Long-Term Care Updates
|
|
|
- Annabella Bennett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Long-Term Care Updates January 2016 By Yunuo (Enora) Wu, PharmD Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is defined as kidney damage (including structural or functional abnormalities) or glomerular filtration rate (GFR) <60 ml/min/1.73m 2 (with or without kidney damage) for 3 months. 1 CKD can progress and worsen over time, increasing the risk of adverse outcomes. Currently, 10% of the global population is diagnosed with CKD. 2 Lack of access to affordable treatment leads to millions of deaths each year, raising CKD to the 18 th cause of death worldwide in In the geriatric population specifically, it is estimated that one in five men and one in four women between the ages of 65 and 74 years have CKD. 2 CKD can often progress to kidney failure due to other comorbidities such as diabetes and hypertension. In addition, CKD can affect drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion. In the presence of kidney disease, certain medications may accumulate and lead to an increased therapeutic effect or adverse drug effects. Addressing CKD early and adjusting medication therapy where necessary can help to prevent progression of the disease and ultimately improve patient outcomes. The article that follows will summarize and synthesize clinical practice guidance on the pharmacologic management of CKD from the National Kidney Foundation (NKF). While these documents provide significant evidence-based guidance on the management of CKD, patient-specific factors and the clinician s judgement should ultimately dictate an appropriate care plan. Clinical practice guidelines from the NKF are available for evaluating, classifying, and slowing the progression of CKD. These include the Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative (KDOQI) published in 2002 and the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) international guidelines published in 2013 as an update and clarification of the 2002 guidelines.
2 Current guidelines recommend that CKD be classified based on cause, GFR category, and albuminuria category. CKD is mainly detected and monitored by the calculated GFR and the urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (UACR). GFR reflects the rate of total filtration by all of the functioning nephrons in the kidney. As kidney damage progresses, GFR declines as the nephrons are damaged or destroyed. UACR (mg albumin/gram creatinine) indicates albuminuria at a ratio 30 mg/gram and is an early indication of kidney damage. Important laboratory tests to monitor include serum creatinine (SCr) and albumin, in order to estimate and calculate GFR and UACR in the presence of kidney disease. Guidelines recommend assessing GFR and albuminuria at least annually in those with stable CKD, and more frequently in those at higher risk of progressing CKD. KDIGO also suggests additional laboratory tests such as cystatin C or its clearance in order to confirm CKD in instances where GFR based on SCr is not as reliable. 4 Although neither KDOQI nor KDIGO focus their recommendations on the long-term care setting specifically, the goals of managing CKD are similar in all patient populations. It is important to identify CKD early to avoid progression to kidney failure. Tables 1 and 2 provide a summary of GFR and albuminuria categories used in the classification of CKD. 4 Whereas KDOQI guidelines recommended classification of CKD based on GFR alone, KDIGO updated this classification to include both GFR and albuminuria measurements. Table 1. CKD Categories Based on GFR 4 Stage Description GFR (ml/min ) G1 Normal or high 90 G2 Mildly decreased (relative to young adult level) G3a Mildly to moderately decreased G3b Moderately to severely decreased G4 Severely decreased G5 Kidney failure <15, or dialysis Category Table 2. CKD Categories Based on Albuminuria 4 Description AER (mg/24hr) ACR (mg/mmol) Abbreviations: AER = albumin excretion rate; ACR = albumin-to-creatinine ratio * Includes nephrotic syndrome (albumin excretion >2200mg/24hr or ACR >220mg/mmol or ACR >2200mg/g ACR (mg/g) A1 Normal to mildly increased <30 <3 <30 A2 Moderately increased (relative to young adult level) A3 Severely increased* >300 >30 >300
3 According to both the KDOQI and KDIGO guidelines, factors associated with CKD progression and prognosis may include GFR, level of albuminuria, elevated blood pressure, hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, smoking, obesity, history of cardiovascular disease (CVD), and exposure to nephrotoxic medications. It is important to note that small fluctuations in GFR do not always indicate CKD progression. KDIGO describes CKD progression as a decline in GFR category, a drop in GFR 25% from baseline, a sustained decline in GFR >5 ml/min/1.73m 2 per year, and increased SCr measurements. 4 Age, sex, race/ethnicity, and socioeconomic development are associated with CKD progression. The prevalence of CKD is quickly growing among the poorest parts of the world. A strong association has been observed between availability of renal replacement therapy and economic development. In addition, the risk of CKD increases with age and is most prominent in the African American, Asian, Hispanic, and Native American populations. 3 High blood pressure has been identified as both a cause and complication of CKD. Uncontrolled blood pressure can lead to a faster decline in kidney function and development of CVD. KDOQI and KDIGO recommend that all adults with CKD and urine albumin excretion <30 mg/24hr should have a blood pressure target of 140/90 mmhg. Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) should be used as first line treatment in both diabetic and non-diabetic patients for blood pressure control. 5 In the case that a patient cannot tolerate ACE inhibitor or ARB therapy due to worsening renal function, other alternatives such as diuretics, beta-blockers, or calcium-channel blockers that do not require renal dosage adjustment can be considered. 5 Glycemic control is also important in the CKD population with a recommended target hemoglobin A1C (HbA1C) of <7% to prevent progression of microvascular complications, such as diabetic kidney disease. 6 HbA1C goals should be individualized to the specific patient, with a higher HbA1C goal for those at risk of hypoglycemia, other comorbidities, and/or limited life expectancy. While the guidelines do not list specific preferred agents for diabetic patients with CKD, hypoglycemic therapy should also be individualized to each individual patient depending on response and glycemic control. Certain diabetes medications may require dosage adjustments in patients with CKD as inappropriate dosing can lead to toxic or suboptimal treatment. 4,6 Another therapeutic goal in slowing the progression of CKD is preventing acute kidney injury (AKI). KDIGO defines AKI as: an increase in SCr by 0.3 mg/dl within 48 hours; an increase in SCr to 1.5 times the baseline value within the past 7 days of monitoring time; or urine volume <0.5 ml/kg/h for 6 hours. Guidelines recommend that patients be monitored for increased AKI risk via SCr and urine output. 7 Patients who develop AKI should be evaluated 3 months after the event for resolution of AKI, new AKI onset, or progression of pre-existing CKD. In order to avoid development of AKI, guidelines suggest discontinuing potentially nephrotoxic agents that are renally eliminated when GFR <60 ml/min/1.73m 2, controlling plasma glucose between mg/dl, monitoring SCr and urine output, and considering alternatives to radiocontrast procedures. 7 Table 3 provides a list of commonly prescribed nephrotoxic medications that should be discontinued in the presence of CKD. Patients taking potentially nephrotoxic agents should be regularly monitored to assess GFR, electrolytes, and drug levels. 4 Table 4 provides a summary of recommended interventions for achieving therapeutic goals in slowing CKD progression.
4 Table 3. Nephrotoxic Medications Analgesics Acetaminophen Aspirin NSAIDs Benzodiazepines Alprazolam Clonazepam Diazepam Antidepressants / Mood Stabilizers Amitriptyline Doxepin Fluoxetine Lithium Cardiovascular Agents ACE inhibitors ARBs Clopidogrel Statins Diuretics Antihistamines Diphenhydramine Doxylamine Proton Pump Inhibitors Lansoprazole Omeprazole Pantoprazole Antimicrobials Acyclovir Aminoglycosides Amphotericin B Beta-Lactams Quinolones Rifampin Sulfonamides Vancomycin Others Allopurinol Haloperidol Phenytoin Quinine Ranitidine Zoledronic acid Abbreviations: ACE = angiotensin converting enzyme; ARB = angiotensin receptor blocker; NSAID = non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug
5 Table 4. Goals and Recommendations for Slowing CKD Progression 4-7 Therapeutic Goal Target Intervention Improve Lifestyle Slow CKD progression 1. Reduce sodium intake (<2 grams/day) 2. Reduce excessive protein intake 3. Smoking cessation 4. Weight management (BMI <30 kg/m 2 ) Control Blood Pressure Control Diabetes <140/90mmHg HbA1c <7%; Meet target blood glucose range; Goals should be individualized 1. ACE inhibitor or ARB (first line) 2. Diuretics Thiazides preferred 3. Beta-blockers Carvedilol, propranolol, or metoprolol preferred for CKD patients with heart failure 4. Calcium channel blockers Avoid nicardipine in elderly patients with CKD 5. Monitor serum potassium ACE inhibitors and ARBs may increase levels Dietary potassium restriction if needed 1. Dose adjust diabetes medications as needed 2. Consider less stringent HbA1c and blood glucose goals for: Elderly patients Patients with multiple comorbidities Patients with a history of hypoglycemia 3. Annual eye and feet screenings 4. Biannual dental exams 5. Quarterly HbA1c if uncontrolled; biannual HbA1c if controlled Prevent AKI Lower risk of AKI 1. Avoid nephrotoxic medications (see Table 3) 2. Control blood glucose between mg/dl 3. Monitor SCr and urine output 3. Avoid other nephrotoxic agents Iodinated contrast media Abbreviations: ACE=angiotensin converting enzyme; AKI=acute kidney injury; ARB=angiotensin receptor blocker; BMI=body mass index; HbA1C=hemoglobin A1C; SCr=serum creatinine
6 Current guidelines also make recommendations for managing complications related to CKD. Dyslipidemia or uncontrolled cholesterol is a common presentation in CKD patients due to decreased GFR and the presence of comorbidities such as hypertension and diabetes. Although there is limited data showing improved renal outcomes with the treatment of dyslipidemia, the guidelines still make recommendations for treatment in order to prevent possible complications such as atherosclerosis or CVD. KDIGO recommends an initial lipid profile evaluation upon diagnosis of CKD, including total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, and triglyceride levels. Statin therapy has been shown to reduce mortality associated with CVD in the CKD population; thus, the guidelines focus recommendations on the use of statins in the CKD population at higher risk of future cardiovascular events. KDIGO recommends that adults 50 years of age with GFR <60 ml/min/1.73m 2 (stage G3a-G5) should be treated with a statin or statin with ezetimibe combination therapy. In adults 50 years of age with GFR 60 ml/min/1.73m 2 (stage G1-G2), statin monotherapy should be recommended. Lifestyle modifications are recommended for patients with hypertriglyceridemia or triglycerides >500 mg/dl. 9 Anemia is diagnosed as hemoglobin (Hgb) <13 grams/dl in males and Hgb <12 grams/dl in females. KDIGO recommends that all CKD patients should be monitored for anemia at least annually in those with CKD stage G3, at least twice per year in those with CKD stage G4- G5, and at least every 3 months in patients with CKD stage G5. The presence of anemia should be evaluated based on a complete blood count, including Hgb concentration, red blood cell (RBC) count, white blood cell count, and platelet count. Anemia should also be assessed via absolute reticulocyte count, serum ferritin levels, serum transferrin saturation, and serum vitamin B12 and folate levels. 10 Bone mineral metabolism, as well as calcium and phosphate homeostasis, change as CKD progresses. KDIGO recommends measuring serum levels of calcium, phosphate, parathyroid hormone, and alkaline phosphatase activity at baseline in adults with GFR <45 ml/min/1.73m 2 (stage G3b-G5) in order to evaluate the values and determine progression of the disease. 11 Guidelines do not recommend routinely supplementing with vitamin D analogs if there is no suspected deficiency as there are a lack of robust data to support the treatment of vitamin D deficiency in non-dialysis patients. 11 Other complications that may occur with CKD include hyperkalemia (due to concomitant medication therapy) and malnutrition. 4 Table 5 summarizes complications as a result of decreased GFR and albuminuria over time, treatment targets, and recommended interventions. KDIGO guidelines recommend referring CKD patients to a nephrology specialist when there is an acute or chronic reduction in renal function, treatment-resistant hypertension, severe electrolyte disturbances, urinary tract structure abnormalities, or other systemic diseases with renal involvement. Patients should also be referred for education on progressive diseases and psychological implications that could be associated with CKD. Box 1 summarizes the specific situations in which patients should be referred to specialist nephrology services. 4
7 Table 5. Treating CKD Complications 4,9-11 Complication Target Intervention Cardiovascular Disease LDL cholesterol <100mg/dL; Refer also to current ACC/AHA lipid guidelines 1. Statin or 2. Statin + ezetimibe combination 3. Lifestyle modifications for high triglycerides Anemia Hgb 13 g/dl (males) Hgb 12 g/dl (females) 1. Oral iron supplements 2. IV iron supplements (if oral treatment is not tolerated) 3. Injectable ESAs: For dialysis patients If not on dialysis: Hgb <10 g/dl AND Hgb decline requiring RBC transfusion AND Increased RBC transfusion-related risk Mineral and Bone Disorders Hypocalcemia Hyperphosphatemia Secondary parathyroidism Vitamin D deficiency Calcium mg/dl Phosphorous mg/dl PTH <65 pg/ml Vitamin D 20 ng/ml 1. Calcium-based phosphate-binding medications 2. Phosphorous binders 3. Restrict dietary phosphorous 4. Vitamin D supplement Ergocalciferol (Vitamin D2) Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3) Calcitriol (Vitamin D) Hyperkalemia Potassium meq/l 1. Discontinue use of NSAIDs 2. Monitor potassium levels during ACE inhibitor or ARB therapy 3. Add diuretic therapy Malnutrition Hypoalbumineria Albumin >4.0 g/dl (range g/dl) 1. Biannual dental exam 2. Optimize diet Abbreviations: ACE = angiotensin converting enzyme; ARB = angiotensin receptor blocker; ESA = erythropoiesis-stimulating agent; Hgb = hemoglobin; LDL = low-density lipoprotein; NSAID = non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug; PTH = parathyroid hormone; RBC = red blood cell
8 Box 1. When to Refer Patients to Nephrology Specialists AKI or an abrupt and sustained decline in GFR CKD progression CKD stages G4-G5 (GFR <30 ml/min/1.73m 2 ) CKD with treatment-resistant hypertension while on 4 antihypertensive agents Hematic cylindruria and hematuria not otherwise explainable Hereditary kidney disease Persistent changes in serum potassium Significant albuminuria (defined as UACR >300 mg/g, albuminuria >300 mg/24hr) Abbreviations: AKI=acute kidney injury; UACR=urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio CKD is a worldwide health issue that causes millions of death each year, with the majority of death due to progression of concomitant chronic diseases. Early diagnosis and treatment is important as it can help to slow the progression of kidney disease in the long-term care population. Current guidelines recommend identifying and controlling diseases that can lead to kidney disease and making necessary lifestyle modifications and therapeutic interventions in order to manage the progression of CKD. 1. National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: Evaluation, classification, and stratification. 2002;39(2 Suppl 1):S Chronic Kidney Disease. World Kidney Day Web site. Available at: Accessed December 21, Jha V, Garcia-Garcia G, Iseki K, et al. Chronic kidney disease: Global dimension and perspectives. 2013;382(9888): Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. 2013;3: Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Blood Pressure Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the management of blood pressure in chronic kidney disease. 2012;2: Standards of medical care in diabetes--2015: Summary of revisions. 2015;38 Suppl:S4. 7. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. 2012;2: Naughton CA. Drug-induced nephrotoxicity. 2008;78(6): Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Lipid Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for lipid management in chronic kidney disease. 2013;3: Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Anemia Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for anemia in chronic kidney disease. 2012;2: Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD MBD Work Group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of chronic kidney disease mineral and bone disorder (CKD MBD). 2009;76(Suppl 113):S1 S130.
9
Applying clinical guidelines treating and managing CKD
 Applying clinical guidelines treating and managing CKD Develop patient treatment plan according to level of severity. Source: Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012
Applying clinical guidelines treating and managing CKD Develop patient treatment plan according to level of severity. Source: Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012
The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009
 The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009 Teresa Northcutt, RN BSN Primaris Program Manager, Prevention - CKD MO-09-01-CKD This material was prepared by Primaris,
The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009 Teresa Northcutt, RN BSN Primaris Program Manager, Prevention - CKD MO-09-01-CKD This material was prepared by Primaris,
CKD FOR INTERNISTS. Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College
 CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
CKD FOR INTERNISTS Dr Ahmed Hossain Associate professor Medicine Sir Salimullah Medical College INTRODUCTION In 2002, the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative(KDOQI)
Management of early chronic kidney disease
 Management of early chronic kidney disease GREENLANE SUMMER GP SYMPOSIUM 2018 Jonathan Hsiao Renal and General Physician Introduction A growing public health problem in NZ and throughout the world. Unknown
Management of early chronic kidney disease GREENLANE SUMMER GP SYMPOSIUM 2018 Jonathan Hsiao Renal and General Physician Introduction A growing public health problem in NZ and throughout the world. Unknown
CKDinform: A PCP s Guide to CKD Detection and Delaying Progression
 CKDinform: A PCP s Guide to CKD Detection and Delaying Progression Learning Objectives Describe suitable screening tools, such as GFR and ACR, for proper utilization in clinical practice related to the
CKDinform: A PCP s Guide to CKD Detection and Delaying Progression Learning Objectives Describe suitable screening tools, such as GFR and ACR, for proper utilization in clinical practice related to the
Primary Care Approach to Management of CKD
 Primary Care Approach to Management of CKD This PowerPoint was developed through a collaboration between the National Kidney Foundation and ASCP. Copyright 2018 National Kidney Foundation and ASCP Low
Primary Care Approach to Management of CKD This PowerPoint was developed through a collaboration between the National Kidney Foundation and ASCP. Copyright 2018 National Kidney Foundation and ASCP Low
Supplement: Summary of Recommendation Statements CHAPTER 1: DEFINITION AND CLASSIFICATION OF CKD
 Supplement: Summary of Recommendation Statements CHAPTER 1: DEFINITION AND CLASSIFICATION OF CKD 1.1 DEFINITION OF CKD 1.1.1: CKD is defined as abnormalities of kidney structure or function, present for
Supplement: Summary of Recommendation Statements CHAPTER 1: DEFINITION AND CLASSIFICATION OF CKD 1.1 DEFINITION OF CKD 1.1.1: CKD is defined as abnormalities of kidney structure or function, present for
Transforming Diabetes Care
 Transforming Diabetes Care Diabetic Kidney Disease: Prevention, Detection and Treatment Alexis Chettiar, ACNP-BC, PhD(c) 1 Polling Question - 1 What is your role as a healthcare provider? a) Dietitian
Transforming Diabetes Care Diabetic Kidney Disease: Prevention, Detection and Treatment Alexis Chettiar, ACNP-BC, PhD(c) 1 Polling Question - 1 What is your role as a healthcare provider? a) Dietitian
Outpatient Management of Chronic Kidney Disease for the Internist
 Outpatient Management of Chronic Kidney Disease for the Internist Annual Meeting of Maryland Chapter of the American College of Physicians February 3, 2018 MARY (TESSIE) BEHRENS, MD, FACP, FASN, FNKF MID-ATLANTIC
Outpatient Management of Chronic Kidney Disease for the Internist Annual Meeting of Maryland Chapter of the American College of Physicians February 3, 2018 MARY (TESSIE) BEHRENS, MD, FACP, FASN, FNKF MID-ATLANTIC
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin and
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, et al. Empagliflozin and
Diabetes and Hypertension
 Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS
 KEY MESSAGES 1 SCREENING CRITERIA Screen: Patients with DM and/or hypertension at least yearly. Consider screening patients with: Age >65 years old Family history of stage 5 CKD or hereditary kidney disease
KEY MESSAGES 1 SCREENING CRITERIA Screen: Patients with DM and/or hypertension at least yearly. Consider screening patients with: Age >65 years old Family history of stage 5 CKD or hereditary kidney disease
CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE: WHAT THE PRIMARY CARE CAN OFFER. The annual conference of the Lebanese Society of Family Medicine October 2017 Dr Hiba AZAR
 CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE: WHAT THE PRIMARY CARE CAN OFFER The annual conference of the Lebanese Society of Family Medicine October 2017 Dr Hiba AZAR OUTLINE: A journey through CKD Screening for CKD: The why,
CHRONIC RENAL FAILURE: WHAT THE PRIMARY CARE CAN OFFER The annual conference of the Lebanese Society of Family Medicine October 2017 Dr Hiba AZAR OUTLINE: A journey through CKD Screening for CKD: The why,
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERENCE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERECE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease CKD VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care (2008) PROVIDER REFERECE CARDS Chronic Kidney Disease CKD VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management
Management of Early Kidney Disease: What to do Before Referring to the Nephrologist
 Management of Early Kidney Disease: What to do Before Referring to the Nephrologist Andrew S. Narva, MD, NIDDK Saturday, February 18, 2017 8:45 a.m. 9:30 a.m. Although evidence-based guidelines for managing
Management of Early Kidney Disease: What to do Before Referring to the Nephrologist Andrew S. Narva, MD, NIDDK Saturday, February 18, 2017 8:45 a.m. 9:30 a.m. Although evidence-based guidelines for managing
Addressing Chronic Kidney Disease in People with Multiple Chronic Conditions
 Addressing Chronic Kidney Disease in People with Multiple Chronic Conditions Andrew S Narva, MD Na/onal Kidney Disease Educa/on Program U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institute of
Addressing Chronic Kidney Disease in People with Multiple Chronic Conditions Andrew S Narva, MD Na/onal Kidney Disease Educa/on Program U.S. Department of Health and Human Services National Institute of
Office Management of Reduced GFR Practical advice for the management of CKD
 Office Management of Reduced GFR Practical advice for the management of CKD CKD Online Education CME for Primary Care April 27, 2016 Monica Beaulieu, MD FRCPC MHA CHAIR PROVINCIAL KIDNEY CARE COMMITTEE
Office Management of Reduced GFR Practical advice for the management of CKD CKD Online Education CME for Primary Care April 27, 2016 Monica Beaulieu, MD FRCPC MHA CHAIR PROVINCIAL KIDNEY CARE COMMITTEE
Primary Care Physicians and Clinicians. XXX on behalf of the Upper Midwest Fistula First Coalition. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Resources
 August 10, 2007 To: From: RE: Primary Care Physicians and Clinicians XXX on behalf of the Upper Midwest Fistula First Coalition Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Resources Caring for patients with chronic kidney
August 10, 2007 To: From: RE: Primary Care Physicians and Clinicians XXX on behalf of the Upper Midwest Fistula First Coalition Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Resources Caring for patients with chronic kidney
DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
 DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes
DIABETES AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Stages 1 4 www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation's Kidney Disease Outcomes
Elevation of Serum Creatinine: When to Screen, When to Refer. Bruce F. Culleton, MD, FRCPC; and Jolanta Karpinski, MD, FRCPC
 Elevation of Serum Creatinine: When to Screen, When to Refer Bruce F. Culleton, MD, FRCPC; and Jolanta Karpinski, MD, FRCPC Presented at the University of Calgary s CME and Professional Development 2006-2007
Elevation of Serum Creatinine: When to Screen, When to Refer Bruce F. Culleton, MD, FRCPC; and Jolanta Karpinski, MD, FRCPC Presented at the University of Calgary s CME and Professional Development 2006-2007
Irish Practice Nurses Association Annual Conference Tullamore Court Hotel OCTOBER 6 th 2012
 Irish Practice Nurses Association Annual Conference Tullamore Court Hotel OCTOBER 6 th 2012 Susan McKenna Renal Clinical Nurse Specialist Cavan General Hospital Renal patient population ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
Irish Practice Nurses Association Annual Conference Tullamore Court Hotel OCTOBER 6 th 2012 Susan McKenna Renal Clinical Nurse Specialist Cavan General Hospital Renal patient population ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
The biologic price of aging includes progressive
 The Aging Kidney: Physiological Changes The biologic price of aging includes progressive structural and functional deterioration of the kidney, and these changes are among the most dramatic of any organ
The Aging Kidney: Physiological Changes The biologic price of aging includes progressive structural and functional deterioration of the kidney, and these changes are among the most dramatic of any organ
Chronic Kidney Disease
 Chronic Kidney Disease Presence of kidney damage or decreased kidney function for three or more months, - necessary to distinguish CKD from acute kidney disease. Ascertained either by kidney biopsy or
Chronic Kidney Disease Presence of kidney damage or decreased kidney function for three or more months, - necessary to distinguish CKD from acute kidney disease. Ascertained either by kidney biopsy or
DIABETES AND YOUR KIDNEYS
 DIABETES AND YOUR KIDNEYS OR AS WE CALL IT DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY The latest guidelines to keep you safe, healthy, fit, and out of danger from needing dialysis A UCLA HEALTH EDUCATIONAL SEMINAR Ramy M. Hanna
DIABETES AND YOUR KIDNEYS OR AS WE CALL IT DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY The latest guidelines to keep you safe, healthy, fit, and out of danger from needing dialysis A UCLA HEALTH EDUCATIONAL SEMINAR Ramy M. Hanna
American Diabetes Association 2018 Guidelines Important Notable Points
 American Diabetes Association 2018 Guidelines Important Notable Points The Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018 by ADA include the most current evidencebased recommendations for diagnosing and treating
American Diabetes Association 2018 Guidelines Important Notable Points The Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2018 by ADA include the most current evidencebased recommendations for diagnosing and treating
Diabetic Kidney Disease in the Primary Care Clinic
 Diabetic Kidney Disease in the Primary Care Clinic Jess Wheeler, DO Nephrology 2015 Outline: 1. CKD/DKD is a growing problem 2. Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) 3. Diagnosis of Diabetic Kidney
Diabetic Kidney Disease in the Primary Care Clinic Jess Wheeler, DO Nephrology 2015 Outline: 1. CKD/DKD is a growing problem 2. Diagnosis of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) 3. Diagnosis of Diabetic Kidney
CONCORD INTERNAL MEDICINE CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE PROTOCOL. Revised May 30, 2012
 CONCORD INTERNAL MEDICINE CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE PROTOCOL Douglas G. Kelling, Jr., MD C. Gismondi-Eagan, MD, FACP George C. Monroe III, MD Revised May 30, 2012 The information contained in this protocol
CONCORD INTERNAL MEDICINE CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE PROTOCOL Douglas G. Kelling, Jr., MD C. Gismondi-Eagan, MD, FACP George C. Monroe III, MD Revised May 30, 2012 The information contained in this protocol
ARE YOU AT INCREASED RISK FOR CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE?
 ARE YOU AT INCREASED RISK FOR CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE? www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease
ARE YOU AT INCREASED RISK FOR CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE? www.kidney.org National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative Did you know that the National Kidney Foundation s Kidney Disease
Identifying and Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: A Practical Approach
 Identifying and Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: A Practical Approach S. Neil Finkle, MD, FRCPC Associate Professor Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Dalhousie University Program Director,
Identifying and Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: A Practical Approach S. Neil Finkle, MD, FRCPC Associate Professor Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Dalhousie University Program Director,
NATIONAL QUALITY FORUM Renal EM Submitted Measures
 NATIONAL QUALITY FORUM Renal EM Submitted Measures Measure ID/ Title Measure Description Measure Steward Topic Area #1662 Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of CKD ACE/ARB
NATIONAL QUALITY FORUM Renal EM Submitted Measures Measure ID/ Title Measure Description Measure Steward Topic Area #1662 Percentage of patients aged 18 years and older with a diagnosis of CKD ACE/ARB
Indiana Medicaid Drug Utilization Review Board Newsletter
 Indiana Medicaid Drug Utilization Review Board Newsletter Volume 12 Issue 4 October 2009 Indiana Medicaid DUR Board Room W382 Indiana State Government Center, South 402 West Washington Street Indianapolis,
Indiana Medicaid Drug Utilization Review Board Newsletter Volume 12 Issue 4 October 2009 Indiana Medicaid DUR Board Room W382 Indiana State Government Center, South 402 West Washington Street Indianapolis,
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Management
 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Management Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Over the years, high blood glucose damages nerves and blood vessels, which can
Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Management Diabetes is a disease in which blood glucose levels are above normal. Over the years, high blood glucose damages nerves and blood vessels, which can
6/10/2014. Chronic Kidney Disease - General management and standard of care. Management of CKD according to stage (KDOQI 2002)
 Chronic Kidney Disease - General management and standard of care Dr Nathalie Demoulin, Prof Michel Jadoul Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc Université Catholique de Louvain What should and can be done
Chronic Kidney Disease - General management and standard of care Dr Nathalie Demoulin, Prof Michel Jadoul Cliniques universitaires Saint-Luc Université Catholique de Louvain What should and can be done
Chapter 1: CKD in the General Population
 Chapter 1: CKD in the General Population Overall prevalence of CKD (Stages 1-5) in the U.S. adult general population was 14.8% in 2011-2014. CKD Stage 3 is the most prevalent (NHANES: Figure 1.2 and Table
Chapter 1: CKD in the General Population Overall prevalence of CKD (Stages 1-5) in the U.S. adult general population was 14.8% in 2011-2014. CKD Stage 3 is the most prevalent (NHANES: Figure 1.2 and Table
Summary of Recommendation Statements Kidney International Supplements (2013) 3, 5 14; doi: /kisup
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2013 DIGO Summary of Recommendation Statements idney International Supplements (2013) 3, 5 14; doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.77 Chapter 1: Definition and classification of
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2013 DIGO Summary of Recommendation Statements idney International Supplements (2013) 3, 5 14; doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.77 Chapter 1: Definition and classification of
What should you do next? Presenter Disclosure Information. Learning Objectives. Case: George
 2:45 3:45pm Optimizing the Management of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease SPEAKER Jay B. Wish, MD, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation:
2:45 3:45pm Optimizing the Management of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease SPEAKER Jay B. Wish, MD, FACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation:
5/8/2017. Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Division of Kidney Disease and Hypertension
 Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Division of Kidney Disease and Hypertension Clinical Assistant Professor Adjunct Clinical Associate Professor Pharmacy Practice 1 http://ed.ted.com/lessons/how-do-your-kidneys-work-emma-bryce.
Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Division of Kidney Disease and Hypertension Clinical Assistant Professor Adjunct Clinical Associate Professor Pharmacy Practice 1 http://ed.ted.com/lessons/how-do-your-kidneys-work-emma-bryce.
Kidney Disease. Chronic kidney disease (CKD) requiring dialysis. The F.P. s Role in the Management of Chronic. Stages
 Focus on CME at McMaster University The F.P. s Role in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease By David N. Churchill, MD, FRCPC, FACP Presented at McMaster University CME Half-Day in Nephrology for Family
Focus on CME at McMaster University The F.P. s Role in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease By David N. Churchill, MD, FRCPC, FACP Presented at McMaster University CME Half-Day in Nephrology for Family
CKD IN THE CLINIC. Session Content. Recommendations for commonly used medications in CKD. CKD screening and referral
 CKD IN THE CLINIC Family Physician Refresher Course Lisa M. Antes, MD April 19, 2017 No disclosures Session Content 1. 2. Recommendations for commonly used medications in CKD Basic principles /patient
CKD IN THE CLINIC Family Physician Refresher Course Lisa M. Antes, MD April 19, 2017 No disclosures Session Content 1. 2. Recommendations for commonly used medications in CKD Basic principles /patient
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Afkarian M, Zelnick L, Hall YN, et al. Clinical manifestations of kidney disease among US adults with diabetes, 1988-2014. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.10924 emethods efigure
Supplementary Online Content Afkarian M, Zelnick L, Hall YN, et al. Clinical manifestations of kidney disease among US adults with diabetes, 1988-2014. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2016.10924 emethods efigure
Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
 Early Treatment is the Key Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stage Description GFR (ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) >90 1 Kidney damage with normal or GFR 2 Mild decrease in GFR 60-89 3 Moderate decrease in GFR
Early Treatment is the Key Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Stage Description GFR (ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) >90 1 Kidney damage with normal or GFR 2 Mild decrease in GFR 60-89 3 Moderate decrease in GFR
S150 KEEP Analytical Methods. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, Vol 55, No 3, Suppl 2, 2010:pp S150-S153
 S150 KEEP 2009 Analytical Methods American Journal of Kidney Diseases, Vol 55, No 3, Suppl 2, 2010:pp S150-S153 S151 The Kidney Early Evaluation program (KEEP) is a free, communitybased health screening
S150 KEEP 2009 Analytical Methods American Journal of Kidney Diseases, Vol 55, No 3, Suppl 2, 2010:pp S150-S153 S151 The Kidney Early Evaluation program (KEEP) is a free, communitybased health screening
Nice CKD Clinical Guidelines 2014 The challenges and benefits they may bring toprimary care
 Nice CKD Clinical Guidelines 2014 The challenges and benefits they may bring toprimary care Paula D Souza Senior CKD Nurse Specialist Royal Devon and Exeter Healthcare Trust Introduction Background What
Nice CKD Clinical Guidelines 2014 The challenges and benefits they may bring toprimary care Paula D Souza Senior CKD Nurse Specialist Royal Devon and Exeter Healthcare Trust Introduction Background What
SAMPLE. Chronic Kidney Disease, Evidence-Based Practice, and the Nutrition Care Process. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Chronic Kidney Disease, Evidence-Based Practice, and the Nutrition Care Process This guide follows the steps of the Nutrition Care Process (NCP) nutrition assessment, nutrition diagnosis, nutrition
Chapter 1 Chronic Kidney Disease, Evidence-Based Practice, and the Nutrition Care Process This guide follows the steps of the Nutrition Care Process (NCP) nutrition assessment, nutrition diagnosis, nutrition
PRE-DIALYSIS CARE IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE PATIENTS DR O. A ADEJUMO MBBS, FWACP, FMCP
 PRE-DIALYSIS CARE IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE PATIENTS DR O. A ADEJUMO MBBS, FWACP, FMCP OUTLINE INTRODUCTION BURDEN OF CKD DEFINITION OF PRE-DIALYSIS CARE (PDC) GOALS OF PDC IN CKD COMPONENTS OF PDC ADVANTAGES
PRE-DIALYSIS CARE IN CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE PATIENTS DR O. A ADEJUMO MBBS, FWACP, FMCP OUTLINE INTRODUCTION BURDEN OF CKD DEFINITION OF PRE-DIALYSIS CARE (PDC) GOALS OF PDC IN CKD COMPONENTS OF PDC ADVANTAGES
Chronic Kidney Disease. Basics of CKD Terms Diagnosis Management
 Chronic Kidney Disease Basics of CKD Terms Diagnosis Management Review the prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) Review how CKD develops Review populations at risk for CKD Review CKD diagnosis Objectives
Chronic Kidney Disease Basics of CKD Terms Diagnosis Management Review the prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) Review how CKD develops Review populations at risk for CKD Review CKD diagnosis Objectives
Chronic Kidney Disease: Optimal and Coordinated Management
 Chronic Kidney Disease: Optimal and Coordinated Management Michael Copland, MD, FRCPC Presented at University of British Columbia s 42nd Annual Post Graduate Review in Family Medicine Conference, Vancouver,
Chronic Kidney Disease: Optimal and Coordinated Management Michael Copland, MD, FRCPC Presented at University of British Columbia s 42nd Annual Post Graduate Review in Family Medicine Conference, Vancouver,
Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus
 Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 How to Screen for Diabetic Nephropathy... 4 What to Measure... 4 Frequency
Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 How to Screen for Diabetic Nephropathy... 4 What to Measure... 4 Frequency
Outline. Outline CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW 7/23/2013. Question 1: Which of these patients has CKD?
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
PREDIABETES TESTING SERVICES
 PREDIABETES TESTING SERVICES ASSESSING DIABETES RISK IN ASYMPTOMATIC ADULTS Depending upon population characteristics, up to 70% of individuals with prediabetes will ultimately progress to diabetes at
PREDIABETES TESTING SERVICES ASSESSING DIABETES RISK IN ASYMPTOMATIC ADULTS Depending upon population characteristics, up to 70% of individuals with prediabetes will ultimately progress to diabetes at
Outline. Outline CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW. Question 1: Which of these patients has CKD?
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
Analytical Methods: the Kidney Early Evaluation Program (KEEP) The Kidney Early Evaluation program (KEEP) is a free, community based health
 Analytical Methods: the Kidney Early Evaluation Program (KEEP) 2000 2006 Database Design and Study Participants The Kidney Early Evaluation program (KEEP) is a free, community based health screening program
Analytical Methods: the Kidney Early Evaluation Program (KEEP) 2000 2006 Database Design and Study Participants The Kidney Early Evaluation program (KEEP) is a free, community based health screening program
Case #1. Current Management Strategies in Chronic Kidney Disease. Serum creatinine cont. Pitfalls of Serum Cr
 Current Management Strategies in Chronic Kidney Disease Grace Lin, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, University of California San Francisco Case #1 50 y.o. 70 kg man with long-standing hypertension is
Current Management Strategies in Chronic Kidney Disease Grace Lin, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine, University of California San Francisco Case #1 50 y.o. 70 kg man with long-standing hypertension is
Concept and General Objectives of the Conference: Prognosis Matters. Andrew S. Levey, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA
 Concept and General Objectives of the Conference: Prognosis Matters Andrew S. Levey, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA General Objectives Topics to discuss What are the key outcomes of CKD? What progress
Concept and General Objectives of the Conference: Prognosis Matters Andrew S. Levey, MD Tufts Medical Center Boston, MA General Objectives Topics to discuss What are the key outcomes of CKD? What progress
Management of DM in Older Adults: It s not all about sugar! Who needs treatment for DM? Peggy Odegard, Pharm.D., BCPS, CDE
 Management of DM in Older Adults: It s not all about sugar! Peggy Odegard, Pharm.D., BCPS, CDE Who needs treatment for DM? 87 year old, frail male with moderately severe dementia living in NH with persistent
Management of DM in Older Adults: It s not all about sugar! Peggy Odegard, Pharm.D., BCPS, CDE Who needs treatment for DM? 87 year old, frail male with moderately severe dementia living in NH with persistent
Younger adults with a family history of premature artherosclerotic disease should have their cardiovascular risk factors measured.
 Appendix 2A - Guidance on Management of Hypertension Measurement of blood pressure All adults from 40 years should have blood pressure measured as part of opportunistic cardiovascular risk assessment.
Appendix 2A - Guidance on Management of Hypertension Measurement of blood pressure All adults from 40 years should have blood pressure measured as part of opportunistic cardiovascular risk assessment.
Key Elements in Managing Diabetes
 Key Elements in Managing Diabetes Presentor Disclosure No conflicts of interest to disclose Presented by Susan Cotey, RN, CDE Lennon Diabetes Center Stephanie Tubbs Jones Health Center Cleveland Clinic
Key Elements in Managing Diabetes Presentor Disclosure No conflicts of interest to disclose Presented by Susan Cotey, RN, CDE Lennon Diabetes Center Stephanie Tubbs Jones Health Center Cleveland Clinic
Quality ID #119 (NQF 0062): Diabetes: Medical Attention for Nephropathy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care
 Quality ID #119 (NQF 0062): Diabetes: Medical Attention for Nephropathy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process
Quality ID #119 (NQF 0062): Diabetes: Medical Attention for Nephropathy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care 2018 OPTIONS F INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY MEASURE TYPE: Process
Long-Term Care Updates
 Long-Term Care Updates August 2015 By Darren Hein, PharmD Hypertension is a clinical condition in which the force of blood pushing on the arteries is higher than normal. This increases the risk for heart
Long-Term Care Updates August 2015 By Darren Hein, PharmD Hypertension is a clinical condition in which the force of blood pushing on the arteries is higher than normal. This increases the risk for heart
DIABETES MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW
 2014 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: DIABETES MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2014 PQRS MEASURES IN DIABETES MEASURES GROUP: #1. Diabetes: Hemoglobin A1c Poor Control #2. Diabetes: Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL-C)
2014 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: DIABETES MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2014 PQRS MEASURES IN DIABETES MEASURES GROUP: #1. Diabetes: Hemoglobin A1c Poor Control #2. Diabetes: Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL-C)
egfr > 50 (n = 13,916)
 Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
Saxagliptin and Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Moderate or Severe Renal Impairment: Observations from the SAVOR-TIMI 53 Trial Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics according
Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: Reducing Risk for CKD Progression
 Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: Reducing Risk for CKD Progression Arasu Gopinath, MD Clinical Nephrologist, Medical Director, Jordan Landing Dialysis Center Objectives: Identify the most important risks
Managing Chronic Kidney Disease: Reducing Risk for CKD Progression Arasu Gopinath, MD Clinical Nephrologist, Medical Director, Jordan Landing Dialysis Center Objectives: Identify the most important risks
Clinician Blood Panel Results
 Page 1 of 7 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Page 1 of 7 Blood Panel - Markers Out of Range and Patterns (Pattern: proprietary formula using one or more Blood Markers) Blood Panel: Check for Markers that are out of Lab Range ***NOTE*** Only one supplement
Outline. Outline 10/14/2014 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW. Question 1: Which of these patients has CKD?
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE UPDATE: WHAT THE GENERALIST NEEDS TO KNOW MICHAEL G. SHLIPAK, MD, MPH CHIEF-GENERAL INTERNAL MEDICINE, SAN FRANCISCO VA MEDICAL CENTER PROFESSOR OF MEDICINE, EPIDEMIOLOGY AND BIOSTATISTICS,
Objectives. Pre-dialysis CKD: The Problem. Pre-dialysis CKD: The Problem. Objectives
 The Role of the Primary Physician and the Nephrologist in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease () By Brian Young, M.D. Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
The Role of the Primary Physician and the Nephrologist in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease () By Brian Young, M.D. Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
Chronic Kidney Disease for the Primary Care Physician in What do the Kidneys do? CKD in the US
 1:25-2:25pm Managing Chronic Kidney Disease in 2019 SPEAKERS Adriana Dejman, MD Chronic Kidney Disease for the Primary Care Physician in 2019 Adriana Dejman, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine
1:25-2:25pm Managing Chronic Kidney Disease in 2019 SPEAKERS Adriana Dejman, MD Chronic Kidney Disease for the Primary Care Physician in 2019 Adriana Dejman, MD Assistant Professor of Clinical Medicine
Section Questions Answers
 Section Questions Answers Guide to CKD Screening and Evaluation -Alec Otteman, MD Delaying Progression - Paul Drawz, MD, MHS, MS 1. Modifiable risk factors for CKD include: a. Diabetes b. Hypertension
Section Questions Answers Guide to CKD Screening and Evaluation -Alec Otteman, MD Delaying Progression - Paul Drawz, MD, MHS, MS 1. Modifiable risk factors for CKD include: a. Diabetes b. Hypertension
CARE GUIDE for Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
 Screening for and Diagnosis of Chronic (1, 24) Kidney Disease Screen all individuals that have: Clinical risk factors: Diabetes (DM) Hypertension (HTN) Autoimmune diseases Systemic infections Urinary tract
Screening for and Diagnosis of Chronic (1, 24) Kidney Disease Screen all individuals that have: Clinical risk factors: Diabetes (DM) Hypertension (HTN) Autoimmune diseases Systemic infections Urinary tract
DISCLOSURES OUTLINE OUTLINE 9/29/2014 ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE
 ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DISCLOSURES Editor-in-Chief- Nephrology- UpToDate- (Wolters Klewer) Richard J. Glassock, MD, MACP Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA 1 st Annual Internal
ANTI-HYPERTENSIVE MANAGEMENT OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DISCLOSURES Editor-in-Chief- Nephrology- UpToDate- (Wolters Klewer) Richard J. Glassock, MD, MACP Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA 1 st Annual Internal
Faculty/Presenter Disclosure
 CSI for CKD Unravelling the myths surrounding chronic kidney disease Practical Evidence for Informed Practice Oct 21 2016 Dr. Scott Klarenbach University of Alberta Slide 1: Option B (Presenter with NO
CSI for CKD Unravelling the myths surrounding chronic kidney disease Practical Evidence for Informed Practice Oct 21 2016 Dr. Scott Klarenbach University of Alberta Slide 1: Option B (Presenter with NO
Professor Suetonia Palmer
 Professor Suetonia Palmer Department of Medicine Nephrologist Christchurch Hospital Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #108: The Kidney Test - When To Test and When to Refer ( and When Not To) 15:05-16:00 WS
Professor Suetonia Palmer Department of Medicine Nephrologist Christchurch Hospital Christchurch 14:00-14:55 WS #108: The Kidney Test - When To Test and When to Refer ( and When Not To) 15:05-16:00 WS
TABLE OF CONTENTS T-1. A-1 Acronyms and Abbreviations. S-1 Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
 A-1 Acronyms and Abbreviations TABLE OF CONTENTS S-1 Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Chapter 1: Nutrition Assessment Charts, Tables and Formulas 1-2 Practical Steps to Nutrition Assessment Adult
A-1 Acronyms and Abbreviations TABLE OF CONTENTS S-1 Stages of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Chapter 1: Nutrition Assessment Charts, Tables and Formulas 1-2 Practical Steps to Nutrition Assessment Adult
Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care
 Clinical Stream Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care Dr Gerald Waters Dr Gerald Waters Renal Physician Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Kidney Disease Normal functions of Kidneys Management of CKD Drugs
Clinical Stream Chronic Kidney Disease in Primary Care Dr Gerald Waters Dr Gerald Waters Renal Physician Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Kidney Disease Normal functions of Kidneys Management of CKD Drugs
2019 COLLECTION TYPE: MIPS CLINICAL QUALITY MEASURES (CQMS) MEASURE TYPE: Process
 Quality ID #119 (NQF 0062): Diabetes: Medical Attention for Nephropathy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care Meaningful Measure Area: Management of Chronic Conditions 2019 COLLECTION
Quality ID #119 (NQF 0062): Diabetes: Medical Attention for Nephropathy National Quality Strategy Domain: Effective Clinical Care Meaningful Measure Area: Management of Chronic Conditions 2019 COLLECTION
Figure 1 LVH: Allowed Cost by Claim Volume (Data generated from a Populytics analysis).
 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): The New Silent Killer Nelson Kopyt D.O. Chief of Nephrology, LVH Valley Kidney Specialists For the past several decades, the health care needs of Americans have shifted from
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): The New Silent Killer Nelson Kopyt D.O. Chief of Nephrology, LVH Valley Kidney Specialists For the past several decades, the health care needs of Americans have shifted from
만성콩팥병환자에서의혈압관리 분당서울대병원신장내과 안신영
 만성콩팥병환자에서의혈압관리 분당서울대병원신장내과 안신영 Contents Introduction Lifestyle and Pharmacological Tx CKD ND ptswithout diabetes CKD ND ptswith diabetes In elderly ptswith CKD ND 2013 대한고혈압학회진료지침 JNC 8th Introduction
만성콩팥병환자에서의혈압관리 분당서울대병원신장내과 안신영 Contents Introduction Lifestyle and Pharmacological Tx CKD ND ptswithout diabetes CKD ND ptswith diabetes In elderly ptswith CKD ND 2013 대한고혈압학회진료지침 JNC 8th Introduction
8 th Annual Congress of the Bangladesh Society of Medicine Dhaka, Bangladesh March 23-24, Jeffrey P. Harris MD, FACP
 8 th Annual Congress of the Bangladesh Society of Medicine Dhaka, Bangladesh March 23-24, 2008 The Internist and the Pre-End Stage Renal Disease Patient Jeffrey P. Harris MD, FACP Country: Bangladesh Population:
8 th Annual Congress of the Bangladesh Society of Medicine Dhaka, Bangladesh March 23-24, 2008 The Internist and the Pre-End Stage Renal Disease Patient Jeffrey P. Harris MD, FACP Country: Bangladesh Population:
Diabetes: Use of Adjunctive Therapy ACEs, ARBs, ASA & STATINs --Oh My! Veronica J. Brady, PhD, FNP-BC, BC-ADM, CDE Project ECHO April 19, 2018
 Diabetes: Use of Adjunctive Therapy ACEs, ARBs, ASA & STATINs --Oh My! Veronica J. Brady, PhD, FNP-BC, BC-ADM, CDE Project ECHO April 19, 2018 Points to Ponder ASCVD is the leading cause of morbidity
Diabetes: Use of Adjunctive Therapy ACEs, ARBs, ASA & STATINs --Oh My! Veronica J. Brady, PhD, FNP-BC, BC-ADM, CDE Project ECHO April 19, 2018 Points to Ponder ASCVD is the leading cause of morbidity
Diabetes Complications Guideline Based Screening, Management, and Referral
 Diabetes Complications Guideline Based Screening, Management, and Referral Eric L. Johnson, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Family and Community Medicine Assistant Medical Director Altru Diabetes
Diabetes Complications Guideline Based Screening, Management, and Referral Eric L. Johnson, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Family and Community Medicine Assistant Medical Director Altru Diabetes
Kidney Disease, Hypertension and Cardiovascular Risk
 1 Kidney Disease, Hypertension and Cardiovascular Risk George Bakris, MD, FAHA, FASN Professor of Medicine Director, Hypertensive Diseases Unit The University of Chicago-Pritzker School of Medicine Chicago,
1 Kidney Disease, Hypertension and Cardiovascular Risk George Bakris, MD, FAHA, FASN Professor of Medicine Director, Hypertensive Diseases Unit The University of Chicago-Pritzker School of Medicine Chicago,
Cardiovascular Health Practice Guideline Outpatient Management of Coronary Artery Disease 2003
 Authorized By: Medical Management Guideline Committee Approval Date: 12/13/01 Revision Date: 12/11/03 Beta-Blockers Nitrates Calcium Channel Blockers MEDICATIONS Indicated in post-mi, unstable angina,
Authorized By: Medical Management Guideline Committee Approval Date: 12/13/01 Revision Date: 12/11/03 Beta-Blockers Nitrates Calcium Channel Blockers MEDICATIONS Indicated in post-mi, unstable angina,
Hypertension Update. Sarah J. Payne, MS, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacotherapy UNT System College of Pharmacy
 Hypertension Update Sarah J. Payne, MS, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacotherapy UNT System College of Pharmacy Introduction 1/3 of US adults have HTN More prevalent in non-hispanic
Hypertension Update Sarah J. Payne, MS, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Professor, Department of Pharmacotherapy UNT System College of Pharmacy Introduction 1/3 of US adults have HTN More prevalent in non-hispanic
Diabetes and the Elderly: Medication Considerations When Determining Benefits and Risks
 Diabetes and the Elderly: Medication Considerations When Determining Benefits and Risks Gretchen M. Ray, PharmD, PhC, BCACP, CDE Associate Professor UNM College of Pharmacy September 7 th, 2018 DISCLOSURES
Diabetes and the Elderly: Medication Considerations When Determining Benefits and Risks Gretchen M. Ray, PharmD, PhC, BCACP, CDE Associate Professor UNM College of Pharmacy September 7 th, 2018 DISCLOSURES
Long-Term Complications of Diabetes Mellitus Macrovascular Complication
 Long-Term Complications of Diabetes Mellitus Macrovascular Complication Sung Hee Choi MD, PhD Professor, Seoul National University College of Medicine, SNUBH, Bundang Hospital Diabetes = CVD equivalent
Long-Term Complications of Diabetes Mellitus Macrovascular Complication Sung Hee Choi MD, PhD Professor, Seoul National University College of Medicine, SNUBH, Bundang Hospital Diabetes = CVD equivalent
HIV AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE. Understanding GFR
 HIV AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Understanding GFR in PEOPLE WITH HIV contents Introduction... 4 Chronic Kidney Disease... 5 What are kidneys and what do they do?... 5 What is glomerular filtration rate
HIV AND CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Understanding GFR in PEOPLE WITH HIV contents Introduction... 4 Chronic Kidney Disease... 5 What are kidneys and what do they do?... 5 What is glomerular filtration rate
Summary of KDIGO 2012 CKD Guideline: behind the scenes, need for guidance, and a framework for moving forward
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2013 International Society of Nephrology Summary of KDIGO 2012 CKD Guideline: behind the scenes, need for guidance, and a framework for moving forward Adeera Levin
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2013 International Society of Nephrology Summary of KDIGO 2012 CKD Guideline: behind the scenes, need for guidance, and a framework for moving forward Adeera Levin
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGNOSIS
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD Offer testing for CKD using egfr, serum creatinine and urinary ACR to people with any of the following risk factors: diabetes hypertension acute
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD Offer testing for CKD using egfr, serum creatinine and urinary ACR to people with any of the following risk factors: diabetes hypertension acute
Disclosures. Topics. Staging and GFR. K-DOQI Staging of Chronic Kidney Disease. Definition of Chronic Kidney Disease. Chronic Kidney Disease
 Disclosures Chronic Kidney Disease Consultant: Baxter Healthcare J. Kevin Tucker, M.D. Brigham and Women s Hospital Massachusetts General Hospital Topics Staging of chronic kidney disease (CKD) How to
Disclosures Chronic Kidney Disease Consultant: Baxter Healthcare J. Kevin Tucker, M.D. Brigham and Women s Hospital Massachusetts General Hospital Topics Staging of chronic kidney disease (CKD) How to
Chronic Kidney Disease. Paul Cockwell Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham
 Chronic Kidney Disease Paul Cockwell Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham Paradigms for chronic disease 1. Acute and chronic disease is closely linked 2. Stratify risk and tailor interventions around failure
Chronic Kidney Disease Paul Cockwell Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham Paradigms for chronic disease 1. Acute and chronic disease is closely linked 2. Stratify risk and tailor interventions around failure
HYPERTENSION IN CKD. LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL
 HYPERTENSION IN CKD LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL Stages in Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Therapeutic Strategies Complications Normal Increased risk Damage GFR
HYPERTENSION IN CKD LEENA ONGAJYOOTH, M.D., Dr.med RENAL UNIT SIRIRAJ HOSPITAL Stages in Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Therapeutic Strategies Complications Normal Increased risk Damage GFR
Modified version focused on CCNC Quality Measures and Feedback Processes
 Executive Summary: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2010 Modified version focused on CCNC Quality Measures and Feedback Processes See http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/33/supplement_1/s11.full
Executive Summary: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2010 Modified version focused on CCNC Quality Measures and Feedback Processes See http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/33/supplement_1/s11.full
Session 9: Optimizing the Management of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Learning Objectives
 Session 9: Optimizing the Management of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Learning Objectives 1. Understand the impact of chronic kidney disease (CKD) as a common condition of the adult US population.
Session 9: Optimizing the Management of Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease Learning Objectives 1. Understand the impact of chronic kidney disease (CKD) as a common condition of the adult US population.
Diabetes in Renal Patients. Contents. Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetes in Renal Patients Contents Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy What effect does CKD have on a patient s diabetic control? Diabetic Drugs in CKD and Dialysis Patients Hyper and Hypoglycaemia in
Diabetes in Renal Patients Contents Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy What effect does CKD have on a patient s diabetic control? Diabetic Drugs in CKD and Dialysis Patients Hyper and Hypoglycaemia in
Multiphasic Blood Analysis
 Understanding Your Multiphasic Blood Analysis Test Results Mon General thanks you for participating in the multiphasic blood analysis. This test can be an early warning of health problems, including coronary
Understanding Your Multiphasic Blood Analysis Test Results Mon General thanks you for participating in the multiphasic blood analysis. This test can be an early warning of health problems, including coronary
Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2018
 Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2018 Eric L. Johnson, M.D. Associate Professor University of North Dakota School of Medicine and Health Sciences Assistant Medical Director Altru Diabetes Center Grand
Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2018 Eric L. Johnson, M.D. Associate Professor University of North Dakota School of Medicine and Health Sciences Assistant Medical Director Altru Diabetes Center Grand
5.2 Key priorities for implementation
 5.2 Key priorities for implementation From the full set of recommendations, the GDG selected ten key priorities for implementation. The criteria used for selecting these recommendations are listed in detail
5.2 Key priorities for implementation From the full set of recommendations, the GDG selected ten key priorities for implementation. The criteria used for selecting these recommendations are listed in detail
Disclosures. Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management. Learning Objectives. Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
 Disclosures Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Tony Hampton, MD, MBA Medical Director Advocate Aurora Operating System Advocate Aurora Healthcare Downers Grove, IL No conflicts or disclosures
Disclosures Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Tony Hampton, MD, MBA Medical Director Advocate Aurora Operating System Advocate Aurora Healthcare Downers Grove, IL No conflicts or disclosures
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGNOSIS
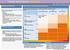 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS GFR categories, description and range WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD CLASSIFICATION OF CKD USING egfr AND ACR CATEGORIES Offer testing for CKD using egfr, creatinine and ACR
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS GFR categories, description and range WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD CLASSIFICATION OF CKD USING egfr AND ACR CATEGORIES Offer testing for CKD using egfr, creatinine and ACR
Chronic Kidney Disease
 Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Guideline (2010) Chronic Kidney Disease CKD: Executive Summary of Recommendations (2010) Executive Summary of Recommendations Below are the major recommendations
Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Guideline (2010) Chronic Kidney Disease CKD: Executive Summary of Recommendations (2010) Executive Summary of Recommendations Below are the major recommendations
Chronic Kidney Disease
 Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Educational Objectives Outline Demographics Propose Strategies to slow progression and improve outcomes Plan for treatment of CKD Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Educational Objectives Outline Demographics Propose Strategies to slow progression and improve outcomes Plan for treatment of CKD Chronic Kidney Disease
