Solubility Profiles of Amyloidogenic Molecular Structures
|
|
|
- Ferdinand Flowers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Solubility Profiles of Amyloidogenic Molecular Structures Key Theories Towards Meaningful Experiments Florin Despa, PhD Department of Pharmacology The University of California, Davis
2 Outline A. Hydration profiles of amyloid proteins, embryonic amyloid composites and mature amyloid fibrils each structural archetype has distinct long-lived water structures; magnetic resonance (MR) signals of these waters are structure-specific and differ from the MR signal of normal protein background. (theory & experiment) Despa, Fernandez, Scott & Berry, JBP (008) B. hiapp: relationship between the state of aggregation of the protein and the degree of toxicity induced in cells
3
4 How does human islet amyloid polypeptide (amylin, hiapp) become toxic? P agg Amyloid Formation Beta Cell dysfunction Hyperinsulinemia & Hyperamylinemia Molecular denaturation induced by molecular crowding Time (min) Despa, Biophys. Chem. (009) Oversecretion of PPinsulin & PPamylin in the ER hiapp: KCNTATCATQRLANFLVHSSNNFGAILSSTNVGSNTY riapp: KCNTATCATQRLANFLVRSSNNLGPVLPPTNVGSNTY Hyperglycemia & Increased Metabolic Demands
5 toxic molecular species 1 nm 10 nm 100 nm 100 nm 1 μm 100 μm ex vivo detection electron microscopy light microscopy non invasive detection NO YES adapted from
6 In Vivo MR Microimaging of Individual Amyloid Plaques in Alzheimer s Transgenic Mice Jack et al., J. Neurosci. 5: , 005
7 Amyloidogenic Proteins are characterized by: an increased number of poorly dehydrated backbone HBs Fernandez, Kardos, Scott, Goto & Berry, PNAS, (003) Fernandez & Berry, PNAS, (003) large surface densities of patches of bulk-like water De Simone et al., PNAS, 005 favor protein association Despa, Fernandez & Berry, PRL, 004 Despa and Berry, Biophys. J, (007); Biophys. J, (008)
8 Pathogenic Proteins Have Poor Desolvations of the Intramolecular HBs Fernandez, Kardos, Scott, Goto & Berry, PNAS, (003) Fernandez & Berry, PNAS, (003)
9 The DEHYDRON is a hydrophilic structural defect Fernandez, Kardos, Scott, Goto & Berry, PNAS, (003) Water in the desolvation region is mostly in contact with hydrophobes.
10 Water Molecular Dipoles Correlated in Pairs Through an Entropic Effect P r ( E) = ( A π ) E 1 4 A e Polarized Water f =1 f = r ( μ f ) α ( f ) A = r μ N EL r, μ N 18 = r dep r 0 r r ( E) μ( E) Q Nd f =3 Despa, Fernandez & Berry, PRL, 004 τ S ( ps) η βe L d correlated water l = 0 1 nm l0 = 0. 75nm Despa, PCCP, 008 experiment Tan et al., JCP (005) R ( nm) Despa, PCCP, R (nm) The fraction of correlated water and its characteristic relaxation time depend on the degree of confinement.
11 r c b b Water structured at the interface between hydrophobes is a source of induction-dispersion effects that favor protein association () () r r g f v ASAr d l r b r b r U c h = μ πε γ ε r ( ) 1 Kcal mol U h ( ) o A r wetting regime Despa and Berry, Biophys. J, (007) Despa and Berry, Biophys. J, (008)
12 Proteins presenting structural defects are characterized by an increased fraction of water with a bulk-like behavior. τ np ~ s (bulk-like water) (structural defects) τ ~ 10 b 1 s (bulk water) τ >10 8 s c (caged water) τ p ~10 9 s (highly structured water) Prion (PrP C ) Solvation Map De Simone et al., PNAS, 005
13 Association of Proteins to Form Oligomers and Fibrils Rescales the Long-lived Water Structures Oligomers Fibrils The change in the distribution of long-lived water structures provides the MRI signal.
14 Aqueous Environment Containing Protein Background + Test Isomers η 0.69 C test isomer native protein η A protein background N0 1mM V 1μm 3 B + ΔN ( 0. mm + ΔN ) Dimers Compact Aggregates negative control η 0.69 Floppy Aggregates
15 Partition of Water in the Protein System f ( A) test isomer (increased number of surface defects) native protein f surface density of defects ( f A ) > f ( A) ( A) V water = N ( Vs + Vc ) + ΔN ( Vs + Vc ) + V r (surface water) V s V ( 1 f ) V p V s f np V s τ τ p np ~10 ~ 10 9 s 10 s (highly structured water) (bulk-like water) (structural defects) (caged water) V c ( ρ ρ ) = Vm VW = Vm max τ >10 8 s c (caged water) Despa, Fernandez, Scott & Berry, JBP (008)
16 Water Fractions protein background + test isomers scaling theory (Reiss, 1965) VS 0. 11V m c p np r = ( ρ ρ)( 1 η) 1 η = η 1 η Nf + ΔNf = 0.11 η N + ΔN = 1 max c η p ( A) fn + f ΔN N + ΔN np ( A) (caged water) (highly structured water) (bulk-like water) (bulk water) f ( A) f ( A) m (soluble oligomers) Despa, Fernandez, Scott & Berry, JBP (008)
17 Histograms describing the partition of constrained water in a system of protein background plus test isomers water fractions highly structured water caged water less structured water (bulk-like) τ >10 8 s c τ p ~10 9 s residence time τ np ~ s ( ) f A f f ( A) ( A) = f = 0.3 = 0.5 = 0.1 (control)
18 Change of the hydration profile following the formation of fibrils and plaques.
19 1. at equilibrium, most of the surface defects are buried inside the fibril:. packing density of fibrils is high so they exclude surrounding water (Petkova et al., Science, 005) f ( A) f ( ASA) c = ( ρ ρ )( 1 η) max η (caged water) Compact Aggregates ( ASA) np = 0.11 f 1 η N + ΔN η N + ΔN / 3 (bulk-like water) ( ASA) p = 0.11 ( 1 f ) 1 η N + ΔN η N + ΔN / 3 (highly structured water) ( ASA) r = 1 ( ASA) c ( ASA) np ( ASA) p (bulk water) Despa, Fernandez, Scott & Berry, JBP (008)
20 1. most of the surface defects are buried inside the aggregate;. packing density of fibrils in a plaque is sufficiently low so that, plaques contain additional caged water molecules (Nelson et al., Nature, 005) Floppy Aggregates ( agg ) c = ( ρ ρ )( 1 η) max η ΔN N + ΔN 1 η η ( ρ ρ ) a (caged water) ( agg ) np ( agg ) p ( agg ) r = 0.11 f = 0.11 = 1 1 η N + ΔN η N + ΔN ( 1 f ) ( agg ) c ( agg ) np / 3 1 η N + ΔN η N + ΔN / 3 ( agg ) p (bulk-like water) (highly structured water) (bulk water) caged water Despa, Fernandez, Scott & Berry, JBP (008)
21 Histograms describing the partition of constrained water in a system of protein background plus test isomers water fractions highly structured water caged water less structured water (bulk-like) τ >10 8 s c τ p ~10 9 s τ np ~ s residence time control protein background + test isomers dimers of test isomers compact protein aggregates Despa, Fernandez, Scott & Berry, JBP (008) floppy protein aggregates
22 = j j j j k T k TE T TR S S, 1, max exp exp 1 = j j j T T, 1 ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) = =, 1, j L j j L j j j j L j j L j j C T C T ω τ τ ω τ τ τ ω τ τ ω τ τ Magnetic Relaxation Response
23 A Control Protein Background D Protein Background + Compact Aggregates B Protein Background + Test Isomers E Protein Background + Floppy Aggregates C Protein Background + Dimers Less Structured Water MR Intensity Signal (grayscale) S S max C D B ( c) ( b) T > T > T ( b) T > T T ( control) ( control) ( control) A (control) ( a) T < T ( control) 9.5 Highly Structured Water E TE (ms) AD samples can display both bright and dark spots on MR images; Bright spots are likely to indicate oligomers and protofibrils.
24 Water Proton NMR Spectroscopy of Amyloidogenic Structures Objectives: To detect the MR response of water following structural modifications of the amyloidogenic assemblies; To test the hypothesis that the formation of oligomers and/or fibrils leads to an increase of the T values, shifting the MR signal towards values corresponding to bulk-like water. hiapp in serum Aβ 1-40 in serum serum+water µm 50 µm 100 µm 5 µm 50 µm 100 µm
25 NMR Setup Dr. J. Walton Dr. S. Anderson
26 Data Analysis ParaVision 3.0. to collect data, Nonlinear least square (NNLS) fit to analyze data
27 Water Proton NMR Spectroscopy of Amyloidogenic Structures T (ms) hiapp Abeta 5 m µm 50 c1 µm 100 cµm % of sample hiapp Abeta % of sample hiapp Abeta T (ms) 9 m c1 c 5 µm 50 µm 100 µm
28 Water Proton NMR Spectroscopy of Amyloidogenic Structures T (A) (ms) % of sample T (B) (ms) % of sample T (C) (ms) % of sample hiapp(m) 1.5, 7., , 1.11, , 0, , 97.38, 97.7 (96.33) control 0.95, 1.5, , 1.1, , 8.1, , 0.77, , 00, , 96.58, 96.8 (95.59) hiapp(c1) 1.4, 5.1, , 1.11, , 50, , 97.38, 97.4 (96.39) control (1) 1.1,.4, , 1.5, , 50, 50 (43.33) 95, 97.5, 97 (96.5) 5.4, , 0.58 hiapp(c) 1.8, 8.1, 6.8 3, 0.58, , 310, , 97.99, 97.7 (97.3) control().1, 7., 7.., 0.4, , 310, , 98.7, 98.1 (97.76) Abeta(m) 1.1, 1.9, , 1.88,.01 7., , , 10, , 95.97, 96.8 (95.76) Abeta(c1) 0.85,.4, , 1.7, , 5.7, , 0.47, , 310, , 96.8, 95.9 (95.4) Abeta(c) 0.71, 7., 1 6.3, 0.48, , 370, , 97.48, 96.3 (95.46) 1., , 0.44
29 The formation of oligomers and/or fibrils leads to an increase of the T value T (ms) Control hiapp Abeta m c1 c 5 µm 50 µm 100 µm % of sample Control hiapp Abeta m c1 c 5 µm 50 µm 100 µm hiapp in serum Aβ 1-40 in serum serum+water µm 50 µm100 µm 5 µm 50 µm 100 µm
30 How does the amyloid toxicity manifest at the cellular level?
31 Amylin-Induced Toxicity in Cardiac Myocytes cardiac myocyte Objective: To assess the functional alteration of myocytes induced by hiapp. Method: Monitor the intracellular Ca signal.
32 3Na Na Na K Sarcolemma ATP NC NHE PLM ATP Ca RyR Ca Ca H 3Na I Ca SR PLB ATP Ca T-Tubule Ca Ca Na- Ca 3Na Ca AP (E m ) Myofil [Ca] i Contraction Na H Cyt H Ca Ca Na Mito
33 Amylin-Induced Toxicity in Cardiac Myocytes Experimental Protocol: - myocytes were plated on laminin-coated coverslips; - loaded with Fura-AM (10 μmol/l, for 45 min); - Fura was alternately excited at 340 and 380 nm (F340 and F380) using an Optoscan monochromator (Cairn Research, Faversham, UK); - fluorescence was collected at 510±0 nm; - the fluorescence ratio F340/F380 was calculated after background subtraction.
34 Ca-mediated Cardiomyocyte Contraction AP (E m ) [Ca] i Contraction
35
36 Intensity of Magnetic Response of Water Concluding Remarks S bulk-like water fibrils soluble amyloidogenic proteins Amyloid proteins and embryonic amyloid composites can be differentiated based on their hydration profiles and characteristic MR signals of the surrounding water. 0.5 normal protein background structured water large, floppy aggregates TE (ms)
37 Clinical Implication: MRI Contrast Mechanism for Detection of AD In Vivo Magnetic Resonance Microimaging of Individual Amyloid Plaques in Alzheimer s Transgenic Mice Jack et al., J. Neurosci. 5: , 005
38 Intensity of Magnetic Response of Water Concluding Remarks S bulk-like water fibrils soluble amyloidogenic proteins normal protein background structured water large, floppy aggregates TE (ms) Amyloid proteins and embryonic amyloid composites can be differentiated based on their hydration profiles and characteristic MR signals of the surrounding water. Toxicity induced by soluble amyloid composites manifests at the cellular level in a time-dependent manner: progressive damage of the membranes. Oligomers are the most toxic species. Fibril growth at the membrane is equally toxic. T 13ms T 53ms 5 µm 50 µm
39 Acknowledgements R. Stephen Berry (Chicago) Ariel Fernandez (Rice) L. Ridgway Scott (Chicago) Christopher Rhodes (Chicago) Donald Steiner (Chicago) Ulrich Hansmann (Juelich) Sanda Despa (Davis) Jeff Walton (Davis) Steve Anderson (Davis)
Cardiotoxicity of Hyperamylinemia
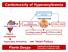 Cardiotoxicity of Hyperamylinemia β-cell Dysfunction & Apoptosis Pancreatic β-cell Amylin Oligomers BLOO OD AMYLIN OLIGOMERIZATION HYPERGLYCEMIA Calcium dsreglation dysregulation HYPERAMYLINEMIA HYPERINSULINEMIA
Cardiotoxicity of Hyperamylinemia β-cell Dysfunction & Apoptosis Pancreatic β-cell Amylin Oligomers BLOO OD AMYLIN OLIGOMERIZATION HYPERGLYCEMIA Calcium dsreglation dysregulation HYPERAMYLINEMIA HYPERINSULINEMIA
Cholesterol modulates amyloid beta peptide 1-42 channel formation in planar lipid membranes
 Cholesterol modulates amyloid beta peptide 1-42 channel formation in planar lipid membranes Meleleo D., Notarachille G., Gallucci E. and Micelli S. Dept. Farmaco-Biologico, Università degli Studi di Bari,
Cholesterol modulates amyloid beta peptide 1-42 channel formation in planar lipid membranes Meleleo D., Notarachille G., Gallucci E. and Micelli S. Dept. Farmaco-Biologico, Università degli Studi di Bari,
Inter-Species Cross-Seeding: Stability and Assembly of Rat - Human Amylin Aggregates. Workalemahu M. Berhanu
 Inter-Species Cross-Seeding: Stability and Assembly of Rat - Human Amylin Aggregates Workalemahu M. Berhanu University of Oklahoma Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry STRUCTURE OF AMYLOIDS & ROLE
Inter-Species Cross-Seeding: Stability and Assembly of Rat - Human Amylin Aggregates Workalemahu M. Berhanu University of Oklahoma Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry STRUCTURE OF AMYLOIDS & ROLE
Using Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry to Measure Oligomer-size Distributions and Structures for the Early Stages of Aβ Assembly
 Using Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry to Measure Oligomer-size Distributions and Structures for the Early Stages of Aβ Assembly Michael T. Bowers, Summer L. Bernstein, Nicholas F. Dupuis, Thomas Wyttenbach,
Using Ion Mobility Mass Spectrometry to Measure Oligomer-size Distributions and Structures for the Early Stages of Aβ Assembly Michael T. Bowers, Summer L. Bernstein, Nicholas F. Dupuis, Thomas Wyttenbach,
Zn(II) as a minimal chaperone mimic to retard Aβ peptide fibril formation
 Zn(II) as a minimal chaperone mimic to retard Aβ peptide fibril formation Astrid Gräslund Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics Stockholm University Lorentz workshop, Leiden, April 17, 215 Potential
Zn(II) as a minimal chaperone mimic to retard Aβ peptide fibril formation Astrid Gräslund Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics Stockholm University Lorentz workshop, Leiden, April 17, 215 Potential
The Amyloid Precursor Protein Has a Flexible Transmembrane Domain and Binds Cholesterol
 The Amyloid Precursor Protein Has a Flexible Transmembrane Domain and Binds Cholesterol Science 336, 1171 (2013) Coach Prof. : Dr. Chung-I Chang Sit-in Prof.: Dr. Wei Yuan Yang Presenter: Han-Ying Wu Date:
The Amyloid Precursor Protein Has a Flexible Transmembrane Domain and Binds Cholesterol Science 336, 1171 (2013) Coach Prof. : Dr. Chung-I Chang Sit-in Prof.: Dr. Wei Yuan Yang Presenter: Han-Ying Wu Date:
JBB2026, Dec 2, Amyloid structure and assembly
 JBB2026, Dec 2, 2016 - Amyloid structure and assembly Disordered Folded? Douglas and Dillin, 2010, J. Cell. Biol. Cell death Loss of organ function Disease pathogenesis Vendruscolo et al, Cold Spring Harbor
JBB2026, Dec 2, 2016 - Amyloid structure and assembly Disordered Folded? Douglas and Dillin, 2010, J. Cell. Biol. Cell death Loss of organ function Disease pathogenesis Vendruscolo et al, Cold Spring Harbor
ORGANIZATION OF ANTIBIOTIC AMPHOTERICIN B IN MODEL LIPID MEMBRANES. A MINI REVIEW
 CELLULAR & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY LETTERS Volume 8, (2003) pp 161 170 http://www.cmbl.org.pl Received 30 September 2002 Accepted 13 February 2003 ORGANIZATION OF ANTIBIOTIC AMPHOTERICIN B IN MODEL LIPID MEMBRANES.
CELLULAR & MOLECULAR BIOLOGY LETTERS Volume 8, (2003) pp 161 170 http://www.cmbl.org.pl Received 30 September 2002 Accepted 13 February 2003 ORGANIZATION OF ANTIBIOTIC AMPHOTERICIN B IN MODEL LIPID MEMBRANES.
If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out.
 Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
Sign In Forgot Password Register username username password password Sign In If you like us, please share us on social media. The latest UCD Hyperlibrary newsletter is now complete, check it out. ChemWiki
Modern Aspects of Colloid Science MICELLES
 Modern Aspects of Colloid Science MICELLES critical micelle concentration (CMC) micellar shape determination of critical micelle concentration purity of surfactants Krafft temperature micellar equilibria
Modern Aspects of Colloid Science MICELLES critical micelle concentration (CMC) micellar shape determination of critical micelle concentration purity of surfactants Krafft temperature micellar equilibria
Adding dimensions to femtosecond spectroscopy: id, 2D and 3D infrared and visiblespectroscopies Martin T. Zanni
 Adding dimensions to femtosecond spectroscopy: id, 2D and 3D infrared and visiblespectroscopies Martin T. Zanni Department ofchemistry, University of Wisconsin-Madison, USA TuesdaY,3 May- 4:00 p.m, The
Adding dimensions to femtosecond spectroscopy: id, 2D and 3D infrared and visiblespectroscopies Martin T. Zanni Department ofchemistry, University of Wisconsin-Madison, USA TuesdaY,3 May- 4:00 p.m, The
Chapter 9. Protein Folding, Dynamics, and Structural Evolution
 Chapter 9 Protein Folding, Dynamics, and Structural Evolution Proteins folding Self-assembly Primary sequence dictates three dimensional structure Folding accessory proteins Protein disulfide isomerases
Chapter 9 Protein Folding, Dynamics, and Structural Evolution Proteins folding Self-assembly Primary sequence dictates three dimensional structure Folding accessory proteins Protein disulfide isomerases
Digital Biology, Spring 2015 Project Suggestions and Reading List
 Digital Biology, Spring 2015 Project Suggestions and Reading List April 22, 2015 The course will require presentation in class of one significant paper, the execution of a research project, and presentation
Digital Biology, Spring 2015 Project Suggestions and Reading List April 22, 2015 The course will require presentation in class of one significant paper, the execution of a research project, and presentation
Chemical Surface Transformation 1
 Chemical Surface Transformation 1 Chemical reactions at Si H surfaces (inorganic and organic) can generate very thin films (sub nm thickness up to µm): inorganic layer formation by: thermal conversion:
Chemical Surface Transformation 1 Chemical reactions at Si H surfaces (inorganic and organic) can generate very thin films (sub nm thickness up to µm): inorganic layer formation by: thermal conversion:
Structure of proteins
 Structure of proteins Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Structure of proteins The 20 a.a commonly found
Structure of proteins Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Structure of proteins The 20 a.a commonly found
Lecture 4: 8/26. CHAPTER 4 Protein Three Dimensional Structure
 Lecture 4: 8/26 CHAPTER 4 Protein Three Dimensional Structure Summary of the Lecture 3 There are 20 amino acids and only the L isomer amino acid exist in proteins Each amino acid consists of a central
Lecture 4: 8/26 CHAPTER 4 Protein Three Dimensional Structure Summary of the Lecture 3 There are 20 amino acids and only the L isomer amino acid exist in proteins Each amino acid consists of a central
Supplementary Figure 1. Comparative analysis of thermal denaturation of enzymatically
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Comparative analysis of thermal denaturation of enzymatically synthesized polyubiquitin chains of different length. a, Differential scanning calorimetry traces
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Comparative analysis of thermal denaturation of enzymatically synthesized polyubiquitin chains of different length. a, Differential scanning calorimetry traces
Exploring the Energy Landscape for Amyloid Formation
 Exploring the Energy Landscape for Amyloid Formation Telluride, 4th April 2007 Birgit Strodel University of Cambridge Department of Chemistry What are Amyloid Fibrils? Amyloid fibrils are encountered in
Exploring the Energy Landscape for Amyloid Formation Telluride, 4th April 2007 Birgit Strodel University of Cambridge Department of Chemistry What are Amyloid Fibrils? Amyloid fibrils are encountered in
Protein structure. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester,
 Protein structure Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Overview of proteins Proteins have different structures and some have repeating inner structures, other do not. A protein may have gazillion
Protein structure Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Overview of proteins Proteins have different structures and some have repeating inner structures, other do not. A protein may have gazillion
ALZHEIMER S DISEASE FACTOIDS & STATISTICS
 ALZHEIMER S DISEASE FACTOIDS & STATISTICS ~ 4 million affected in US alone 6-8% if 65+ years old, 30-50% if 80+ By 2030, in US >65 million people >65+ (---> ~14 million with AD) AD is one of the top 10
ALZHEIMER S DISEASE FACTOIDS & STATISTICS ~ 4 million affected in US alone 6-8% if 65+ years old, 30-50% if 80+ By 2030, in US >65 million people >65+ (---> ~14 million with AD) AD is one of the top 10
The role of amyloid beta peptide variability toward progress of Alzheimer disease
 The role of amyloid beta peptide variability toward progress of Alzheimer disease Kerensa Broersen Brain Disorders and Therapeutics London, August 26 1 Alzheimer s disease Amyloid β peptide 2 Alzheimer
The role of amyloid beta peptide variability toward progress of Alzheimer disease Kerensa Broersen Brain Disorders and Therapeutics London, August 26 1 Alzheimer s disease Amyloid β peptide 2 Alzheimer
BIOCHEMISTRY 460 FIRST HOUR EXAMINATION FORM A (yellow) ANSWER KEY February 11, 2008
 WRITE YOUR AND I.D. NUMBER LEGIBLY ON EVERY PAGE PAGES WILL BE SEPARATED FOR GRADING! CHECK TO BE SURE YOU HAVE 6 PAGES, (print): ANSWERS INCLUDING COVER PAGE. I swear/affirm that I have neither given
WRITE YOUR AND I.D. NUMBER LEGIBLY ON EVERY PAGE PAGES WILL BE SEPARATED FOR GRADING! CHECK TO BE SURE YOU HAVE 6 PAGES, (print): ANSWERS INCLUDING COVER PAGE. I swear/affirm that I have neither given
Sheet #5 Dr. Mamoun Ahram 8/7/2014
 P a g e 1 Protein Structure Quick revision - Levels of protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary. - Primary structure is the sequence of amino acids residues. It determines the other
P a g e 1 Protein Structure Quick revision - Levels of protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary & quaternary. - Primary structure is the sequence of amino acids residues. It determines the other
Skeletal Muscle : Structure
 1 Skeletal Muscle : Structure Dr.Viral I. Champaneri, MD Assistant Professor Department of Physiology 2 Learning objectives 1. Gross anatomy of the skeletal muscle 2. Myofilaments & their molecular structure
1 Skeletal Muscle : Structure Dr.Viral I. Champaneri, MD Assistant Professor Department of Physiology 2 Learning objectives 1. Gross anatomy of the skeletal muscle 2. Myofilaments & their molecular structure
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Protein conformation Many conformations are possible for proteins due to flexibility of amino acids linked by peptide
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Protein conformation Many conformations are possible for proteins due to flexibility of amino acids linked by peptide
Paper No. 01. Paper Title: Food Chemistry. Module-16: Protein Structure & Denaturation
 Paper No. 01 Paper Title: Food Chemistry Module-16: Protein Structure & Denaturation The order of amino acids in a protein molecule is genetically determined. This primary sequence of amino acids must
Paper No. 01 Paper Title: Food Chemistry Module-16: Protein Structure & Denaturation The order of amino acids in a protein molecule is genetically determined. This primary sequence of amino acids must
Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology FACULTY OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES. Lipid rafts in neurodegenerative diseases. Nigel M.
 Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology FACULTY OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES Lipid rafts in neurodegenerative diseases Nigel M. Hooper Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology FACULTY OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES
Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology FACULTY OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES Lipid rafts in neurodegenerative diseases Nigel M. Hooper Institute of Molecular and Cellular Biology FACULTY OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES
Globular proteins Proteins globular fibrous
 Globular proteins Globular proteins Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form in a biologically functional way. Globular
Globular proteins Globular proteins Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form in a biologically functional way. Globular
Alzheimer's Disease A mind in darkness awaiting the drink of a gentle color.
 Alzheimer's Disease A mind in darkness awaiting the drink of a gentle color. Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Gabriel García Márquez One Hundred Years of Solitude Alois Alzheimer
Alzheimer's Disease A mind in darkness awaiting the drink of a gentle color. Mary ET Boyle, Ph. D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Gabriel García Márquez One Hundred Years of Solitude Alois Alzheimer
Supporting Information. Kinetic and Conformational Insights into Islet Amyloid Polypeptide Self-Assembly using a Biarsenical Fluorogenic Probe
 Kinetic and Conformational Insights into Islet Amyloid Polypeptide Self-Assembly using a Biarsenical Fluorogenic Probe Noé Quittot, Mathew Sebastiao, Soultan Al-Halifa and Steve Bourgault* Department of
Kinetic and Conformational Insights into Islet Amyloid Polypeptide Self-Assembly using a Biarsenical Fluorogenic Probe Noé Quittot, Mathew Sebastiao, Soultan Al-Halifa and Steve Bourgault* Department of
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Fig. S1. SDSPAGE of crosslinked Aβ42 oligomers after SEC. After crosslinking of Aβ42 with or without Myr or RA, APS and Ru(bpy) were removed by SEC. The resulting products were
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Fig. S1. SDSPAGE of crosslinked Aβ42 oligomers after SEC. After crosslinking of Aβ42 with or without Myr or RA, APS and Ru(bpy) were removed by SEC. The resulting products were
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Heme Proteins
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Heme Proteins 1.1 Techniques Used to Study Protein Folding Pathways Proteins are synthesized by the ribosome in a stepwise fashion, emerging as long, linear polypeptides that
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Heme Proteins 1.1 Techniques Used to Study Protein Folding Pathways Proteins are synthesized by the ribosome in a stepwise fashion, emerging as long, linear polypeptides that
Supporting Information for
 Supporting Information for Rupture of Lipid Membranes Induced by Amphiphilic Janus Nanoparticles Kwahun Lee, Liuyang Zhang, Yi Yi, Xianqiao Wang, Yan Yu* Department of Chemistry, Indiana University, Bloomington,
Supporting Information for Rupture of Lipid Membranes Induced by Amphiphilic Janus Nanoparticles Kwahun Lee, Liuyang Zhang, Yi Yi, Xianqiao Wang, Yan Yu* Department of Chemistry, Indiana University, Bloomington,
We are going to talk about two classifications of proteins: fibrous & globular.
 Slide # 13 (fibrous proteins) : We are going to talk about two classifications of proteins: fibrous & globular. *fibrous proteins: (dense fibers) *Their structures are mainly formed of the secondary structure
Slide # 13 (fibrous proteins) : We are going to talk about two classifications of proteins: fibrous & globular. *fibrous proteins: (dense fibers) *Their structures are mainly formed of the secondary structure
Chapter VI. Increased affinity in the complex of yeast cytochrome c and cytochrome c peroxidase
 Chapter VI Increased affinity in the complex of yeast cytochrome c and cytochrome c peroxidase Chapter VI Abstract We report the study of T12A Cyt c CcP complex using isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC),
Chapter VI Increased affinity in the complex of yeast cytochrome c and cytochrome c peroxidase Chapter VI Abstract We report the study of T12A Cyt c CcP complex using isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC),
Nigel Hooper. University of Manchester UK
 Prion protein as a therapeutic target in Alzheimer s disease Nigel Hooper University of Manchester UK Prion protein and Alzheimer s a connection? - causative agent of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies
Prion protein as a therapeutic target in Alzheimer s disease Nigel Hooper University of Manchester UK Prion protein and Alzheimer s a connection? - causative agent of transmissible spongiform encephalopathies
Interaction of Functionalized C 60 Nanoparticles with Lipid Membranes
 Interaction of Functionalized C 60 Nanoparticles with Lipid Membranes Kevin Gasperich Advisor: Dmitry Kopelevich ABSTRACT The recent rapid development of applications for fullerenes has led to an increase
Interaction of Functionalized C 60 Nanoparticles with Lipid Membranes Kevin Gasperich Advisor: Dmitry Kopelevich ABSTRACT The recent rapid development of applications for fullerenes has led to an increase
Unveiling transient protein-protein interactions that modulate inhibition of alpha-synuclein aggregation
 Supplementary information Unveiling transient protein-protein interactions that modulate inhibition of alpha-synuclein aggregation by beta-synuclein, a pre-synaptic protein that co-localizes with alpha-synuclein.
Supplementary information Unveiling transient protein-protein interactions that modulate inhibition of alpha-synuclein aggregation by beta-synuclein, a pre-synaptic protein that co-localizes with alpha-synuclein.
Chem Lecture 2 Protein Structure
 Chem 452 - Lecture 2 Protein Structure 110923 Proteins are the workhorses of a living cell and involve themselves in nearly all of the activities that take place in a cell. Their wide range of structures
Chem 452 - Lecture 2 Protein Structure 110923 Proteins are the workhorses of a living cell and involve themselves in nearly all of the activities that take place in a cell. Their wide range of structures
CS612 - Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL
 Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL For Questions 1-10 choose ONE INCORRECT answer. 1. Which ONE of the following statements concerning the
Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL For Questions 1-10 choose ONE INCORRECT answer. 1. Which ONE of the following statements concerning the
Proteins are linear polymers built of monomer units called amino acids. Proteins contain a wide range of functional groups.
 Chapter 2: Protein Structure and Function Proteins arevery versatile with regards to functions for the cell Uses? Proteins are linear polymers built of monomer units called amino acids. One dimensional
Chapter 2: Protein Structure and Function Proteins arevery versatile with regards to functions for the cell Uses? Proteins are linear polymers built of monomer units called amino acids. One dimensional
AFM In Liquid: A High Sensitivity Study On Biological Membranes
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2006 AFM In Liquid: A High Sensitivity Study On Biological Membranes Michael J. Higgins
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2006 AFM In Liquid: A High Sensitivity Study On Biological Membranes Michael J. Higgins
Colloid Chemistry. Lecture #2 Association colloid
 Colloid Chemistry Lecture #2 Association colloid 1 https://ilustracionmedica.wordpress.com/2014/08/27/fisicos-haciendo-medicina-john-tyndall/ Solution Classical vs. Colloid solution Tyndall effect Increased
Colloid Chemistry Lecture #2 Association colloid 1 https://ilustracionmedica.wordpress.com/2014/08/27/fisicos-haciendo-medicina-john-tyndall/ Solution Classical vs. Colloid solution Tyndall effect Increased
Q1: Circle the best correct answer: (15 marks)
 Q1: Circle the best correct answer: (15 marks) 1. Which one of the following incorrectly pairs an amino acid with a valid chemical characteristic a. Glycine, is chiral b. Tyrosine and tryptophan; at neutral
Q1: Circle the best correct answer: (15 marks) 1. Which one of the following incorrectly pairs an amino acid with a valid chemical characteristic a. Glycine, is chiral b. Tyrosine and tryptophan; at neutral
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction. Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry
 Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
H C. C α. Proteins perform a vast array of biological function including: Side chain
 Topics The topics: basic concepts of molecular biology elements on Python overview of the field biological databases and database searching sequence alignments phylogenetic trees microarray data analysis
Topics The topics: basic concepts of molecular biology elements on Python overview of the field biological databases and database searching sequence alignments phylogenetic trees microarray data analysis
Phase transitions in cell biology
 Institute of Bioengineering Queen Mary University of London Oct 16, 2013 Phase transitions in cell biology Chiu Fan Lee Department of Bioengineering Imperial College London A cell Figure from Wikipedia
Institute of Bioengineering Queen Mary University of London Oct 16, 2013 Phase transitions in cell biology Chiu Fan Lee Department of Bioengineering Imperial College London A cell Figure from Wikipedia
NANO 243/CENG 207 Course Use Only
 L9. Drug Permeation Through Biological Barriers May 3, 2018 Lipids Lipid Self-Assemblies 1. Lipid and Lipid Membrane Phospholipid: an amphiphilic molecule with a hydrophilic head and 1~2 hydrophobic tails.
L9. Drug Permeation Through Biological Barriers May 3, 2018 Lipids Lipid Self-Assemblies 1. Lipid and Lipid Membrane Phospholipid: an amphiphilic molecule with a hydrophilic head and 1~2 hydrophobic tails.
Rheology of Wormlike Micelles
 Rheology of Wormlike Micelles (ITP Complex Fluids Program 3/27/2) T1 Rheology of Wormlike Micelles Grégoire Porte Denis Roux Jean-François Berret* Sandra Lerouge Jean-Paul Decruppe Peter Lindner Laurence
Rheology of Wormlike Micelles (ITP Complex Fluids Program 3/27/2) T1 Rheology of Wormlike Micelles Grégoire Porte Denis Roux Jean-François Berret* Sandra Lerouge Jean-Paul Decruppe Peter Lindner Laurence
Amino Acids and Proteins Hamad Ali Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS, HSC, KU Biochemistry 210 Chapter 22
 Amino Acids and Proteins Hamad Ali Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS, HSC, KU Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw Biochemistry 210 Chapter 22 Importance of Proteins Main catalysts in biochemistry: enzymes (involved in
Amino Acids and Proteins Hamad Ali Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS, HSC, KU Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw Biochemistry 210 Chapter 22 Importance of Proteins Main catalysts in biochemistry: enzymes (involved in
Modeling of Thermal Damage from Focused Ultrasound Exposures for Heterogeneous Tissues
 Modeling of Thermal Damage from Focused Ultrasound Exposures for Heterogeneous Tissues Adam C. Waspe, PhD adam.waspe@sickkids.ca Aug. 11, 2014 * Some content adapted from lecture notes from Rajiv Chopra
Modeling of Thermal Damage from Focused Ultrasound Exposures for Heterogeneous Tissues Adam C. Waspe, PhD adam.waspe@sickkids.ca Aug. 11, 2014 * Some content adapted from lecture notes from Rajiv Chopra
Supporting material. Membrane permeation induced by aggregates of human islet amyloid polypeptides
 Supporting material Membrane permeation induced by aggregates of human islet amyloid polypeptides Chetan Poojari Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH, Institute of Complex Systems: Structural Biochemistry (ICS-6),
Supporting material Membrane permeation induced by aggregates of human islet amyloid polypeptides Chetan Poojari Forschungszentrum Jülich GmbH, Institute of Complex Systems: Structural Biochemistry (ICS-6),
Common Core Structure of Amyloid Fibrils by Synchrotron X-Ray Diffraction
 Common Core Structure of Amyloid Fibrils by Synchrotron X-Ray Diffraction Michael Foody May 5 th, 2015 M. Sunde, L.C. Serpell, M. Bartlam, P. Fraser, M. Pepys, C. Blake, J. Mol. Biol. 273, 729-739, (1997)
Common Core Structure of Amyloid Fibrils by Synchrotron X-Ray Diffraction Michael Foody May 5 th, 2015 M. Sunde, L.C. Serpell, M. Bartlam, P. Fraser, M. Pepys, C. Blake, J. Mol. Biol. 273, 729-739, (1997)
Supporting Information for:
 Supporting Information for: A Robust Liposomal Platform for Direct Colorimetric Detection of Sphingomyelinase Enzyme and Inhibitors Margaret N. Holme, 1,2,3,4 Subinoy Rana, 1,2,3,5 Hanna M. G. Barriga,
Supporting Information for: A Robust Liposomal Platform for Direct Colorimetric Detection of Sphingomyelinase Enzyme and Inhibitors Margaret N. Holme, 1,2,3,4 Subinoy Rana, 1,2,3,5 Hanna M. G. Barriga,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Early detection of amyloidopathy in Alzheimer's mice by hyperspectral endoscopy. Swati S. More 1, James Beach 2, Robert Vince 1* 1 Center for Drug Design, Academic Health Center,
Supporting Information Early detection of amyloidopathy in Alzheimer's mice by hyperspectral endoscopy. Swati S. More 1, James Beach 2, Robert Vince 1* 1 Center for Drug Design, Academic Health Center,
What is superhydrophobicity? How it is defined? What is oleophobicity?
 Avijit Baidya 12.11.2016 What is superhydrophobicity? How it is defined? What is oleophobicity? Introduction : Hydrophobic and amphiphobic surfaces have been studied in great depth over the past couple
Avijit Baidya 12.11.2016 What is superhydrophobicity? How it is defined? What is oleophobicity? Introduction : Hydrophobic and amphiphobic surfaces have been studied in great depth over the past couple
Proteins. (b) Protein Structure and Conformational Change
 Proteins (b) Protein Structure and Conformational Change Protein Structure and Conformational Change Proteins contain the elements carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O2) and nitrogen (N2) Some may also
Proteins (b) Protein Structure and Conformational Change Protein Structure and Conformational Change Proteins contain the elements carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O2) and nitrogen (N2) Some may also
Reading for lecture 6
 Reading for lecture 6 1. Lipids and Lipid Bilayers 2. Membrane Proteins Voet and Voet, Chapter 11 Alberts et al Chapter 6 Jones, R.A.L, Soft Condensed Matter 195pp Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-850590-6
Reading for lecture 6 1. Lipids and Lipid Bilayers 2. Membrane Proteins Voet and Voet, Chapter 11 Alberts et al Chapter 6 Jones, R.A.L, Soft Condensed Matter 195pp Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-850590-6
Liver Fat Quantification
 Liver Fat Quantification Jie Deng, PhD, DABMP Department of Medical Imaging May 18 th, 2017 Disclosure Research agreement with Siemens Medical Solutions 2 Background Non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases
Liver Fat Quantification Jie Deng, PhD, DABMP Department of Medical Imaging May 18 th, 2017 Disclosure Research agreement with Siemens Medical Solutions 2 Background Non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases
Interactions between Bisphosphate. Geminis and Sodium Lauryl Ether
 Chapter 5 Interactions between Bisphosphate Geminis and Sodium Lauryl Ether Sulphate 110 5.1 Introduction The physiochemical and surface active properties of mixed surfactants are of more interest and
Chapter 5 Interactions between Bisphosphate Geminis and Sodium Lauryl Ether Sulphate 110 5.1 Introduction The physiochemical and surface active properties of mixed surfactants are of more interest and
Biological Membranes. Lipid Membranes. Bilayer Permeability. Common Features of Biological Membranes. A highly selective permeability barrier
 Biological Membranes Structure Function Composition Physicochemical properties Self-assembly Molecular models Lipid Membranes Receptors, detecting the signals from outside: Light Odorant Taste Chemicals
Biological Membranes Structure Function Composition Physicochemical properties Self-assembly Molecular models Lipid Membranes Receptors, detecting the signals from outside: Light Odorant Taste Chemicals
Cellular Neurophysiology I Membranes and Ion Channels
 Cellular Neurophysiology I Membranes and Ion Channels Reading: BCP Chapter 3 www.bioelectriclab All living cells maintain an electrical potential (voltage) across their membranes (V m ). Resting Potential
Cellular Neurophysiology I Membranes and Ion Channels Reading: BCP Chapter 3 www.bioelectriclab All living cells maintain an electrical potential (voltage) across their membranes (V m ). Resting Potential
HOMOTAURINE INVESTIGATIONAL SUMMARY
 HOMOTAURINE INVESTIGATIONAL SUMMARY Amyloid Precursor Protein (brain) Amyloid Aß Amyloid fibril Amyloid plaque action mechanism Aisen PS. Presented at: 9th International Geneva Springfield Symposium on
HOMOTAURINE INVESTIGATIONAL SUMMARY Amyloid Precursor Protein (brain) Amyloid Aß Amyloid fibril Amyloid plaque action mechanism Aisen PS. Presented at: 9th International Geneva Springfield Symposium on
Cellular Bioelectricity
 ELEC ENG 3BB3: Cellular Bioelectricity Notes for Lecture 22 Friday, February 28, 2014 10. THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION We will look at: Structure of the neuromuscular junction Evidence for the quantal nature
ELEC ENG 3BB3: Cellular Bioelectricity Notes for Lecture 22 Friday, February 28, 2014 10. THE NEUROMUSCULAR JUNCTION We will look at: Structure of the neuromuscular junction Evidence for the quantal nature
Bear: Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain 3e
 Bear: Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain 3e Chapter 03: The Neuronal Membrane at Rest Introduction Action potential in the nervous system Action potential vs. resting potential Slide 1 Slide 2 Cytosolic
Bear: Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain 3e Chapter 03: The Neuronal Membrane at Rest Introduction Action potential in the nervous system Action potential vs. resting potential Slide 1 Slide 2 Cytosolic
Carbohydrates and Lipids
 Carbohydrates and Lipids Chapter 5: Macromolecules Macromolecules Smaller organic molecules join together to form larger molecules o macromolecules 4 major classes of macromolecules: o Carbohydrates o
Carbohydrates and Lipids Chapter 5: Macromolecules Macromolecules Smaller organic molecules join together to form larger molecules o macromolecules 4 major classes of macromolecules: o Carbohydrates o
Lecture 15. Membrane Proteins I
 Lecture 15 Membrane Proteins I Introduction What are membrane proteins and where do they exist? Proteins consist of three main classes which are classified as globular, fibrous and membrane proteins. A
Lecture 15 Membrane Proteins I Introduction What are membrane proteins and where do they exist? Proteins consist of three main classes which are classified as globular, fibrous and membrane proteins. A
THE INS AND OUTS OF YOUR SKIN. Emma Sparr Physical Chemistry Lund University
 THE INS AND OUTS OF YOUR SKIN Emma Sparr Physical Chemistry Lund University The skin - A Responding Barrier Membrane stratum corneum (10 20 µm) Water CO 2 Temperature ph 5.5 O 2 Moisturizers, Drugs etc
THE INS AND OUTS OF YOUR SKIN Emma Sparr Physical Chemistry Lund University The skin - A Responding Barrier Membrane stratum corneum (10 20 µm) Water CO 2 Temperature ph 5.5 O 2 Moisturizers, Drugs etc
Due in class on Thursday Sept. 8 th
 Problem Set #1 Chem 391 Due in class on Thursday Sept. 8 th Name Solutions 1. For the following processes, identify whether G, H and S are positive (+), negative (-) or about zero (~0) at the standard
Problem Set #1 Chem 391 Due in class on Thursday Sept. 8 th Name Solutions 1. For the following processes, identify whether G, H and S are positive (+), negative (-) or about zero (~0) at the standard
Skeletal Muscle Contraction and ATP Demand
 Skeletal Muscle Contraction and ATP Demand Anatomy & Structure Contraction Cycling Calcium Regulation Types of Contractions Force, Power, and Contraction Velocity Epimysium - separates fascia and muscle
Skeletal Muscle Contraction and ATP Demand Anatomy & Structure Contraction Cycling Calcium Regulation Types of Contractions Force, Power, and Contraction Velocity Epimysium - separates fascia and muscle
The Transport and Organization of Cholesterol in Planar Solid-Supported Lipid Bilayer Depend on the Phospholipid Flip-Flop Rate
 Supporting Information The Transport and Organization of Cholesterol in Planar Solid-Supported Lipid Bilayer Depend on the Phospholipid Flip-Flop Rate Ting Yu, 1,2 Guangnan Zhou, 1 Xia Hu, 1,2 Shuji Ye
Supporting Information The Transport and Organization of Cholesterol in Planar Solid-Supported Lipid Bilayer Depend on the Phospholipid Flip-Flop Rate Ting Yu, 1,2 Guangnan Zhou, 1 Xia Hu, 1,2 Shuji Ye
Transport through biological membranes. Christine Carrington Biochemistry Unit Apr 2010
 Transport through biological membranes Christine Carrington Biochemistry Unit Apr 2010 Biological membranes Membranes control the structures and environments of the compartments they define and thereby
Transport through biological membranes Christine Carrington Biochemistry Unit Apr 2010 Biological membranes Membranes control the structures and environments of the compartments they define and thereby
Lipid Bilayers Are Excellent For Cell Membranes
 Lipid Bilayers Are Excellent For Cell Membranes ydrophobic interaction is the driving force Self-assembly in water Tendency to close on themselves Self-sealing (a hole is unfavorable) Extensive: up to
Lipid Bilayers Are Excellent For Cell Membranes ydrophobic interaction is the driving force Self-assembly in water Tendency to close on themselves Self-sealing (a hole is unfavorable) Extensive: up to
Ch5: Macromolecules. Proteins
 Ch5: Macromolecules Proteins Essential Knowledge 4.A.1 The subcomponents of biological molecules and their sequence determine the properties of that molecule A. Structure and function of polymers are derived
Ch5: Macromolecules Proteins Essential Knowledge 4.A.1 The subcomponents of biological molecules and their sequence determine the properties of that molecule A. Structure and function of polymers are derived
Supplementary Information
 Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Photoswitchable Assembly and Disassembly Xiaoyan Zheng, Dong Wang,* Zhigang Shuai,* MOE Key Laboratory of Organic Optoelectronics and Molecular Engineering,
Coarse-Grained Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Photoswitchable Assembly and Disassembly Xiaoyan Zheng, Dong Wang,* Zhigang Shuai,* MOE Key Laboratory of Organic Optoelectronics and Molecular Engineering,
Chapter 3. Protein Structure and Function
 Chapter 3 Protein Structure and Function Broad functional classes So Proteins have structure and function... Fine! -Why do we care to know more???? Understanding functional architechture gives us POWER
Chapter 3 Protein Structure and Function Broad functional classes So Proteins have structure and function... Fine! -Why do we care to know more???? Understanding functional architechture gives us POWER
6. The catalytic mechanism of arylsulfatase A and its theoretical investigation
 6. The catalytic mechanism of arylsulfatase A and its theoretical investigation When the crystal structure of arylsulfatase A was solved, a remarkable structural analogy to another hydrolytic enzyme, the
6. The catalytic mechanism of arylsulfatase A and its theoretical investigation When the crystal structure of arylsulfatase A was solved, a remarkable structural analogy to another hydrolytic enzyme, the
Chapter CHAPTER 7. ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF ZnO DOPED MAGESIUM ALUMIUM SILICATE GLASS-CERAMICS
 Chapter 7 102 CHAPTER 7 ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF ZnO DOPED MAGESIUM ALUMIUM SILICATE GLASS-CERAMICS Chapter 7 103 CHAPTER 7 ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF ZnO DOPED MAGNESIUM ALUMINUM SILICATE GLASS-CERAMICS
Chapter 7 102 CHAPTER 7 ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF ZnO DOPED MAGESIUM ALUMIUM SILICATE GLASS-CERAMICS Chapter 7 103 CHAPTER 7 ELECTRICAL PROPERTIES OF ZnO DOPED MAGNESIUM ALUMINUM SILICATE GLASS-CERAMICS
Biology Movement Across the Cell Membrane
 Biology 160 - Movement Across the Cell Membrane Prelab Information Movement is one of the characteristics of life. The ability to control the movement of material across the cell membrane is an incredibly
Biology 160 - Movement Across the Cell Membrane Prelab Information Movement is one of the characteristics of life. The ability to control the movement of material across the cell membrane is an incredibly
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Lu et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201012063/dc1 Figure S1. Kinetics of nuclear envelope assembly, recruitment of Nup133
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Lu et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201012063/dc1 Figure S1. Kinetics of nuclear envelope assembly, recruitment of Nup133
Diagnosis of Amyloidosis. Maria M. Picken MD, PhD Loyola University Medical Center Chicago
 Diagnosis of Amyloidosis Maria M. Picken MD, PhD Loyola University Medical Center Chicago mpicken@lumc.edu 1 Outline Diagnosis of amyloidosis Fat pad Other 2 Amyloidoses protein folding disorders protein
Diagnosis of Amyloidosis Maria M. Picken MD, PhD Loyola University Medical Center Chicago mpicken@lumc.edu 1 Outline Diagnosis of amyloidosis Fat pad Other 2 Amyloidoses protein folding disorders protein
Multi-modal fluorescence imaging of contracting intact hearts
 Multi-modal fluorescence imaging of contracting intact hearts ESR4: Vineesh Kappadan Project Supervisor: Prof.Ulrich Parlitz & Dr.Jan Christoph Biomedical Physics Group Max Planck Institute for Dynamics
Multi-modal fluorescence imaging of contracting intact hearts ESR4: Vineesh Kappadan Project Supervisor: Prof.Ulrich Parlitz & Dr.Jan Christoph Biomedical Physics Group Max Planck Institute for Dynamics
Characterization of Starch Polysaccharides in Aqueous Systems: de facto molar masses vs supermolecular structures
 Characterization of Starch Polysaccharides in Aqueous Systems: de facto molar masses vs supermolecular structures Werner Praznik and Anton uber Department of Chemistry BKU - University of Natural Resourses
Characterization of Starch Polysaccharides in Aqueous Systems: de facto molar masses vs supermolecular structures Werner Praznik and Anton uber Department of Chemistry BKU - University of Natural Resourses
Thioflavin T Binding to Amyloid Fibrils Lauren Riggs North Carolina State University University of Florida REU Summer 2006
 Thioflavin T Binding to Amyloid Fibrils Lauren Riggs North Carolina State University University of Florida REU Summer 2006 Abstract Treatment of Alzheimer s disease (AD) is hampered by the fact that the
Thioflavin T Binding to Amyloid Fibrils Lauren Riggs North Carolina State University University of Florida REU Summer 2006 Abstract Treatment of Alzheimer s disease (AD) is hampered by the fact that the
Protein Structure and Function
 Protein Structure and Function Protein Structure Classification of Proteins Based on Components Simple proteins - Proteins containing only polypeptides Conjugated proteins - Proteins containing nonpolypeptide
Protein Structure and Function Protein Structure Classification of Proteins Based on Components Simple proteins - Proteins containing only polypeptides Conjugated proteins - Proteins containing nonpolypeptide
Interaction Between Amyloid-b (1 42) Peptide and Phospholipid Bilayers: A Molecular Dynamics Study
 Biophysical Journal Volume 96 February 2009 785 797 785 Interaction Between Amyloid-b (1 42) Peptide and Phospholipid Bilayers: A Molecular Dynamics Study Charles H. Davis and Max L. Berkowitz * Department
Biophysical Journal Volume 96 February 2009 785 797 785 Interaction Between Amyloid-b (1 42) Peptide and Phospholipid Bilayers: A Molecular Dynamics Study Charles H. Davis and Max L. Berkowitz * Department
Life Sciences 1a. Practice Problems 4
 Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 4 1. KcsA, a channel that allows K + ions to pass through the membrane, is a protein with four identical subunits that form a channel through the center of the tetramer.
Life Sciences 1a Practice Problems 4 1. KcsA, a channel that allows K + ions to pass through the membrane, is a protein with four identical subunits that form a channel through the center of the tetramer.
Distinct Helix Propensities and Membrane Interactions of Human and Rat IAPP 1 19 Monomers in Anionic Lipid Bilayers
 pubs.acs.org/jpcb Distinct Helix Propensities and Membrane Interactions of Human and Rat IAPP 1 19 Monomers in Anionic Lipid Bilayers Cong Guo, Se bastien Co te, Normand Mousseau, and Guanghong Wei*, State
pubs.acs.org/jpcb Distinct Helix Propensities and Membrane Interactions of Human and Rat IAPP 1 19 Monomers in Anionic Lipid Bilayers Cong Guo, Se bastien Co te, Normand Mousseau, and Guanghong Wei*, State
the contents of the cell from the environment.
 Name: Date: Period: Living Environment Unit 3: Cellular Processes Study Guide Due Date: Test Date: Unit 3 Important Topics: I. Aim # 14 Cell Membrane II. Aim # 15 NYS Diffusion Lab III. Aim # 16 Photosynthesis
Name: Date: Period: Living Environment Unit 3: Cellular Processes Study Guide Due Date: Test Date: Unit 3 Important Topics: I. Aim # 14 Cell Membrane II. Aim # 15 NYS Diffusion Lab III. Aim # 16 Photosynthesis
Structural Characterization of Prion-like Conformational Changes of the Neuronal Isoform of Aplysia CPEB
 Structural Characterization of Prion-like Conformational Changes of the Neuronal Isoform of Aplysia CPEB Bindu L. Raveendra, 1,5 Ansgar B. Siemer, 2,6 Sathyanarayanan V. Puthanveettil, 1,3,7 Wayne A. Hendrickson,
Structural Characterization of Prion-like Conformational Changes of the Neuronal Isoform of Aplysia CPEB Bindu L. Raveendra, 1,5 Ansgar B. Siemer, 2,6 Sathyanarayanan V. Puthanveettil, 1,3,7 Wayne A. Hendrickson,
Colloid chemistry. Lecture 10: Surfactants
 Colloid chemistry Lecture 10: Surfactants Applications of surfactants: cleaning/detergents (40%); textiles; cosmetics; pharmacy; paint; food; etc. Etymology Surfactant micelles surfactant molecule spherical
Colloid chemistry Lecture 10: Surfactants Applications of surfactants: cleaning/detergents (40%); textiles; cosmetics; pharmacy; paint; food; etc. Etymology Surfactant micelles surfactant molecule spherical
Reading from the NCBI
 Reading from the NCBI http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?highlight=thermodyn amics&rid=stryer.section.156#167 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?highlight=stability,pr otein&rid=stryer.section.365#371
Reading from the NCBI http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?highlight=thermodyn amics&rid=stryer.section.156#167 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?highlight=stability,pr otein&rid=stryer.section.365#371
Electronic Supporting Information
 Modulation of raft domains in a lipid bilayer by boundary-active curcumin Manami Tsukamoto a, Kenichi Kuroda* b, Ayyalusamy Ramamoorthy* c, Kazuma Yasuhara* a Electronic Supporting Information Contents
Modulation of raft domains in a lipid bilayer by boundary-active curcumin Manami Tsukamoto a, Kenichi Kuroda* b, Ayyalusamy Ramamoorthy* c, Kazuma Yasuhara* a Electronic Supporting Information Contents
Effects of Cholesterol on Membranes: Physical Properties
 Effects of Cholesterol on Membranes: Physical Properties Removes gel to liquid crystal phase transition New intermediate phase called liquid ordered - ordering of the membrane lipids due to condensation
Effects of Cholesterol on Membranes: Physical Properties Removes gel to liquid crystal phase transition New intermediate phase called liquid ordered - ordering of the membrane lipids due to condensation
Quiz 8 Introduction to Polymers (Chemistry)
 051117 Quiz 8 Introduction to Polymers (Chemistry) (Figures from Heimenz Colloid Sci.) 1) Surfactants are amphiphilic molecules (molecules having one end hydrophobic and the other hydrophilic) and are
051117 Quiz 8 Introduction to Polymers (Chemistry) (Figures from Heimenz Colloid Sci.) 1) Surfactants are amphiphilic molecules (molecules having one end hydrophobic and the other hydrophilic) and are
Physical Pharmacy. Interfacial phenomena. Khalid T Maaroof MSc. Pharmaceutical sciences School of pharmacy Pharmaceutics department
 Physical Pharmacy Interfacial phenomena Khalid T Maaroof MSc. Pharmaceutical sciences School of pharmacy Pharmaceutics department 1 Introduction The boundary between two phases is generally described as
Physical Pharmacy Interfacial phenomena Khalid T Maaroof MSc. Pharmaceutical sciences School of pharmacy Pharmaceutics department 1 Introduction The boundary between two phases is generally described as
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature6416 Supplementary Notes Spine Ca 2+ signals produced by glutamate uncaging We imaged uncaging-evoked [Ca 2+ ] transients in neurons loaded with a green Ca 2+ - sensitive indicator (G;
doi: 1.138/nature6416 Supplementary Notes Spine Ca 2+ signals produced by glutamate uncaging We imaged uncaging-evoked [Ca 2+ ] transients in neurons loaded with a green Ca 2+ - sensitive indicator (G;
6 MEMBRANES AND TRANSPORT
 6 MEMBRANES AND TRANSPORT Chapter Outline 6.1 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Biological membranes contain both lipid and protein molecules The fluid mosaic model explains membrane structure The fluid mosaic model
6 MEMBRANES AND TRANSPORT Chapter Outline 6.1 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE Biological membranes contain both lipid and protein molecules The fluid mosaic model explains membrane structure The fluid mosaic model
Note: During 30 minute incubation; proceed thru appropriate sections below (e.g. sections II, III and V).
 LEGEND MAX β Amyloid x 40 LEGEND MAX β Amyloid x 40 ELISA Kit Components and Protocol Kit Components Capture Antibody Coated Plate 1 stripwell plate 1 40 Standard (2) 20μg vial 5X Wash Buffer 125mL Standard
LEGEND MAX β Amyloid x 40 LEGEND MAX β Amyloid x 40 ELISA Kit Components and Protocol Kit Components Capture Antibody Coated Plate 1 stripwell plate 1 40 Standard (2) 20μg vial 5X Wash Buffer 125mL Standard
