Ruben J. Boado, Eric Ka-Wai Hui, Jeff Zhiqiang Lu, and William M. Pardridge
|
|
|
- Chester Lewis
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 X/12/ $25.00 DRUG METABOLISM AND DISPOSITION Vol. 40, No. 10 Copyright 2012 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 46375/ DMD 40: , 2012 Glycemic Control and Chronic Dosing of Rhesus Monkeys with a Fusion Protein of Iduronidase and a Monoclonal Antibody Against the Human Insulin Receptor Ruben J. Boado, Eric Ka-Wai Hui, Jeff Zhiqiang Lu, and William M. Pardridge Department of Medicine, University of California Los Angeles, Los Angeles, California (R.J.B., W.M.P.); and, ArmaGen Technologies, Inc., Santa Monica, California (R.J.B., E.K.-W.H., J.Z.L.) Received April 21, 2012; accepted July 20, 2012 ABSTRACT: Hurler s syndrome, or mucopolysaccharidosis type I, is a lysosomal storage disorder caused by mutations in the gene encoding the lysosomal enzyme iduronidase (IDUA). The disease affects both peripheral tissues and the central nervous system (CNS). Recombinant IDUA treatment does not affect the CNS, because IDUA does not cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB). To enable BBB penetration, human IDUA was re-engineered as an IgG-IDUA fusion protein, where the IgG domain is a genetically engineered monoclonal antibody (MAb) against the human insulin receptor (HIR). The HIRMAb penetrates the brain from the blood via transport on the endogenous BBB insulin receptor and acts as a molecular Trojan horse to deliver the fused IDUA to the brain. Before human testing, the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein was evaluated in Introduction Mucopolysaccaridosis Type I, also called MPSI, is a lysosomal storage disorder caused by mutations in the gene encoding the lysosomal enzyme -L-iduronidase (IDUA). MPSI patients are treated with enzyme replacement therapy (Brady and Schiffmann, 2004) and weekly intravenous infusions of the recombinant IDUA enzyme. However, many patients with MPSI have Hurler s syndrome, where the disorder also affects the central nervous system (CNS). Enzyme replacement therapy is not effective for the CNS (Wraith, 2001), because IDUA, a large molecule drug, does not cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and does not penetrate the brain from the blood (Miebach, 2005). Recombinant enzymes such as IDUA can be re-engineered as BBB-penetrating pharmaceuticals by the fusion of IDUA to a genetically engineered monoclonal antibody (MAb) against the human insulin receptor (HIR) (Boado et al., 2008). The insulin receptor is expressed at the human BBB (Pardridge et al., 1985). The HIRMAb binds the BBB insulin receptor and acts as a molecular Trojan horse to ferry the fused IDUA enzyme across the BBB. The insulin receptor This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke [Grant U44-NS064602]. Article, publication date, and citation information can be found at a 6-month weekly dosing toxicology study at doses of 0, 3, 9, and 30 mg/kg/week of the fusion protein administered to 40 rhesus monkeys. The focus of the present study is the effect of chronic high dose administration of this fusion protein on plasma glucose and long-term glycemic control. The results show that the HIRMAb has weak insulin agonist activity and causes hypoglycemia at the high dose, 30 mg/kg, after intravenous infusion in normal saline. When dextrose is added to the saline infusion solution, no hypoglycemia is observed at any dose. An intravenous glucose tolerance test performed at the end of the 6 months of chronic treatment showed no change in glucose tolerance at any dose of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein. also is expressed on brain cells, and the HIRMAb also mediates endocytosis into target cells, where the fusion protein then is triaged to the lysosomal compartment of the cell (Boado et al., 2008). Treatment of Hurler s syndrome with HIRMAb-IDUA fusion proteins requires chronic dosing with weekly intravenous infusions of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein. Under these conditions, it is possible that the HIRMAb domain of the fusion protein could have either agonist or antagonist properties at the HIR, causing either hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia, respectively. The HIRMAb cross-reacts with the insulin receptor in Old World primates such as the rhesus monkey but does not cross-react with the insulin receptor of lower animals or even New World primates (Pardridge et al., 1995). Therefore, chronic dosing studies must be performed in the rhesus monkey. In a prior study, rhesus monkeys were treated twice weekly for 4 weeks with 0.2, 2, and 20 mg/kg doses of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein (Boado et al., 2009). No evidence of hypo- or hyperglycemia was observed at these doses of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein (Boado et al., 2009). In the present investigation, the dose of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein is increased to 3, 9, and 30 mg/kg/dose, and the duration of the weekly dosing is increased to 6 months. Glucose concentrations in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) are measured at each dose of the fusion protein. Glycemic control at the end of the study is evaluated with intravenous glucose tolerance tests. ABBREVIATIONS: BBB, blood-brain barrier; CNS, central nervous system; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; HIR, human insulin receptor; HIRMAb, MAb against HIR; IDUA, iduronidase; HIRMAb-IDUA, fusion protein of HIRMAb and IDUA; MAb, monoclonal antibody. 2021
2 2022 BOADO ET AL. Materials and Methods Production of the HIRMAb-IDUA Fusion Protein. The HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein, also called AGT-181, is a heterotetrameric protein comprised of two heavy chains and two light chains; an IDUA protein is fused to the C terminus of each heavy chain (Boado et al., 2008). The HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein was produced in Chinese hamster ovary cells in serum-free medium in a 50-L perfusion mode Wave bioreactor (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Pittsburgh, PA) as described previously (Boado et al., 2009). The conditioned medium was clarified by depth filtration, and the fusion protein was purified with three columns: a 1.8-L protein A column (MAb Select; GE Healthcare Life Sciences), a 1.8-L cation exchange column (SP Sepharose; GE Healthcare Life Sciences), and a 1.2-L anion exchange column (Q Sepharose; GE Healthcare Life Sciences) followed by nanofiltration and diafiltration in the final diluent, which is 10 mm sodium acetate/140 mm NaCl (ph 5.5)/0.001% Tween 80. The purity, identity, and potency of the fusion protein were verified by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, size exclusion chromatography, human IgG and IDUA Western blot analysis, HIR receptor binding assay, IDUA fluorometric enzymatic assay, host cell protein impurity, protein A impurity, host cell DNA impurity, endotoxin, and subvisible particles. The identity of the protein was confirmed by peptide mapping with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry at The Scripps Research Institute (La Jolla, CA). The final formulation contained 5 mg/ml fusion protein, which was stored upright as a sterile liquid at 4 C. Stability studies, based on eight analytical methods on purity, identity, potency, and sterility, showed that the protein was stable at this formulation for 2 years. Chronic Dosing of Rhesus Monkeys. Juvenile rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta) of mixed sex (20 males, 20 females) were used for all of the studies and were housed at MPI Research, Inc. (Mattawan, MI) in stainless steel cages in a controlled environment (18 28 C and 30 70% relative humidity) on a 12-h light/dark cycle. LabDiet Certified Primate Diet (PMI Nutrition International, Crystal, MN) was provided twice daily. Animals were fasting before all of the study drug infusions, as food was withheld the morning before drug infusion. Tap water was provided ab libitum. All of the aspects of the primate study performed at MPI Research, Inc. were conducted in strict compliance with the United States Food and Drug Administration Good Laboratory Practice Regulations, 21 CFR Part 58. All of the procedures were in compliance with the Animal Welfare Act Regulations and were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. The primates were treated with 0 mg/kg (6 males, 6 females), 3 mg/kg (4 males, 4 females), 9 mg/kg (4 males, 4 females), or 30 mg/kg (6 males, 6 females) of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein administered as an intravenous infusion over a 30-min period in 50 ml of either normal saline or 10% dextrose in normal saline. In the 26-week toxicity study, the doses were administered every 7 days for 26 consecutive weeks. The HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein was administered on a weekly basis, because this parallels the current standard practice in the treatment of Hurler s syndrome, which uses weekly intravenous infusions of the recombinant IDUA (Wraith, 2001; Miebach, 2005). For study drug infusion at week 1 and week 25, blood was removed from the femoral vein and collected in tubes with K 2 -EDTA at 0, 2, 5, 30, 35, 90, min and 3, 6, and 23 h after the start of the 30-min intravenous infusion of the HIRMAb- IDUA fusion protein. The blood was separated into plasma, which then was stored at 70 C until analysis. Fasting plasma glucose was measured monthly during the study. During the first week, CSF was removed via the cisterna magna at 0, 3, and 23 h after the intravenous infusion of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein. Fasting plasma glucose was measured in blood removed at weeks 0, 4, 8, 13, 16, 20, and 24. Glucose Assays. Plasma glucose was determined at MPI Research, Inc. with an Olympus AU2700 chemistry analyzer (Olympus America, Inc., Center Valley, PA). CSF glucose was determined with a glucose assay kit from BioVision (Mountain View, CA) using a spectrophotometric method and absorbance at 570 nm. The assay is run in 96-well plates with a standard curve of D-glucose of 0 to 10 nmol/well and 50- l samples per well of a 1:50 dilution of primate CSF. Intravenous Glucose Tolerance Test. The HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein was infused in 50 ml of 10% dextrose/normal saline over 30 min, and plasma glucose was measured at 0, 2, 5, 30, 35, 60, 90, 180, and 360 min after the start of the infusion. The plasma glucose, A(t), was plotted versus the time (t) of infusion between 30 and 90 min and fit to the equation ln[a(t)] ln(a max ) kt, where A max is the maximal plasma glucose at zero time and k is the rate constant of glucose clearance from the plasma. The half-time of plasma glucose clearance, T 1/2, was determined from ln(2)/k. The intravenous glucose tolerance test was performed on fasting monkeys with the end of study (week 25) drug infusion. Statistical Analysis. Data are reported as mean S.E., and statistically significant differences were assessed at the P 0.05 level using analysis of variance with Bonferroni correction. Results The HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein was infused intravenously over 30 min in 50 ml of normal saline in rhesus monkeys at four doses (0, 3, 9, and 30 mg/kg). Plasma glucose was measured at 0, 2, 5, 30, 35, 90, 180, 360, and 1380 min after the start of the 30-min infusion, and the values are reported in Table 1 by either sex or combined sexes. There are no significant differences between sexes at any time point (Table 1). The glucose in the fusion protein-treated animals (combined sexes) was 20 to 29% lower than that of the saline controls at 30 and 35 min after start of the 30-min drug infusion at all three doses of the fusion protein, with no dose relationships (Table 1). The plasma glucose is decreased 31 and 47% at 90 and 180 min only in the high dose group, 30 mg/kg (Table 1). Figure 1 shows the plasma glucose for individual monkeys in the saline group and in the high dose group (30 mg/kg). One monkey in the saline group and four monkeys in the 30 mg/kg group have plasma glucose values of 40 mg%, and the nadir is at 180 min after the start of the 30-min infusion (Fig. 1). The level of hypoglycemia in two monkeys at 180 min was severe, with plasma glucose values of 11 mg% after the intravenous infusion of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein in normal saline at a dose of 30 mg/kg (Fig. 1). During the last week of the 26-week treatment study, the HIRMAb- IDUA fusion protein was formulated in 50 ml of 10% dextrose/normal TABLE 1 Plasma glucose at start of study Data are in mg/dl. Mean S.E. (n 8 12 per group in combined sexes and 4 6 per group in male or female groups). Sex Minutes HIRMAb-IDUA Injection Dose Combined * 60 3* * Male * 57 3* * Female * * P 0.05 difference from 0 mg/kg by analysis of variance. P 0.01 difference from 0 mg/kg by analysis of variance.
3 GLUCOSE CONTROL AND INSULIN RECEPTOR MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY 2023 FIG. 1. Plasma glucose is plotted versus time after the start of a 30 min infusion of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein at a dose of either 0 mg/kg (left) or 30 mg/kg (right). Data are shown for individual monkeys (6 males and 6 females in each treatment group). The HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein is infused in 50 ml of normal saline with no glucose supplement at the start (week 1) of the study. The horizontal bar defines a plasma glucose of 40 mg%, which is a minimum value for all but one of the saline-infused monkeys. saline and infused over 30 min in the same group of rhesus monkeys at doses of 0, 3, 9, and 30 mg/kg. No hypoglycemia was observed in any animal, and the plasma glucose values are shown in Fig. 2. The plasma glucose peaked at the end of the 30 min of fusion protein infusion (Fig. 2). The rate of decline in the plasma glucose was evaluated by linear regression analysis to produce the half-time (T 1/2 ) of glucose clearance from plasma for each of the four treatment doses of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein. There were no differences in the T 1/2 among all of the treatment groups, and glucose was cleared from plasma with a T 1/2 of 32 to 35 min (Table 2). Plasma glucose was measured monthly in all of the monkeys before the intravenous infusion of the study drug, and the plasma glucose values are shown in Table 3 by sex and for combined groups. There are no sex differences and no upward or downward trends in plasma glucose over the course of 24 weeks. Glucose was measured in CSF at 0, 3, and 23 h after the 30-min infusion of HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein at each of the four doses (0, 3, 9, and 30 mg/kg) in normal saline. The only significant difference in CSF glucose was a 48% decrease at 3hinthe30mg/kg treatment group (Fig. 3). The CSF glucose, at 3 h after drug infusion, in all 40 monkeys in the study correlated with the plasma glucose, at 3 h after drug infusion, and the average CSF/plasma glucose ratio was 54% for all of the monkeys (Fig. 4). There were no significant differences in the glucose concentrations in CSF at 0 and 23 h in any of the four treatment groups. The CSF glucose at 0 h was 63 16, 69 20, 58 6, and mg% and at 23 h was 54 9, 67 18, 52 8, and mg%, respectively, after the administration of 0, 3, 9, and 23 mg/kg HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein (mean S.D.). Discussion The results of the studies are consistent with the following conclusions. First, high doses, 30 mg/kg, of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein in fasting rhesus monkeys cause hypoglycemia with a nadir of 39 5 mg% at 180 min after a 30-min infusion of the fusion protein in 50 ml of normal saline (Table 1). Second, the hypoglycemia can be severe in some monkeys, because the nadir was as low as 11 mg% in two monkeys at the 30 mg/kg dose of the fusion protein (Fig. 1). Third, the hypoglycemia is eliminated by the inclusion of glucose in the infusion solution (Fig. 2). Fourth, the rate of clearance of glucose from plasma, which is a measure of glucose tolerance, is unchanged in all of the treatment groups at the end of the 26 weeks of fusion protein dosing (Fig. 2), and the half-time of glucose clearance at all of the doses is the same, 32 to 35 min (Table 2). Fifth, there is no evidence of impaired glucose tolerance with chronic fusion protein treatment, because the monthly fasting plasma glucose is unchanged in all of the treatment groups over the course of the 6 months of treatment (Table 3). Sixth, the CSF glucose is decreased at 3 h after intravenous infusion of 30 mg/kg of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein in normal saline, and the CSF glucose parallels the corresponding plasma glucose in each monkey (Fig. 4). A monoclonal antibody against the subunit of the human insulin receptor may have either agonist or antagonist properties. Antibodies against the insulin receptor that demonstrate agonist properties cause an increase in glucose uptake by cells (Brunetti et al., 1989), which is associated with an increase in glucose clearance from plasma (Bhaskar et al., 2012). The HIRMAb domain of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein shows agonist properties, albeit only at the highest treatment dose of 30 mg/kg. At this dose, hypoglycemia is induced, which peaks at 3 h after a 30-min infusion of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein in normal saline (Fig. 1; Table 1). The hypoglycemia is eliminated when glucose is added to the fusion protein infusion solution (Fig. 2). An insulin receptor antibody with antagonist action can cause hyperglycemia and impaired glucose tolerance (Malek et al., 2010). The HIRMAb domain of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein exhibits no antagonist properties, because fasting hyperglycemia is not induced (Table 3) and the rate constant of glucose clearance from plasma is unchanged (Table 2) after 6 months of weekly dosing of the fusion protein at doses of 3, 9, or 30 mg/kg. The lack of an effect of chronic treatment with the HIRMAb fusion protein on glycemic control is not due to a change in the exposure over the course of 6 months of treatment. A pharmacokinetics analysis shows that there is no change in the rate of clearance of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein from the blood at the start (week 1) and end (week 25) FIG. 2. Plasma glucose is plotted versus time after the start of a 30-min infusion of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein at a dose of 0, 3, 9, or 30 mg/kg. The HIRMAb- IDUA fusion protein is infused in 50 ml of 10% dextrose/normal saline at the end (week 25) of the study. The 23-h plasma glucose was 80 4, 80 5, 78 7, and 80 4 mg% for the 0, 3, 9, and 30 mg/kg treatment groups, respectively. Data are mean S.E. (n 6 12 combined sexes in each group).
4 2024 BOADO ET AL. TABLE 2 Intravenous glucose tolerance test at end of 26-week dosing Parameters were determined by nonlinear regression analysis of the plasma glucose between 30 and 90 min after a 30-min infusion of 10% glucose. Data are means S.E. for combined sexes. T 1/2 half-time of glucose clearance from blood after termination of the glucose infusion. Parameter Units HIRMAb-IDUA Dose k min T 1/2 min of the 6 months of treatment (R. J. Boado, E. K.-W. Hui, J. Z. Lu, and W. M. Pardridge, manuscript in preparation). The concentration of glucose in CSF also is reduced at 3 h after intravenous infusion of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein at a dose of 30 mg/kg in normal saline (Fig. 3). Insulin does not affect glucose uptake by the brain (Hasselbalch et al., 1999), and the CSF glucose is regulated by the plasma glucose concentration. The direct relationship between CSF and plasma glucose is demonstrated in this study (Fig. 4), and the mean CSF/plasma glucose ratio is 0.54 (Fig. 4). This value is in agreement with the CSF/plasma ratio reported in either humans or rhesus monkeys, which is 0.5 to 0.6 (Powers, 1981; Davis et al., 1993). Therefore, high doses of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein have no direct effect on glucose distribution in CSF, and CSF glucose concentrations parallel the corresponding concentrations of glucose in plasma. Reductions in plasma and CSF glucose are observed at 3 h after HIRMAb-IDUA infusion only at the high dose of 30 mg/kg. Reductions in glucose in either plasma or CSF are not observed after 3 or 9 mg/kg doses of the fusion protein. Because the projected therapeutic dose of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein is 0.6 to 1 mg/kg (Boado et al., 2008, 2011), no alterations in plasma or CSF glucose are expected in humans. The effect of high doses of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein on plasma glucose is transient, because the plasma glucose increases between 180 and 360 min after the infusion (Fig. 1). The rapid reversal of the plasma glucose is consistent with the rapid removal of the HIRMAb- IDUA fusion protein from plasma, owing to uptake by peripheral tissues. At a dose of 20 mg/kg in rhesus monkeys, the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion TABLE 3 Plasma glucose by week of study Data are in mg/dl. Mean S.E. (n 8 12 per group in combined sexes and 4 6 per group in male or female groups). Blood was removed for plasma glucose 1 week after the previous dosing of the study drug. Sex Weeks HIRMAb-IDUA Injection Dose Combined Male Female protein is cleared rapidly from plasma with a systemic clearance of ml/min/kg and a high systemic volume of distribution of ml/kg (Boado et al., 2009). The mean residence time of the fusion protein in the circulation in rhesus monkeys is min (Boado et al., 2009). Therefore, the return to normoglycemia by 6 h after drug infusion (Table 1) is consistent with nearly complete removal of the fusion protein from the circulation. Lower doses of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein do not cause hypoglycemia. In a previous study with a 20 mg/kg dose of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein in rhesus monkeys, no reduction in plasma or CSF glucose was observed (Boado et al., 2009). In another study, a HIRMAb fusion protein was administered to rhesus monkeys by bolus intravenous injection at 10 mg/kg every 12 h for five consecutive doses, and no hypoglycemia was observed (Pardridge and Boado, 2009). In the present study, there are only modest reductions in glucose at 0 to 5 min after the termination of the 30-min infusion and no significant reductions in plasma glucose at 90 to 1380 min after the start of the 30-min intravenous infusion of 3 or 9 mg/kg doses of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein in normal saline (Table 1). The 3 or 9 mg/kg doses are higher than the expected therapeutic dose of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein, which may be on the order of 1 mg/kg. The CNS lysosomal inclusion bodies are reduced in Hurler mice after chronic treatment with the mouse homolog of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein, and the treatment dose is 1 mg/kg of fusion protein intravenously (Boado et al., 2011). The level of IgGenzyme penetration of the brain after intravenous administration is comparable in mice and rhesus monkeys, where the brain uptake in either species is approximately 1% of the injected dose per brain (Boado et al., 2008; Zhou et al., 2012). On the basis of the brain uptake in the primate of 1% of the injected dose per brain and the endogenous IDUA enzyme activity in the human brain, a treatment dose of 0.6 mg/kg is predicted to replace 50% of the IDUA enzyme activity in the brain (Boado et al., 2008). In conclusion, these studies show that the HIRMAb domain of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein has weak insulin agonist properties FIG. 3. CSF glucose at 0, 3, and 23 h after HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein infusion is shown for 0, 3, 9, and 30 mg/kg doses of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein. Data are mean S.E. (n 8 12 combined sexes in each group). The HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein is infused in 50 ml of normal saline at the start (week 1) of the study., P 0.05 difference from control (0 mg/kg) as determined by analysis of variance.
5 GLUCOSE CONTROL AND INSULIN RECEPTOR MONOCLONAL ANTIBODY 2025 Contributed new reagents or analytic tools: Boado. Performed data analysis: Boado, Hui, Lu, and Pardridge. Wrote or contributed to the writing of the manuscript: Boado, Hui, Lu, and Pardridge. FIG. 4. CSF glucose is plotted versus the corresponding plasma glucose at 3 h after the intravenous infusion of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein for all four treatment groups (0, 3, 9, and 30 mg/kg). Data for individual monkeys is shown. The slope was determined by linear regression analysis. CSF and plasma glucose were determined after HIRMAb-IDUA infusion during the first week of the study. that are observed only at the highest dose of 30 mg/kg, which may be as much as 30-fold greater than planned therapeutic doses of the fusion protein. Hypoglycemia is not observed after the administration of doses lower than 30 mg/kg. These observations are corroborated by a prior study, which showed no hypoglycemia after intravenous infusion of the HIRMAb-IDUA fusion protein in saline at doses up to 20 mg/kg in rhesus monkeys (Boado et al., 2009). Any concern about hypoglycemia is mitigated by simply adding dextrose to the saline infusion of drug. The present study shows that a 10% dextrose additive is not necessary, because this dose of glucose causes transient hyperglycemia (Fig. 2). A preferred formulation is normal saline with 5% dextrose for routine administration of HIRMAb-derived fusion proteins. Acknowledgments We thank Winnie Tai and Phuong Tram for providing technical assistance. We are also indebted to MPI Research, Inc., for participation in the Good Laboratory Practice primate studies. Authorship Contributions Participated in research design: Boado and Pardridge. Conducted experiments: Boado, Hui, and Lu. References Bhaskar V, Goldfine ID, Bedinger DH, Lau A, Kuan HF, Gross LM, Handa M, Maddux BA, Watson SR, Zhu S, et al. (2012) A fully human, allosteric monoclonal antibody that activates the insulin receptor and improves glycemic control. Diabetes 61: Boado RJ, Hui EK, Lu JZ, and Pardridge WM (2009) AGT-181: expression in CHO cells and pharmacokinetics, safety, and plasma iduronidase enzyme activity in Rhesus monkeys. J Biotechnol 144: Boado RJ, Hui EK, Lu JZ, Zhou QH, and Pardridge WM (2011) Reversal of lysosomal storage in brain of adult MPS-I mice with intravenous Trojan horse-iduronidase fusion protein. Mol Pharm 8: Boado RJ, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Xia CF, Wang Y, and Pardridge WM (2008) Genetic engineering of a lysosomal enzyme fusion protein for targeted delivery across the human blood-brain barrier. Biotechnol Bioeng 99: Brady RO and Schiffmann R (2004) Enzyme-replacement therapy for metabolic storage disorders. Lancet Neurol 3: Brunetti A, Maddux BA, Wong KY, Hofmann C, Whittaker J, Sung C, and Goldfine ID (1989) Monoclonal antibodies to the human insulin receptor mimic a spectrum of biological effects in transfected 3T3/HIR fibroblasts without activating receptor kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 165: Davis TM, Brown AE, and Smith CD (1993) Metabolic disturbances in Plasmodium coatneyiinfected rhesus monkeys. Int J Parasitol 23: Hasselbalch SG, Knudsen GM, Videbaek C, Pinborg LH, Schmidt JF, Holm S, and Paulson OB (1999) No effect of insulin on glucose blood-brain barrier transport and cerebral metabolism in humans. Diabetes 48: Malek R, Chong AY, Lupsa BC, Lungu AO, Cochran EK, Soos MA, Semple RK, Balow JE, and Gorden P (2010) Treatment of type B insulin resistance: a novel approach to reduce insulin receptor autoantibodies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95: Miebach E (2005) Enzyme replacement therapy in mucopolysaccharidosis type I. Acta Paediatr Suppl 94: Pardridge WM and Boado RJ (2009) Pharmacokinetics and safety in rhesus monkeys of a monoclonal antibody-gdnf fusion protein for targeted blood-brain barrier delivery. Pharm Res 26: Pardridge WM, Eisenberg J, and Yang J (1985) Human blood-brain barrier insulin receptor. J Neurochem 44: Pardridge WM, Kang YS, Buciak JL, and Yang J (1995) Human insulin receptor monoclonal antibody undergoes high affinity binding to human brain capillaries in vitro and rapid transcytosis through the blood-brain barrier in vivo in the primate. Pharm Res 12: Powers WJ (1981) Cerebrospinal fluid to serum glucose ratios in diabetes mellitus and bacterial meningitis. Am J Med 71: Wraith JE (2001) Enzyme replacement therapy in mucopolysaccharidosis type I: progress and emerging difficulties. J Inherit Metab Dis 24: Zhou QH, Boado RJ, Lu JZ, Hui EK, and Pardridge WM (2012) Brain-penetrating IgG-iduronate 2-sulfatase fusion protein for the mouse. Drug Metab Dispos 40: Address correspondence to: Dr. William M. Pardridge, Department of Medicine, University of California Los Angeles, Warren Hall , 900 Veteran Ave., Los Angeles, CA wpardridge@mednet.ucla.edu
In 2017, there are no biologics that are FDA approved for CNS disease, wherein drug action requires transport into the brain across the BBB
 The Brain and Biotechnology In 2017, there are no biologics that are FDA approved for CNS disease, wherein drug action requires transport into the brain across the BBB History of biologic drug development
The Brain and Biotechnology In 2017, there are no biologics that are FDA approved for CNS disease, wherein drug action requires transport into the brain across the BBB History of biologic drug development
Treatment of Hurler MPSI with a Blood-Brain Barrier Penetrating IgG-Lysosomal Enzyme Fusion Protein
 Treatment of Hurler MPSI with a Blood-Brain Barrier Penetrating IgG-Lysosomal Enzyme Fusion Protein Ruben Boado TRAVERSING THE BBB PRE-CLINICAL TO CLINICAL TRANSLATION Enabling Novel Treatments for Nervous
Treatment of Hurler MPSI with a Blood-Brain Barrier Penetrating IgG-Lysosomal Enzyme Fusion Protein Ruben Boado TRAVERSING THE BBB PRE-CLINICAL TO CLINICAL TRANSLATION Enabling Novel Treatments for Nervous
Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
S2 Protein augmentation therapies for inherited disorders 1
 Disease category Disorder S2 Protein augmentation therapies for inherited 1 Augmented protein 2 Source of therapeutic protein / peptide Outcome References 3 Membrane transport Coagulation Cystic fibrosis
Disease category Disorder S2 Protein augmentation therapies for inherited 1 Augmented protein 2 Source of therapeutic protein / peptide Outcome References 3 Membrane transport Coagulation Cystic fibrosis
1. If the MTC is 100 ng/ml and the MEC is 0.12 ng/ml, which of the following dosing regimen(s) are in the therapeutic window?
 Page 1 PHAR 750: Biopharmaceutics/Pharmacokinetics October 23, 2009 - Form 1 Name: Total 100 points Please choose the BEST answer of those provided. For numerical answers, choose none of the above if your
Page 1 PHAR 750: Biopharmaceutics/Pharmacokinetics October 23, 2009 - Form 1 Name: Total 100 points Please choose the BEST answer of those provided. For numerical answers, choose none of the above if your
Basic Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics: An Integrated Textbook with Computer Simulations
 Basic Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics: An Integrated Textbook with Computer Simulations Rosenbaum, Sara E. ISBN-13: 9780470569061 Table of Contents 1 Introduction to Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics.
Basic Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics: An Integrated Textbook with Computer Simulations Rosenbaum, Sara E. ISBN-13: 9780470569061 Table of Contents 1 Introduction to Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics.
Osimertinib Activity in Patients With Leptomeningeal Disease From Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Updated Results From the BLOOM Study
 Osimertinib Activity in Patients With Leptomeningeal Disease From Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Updated Results From the BLOOM Study Abstract 9002 Yang JC, Kim DW, Kim SW, Cho BC, Lee JS, Ye X, Yin X, Yang
Osimertinib Activity in Patients With Leptomeningeal Disease From Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Updated Results From the BLOOM Study Abstract 9002 Yang JC, Kim DW, Kim SW, Cho BC, Lee JS, Ye X, Yin X, Yang
Glucose Assay Kit. Catalog Number KA assays Version: 07. Intended for research use only.
 Glucose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0831 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials Supplied...
Glucose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0831 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials Supplied...
Mouse C-peptide EIA. Cat. No. YII-YK013-EX FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY
 Mouse C-peptide EIA Cat. No. YII-YK013-EX FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY TOYO 2CHOME, KOTO-KU, TOKYO, 135-0016, JAPAN http://www.cosmobio.co.jp e-mail : export@cosmobio.co.jp Phone : +81-3-5632-9617 FAX : +81-3-5632-9618
Mouse C-peptide EIA Cat. No. YII-YK013-EX FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY TOYO 2CHOME, KOTO-KU, TOKYO, 135-0016, JAPAN http://www.cosmobio.co.jp e-mail : export@cosmobio.co.jp Phone : +81-3-5632-9617 FAX : +81-3-5632-9618
Glucose Assay Kit. Catalog Number KA assays Version: 03. Intended for research use only.
 Glucose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1648 100 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Glucose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1648 100 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Prothrombin (Human) ELISA Kit
 Prothrombin (Human) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0496 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General
Prothrombin (Human) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0496 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General
Lipoprotein Lipase Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric)
 Lipoprotein Lipase Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Catalog Number KA4538 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General
Lipoprotein Lipase Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Catalog Number KA4538 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General
GLYCEMIC CONTROL IN NEUROCRITICAL CARE PATIENTS
 GLYCEMIC CONTROL IN NEUROCRITICAL CARE PATIENTS David Zygun MD MSc FRCPC Professor and Director Division of Critical Care Medicine University of Alberta Zone Clinical Department Head Critical Care Medicine,
GLYCEMIC CONTROL IN NEUROCRITICAL CARE PATIENTS David Zygun MD MSc FRCPC Professor and Director Division of Critical Care Medicine University of Alberta Zone Clinical Department Head Critical Care Medicine,
Basics of Pharmacology
 Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Metabolic Syndrome. Antibodies and antigens
 Metabolic Syndrome Antibodies and antigens HYTEST METABOLIC SYNDROME Introduction Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions that increases the likelihood of cardiovascular heart diseases and diabetes.
Metabolic Syndrome Antibodies and antigens HYTEST METABOLIC SYNDROME Introduction Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions that increases the likelihood of cardiovascular heart diseases and diabetes.
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Tryptic digestion protection experiments - PCSK9 with Ab-3D5 (1:1 molar ratio) in 50 mm Tris, ph 8.0, 150 mm NaCl was incubated overnight at 4 o C. The
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Tryptic digestion protection experiments - PCSK9 with Ab-3D5 (1:1 molar ratio) in 50 mm Tris, ph 8.0, 150 mm NaCl was incubated overnight at 4 o C. The
General Principles of Pharmacology and Toxicology
 General Principles of Pharmacology and Toxicology Parisa Gazerani, Pharm D, PhD Assistant Professor Center for Sensory-Motor Interaction (SMI) Department of Health Science and Technology Aalborg University
General Principles of Pharmacology and Toxicology Parisa Gazerani, Pharm D, PhD Assistant Professor Center for Sensory-Motor Interaction (SMI) Department of Health Science and Technology Aalborg University
Immune Globulin Comparison Table
 I. Formulation data Gamunex /IGIVnex Gammagard Liquid Privigen Vivaglobin Formulation Lyophilized Liquid Liquid Liquid Liquid Concentration 5% or 10% upon reconstitution Administration set provided? IgA
I. Formulation data Gamunex /IGIVnex Gammagard Liquid Privigen Vivaglobin Formulation Lyophilized Liquid Liquid Liquid Liquid Concentration 5% or 10% upon reconstitution Administration set provided? IgA
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Nair S, Branagan AR, Liu J, Boddupalli CS, Mistry PK, Dhodapkar
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Nair S, Branagan AR, Liu J, Boddupalli CS, Mistry PK, Dhodapkar
MALDI-TOF analysis of whole blood: its usefulness and potential in the assessment of HbA1c levels
 MALDI-TOF analysis of whole blood: its usefulness and potential in the assessment of HbA1c levels Jane Y. Yang, David A. Herold Department of Pathology, University of California San Diego, 9500 Gilman
MALDI-TOF analysis of whole blood: its usefulness and potential in the assessment of HbA1c levels Jane Y. Yang, David A. Herold Department of Pathology, University of California San Diego, 9500 Gilman
Fructose Assay Kit. Catalog Number KA assays Version: 02. Intended for research use only.
 Fructose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1668 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Fructose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1668 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
MANUAL RBP4 (human) Competitive ELISA Kit Cat. No. AG-45A-0010YEK-KI01 For research use only. Not for diagnostic use.
 MANUAL RBP4 (human) Competitive ELISA Kit For research use only. Not for diagnostic use. Version 3 (04-May-2015) Cat. No. AG-45A-0010YEK-KI01 www.adipogen.com Table of Contents 1. Intended Use 3 2. Introduction
MANUAL RBP4 (human) Competitive ELISA Kit For research use only. Not for diagnostic use. Version 3 (04-May-2015) Cat. No. AG-45A-0010YEK-KI01 www.adipogen.com Table of Contents 1. Intended Use 3 2. Introduction
Report Reference Guide. THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES CareLink Report Reference Guide 1
 Report Reference Guide THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES CareLink Report Reference Guide 1 How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections.
Report Reference Guide THERAPY MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE FOR DIABETES CareLink Report Reference Guide 1 How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections.
Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit
 PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
Determination of bioavailability
 Pharmaceutics 2 Bioavailability Bioavailability is the rate and extent to which an administered drug reaches the systemic circulation. For example, if 100 mg of a drug is administered orally and 70 mg
Pharmaceutics 2 Bioavailability Bioavailability is the rate and extent to which an administered drug reaches the systemic circulation. For example, if 100 mg of a drug is administered orally and 70 mg
Research and Reviews: Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences
 Research and Reviews: Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences A Validated Spectrophotometric Method for Determination of Paliperidone Palmitate in Bulk Drug and its Pharmaceutical Dosage Form.
Research and Reviews: Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences A Validated Spectrophotometric Method for Determination of Paliperidone Palmitate in Bulk Drug and its Pharmaceutical Dosage Form.
Mouse Cathepsin B ELISA Kit
 GenWay Biotech, Inc. 6777 Nancy Ridge Drive San Diego, CA 92121 Phone: 858.458.0866 Fax: 858.458.0833 Email: techline@genwaybio.com http://www.genwaybio.com Mouse Cathepsin B ELISA Kit Catalog No. GWB-ZZD154
GenWay Biotech, Inc. 6777 Nancy Ridge Drive San Diego, CA 92121 Phone: 858.458.0866 Fax: 858.458.0833 Email: techline@genwaybio.com http://www.genwaybio.com Mouse Cathepsin B ELISA Kit Catalog No. GWB-ZZD154
Vishwanath Pattan Endocrinology Wyoming Medical Center
 Vishwanath Pattan Endocrinology Wyoming Medical Center Disclosure Holdings in Tandem Non for this Training Introduction In the United States, 5 to 6 percent of pregnancies almost 250,000 women are affected
Vishwanath Pattan Endocrinology Wyoming Medical Center Disclosure Holdings in Tandem Non for this Training Introduction In the United States, 5 to 6 percent of pregnancies almost 250,000 women are affected
Cortisol (Sheep) ELISA Kit
 Cortisol (Sheep) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0919 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the
Cortisol (Sheep) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0919 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the
Practical application of analytical tools for characterization of an impurity-related particle formation mechanism
 Practical application of analytical tools for characterization of an impurity-related particle formation mechanism Jared S. Bee, Ph.D. Protein aggregation measurement in biotherapeutics Maryland Center
Practical application of analytical tools for characterization of an impurity-related particle formation mechanism Jared S. Bee, Ph.D. Protein aggregation measurement in biotherapeutics Maryland Center
Fructose Assay Kit. Catalog Number KA assays Version: 03. Intended for research use only.
 Fructose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1668 100 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Fructose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1668 100 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Spectrophotometric Method for Estimation of Sitagliptin Phosphate in Bulk...
 Spectrophotometric Method for Estimation of Sitagliptin Phosphate in Bulk... I J P F A International Science Press Spectrophotometric Method for Estimation of Sitagliptin Phosphate in Bulk and Tablet Dosage
Spectrophotometric Method for Estimation of Sitagliptin Phosphate in Bulk... I J P F A International Science Press Spectrophotometric Method for Estimation of Sitagliptin Phosphate in Bulk and Tablet Dosage
MEDAK DIST. ANDHRA PRADESH STATE, INDIA. Research Article RECEIVED ON ACCEPTED ON
 Page67 Available Online through IJPBS Volume 1 Issue 2 APRIL- JUNE 2011 SIMPLE QUANTITATIVE METHOD DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF VALSARTAN IN PUREFORM AND PHARMACEUTICAL DOSAGE FORMS BYUV SPECTROSCOPY
Page67 Available Online through IJPBS Volume 1 Issue 2 APRIL- JUNE 2011 SIMPLE QUANTITATIVE METHOD DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION OF VALSARTAN IN PUREFORM AND PHARMACEUTICAL DOSAGE FORMS BYUV SPECTROSCOPY
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
Basic Concepts of TDM
 TDM Lecture 1 5 th stage What is TDM? Basic Concepts of TDM Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is a branch of clinical pharmacology that specializes in the measurement of medication concentrations in blood.
TDM Lecture 1 5 th stage What is TDM? Basic Concepts of TDM Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) is a branch of clinical pharmacology that specializes in the measurement of medication concentrations in blood.
Monitoring intracellular activity of Arylsulfatase B on its natural substrates in a functional bioassay using LIF-CZE
 Monitoring intracellular activity of Arylsulfatase B on its natural substrates in a functional bioassay using LIF-CZE Erno Pungor Jr; Charles M. Hague; Ginger Chen; Jeffrey F. Lemontt; William S. Prince
Monitoring intracellular activity of Arylsulfatase B on its natural substrates in a functional bioassay using LIF-CZE Erno Pungor Jr; Charles M. Hague; Ginger Chen; Jeffrey F. Lemontt; William S. Prince
Experiment 3: Activity Determination
 Experiment 3: Activity Determination Introduction: Specific activity is a method for measuring enzymatic activity and the enzyme purity in a mixture. In order to determine the specific activity of an enzyme,
Experiment 3: Activity Determination Introduction: Specific activity is a method for measuring enzymatic activity and the enzyme purity in a mixture. In order to determine the specific activity of an enzyme,
Human Creatinine Urinary Detection Kit
 Human Creatinine Urinary CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2509 Detection Kit LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Urinary Creatinine kit is designed to quantitatively measure creatinine present in urine samples. BACKGROUND
Human Creatinine Urinary CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2509 Detection Kit LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Urinary Creatinine kit is designed to quantitatively measure creatinine present in urine samples. BACKGROUND
Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set
 Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10231 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in
Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10231 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in
YK052 Mouse Leptin ELISA
 YK052 Mouse Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA-SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Ⅰ. Introduction 2 Ⅱ. Characteristics 3 Ⅲ. Composition 4 Ⅳ. Method
YK052 Mouse Leptin ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA-SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418-0011 Contents Ⅰ. Introduction 2 Ⅱ. Characteristics 3 Ⅲ. Composition 4 Ⅳ. Method
Human LDL ELISA Kit. Innovative Research, Inc.
 Human LDL ELISA Kit Catalog No: IRKTAH2582 Lot No: SAMPLE INTRODUCTION Human low-density lipoprotein (LDL) transports cholesterol from the liver to tissues where it is incorporated into cell membranes.
Human LDL ELISA Kit Catalog No: IRKTAH2582 Lot No: SAMPLE INTRODUCTION Human low-density lipoprotein (LDL) transports cholesterol from the liver to tissues where it is incorporated into cell membranes.
Report Reference Guide
 Report Reference Guide How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections. Report data used to generate the sample reports was from sample patient
Report Reference Guide How to use this guide Each type of CareLink report and its components are described in the following sections. Report data used to generate the sample reports was from sample patient
Insulin Aspart ELISA Kit
 Insulin Aspart ELISA Kit Catalogue DEIABL215 For the qualitative determination of antibodies to insulin aspart in human serum and plasma FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Creative Diagnostics. All rights reserved
Insulin Aspart ELISA Kit Catalogue DEIABL215 For the qualitative determination of antibodies to insulin aspart in human serum and plasma FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Creative Diagnostics. All rights reserved
PFK Activity Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
 PFK Activity Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA3761 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
PFK Activity Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number KA3761 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176
 human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176 This DuoSet ELISA Development kit contains the basic components required for the development of sandwich ELISAs to measure natural and recombinant human Total
human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176 This DuoSet ELISA Development kit contains the basic components required for the development of sandwich ELISAs to measure natural and recombinant human Total
Dose response relationships: biological and modeling aspects
 Dose response relationships: biological and modeling aspects Jason Aungst, Ph.D. Office of Food Additive Safety Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition U.S. Food and Drug Administration The findings
Dose response relationships: biological and modeling aspects Jason Aungst, Ph.D. Office of Food Additive Safety Center for Food Safety and Applied Nutrition U.S. Food and Drug Administration The findings
INTERACTION DRUG BODY
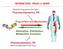 INTERACTION DRUG BODY What the drug does to the body What the body does to the drug Receptors - intracellular receptors - membrane receptors - Channel receptors - G protein-coupled receptors - Tyrosine-kinase
INTERACTION DRUG BODY What the drug does to the body What the body does to the drug Receptors - intracellular receptors - membrane receptors - Channel receptors - G protein-coupled receptors - Tyrosine-kinase
Dense and Dynamic Polyethylene Glycol Shells Cloak Nanoparticles. from Uptake by Liver Endothelial Cells for Long Blood Circulation
 Dense and Dynamic Polyethylene Glycol Shells Cloak Nanoparticles from Uptake by Liver Endothelial Cells for Long Blood Circulation Hao Zhou, Zhiyuan Fan, Peter Y. Li, Junjie Deng,, Dimitrios C. Arhontoulis,
Dense and Dynamic Polyethylene Glycol Shells Cloak Nanoparticles from Uptake by Liver Endothelial Cells for Long Blood Circulation Hao Zhou, Zhiyuan Fan, Peter Y. Li, Junjie Deng,, Dimitrios C. Arhontoulis,
Fructose Assay Kit. Catalog Number KA assays Version: 04. Intended for research use only.
 Fructose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1668 100 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Fructose Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1668 100 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
<Supplemental information>
 The Structural Basis of Endosomal Anchoring of KIF16B Kinesin Nichole R. Blatner, Michael I. Wilson, Cai Lei, Wanjin Hong, Diana Murray, Roger L. Williams, and Wonhwa Cho Protein
The Structural Basis of Endosomal Anchoring of KIF16B Kinesin Nichole R. Blatner, Michael I. Wilson, Cai Lei, Wanjin Hong, Diana Murray, Roger L. Williams, and Wonhwa Cho Protein
Human Hemoglobin Colorimetric Detection Kit
 Human Hemoglobin Colorimetric Detection Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2522 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Hemoglobin detection kit is designed to quantitatively measure all forms of hemoglobin present in blood
Human Hemoglobin Colorimetric Detection Kit CATALOG NO: IRAAKT2522 LOT NO: SAMPLE INTENDED USE The Hemoglobin detection kit is designed to quantitatively measure all forms of hemoglobin present in blood
Lippincott Questions Pharmacology
 Lippincott Questions Pharmacology Edition Two: Chapter One: 1.Which one of the following statements is CORRECT? A. Weak bases are absorbed efficiently across the epithelial cells of the stomach. B. Coadministration
Lippincott Questions Pharmacology Edition Two: Chapter One: 1.Which one of the following statements is CORRECT? A. Weak bases are absorbed efficiently across the epithelial cells of the stomach. B. Coadministration
Human Obestatin ELISA
 K-ASSAY Human Obestatin ELISA For the quantitative determination of obestatin in human serum and plasma Cat. No. KT-495 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 081309 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION Human Obestatin
K-ASSAY Human Obestatin ELISA For the quantitative determination of obestatin in human serum and plasma Cat. No. KT-495 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 081309 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION Human Obestatin
Rat Leptin-HS ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN
 YK051 Rat Leptin-HS ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418 0011 Contents Introduction 2 Characteristics 3 Composition 4 Method 5-6 Notes
YK051 Rat Leptin-HS ELISA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY YANAIHARA INSTITUTE INC. 2480-1 AWAKURA, FUJINOMIYA - SHI SHIZUOKA, JAPAN 418 0011 Contents Introduction 2 Characteristics 3 Composition 4 Method 5-6 Notes
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/4/e1500980/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The crystal structure of human dopamine -hydroxylase at 2.9 Å resolution Trine V. Vendelboe, Pernille Harris, Yuguang
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/4/e1500980/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The crystal structure of human dopamine -hydroxylase at 2.9 Å resolution Trine V. Vendelboe, Pernille Harris, Yuguang
Available Online through Research Article
 ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC METHODS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF FROVATRIPTAN SUCCINATE MONOHYDRATE IN BULK AND PHARMACEUTICAL DOSAGE FORMS
ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com SPECTROPHOTOMETRIC METHODS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF FROVATRIPTAN SUCCINATE MONOHYDRATE IN BULK AND PHARMACEUTICAL DOSAGE FORMS
Serrata) Alkaline Phosphatase
 Vol. 41, No. 5, April 1997 BIOCHEMISTRY and MOLECULAR BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Pages 951-959 An Essential Tryptophan Residue of Green Crab (Syclla Serrata) Alkaline Phosphatase Wen-Zhu Zheng 1, Qing-Xi Chen
Vol. 41, No. 5, April 1997 BIOCHEMISTRY and MOLECULAR BIOLOGY INTERNATIONAL Pages 951-959 An Essential Tryptophan Residue of Green Crab (Syclla Serrata) Alkaline Phosphatase Wen-Zhu Zheng 1, Qing-Xi Chen
Gastric, intestinal and colonic absorption of metoprolol in
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1985), 19, 85S-89S Gastric, intestinal and colonic absorption of metoprolol in the rat J. DOMENECH', M. ALBA', J. M. MORERA', R. OBACH' & J. M. PLA DELFINA2 'Department of Pharmaceutics,
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1985), 19, 85S-89S Gastric, intestinal and colonic absorption of metoprolol in the rat J. DOMENECH', M. ALBA', J. M. MORERA', R. OBACH' & J. M. PLA DELFINA2 'Department of Pharmaceutics,
Human Leptin ELISA Kit
 Product Manual Human Leptin ELISA Kit Catalog Numbers MET-5057 MET-5057-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Leptin is a polypeptide hormone
Product Manual Human Leptin ELISA Kit Catalog Numbers MET-5057 MET-5057-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Leptin is a polypeptide hormone
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit
 Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Phospho-AKT Sampler Kit E 0 5 1 0 0 3 Kits Includes Cat. Quantity Application Reactivity Source Akt (Ab-473) Antibody E021054-1 50μg/50μl IHC, WB Human, Mouse, Rat Rabbit Akt (Phospho-Ser473) Antibody
Drug transport across the blood brain barrier
 Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism (2012) 32, 1959 1972 & 2012 ISCBFM All rights reserved 0271-678X/12 $32.00 www.jcbfm.com REVIEW ARTICLE Drug transport across the blood brain barrier William
Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism (2012) 32, 1959 1972 & 2012 ISCBFM All rights reserved 0271-678X/12 $32.00 www.jcbfm.com REVIEW ARTICLE Drug transport across the blood brain barrier William
Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting
 The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol. absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1
 The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1 Pei-Shan Li 1, Zhen-Yan Fu 1,2, Ying-Yu Zhang 1, Jin-Hui Zhang 1, Chen-Qi Xu 1, Yi-Tong Ma
The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1 Pei-Shan Li 1, Zhen-Yan Fu 1,2, Ying-Yu Zhang 1, Jin-Hui Zhang 1, Chen-Qi Xu 1, Yi-Tong Ma
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Supporting Information. Maximizing the Supported Bilayer Phenomenon: LCP Liposomes Comprised Exclusively
 S-1 Supporting Information Maximizing the Supported Bilayer Phenomenon: LCP Liposomes Comprised Exclusively of PEGylated Phospholipids for Enhanced Systemic and Lymphatic Delivery Matthew T. Haynes and
S-1 Supporting Information Maximizing the Supported Bilayer Phenomenon: LCP Liposomes Comprised Exclusively of PEGylated Phospholipids for Enhanced Systemic and Lymphatic Delivery Matthew T. Haynes and
Protease Activity Assay Kit (Red)
 Protease Activity Assay Kit (Red) Catalog Number KA2524 500 assays Version: 11 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4
Protease Activity Assay Kit (Red) Catalog Number KA2524 500 assays Version: 11 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4
v o = V max [S] rate = kt[s] e V max = k cat E t ΔG = -RT lnk eq K m + [S]
![v o = V max [S] rate = kt[s] e V max = k cat E t ΔG = -RT lnk eq K m + [S] v o = V max [S] rate = kt[s] e V max = k cat E t ΔG = -RT lnk eq K m + [S]](/thumbs/81/84404059.jpg) Exam 3 Spring 2017 Dr. Stone 8:00 Name There are 100 possible points on this exam. -ΔG / RT v o = V max [S] rate = kt[s] e V max = k cat E t ΔG = -RT lnk eq K m + [S] h rate forward = k forward [reactants]
Exam 3 Spring 2017 Dr. Stone 8:00 Name There are 100 possible points on this exam. -ΔG / RT v o = V max [S] rate = kt[s] e V max = k cat E t ΔG = -RT lnk eq K m + [S] h rate forward = k forward [reactants]
INTRATHECAL APPLICATION OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES. Samo Rožman Institute of Oncology Ljubljana Slovenia
 INTRATHECAL APPLICATION OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES Samo Rožman Institute of Oncology Ljubljana Slovenia AGENDA 1. INTRATHECAL APPLICATION 2. MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES 3. MALIGNANT CARCINOMATOSIS 4. INTRATHECAL
INTRATHECAL APPLICATION OF MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES Samo Rožman Institute of Oncology Ljubljana Slovenia AGENDA 1. INTRATHECAL APPLICATION 2. MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES 3. MALIGNANT CARCINOMATOSIS 4. INTRATHECAL
Lipid Peroxidation Assay
 Package Insert Lipid Peroxidation Assay 96 Wells For Research Use Only v. 1.0 Eagle Biosciences, Inc. 82 Broad Street, Suite 383, Boston, MA 02110 Phone: 866-419-2019 Fax: 617-419-1110 INTRODUCTION Lipid
Package Insert Lipid Peroxidation Assay 96 Wells For Research Use Only v. 1.0 Eagle Biosciences, Inc. 82 Broad Street, Suite 383, Boston, MA 02110 Phone: 866-419-2019 Fax: 617-419-1110 INTRODUCTION Lipid
Supplementary materials for manuscript entitled Development and Analytical
 Supplementary materials for manuscript entitled Development and Analytical Validation of An Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the detection of Copper in Human Hair and Serum Samples Manuscripte
Supplementary materials for manuscript entitled Development and Analytical Validation of An Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for the detection of Copper in Human Hair and Serum Samples Manuscripte
GUIDELINES FOR WEIGHT-BASED DOSING AND INFUSION
 GUIDELINES FOR WEIGHT-BASED DOSING AND INFUSION Includes Example dose calculation wheel Preparation and administration information for healthcare professionals Please see enclosed full Prescribing Information,
GUIDELINES FOR WEIGHT-BASED DOSING AND INFUSION Includes Example dose calculation wheel Preparation and administration information for healthcare professionals Please see enclosed full Prescribing Information,
Kinetic assay of serum and urine for urea with use of urease and leucine dehydrogenase
 Clinical Chemistry 43:10 1932 1936 (1997) Automation and Analytical Techniques Kinetic assay of serum and urine for urea with use of urease and leucine dehydrogenase Yoshitaka Morishita, 1 * Kiyoshi Nakane,
Clinical Chemistry 43:10 1932 1936 (1997) Automation and Analytical Techniques Kinetic assay of serum and urine for urea with use of urease and leucine dehydrogenase Yoshitaka Morishita, 1 * Kiyoshi Nakane,
To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank
 Supplementary Discussion The source of hepatitis B virus infection To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank and HBV Database (http://hbvdb.ibcp.fr),
Supplementary Discussion The source of hepatitis B virus infection To test the possible source of the HBV infection outside the study family, we searched the Genbank and HBV Database (http://hbvdb.ibcp.fr),
Structural Characterization of Prion-like Conformational Changes of the Neuronal Isoform of Aplysia CPEB
 Structural Characterization of Prion-like Conformational Changes of the Neuronal Isoform of Aplysia CPEB Bindu L. Raveendra, 1,5 Ansgar B. Siemer, 2,6 Sathyanarayanan V. Puthanveettil, 1,3,7 Wayne A. Hendrickson,
Structural Characterization of Prion-like Conformational Changes of the Neuronal Isoform of Aplysia CPEB Bindu L. Raveendra, 1,5 Ansgar B. Siemer, 2,6 Sathyanarayanan V. Puthanveettil, 1,3,7 Wayne A. Hendrickson,
Pharmacokinetics and allometric scaling of levormeloxifene, a selective oestrogen receptor modulator
 BIOPHARMACEUTICS & DRUG DISPOSITION Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 24: 121 129 (2003) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/bdd.344 Pharmacokinetics and allometric scaling
BIOPHARMACEUTICS & DRUG DISPOSITION Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 24: 121 129 (2003) Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/bdd.344 Pharmacokinetics and allometric scaling
Coenzyme A Assay Kit. Catalog Number KA assays Version: 02. Intended for research use only.
 Coenzyme A Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0809 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials Supplied...
Coenzyme A Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0809 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials Supplied...
Mouse Leptin ELISA Kit (mleptin-elisa)
 Mouse Leptin ELISA Kit (mleptin-elisa) Cat. No. EK0438 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Leptin (or obese, OB) is a circulating hormone that is expressed abundantly and specifically in the
Mouse Leptin ELISA Kit (mleptin-elisa) Cat. No. EK0438 96 Tests in 8 x 12 divisible strips Background Leptin (or obese, OB) is a circulating hormone that is expressed abundantly and specifically in the
VIROMER ONE. standardized transfection reagent
 VIROMER ONE standardized transfection reagent 1 Doing transfection is like making coffee. Same procedure, somewhat different result each time you do it. Then came Nespresso. An easy, comfortable and clean
VIROMER ONE standardized transfection reagent 1 Doing transfection is like making coffee. Same procedure, somewhat different result each time you do it. Then came Nespresso. An easy, comfortable and clean
Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set
 Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10815 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10815 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
ALLOSTERIC REGULATION OF GPCR ACTIVITY BY PHOSPHOLIPIDS
 Supplementary Information ALLOSTERIC REGULATION OF GPCR ACTIVITY BY PHOSPHOLIPIDS Rosie Dawaliby 1, Cataldo Trubbia 1, Cédric Delporte 3,4, Matthieu Masureel 2, Pierre Van Antwerpen 3,4, Brian K. Kobilka
Supplementary Information ALLOSTERIC REGULATION OF GPCR ACTIVITY BY PHOSPHOLIPIDS Rosie Dawaliby 1, Cataldo Trubbia 1, Cédric Delporte 3,4, Matthieu Masureel 2, Pierre Van Antwerpen 3,4, Brian K. Kobilka
Pharmacokinetic overview of Ortho Evra /Evra
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY VOL. 77, NO. 2, SUPPL 2 FEBRUARY 2002 Copyright 2002 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Published by Elsevier Science Inc. Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. Pharmacokinetic
FERTILITY AND STERILITY VOL. 77, NO. 2, SUPPL 2 FEBRUARY 2002 Copyright 2002 American Society for Reproductive Medicine Published by Elsevier Science Inc. Printed on acid-free paper in U.S.A. Pharmacokinetic
Exendin-4 (Exenatide) ELISA Kit
 Exendin-4 (Exenatide) ELISA Kit Catalog: DEIABL227 For the quantitative determination of Exendin-4 in serum or plasma using competitive ELISA method For Research Use Only. Protocol Provided for Informational
Exendin-4 (Exenatide) ELISA Kit Catalog: DEIABL227 For the quantitative determination of Exendin-4 in serum or plasma using competitive ELISA method For Research Use Only. Protocol Provided for Informational
Francesco Parlati, Ph.D.
 Novel Pharmacodynamic Assays to Measure Glutaminase Inhibition Following Oral Administration of CB-839 Francesco Parlati, Ph.D. Calithera Biosciences South San Francisco, California Disclosure Information
Novel Pharmacodynamic Assays to Measure Glutaminase Inhibition Following Oral Administration of CB-839 Francesco Parlati, Ph.D. Calithera Biosciences South San Francisco, California Disclosure Information
Human Neurology 3-Plex A
 Human Neurology 3-Plex A SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION OF THE TEST The Human N3PA assay is a digital immunoassay for the quantitative determination of total Tau, Aβ42, and Aβ40 in human plasma and CSF. Determination
Human Neurology 3-Plex A SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION OF THE TEST The Human N3PA assay is a digital immunoassay for the quantitative determination of total Tau, Aβ42, and Aβ40 in human plasma and CSF. Determination
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Analysis
 139 International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Analysis e-issn: 2249 7781 Print ISSN: 2249 779X www.ijpra.com A VALIDATED SIMULTANEOUS ESTIMATION OF DOXYLAMINE SUCCINATE AND PYRIDOXINE HYDROCHLORIDE
139 International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Analysis e-issn: 2249 7781 Print ISSN: 2249 779X www.ijpra.com A VALIDATED SIMULTANEOUS ESTIMATION OF DOXYLAMINE SUCCINATE AND PYRIDOXINE HYDROCHLORIDE
BabyBio IMAC columns DATA SHEET DS
 BabyBio IMAC columns DATA SHEET DS 45 655 010 BabyBio columns for Immobilized Metal Ion Affinity Chromatography (IMAC) are ready-to-use for quick and easy purification of polyhistidine-tagged (His-tagged)
BabyBio IMAC columns DATA SHEET DS 45 655 010 BabyBio columns for Immobilized Metal Ion Affinity Chromatography (IMAC) are ready-to-use for quick and easy purification of polyhistidine-tagged (His-tagged)
Product: Omecamtiv Mecarbil Clinical Study Report: Date: 02 April 2014 Page 1
 Date: 02 April 2014 Page 1. 2. SYNOPSIS Name of Sponsor: Amgen Inc. Name of Finished Product: Omecamtiv mecarbil injection Name of Active Ingredient: Omecamtiv mecarbil (AMG 423) Title of Study: A double-blind,
Date: 02 April 2014 Page 1. 2. SYNOPSIS Name of Sponsor: Amgen Inc. Name of Finished Product: Omecamtiv mecarbil injection Name of Active Ingredient: Omecamtiv mecarbil (AMG 423) Title of Study: A double-blind,
Preparation of SG3249 antibody-drug conjugates
 Preparation of SG3249 antibody-drug conjugates Conjugate A: Herceptin-SG3249 (ConjA) Antibody (15 mg, 100 nanomoles) was diluted into 13.5 ml of a reduction buffer containing 10 mm sodium borate ph 8.4,
Preparation of SG3249 antibody-drug conjugates Conjugate A: Herceptin-SG3249 (ConjA) Antibody (15 mg, 100 nanomoles) was diluted into 13.5 ml of a reduction buffer containing 10 mm sodium borate ph 8.4,
Insulin therapy in gestational diabetes mellitus
 Insulin therapy in gestational diabetes mellitus October 15, 2015 Kyung-Soo Kim Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University Contents
Insulin therapy in gestational diabetes mellitus October 15, 2015 Kyung-Soo Kim Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, CHA Bundang Medical Center, CHA University Contents
Available online Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(3):289-294 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Simultaneous UV-spectrophotometric estimation of
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(3):289-294 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Simultaneous UV-spectrophotometric estimation of
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Transplant Proc. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2011 April 6.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Transplant Proc. 1991 December ; 23(6): 2777 2779. Pharmacokinetics of Cyclosporine and Nephrotoxicity in Orthotopic Liver Transplant
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Transplant Proc. 1991 December ; 23(6): 2777 2779. Pharmacokinetics of Cyclosporine and Nephrotoxicity in Orthotopic Liver Transplant
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis
 Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis Soluble CD8αα and was manufactured as described previously. 1,2 The C12C heterodimeric TCR was produced using an engineered disulfide bridge between the constant
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis Soluble CD8αα and was manufactured as described previously. 1,2 The C12C heterodimeric TCR was produced using an engineered disulfide bridge between the constant
2009 H1N1 Influenza ( Swine Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA kit
 2009 H1N1 Influenza ( Swine Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA kit Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as
2009 H1N1 Influenza ( Swine Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA kit Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as
ACTIVITY OF BRINCIDOFOVIR (BCV) AGAINST MURINE POLYOMAVIRUS (MUPYV) IN A MOUSE INFECTION MODEL
 ACTIVITY OF BRINCIDOFOVIR (BCV) AGAINST MURINE POLYOMAVIRUS (MUPYV) IN A MOUSE INFECTION MODEL Kidney Week 2018 Poster # SA-PO642 BRINCIDOFOVIR(BCV) DEMONSTRATES ANTIVIRAL ACTIVITY AGAINST MURINE POLYOMAVIRUS
ACTIVITY OF BRINCIDOFOVIR (BCV) AGAINST MURINE POLYOMAVIRUS (MUPYV) IN A MOUSE INFECTION MODEL Kidney Week 2018 Poster # SA-PO642 BRINCIDOFOVIR(BCV) DEMONSTRATES ANTIVIRAL ACTIVITY AGAINST MURINE POLYOMAVIRUS
Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range
 Product Name: DynaMarker Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range Code No: DM670L Lot No: ******* Size: 200 μl x 3 (DM670 x 3) (120 mini-gel lanes) Storage: 4 C Stability: 12 months at 4 C Storage Buffer:
Product Name: DynaMarker Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range Code No: DM670L Lot No: ******* Size: 200 μl x 3 (DM670 x 3) (120 mini-gel lanes) Storage: 4 C Stability: 12 months at 4 C Storage Buffer:
Nanoparticles as Drug-Delivery D Systems
 Nanoparticles as Drug-Delivery D Systems Melissa Herman Infectious Minds Jan 19 th 2012 Advantages in drug delivery Small: allows uptake into cells and areas that are not easily accessible by larger particles
Nanoparticles as Drug-Delivery D Systems Melissa Herman Infectious Minds Jan 19 th 2012 Advantages in drug delivery Small: allows uptake into cells and areas that are not easily accessible by larger particles
UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations Department: BIOLOGY. Title of Exam: Cell Biology
 Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Cell Biology Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Total marks available
Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Cell Biology Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Total marks available
