Hyperammonemia in Pediatric Clinics: A review of ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency (OTCD) based on our case studies
|
|
|
- Hugo Clark
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JMA Medical Awards Hyperammonemia in Pediatric Clinics: A review of ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency (OTCD) based on our case studies JMAJ 47(4): , 2004 Ichiro MATSUDA Professor Emeritus, Kumamoto University Abstract: Ornithine transcarbamylase, which is the enzyme to synthesize citrulline from carbamyl phosphate and ornithine, is located on the X chromosome. Male patients with OTCD present a wide clinical picture, as shown in the neonatal type (usually ending in death within one year) and the late-onset type (appearing between 2 and 56 years and characterized by long-term survival). OTC activity in the neonatal type is essentially undetectable, whereas those with the late-onset type have % of the control level. Mutations of male patients with the neonatal type (n 23) include base insertion/deletion, exon skipping, and nonsense and missense mutations. Mutations may lead to unstable mrna or truncated protein, or involve the active site or cord domain of the enzyme, leading to structural changes. Mutations associated with the late-onset type (n 25) are only of the missense type, with most occurring on the surface of the enzyme. We performed prenatal monitoring for OTCD in 21 cases, among which one male fetus with Arg129His and two male fetuses with Arg40His (both belonging to the lateonset type) were diagnosed on the basis of gene analysis of amniotic cells. Treatment was initiated immediately after birth, enabling them to enjoy a normal school life. Two fetuses diagnosed as having neonatal-type mutations were terminated. Gene analysis provides the most reliable information about the future consequences of OTCD, especially in male patients. Key words: Hyperammonemia; Urea cycle disorder; Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency (OTCD); Genotype-phenotype correlation Introduction Hyperammonemia in children is observed in association with a variety of diseases and con- ditions including liver diseases accompanied with liver cirrhosis (e.g., congenital biliary atresia) and hereditary diseases such as urea-cycle enzyme defects, defective transport of ornithine This article is a revised English version of a paper originally published in the Journal of the Japan Medical Association (Vol. 129, No. 1, 2003, pages 60 64). This research was awarded the Medical Prize of the Japan Medical Association for 2002 in Clinical Medicine. 160 JMAJ, April 2004 Vol. 47, No. 4
2 ORNITHINE TRANSCARBAMYLASE DEFICIENCY into mitochondria, and certain organic acidemias. In recent years, gene analysis of certain hereditary diseases has revealed the relationship between genotype and phenotype (the pathologic condition), and the results of analysis have come to be applied in clinical practice. This paper describes ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency (OTCD), one of the most frequent of such hereditary diseases in Japan and the subject of our research since we reported the first case of this disease in Japan in ) Our group was the first to succeed in elucidating the structure of the OTC gene in ) In addition, identification of the carbamyl phosphate synthetase and arginase genes and elucidation of their mutant genes were also initially carried out by our group. 3 6) OTC, a urea cycle enzyme localized in mitochondria of the liver, is involved in synthesizing citrulline from carbamyl phosphate and ornithine. This enzyme is first synthesized as a precursor protein with a molecular mass of about 40,000 daltons in the cytosol, then transported to the mitochondrial matrix, where it is processed to the mature enzyme of about 36,000 daltons. It becomes active after being formed into a trimer. The OTC gene maps to Xp21.1 and is 73 kb long with 10 exons. 1) OTC deficiency is an X-linked semidominant urea cycle disorder, and has the highest incidence (1 out of 50,000 people) among the various urea cycle disorders. Clinically, the age of onset is wideranging, involving infants to adults. The reason for such variety remained unclear until gene analysis provided relevant information. Classification of Disease Types About half of male patients (hemizygotes) have a neonatal onset, with the disease occurring within 1 month after birth; the other half experience late-onset disease. Most female patients (heterozygotes) have late-onset disease. 7) 1. Neonatal-onset type OTCD in neonates is severe and manifests with central nervous system (CNS) symptoms such as vomiting, spasm, coma, and lethargy, within 30 days after birth. In most cases, it ends in patient death within the first several months of life. Even if the patient survives, severe neurological disorders will remain. OTC activity in the liver is below the limit of detection. 7) 2. Late-onset type Late-onset disease occurs in patients of various ages, ranging from those in infancy, puberty, and adolescence, to middle age or even later. One patient had been known to be asymptomatic until the age of 65 years. Patients commonly lead a normal life until the onset of disease. However, some patients have been reported to have mild symptoms (vomiting and mild neural confusion) particularly when they have fever. Hepatic OTC activity in patients with normal IQ and normal electrocardiographic findings corresponds to % of the normal level. 7) 3. Female patients Signs and symptoms vary widely among female patients (heterozygotes). Some are asymptomatic, while others eventually die after onset. Differences in the rate of inactivation of the X chromosome owing to lyonization are involved in how the disease manifests. 7) Relation between Disease Type (Phenotype) and Mutant Gene (Fig. 1) Mutation of the OTC gene is basically individual, varying among those who are affected. 8) 1. Gene mutation of neonatal-onset OTCD About half the patients with neonatal-onset disease have nonsense mutations (mutations with a stop codon present in the sequence), base insertion, and base deletion. In this case, enzyme protein is always greatly decreased, and the activity level is virtually nil. The other half of patients have missense mutations (mutations accompanied with substitution of amino JMAJ, April 2004 Vol. 47, No
3 I. MATSUDA Mutation R40H Y55D D126G R129H R141Q I172M Q180H S192R D196V L201R S207R H214Y L221L (AAG AAA) T264A T264I M268T R277W L304F V337L Exon month 1 year 10 years 50 years Age at first episode Age at detection of mutation on genetic screening in the absence of symptoms Fig. 1 Relationship between patient age at the first episode of OTCD and missense mutant genes Mutations in patients who died within one month after birth (neonatal-onset disease) were located at the active site of the enzyme protein or at the site indispensable for composition of a trimer. Mutations in patients with late-onset disease were located on the surface of the enzyme protein. (From Matsuda, I.: Iden 54; 2000: 48 54) acids: e.g., D126G, R141Q, I172M, S192R, D196V, or L201R). All these mutations are missense mutations at sites important for enzyme activity, such as the site responsible for trimer formation and the active site of the enzyme. 8) In any case, OTC activity as examined in gene expression studies was below the limit of detection. 8,9) 2. Gene mutation of late-onset OTCD In late-onset cases, all mutations are missense mutations, and most of them are located on the surface of the enzyme protein. The OTC activity corresponds to 10 15% of the normal level. Unlike neonatal-onset disease, identical gene mutations (R40H, R277W, R129H, M268T) are found in about 30% of the families of patients. The R4OH mutation, in particular, has been found in 6 families. In these families, there was a male patient who was 65 years old at the first examination and had never experienced episodes of hyperammonemia, as well as male patients who developed the disease at the ages of 9, 15, 17, and 48 years. The 65-year-old patient was found to have a daily protein intake of less than 65 g. Interestingly, the disease manifested in all these patients in the 1980s, when the protein intake among Japanese adult men reached about 80 g/day. 10) 3. Gene mutation of OTCD in females In female patients, nonsense mutation, base insertion, base deletion, exon skipping, and missense mutation have been observed. However, mutations in female patients are basically of the same nature as those in male patients with neonatal-onset disease. 8) 4. Patient gender and carrier diagnosis It is known empirically that the percentage 162 JMAJ, April 2004 Vol. 47, No. 4
4 ORNITHINE TRANSCARBAMYLASE DEFICIENCY Table 1 Prenatal Diagnosis of OTCD Site of mutation Case Family Specimen Sex targeted for diagnosis Mutation Exon/Intron Restriction enzyme Result Consequence 1 1 Villi Male Intron 1 ( 4. A C) Rsa I Patient Aborted 2 1 Villi Male Normal Continued 3 1 Villi Female Normal Continued 4 2 Villi Male Exon 2 CGT CAT Arg 40 His Nla III, Mae II Patient Continued 5 3 Villi Male Exon 2 CGT CAT Arg 40 His Nla III, Mae II Patient Continued 6 4 Villi Male Exon 4 GAC GGC Arg 126 Gly Sdu I Patient Aborted 7 5 Male Exon 4 CGT CAT Arg 129 His Msp I Patient Continued 8 6 Villi Female Exon 5 CGA TGA Arg 141 Ter Taq I Carrier Continued 9 6 Female Carrier Continued 10 7 Villi Female Exon 5 CGA CAA Arg 141 Gln Taq I Carrier Continued 11 7 Villi Male Normal Continued 12 8* Male Exon 6 AGC AGG Ser 192 Arg Pvu II Unevaluable Continued (patient) 13 8 Villi Male Patient Aborted 14 9 Female Exon 9 TGG TGA Ser 332 Ter Base sequence analysis Carrier Continued Male Intron 8 ( 1. G A) Msp I, RFLP Normal Continued Female Msp I, RFLP Normal Continued 17 12** Unknown Unevaluable Continued (patient) Villi Male SSCP (Normal) Continued (normal) *Maternal blood contamination **Bacterial contamination SSCP: single-strand conformation polymorphism, RFLP: restriction fragment length polymorphism (From Matsuda, I.: Ethical issues around prenatal diagnosis: From the standpoint of molecular biology. Shusanki Igaku 1998; 28: (in Japanese)) of carriers among mothers of male patients is not the same as that among mothers of female patients. Whereas 92% of mothers of male patients are carriers, fresh mutation was common in female patients, with only 20% of mothers of female patients being carriers. 11) or R129H mutant gene. In these cases, treatment was begun just after delivery without abortion. The patients are currently in elementary school and are showing healthy growth. Three of the 18 cases underwent abortion after prenatal diagnosis. 12) Prenatal Diagnosis of OTCD The author has been involved in prenatal monitoring for OTCD in 18 patients from 13 families (Table 1). The male-female ratio was 11:7. Four of the 7 females were carriers, and 6 of the 11 males had a mutant gene. Three of these 6 had late-onset OTCD, showing an R40H Treatment and Prognosis Administration of sodium benzoate or sodium phenylacetate is employed as pharmacotherapy, and a low protein diet (protein g/kg/ day plus essential amino acids at the required level) is used as nutritional therapy. However, since arginine is essential in this disease, in JMAJ, April 2004 Vol. 47, No
5 I. MATSUDA Survival rate (%) (Years) Age Fig. 2 Survival rate in patients with late-onset OTCD Death of female patients (thin line) begins at about 5 years and follows a course similar to that in male patients (thick line). (From Uchino, T. et al.: Neurodevelopmental outcome of long-term therapy of urea cycle disorders in Japan. J Inherit Metab Dis 1998; 21(Suppl1): ) Conclusion In OTCD, gene mutations that severely affect the structure and function of OTC enzyme protein are associated with the complete absence of enzyme activity and neonatal onset, whereas gene mutations affecting the protein surface are associated with a 10 20% enzyme activity level and onset in late childhood or adulthood. In addition, a close association has been found between protein intake and disease onset. These findings represent a useful set of information for genetic counseling in relation to treatment of the patient and prenatal diagnosis of the disease. addition to the usual essential amino acids, arginine (400 mg/kg/day) should be given to the patient in conjunction with other essential amino acids. With regard to prognosis, most neonatalonset cases end in death within several months after birth, as mentioned previously. In contrast, male patients with late-onset disease and female patients show various courses of illness ranging from a complete lack of symptoms to death after the initial onset, under the strong influences of both the gene mutation (remaining enzyme activity) and treatment. 13) In general, patients with an initial blood ammonia level exceeding 1,000 g/dl have a poor prognosis. Figure 2 shows the survival rate of Japanese patients. In recent years, liver transplantation has been performed with the aim of radical treatment, achieving successful results in many cases. Although gene therapy is still in the experimental stage, AdexCAGhOTC, developed in Japan, has been demonstrated to be a considerably more efficient vector than AdexSR- hotc, developed in the US. 14) However, application to human subjects is not practical as long as basic immunological issues associated with adenovirus vectors remain unsolved. REFERENCES 1) Matsuda, I., Arashima, S., Nanbu, H. et al.: Hyperammonemia due to a mutant enzyme of ornithine transcarbamylase. Pediatrics 1971; 48: ) Hata, A., Tsuzuki, T., Shimada, K. et al.: Structure of the human ornithine transcarbamylase gene. J Biochem 1988; 103: ) Haraguchi, Y., Uchino, T., Takiguchi, M. et al.: Cloning and sequence of a cdna encoding human carbamyl phosphate synthetase I: Molecular analysis of hyperammonemia. Gene 1991: 107: ) Hoshide, R., Matsuura, T., Haraguchi, Y. et al.: Carbamyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency. One base substitution in an exon of the CPS 1 gene causes a 9-basepair deletion to aberrant splicing. J Clin Invest 1993; 91: ) Uchino, T., Snyderman, S.E., Lambert, M. et al.: Molecular basis of phenotypic variation in patients with argininemia. Hum Genet 1995: 96: ) Haraguchi, Y., Aparicio, J.M., Takiguchi, M. et al.: Molecular basis of argininemia. Identification of two discrete frame-shift deletions in the liver-type arginase gene. J Clin Invest 1990: 86: ) Matsuda, I., Nagata, N., Matsuura, T. et al.: Retrospective survey of urea cycle disorders: Part 1. Clinical and laboratory observations of thirty-two Japanese male patients with ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency. Am 164 JMAJ, April 2004 Vol. 47, No. 4
6 ORNITHINE TRANSCARBAMYLASE DEFICIENCY J Med Genet 1991; 38: ) Matsuda, I. and Tanase, S.: The ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) gene: Mutations in 50 Japanese families with OTC deficiency. Am J Med Genet 1997; 71: ) Matsuura, T., Hoshide, R., Setoyama, C. et al.: Expression of four mutant human ornithine transcarbamylase genes in cultured Cos-I cells relates to clinical phenotypes. Hum Genet 1994; 93: ) Matsuda, I., Matsuura, T., Nishiyori, A. et al.: Phenotype variability in male patients carrying the mutant ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) allele, Arg40His, ranging from a child with an unfavorable prognosis to a symptomatic older adult. J Med Genet 1996; 33: ) Tuchman, M., Matsuda, I., Munnich, A. et al.: Proportions of spontaneous mutations in males and females with ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. Am J Med Genet 1995; 55: ) Matsuda, I.: Ethical issues around prenatal diagnosis: From the standpoint of molecular biology. Shusanki Igaku 1998; 28: (in Japanese) 13) Uchino, T., Endo, F. and Matsuda, I.: Neurodevelopmental outcome of long-term therapy of urea cycle disorders in Japan. J Inherit Metab Dis 1998; 21(Suppl1): ) Kiwaki, K., Kanegae, Y., Saito, I. et al.: Correction of ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency in adult Spf ash mice and in OTC-deficient human hepatocytes with recombinant adenoviruses bearing the CAG promoter. Hum Gene Ther 1996; 7: JMAJ, April 2004 Vol. 47, No
Urea Cycle Defects. Dr Mick Henderson. Biochemical Genetics Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust. MetBioNet IEM Introductory Training
 Urea Cycle Defects Dr Mick Henderson Biochemical Genetics Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust The Urea Cycle The urea cycle enables toxic ammonia molecules to be converted to the readily excreted and non toxic
Urea Cycle Defects Dr Mick Henderson Biochemical Genetics Leeds Teaching Hospitals Trust The Urea Cycle The urea cycle enables toxic ammonia molecules to be converted to the readily excreted and non toxic
TRANSAMINATION AND UREA CYCLE
 TRANSAMINATION AND UREA CYCLE USMAN SUMO FRIEND TAMBUNAN ARLI ADITYA PARIKESIT SEPTIANA BIOINFORMATICS GROUP DEPARTEMENT OF CHEMISTRY FACULTY OF MATHEMATIC AND SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF INDONESIA What is transamination?
TRANSAMINATION AND UREA CYCLE USMAN SUMO FRIEND TAMBUNAN ARLI ADITYA PARIKESIT SEPTIANA BIOINFORMATICS GROUP DEPARTEMENT OF CHEMISTRY FACULTY OF MATHEMATIC AND SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF INDONESIA What is transamination?
Jana Novotná, Bruno Sopko. Department of the Medical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry The 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles Univ.
 Amino acid metabolism II. Urea cycle Jana Novotná, Bruno Sopko Department of the Medical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry The 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles Univ. Nitrogen balance Tissue proteins
Amino acid metabolism II. Urea cycle Jana Novotná, Bruno Sopko Department of the Medical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry The 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles Univ. Nitrogen balance Tissue proteins
UREA CYCLE DISORDERS - The What, Why, How and When
 UREA CYCLE DISORDERS - The What, Why, How and When George A. Diaz, MD, PhD Program for Inherited Metabolic Diseases Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences Department of Pediatrics Icahn School of
UREA CYCLE DISORDERS - The What, Why, How and When George A. Diaz, MD, PhD Program for Inherited Metabolic Diseases Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences Department of Pediatrics Icahn School of
Beta Thalassemia Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Spring 2015
 Bioinformatics in Medical Product Development SMPD 287 Three Beta Thalassemia Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Hemoglobin Outline Anatomy of a gene Hemoglobinopathies
Bioinformatics in Medical Product Development SMPD 287 Three Beta Thalassemia Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Hemoglobin Outline Anatomy of a gene Hemoglobinopathies
UNDERSTANDING UREA CYCLE DISORDERS
 UNDERSTANDING UREA CYCLE DISORDERS What is a urea cycle disorder? A urea cycle disorder is a genetic disease that affects how protein is broken down in the body. It is therefore classified as a metabolic
UNDERSTANDING UREA CYCLE DISORDERS What is a urea cycle disorder? A urea cycle disorder is a genetic disease that affects how protein is broken down in the body. It is therefore classified as a metabolic
Urea Cycle Disorders Prior Authorization Program Summary
 Urea Cycle Disorders Prior Authorization Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1,2 Agent(s) Indication(s) Dosing -Adjunctive therapy in the chronic management of patients with urea cycle disorders
Urea Cycle Disorders Prior Authorization Program Summary FDA APPROVED INDICATIONS DOSAGE 1,2 Agent(s) Indication(s) Dosing -Adjunctive therapy in the chronic management of patients with urea cycle disorders
Clinical Spectrum and Genetic Mechanism of GLUT1-DS. Yasushi ITO (Tokyo Women s Medical University, Japan)
 Clinical Spectrum and Genetic Mechanism of GLUT1-DS Yasushi ITO (Tokyo Women s Medical University, Japan) Glucose transporter type 1 (GLUT1) deficiency syndrome Mutation in the SLC2A1 / GLUT1 gene Deficiency
Clinical Spectrum and Genetic Mechanism of GLUT1-DS Yasushi ITO (Tokyo Women s Medical University, Japan) Glucose transporter type 1 (GLUT1) deficiency syndrome Mutation in the SLC2A1 / GLUT1 gene Deficiency
Urea is the major end product of nitrogen catabolism in humans One nitrogen free NH3 other nitrogen aspartate. carbon oxygen CO2 liver,
 Urea is the major end product of nitrogen catabolism in humans Urea is the major disposal form of amino groups derived from amino acids, and accounts about 90% percent of the nitrogencontaining components
Urea is the major end product of nitrogen catabolism in humans Urea is the major disposal form of amino groups derived from amino acids, and accounts about 90% percent of the nitrogencontaining components
Beta Thalassemia Case Study Introduction to Bioinformatics
 Beta Thalassemia Case Study Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University San José, California, USA sami.khuri@sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Outline v Hemoglobin v Alpha
Beta Thalassemia Case Study Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University San José, California, USA sami.khuri@sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Outline v Hemoglobin v Alpha
THIAMINE TRANSPORTER TYPE 2 DEFICIENCY
 THIAMINE TRANSPORTER TYPE 2 DEFICIENCY WHAT IS THE THIAMINE TRANSPORTER TYPE 2 DEFICIENCY (hthtr2)? The thiamine transporter type 2 deficiency (hthtr2) is a inborn error of thiamine metabolism caused by
THIAMINE TRANSPORTER TYPE 2 DEFICIENCY WHAT IS THE THIAMINE TRANSPORTER TYPE 2 DEFICIENCY (hthtr2)? The thiamine transporter type 2 deficiency (hthtr2) is a inborn error of thiamine metabolism caused by
LOW CITRULLINE AS A MARKER FOR THE PROXIMAL UREA CYCLE DEFECTS EXPERIENCE OF THE NEW ENGLAND NEWBORN SCREENING PROGRAM
 LOW CITRULLINE AS A MARKER FOR THE PROXIMAL UREA CYCLE DEFECTS EXPERIENCE OF THE NEW ENGLAND NEWBORN SCREENING PROGRAM Inderneel Sahai, MD, FACMG Newborn Screening and Genetic Testing Symposium Oct 2014
LOW CITRULLINE AS A MARKER FOR THE PROXIMAL UREA CYCLE DEFECTS EXPERIENCE OF THE NEW ENGLAND NEWBORN SCREENING PROGRAM Inderneel Sahai, MD, FACMG Newborn Screening and Genetic Testing Symposium Oct 2014
UPDATE ON UREA CYCLE DISORDERS TREATMENT
 UPDATE ON UREA CYCLE DISORDERS TREATMENT George A. Diaz, MD, PhD Program for Inherited Metabolic Diseases Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Disclosure
UPDATE ON UREA CYCLE DISORDERS TREATMENT George A. Diaz, MD, PhD Program for Inherited Metabolic Diseases Department of Genetics and Genomic Sciences Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai Disclosure
Supplementary Document
 Supplementary Document 1. Supplementary Table legends 2. Supplementary Figure legends 3. Supplementary Tables 4. Supplementary Figures 5. Supplementary References 1. Supplementary Table legends Suppl.
Supplementary Document 1. Supplementary Table legends 2. Supplementary Figure legends 3. Supplementary Tables 4. Supplementary Figures 5. Supplementary References 1. Supplementary Table legends Suppl.
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Urea Cycle Disorders Page 1 of 7 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Urea Cycle Disorders Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
Urea Cycle Disorders Page 1 of 7 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: Urea Cycle Disorders Prime Therapeutics will review Prior Authorization requests
Urea Cycle Disorders and Hyperammonemia: Diagnosable Treatable Screenable
 Urea Cycle Disorders and Hyperammonemia: Diagnosable Treatable Screenable Marshall L. Summar, M.D. Chief, Division of Genetics and Metabolism Children s National Medical Center Washington, DC, USA Disclosure
Urea Cycle Disorders and Hyperammonemia: Diagnosable Treatable Screenable Marshall L. Summar, M.D. Chief, Division of Genetics and Metabolism Children s National Medical Center Washington, DC, USA Disclosure
Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase (code 50470) Notice of Assessment
 Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase (code 50470) Notice of Assessment June 2013 DISCLAIMER: This document was originally drafted in French by the Institut national d'excellence en santé et en services sociaux
Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase (code 50470) Notice of Assessment June 2013 DISCLAIMER: This document was originally drafted in French by the Institut national d'excellence en santé et en services sociaux
Muscular Dystrophy. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
Muscular Dystrophy Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Duchenne muscular dystrophy Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a neuromuscular disease that occurs in ~ 1/3,500 male births. The disease causes developmental
Integration Solutions
 Integration Solutions (1) a) With no active glycosyltransferase of either type, an ii individual would not be able to add any sugars to the O form of the lipopolysaccharide. Thus, the only lipopolysaccharide
Integration Solutions (1) a) With no active glycosyltransferase of either type, an ii individual would not be able to add any sugars to the O form of the lipopolysaccharide. Thus, the only lipopolysaccharide
Phenylketonuria (PKU) the Biochemical Basis. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Phenylketonuria (PKU) the Biochemical Basis Biol 405 Molecular Medicine PKU a history In 1934 Følling identified a clinical condition - imbecillitas phenylpyruvica. Mental retardation associated with this
Phenylketonuria (PKU) the Biochemical Basis Biol 405 Molecular Medicine PKU a history In 1934 Følling identified a clinical condition - imbecillitas phenylpyruvica. Mental retardation associated with this
Pathophysiology of the Phenylketonuria
 Problem 4. Pathophysiology of the Phenylketonuria Readings for this problem are found on pages: 79-82, 84, 85-6, 945-6 and 1019 of your Pathophysiology (5 th edition) textbook. (This problem was based
Problem 4. Pathophysiology of the Phenylketonuria Readings for this problem are found on pages: 79-82, 84, 85-6, 945-6 and 1019 of your Pathophysiology (5 th edition) textbook. (This problem was based
Transgenic Mice and Genetargeting
 Transgenic Mice and Genetargeting mice In Biomedical Science Techniques of transgenic and gene-targeting mice are indispensable for analyses of in vivo functions of particular genes and roles of their
Transgenic Mice and Genetargeting mice In Biomedical Science Techniques of transgenic and gene-targeting mice are indispensable for analyses of in vivo functions of particular genes and roles of their
George R. Honig Junius G. Adams III. Human Hemoglobin. Genetics. Springer-Verlag Wien New York
 George R. Honig Junius G. Adams III Human Hemoglobin Genetics Springer-Verlag Wien New York George R. Honig, M.D., Ph.D. Professor and Head Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine University of Illinois
George R. Honig Junius G. Adams III Human Hemoglobin Genetics Springer-Verlag Wien New York George R. Honig, M.D., Ph.D. Professor and Head Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine University of Illinois
BIOLOGY 621 Identification of the Snorks
 Name: Date: Block: BIOLOGY 621 Identification of the Snorks INTRODUCTION: In this simulation activity, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism - the Snork. Snorks were discovered on
Name: Date: Block: BIOLOGY 621 Identification of the Snorks INTRODUCTION: In this simulation activity, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism - the Snork. Snorks were discovered on
Identification of a novel duplication mutation in the VHL gene in a large Chinese family with Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome
 Identification of a novel duplication mutation in the VHL gene in a large Chinese family with Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome L.H. Cao 1, B.H. Kuang 2, C. Chen 1, C. Hu 2, Z. Sun 1, H. Chen 2, S.S. Wang
Identification of a novel duplication mutation in the VHL gene in a large Chinese family with Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) syndrome L.H. Cao 1, B.H. Kuang 2, C. Chen 1, C. Hu 2, Z. Sun 1, H. Chen 2, S.S. Wang
New developments in Urea Cycle Disorders and its impact on patients
 New developments in Urea Cycle Disorders and its impact on patients Johannes Häberle University Children s Hospital Zurich, Division of Metabolism 16 June 2015 SFEIM 2015, Lille, France The urea cycle
New developments in Urea Cycle Disorders and its impact on patients Johannes Häberle University Children s Hospital Zurich, Division of Metabolism 16 June 2015 SFEIM 2015, Lille, France The urea cycle
Proceedings of a Consensus Conference for the
 Proceedings of a Consensus Conference for the Management of Patients with Urea Cycle Disorders Marshall Summar, MD, and Mendel Tuchman, MD In an effort to develop standards for the treatment of patients
Proceedings of a Consensus Conference for the Management of Patients with Urea Cycle Disorders Marshall Summar, MD, and Mendel Tuchman, MD In an effort to develop standards for the treatment of patients
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Amino Acid Metabolism
 Amino Acid Metabolism The continuous degradation and synthesis of cellular proteins occur in all forms of life. Each day humans turn over 1 2% of their total body protein, principally muscle protein. Approximately
Amino Acid Metabolism The continuous degradation and synthesis of cellular proteins occur in all forms of life. Each day humans turn over 1 2% of their total body protein, principally muscle protein. Approximately
ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018
 ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018 Inborn Errors Of Metabolism Urea Cycle Disorders Diagnosis And Care F. Feillet (FR) Urea cycle disorders, diagnosis and care F Feillet National reference centre for Inborn errors
ESPEN Congress Madrid 2018 Inborn Errors Of Metabolism Urea Cycle Disorders Diagnosis And Care F. Feillet (FR) Urea cycle disorders, diagnosis and care F Feillet National reference centre for Inborn errors
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein
 Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 333, skip the beginning of Concept 17.1 from p. 334 to the bottom of the first column on p. 336, and
Bio 111 Study Guide Chapter 17 From Gene to Protein BEFORE CLASS: Reading: Read the introduction on p. 333, skip the beginning of Concept 17.1 from p. 334 to the bottom of the first column on p. 336, and
Genotype-Phenotype in Egyptian Patients with Nephropathic Cystinosis. (December 2012 report)
 Genotype-Phenotype in Egyptian Patients with Nephropathic Cystinosis (December 2012 report) This is the first study of the genotype of Nephropathic Cystinosis (NC) patients in Egypt and the region of North
Genotype-Phenotype in Egyptian Patients with Nephropathic Cystinosis (December 2012 report) This is the first study of the genotype of Nephropathic Cystinosis (NC) patients in Egypt and the region of North
TRANSLATION: 3 Stages to translation, can you guess what they are?
 TRANSLATION: Translation: is the process by which a ribosome interprets a genetic message on mrna to place amino acids in a specific sequence in order to synthesize polypeptide. 3 Stages to translation,
TRANSLATION: Translation: is the process by which a ribosome interprets a genetic message on mrna to place amino acids in a specific sequence in order to synthesize polypeptide. 3 Stages to translation,
Computational Systems Biology: Biology X
 Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#4:(October-0-4-2010) Cancer and Signals 1 2 1 2 Evidence in Favor Somatic mutations, Aneuploidy, Copy-number changes and LOH
Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#4:(October-0-4-2010) Cancer and Signals 1 2 1 2 Evidence in Favor Somatic mutations, Aneuploidy, Copy-number changes and LOH
First report of carglumic acid in a patient with citrullinemia type 1 (argininosuccinate synthetase deficiency)
 Received: 14 June 2017 Accepted: 20 June 2017 DOI: 10.1111/jcpt.12593 CASE REPORT First report of carglumic acid in a patient with citrullinemia type 1 (argininosuccinate synthetase deficiency) E. Kose
Received: 14 June 2017 Accepted: 20 June 2017 DOI: 10.1111/jcpt.12593 CASE REPORT First report of carglumic acid in a patient with citrullinemia type 1 (argininosuccinate synthetase deficiency) E. Kose
Disorder name: Argininemia / Arginase deficiency Acronym: ARG 1 deficiency
 Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Amino Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
Genetic Fact Sheets for Parents Amino Acid Disorders Screening, Technology, and Research in Genetics is a multi-state project to improve information about the financial, ethical, legal, and social issues
MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS. (Start your clickers)
 MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS (Start your clickers) How do mutations arise? And how do they affect a cell and its organism? Mutations: heritable changes in genes Mutations occur in DNA But
MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS (Start your clickers) How do mutations arise? And how do they affect a cell and its organism? Mutations: heritable changes in genes Mutations occur in DNA But
DMD Genetics: complicated, complex and critical to understand
 DMD Genetics: complicated, complex and critical to understand Stanley Nelson, MD Professor of Human Genetics, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, and Psychiatry Co Director, Center for Duchenne Muscular
DMD Genetics: complicated, complex and critical to understand Stanley Nelson, MD Professor of Human Genetics, Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, and Psychiatry Co Director, Center for Duchenne Muscular
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions
 Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
Mutation Screening and Association Studies of the Human UCP 3 Gene in Normoglycemic and NIDDM Morbidly Obese Patients
 Mutation Screening and Association Studies of the Human UCP 3 Gene in Normoglycemic and NIDDM Morbidly Obese Patients Shuichi OTABE, Karine CLEMENT, Séverine DUBOIS, Frederic LEPRETRE, Veronique PELLOUX,
Mutation Screening and Association Studies of the Human UCP 3 Gene in Normoglycemic and NIDDM Morbidly Obese Patients Shuichi OTABE, Karine CLEMENT, Séverine DUBOIS, Frederic LEPRETRE, Veronique PELLOUX,
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis-Inheritance Connection. Chapter 13
 Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis-Inheritance Connection Chapter 13 Chromosome Theory Chromosomal theory of inheritance - developed in 1902 by Walter Sutton - proposed that genes are present on chromosomes
Chromosomes, Mapping, and the Meiosis-Inheritance Connection Chapter 13 Chromosome Theory Chromosomal theory of inheritance - developed in 1902 by Walter Sutton - proposed that genes are present on chromosomes
CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE. Dr. Bahar Naghavi
 2 CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE Dr. Bahar Naghavi Assistant professor of Basic Science Department, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran,Iran 3 Introduction Over 4000
2 CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE Dr. Bahar Naghavi Assistant professor of Basic Science Department, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran,Iran 3 Introduction Over 4000
Insulin Resistance. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Insulin Resistance Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Insulin resistance: a subnormal biological response to insulin. Defects of either insulin secretion or insulin action can cause diabetes mellitus. Insulin-dependent
Insulin Resistance Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Insulin resistance: a subnormal biological response to insulin. Defects of either insulin secretion or insulin action can cause diabetes mellitus. Insulin-dependent
c Tuj1(-) apoptotic live 1 DIV 2 DIV 1 DIV 2 DIV Tuj1(+) Tuj1/GFP/DAPI Tuj1 DAPI GFP
 Supplementary Figure 1 Establishment of the gain- and loss-of-function experiments and cell survival assays. a Relative expression of mature mir-484 30 20 10 0 **** **** NCP mir- 484P NCP mir- 484P b Relative
Supplementary Figure 1 Establishment of the gain- and loss-of-function experiments and cell survival assays. a Relative expression of mature mir-484 30 20 10 0 **** **** NCP mir- 484P NCP mir- 484P b Relative
Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over Why? Double crossovers
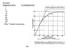 Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over 1 5 10 15 50 80 100 107 Why? Double crossovers 232 .. A B. a b. 1. A fully heterozygous gray-bodied (b+), normal winged (vg+) female F 1 fruit fly crossed with
Example: Distance in M.U. % Crossing Over 1 5 10 15 50 80 100 107 Why? Double crossovers 232 .. A B. a b. 1. A fully heterozygous gray-bodied (b+), normal winged (vg+) female F 1 fruit fly crossed with
Bacterial Gene Finding CMSC 423
 Bacterial Gene Finding CMSC 423 Finding Signals in DNA We just have a long string of A, C, G, Ts. How can we find the signals encoded in it? Suppose you encountered a language you didn t know. How would
Bacterial Gene Finding CMSC 423 Finding Signals in DNA We just have a long string of A, C, G, Ts. How can we find the signals encoded in it? Suppose you encountered a language you didn t know. How would
CYP21A2 Mutations Found in Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Patients in the California Population
 CYP21A2 Mutations Found in Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Patients in the California Population Christopher N. Greene, Ph.D. Newborn Screening and Molecular Biology Branch National Center for Environmental
CYP21A2 Mutations Found in Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Patients in the California Population Christopher N. Greene, Ph.D. Newborn Screening and Molecular Biology Branch National Center for Environmental
Psych 3102 Lecture 3. Mendelian Genetics
 Psych 3102 Lecture 3 Mendelian Genetics Gregor Mendel 1822 1884, paper read 1865-66 Augustinian monk genotype alleles present at a locus can we identify this? phenotype expressed trait/characteristic can
Psych 3102 Lecture 3 Mendelian Genetics Gregor Mendel 1822 1884, paper read 1865-66 Augustinian monk genotype alleles present at a locus can we identify this? phenotype expressed trait/characteristic can
What we know about Li-Fraumeni syndrome
 What we know about Li-Fraumeni syndrome Dr Helen Hanson Consultant in Cancer Genetics St Georges Hospital, South-West Thames Regional Genetics Service History of LFS 1969 Li and Fraumeni describe four
What we know about Li-Fraumeni syndrome Dr Helen Hanson Consultant in Cancer Genetics St Georges Hospital, South-West Thames Regional Genetics Service History of LFS 1969 Li and Fraumeni describe four
Basic Definitions. Dr. Mohammed Hussein Assi MBChB MSc DCH (UK) MRCPCH
 Basic Definitions Chromosomes There are two types of chromosomes: autosomes (1-22) and sex chromosomes (X & Y). Humans are composed of two groups of cells: Gametes. Ova and sperm cells, which are haploid,
Basic Definitions Chromosomes There are two types of chromosomes: autosomes (1-22) and sex chromosomes (X & Y). Humans are composed of two groups of cells: Gametes. Ova and sperm cells, which are haploid,
Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency (OTCD) Recommendations on Emergency Management of Metabolic Disease
 Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency (OTCD) Recommendations on Emergency Management of Metabolic Disease Patient s Name: Date of Birth: MRN in KFSH&RC: Please read carefully. Meticulous and prompt treatment
Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency (OTCD) Recommendations on Emergency Management of Metabolic Disease Patient s Name: Date of Birth: MRN in KFSH&RC: Please read carefully. Meticulous and prompt treatment
Metabolic Disorders. Chapter Thomson - Wadsworth
 Metabolic Disorders Chapter 28 1 Metabolic Disorders Inborn errors of metabolism group of diseases that affect a wide variety of metabolic processes; defective processing or transport of amino acids, fatty
Metabolic Disorders Chapter 28 1 Metabolic Disorders Inborn errors of metabolism group of diseases that affect a wide variety of metabolic processes; defective processing or transport of amino acids, fatty
Genetic information flows from mrna to protein through the process of translation
 Genetic information flows from mrn to protein through the process of translation TYPES OF RN (RIBONUCLEIC CID) RN s job - protein synthesis (assembly of amino acids into proteins) Three main types: 1.
Genetic information flows from mrn to protein through the process of translation TYPES OF RN (RIBONUCLEIC CID) RN s job - protein synthesis (assembly of amino acids into proteins) Three main types: 1.
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names you wish listed) (A)-Testing
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names you wish listed) (A)-Testing
JULY 21, Genetics 101: SCN1A. Katie Angione, MS CGC Certified Genetic Counselor CHCO Neurology
 JULY 21, 2018 Genetics 101: SCN1A Katie Angione, MS CGC Certified Genetic Counselor CHCO Neurology Disclosures: I have no financial interests or relationships to disclose. Objectives 1. Review genetic
JULY 21, 2018 Genetics 101: SCN1A Katie Angione, MS CGC Certified Genetic Counselor CHCO Neurology Disclosures: I have no financial interests or relationships to disclose. Objectives 1. Review genetic
Abstract. Introduction. RBMOnline - Vol 8. No Reproductive BioMedicine Online; on web 10 December 2003
 RBMOnline - Vol 8. No 2. 224-228 Reproductive BioMedicine Online; www.rbmonline.com/article/1133 on web 10 December 2003 Article Preimplantation genetic diagnosis for early-onset torsion dystonia Dr Svetlana
RBMOnline - Vol 8. No 2. 224-228 Reproductive BioMedicine Online; www.rbmonline.com/article/1133 on web 10 December 2003 Article Preimplantation genetic diagnosis for early-onset torsion dystonia Dr Svetlana
Volume 3 (2017) Issue 10 ISSN Keywords. Introduction. Case Report. Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports
 Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 3 (2017) Issue 10 ISSN 2379-1039 Recurrent hyperammonemia in an 80-year-old woman with congenital urea cycle abnormality Junji Yamaguchi, MD*; Koichi
Open Journal of Clinical & Medical Case Reports Volume 3 (2017) Issue 10 ISSN 2379-1039 Recurrent hyperammonemia in an 80-year-old woman with congenital urea cycle abnormality Junji Yamaguchi, MD*; Koichi
Col Rama Krishna Sanjeev Military Hospital Chennai Prof Shanmughasundaram Mehta Hospital, Chennai
 Col Rama Krishna Sanjeev Military Hospital Chennai Prof Shanmughasundaram Mehta Hospital, Chennai 11 day old male neonate admitted on 26/6 to our Hospital with c/olethargy -since day1 abnormal movements
Col Rama Krishna Sanjeev Military Hospital Chennai Prof Shanmughasundaram Mehta Hospital, Chennai 11 day old male neonate admitted on 26/6 to our Hospital with c/olethargy -since day1 abnormal movements
Tay Sachs, Cystic Fibrosis, Sickle Cell Anemia and PKU. Tay Sachs Disease (also called Hexosaminidase deficiency)
 Tay Sachs, Cystic Fibrosis, Sickle Cell Anemia and PKU Tay Sachs Disease (also called Hexosaminidase deficiency) Introduction 1. Tay Sachs is a rare condition named after 2 physicians, Tay and Sachs, who
Tay Sachs, Cystic Fibrosis, Sickle Cell Anemia and PKU Tay Sachs Disease (also called Hexosaminidase deficiency) Introduction 1. Tay Sachs is a rare condition named after 2 physicians, Tay and Sachs, who
Educational Items Section
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL AT INIST-CNRS Educational Items Section Hemoglobin genes; Sickle-cell anemia - Thalassemias Jean-Loup Huret, Xavier Troussard
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL AT INIST-CNRS Educational Items Section Hemoglobin genes; Sickle-cell anemia - Thalassemias Jean-Loup Huret, Xavier Troussard
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Choroideremia OMIM number for disease 303100 Disease alternative names please
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name Choroideremia OMIM number for disease 303100 Disease alternative names please
Laboratory Testing for Chronic Granulomatous Disease: Challenges and Recommendations 3/20/2017
 1 2 I have no disclosures. 3 As you view this presentation, consider the following important points regarding testing: How is the testing going to be used in your practice? When should the test be used?
1 2 I have no disclosures. 3 As you view this presentation, consider the following important points regarding testing: How is the testing going to be used in your practice? When should the test be used?
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008
 BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
The breakdown of fats to provide energy occurs in segregated membrane-bound compartments
 CPT1a deficiency The breakdown of fats to provide energy occurs in segregated membrane-bound compartments of the cell known as mitochondria. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase Ia (CPT1a) is a protein that
CPT1a deficiency The breakdown of fats to provide energy occurs in segregated membrane-bound compartments of the cell known as mitochondria. Carnitine palmitoyltransferase Ia (CPT1a) is a protein that
Variant Classification. Author: Mike Thiesen, Golden Helix, Inc.
 Variant Classification Author: Mike Thiesen, Golden Helix, Inc. Overview Sequencing pipelines are able to identify rare variants not found in catalogs such as dbsnp. As a result, variants in these datasets
Variant Classification Author: Mike Thiesen, Golden Helix, Inc. Overview Sequencing pipelines are able to identify rare variants not found in catalogs such as dbsnp. As a result, variants in these datasets
MMB (MGPG) Non traditional Inheritance Epigenetics. A.Turco
 MMB (MGPG) 2017 Non traditional Inheritance Epigenetics A.Turco NON TRADITIONAL INHERITANCE EXCEPTIONS TO MENDELISM - Genetic linkage (2 loci close to each other) - Complex or Multifactorial Disease (MFD)
MMB (MGPG) 2017 Non traditional Inheritance Epigenetics A.Turco NON TRADITIONAL INHERITANCE EXCEPTIONS TO MENDELISM - Genetic linkage (2 loci close to each other) - Complex or Multifactorial Disease (MFD)
Proteins. Length of protein varies from thousands of amino acids to only a few insulin only 51 amino acids
 Proteins Protein carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and often sulphur Length of protein varies from thousands of amino acids to only a few insulin only 51 amino acids During protein synthesis, amino acids
Proteins Protein carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and often sulphur Length of protein varies from thousands of amino acids to only a few insulin only 51 amino acids During protein synthesis, amino acids
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 deficiency: First report of this rare metabolic disorder in Kingdom of Bahrain with novel mutation
 Alsahlawi et al. 1 CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 deficiency: First report of this rare metabolic disorder in Kingdom of Bahrain with novel mutation Z. Alsahlawi,
Alsahlawi et al. 1 CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 deficiency: First report of this rare metabolic disorder in Kingdom of Bahrain with novel mutation Z. Alsahlawi,
Mutants and HBV vaccination. Dr. Ulus Salih Akarca Ege University, Izmir, Turkey
 Mutants and HBV vaccination Dr. Ulus Salih Akarca Ege University, Izmir, Turkey Geographic Distribution of Chronic HBV Infection 400 million people are carrier of HBV Leading cause of cirrhosis and HCC
Mutants and HBV vaccination Dr. Ulus Salih Akarca Ege University, Izmir, Turkey Geographic Distribution of Chronic HBV Infection 400 million people are carrier of HBV Leading cause of cirrhosis and HCC
Truncation and microdeletion of EVC accompanied by novel EFCAB7 missense mutation in Ellis-van Creveld syndrome with atypical congenital heart defect
 Truncation and microdeletion of EVC accompanied by novel EFCAB7 missense mutation in Ellis-van Creveld syndrome with atypical congenital heart defect NGUYEN Tran Quynh Nhu, MD. Department of Developmental
Truncation and microdeletion of EVC accompanied by novel EFCAB7 missense mutation in Ellis-van Creveld syndrome with atypical congenital heart defect NGUYEN Tran Quynh Nhu, MD. Department of Developmental
Diagnostic difficulties in prevention and control program for thalassemia in Thailand: atypical thalassemia carriers
 Diagnostic difficulties in prevention and control program for thalassemia in Thailand: atypical thalassemia carriers Pranee Winichagoon Fucharoen Thalassemia Research Center Institute of Molecular Biosciences
Diagnostic difficulties in prevention and control program for thalassemia in Thailand: atypical thalassemia carriers Pranee Winichagoon Fucharoen Thalassemia Research Center Institute of Molecular Biosciences
BIOCHEMICAL AND MOLECULAR HETEROGENEITY IN CARNITINE PALMITOYLTRANSFERASE II DEFICIENCY
 BIOCHEMICAL AND MOLECULAR HETEROGENEITY IN CARNITINE PALMITOYLTRANSFERASE II DEFICIENCY Carmen Sousa, Helena Fonseca, Hugo Rocha, Ana Marcão, Laura Vilarinho, Luísa Diogo, Sílvia Sequeira, Cristina Costa,
BIOCHEMICAL AND MOLECULAR HETEROGENEITY IN CARNITINE PALMITOYLTRANSFERASE II DEFICIENCY Carmen Sousa, Helena Fonseca, Hugo Rocha, Ana Marcão, Laura Vilarinho, Luísa Diogo, Sílvia Sequeira, Cristina Costa,
The spectrum and outcome of the. neonates with inborn errors of. metabolism at a tertiary care hospital
 The spectrum and outcome of the neonates with inborn errors of metabolism at a tertiary care hospital Dr. Sevim Ünal Neonatology Division, Ankara Children s Hematology Oncology Research Hospital, Ankara,
The spectrum and outcome of the neonates with inborn errors of metabolism at a tertiary care hospital Dr. Sevim Ünal Neonatology Division, Ankara Children s Hematology Oncology Research Hospital, Ankara,
Altered mental status: a common complaint that led to a rare diagnosis - Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency
 Altered mental status: a common complaint that led to a rare diagnosis - Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency Joshua J. White, OMS3 Charles C. Finch, D.O., FACOEP Arizona College Of Osteopathic Medicine
Altered mental status: a common complaint that led to a rare diagnosis - Ornithine Transcarbamylase Deficiency Joshua J. White, OMS3 Charles C. Finch, D.O., FACOEP Arizona College Of Osteopathic Medicine
Human inherited diseases
 Human inherited diseases A genetic disorder that is caused by abnormality in an individual's DNA. Abnormalities can range from small mutation in a single gene to the addition or subtraction of a whole
Human inherited diseases A genetic disorder that is caused by abnormality in an individual's DNA. Abnormalities can range from small mutation in a single gene to the addition or subtraction of a whole
Understanding genetics, mutation and other details. Stanley F. Nelson, MD 6/29/18
 Understanding genetics, mutation and other details Stanley F. Nelson, MD 6/29/18 1 6 11 16 21 Duchenne muscular dystrophy 26 31 36 41 46 51 56 61 66 71 76 81 86 91 96 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 Duchenne/Becker
Understanding genetics, mutation and other details Stanley F. Nelson, MD 6/29/18 1 6 11 16 21 Duchenne muscular dystrophy 26 31 36 41 46 51 56 61 66 71 76 81 86 91 96 600 500 400 300 200 100 0 Duchenne/Becker
AMINO ACID METABOLISM
 AMINO ACID METABOLISM Synthesis of Urea in Liver The series of reactions that form urea is known as the Urea Cycle or the Krebs-Henseleit Cycle. The urea cycle operates only to eliminate excess nitrogen.
AMINO ACID METABOLISM Synthesis of Urea in Liver The series of reactions that form urea is known as the Urea Cycle or the Krebs-Henseleit Cycle. The urea cycle operates only to eliminate excess nitrogen.
Section Chapter 14. Go to Section:
 Section 12-3 Chapter 14 Go to Section: Content Objectives Write these Down! I will be able to identify: The origin of genetic differences among organisms. The possible kinds of different mutations. The
Section 12-3 Chapter 14 Go to Section: Content Objectives Write these Down! I will be able to identify: The origin of genetic differences among organisms. The possible kinds of different mutations. The
Wilson Disease Robert Baumgartner, Kira Melamud and Amelia Wnorowski
 Wilson Disease Robert Baumgartner, Kira Melamud and Amelia Wnorowski Basic Genetics Wilson Disease is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder of impaired copper metabolism. The Wilson Disease gene is composed
Wilson Disease Robert Baumgartner, Kira Melamud and Amelia Wnorowski Basic Genetics Wilson Disease is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder of impaired copper metabolism. The Wilson Disease gene is composed
Arginine as an Example of a Conditionally Essential Nutrient: Sickle Cell Disease & Trauma Claudia R. Morris MD, FAAP
 Arginine as an Example of a Conditionally Essential Nutrient: Sickle Cell Disease & Trauma Claudia R. Morris MD, FAAP Examining Special Nutritional Requirements in Disease States, A Workshop April 1, 2018
Arginine as an Example of a Conditionally Essential Nutrient: Sickle Cell Disease & Trauma Claudia R. Morris MD, FAAP Examining Special Nutritional Requirements in Disease States, A Workshop April 1, 2018
MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS
 MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS How do different alleles arise? ( allele : form of a gene; specific base sequence at a site on DNA) Mutations: heritable changes in genes Mutations occur in DNA
MUTATIONS, MUTAGENESIS, AND CARCINOGENESIS How do different alleles arise? ( allele : form of a gene; specific base sequence at a site on DNA) Mutations: heritable changes in genes Mutations occur in DNA
Agro/Ansc/Bio/Gene/Hort 305 Fall, 2017 MEDICAL GENETICS AND CANCER Chpt 24, Genetics by Brooker (lecture outline) #17
 Agro/Ansc/Bio/Gene/Hort 305 Fall, 2017 MEDICAL GENETICS AND CANCER Chpt 24, Genetics by Brooker (lecture outline) #17 INTRODUCTION - Our genes underlie every aspect of human health, both in function and
Agro/Ansc/Bio/Gene/Hort 305 Fall, 2017 MEDICAL GENETICS AND CANCER Chpt 24, Genetics by Brooker (lecture outline) #17 INTRODUCTION - Our genes underlie every aspect of human health, both in function and
Genetic Assessment and Counseling
 Genetic Assessment and Counseling Genetic counseling is the communication of information and advice about inherited conditions and a person seeking such advice is called a consultand. This process includes
Genetic Assessment and Counseling Genetic counseling is the communication of information and advice about inherited conditions and a person seeking such advice is called a consultand. This process includes
Chapter 11 Gene Expression
 Chapter 11 Gene Expression 11-1 Control of Gene Expression Gene Expression- the activation of a gene to form a protein -a gene is on or expressed when it is transcribed. -cells do not always need to produce
Chapter 11 Gene Expression 11-1 Control of Gene Expression Gene Expression- the activation of a gene to form a protein -a gene is on or expressed when it is transcribed. -cells do not always need to produce
What do you think of when you here the word genome?
 What do you think of when you here the word genome? What do you think of when you here the word genome? Personal Genomics Outline Review of pre-lab work Genomics and Medicine Case Overview & Assignment
What do you think of when you here the word genome? What do you think of when you here the word genome? Personal Genomics Outline Review of pre-lab work Genomics and Medicine Case Overview & Assignment
Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Oxidation Deficiencies Prof. Niels Gregersen
 Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Oxidation Deficiencies Research Unit for Molecular Medicine Clinical Institute Aarhus University Hospital and Faculty of Health Sciences Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark 1 Menu
Mitochondrial Fatty Acid Oxidation Deficiencies Research Unit for Molecular Medicine Clinical Institute Aarhus University Hospital and Faculty of Health Sciences Aarhus University, Aarhus, Denmark 1 Menu
SEX-LINKED INHERITANCE. Dr Rasime Kalkan
 SEX-LINKED INHERITANCE Dr Rasime Kalkan Human Karyotype Picture of Human Chromosomes 22 Autosomes and 2 Sex Chromosomes Autosomal vs. Sex-Linked Traits can be either: Autosomal: traits (genes) are located
SEX-LINKED INHERITANCE Dr Rasime Kalkan Human Karyotype Picture of Human Chromosomes 22 Autosomes and 2 Sex Chromosomes Autosomal vs. Sex-Linked Traits can be either: Autosomal: traits (genes) are located
Objectives. Genetics and Rett syndrome: As easy as apple pie! Chromosome to gene to protein
 Genetics and Rett syndrome: As easy as apple pie! Victoria Mok Siu M.D., FRCPC, FCCMG ORSA conference Ottawa April 24, 2016 Objectives Review chromosomes and genes Understand s Explore the reasons behind
Genetics and Rett syndrome: As easy as apple pie! Victoria Mok Siu M.D., FRCPC, FCCMG ORSA conference Ottawa April 24, 2016 Objectives Review chromosomes and genes Understand s Explore the reasons behind
Asingle inherited mutant gene may be enough to
 396 Cancer Inheritance STEVEN A. FRANK Asingle inherited mutant gene may be enough to cause a very high cancer risk. Single-mutation cases have provided much insight into the genetic basis of carcinogenesis,
396 Cancer Inheritance STEVEN A. FRANK Asingle inherited mutant gene may be enough to cause a very high cancer risk. Single-mutation cases have provided much insight into the genetic basis of carcinogenesis,
Advances in genetic diagnosis of neurological disorders
 Acta Neurol Scand 2014: 129 (Suppl. 198): 20 25 DOI: 10.1111/ane.12232 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd ACTA NEUROLOGICA SCANDINAVICA Review Article Advances in genetic diagnosis
Acta Neurol Scand 2014: 129 (Suppl. 198): 20 25 DOI: 10.1111/ane.12232 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd ACTA NEUROLOGICA SCANDINAVICA Review Article Advances in genetic diagnosis
BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease. Metabolic Disorders - Obesity
 BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders - Obesity Obesity Approx. 23% of adults are obese in the U.K. The number of obese children has tripled in 20 years. 10% of six year olds are obese, rising
BIOL212 Biochemistry of Disease Metabolic Disorders - Obesity Obesity Approx. 23% of adults are obese in the U.K. The number of obese children has tripled in 20 years. 10% of six year olds are obese, rising
Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 deficiency (CPT2) is a rare inherited disorder that occurs when
 CPT2 Deficiency Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 deficiency (CPT2) is a rare inherited disorder that occurs when the last step in the entry of fats into sac-like bodies called mitochondria is blocked.
CPT2 Deficiency Carnitine palmitoyl transferase 2 deficiency (CPT2) is a rare inherited disorder that occurs when the last step in the entry of fats into sac-like bodies called mitochondria is blocked.
A Comprehensive Study of TP53 Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Analysis of 1,287 Diagnostic CLL Samples
 A Comprehensive Study of TP53 Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Analysis of 1,287 Diagnostic CLL Samples Sona Pekova, MD., PhD. Chambon Ltd., Laboratory for molecular diagnostics, Prague, Czech
A Comprehensive Study of TP53 Mutations in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Analysis of 1,287 Diagnostic CLL Samples Sona Pekova, MD., PhD. Chambon Ltd., Laboratory for molecular diagnostics, Prague, Czech
Hyperammonemia: Diagnostic Experience At The Metabolism Laboratory
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Laboratory Medicine Volume 1 Number 2 Hyperammonemia: Diagnostic Experience At The Metabolism Laboratory A Rao, P Varma, Sumitra, S Dhanya Citation A Rao, P Varma, Sumitra,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Laboratory Medicine Volume 1 Number 2 Hyperammonemia: Diagnostic Experience At The Metabolism Laboratory A Rao, P Varma, Sumitra, S Dhanya Citation A Rao, P Varma, Sumitra,
Chapter 12-4 DNA Mutations Notes
 Chapter 12-4 DNA Mutations Notes I. Mutations Introduction A. Definition: Changes in the DNA sequence that affect genetic information B. Mutagen= physical or chemical agent that interacts with DNA to cause
Chapter 12-4 DNA Mutations Notes I. Mutations Introduction A. Definition: Changes in the DNA sequence that affect genetic information B. Mutagen= physical or chemical agent that interacts with DNA to cause
Dr Rosline Hassan Haematology Department, School of Medical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Kelantan
 Dr Rosline Hassan Haematology Department, School of Medical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Kelantan THE FIRST ASEAN FEDERATION OF HAEMATOLOGY AND THE VIIITH MALAYSIAN NATIONAL HAEMATOLOGY SCIENTIFIC
Dr Rosline Hassan Haematology Department, School of Medical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Kelantan THE FIRST ASEAN FEDERATION OF HAEMATOLOGY AND THE VIIITH MALAYSIAN NATIONAL HAEMATOLOGY SCIENTIFIC
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
AMINOACID METABOLISM FATE OF AMINOACIDS & UREA CYCLE
 AMINOACID METABOLISM FATE OF AMINOACIDS & UREA CYCLE SOURCE & FATE OF AA The aminoacids obtained from DIETARY SOURCE or BODY PROTEIN TURNOVER are utilized for protein biosynthesis and the production of
AMINOACID METABOLISM FATE OF AMINOACIDS & UREA CYCLE SOURCE & FATE OF AA The aminoacids obtained from DIETARY SOURCE or BODY PROTEIN TURNOVER are utilized for protein biosynthesis and the production of
In adults, the predominant Hb (HbA) molecule has four chains: two α and two β chains. In thalassemias, the synthesis of either the α or the β chains
 Thalassaemias Thalassemia Thalassemia is an inherited autosomal recessive blood disease. Associated with absence or reduction in a or b globin chains. Reduced synthesis of one of the globin chains can
Thalassaemias Thalassemia Thalassemia is an inherited autosomal recessive blood disease. Associated with absence or reduction in a or b globin chains. Reduced synthesis of one of the globin chains can
Lecture 17: Human Genetics. I. Types of Genetic Disorders. A. Single gene disorders
 Lecture 17: Human Genetics I. Types of Genetic Disorders A. Single gene disorders B. Multifactorial traits 1. Mutant alleles at several loci acting in concert C. Chromosomal abnormalities 1. Physical changes
Lecture 17: Human Genetics I. Types of Genetic Disorders A. Single gene disorders B. Multifactorial traits 1. Mutant alleles at several loci acting in concert C. Chromosomal abnormalities 1. Physical changes
