Gillian Kreugel, M.S.C., Joost C. Keers, Ph.D., Michiel N. Kerstens, M.D., Ph.D., and Bruce H.R. Wolffenbuttel, M.D., Ph.D.
|
|
|
- Angel Sherilyn Stephens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 13, Number 7, 2011 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: /dia Randomized Trial on the Influence of the Length of Two Insulin Pen Needles on Glycemic Control and Patient Preference in Obese Patients with Diabetes Gillian Kreugel, M.S.C., Joost C. Keers, Ph.D., Michiel N. Kerstens, M.D., Ph.D., and Bruce H.R. Wolffenbuttel, M.D., Ph.D. Abstract Objective: This study determined the influence of needle length for insulin administration on metabolic control and patient preference in obese patients with diabetes mellitus. Methods: In this multicenter, open-label crossover study, insulin pen needles of two different lengths (5 mm and 8 mm) were compared. A total of 130 insulin-treated type 1 and type 2 diabetes patients with a body mass index 30 kg/m 2 were randomized, and 126 patients completed the study. Patients started using the 5-mm needle for 3 months, after which they switched to injecting insulin with the 8-mm needle for another 3 months, or vice versa. Hemoglobin A1c (A1C), fructosamine, and 1,5-anhydroglucitol were measured, and self-reported side effects and patient preference were recorded. Results: No within-group changes were observed with respect to A1C, serum fructosamine, 1,5-anhydroglucitol, hypoglycemic events, bruising, and pain. When data of all 126 subjects were pooled, there was a small, but significant, difference between needle lengths (5-mm, A1C %; 8-mm, %; P ¼ 0.02). Patients reported less bleeding with the 5-mm needle (P ¼ 0.04) and less insulin leakage from the skin with the 8-mm needle (P ¼ 0.01). There were no significant differences in patient preference, with 46% of the patients preferring the 5-mm needle, 41% the 8-mm needle, and 13% not preferring a particular needle length. Conclusions: A 5-mm needle is similar to an 8-mm needle in obese patients with diabetes with respect to metabolic control, injection-related complaints, or patient preference and can be used safely. Introduction Acorrect injection technique during subcutaneous insulin administration is important for optimal glucose control. 1 5 Preferred insulin injection sites are the upper arm and the anterior and lateral aspects of the thigh, buttocks, and abdomen. 6 Insulin can be injected with a conventional syringe or with an insulin pen and pen needle. Pen needles vary by length and diameter (gauge). According to a recent study in Europe, 92% of adult patients on insulin treatment were using an insulin pen with a disposable needle, and 63% were using an 8-mm needle or longer. 7 In many countries use of a 8-mm needle or longer is recommended for obese adults. 8,9 The Canadian Diabetes Association writes, short needles are not suitable for everyone; in people who are overweight, the short needle might not penetrate deeply enough to reach the layer where the insulin can be absorbed into the body. 8 Contrary to the previous assertion, research suggests the needle only needs to pass through the skin, which has been shown to be less than 2.88 mm thick in more than 95% of healthy subjects with a wide range of anthropometric characteristics. 10,11 Patients injecting insulin can experience local injectionrelated side effects, such as pain, bruising, and bleeding, but also insulin backflow (i.e., leakage) from the skin after needle withdrawal. Several studies (including one by Schwarz et al., 12 which compared the use of relatively long needles by obese patients) have reported that the majority of patients prefer to use a shorter needle Nevertheless, there is still some reluctance to recommend the use of shorter needles to obese adults. Therefore, we conducted a randomized study comparing the effects of two insulin pen needles on glycemic control and patient preference in obese subjects with diabetes mellitus. Department of Endocrinology, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands. This trial is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov with trial number NCT Portions of this study have been presented as a poster during the 2009 Scientific Meeting of the American Diabetes Association. 737
2 738 KREUGEL ET AL. Research Design and Methods In this multicenter, open label, crossover study, 130 obese patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes treated with insulin and using an insulin pen were randomized into two groups. Group A started using a 31-gauge 5-mm insulin pen needle for 3 consecutive months, after which they switched to a 31-gauge 8-mm needle for another 3 months (BD Micro-Fine Ò Mini and Short insulin pen needles, Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ); group B used these two different needles in reverse order. Patients were recruited from the outpatient clinics of one university medical center and four non-university hospitals in The Netherlands (see Appendix). Male and female patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes were eligible if they injected insulin with a pen device for at least 1 year, were 18 years of age, and had a body mass index (BMI) of 30 kg/m 2. Exclusion criteria were self-adjustments of insulin doses that were incompletely recorded by the patient, hemoglobin A1c (A1C) levels showing >15% variation during the year prior to inclusion, hypoglycemia unawareness, pregnancy or an intention to become pregnant, hemoglobinopathies, or the presence of lipodystrophy. Patients were advised to use a new needle for each injection and to rotate injections within a specific body area. Thigh and abdomen were the recommended body areas for long-acting and fast-acting insulin, respectively, and these remained unchanged throughout the study. The volume threshold of insulin was 50 IU per injection. With a dose of more than 50 IU patients were advised to split the dose and administer the insulin in two injections within the same specific body area. With the 5-mm needle, patients did not use a skin fold and inserted the needle at an angle of 908. When using the 8-mm needle, patients were advisedtoinjectinaliftedskinfold. A1C, fructosamine, and 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG) were measured at baseline and after each 3-month treatment period. Both A1C and fructosamine measure the mean blood glucose concentration over a period of time, with A1C measuring control over the previous 2 3 months whereas fructosamine measures control over the previous 2 3 weeks. Another marker of glycemia is plasma 1,5-AG. Levels of 1,5- AG are inversely correlated with glycemia and reflect the 2-h postprandial glucose values of the previous 2 weeks. 17 In addition, information on insulin injection doses was collected, and body weight was measured at each visit. Waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) was measured at baseline. The number of hypoglycemic events and injection-related side effects (bleeding, bruising, and insulin backflow) were evaluated with a validated questionnaire with a 4-point Likert-scale. 14 The degree of pain experienced during insulin injection was measured using a 100-mm Visual Analog Scale (VAS), where 0 is no pain and 100 is worst possible pain. The study was approved by the medical ethics review committee of the University Medical Center Groningen, and all participants gave their written informed consent. A sample size calculation was made by means of a power analysis with patient s preference as the primary objective. It was thus calculated that 131 patients are needed to demonstrate a preference of 65% (i.e., an absolute difference of 15% compared with 50% in case of no preference) with a power of 85% and a two-sided P value < For A1C, 49 patients are needed to show that the treatment with 5-mm needles will not be inferior compared with 8-mm needles, defined as a difference in A1C not exceeding the outer bound of the 95% confidence interval (i.e., 0.4% [SD of the changes within a group of 0.92 and correlation coefficient between two measurements of 0.8; power 85%, bilaterally tested at a 0.05 level of significance]). In this power analysis, intra-individual variation of the glycemic control of patients has been taken into account. Data are presented as mean SD, or median and interquartile range, where appropriate. Paired t test and Wilcoxon s Signed Ranks test were used for within group analysis, and t test, w 2, and Mann Whitney U tests were used for between-group analysis, where appropriate. Bivariate relationships between parameters were evaluated by w 2 test, Spearman s rank correlation analysis, or Pearson s correlation analysis, where appropriate. SPSS (version 16.0, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL) was used for statistical analysis. The level of significance for all tests was P < Results Of 130 patients enrolled, 126 with type 1 (n ¼ 5) or type 2 (n ¼ 121) diabetes with a mean BMI of 36.4 kg/m 2 (range, kg/m 2 ) completed the study. Baseline characteristics for the two groups of patients with different sequence of needle use are presented in Table 1. Reasons for not completing the study were no reported reason (n ¼ 1), use of an autocover needle (n ¼ 1), and patient preference (n ¼ 2). One patient withdrew because of her impression that glucose regulation was better with the 6-mm needle she used before the start of the study (not supported by any changes in A1C level), and one patient withdrew because she experienced an increase of subcutaneous nodules with the 8-mm needle. There were 34 patients who did not apply the skin fold technique while using a 8-mm needle. During the study, body weight remained unchanged in both groups, and there were no significant within-group changes of A1C, fructosamine, or 1,5-AG levels (Table 2). The insulin dose in group A was unaffected but was slightly Table 1. Baseline Characteristics of the Participants According to Treatment Sequence Variable Group A (n ¼ 64) Group B (n ¼ 62) Gender (M/F ratio) 34/30 36/26 Age (years) BMI (kg/m 2 ) Waist-hip ratio Type 1/type 2 diabetes 3/61 2/60 Previously used needles Length 5 mm and/or 6 mm Length 5 mm/6mm and 8 mm 3 2 Length 8 mm Length 12.7 mm 1 2 A1C (%) FA (mmol/l) ,5-AG (mg/l) TDI (units/day) Data are given as absolute numbers or mean SD values. Group A first used the 31-gauge 5-mm pen needle and then the 31-gauge 8-mm pen needle; Group B used them in the reverse order. A1C, hemoglobin A1c; 1,5-AG, 1,5-anhydroglucitol; BMI, body mass index; F, female; FA, fructosamine; M, male; TDI, total daily insulin dose.
3 INFLUENCE OF NEEDLE LENGTH IN DIABETES 739 higher with the 8-mm needle in group B only ( vs U/day, P ¼ 0.03). When all 126 patients were pooled, mean A1C was slightly lower when using the 5-mm needle: baseline A1C was %; after 3 months use of the 5-mm needle was %, and with the 8-mm needle it was % (P ¼ 0.02 for 5-mm vs. 8-mm). No differences were demonstrated in concentrations of serum fructosamine ( vs mmol/l) and 1,5-AG ( vs mg/l) when pooled data for 5-mm versus 8-mm needle length were compared. There were no significant differences in self-reported hypoglycemic events (Table 3) during both periods. Patients reported less bleeding (P ¼ 0.04) with the 5-mm needle and less insulin backflow with the 8-mm needle (P ¼ 0.01), but no difference in bruising. Pain perception was low for both needles, as reflected by a median VAS score of 7 mm (interquartile range, 0 22) for the 5-mm needle and 9 mm (interquartile range, 0 23) for the 8-mm needle (difference not significant). There was no correlation (for both needle lengths) between insulin backflow from the skin and determinants as BMI, WHR, A1C, the total amount of daily insulin use, injection site, or application of skin fold (the latter injection technique only for the 8-mm needle). As expected, there was a strong correlation between reports of bleeding and of bruising (r ¼ 0.48 and 0.53, P < 0.01 for the 8-mm and 5-mm needle, respectively). There was no difference in patient preference, with 46% of patients preferring the 5-mm and 41% preferring the 8-mm needle, and 13% of patients expressing no specific preference for either needle length. Needle length before inclusion, WHR, or baseline BMI did not predict patients preference. Finally, at the individual level there was a strong correlation with respect to the occurrence of hypoglycemic events during the period using the 5-mm or the 8-mm needle (P < 0.01). This strong correlation was also seen with respect to the occurrence of bleeding, bruising, backflow of insulin, and pain. Discussion In the present study, we compared the effects of using either a 5-mm or an 8-mm needle for injecting insulin in a large group of obese patients with diabetes. Besides a small, but statistically significant, difference of A1C (0.12%, P ¼ 0.02) in favor of the 5-mm needle, there were no significant differences Table 3. Reported Hypoglycemic Symptoms According to Treatment Group 5-mm (n ¼ 126) Needle length 8-mm (n ¼ 126) Never Less than once a week Once or twice a week More than twice a week 7 5 w 2 ¼ 3.37, P ¼ in other parameters of glycemic control, incidence of hypoglycemia, or patient preference. In addition, there was no clinically relevant influence of needle length on injectionrelated side effects. The absence of effects of needle length on glycemic control is in agreement with the results obtained in other studies. 12,14 16 Schwartz et al. 12 reported a lack of change in A1C in 62 obese patients who used either a 31-gauge 6-mm needle or a 29- gauge 12.7-mm needle, each for 12 weeks. Our group has reported that the use of a 5-mm needle was associated with similar levels of A1C and frequency or severity of hypoglycemic events but less discomfort compared with 8-mm or 12-mm needles in a group of 68 patients with diabetes and a mean BMI of 28.2 kg/m In a very recent study, Hirsch et al. 15 reported comparative glycemic control in a 3-week two-period crossover study for a new 32-gauge 4-mm insulin pen needle compared with both 5-mm and 8-mm 31-gauge needles, using serum fructosamine as the measure of glycemic control. Unique in our study is the 1,5-AG measurement. Because 1,5-AG is influenced by postprandial elevations, any influences of needle length on postprandial glucose levels would be expected to have an influence on 1,5-AG. As reported, there were no changes in 1,5-AG levels. The percentage of patients preferring the shorter needle is lower than that found in an earlier study by our group in patients with varying degrees of obesity. 14 Schwartz et al. 12 reported a higher preference for a 6-mm needle versus a mm needle in obese patients with diabetes mellitus, although Table 2. Relevant Metabolic Parameters in the Two Treatment Groups After a 3-Month Period of Administering Insulin Injections with 5-mm or 8-mm Needles Use of needle length Group A (n ¼ 64) Group B (n ¼ 62) Variable 5-mm 8-mm 8-mm 5-mm Weight (kg) A1C (%) FA (mmol/l) ,5-AG (mg/l) TDI (IU) * Data are mean SD values. Group A first used the 31-gauge 5-mm pen needle and then the 31-gauge 8-mm pen needle; Group B used them in the reverse order. *P < 0.05 versus baseline. A1C, hemoglobin A1c; 1,5-AG, 1,5-anhydroglucitol; FA, fructosamine; TDI, total daily insulin dose.
4 740 KREUGEL ET AL. it is interesting that the patients did not distinguish between the two different needles when given injections in which they were blinded to the needle used. In several studies it was reported that using a shorter needle coincided with a lower injection-related pain score In these earlier studies, investigators not only have used needles of different length but also of different diameter, which could influence the results of patient preference and pain scores. In the present study only the length of both needle types was different. This supports the concept that needle diameter is a stronger determinant of injection-related pain than needle length, especially in obese patients. Indeed, several studies reported that a greater outer needle diameter (smaller gauge) was positively and significantly associated with increased pain at the site of insertion. 13,18,19 For example, in the study of Iwanaga and Kamoi 19 patients using a 32- gauge 6-mm needle, which has a smaller diameter, reported a lower pain score than when using a 31-gauge 5-mm needle, with the difference of outer diameter between both needle types being mm. However, these authors suggested that the difference in pain score may also be in part explained by a difference in needle manufacturing (standard vs. tapered needle) and coating. 20 In our study only needle length was different; diameter, manufacturing technique, and coating of the needle were similar. Our findings are not dissimilar from those reported by Hirsch et al., 15 where patients with a BMI of kg/m 2 rated the 32-gauge 4-mm pen needle as less painful and preferred it significantly more than the 31-gauge 5-mm and 8-mm comparator needles all of which had similar manufacturing technique and lubrication. However, both length and diameter/gauge differed in that trial (the 5-mm and 8-mm needles were not compared). A particular strength of our study is the large number of patients who participated, and the robustness of our findings supporting the safety of the use of short needles even in obese patients. There are also some limitations. Injectionrelated pain was assessed retrospectively during the second and third visit using a VAS. Such an assessment precludes the possibility of detecting variations in pain intensity between multiple injections and might be prone to recall bias. In addition, occurrence of hypoglycemic episodes was based on patient self-report, and confirmation by self-measurement of blood glucose was not required. This could have resulted in overestimation or underestimation of the hypoglycemia frequency as certain symptoms might have been incorrectly ascribed to a low blood glucose. However, we do not expect that confirmation of all hypoglycemic episodes by measurement of blood glucose would have significantly altered our conclusions because it is unlikely that patient perception in this respect would be different between both study periods. We conclude that the findings of this study provide strong support for the current Danish guidelines 21 and the new injection recommendations for patients with diabetes 22 emphasizing greater use of shorter-length pen needles. Our data suggest that there is no additional benefit and no major clinical difference in insulin action (as reflected by A1C, fructosamine, and 1,5-AG), when insulin is injected with either of the two needle lengths, in an obese population. Contrary to some patient instruction information, 8 the 5-mm needles can be safely used for insulin injections in obese patients with diabetes mellitus. Appendix Participating centers (diabetes nurse specialists) Department of Endocrinology, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, Groningen, The Netherlands: B. De Boer, I. Hoekstra, C. Janson, A.J. Jongbloed, L.G.J. Smit, and R. Zuur. Department of Internal Medicine, Refaja Hospital, Stadskanaal, The Netherlands: G.A.T. Eleveld-Hoezen, M. Steenge, and A.H. Verweij-Gjaltema. Department of Internal Medicine, Delfzicht Hospital, Delfzijl, The Netherlands: L. Hoffman, H.M. Spoelstra-Knol, and H. Van Dijken. Department of Internal Medicine, Martini Hospital, Groningen: S.M. Snel. Department of Internal Medicine, Wilhelmina Hospital, Assen, The Netherlands: J.M.C. Luttmer. Acknowledgments We thank Dr. L. Hirsch and Dr. K. Strauss (Becton Dickinson) for their review of the manuscript. We thank the diabetes nurse specialists from the participating hospitals (see Appendix) for their skillful and enthusiastic participation and Dr. W. Sluiter for his statistical advice. Author Disclosure Statement This project was supported by an unrestricted research grant from Becton Dickinson. The authors of this paper independently wrote the study protocol, collected and analyzed the data, and wrote the entire manuscript including the discussion. The sponsor has reviewed the study manuscript, but this review had no influence on the content of the manuscript or its conclusions. The principal investigator fully controlled the decision to submit for publication. No other potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported. References 1. Thow JC, Johnson AB, Fulcher G, Home PD: Different absorption of isophane (NPH) insulin from subcutaneous and intramuscular sites suggests a need to reassess recommended insulin injection technique. Diabet Med 1990;7: Thow JC, Coulthard A, Home PD: Insulin injection site tissue depths and localization of a simulated insulin bolus using a novel air contrast ultrasonographic technique in insulin treated diabetic subjects. Diabet Med 1992;9: Bantle JP, Neal L, Frankamp LM: Effects of the anatomical region used for insulin injections on glycemia in type I diabetes subjects. Diabetes Care 1993;16: Engstrom L, Bergman A: A new injection technique for insulin treatment, simpler to use and as effective? Scand J Caring Sci 1993;7: Strauss K, De Gols H, Hannet I, Partanen TM, Frid A: A pan- European epidemiologic study of insulin injection technique in patients with diabetes. Pract Diabetes Int 2002;19: American Diabetes Association: Insulin administration. Diabetes Care 2004;27(Suppl 1):S106 S De Coninck C, Frid A, Gaspar R, Hicks D, Hirsch L, Kreugel G, Liersch J, Letondeur C, Sauvanet JP, Tubiana N, Strauss K: The Insulin Injection Technique Questionnaire Survey: results and analysis. J Diabetes 2010;2:
5 INFLUENCE OF NEEDLE LENGTH IN DIABETES Canadian Diabetes Association: Guide to Diabetes Products and Diabetes Medications. (accessed November 2010). 9. Hanicotte B: Recommendations de Bonnes Pratiques. Alfediam Paramedical. (accessed November 2010). 10. Laurent A, Mistretta F, Bottigioli D, Dahel K, Goujon C, Nicolas JF, Hennino A, Laurent PE: Echographic measurement of skin thickness in adults by high frequency ultrasound to assess the appropriate microneedle length for intradermal delivery of vaccines. Vaccine 2007;25: Gibney MA, Arce CH, Byron KJ, Hirsch LJ: Skin and subcutaneous adipose layer thickness in adults with diabetes at sites used for insulin injections: implications for needle length recommendations. Curr Med Res Opin 2010;26: Schwartz S, Hassman D, Shelmet J, Sievers R, Weinstein R, Liang J, Lyness WA: A multicenter, open-label, randomized, two-period crossover trial comparing glycemic control, satisfaction, and preference achieved with a 31 gauge 6mm needle versus a 29 gauge12.7 mm needle in obese patients with diabetes mellitus. Clin Ther 2004;26: McKay M, Compion G, Lytzen L: A comparison of insulin injection needles on patients perceptions of pain, handling, and acceptability: a randomized, open-label, crossover study in subjects with diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther 2009;11: Kreugel G, Beijer HJM, Kerstens MN, Maaten ter JC, Sluiter WJ, Boot BS: Influence of needle size for subcutaneous insulin administration on metabolic control and patient acceptance. Eur Diabetes Nurs 2007;4: Hirsch LJ, Gibney MA, Albanese J, Qu S, Kassler-Taub K, Klaff LJ, Bailey TS: Comparative glycemic control, safety and patient ratings for a new 4 mm32g insulin pen needle in adults with diabetes. Curr Med Res Opin 2010;26: Van Doorn LG, Albeda A, Lytzen L: Insulin leakage and pain perception with NovoFine, 6mm and NovoFine, 12mm needle lengths in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes [abstract]. Diabet Med 1998;15:S Stettler C, Stahl M, Allemann S, Diem P, Schmidlin K, Zwahlen M, Riesen W, Keller U, Christ E: Association of 1,5- anhydroglucitol and 2-h postprandial blood glucose in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2008;31: Arendt-Nielsen L, Egekvist H, Bjerring P: Pain following controlled cutaneous insertion of needles with different diameters. Somatosens Mot Res 2006;23: Iwanaga M, Kamoi K: Patient perceptions of injection pain and anxiety: a comparison of NovoFine 32-gauge tip 6mm and Micro Fine Plus 31-gauge 5mm needles. Diabetes Technol Ther 2009;11: Miyakoshi M, Kamoi K, Iwanaga M, Hoshiyama A, Yamada A: Comparison of patient s preference, pain perception, and usability between Micro Fine Plus 31-gauge needle and Microtapered NanoPass 33-gauge needle for insulin therapy. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2007;1: Danish Nurses Association: Evidence-Based Clinical Guidelines for Injection of Insulin for Adults with Diabetes Mellitus, 2nd ed. Updated (accessed December 2010). 22. Frid A, Hirsch L, Gaspar R, Hicks D, Kreugel G, Liersch J, Letondeur C, Sauvanet JP, Tubiana-Rufi N, Strauss K: New injection recommendations for patients with diabetes. Diabetes Metab 2010;36(Suppl 2):S3 S18. Address correspondence to: Bruce H.R. Wolffenbuttel, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Endocrinology University Medical Center Groningen P.O. Box RB Groningen, The Netherlands bwo@int.umcg.nl
6
The Advantages of Short Pen Needles. Insulin injection with pen needles
 Clinical Evidence Folder The Advantages of Short Pen Needles Insulin injection with pen needles 1. Introduction 3 2. Utilization of Shorter Pen Needles 4 2.1. Injection Sites 4 2.2. Injection Site and
Clinical Evidence Folder The Advantages of Short Pen Needles Insulin injection with pen needles 1. Introduction 3 2. Utilization of Shorter Pen Needles 4 2.1. Injection Sites 4 2.2. Injection Site and
BD Nano 4mm Pen Needles
 BD Nano mm Pen Needles Preferred by patients₉ Less effort to inject medication for people with hand strength issues₉* BD's smallest, thinnest pen needle was rated as less painful and easier to insert₉
BD Nano mm Pen Needles Preferred by patients₉ Less effort to inject medication for people with hand strength issues₉* BD's smallest, thinnest pen needle was rated as less painful and easier to insert₉
If you inject diabetes medication, you should know how important correct injection technique is for effectively managing your diabetes.
 Insulin injection technique best practices Expert recommendations on injecting insulin with pen and insulin syringe needles If you inject diabetes medication, you should know how important correct injection
Insulin injection technique best practices Expert recommendations on injecting insulin with pen and insulin syringe needles If you inject diabetes medication, you should know how important correct injection
Injection technique for different needle lengths
 Injection technique for different needle lengths Use the correct technique to better manage your diabetes 1 Why it s important to use the shortest needles available Reduce your risk of injecting into the
Injection technique for different needle lengths Use the correct technique to better manage your diabetes 1 Why it s important to use the shortest needles available Reduce your risk of injecting into the
Copyright 2010 Informa UK Limited Not for Sale or Commercial Distribution
 Current Medical Research & Opinion Vol. 26, No. 6, 2010, 1519 1530 0300-7995 Article 5499/481203 doi:10.1185/03007995.2010.481203 All rights reserved: reproduction in whole or part not permitted Original
Current Medical Research & Opinion Vol. 26, No. 6, 2010, 1519 1530 0300-7995 Article 5499/481203 doi:10.1185/03007995.2010.481203 All rights reserved: reproduction in whole or part not permitted Original
Living Well Successfully managing diabetes
 Living Well Successfully managing diabetes with 4mm Pen Needles Helping all people live healthy lives Our most comfortable injection experience ever Successfully managing diabetes with BD Micro-Fine +
Living Well Successfully managing diabetes with 4mm Pen Needles Helping all people live healthy lives Our most comfortable injection experience ever Successfully managing diabetes with BD Micro-Fine +
Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s): insulin glargine (HOE901) According to template: QSD VERSION N 4.0 (07-JUN-2012) Page 1
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
Evaluation of the Use of PenNeedle 32G Taper in Children being Treated with Growth Hormone
 Clin Pediatr Endocrinol 2008; 17(1), 1-7 Copyright 2008 by The Japanese Society for Pediatric Endocrinology Original Article Evaluation of the Use of PenNeedle 32G Taper in Children being Treated with
Clin Pediatr Endocrinol 2008; 17(1), 1-7 Copyright 2008 by The Japanese Society for Pediatric Endocrinology Original Article Evaluation of the Use of PenNeedle 32G Taper in Children being Treated with
Lessons learned from working with international injection technique guidelines
 Lessons learned from working with international injection technique guidelines Anders Frid, MD, PhD Clinic of Endocrinology, Skåne University Hospital, Malmö Oslo 23rd March 2012 INJECTION TECHNIQUE IS
Lessons learned from working with international injection technique guidelines Anders Frid, MD, PhD Clinic of Endocrinology, Skåne University Hospital, Malmö Oslo 23rd March 2012 INJECTION TECHNIQUE IS
Setting The setting was primary care. The economic study was carried out in the USA.
 Preference and resource utilization in elderly patients: InnoLet (R) versus vial/syringe Shelmet J, Schwartz S, Cappleman J, Peterson G, Skovlund S, Lytzen L, Nicklasson L, Liang J, Lyness W Record Status
Preference and resource utilization in elderly patients: InnoLet (R) versus vial/syringe Shelmet J, Schwartz S, Cappleman J, Peterson G, Skovlund S, Lytzen L, Nicklasson L, Liang J, Lyness W Record Status
Defining the ideal injection techniques when using 5-mm needles in children and adults
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online June 28, 2010 Defining the ideal injection techniques when using 5-mm needles in children and adults Paul Leslie Hofman MD 1, José Guilherme Behrensdorf
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online June 28, 2010 Defining the ideal injection techniques when using 5-mm needles in children and adults Paul Leslie Hofman MD 1, José Guilherme Behrensdorf
Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s): Insulin Glargine. Study Identifiers: NCT
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
Safe and Gentle Injection of Insulin. Guide for correct injection technique. Englische Ausgabe
 Safe and Gentle Injection of Insulin Guide for correct injection technique Englische Ausgabe Insulin injection basics 1 Insulin has to be injected into the subcutaneous fat layer 3 Rotate the injection
Safe and Gentle Injection of Insulin Guide for correct injection technique Englische Ausgabe Insulin injection basics 1 Insulin has to be injected into the subcutaneous fat layer 3 Rotate the injection
Injection Technique (I.T.), Glycemic Variability, and Lipohypertrophy. Why I.T. All Matters
 Injection Technique (I.T.), Glycemic Variability, and Lipohypertrophy Why I.T. All Matters Larry Hirsch, MD Vice-President, Global Medical Affairs BD Diabetes Care Seoul, South Korea KDA-ICDM 29 September
Injection Technique (I.T.), Glycemic Variability, and Lipohypertrophy Why I.T. All Matters Larry Hirsch, MD Vice-President, Global Medical Affairs BD Diabetes Care Seoul, South Korea KDA-ICDM 29 September
Switch protocol: Insulin pen needles to cost effective brand
 Switch protocol: Insulin pen needles to cost effective brand Applies to HaRD CCG employed Pharmacists and Medicines Optimisation Technicians. These protocols are produced by the NY&AWC MM team hosted by
Switch protocol: Insulin pen needles to cost effective brand Applies to HaRD CCG employed Pharmacists and Medicines Optimisation Technicians. These protocols are produced by the NY&AWC MM team hosted by
Switch protocol: Insulin pen needles to cost effective brand
 Switch protocol: Insulin pen needles to cost effective brand Applies to HaRD CCG employed Pharmacists and Medicines Optimisation Technicians. These protocols are produced by the NY&AWC MM team hosted by
Switch protocol: Insulin pen needles to cost effective brand Applies to HaRD CCG employed Pharmacists and Medicines Optimisation Technicians. These protocols are produced by the NY&AWC MM team hosted by
Insulin Delivery System and Self Monitoring Blood Sugar (SMBG ) Leyden V. Florido, RN, MAN
 Insulin Delivery System and Self Monitoring Blood Sugar (SMBG ) Leyden V. Florido, RN, MAN Management of Diabetes Mellitus Pharmacological Glucose Lowering Agents/Oral Antidiabetes Drug/Oral Hypogycemic
Insulin Delivery System and Self Monitoring Blood Sugar (SMBG ) Leyden V. Florido, RN, MAN Management of Diabetes Mellitus Pharmacological Glucose Lowering Agents/Oral Antidiabetes Drug/Oral Hypogycemic
Injection Techniques Questionnaire (ITQ) WorldWide Results Needle Gauge
 Injection Techniques Questionnaire (ITQ) WorldWide Results 2014-2015 Needle Gauge BACKGROUND All needles are at least twice as long as the skin is thick More than twice as long 31G =.26mm Surface = 1
Injection Techniques Questionnaire (ITQ) WorldWide Results 2014-2015 Needle Gauge BACKGROUND All needles are at least twice as long as the skin is thick More than twice as long 31G =.26mm Surface = 1
The Effect of Microneedle Thickness on Pain During Minimally Invasive Facial Procedures: A Clinical Study
 532941AESXXX10.1177/1090820X14532941Aesthetic Surgery JournalSezgin et al research-article2014 INTERNATIONAL CONTRIBUTION Cosmetic Medicine The Effect of Microneedle Thickness on Pain During Minimally
532941AESXXX10.1177/1090820X14532941Aesthetic Surgery JournalSezgin et al research-article2014 INTERNATIONAL CONTRIBUTION Cosmetic Medicine The Effect of Microneedle Thickness on Pain During Minimally
Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s): HOE901-U300 (insulin glargine) According to template: QSD VERSION N 4.0 (07-JUN-2012) Page 1
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
Gentle and safe injections. Tips and tricks for injecting insulin.
 Gentle and safe injections. Tips and tricks for injecting insulin. Freedom. Confidence. With mylife. Gentle and safe injections The correct injection technique The insulin is injected into the subcutaneous
Gentle and safe injections. Tips and tricks for injecting insulin. Freedom. Confidence. With mylife. Gentle and safe injections The correct injection technique The insulin is injected into the subcutaneous
Hamdiye Arda Sürücü 1*, Hatice Okur Arslan 2
 Journal of Caring Sciences 2018; 7 (2): 67-74 doi:10.15171/jcs.2018.011 http:// journals.tbzmed.ac.ir/ JCS Original Article in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes: Prevalence and Risk Factors Hamdiye Arda
Journal of Caring Sciences 2018; 7 (2): 67-74 doi:10.15171/jcs.2018.011 http:// journals.tbzmed.ac.ir/ JCS Original Article in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes: Prevalence and Risk Factors Hamdiye Arda
INSULIN INJECTION KNOW-HOW
 0-1- INSULIN INJECTION KNOW-HOW Learning how to Congratulations for making the move to insulin therapy. It won t be long before you start enjoying better blood sugar control, more energy, and a host of
0-1- INSULIN INJECTION KNOW-HOW Learning how to Congratulations for making the move to insulin therapy. It won t be long before you start enjoying better blood sugar control, more energy, and a host of
Agreement between Glucose Trends Derived from Three Simultaneously Worn Continuous Glucose Sensors
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 5, September 2008 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLES Agreement between Glucose Trends Derived from Three Simultaneously Worn Continuous
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 5, September 2008 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLES Agreement between Glucose Trends Derived from Three Simultaneously Worn Continuous
Efficacy/pharmacodynamics: 85 Safety: 89
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor/Company: Sanofi Drug substance:
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor/Company: Sanofi Drug substance:
Correct Site Rotation
 Injection Techniques Questionnaire (ITQ) WorldWide Results 2014-2015 Correct Site Rotation BACKGROUND Correct Rotation = at least 1 cm between successive injections Lipohypertrophy and Observed Correct
Injection Techniques Questionnaire (ITQ) WorldWide Results 2014-2015 Correct Site Rotation BACKGROUND Correct Rotation = at least 1 cm between successive injections Lipohypertrophy and Observed Correct
Things you need to know about injections
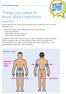 www.trend-uk.org Things you need to know about injections Injection sites: You can see from the picture below the best sites for injecting insulin or GLP-1 medications are: Back of the upper arms (difficult
www.trend-uk.org Things you need to know about injections Injection sites: You can see from the picture below the best sites for injecting insulin or GLP-1 medications are: Back of the upper arms (difficult
Protocol. Title: The Effect of Needle Size on Pain Perception in Patients Treated with Botulinum Toxin A Injections
 Protocol Title: The Effect of Needle Size on Pain Perception in Patients Treated with Botulinum Toxin A Injections Principal Investigator: Murad Alam, MD 1 Table of contents Table of contents List of abbreviations
Protocol Title: The Effect of Needle Size on Pain Perception in Patients Treated with Botulinum Toxin A Injections Principal Investigator: Murad Alam, MD 1 Table of contents Table of contents List of abbreviations
Gentle and safe injections. Tips and tricks for injecting insulin.
 Gentle and safe injections. Tips and tricks for injecting insulin. More freedom. More confidence. With mylife. Gentle and safe injections The correct injection technique The insulin is injected into the
Gentle and safe injections. Tips and tricks for injecting insulin. More freedom. More confidence. With mylife. Gentle and safe injections The correct injection technique The insulin is injected into the
BEST 4 Diabetes. Optimisation of insulin module
 BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
These results are supplied for informational purposes only.
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription Sponsor/company: sanofi-aventis ClinialTrials.gov
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription Sponsor/company: sanofi-aventis ClinialTrials.gov
PREVENTION OF NOCTURNAL HYPOGLYCEMIA USING PREDICTIVE LOW GLUCOSE SUSPEND (PLGS)
 PREVENTION OF NOCTURNAL HYPOGLYCEMIA USING PREDICTIVE LOW GLUCOSE SUSPEND (PLGS) Pathways for Future Treatment and Management of Diabetes H. Peter Chase, MD Carousel of Hope Symposium Beverly Hilton, Beverly
PREVENTION OF NOCTURNAL HYPOGLYCEMIA USING PREDICTIVE LOW GLUCOSE SUSPEND (PLGS) Pathways for Future Treatment and Management of Diabetes H. Peter Chase, MD Carousel of Hope Symposium Beverly Hilton, Beverly
BEST 4 Diabetes. Optimisation of insulin module
 BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
BEST 4 Diabetes Optimisation of insulin module Confidence and competence Where would you rate yourself? Why do all of our patient not achieve optimal blood glucose control? Insulin Therapy Goals and Purpose
Safe use of insulin regular concentrated (500 units/ml) in severe insulin resistance
 Safe use of insulin regular concentrated (500 units/ml) in severe insulin resistance Jodie S. Gee, Pharm.D., BCACP, CDE Clinical Pharmacy Specialist-Ambulatory Care Harris Health System Objectives To be
Safe use of insulin regular concentrated (500 units/ml) in severe insulin resistance Jodie S. Gee, Pharm.D., BCACP, CDE Clinical Pharmacy Specialist-Ambulatory Care Harris Health System Objectives To be
Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s): Insulin Glargine (HOE901) Insulin Glulisine (HMR1964)
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
Frequency of Lipohypertrophy and Associated Risk Factors in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study
 Diabetes Ther (2016) 7:259 267 DOI 10.1007/s13300-016-0161-3 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Frequency of Lipohypertrophy and Associated Risk Factors in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study Ayman
Diabetes Ther (2016) 7:259 267 DOI 10.1007/s13300-016-0161-3 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Frequency of Lipohypertrophy and Associated Risk Factors in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study Ayman
Country Health SA Local Health Network. Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in the Community Setting
 Protocol (Clinical) Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in the Community Setting Protocol developed by: CHSALHN Diabetes Service Protocol Sponsor: CHSALHN, Executive Director, Medical Services Approved
Protocol (Clinical) Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in the Community Setting Protocol developed by: CHSALHN Diabetes Service Protocol Sponsor: CHSALHN, Executive Director, Medical Services Approved
Starting and Helping People with Type 2 Diabetes on Insulin
 Starting and Helping People with Type 2 Diabetes on Insulin Elaine Cooke, BSc(Pharm), RPh, CDE Pharmacist and Certified Diabetes Educator Maple Ridge, BC Objectives After attending this session, participants
Starting and Helping People with Type 2 Diabetes on Insulin Elaine Cooke, BSc(Pharm), RPh, CDE Pharmacist and Certified Diabetes Educator Maple Ridge, BC Objectives After attending this session, participants
Enjoy brilliance. mylife Clickfine DiamondTip more comfort with the perfect tip.
 Enjoy brilliance. mylife Clickfine DiamondTip more comfort with the perfect tip. 6-bevel needle tip for a smoother injection 1,2 Thin wall technology for a faster flux of medication Special silicone surface
Enjoy brilliance. mylife Clickfine DiamondTip more comfort with the perfect tip. 6-bevel needle tip for a smoother injection 1,2 Thin wall technology for a faster flux of medication Special silicone surface
Factors Affecting Use of Insulin Pens by Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online November 26, 2007 Factors Affecting Use of Insulin Pens by Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Richard R. Rubin, PhD 1,2 Mark Peyrot, PhD 1,3 1= Department
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online November 26, 2007 Factors Affecting Use of Insulin Pens by Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Richard R. Rubin, PhD 1,2 Mark Peyrot, PhD 1,3 1= Department
Comparison of the Dose Accuracy of Prefilled Insulin Pens
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 3, Issue 1, January 2009 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLES Comparison of the Dose Accuracy of Prefilled Insulin Pens Alexander, M.Sc., Johannes
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 3, Issue 1, January 2009 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLES Comparison of the Dose Accuracy of Prefilled Insulin Pens Alexander, M.Sc., Johannes
Important Safety Information for Adlyxin (lixisenatide) injection
 A GLP-1 receptor agonist (RA) Adlyxin (lixisenatide) injection 20 mcg Information To Help Answer Patients Questions This booklet contains information about Adlyxin to help you answer patients questions
A GLP-1 receptor agonist (RA) Adlyxin (lixisenatide) injection 20 mcg Information To Help Answer Patients Questions This booklet contains information about Adlyxin to help you answer patients questions
Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s): Insulin Glargine (HOE901) Insulin Glulisine (HMR1964)
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
Sensor-augmented pump systems provide insulin delivery
 DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 18, Number 10, 2016 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/dia.2016.0216 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effectiveness of Automated Insulin Management Features of the MiniMed c
DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 18, Number 10, 2016 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/dia.2016.0216 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effectiveness of Automated Insulin Management Features of the MiniMed c
KEEPING SAFE WITH INSULIN THERAPY
 KEEPING SAFE WITH INSULIN THERAPY kk WHY IS THIS LEAFLET FOR YOU? Insulin treatment improves the quality of life in many people and saves the lives of others. It is used to lower blood glucose levels.
KEEPING SAFE WITH INSULIN THERAPY kk WHY IS THIS LEAFLET FOR YOU? Insulin treatment improves the quality of life in many people and saves the lives of others. It is used to lower blood glucose levels.
Protocol (Clinical) Country Health SA Local Health Network. Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in Hospital and Aged Care
 Protocol (Clinical) Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in Hospital and Aged Care Protocol developed by: CHSALHN Diabetes Service Protocol Sponsor: CHSALHN, Executive Director, Medical Services
Protocol (Clinical) Title: Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in Hospital and Aged Care Protocol developed by: CHSALHN Diabetes Service Protocol Sponsor: CHSALHN, Executive Director, Medical Services
Performance-powered. The OneTouch. Ping insulin pump and meter-remote.
 Performance-powered. The OneTouch Ping insulin pump and meter-remote. I We don t just deliver insulin. We deliver outstanding clinical performance. P36337_OTP_DetAid_OmniPodUpdate_r12.indd 1 OneTouch Ping.
Performance-powered. The OneTouch Ping insulin pump and meter-remote. I We don t just deliver insulin. We deliver outstanding clinical performance. P36337_OTP_DetAid_OmniPodUpdate_r12.indd 1 OneTouch Ping.
ADMELOG, NOVOLIN, NOVOLOG, and FIASP
 ADMELOG, NOVOLIN, NOVOLOG, and FIASP Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
ADMELOG, NOVOLIN, NOVOLOG, and FIASP Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This Pharmacy
iglarlixi Reduces Glycated Hemoglobin to a Greater Extent Than Basal Insulin Regardless of Levels at Screening: Post Hoc Analysis of LixiLan-L
 Diabetes Ther (2018) 9:373 382 https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-017-0336-6 BRIEF REPORT iglarlixi Reduces Glycated Hemoglobin to a Greater Extent Than Basal Insulin Regardless of Levels at Screening: Post
Diabetes Ther (2018) 9:373 382 https://doi.org/10.1007/s13300-017-0336-6 BRIEF REPORT iglarlixi Reduces Glycated Hemoglobin to a Greater Extent Than Basal Insulin Regardless of Levels at Screening: Post
Your guide to diabetes management
 Your guide to diabetes management Injecting insulin and making healthy lifestyle choices Understanding insulin therapy How do I inject insulin? In general, there are two ways you can inject insulin. Talk
Your guide to diabetes management Injecting insulin and making healthy lifestyle choices Understanding insulin therapy How do I inject insulin? In general, there are two ways you can inject insulin. Talk
A Study Assessing an Injection Port for Administration of Insulin
 Feature Article / Blevins et al. A Study Assessing an Injection Port for Administration of Insulin Thomas Blevins, MD; Sherwyn L. Schwartz, MD; Bruce Bode, MD; Stephen Aronoff, MD; Claire Baker, MD; Kay
Feature Article / Blevins et al. A Study Assessing an Injection Port for Administration of Insulin Thomas Blevins, MD; Sherwyn L. Schwartz, MD; Bruce Bode, MD; Stephen Aronoff, MD; Claire Baker, MD; Kay
Effective Health Care Program
 Comparative Effectiveness Review Number 57 Effective Health Care Program Methods for Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring: Comparative Effectiveness Executive Summary Background Diabetes mellitus is
Comparative Effectiveness Review Number 57 Effective Health Care Program Methods for Insulin Delivery and Glucose Monitoring: Comparative Effectiveness Executive Summary Background Diabetes mellitus is
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online June 22, 2007
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online June 22, 2007 Coverage of Postprandial Blood Glucose Excursions With Inhaled Technosphere Insulin in Comparison to Subcutaneously Injected Regular
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online June 22, 2007 Coverage of Postprandial Blood Glucose Excursions With Inhaled Technosphere Insulin in Comparison to Subcutaneously Injected Regular
Insulin Basic facts. Patient Education Patient Care Services. What is insulin? What types of insulin are there? Basal Insulin
 Patient Education Insulin Basic facts Insulin is a protein made by the pancreas that allows your cells to use glucose for energy. There are different types of insulin: Basal long-acting insulin that controls
Patient Education Insulin Basic facts Insulin is a protein made by the pancreas that allows your cells to use glucose for energy. There are different types of insulin: Basal long-acting insulin that controls
Clinical Study Synopsis
 Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
INSULIN IN THE OBESE PATIENT JACQUELINE THOMPSON RN, MAS, CDE SYSTEM DIRECTOR, DIABETES SERVICE LINE SHARP HEALTHCARE
 INSULIN IN THE OBESE PATIENT JACQUELINE THOMPSON RN, MAS, CDE SYSTEM DIRECTOR, DIABETES SERVICE LINE SHARP HEALTHCARE OBJECTIVES DESCRIBE INSULIN, INCLUDING WHERE IT COMES FROM AND WHAT IT DOES STATE THAT
INSULIN IN THE OBESE PATIENT JACQUELINE THOMPSON RN, MAS, CDE SYSTEM DIRECTOR, DIABETES SERVICE LINE SHARP HEALTHCARE OBJECTIVES DESCRIBE INSULIN, INCLUDING WHERE IT COMES FROM AND WHAT IT DOES STATE THAT
A Prefilled Insulin Pen with a Novel Injection Mechanism and a Lower Injection Force than Other Prefilled Insulin Pens
 DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 13, Number 12, 2011 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/dia.2011.0110 A Prefilled Insulin Pen with a Novel Injection Mechanism and a Lower Injection Force than
DIABETES TECHNOLOGY & THERAPEUTICS Volume 13, Number 12, 2011 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. DOI: 10.1089/dia.2011.0110 A Prefilled Insulin Pen with a Novel Injection Mechanism and a Lower Injection Force than
Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim
 Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim Chosun University Hospital Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Committee of Scientific Affairs Insulin therapy is the mainstay
Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim Chosun University Hospital Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Committee of Scientific Affairs Insulin therapy is the mainstay
Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s): HOE901-U300 (insulin glargine)
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor / Company: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
Enjoy brilliance. mylife Clickfine DiamondTip more comfort with the perfect tip.
 Enjoy brilliance. mylife Clickfine DiamondTip more comfort with the perfect tip. 6-bevel needle tip for a smoother injection 1,2 Thin wall technology for a faster flux of medication Special silicone surface
Enjoy brilliance. mylife Clickfine DiamondTip more comfort with the perfect tip. 6-bevel needle tip for a smoother injection 1,2 Thin wall technology for a faster flux of medication Special silicone surface
Long-term effects of continuous glucose monitoring on HbA 1c levels: An audit
 Long-term effects of continuous glucose monitoring on Julie Brake Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has become a common and useful tool in diabetes care. To understand whether a 72-hour glucose profile
Long-term effects of continuous glucose monitoring on Julie Brake Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has become a common and useful tool in diabetes care. To understand whether a 72-hour glucose profile
Evaluation of a Continuous Glucose Monitoring System for Home-Use Conditions
 Evaluation of a Continuous Glucose Monitoring System for Home-Use Conditions Bruce Bode, MD 1, Michael Silver, MD 2, Richard Weiss, MS, 3 Kathryn Martin, PharmD. 3 1 Atlanta Diabetes Associates; 2 Medical
Evaluation of a Continuous Glucose Monitoring System for Home-Use Conditions Bruce Bode, MD 1, Michael Silver, MD 2, Richard Weiss, MS, 3 Kathryn Martin, PharmD. 3 1 Atlanta Diabetes Associates; 2 Medical
Initiation and Titration of Insulin in Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
 Initiation and Titration of Insulin in Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Greg Doelle MD, MS April 6, 2016 Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflicts of interest in relation to the content of this lecture.
Initiation and Titration of Insulin in Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Greg Doelle MD, MS April 6, 2016 Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflicts of interest in relation to the content of this lecture.
Guide to Starting and Adjusting Insulin for Type 2 Diabetes*
 Guide to Starting and Adjusting Insulin for Type 2 Diabetes* www.cadth.ca * Adapted from Guide to Starting and Adjusting Insulin for Type 2 Diabetes, 2008 International Diabetes Center, Minneapolis, MN.
Guide to Starting and Adjusting Insulin for Type 2 Diabetes* www.cadth.ca * Adapted from Guide to Starting and Adjusting Insulin for Type 2 Diabetes, 2008 International Diabetes Center, Minneapolis, MN.
Policy for the safe administration of Insulin
 Policy for the safe administration of Insulin This is a working document and any changes that become necessary to this policy must be Notified in writing to the Medicine Management Group via the Chief
Policy for the safe administration of Insulin This is a working document and any changes that become necessary to this policy must be Notified in writing to the Medicine Management Group via the Chief
New Drug Evaluation: Insulin degludec/aspart, subcutaneous injection
 New Drug Evaluation: Insulin degludec/aspart, subcutaneous injection Date of Review: March 2016 End Date of Literature Search: November 11, 2015 Generic Name: Insulin degludec and insulin aspart Brand
New Drug Evaluation: Insulin degludec/aspart, subcutaneous injection Date of Review: March 2016 End Date of Literature Search: November 11, 2015 Generic Name: Insulin degludec and insulin aspart Brand
Country Health SA Local Health Network Protocol Subcutaneous Insulin Administration in the Community Setting
 1. Rationale Correct supervision and/or administration and documentation of subcutaneous insulin for diabetes management. Promote independence towards self or assisted administration of insulin and blood
1. Rationale Correct supervision and/or administration and documentation of subcutaneous insulin for diabetes management. Promote independence towards self or assisted administration of insulin and blood
Effect of an Experiential Exercise in Diabetes Management on Pharmacy Students Fear and Perceived Pain of Injection and Fingertip Lancing
 RESEARCH Effect of an Experiential Exercise in Diabetes Management on Pharmacy Students Fear and Perceived Pain of Injection and Fingertip Lancing Amitjeet Sahnan, BSc(Pharm), and Scot H. Simpson, BSP,
RESEARCH Effect of an Experiential Exercise in Diabetes Management on Pharmacy Students Fear and Perceived Pain of Injection and Fingertip Lancing Amitjeet Sahnan, BSc(Pharm), and Scot H. Simpson, BSP,
To assess the safety and tolerability in each treatment group.
 These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
These results are supplied for informational purposes only. Prescribing decisions should be made based on the approved package insert in the country of prescription. Sponsor: Sanofi Drug substance(s):
Dose Accuracy of the ClikSTAR, NovoPen 4, and Luxura Insulin Pens: Results of Laboratory and Field Studies
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 5, Issue 5, September 2011 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLE Arnd, Ph.D., 1 Nils Basso, Ph.D., 2 and Steffen Adler, Ph.D. 1 Abstract Background:
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 5, Issue 5, September 2011 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLE Arnd, Ph.D., 1 Nils Basso, Ph.D., 2 and Steffen Adler, Ph.D. 1 Abstract Background:
My Doctor Says I Need to Inject Insulin In Special Sites... Which Ones Should I Use? Getting Started. Site Selection
 My Doctor Says I Need to Inject Insulin In Special Sites... Which Ones Should I Use? Getting Started Site Selection You need to know where to inject insulin so that your injections will be easier, safer
My Doctor Says I Need to Inject Insulin In Special Sites... Which Ones Should I Use? Getting Started Site Selection You need to know where to inject insulin so that your injections will be easier, safer
BRIEF REPORTS. Providing Long-Acting Reversible Contraception in an Academic Family Medicine Center Jennifer Amico, MD, MPH; Justine Wu, MD, MPH
 Providing Long-Acting Reversible Contraception in an Academic Family Medicine Center Jennifer Amico, MD, MPH; Justine Wu, MD, MPH BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Providing long-acting reversible contraception
Providing Long-Acting Reversible Contraception in an Academic Family Medicine Center Jennifer Amico, MD, MPH; Justine Wu, MD, MPH BACKGROUND AND OBJECTIVES: Providing long-acting reversible contraception
Faculty. Concentrated Insulin: Examining the Necessity of Newer Insulins for In-Hospital Diabetes Management. Disclosures. Learning Objectives
 Examining the Necessity of Newer Insulins for In-Hospital Diabetes Management Faculty Susan Cornell, PharmD, CDE, FAPhA, FAADE Associate Professor of Pharmacy Practice Associate Director of Experiential
Examining the Necessity of Newer Insulins for In-Hospital Diabetes Management Faculty Susan Cornell, PharmD, CDE, FAPhA, FAADE Associate Professor of Pharmacy Practice Associate Director of Experiential
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online February 25, 2010
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online February 25, 2010 Quality of Life and costs of IP vs. Health related quality of life, treatment satisfaction and costs associated with intraperitoneal
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online February 25, 2010 Quality of Life and costs of IP vs. Health related quality of life, treatment satisfaction and costs associated with intraperitoneal
Best Practice Guideline to support Correct Injection Technique in Diabetes Care
 Best Practice Guideline to support Correct Injection Technique in Diabetes Care B e s t P r a c t i c e i n D i a b e t e s C a r e PAGE 2 Contents Introduction Our Supporters Endorsements SECTION 1. THE
Best Practice Guideline to support Correct Injection Technique in Diabetes Care B e s t P r a c t i c e i n D i a b e t e s C a r e PAGE 2 Contents Introduction Our Supporters Endorsements SECTION 1. THE
Intradermal influenza vaccination. Clinical data and first experience from its use in a routine vaccination programme
 VI. Hradecké Vakcinologické Dny Hradec Kralove, 1st October 21 Intradermal influenza vaccination Clinical data and first experience from its use in a routine vaccination programme Clemens Vlasich, MD,
VI. Hradecké Vakcinologické Dny Hradec Kralove, 1st October 21 Intradermal influenza vaccination Clinical data and first experience from its use in a routine vaccination programme Clemens Vlasich, MD,
MIDDLE EAST AND NORTH AFRICA INSULIN DELIVERY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR CHILDREN AND YOUNG ADULTS
 MIDDLE EAST AND NORTH AFRICA INSULIN DELIVERY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR CHILDREN AND YOUNG ADULTS Sponsored by Content Introduction 3 Contributors 4 KEY 4 Acknowledgment 4 1.0 Insulin Injection 5 2.0 Insulin
MIDDLE EAST AND NORTH AFRICA INSULIN DELIVERY RECOMMENDATIONS FOR CHILDREN AND YOUNG ADULTS Sponsored by Content Introduction 3 Contributors 4 KEY 4 Acknowledgment 4 1.0 Insulin Injection 5 2.0 Insulin
Insulin Pump Therapy for Type 2
 9501172-011 Insulin Pump Therapy for Type 2 Objective To show the effectiveness of CSII for insulin-taking type 2 patients Key Points Tight glycemic control decreases risk of diabetes-related complications
9501172-011 Insulin Pump Therapy for Type 2 Objective To show the effectiveness of CSII for insulin-taking type 2 patients Key Points Tight glycemic control decreases risk of diabetes-related complications
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Continuous or Intermittent Monitoring of Glucose in Interstitial Fluid Page 1 of 26 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Continuous or Intermittent Monitoring
Continuous or Intermittent Monitoring of Glucose in Interstitial Fluid Page 1 of 26 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Continuous or Intermittent Monitoring
What is a CGM? (Continuous Glucose Monitor) The Bionic Pancreas Is Coming
 The Bionic Pancreas Is Coming Montana Diabetes Professional Conference October 23, 2014 H. Peter Chase, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Colorado Barbara Davis Center Stanford: Bruce Buckingham,
The Bionic Pancreas Is Coming Montana Diabetes Professional Conference October 23, 2014 H. Peter Chase, MD Professor of Pediatrics University of Colorado Barbara Davis Center Stanford: Bruce Buckingham,
Workshop 4 Making the complex simple
 Workshop 4 Making the complex simple Goal of workshop Insulin commencement making the complex simple Ensure participants are confident with Selecting and using devices Troubleshooting injection issues
Workshop 4 Making the complex simple Goal of workshop Insulin commencement making the complex simple Ensure participants are confident with Selecting and using devices Troubleshooting injection issues
Update on New Basal Insulins and Combinations: Starting, Titrating and Adding to Therapy
 Update on New Basal Insulins and Combinations: Starting, Titrating and Adding to Therapy Jerry Meece, BPharm, CDE, FACA, FAADE Director of Clinical Services Plaza Pharmacy and Wellness Center Gainesville,
Update on New Basal Insulins and Combinations: Starting, Titrating and Adding to Therapy Jerry Meece, BPharm, CDE, FACA, FAADE Director of Clinical Services Plaza Pharmacy and Wellness Center Gainesville,
Horizon Scanning Technology Summary. Liraglutide for type 2 diabetes. National Horizon Scanning Centre. April 2007
 Horizon Scanning Technology Summary National Horizon Scanning Centre Liraglutide for type 2 diabetes April 2007 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited
Horizon Scanning Technology Summary National Horizon Scanning Centre Liraglutide for type 2 diabetes April 2007 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited
Comparison of glucose monitoring between Freestyle Libre Pro and ipro2 in patients with diabetes mellitus
 Comparison of glucose monitoring between Freestyle Libre Pro and ipro2 in patients with diabetes mellitus Ryo Kumagai 1, iko Muramatsu 1, Masanao Fujii 1, Yukino Katakura 1,KeiIto 1,KeikoFujie 2, Yoshio
Comparison of glucose monitoring between Freestyle Libre Pro and ipro2 in patients with diabetes mellitus Ryo Kumagai 1, iko Muramatsu 1, Masanao Fujii 1, Yukino Katakura 1,KeiIto 1,KeikoFujie 2, Yoshio
Anneloes Kerssen, a Harold W. de Valk, b Gerard H.A. Visser a. D RCOG 2004 BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology
 BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology September 2004, Vol. 111, pp. 919 924 DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2004.00203.x Day-to-day glucose variability during pregnancy in women with Type
BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology September 2004, Vol. 111, pp. 919 924 DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2004.00203.x Day-to-day glucose variability during pregnancy in women with Type
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Methods
 Supplementary Methods Chronic kidney disease stage 4 or 5 Current diabetic foot with ulcer, soft tissue infection or necrosis Unstable angina, myocardial infarction, or cerebrovascular accident over the
Supplementary Methods Chronic kidney disease stage 4 or 5 Current diabetic foot with ulcer, soft tissue infection or necrosis Unstable angina, myocardial infarction, or cerebrovascular accident over the
What is the role of insulin pumps in the modern day care of patients with Type 1 diabetes?
 What is the role of insulin pumps in the modern day care of patients with Type 1 diabetes? Dr. Fiona Wotherspoon Consultant in Diabetes and Endocrinology Dorset County Hospital Fiona.Wotherspoon@dchft.nhs.uk
What is the role of insulin pumps in the modern day care of patients with Type 1 diabetes? Dr. Fiona Wotherspoon Consultant in Diabetes and Endocrinology Dorset County Hospital Fiona.Wotherspoon@dchft.nhs.uk
Control of Glycemic Variability for Reducing Hypoglycemia Jae Hyeon Kim
 Control of Glycemic Variability for Reducing Hypoglycemia Jae Hyeon Kim Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Conflict of interest
Control of Glycemic Variability for Reducing Hypoglycemia Jae Hyeon Kim Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine Conflict of interest
PATIENT INFORMATION. D iabetes. What You Need to Know About. Insulin
 PATIENT INFORMATION Medicine To Treat: D iabetes What You Need to Know About Insulin INTRODUCTION The insulin preparations currently available in Singapore are mostly from human origin; pork or bovine
PATIENT INFORMATION Medicine To Treat: D iabetes What You Need to Know About Insulin INTRODUCTION The insulin preparations currently available in Singapore are mostly from human origin; pork or bovine
Diabetes Technology Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Therapy And Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Adults: An Endocrine Society Clinical
 Diabetes Technology Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Therapy And Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Adults: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline Task Force Members Anne Peters, MD (Chair)
Diabetes Technology Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion Therapy And Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Adults: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline Task Force Members Anne Peters, MD (Chair)
FIT Forum for Injection Technique
 DIABETES CARE IN IRELAND FIT Forum for Injection Technique Irish Injection and Infusion Technique Recommendations 2nd Edition The Irish Injection and Infusion Technique Recommendations have been endorsed
DIABETES CARE IN IRELAND FIT Forum for Injection Technique Irish Injection and Infusion Technique Recommendations 2nd Edition The Irish Injection and Infusion Technique Recommendations have been endorsed
CAM2038 A new liquid-lipid crystal depot buprenorphine: A dose-ranging suite of weekly and monthly subcutaneous depot injections
 CAM2038 A new liquid-lipid crystal depot buprenorphine: A dose-ranging suite of weekly and monthly subcutaneous depot injections Dr. Fredrik Tiberg Assoc. Prof. President & CEO, Head R&D, Camurus Lund,
CAM2038 A new liquid-lipid crystal depot buprenorphine: A dose-ranging suite of weekly and monthly subcutaneous depot injections Dr. Fredrik Tiberg Assoc. Prof. President & CEO, Head R&D, Camurus Lund,
TAKING THE OUT OF INSULIN DELIVERY
 G N I T S TAKING THE OUT OF INSULIN DELIVERY PHOTO: THINKSTOCK Nearly a century after its discovery, most insulin is still delivered via a needle, which many people with diabetes find painful and inconvenient.
G N I T S TAKING THE OUT OF INSULIN DELIVERY PHOTO: THINKSTOCK Nearly a century after its discovery, most insulin is still delivered via a needle, which many people with diabetes find painful and inconvenient.
This supplement contains the following items:
 This supplement contains the following items: 1. Original protocol, final protocol, summary of changes 2. Original statistical analysis plan, final statistical analysis plan, summary of changes Original
This supplement contains the following items: 1. Original protocol, final protocol, summary of changes 2. Original statistical analysis plan, final statistical analysis plan, summary of changes Original
nocturnal hypoglycemia percentage of Hispanics in the insulin glargine than NPH during forced patients who previously This study excluded
 Clinical Trial Design/ Primary Objective Insulin glargine Treat-to-Target Trial, Riddle et al., 2003 (23) AT.LANTUS trial, Davies et al., 2005 (24) INSIGHT trial, Gerstein et al., 2006 (25) multicenter,
Clinical Trial Design/ Primary Objective Insulin glargine Treat-to-Target Trial, Riddle et al., 2003 (23) AT.LANTUS trial, Davies et al., 2005 (24) INSIGHT trial, Gerstein et al., 2006 (25) multicenter,
Dermatological complications of insulin therapy in children with type 1 diabetes
 in children with type 1 diabetes Hilde E van Munster, MSc 2 Cathelijne PM van de Sande 2 Paul G Voorhoeve, MD, PhD 2,3 Janiëlle AEM van Alfen-van der Velden, MD, PhD 1,2 1 Department of Pediatric Endocrinology,
in children with type 1 diabetes Hilde E van Munster, MSc 2 Cathelijne PM van de Sande 2 Paul G Voorhoeve, MD, PhD 2,3 Janiëlle AEM van Alfen-van der Velden, MD, PhD 1,2 1 Department of Pediatric Endocrinology,
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE
 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN 07/81 9/10 1 of 5 PURPOSE: 1. To maintain aseptic technique in preparing and administering
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL NURSING PROCEDURE TITLE: ISSUED FOR: Nursing DATE: REVIEWED: PAGES: RESPONSIBILITY: RN, LPN 07/81 9/10 1 of 5 PURPOSE: 1. To maintain aseptic technique in preparing and administering
Disclosure. Learning Objectives. Case. Diabetes Update: Incretin Agents in Diabetes-When to Use Them? I have no disclosures to declare
 Disclosure Diabetes Update: Incretin Agents in Diabetes-When to Use Them? I have no disclosures to declare Spring Therapeutics Update 2011 CSHP BC Branch Anar Dossa BScPharm Pharm D CDE April 20, 2011
Disclosure Diabetes Update: Incretin Agents in Diabetes-When to Use Them? I have no disclosures to declare Spring Therapeutics Update 2011 CSHP BC Branch Anar Dossa BScPharm Pharm D CDE April 20, 2011
Andrejs Kalvelis 1, MD, PhD, Inga Stukena 2, MD, Guntis Bahs 3 MD, PhD & Aivars Lejnieks 4, MD, PhD ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION. Riga Stradins University
 CARDIOVASCULAR RISK FACTORS ORIGINAL ARTICLE Do We Correctly Assess the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease? Characteristics of Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease Depending on the Sex and Age of Patients
CARDIOVASCULAR RISK FACTORS ORIGINAL ARTICLE Do We Correctly Assess the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease? Characteristics of Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease Depending on the Sex and Age of Patients
