Whole body and regional body composition analysis by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in cirrhotic patients
|
|
|
- Bruno Walker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 810±814 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Whole body and regional body composition analysis by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in cirrhotic patients O Riggio 1, A Andreoli 2, F Diana 1, P Fiore 1, P Meddi 1, R Lionetti 1, F Montagnese 1, M Merli 1, L Capocaccia 1 and A De Lorenzo 2 1 II Gastroenterologia, UniversitaÁ, La Sapienza and 2 Fisiologia Umana, UniversitaÁ di Tor Vergata, Rome, Italy Objectives: To compare whole body and regional (arms, legs and trunk) fat mass, fat-free mineral-free mass, bone mineral content and bone mineral density, measured by DXA, in cirrhotic patients and age, sex and BMI matched healthy volunteers. Design: Cross-sectional study. Setting: Two medical research institutions. Subjects: Twenty-two non ascitic cirrhotic patients and 16 age, sex and BMI matched healthy volunteers. Interventions: The Lunar DPX whole-body X-ray densitometer with Lunar software version 3.6z (Lunar Radiation Corp., Madison WI, USA) was used. Regional analysis was performed on the arms, legs, trunk and head. Results: Compared to controls, cirrhotic patients showed a signi cant reduction in percentage body fat. When differentiated by gender, however, the reduction in percentage body fat was evident in female cirrhotics only, particularly in the trunk. In male cirrhotic patients fat-free mineral-free mass was reduced in absolute terms in the whole body and the limbs. For both genders and in each body segment bone mineral content and density were reduced in cirrhotics compared to controls. In cirrhotic patients bone mineral density was signi cantly correlated to both fat-free, mineral-free mass (r ˆ 0.85; P < 0.001) and to the Physical Activity Index (r ˆ 0.52; P < 0.01). Conclusions: Two different patterns of soft tissue loss may be found in cirrhotic patients: in women lean tissue is maintained while fat stores are reduced, as in early starvation; in men lean tissue is reduced, as seen under conditions of stress. Moreover, factors in uencing lean body mass, such as nutritional depletion and physical inactivity, may contribute to the reduction of bone density frequently observed in cirrhotic patients. Sponsorship: This work has been funded by the University of Rome, `La Sapienza' research grant MURST 60%, Descriptors: body composition; dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry; cirrhosis Introduction The measurement of body composition in cirrhotic patients is of particular interest, not only because it can provide additional and more precise information on their nutritional status, but also because the estimation of metabolically active body compartments by means of body composition analysis is essential in standardizing physiological processes, such as energy expenditure and protein turnover. A comparison of these processes between cirrhotics and healthy individuals may help explain the mechanism by which malnutrition arises in these patients. Although several methods have been applied (Madden & Morgan, 1994; Muller et al, 1992; McCullough et al, 1991; Crawford et al, 1994; Olroyd et al, 1993; Prijatmoko et al, 1993), an analysis of body composition in cirrhotic patients is not easy to perform. Simple bed-side methods, skinfold anthropometry for example, while useful for epidemiological purposes (Italian Multicentre Cooperative Project on nutrition in liver cirrhosis, 1994; Merli et al, 1996), are not always accurate (Frost & Corish, 1989). Bioelectrical impedance analysis may not provide valid data on body composition in patients whose state of Correspondence: Dr O Riggio, Via Costantino MAES 68, Roma, Italy. Received 30 December 1996; revised 8 July 1997; accepted 22 July 1997 hydratation is variable (Katch et al, 1986; Jebb & Elia, 1991; De Lorenzo et al, 1991), as is the case with cirrhotic patients (McCullough et al, 1991; Olroyd et al, 1993; Prijatmoko et al, 1993; Guglielmi et al, 1991). The estimation of body composition from Total Body Potassium (TBK) or Total Body Water (TBW) is based on assumptions made regarding healthy individuals and has never been validated in cirrhotic patients in whom TBK may be reduced (Podolsky et al, 1973) and fractional hydratation of body lean and cell mass may be increased (McCullough et al, 1991; Olroyd et al, 1993; Prijatmoko et al, 1993). Finally, the application of in vivo neutral activation analysis (IVNAA) can only be performed in a few specialized centers and thus in a limited number of patients. Dual X-ray absorptiometry is a safe, convenient and non invasive technique for assessing body composition (Mazess et al, 1990). By applying this method Fat Mass (FM), Bone Mineral Content (BMC), namely mass in grams of the inorganic calci ed content of bone, Bone Mineral Density (BMD), namely bone mass per unit of projected bone area in g=cm 2 ) and Fat-Free Mineral- Free Mass (FFMFM) can be estimated, and whole body and regional analysis (arms, legs and trunk) may be performed. This study aimed to determine the above three body compartments in non ascitic cirrhotic patients and age, gender and body size-matched controls.
2 Table 1 Etiology and functional severity of liver injury in the 22 cirrhotic patients 811 Etiology Patients HCV 10 Alcoholic 4 Cryptogenetic 2 HCV alcoholic 2 HBV HDV 2 HBV alcoholic 1 PBC 1 Child±PUGH A 9 B 12 C 1 Bilirubin (mg/dl) Prothrombin activity (%) Albumin (g/dl) HCV ˆ Hepatitis C virus; HBV ˆ Hepatitis B virus; HDV ˆ Hepatitis Delta virus; PBC ˆ Primary Biliary Cirrhosis. Table 2 Comparison between cirrhotic patients and matched healthy volunteers Cirrhotics Controls Sex (M/F) 12/10 7/9 Age NS Weight (kg) NS Height (cm) NS BMI (kg/m 2 ) NS Mean SD. Patients and methods Twenty-two cirrhotic patients hospitalised for diagnostic and=or therapeutic reasons were included in the study. Patient's characteristics are reported in Table 1. Aetiology of liver disease was based on histological, clinical and laboratory variables. The severity of cirrhosis was assessed using the Child-Pugh grading system, performed in each patient on entry. Ten of these patients had clinical and ultrasonographical evidence of uid retention at entry. Fluid retention was treated with diuretics or paracenthesis and body composition measurements were made when ascites (at ultrasonography) or oedema was no longer detectable. Sixteen healthy volunteers of similar age and Body Mass Index were used as controls. The comparison Figure 1 Correlation between whole body mass by DXA and body weight by gravimetry. between cirrhotics and matched controls is reported in Table 2. DXA measurements were made on subjects in the postabsorptive state immediately after emptying the bladder and with no uid intake in the previous 4 hrs. The Lunar DPX whole-body X-ray densitometer with Lunar software version 3.6z (Lunar Radiation Corp., Madison WI, USA) was used. This instrument used a rectilinear scanner, running at medium speed, to detect density differences through the subject, lying undressed on a scan table. Regional analysis was performed on the arms, legs, trunk and head. This analysis provides mass in grams of bone mineral content, fat, lean (fat-free, mineral-free mass) and the sum of the body tissues for segments and whole body. The determination of whole body mass by DXA and body weight by gravimetry were compared (Figure 1). Each patient lled in a questionnaire regarding their usual daily routine. Questions were asked about how many hours are spent sleeping, awake but in repose or in physical activity (housework, personal care, outdoor pursuits, etc.) (Wilson et al, 1986). An index (in percent) was calculated by simply dividing the number of hours devoted to physical activity by 24. Data from cirrhotics and controls were compared using the Student t-test. All results are espressed as mean SD Table 3 Regional analysis of body composition in cirrhotics and controls (MeanSD) (kg) (g=cm 2 ) (kg) (kg) (kg) ( % ) Cirrhotics Arms Controls t-test ns ns ns ns ns ns Cirrhotics Trunk Controls t-test P < P < P < 0.05 ns ns P < Cirrhotics Legs Controls t-test ns ns ns ns ns ns Cirrhotics Total body Controls t-test P < 0.05 P < 0.01 ns ns ns P < 0.05 BMC ˆ Bone Mineral Content; BMD ˆ Bone Mineral Density; FM ˆ Fat Mass; FF-MFM ˆ Fat Free Mineral-Free Mass.
3 812 5), BMC and BMD were signi cantly reduced in both genders and in each body segment compared with respective controls, while percent body fat was signi cantly reduced in female cirrhotics only, particularly in the trunk. In male cirrhotic patients fat-free, mineral-free mass was lower in absolute terms but not in percentage in the whole body or in the limbs (Table 4). In the cirrhotic group the BMD was signi cantly correlated to both body weight (r ˆ 0.65; P < 0.001) and fat-free, mineral-free mass (r ˆ 0.85; P < 0.001), but not to body fat (r ˆ 0.19; ns) (Figure 2). BMD was also correlated to the physical activity index (r ˆ 0.52; P < 0.01). The mean physical activity index of cirrhotic patients was 18 10%. Figure 2 Correlation between whole body BMD and Fat-Free Mineral- Free Mass, Fat Mass and Body Weight in cirrhotic patients. Results Regional and whole body composition analysis in the entire group of cirrhotics and controls is reported in Table 3. A signi cant reduction in whole body bone mineral content, bone mineral density and percent fat was observed in cirrhotics. By dividing the subjects by sex (Tables 4 and Discussion DXA has been introduced as a precise, safe and relatively inexpensive tool to measure body composition in humans. DXA is associated with a low radiation exposure (Lang et al, 1991) and provides bone mineral as well as fat and lean tissue mass, and thus body composition may be estimated according to the three-component model (Lukasky, 1993). DXA has been validated in animal studies where carcass analysis is possible (Svendsen et al, 1993) and in humans by comparing other methods for estimating body composition, such as under-water weighing (Johansson et al, 1993), skinfold thickness, bioelectrical impedance and TBW (Pritchard et al, 1993), TBK and TBN (Aloia et al, 1995). Both the precision and the agreement of DXA with other methods are considered excellent for bone mineral content, and very good for fat mass. On the other hand, DXA tends to underestimate lean mass, especially at highest values (Aloia et al, 1995). In cirrhotic patients DXA has been compared to TBK, BIA and skinfold anthropometry (Bramley et al, 1993) and to a multicompartmental model based on IVNAA and TBW measurements (Prijatmoko et al, 1993). Again a good agreement for fat mass estimation was found for the different methods. The main advantage of DXA is that regional measurements may be made (for each arm, leg, the head and trunk), which are particularly useful in bone mass estimation. In this study, DXA was applied to a group of cirrhotic patients without overt uid retention. This does not exclude slight over-hydration in our patients. However it has been recently shown that slight changes in hydration have little in uence on the estimation of soft tissue composition by DXA (Pietrobelli et al, 1996). The comparison with age Table 4 Regional analysis of body composition in male cirrhotics and controls (Mean s.d.) (kg) (g=cm 2 ) (kg) (kg) (kg) ( % ) Cirrhotics Arms Controls t-test P < P < NS P < NS NS Cirrhotics Trunk Controls t-test P < P < NS NS NS NS Cirrhotics Legs Controls t-test P < P < NS P < P < 0.05 NS Cirrhotics Total body Controls t-test P < P < NS P < 0.01 NS NS BMC ˆ Bone Mineral Content; BMD ˆ Bone Mineral Density; FM ˆ Fat Mass; FF MFM ˆ Fat-Free Mineral-Free Mass.
4 Table 5 Regional analysis of body composition in female cirrhotics and controls (Mean s.d.) (kg) (g=cm (kg) (kg) (kg) ( % ) 813 Cirrhotics Arms Controls t-test NS P < 0.05 NS NS NS NS Cirrhotics Trunk Controls t-test P < 0.01 P < P < 0.05 NS NS P < Cirrhotics Legs Controls t-test P < 0.05 P < NS NS NS NS Cirrhotics Total body Controls t-test P < 0.01 P < 0.01 NS NS NS P < 0.05 BMC ˆ Bone Mineral Content; BMD ˆ Bone Mineral Density; FM ˆ Fat Mass; FF-MFM ˆ Fat Free Mineral-Free Mass. and BMI-matched healthy controls shows that in cirrhotic patients soft tissue is characterised by a reduced percent of fat mass. This agreees with what has already been reported using other methodologies, such as skinfold anthropometry (Madden & Morgan, 1994), TBK (Crawford et al, 1994) and TBW (McCoullogh et al, 1991). However, if a distinction is made between genders, reduced percent fat mass was only evident in females. Gender differences in body tissue loss have already been reported in epidemiological studies on the prevalence of malnutrition in cirrhotic patients (Italian Multicentre Cooperative Project on nutrition in liver cirrhosis 1994; Caregaro et al, 1996). In such studies adipose tissue was more frequently depleted in females than in males with cirrhosis, while lean tissue was more often affected in males. Also, in the present study, fat-free mineral-free mass was signi cantly lower, in absolute terms, in male cirrhotics only. Thus, according to the present and previous observations, two different patterns of tissue loss may be found in cirrhotic patients: in women lean tissue is maintained while fat stores are reduced, as in early starvation; in men lean tissue is reduced and body fat is normal, as seen under conditions of stress. These two patterns of tissue loss have also been observed in cirrhotics by Crawford et al, in 1994, who unfortunately did not provide gender differentiated data. The reason for a gender difference in tissue loss in cirrhotic patients could be merely related to the abundance of fat stores in female, which are progressively used to cope with the metabolic needs until muscle mass remains the exclusive energy store. Conclusions Previous observations on reduced bone mineral content and density in cirrhotic patients (Bonkovsky et al, 1990) are con rmed in our study. Bone loss in patients with cirrhosis of various etiology and not only in those affected by alcoholic or cholestatic liver diseases has emerged as a clinical problem, because bone alterations are not corrected but are even accentuated after liver transplantation (Meys et al, 1994). The mechanism underlying bone loss in cirrhotic patients is complex and multifactorial. One basic assumption, however, is that skeletal mass and density are both in uenced by mechanical loading, namely gravitational forces and muscular activity (Slemenda, 1995). In the present study, signi cant correlations were found in cirrhotics between BMD and both fat-free mineral-free mass and the physical activity index, emphasising the role of lean (muscle) tissue as an important factor for bone maintenance. Thus, factors in uencing muscle mass, such as nutritional depletion, altered protein turnover and physical inactivity may also, at least in part, negatively affect bone density. Although these factors are probably not speci c for liver cirrhosis, they should be taken into consideration in future studies on bone alteration in these patients. References Aloia JF, Vaswani A, Ma R & Flaster E (1995): Comparative study of body composition by Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry. J. Nucl. Med. 36, 1392±1397. Bonkovsky H, Hawkins M, Steinberg K, Hersh T, Galambos J, Henderson J, Millikan W & Galloway J (1990): Prevalence and prediction of osteopenia in chronic liver disease. Hepatology 12, 273±280. Bramley P, Oldroyd B, Stewart S, Simpson M, Truscott J, Losowsky M & Smith M (1993): Body composition analysis in liver cirrhosis. The measurement of body fat by Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry in comparison to skinfolds anthropometry, bioelectrical impedance and total body potassium. In Human body composition. eds. KJ Kellis & JD Eastman. New York: Plenum Press. 211±214 Caregaro L, Alberino F, Amodio P, Markel C, Bolognesi M, Angeli P & Gatta A (1996): Malnutrition in alcoholic and virus-related cirrhosis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 63, 602±609. Crawford DHG, Shepherd RW, Halliday JW, Cooksley GWGE, Golding SD, Cheng WSC & Powell LW (1994): Body composition in nonalcoholic cirrhosis: the effects of disease etiology and severity on nutritional compartments. Gastroenterology 106, 1611±1617. De Lorenzo A, Barra PFA, Sasso GF, Battistini NC & Deurenberg P (1991): Body impedance measurement during dialysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 45, 321±325. Frost GS & Corish C (1989): Reproducibility of upper-arm anthropometry in subjects of differing body mass. J. Human Nutr. Dietology 2, 403± 406. Guglielmi FW, Contento F, Laddaga L, Panella C & Francavilla A (1991): Bioelectrical impedance analysis: experience with male patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 13, 892±895. Italian Multicentre Cooperative Project on nutrition in liver cirrhosis (1994): Nutritional status in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 21, 317±325. Jebb SA & Elia M (1991): Assessment of changes in total body water in patients undergoing renal dialysis using bioelectrical analysis. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 50, 153A. Johansson AG, Forslund A, Sjodin A, Mallmin H, Hambraeus L & Ljunghall S (1993): Determination of body compositionða comparison of Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry and hidrodensitometry. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 57, 323±326. Katch FI, Soloman RT, Shayevitz M & Shayevitz B (1986): Validity of bioelectrical impedance to estimate body composition in cardiac and pulmonary patients. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 43, 972±973. Lang P, Steiger P, Faulkner K, Gluer C & Genant HK (1991): Osteoporosis: current techniques and recent developments in quantitative bone densitometry. Radiol. Clin. North Am. 29, 49±76.
5 814 Lukasky HC (1993): Soft tissue composition and bone mineral status: evaluation by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry. J. Nutr. 123, 438± 443. Madden AM & Morgan MY (1994): A comparison of skinfold anthropometry and bioelectrical impedance analysis for measuring percentage body fat in patients with cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 21, 878± 883. Mazess RB, Bardin HS, Bisek JP & Hanson J (1990): Dual energy x-ray absorptiometry for total body and regional bone mineral and soft tissue composition. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 51, 1106±1112. McCullough AJ, Mullen KD & Kalhan SC (1991): Measurements of total body and extracellular water in cirrhotic patients with and without ascites. Hepatology 14, 1102±1111. Merli M, Riggio O, Dally L & PINC (1996): Does malnutrition affect survival in cirrhosis. Hepatology 23, 1041±1046 Meys E, Fontages E, Fourcade N, Thomasson A, Pouyet M & Delmas PD (1994): Bone loss after orthotopic liver transplantation. Am. J. Med. 97, 445±450. Muller MJ, Lautz HU, Plogmann B, Burger M, Korber J & Schmidt FW (1992): Energy expenditure and substrate oxidation in patients with cirrhosis: the impact of cause, clinical staging and nutritional state. Hepatology 15, 782±794. Olroyd B, Bramley PN, Stewart SP, Simpson M, Truscott JC, Losowsky MS & Smith MA (1993): A four-compartment model to determine body composition in liver cirrhosis. In Human Body Composition, eds. KJ Kellis & JD Eastman. New York: Plenum Press. 221±224 Pietrobelli A, Formica C, Wang Z & Heyms eld SB (1996): Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry body composition model:review of physical concepts. Am. J. Physiol. 271, E941±E951. Podolsky S, Zimmerman HJ, Burrows BA, Cardarelli JA & Pattavina CG (1973): Potassium depletion in hepatic cirrhosis. A reversible cause of impaired growth-hormone and insulin response to stimulation. New England J. Med. 288, 644±648. Prijatmoko DWI, Strauss BJG, Lambert JR, Sievert W, Stroud DB, Wahlqvist ML, Katz B, Colman J, Jones P & Korman MG (1993): Early detection of protein depletion in alcoholic cirrhosis: role of body composition analysis. Gastroenterology 105, 1839±1845. Pritchard JE, Nowson CA, Strauss BJ, Carlson JS, Kaymakci B & Wark JD (1993): Evaluation of Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry as a method of measurement of body fat. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 47, 216±228. Slemenda CW (1995): Editorial: Body composition and skeletal densityð Mechanical loading or something more? J. Clin. End. Met. 80, 1761± Svendsen OL, Haarbo J, Hassager C & Christiansen C (1993): Accuracy of measurements of body composition by Dual Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry in vivo. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 57, 605±608. Wilson PWF, Paffenbarger RS, Morris JN & Havlink RJ (1986): Assessment methods for physical activity and physical tness in population studies: Report of a NHLBI workshop. Am. Heart J. 111, 1177±1192.
Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics differ between manufacturers
 European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 449±454 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 449±454 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics
Cross-calibration of fat and lean measurements by dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry to pig carcass analysis in the pediatric body weight range13
 Cross-calibration of fat and lean measurements by dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry to pig carcass analysis in the pediatric body weight range13 Stephen J Pintauro, Tim R Nagy, Christa M Duthie, and Michael
Cross-calibration of fat and lean measurements by dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry to pig carcass analysis in the pediatric body weight range13 Stephen J Pintauro, Tim R Nagy, Christa M Duthie, and Michael
Differences in whole body measurements by DXA-scanning using two Lunar DPX-L machines
 International Journal of Obesity (1999) 23, 764±770 ß 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ijo Short Communication Differences in whole body measurements
International Journal of Obesity (1999) 23, 764±770 ß 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ijo Short Communication Differences in whole body measurements
Segmental Body Composition Assessment for Obese Japanese Adults by Single-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with 8-point Contact Electrodes
 Segmental Body Composition Assessment for Obese Japanese Adults by Single-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with 8-point Contact Electrodes Susumu Sato 1), Shinichi Demura 2), Tamotsu Kitabayashi
Segmental Body Composition Assessment for Obese Japanese Adults by Single-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with 8-point Contact Electrodes Susumu Sato 1), Shinichi Demura 2), Tamotsu Kitabayashi
Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment
 Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott,
Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott,
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry to Determine Body Composition
 Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Determine Body Composition Description Using low dose x-rays of two different energy levels, whole body dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measures lean tissue
Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Determine Body Composition Description Using low dose x-rays of two different energy levels, whole body dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measures lean tissue
The Influence of Exogenous Fat and Water on Lumbar Spine Bone Mineral Density in Healthy Volunteers
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.2.289 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 53(2):289-293, 2012 The Influence of Exogenous Fat and Water on Lumbar Spine Bone Mineral Density
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2012.53.2.289 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 53(2):289-293, 2012 The Influence of Exogenous Fat and Water on Lumbar Spine Bone Mineral Density
Estimation of body composition from bioelectrical impedance of body segments : comparison with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
 British Journal of Nutrition (1993), 69, 645-655 645 Estimation of body composition from bioelectrical impedance of body segments : comparison with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry BY S. P. STEWART1, P.
British Journal of Nutrition (1993), 69, 645-655 645 Estimation of body composition from bioelectrical impedance of body segments : comparison with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry BY S. P. STEWART1, P.
9 Quality Assurance in Bone Densitometry section
 9 Quality Assurance in Bone Densitometry section Introduction Bone densitometry is frequently used to determine an individual's fracture risk at a particular point in time but may also be used to assess
9 Quality Assurance in Bone Densitometry section Introduction Bone densitometry is frequently used to determine an individual's fracture risk at a particular point in time but may also be used to assess
J EisenkoÈlbl 1, M Kartasurya 1 and K Widhalm 1 * Introduction
 (2001) 55, 423±429 ß 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954±3007/01 $15.00 www.nature.com/ejcn Original Communication Underestimation of percentage fat mass measured by bioelectrical impedance
(2001) 55, 423±429 ß 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954±3007/01 $15.00 www.nature.com/ejcn Original Communication Underestimation of percentage fat mass measured by bioelectrical impedance
Bioelectrical impedance analysis to assess body composition in obese adult women: The effect of ethnicity
 International Journal of Obesity (1998) 22, 243±249 ß 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/98 $12.00 Bioelectrical impedance analysis to assess body composition in obese adult women: The effect
International Journal of Obesity (1998) 22, 243±249 ß 1998 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/98 $12.00 Bioelectrical impedance analysis to assess body composition in obese adult women: The effect
A multi-center comparison of dual energy X-ray absorptiometers: In vivo and in vitro soft tissue measurement
 European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 312±317 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 A multi-center comparison of dual energy X-ray absorptiometers: In vivo and in vitro
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 312±317 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 A multi-center comparison of dual energy X-ray absorptiometers: In vivo and in vitro
DUAL ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY (DXA) GOLD STANDARD FOR BONE HEALTH AND BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT
 DUAL ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY (DXA) GOLD STANDARD FOR BONE HEALTH AND BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT Prof d-r Slavica Šubeska Stratrova Clinic of Endocrinology, Skopje, Macedonia Definition and classification
DUAL ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY (DXA) GOLD STANDARD FOR BONE HEALTH AND BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT Prof d-r Slavica Šubeska Stratrova Clinic of Endocrinology, Skopje, Macedonia Definition and classification
Understanding Body Composition
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines 7 Understanding Body Composition Objectives Define body composition. Explain why the assessment of body size, shape, and composition is useful. Explain how to perform assessments
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines 7 Understanding Body Composition Objectives Define body composition. Explain why the assessment of body size, shape, and composition is useful. Explain how to perform assessments
Body composition A tool for nutritional assessment
 Body composition A tool for nutritional assessment Ingvar Bosaeus Clinical Nutrition Unit Sahlgrenska University Hospital NSKE Oslo 2012-01-18 Outline What is body composition? What is nutritional assessment?
Body composition A tool for nutritional assessment Ingvar Bosaeus Clinical Nutrition Unit Sahlgrenska University Hospital NSKE Oslo 2012-01-18 Outline What is body composition? What is nutritional assessment?
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Birth Date: 40.2 years Height / Weight: 158.0 cm 52.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 50% 40% 30% 20% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Birth Date: 40.2 years Height / Weight: 158.0 cm 52.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 50% 40% 30% 20% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Body composition in children and adults by air displacement plethysmography
 European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1999) 53, 382±387 ß 1999 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ejcn Body composition in children and adults by
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1999) 53, 382±387 ß 1999 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/ejcn Body composition in children and adults by
Anthropometry and methods of body composition measurement for research and eld application in the elderly
 (2000) 54, Suppl 3, S26±S32 ß 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0954±3007/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/ejcn Anthropometry and methods of body composition measurement for research and eld application
(2000) 54, Suppl 3, S26±S32 ß 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0954±3007/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/ejcn Anthropometry and methods of body composition measurement for research and eld application
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in Dexa Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Birth Date: 24.7 years Height / Weight: 8.0 cm 79.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 40% 30% 20% 0% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 00 Centile
Birth Date: 24.7 years Height / Weight: 8.0 cm 79.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 40% 30% 20% 0% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 00 Centile
Medical Policy. MP Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry to Determine Body Composition
 Medical Policy MP 6.01.40 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 6.01.40 Last Review: 09/28/2017 Effective Date: 09/28/2017 Section: Radiology End Date: 09/18/2018 Related Policies 6.01.44 Vertebral Fracture Assessment With
Medical Policy MP 6.01.40 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 6.01.40 Last Review: 09/28/2017 Effective Date: 09/28/2017 Section: Radiology End Date: 09/18/2018 Related Policies 6.01.44 Vertebral Fracture Assessment With
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 48.2 years Height / Weight: 150.0 cm 72.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 48.2 years Height / Weight: 150.0 cm 72.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
NUTRITIONAL OPTIMIZATION IN PRE LIVER TRANSPLANT PATIENTS
 NUTRITIONAL OPTIMIZATION IN PRE LIVER TRANSPLANT PATIENTS ACHIEVING NUTRITIONAL ADEQUACY Dr N MURUGAN Consultant Hepatologist Apollo Hospitals Chennai NUTRITION IN LIVER FAILURE extent of problem and consequences
NUTRITIONAL OPTIMIZATION IN PRE LIVER TRANSPLANT PATIENTS ACHIEVING NUTRITIONAL ADEQUACY Dr N MURUGAN Consultant Hepatologist Apollo Hospitals Chennai NUTRITION IN LIVER FAILURE extent of problem and consequences
The Assessment of Body Composition in Health and Disease
 The Assessment of Body Composition in Health and Disease Giorgio Bedogni, Paolo Brambilla, Stefano Bellentani and Claudio Tiribelli CHAPTER 3 BODY AND NUTRITIONAL STATUS Nutritional status can be operationally
The Assessment of Body Composition in Health and Disease Giorgio Bedogni, Paolo Brambilla, Stefano Bellentani and Claudio Tiribelli CHAPTER 3 BODY AND NUTRITIONAL STATUS Nutritional status can be operationally
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 43.4 years Height / Weight: 170.0 cm 66.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 43.4 years Height / Weight: 170.0 cm 66.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
Kosuke Yoshida, MD, Yoko Aburakawa, MD, PhD, Yasuhiro Suzuki, MD, PhD, Kenji Kuroda, MD, PhD and Takashi Kimura, MD, PhD
 Kosuke Yoshida, MD, Yoko Aburakawa, MD, PhD, Yasuhiro Suzuki, MD, PhD, Kenji Kuroda, MD, PhD and Takashi Kimura, MD, PhD Depertment of Neurology, Asahikawa Medical Center, National Hospital Organization,
Kosuke Yoshida, MD, Yoko Aburakawa, MD, PhD, Yasuhiro Suzuki, MD, PhD, Kenji Kuroda, MD, PhD and Takashi Kimura, MD, PhD Depertment of Neurology, Asahikawa Medical Center, National Hospital Organization,
BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES. Abstract. Introduction. Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, UDC :572.
 EXERCISE AND QUALITY OF LIFE Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, 43-48 UDC 796.034.6-051:572.087 Research article BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES Jelena Popadiã Gaãeša *, Otto Barak, Dea Karaba
EXERCISE AND QUALITY OF LIFE Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, 43-48 UDC 796.034.6-051:572.087 Research article BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES Jelena Popadiã Gaãeša *, Otto Barak, Dea Karaba
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017
 ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Paediatric specificities of nutritional assessment Body composition measurement in children N. Mehta (US) 39 th ESPEN Congress The Hague, Netherlands Body Composition Measurement
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Paediatric specificities of nutritional assessment Body composition measurement in children N. Mehta (US) 39 th ESPEN Congress The Hague, Netherlands Body Composition Measurement
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) to Determine Body Composition
 Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) to Determine Body Composition Policy Number: 6.01.40 Last Review: 4/2018 Origination: 4/2005 Next Review: 4/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) to Determine Body Composition Policy Number: 6.01.40 Last Review: 4/2018 Origination: 4/2005 Next Review: 4/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City
Adult BMI Calculator
 For more information go to Center for Disease Control http://search.cdc.gov/search?query=bmi+adult&utf8=%e2%9c%93&affiliate=cdc-main\ About BMI for Adults Adult BMI Calculator On this page: What is BMI?
For more information go to Center for Disease Control http://search.cdc.gov/search?query=bmi+adult&utf8=%e2%9c%93&affiliate=cdc-main\ About BMI for Adults Adult BMI Calculator On this page: What is BMI?
Bone Mineral Density in Thai Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C, before and after Treatment with Pegylated Interferon/Ribavirin Combination ABSTRACT
 Original Article 73 before and after Treatment with Pegylated Interferon/Ribavirin Combination Bunchorntavakul C 1 Chotiyaputta W 1 Sriussadaporn S 2 Tanwandee T 1 ABSTRACT Background: Loss of bone mineral
Original Article 73 before and after Treatment with Pegylated Interferon/Ribavirin Combination Bunchorntavakul C 1 Chotiyaputta W 1 Sriussadaporn S 2 Tanwandee T 1 ABSTRACT Background: Loss of bone mineral
C H A P T E R 14 BODY WEIGHT, BODY COMPOSITION, AND SPORT
 C H A P T E R 14 BODY WEIGHT, BODY COMPOSITION, AND SPORT Learning Objectives Differentiate among body build, body size, and body composition. Find out what tissues of the body constitute fat-free mass.
C H A P T E R 14 BODY WEIGHT, BODY COMPOSITION, AND SPORT Learning Objectives Differentiate among body build, body size, and body composition. Find out what tissues of the body constitute fat-free mass.
Nutrition Assessment in CKD
 Nutrition Assessment in CKD Shiaw-Wen Chien, MD, EMBA Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Tungs Taichung MetroHarbor Hospital Taichung, Taiwan September 10, 2017 Outline Introduction Composite
Nutrition Assessment in CKD Shiaw-Wen Chien, MD, EMBA Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Tungs Taichung MetroHarbor Hospital Taichung, Taiwan September 10, 2017 Outline Introduction Composite
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 29.5 years Height / Weight: 156.0 cm 57.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 29.5 years Height / Weight: 156.0 cm 57.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
Validation Study of Multi-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance with Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Among Obese Patients
 OBES SURG (2014) 24:1476 1480 DOI 10.1007/s11695-014-1190-5 OTHER Validation Study of Multi-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance with Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Among Obese Patients Silvia L. Faria
OBES SURG (2014) 24:1476 1480 DOI 10.1007/s11695-014-1190-5 OTHER Validation Study of Multi-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance with Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Among Obese Patients Silvia L. Faria
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in Dexa Total Body 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
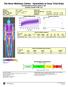 Patient: Obese, Sample Birth Date: 0/Jan/966 44.4 years Height / Weight: 72.0 cm 95.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Referring Physician: DR. SMITH Measured: 07/Jun/200 7:0:52 PM (.40) Analyzed: 02/Apr/203
Patient: Obese, Sample Birth Date: 0/Jan/966 44.4 years Height / Weight: 72.0 cm 95.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Referring Physician: DR. SMITH Measured: 07/Jun/200 7:0:52 PM (.40) Analyzed: 02/Apr/203
Bone Mineral and Body Composition Measurements: Cross-Calibration of Pencil-Beam and Fan-Beam Dual- Energy X-Ray Absorptiometers*
 JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH Volume 13, Number 10, 1998 Blackwell Science, Inc. 1998 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Bone Mineral and Body Composition Measurements: Cross-Calibration
JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH Volume 13, Number 10, 1998 Blackwell Science, Inc. 1998 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Bone Mineral and Body Composition Measurements: Cross-Calibration
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) to Determine Body Composition. Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 6.01.28 Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) to Determine Body Composition Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 12:2012 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date reviewed
MP 6.01.28 Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) to Determine Body Composition Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 12:2012 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date reviewed
Understanding & Interpreting Body Composition Measures
 BODY COMPOSITION Understanding & Interpreting Body Composition Measures Body composition = component of health-related fitness & = component of metabolic fitness Unlike other health-related fitness Not
BODY COMPOSITION Understanding & Interpreting Body Composition Measures Body composition = component of health-related fitness & = component of metabolic fitness Unlike other health-related fitness Not
ESPEN Congress Prague 2007
 ESPEN Congress Prague 2007 Nutrition implication of obesity and Type II Diabetes Nutrition support in obese patient Claude Pichard Nutrition Support in Obese Patients Prague, 2007 C. Pichard, MD, PhD,
ESPEN Congress Prague 2007 Nutrition implication of obesity and Type II Diabetes Nutrition support in obese patient Claude Pichard Nutrition Support in Obese Patients Prague, 2007 C. Pichard, MD, PhD,
Evaluation of two foot-to-foot bioelectrical impedance analysers to assess body composition in overweight and obese adolescents
 British Journal of Nutrition (2003), 90, 987 992 q The Authors 2003 DOI: 10.1079/BJN2003983 Evaluation of two foot-to-foot bioelectrical impedance analysers to assess body composition in overweight and
British Journal of Nutrition (2003), 90, 987 992 q The Authors 2003 DOI: 10.1079/BJN2003983 Evaluation of two foot-to-foot bioelectrical impedance analysers to assess body composition in overweight and
Association of Lean Tissue and Fat Mass with Bone Mineral Content in Children and Adolescents
 Association of Lean Tissue and Fat Mass with Bone Mineral Content in Children and Adolescents Angelo Pietrobelli,* Myles S. Faith,* Jack Wang,* Paolo Brambilla, Giuseppe Chiumello, and Steven B. Heymsfield*
Association of Lean Tissue and Fat Mass with Bone Mineral Content in Children and Adolescents Angelo Pietrobelli,* Myles S. Faith,* Jack Wang,* Paolo Brambilla, Giuseppe Chiumello, and Steven B. Heymsfield*
High Prevalence of Vitamin A Deficiency and Vitamin D Deficiency in Patients Evaluated for Liver Transplantation
 LIVER TRANSPLANTATION 19:627 633, 2013 ORIGINAL ARTICLE High Prevalence of Vitamin A Deficiency and Vitamin D Deficiency in Patients Evaluated for Liver Transplantation Mukund Venu, Eric Martin, Kia Saeian,
LIVER TRANSPLANTATION 19:627 633, 2013 ORIGINAL ARTICLE High Prevalence of Vitamin A Deficiency and Vitamin D Deficiency in Patients Evaluated for Liver Transplantation Mukund Venu, Eric Martin, Kia Saeian,
Evidence Analysis Library Research Project
 Evidence Analysis Library Research Project EAL question: What is the evidence to support the use of supplementing BCAA in patients with cirrhosis to 1) prevent further liver damage or improve liver function;
Evidence Analysis Library Research Project EAL question: What is the evidence to support the use of supplementing BCAA in patients with cirrhosis to 1) prevent further liver damage or improve liver function;
Body Composition. Lecture Overview. Measuring of Body Composition. Powers & Howely pp Methods of measuring body composition
 Body Composition Powers & Howely pp 344-356 Lecture Overview Methods of measuring body composition Two-component system Body fatness for health & fitness Obesity and weight control Diet, exercise, and
Body Composition Powers & Howely pp 344-356 Lecture Overview Methods of measuring body composition Two-component system Body fatness for health & fitness Obesity and weight control Diet, exercise, and
Duncan Macfarlane IHP, HKU Parts of this lecture were based on lecture notes provided by the Lindsay Carter Anthropometric Archive, AUT, NZ
 Body composition assessment issues in athletes 1 Duncan Macfarlane IHP, HKU Parts of this lecture were based on lecture notes provided by the Lindsay Carter Anthropometric Archive, AUT, NZ LEARNING OUTCOMES:
Body composition assessment issues in athletes 1 Duncan Macfarlane IHP, HKU Parts of this lecture were based on lecture notes provided by the Lindsay Carter Anthropometric Archive, AUT, NZ LEARNING OUTCOMES:
BODY COMPOSITION: AN ANALYSIS BETWEEN THE FOOTBALLER AND THANG-TA PRACTITIONER OF MANIPUR
 BODY COMPOSITION: AN ANALYSIS BETWEEN THE FOOTBALLER AND THANG-TA PRACTITIONER OF MANIPUR T. INAOBI SINGH 1, MAIBAM CHOURJIT SINGH 2, CHETAN MAIBAM 3 1 Department of Physical Education & Sports Science,
BODY COMPOSITION: AN ANALYSIS BETWEEN THE FOOTBALLER AND THANG-TA PRACTITIONER OF MANIPUR T. INAOBI SINGH 1, MAIBAM CHOURJIT SINGH 2, CHETAN MAIBAM 3 1 Department of Physical Education & Sports Science,
MP Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry to Determine Body Composition
 Medical Policy MP 6.01.40 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 6.01.40 Last Review: 09/19/2018 Effective Date: 09/19/2018 Section: Radiology Related Policies 6.01.44 Vertebral Fracture Assessment With Densitometry 9.01.502
Medical Policy MP 6.01.40 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 6.01.40 Last Review: 09/19/2018 Effective Date: 09/19/2018 Section: Radiology Related Policies 6.01.44 Vertebral Fracture Assessment With Densitometry 9.01.502
Nutritional Support in Paediatric Patients
 Nutritional Support in Paediatric Patients Topic 4 Module 4.5 Nutritional Evaluation of the Hospitalized Children Learning objectives Olivier Goulet To be aware of how malnutrition presents and how to
Nutritional Support in Paediatric Patients Topic 4 Module 4.5 Nutritional Evaluation of the Hospitalized Children Learning objectives Olivier Goulet To be aware of how malnutrition presents and how to
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies
 Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Femur Bone Measurements Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: DXXFEM_D.XPT January 2009 NHANES 2005 2006 Data
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Femur Bone Measurements Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: DXXFEM_D.XPT January 2009 NHANES 2005 2006 Data
Interpreting DEXA Scan and. the New Fracture Risk. Assessment. Algorithm
 Interpreting DEXA Scan and the New Fracture Risk Assessment Algorithm Prof. Samir Elbadawy *Osteoporosis affect 30%-40% of women in western countries and almost 15% of men after the age of 50 years. Osteoporosis
Interpreting DEXA Scan and the New Fracture Risk Assessment Algorithm Prof. Samir Elbadawy *Osteoporosis affect 30%-40% of women in western countries and almost 15% of men after the age of 50 years. Osteoporosis
Premium solution for your health
 770 Premium solution for your health See What You re Made of Reveal the efficiency of your consultation throughout the InBody Test The InBody Test clearly visualize internal change of the body. Weight
770 Premium solution for your health See What You re Made of Reveal the efficiency of your consultation throughout the InBody Test The InBody Test clearly visualize internal change of the body. Weight
Effect of Precision Error on T-scores and the Diagnostic Classification of Bone Status
 Journal of Clinical Densitometry, vol. 10, no. 3, 239e243, 2007 Ó Copyright 2007 by The International Society for Clinical Densitometry 1094-6950/07/10:239e243/$32.00 DOI: 10.1016/j.jocd.2007.03.002 Original
Journal of Clinical Densitometry, vol. 10, no. 3, 239e243, 2007 Ó Copyright 2007 by The International Society for Clinical Densitometry 1094-6950/07/10:239e243/$32.00 DOI: 10.1016/j.jocd.2007.03.002 Original
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) to Determine Body Composition
 Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) to Determine Body Composition Policy Number: 6.01.40 Last Review: 4/2014 Origination: 4/2005 Next Review: 4/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DEXA) to Determine Body Composition Policy Number: 6.01.40 Last Review: 4/2014 Origination: 4/2005 Next Review: 4/2015 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
Malnutrition in advanced CKD
 Malnutrition in advanced CKD Malnutrition Lack of proper nutrition, caused by not having enough to eat, not eating enough of the right things or being unable to use the food that one does eat Jessica Stevenson
Malnutrition in advanced CKD Malnutrition Lack of proper nutrition, caused by not having enough to eat, not eating enough of the right things or being unable to use the food that one does eat Jessica Stevenson
DEXA Bone Mineral Density Tests and Body Composition Analysis Information for Health Professionals
 DEXA Bone Mineral Density Tests and Body Composition Analysis Information for Health Professionals PERFORMANCE DEXA is an advanced technology originally used to, and still capable of assessing bone health
DEXA Bone Mineral Density Tests and Body Composition Analysis Information for Health Professionals PERFORMANCE DEXA is an advanced technology originally used to, and still capable of assessing bone health
Obesity Increases Precision Errors in Total Body Dual X-ray Absorptiometry Measurements.
 Obesity Increases Precision Errors in Total Body Dual X-ray Absorptiometry Measurements. 1 K.M.Knapp, 1 J.R.Welsman, 1 S.J.Hopkins, 1 A.Shallcross, 2 I.Fogelman and 2 G.M.Blake 1. University of Exeter,
Obesity Increases Precision Errors in Total Body Dual X-ray Absorptiometry Measurements. 1 K.M.Knapp, 1 J.R.Welsman, 1 S.J.Hopkins, 1 A.Shallcross, 2 I.Fogelman and 2 G.M.Blake 1. University of Exeter,
FAT MASS ESTIMATION BY BIOELECTRICAL IMPEDANCE ANALYSIS
 FAT MASS ESTIMATION BY BIOELECTRICAL IMPEDANCE ANALYSIS FAT MASS ESTIMATION BY BIOELECTRICAL IMPEDANCE ANALYSIS Epidemiological studies have shown that relative risk of diabetes and cardiovascular diseases
FAT MASS ESTIMATION BY BIOELECTRICAL IMPEDANCE ANALYSIS FAT MASS ESTIMATION BY BIOELECTRICAL IMPEDANCE ANALYSIS Epidemiological studies have shown that relative risk of diabetes and cardiovascular diseases
Fitness Concepts + Principles Packet. Name: Period:
 Fitness Concepts + Principles Packet Name: Period: Content Pages + Directions 5 Components of Fitness.................................................... Slides 3-12 FITT Principle.........................................................
Fitness Concepts + Principles Packet Name: Period: Content Pages + Directions 5 Components of Fitness.................................................... Slides 3-12 FITT Principle.........................................................
New bioelectrical impedance formula for patients with respiratory insufficiency: comparison to dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry
 Eur Respir J 1998; 12: 960 966 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.98.12040960 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1998 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 New bioelectrical impedance
Eur Respir J 1998; 12: 960 966 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.98.12040960 Printed in UK - all rights reserved Copyright ERS Journals Ltd 1998 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 0903-1936 New bioelectrical impedance
Body Composition Changes Following a Very Low Calorie Pre-Operative Diet in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery
 Body Composition Changes Following a Very Low Calorie Pre-Operative Diet in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery 03 September 2018 Jonathan Sivakumar, Lynn Chong, Salena Ward, Tom R Sutherland, Michael
Body Composition Changes Following a Very Low Calorie Pre-Operative Diet in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery 03 September 2018 Jonathan Sivakumar, Lynn Chong, Salena Ward, Tom R Sutherland, Michael
Introduction. Methods
 (2000) 24, 627±632 ß 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0307±0565/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/ijo Overweight and obese children have low bone mass and area for their weight A Goulding 1 *,
(2000) 24, 627±632 ß 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0307±0565/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/ijo Overweight and obese children have low bone mass and area for their weight A Goulding 1 *,
Interpretation Guide. What you are made of? Find out with - Vital Body Scan NZ Ltd. Mobile Body Composition Analysis
 Interpretation Guide Vital Body Scan NZ Ltd What you are made of? Find out with - Vital Body Scan NZ Ltd Mobile Body Composition Analysis Interpreting your results Total Body Water (TBW) TBW is all the
Interpretation Guide Vital Body Scan NZ Ltd What you are made of? Find out with - Vital Body Scan NZ Ltd Mobile Body Composition Analysis Interpreting your results Total Body Water (TBW) TBW is all the
Simopoulos AP (ed): Nutrition and Fitness: Obesity, the Metabolic Syndrome, Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer. Basel, Karger, 2005, vol 94, pp 60 67
 WRN94060.qxd 4/11/05 4:57 PM Page 60 Simopoulos AP (ed): Nutrition and Fitness: Obesity, the Metabolic Syndrome, Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer. Basel, Karger, 2005, vol 94, pp 60 67 Physical Activity
WRN94060.qxd 4/11/05 4:57 PM Page 60 Simopoulos AP (ed): Nutrition and Fitness: Obesity, the Metabolic Syndrome, Cardiovascular Disease and Cancer. Basel, Karger, 2005, vol 94, pp 60 67 Physical Activity
Resting Energy Expenditure and Substrate Metabolism in Chinese Patients with Acute or Chronic Hepatitis B or Liver Cirrhosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Resting Energy Expenditure and Substrate Metabolism in Chinese Patients with Acute or Chronic Hepatitis B or Liver Cirrhosis Qing-Hua Meng 1,Jin-HuanWang 1, Hong-Wei Yu 1,JuanLi 1, Yan-Mei
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Resting Energy Expenditure and Substrate Metabolism in Chinese Patients with Acute or Chronic Hepatitis B or Liver Cirrhosis Qing-Hua Meng 1,Jin-HuanWang 1, Hong-Wei Yu 1,JuanLi 1, Yan-Mei
In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in
 1 2 In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in adults: the influence of body mass index 3 4 Running title: Precision of the idxa for the measurement of visceral
1 2 In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in adults: the influence of body mass index 3 4 Running title: Precision of the idxa for the measurement of visceral
Effects of different sports on bone density and muscle mass in highly trained athletes
 CLINICAL SCIENCES Clinically Relevant Effects of different sports on bone density and muscle mass in highly trained athletes ANGELA ANDREOLI, MAURIZIO MONTELEONE, MARTA VAN LOAN, LUIGI PROMENZIO, UMBERTO
CLINICAL SCIENCES Clinically Relevant Effects of different sports on bone density and muscle mass in highly trained athletes ANGELA ANDREOLI, MAURIZIO MONTELEONE, MARTA VAN LOAN, LUIGI PROMENZIO, UMBERTO
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), body composition assessment 62
 Subject Index 3 -Adrenergic receptor, gene polymorphisms and obesity 10 Aging, body composition effects 64, 65 Air-displacement plethysmography, body composition assessment 62 Bioelectrical impedance analysis
Subject Index 3 -Adrenergic receptor, gene polymorphisms and obesity 10 Aging, body composition effects 64, 65 Air-displacement plethysmography, body composition assessment 62 Bioelectrical impedance analysis
Longitudinal Study of Total Body Potassium in Healthy Men
 Original Research Longitudinal Study of Total Body Potassium in Healthy Men Angela Andreoli, MD, PhD, Stella L. Volpe, PhD, Sarah J. Ratcliffe, PhD, Nicola Di Daniele, MD, Antonio Imparato, PhD, Luigi
Original Research Longitudinal Study of Total Body Potassium in Healthy Men Angela Andreoli, MD, PhD, Stella L. Volpe, PhD, Sarah J. Ratcliffe, PhD, Nicola Di Daniele, MD, Antonio Imparato, PhD, Luigi
Development of Bio-impedance Analyzer (BIA) for Body Fat Calculation
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Development of Bio-impedance Analyzer (BIA) for Body Fat Calculation Recent citations - Munawar A Riyadi et al To cite this article:
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Development of Bio-impedance Analyzer (BIA) for Body Fat Calculation Recent citations - Munawar A Riyadi et al To cite this article:
Review Comparison of body composition methods: a literature analysis
 European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 495±503 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Review Comparison of body composition methods: a literature analysis M Fogelholm
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 495±503 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Review Comparison of body composition methods: a literature analysis M Fogelholm
Suprailiac or Abdominal Skinfold Thickness Measured with a Skinfold Caliper as a Predictor of Body Density in Japanese Adults
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2007, Measurement 213, 51-61Error Characteristics of Skinfold Caliper 51 Suprailiac or Abdominal Skinfold Thickness Measured with a Skinfold Caliper as a Predictor of Body Density
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2007, Measurement 213, 51-61Error Characteristics of Skinfold Caliper 51 Suprailiac or Abdominal Skinfold Thickness Measured with a Skinfold Caliper as a Predictor of Body Density
Module 2: Metabolic Syndrome & Sarcopenia. Lori Kennedy Inc & Beyond
 Module 2: Metabolic Syndrome & Sarcopenia 1 What You Will Learn Sarcopenia Metabolic Syndrome 2 Sarcopenia Term utilized to define the loss of muscle mass and strength that occurs with aging Progressive
Module 2: Metabolic Syndrome & Sarcopenia 1 What You Will Learn Sarcopenia Metabolic Syndrome 2 Sarcopenia Term utilized to define the loss of muscle mass and strength that occurs with aging Progressive
The bone mass concept: problems in short stature
 European Journal of Endocrinology (2004) 151 S87 S91 ISSN 0804-4643 The bone mass concept: problems in short stature E Schoenau, C Land, A Stabrey, T Remer 1 and A Kroke 1 Children s Hospital, University
European Journal of Endocrinology (2004) 151 S87 S91 ISSN 0804-4643 The bone mass concept: problems in short stature E Schoenau, C Land, A Stabrey, T Remer 1 and A Kroke 1 Children s Hospital, University
This article may be used for non-commercial purposes in accordance with Wiley Terms and Conditions for Self-Archiving.
 This is the peer reviewed version of the following article: S, Smith & A. M. Madden (2016) Body Composition and functional assessment of nutritional status in adults: a narrative review of imaging, impedance,
This is the peer reviewed version of the following article: S, Smith & A. M. Madden (2016) Body Composition and functional assessment of nutritional status in adults: a narrative review of imaging, impedance,
2013 ISCD Official Positions Adult
 2013 ISCD Official Positions Adult These are the Official Positions of the ISCD as updated in 2013. The Official Positions that are new or revised since 2007 are in bold type. Indications for Bone Mineral
2013 ISCD Official Positions Adult These are the Official Positions of the ISCD as updated in 2013. The Official Positions that are new or revised since 2007 are in bold type. Indications for Bone Mineral
Note that metric units are used in the calculation of BMI. The following imperial-metric conversions are required:
 Body Composition Body Composition: Assessment and Interpretation Body composition has great practical and functional significance for many of us: scientists, clinicians and the general population. It can
Body Composition Body Composition: Assessment and Interpretation Body composition has great practical and functional significance for many of us: scientists, clinicians and the general population. It can
STUDY OF CORRELATION OF SEVERITY OF HEPATIC CIRRHOSIS WITH SEVERITY OF BONE CHANGES MEASURED BY BMD (BONE MINERAL DENSITY)
 STUDY OF CORRELATION OF SEVERITY OF HEPATIC CIRRHOSIS WITH SEVERITY OF BONE CHANGES MEASURED BY BMD (BONE MINERAL DENSITY) MD. ASHRAFUL ALAM 1, NOORUDDIN AHMED 2, SHAHINUL ALAM 2, MAMUN AL MAHTAB 2 Abstract
STUDY OF CORRELATION OF SEVERITY OF HEPATIC CIRRHOSIS WITH SEVERITY OF BONE CHANGES MEASURED BY BMD (BONE MINERAL DENSITY) MD. ASHRAFUL ALAM 1, NOORUDDIN AHMED 2, SHAHINUL ALAM 2, MAMUN AL MAHTAB 2 Abstract
Body composition. Body composition models Fluid-metabolism ECF. Body composition models Elemental. Body composition models Anatomic. Molnár Dénes.
 Body composition models Fluid-metabolism Fat Body composition ECF Molnár Dénes BCM ICF ICS ECS FFM Body composition models Anatomic Fat NSMST SM Body composition models Elemental Miscellaneous Calcium
Body composition models Fluid-metabolism Fat Body composition ECF Molnár Dénes BCM ICF ICS ECS FFM Body composition models Anatomic Fat NSMST SM Body composition models Elemental Miscellaneous Calcium
Luis S. Marsano, MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Louisville and Louisville VAMC 2015
 Luis S. Marsano, MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Louisville and Louisville VAMC 2015 Protein-calorie malnutrition (PCM) is extremely common
Luis S. Marsano, MD Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition University of Louisville and Louisville VAMC 2015 Protein-calorie malnutrition (PCM) is extremely common
Validation of bioimpedance body composition assessment by TANITA BC-418 in 7 years-
 Validation of bioimpedance body composition assessment by TANITA BC-418 in 7 years- old children vs. Dual X-ray absorptiometry Veronica Luque on behalf to URV Team 18th November 2012 Milano, 10th Bi-annual
Validation of bioimpedance body composition assessment by TANITA BC-418 in 7 years- old children vs. Dual X-ray absorptiometry Veronica Luque on behalf to URV Team 18th November 2012 Milano, 10th Bi-annual
Author's response to reviews
 Author's response to reviews Title:The association between lean mass and bone mineral content in the high disease activity group of adult patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis Authors: Kristyna Brabnikova
Author's response to reviews Title:The association between lean mass and bone mineral content in the high disease activity group of adult patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis Authors: Kristyna Brabnikova
Prospective study of profile of hepatic osteodystrophy in patients with non-choleastatic liver cirrhosis and impact of bisphosphonate supplementation
 Original Article Prospective study of profile of hepatic osteodystrophy in patients with non-choleastatic liver cirrhosis and impact of bisphosphonate supplementation United European Gastroenterology Journal
Original Article Prospective study of profile of hepatic osteodystrophy in patients with non-choleastatic liver cirrhosis and impact of bisphosphonate supplementation United European Gastroenterology Journal
Evaluation of DXA against the four-component model of body composition in obese children and adolescents aged 5 to 21 years
 Europe PMC Funders Group Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Int J Obes (Lond). 2010 April ; 34(4): 649 655. doi:10.1038/ijo.2009.249. Evaluation of DXA against the four-component model
Europe PMC Funders Group Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Int J Obes (Lond). 2010 April ; 34(4): 649 655. doi:10.1038/ijo.2009.249. Evaluation of DXA against the four-component model
Relationship between Family History of Osteoporotic Fracture and Femur Geometry
 Iranian J Publ Health, 2007, Iranian A supplementary J Publ Health, issue 2007, on Osteoporosis, A supplementary pp.70-74 issue on Osteoporosis, pp.70-74 Relationship between Family History of Osteoporotic
Iranian J Publ Health, 2007, Iranian A supplementary J Publ Health, issue 2007, on Osteoporosis, A supplementary pp.70-74 issue on Osteoporosis, pp.70-74 Relationship between Family History of Osteoporotic
Copyright 2014 ChaBiotech. All Rights Reserved. 차의과학대학교분당차병원소화기내과이주호, MD, PhD
 Copyright 2014 ChaBiotech. All Rights Reserved. 차의과학대학교분당차병원소화기내과이주호, MD, PhD Contents 1. Prevalence of Malnutrition in End Stage Liver Disease 2. Assessment of Malnutrition in Liver cirrhosis 3. Prognosis
Copyright 2014 ChaBiotech. All Rights Reserved. 차의과학대학교분당차병원소화기내과이주호, MD, PhD Contents 1. Prevalence of Malnutrition in End Stage Liver Disease 2. Assessment of Malnutrition in Liver cirrhosis 3. Prognosis
Dual-energy Vertebral Assessment
 Dual-energy Vertebral Assessment gehealthcare.com Dual-energy Vertebral Assessment More than 40% of women with normal or osteopenic BMD had a moderate or severe vertebral deformation seen with DVA. Patrick
Dual-energy Vertebral Assessment gehealthcare.com Dual-energy Vertebral Assessment More than 40% of women with normal or osteopenic BMD had a moderate or severe vertebral deformation seen with DVA. Patrick
Multi-Compartment Model (MCM) and Body Composition Measurement Techniques
 White Paper Contents Multi Compartment Model (MCM) 1 Methods comparable to MCM 2 Methods NOT comparable to MCMC 3 References 6 Multi-Compartment Model (MCM) and Body Composition Measurement Techniques
White Paper Contents Multi Compartment Model (MCM) 1 Methods comparable to MCM 2 Methods NOT comparable to MCMC 3 References 6 Multi-Compartment Model (MCM) and Body Composition Measurement Techniques
Norland Densitometry A Tradition of Excellence
 Norland Densitometry A Tradition of Excellence Norland DXA Bone Density Measurement Osteoporosis is a disease marked by reduced bone strength leading to an increased risk of fractures. About 54 million
Norland Densitometry A Tradition of Excellence Norland DXA Bone Density Measurement Osteoporosis is a disease marked by reduced bone strength leading to an increased risk of fractures. About 54 million
Potassium per kilogram fat-free mass and total body potassium: predictions from sex, age, and anthropometry
 Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 284: E416 E423, 2003. First published October 15, 2002; 10.1152/ajpendo.00199.2001. Potassium per kilogram fat-free mass and total body potassium: predictions from sex, age,
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 284: E416 E423, 2003. First published October 15, 2002; 10.1152/ajpendo.00199.2001. Potassium per kilogram fat-free mass and total body potassium: predictions from sex, age,
PhenX Measure: Body Composition (#020300) PhenX Protocol: Body Composition - Body Composition by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (#020302)
 PhenX Measure: Body Composition (#020300) PhenX Protocol: Body Composition - Body Composition by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (#020302) Date of Interview/Examination (MM/DD/YYYY): A downloadable PDF
PhenX Measure: Body Composition (#020300) PhenX Protocol: Body Composition - Body Composition by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (#020302) Date of Interview/Examination (MM/DD/YYYY): A downloadable PDF
Bedside methods versus dual energy X-ray absorptiometry for body composition measurement in COPD
 Eur Respir J ; 19: 66 631 DOI: 1.1183/931936..796 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Bedside methods versus dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
Eur Respir J ; 19: 66 631 DOI: 1.1183/931936..796 Printed in UK all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 Bedside methods versus dual energy X-ray absorptiometry
Evaluation of Bone Mineral Status in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:180-184 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.2.180 Evaluation of Bone Mineral Status in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Babak Pourabbas Tahvildari,
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:180-184 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.2.180 Evaluation of Bone Mineral Status in Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Babak Pourabbas Tahvildari,
Body-fat measurement in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: which method should be used?13
 Original Research Communications-general Body-fat measurement in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: which method should be used?13 Jack Wang, Donald P Koiler, Man Russell, Santiago Burasiero,
Original Research Communications-general Body-fat measurement in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: which method should be used?13 Jack Wang, Donald P Koiler, Man Russell, Santiago Burasiero,
Lateral Vertebral Analysis DXA Body Composition Quality Assurance in DXA
 Strong Bone Asia 2013 Osteoporosis in ASEAN Lateral Vertebral Analysis DXA Body Composition Quality Assurance in DXA Chris Schultz Scientist-in-Charge (Bone Densitometry) Royal Adelaide Hospital, Adelaide,
Strong Bone Asia 2013 Osteoporosis in ASEAN Lateral Vertebral Analysis DXA Body Composition Quality Assurance in DXA Chris Schultz Scientist-in-Charge (Bone Densitometry) Royal Adelaide Hospital, Adelaide,
Analysis of Body Compositions and Energy Expenditure of Sedentary Teaching Employees of SDAU, Gujarat, India
 International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Special Issue-7 pp. 914-921 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Analysis of Body Compositions
International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences ISSN: 2319-7706 Special Issue-7 pp. 914-921 Journal homepage: http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Analysis of Body Compositions
Definition and Diagnosis of Sarcopenia for Asian the Basic Science
 Definition and Diagnosis of Sarcopenia for Asian the Basic Science Simon Chow Educational Workshop on Sarcopenia and its Related Orthopaedic Problems February 13th, 2015. Prince of Wales Hospital. Sarcopenia
Definition and Diagnosis of Sarcopenia for Asian the Basic Science Simon Chow Educational Workshop on Sarcopenia and its Related Orthopaedic Problems February 13th, 2015. Prince of Wales Hospital. Sarcopenia
Body Composition. Sport Books Publisher 1
 Body Composition Sport Books Publisher 1 The body composition The body composition is affected by the proportions of the body component (bones, muscles, and other tissues) It can be seen that the major
Body Composition Sport Books Publisher 1 The body composition The body composition is affected by the proportions of the body component (bones, muscles, and other tissues) It can be seen that the major
Adaptation and re-feeding Hypokalemia Bone complications
 Adaptation and re-feeding Hypokalemia Bone complications René Klinkby Støving Odense University Hospital Denmark 10% 20% 30% 40% BMI 18.5 BMI 16.5 BMI 14.5 BMI 12.5 Willmore DW, The Metabolic Management
Adaptation and re-feeding Hypokalemia Bone complications René Klinkby Støving Odense University Hospital Denmark 10% 20% 30% 40% BMI 18.5 BMI 16.5 BMI 14.5 BMI 12.5 Willmore DW, The Metabolic Management
Clinical Study Body Fat Mass Assessment: A Comparison between an Ultrasound-Based Device and a Discovery A Model of DXA
 ISRN Obesity Volume 2013, Article ID 462394, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/462394 Clinical Study Body Fat Mass Assessment: A Comparison between an Ultrasound-Based Device and a Discovery A Model
ISRN Obesity Volume 2013, Article ID 462394, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/462394 Clinical Study Body Fat Mass Assessment: A Comparison between an Ultrasound-Based Device and a Discovery A Model
Evaluating body fat in girls and female adolescents: advantages and disadvantages of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry 1 4
 Evaluating body fat in girls and female adolescents: advantages and disadvantages of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry 1 4 William W Wong, Albert C Hergenroeder, Janice E Stuff, Nancy F Butte, E O Brian
Evaluating body fat in girls and female adolescents: advantages and disadvantages of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry 1 4 William W Wong, Albert C Hergenroeder, Janice E Stuff, Nancy F Butte, E O Brian
