Orexins (hypocretins) are novel neuropeptides. Glucose Regulates the Release of Orexin-A From the Endocrine Pancreas
|
|
|
- Moris Ramsey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Glucose Regulates the Release of Orexin-A From the Endocrine Pancreas Raogo Ouedraogo, 1 Erik Näslund, 2 and Annette L. Kirchgessner 1 Orexins (hypocretins) are novel neuropeptides that appear to play a role in the regulation of energy balances. Orexin-A (OXA) increases food intake in rodents, and fasting activates OXA neurons in both the lateral hypothalamic area and gut. OXA is also found in the endocrine pancreas; however, little is known about its release or functional significance. In this study, we show that depolarizing stimuli evoke the release of OXA from rat pancreatic islets in a calcium-dependent manner. Moreover, OXA release is stimulated by low glucose (2.8 mmol/l), similar to glucagon secretion, and inhibited by high glucose (16.7 mmol/l). Fasting increases plasma OXA, supporting the idea that orexin is released in response to hypoglycemia. Cells that secrete glucagon and insulin contain OXA and both cell types express orexin receptors. OXA increases glucagon secretion and decreases glucose-stimulated insulin release from isolated islets. OXA infusion increases plasma glucagon and glucose levels and decreases plasma insulin in fasted rats. We conclude that orexin-containing islet cells, like those in the brain and gut, are glucosensitive and part of a network of glucose sensing cells that becomes activated when blood glucose levels fall. OXA may modulate islet hormone secretion to maintain blood glucose levels during fasting. Diabetes 52: , 2003 Orexins (hypocretins) are novel neuropeptides that play a role in arousal and the regulation of energy balances (1 3). Orexin-A (OXA) and -B are 33- and 28-residue peptides, respectively, that are isolated from the rat hypothalamus and named for their ability to stimulate feeding when injected into the brain (2). Their common precursor, prepro-orexin, is expressed in a specific population of neurons in and around the lateral hypothalamic area (LHA) (2), a region classically implicated in the control of mammalian feeding behavior (4). The LHA contains glucosensitive neurons that are stimulated by falls in circulating glucose (5) and From the 1 Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, State University of New York, Downstate Medical Center, Brooklyn, New York; and the 2 Division of Surgery, Karolinska Institutet, Danderyd Hospital, Stockholm, Sweden. Address correspondence and reprint requests to Dr. Annette Kirchgessner, Neurology and GI CEDD, GlaxoSmithKline, New Frontiers Science Park, Third Avenue, Harlow, Essex CM19 5AW. annette_2_kirchgessner@gsk.com. Received for publication 19 June 2002 and accepted in revised form 9 October A.L.K. is employed by and holds stock in GlaxoSmithKline. EIA, enzyme immunoassay; ENS, enteric nervous system; FITC, fluorescein isothiocyanate; HPLC, high-performance liquid chromatography; IR-OXA, immunoreactive Orexin-A; LHA, lateral hypothalamic area; NTS, nucleus of the solitary tract; OXA, Orexin-A; OXR1, orexin receptor 1; TFA, trifluoroacetic acid; TTX, tetrodotoxin. inhibited by prandial signals, such as the presence of food in the gut and/or a rise in portal glucose concentration (4). Previous studies have suggested that orexin neurons might correspond to this neuronal population, since orexin neurons are activated by hypoglycemia (6) and increased hypothalamic prepro-orexin mrna levels are observed in response to fasting (1,7); however, glucosensitive neurons do not contain OXA (8). They are excited by the peptide (8), implying that orexin acts as a neuromodulator at glucosensitive cells, stimulating them under conditions of hunger. Glucosensitive neurons are also found in regions outside the hypothalamus, including the nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS) (9) and enteric nervous system (ENS) (10). The NTS relays visceral afferent signals to the LHA (8). Orexin fibers are distributed extensively in the NTS (11), and glucosensitive neurons are activated by the same conditions that stimulate orexin neurons in the LHA (6). The ENS participates in the regulation of food intake by directly sensing, integrating, and regulating the machinery of the gut involved in energy metabolism (3). We have previously shown that orexin neurons are located throughout the ENS and, like their hypothalamic counterparts, are activated by fasting (12). Orexins may sense nutritional status in the gut, modulating secretion and motility in order to prime the digestive tract in preparation for food ingestion and energy uptake. Endocrine cells in the gastric and intestinal mucosa (12,13), as well as in the pancreas (12), also contain orexins; therefore, orexins may function as circulating hormones and/or paracrine or autocrine transmitters. The presence of OXA in human plasma supports this idea (14,15). Little is known about the regulation and role of the orexins in the endocrine pancreas. We have previously shown that OXA and orexin receptor immunoreactivity is displayed by the insulin-secreting -cells in the rat pancreas (12). OXA release in the extracellular medium might allow -cells to regulate neighboring cells that express orexin receptors. The present study was conducted to determine whether 1) endogenous OXA is secreted from rat pancreatic islets, 2) OXA release is modulated by extracellular glucose concentrations, and 3) OXA affects pancreatic hormone secretion. RESEARCH DESIGN AND METHODS Animals. Adult female or male Sprague-Dawley rats ( g) were used. Animals were killed by CO 2 inhalation and exsanguinated. The Animal Care and Use Committee of the State University of New York Downstate Medical Center and the local ethics committee for animal experimentation in Stockholm, Sweden, approved the experimental protocols. Isolation and culture of pancreatic islets. Pancreatic islets were isolated by digestion with collagenase as previously described (16). Islets were DIABETES, VOL. 52, JANUARY
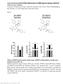
2 OXA RELEASE FROM ISLETS FIG. 1. Effects of depolarizing stimuli on OXA release from islets isolated from the rat pancreas. A: Reversed-phase HPLC. Islet IR-OXA elutes as a single peak that is superimposible with the peak observed with commercial rat OXA. B: High KCl (80 mmol/l) increases the release of IR-OXA. The effect of high KCl is completely blocked by the L-type Ca 2 channel blocker nifedipine (25 mol/l). C: Veratridine increases the release of IR-OXA in a concentration-dependent manner, and the effect is blocked by TTX (3 mol/l). Results are expressed as percentages of control IR-OXA release in the presence of 2.8 mmol/l glucose ( fmol islet 1 min 1, n 8). *P < 0.05 vs. control. selected under a dissecting microscope, transferred to Petri dishes, and cultured for h in RPMI-1640 medium (Gibco BRL, Grand Island, NY) supplemented with 10 mmol/l glucose. Static incubation of pancreatic islets. Incubation of pancreatic islets was performed as previously described (16,17). Briefly, groups of 10 islets were preincubated in 1 ml of Krebs bicarbonate-buffered solution (115 mmol/l NaCl, 5 mmol/l KCl, 2.56 mmol/l CaCl 2, 1 mmol/l MgCl 2, and 24 mmol/l NaHCO 3 ) containing 0.5% (wt/vol) albumin (fraction V, radioimmunoassay grade; Sigma Chemical, St. Louis, MO) and 2.8 mmol/l glucose for 30 min at 37 C. The preincubation medium was aspirated and replaced with the same medium in the absence and presence of test compounds. Final incubations were carried out for 90 min at 37 C in a shaking water bath. At the end of the test incubations, the medium was aspirated and stored at 20 C. The effects of high KCl, veratridine (Sigma Chemical), OXA (Peninsula Laboratories, San Carlos, CA), and glucose were studied. In experiments with tetrodotoxin (TTX), diazoxide, and nifedipine (Sigma Chemical), the test substances were present in the medium during both the prestimulation and stimulation incubations. OXA extraction and measurement. Samples were loaded onto a Sep-Pak C18 cartridge (Peninsula Laboratories), which was pretreated with acetonitrile (CH 3 CN) and then washed with 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid (TFA). After washing with TFA, adsorbed peptides in the cartridge were eluted with 60% CH 3 CN/0.1% TFA. The eluate was dried under vacuum in a Speed Vac SC100 Savant apparatus and stored at 20 C until the time of OXA assay. OXA was measured in triplicate using a commercial enzyme immunoassay (EIA) kit (Peninsula Labs) that uses a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against human OXA. The antibody does not cross-react with orexin-b, neuropeptide Y, or leptin. OXA concentrations were determined against a known standard (0 25 ng/ml), and the detection limit of the assay was pg/ml of sample. Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Chromatographic characterization of the extracts was performed by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) using an Aquapore C4 column (BU-300, mm; Aquapore, Bodman, PA). The column was eluted with a linear gradient of CH 3 CN containing 0.1% TFA at a flow rate of 0.7 ml/min. Fractions (0.7 ml) were collected continuously. Each fraction was dried, reconstituted with assay buffer, and assayed. OXA infusion. Rats were anesthetized with sodium pentobarbital (50 mg/kg i.p.; Apoteksbolaget, Stockholm, Sweden) and implanted with a jugular vein catheter for administration of drugs. The catheter was tunneled subcutaneously to exit at the back of the animal s neck. The rats were housed singly and allowed to recover for at least 7 days before experiments were undertaken. During recovery, the rats were trained to accept experimental conditions. Experiments were then carried out in conscious animals placed in Bollman cages after an 18-h fasting period with free access to water. OXA (100 pmol kg 1 min 1 ; Bachem AG, Bubendorf, Switzerland) or vehicle was administered for 20 min using a microinjection pump (CMA 100; CMA Microdialysis, Sǒlna, Sweden). A blood sample was obtained at the termination of the infusion, and insulin and glucagon were measured as described below. For glycemia studies, OXA (80 pmol kg 1 min 1 ) was infused for 60 min. Blood samples were taken at 20-min intervals before, during, and after OXA injection. Vehicle was administered as a control. Blood sampling. Blood was collected in propylene tubes containing EDTA (1 mg/ml blood) and aprotinin (500 KIU/ml), centrifuged, and then stored at 80 C. Plasma-immunoreactive OXA, insulin, and glucagon levels were measured in triplicate. Blood glucose was determined by the glucose oxidase method using a glucose analyzer. Glucagon and insulin measurement. Glucagon was measured using a rat glucagon EIA kit (Peninsula Labs) and human glucagon as standard. Glucagon concentrations were determined against a known standard (0 25 ng/ml), and the detection limit of the assay was pg/ml of sample. Insulin was quantified using High Range Rat Insulin ELISA kit (ALPCO Diagnostics), with rat insulin as standard. The range for insulin measurement was ng/ml with a limit of 3 ng/ml. Immunocytochemistry. The pancreas was fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 mol/l phosphate buffer (ph 7.4), embedded in OCT (TissueTek), and sectioned (10 m) using a cryostat-microtome. To locate proteins in the tissue by immunocytochemistry, preparations were exposed to PBS containing 1% Triton X-100 and 4% horse serum for 30 min. Primary antibodies were against OXA (affinity-purified rabbit polyclonal, diluted 1:500; Alpha Diagnostic Inter- 112 DIABETES, VOL. 52, JANUARY 2003
3 R. OUEDRAOGO, E. NÄSLUND, AND A.L. KIRCHGESSNER FIG. 2. Effects of glucose on IR-OXA, immunoreactive glucagon, and immunoreactive insulin release from isolated pancreatic islets. A: High glucose (16.7 mmol/l) inhibits the release of OXA. In contrast, glucose stimulates the release of insulin and the effect is dose dependently reduced by the ATP-sensitive K channel opener diazoxide. Diazoxide has no effect on the release of OXA. B: Low glucose (2.8 mmol/l) stimulates the release of both OXA and glucagon. Results are expressed as percentages of control IR-OXA ( fmol islet 1 min 1, n 8), immunoreactive (IR) glucagon ( fmol islet 1 min 1, n 8), or immunoreactive insulin ( fmol islet 1 min 1, n 8) release in the presence of 2.8 mmol/l. *P < 0.05 vs. control. national, San Antonio, TX) and orexin receptor 1 (OXR1) (affinity-purified rabbit polyclonal, diluted 1:500; Alpha Diagnostic International) (13) followed by incubation with donkey anti-rabbit secondary antibodies coupled with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) (Jackson ImmunoResearch Labs, West Grove, PA) diluted 1:500 for 3 h. Double labeling was made possible by using primary antibodies raised in different species in conjunction with speciesspecific secondary antibodies (donkey anti-mouse, donkey anti guinea pig; Jackson ImmunoResearch Labs) coupled to contrasting fluorophores FITC or Cy 3 (Kirkegaard and Perry, Gaithesburg, MD). Primary antibodies were against insulin (mouse monoclonal, diluted 1:1,000; ICN ImmunoBiologicals, Lisle, IL) and glucagon (guinea pig polyclonal, diluted 1:1,000; Linco Research). The sections were coverslipped with Vectashield (Vector Labs, Burlingame, CA). No staining was observed in control sections incubated without primary antibody. Sections were examined by using a Radiance 2000 laser scanning confocal microscope (Bio-Rad, San Francisco, CA) attached to an Axioskop 2 microscope (Zeiss, New York). Data analysis. Data are expressed as means SE. Statistical significance was evaluated using ANOVA followed by ad hoc analysis using Tukey s test. Differences were considered significant at P RESULTS Depolarizing stimuli evoke the release of OXA. In the first part of this study, we characterized the in vitro release of immunoreactive OXA (IR-OXA) from isolated islets in response to various depolarizing stimuli. Basal IR-OXA release in the presence of 2.8 mmol/l glucose was fmole islet 1 min 1 (n 8). When characterized by reversed-phase HPLC, islet IR-OXA eluted as a peak that was superimposible with the peak of synthetic OXA (Fig. 1A). Depolarization of the incubated islets with 80 mmol/l KCl induced a 61% (n 8, P 0.05) increase in IR-OXA release over the basal level (Fig. 1B), suggesting that at least some OXA is stored and released via a regulated pathway. The release of IR-OXA was also significantly increased by the alkaloid veratridine, a Na channel activator (Fig. 1C). Veratridine (10 mol/l) induced a 47% (n 5, P 0.05) increase in the release of IR-OXA over the mean basal level. The effect of veratridine was concentration dependent and blocked by the Na channel inhibitor TTX (3 mol/l; % vs % of basal level, n 6) (Fig. 1C). IR-OXA release produced by high KCl (80 mmol/l) was completely inhibited by pretreating islets with the L-type Ca 2 channel blocker nifedipine (25 mol/l, n 8) (Fig. 1B). Thus, the stimulated release of OXA depends on membrane depolarization and Ca 2 influx through L-type Ca 2 channels. The release of OXA is regulated by glucose. Next, we examined whether the release of OXA from islets is regulated by extracellular glucose concentrations. An increase of the glucose concentration from 2.8 to 16.7 mmol/l caused a significant decrease in islet IR-OXA release from to % of control (P 0.05) (Fig. 2A). Insulin release was determined from the same samples that were used to determine OXA release. Insulin secretion increased from to % of control (n 8, P 0.05) (Fig. 2A). The finding that IR-OXA release was still reduced in the presence of the ATP-sensitive K channel opener diazoxide (25 and 50 mol/l) (Fig. 2A) indicates that the inhibitory effect of glucose is not due to insulin- or glucoseinduced membrane depolarization. Conversely, when the glucose concentration was decreased from 16.7 to 2.8 mmol/l, IR-OXA release significantly increased from to % (P 0.05) (Fig. 2B, top). As expected, glucagon release was also significantly increased (from to %, P 0.05) (Fig. 2B, bottom). Thus, a negative relationship between glucose concentration and OXA release by pancreatic islets was observed in the present study. Plasma OXA is increased during fasting. Since the release of OXA is stimulated by low glucose, we hypothesized that the release of OXA is increased during fasting. To test this idea, IR-OXA was measured in the plasma of fasted rats. Plasma IR-OXA eluted as a single peak that was superimposible with the peak of islet release (data not DIABETES, VOL. 52, JANUARY
4 OXA RELEASE FROM ISLETS FIG. 3. Localization of OXA and OXR1 in pancreatic islets. A F: Cryostat sections of rat pancreas were immunostained for OXA (green) and glucagon (red). Specific staining is observed in a subset of cells (arrow). The merged confocal images (D and F) demonstrate the presence of OXA and OXR1 in glucagon-secreting islet cells (yellow, arrow). Note that non glucagon-containing cells also display peptide and receptor immunoreactivity. Scale bars, 15 m. shown). Food deprivation resulted in a significant (P 0.05) rise in plasma IR-OXA (from to pg/ml, n 6). These findings are consistent with the hypothesis of increased OXA release during fasting. Islet cells display OXA and orexin receptor immunoreactivity. The increase in release of islet IR-OXA and glucagon by low glucose prompted us to determine whether the same cells produce OXA and glucagon. As 114 DIABETES, VOL. 52, JANUARY 2003
5 R. OUEDRAOGO, E. NÄSLUND, AND A.L. KIRCHGESSNER FIG. 4. Effect of OXA on glucagon and insulin secretion from isolated pancreatic islets. A: OXA (80 and 100 nmol/l) potentiates the release of glucagon from rat islets in the presence of low glucose (2.8 mmol/l). B: OXA (100 and 150 nmol/l) inhibits glucose (16.7 mmol/l)-stimulated insulin secretion. Results are expressed as percentages of control immunoreactive (IR) glucagon ( fmol islet 1 min 1, n 8) or insulin ( fmol islet 1 min 1, n 8) release in the presence of 2.8 mmol/l glucose. *P < 0.05 vs. without drug. previously reported (12), OXA immunoreactivity was observed in the cytoplasm of -cells (Fig. 3A); however, intense OXA immunoreactivity was also observed in cells located at the periphery of a subset of islets (Fig. 3B). Double labeling with antibodies to OXA and glucagon revealed that OXA immunoreactivity is displayed by the glucagon-secreting -cells (Figs. 3C and D). In addition, both - and -cells display OXR1 immunoreactivity (12) (Figs. 3E and F), suggesting that OXA might affect insulin and/or glucagon secretion. OXA modulates glucagon and insulin secretion from isolated islets. We examined the effects of OXA on hormone release from isolated islets. OXA (100 nmol/l) significantly (P 0.001) increased glucagon secretion (from to %, n 8) from islets incubated in low (2.8 mmol/l) glucose (Fig. 4A) and had no effect on the insulin level (not shown). A significant increase (P 0.05) in glucagon secretion was also observed in the presence of 80 nmol/l OXA; however, no effect was observed at concentrations in the range of 1 50 nmol/l (Fig. 4A). When the glucose concentration was raised to 16.7 mmol/l, OXA (100 nmol/l) significantly (P 0.05) decreased glucose-stimulated insulin secretion ( to %, n 8) (Fig. 4B). A significant (P 0.001) decrease in glucose-stimulated insulin secretion was also observed in the presence of 150 nmol/l of OXA (from to %) (Fig. 4B); however, no effect was observed at concentrations in the range of 1 80 nmol/l (Fig. 4B). OXA modulates plasma insulin, glucagon, and glucose in fasted rats. Next, we determined whether OXA modulates plasma insulin, glucagon, and/or glucose level. Like the exogenous application of OXA to islets incubated in low glucose, the intravenous administration of the peptide (100 pmol kg 1 min 1 for 20 min) significantly (P 0.05) increased plasma glucagon in fasted rats (from to pg/ml, n 4). In contrast, FIG. 5. Effect of OXA on blood glucose levels. Animals were food deprived for 12 h before infusion of vehicle (isotonic saline; f) or OXA (80 pmol kg 1 min 1 ; ). Glucose concentrations were measured every 20 min. Time 0 corresponds to the beginning of vehicle or OXA infusion. Blood glucose levels are expressed as percentages of mean blood glucose concentration observed at time 0. Values represent means SE of five independent experiments. *P < 0.05 vs. control. DIABETES, VOL. 52, JANUARY
6 OXA RELEASE FROM ISLETS plasma insulin concentration significantly (P 0.05) decreased (from to ng/ml, n 4). Interestingly, plasma glucose concentrations were significantly higher during and after OXA (80 pmol kg 1 min 1 ) administration (Fig. 5), as might be expected due to increased glucagon and reduced plasma insulin levels. DISCUSSION We have previously reported that OXA and orexin receptors are expressed in the endocrine pancreas (12); however, the physiological significance of this expression was unclear. Many neuropeptides are contained in granule-like structures within endocrine cells, from which they can be released into the extracellular space. The study of this secretion represents an important step toward the identification of mechanisms involved in the modulation of its function and, ultimately, an understanding of its function. The present study demonstrates that OXA is released from pancreatic islet cells and that glucose levels regulate its release. In addition, it shows that OXA can modulate pancreatic hormone secretion and blood glucose levels. We characterized the release of OXA from isolated pancreatic islets using an EIA capable of detecting 1 fmol of IR-OXA and confirmed the authenticity of the released peptide by reversed-phase HPLC. As is typical of the release of peptides, depolarizing stimuli produced a dose-dependent increase in the release of OXA that was TTX sensitive. Furthermore, the release of OXA evoked by 80 mmol/l KCl was abolished in the presence of nifedipine; therefore, OXA is stored and released by islet cells, and L-type Ca 2 channels are involved in the response. OXA release from pancreatic islet cells is regulated by glucose. A decrease in the glucose concentration from 16.7 to 2.8 mmol/l more than doubled OXA release. In contrast, when the glucose concentration was increased from 2.8 to 16.7 mmol/l, OXA release decreased by 90%. These findings indicate that OXA release is stimulated by decreased glucose levels and suggest that OXA-containing pancreatic islet cells, like those in the brain (18) and gut (12), are glucosensitive and part of a network of glucose- sensing cells that becomes activated when blood glucose levels fall. Orexin neurons in the LHA are activated by hypoglycemia (6), and blood glucose inhibits prepro-orexin mrna expression in these cells (1,7). Thus, orexin cells are somehow sensing the animal s nutritional state, and OXA is released in response to nutritional depletion. In support of this idea, we found a significant increase in plasma OXA level in fasted lean rats similar to that reported in humans (14,15). The origin of plasma OXA was not identified; however, in light of the present findings, one potential source is the pancreatic islets. Other peripheral sites of synthesis include neurons and/or endocrine cells in the gut (12), adrenal glands (19), and testis (2,19,20). Furthermore, since cells outside the central nervous system express orexin receptors (12,19), the findings support the existence of a peripheral orexin system and suggest that OXA may function as a hormone and/or neuromodulator. Peripheral plasma OXA may modulate brain regulatory centers, since OXA crosses the blood-brain barrier (21). In the rat hypothalamus, OXA is colocalized with dynorphin (22) and galanin (23), two other orexigenic peptides, suggesting that this colocalization might have an important physiological role. In the endocrine pancreas of the rat, OXA immunoreactivity is displayed by both the - and -cells, which secrete hormones that antagonistically control the balance between glucose storage and consumption and maintain plasma glucose levels within a very narrow range. Glucagon secretion is increased in the fasting state to activate glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, whereas insulin is secreted in response to nutrients to promote energy storage. Interestingly, the regulation of OXA release from isolated islets is similar to that of glucagon secretion. For instance, both OXA and glucagon release are suppressed by high glucose levels, stimulated by low glucose, and increased during periods of fasting. Stimulation of OXA release by low glucose is compatible with a role in the regulation of metabolic states, particularly when food availability is reduced to the organism. The resulting increase in orexinergic activity could then lead to increased glucagon secretion, which is essential for the maintenance of plasma glucose levels during fasting. The expression of orexin receptors in both pancreatic and -cells suggests that locally released OXA may modulate glucagon and/or insulin secretion. In this study, we show that extracellular OXA significantly increases glucagon secretion from isolated islets incubated in low glucose, while it decreases glucose-stimulated insulin release. Furthermore, the effect of OXA on glucagon and insulin release is concentration dependent. The concentration of OXA necessary to see an effect is higher than that of circulating OXA; however, if OXA were released locally within the islets, the islet cells would be exposed to high concentrations of peptide. Like the application of OXA to islets incubated in the presence of low glucose, the intravenous administration of OXA to fasted rats increased plasma glucagon and decreased insulin levels. Interestingly, there was a rise in blood glucose, suggesting that OXA may play a role in the physiological control of blood glucose. A role in the control of energy metabolism and maintaining homeostasis has been suggested (24). This may serve to stimulate food intake. Also, an effect on plasma insulin has been confirmed by several approaches (25 28); however, a strong link with glucagon secretion and glycemia is suggested by the present findings. It may be speculated that fasting, which is associated with a decline in blood glucose, induces an increase in plasma OXA levels. OXA facilitates glucagon secretion, while inhibition of insulin release may become important until normoglycemia is restored. When a meal is ingested and blood glucose rises, a decline in OXA is parallel to that of glucagon and inversely related to insulin. Experiments are in progress to further elucidate the role of OXA in the physiological regulation of blood glucose. A complete understanding will require strict temporal parameters that can only be addressed in future in vivo studies. In conclusion, the present study demonstrates that OXA is released by islet cells and that these cells, like those in the brain and gut, are glucosensitive and part of a network of glucose sensing cells that becomes activated when blood glucose levels fall. We propose that islet OXA acts to signal the need to conserve energy and restore blood glucose levels by modulating glucagon and insulin secretion. 116 DIABETES, VOL. 52, JANUARY 2003
7 R. OUEDRAOGO, E. NÄSLUND, AND A.L. KIRCHGESSNER ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This study was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant NS27645, the American Diabetes Association, and the Swedish Research council. We thank Jimmy Calaycay and Dr. Rushbrook for their guidance with HPLC and comments on the manuscript and Dr. Gintzler for his advice on protein extraction. We also thank Dr. Bianchi for comments on the manuscript and Jie Ma and Qingchun Tong for assistance with immunocytochemistry and animal surgery. REFERENCES 1. de Lecea L, Kilduff TS, Peyron C, Gao X, Foye PE, Danielson PE, Fukuhara C, Battenberg EL, Gautvik VT, Bartlett FS 2nd, Frankel WN, van den Pol AN, Bloom FE, Gautvik KM, Sutcliffe JG: The hypocretins: hypothalamusspecific peptides with neuroexcitatory activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95: , Sakurai T, Amemiya A, Ishii M, Matsuzaki I, Chemelli RM, Tanaka H, Williams SC, Richarson JA, Kozlowski GP, Wilson S, Arch JR, Buckingham RE, Haynes AC, Carr SA, Annan RS, McNulty DE, Liu WS, Terrett JA, Elshourbagy NA, Bergsma DJ, Yanagisawa M: Orexins and orexin receptors: a family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell 92: , Kirchgessner AL: Orexins in the brain-gut axis. Endocrine Rev 23:1 15, Bernardis LL, Bellinger LL: The lateral hypothalamic area revisited: ingestive behavior. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 20: , Oomura Y, Onyama H, Sugimori M, Nakemura T, Yamada Y: Glucose inhibition of the glucose-sensitive neurons in the rat lateral hypothalamus. Nature 247: , Cai XJ, Evans ML, Lister CA, Leslie RA, Arch JR, Wilson S, Williams G: Hypoglycemia activates orexin neurons and selectively increases hypothalamic orexin-b levels: responses inhibited by feeding and possibly mediated by the nucleus of the solitary tract. Diabetes 50: , Cai XJ, Widdowson PS, Harrold J, Wilson S, Buckingham RE, Arch JR, Tadayyon M, Clapham JC, Wilding J, Williams G: Hypothalamic orexin expression: modulation by blood glucose and feeding. Diabetes 48: , Williams G, Bing C, Cai XJ, Harrold JA, King PJ, Liu XH: The hypothalamus and the control of energy homeostasis: different circuits, different purposes. Physiol Behav 74: , Mizuno Y, Oomura Y: Glucose responding neurons in the nucleus tractus solitarius of the rat: in vitro study. Brain Res 30: , Liu MT, Seino S, Kirchgessner AL: Identification and characterization of glucoresponsive neurons in the enteric nervous system. J Neurosci 19: , Peyron C, Tighe DK, van den Pol AN, de Lecea L, Heller HC, Sutcliffe JG, Kilduff TS: Neurons containing hypocretin (orexin) project to multiple neuronal systems. J Neurosci 18: , Kirchgessner AL, Liu M-L: Orexin synthesis and response in the gut. Neuron 24: , demiguel MJ, Burrell MA: Immunocytochemical detection of orexin A in endocrine cells of the developing mouse gut. J Histochem Cytochem 50:63 69, Arihara Z, Takahashi K, Murakami O, Totsune K, Sone M, Satoh F, Ito S, Mouri T: Immunoreactive orexin-a in human plasma. Peptides 22: , Komaki G, Matsumoto Y, Nishikata H, Kawai K, Nozaki T, Takii M, Sogawa H, Kubo C: Orexin-A and leptin change inversely in fasting non-obese subjects. Eur J Endocrino 144: , Tong Q, Ouedraogo R, Kirchgessner AL: Localization and function of group III metabotropic glutamate receptors in rat pancreatic islets. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 282: E1324 E1333, Lebrun P, Antoine MH, Ouedraogo R, Kane C, Dunne M, Hermann M, Herchuelz A, Masereel B, Delarge J, de Tullio P, Pirotte B: Activation of ATP-dependent K channels and inhibition of insulin release: effect of BPDZ 62. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 277: , Muroya S, Uramura K, Sakurai T, Takigawa M, Yada T: Lowering glucose concentrations increases cytosolic Ca 2 in orexin neurons of the rat lateral hypothalamus. Neurosci Lett 309: , Randeva HS, Karteris E, Grammatopoulos D, Hillhouse EW: Expression of orexin-a and functional orexin type receptors in the adult adrenals: implications for adrenal function and energy homeostasis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86: , Johren O, Neidert SJ, Kummer M, Dendorfer A, Dominiak P: Prepro-orexin and orexin receptor mrnas are differentially expressed in peripheral tissues of male and female rats. Endocrinology 142: , Kastin AJ, Akerstrom V: Orexin A but not orexin B rapidly enters brain from blood by simple diffusion. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 289: , Chou TC, Lee CE, Lu J, Elmquist JK, Hara J, Willie JT, Beuckmann CT, Chemelli RM, Sakurai T, Yanagisawa M, Saper CB, Scammell TE: Orexin (hypocretin) neurons contain dynorphin. J Neurosci 21:RC168, Hakansson M, de Lecea L, Sutcliffe JG, Yanagisawa M, Meister B: Leptin receptor- and STAT3-immunoreactivities in hypocretin/orexin neurones of the lateral hypothalamus. J Neuroendocrinol 11: , Lubkin M, Stricker-Krongrad A: Independent feeding and metabolic actions of orexins in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 253: , Nowak KW, Mackowiak P, Switonska MM, Fabis M, Malendowicz LK: Acute orexin effects on insulin secretion in the rat: in vivo and in vitro studies. Life Sci 66: , Switonska MM, Kaczmarek P, Malendowicz LK, Nowak KW: Orexins and adipoinsular axis function in the rat. Regul Pept 104:69 73, Tsuneki H, Sugihara Y, Honda R, Wada T, Sasaoka T, Kimura I: Reduction of blood glucose level by orexins in fasting normal and streptozotocindiabetic mice. Eur J Pharmacol 448: , Russell SH, Small CJ, Dakin CL, Abbott CR, Morgan DG, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR: The central effects of orexin-a in the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in vivo and in vitro in male rats. J Neuroendocrinol 13: , 2001 DIABETES, VOL. 52, JANUARY
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Regul Pept. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2009 April 10.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Regul Pept. 2008 April 10; 147(1-3): 1 3. Do enteric neurons make hypocretin? Christian R. Baumann a,c,*, Erika L. Clark a, Nigel
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Regul Pept. 2008 April 10; 147(1-3): 1 3. Do enteric neurons make hypocretin? Christian R. Baumann a,c,*, Erika L. Clark a, Nigel
Reduced availability of glucose, the brain s main
 Orexin A Preferentially Excites Glucose-Sensitive Neurons in the Lateral Hypothalamus of the Rat In Vitro Xiao Hui Liu, 1 Richard Morris, 2 David Spiller, 3 Michael White, 3 and Gareth Williams 1 Falls
Orexin A Preferentially Excites Glucose-Sensitive Neurons in the Lateral Hypothalamus of the Rat In Vitro Xiao Hui Liu, 1 Richard Morris, 2 David Spiller, 3 Michael White, 3 and Gareth Williams 1 Falls
CNS Control of Food Intake. Adena Zadourian & Andrea Shelton
 CNS Control of Food Intake Adena Zadourian & Andrea Shelton Controlling Food Intake Energy Homeostasis (Change in body adiposity + compensatory changes in food intake) Background Information/Review Insulin
CNS Control of Food Intake Adena Zadourian & Andrea Shelton Controlling Food Intake Energy Homeostasis (Change in body adiposity + compensatory changes in food intake) Background Information/Review Insulin
Appetite and feeding behavior are regulated by many
 Central Orexin-A Augments Sympathoadrenal Outflow in Conscious Rabbits Kiyoshi Matsumura, Takuya Tsuchihashi, Isao Abe Abstract We determined the cardiovascular and neurohormonal responses to intracerebroventricular
Central Orexin-A Augments Sympathoadrenal Outflow in Conscious Rabbits Kiyoshi Matsumura, Takuya Tsuchihashi, Isao Abe Abstract We determined the cardiovascular and neurohormonal responses to intracerebroventricular
Human Obestatin ELISA
 K-ASSAY Human Obestatin ELISA For the quantitative determination of obestatin in human serum and plasma Cat. No. KT-495 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 081309 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION Human Obestatin
K-ASSAY Human Obestatin ELISA For the quantitative determination of obestatin in human serum and plasma Cat. No. KT-495 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 081309 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION Human Obestatin
Gut hormones KHATTAB
 Gut hormones PROF:ABD ALHAFIZ HASSAN KHATTAB Gut as an endocrine gland The talk will cover the following : Historical background. Why this subject is chosen. Gastro-intestinal hormones and their function.
Gut hormones PROF:ABD ALHAFIZ HASSAN KHATTAB Gut as an endocrine gland The talk will cover the following : Historical background. Why this subject is chosen. Gastro-intestinal hormones and their function.
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Orexins/hypocretins excite rat sympathetic preganglionic neurons in vivo and in vitro
 Am J Physiol Regulatory Integrative Comp Physiol 281: R1801 R1807, 2001. Orexins/hypocretins excite rat sympathetic preganglionic neurons in vivo and in vitro VAGNER R. ANTUNES, G. CRISTINA BRAILOIU, ERNEST
Am J Physiol Regulatory Integrative Comp Physiol 281: R1801 R1807, 2001. Orexins/hypocretins excite rat sympathetic preganglionic neurons in vivo and in vitro VAGNER R. ANTUNES, G. CRISTINA BRAILOIU, ERNEST
Orexin 2 Receptor Reporter Assay Kit
 Orexin 2 Receptor Reporter Assay Kit Item No. 600250 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Orexin 2 Receptor Reporter Assay Kit Item No. 600250 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Chapter 12. Ingestive Behavior
 Chapter 12 Ingestive Behavior Drinking a. fluid compartments b. osmometric thirst c. volumetric thirst Eating a. energy sources b. starting a meal c. stopping a meal d. eating disordersd Drinking a. fluid
Chapter 12 Ingestive Behavior Drinking a. fluid compartments b. osmometric thirst c. volumetric thirst Eating a. energy sources b. starting a meal c. stopping a meal d. eating disordersd Drinking a. fluid
Human Leptin ELISA Kit
 Product Manual Human Leptin ELISA Kit Catalog Numbers MET-5057 MET-5057-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Leptin is a polypeptide hormone
Product Manual Human Leptin ELISA Kit Catalog Numbers MET-5057 MET-5057-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Leptin is a polypeptide hormone
Orexin and Sleep. Team: A Little Bit of Leptin
 Orexin and Sleep Team: A Little Bit of Leptin Intro to Orexin 1997 -Scripps Research Institute gene expression in the hypothalamus Found gene clone 35 - expression limited to the lateral hypothalamus NTs
Orexin and Sleep Team: A Little Bit of Leptin Intro to Orexin 1997 -Scripps Research Institute gene expression in the hypothalamus Found gene clone 35 - expression limited to the lateral hypothalamus NTs
Motility Conference Ghrelin
 Motility Conference Ghrelin Emori Bizer, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology November 21, 2007 Ghrelin: Basics Hormone produced by the A-like A endocrine cells in the oxyntic mucosa (stomach body
Motility Conference Ghrelin Emori Bizer, M.D. Division of Gastroenterology/Hepatology November 21, 2007 Ghrelin: Basics Hormone produced by the A-like A endocrine cells in the oxyntic mucosa (stomach body
OREXINS, ENERGY BALANCE, TEMPERATURE, SLEEP-WAKE CYCLE. Miklós Székely
 Page Articles 1 of 15 in PresS. Am J Physiol AJP: Regul Regulatory, Integr Integrative Comp Physiol and Comparative (March 23, Physiology 2006). doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00179.2006 R-00179-2006 1 FINAL ACCEPTED
Page Articles 1 of 15 in PresS. Am J Physiol AJP: Regul Regulatory, Integr Integrative Comp Physiol and Comparative (March 23, Physiology 2006). doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00179.2006 R-00179-2006 1 FINAL ACCEPTED
Pancreas Fox Chapter 18 part 2 (also Chapter 19.3 & 19.4)
 Vert Phys PCB3743 Pancreas Fox Chapter 18 part 2 (also Chapter 19.3 & 19.4) T. Houpt, Ph.D. Anatomy of Digestive System Peristalsis Stomach and Acid Secretion Liver and Bile Secretion Pancreas and pancreatic
Vert Phys PCB3743 Pancreas Fox Chapter 18 part 2 (also Chapter 19.3 & 19.4) T. Houpt, Ph.D. Anatomy of Digestive System Peristalsis Stomach and Acid Secretion Liver and Bile Secretion Pancreas and pancreatic
Chapter 16: Endocrine System 1
 Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
Ch 16 Endocrine System Bi 233 Endocrine system Endocrine System: Overview Body s second great controlling system Influences metabolic activities of cells by means of hormones Slow signaling Endocrine glands
History of Investigation
 Acini - Pancreatic juice (1º) (2º) Secretions- neuronal and hormonal mechanisms 1) Secretin - bicarbonate rich 2) Cholecystokinin - enzyme rich Islets of Langerhans (contain 4 cell types) Alpha cells (α)-
Acini - Pancreatic juice (1º) (2º) Secretions- neuronal and hormonal mechanisms 1) Secretin - bicarbonate rich 2) Cholecystokinin - enzyme rich Islets of Langerhans (contain 4 cell types) Alpha cells (α)-
Supplemental methods. Total RNA was extracted from the stomach, liver, pancreas, pituitary, and
 Supplemental methods Real-time quantitative RT-PCR and Semi-quantitative PCR Total RNA was extracted from the stomach, liver, pancreas, pituitary, and hypothalamus as previously described (). Primers and
Supplemental methods Real-time quantitative RT-PCR and Semi-quantitative PCR Total RNA was extracted from the stomach, liver, pancreas, pituitary, and hypothalamus as previously described (). Primers and
What systems are involved in homeostatic regulation (give an example)?
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
Autonomic regulation of islet hormone secretion
 Autonomic regulation of islet hormone secretion Implications for health and disease Billy & Bree Paper 1: Autonomic regulation of islet hormone secretion : Implications for health and disease By Team BBB
Autonomic regulation of islet hormone secretion Implications for health and disease Billy & Bree Paper 1: Autonomic regulation of islet hormone secretion : Implications for health and disease By Team BBB
UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
Internal Regulation II Energy
 Internal Regulation II Energy Reading: BCP Chapter 16 lookfordiagnosis.com Homeostasis Biologically, what is necessary for life is a coordinated set of chemical reactions. These reactions take place in
Internal Regulation II Energy Reading: BCP Chapter 16 lookfordiagnosis.com Homeostasis Biologically, what is necessary for life is a coordinated set of chemical reactions. These reactions take place in
I. Introduction. II. Characteristics
 YK050 Rat Leptin ELISA I. Introduction Leptin, which is a product of ob gene, is a protein consisting of 167 amino acids and it is secreted from white adipose tissue. It is known that leptin acts on hypothalamus
YK050 Rat Leptin ELISA I. Introduction Leptin, which is a product of ob gene, is a protein consisting of 167 amino acids and it is secreted from white adipose tissue. It is known that leptin acts on hypothalamus
THE ROLE OF INSULIN RECEPTOR SIGNALING IN THE BRAIN. COGS 163 By: Pranav Singh Alexandra Villar
 THE ROLE OF INSULIN RECEPTOR SIGNALING IN THE BRAIN COGS 163 By: Pranav Singh Alexandra Villar INTRODUCTION Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas by the islets of Langerhans that regulates the
THE ROLE OF INSULIN RECEPTOR SIGNALING IN THE BRAIN COGS 163 By: Pranav Singh Alexandra Villar INTRODUCTION Insulin is a hormone produced in the pancreas by the islets of Langerhans that regulates the
Hormones. Prof. Dr. Volker Haucke Institut für Chemie-Biochemie Takustrasse 6
 Hormones Prof. Dr. Volker Haucke Institut für Chemie-Biochemie Takustrasse 6 Tel. 030-8385-6920 (Sekret.) 030-8385-6922 (direkt) e-mail: vhaucke@chemie.fu-berlin.de http://userpage.chemie.fu-berlin.de/biochemie/aghaucke/teaching.html
Hormones Prof. Dr. Volker Haucke Institut für Chemie-Biochemie Takustrasse 6 Tel. 030-8385-6920 (Sekret.) 030-8385-6922 (direkt) e-mail: vhaucke@chemie.fu-berlin.de http://userpage.chemie.fu-berlin.de/biochemie/aghaucke/teaching.html
Rat Glicentin EIA FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. <Distributed by> DF Kasumigaseki Place, 3-6-7, Kasumigaseki, Chiyoda-ku Tokyo Japan
 YK111 Rat Glicentin EIA FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY DF Kasumigaseki Place, 3-6-7, Kasumigaseki, Chiyoda-ku Tokyo 100-0013 Japan URL: http://www.sceti.co.jp/export/ e-mail: exp-pet@sceti.co.jp
YK111 Rat Glicentin EIA FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY DF Kasumigaseki Place, 3-6-7, Kasumigaseki, Chiyoda-ku Tokyo 100-0013 Japan URL: http://www.sceti.co.jp/export/ e-mail: exp-pet@sceti.co.jp
A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets
 Diabetologia () 5:77 DOI.7/s5--- SHORT COMMUNICATION A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets Q. Cheng & Y. C.
Diabetologia () 5:77 DOI.7/s5--- SHORT COMMUNICATION A novel role for vitamin D: modulation of expression and function of the local renin angiotensin system in mouse pancreatic islets Q. Cheng & Y. C.
Rat Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN
 YK050 Rat Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Introduction 2 Characteristics 3 Composition 4 Method 5-6 Notes
YK050 Rat Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Introduction 2 Characteristics 3 Composition 4 Method 5-6 Notes
Rat Leptin-HS ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN
 YK051 Rat Leptin-HS ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418 0011 Contents Introduction 2 Characteristics 3 Composition 4 Method 5-6 Notes
YK051 Rat Leptin-HS ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418 0011 Contents Introduction 2 Characteristics 3 Composition 4 Method 5-6 Notes
Research Article A TRPM4 Inhibitor 9-Phenanthrol Inhibits Glucose- and Glucagon-Like Peptide 1-Induced Insulin Secretion from Rat Islets of Langerhans
 Hindawi Diabetes Research Volume 217, Article ID 5131785, 5 pages https://doi.org/1.1155/217/5131785 Research Article A TRPM4 Inhibitor 9-Phenanthrol Inhibits Glucose- and Glucagon-Like Peptide 1-Induced
Hindawi Diabetes Research Volume 217, Article ID 5131785, 5 pages https://doi.org/1.1155/217/5131785 Research Article A TRPM4 Inhibitor 9-Phenanthrol Inhibits Glucose- and Glucagon-Like Peptide 1-Induced
The Influence of Orexin Antagonist, SB , on Cognitive Flexibility
 The Influence of Orexin Antagonist, SB-334867, on Cognitive Flexibility Zoey Forrester-Fronstin Mentor: Dr. Aileen Bailey, Ph.D. St. Mary s College of Maryland Alzheimer s Disease Alzheimer s Association,
The Influence of Orexin Antagonist, SB-334867, on Cognitive Flexibility Zoey Forrester-Fronstin Mentor: Dr. Aileen Bailey, Ph.D. St. Mary s College of Maryland Alzheimer s Disease Alzheimer s Association,
Ghrelin Stimulates Porcine Somatotropes
 Animal Industry Report AS 650 ASL R1957 2004 Ghrelin Stimulates Porcine Somatotropes Aleksandra Glavaski-Joksimovic Ksenija Jeftinija Colin G. Scanes Lloyd L. Anderson Srdija Jeftinija Recommended Citation
Animal Industry Report AS 650 ASL R1957 2004 Ghrelin Stimulates Porcine Somatotropes Aleksandra Glavaski-Joksimovic Ksenija Jeftinija Colin G. Scanes Lloyd L. Anderson Srdija Jeftinija Recommended Citation
Mouse C-peptide EIA. Cat. No. YII-YK013-EX FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY
 Mouse C-peptide EIA Cat. No. YII-YK013-EX FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY TOYO 2CHOME, KOTO-KU, TOKYO, 135-0016, JAPAN http://www.cosmobio.co.jp e-mail : export@cosmobio.co.jp Phone : +81-3-5632-9617 FAX : +81-3-5632-9618
Mouse C-peptide EIA Cat. No. YII-YK013-EX FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY TOYO 2CHOME, KOTO-KU, TOKYO, 135-0016, JAPAN http://www.cosmobio.co.jp e-mail : export@cosmobio.co.jp Phone : +81-3-5632-9617 FAX : +81-3-5632-9618
ENDOCRINOLOGY. Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE
 ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
ENDOCRINOLOGY Dr.AZZA SAJID ALKINANY 2 nd STAGE THE RELATIONSHIP AMONG THE HYPOTHALMUS,POSTERIOR PITUITARY AND TARGET TISSUES. The posterior pituitary does not produce its own hormones, but stores and
Mouse GLP-2 EIA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY
 YK142 Mouse GLP-2 EIA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY Kasumigaseki place, 3-6-7, Kasumigaseki, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-0013 Japan http://www.sceti.co.jp/english/export e-mail exp-pet@sceti.co.jp
YK142 Mouse GLP-2 EIA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY Kasumigaseki place, 3-6-7, Kasumigaseki, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-0013 Japan http://www.sceti.co.jp/english/export e-mail exp-pet@sceti.co.jp
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
ENERGY HOMEOSTASIS IS regulated by discrete central
 0013-7227/03/$15.00/0 Endocrinology 144(9):3774 3778 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2003 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/en.2003-0274 Fasting Activates the Nonhuman Primate Hypocretin (Orexin) System
0013-7227/03/$15.00/0 Endocrinology 144(9):3774 3778 Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2003 by The Endocrine Society doi: 10.1210/en.2003-0274 Fasting Activates the Nonhuman Primate Hypocretin (Orexin) System
Dynamic Changes of Orexin A and Leptin in Obese Children during Body Weight Reduction
 Physiol. Res. 56: 89-96, 2007 Dynamic Changes of Orexin A and Leptin in Obese Children during Body Weight Reduction J. BRONSKÝ 1,2, J. NEDVÍDKOVÁ 3, H. ZAMRAZILOVÁ 4, M. PECHOVÁ 2, M. CHADA 2,5, K. KOTAŠKA
Physiol. Res. 56: 89-96, 2007 Dynamic Changes of Orexin A and Leptin in Obese Children during Body Weight Reduction J. BRONSKÝ 1,2, J. NEDVÍDKOVÁ 3, H. ZAMRAZILOVÁ 4, M. PECHOVÁ 2, M. CHADA 2,5, K. KOTAŠKA
Endocrine System Notes
 Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Endocrine System Notes is the tendency to maintain a stable internal environment. - parts of the body that secrete hormones directly into the body. - parts of the body that make secretions which travel
Neurophysiology of the Regulation of Food Intake and the Common Reward Pathways of Obesity and Addiction. Laura Gunter
 Neurophysiology of the Regulation of Food Intake and the Common Reward Pathways of Obesity and Addiction Laura Gunter The Brain as the Regulatory Center for Appetite The brain is the integration center
Neurophysiology of the Regulation of Food Intake and the Common Reward Pathways of Obesity and Addiction Laura Gunter The Brain as the Regulatory Center for Appetite The brain is the integration center
18. PANCREATIC FUNCTION AND METABOLISM. Pancreatic secretions ISLETS OF LANGERHANS. Insulin
 18. PANCREATIC FUNCTION AND METABOLISM ISLETS OF LANGERHANS Some pancreatic functions have already been discussed in the digestion section. In this one, the emphasis will be placed on the endocrine function
18. PANCREATIC FUNCTION AND METABOLISM ISLETS OF LANGERHANS Some pancreatic functions have already been discussed in the digestion section. In this one, the emphasis will be placed on the endocrine function
Ingestive Behaviors 21. Introduction. Page 1. control and story lines. (a review of general endocrinology) Integration (or the basic reflex arc model)
 Ingestive Behaviors 21 (a review of general endocrinology) A neuroendocrine system: components, a reflex arc, the endocrine system, the AN, endocrine / nervous systems as afferents and efferents, the theoretical
Ingestive Behaviors 21 (a review of general endocrinology) A neuroendocrine system: components, a reflex arc, the endocrine system, the AN, endocrine / nervous systems as afferents and efferents, the theoretical
VaTx1 VaTx2 VaTx3. VaTx min Retention Time (min) Retention Time (min)
 a Absorbance (mau) 5 2 5 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 6 2 3 4 5 6 VaTx2 High Ca 2+ Low Ca 2+ b 38.2 min Absorbance (mau) 3 2 3 4 5 3 2 VaTx2 39.3 min 3 4 5 3 2 4. min 3 4 5 Supplementary Figure. Toxin Purification For
a Absorbance (mau) 5 2 5 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 6 2 3 4 5 6 VaTx2 High Ca 2+ Low Ca 2+ b 38.2 min Absorbance (mau) 3 2 3 4 5 3 2 VaTx2 39.3 min 3 4 5 3 2 4. min 3 4 5 Supplementary Figure. Toxin Purification For
Appeal decision. Appeal No USA HILL'S PET NUTRITION, INC. Osaka, Japan
 Appeal decision Appeal No. 2015-17056 USA Appellant HILL'S PET NUTRITION, INC. Osaka, Japan Patent Attorney MURAI, Koji The case of appeal against the examiner's decision of refusal of Japanese Patent
Appeal decision Appeal No. 2015-17056 USA Appellant HILL'S PET NUTRITION, INC. Osaka, Japan Patent Attorney MURAI, Koji The case of appeal against the examiner's decision of refusal of Japanese Patent
Low ambient temperature lowers cholecystokinin and leptin plasma concentrations in adult men
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gastroenterology Volume 7 Number 2 Low ambient temperature lowers cholecystokinin and leptin plasma concentrations in adult men M Pizon, P Tomasic, K Sztefko, Z Szafran
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Gastroenterology Volume 7 Number 2 Low ambient temperature lowers cholecystokinin and leptin plasma concentrations in adult men M Pizon, P Tomasic, K Sztefko, Z Szafran
Growth Hormone, Somatostatin, and Prolactin 1 & 2 Mohammed Y. Kalimi, Ph.D.
 Growth Hormone, Somatostatin, and Prolactin 1 & 2 Mohammed Y. Kalimi, Ph.D. I. Growth Hormone (somatotropin): Growth hormone (GH) is a 191 amino acid single chain polypeptide (MW 22,000 daltons). Growth
Growth Hormone, Somatostatin, and Prolactin 1 & 2 Mohammed Y. Kalimi, Ph.D. I. Growth Hormone (somatotropin): Growth hormone (GH) is a 191 amino acid single chain polypeptide (MW 22,000 daltons). Growth
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
YK052 Mouse Leptin ELISA
 YK052 Mouse Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA-SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Ⅰ. Introduction 2 Ⅱ. Characteristics 3 Ⅲ. Composition 4 Ⅳ. Method
YK052 Mouse Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA-SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Ⅰ. Introduction 2 Ⅱ. Characteristics 3 Ⅲ. Composition 4 Ⅳ. Method
YK160 GLP-1 EIA Kit. For Measurement of Rat, Mouse & Human GLP-1 FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY. <Distributed by>
 YK160 GLP-1 EIA Kit For Measurement of Rat, Mouse & Human GLP-1 FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY 3-6-7, Kasumigaseki, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-0013 Japan URL: www.sceti.co.jp/export/ e-mail: exp-pet@sceti.co.jp
YK160 GLP-1 EIA Kit For Measurement of Rat, Mouse & Human GLP-1 FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY 3-6-7, Kasumigaseki, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-0013 Japan URL: www.sceti.co.jp/export/ e-mail: exp-pet@sceti.co.jp
Chapter 41. Lecture 14. Animal Hormones. Dr. Chris Faulkes
 Chapter 41 Lecture 14 Animal Hormones Dr. Chris Faulkes Animal Hormones Aims: To appreciate the variety and roles of hormones in the body To understand the basic types of hormones To understand how hormones
Chapter 41 Lecture 14 Animal Hormones Dr. Chris Faulkes Animal Hormones Aims: To appreciate the variety and roles of hormones in the body To understand the basic types of hormones To understand how hormones
Monday, 17 April 2017 BODY FLUID HOMEOSTASIS
 Monday, 17 April 2017 BODY FLUID HOMEOSTASIS Phenomenon: shipwrecked sailor on raft in ocean ("water, water everywhere but not a drop to drink") Why are the sailors thirsty? (What stimulated thirst?) Why
Monday, 17 April 2017 BODY FLUID HOMEOSTASIS Phenomenon: shipwrecked sailor on raft in ocean ("water, water everywhere but not a drop to drink") Why are the sailors thirsty? (What stimulated thirst?) Why
Secondary Negative Effects of Isolation Enzyme (s) On Human Islets. A.N.Balamurugan
 Secondary Negative Effects of Isolation Enzyme (s) On Human Islets A.N.Balamurugan Human Islets Functional Mass Preservation 18-25 min 10 min 8-12 min 10-15 min 45-60 min pancreas in chamber 37º Sub-Optimal
Secondary Negative Effects of Isolation Enzyme (s) On Human Islets A.N.Balamurugan Human Islets Functional Mass Preservation 18-25 min 10 min 8-12 min 10-15 min 45-60 min pancreas in chamber 37º Sub-Optimal
ENERGY FROM INGESTED NUTREINTS MAY BE USED IMMEDIATELY OR STORED
 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 SHORT TERM METABOLISM [METABOLISM] Learning Objectives: Identify primary energy stores of the body Differentiate the metabolic processes of the fed and fasted states Explain
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 SHORT TERM METABOLISM [METABOLISM] Learning Objectives: Identify primary energy stores of the body Differentiate the metabolic processes of the fed and fasted states Explain
Scope. History. History. Incretins. Incretin-based Therapy and DPP-4 Inhibitors
 Plasma Glucose (mg/dl) Plasma Insulin (pmol/l) Incretin-based Therapy and Inhibitors Scope Mechanism of action ผศ.ดร.นพ.ว ระเดช พ ศประเสร ฐ สาขาว ชาโภชนว ทยาคล น ก ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล
Plasma Glucose (mg/dl) Plasma Insulin (pmol/l) Incretin-based Therapy and Inhibitors Scope Mechanism of action ผศ.ดร.นพ.ว ระเดช พ ศประเสร ฐ สาขาว ชาโภชนว ทยาคล น ก ภาคว ชาอาย รศาสตร คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล
Investigation of the role of nesfatin-1/nucb2 in the central nervous system. Ph.D. thesis Katalin Könczöl
 Investigation of the role of nesfatin-1/nucb2 in the central nervous system Ph.D. thesis Katalin Könczöl Semmelweis University János Szentágothai Doctoral School of Neurosciences Supervisor: Official reviewers:
Investigation of the role of nesfatin-1/nucb2 in the central nervous system Ph.D. thesis Katalin Könczöl Semmelweis University János Szentágothai Doctoral School of Neurosciences Supervisor: Official reviewers:
Control of Glucose Metabolism
 Glucose Metabolism Control of Glucose Metabolism The pancreas is both an exocrine and endocrine gland. It secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum (exocrine) and 3 specific hormones into the bloodstream
Glucose Metabolism Control of Glucose Metabolism The pancreas is both an exocrine and endocrine gland. It secretes digestive enzymes into the duodenum (exocrine) and 3 specific hormones into the bloodstream
Daily Intraparaventricular Orexin-A Treatment Induces Weight Loss in Rats
 nature publishing group articles Daily Intraparaventricular -A Treatment Induces Weight Loss in Rats Colleen M. Novak 1 and James A. Levine 1 The neuropeptide orexin (hypocretin) increases energy expenditure
nature publishing group articles Daily Intraparaventricular -A Treatment Induces Weight Loss in Rats Colleen M. Novak 1 and James A. Levine 1 The neuropeptide orexin (hypocretin) increases energy expenditure
Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane
 Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane potential recorded from POMC neurons following treatment with
Supplementary Figure 1) GABAergic enhancement by leptin hyperpolarizes POMC neurons A) Representative recording samples showing the membrane potential recorded from POMC neurons following treatment with
Chapter 9. The Endocrine System. Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Intro to the Endocrine System Chief Complaint:8-year-old girl with excessive thirst, frequent
Chapter 9 The Endocrine System Lecture Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor Florence-Darlington Technical College Intro to the Endocrine System Chief Complaint:8-year-old girl with excessive thirst, frequent
Cholecystokinin antagonist, proglumide, stimulates growth hormone release in the rat
 J. Biosci., Vol. 15, Number 1, March 1990, pp. 17 21. Printed in India. Cholecystokinin antagonist, proglumide, stimulates growth hormone release in the rat E. VIJAYAN* and S. M. McCANN Department of Physiology,
J. Biosci., Vol. 15, Number 1, March 1990, pp. 17 21. Printed in India. Cholecystokinin antagonist, proglumide, stimulates growth hormone release in the rat E. VIJAYAN* and S. M. McCANN Department of Physiology,
Hormonal regulation of. Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara
 Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
Hormonal regulation of nutrient metabolism Physiology Department Medical School, University of Sumatera Utara Homeostasis & Controls Successful compensation Homeostasis reestablished Failure to compensate
Human Total GIP Kit v1-2016Apr 1
 Human Total GIP Kit 1-Plate Kit 5-Plate Kit 25-Plate Kit K151RPD-1 K151RPD-2 K151RPD-4 18067-v1-2016Apr 1 MSD Metabolic Assays Human Total GIP Kit This package insert must be read in its entirety before
Human Total GIP Kit 1-Plate Kit 5-Plate Kit 25-Plate Kit K151RPD-1 K151RPD-2 K151RPD-4 18067-v1-2016Apr 1 MSD Metabolic Assays Human Total GIP Kit This package insert must be read in its entirety before
GLP-2 ELISA. For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in human serum and plasma samples.
 GLP-2 ELISA For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in human serum and plasma samples. For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 48-GP2HU-E01.1 Size: 96 wells Version:
GLP-2 ELISA For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in human serum and plasma samples. For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 48-GP2HU-E01.1 Size: 96 wells Version:
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/312/5779/1533/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Long-Term Potentiation of Neuron-Glia Synapses Mediated by Ca 2+ - Permeable AMPA Receptors Woo-Ping Ge, Xiu-Juan Yang,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/312/5779/1533/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Long-Term Potentiation of Neuron-Glia Synapses Mediated by Ca 2+ - Permeable AMPA Receptors Woo-Ping Ge, Xiu-Juan Yang,
Hormones. BIT 230 Walsh Chapter 8
 Hormones BIT 230 Walsh Chapter 8 Hormones Regulatory molecules Affect all areas of metabolism Endocrine- hormones travel via the bloodstream to its target cell: true hormone Modern definition- any regulatory
Hormones BIT 230 Walsh Chapter 8 Hormones Regulatory molecules Affect all areas of metabolism Endocrine- hormones travel via the bloodstream to its target cell: true hormone Modern definition- any regulatory
Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes
 Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes T Jourdan, G Godlewski, R Cinar, A Bertola, G Szanda, J Liu, J Tam, T Han, B Mukhopadhyay,
Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes T Jourdan, G Godlewski, R Cinar, A Bertola, G Szanda, J Liu, J Tam, T Han, B Mukhopadhyay,
Mouse C-Peptide I EIA
 Mouse C-Peptide I EIA Cat. No. YII-YK011-EX FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY TOYO 2CHOME, KOTO-KU, TOKYO, 135-0016, JAPAN http://www.cosmobio.co.jp e-mail : export@cosmobio.co.jp Phone : +81-3-5632-9617 FAX : +81-3-5632-9618
Mouse C-Peptide I EIA Cat. No. YII-YK011-EX FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY TOYO 2CHOME, KOTO-KU, TOKYO, 135-0016, JAPAN http://www.cosmobio.co.jp e-mail : export@cosmobio.co.jp Phone : +81-3-5632-9617 FAX : +81-3-5632-9618
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Effects of orexins A and B on the secretory and proliferative activity of immature and regenerating rat adrenal glands
 Histol Histopathol (2001) 16: 713-717 001 : 10.14670/HH-16.713 http://www.ehu.es/histol-histopathol Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Effects of orexins A and B on the secretory
Histol Histopathol (2001) 16: 713-717 001 : 10.14670/HH-16.713 http://www.ehu.es/histol-histopathol Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Effects of orexins A and B on the secretory
A Comparison of Leucine- and Acetoacetate-induced Hypoglycemia in Man *
 Journal of Clinical Investigation Vol. 43, No. 1, 1964 A Comparison of Leucine- and Acetoacetate-induced Hypoglycemia in Man * STEFAN S. FAJANS, JOHN C. FLOYD, JR., RALPH F. KNOPF, AND JEROME W. CONN (From
Journal of Clinical Investigation Vol. 43, No. 1, 1964 A Comparison of Leucine- and Acetoacetate-induced Hypoglycemia in Man * STEFAN S. FAJANS, JOHN C. FLOYD, JR., RALPH F. KNOPF, AND JEROME W. CONN (From
Eliades, Erlandson, Ruiz UW-L Journal of Undergraduate Research XVII (2014)
 Effects of Hibernation on the Enteric Nervous System of the Thirteenlined Ground Squirrels. Lauren Eliades, Martin Erlandson, Amelia Ruiz Faculty Sponsors: Dr. Sumei Liu and Dr. Scott Cooper, Department
Effects of Hibernation on the Enteric Nervous System of the Thirteenlined Ground Squirrels. Lauren Eliades, Martin Erlandson, Amelia Ruiz Faculty Sponsors: Dr. Sumei Liu and Dr. Scott Cooper, Department
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1
 GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
GLP-2 (Rat) ELISA. For the quantitative determination of glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2) in rat serum and plasma
 GLP-2 (Rat) ELISA For the quantitative determination of glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2) in rat serum and plasma For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 48-GP2RT-E01
GLP-2 (Rat) ELISA For the quantitative determination of glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2) in rat serum and plasma For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 48-GP2RT-E01
Adrenocorticotropin Responses to Corticotropin Releasing Factor and Vasopressin in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
 Laboratory Studies Adrenocorticotropin Responses to Corticotropin Releasing Factor and Vasopressin in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats TERUHIKO HATTORI, KOZO HASHIMOTO, AND ZENSUKE OTA SUMMARY The effects
Laboratory Studies Adrenocorticotropin Responses to Corticotropin Releasing Factor and Vasopressin in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats TERUHIKO HATTORI, KOZO HASHIMOTO, AND ZENSUKE OTA SUMMARY The effects
Motivation 1 of 6. during the prandial state when the blood is filled
 Motivation 1 of 6 I. INTRODUCTION A. Motivation: a condition (usually internal) that initiates, activates, or maintains goal-directed behavior. B. Archery analogy 1. undrawn bow has no potential energy
Motivation 1 of 6 I. INTRODUCTION A. Motivation: a condition (usually internal) that initiates, activates, or maintains goal-directed behavior. B. Archery analogy 1. undrawn bow has no potential energy
PYY (Human/Mouse/Rat) ELISA Kit
 PYY (Human/Mouse/Rat) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA1686 96 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3
PYY (Human/Mouse/Rat) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA1686 96 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3
Pancreatic Insulinoma Presenting. with Episodes of Hypoinsulinemic. Hypoglycemia in Elderly ---- A Case Report
 2008 19 432-436 Pancreatic Insulinoma Presenting with Episodes of Hypoinsulinemic Hypoglycemia in Elderly ---- A Case Report Chieh-Hsiang Lu 1, Shih-Che Hua 1, and Chung-Jung Wu 2,3 1 Division of Endocrinology
2008 19 432-436 Pancreatic Insulinoma Presenting with Episodes of Hypoinsulinemic Hypoglycemia in Elderly ---- A Case Report Chieh-Hsiang Lu 1, Shih-Che Hua 1, and Chung-Jung Wu 2,3 1 Division of Endocrinology
Week 3, Lecture 5a. Pathophysiology of Diabetes. Simin Liu, MD, ScD
 Week 3, Lecture 5a Pathophysiology of Diabetes Simin Liu, MD, ScD General Model of Peptide Hormone Action Hormone Plasma Membrane Activated Nucleus Cellular Trafficking Enzymes Inhibited Receptor Effector
Week 3, Lecture 5a Pathophysiology of Diabetes Simin Liu, MD, ScD General Model of Peptide Hormone Action Hormone Plasma Membrane Activated Nucleus Cellular Trafficking Enzymes Inhibited Receptor Effector
Ingestive Behavior: Feeding & Weight Regulation. Hypovolemic vs. Osmotic Thirst
 Ingestive Behavior: Feeding & Weight Regulation 1 Hypovolemic Thirst Receptors, CNS, Responses Salt Appetite Digestive components Glucose Homeostasis: Insulin & Glucagon Diabetes Mellitus 1 & 2 CNS Hypothalamic
Ingestive Behavior: Feeding & Weight Regulation 1 Hypovolemic Thirst Receptors, CNS, Responses Salt Appetite Digestive components Glucose Homeostasis: Insulin & Glucagon Diabetes Mellitus 1 & 2 CNS Hypothalamic
Research Article Plasma Orexin-A Levels in COPD Patients with Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure
 Mediators of Inflammation Volume 2011, Article ID 754847, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/754847 Research Article Plasma Orexin-A Levels in COPD Patients with Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure Lin-Yun Zhu, 1 Hanssa
Mediators of Inflammation Volume 2011, Article ID 754847, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/754847 Research Article Plasma Orexin-A Levels in COPD Patients with Hypercapnic Respiratory Failure Lin-Yun Zhu, 1 Hanssa
Human Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (7-36 amide) (GLP-1 (7-36 amide)) Kit
 TECHNICAL DATA SHEET AlphaLISA Research Reagents Caution: For Laboratory Use. A research chemical for research purposes only. Human Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (7-36 amide) (GLP-1 (7-36 amide)) Kit Product
TECHNICAL DATA SHEET AlphaLISA Research Reagents Caution: For Laboratory Use. A research chemical for research purposes only. Human Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (7-36 amide) (GLP-1 (7-36 amide)) Kit Product
Endocrine System. Chapter 20. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. The Endocrine System. Endocrine glands
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Chapter 20 Endocrine System Endocrine Glands and Hormones The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete hormones Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times
Solid-in-oil peptide nanocarriers for transcutaneous cancer vaccine delivery. against melanoma
 Supplementary Information for Solid-in-oil peptide nanocarriers for transcutaneous cancer vaccine delivery against melanoma Rie Wakabayashi,,a,b Masato Sakuragi,,a Shuto Kozaka, a Yoshiro Tahara, a Noriho
Supplementary Information for Solid-in-oil peptide nanocarriers for transcutaneous cancer vaccine delivery against melanoma Rie Wakabayashi,,a,b Masato Sakuragi,,a Shuto Kozaka, a Yoshiro Tahara, a Noriho
Supplementary Information. Glycogen shortage during fasting triggers liver-brain-adipose. neurocircuitry to facilitate fat utilization
 Supplementary Information Glycogen shortage during fasting triggers liver-brain-adipose neurocircuitry to facilitate fat utilization Supplementary Figure S1. Liver-Brain-Adipose neurocircuitry Starvation
Supplementary Information Glycogen shortage during fasting triggers liver-brain-adipose neurocircuitry to facilitate fat utilization Supplementary Figure S1. Liver-Brain-Adipose neurocircuitry Starvation
Chemical Regulation. Chapter 26. Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? THE NATURE OF CHEMICAL REGULATION
 Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
Chapter 6 Chemical Regulation PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Testosterone and Male Aggression: Is There a Link? Among male animals,
INTRODUCTION TO THE BIOCHEMISTRY OF HORMONES AND THEIR RECPTORS
 INTRODUCTION TO THE BIOCHEMISTRY OF HORMONES AND THEIR RECPTORS 1 Introduction to the Biochemistry of Hormones and their Receptors Lectuctre1 Sunday 17/2/ Objectives: 1. To understand the biochemical nature
INTRODUCTION TO THE BIOCHEMISTRY OF HORMONES AND THEIR RECPTORS 1 Introduction to the Biochemistry of Hormones and their Receptors Lectuctre1 Sunday 17/2/ Objectives: 1. To understand the biochemical nature
Analysis of AVP functions via V1a and V1b receptors with knockout mice. Akito Tanoue
 Analysis of AVP functions via V1a and V1b receptors with knockout mice Akito Tanoue Department of Pharmacology, National Research Institute for Child Health and Development Arginine-Vasopressin (AVP) is
Analysis of AVP functions via V1a and V1b receptors with knockout mice Akito Tanoue Department of Pharmacology, National Research Institute for Child Health and Development Arginine-Vasopressin (AVP) is
Human Physiology 6.6- Hormones, Homeostasis, and Reproduction
 Human Physiology 6.6- Hormones, Homeostasis, and Reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Application: William Harvey s investigation of sexual reproduction
Human Physiology 6.6- Hormones, Homeostasis, and Reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Application: William Harvey s investigation of sexual reproduction
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Chapter 6 Communication, Integration, and Homeostasis
 Chapter 6 Communication, Integration, and Homeostasis About This Chapter Cell-to-cell communication Signal pathways Novel signal molecules Modulation of signal pathways Homeostatic reflex pathways Cell-to-Cell
Chapter 6 Communication, Integration, and Homeostasis About This Chapter Cell-to-cell communication Signal pathways Novel signal molecules Modulation of signal pathways Homeostatic reflex pathways Cell-to-Cell
Digestion: Endocrinology of Appetite
 Digestion: Endocrinology of Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one on one relationship with a qualified health care professional
Digestion: Endocrinology of Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one on one relationship with a qualified health care professional
Electronic Supplementary Material to the article entitled Altered pattern of the
 Electronic Supplementary Material to the article entitled Altered pattern of the incretin effect as assessed by modelling in individuals with glucose tolerance ranging from normal to diabetic Integrated
Electronic Supplementary Material to the article entitled Altered pattern of the incretin effect as assessed by modelling in individuals with glucose tolerance ranging from normal to diabetic Integrated
Pancreas. Endocrine pancreas - Islets of Langerhans A or alpha cells glucagon B or beta cells insulin Delta cells somatostatin
 Endocrine System Pancreas Endocrine pancreas - Islets of Langerhans A or alpha cells glucagon B or beta cells insulin Delta cells somatostatin Glucagon & Metabolism Produced by beta cells of Islets Primary
Endocrine System Pancreas Endocrine pancreas - Islets of Langerhans A or alpha cells glucagon B or beta cells insulin Delta cells somatostatin Glucagon & Metabolism Produced by beta cells of Islets Primary
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary
 Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
Hypothalamic Control of Posterior Pituitary Hypothalamus neuron cell bodies produce ADH: supraoptic nuclei Oxytocin: paraventricular nuclei Transported along the hypothalamohypophyseal tract Stored in
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
SensoLyte pnpp Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit *Colorimetric*
 SensoLyte pnpp Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit *Colorimetric* Catalog # 72146 Kit Size 500 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect alkaline phosphatase activity Enhanced
SensoLyte pnpp Alkaline Phosphatase Assay Kit *Colorimetric* Catalog # 72146 Kit Size 500 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect alkaline phosphatase activity Enhanced
Gastric Artery Embolization for Weight Loss: Rationale
 Gastric Artery Embolization for Weight Loss: Rationale Gary Siskin, MD FSIR Professor and Chairman Department of Radiology Albany Medical Center Albany, New York Gary Siskin, M.D. Consultant/Advisory Board:
Gastric Artery Embolization for Weight Loss: Rationale Gary Siskin, MD FSIR Professor and Chairman Department of Radiology Albany Medical Center Albany, New York Gary Siskin, M.D. Consultant/Advisory Board:
Developmental changes in CSF hypocretin-1 (orexin-a) levels in normal and genetically narcoleptic Doberman pinschers
 J Physiol 560.2 (2004) pp 587 592 587 Developmental changes in CSF hypocretin-1 (orexin-a) levels in normal and genetically narcoleptic Doberman pinschers Joshi John 1,2, Ming-Fung Wu 1,2, Nigel T. Maidment
J Physiol 560.2 (2004) pp 587 592 587 Developmental changes in CSF hypocretin-1 (orexin-a) levels in normal and genetically narcoleptic Doberman pinschers Joshi John 1,2, Ming-Fung Wu 1,2, Nigel T. Maidment
