Diabetologia 9 by Springer-Verlag 1978
|
|
|
- Georgia Ryan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Diabetologia 15, (1978) Diabetologia 9 by Springer-Verlag 1978 Intracellular Pancreatic B Cell Serotonin and the Dynamics of Insulin Release O. M. Pulido, S. A. Bencosme, M. L. de Bold, and A. J. de Bold Department of Pathology, Queen's University, Kingston General and Hotel Dieu Hospitals, Kingston, Ontario, Canada Summary. The role of intracellular pancreatic B cell serotonin in the dynamics of insulin release was investigated in an in situ perfused rat pancreas preparation. Animals were pretreated with 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) to increase the intracellular levels of serotonin (5-HT) as shown by fluorescence histochemistry. Despite a clear induction of intracellular 5-HT fluorescence in pancreatic islets neither the pattern nor the total amount of insulin released were significantly modified after perfusion with either glucose or tolbutamide. However, the L-amino acid decarboxylase inhibitor, RO , significantly decreased both phases of glucose-mediated insulin release in normal animals as well as in those receiving 5-HTP. Key words: Insulin, pancreatic B cells, serotonin, fluorescence microscopy, monoamine oxidase, L- aromatic amino acid decarboxylase. release caused by these serotonin antagonists has not been established and may be unrelated to their antiserotoninergic action [13, 17, 35]. In addition to this uncertainty, a conflict arises from other in vivo studies in which no inhibition of glucose-mediated insulin release was observed in either mice [28] or humans [34] pretreated with 5-HTP. We have previously found [9, 10, 13] that serotonin, incorporated into the perfusion fluid of the in situ perfused pancreas preparation at a concentration of 1.0 X 10-SM significantly inhibited the glucosemediated first phase of insulin release but did not affect the basal release of insulin. In the present study we have evaluated the role of intracellular B cell serotonin in the dynamics of insulin release using the same in situ perfused pancreas preparation. Rat pancreases containing high levels of experimentally induced intracellular B cell serotonin, as indicated by fluorescence histochemistry [31], were perfused with glucose or tolbutamide. Evidence accumulated over the past few years has led to the hypothesis that intracellular B cell serotonin (5-HT) acts as a tonic inhibitor of insulin release. Serotonin is reported to inhibit glucose-mediated insulin release in vitro after administration of the precursor 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP) [ 18, 26, 36, 37]. Additionally, drugs reported to be specific serotonin antagonists have been shown to potentiate the glucose- and tolbutamide-induced insulin release in adult onset diabetic patients [1, 2, 33], acromegalic patients with glucose intolerance [4, 20] and normal subjects [30]. Similar results have been obtained in vitro using pieces of rabbit pancreas [18, 19] and in the in situ perfused rat pancreas [11]. The precise mechanism of potentiation of glucose-induced insulin Materials and Methods Chemica~ L-5-hydroxytyptophan (5-HTP) and the monoaminoxidase (MAO) inhibitor, nialamide, were obtained from the Sigma Chemical Company (St. Louis, Missouri, U.S.A.); Tolbutamide (Orinase R) from Upjohn (Kalamazoo, Michigan, U.S.A.); Sodium Amytal R from Eli Lilly Company (Toronto, Ontario, Canada); Kits for insulin radioimmunoassay (Phadebas R) from Pharmacia (Montreal, Quebec, Canada). The L-aromatic amino acid deearboxylase inhibitor, RO , was a gift from Hoffman-LaRoche Limited (Vaudreuil, Quebec, Canada). Induction of 5-HT Fluorescence in Pancreatic Islets Serotonin within islet cells was visualized using the formaldehyde condensation technique [5]. Pancreatic biopsies were frozen in X/78/0015/0197/$01.60
2 198 O.M. Pulido et al.: Serotonin and Insulin Release Table L Summary of experimental protocol used to assess the effect of elevated intracellular B cell serotonin on dynamics of glucose- and tolbutamide-mediated insulin release. In the glucose stimulation experiments the pancreases from four animals in each group were biopsied before and after surgery; in groups B and E the pancreases from three animals were perfused with 4.4 mmol/1 glucose; in all groups the pancreases from the remaining animals were perfused with 16.6 mmol/1 glucose. In all instances a pancreatic biopsy was taken at the end of perfusion Stimulus Group (n) b Treatment A (16) No treatment B (19) Saline & Saline a C (10) Nialamide & Saline a D (10) Saline & 5-HTP a Glucose E (13) Nialamide & 5-HTP a F (10) RO immediately prior to Nialamide & 5-HTP a G (10) RO immediately prior to Saline & Saline a Tolbutamide H (5) Saline & Saline a I (5) Nialamide & 5-HTP a a Given after an interval of i h b (n) number of animals used in each group isopentane/liquid nitrogen and freeze-dried under vacuum for 24 h in an Edward-Pearse tisgue dryer. The tissue was then treated with paraformaldehyde vapour at 80 ~ C for 1 h and embedded in paraffin. Slides were examined under a fluorescence microscope equipped with a combination of KP500/K510 filters. The intensity of the fluorescence observed within islet cells was evaluated and graded as slight, moderate, or intense. In a previous communication [31] we have described conditions to induce accumulation of serotonin in rat pancreatic islet cells. Briefly, injection of nialamide (5 mg/kg body weight) followed by 5-HTP (50 mg/kg body weight) one hour later, resulted in intense serotonin fluorescence observed at 120 rain after injection of 5-HTP. Injection of 5-HTP alone produced similar but weaker results in terms of serotonin fluorescence. In the present investigations we carried out pilot experiments to determine changes in serotonin fluorescence at different time intervals after 5-HTP injection. To this purpose, two groups of 12 animals each were injected intraperitoneally with either nialamide (5 mg/kg body weight) and, 60 min later, with 5-HTP (50 mg/kg body weight) or with 5-HTP alone (50 mg/kg body weight). At 15, 30, 60 and 120 min after 5-HTP injection, 3 animals from each group were anaesthetized with Na Amytal R and pieces of pancreas were taken for histochemieal evaluation. Serotonin fluorescence was evident in pancreatic islets from both groups as early as 15 min after 5-HTP injection, increasing through 60 min and remaining unaltered for up to 120 min. The fluorescence displayed by islet cells in animals treated with 5-HTP alone was consistently lower than that observed in animals treated with both nialamide and 5-HTP. As no change in fluorescence was apparent after 60 min of 5-HTP administration, this time period was chosen to perform the investigations described below. Perfusion Technique Male Sprague-Dawley rats weighing g were fasted for h, anaesthetized with sodium Amytal R (100mg/kg body weight) and the pancreas isolated in situ [29]. The basic buffer used for peffusion of the gland was supplemented Krebs-Ringer bicarbonate [2], ph: 7.4, containing glucose 4.4 mmol/1 and Dextran T40, 60 mg/ml [12]. The integrity of this type of preparation has been established by electron microscopy [7, 8, 12, 26]. Following surgery, lasting approximately 20 min, the pancreases were perfused for a 15 min stabilization period followed by a period of 3 min to obtain the basal immunoreactive insulin (IRI) levels. The release of insulin was then stimulated by perfusion with either 16.6 mmol/1 glucose or 0.27 mmol/1 tolbutamide in the basic buffer. In selected groups, some of the pancreases were perfused with basic buffer to obtain the basal insulin release corresponding to the period of stimulation of test pancreases of the same groups. During the one hour of perfusion, flow rates ranged from 5 to 10 ml/min, and the perfusion pressure was 8.0 KPa. Insulin released into the perfusate was measured by radioimmunoassay. Experimental Design Table 1 summarises the protocol used in the glucose and tolbutamide experiments. The glucose stimulation experiments were composed of 7 groups (A-G). Groups A and B were controls. Groups C to G received one or more of the following drugs intraperitoneally: 5-HTP (50 mg/kg body weight), nialamide (5 mg/kg body weight) and RO (100 mg/kg body weight). Normal saline (9 g NaC1/1) was used as a drug substitute. Pancreatic biopsies were obtained from 4 animals in each group immediately before and also after isolation of the pancreas for perfusion, to see if surgical manipulation altered the induced serotonin fluorescence in pancreatic islet cells. The pancreases of 12 animals from groups A and B, and 6 animals from groups C to G were perfused with 16.6 mmol/1 glucose (Table 2). In addition 3 animals from groups B and E were perfused with basic buffer to provide the basal levels of IRI release for control and for animals with elevated pancreatic islet cell serotonin. In all instances pancreatic biopsies were obtained at the end of perfusion for histochemical evaluation of change in the intraceuular serotonin content. The tolbutamide stimulation experiments were composed of 2 groups (H and I) as shown in Table 1. The pancreases of 5 saline control animals (Group H) and 5 animals treated with nialamide and 5-HTP (Group 1) were challenged with 0.27mmol/1 tolbutamide (Table 2). Pancreatic biopsies for histochemical evaluation were taken following perfusion. Data Calculation The total insulin output is expressed as the integrated area under the insulin curve, which was 4 to 8 minutes (Z 8) for the first phase and 9 to 23 minutes (Z 23) for the second phase. Student's ttest was used to determine statistical significance for all comparisons between means. Differences were considered to be significant if p < Results are presented as mean -+ SEM. Results The surgical procedure used to isolate the pancreas did not cause a detectable change of intesity of 5-HT formaldehyde-induced fluorescence (Fig. 1 and 2) nor the blocking effect of RO (Fig. 3). Fur-
3 O. M. Pulido et al.: Serotonin and Insulin Release 199 Table 2. Effect of elevated intracellular B cell serotonin on the biphasic glucose- and tolbutamide-mediated insulin release. The total insulin released (mean + SEM) and its distribution in Phase I and Phase II, in terms of amount (gu) and percentage, are presented for each group Stimulus Group (n) Treatment Total Insulin ad Phase I b Phase II c Insulin (~U) p % of Total Insulin (gu) p % of Total Glucose A (12) Untreated 9577_ _+159 NS _+896 NS 82.8 B (12) Saline + Saline d 11495_ _ _ C (6) Nialamide + Saline a 11317_ _+197 NS _+1025 NS 80.0 D (6) Saline + 5-HTP d NS NS 80.8 E (6) Nialamide + 5-HTP d 10098_ NS _+739 NS 81.7 F (6) RO Nialamide 6662_ _+86 < _+459 < HTP d G (6) RO Saline < _+963 < Saline d Tolbutamide H (5) Saline + Saline a _ _ I (5) Nialamide + 5-HTP a 2462_+_ _+138 NS _+519 NS 72.3 a Values for total insulin are expressed as integrated areas under the insulin curve [4-23 min] b Phase I was determined by the first peak response which was over 5 min after initiation of the stimulus. Values are expressed as integrated areas under the insulin curve [4-8 min] c Phase II was arbitrarily determined beginning by rain 6 after initiation of the stimulus and lasting until the end of the glucose infusion. Values are expressed as integrated area under the insulin curve [9-23 mini d Given after an interval of 1 h NS Not significantly different relative to saline controls (values were considered significant when p < 0.05) thermore, the apparent intensity of 5-HT formaldehyde-induced fluorescence (Fig. 4) and the basal IRI release (Fig. 5) were not modified by perfusion with the basic buffer. Effect of Intracellular B Cell Serotonin on Glucose-mediated Insulin Release Controls (Groups A and B). Glucose elicited a typical biphasic IRI secretion pattern in untreated (Group A) as well as in saline-injected (Group B) controls (Table 2, Fig. 5). Since no significant difference was found between groups A and B, all treated groups were compared to saline controls for analysis of drug effects. Test Animals (Groups C-G). The biphasic pattern of glucose-mediated insulin release was observed in all instances. In Group C, treated with nialamide alone, the first peak was slightly higher ('/3) and shorter lived (3 min) than that obtained in Group B. Nevertheless, the total insulin release in each phase did not differ significantly from the corresponding phase in the saline controls (Table 2 and Fig. 5). Despite the elevated intracellular B cell serotonin in Group D (5-HTP alone) and Group E (nialamide and 5-HTP), neither the pattern nor the total amount of insulin released were found to be statistically different from that of the saline controls (Table 2 and Fig. 5). The biphasic pattern was repeated in Group F (RO , nialamide and 5-HTP) and Group G (RO alone). However, total insulin release was significantly reduced. In Group F, Phase I was reduced by 44.6% and Phase II by 41.6%. In group G Phase I was reduced by 34.1% and Phase II by 35.2%. Thus, the proportion of insulin release in Phase I and II was essentially the same as in Group B (Table 2 and Fig. 5). After glucose stimulation, islet cells of pancreases from Groups A, B, C, F and G were not fluorescent, whereas, those from Groups D (Fig. 7) and E (Fig. 6) exhibited a yellow fluorescence that was most intense in Group E.
4 200 O.M. Pulido et al.: Serotonin and Insulin Release Fig. 1. Intense cytoplasmic fluorescence is desplayed by islet ceils from a rat pretreated with nialamide (5 mg/kg body weight) and 5-HTP (50 mg/kg body weight). Tissue was removed after isolation of pancreas and before perfusion. 360 Fig. 2. Moderate cytoplasmic fluorescence is displayed by islet cells from a rat pretreated with 5-HTP (50 mg/kg body weight alone). Tissue removed after isolation of pancreas and before peffusion. 360 Fig. 3. Non-fluorescent islet cells from a rat pretreated with RO (100 mg/kg body weight), nialamide (5 mg/kg body weight) and 5-HTP (50 mg/kg body weight). Tissue was removed after isolation of pancreas and before perfusion. 360 Fig. 4. Intense cytoplasmic fluorescence is displayed by pancreatic islet cells from a rat pretreated with nialamide (5 mg/kg body weight) and 5-HTP (50 mg/kg body weight). Pancreas was removed at the end of perfusion with 4.4 mmol/1 glucose. 360 x Effect of Intracellular B Cell Serotonin on Tolbutamide-Stimulated Insulin Release Saline Control (Group H). Stimulation with tolbutamide elicited the characteristic single peak in Phase I followed by a sustained secretion rate above the basal level lasting until the termination of the stimulus in Phase II (Fig. 5). Nialamide and 5-HTP (Group I). Despite the elevated intracellular B cell serotonin in Group I, the pattern and the total amount of insulin released in
5 O. M. Pulido et al.: Serotonin and Insulin Release 201 / I00( L 500 O I GROUP A UNTREATED ~ L o w gl n=12 Ucose IT_ r. ~ TT n=3 0 5 I GROUP B SALINE 8= SALINE S 6 5,b i5 2'o GROUP c N,ALAM,DE 8= SALINE C -- IOOC E D :::k 5O( 0_ D 0 O z b g io t5 ~o GROUP D SALINE 5-HTP 11=6 6 g ib ig s'o GROUP E NiALAMIDE 8 5- I-ITP 6 g ib Ig 2'0 GROUP F RO NIALAMIDE 8= 5-HTP 03 Z IO S GROUP G R SALINE 8, SALINE t TOLB UTAMIDE! 9 n=5 6 g,b i5 2'0 GROUP H SALINE 8= SALINE TIME (rain) b 5 TOLB UTAMIDE n=5 ib 15 zb GROUP I NIALAMIDE 8= 5-HTP Fig. 5. Dynamics of insulin release in each test group. The first three points in each curve depict the basal IRI levels obtained during perfusion with 4.4 mmol/1 glucose. The stimulation period is designated by a horizontal line above each curve. The superscript identifies the stimulus, either 16.6 mmol/1 glucose (e--o) or 0.27 mmol/1 tolbutamide (x--x). In Groups B and E the basal insulin levels obtained by perfusign with low glucose (Q--o) are indicated by an arrow response to tolbutamide was similar to that of Group H (Table 2 and Fig. 5). The persistence of high levels of intracellular B cell serotonin during tolbutamide stimulation was confirmed by histochemical examination of islet cells which revealed an intense yellow fluorescence in Group I (Fig. 8). This reaction was absent in islet cells of saline controls. Discussion In the present work, it has been demonstrated that elevated intracellular B cell serotonin did not affect the pattern or amount of insulin released from the rat pancreas challenged with glucose or tolbutamide. These observations are in agreement with previous in vivo studies of glucose-mediated insulin release in mice [28] and humans [34] both pretreated with 5-HTP. Disparate to these findings is the inhibitory effect of elevated intracellular B cell serotonin on the release of insulin observed during incubation of tissue obtained from animals treated with the 5-HT precursor 5-HTP [18, 27, 36, 37]. Whether this discrepancy is due to differences in experimental technique (i. e. incubation vs. peffusion), to species differences or other as yet unknown reasons remains to be determined. It is worth noting that previous studies in our laboratory [9, 10, 13] have shown that serotonin inhibited insulin response to a glucose challenge when it was incorporated into the perfusion fluid of a similar preparation to that used in the present studies. From this and the present study, it is concluded that under our experimental conditions, elevated intracellular B cell serotonin does not have an effect on insulin release, whereas extracellular serotonin inhibits this B cell function. It is not clear where this inhibition is effected. Since some evidence [6, 18] indicates
6 202 O.M. Pulido et al.: Serotonin and Insulin Release that serotonin penetrates cell membranes very poorly it is possible that extracellular serotonin acts on the cell membrane. However, these findings do not totally preclude penetration of some serotonin into B cells. In view of the inhibitory action of extracellular serotonin on insulin release observed in our preparation, the question arises as to whether intracellular serotonin leakage from B cells, either physiologically [23] or through cell necrosis [2, 3], may result in sufficiently high local concentration of this amine to affect insulin release in vitro. This consideration appears relevant in the interpretation of data obtained using incubation of tissues from animals pretreated with 5-HTP [18, 27, 36, 37]. Species differences may also account for the disparity between our results and the inhibitory effect of elevated intracellular B cell serotonin observed in vitro by others [18, 27, 37]. In guinea pigs the B cell contains high levels of intracellular serotonin which does not appear to compromise cellular function [6, 24]. However, if intracellular B cell serotonin, which is not demonstrable in mice and rabbits, is elevated by the administration of 5-HTP, insulin release is abolished in mice [27] but only partially inhibited in rabbits [18, 36, 37]. In studies in which the sulphonamide glibenclamide, or isoproterenol were used as the insulinogenic stimulus, pretreatment of mice with 5-HTP inhibited insulin release but did not affect the insulin response to a glucose callenge [28]. In our experiments the insulin release elicited by the sulphonamide tolbutamide was not inhibited after pretreatment with 5-HTP. The different insulin response to tolbutamide as compared to that of glibenclamide, in the presence of elevated intracellular B cell serotonin, may be the result of differences in the mechanisms of action of these two sulphonamides [21] or in experimental models. The results of the perfusion experiments obtained when RO was administered to verify that the Fig. 6. Intense cytoplasmic fluorescence is displayed by islet cells from a rat pretreated with nialamide (5 mg/kg body weight) and 5-HTP (50 mg/kg body weight). Pancreas was removed at the end of perfusion with 16.6 mmol/1 glucose. 325 x Fig, 7, Moderate cytoplasmic fluorescence is displayed by islet cells from a rat pretreated with 5-HTP alone (50 mg/kg body weight). Pancreas was removed at the end of perfusion with 16.6 mmol/1 glucose. 325 Fig. 8. Intense cytoplasmic fluorescence is displayed by islet cells from a rat pretreated with nialamide (5 mg/kg body weight) and 5-HTP (50 mg/kg body weight). Pancreas was removed at the end of perfusion with 0.27 mmol/1 tolbutamide. 325 x
7 O. M. Pulido et al.: Serotonin and Insulin Release 203 formaldehyde induced fluorescence was due to serotonin, were unexpected. The administration of RO , which blocks the synthesis of 5-HT from 5-HTP, resulted in an inhibition of glucose mediated insulin release whether or not pretreatment with 5-HTP was carried out. The implication of this finding is not clear. A possible explanation is that RO exerts an independent pharmacological effect responsible for the observed inhibition of insulin release. The above findings with our experimental model precludes the generalisation of the hypothesis that intracellular B cell serotonin acts as inhibitor of insulin release [18, 25]. Clearly, further work on the role of intracellular B cell serotonin is required. Such studies must include the rat together with other species so that the question of species differences in sensitivity to increased levels of intracellular B cell serotonin may be answered. Acknowledgements. It is a pleasure to acknowledge the excellent technical assistance of Mr. B. Gubbins and Miss M. Chiong, and the expert secretarial assistance of Mrs. B. Fluhrer and Mrs. Audrey Davison. References 1. Baldrigde, J. A., Quickel, K. E., Jr., Feldman, J. M., Lebovitz, H. E.: Potentiation of tolbutamide-mediated insulin release in adult onset diabetics by methysergide maleate. Diabetes 23, (1974) 2. Beneosme, S.A., Wilson, M.B., Aleyassine, H., de Bold, A. J., de Bold, M. L.: Rabbit pancreatic B cell. Morphological and functional studies during embryonal and post-natal development. Diabetologia 6, (1970) 3. Bencosme, S.A., Tsutsumi, V., Martin, J.M., Nkerblom, H.K.: Ultrastructural changes in B cells of pancreatic islets from rats with elevated levels of circulating growth hormone secreted by MtT-Wl5 tumor. Diabetes 20, (1971) 4. Bivens, C.H., Lebovitz, H.E., Skyler, J.S., Feldman, J.M.: Enhancement of insulin secretion in acromegaly by serotonin antagonists (Abstract). Diabetes 21 (Suppl 1), 352 (1972) 5. Bj6rklund, A., Falck, B., Owman, Ch.: Fluorescence microscopic and microspectrofluorometric technique for the cellular localization and characterization of biogenic amines. In: S. A. Berson (Ed.): Methods in investigative and diagnostic endocrinology; J. E. Rall, I. J. Kopin (Eds.): The thyroid and biogenic amines, p Amsterdam: North-Holland Publishing Company (Publishers); New York: American Elsevier Publishing Company, Inc. (Distributors) Cegrell, L.: The occurrence of biogenic monoamines in the mammalian endocrine pancreas. Acta Physiol. Scand. [Suppl.] 314, 1-60 (1968) 7. Curry, D.L., Bennet, L.L., Grodsky, G.M.: Dynamics of insulin secretion by the peffused rat pancreas. Endocrinology 83, (1968) 8. de Bold, M. L.: Establishment of an in situ perfused pancreas preparation to study the biphasic release of insulin. In: regulatory role of serotonin during the first phase of insulin release. A morphological and functional study, p Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Pathology, Queen's University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada de Bold, M. L.: The effects of serotonin on B cell structure and function during the glucose-mediated first phase of insulin release. In: Regulatory role of serotonin during the first phase of insulin release. A morphological and functional study, p Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Pathology, Queen's University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada de Bold, M. L., Bencosme, S. A.: Inhibition of the first phase of glucose mediated insulin release by serotonin in an in situ perfused pancreas preparation (Abstract). Fed. Proc. 42, 253 (1975) 11. de Bold, M.L., Bencosme, S.A.: Morphological changes occurring in rat B cells following stimulation or inhibition of the first phase of insulin release (Abstract). Anat. Rec. 181, 342 (1975) 12. de Bold, M.L., Bencosme, S.A., Penhos, J.C.: The ultrastructure of B-cell during the biphasic release of insulin after using dextran as albumin substitute (Abstract). Lab. Invest. 32, 422 (1975) 13. de Bold, M. L., Bencosme, S.A.: Effects of serotonin and its antagonists on the first phase of insulin release in normal and hypersomatotropie rats. Horm. Metab. Res. (Accepted for publication) (1978) 14. Feldman J. M., Lebovitz, H. E.: Specificity of serotonin inhibition of insulin release from golden hamster pancreas. Diabetes 19, (1970) 15. Feldman, J.M., Lebovitz, H.E.: Mechanism of epinephrine and serotonin inhibition of insulin release in the golden hamster in vitro. Diabetes 19, (1970) 16. Feldman, J.M., Lebovitz, H.E.: Serotonin inhibition of in vitro insulin release from golden hamster pancreas. Endocrinology 86, (1970) 17. Feldman, J. M., Lebovitz, H. E.: Antagonism of catecholamine inhibition of insulin secretion by methysergide. Experientia 28, (1972) 18. Feldman, J. M., Lebovitz, H. E.: A serotoninergic mechanism for the control of insulin secretion. Trans. Assoc. Am. Physicians 85, (1972) 19. Feldman, J.M., Quickel, K. E., Jr., Lebovitz, H. E.: Potentiation of insulin secretion in vitro by serotonin antagonists. Diabetes 21, (1972) 20. Feldman, J.M., Bivens, C.H., Skyler, J. S., Lebovitz, H.E.: Effect of eyproheptadiene administration on insulin secretion in acromegalic, diabetic and normal subjects. Horm. Metab. Res. 7, (1975) 21. Fubganger, R.D., Goberna, R., Hinz, M., Jaros, P., Karsten, C., Pfeiffer, E.F., Raptis, S.: Comparative studies on the dynamics of insulin secretion following HB 419 and tolbutamide of the perfused isolated rat pancreas and the perifused isolated pieces and islets of rat pancreas. Horm. Metab. Res. (Suppl), (1969) 22. Gagliardino, J.J., Nierle, C., Pfeiffer, E.F.: The effect of serotonin on in vitro insulin secretion and biosynthesis in mice. Diabetologia 10, (1974) 23. Gylfe, E.: Concomitant release of serotonin and insulin from perifused pancreatic islets (Abstract). Diabetologia 13, 398 (1977) 24. Jaim-Etcheverry, G., Zieher, L.M.: Electron microscopic cytochemistry of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) in the beta cells of guinea pig endocrine pancreas. Endocrinology 83, (1968) 25. Lebovitz, H.E., Feldman, J.M.: Pancreatic biogenic amines and insulin secretion in health and disease. Fed. Proc. 32, (1973) 26. Lee, J. C., Grodsky, G. M., Bennett, L. L., Smith-Kyle, D. F., Craw, L.: Ultrastructure of B ceils during the dynamic response to glucose and tolbutamide in vitro. Diabetologia 6, (1970)
8 204 O.M. Pulido et al.: Serotonin and Insulin Release 27. Lernmark, A.: The significance of 5-hydroxytryptamine for insulin secretion in the mouse. Horm. Metab. Res. 3, (1971) 28. Lundquist, I., Ekholm, R., ~Ericson, L. E.: Monoamines in the pancreatic islets of the mouse. 5-hydroxytryptamine as an intracellular modifier of insulin secretion and the hypoglycaemic action of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Diabetologia 7, (1971) 29. Penhos, J.C., Wu, C.H., Basabe, J.C., Lopez, N., Wolff, F.W.: A rat pancreas-small gut preparation for the study of intestinal factor(s) and insulin release. Diabetes 18, (1969) 30. Pontiroli, A. E., Viberti, G. C., Tognetti, A., Pozza, G.: Effect of metergoline, a powerful and long-acting antiserotoninergic agent, on insulin secretion in normal subjects and in patients with chemical diabetes. Diabetologia 11, (1975) 31. Pulido, O., de Bold, A., de Bold, M.L., Bencosme, S.A.: Demonstration of a tryptaminergic mechanism in the rat B cell. Experientia 33, (1977) 32. Quickel, K. E., Jr., Feldman, J. M., Lebovitz, H. E.: Inhibition of insulin secretion by serotonin and dopamine. Species variation. Endocrinology 89, (1971) 33. Quickel, K. E., Jr., Feldman, J. M., Lebovitz, H. E.: Enhancement of insulin secretion in adult onset diabetics by methysergide maleate: Evidence for an endogenous biogenic monoamine mechanism as a factor in the impaired insulin secretion in diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 33, (1971) 34. Seino, Y., Ikeda, M., Kuzuya, H., Sakurai, H., Imura, H.: Effect of 5-hydroxytryptophan (5-HTP), L-Dopa and Bethanidine on plasma insulin response to intravenous glucose loading in normal subjects. Horm. Metab. Res. 7, (1975) 35. Smith, P. H., Porte, D., Jr.: Neuropharmacology of the pancreatic islets. Annu. Rev. Pharmacoi. Toxicol. 16, (1976) 36. Tjalve, H.: Catechol- and indolamines in some endocrine cell systems. An autoradiographical, histochemical and radioimmunological study. Acta Physiol. Scand. [Suppl 360] 81, (1971) 37. Wilson, J.P., Downs, R.W., Jr., Feldman, J.M., Lebovitz, H.E.: Beta cell monoamines: Further evidence for their role in modulating insulin secretion. Am. J. Physiol. 227, (1974) Received. November 11, 1977, and in revised form: April 21, 1978 Dr. A. J. de Bold Department of Pathology Hotel Dieu Hospital Kingston, Ontario Canada K7L 3H6
EFFECT OF 5-HYDROXYTRYPTOPHAN
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1974), 50, 575-580 THE HYPOGLYCAEMIC EFFECT OF 5-HYDROXYTRYPTOPHAN B.L. FURMAN Department of Pharmacology, University of Strathclyde, George Street, Glasgow Gl 1XW, Scotland 1 In nialamide-treated
Br. J. Pharmac. (1974), 50, 575-580 THE HYPOGLYCAEMIC EFFECT OF 5-HYDROXYTRYPTOPHAN B.L. FURMAN Department of Pharmacology, University of Strathclyde, George Street, Glasgow Gl 1XW, Scotland 1 In nialamide-treated
Effect of L-5-HTP on the Release of Growth Hormone, TSH and Insulin
 Endocrinol. Japon. 1973, 20 (2), 135,-441 Effect of L-5-HTP on the Release of Growth Hormone, TSH and Insulin MANABU YOSHIMURA, YUKIO OCHI, TADAYOSHI MIYAZAKI, KATSUHIKO SHIOMI AND TAKASHI HACHIYA 2nd
Endocrinol. Japon. 1973, 20 (2), 135,-441 Effect of L-5-HTP on the Release of Growth Hormone, TSH and Insulin MANABU YOSHIMURA, YUKIO OCHI, TADAYOSHI MIYAZAKI, KATSUHIKO SHIOMI AND TAKASHI HACHIYA 2nd
Reversal by Methysergide of Inhibition of Insulin
 Reversal by Methysergide of Inhibition of Insulin Secretion by Prostaglandin E in the Dog R. PAUL ROBERTSON and ROBERT J. GUEST, Division of Clinical Pharmacology, Department of Medicine, University of
Reversal by Methysergide of Inhibition of Insulin Secretion by Prostaglandin E in the Dog R. PAUL ROBERTSON and ROBERT J. GUEST, Division of Clinical Pharmacology, Department of Medicine, University of
Diabetologia by Springer-Verlag 1978
 Diabetologia 15, 343-347 (1978) Diabetologia by Springer-Verlag 1978 Haloperidol, a Dopaminergic Antagonist: Somatostatin-Like Inhibition of Glucagon and Insulin Release from the Isolated, Perfused Canine
Diabetologia 15, 343-347 (1978) Diabetologia by Springer-Verlag 1978 Haloperidol, a Dopaminergic Antagonist: Somatostatin-Like Inhibition of Glucagon and Insulin Release from the Isolated, Perfused Canine
LOCALIZATION OF MONOAMINE OXIDASE IN MAMMALIAN
 Brit. Heart J., 1965, 27, 116. LOCALIZATION OF MONOAMINE OXIDASE IN MAMMALIAN AND REPTILIAN HEART BY E. MULLER* AND A. G. E. PEARSEt From the Department ofpathology, Postgraduate Medical School, London
Brit. Heart J., 1965, 27, 116. LOCALIZATION OF MONOAMINE OXIDASE IN MAMMALIAN AND REPTILIAN HEART BY E. MULLER* AND A. G. E. PEARSEt From the Department ofpathology, Postgraduate Medical School, London
Effect of glucose on beta cell proliferation and population size in organ culture of foetal and neonatal rat pancreases
 J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 74, 303-312 (1983) 3Q3 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1983 Effect of glucose on beta cell proliferation and population size in organ culture of foetal
J. Embryol. exp. Morph. 74, 303-312 (1983) 3Q3 Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1983 Effect of glucose on beta cell proliferation and population size in organ culture of foetal
Diabetologia 9 by Springer-Verlag 1976
 Diabetologia 12, 263-267 (1976) Diabetologia 9 by Springer-Verlag 1976 The Comparative Effects of Barbituric Acid and Phenobarbital on Blood Glucose and Insulin Secretion in Mice* J. H. Mennear, C. Schonwalder
Diabetologia 12, 263-267 (1976) Diabetologia 9 by Springer-Verlag 1976 The Comparative Effects of Barbituric Acid and Phenobarbital on Blood Glucose and Insulin Secretion in Mice* J. H. Mennear, C. Schonwalder
Experiments were carried out then with the object of producing complete disappearance of the A
 Relation of Glucagon to A Cells of the Pancreas*. (22339) SERGIO A. BENCOSME AND J. FREI. (Introduced by J.S.L. Browne Departament of pathology, Queen`s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada. In spite
Relation of Glucagon to A Cells of the Pancreas*. (22339) SERGIO A. BENCOSME AND J. FREI. (Introduced by J.S.L. Browne Departament of pathology, Queen`s University, Kingston, Ontario, Canada. In spite
INFLUENCE OF METHYLDOPA ON CENTRAL EFFECTS OF RESERPINE
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1964), 22, 366-370. INFLUENCE OF METHYLDOPA ON CENTRAL EFFECTS OF RESERPINE BY B. G. BENFEY AND D. R. VARMA From the Department of Pharmacology, McGill University, Montreal, Canada
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1964), 22, 366-370. INFLUENCE OF METHYLDOPA ON CENTRAL EFFECTS OF RESERPINE BY B. G. BENFEY AND D. R. VARMA From the Department of Pharmacology, McGill University, Montreal, Canada
Adrenergic fibres in the human intestine
 Gut, 1968, 9, 678-682 Adrenergic fibres in the human intestine L. CAPURSO,1 C. A. FRIEDMANN, AND A. G. PARKS From the Research Department, St Mark's Hospital, London, and the London Hospital, Whitechapel,
Gut, 1968, 9, 678-682 Adrenergic fibres in the human intestine L. CAPURSO,1 C. A. FRIEDMANN, AND A. G. PARKS From the Research Department, St Mark's Hospital, London, and the London Hospital, Whitechapel,
Article. Reference. Effect of insulin on glucose- and arginine-stimulated somatostatin secretion from the isolated perfused rat pancreas
 Article Effect of insulin on glucose- and arginine-stimulated somatostatin secretion from the isolated perfused rat pancreas GERBER, Pietro, et al. Abstract The effects of exogenous insulin on somatostatin
Article Effect of insulin on glucose- and arginine-stimulated somatostatin secretion from the isolated perfused rat pancreas GERBER, Pietro, et al. Abstract The effects of exogenous insulin on somatostatin
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION
 ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
A Comparison of Leucine- and Acetoacetate-induced Hypoglycemia in Man *
 Journal of Clinical Investigation Vol. 43, No. 1, 1964 A Comparison of Leucine- and Acetoacetate-induced Hypoglycemia in Man * STEFAN S. FAJANS, JOHN C. FLOYD, JR., RALPH F. KNOPF, AND JEROME W. CONN (From
Journal of Clinical Investigation Vol. 43, No. 1, 1964 A Comparison of Leucine- and Acetoacetate-induced Hypoglycemia in Man * STEFAN S. FAJANS, JOHN C. FLOYD, JR., RALPH F. KNOPF, AND JEROME W. CONN (From
Cytochemical Quantification of Physiologic Regulation of Oxyntic Cell Carbonic Anhydrase a
 Cytochemical Quantification of Physiologic Regulation of Oxyntic Cell Carbonic Anhydrase a A. I. VINIKb and A. A. HELDSINGER Department of Internal Medicine University of Michigan Medical School Ann Arbor,
Cytochemical Quantification of Physiologic Regulation of Oxyntic Cell Carbonic Anhydrase a A. I. VINIKb and A. A. HELDSINGER Department of Internal Medicine University of Michigan Medical School Ann Arbor,
Insulin and glucagon release from the isolated pancreas of foetal and newborn mice
 /. Embryol. exp. Morph. Vol. 28, 3, pp. 607-614, 1972 607 Printed in Great Britain Insulin and glucagon release from the isolated pancreas of foetal and newborn mice ByAKE LERNMARK 1 AND BRITT INGER WENNGREN
/. Embryol. exp. Morph. Vol. 28, 3, pp. 607-614, 1972 607 Printed in Great Britain Insulin and glucagon release from the isolated pancreas of foetal and newborn mice ByAKE LERNMARK 1 AND BRITT INGER WENNGREN
The influence of light and dark on the catecholamine content of the retina and choroid. Charles W. Nichols, David Jacobowitz, and Marianne Hottenstein
 The influence of light and dark on the catecholamine content of the retina and choroid Charles W. Nichols, David Jacobowitz, and Marianne Hottenstein Recent histochemical studies with the use of a fluorescence
The influence of light and dark on the catecholamine content of the retina and choroid Charles W. Nichols, David Jacobowitz, and Marianne Hottenstein Recent histochemical studies with the use of a fluorescence
Chapter 16: Endocrine System 1
 Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
C'4-tryptophan in rat pineals in organ culture. Other compounds related in
 STIMULATION OF C14-MELATONIN SYNTHESIS FROM C14-TRYPTOPHAN BY NORADRENALINE IN RAT PINEAL IN ORGAN CULTURE* BY JULIUS AXELROD, HARVEY M. SHEIN, AND RICHARD J. WURTMAN LABORATORY OF CLINICAL SCIENCE, NATIONAL
STIMULATION OF C14-MELATONIN SYNTHESIS FROM C14-TRYPTOPHAN BY NORADRENALINE IN RAT PINEAL IN ORGAN CULTURE* BY JULIUS AXELROD, HARVEY M. SHEIN, AND RICHARD J. WURTMAN LABORATORY OF CLINICAL SCIENCE, NATIONAL
Passage into the rat brain of dopa and dopamine injected into the lateral ventricle
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 43, 32-38. Passage into the rat brain of dopa and dopamine injected into the lateral ventricle J. CONSTANTINIDIS, J. M. GAILLARD, F. GEISSBUHLER AND R. TISSOT The University Psychiatric
Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 43, 32-38. Passage into the rat brain of dopa and dopamine injected into the lateral ventricle J. CONSTANTINIDIS, J. M. GAILLARD, F. GEISSBUHLER AND R. TISSOT The University Psychiatric
A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets
 Diabetologia () 5:77 DOI.7/s5--- SHORT COMMUNICATION A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets Q. Cheng & Y. C.
Diabetologia () 5:77 DOI.7/s5--- SHORT COMMUNICATION A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets Q. Cheng & Y. C.
Effects of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I on Insulin and Glucagon Release from Isolated Perfused Rat Pancreas
 Effects of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I on Insulin and Glucagon Release from Isolated Perfused Rat Pancreas KOICHI KAWAI, SEIJI SUZUKI, KAZUE TAKANO*, NAOMI HIZUKA*, YASUKO WATANABE AND KAMEJIRO YAMASHITA
Effects of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I on Insulin and Glucagon Release from Isolated Perfused Rat Pancreas KOICHI KAWAI, SEIJI SUZUKI, KAZUE TAKANO*, NAOMI HIZUKA*, YASUKO WATANABE AND KAMEJIRO YAMASHITA
Tumor markers. Chromogranin A. Analyte Information
 Tumor markers Chromogranin A Analyte Information -1-2018-04-22 Chromogranin A Introduction Chromogranin A (CgA) is a 439-amino acid protein with a molecular weight of 48 to 60 kda, depending on glycosylation
Tumor markers Chromogranin A Analyte Information -1-2018-04-22 Chromogranin A Introduction Chromogranin A (CgA) is a 439-amino acid protein with a molecular weight of 48 to 60 kda, depending on glycosylation
Uniphasic Insulin Responses to Secretin Stimulation in Man
 Uniphasic Insulin Responses to Stimulation in Man ROGER L. LERNER and DANIEL PORTE, JR. From the University of Washington School of Medicine and Veterans Administration Hospital, Seattle, Washington 98108
Uniphasic Insulin Responses to Stimulation in Man ROGER L. LERNER and DANIEL PORTE, JR. From the University of Washington School of Medicine and Veterans Administration Hospital, Seattle, Washington 98108
University of Groningen. Melatonin on-line Drijfhout, Willem Jan
 University of Groningen Melatonin on-line Drijfhout, Willem Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Melatonin on-line Drijfhout, Willem Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Diabetologia 9 by Springer-Verlag 1978
 Diabetologia 15, 159-164 (1978) Diabetologia 9 by Springer-Verlag 1978 Characterisation of the Effect of Intravenous Infusion of Glucose and Tolbutamide on the Insulin Delivery Rate in Man T. Asano, H.
Diabetologia 15, 159-164 (1978) Diabetologia 9 by Springer-Verlag 1978 Characterisation of the Effect of Intravenous Infusion of Glucose and Tolbutamide on the Insulin Delivery Rate in Man T. Asano, H.
STUDIES ON INSULIN RELEASE FROM THE ISOLATED MOUSE ISLET
 STUDIES ON INSULIN RELEASE FROM THE ISOLATED MOUSE ISLET AKADEMISK AVHANDLING som med vederbörligt tillstånd av Medicinska Fakulteten i Umeå för vinnande av medicine doktorsgrad offentligen försvaras i
STUDIES ON INSULIN RELEASE FROM THE ISOLATED MOUSE ISLET AKADEMISK AVHANDLING som med vederbörligt tillstånd av Medicinska Fakulteten i Umeå för vinnande av medicine doktorsgrad offentligen försvaras i
COLLOID DROPLET FORMATION IN DOG THYROID IN VITRO
 COLLOID DROPLET FORMATION IN DOG THYROID IN VITRO Induction by Dibutyryl Cyclic-AMP I. PASTAN and S. HI. WOLLMAN. Froml the National Institute of Arthritis and Metabolic Diseases and the National Cancer
COLLOID DROPLET FORMATION IN DOG THYROID IN VITRO Induction by Dibutyryl Cyclic-AMP I. PASTAN and S. HI. WOLLMAN. Froml the National Institute of Arthritis and Metabolic Diseases and the National Cancer
CONVERSION OF AMINO ACIDS TO SPECIALIZED PRODUCTS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU
 CONVERSION OF AMINO ACIDS TO SPECIALIZED PRODUCTS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU In addition to serving as building blocks for proteins, amino acids are precursors of many nitrogen-containing
CONVERSION OF AMINO ACIDS TO SPECIALIZED PRODUCTS DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU In addition to serving as building blocks for proteins, amino acids are precursors of many nitrogen-containing
Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1984
 Diabetologia (1984) 26:203 207 Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1984 How does glucose regulate the human pancreatic A cell in vivo? C. M. Asplin*, P. M. Hollander** and J. P. Palmer Diabetes Research Center
Diabetologia (1984) 26:203 207 Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1984 How does glucose regulate the human pancreatic A cell in vivo? C. M. Asplin*, P. M. Hollander** and J. P. Palmer Diabetes Research Center
Control of Glucose Metabolism
 Glucose Metabolism Control of Glucose Metabolism The pancreas is both an exocrine and endocrine gland. It secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum (exocrine) and 3 specific hormones into the bloodstream
Glucose Metabolism Control of Glucose Metabolism The pancreas is both an exocrine and endocrine gland. It secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum (exocrine) and 3 specific hormones into the bloodstream
Immunohistochemical Study on the C-cells in the Internal Parathyroid Gland of the Goat
 Immunohistochemical Study on the C-cells in the Internal Parathyroid Gland of the Goat Takeshi TSUCHIYA Department of Animal Morphology, Faculty of Agriculture, Tohoku University, Sendai-Shi 980 (Received
Immunohistochemical Study on the C-cells in the Internal Parathyroid Gland of the Goat Takeshi TSUCHIYA Department of Animal Morphology, Faculty of Agriculture, Tohoku University, Sendai-Shi 980 (Received
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 1. Primers used for PCR and qpcr Primer Name
 Supplementary Table. Primers used for PCR and qpcr Primer Name ccession Number Fwd Rev Type of PCR Cre NC_8 GGCGTCTTCCGC GTGCCCCTCGTTTG Standard PCR LoUcp CCGGGCTGTCTCCGCGG GGCTGTTCGCCCGGCC Standard PCR
Supplementary Table. Primers used for PCR and qpcr Primer Name ccession Number Fwd Rev Type of PCR Cre NC_8 GGCGTCTTCCGC GTGCCCCTCGTTTG Standard PCR LoUcp CCGGGCTGTCTCCGCGG GGCTGTTCGCCCGGCC Standard PCR
GRANULOLYSIS IN A CELLS OF ENDOCRINE PANCREAS AND EXPERIMENTAL DIABETES IN ANIMALS
 Published Online: 1 August, 1968 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.38.2.462 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on December 25, 2018 GRANULOLYSIS IN A CELLS OF ENDOCRINE PANCREAS IN SPONTANEOUS AND EXPERIMENTAL
Published Online: 1 August, 1968 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.38.2.462 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on December 25, 2018 GRANULOLYSIS IN A CELLS OF ENDOCRINE PANCREAS IN SPONTANEOUS AND EXPERIMENTAL
THE ACTION OF PHYSOSTIGMINE AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF CHOLINESTERASES IN THE CHICKEN OESOPHAGUS
 Br. J. Phannac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 531-536. THE ACTION OF PHYSOSTIGMINE AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF CHOLINESTERASES IN THE CHICKEN OESOPHAGUS BY A. L. BARTLET AND T. HASSAN From the Department of Veterinary
Br. J. Phannac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 531-536. THE ACTION OF PHYSOSTIGMINE AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF CHOLINESTERASES IN THE CHICKEN OESOPHAGUS BY A. L. BARTLET AND T. HASSAN From the Department of Veterinary
AUGMENTATIVE EFFECT OF PROSTAGLANDIN E 1 ON PENTOBARBITAL HYPNOSIS MEDIATED BY 5-HT IN CHICKS
 Explor. Anim. Med. Res., Vol. 1, Issue - 2, 2012. p- 145-150 AUGMENTATIVE EFFECT OF PROSTAGLANDIN E 1 ON PENTOBARBITAL HYPNOSIS MEDIATED BY 5-HT IN CHICKS Amalendu Chanda 1, A.K Chakraborty 1, T.K. Mandal
Explor. Anim. Med. Res., Vol. 1, Issue - 2, 2012. p- 145-150 AUGMENTATIVE EFFECT OF PROSTAGLANDIN E 1 ON PENTOBARBITAL HYPNOSIS MEDIATED BY 5-HT IN CHICKS Amalendu Chanda 1, A.K Chakraborty 1, T.K. Mandal
On the role of central nervous system catecholamines and 5-hydroxytryptamine in the nialamide-induced behavioural syndrome
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1972), 46, 3245. On the role of central nervous system catecholamines and 5-hydroxytryptamine in the nialamide-induced behavioural syndrome K. MODIGH AND T. H. SVENSSON Department of Pharmacology,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1972), 46, 3245. On the role of central nervous system catecholamines and 5-hydroxytryptamine in the nialamide-induced behavioural syndrome K. MODIGH AND T. H. SVENSSON Department of Pharmacology,
Relationship between rat brain and cisternal CSF
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 239-243 Relationship between rat brain and cisternal CSF tryptophan concentrations' SIMON N. YOUNG,2 PIERRE ETIENNE,3 AND THEODORE L. SOURKES
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 239-243 Relationship between rat brain and cisternal CSF tryptophan concentrations' SIMON N. YOUNG,2 PIERRE ETIENNE,3 AND THEODORE L. SOURKES
Adrenergic agonists Sympathomimetic drugs. ANS Pharmacology Lecture 4 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy/University of Sulaimani
 Adrenergic agonists Sympathomimetic drugs ANS Pharmacology Lecture 4 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy/University of Sulaimani 2017-2018 Adrenergic agonists The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that
Adrenergic agonists Sympathomimetic drugs ANS Pharmacology Lecture 4 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy/University of Sulaimani 2017-2018 Adrenergic agonists The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that
Sympathetic Innervation of the Juxtaglomerular Cells of the Kidney
 Sympathetic Innervation of the Juxtaglomerular Cells of the Kidney By Jan Wagermark, M.D., Urban Ungerstedt, M.D., and Arne Ljungqvist, M.D., Ph.D. ABSTRACT Combination of a histochemical fluorescence
Sympathetic Innervation of the Juxtaglomerular Cells of the Kidney By Jan Wagermark, M.D., Urban Ungerstedt, M.D., and Arne Ljungqvist, M.D., Ph.D. ABSTRACT Combination of a histochemical fluorescence
RELATIONS BETWEEN INSULIN AND PITUITARY HORMONES IN AMINO ACID METABOLISM
 RELATIONS BETWEEN INSULIN AND PITUITARY HORMONES IN AMINO ACID METABOLISM BY WILLIAM D. LOTSPEICH* WITH THE TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE OF JOAN B. SHELTON (From the Department of Physiology, Syracuse University
RELATIONS BETWEEN INSULIN AND PITUITARY HORMONES IN AMINO ACID METABOLISM BY WILLIAM D. LOTSPEICH* WITH THE TECHNICAL ASSISTANCE OF JOAN B. SHELTON (From the Department of Physiology, Syracuse University
Monday, 7 th of July 2008 ( ) University of Buea MED30. (GENERAL ENDOCRINOLOGY) Exam ( )
 .. Monday, 7 th of July 2008 (8 30-11. 30 ) Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea MED30 304 Programme in Medicine (GENERAL ENDOCRINOLOGY) Exam (2007-2008).. Multiple Choice Identify the letter
.. Monday, 7 th of July 2008 (8 30-11. 30 ) Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea MED30 304 Programme in Medicine (GENERAL ENDOCRINOLOGY) Exam (2007-2008).. Multiple Choice Identify the letter
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells.
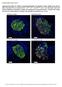 Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
Supplementary Figure S1. Distinct compartmentalization of proinsulin in obese db/db mouse islet ß- cells. Pancreata from 16-weeks-old 6J +/+, 6J db/db, KS +/+ and KS db/db mice were harvested, fixed with
About This Chapter. Hormones The classification of hormones Control of hormone release Hormone interactions Endocrine pathologies Hormone evolution
 About This Chapter Hormones The classification of hormones Control of hormone release Hormone interactions Endocrine pathologies Hormone evolution Hormones: Function Control Rates of enzymatic reactions
About This Chapter Hormones The classification of hormones Control of hormone release Hormone interactions Endocrine pathologies Hormone evolution Hormones: Function Control Rates of enzymatic reactions
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Neurotransmitter Systems III Neurochemistry Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important
Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets
 Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets Gene 5 Forward 3 5 Reverse 3.T. Product (bp) ( C) mnox1 GTTCTTGGGCTGCCTTGG GCTGGGGCGGCGG 60 300 mnoxa1 GCTTTGCCGCGTGC GGTTCGGGTCCTTTGTGC
Supplementary Table 1. Primer sequences for conventional RT-PCR on mouse islets Gene 5 Forward 3 5 Reverse 3.T. Product (bp) ( C) mnox1 GTTCTTGGGCTGCCTTGG GCTGGGGCGGCGG 60 300 mnoxa1 GCTTTGCCGCGTGC GGTTCGGGTCCTTTGTGC
Pharmacologyonline 2: (2009) Pharmacodynamic Drug Interaction of Gliclazide and Mexiletine in Rats
 Pharmacodynamic Drug Interaction of Gliclazide and Mexiletine in Rats K. Abedulla Khan 1, S. Satyanarayana 2, K. Eswar Kumar 2, K. Pavan Kumar 1, K. Anupama 1 1 Sultan-ul-uloom College of pharmacy, Banjarahills,
Pharmacodynamic Drug Interaction of Gliclazide and Mexiletine in Rats K. Abedulla Khan 1, S. Satyanarayana 2, K. Eswar Kumar 2, K. Pavan Kumar 1, K. Anupama 1 1 Sultan-ul-uloom College of pharmacy, Banjarahills,
In Vitro Studies on Insulin Secretion in the Genetically Obese Mouse
 Diabetologia 9, 447--452 (1973) 9 by Springer-Verlag 1973 In Vitro Studies on Insulin Secretion in the Genetically Obese Mouse A. Beloff-Chain, M.E. Newman and K.R.L. Mansford Department of Biochemistry,
Diabetologia 9, 447--452 (1973) 9 by Springer-Verlag 1973 In Vitro Studies on Insulin Secretion in the Genetically Obese Mouse A. Beloff-Chain, M.E. Newman and K.R.L. Mansford Department of Biochemistry,
Glucose Homeostasis. Liver. Glucose. Muscle, Fat. Pancreatic Islet. Glucose utilization. Glucose production, storage Insulin Glucagon
 Glucose Homeostasis Liver Glucose Glucose utilization Glucose production, storage Insulin Glucagon Muscle, Fat Pancreatic Islet Classification of Diabetes Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes Other types of
Glucose Homeostasis Liver Glucose Glucose utilization Glucose production, storage Insulin Glucagon Muscle, Fat Pancreatic Islet Classification of Diabetes Type 1 diabetes Type 2 diabetes Other types of
Neurotransmitters acting on G-protein coupled receptors
 Neurotransmitters acting on G-protein coupled receptors Part 2: Serotonin and Histamine BIOGENIC AMINES Monoamines Diamine Indolamines: Serotonin Basic Neurochemistry. FIGURE 15-1: Chemical structure of
Neurotransmitters acting on G-protein coupled receptors Part 2: Serotonin and Histamine BIOGENIC AMINES Monoamines Diamine Indolamines: Serotonin Basic Neurochemistry. FIGURE 15-1: Chemical structure of
Impaired glucose tolerance and growth hormone in chronic liver disease
 Gut, 1981, 22, 3135 Impaired glucose tolerance and growth hormone in chronic liver disease W J RILY* AND V J McCANN From the Department of Biochemistry and Diabetic Unit, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Western
Gut, 1981, 22, 3135 Impaired glucose tolerance and growth hormone in chronic liver disease W J RILY* AND V J McCANN From the Department of Biochemistry and Diabetic Unit, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Western
Interrelationship between Angiotensin Catecholamines. Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Masaru MAEBASHI, M.D., Koji GOTO, M.D., and Kaoru YOSHINAGA, M.D.
 Interrelationship between Angiotensin and Catecholamines Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Masaru MAEBASHI, M.D., Koji GOTO, M.D., and Kaoru YOSHINAGA, M.D. SUMMARY Urinary catecholamines were measured with an attempt
Interrelationship between Angiotensin and Catecholamines Tatsuo SATO, M.D., Masaru MAEBASHI, M.D., Koji GOTO, M.D., and Kaoru YOSHINAGA, M.D. SUMMARY Urinary catecholamines were measured with an attempt
Effect of Cobalt Chloride on Blood Glucose, Plasma Insulin and Lipids in Rabbits.
 Effect of Cobalt Chloride on Blood Glucose, Plasma Insulin and Lipids in Rabbits. Masayoshi Ohmichi, Hiroyuki Morita, Yoko Onuma and Shigeo Koike Department of Hygiene, School of Medicine, Showa University,
Effect of Cobalt Chloride on Blood Glucose, Plasma Insulin and Lipids in Rabbits. Masayoshi Ohmichi, Hiroyuki Morita, Yoko Onuma and Shigeo Koike Department of Hygiene, School of Medicine, Showa University,
Monoamine oxidase in sympathetic nerves: a transmitter specific enzyme type
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 43, 814-818. Monoamine oxidase in sympathetic nerves: a transmitter specific enzyme type C. GORIDIS AND N. H. NEFF Laboratory of Preclinical Pharmacology, National Institute of
Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 43, 814-818. Monoamine oxidase in sympathetic nerves: a transmitter specific enzyme type C. GORIDIS AND N. H. NEFF Laboratory of Preclinical Pharmacology, National Institute of
norepinephrinee." 2 PNMT activity is stimulated by certain adrenocortical markedly,3' 4 but can be restored to normal by the administration of
 IMPAIRED SECRETION OF EPINEPHRINE IN RESPONSE TO INSULIN AMONG HYPOPHYSECTOMIZED DOGS* BY RICHARD J. WURTMAN, ALFRED CASPER, LARISSA A. POHORECKY, AND FREDERIC C. BARTTER DEPARTMENT OF NUTRITION AND FOOD
IMPAIRED SECRETION OF EPINEPHRINE IN RESPONSE TO INSULIN AMONG HYPOPHYSECTOMIZED DOGS* BY RICHARD J. WURTMAN, ALFRED CASPER, LARISSA A. POHORECKY, AND FREDERIC C. BARTTER DEPARTMENT OF NUTRITION AND FOOD
Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1982
 Diabetologia (1982) 22:245-249 Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1982 Twenty-Four Hour Profiles of Plasma C-Peptide in Type 1 (Insulin-Dependent) Diabetic Children G. A. Werther 1 *, R. C. Turner 2, P. A.
Diabetologia (1982) 22:245-249 Diabetologia 9 Springer-Verlag 1982 Twenty-Four Hour Profiles of Plasma C-Peptide in Type 1 (Insulin-Dependent) Diabetic Children G. A. Werther 1 *, R. C. Turner 2, P. A.
Physiological processes controlled by hormones?
 : the study of hormones, their receptors, the intracellular signaling pathways they invoke, and the diseases and conditions associated with them. What are hormones? Major endocrine glands? Fig 7-2 Physiological
: the study of hormones, their receptors, the intracellular signaling pathways they invoke, and the diseases and conditions associated with them. What are hormones? Major endocrine glands? Fig 7-2 Physiological
Part 2: How Your Brain and Nervous System Work
 Part 2: How Your Brain and Nervous System Work with Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one onone relationship with a qualified
Part 2: How Your Brain and Nervous System Work with Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one onone relationship with a qualified
INTESTINAL ABSORPTION OF AMINO ACIDS I. THE EFFECT OF VITAMIN B6 ON THE ABSORPTION OF L-AMINO ACIDS THROUGH THE INTESTINE
 The Journal of Biochemistry, Vol. 47, No. 1, 1960 INTESTINAL ABSORPTION OF AMINO ACIDS I. THE EFFECT OF VITAMIN B6 ON THE ABSORPTION OF L-AMINO ACIDS THROUGH THE INTESTINE By HITOSHI AKEDO, TADASHI SUGAWA,
The Journal of Biochemistry, Vol. 47, No. 1, 1960 INTESTINAL ABSORPTION OF AMINO ACIDS I. THE EFFECT OF VITAMIN B6 ON THE ABSORPTION OF L-AMINO ACIDS THROUGH THE INTESTINE By HITOSHI AKEDO, TADASHI SUGAWA,
Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species
 Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Disappearance of small vesicles from adrenergic nerve endings in the rat vas deferens caused by red back spider venom
 Journal of Neurocytology z, 465-469 (I973) Disappearance of small vesicles from adrenergic nerve endings in the rat vas deferens caused by red back spider venom R. C. HAMILTON 1 and P. M. ROBINSON~ 1Commonwealth
Journal of Neurocytology z, 465-469 (I973) Disappearance of small vesicles from adrenergic nerve endings in the rat vas deferens caused by red back spider venom R. C. HAMILTON 1 and P. M. ROBINSON~ 1Commonwealth
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum
 Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
ENERGY FROM INGESTED NUTREINTS MAY BE USED IMMEDIATELY OR STORED
 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 SHORT TERM METABOLISM [METABOLISM] Learning Objectives: Identify primary energy stores of the body Differentiate the metabolic processes of the fed and fasted states Explain
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 SHORT TERM METABOLISM [METABOLISM] Learning Objectives: Identify primary energy stores of the body Differentiate the metabolic processes of the fed and fasted states Explain
Hormones, Receptors and Receptor-Hormone Interactions
 Classification of Hormones Hormones, Receptors and Receptor-Hormone Interactions Synthesis of Protein Hormones and Amine Hormones Hormone Activity Locations of Receptors Mechanisms of Hormone Action Types
Classification of Hormones Hormones, Receptors and Receptor-Hormone Interactions Synthesis of Protein Hormones and Amine Hormones Hormone Activity Locations of Receptors Mechanisms of Hormone Action Types
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum
 Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Study of the main chemical components of Ganoderma lucidum Yasuo Komota et al Tokyo Medical and Dental University [Purpose] As part of the means for exerting quality control on Ganoderma lucidum 50% ethanol
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Stimulation of Active K + Transport by Anti-L Antibodies in Trypsin-Treated Low Potassium Sheep Erythrocytes
 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Stimulation of Active K + Transport by Anti-L Antibodies in Trypsin-Treated Low Potassium Sheep Erythrocytes Dear Sir: In this letter we attempt to resolve a discrepancy on the effect
LETTER TO THE EDITOR Stimulation of Active K + Transport by Anti-L Antibodies in Trypsin-Treated Low Potassium Sheep Erythrocytes Dear Sir: In this letter we attempt to resolve a discrepancy on the effect
Diabetologia 9 by Springer-Verlag 1978
 Diabetologia 14, 223-227 (1978) Diabetologia 9 by Springer-Verlag 1978 Originals Sustained Insulin-Induced Remissions of Juvenile Diabetes by Means of an External Artificial Pancreas J. Mirouze, J. L.
Diabetologia 14, 223-227 (1978) Diabetologia 9 by Springer-Verlag 1978 Originals Sustained Insulin-Induced Remissions of Juvenile Diabetes by Means of an External Artificial Pancreas J. Mirouze, J. L.
The Nervous System Mark Stanford, Ph.D.
 The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
Fluoro: MAO TM. Monoamine Oxidase A & B Detection Kit. Contact Information. This version to be used for kits shipped on or after April 27 th 2006
 Fluoro: MAO TM Monoamine Oxidase A & B Detection Kit This version to be used for kits shipped on or after April 27 th 2006 Contact Information Notes Revised protocol 5/06 Updated 1/07 I. Assay Principle:
Fluoro: MAO TM Monoamine Oxidase A & B Detection Kit This version to be used for kits shipped on or after April 27 th 2006 Contact Information Notes Revised protocol 5/06 Updated 1/07 I. Assay Principle:
Goals and Challenges of Communication. Communication and Signal Transduction. How Do Cells Communicate?
 Goals and Challenges of Communication Reaching (only) the correct recipient(s) Imparting correct information Timeliness Causing the desired effect Effective termination Communication and Signal Transduction
Goals and Challenges of Communication Reaching (only) the correct recipient(s) Imparting correct information Timeliness Causing the desired effect Effective termination Communication and Signal Transduction
Effects of Calcium Antagonists on Insulin Release
 Effects of Calcium Antagonists on Insulin Release Prof. Mashori Ghulam Rasool, Pakistan Introduction Cardiovascular diseases are the main cause of death in many countries and pose health problems not only
Effects of Calcium Antagonists on Insulin Release Prof. Mashori Ghulam Rasool, Pakistan Introduction Cardiovascular diseases are the main cause of death in many countries and pose health problems not only
Distribution of Pancreatic Polypeptide in the Head of the Human Pancreas. By Andrew Kringas
 Distribution of Pancreatic Polypeptide in the Head of the Human Pancreas By Andrew Kringas Diabetes (Diabetes mellitus) A condition when the body doesn t properly respond to insulin Type 1 Type 2 Gestational
Distribution of Pancreatic Polypeptide in the Head of the Human Pancreas By Andrew Kringas Diabetes (Diabetes mellitus) A condition when the body doesn t properly respond to insulin Type 1 Type 2 Gestational
Insulin release, insulin sensitivity, and glucose intolerance (early diabetes/pathogenesis)
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 77, No. 12, pp. 7425-7429, December 1980 Medical Sciences nsulin release, insulin sensitivity, and glucose intolerance (early diabetes/pathogenesis) SUAD EFENDt, ALEXANDRE
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 77, No. 12, pp. 7425-7429, December 1980 Medical Sciences nsulin release, insulin sensitivity, and glucose intolerance (early diabetes/pathogenesis) SUAD EFENDt, ALEXANDRE
INDUCTION OF OVULATION IN URETHANE-TREATED RATS
 5 INDUCTION OF OVULATION IN URETHANE-TREATED RATS Ronald D. Johnson* and Barbara Shirley Faculty of Natural Sciences, University of Tulsa, Tulsa, Oklahoma 74104 Subcutaneous injection of urethane (1 g/kg
5 INDUCTION OF OVULATION IN URETHANE-TREATED RATS Ronald D. Johnson* and Barbara Shirley Faculty of Natural Sciences, University of Tulsa, Tulsa, Oklahoma 74104 Subcutaneous injection of urethane (1 g/kg
Comprehensive assessments of neuroendocrine status. Salivary Sex Steroid Hormones and Adrenal/HPA Axis Function
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Comprehensive assessments of neuroendocrine status Salivary Sex Steroid Hormones and Adrenal/HPA Axis Function Neuro-Biogenic Amine and Metabolite Profiles (Neurotransmitters) Metabolomic
ENDOCRINOLOGY Comprehensive assessments of neuroendocrine status Salivary Sex Steroid Hormones and Adrenal/HPA Axis Function Neuro-Biogenic Amine and Metabolite Profiles (Neurotransmitters) Metabolomic
Clinical abstracts. Diabetes
 Clinical abstracts Diabetes Antidiabetic Activity Of Aloes: Preliminary Clinical & Experimental Observations Ghannam N; Kingston M; Al-Meshaal IA; Tariq M; Parman NS; Woodhouse N Horm Res 24(4):288-94
Clinical abstracts Diabetes Antidiabetic Activity Of Aloes: Preliminary Clinical & Experimental Observations Ghannam N; Kingston M; Al-Meshaal IA; Tariq M; Parman NS; Woodhouse N Horm Res 24(4):288-94
neoplastic mast cells (Giarman, Potter & Day, 1960). According to Toh
 J. Phy8iol. (1963), 165, pp. 83-88 83 Printed in Great Britain RELEASE OF HISTAMINE FROM SPLEEN BY KIDNEY EXTRACT, RESERPINE AND COMPOUND 48/80 BY ANNIE B. ELLIOTT From the Department of Physiology, University
J. Phy8iol. (1963), 165, pp. 83-88 83 Printed in Great Britain RELEASE OF HISTAMINE FROM SPLEEN BY KIDNEY EXTRACT, RESERPINE AND COMPOUND 48/80 BY ANNIE B. ELLIOTT From the Department of Physiology, University
History of Investigation
 Acini - Pancreatic juice (1º) (2º) Secretions- neuronal and hormonal mechanisms 1) Secretin - bicarbonate rich 2) Cholecystokinin - enzyme rich Islets of Langerhans (contain 4 cell types) Alpha cells (α)-
Acini - Pancreatic juice (1º) (2º) Secretions- neuronal and hormonal mechanisms 1) Secretin - bicarbonate rich 2) Cholecystokinin - enzyme rich Islets of Langerhans (contain 4 cell types) Alpha cells (α)-
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
METABOLIC EFFECTS OF SULFONYLUREAS IN NORMAL MEN AND IN VARIOUS TYPES OF DIABETIC PATIENTS*
 METABOLC EFFECTS OF SULFONYLUREAS N NORMAL MEN AND N VAROUS TYPES OF DABETC PATENTS* By Stefan S. Fajans, Lawrence H. Louis, Allen R. Hennest, Bernard0 L. Wajchenbergt, Robert D. Johnson, Robert D. Gittler,
METABOLC EFFECTS OF SULFONYLUREAS N NORMAL MEN AND N VAROUS TYPES OF DABETC PATENTS* By Stefan S. Fajans, Lawrence H. Louis, Allen R. Hennest, Bernard0 L. Wajchenbergt, Robert D. Johnson, Robert D. Gittler,
BIO 5 Human Physiology Pre-Lab Assignment #1 Exercise #2: Acids, Bases, Buffers
 Pre-Lab Assignment #1 Exercise #2: Acids, Bases, Buffers 1. What is the chemical equation for converting carbon dioxide into bicarbonate ion? 2. What is the source of carbon dioxide in this lab exercise?
Pre-Lab Assignment #1 Exercise #2: Acids, Bases, Buffers 1. What is the chemical equation for converting carbon dioxide into bicarbonate ion? 2. What is the source of carbon dioxide in this lab exercise?
PLASMA INSULIN ACTIVITY IN DIABETICS
 266 PLASMA INSULIN ACTIVITY IN DIABETICS By J. VALLANCE-OWEN, M.A., M.D.(CANTAB.), M.R.C.P. Department of Medicine, King's College, University of Durham, Newcastle upon Tyne A reasonably accurate and reliable
266 PLASMA INSULIN ACTIVITY IN DIABETICS By J. VALLANCE-OWEN, M.A., M.D.(CANTAB.), M.R.C.P. Department of Medicine, King's College, University of Durham, Newcastle upon Tyne A reasonably accurate and reliable
Week 3, Lecture 5a. Pathophysiology of Diabetes. Simin Liu, MD, ScD
 Week 3, Lecture 5a Pathophysiology of Diabetes Simin Liu, MD, ScD General Model of Peptide Hormone Action Hormone Plasma Membrane Activated Nucleus Cellular Trafficking Enzymes Inhibited Receptor Effector
Week 3, Lecture 5a Pathophysiology of Diabetes Simin Liu, MD, ScD General Model of Peptide Hormone Action Hormone Plasma Membrane Activated Nucleus Cellular Trafficking Enzymes Inhibited Receptor Effector
EFFECTS OF VANADATE ON OLEIC ACID INDUCED INSULIN RESISTANCE IN CULTURED RAT HEPATOCYTES
 1 Department of Physiology, School of Dentistry, University of Zagreb, Gunduliæeva 5, HR-1 Zagreb, Croatia Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, University of Zagreb, Šalata 3, HR-1 Zagreb, Croatia
1 Department of Physiology, School of Dentistry, University of Zagreb, Gunduliæeva 5, HR-1 Zagreb, Croatia Department of Physiology, School of Medicine, University of Zagreb, Šalata 3, HR-1 Zagreb, Croatia
Fig. S4. Current-voltage relations of iglurs. A-C: time courses of currents evoked by 100 ms pulses
 Fig. S1. Immunohistochemical detection of iglur2 protein in single islet cells. A: α cells identified using glucagon-specific antibody express the iglur2 subtype of AMPA receptor. 24 out of 26 identified
Fig. S1. Immunohistochemical detection of iglur2 protein in single islet cells. A: α cells identified using glucagon-specific antibody express the iglur2 subtype of AMPA receptor. 24 out of 26 identified
Insulin Resistance. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Insulin Resistance Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Insulin resistance: a subnormal biological response to insulin. Defects of either insulin secretion or insulin action can cause diabetes mellitus. Insulin-dependent
Insulin Resistance Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Insulin resistance: a subnormal biological response to insulin. Defects of either insulin secretion or insulin action can cause diabetes mellitus. Insulin-dependent
suggesting that the release of noradrenaline from sympathetic fibres was dependent on the concentration of Ca2+ outside the fibre.
 214 J. Phy8iol. (1965), 181, pp. 214-223 With 4 text-figurem Printed in Great Britain THE RELEASE OF NORADRENALINE FROM SYMPATHETIC FIBRES IN RELATION TO CALCIUM CONCENTRATION BY J. H. BURN AND W. R. GIBBONS
214 J. Phy8iol. (1965), 181, pp. 214-223 With 4 text-figurem Printed in Great Britain THE RELEASE OF NORADRENALINE FROM SYMPATHETIC FIBRES IN RELATION TO CALCIUM CONCENTRATION BY J. H. BURN AND W. R. GIBBONS
ROLE OF ADRENAL HORMONES IN MAINTAINING TISSUE STORES OF NORADRENALINE DURING INCREASED SYMPATHETIC ACTIVITY
 Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1966), 27, 532-535. ROLE OF ADRENAL HORMONES IN MAINTAINING TISSUE STORES OF NORADRENALINE DURING INCREASED SYMPATHETIC ACTIVITY BY V. M. AVAKIAN* AND MARTHE VOGT From the Agricultural
Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1966), 27, 532-535. ROLE OF ADRENAL HORMONES IN MAINTAINING TISSUE STORES OF NORADRENALINE DURING INCREASED SYMPATHETIC ACTIVITY BY V. M. AVAKIAN* AND MARTHE VOGT From the Agricultural
Chapter 9. The Endocrine System. Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Intro to the Endocrine System Chief Complaint:8-year-old girl with excessive thirst, frequent
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Intro to the Endocrine System Chief Complaint:8-year-old girl with excessive thirst, frequent
Elevated Serum Human Growth Hormone and
 Elevated Serum Human Growth Hormone and Decreased Serum Insulin in Prediabetic Males after Intravenous Tolbutamide and Glucose G. BODEN, J. S. SOELDNER, R. E. GLEASON, and A. MARBLE From the Elliott P.
Elevated Serum Human Growth Hormone and Decreased Serum Insulin in Prediabetic Males after Intravenous Tolbutamide and Glucose G. BODEN, J. S. SOELDNER, R. E. GLEASON, and A. MARBLE From the Elliott P.
Chapter 6 Communication, Integration, and Homeostasis
 Chapter 6 Communication, Integration, and Homeostasis About This Chapter Cell-to-cell communication Signal pathways Novel signal molecules Modulation of signal pathways Homeostatic reflex pathways Cell-to-Cell
Chapter 6 Communication, Integration, and Homeostasis About This Chapter Cell-to-cell communication Signal pathways Novel signal molecules Modulation of signal pathways Homeostatic reflex pathways Cell-to-Cell
I. Introduction. II. Characteristics
 YK050 Rat Leptin ELISA I. Introduction Leptin, which is a product of ob gene, is a protein consisting of 167 amino acids and it is secreted from white adipose tissue. It is known that leptin acts on hypothalamus
YK050 Rat Leptin ELISA I. Introduction Leptin, which is a product of ob gene, is a protein consisting of 167 amino acids and it is secreted from white adipose tissue. It is known that leptin acts on hypothalamus
samples and assayed for 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) on the rat stomachstrip preparation. Rectal temperature was monitored continuously.
 J. Phy8iol. (1967), 188, pp. 131-140 131 With 3 text-fitgurem Printed in Great Britain MONOAMINE OXIDASE INHIBITION: EFFECT ON 5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE OUTPUT FROM PERFUSED THIRD VENTRICLE AND BODY TEMPERATURE
J. Phy8iol. (1967), 188, pp. 131-140 131 With 3 text-fitgurem Printed in Great Britain MONOAMINE OXIDASE INHIBITION: EFFECT ON 5-HYDROXYTRYPTAMINE OUTPUT FROM PERFUSED THIRD VENTRICLE AND BODY TEMPERATURE
Diabetologia. NSILA-Carrier Protein Abolishes the Action of Nonsuppressible Insulin-Like Activity (NSILA-S) on Perfused Rat Heart
 Diabetologia 14, 255-259 (1978) Diabetologia 9 by Springer-Verlag 1978 NSLA-Carrier Protein Abolishes the Action of Nonsuppressible nsulin-like Activity (NSLA-S) on Perfused Rat Heart C. Meuli, J. Zapf,
Diabetologia 14, 255-259 (1978) Diabetologia 9 by Springer-Verlag 1978 NSLA-Carrier Protein Abolishes the Action of Nonsuppressible nsulin-like Activity (NSLA-S) on Perfused Rat Heart C. Meuli, J. Zapf,
human anatomy & physiology sampler questions
 human anatomy & physiology sampler questions Please note that there are questions within this set that test material that may not have been covered in your lecture; unless otherwise specified, lecture
human anatomy & physiology sampler questions Please note that there are questions within this set that test material that may not have been covered in your lecture; unless otherwise specified, lecture
2) Storehouse for the hormones produced by the hypothalamus of the brain. 2)
 AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs. morning 4/23 Name: Matching; match the labeled organ with the most appropriate response or identification. Figure 16.1 Using Figure 16.1, match
Pancreas. Endocrine pancreas - Islets of Langerhans A or alpha cells glucagon B or beta cells insulin Delta cells somatostatin
 Endocrine System Pancreas Endocrine pancreas - Islets of Langerhans A or alpha cells glucagon B or beta cells insulin Delta cells somatostatin Glucagon & Metabolism Produced by beta cells of Islets Primary
Endocrine System Pancreas Endocrine pancreas - Islets of Langerhans A or alpha cells glucagon B or beta cells insulin Delta cells somatostatin Glucagon & Metabolism Produced by beta cells of Islets Primary
Scanning Electron Microscopic Observations on the Sperm Penetration through the Zona Pellucida of Mouse Oocytes Fertilized in vitro
 Scanning Electron Microscopic Observations on the Sperm Penetration through the Zona Pellucida of Mouse Oocytes Fertilized in vitro Masatsugu MOTOMURA and Yutaka TOYODA School of Veterinary Medicine and
Scanning Electron Microscopic Observations on the Sperm Penetration through the Zona Pellucida of Mouse Oocytes Fertilized in vitro Masatsugu MOTOMURA and Yutaka TOYODA School of Veterinary Medicine and
My Journey in Endocrinology. Samuel Cataland M.D
 My Journey in Endocrinology Samuel Cataland M.D. 1968-2015 Drs Berson M.D. Yalow phd Insulin Radioimmunoassay Nobel Prize Physiology or Medicine 1977 Rosalyn Yalow: Radioimmunoassay Technology Andrew Schally
My Journey in Endocrinology Samuel Cataland M.D. 1968-2015 Drs Berson M.D. Yalow phd Insulin Radioimmunoassay Nobel Prize Physiology or Medicine 1977 Rosalyn Yalow: Radioimmunoassay Technology Andrew Schally
2017, Pharmapex USA, A Member of Apex Group of Companies
 2017, Pharmapex USA, A Member of Apex Group of Companies Natural Blood Health Aid uses a proprietary and licensed Virgin Isolate Technology, invented which recreates the Ayurvedic method used in ancient
2017, Pharmapex USA, A Member of Apex Group of Companies Natural Blood Health Aid uses a proprietary and licensed Virgin Isolate Technology, invented which recreates the Ayurvedic method used in ancient
