Dr Rick Cutfield Physician, Diabetologist and Endocrinologist Mercy Specialist Centre
|
|
|
- Erick Holland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dr Rick Cutfield Physician, Diabetologist and Endocrinologist Mercy Specialist Centre
2 Diabetes Case Studies from the clinic Dr Rick Cutfield Physician and Endocrinologist Waitemata District Health Board Mercy Specialist Centre
3
4 Case 1: 48 year old Mrs DM: BMI = 35 HbA1c = 64 mmol/mol Type 2 diabetes 5 years On Metformin 500mg t.d.s. N.B.: HbA1c 64 = 8% Remember: 9% = 75 mmol/mol 8% = 64 mmol/mol 7% = 53 mmol/mol
5 Metformin Points a) How do you prescribe Metformin? How often and maximum dose? b) What if egfr is down to 36/ml/min? Do you stop Metformin? c) Metformin causes hypoglycaemia. T / F d) Metformin affects B12 levels? T / F e) Metformin may reduce cancer risk in Mrs DM f) Metformin will reduce C/V risk in a patient like Mrs DM T / F T / F
6 What is next drug of choice to reach glycaemic target of 53 (7%) a) Sulphonylureas (NOT GLIBENCLAMIDE) Pro Known for years Can glucose levels effectively in most people Cheap Given twice daily Con Slight weight Hypoglycaemia May only work for 2-5 years
7 What is next drug of choice to reach glycaemic target of 53 (7%) b) TZDs (Thiazolidinedione) Pioglitazone Pro glucose in insulin resistant patients Once daily fat in liver T.G. levels No hypoglycaemia given alone or with Metformin Con risk of Fracture (2x) Weight gain ++ Fluid retention in some Rarely heart failure Takes 4-6 weeks to work
8 What is next drug of choice to reach glycaemic target of 53 (7%) c) Incretins 1. DPP 4 inhibitors, GLP Levels e.g. Sitagliptin Pro Insulin release after meals. Glucagon 100mg once daily Weight neutral NO hypoglycaemia Ideal for elderly Type 2, or those at risk of hypos Con These are new oral agents not funded currently ($100 / month) Not a powerful agent
9 What is next drug of choice to reach glycaemic target of 53 (7%) c) Incretins 2. GLP Analogues, e.g. Exanatide Pro S.C. injection B.D. Weight loss an advantage An option for those overweight wealthier Type 2 patients instead of insulin May decrease BP slightly Con Expensive (over $200 / month) Nausea (often temporary) N.B.: New once/week analogue soon to be released in U.S.
10 What is next treatment of choice to reach glycaemic target of 53 (7%) d) Bariatric Surgery A real option Which operation best? What ages? What B.M.I. to include? Public vs Private Long Term Benefits vs Long Term side effects
11 If your patient is not at TARGET after maximising oral agents HOW DO YOU START INSULIN
12 Insulin in Type 2 Diabetes Keep it safe Keep it simple Introduce concept early Explain concept of B cell failure Discuss barriers BUT DO NOT DELAY if patient adhering to programme but not reaching TARGET.
13 If fasting glucose elevated start NPH at bedtime,.e.g. Protophane or Humulin N. N.B: We are currently not funded to use insulin Glargine in this setting in Type 2 Diabetes (unlike US/Europe)
14 DOSE Try 8-12u and titrate dose by 1-2 units every 4 days to reach fasting glucose target of 6 mmol/l Teach patient to do this but arrange f/up after 1 week May use B.D. NPH Insulin or pre-mixed insulin depending on results of capillary glucose
15 Case 2: 65 year old with tiredness and diabetes for 3 years on Gliclazide 120 mg b.d. BMI 33 HbA1c 8.1% Cholesterol LDL TG HDL 1.0 Bili 14 - GGT 78 - AST 89 - ALT AlkPO4 110 Testosterone 10.2 Ferritin 420 (iron saturation normal) egfr 42. S.Creatinine 140 These findings are most consistent with: Chronic Hep C Haemachromatosis Alcohol abuse Hepatic steatosis Sulphonylurea sensitivity.
16 Next step would include: a) Lifestyle change for 6-12 months. b) Add Metformin. c) Add Pioglitazone. d) Increase Gliclazide. e) Check Haemachromatosis gene. f) Liver ultrasound.
17 Teaching Points: Hepatic steatohepatitis is very common in insulin resistant states. ALT & GGT reflect liver fat and insulin resistance, and predict diabetes. Hepatic steatohepatitis can occasionally lead to fibrosis/cirrhosis. Haemachromatosis is associated with diabetes and testosterone deficiency, and while not rare is a much less common cause of abnormal LFT in diabetes. Glitazones not contraindicated unless significant fibrosis/cirrhosis and may be helpful in reducing liver fat. Hep C is associated with incidence of diabetes. Metformin is safe with mild-moderate liver function abnormalities. Lactic acidosis is very rare and safe to use if egfr is over 30.
18 Case 3: A woman aged 42 with Type 1 Diabetes for 8 years has a history of recent severe daytime and nocturnal hypoglycaemia and mild weight loss. Which is least likely?: a) She should have diet / exercise reviewed. b) She should have a screen for celiac disease. c) She should have Addison s disease ruled out. d) She likely has renal impairment reducing insulin clearance. e) Insulin Glargine and Determir have been demonstrated to reduce nocturnal hypoglycaemia and would be useful here.
19 Treatment Issues with Hypoglycaemia: Types of insulin: Rapid acting analogues - most should benefit Long acting analogues - most should benefit espec noct. hypos. [Lantus, Determir] Timing of insulin. NPH at bed not dinner; Glargine AM or PM or B.D.
20 Treatment Issues with Hypoglycaemia: Severe hypoglycaemia with Sulphonylureas may be prolonged especially with glibenclamide. Consider admission for 24 hours for IV glucose ± somatostatin. Meals, exercise, alcohol, age. If SMBG doesn t reveal answer; search for nocturnal hypos. Sometimes use continuous glucose monitoring. Consider Addison s, celiac disease in T1DM. Consider renal failure. Reduce medication. Prevention of hypoglycaemia for 2-3 weeks can improve hypoglycaemic awareness.
21 Case 4: Mr L.G.: Aged 75 with PHX of I.H.D. Diabetes 15 years On: Novorapid 8u Protophane 18u Novorapid 10u Protophane 14u Pre-breakfast Pre-dinner C/O Nocturnal hypos What to do next?
22 Are nocturnal hypos of concern in patients with I.H.D.?
23 Reduce Nocturnal Hypos by: Adding supper? Move Protophane to bed ± reduce dose Consider Insulin Glargine replace NPH using 20% lower dose i.e.: Glargine 24u breakfast Novorapid 6u-8u breakfast Novorapid 8u-10u dinner
24 Case 5: 48 year old man with type 2 diabetes. HbA1c 8.8% - BP 130/84 Urine microalbumin 48mg/l ACR 3.2 S. Creatinine 112
25 Case 5: continued Which would you do? a) Add ACE inhibitor. b) Add Angiotensin 2 antagonist. c) Repeat microalbumin after attempt at improved glycaemic control. d) Do nothing as ACR is normal. e) Check MSU.
26 Case 5: continued If microalbuminuria persists, but BP settles to 130/80 should he be on: Ace inhibitor? Statin? Aspirin? All of above?
27 Microalbuminuria: Persistent albumin excretion mg/day. If > 300mg/d overt proteinuria. ACR 2.5(m) 3.5(f). Marker of diabetic nephropathy. Marker of endothelial dysfunction. Associated with C/V mortality. May be present at diagnosis and reflect underlying C/V disease. Transient microalbuminuria. Fever; exercise; heart failure. Poor glycaemic control.
28 Microalbuminuria in Type I Diabetes: Strict glycaemic, lipid control, aspirin. If BP > 130/80 ACE. If BP < 130/80 treat with ACE If in albumin excretion. Use ARB if intol of ACE, but not both. Do not treat normotensive patients with normal microalbumin with ACE-I.
29 Microalbuminuria in Type 2 Diabetes: ACE or ARB if: Microalbuminuria. BP > 130/80. Aggressive combined approach with statin, aspirin, tight glycaemic control and BP control (Steno 2) reduces mortality by ½.
30 Case 6: Mrs D.G.: T2 diabetes HbA1c 7.2% microalbumin level of 68 ACR of 8.4. She is on maximum ACE inhibitor plus Metformin. BP is 140/90 NEXT?
31 Would you add? A 2 antagonist, e.g. Cozaar Thiazide Calcium antagonist β Blocker α Blocker Frusemide
32 Would you add STATIN? If LDL cholesterol 2.5 Y / N Would you add Aspirin? Y / N
33 If C/O muscle pains on Simvastatin 40mg/d. What do you do?
34 Check CK (can have myalgia 2 statin without CK rise) Consider: Reducing dose Changing statin, e.g. Lipitor, Crestor Review indication for treatment Consider: Ezetemide Fibrate (evidence for in microalbuminuria retinopathy) Nicotinic Acid (or Tredaptive)
35 Case 7: 69 year old smoker; type 2 diabetes on: Metformin 850 mg b.d. Gliclazide 80mg b.d. Accupril 10 mg b.d. Bezalip 400 mg plus Simvastatin 40mg O/E BP 130/85 BMI 32 Femoral bruit with no foot pulses. Creatinine 0.18 (creatinine year ago) egfr 32ml/min. Urine microalbumin 54 mg/l MSU 10 rbc. ACR 4.3 HbA1c 7.5%. Cholesterol 4.3 LDL HDL TG 2.1.
36 Case 7: Continued Next best step is: a) Stop Bezalip. b) Order MRI renal arteries. c) Stop accupril. d) Increase Metformin to improve HbA1c.
37 Teaching Points: Renal artery stenosis is common in Type 2 diabetes but usually does not need intervention. MRI of Renal Artery may be best test if BP troublesome. ACE inhibitor can be continued unless creatinine rises 30% soon after initiation. Fibrates should be avoided if abnormal creatinine. Consider use with fasting TG over 3 mmol/l if egfr > 60. Proteinuria is almost always present if significantly elevated creatinine is due to diabetic renal disease.
38 Teaching Points: continued Diabetic nephropathy can be associated with some microscopic haematuria. If significant haematuria; urine casts; no proteinuria; no retinopathy think of nondiabetic cause of renal failure, especially if diabetes of very short duration. NB: In patients with T2DM and proteinuria up to 20% have nondiabetic causes of nephropathy. Only 60% of diabetic nephropathy in T2DM have significant retinopathy.
39 Teaching Points: continued If creatinine in diabetes always check if recent use of contrast media; diuretics, NSAID; Fibrates. Patient with renal disease and diabetes, esp smokers, esp with femoral bruits WILL have coronary disease. look for subtle symptoms, e.g. SOB, minimal chest discomfort, diaphoresis and plan ex ECG. Aggressive C.V. management: Statin - aim LDL < 2.0 Aspirin BP to < 130/80 but not less than 120/80.
40 Case 8: 19 year old female presents with fasting hyperglycaemia. A repeat fasting glucose is 7.2mmo/l. She has BMI 23 and a family history of diabetes in mother and grandmother. Which of the following tests would you find the most clinically useful: a) Islet Cell and GAD Ab. b) Serum Insulin. c) Thyroid function test. d) HNF-1α check for MODY3 diabetes. e) HbA1c.
41 Case 8: Indeed she could have: Early autoimmune Type I diabetes Monogonic Diabetes autosomal dominant MODY3 due to HNF 1 α mutation
42 Case 9: 64 year old presents with: Glucose 15.3 HbA1c 9.2% O/E Enlarged liver Ferritin 4000 Iron saturation Positive Gene for haemachromatosis. He begins weekly venesection & remains on Metformin 850mg bd with gliclazide 40mg bd added After 16 weeks he has HbA1c of 5.9% with pre-meal glucose tests 6-9 mmol/l on his 2 year old meter. The low HbA1c most likely represents: a) Nocturnal hypoglycaemia 2 gliclazide use and possible cirrhosis of liver. b) Iron interference with capillary glucose measurement. c) Increased red cell turnover.
43 Teaching Points: RBC turnover can cause falsely low HbA1c, e.g. Blood loss, haemolysis, venesection. HbA1c < 6.5% should prompt a search for hypoglycaemia (especially nocturnal) in those on Insulin or sulphonylurea.
44 Case 10: 28 year old with poorly controlled diabetes HbA1c 12% achieves excellent control after a rev-up from her new boyfriend after mild retinopathy discovered. Her HbA1c improves to 7.2% over four months, but her repeat eye check shows worsening retinopathy and she c/o burning slightly swollen feet?
45 Teaching Point: When glucose control is improved rapidly and especially when HbA1c drops from over 11% quickly to 7% Patients can develop a self limiting neuritis with severe pain in lower limbs and occasionally over trunk. Can be temporary worsening of retinopathy. Usually returns to normal after months.
46 Case 11: 70 year old with diabetes for many years and moderate neuropathy presents with swollen and hot foot. CRP is 7. W.C.C. normal. Afebrile. Xray shows possible fracture and disorganisation of mid-tarsal bones. What is the clinical problem to rule out, and what other tests to order? What is probable diagnosis?
47 Charcot Neuroarthropathy: Peripheral neuropathy insensate foot. Increased A-V shunting with peripheral blood flow and bone flow. Minor mechanical trauma / mico-fractures. Unilateral warmth, oedema, redness in foot with minor trauma, with little or no pain. Collapse of arch and bony prominence. Local osteopenia. Differential diagnosis is septic arthritis; gout; other arthritis. MRI & serial xray ortho opinion. Avoid weight bearing / offloading cast essential. Pamidronate infusion?
48 Case 12: 72 year old with T2DM with good control: HbA1c 7.2%. No Retinopathy or significant peripheral neuropathy. Develops severe pain in L) thigh with: weight loss thigh wasting weakness of hip flexion loss of knee reflex.
49 Acute femoral neuropathy (amyotrophy-proximal motor neuropathy) Rapid onset. Usually reversible in 6-24 months. Seldom recurs but can do. No relation to other long term complications. Often older, T2DM and M > F. Severe neuropathic pain and yet mild sensory deficit. Cause -? Perivascular? Immunological?
50 Case 13: 38 year old with Type I Diabetes for 25 years. C/O: Intermittent Diarrhoea Dizziness on standing Facial sweating after some foods O/E: Pulse 90min BP 130/70 Lying 90/60 Standing
51 Investigations: Thyroid function normal. 9:00am Cortisol 480 Stool sample: No pathogens No RBC No WCC. Celiac Screen negative Colonoscopy normal
52 Clinical & subclinical features of diabetic autonomic neuropathy
53 Cardiovascular autonomic function tests Normal Abnormal Heart rate variation during deep breathing Maximum-minimum (bpm) > 15 < 10 Heart-rate increase on standing 15 secs after standing (bpm) 30 : 15 ratio > 15 > 1.04 < 12 < 1.00 Heart-rate change during Valsalva Maximum : minimum ratio > 1.21 < 1.20 Postural fall in systolic BP 2 min after standing (mmhg) < 10 > 30 Note that these tests normally decline with age; the normal values given here generally apply to subjects less than 60 years of age.
54 Classification of diabetic Neuropathies Progressive neuropathies Reversible neuropathies Pressure palsies Distal symmetrical polyneuropathy Predominately sensory Autonomic involvement common (mostly asymptomatic) Clinical Motor involvement very rare Small-fibre neuropathy Autonomic involvement common and usually symptomatic Gradual onset No recovery Associated with increasing duration of diabetes Associated with other chronic diabetic complications Mononeuropathies Femoral (amyotrophy) Cranial-nerve palsies (III and VI) Truncal radiculopathies Acute diffuse painful neuropathy Stocking distribution Sudden onset Spontaneous recovery No association with duration of diabetes No association with other chronic diabetic complications Median nerve Carpal-tunnel syndrome Ulnar nerve Lateral popliteal nerve (very rare) More common than in the non-diabetic population No association with duration of diabetes
Guidelines to assist General Practitioners in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes. April 2010
 Guidelines to assist General Practitioners in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes April 2010 Foreword The guidelines were devised by the Diabetes Day Centre in Beaumont Hospital in consultation with a number
Guidelines to assist General Practitioners in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes April 2010 Foreword The guidelines were devised by the Diabetes Day Centre in Beaumont Hospital in consultation with a number
Mr Rab Burtun. Dr David Kim. 8:30-10:30 WS #2: Diabetes Basic 11:00-13:00 WS #9: Diabetes Basic (Repeated)
 Dr David Kim Endocrinologist and General Physician Waitemata DHB and Apollo Specialist Clinic Albany Auckland Mr Rab Burtun Diabetes Nurse Specialist Waitemata DHB Waitakere Hospital Auckland 8:30-10:30
Dr David Kim Endocrinologist and General Physician Waitemata DHB and Apollo Specialist Clinic Albany Auckland Mr Rab Burtun Diabetes Nurse Specialist Waitemata DHB Waitakere Hospital Auckland 8:30-10:30
Glucose Control drug treatments
 Glucose Control drug treatments It should be noted that glitazones are under suspicion of precipitating acute cardiac events and current recommendations contraindicate the use of glitazones in patients
Glucose Control drug treatments It should be noted that glitazones are under suspicion of precipitating acute cardiac events and current recommendations contraindicate the use of glitazones in patients
Dept of Diabetes Main Desk
 Dept of Diabetes Main Desk 01202 448060 Glucose management in Type 2 Diabetes in Adults The natural history of type 2 diabetes is for HbA1c to deteriorate with time. A stepwise approach to treatment is
Dept of Diabetes Main Desk 01202 448060 Glucose management in Type 2 Diabetes in Adults The natural history of type 2 diabetes is for HbA1c to deteriorate with time. A stepwise approach to treatment is
Type 2 Diabetes. Stopping Smoking. Consider referral to smoking cessation. Consider referring for weight management advice.
 Type 2 Diabetes Stopping Smoking Consider referral to smoking cessation BMI > 25 kg m² Set a weight loss target of a 5-10% reduction Consider referring for weight management advice Control BP to
Type 2 Diabetes Stopping Smoking Consider referral to smoking cessation BMI > 25 kg m² Set a weight loss target of a 5-10% reduction Consider referring for weight management advice Control BP to
Metformin should be considered in all patients with type 2 diabetes unless contra-indicated
 November 2001 N P S National Prescribing Service Limited PPR fifteen Prescribing Practice Review PPR Managing type 2 diabetes For General Practice Key messages Metformin should be considered in all patients
November 2001 N P S National Prescribing Service Limited PPR fifteen Prescribing Practice Review PPR Managing type 2 diabetes For General Practice Key messages Metformin should be considered in all patients
Volume 2; Number 14 September 2008 NICE CLINICAL GUIDELINE 66: TYPE 2 DIABETES THE MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES (MAY 2008)
 Volume 2; Number 14 September 2008 NICE CLINICAL GUIDELINE 66: TYPE 2 DIABETES THE MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES (MAY 2008) The purpose of this special edition of the PACE Bulletin is to summarize the
Volume 2; Number 14 September 2008 NICE CLINICAL GUIDELINE 66: TYPE 2 DIABETES THE MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES (MAY 2008) The purpose of this special edition of the PACE Bulletin is to summarize the
Cardiovascular risk reduction in diabetes Lipids (NICE CG181)
 Cardiovascular risk reduction in diabetes Lipids (NICE CG181) Primary Prevention T1DM Offer Atorvastatin 20mg if >40 years old Diabetes duration >10 years Established nephropathy Other CVS risk factors
Cardiovascular risk reduction in diabetes Lipids (NICE CG181) Primary Prevention T1DM Offer Atorvastatin 20mg if >40 years old Diabetes duration >10 years Established nephropathy Other CVS risk factors
MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES
 MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES 3 Month trial of lifestyle changes. Refer to DESMOND structured education programme. Set glycaemic target HbA1c < 7.0% (53mmol/mol) or individualised If HbA1c > 53mmol/mol
MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES 3 Month trial of lifestyle changes. Refer to DESMOND structured education programme. Set glycaemic target HbA1c < 7.0% (53mmol/mol) or individualised If HbA1c > 53mmol/mol
Dr A Pokrajac MD MSc MRCP Consultant
 Dr A Pokrajac MD MSc MRCP Consultant Onset at 5-15 years of T1DM Can be present at diagnosis of T2DM Detect in regular MA/Cr screening (2X first urine sample, no UTI, no other causes) Contributing Factors
Dr A Pokrajac MD MSc MRCP Consultant Onset at 5-15 years of T1DM Can be present at diagnosis of T2DM Detect in regular MA/Cr screening (2X first urine sample, no UTI, no other causes) Contributing Factors
Diabetes Complications Guideline Based Screening, Management, and Referral
 Diabetes Complications Guideline Based Screening, Management, and Referral Eric L. Johnson, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Family and Community Medicine Assistant Medical Director Altru Diabetes
Diabetes Complications Guideline Based Screening, Management, and Referral Eric L. Johnson, M.D. Associate Professor Department of Family and Community Medicine Assistant Medical Director Altru Diabetes
Abbreviations DPP-IV dipeptidyl peptidase IV DREAM Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone
 Index Abbreviations DPP-IV dipeptidyl peptidase IV DREAM Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication GAD glutamic acid decarboxylase GLP-1 glucagon-like peptide 1 NPH neutral
Index Abbreviations DPP-IV dipeptidyl peptidase IV DREAM Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication GAD glutamic acid decarboxylase GLP-1 glucagon-like peptide 1 NPH neutral
Dr Tahseen A. Chowdhury Royal London Hospital. New Guidelines in Diabetes: NICE or Nasty?
 Dr Tahseen A. Chowdhury Royal London Hospital New Guidelines in Diabetes: NICE or Nasty? I have no conflicts of interest I do not undertake talks / advisory bodies / research for any pharma company Consultant
Dr Tahseen A. Chowdhury Royal London Hospital New Guidelines in Diabetes: NICE or Nasty? I have no conflicts of interest I do not undertake talks / advisory bodies / research for any pharma company Consultant
Diabetes Mellitus. Eiman Ali Basheir. Mob: /1/2019
 Diabetes Mellitus Eiman Ali Basheir Mob: 091520385 27/1/2019 Learning Outcomes Discuss the WHO criteria for Diabetes Mellitus diagnosis Describe the steps taken to confirm diagnosis Interpret GTT. Discuss
Diabetes Mellitus Eiman Ali Basheir Mob: 091520385 27/1/2019 Learning Outcomes Discuss the WHO criteria for Diabetes Mellitus diagnosis Describe the steps taken to confirm diagnosis Interpret GTT. Discuss
Practical Diabetes. Nic Crook. (and don t use so many charts) Kuirau Specialists 1239 Ranolf Street Rotorua. Rotorua Hospital Private Bag 3023 Rotorua
 Practical Diabetes (and don t use so many charts) Nic Crook Rotorua Hospital Private Bag 3023 Rotorua Kuirau Specialists 1239 Ranolf Street Rotorua Worldwide rates of diabetes mellitus: predictions 80
Practical Diabetes (and don t use so many charts) Nic Crook Rotorua Hospital Private Bag 3023 Rotorua Kuirau Specialists 1239 Ranolf Street Rotorua Worldwide rates of diabetes mellitus: predictions 80
YOU HAVE DIABETES. Angie O Connor Community Diabetes Nurse Specialist 25th September 2013
 YOU HAVE DIABETES Angie O Connor Community Diabetes Nurse Specialist 25th September 2013 Predicated 2015 figures are already met 1 in 20 have diabetes:1in8 over 60years old Definite Diagnosis is key Early
YOU HAVE DIABETES Angie O Connor Community Diabetes Nurse Specialist 25th September 2013 Predicated 2015 figures are already met 1 in 20 have diabetes:1in8 over 60years old Definite Diagnosis is key Early
Diabetes in the Elderly 1, 2, 3
 Diabetes in the Elderly 1, 2, 3 WF Mollentze Feb 2010 Diabetes in the elderly differs from diabetes in younger people Prevalence: o Diabetes increases with age affecting approximately 10% of people over
Diabetes in the Elderly 1, 2, 3 WF Mollentze Feb 2010 Diabetes in the elderly differs from diabetes in younger people Prevalence: o Diabetes increases with age affecting approximately 10% of people over
New Treatments for Type 2 diabetes. Nandini Seevaratnam April 2016 Rushcliffe Patient Forum
 New Treatments for Type 2 diabetes Nandini Seevaratnam April 2016 Rushcliffe Patient Forum Overview Growing population of Type 2 diabetes Basic science on what goes wrong Current treatments Why there is
New Treatments for Type 2 diabetes Nandini Seevaratnam April 2016 Rushcliffe Patient Forum Overview Growing population of Type 2 diabetes Basic science on what goes wrong Current treatments Why there is
bpac better e m dicine
 bpac nz better medicin e bpac nz Development Team: Rachael Clarke Sonia Ross Dr Trevor Walker David Woods bpac nz Clinical Advisory Group (laboratory programme): Tracey Barron Dr Dave Colquhoun Michele
bpac nz better medicin e bpac nz Development Team: Rachael Clarke Sonia Ross Dr Trevor Walker David Woods bpac nz Clinical Advisory Group (laboratory programme): Tracey Barron Dr Dave Colquhoun Michele
DR HJ BODANSKY MD FRCP CONSULTANT PHYSICIAN LEEDS TEACHING HOSPITALS ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, UNIVERSITY OF LEEDS
 DR HJ BODANSKY MD FRCP CONSULTANT PHYSICIAN LEEDS TEACHING HOSPITALS ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, UNIVERSITY OF LEEDS DIABETETES UPDATE 2015 AIMS OF THE SEMINAR Diagnosis Investigation Management When to refer
DR HJ BODANSKY MD FRCP CONSULTANT PHYSICIAN LEEDS TEACHING HOSPITALS ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR, UNIVERSITY OF LEEDS DIABETETES UPDATE 2015 AIMS OF THE SEMINAR Diagnosis Investigation Management When to refer
Disclosures. Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management. Learning Objectives. Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
 Disclosures Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Tony Hampton, MD, MBA Medical Director Advocate Aurora Operating System Advocate Aurora Healthcare Downers Grove, IL No conflicts or disclosures
Disclosures Diabetes and Cardiovascular Risk Management Tony Hampton, MD, MBA Medical Director Advocate Aurora Operating System Advocate Aurora Healthcare Downers Grove, IL No conflicts or disclosures
TREATMENTS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES. Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse
 TREATMENTS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse How can we improve outcomes in Type 2 diabetes? Earlier diagnosis Better patient education Stress central role of lifestyle management
TREATMENTS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES Susan Henry Diabetes Specialist Nurse How can we improve outcomes in Type 2 diabetes? Earlier diagnosis Better patient education Stress central role of lifestyle management
Drugs used in Diabetes. Dr Andrew Smith
 Drugs used in Diabetes Dr Andrew Smith Plan Introduction Insulin Sensitising Drugs: Metformin Glitazones Insulin Secretagogues: Sulphonylureas Meglitinides Others: Acarbose Incretins Amylin Analogues Damaglifozin
Drugs used in Diabetes Dr Andrew Smith Plan Introduction Insulin Sensitising Drugs: Metformin Glitazones Insulin Secretagogues: Sulphonylureas Meglitinides Others: Acarbose Incretins Amylin Analogues Damaglifozin
Case study for CME Diabetes up-to-date management
 Case study for CME Diabetes up-to-date management Dr Ole Schmiedel, MRCP MD FRACP Physician and Endocrinologist Service Clinical Director Auckland Diabetes Centre GP referral to Auckland Diabetes Centre
Case study for CME Diabetes up-to-date management Dr Ole Schmiedel, MRCP MD FRACP Physician and Endocrinologist Service Clinical Director Auckland Diabetes Centre GP referral to Auckland Diabetes Centre
Diabetic & Complications. Dr. A K Viswanath Consultant Diabetologist
 Diabetic & Complications Dr. A K Viswanath Consultant Diabetologist Outline Challenges in diabetes How do we fare? Diabetes complications Improving outcomes in diabetes Types of Diabetes Type-1 DM Genetic
Diabetic & Complications Dr. A K Viswanath Consultant Diabetologist Outline Challenges in diabetes How do we fare? Diabetes complications Improving outcomes in diabetes Types of Diabetes Type-1 DM Genetic
Pharmacological Glycaemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes
 Pharmacological Glycaemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Aim(s) and Objective(s) This guideline aims to offer advice on the pharmacological management for those who require measures beyond diet and exercise
Pharmacological Glycaemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes Aim(s) and Objective(s) This guideline aims to offer advice on the pharmacological management for those who require measures beyond diet and exercise
Diabetes Mellitus: Implications of New Clinical Trials and New Medications
 Diabetes Mellitus: Implications of New Clinical Trials and New Medications Estimates of Diagnosed Diabetes in Adults, 2005 Alka M. Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine UCSF, Primary Care CME October
Diabetes Mellitus: Implications of New Clinical Trials and New Medications Estimates of Diagnosed Diabetes in Adults, 2005 Alka M. Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine UCSF, Primary Care CME October
STEP 3: Add or Substitute with one of
 Prescribing of Hypoglycaemic Agents for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Sunderland Refer to DESMOND Structured Education classes to promote Increased Physical Activity, Weight Loss and Calories Reduction
Prescribing of Hypoglycaemic Agents for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Sunderland Refer to DESMOND Structured Education classes to promote Increased Physical Activity, Weight Loss and Calories Reduction
Case study: Lean adult with no complications, newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes
 Case study: Lean adult with no complications, newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes Authored by Clifford Bailey and James LaSalle on behalf of the Global Partnership for Effective Diabetes Management. The
Case study: Lean adult with no complications, newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes Authored by Clifford Bailey and James LaSalle on behalf of the Global Partnership for Effective Diabetes Management. The
Professor Rudy Bilous James Cook University Hospital
 Professor Rudy Bilous James Cook University Hospital Rate per 100 patient years Rate per 100 patient years 16 Risk of retinopathy progression 16 Risk of developing microalbuminuria 12 12 8 8 4 0 0 5 6
Professor Rudy Bilous James Cook University Hospital Rate per 100 patient years Rate per 100 patient years 16 Risk of retinopathy progression 16 Risk of developing microalbuminuria 12 12 8 8 4 0 0 5 6
Insulin use in Type 2 Diabetes
 Insulin use in Type 2 Diabetes 1 Conflict of Interest I have been on advisory boards or had speaker fees from the following pharmaceutical companies: - Eli Lilly - Novo Nordisk - Sanofi Aventis - MSD -
Insulin use in Type 2 Diabetes 1 Conflict of Interest I have been on advisory boards or had speaker fees from the following pharmaceutical companies: - Eli Lilly - Novo Nordisk - Sanofi Aventis - MSD -
DIABETES Self Directed Test (12 Hours) Name: Ward/Practice Area: Mailing Address:
 1 DIABETES Self Directed Test (12 Hours) Name: Ward/Practice Area: Mailing Address: 2 Learning Outcomes All nurses, regardless of practice setting, are required to work collaboratively with the person
1 DIABETES Self Directed Test (12 Hours) Name: Ward/Practice Area: Mailing Address: 2 Learning Outcomes All nurses, regardless of practice setting, are required to work collaboratively with the person
The York Diabetes Care Model
 This Session The York Diabetes Care Model The annual review what s it for and how to do it How to make the diagnosis of diabetes and who to test Categorisation of diabetes at diagnosis Basics of Insulin
This Session The York Diabetes Care Model The annual review what s it for and how to do it How to make the diagnosis of diabetes and who to test Categorisation of diabetes at diagnosis Basics of Insulin
Diabetes in Renal Patients. Contents. Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy
 Diabetes in Renal Patients Contents Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy What effect does CKD have on a patient s diabetic control? Diabetic Drugs in CKD and Dialysis Patients Hyper and Hypoglycaemia in
Diabetes in Renal Patients Contents Understanding Diabetic Nephropathy What effect does CKD have on a patient s diabetic control? Diabetic Drugs in CKD and Dialysis Patients Hyper and Hypoglycaemia in
HIHIM Clinical Cocepts for Managers 7/31/2009. Fernando Vega, MD 1
 Fernando Vega, MD HIHIM 409 July 31, 2008 Hyperglycemia characterized by relative or absolute lack of insulin secretion Varying degrees of insulin resistance Often associated with symptoms: polyruia, polydipsia,
Fernando Vega, MD HIHIM 409 July 31, 2008 Hyperglycemia characterized by relative or absolute lack of insulin secretion Varying degrees of insulin resistance Often associated with symptoms: polyruia, polydipsia,
Insulin Initiation, titration & Insulin switch in the Primary Care-KISS
 Insulin Initiation, titration & Insulin switch in the Primary Care-KISS Rotorua GP CME 9 June 2012 Dr Kingsley Nirmalaraj FRACP Endocrinologist, BOPDHB & Suite 9, Promed House, Tenth Ave, Tauranga Linda
Insulin Initiation, titration & Insulin switch in the Primary Care-KISS Rotorua GP CME 9 June 2012 Dr Kingsley Nirmalaraj FRACP Endocrinologist, BOPDHB & Suite 9, Promed House, Tenth Ave, Tauranga Linda
Arrange 3 Monthly Review Re-enforce LIFESTYLE advice and check DRUG COMPLIANCE at each visit Target HbA1c < 53mmol/mol
 Prescribing of Hypoglycaemic Agents for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Sunderland Refer to DESMOND Structured Education classes to promote Increased Physical Activity, Weight Loss and Calories Reduction
Prescribing of Hypoglycaemic Agents for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Sunderland Refer to DESMOND Structured Education classes to promote Increased Physical Activity, Weight Loss and Calories Reduction
Chronic Benefit Application Form Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes
 Chronic Benefit Application Form Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes 19 West Street, Houghton, South Africa, 2198 Postnet Suite 411, Private Bag X1, Melrose Arch, 2076 Tel: +27 (11) 715 3000 Fax: +27 (11)
Chronic Benefit Application Form Cardiovascular Disease and Diabetes 19 West Street, Houghton, South Africa, 2198 Postnet Suite 411, Private Bag X1, Melrose Arch, 2076 Tel: +27 (11) 715 3000 Fax: +27 (11)
Diabetic Neuropathy An Overview. Dr. Mark Hannon MD MSc FRCPI Consultant Physician and Endocrinologist Bantry General Hospital Septebmer 20 th 2017
 Diabetic Neuropathy An Overview Dr. Mark Hannon MD MSc FRCPI Consultant Physician and Endocrinologist Bantry General Hospital Septebmer 20 th 2017 Neuropathy in Diabetes Overall, one of the most common
Diabetic Neuropathy An Overview Dr. Mark Hannon MD MSc FRCPI Consultant Physician and Endocrinologist Bantry General Hospital Septebmer 20 th 2017 Neuropathy in Diabetes Overall, one of the most common
Challenges in type 2 diabetes control: slipping control and weight gain
 control Earn 3 CPD Points online Case study Challenges in type 2 diabetes control: slipping control and weight gain Presenter Dr Sedeshan Govender Specialist Physician, Endocrinologist and Diabetologists
control Earn 3 CPD Points online Case study Challenges in type 2 diabetes control: slipping control and weight gain Presenter Dr Sedeshan Govender Specialist Physician, Endocrinologist and Diabetologists
Management of Type 2 Diabetes. Why Do We Bother to Achieve Good Control in DM2. Insulin Secretion. The Importance of BP and Glucose Control
 Insulin Secretion Management of Type 2 Diabetes DG van Zyl Why Do We Bother to Achieve Good Control in DM2 % reduction 0-5 -10-15 -20-25 -30-35 -40 The Importance of BP and Glucose Control Effects of tight
Insulin Secretion Management of Type 2 Diabetes DG van Zyl Why Do We Bother to Achieve Good Control in DM2 % reduction 0-5 -10-15 -20-25 -30-35 -40 The Importance of BP and Glucose Control Effects of tight
Complications of Diabetes mellitus. Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015
 Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
Complications of Diabetes mellitus Dr Bill Young 16 March 2015 Complications of diabetes Multi-organ involvement 2 The extent of diabetes complications At diagnosis as many as 50% of patients may have
CHALLENGING CASE PRESENTATION Steroid Induced Hyperglycemia
 CHALLENGING CASE PRESENTATION Steroid Induced Hyperglycemia Javier Carrasco, MD, PhD Juan Ramón Jiménez Hospital University of Huelva, Spain Case Study: Medical and Social History A 60 years old female
CHALLENGING CASE PRESENTATION Steroid Induced Hyperglycemia Javier Carrasco, MD, PhD Juan Ramón Jiménez Hospital University of Huelva, Spain Case Study: Medical and Social History A 60 years old female
Colin Edwards. Cardiologist Auckland Heart Group Waitemata Health
 Colin Edwards Cardiologist Auckland Heart Group Waitemata Health AUG 2012 Introduction Case Summary BP MEASUREMENTS measured seated mean of 2 BP recordings per visit at least 2 visits Diet Exercise Weight
Colin Edwards Cardiologist Auckland Heart Group Waitemata Health AUG 2012 Introduction Case Summary BP MEASUREMENTS measured seated mean of 2 BP recordings per visit at least 2 visits Diet Exercise Weight
Diabetes in the UK: Update on Diabetes Treatment and Care. Why is diabetes increasing? Obesity Increased waist circumference.
 Update on Diabetes Treatment and Care Tahseen A Chowdhury Consultant Diabetologist Royal London and Mile End Hospitals Diabetes prevalence (thousands) Diabetes in the UK: 1995-21 3 25 2 15 1 5 Type 1 Type
Update on Diabetes Treatment and Care Tahseen A Chowdhury Consultant Diabetologist Royal London and Mile End Hospitals Diabetes prevalence (thousands) Diabetes in the UK: 1995-21 3 25 2 15 1 5 Type 1 Type
Diabetes Diagnosis 2011 Does your patient have diabetes?
 Diabetes Diagnosis 2011 Does your patient have diabetes? Dr Rick Cutfield Physician and Endocrinologist Waitemata District Health Board Mercy Specialist Centre Case 1: A 24 year old stockcar driver presents
Diabetes Diagnosis 2011 Does your patient have diabetes? Dr Rick Cutfield Physician and Endocrinologist Waitemata District Health Board Mercy Specialist Centre Case 1: A 24 year old stockcar driver presents
ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES
 ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Pr. Michel KOMAJDA Institute of Cardiology - IHU ICAN Pitie Salpetriere Hospital - University Pierre and Marie Curie, Paris (France) DEFINITION A
ESC GUIDELINES ON DIABETES AND CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES Pr. Michel KOMAJDA Institute of Cardiology - IHU ICAN Pitie Salpetriere Hospital - University Pierre and Marie Curie, Paris (France) DEFINITION A
Colin Edwards. Cardiologist Auckland Heart Group Waitemata Health
 Colin Edwards Cardiologist Auckland Heart Group Waitemata Health August 2011 BP MEASUREMENTS measured seated mean of 2 or BP recordings at least 2 visits 2 x risk of developing true hypertension Size of
Colin Edwards Cardiologist Auckland Heart Group Waitemata Health August 2011 BP MEASUREMENTS measured seated mean of 2 or BP recordings at least 2 visits 2 x risk of developing true hypertension Size of
Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus
 Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 How to Screen for Diabetic Nephropathy... 4 What to Measure... 4 Frequency
Swindon Diabetes Guidelines: Management of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Diabetes Mellitus 1 Contents Executive Summary... 3 How to Screen for Diabetic Nephropathy... 4 What to Measure... 4 Frequency
Diabetes Renal Disease Management. Dr Paul Laboi Dr Vijay Jayagopal York Hospital
 Diabetes Renal Disease Management Dr Paul Laboi Dr Vijay Jayagopal York Hospital 0 Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is a clinical syndrome characterised by the following: Persistent albuminuria
Diabetes Renal Disease Management Dr Paul Laboi Dr Vijay Jayagopal York Hospital 0 Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy is a clinical syndrome characterised by the following: Persistent albuminuria
Newer Drugs in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 Newer Drugs in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Dr. C. Dinesh M. Naidu Professor of Pharmacology, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences, Narketpally. 1 Presentation Outline Introduction Pathogenesis
Newer Drugs in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Dr. C. Dinesh M. Naidu Professor of Pharmacology, Kamineni Institute of Medical Sciences, Narketpally. 1 Presentation Outline Introduction Pathogenesis
Hot Topics in Diabetic Kidney Disease a primary care perspective
 Hot Topics in Diabetic Kidney Disease a primary care perspective DR SARAH DAVIES GP PARTNER WITH SPECIAL INTEREST IN DIABETES, CARDIFF DUK CLINICAL CHAMPION NB MEDICAL HOT TOPICS PRESENTER AND DIABETES
Hot Topics in Diabetic Kidney Disease a primary care perspective DR SARAH DAVIES GP PARTNER WITH SPECIAL INTEREST IN DIABETES, CARDIFF DUK CLINICAL CHAMPION NB MEDICAL HOT TOPICS PRESENTER AND DIABETES
Oral Treatments for Type 2 Diabetes. Prescribing Support Pharmacist
 Oral Treatments for Type 2 Diabetes Prescribing Support Pharmacist Learning Outcomes Familiar with classes of oral hypoglycaemic agents (OHAs) used in controlling blood glucose levels When to use each
Oral Treatments for Type 2 Diabetes Prescribing Support Pharmacist Learning Outcomes Familiar with classes of oral hypoglycaemic agents (OHAs) used in controlling blood glucose levels When to use each
The older person with co morbidities. Eugene Hughes General Practitioner Isle of Wight
 The older person with co morbidities Eugene Hughes General Practitioner Isle of Wight Eugene Hughes Age 60 BMI 26.5 BP 125/70 Alcohol intake moderate (?) TC 5.6 Regular exercise Non smoker Stress free
The older person with co morbidities Eugene Hughes General Practitioner Isle of Wight Eugene Hughes Age 60 BMI 26.5 BP 125/70 Alcohol intake moderate (?) TC 5.6 Regular exercise Non smoker Stress free
Diabetic Nephropathy 2009
 Diabetic Nephropathy 2009 Michael T McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Michael.mcdermott@ucdenver.edu Diabetic Nephropathy Clinical Stages Hyperfunction
Diabetic Nephropathy 2009 Michael T McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Michael.mcdermott@ucdenver.edu Diabetic Nephropathy Clinical Stages Hyperfunction
Joslin Diabetes Center Joslin Diabetes Forum 2013: The Impact of Comorbidities on Glucose Control Scenario 2: Reduced Renal Function
 Scenario 2: Reduced Renal Function 62 y.o. white man with type 2 diabetes for 18 years Hypertension and hypercholesterolemia Known proliferative retinopathy Current medications: Metformin 1000 mg bid Glyburide
Scenario 2: Reduced Renal Function 62 y.o. white man with type 2 diabetes for 18 years Hypertension and hypercholesterolemia Known proliferative retinopathy Current medications: Metformin 1000 mg bid Glyburide
Optimal glucose control. DM Treatment. Glucose Control one out of many. Many guidelines: Confusing. Theorectically easy
 DM Treatment How to Achieve Optimal Glycaemic Control The Tung Wah Eastern Hospital Experience of DM Share Care Experience Optimal glucose control Theorectically easy More challenging in the real world
DM Treatment How to Achieve Optimal Glycaemic Control The Tung Wah Eastern Hospital Experience of DM Share Care Experience Optimal glucose control Theorectically easy More challenging in the real world
Diabetes and Hypertension
 Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Diabetes and Hypertension M.Nakhjvani,M.D Tehran University of Medical Sciences 20-8-96 Hypertension Common DM comorbidity Prevalence depends on diabetes type, age, BMI, ethnicity Major risk factor for
Application of the Diabetes Algorithm to a Patient
 Application of the Diabetes Algorithm to a Patient Apply knowledge gained from this activity to improve disease management and outcomes for patients with T2DM and obesity Note: The cases in this deck represent
Application of the Diabetes Algorithm to a Patient Apply knowledge gained from this activity to improve disease management and outcomes for patients with T2DM and obesity Note: The cases in this deck represent
Hypertension Clinical case scenarios for primary care
 Hypertension Clinical case scenarios for primary care Implementing NICE guidance August 2011 NICE clinical guideline 127 What this presentation covers Five clinical case scenarios, including: presentation
Hypertension Clinical case scenarios for primary care Implementing NICE guidance August 2011 NICE clinical guideline 127 What this presentation covers Five clinical case scenarios, including: presentation
DIABETES AND LABORATORY TESTS. Author: Josephine Davis
 DIABETES AND LABORATORY TESTS Author: Josephine Davis LAB TESTS Think twice before you test. What is the reason for testing? Laboratory tests are generally requested in primary care for one of the following
DIABETES AND LABORATORY TESTS Author: Josephine Davis LAB TESTS Think twice before you test. What is the reason for testing? Laboratory tests are generally requested in primary care for one of the following
Diabetes and Kidney Disease. Kris Bentley Renal Nurse practitioner 2018
 Diabetes and Kidney Disease Kris Bentley Renal Nurse practitioner 2018 Aims Develop an understanding of Chronic Kidney Disease Understand how diabetes impacts on your kidneys Be able to recognise the risk
Diabetes and Kidney Disease Kris Bentley Renal Nurse practitioner 2018 Aims Develop an understanding of Chronic Kidney Disease Understand how diabetes impacts on your kidneys Be able to recognise the risk
PLEASE CHECK FULL SPECIFIC PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS FOR MORE DETAILED AND CURRENT INFORMATION:
 Metformin Standard tablets Modified-release tablets Metformin 1g sachets Metformin liquid 500mg/5ml (avoid use as expensive) < 2.00 5.32 for 56 tabs 500mg 13.16 for 60 sachets > 120 Ketoacidosis General
Metformin Standard tablets Modified-release tablets Metformin 1g sachets Metformin liquid 500mg/5ml (avoid use as expensive) < 2.00 5.32 for 56 tabs 500mg 13.16 for 60 sachets > 120 Ketoacidosis General
Drug Therapy for Diabetes Mellitus. Adj A/Prof Daniel Chew Dept of Endocrinology 8 th July 2017
 Drug Therapy for Diabetes Mellitus Adj A/Prof Daniel Chew Dept of Endocrinology 8 th July 2017 Diabetes Subtypes Optimal Treatment Ominous Octet DeFronzo. DIABETES, VOL. 58, APRIL 2009 Schematic Overview
Drug Therapy for Diabetes Mellitus Adj A/Prof Daniel Chew Dept of Endocrinology 8 th July 2017 Diabetes Subtypes Optimal Treatment Ominous Octet DeFronzo. DIABETES, VOL. 58, APRIL 2009 Schematic Overview
How can we improve outcomes in Type 2 diabetes?
 How can we improve outcomes in Type 2 diabetes? Earlier diagnosis Better patient education Stress central role of lifestyle management Identify and treat all risk factors Use rational pharmacological therapy
How can we improve outcomes in Type 2 diabetes? Earlier diagnosis Better patient education Stress central role of lifestyle management Identify and treat all risk factors Use rational pharmacological therapy
Insulin Optimisation Workshop. Theingi Aung & Claire Rowell
 Insulin Optimisation Workshop Theingi Aung & Claire Rowell Insulin initiation and titration Insulin Preparations Rapid-acting insulin analogues: onset of action of approximately 15 minutes and a duration
Insulin Optimisation Workshop Theingi Aung & Claire Rowell Insulin initiation and titration Insulin Preparations Rapid-acting insulin analogues: onset of action of approximately 15 minutes and a duration
GLP-1 agonists. Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK
 GLP-1 agonists Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK What do GLP-1 agonists do? Physiology of postprandial glucose regulation Meal ❶ ❷ Insulin Rising plasma
GLP-1 agonists Ian Gallen Consultant Community Diabetologist Royal Berkshire Hospital Reading UK What do GLP-1 agonists do? Physiology of postprandial glucose regulation Meal ❶ ❷ Insulin Rising plasma
Treatment Options for Diabetes: An Update
 Treatment Options for Diabetes: An Update A/Prof. Marg McGill Manager, Diabetes Centre Dr. Ted Wu Staff Specialist Endocrinologist Diabetes Centre Centre of Health Professional Education Education Provider
Treatment Options for Diabetes: An Update A/Prof. Marg McGill Manager, Diabetes Centre Dr. Ted Wu Staff Specialist Endocrinologist Diabetes Centre Centre of Health Professional Education Education Provider
Diabetes and New Meds for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction. F. Dwight Chrisman, MD, FACC. Disclosures: BI Boehringer Ingelheim speaker
 Diabetes and New Meds for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction F. Dwight Chrisman, MD, FACC Disclosures: BI Boehringer Ingelheim speaker 1 Prevalence of DM DM state specific prevalence 2006 4%-6% 6-8% 8-10% 10-12%
Diabetes and New Meds for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction F. Dwight Chrisman, MD, FACC Disclosures: BI Boehringer Ingelheim speaker 1 Prevalence of DM DM state specific prevalence 2006 4%-6% 6-8% 8-10% 10-12%
Case study: Adult with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes of long duration and cardiovascular disease
 Case study: Adult with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes of long duration and cardiovascular disease Authored by Paul Zimmet and Richard Nesto on behalf of the Global Partnership for Effective Diabetes Management.
Case study: Adult with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes of long duration and cardiovascular disease Authored by Paul Zimmet and Richard Nesto on behalf of the Global Partnership for Effective Diabetes Management.
Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim
 Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim Chosun University Hospital Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Committee of Scientific Affairs Insulin therapy is the mainstay
Non-insulin treatment in Type 1 DM Sang Yong Kim Chosun University Hospital Conflict of interest disclosure None Committee of Scientific Affairs Committee of Scientific Affairs Insulin therapy is the mainstay
Management of Type 2 Diabetes
 Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Pathophysiology Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency/ defective secretion Not immune mediated No evidence of β cell destruction Increased risk with age, obesity
Comprehensive Diabetes Treatment
 Comprehensive Diabetes Treatment Joshua L. Cohen, M.D., F.A.C.P. Professor of Medicine Interim Director, Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism The George Washington University School of Medicine Diabetes
Comprehensive Diabetes Treatment Joshua L. Cohen, M.D., F.A.C.P. Professor of Medicine Interim Director, Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism The George Washington University School of Medicine Diabetes
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGNOSIS
 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD Offer testing for CKD using egfr, serum creatinine and urinary ACR to people with any of the following risk factors: diabetes hypertension acute
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD Offer testing for CKD using egfr, serum creatinine and urinary ACR to people with any of the following risk factors: diabetes hypertension acute
DIABETES MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW
 2014 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: DIABETES MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2014 PQRS MEASURES IN DIABETES MEASURES GROUP: #1. Diabetes: Hemoglobin A1c Poor Control #2. Diabetes: Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL-C)
2014 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: DIABETES MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2014 PQRS MEASURES IN DIABETES MEASURES GROUP: #1. Diabetes: Hemoglobin A1c Poor Control #2. Diabetes: Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL-C)
ABFM Diabetes SAM Part 4
 ABFM Diabetes SAM Part 4 37. A 55-year-old male with type 2 diabetes mellitus has a chronic history of reduced libido and erectile dysfunction. On examination you note hepatomegaly and mild testicular
ABFM Diabetes SAM Part 4 37. A 55-year-old male with type 2 diabetes mellitus has a chronic history of reduced libido and erectile dysfunction. On examination you note hepatomegaly and mild testicular
130/80 vs. 140/90 If nephropathy is present the target should be 120/ /10/07
 DG van Zyl Macro vascular Micro vascular Neuropathy Infections Genetic susceptibility *Repeated acute changes in cellular metabolism Hyperglycemia Tissue damage **Cumulative long term changes in stable
DG van Zyl Macro vascular Micro vascular Neuropathy Infections Genetic susceptibility *Repeated acute changes in cellular metabolism Hyperglycemia Tissue damage **Cumulative long term changes in stable
Diabetic Nephropathy. Objectives:
 There are, in truth, no specialties in medicine, since to know fully many of the most important diseases a man must be familiar with their manifestations in many organs. William Osler 1894. Objectives:
There are, in truth, no specialties in medicine, since to know fully many of the most important diseases a man must be familiar with their manifestations in many organs. William Osler 1894. Objectives:
Objectives. Objectives. Alejandro J. de la Torre, MD Cook Children s Hospital May 30, 2015
 Alejandro J. de la Torre, MD Cook Children s Hospital May 30, 2015 Presentation downloaded from http://ce.unthsc.edu Objectives Understand that the obesity epidemic is also affecting children and adolescents
Alejandro J. de la Torre, MD Cook Children s Hospital May 30, 2015 Presentation downloaded from http://ce.unthsc.edu Objectives Understand that the obesity epidemic is also affecting children and adolescents
Diabetes Complications. Rezvan Salehidoost, M.D., Endocrinologist
 Diabetes Complications Rezvan Salehidoost, M.D., Endocrinologist Different Diabetes Complications Macro vascular Micro vascular Infections Macro vascular Complications Macro-vascular Complications Ischemic
Diabetes Complications Rezvan Salehidoost, M.D., Endocrinologist Different Diabetes Complications Macro vascular Micro vascular Infections Macro vascular Complications Macro-vascular Complications Ischemic
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGNOSIS
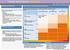 CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS GFR categories, description and range WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD CLASSIFICATION OF CKD USING egfr AND ACR CATEGORIES Offer testing for CKD using egfr, creatinine and ACR
CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE DIAGSIS GFR categories, description and range WHO SHOULD BE TESTED FOR CKD CLASSIFICATION OF CKD USING egfr AND ACR CATEGORIES Offer testing for CKD using egfr, creatinine and ACR
Adult Diabetes Clinician Guide NOVEMBER 2017
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Diabetes Clinician Guide Introduction NOVEMBER 2017 This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2017 KP National Diabetes Guideline.
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Diabetes Clinician Guide Introduction NOVEMBER 2017 This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2017 KP National Diabetes Guideline.
Oral Treatments. SaminaAli Prescribing Support Pharmacist
 Oral Treatments for Type 2 Diabetes SaminaAli Prescribing Support Pharmacist Learning Outcomes National Guidance Familiar with classes of oral hypoglycaemic agents (OHAs) used in controlling blood glucose
Oral Treatments for Type 2 Diabetes SaminaAli Prescribing Support Pharmacist Learning Outcomes National Guidance Familiar with classes of oral hypoglycaemic agents (OHAs) used in controlling blood glucose
Injectable Therapies in Diabetes
 Injectable Therapies in Diabetes Diabetes Specialist Nurse Joyce Robson Learning Outcomes Think about the place of injectible therapies in diabetes Think about when / why patients require insulin therapy
Injectable Therapies in Diabetes Diabetes Specialist Nurse Joyce Robson Learning Outcomes Think about the place of injectible therapies in diabetes Think about when / why patients require insulin therapy
Modified version focused on CCNC Quality Measures and Feedback Processes
 Executive Summary: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2010 Modified version focused on CCNC Quality Measures and Feedback Processes See http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/33/supplement_1/s11.full
Executive Summary: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2010 Modified version focused on CCNC Quality Measures and Feedback Processes See http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/33/supplement_1/s11.full
There have been important changes in diabetes care which may not be covered in undergraduate textbooks.
 Diabetes Clinical update There have been important changes in diabetes care which may not be covered in undergraduate textbooks. Changes in the diagnosis of diabetes a) HbA1C Since 2011, World Health Organisation
Diabetes Clinical update There have been important changes in diabetes care which may not be covered in undergraduate textbooks. Changes in the diagnosis of diabetes a) HbA1C Since 2011, World Health Organisation
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. Type 2 diabetes. Stakeholder Comments Draft Guideline
 National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Type 2 diabetes Stakeholder Comments Draft Guideline NOTE: NICE is unable to accept comments from non-registered organisations or individuals. If you wish
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence Type 2 diabetes Stakeholder Comments Draft Guideline NOTE: NICE is unable to accept comments from non-registered organisations or individuals. If you wish
A Practical Approach to the Use of Diabetes Medications
 A Practical Approach to the Use of Diabetes Medications Juan Pablo Frias, M.D., FACE President, National Research Institute, Los Angles, CA Clinical Faculty, University of California, San Diego, CA OUTLINE
A Practical Approach to the Use of Diabetes Medications Juan Pablo Frias, M.D., FACE President, National Research Institute, Los Angles, CA Clinical Faculty, University of California, San Diego, CA OUTLINE
Type 1 Diabetes & Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Dr Sheila Cook Director of Diabetes & Endocrinology Toowoomba Hospital
 Type 1 Diabetes & Continuous Glucose Monitoring Dr Sheila Cook Director of Diabetes & Endocrinology Toowoomba Hospital Let s consider the traditional diabetes clinic The Diabetes Clinic Whenever I check
Type 1 Diabetes & Continuous Glucose Monitoring Dr Sheila Cook Director of Diabetes & Endocrinology Toowoomba Hospital Let s consider the traditional diabetes clinic The Diabetes Clinic Whenever I check
Diabetes Management in New Brunswick Nursing Homes
 Diabetes Management in New Brunswick Nursing Homes Prepared by Dr. Angela McGibbon March, 2016 As the population ages and with the rising incidence of diabetes, there are increasing numbers of people with
Diabetes Management in New Brunswick Nursing Homes Prepared by Dr. Angela McGibbon March, 2016 As the population ages and with the rising incidence of diabetes, there are increasing numbers of people with
Complete this CE activity online at ProCE.com/InsulinPart2
 Complete this CE activity online at ProCE.com/InsulinPart2 Case 1: A 67 year old male with T2DM History and Presentation John is a 67 year old retiree who has been visiting your pharmacy/clinic for over
Complete this CE activity online at ProCE.com/InsulinPart2 Case 1: A 67 year old male with T2DM History and Presentation John is a 67 year old retiree who has been visiting your pharmacy/clinic for over
Management of early chronic kidney disease
 Management of early chronic kidney disease GREENLANE SUMMER GP SYMPOSIUM 2018 Jonathan Hsiao Renal and General Physician Introduction A growing public health problem in NZ and throughout the world. Unknown
Management of early chronic kidney disease GREENLANE SUMMER GP SYMPOSIUM 2018 Jonathan Hsiao Renal and General Physician Introduction A growing public health problem in NZ and throughout the world. Unknown
RISK FACTORS OR COMPLICATIONS AND RECOMMENDED TREATMENT GOALS AND FREQUENCY OF EVALUATION FOR ADULTS WITH DIABETES
 RISK FACTORS OR COMPLICATIONS AND RECOMMENDED TREATMENT GOALS AND FREQUENCY OF EVALUATION FOR ADULTS WITH DIABETES Risk Factors or Complications Glycemic Control Fasting & Capillary Plasma Glucose Anti-platelet
RISK FACTORS OR COMPLICATIONS AND RECOMMENDED TREATMENT GOALS AND FREQUENCY OF EVALUATION FOR ADULTS WITH DIABETES Risk Factors or Complications Glycemic Control Fasting & Capillary Plasma Glucose Anti-platelet
More Than Just the Numbers:
 More Than Just the Numbers: Individualising Patient Care ADEA-QLD Branch Conference 20 April 2018 Case Study 1 Child with Type 1 Diabetes 2 Background and Social History 10 year old female with T1DM since
More Than Just the Numbers: Individualising Patient Care ADEA-QLD Branch Conference 20 April 2018 Case Study 1 Child with Type 1 Diabetes 2 Background and Social History 10 year old female with T1DM since
Mr Gavin Hendry. Mr Rab Burtun. Prof Jim Mann. Diabetes Nurse Facilitator, Auckland. Dunedin. Human Nutrition & Medicine University of Otago, Dunedin
 Mr Rab Burtun Diabetes Nurse Facilitator, Auckland Mr Gavin Hendry Dunedin Prof Jim Mann Human Nutrition & Medicine University of Otago, Dunedin Insulin Master Class Presented by: Prof Jim Mann Gavin Hendry
Mr Rab Burtun Diabetes Nurse Facilitator, Auckland Mr Gavin Hendry Dunedin Prof Jim Mann Human Nutrition & Medicine University of Otago, Dunedin Insulin Master Class Presented by: Prof Jim Mann Gavin Hendry
USING INSULIN IN TYPE 2 DIABETES. Patrick Manning 2016
 USING INSULIN IN TYPE 2 DIABETES Patrick Manning 2016 NATURAL HISTORY OF TYPE 2 DIABETES It has been estimated using the homeostasis multiple assessment (HOMA) that, at the time of diagnosis, 50% of pancreatic
USING INSULIN IN TYPE 2 DIABETES Patrick Manning 2016 NATURAL HISTORY OF TYPE 2 DIABETES It has been estimated using the homeostasis multiple assessment (HOMA) that, at the time of diagnosis, 50% of pancreatic
What s New in Type 2? Peter Hammond Consultant Physician Harrogate District Hospital
 What s New in Type 2? Peter Hammond Consultant Physician Harrogate District Hospital Therapy considerations in T2DM Thiazoledinediones DPP IV inhibitors GLP 1 agonists Insulin Type Delivery Horizon scanning
What s New in Type 2? Peter Hammond Consultant Physician Harrogate District Hospital Therapy considerations in T2DM Thiazoledinediones DPP IV inhibitors GLP 1 agonists Insulin Type Delivery Horizon scanning
Diabetes, Type 2 Management
 CLINICAL GUIDELINE Diabetes, Type 2 Management A guideline is intended to assist healthcare professionals in the choice of disease-specific treatments. Clinical judgement should be exercised on the applicability
CLINICAL GUIDELINE Diabetes, Type 2 Management A guideline is intended to assist healthcare professionals in the choice of disease-specific treatments. Clinical judgement should be exercised on the applicability
Overview. NOT A REPETION OF LOCAL GUIDELINE Dr Diviash Thakrar
 Overview 1. Why hypertension is important? 2. What are basic principles in treatment? 3. Different ways of measuring 4. Hypercholesterolemia NOT A REPETION OF LOCAL GUIDELINE CVD risk factors? Non modifiable
Overview 1. Why hypertension is important? 2. What are basic principles in treatment? 3. Different ways of measuring 4. Hypercholesterolemia NOT A REPETION OF LOCAL GUIDELINE CVD risk factors? Non modifiable
Case Study: Chris Arden. Peripheral Arterial Disease
 Case Study: Chris Arden Peripheral Arterial Disease Patient Presentation Diane is a 65-year-old retired school teacher She complains of left calf pain when walking 50 metres; the pain goes away after she
Case Study: Chris Arden Peripheral Arterial Disease Patient Presentation Diane is a 65-year-old retired school teacher She complains of left calf pain when walking 50 metres; the pain goes away after she
