Foundations of Exercise-Based Dysphagia Treatments
|
|
|
- Ann Collins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Foundations of Exercise-Based Dysphagia Treatments Lori Burkhead Morgan, PhD, CCC-SLP Communication Science & Special Neurology
2 Disclosures Passy-Muir Educational Consultant ACP Provided semg device today for 2PM session
3 Always begin with the end in mind
4 Why we are all here today
5 My perspective Practicing SLP since 1994 Completed PhD in Rehabilitation Science, 2005 Focus on exercise science & sports training How can we (SLP s) truly do swallowing exercise?? 5
6 Purpose of this talk Muscle structure & function Response to deconditioning & conditioning Activity vs. exercise Application of exercise principles in dysphagia rehabilitation 6
7 The Challenge Critically evaluate & implement findings from research to solve clinical problems Provide the best patient care possible Treatment must be both time-efficient & costefficient
8 Evidence Based Practice Treatment should be based on: Best available evidence Patients wishes Clinicians knowledge & experience
9 Wisdom from a Snapple cap Relative to size, the tongue is the strongest muscle in the human body Snapple Real Fact #810
10 Neuromuscular Development 10
11 How muscles work 11
12 Skeletal Muscle Composition Type I Type II IIa IIb Slow-twitch, fatigue resistant Fast-twitch, fatigable Adaptable, more efficient Type II fiber Best force generation, but inefficient Whole muscle contains blend with a predominance of one type 12
13 Oropharyngeal Muscle Composition Type II is predominant Type I, IIa, IIb and hybrid fibers Unique architecture Regional differences in proportion & diameter of fiber types Complex arrangement Kent,
14 Oropharyngeal Muscle Composition Muscular hydrostat Tongue Kier & Smith (1985) Pharynx? Kairaitis (2010) Kairaitis,
15 Muscular Hydrostat Composed entirely of muscle with complex, 3- dimentional fiber arrangement. Maintains constant volume, as a fluid-based muscle structure. Shape alteration is dependent on redistribution of hydrostatic tissue pressure. Mechanical effect depends upon integrated activity of other muscles within the organ. Kairaitis,
16 Why do we care? Do contemporary exercise principles apply to these unique structures? In what ways can we maximize function of these muscles? 16
17 For more detail Burkhead LM, Sapienza CM, Rosenbek JC. Strength-training exercise in dysphagia rehabilitation: Principles, procedures, and directions for future research. Dysphagia 22: ,
18 Muscle response to deconditioning & conditioning Deconditioned: Muscle-wasting, cachexia Conditioned: John Burkhead World record bench press, 515 lbs. 18
19 Deconditioning PERIPHERAL Atrophy Loss in cross sectional area Decreased size Force-generating capacity ( strength ) Fiber-type shift More easily fatigued CENTRAL Decreased neural activation ( drive ) Decrease in number of motor units Remodeling of motor units Sarcopenia Age-related reduction in muscle fibers Preferentially affects Type II 19
20 Deconditioning Muscle atrophy & deconditioning 4-6 wks bed rest (young, healthy) up to 40% decrease in strength* Ill & elderly even more susceptible** *Bloomfield, **Urso et al,
21 Vicious Loops in sarcopenia 21 Muhlberg & Sieber, 2004
22 Vicious Loops in Dysphagia? Dysphagia - NPO ecreased swallow frequency Deconditioning Murray et al, 1996 Swallow frequency/min: Normals = 3 Dysphagia, - asp = 1.16 Dysphagia, + asp =.71 Exacerbation of dysfunction 22
23 Deconditioning and Non-Functional Function Synkinesis Involuntary movements that accompany voluntary movements Results from re-wiring of mis-firing nerves Functional Decompensation (Crary, 1995) Compensatory gestures that interfere with rather than help swallowing function. Excessive throat-clearing, tongue pumping, etc.
24 Conditioning PERIPHERAL Hypertrophy Increased cross sectional area Increased force-generating capacity Fiber type shift Increased endurance CENTRAL Increased neural activation ( drive ) Increased number of motor units 4-8 wks. 6-12wks. 24
25 ***Plasticity*** Cortical reorganization Blood flow changes Peripheral muscle changes 25
26 Therapeutic Exercise: Exercise vs. Activity
27 Exercise: What is it? Strength, Timing, Coordination, ROM* Specificity Intensity Overload principle (> 60% MVC) Progressive resistance Volume & frequency of exercise *Burkhead LM, Sapienza CM, Rosenbek JC (2007) 27
28 Motor Learning What is it? Process for learning voluntary control of more automatic physiological processes If swallowing is a sensory motor task, is motor learning part of re-training swallow behaviors? SURE!
29 Motor Learning Performance is temporary Learning is permanent change due to practice
30 Motor Learning 3-stage model (Fitts & Poser, 1967) Cognitive Stage Understanding task Associative Stage Refining movement pattern Autonomous Stage Developing independent, transferable skill
31 What qualifies as EXERCISE? Exercise is activity that challenges the body beyond it s typical level of activity Exercise that does not force the neuromuscular system beyond usual activity will not elicit an adaptation Resistance training recruiting 60-75% effort is required to achieve the greatest improvement 31
32 As your muscles get stronger, the challenge must also increase to elicit continued improvement! 32
33 Strength Defined The force-generating capacity of a muscle. Lifting a heavy weight Swallowing a large bolus of peanut butter 33
34 Endurance Defined The ability to continually produce force over a period of time. Marathon runner Eating a meal 34
35 Power Defined Combination of strength & speed Ability to exert force quickly in a burst Jumping, sprint start Strong, forceful BOT retraction
36 Speed Defined Maximal velocity achieved (how fast one can go!) Sprinter Swallowing liquids
37 Coordination Defined All of the previous components mentioned working in concert to efficiently and effectively perform functional tasks Basketball player in a game Ballet dancer performing My husband ingesting a rack of ribs & a beer.
38 Functional Reserve The proportion of potential force-generating capacity in relation to the effort required to perform a certain task. 38
39 Exercise Methods: Borrowing from Physical Therapy & Athletic Training 39
40 Think outside of the box or the cage.
41 Exercise: What? Strength, Timing, Coordination, ROM* Intensity Overload principle (> 60% MVC) Progressive resistance Volume & frequency of exercise Specificity *Burkhead LM, Sapienza CM, Rosenbek JC (2007) 41
42 Exercise: What? Direct versus indirect exercises Direct exercise Mendelsohn Effortful swallow Tongue hold swallow (Masako) Etc. Indirect exercise Shaker head lift EMST Lingual strengthening 42
43 Specificity in Oropharygneal Musculature Clark, HM (2012) Pilot study of 22 healthy volunteers Exercised 3/wk for 4 wks using IOPI STRENGTH ENDURANCE POWER SPEED Maximal anterior elevation press (5 sets of 5) with IOPI. Anterior elevation at 50% max. 5 sets at 75% of most recent endurance measure on IOPI. Anterior elevation at 75% Max, attempting to produce /t/ while achieving pressure goal on IOPI. 5 sets of 10. Produce /t/ as fast as possible. 5 sets of 10-second trials. No IOPI.
44 Specificity in Oropharyngeal Musculature Study limitations: Small N and gender imbalance Effect sizes demonstrated trends for strength, endurance, power (force & speed) but not speed alone. Potential for specificity of exercise in oropharyngeal muscle
45 Specificity in Oropharyngeal Musculature Clark, HM & Shelton, N (2014) 40 Healthy Volunteers 35 females (mean age = 22.3 yrs.) 5 males (mean age = 34 yrs.) 4 weeks of training (3 sets of 10, 7d/wk) Condition 1 Condition 2 Condition 3 Condition 4 High effort Sips from small- diameter straw Eff. swallow preceded by high-effort sips Eff. swallow preceded by max. lingual elevation Eff. Swallow
46 Specificity in Oropharyngeal Musculature RESULTS Poor compliance (avg.= 3 sets 10, 5d/wk) Swallowing pressures did not vary significantly across different straw diameters Larger volume w/ larger diameter = greater pressure Effortful swallow showed greatest pressure gains during swallowing
47 Specificity in Oropharyngeal Musculature RESULTS Swallowing pressures measured in BOTH a usual swallow and effortful swallow condition MOST dramatic improvement noted with EFFORTFUL SWALLOW since THAT is what was trained! What does this mean?
48 Specificity in Oropharyngeal Musculature If your patient is training EFFORTFUL SWALLOWS in therapy better FUNCTIONAL carryover with THAT swallow during deglutition (vs. usual swallow )
49 Specificity in Oropharyngeal Musculature Perhaps specificity training will yield greater outcomes with swallowing function Steele, C. et al, Toronto Rehabilitation Institute Case series reveal increased liquid swallowing when accuracy targeted in addition to lingual strengthening tasks* Ongoing exploratory RCT currently underway *Yeates et al, 2008; Steele et al, 2011; Steele et al 2013
50 Skill vs. Strength? Maybe both? Stonger musles move more quicly (power) Must have some base of strength for movement first
51 The sooner the better Exercise: When? Use it or lose it principle* Early intervention can improve diet tolerance, airway protection & overall nutrition** Pre-Treatment exercise beneficial in H&N Ca*** *Kleim & Jones, ** Emstahl et al, 1999; Carnaby et al, ***Kulbersh et al, 2006; Carroll et al,
52 52
53 Exercise When??
54 Our patients are too sick If you do nothing you will improve nothing. Function may only get worse as you wait for the patient to get better. Remember the concept of vicious loops. 54
55 Major culprits in the ICU patient Systemic inflammatory response syndrome Critical illness myopathy Critical illness polyneuropathy
56 Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome (SIRS) HR > 90 bpm Body temperature, 36 or >38 C WBC count, 4000cells/mm 3 SIRS + infection = sepsis
57 SIRS Occurs in adults and children Up to 50% of ICU pts on vent have SIRS 50-70% of those pts develop diffuse myopathy and polyneuropathy
58 Results in SIRS Muscle weakness Difficulty weaning from the ventilator
59 Critical Illness Myopathy (CIM) & Polyneuropathy (CIP) Usually co-occurring Presents as ventilator weaning difficulty Seen in 25-63% of pts on vent >1 week Sensorimotor with motor predominance Limbs & respiratory muscle affected most Cranial nerves usually spared
60 Critical Illness Myopathy (CIM) Diffuse weakness Diagnosed with EMG studies & biopsy Type II muscle atrophy or undergo necrosis
61 Offenders specifically impacting communication & swallowing Deconditioning Endotracheal intubation Tracheostomy Ventilator dependency
62 Deconditioning Negatively Impacts Structure & Function Muscle atrophy Reduced force-generating capacity A.K.A., strength Lower endurance
63 What about communication & Intubation swallowing in the ICU? Tracheostomy Ventilator dependency NPO
64 Endotracheal Intubation Bypasses use of upper airway Disuse atrophy Desensitization Trauma to mucosa, particularly larynx Cuff over inflation is common
65 Airflow Changes with tracheostomy Airflow bypasses upper airway Deflated cuff and/or fenestration can facilitate some upper airway airflow AIRFLOW
66 Normal Larynx (for reference)
67 Granuloma
68 Subglottic Stenosis
69 Glottic & subglottic trauma
70 Post-Intubation Ulceration
71 What contributes to structural deficits? Prolonged intubation (>2 weeks) Can happen quickly, not just in long-term intubation Whited (1984); Colice (1992); De Larminat et al (1995) Trauma due to movement/friction
72 Incidence & Prevalence Laryngotracheal injury in 95% (39/41) of previously intubated patients. Stauffer, Olson, & Petty (1981) Dysphagia as high as 56% (27/48), with nearly half those pts aspirating silently Ajemian, Nirmul, Anderson, Zirlen, & Kwasnik (2001)
73 But we CAN do something.
74 Are Our Patients Too Sick? If you do nothing, you will improve nothing - function commonly gets worse as you wait for the patient to get better.
75 Lessons from Physical Therapy Early intervention ROM and facilitation are precursors to rehabilitating functional movement.
76 Exercise: When? The sooner the better Muscle atrophy & deconditioning 4-6 weeks bedrest = ~40% decrease in strength* Ill & elderly even more susceptible** *Bloomfield, 1997 **Urso et al, 2006
77 First things first. Restore the system to the most normal condition as possible Passy-Muir Valve use (in-line ventilator use or trach alone)
78 Approaching Assessment with Exercise Principles in Mind Hey, what do you say we get this fella up for nice walk? Yeah I bet that would feel good to stretch in those legs! If he falls, we can call PT for a consult!
79 Instrumental assessment not just a tool for diagnosis of dysphagia think physiology! Coordination Speed Endurance Strength Various conditions
80 Evaluation: Lessons from Physical Rehabilitation Ambulation Leg strength/rom Standing, balance Few steps Swallowing O-P-L strength/rom Dry Swallow, cough, breath-hold Few bites/sips Greater distance, speed Greater volume, rate Variety of terrain Variety of consistency & situation
81 The Biggest Lesson from Physical Rehabilitation One successful step ambulation One successful swallow eating
82 Thank you for your attention.
Cardiovascular system progress chart
 Neural muscular system Topic 3A: Characteristics and functions of different muscle fibre types for a variety of sporting activities Term Muscle fibre Slow twitch (type I) Fast oxidative glycolytic (type
Neural muscular system Topic 3A: Characteristics and functions of different muscle fibre types for a variety of sporting activities Term Muscle fibre Slow twitch (type I) Fast oxidative glycolytic (type
Strength and conditioning? Chapter 4 Training Techniques. Weight gain (24yr, 73kg, 177cm, takes 18% protein) Guidelines.
 Strength and conditioning? Chapter 4 Training Techniques Minimise the probability of injury Maximise performance Athletic Training Spring 2014 Jihong Park Guidelines Safety: environment, technique, nutrition
Strength and conditioning? Chapter 4 Training Techniques Minimise the probability of injury Maximise performance Athletic Training Spring 2014 Jihong Park Guidelines Safety: environment, technique, nutrition
Swallow Function: Passy-Muir Valve Use for Evaluation & Rehabilitation David A. Muir Course Outline Physiology of Swallow
 Swallow Function: Passy-Muir Valve Use for Evaluation & Rehabilitation Mary Spremulli, MA, CCC-SLP Passy-Muir Clinical Consultant spre713@hotmail.com (949) 833-8255 David A. Muir 23 year-old ventilator
Swallow Function: Passy-Muir Valve Use for Evaluation & Rehabilitation Mary Spremulli, MA, CCC-SLP Passy-Muir Clinical Consultant spre713@hotmail.com (949) 833-8255 David A. Muir 23 year-old ventilator
Radiation Therapy to the Head and Neck: What You Need to Know About Swallowing
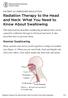 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Radiation Therapy to the Head and Neck: What You Need to Know About Swallowing This information describes swallowing problems that can be caused by radiation therapy to the
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Radiation Therapy to the Head and Neck: What You Need to Know About Swallowing This information describes swallowing problems that can be caused by radiation therapy to the
Improving Muscular Strength and Endurance
 Improving Muscular Strength and Endurance Introduction Outline Structure of Skeletal Muscle How Skeletal Muscle Contracts Motor Neurons Actin and Myosin Types of Contractions Muscle Fiber Types Determinants
Improving Muscular Strength and Endurance Introduction Outline Structure of Skeletal Muscle How Skeletal Muscle Contracts Motor Neurons Actin and Myosin Types of Contractions Muscle Fiber Types Determinants
Daniels SK & Huckabee ML (2008). Dysphagia Following Stroke. Muscles of Deglutition. Lateral & Mesial Premotor Area 6. Primary Sensory
 An Overview of Dysphagia in the Stroke Population Stephanie K. Daniels, PhD Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center PM & R, Baylor College of Medicine Communication Sciences and Disorders, University of Houston
An Overview of Dysphagia in the Stroke Population Stephanie K. Daniels, PhD Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center PM & R, Baylor College of Medicine Communication Sciences and Disorders, University of Houston
COMMUNICATION. Communication and Swallowing post Tracheostomy. Role of SLT. Impact of Tracheostomy. Normal Speech. Facilitating Communication
 Communication and Swallowing post Tracheostomy. Role of SLT 1. 2. 3. Management of communication needs. Management of swallowing issues. Working with the multidisciplinary team to facilitate weaning. Impact
Communication and Swallowing post Tracheostomy. Role of SLT 1. 2. 3. Management of communication needs. Management of swallowing issues. Working with the multidisciplinary team to facilitate weaning. Impact
Exercise for Frailty and Debility in Injury Recovery and Re-Injury Prevention
 Exercise for Frailty and Debility in Injury Recovery and Re-Injury Prevention Matthew N. Bartels, MD, MPH Professor and Chairman of Rehabilitation Medicine Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY
Exercise for Frailty and Debility in Injury Recovery and Re-Injury Prevention Matthew N. Bartels, MD, MPH Professor and Chairman of Rehabilitation Medicine Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY
Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment
 Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott, Williams
Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott, Williams
TeachPE.com progress charts
 Exercise Physiology topic 2: Preparation and training methods in relation to maintaining physical activity and performance Topic 2A: Physiological effects and benefits of a warm up and cool down Term Identify
Exercise Physiology topic 2: Preparation and training methods in relation to maintaining physical activity and performance Topic 2A: Physiological effects and benefits of a warm up and cool down Term Identify
Evidence-Based Swallowing Related Issues in Patients with Tracheotomy Tubes
 Evidence-Based Swallowing Related Issues in Patients with Tracheotomy Tubes Steven B. Leder, Ph.D. Yale University School of Medicine Debra M. Suiter,, Ph.D. University of Memphis Impetus Swallowing Rx
Evidence-Based Swallowing Related Issues in Patients with Tracheotomy Tubes Steven B. Leder, Ph.D. Yale University School of Medicine Debra M. Suiter,, Ph.D. University of Memphis Impetus Swallowing Rx
Btec Exam Guide Practice Questions - Unit 1.1 Components of Fitness
 Btec Exam Guide Practice Questions - Unit 1.1 Components of Fitness 1) What is the main difference between aerobic endurance and muscular endurance? (2 marks) 2) Explain the following components of physical
Btec Exam Guide Practice Questions - Unit 1.1 Components of Fitness 1) What is the main difference between aerobic endurance and muscular endurance? (2 marks) 2) Explain the following components of physical
BTEC. Name: Student Guide. BTEC Level 2 Unit 1- Fitness for Sport and Exercise
 BTEC BTEC Level 2 Unit 1- Fitness for Sport and Exercise Student Guide Name: 1 Before we start Overview This unit covers four keys areas (learning aims): A: Know about the components of fitness and the
BTEC BTEC Level 2 Unit 1- Fitness for Sport and Exercise Student Guide Name: 1 Before we start Overview This unit covers four keys areas (learning aims): A: Know about the components of fitness and the
Oral care & swallowing
 Oral care & swallowing Oral care is important as it has a role to play in preventing healthcare associated infections. Dental plaque and the oropharynx can become colonized by bacteria and a biofilm can
Oral care & swallowing Oral care is important as it has a role to play in preventing healthcare associated infections. Dental plaque and the oropharynx can become colonized by bacteria and a biofilm can
DEVELOPING PHYSICAL CAPACITIES - SPEED
 DEVELOPING PHYSICAL CAPACITIES - SPEED Speed is one of the main fitness components, whether one plays sports or not, everybody needs speed because movements in everyday situations have to be performed
DEVELOPING PHYSICAL CAPACITIES - SPEED Speed is one of the main fitness components, whether one plays sports or not, everybody needs speed because movements in everyday situations have to be performed
Chapter 4. Muscular Strength and Endurance KIN 217 3/28/18 1
 Chapter 4 Muscular Strength and Endurance KIN 217 1 Functions of Muscle Tissues Functions: provide stability and postural tone, allow purposeful movement, heat production. Muscle mass constitutes: 40 to
Chapter 4 Muscular Strength and Endurance KIN 217 1 Functions of Muscle Tissues Functions: provide stability and postural tone, allow purposeful movement, heat production. Muscle mass constitutes: 40 to
Respiratory Compromise and Swallowing
 Speech Pathology and Respiratory Care April 11, 2013 By Angela Parcaro-Tucker, MA, CCC-SLP, LSVT How can Speech Therapy help? 1 Respiratory Compromise and Swallowing Swallowing is a complex sequence of
Speech Pathology and Respiratory Care April 11, 2013 By Angela Parcaro-Tucker, MA, CCC-SLP, LSVT How can Speech Therapy help? 1 Respiratory Compromise and Swallowing Swallowing is a complex sequence of
DYSPHAGIA MANAGEMENT IN ACUTE CARE AMANDA HEREFORD, MA, CCC- SLP
 DYSPHAGIA MANAGEMENT IN ACUTE CARE AMANDA HEREFORD, MA, CCC- SLP OVERVIEW Decision making re: swallowing in the medically compromised patient Swallow evaluation vs. Nursing Swallow Screening Instrumental
DYSPHAGIA MANAGEMENT IN ACUTE CARE AMANDA HEREFORD, MA, CCC- SLP OVERVIEW Decision making re: swallowing in the medically compromised patient Swallow evaluation vs. Nursing Swallow Screening Instrumental
The Role of the Speech Language Pathologist & Spinal Cord Injury
 The Role of the Speech Language Pathologist & Spinal Cord Injury Facts According to the National Spinal Cord Injury Statistical Center (NSCISC) there are approxiamtely 12,000 new spinal cord injuries (SCI)
The Role of the Speech Language Pathologist & Spinal Cord Injury Facts According to the National Spinal Cord Injury Statistical Center (NSCISC) there are approxiamtely 12,000 new spinal cord injuries (SCI)
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education Methods of Training These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
KS4 Physical Education Methods of Training These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
Evidence-Based, Optimal Strength Exercise Parameters: Practice Considerations for Speech Therapists
 Evidence-Based, Optimal Strength Exercise Parameters: Practice Considerations for Speech Therapists Mark Richards, PT, MS, CEEAA Vice President of Clinical Services Accelerated Care Plus markprichards@comcast.net
Evidence-Based, Optimal Strength Exercise Parameters: Practice Considerations for Speech Therapists Mark Richards, PT, MS, CEEAA Vice President of Clinical Services Accelerated Care Plus markprichards@comcast.net
Temporal (time related) aspects of job design the main concern is fatigue: over worked, over stressed etc., rest is required for recovery.
 Temporal Ergonomics Temporal (time related) aspects of job design the main concern is fatigue: over worked, over stressed etc., rest is required for recovery. Fatigue is associated with (1) Gradual decrement
Temporal Ergonomics Temporal (time related) aspects of job design the main concern is fatigue: over worked, over stressed etc., rest is required for recovery. Fatigue is associated with (1) Gradual decrement
Section III: Concept 11: Muscular Fitness
 Section III: Concept 11: Muscular Fitness ١ Health Benefits of Muscular Fitness Include muscular strength and ٢ endurance Promote many health benefits Avoiding back problems Reducing risks of injury Reducing
Section III: Concept 11: Muscular Fitness ١ Health Benefits of Muscular Fitness Include muscular strength and ٢ endurance Promote many health benefits Avoiding back problems Reducing risks of injury Reducing
TREATMENT OF DYSPHAGIA IN PATIENTS AFTER STROKE IN ESTONIA
 TREATMENT OF DYSPHAGIA IN PATIENTS AFTER STROKE IN ESTONIA ANNE URIKO SPORTS MEDICINE AND REHABILITATION CLINIG OF TARTU UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL 17.09.2010 DYSPHAGIA DIFFICULTY MOVING FOOD FROM MOUTH TO STOMACH
TREATMENT OF DYSPHAGIA IN PATIENTS AFTER STROKE IN ESTONIA ANNE URIKO SPORTS MEDICINE AND REHABILITATION CLINIG OF TARTU UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL 17.09.2010 DYSPHAGIA DIFFICULTY MOVING FOOD FROM MOUTH TO STOMACH
D: there are no strength gains typically at this early stage in training
 Name: KIN 410 Final Motor Control (B) units 6, + FALL 2016 1. Place your name at the top of this page of questions, and on the answer sheet. 2. Both question and answer sheets must be turned in. 3. Read
Name: KIN 410 Final Motor Control (B) units 6, + FALL 2016 1. Place your name at the top of this page of questions, and on the answer sheet. 2. Both question and answer sheets must be turned in. 3. Read
VO2MAX TEST.
 AEROBIC CAPACITY Aerobic capacity refers to the maximum amount of oxygen that the body can utilize in an exercise session It is possible to improve aerobic capacity over time, and it is also possible to
AEROBIC CAPACITY Aerobic capacity refers to the maximum amount of oxygen that the body can utilize in an exercise session It is possible to improve aerobic capacity over time, and it is also possible to
POST POLIO SYNDROME (PPS) AND ITS EFFECTS ON SWALLOWING BY: LINDSAY JORDAN
 POST POLIO SYNDROME (PPS) AND ITS EFFECTS ON SWALLOWING BY: LINDSAY JORDAN WHAT IS POST POLIO SYNDROME (PPS)? Post-polio syndrome (PPS) is a condition that affects polio survivors years after recovery
POST POLIO SYNDROME (PPS) AND ITS EFFECTS ON SWALLOWING BY: LINDSAY JORDAN WHAT IS POST POLIO SYNDROME (PPS)? Post-polio syndrome (PPS) is a condition that affects polio survivors years after recovery
Radiation Therapy to the Head and Neck: What You Need to Know About Swallowing
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Radiation Therapy to the Head and Neck: What You Need to Know About Swallowing This information describes swallowing problems that can be caused by radiation therapy to the
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Radiation Therapy to the Head and Neck: What You Need to Know About Swallowing This information describes swallowing problems that can be caused by radiation therapy to the
Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle
 Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle Course: Introduction to Exercise Science-Level 2 (Exercise Physiology) Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.ED, ACSM-H/FI Copyright EFS Inc. All Rights Reserved. Skeletal
Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle Course: Introduction to Exercise Science-Level 2 (Exercise Physiology) Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.ED, ACSM-H/FI Copyright EFS Inc. All Rights Reserved. Skeletal
Muscle Function: Understanding the Unique Characteristics of Muscle. Three types of muscle. Muscle Structure. Cardiac muscle.
 : Understanding the Unique Characteristics of Muscle Scott Riewald United States Olympic Committee Three types of muscle Cardiac muscle Involuntary Smooth muscle Involuntary Skeletal muscle Voluntary Involuntary
: Understanding the Unique Characteristics of Muscle Scott Riewald United States Olympic Committee Three types of muscle Cardiac muscle Involuntary Smooth muscle Involuntary Skeletal muscle Voluntary Involuntary
Swallowing Disorders and Their Management in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
 National Multiple Sclerosis Society 733 Third Avenue New York, NY 10017-3288 Clinical Bulletin Information for Health Professionals Swallowing Disorders and Their Management in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
National Multiple Sclerosis Society 733 Third Avenue New York, NY 10017-3288 Clinical Bulletin Information for Health Professionals Swallowing Disorders and Their Management in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
PMV ON OR OFF WITH SWALLOWING DOES IT MAKE A DIFFERENCE?
 PMV ON OR OFF WITH SWALLOWING DOES IT MAKE A DIFFERENCE? 1 Tedd Masiongale, MA, CCC-SLP Lorry Lewis, MS, CCC-SLP REASON FOR STUDY After several years of working with trach and ventilator dependent patients,
PMV ON OR OFF WITH SWALLOWING DOES IT MAKE A DIFFERENCE? 1 Tedd Masiongale, MA, CCC-SLP Lorry Lewis, MS, CCC-SLP REASON FOR STUDY After several years of working with trach and ventilator dependent patients,
GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION PE2 UNIT GUIDE
 GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION PE2 UNIT GUIDE Content Title: Application of Principles of Training Key points Application of the principles of training Specific examples of how to apply the principles of specificity,
GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION PE2 UNIT GUIDE Content Title: Application of Principles of Training Key points Application of the principles of training Specific examples of how to apply the principles of specificity,
Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy
 Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy Disclaimer This material is intended for use by trained family members and caregivers of children with tracheostomies who are
Tracheostomy and Ventilator Education Program Module 2: Respiratory Anatomy Disclaimer This material is intended for use by trained family members and caregivers of children with tracheostomies who are
NZQA Expiring unit standard version 2 Page 1 of 5. Demonstrate knowledge of exercise physiology and human anatomy
 Page 1 of 5 Title Demonstrate knowledge of exercise physiology and human anatomy Level 3 Credits 10 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: explain the nervous system and its functions;
Page 1 of 5 Title Demonstrate knowledge of exercise physiology and human anatomy Level 3 Credits 10 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: explain the nervous system and its functions;
Vertical Jump Training Exposed: The 3 Biggest Training Mistakes Athletes Make & How These Mistakes Are Severely Diminishing Their Results
 Vertical Jump Training Exposed: The 3 Biggest Training Mistakes Athletes Make & How These Mistakes Are Severely Diminishing Their Results Have you been working your tail off in the gym trying to increase
Vertical Jump Training Exposed: The 3 Biggest Training Mistakes Athletes Make & How These Mistakes Are Severely Diminishing Their Results Have you been working your tail off in the gym trying to increase
BTEC First Award in Sport NQF Unit 1 Fitness for Sport and Exercise Topic A Revision Test
 BTEC First Award in Sport NQF Unit 1 Fitness for Sport and Exercise Topic A Revision Test 1 What are the two different types of Components of Fitness? 2 Aerobic Endurance, Muscular Endurance and Flexibility
BTEC First Award in Sport NQF Unit 1 Fitness for Sport and Exercise Topic A Revision Test 1 What are the two different types of Components of Fitness? 2 Aerobic Endurance, Muscular Endurance and Flexibility
DIFFERENT WAYS TO TRAIN
 DIFFERENT WAYS TO TRAIN There are 5 principle training methods: 1. INTERVAL TRAINING 2.CONTINUOUS TRAINING 3.FARTLEK TRAINING 4.CIRCUIT TRAINING 5.WEIGHT TRAINING 1. INTERVAL TRAINING This involves periods
DIFFERENT WAYS TO TRAIN There are 5 principle training methods: 1. INTERVAL TRAINING 2.CONTINUOUS TRAINING 3.FARTLEK TRAINING 4.CIRCUIT TRAINING 5.WEIGHT TRAINING 1. INTERVAL TRAINING This involves periods
Assignment 4: Muscle Structure and Function
 Assignment 4: Muscle Structure and Function Unit 2: Chapter 5 Part A Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about skeletal muscle is true: A) Skeletal muscles are usually linked
Assignment 4: Muscle Structure and Function Unit 2: Chapter 5 Part A Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about skeletal muscle is true: A) Skeletal muscles are usually linked
Supporting information leaflet (5): Stretches and Activity (Exercise) for people with Neuromuscular Disorders
 Acute Services Division Supporting information leaflet (5): Stretches and Activity (Exercise) for people with Neuromuscular Disorders Introduction Exercise is an important part of all of our daily lives.
Acute Services Division Supporting information leaflet (5): Stretches and Activity (Exercise) for people with Neuromuscular Disorders Introduction Exercise is an important part of all of our daily lives.
PHYSICAL FITNESS 1.- ENDURANCE TRAINING SYSTEMS
 PHYSICAL FITNESS 1.- ENDURANCE TRAINING SYSTEMS 1.1.- TYPES Last year we learnt that there are two types, depending on the intensity of the exertion: this intensity depends on whether the oxygen for the
PHYSICAL FITNESS 1.- ENDURANCE TRAINING SYSTEMS 1.1.- TYPES Last year we learnt that there are two types, depending on the intensity of the exertion: this intensity depends on whether the oxygen for the
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education Muscles and Muscle Action These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities
KS4 Physical Education Muscles and Muscle Action These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities
Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Patients with COPD: A Systematic Review
 Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Patients with COPD: A Systematic Review Lisa O Kane, B.A. Michael Groher, Ph.D. Boston University University of Redlands Boston, MA Redlands, CA ASHA Convention 2009 New Orleans
Oropharyngeal Dysphagia in Patients with COPD: A Systematic Review Lisa O Kane, B.A. Michael Groher, Ph.D. Boston University University of Redlands Boston, MA Redlands, CA ASHA Convention 2009 New Orleans
2013 Charleston Swallowing Conference
 Providing Quality Affordable Continuing Education and Treatment Materials for over 30 years. 2013 Charleston Swallowing Conference Session 9 Bedside Assessment: What Does It Tell You? 10:00 11:30 am Saturday,
Providing Quality Affordable Continuing Education and Treatment Materials for over 30 years. 2013 Charleston Swallowing Conference Session 9 Bedside Assessment: What Does It Tell You? 10:00 11:30 am Saturday,
Yearly Training program - plan of attack (goals and methods of attaining goals)
 Yearly Training program - plan of attack (goals and methods of attaining goals) Single (one peak) verses Double Periodization (two peaks) 3 phases of training plus 1 transition phase for each Each phase
Yearly Training program - plan of attack (goals and methods of attaining goals) Single (one peak) verses Double Periodization (two peaks) 3 phases of training plus 1 transition phase for each Each phase
Where do we come from?
 Interdisciplinary Decision-Making with Patients Requiring Tracheostomy and Carrie Windhorst MS CCC-SLP Cheryl Wagoner MS CCC-SLP Ricque Harth MEd CCC-SLP Where do we come from? Welcome to Madonna Rehabilitation
Interdisciplinary Decision-Making with Patients Requiring Tracheostomy and Carrie Windhorst MS CCC-SLP Cheryl Wagoner MS CCC-SLP Ricque Harth MEd CCC-SLP Where do we come from? Welcome to Madonna Rehabilitation
Author: Max Schmarzo Draft. Purpose
 Author: Max Schmarzo Draft Purpose The purpose of this paper is to introduce the concepts of accessible strength and strength ceiling and its relationship with muscular force in regards to both the structural
Author: Max Schmarzo Draft Purpose The purpose of this paper is to introduce the concepts of accessible strength and strength ceiling and its relationship with muscular force in regards to both the structural
The Biomechanics of Human Skeletal Muscle
 AML2506 Biomechanics and Flow Simulation Day 03B The Biomechanics of Human Skeletal Muscle Session Speaker Dr. M. D. Deshpande 1 Session Objectives At the end of this session the delegate would have understood
AML2506 Biomechanics and Flow Simulation Day 03B The Biomechanics of Human Skeletal Muscle Session Speaker Dr. M. D. Deshpande 1 Session Objectives At the end of this session the delegate would have understood
MY SPORTFOLIO ISM PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND FITNESS TEACHER: BLOCK: GRADE:
 MY SPORTFOLIO ISM PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND FITNESS TEACHER: BLOCK: GRADE: WHAT IS HEALTHY ACTIVE LIVING? Before starting off on a journey, you need to know what your starting point is. This exercise will
MY SPORTFOLIO ISM PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND FITNESS TEACHER: BLOCK: GRADE: WHAT IS HEALTHY ACTIVE LIVING? Before starting off on a journey, you need to know what your starting point is. This exercise will
Program Design The Science of Fat Loss and changing your Bodies Composition for the Long Term.
 Program Design The Science of Fat Loss and changing your Bodies Composition for the Long Term. It is impossible to write this article without it going into depth about scientific processes. It would also
Program Design The Science of Fat Loss and changing your Bodies Composition for the Long Term. It is impossible to write this article without it going into depth about scientific processes. It would also
Optimal Interval Training for MMA By Eric Wong, BSc, CSCS
 Optimal Interval Training for MMA By Eric Wong, BSc, CSCS Interval training has quickly become the go-to choice for mixed martial artists looking to maximize their cardio. The most popular form of intervals
Optimal Interval Training for MMA By Eric Wong, BSc, CSCS Interval training has quickly become the go-to choice for mixed martial artists looking to maximize their cardio. The most popular form of intervals
What is Physical Fitness?
 What is Physical Fitness? The Body Systems ability to work together efficiently Daily activities require no effort Have the energy to respond in an emergency Can enjoy leisure activities Both Health and
What is Physical Fitness? The Body Systems ability to work together efficiently Daily activities require no effort Have the energy to respond in an emergency Can enjoy leisure activities Both Health and
VCERT PE Final Test Revision
 VCERT PE Final Test Revision Skeletal System This one is known as the Condyloid Joint Definition: The point at which two or more bones meet to produce movement. Slightly Moveable Joints- spine Fix Joints-
VCERT PE Final Test Revision Skeletal System This one is known as the Condyloid Joint Definition: The point at which two or more bones meet to produce movement. Slightly Moveable Joints- spine Fix Joints-
Muscle Function and Exercise
 Muscle Function and Exercise The muscle cell is the basic unit that makes up a muscle. When looking at a whole muscle, we are actually seeing a collection of muscle cells grouped together. If we were to
Muscle Function and Exercise The muscle cell is the basic unit that makes up a muscle. When looking at a whole muscle, we are actually seeing a collection of muscle cells grouped together. If we were to
Guidance. Name and describe the 4 types of guidance. What are the key features of each of the types of guidance?
 Skill What components make up skill? Describe a motor skill Explain what a skilled performer is What are the main characteristics of skilful movement? Classification What is a continuum? Describe a closed
Skill What components make up skill? Describe a motor skill Explain what a skilled performer is What are the main characteristics of skilful movement? Classification What is a continuum? Describe a closed
Clinical Swallowing Exam
 Clinical Evaluation Template 1 Clinical Exam Name: ID/Medical record number: Date of exam: Referred by: Reason for referral: Medical diagnosis: Date of onset of diagnosis: Other relevant medical history/diagnoses/surgery
Clinical Evaluation Template 1 Clinical Exam Name: ID/Medical record number: Date of exam: Referred by: Reason for referral: Medical diagnosis: Date of onset of diagnosis: Other relevant medical history/diagnoses/surgery
Implementation of the Dance Head and Neck Clinical Pathway
 Implementation of the Dance Head and Neck Clinical Pathway Barbara Messing, MA, CCC-SLP, BCS-S, FASHA & Head and Neck Team GBMC Head and Neck Grand Rounds Acknowledgements Acknowledgements Background Evidence
Implementation of the Dance Head and Neck Clinical Pathway Barbara Messing, MA, CCC-SLP, BCS-S, FASHA & Head and Neck Team GBMC Head and Neck Grand Rounds Acknowledgements Acknowledgements Background Evidence
What are the Challenges? Spreading the Word in NICU. Need for NICU Care: Impact. Baby Trachs: Use of the Passy Muir Valve in the NICU to
 What are the Challenges? Baby Trachs: Use of the Passy Muir Valve in the NICU to Optimize Swallowing and Feeding Catherine S Shaker, MS/CCC SLP, BRS S and Cari Mutnick, MS/CCC SLP Florida Hospital for
What are the Challenges? Baby Trachs: Use of the Passy Muir Valve in the NICU to Optimize Swallowing and Feeding Catherine S Shaker, MS/CCC SLP, BRS S and Cari Mutnick, MS/CCC SLP Florida Hospital for
On-line Text: Hawkins, Skeletal Muscle Mechanics available via Canvas/Pages/Hawkins On-line Textbook.
 BIM 228 Skeletal Muscle Mechanics: Form, Function, Adaptability and Implications for Human Movement Instructor: Dave Hawkins Office: 275 Hickey Gym Phone: 752-2748 email: dahawkins@ucdavis.edu Office Hrs:
BIM 228 Skeletal Muscle Mechanics: Form, Function, Adaptability and Implications for Human Movement Instructor: Dave Hawkins Office: 275 Hickey Gym Phone: 752-2748 email: dahawkins@ucdavis.edu Office Hrs:
CHAPTER 3: The neuromuscular system. Practice questions - text book pages QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Answers
 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 3: The neuromuscular system Practice questions - text book pages 46-48 1) Which type of muscle fibre is associated with endurance? a. fast twitch muscle fibres, because they
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 3: The neuromuscular system Practice questions - text book pages 46-48 1) Which type of muscle fibre is associated with endurance? a. fast twitch muscle fibres, because they
2011 USTFCCCA Annual Meeting
 Caryl Smith Gilbert Caryl Smith Gilbert 2011 USTFCCCA Annual Meeting What t is Power? Why y do we need Power? Where do we use Power? When do we use Power? How do we develop Power? As horizontal velocity
Caryl Smith Gilbert Caryl Smith Gilbert 2011 USTFCCCA Annual Meeting What t is Power? Why y do we need Power? Where do we use Power? When do we use Power? How do we develop Power? As horizontal velocity
Aerobic Endurance. Muscular Strength
 Fitness can be defined in many different ways. To some people fitness might mean a slim waistline. To others it could be the ability to bench-press their body weight. And to others it might be a general
Fitness can be defined in many different ways. To some people fitness might mean a slim waistline. To others it could be the ability to bench-press their body weight. And to others it might be a general
Physical Education Studies Year 11 ATAR. CHAPTER 5: Exercise Physiology NEXT
 Physical Education Studies Year 11 ATAR CHAPTER 5: Exercise Physiology NEXT Welcome to the quiz for Chapter 5 You will be given 30 multiple choice questions Click on the correct answer Use the links to
Physical Education Studies Year 11 ATAR CHAPTER 5: Exercise Physiology NEXT Welcome to the quiz for Chapter 5 You will be given 30 multiple choice questions Click on the correct answer Use the links to
MUSCLE FIBERS. EXSC- Std. 9
 MUSCLE FIBERS EXSC- Std. 9 BELL WORK Page 117-118 in small A&P book. Define: Muscle fatigue Muscle tone Atrophy Hypertrophy Review 14 must know muscles from previous lesson!!! MUSCLE TONE MUSCLE ATROPHY
MUSCLE FIBERS EXSC- Std. 9 BELL WORK Page 117-118 in small A&P book. Define: Muscle fatigue Muscle tone Atrophy Hypertrophy Review 14 must know muscles from previous lesson!!! MUSCLE TONE MUSCLE ATROPHY
Year 7 End of Year Exam Revision
 Year 7 End of Year Exam Revision Physical Education https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=el1_enlemka Starter Video The Exam The exam you will sit is out of 40 marks. 25 of these are multiple choice, 7 are short
Year 7 End of Year Exam Revision Physical Education https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=el1_enlemka Starter Video The Exam The exam you will sit is out of 40 marks. 25 of these are multiple choice, 7 are short
PSK4U THE NEUROMUSCULAR SYSTEM
 PSK4U THE NEUROMUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW Review of muscle so we can see how the neuromuscular system works This is not on today's note Skeletal Muscle Cell: Cellular System A) Excitation System Electrical
PSK4U THE NEUROMUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW Review of muscle so we can see how the neuromuscular system works This is not on today's note Skeletal Muscle Cell: Cellular System A) Excitation System Electrical
Chapter 13, 21. The Physiology of Training: Physiological Effects of Strength Training pp Training for Anaerobic Power p.
 Chapter 13, 21 The Physiology of Training: Physiological Effects of Strength Training pp. 267-270 270 Training for Anaerobic Power p. 430-431 431 Types of Contractions Dynamic, Isotonic, or concentric
Chapter 13, 21 The Physiology of Training: Physiological Effects of Strength Training pp. 267-270 270 Training for Anaerobic Power p. 430-431 431 Types of Contractions Dynamic, Isotonic, or concentric
Action and Support: The Muscles and Skeleton
 Lesson 15 Action and Support: The Muscles and Skeleton Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Muscle Contraction Muscles: tissues that produce movement by contracting Vertebrates have three types of
Lesson 15 Action and Support: The Muscles and Skeleton Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Muscle Contraction Muscles: tissues that produce movement by contracting Vertebrates have three types of
SWALLOW PHYSIOLOGY IN PATIENTS WITH TRACH CUFF INFLATED OR DEFLATED: A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY
 SWALLOW PHYSIOLOGY IN PATIENTS WITH TRACH CUFF INFLATED OR DEFLATED: A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Ruiying Ding, PhD, 1 Jeri A. Logemann, PhD 2 1 University of Wisconsin-Whitewater, Department of Communicative
SWALLOW PHYSIOLOGY IN PATIENTS WITH TRACH CUFF INFLATED OR DEFLATED: A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY Ruiying Ding, PhD, 1 Jeri A. Logemann, PhD 2 1 University of Wisconsin-Whitewater, Department of Communicative
Respiratory Guard System: New Technology
 Respiratory Guard System: New Technology Zvi Peled, Avishai Zisser, Michal Fertouk, Victor Kerzman, Keren Bitton-Worms and Gil Bolotin. Department of Cardiac Surgery, Rambam Health Care Campus, Technion
Respiratory Guard System: New Technology Zvi Peled, Avishai Zisser, Michal Fertouk, Victor Kerzman, Keren Bitton-Worms and Gil Bolotin. Department of Cardiac Surgery, Rambam Health Care Campus, Technion
Fitness Intro. Freshmen PE
 Fitness Intro Freshmen PE Physical Fitness Are you able to get through your day easily without tiring? Does your body respond quickly when it needs to? Are you mentally alert in class? Do you feel good
Fitness Intro Freshmen PE Physical Fitness Are you able to get through your day easily without tiring? Does your body respond quickly when it needs to? Are you mentally alert in class? Do you feel good
PE Assessment Point 2 Revision booklet
 PE Assessment Point 2 Revision booklet Assessment point 2 PE assessment Theory Practical Theory Topics Locations of major bones Functions of the skeletal system Aerobic and anaerobic Warm ups and cool
PE Assessment Point 2 Revision booklet Assessment point 2 PE assessment Theory Practical Theory Topics Locations of major bones Functions of the skeletal system Aerobic and anaerobic Warm ups and cool
How does training affect performance?
 Name: How does training affect performance? CQ1 DP2 types of training and training methods aerobic, eg continuous, Fartlek, aerobic interval, circuit anaerobic, eg anaerobic interval flexibility, eg static,
Name: How does training affect performance? CQ1 DP2 types of training and training methods aerobic, eg continuous, Fartlek, aerobic interval, circuit anaerobic, eg anaerobic interval flexibility, eg static,
CHAPTER 5: Training methods and aerobic training Practice questions - text book pages 91-92
 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 5: Training methods and aerobic training Practice questions - text book pages 91-92 1) Mary is a 20 year old college student What is her theoretical maximum heart rate? a
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS CHAPTER 5: Training methods and aerobic training Practice questions - text book pages 91-92 1) Mary is a 20 year old college student What is her theoretical maximum heart rate? a
9/16/2009. Fast and slow twitch fibres. Properties of Muscle Fiber Types Fast fibers Slow fibers
 Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils Fast and slow twitch fibres Rat hindlimb muscle ATPase staining at different ph and NADH Muscle fibre shortening velocity lengths/second Properties of Muscle Fiber
Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils Fast and slow twitch fibres Rat hindlimb muscle ATPase staining at different ph and NADH Muscle fibre shortening velocity lengths/second Properties of Muscle Fiber
Types of Flexibility. Types of Flexibility. What is Flexibility? What is Flexibility? Or rather a lack of it! 8/22/2012
 Or rather a lack of it! Types of Flexibility Types of Flexibility STATIC FLEXIBILITY Slowly moving into a stretched position Holding the stretched position Sitting in the splits DYNAMIC FLEXIBILITY Involves
Or rather a lack of it! Types of Flexibility Types of Flexibility STATIC FLEXIBILITY Slowly moving into a stretched position Holding the stretched position Sitting in the splits DYNAMIC FLEXIBILITY Involves
Neuromuscular diseases (NMDs) include both hereditary and acquired diseases of the peripheral neuromuscular system. They are diseases of the
 Neuromuscular diseases (NMDs) include both hereditary and acquired diseases of the peripheral neuromuscular system. They are diseases of the peripheral nerves (neuropathies and anterior horn cell diseases),
Neuromuscular diseases (NMDs) include both hereditary and acquired diseases of the peripheral neuromuscular system. They are diseases of the peripheral nerves (neuropathies and anterior horn cell diseases),
Applied anatomy and physiology: definitions of key terms
 Applied anatomy and physiology: definitions of key terms See pages 5 46 These are the key terms from Chapter 1. Try cutting them out and then matching the key terms with their definitions, or asking friends
Applied anatomy and physiology: definitions of key terms See pages 5 46 These are the key terms from Chapter 1. Try cutting them out and then matching the key terms with their definitions, or asking friends
Year 9 Options PE. Knowledge Book
 Year 9 Options PE Knowledge Book Topic 3 - Physical Training - Definitions and relationships between terms Grade 1-3 Grade 4-5 Grade 6-9 Curriculum Content Students will be expected to know and understand:
Year 9 Options PE Knowledge Book Topic 3 - Physical Training - Definitions and relationships between terms Grade 1-3 Grade 4-5 Grade 6-9 Curriculum Content Students will be expected to know and understand:
Fitness Intro. Freshmen PE
 Fitness Intro Freshmen PE Physical Fitness Are you able to get through your day easily without tiring? Does your body respond quickly when it needs to? Are you mentally alert in class? Do you feel good
Fitness Intro Freshmen PE Physical Fitness Are you able to get through your day easily without tiring? Does your body respond quickly when it needs to? Are you mentally alert in class? Do you feel good
THEORY OF FIRST TERM. PHYSICAL EDUCATION: 3rd E.S.O.
 THEORY OF FIRST TERM. PHYSICAL EDUCATION: 3rd E.S.O. 1.- WHAT IS THE PHYSICAL CONDITION? It is a set of characteristics of our body that allows us to perform any physical activity in an appropriate way.
THEORY OF FIRST TERM. PHYSICAL EDUCATION: 3rd E.S.O. 1.- WHAT IS THE PHYSICAL CONDITION? It is a set of characteristics of our body that allows us to perform any physical activity in an appropriate way.
Early Physical Rehabilitation in the ICU and Ventilator Liberation
 Early Physical Rehabilitation in the ICU and Ventilator Liberation 本檔僅供內部教學使用檔案內所使用之照片之版權仍屬於原期刊公開使用時, 須獲得原期刊之同意授權 Respiratory Care 2012 Oct Vol 57 No 10 Pedro A Mendez-Tellez MD and Dale M Needham MD PhD
Early Physical Rehabilitation in the ICU and Ventilator Liberation 本檔僅供內部教學使用檔案內所使用之照片之版權仍屬於原期刊公開使用時, 須獲得原期刊之同意授權 Respiratory Care 2012 Oct Vol 57 No 10 Pedro A Mendez-Tellez MD and Dale M Needham MD PhD
Personalized Blood Flow Restriction Rehabilitation. Knee Arthroscopy. (Debridements, Meniscectomies, Synovectomy, Chondroplasty)
 Personalized Blood Flow Restriction Rehabilitation Knee Arthroscopy (Debridements, Meniscectomies, Synovectomy, Chondroplasty) Knee Arthroscopy 2 The primary goals after knee arthroscopy debridement is
Personalized Blood Flow Restriction Rehabilitation Knee Arthroscopy (Debridements, Meniscectomies, Synovectomy, Chondroplasty) Knee Arthroscopy 2 The primary goals after knee arthroscopy debridement is
Surgical Effects on Swallowing DYSPHAGIA AFTER TREATMENT FOR HNC: WHAT CAUSES IT? WHAT TREATMENT WORKS? Surgical Effects on Swallowing
 Susan Langmore, PhD, CCC-SLP, BRS-S Professor, BUMC, BU September 27, 2010 DYSPHAGIA AFTER TREATMENT FOR HNC: WHAT CAUSES IT? WHAT TREATMENT WORKS? Incidence of dysphagia after XRT VA study (Wolf; Terrell
Susan Langmore, PhD, CCC-SLP, BRS-S Professor, BUMC, BU September 27, 2010 DYSPHAGIA AFTER TREATMENT FOR HNC: WHAT CAUSES IT? WHAT TREATMENT WORKS? Incidence of dysphagia after XRT VA study (Wolf; Terrell
Chapter 14 Training Muscles to Become Stronger
 Chapter 14 Training Muscles to Become Stronger Slide Show developed by: Richard C. Krejci, Ph.D. Professor of Public Health Columbia College 11.22.11 Objectives 1. Describe the following four methods to
Chapter 14 Training Muscles to Become Stronger Slide Show developed by: Richard C. Krejci, Ph.D. Professor of Public Health Columbia College 11.22.11 Objectives 1. Describe the following four methods to
Muscles. (=striated muscle) Supply power (with skeletal system) Restrain Heat Viscera Specialized. Electric Organs. Muscle organ.
 Muscles Electric Organs Supply power (with skeletal system) Restrain Heat Viscera Specialized =muscle cell (multinucleate) Muscle fiber Muscle organ Skeletal Striated muscle Muscle (skeletal muscle) (=striated
Muscles Electric Organs Supply power (with skeletal system) Restrain Heat Viscera Specialized =muscle cell (multinucleate) Muscle fiber Muscle organ Skeletal Striated muscle Muscle (skeletal muscle) (=striated
Muscular Strength and Endurance:
 PE 1- Assignment #5 6 1 Name: Per: Date: Teacher: STRESS BREAK Participating in physical activities that improve your self-esteem is a great way to deal with stress. The better you feel about yourself,
PE 1- Assignment #5 6 1 Name: Per: Date: Teacher: STRESS BREAK Participating in physical activities that improve your self-esteem is a great way to deal with stress. The better you feel about yourself,
PE10U2L5 - Strength Training. Unit 2: Active Living
 Page 1 of 6 Unit 2: Active Living Lesson 5 - Strength Training Label your Assignment as: PE10U2L5 Introduction In today's lesson, we are going to look at the many benefits to be gained by participating
Page 1 of 6 Unit 2: Active Living Lesson 5 - Strength Training Label your Assignment as: PE10U2L5 Introduction In today's lesson, we are going to look at the many benefits to be gained by participating
GCSE Physical Education
 GCSE Physical Education Extension Work Booklet Name Tutor Group 2 Introduction and Contents Welcome to GCSE Physical Education! This work booklet will be like your bible! Please ensure you have this with
GCSE Physical Education Extension Work Booklet Name Tutor Group 2 Introduction and Contents Welcome to GCSE Physical Education! This work booklet will be like your bible! Please ensure you have this with
Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils
 Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils Properties of Muscle Fiber Types Fast fibers Slow fibers Characteristic IIb IIx IIa Type I V max (speed of shortening) Highest Intermediate Low Resistance to fatigue
Muscles, muscle fibres and myofibrils Properties of Muscle Fiber Types Fast fibers Slow fibers Characteristic IIb IIx IIa Type I V max (speed of shortening) Highest Intermediate Low Resistance to fatigue
Chapter 13. Development of Muscular, Strength, Endurance, and Flexibility
 Chapter 13 Development of Muscular, Strength, Endurance, and Flexibility Types of Contractions Dynamic, Isotonic, or concentric Muscle shortens with varying tension while lifting constant load Isometric,
Chapter 13 Development of Muscular, Strength, Endurance, and Flexibility Types of Contractions Dynamic, Isotonic, or concentric Muscle shortens with varying tension while lifting constant load Isometric,
Motor systems.... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington
 Motor systems... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington 1 Descending pathways: CS corticospinal; TS tectospinal; RS reticulospinal; VS
Motor systems... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington 1 Descending pathways: CS corticospinal; TS tectospinal; RS reticulospinal; VS
X-Plain Muscles Reference Summary
 X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
X-Plain Reference Summary Introduction are very important elements of the human body. They account for about half of a person s weight. Understanding how muscles work and how they can be injured is necessary
Physical Education. Year 9 Theory Curriculum Year 9 40% 60%
 Physical Education Year 9 Theory Curriculum 2016-17 This year students will be given a final end of year grade which will be based on 2 areas: Practical abilities (their end of year level) Performance
Physical Education Year 9 Theory Curriculum 2016-17 This year students will be given a final end of year grade which will be based on 2 areas: Practical abilities (their end of year level) Performance
Swallowing after a Total Laryngectomy
 Swallowing after a Total Laryngectomy Diane Longnecker, M.S.,CCC-SLP, BCS-S Baylor Institute for Rehabilitation at Baylor University Medical Center Dallas, TX Disclosure Statement No relevant financial
Swallowing after a Total Laryngectomy Diane Longnecker, M.S.,CCC-SLP, BCS-S Baylor Institute for Rehabilitation at Baylor University Medical Center Dallas, TX Disclosure Statement No relevant financial
Warm-up Questions: write and answer each of the below questions (hint these make great test questions)
 Warm-up Questions: write and answer each of the below questions (hint these make great test questions) 1. is the process in which your body gets energy from food. 2. A is a way of life that involves little
Warm-up Questions: write and answer each of the below questions (hint these make great test questions) 1. is the process in which your body gets energy from food. 2. A is a way of life that involves little
Dysphagia and Swallowing. Jan Adams, DNP, MPA, RN and Karen Kern
 Dysphagia and Swallowing Jan Adams, DNP, MPA, RN and Karen Kern Scope of the Problem and Incidence 15 million people in the US have some form of Dysphagia. Every year, 1 million people are diagnosed with
Dysphagia and Swallowing Jan Adams, DNP, MPA, RN and Karen Kern Scope of the Problem and Incidence 15 million people in the US have some form of Dysphagia. Every year, 1 million people are diagnosed with
PHYSICAL FITNESS 1 MOTOR SKILLS
 PHYSICAL FITNESS The concept of physical fitness first arose in 1916, in a scientific study that tried to accurately measure the different physical characteristics of individuals. The idea of fitness suggests
PHYSICAL FITNESS The concept of physical fitness first arose in 1916, in a scientific study that tried to accurately measure the different physical characteristics of individuals. The idea of fitness suggests
The Clinical Swallow Evaluation: What it can and cannot tell us. Introduction
 The Clinical Swallow Evaluation: What it can and cannot tell us Debra M. Suiter, Ph.D., CCC-SLP, BCS-S Director, Voice & Swallow Clinic Associate Professor, Division of Communication Sciences & Disorders
The Clinical Swallow Evaluation: What it can and cannot tell us Debra M. Suiter, Ph.D., CCC-SLP, BCS-S Director, Voice & Swallow Clinic Associate Professor, Division of Communication Sciences & Disorders
C2 Qu1 DP2 How does training affect performance?
 C2 Qu1 DP2 How does training affect performance? Hi Guys In this video, we will be explore Core two question 1 - dot point 2 If you look at the syllabus you can see this dot point is about types of training
C2 Qu1 DP2 How does training affect performance? Hi Guys In this video, we will be explore Core two question 1 - dot point 2 If you look at the syllabus you can see this dot point is about types of training
