PHAR763: Pathophysiology and Therapeutics Ophthalmic Disorders: Glaucoma June 4, Julianne E. Himstreet, Pharm.D., BCPS
|
|
|
- Jordan Scott
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PHAR763: Pathophysiology and Therapeutics Ophthalmic Disorders: Glaucoma June 4, 2008 Julianne E. Himstreet, Pharm.D., BCPS Recommended Reading: Applied Therapeutics Chapter 51. I. Learning Objectives 1. Be familiar with the anatomy and physiology of the eye. 2. Know the medications used to treat primary open-angle glaucoma. 3. Describe the most common side effects of the medications used to treat primary open-angle glaucoma. 4. Know the medications used to treat closed-angle glaucoma. 5. Counsel a patient on administration and storage of medications for glaucoma including nasolacrimal occlusion. 6. Identify which systemic medications can cause ocular side effects. II. Ocular Anatomy and Physiology DIAGRAM OF THE EYE 1
2 A. Outer coat of the eye 1. sclera: white, dense, fibrous protective coating a. episclera: a thin layer of loose connective tissue covering the sclera, contains the blood vessels for the sclera 2. conjunctiva: mucous membrane covering the anterior portion of the eye and lines the eyelids 3. cornea: transparent avascular tissue that functions as a refractive and protective window membrane where light rays pass to the retina a. cornea involved in drug penetration b. best penetration through intact cornea with biphasic preparations (both fat and water soluble) B. Inner segment of the eye 1. retina: contains all sensory receptors for light transmission 2. optic nerve: transmits visual impulses from the retina to the brain 3. crystalline lens, aq ueous humor and vitreous: assist cornea with process of refraction C. Outermost part of the eye 1. eyelids and eyelashes a. protection for the eye b. eyelids contain sebaceous and sweat glands D. Innervation of the eye 1. Parasympathetic fibers a. originate from occulomotor nerve in the brain b. innervate the ciliary muscle and sphincter pupillae muscle c. involved in constriction of the pupil i. parasympathomimetics (cholinergics): miosis (contraction) ii. parasympatholytics (anticholinergics): mydriasis (dilation) and cytoplegia (paralysis of ciliary muscle and zonules that results in decreased accommodation and blurred vision) d. tear secretion by lacrimal glands controlled by parasympathetic system 2. Sympathetic fibers a. originate from the superior cervical ganglion in spinal cord b. innervate the dilator pupillae muscle, blood vessels of the ciliary body, episclera, and extraocular muscles c. involved in dilation of pupil i. sympathomimetics cause mydriasis (dilation) without affecting accommodation ii. sympatholytics cause miosis (contraction) 2
3 III. Glaucoma A. Definition: ocular disorder involving optic neuropathy with changes in the optic disk and loss of visual sensitivity and field; increased intraocular pressure (IOP) is thought to play an important role in pathogenesis of glaucoma but is not a diagnostic criterion 1. Influenced by a. production of aqueous humor by the ciliary processes b. outflow of aqueous humor through the trabecular meshwork 2. Intraocular pressure a. normal IOP: 10 to 20 mmhg b. IOP over 22 mmhg can indicate glaucoma B. Ocular Hypertension 1. Background a. IOP greater than 21 mmhg b. normal visual fields c. normal optic discs d. open angles e. absence of any ocular disease contributing to the elevated IOP 2. Treatment a. Only in pts with elevated IOP (> 30mmHg), family history of glaucoma, black patients, high myopia, and patients with one eye b. Beta blocker: timolol, levobunolol c. α 2 adrenergic agonist: brimonidine, apraclonidine d. Topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor (CAI): brinzolamide, dorzolamide e. Prostaglandin analogue: latanoprost, travaprost, brimatoprost f. Goal of treatment: lower IOP by 25-30% to decrease risk of optic nerve damage C. Open Angle Glaucoma 1. Background a. 1.5% people over 30 years b. 2-3% of people older than 70 years c. Accounts for most cases of glaucoma 2. Primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) a. Background i % of primary glaucomas are POAG ii. Manifests as optic nerve degeneration characterized by disk changes and visual field loss iii. Involves decreased aqueous humor outflow from anterior chamber from degenerative process in trabecular meshwork iv. IOP varies throughout the day from normal to significantly elevated v. Onset is gradual and asymptomatic until substantial visual field constriction occurs vi. Increase in IOP not required for diagnosis 3
4 b. Treatment i. First line - Beta blockers - Prostaglandin analogs ii. Alternative agents - α 2 -Adrenergic Agonists - Topical CAIs iii. Second line agents - Pilocarpine - Epinephrine or dipivefrin - Apraclonidine c. Approach to therapy i. Start with single agent in one eye to evaluate drug efficacy and tolerance ii. Monitor IOP and optic disk after 2-4 weeks, then every 1-6 months until stabilized iii. Measure visual field every 3-12 months (or after changes in drug therapy) iii. If single agent not tolerated, change to alternative agent iv. If single agent not effective at highest dose - switch to alternative agent (overlap by 1 day) or - addition of another optical drug used in combination v. If drug therapy not effective or tolerated, then surgical procedures are considered - argon laser trabeculoplasty (ALT) - surgical trabeculectomy vi. Goal - reduce IOP initially by 25-30% with goal of IOP < 21mmHg 4
5 Pharmacologic Agents used in Primary Open-angle glaucoma Mechanism of action Drug Dosing Interval Expected IOP Decreased production of aqueous humor Decrease production of aqueous humor and may increase outflow β-blockers Nonselective Timolol (Timoptic) Timolol (Timoptic XE) Levobunolol (Betagan) Metipranolol (Optipranolol) Selective Betaxolol (Betoptic) Nonselective with ISA Carteolol (Ocupress) Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (CAIs) Dorzolamide (Trusopt) Brinzolamide (Azopt) α 2 -Adrenergic Agonists brimonidine (Alphagan) apraclonidine (Iopidine) Once daily 2-3 times daily 2-3 times daily 2-3 times daily 2-3 times daily lowering % *timolol and levobunolol have greater IOP lowering than betaxolol 5 Side effects Cautions Cost/ month Most common local effect: Stinging Betaxolol and metipranolol most common Dry eyes, blurred vision, blepharitis, corneal anesthesia Rare local effect: Conjunctivitis, uveitis, keratitis Systemic effects: Heart rate, blood pressure, bronchospasm, CNS effects May be less with betaxolol and carteolol % Most common local effects: Transient burning/stinging, ocular discomfort, transient blurred vision, tearing Superficial punctate keratitis (10-15%) Rare local effect: Conjunctivitis, lid reactions, photophobia Systemic effects: Sulfonamide so caution in sulfa allergic pts 18-27% Most common local effects: Allergic type reaction: lid edema, eye discomfort, itching, hyperemia (must d/c) 30% with alpraclonidine 8% with brimonidine Systemic effects: Dizziness, somnolence, dry mouth, Heart rate, blood pressure (more common with brimonidine) Pulmonary diseases Sinus bradycardia Second/third heart block CHF CAD DM Myasthenia gravis Pts taking oral β- blockers $12.00 $29.00 $ $16.00 $40.00 $20.00 Avoid in patients with hepatic or renal impairment $31.00 $33.00 CAD, Renal impairment Cerebrorvascular dz, Diabetes Pts taking antihypertensives, CAD drugs, MAOIs, tricyclic antidepressants Cosopt $50.00 $33.00 $74.00
6 Pharmacologic Agents used in Primary Open-angle glaucoma Mechanism of action Drug Dosing Interval Expected IOP Increased aqueous outflow Prostaglandin analogs Latanoprost (Xalatan) Travaprost (Travatan) Bimatoprost (Lumigan) Unoprostone (Rescula) Once daily Once daily Once daily lowering 25-35% Most common local effects: Iris pigmentation (15-30%) Most common in pts with light colored eyes Uveitis Caution in pts with ocular inflammatory conditions Rare local effects: Ocular irritation, conjuntival hyperemia, superficial punctate keratitis Systemic effects: Rarely occur Side effects Cautions Cost/ month $50.00 $57.00 $65.00 $47.00 Parasympathomimetics Pilocarpine (Pilocar) soln Pilocarpine (Pilocar) gel Pilocarpine ocular insert (Ocusert) Carbachol Sympathomimetics Diprivefrin (Propine) Epinephrine (Glaucon) 3-4 times daily once daily once weekly 2-3 times daily 20-30% Local effects: Miosis and decreased night vision in pts with cataracts Frontal headache/browache Periorbital pain, Eyelid twitching Conjunctival irritation Systemic effects: Diaphoresis, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, cramping, urinary frequency, bronchospasm, heart block More with higher doses 15-25% Most common local effects: Tearing, burning, ocular discomfort, browache, conjunctival hyperemia, punctate keratopathy, allergic blepharoconjunctivitis Rare local effects: Loss of eyelashes, stenosis of nasolacrimal duct, blurred vision, pigmentation of conjuctiva and cornea (less with diprivefrin) Systemic effects: Headache, faintness, increased blood pressure, tachycardia, arrhythmia CAD Acute iritis $7.00 $46.00 CAD, cerebrovascular disease, CAG, hyperthyroidis m, diabetes, Pt undergoing anesthesia with halogenated hydrocarbons $10.00 $
7 D. Closed angle glaucoma (CAG) 1. Background a. Accounts for 5% or less of primary glaucomas b. Many times is an emergency to avoid visual loss c. Results from mechanical blockage of trabecular meshwork by the peripheral iris d. Between attacks IOP is usually normal in absence of POAG e. Occurs in pts with inherited shallow anterior chambers which produce a narrow angle between cornea and iris or tight contact between the iris and lens (pupillary block) f. Determined by visualization of the angle by gonioscopy g. Two types of classic reversible primary CAG i. CAG with pupillary block ii. CAG without pupillary block h. Symptoms i. cloudy, edematous cornea, ocular pain or discomfort, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain and diaphoresis i. Examination i. closed-angle, narrow anterior chamber, hyperemic conjunctiva and edematous and hyperemic optic disc with IOP as high as mm HG 2. Goals of therapy a. rapid reduction of IOP to preserve vision and avoid surgical or laser iridectomy 3. Drug therapy a. Pilocarpine 2-4% 1 drop every 5 minutes for 4-6 administrations b. Hyperosmotic agents i. IV: mannitol ii. Oral: 50% glycerin g/kg or isosorbide iii. no drinking liquids since it will counteract the osmotic effects of the agents iv. Also can add acetazolamide 500mg IV c. Secretory inhibitor (β-blocker, α 2 agonist, prostaglandin F 2α analog or topical CAI) E. Drug induced Glaucoma 1. Open angle glaucoma a. patients with treated, controlled POAG are at minimal risk of increased IOP from systemic meds with anticholinergic properties or vasodilators b. patients with untreated or uncontrolled POAG can be at risk for further increases in IOP c. Topical anticholinergics (mydriasis): increase in IOP most likely with atropine or homatropine d. Inhaled, nasal, topical or oral corticosteroids may increase IOP in patients with POAG and those who do not have POAG; amount of increase in IOP is dose related 7
8 High Risk Medium Risk Low Risk Ophthalmic corticosteroids Systemic corticosteroids Vasodilators Nasal/inhaled corticosteroids Cimetidine Ophthalmic anticholinergics Succinylcholine 2. Closed angle glaucoma a. May be produced by drugs that cause mydriasis (anticholinergics) or swelling of the lens (sulfa compounds) b. Most likely with optical anticholinergics or topical sympathomimetics High-medium Risk Topical anticholinergics Topical sympathomimetics Systemic anticholinergics Heterocyclic antidepressants Low potency phenothiazines Antihistamines Ipratropium Low Risk Benzodiazepines Theophylline Vasodilators Systemic sympathomimetics CNS stimulants Tetracyclines Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors Monoamine oxidase inhibitors Topical cholinergics IV. Patient Education A. Procedure for administration of ophthalmic products 1. Wash and dry hands 2. Shake bottle if a suspension 3. With forefinger pull down on outer portion of lower eyelid to form a pocket to receive the drop 4. Grasp dropper between thumb and fingers with hand braced against cheek or nose and the head held upward 5. Place dropper over the eye while looking at the tip of the bottle then look up and place a single drop in the eye 6. The lids should be closed for 1-3 minutes after instillation to increase ocular availability of the drug (should not squeeze or rub eye) 7. Recap the bottle and store as instructed B. Nasolacrimal Occlusion (NLO) 1. Used to increase ocular bioavailability and reduce systemic absorption 2. Procedure a. For 1-3 minutes close the eyes and place the index finger over the nasolacrimal drainage system in the inner corner of the eye b. This decreases drainage of the drug thereby reducing drug available for systemic absorption 8
9 C. Practical information 1. Many patients are physically unable to administer their own eye drops 2. Use of more than one drop per dose increases costs and does not improve response significantly 3. When 2 drugs are administered, instillation should be separated by 3-5 minutes at least, preferably by 10 minutes 4. Instruct patients not to touch dropper bottle tip with eye, hands or any surface 5. Patients need to be encouraged to continue therapy despite lack of symptoms and warned about the risks of nonadherence 9
10 Eye Drop Tips from the Glaucoma Research Foundation ( Eye drops help maintain the pressure in your eye at a healthy level and are an important part of the treatment routine for most people with glaucoma. Always check with your doctor if you are having any difficulty. Follow doctor s orders. Be sure your doctor knows about any other drugs you may be taking (including over-thecounter items like vitamins and aspirin) and about any allergies you may have. Wash your hands before putting in your eye drops. Be careful not to let the tip of the dropper touch any part of your eye. Make sure the dropper stays clean. If you are putting in more than one drop or more than one type of eye drop, wait five minutes before putting the next drop in. This will keep the first drop from being washed out by the second before it has had time to work. Store eye drops and all medicines out of the reach of children. Start by tilting your head backward while sitting, standing, or lying down. With your index finger placed on the soft spot just below the lower lid, gently pull down to form a pocket. Let a drop fall into the pocket. Slowly let go of the lower lid. Blinking a few times is all right but try not to shut your eyes tight or squint. This may push the drops out of your eye. Gently press on the inside corner of your closed eyes with your index finger and thumb for two to three minutes. This will help keep any drops from getting into your system and keep them in your eye, where they are needed. Blot around your eyes to remove any excess. If you are still having trouble putting eye drops in, here are some tips that may help. If Your Hands Are Shaking: Try approaching your eye from the side so you can rest your hand on your face to help steady your hand. If shaky hands are still a problem, you might try using a 1 or 2 pound wrist weight (you can get these at any sporting goods store). The extra weight around the wrist of the hand you re using can decrease mild shaking. 10
11 Trouble Getting The Drop Into Your Eye: It may be easier to tell if the drop has gone into your eye if you keep your eye drops in the refrigerator. Your eye will feel the liquid when it s cold better than if it s at room temperature. If you are still not sure the drop actually got in your eye, put in another drop. The eyelids can hold only about one drop, so any excess will just run out of the eye. It is better to have excess run out than to not have enough medication in your eye. If pulling the lower lid out to create a pocket isn t working, try this. With your head turned to the side or lying on your side, close your eyes. Place a drop in the inner corner of your eyelid (the side closest to the bridge of your nose). By opening your eyes slowly, the drop should fall right into your eye. Trouble Holding Onto The Bottle: If the eye drop bottle feels too small to hold (in cases where a dropper isn t used and the drop comes directly from the bottle), try wrapping something (like a paper towel) around the bottle. You can use anything that will make the bottle wider. This may be helpful in some mild cases of arthritis in the hands. Products are available to assist you putting in your eye drops. 11
12 V. Ocular Side Effects of Systemic Medications Drug Class Effects Comments Analgesics Ibuprofen Indomethacin Narcotics Antiarrhythmics Amiodarone Anticholinergics Atropine, scopolamine, trihyxylphenidyl Anticonvulsants Carbamzepine Phenytoin Reduced vision Miosis Reduced vision Tearing, irregular pupils, paresis of accommodation, diplopia Keratopathy Cataracts Mydriasis, cycloplegia, decreased accommodation, photophobia Diplopia, blurred vision Nystagmus, cataracts Rare, blurred vision more common Common with therapeutic doses, secondary to Rare, also changes in color vision rarely reported CNS action on pupilloconstrictor center Effects associated with narcotic withdrawal Dose and duration related; corneal deposits are bilateral, reversible and asymptomatic; deposits occur in almost 100% of pts taking 400mg/day or more Anterior subcapsular lens opacities associated with amiodarone therapy; may progress to ultimately cover an area larger than undilated pupil s aperture Systemic and transdermal anticholinergic agents may cause mydriasis and less commonly cycloplegia. Mydriasis can cause angle-closure glaucoma; photophobia is related to the mydriasis. Ocular adverse effects when dosate > 1-2 grams/day, resolve with dose reduction Nystagmus with high blood levels (> 20μg/mL), cataracts may rarely occur with prolonged therapy Anesthetics Propofol Inability to open eyes 6/50 pts undergoing ENT procedures were unable to open eyes for 3-20 minutes after end of anesthetic administration Antidepressants Tricyclic (TCAs) Fluoxetine Antihistamines Chlorpheniramine Antihypertensives Clonidine Diazoxide Guanethidine Reserpine Mydriasis, cycloplegia Eye tics Blurred vision, mydriasis, decreased lacrimal secretions Miosis, dry itchy eyes Lacrimation Miosis, ptosis, conjunctivitis, blurred vision Miosis, conjunctivitis Mydriasis most common ocular side effect, cycloplegia is rare, reports of precipitation of angle-closure glaucoma Fluoxetine 20-40mg/day associated with paroxysmal contractions of the muscles aroung the lateral aspect of the eye; effect occurred 3-4 weeks after initiation and resolved within 2 weeks of discontinuation Blurred vision ~1%of patients taking 12-14mg/day, mydriasis rare Miosis in overdose; itchy eyes rare 20% of patients, may continue after stopping sporatically documented miosis rare; conjunctivitis common secondary to dilation fo conjunctival blood vessels 12
13 Antiinfectives Amantadine Chloramphenicol Chloroquine Ethambutol Gentamicin Isoniazid Sulfonamides Tetracyclines Corneal lesions Optic neuritis Corneal deposits Retrobulbar neuritis Pseudotumor cerebri Optic neuritis Myopia Conjunctivitis Optic neuritis Photosensitivity Myopia Papilledema Diffuse corneal opacities reported, occasionally associated with superficial punctate keratitis, onset 1-2 weeks after initiation of therapy with doses of mg/day, resolves with d/c drug Rare unless total dose of 100 gram and duration > 6 weeks exceeded, vision improves after stopping May occur after few months therapy, of no consequence At doses of 15mg/kg/day, ocular side effects not seen, at doses of 25mg/kg/day side effects are rare; for treatment of greater than 3 months need to do routine eye exams Rare but well documented with secondary papilledema and visual loss Prevalence not well defined but less than peripheral neuritis Acute, reversible, most common ocular side effect Associated with use of sulfisoxazide lid margin therapy Even in low doses, usually reversible with complete recovery of vision Associated with using sulfisoxazole lid margin therapy Appears to be acute, transient and rare More common in children and infants than adults, rare Antilipidemic agents Lovastatin Cataracts Does not appear to effect visual acuity, rare Diuretics Thiazides Myopia Acute myopia that may last from hours, may be reversible even when drug continued Estrogens Clomiphene Oral contraceptives Blurred vision Mydriasis Visual field changes Visual sensations Optic neuritis Pseudotumor cerebri Retrotubular neuritis 5-10% exeperience ocular side effects, blurred vision most common quite rare, pts with retinal vascular abnormalities use with caution Hyperuricemia Allopurinol Cataracts May be associated with anterior and posterior lens capsule changes, 42 cases reported, reports conflicting Phenothiazines Chlorpromazine Thioridazine Erectile dysfunction Sildenafil Deposits on the lens Retinal pigment deposits Pigmentary retinopathy Disturbance of color vision Increased brightness Blurred vision Nonarteritic ischemic optic neuropathy Rare when total dose < 0.5 kg, visible dose > 1kg Reported cases small Usually associated with maximal daily doses over 1000mg, daily doses up to 600mg are relatively safe Color vision alterations are mild to moderate, blurred vision does not impair visual acuity, visual alterations subside usually 4 hours after dose 13
14 Cardiac drugs Calcium channel blockers Digitalis Antineoplastic agents Busulfan Cytarabine Doxorubicin Fluorouracil Tamoxifen Vinca alkaloids Blurred vision Transient blindness Altered color vision, visual acuity Decreased intraocular pressure Catarats Keratoconjunctivitis, ocular burning, photophobia, blurred vision Conjunctivitis Excessive tearing Ocular irritation, lacrimation Corneal opacities, decreased vision Extraocular muscle paresis (EMP), ptosis Primary blurred vision, transient blindness at peak concentrations observed in several pts Changed in color vision, glare phenomenon, small number of cases of reversible reduction in visual acuity Decrease intraocular pressure seen most commonly at doses near toxic dose Reported with high doses Corneal toxicity and conjunctivitis reported with high dose therapy (3g/m 2 ) May last for several days after treatment Reversible and seldom interferes with therapy Generally in higher than normal doses for months Onset on EMP or paralysis seen as early as 2 weeks, dose related, most fully recover after stopping drug Corticosteroids Cataracts Posterior subcapsular cataracts with systemic use, dose dependent and more common in doses over 15mg/day prednisone for > 1 years; rare with nasal or oral use and cases where seen use was over 5 years in higher than recommended dose and use of periodic systemic corticosteroids Increased intraocular pressure More common with topical corticosteroids than systemic; little consequence in pts without preexisting glaucoma, monitor glaucoma pts on systemic steroids Papilledema Intracranial hypertension or pseudomotor cerebri from systemic corticosteroids well documented, incidence greater in children than adults, more common with chronic therapy Table adapted from Chapter 51 (Eye Disorders) Table Applied Therapeutics Textbook. 14
BrightFocus Foundation is the new name for American Health Assistance Foundation.
 In this section, you will find the following: Glaucoma Medications Laser Therapies Conventional Surgical Procedures In the second section, you will find information on how to search for potential treatments
In this section, you will find the following: Glaucoma Medications Laser Therapies Conventional Surgical Procedures In the second section, you will find information on how to search for potential treatments
OCULAR PHARMACOLOGY GLAUCOMA. increased intraocular pressure. normally mm Hg. when to Tx no fixed level.
 OCULAR PHARMACOLOGY GLAUCOMA increased intraocular pressure normally 12 20 mm Hg. when to Tx no fixed level. literature sets ~21 mm Hg as upper limit of normal. some safe at 30 mm Hg some may have damage
OCULAR PHARMACOLOGY GLAUCOMA increased intraocular pressure normally 12 20 mm Hg. when to Tx no fixed level. literature sets ~21 mm Hg as upper limit of normal. some safe at 30 mm Hg some may have damage
A. Incorrect! Acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor given orally or by intravenous injection.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 20: Drugs that Treat Glaucoma Question No. 1 of 10 1. is a topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Question #01 (A) Acetazolamide (B) Clonidine (C) Dorzolamide (D) Apraclonidine
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 20: Drugs that Treat Glaucoma Question No. 1 of 10 1. is a topical carbonic anhydrase inhibitor. Question #01 (A) Acetazolamide (B) Clonidine (C) Dorzolamide (D) Apraclonidine
Vision Health: Conditions, Disorders & Treatments GLAUCOMA
 Vision Health: Conditions, Disorders & Treatments GLAUCOMA Glaucoma is a disease of the optic nerve, which transmits the images you see from the eye to the brain. The optic nerve is made up of many nerve
Vision Health: Conditions, Disorders & Treatments GLAUCOMA Glaucoma is a disease of the optic nerve, which transmits the images you see from the eye to the brain. The optic nerve is made up of many nerve
BETAGAN Allergan Levobunolol HCl Glaucoma Therapy
 BETAGAN Allergan Levobunolol HCl Glaucoma Therapy Action And Clinical Pharmacology: Levobunolol is a noncardioselective beta- adrenoceptor antagonist, equipotent at both beta1 and beta2 receptors. Levobunolol
BETAGAN Allergan Levobunolol HCl Glaucoma Therapy Action And Clinical Pharmacology: Levobunolol is a noncardioselective beta- adrenoceptor antagonist, equipotent at both beta1 and beta2 receptors. Levobunolol
Treatments for Open-Angle Glaucoma. A Review of the Research for Adults
 Treatments for Open-Angle Glaucoma A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is for you if: Your eye doctor has said that you have open-angle glaucoma,
Treatments for Open-Angle Glaucoma A Review of the Research for Adults Is This Information Right for Me? Yes, this information is for you if: Your eye doctor has said that you have open-angle glaucoma,
Financial Disclosure. Prostaglandin Analogs (PGs) The Glaucoma Grab Bag: Practical Guidelines for Effective Glaucoma Therapy
 The Glaucoma Grab Bag: Practical Guidelines for Effective Glaucoma Therapy Danica J. Marrelli, OD, FAAO University of Houston College of Optometry Financial Disclosure I have received I have received speaking
The Glaucoma Grab Bag: Practical Guidelines for Effective Glaucoma Therapy Danica J. Marrelli, OD, FAAO University of Houston College of Optometry Financial Disclosure I have received I have received speaking
8/30/2018. Eye Disorders. Patrick Sarte. Anatomy of the Eye Uveitis Scleritis vs. Episcleritis Glaucoma Retinal Findings Eyelids
 Eye Disorders Patrick Sarte Anatomy of the Eye Uveitis Scleritis vs. Episcleritis Glaucoma Retinal Findings Eyelids 1 Anatomy of the Eye Anatomy of the Eye 2 Anatomy of the Eye 3 4 A 26 year old woman
Eye Disorders Patrick Sarte Anatomy of the Eye Uveitis Scleritis vs. Episcleritis Glaucoma Retinal Findings Eyelids 1 Anatomy of the Eye Anatomy of the Eye 2 Anatomy of the Eye 3 4 A 26 year old woman
East and North Hertfordshire treatment pathway for primary open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension in adults
 East and North Hertfordshire treatment pathway for primary open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension in adults Introduction Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases causing optic nerve damage. In most cases
East and North Hertfordshire treatment pathway for primary open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension in adults Introduction Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases causing optic nerve damage. In most cases
VI.2.2 Summary of treatment benefits
 EU-Risk Management Plan for Bimatoprost V01 aetiology), both OAG and ACG can be secondary conditions. Secondary glaucoma refers to any case in which another disorder (e.g. injury, inflammation, vascular
EU-Risk Management Plan for Bimatoprost V01 aetiology), both OAG and ACG can be secondary conditions. Secondary glaucoma refers to any case in which another disorder (e.g. injury, inflammation, vascular
5/12/2014. Lynn E. Lawrence, CPOT, ABOC, COA
 Lynn E. Lawrence, CPOT, ABOC, COA Glaucoma is an optic neuropathy characterized by a loss of ganglion cells and their axons, in the RNFL. The loss of retinal ganglion cells in glaucoma is irreversible
Lynn E. Lawrence, CPOT, ABOC, COA Glaucoma is an optic neuropathy characterized by a loss of ganglion cells and their axons, in the RNFL. The loss of retinal ganglion cells in glaucoma is irreversible
WORLD GLAUCOMA WEEK What is Glaucoma? Can I develop glaucoma if I have increased eye pressure?
 WORLD GLAUCOMA WEEK What is Glaucoma? Glaucoma is a group of diseases that damage the optic nerve and can result in gradual vision loss and blindness. However, with early detection and treatment, you can
WORLD GLAUCOMA WEEK What is Glaucoma? Glaucoma is a group of diseases that damage the optic nerve and can result in gradual vision loss and blindness. However, with early detection and treatment, you can
Divakar Gupta Glaucoma Fellow, Duke Eye Center 5/14/16
 Divakar Gupta Glaucoma Fellow, Duke Eye Center 5/14/16 Pathophysiology of glaucoma Consider risk factors of glaucoma Understand the side effects of glaucoma medications Diagnostic testing Leading cause
Divakar Gupta Glaucoma Fellow, Duke Eye Center 5/14/16 Pathophysiology of glaucoma Consider risk factors of glaucoma Understand the side effects of glaucoma medications Diagnostic testing Leading cause
Get a grip on your glaucoma Booklet 1
 Information for Patients Glaucoma services Welcome! Get a grip on your glaucoma Booklet 1 Group-based Glaucoma information Course Session 1 What happens in session 1? Finding out what questions you have
Information for Patients Glaucoma services Welcome! Get a grip on your glaucoma Booklet 1 Group-based Glaucoma information Course Session 1 What happens in session 1? Finding out what questions you have
02/03/2014. Average Length: 23mm (Infant ~16mm) Approximately the size of a quarter Volume: ~5mL
 Identify the anatomy of the eye. Explain the basic physiology of the parts of the eye. Briefly discuss various surgeries related to different parts of the anatomy. Average Length: 23mm (Infant ~16mm) Approximately
Identify the anatomy of the eye. Explain the basic physiology of the parts of the eye. Briefly discuss various surgeries related to different parts of the anatomy. Average Length: 23mm (Infant ~16mm) Approximately
Glaucoma. Glaucoma. Glaucoma. Trevor Arnold, MS, DVM, DACVO
 Glaucoma Trevor Arnold, MS, DVM, DACVO Glaucoma Physiology of Aqueous Humor Produced in the ciliary body Flows out the iridocorneal angle and ciliary cleft High intraocular pressures are caused by a decreased
Glaucoma Trevor Arnold, MS, DVM, DACVO Glaucoma Physiology of Aqueous Humor Produced in the ciliary body Flows out the iridocorneal angle and ciliary cleft High intraocular pressures are caused by a decreased
Frequently Asked Questions about General Ophthalmology:
 1. Normal Eye Structure The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The parts of the eye include: Cornea (a clear dome over the iris), Iris (the pigmented part); Pupil (the black
1. Normal Eye Structure The eye is a slightly asymmetrical globe, about an inch in diameter. The parts of the eye include: Cornea (a clear dome over the iris), Iris (the pigmented part); Pupil (the black
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS Patients with Open-Angle Glaucoma or Ocular Hypertension
 3 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Isopto Carpine safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Isopto Carpine. Isopto
3 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Isopto Carpine safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Isopto Carpine. Isopto
The following is a list of medications which are known to have high risk of ocular side effects
 Medications have an established profile of side effects, but ocular side effects are often unrecognized, overlooked or misdiagnosed. While the ophthalmologic literature usually highlights such discoveries,
Medications have an established profile of side effects, but ocular side effects are often unrecognized, overlooked or misdiagnosed. While the ophthalmologic literature usually highlights such discoveries,
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION MYDFRIN * Phenylephrine Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution. Vasoconstrictor and Mydriatic for Use in Ophthalmology
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION MYDFRIN * Phenylephrine Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution Vasoconstrictor and Mydriatic for Use in Ophthalmology Novartis Pharmaceuticals Canada Inc. 385 Bouchard Blvd., Dorval,
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION MYDFRIN * Phenylephrine Hydrochloride Ophthalmic Solution Vasoconstrictor and Mydriatic for Use in Ophthalmology Novartis Pharmaceuticals Canada Inc. 385 Bouchard Blvd., Dorval,
Glaucoma Clinical Update. Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012
 Glaucoma Clinical Update Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Objectives Understand the different categories of glaucoma Recognize the symptoms and signs of open angle and angle-closure
Glaucoma Clinical Update Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Giovanni Caboto Club October 3, 2012 Objectives Understand the different categories of glaucoma Recognize the symptoms and signs of open angle and angle-closure
READ THIS FOR SAFE AND EFFECTIVE USE OF YOUR MEDICINE PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION. IOPIDINE 1% Apraclonidine Ophthalmic Solution, USP
 READ THIS FOR SAFE AND EFFECTIVE USE OF YOUR MEDICINE PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION Pr IOPIDINE 1% Apraclonidine Ophthalmic Solution, USP Read this carefully before you start taking IOPIDINE 1% and each
READ THIS FOR SAFE AND EFFECTIVE USE OF YOUR MEDICINE PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION Pr IOPIDINE 1% Apraclonidine Ophthalmic Solution, USP Read this carefully before you start taking IOPIDINE 1% and each
Pilocarpine 2% w/v Eye Drops, solution. Pilocarpine 4% w/v Eye Drops, solution. Pilocarpine Hydrochloride
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Pilocarpine 2% w/v Eye Drops, solution Pilocarpine 4% w/v Eye Drops, solution Pilocarpine Hydrochloride (Referred to as Pilocarpine Eye Drops in this leaflet)
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER Pilocarpine 2% w/v Eye Drops, solution Pilocarpine 4% w/v Eye Drops, solution Pilocarpine Hydrochloride (Referred to as Pilocarpine Eye Drops in this leaflet)
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION AND CONSUMER INFORMATION ISOPTO * CARPINE. pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution, USP.
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION AND CONSUMER INFORMATION Pr ISOPTO * CARPINE pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution, USP 1%, 2% and 4% w/v Parasympathomimetic Alcon Canada Inc. 2665 Meadowpine Blvd. Mississauga,
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION AND CONSUMER INFORMATION Pr ISOPTO * CARPINE pilocarpine hydrochloride ophthalmic solution, USP 1%, 2% and 4% w/v Parasympathomimetic Alcon Canada Inc. 2665 Meadowpine Blvd. Mississauga,
Core Safety Profile. Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Sterile eye drops 1%, 2% Date of FAR:
 Core Safety Profile Active substance: Carteolol Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Sterile eye drops 1%, 2% P - RMS: SK/H/PSUR/0002/002 Date of FAR: 16.03.2012 4.1 THERAPEUTIC INDICATIONS Ocular hypertension
Core Safety Profile Active substance: Carteolol Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Sterile eye drops 1%, 2% P - RMS: SK/H/PSUR/0002/002 Date of FAR: 16.03.2012 4.1 THERAPEUTIC INDICATIONS Ocular hypertension
Scrub In. What is the function of vitreous humor? What does the pupil do when exposed to bright light? a. Maintain eye shape and provide color vision
 Scrub In What is the function of vitreous humor? a. Maintain eye shape and provide color vision b. Maintain eye shape and refract light rays c. Provide night vision and color vision d. Provide night vision
Scrub In What is the function of vitreous humor? a. Maintain eye shape and provide color vision b. Maintain eye shape and refract light rays c. Provide night vision and color vision d. Provide night vision
KEY MESSAGES. Details of the evidence supporting these recommendations can be found in the above CPG, available on the following websites:
 QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS KEY MESSAGES 1. Glaucoma is a chronic eye disease that damages the optic nerve, & can result in serious vision loss and irreversible blindness. 2. Glaucoma diagnosis
QUICK REFERENCE FOR HEALTHCARE PROVIDERS KEY MESSAGES 1. Glaucoma is a chronic eye disease that damages the optic nerve, & can result in serious vision loss and irreversible blindness. 2. Glaucoma diagnosis
Elements for a public summary. VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology
 VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology The term ocular hypertension usually refers to any situation in which the pressure inside the eye, called intraocular pressure,
VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology The term ocular hypertension usually refers to any situation in which the pressure inside the eye, called intraocular pressure,
IOPIDINE 1% IOPIDINE 0.5% Alcon Apraclonidine HCl Controls Postsurgical Intraocular Pressure Glaucoma Therapy
 IOPIDINE 1% IOPIDINE 0.5% Alcon Apraclonidine HCl Controls Postsurgical Intraocular Pressure Glaucoma Therapy Action And Clinical Pharmacology: Apraclonidine is a relatively selective alpha adrenergic
IOPIDINE 1% IOPIDINE 0.5% Alcon Apraclonidine HCl Controls Postsurgical Intraocular Pressure Glaucoma Therapy Action And Clinical Pharmacology: Apraclonidine is a relatively selective alpha adrenergic
Glaucoma. Cornea. Iris
 Glaucoma Introduction Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can lead to blindness if not treated. Openangle glaucoma, the most common form of glaucoma, affects about 3 million Americans. Half of those
Glaucoma Introduction Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that can lead to blindness if not treated. Openangle glaucoma, the most common form of glaucoma, affects about 3 million Americans. Half of those
Written by Administrator Wednesday, 13 January :27 - Last Updated Thursday, 21 January :34
 angle closure glaucoma A type of glaucoma caused by a sudden and severe rise in eye pressure. Occurs when the pupil enlarges too much or too quickly, and the outer edge of the iris blocks the eye s drainage
angle closure glaucoma A type of glaucoma caused by a sudden and severe rise in eye pressure. Occurs when the pupil enlarges too much or too quickly, and the outer edge of the iris blocks the eye s drainage
GLAUCOMA. An Overview
 GLAUCOMA An Overview Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com --()-- IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your
GLAUCOMA An Overview Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com --()-- IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your
Collaboration in the care of glaucoma patients and glaucoma suspects. Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Nico Ristorante November 29, 2012
 Collaboration in the care of glaucoma patients and glaucoma suspects Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Nico Ristorante November 29, 2012 Goals of Collaboration Patient-centred and evidence based approach Timely access
Collaboration in the care of glaucoma patients and glaucoma suspects Barry Emara MD FRCS(C) Nico Ristorante November 29, 2012 Goals of Collaboration Patient-centred and evidence based approach Timely access
Continuing Education
 Continuing Education Glaucoma: Overview & Treatment Options Authors: Tyler Rinker, Pharm.D. Harrison School of Pharmacy, Auburn University Mary Elizabeth Terrell, Pharm.D. Harrison School of Pharmacy,
Continuing Education Glaucoma: Overview & Treatment Options Authors: Tyler Rinker, Pharm.D. Harrison School of Pharmacy, Auburn University Mary Elizabeth Terrell, Pharm.D. Harrison School of Pharmacy,
2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1. PRODUCT NAME ISOPTO CARPINE pilocarpine hydrochloride eye drops 1% ISOPTO CARPINE pilocarpine hydrochloride eye drops 2% ISOPTO CARPINE pilocarpine hydrochloride eye drops 4%
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1. PRODUCT NAME ISOPTO CARPINE pilocarpine hydrochloride eye drops 1% ISOPTO CARPINE pilocarpine hydrochloride eye drops 2% ISOPTO CARPINE pilocarpine hydrochloride eye drops 4%
Glaucoma. How is Glaucoma Diagnosed? Glaucoma Testing
 Glaucoma How is Glaucoma Diagnosed? Glaucoma Testing There is no single test for glaucoma. The diagnosis is made by evaluating the patient from a number of perspectives, using specialized instruments.
Glaucoma How is Glaucoma Diagnosed? Glaucoma Testing There is no single test for glaucoma. The diagnosis is made by evaluating the patient from a number of perspectives, using specialized instruments.
Update on Rhopressa TM QD (netarsudil ophthalmic solution) 0.02% and Roclatan TM (netarsudil/latanoprost ophthalmic solution) 0.02%/0.
 Update on Rhopressa TM QD (netarsudil ophthalmic solution) 0.02% and Roclatan TM (netarsudil/latanoprost ophthalmic solution) 0.02%/0.005% 1 Important Information Any discussion of the potential use or
Update on Rhopressa TM QD (netarsudil ophthalmic solution) 0.02% and Roclatan TM (netarsudil/latanoprost ophthalmic solution) 0.02%/0.005% 1 Important Information Any discussion of the potential use or
Patient Information COSOPT PF (CO-sopt PEA EHF) (dorzolamide hydrochloride-timolol maleate ophthalmic solution) 2%/0.5%
 Patient Information COSOPT PF (CO-sopt PEA EHF) (dorzolamide hydrochloride-timolol maleate ophthalmic solution) 2%/0.5% Read this information before you start using COSOPT PF and each time you get a refill.
Patient Information COSOPT PF (CO-sopt PEA EHF) (dorzolamide hydrochloride-timolol maleate ophthalmic solution) 2%/0.5% Read this information before you start using COSOPT PF and each time you get a refill.
GLAUCOMA (2006) PHILIPPINE GLAUCOMA SOCIETY
 GLAUCOMA (2006) PHILIPPINE GLAUCOMA SOCIETY CPM 9 TH EDITION Philippine Glaucoma Society (PGS) Correspondence to: Eye Referral Center, T. M. Kalaw Street, Ermita, Manila Telephone: 524-7119/525-9360 Mobile:
GLAUCOMA (2006) PHILIPPINE GLAUCOMA SOCIETY CPM 9 TH EDITION Philippine Glaucoma Society (PGS) Correspondence to: Eye Referral Center, T. M. Kalaw Street, Ermita, Manila Telephone: 524-7119/525-9360 Mobile:
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 28 May 2008
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 28 May 2008 COSOPT 20 mg/5 mg/ml, eye drops, solution in single dose container Box of 60 0.2 ml single dose containers
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 28 May 2008 COSOPT 20 mg/5 mg/ml, eye drops, solution in single dose container Box of 60 0.2 ml single dose containers
Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Solution: 5 mg/ml Suspensions: 2.5 and 5 mg/ml P-RMS:
 0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Betaxolol eyedrops Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Solution: 5 mg/ml Suspensions: 2.5 and 5 mg/ml P-RMS: HU/H/PSUR/0010/002 Date of FAR: 20.03.2013 4.2 Posology
0BCore Safety Profile Active substance: Betaxolol eyedrops Pharmaceutical form(s)/strength: Solution: 5 mg/ml Suspensions: 2.5 and 5 mg/ml P-RMS: HU/H/PSUR/0010/002 Date of FAR: 20.03.2013 4.2 Posology
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS
 THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA? People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA? People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
Ophthalmological preparations
 Ophthalmological preparations Administration of eye preparations Preparations for the eye should be sterile when issued. Use of single-application containers is preferable; multiple-application preparations
Ophthalmological preparations Administration of eye preparations Preparations for the eye should be sterile when issued. Use of single-application containers is preferable; multiple-application preparations
A LITTLE ANATOMY. three layers of eye: 1. outer: corneosclera. 2. middle - uvea. anterior - iris,ciliary body. posterior - choroid
 GLAUCOMA A LITTLE ANATOMY three layers of eye: 1. outer: corneosclera 2. middle - uvea anterior - iris,ciliary body posterior - choroid connection at the pars plana between post and ant uvea 3. retina
GLAUCOMA A LITTLE ANATOMY three layers of eye: 1. outer: corneosclera 2. middle - uvea anterior - iris,ciliary body posterior - choroid connection at the pars plana between post and ant uvea 3. retina
Test Bank for Medical Surgical Nursing An Integrated Approach 3rd Edition by White
 Test Bank for Medical Surgical Nursing An Integrated Approach 3rd Edition by White Link full download : http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-medical-surgical-nursing-anintegrated-approach-3rd-edition-by-white/
Test Bank for Medical Surgical Nursing An Integrated Approach 3rd Edition by White Link full download : http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-medical-surgical-nursing-anintegrated-approach-3rd-edition-by-white/
Differential diagnosis of the red eye. Carol Slight Nurse Practitioner Ophthalmology
 Differential diagnosis of the red eye Carol Slight Nurse Practitioner Ophthalmology The red eye Conjunctivitis HSV Keratitis Acute angle closure glaucoma Anterior Uveitis Red eye Scleritis Subconjunctival
Differential diagnosis of the red eye Carol Slight Nurse Practitioner Ophthalmology The red eye Conjunctivitis HSV Keratitis Acute angle closure glaucoma Anterior Uveitis Red eye Scleritis Subconjunctival
4/22/16. Eye. External Anatomy of Eye. Accessory Structures. Bio 40B Dr. Kandula
 Eye Bio 40B Dr. Kandula External Anatomy of Eye Accessory Structures l Eyebrows l Levator Palpebrae Superioris - opens eye l Eyelashes l Ciliary glands modified sweat glands l Small sebaceous glands l
Eye Bio 40B Dr. Kandula External Anatomy of Eye Accessory Structures l Eyebrows l Levator Palpebrae Superioris - opens eye l Eyelashes l Ciliary glands modified sweat glands l Small sebaceous glands l
Glaucoma What You Should Know
 Glaucoma What You Should Know U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Eye Institute The National Eye Institute (NEI) conducts and supports research that leads
Glaucoma What You Should Know U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES National Institutes of Health National Eye Institute The National Eye Institute (NEI) conducts and supports research that leads
Elements for a Public Summary. Overview of disease epidemiology
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Epidemiology of the disease Incidence and prevalence Increased pressure in the eye occurs in more than 100 million people, and
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Epidemiology of the disease Incidence and prevalence Increased pressure in the eye occurs in more than 100 million people, and
Long Term Care Formulary RS 14. RESTRICTED STATUS Topical Medical Treatment of Glaucoma 1 of 5
 RESTRICTED STATUS Topical Medical Treatment of Glaucoma 1 of 5 PREAMBLE Significance: Glaucoma occurs in 1-2% of white people aged over 40 years, rising to 5% at 70 years and exponentially with advancing
RESTRICTED STATUS Topical Medical Treatment of Glaucoma 1 of 5 PREAMBLE Significance: Glaucoma occurs in 1-2% of white people aged over 40 years, rising to 5% at 70 years and exponentially with advancing
Glaucoma. What is glaucoma? Eye Words to Know. What causes glaucoma?
 2014 2015 Glaucoma What is glaucoma? Glaucoma is a disease that damages your eye s optic nerve. It usually happens when fluid builds up in the front part of your eye. That extra fluid increases the pressure
2014 2015 Glaucoma What is glaucoma? Glaucoma is a disease that damages your eye s optic nerve. It usually happens when fluid builds up in the front part of your eye. That extra fluid increases the pressure
Visit Type (Check one)
 Page 1 of 14 OHFV21.01 MULE: Page 1 Visit Type (Check one) Visit prior to 078 month visit enter visit window 0 Semi-Annual: Annual: 078 mo. 090 mo. 102 mo. 114 mo. 126 mo. 138 mo. 150 mo. 162 mo. 084 mo.
Page 1 of 14 OHFV21.01 MULE: Page 1 Visit Type (Check one) Visit prior to 078 month visit enter visit window 0 Semi-Annual: Annual: 078 mo. 090 mo. 102 mo. 114 mo. 126 mo. 138 mo. 150 mo. 162 mo. 084 mo.
2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1. PRODUCT NAME MYDRIACYL (Tropicamide) 0.5% MYDRIACYL (Tropicamide) 1.0% Eye Drops 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each ml of Mydriacyl Eye Drops contains the active
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1. PRODUCT NAME MYDRIACYL (Tropicamide) 0.5% MYDRIACYL (Tropicamide) 1.0% Eye Drops 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each ml of Mydriacyl Eye Drops contains the active
Managing the Patient with POAG
 Managing the Patient with POAG Vision Institute Annual Fall Conference Mitchell W. Dul, OD, MS, FAAO mdul@sunyopt.edu Richard J. Madonna, MA, OD, FAAO rmadonna@sunyopt.edu Ocular Hypertension (OHT) Most
Managing the Patient with POAG Vision Institute Annual Fall Conference Mitchell W. Dul, OD, MS, FAAO mdul@sunyopt.edu Richard J. Madonna, MA, OD, FAAO rmadonna@sunyopt.edu Ocular Hypertension (OHT) Most
Chapter 7, Section 1 Review Questions. Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. Name PER Date
 Name PER Date Chapter 7, Section 1 Review Questions Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. A. the middle layer of the wall of the eye B. the structure between the choroid
Name PER Date Chapter 7, Section 1 Review Questions Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. A. the middle layer of the wall of the eye B. the structure between the choroid
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS
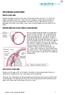 THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
Mild NPDR. Moderate NPDR. Severe NPDR
 Diabetic retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of blindness in adults aged 35-65 years-old. Hyperglycaemia is thought to cause increased retinal blood flow and abnormal metabolism in
Diabetic retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of blindness in adults aged 35-65 years-old. Hyperglycaemia is thought to cause increased retinal blood flow and abnormal metabolism in
Brimonidine/timolol Version 1.2, 16Oct, Elements for a public summary. VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology
 VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology The estimated number of people with vision loss from glaucoma range from 5.2 to 6.7 million. This is approximately 10% of the
VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology The estimated number of people with vision loss from glaucoma range from 5.2 to 6.7 million. This is approximately 10% of the
PRODUCT INFORMATION. 2-(dimethylamino) ethyl (RS)-2-(1-hydroxycyclopentyl)-2- phenylacetate hydrochloride
 PRODUCT INFORMATION MINIMS CYCLOPENTOLATE EYE DROPS NAME OF THE MEDICINE Cyclopentolate hydrochloride Structural formula: Chemical name: Molecular formula: Molecular weight: 327.9 2-(dimethylamino) ethyl
PRODUCT INFORMATION MINIMS CYCLOPENTOLATE EYE DROPS NAME OF THE MEDICINE Cyclopentolate hydrochloride Structural formula: Chemical name: Molecular formula: Molecular weight: 327.9 2-(dimethylamino) ethyl
Medical Treatment in Pediatric Glaucoma
 Medical Treatment in Pediatric Glaucoma By Nader Bayoumi, MD Lecturer of Ophthalmology Ophthalmology Department Alexandria University Alexandria, Egypt ESG 2012 Pediatric glaucoma is a surgical disease
Medical Treatment in Pediatric Glaucoma By Nader Bayoumi, MD Lecturer of Ophthalmology Ophthalmology Department Alexandria University Alexandria, Egypt ESG 2012 Pediatric glaucoma is a surgical disease
Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma
 www.eyesurgeonlondon.co.uk Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Glaucoma is a condition in which there is damage to the optic nerve. This nerve carries visual signals from the eye to the brain.
www.eyesurgeonlondon.co.uk Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma What is Glaucoma? Glaucoma is a condition in which there is damage to the optic nerve. This nerve carries visual signals from the eye to the brain.
Which Drugs Cause Ocular Side Effects?
 Systemic Drugs Causing Eye Side Effects Which Drugs Cause Ocular Side Effects? List of medications If you read drug inset information, almost all say blurred vision. 1 PHOTOSENSITIZERS UV radiation can
Systemic Drugs Causing Eye Side Effects Which Drugs Cause Ocular Side Effects? List of medications If you read drug inset information, almost all say blurred vision. 1 PHOTOSENSITIZERS UV radiation can
PRODUCT INFORMATION NAME OF THE MEDICINE DESCRIPTION PHARMACOLOGY. IOPIDINE (apraclonidine hydrochloride) Eye Drops 0.5%
 PRODUCT INFORMATION IOPIDINE (apraclonidine hydrochloride) Eye Drops 0.5% NAME OF THE MEDICINE IOPIDINE Eye Drops 0.5% contains apraclonidine hydrochloride, an alpha-adrenergic agonist, in a sterile isotonic
PRODUCT INFORMATION IOPIDINE (apraclonidine hydrochloride) Eye Drops 0.5% NAME OF THE MEDICINE IOPIDINE Eye Drops 0.5% contains apraclonidine hydrochloride, an alpha-adrenergic agonist, in a sterile isotonic
South East London Area Prescribing Committee Chronic Open Angle Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension Treatment Pathway
 Proceed to 2 nd line treatment if further reduction in IOP required and there is good response to PGAs or (& no South East London Area Prescribing Committee Chronic Open Angle Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension
Proceed to 2 nd line treatment if further reduction in IOP required and there is good response to PGAs or (& no South East London Area Prescribing Committee Chronic Open Angle Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Contents METHODS... 2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria... 2 Supplementary table S1... 2 Assessment of abnormal ocular signs and symptoms... 3 Supplementary table S2... 3 Ocular
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Contents METHODS... 2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria... 2 Supplementary table S1... 2 Assessment of abnormal ocular signs and symptoms... 3 Supplementary table S2... 3 Ocular
Vision loss in elderly. Erica Weir, April 2015
 Vision loss in elderly Erica Weir, April 2015 1 Burden Enter nursing homes 3 years earlier Twice the risk of falling 4x the risk of hip fracture Independent risk factor for delirium What are the leading
Vision loss in elderly Erica Weir, April 2015 1 Burden Enter nursing homes 3 years earlier Twice the risk of falling 4x the risk of hip fracture Independent risk factor for delirium What are the leading
Glaucoma Basics OVERVIEW GENETICS SIGNALMENT/DESCRIPTION OF PET
 Glaucoma Basics OVERVIEW Glaucoma is a disease of the eye, in which the pressure within the eye is increased (pressure within the eye is known as intraocular pressure or IOP) High intraocular pressure
Glaucoma Basics OVERVIEW Glaucoma is a disease of the eye, in which the pressure within the eye is increased (pressure within the eye is known as intraocular pressure or IOP) High intraocular pressure
Vision loss in elderly
 Vision loss in elderly Erica Weir, February 2016 1 Burden Enter nursing homes 3 years earlier Twice the risk of falling 4x the risk of hip fracture Independent risk factor for delirium What are the leading
Vision loss in elderly Erica Weir, February 2016 1 Burden Enter nursing homes 3 years earlier Twice the risk of falling 4x the risk of hip fracture Independent risk factor for delirium What are the leading
LUMIGAN EYE DROPS (bimatoprost 0.3 mg per ml)
 LUMIGAN EYE DROPS (bimatoprost 0.3 mg per ml) Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about LUMIGAN eye drops. It does not contain all the available
LUMIGAN EYE DROPS (bimatoprost 0.3 mg per ml) Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about LUMIGAN eye drops. It does not contain all the available
Vision I. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Vision I Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Eye Cornea Sclera Conjunctiva 2 Eye The conjunctiva lines the inner surface of the eyelids and outer surface of the sclera. 3
Vision I Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Eye Cornea Sclera Conjunctiva 2 Eye The conjunctiva lines the inner surface of the eyelids and outer surface of the sclera. 3
YOUR VYZULTA TREATMENT GUIDE. Please see Important Safety Information on pages 1, 9, 10, 17 and 18. Please see accompanying Prescribing Information.
 YOUR VYZULTA TREATMENT GUIDE Please see Important Safety Information on pages 1, 9, 10, 17 and 18. Please see accompanying Prescribing Information. INDICATION VYZULTA TM (latanoprostene bunod ophthalmic
YOUR VYZULTA TREATMENT GUIDE Please see Important Safety Information on pages 1, 9, 10, 17 and 18. Please see accompanying Prescribing Information. INDICATION VYZULTA TM (latanoprostene bunod ophthalmic
relative s privacy, do not identify your relative by full name in any assignment.
 Overview Do you or a family member have glaucoma? Do you wonder what this diagnosis means? Glaucoma affects tens of millions of people worldwide. Despite its prevalence, many people lack accurate information
Overview Do you or a family member have glaucoma? Do you wonder what this diagnosis means? Glaucoma affects tens of millions of people worldwide. Despite its prevalence, many people lack accurate information
DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC)
 Guidelines for the medical treatment of chronic open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension Summary: DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Diagnosis and management of ocular hypertension (OHT)
Guidelines for the medical treatment of chronic open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension Summary: DERBYSHIRE JOINT AREA PRESCRIBING COMMITTEE (JAPC) Diagnosis and management of ocular hypertension (OHT)
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION WITH CONSUMER INFORMATION MYDRIACYL. tropicamide ophthalmic solution, USP. 0.5% and 1% w/v.
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION WITH CONSUMER INFORMATION Pr MYDRIACYL tropicamide ophthalmic solution, USP 0.5% and 1% w/v Anticholinergic Alcon Canada Inc. 2665 Meadowpine Blvd. Mississauga, ON L5N 8C7 www.alcon.ca
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION WITH CONSUMER INFORMATION Pr MYDRIACYL tropicamide ophthalmic solution, USP 0.5% and 1% w/v Anticholinergic Alcon Canada Inc. 2665 Meadowpine Blvd. Mississauga, ON L5N 8C7 www.alcon.ca
LOWPROST Eye Drops (Bimatoprost Ophthalmic Solution 0.01%)
 Published on: 14 Apr 2017 LOWPROST Eye Drops (Bimatoprost Ophthalmic Solution 0.01%) For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Composition Each ml contains: Bimatoprost...
Published on: 14 Apr 2017 LOWPROST Eye Drops (Bimatoprost Ophthalmic Solution 0.01%) For the use of a Registered Medical Practitioner or a Hospital or a Laboratory only Composition Each ml contains: Bimatoprost...
APPROVED PACKAGE INSERT FOR XALATAN EYE DROPS. Each millilitre contains latanoprost 50 µg and benzalkonium chloride 0,02 % m/v as preservative.
 SCHEDULING STATUS: S4 APPROVED PACKAGE INSERT FOR XALATAN EYE DROPS PROPRIETARY NAME (and dosage form): XALATAN Eye Drops COMPOSITION: Each millilitre contains latanoprost 50 µg and benzalkonium chloride
SCHEDULING STATUS: S4 APPROVED PACKAGE INSERT FOR XALATAN EYE DROPS PROPRIETARY NAME (and dosage form): XALATAN Eye Drops COMPOSITION: Each millilitre contains latanoprost 50 µg and benzalkonium chloride
Assisting in Ophthalmology. Copyright 2011, 2007, 2003, 1999 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Assisting in Ophthalmology Learning Objectives Define, spell, and pronounce the terms listed in the vocabulary. Apply critical thinking skills in performing patient assessment and care. Explain the differences
Assisting in Ophthalmology Learning Objectives Define, spell, and pronounce the terms listed in the vocabulary. Apply critical thinking skills in performing patient assessment and care. Explain the differences
Trabeculectomy. Draining the aqueous humour reduces the pressure on the optic nerve that causes loss of vision in glaucoma.
 Trabeculectomy Other formats If you need this information in another format such as audio tape or computer disk, Braille, large print, high contrast, British Sign Language or translated into another language,
Trabeculectomy Other formats If you need this information in another format such as audio tape or computer disk, Braille, large print, high contrast, British Sign Language or translated into another language,
PRECISION PROGRAM. Injection Technique Quick-Reference Guide. Companion booklet for the Video Guide to Injection Technique
 Injection Technique Quick-Reference Guide PRECISION PROGRAM Companion booklet for the Video Guide to Injection Technique Available at www.ozurdexprecisionprogram.com Provides step-by-step directions with
Injection Technique Quick-Reference Guide PRECISION PROGRAM Companion booklet for the Video Guide to Injection Technique Available at www.ozurdexprecisionprogram.com Provides step-by-step directions with
OOGZIEKTEN VOOR DE HUISARTS F. GOES, JR.
 OOGZIEKTEN VOOR DE HUISARTS F. GOES, JR. HET RODE OOG F. GOES, JR. Condition Signs Symptoms Causes Conjunctivitis Viral Normal vision, normal pupil size Mild to no pain, diffuse Adenovirus (most common),
OOGZIEKTEN VOOR DE HUISARTS F. GOES, JR. HET RODE OOG F. GOES, JR. Condition Signs Symptoms Causes Conjunctivitis Viral Normal vision, normal pupil size Mild to no pain, diffuse Adenovirus (most common),
ENIDIN EYE DROPS [brimonidine tartrate]
![ENIDIN EYE DROPS [brimonidine tartrate] ENIDIN EYE DROPS [brimonidine tartrate]](/thumbs/81/84520817.jpg) ENIDIN EYE DROPS [brimonidine tartrate] Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about ENIDIN eye drops, including how to use the eye It does not
ENIDIN EYE DROPS [brimonidine tartrate] Consumer Medicine Information What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about ENIDIN eye drops, including how to use the eye It does not
Internal Document code 1 iop041217inz
 NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1. PRODUCT NAME IOPIDINE (apraclonidine hydrochloride) Eye Drops 0.5%. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each ml of Iopidine Eye Drops 0.5% contains apraclonidine hydrochloride
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1. PRODUCT NAME IOPIDINE (apraclonidine hydrochloride) Eye Drops 0.5%. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each ml of Iopidine Eye Drops 0.5% contains apraclonidine hydrochloride
Anatomy: There are 6 muscles that move your eye.
 Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Thyroid Eye Disease Your doctor thinks you have thyroid orbitopathy. This is an autoimmune condition where your body's immune system is producing factors that stimulate enlargement of the muscles that
Phospholine Iodide (echothiophate iodide for ophthalmic solution)
 Phospholine Iodide (echothiophate iodide for ophthalmic solution) Rx Only DESCRIPTION Chemical name: (2-mercaptoethyl) trimethylammonium iodide O,O-diethyl phosphorothioate Structural formula Echothiophate
Phospholine Iodide (echothiophate iodide for ophthalmic solution) Rx Only DESCRIPTION Chemical name: (2-mercaptoethyl) trimethylammonium iodide O,O-diethyl phosphorothioate Structural formula Echothiophate
Special Senses: The Eye
 Unit 4 Special Senses: The Eye ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Senses General senses of touch Temperature Pressure Pain Special senses Smell Taste Sight Hearing Equilibrium The Eye and Vision
Unit 4 Special Senses: The Eye ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY The Senses General senses of touch Temperature Pressure Pain Special senses Smell Taste Sight Hearing Equilibrium The Eye and Vision
LENS INDUCED GLAUCOMA
 LENS INDUCED GLAUCOMA PRESENTER P SHILPA RAVI 2 ND YEAR PG DEPT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY LENS INDUCED GLAUCOMA It is a form of secondary glaucoma where intraocular pressure is raised due to disorder in crystalline
LENS INDUCED GLAUCOMA PRESENTER P SHILPA RAVI 2 ND YEAR PG DEPT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY LENS INDUCED GLAUCOMA It is a form of secondary glaucoma where intraocular pressure is raised due to disorder in crystalline
SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM
 Page 1 of 5 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM FML Liquifilm Sterile Eye Suspension COMPOSITION FML Liquifilm Sterile Eye Suspension contains: Fluorometholone 1,0 mg/ml Liquifilm
Page 1 of 5 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM FML Liquifilm Sterile Eye Suspension COMPOSITION FML Liquifilm Sterile Eye Suspension contains: Fluorometholone 1,0 mg/ml Liquifilm
Objectives. Unexplained Vision Loss: Where Do I Go From Here. History. History. Drug Induced Vision Loss
 Objectives Unexplained Vision Loss: Where Do I Go From Here Denise Goodwin, OD, FAAO Coordinator, Neuro-ophthalmic Disease Clinic Pacific University College of Optometry goodwin@pacificu.edu Know the importance
Objectives Unexplained Vision Loss: Where Do I Go From Here Denise Goodwin, OD, FAAO Coordinator, Neuro-ophthalmic Disease Clinic Pacific University College of Optometry goodwin@pacificu.edu Know the importance
Around The Globe in 60 Minutes
 Around The Globe in 60 Minutes Around the GLOBE in Sixty Minutes Basic Ocular Anatomy, Examination, and Diagnostic Techniques Introduction Focusing on canine and feline ocular anatomy and basic examination
Around The Globe in 60 Minutes Around the GLOBE in Sixty Minutes Basic Ocular Anatomy, Examination, and Diagnostic Techniques Introduction Focusing on canine and feline ocular anatomy and basic examination
The Orbit. The Orbit OCULAR ANATOMY AND DISSECTION 9/25/2014. The eye is a 23 mm organ...how difficult can this be? Openings in the orbit
 The eye is a 23 mm organ...how difficult can this be? OCULAR ANATOMY AND DISSECTION JEFFREY M. GAMBLE, OD COLUMBIA EYE CONSULTANTS OPTOMETRY & UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY CLINICAL
The eye is a 23 mm organ...how difficult can this be? OCULAR ANATOMY AND DISSECTION JEFFREY M. GAMBLE, OD COLUMBIA EYE CONSULTANTS OPTOMETRY & UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY CLINICAL
Cataract Surgery: Patient Information
 Cataract Surgery: Patient Information How do the Eyes Work? As light enters the eye, it first passes through the cornea the clear window of the eye. Because the cornea is curved, the light rays bend (refract).
Cataract Surgery: Patient Information How do the Eyes Work? As light enters the eye, it first passes through the cornea the clear window of the eye. Because the cornea is curved, the light rays bend (refract).
By Darlene Jones, Nurse. May 2017
 By Darlene Jones, Nurse May 2017 Disclosure of potential conflict of interest Darlene Jones, Nurse I have no conflict of interest Course objectives Become familiar with the different pathologies in ophthalmology
By Darlene Jones, Nurse May 2017 Disclosure of potential conflict of interest Darlene Jones, Nurse I have no conflict of interest Course objectives Become familiar with the different pathologies in ophthalmology
The Special Senses: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College CHAPTER 15 The Special Senses: Part A Warm Up What is the function of the eyeball? List any structures of the eyeball that you
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College CHAPTER 15 The Special Senses: Part A Warm Up What is the function of the eyeball? List any structures of the eyeball that you
Ocular Anatomy for the Paraoptometric
 Ocular Anatomy for the Paraoptometric Minnesota Optometric Association Paraoptometric CE Friday September 30, 2016 Lindsay A. Sicks, OD, FAAO Assistant Professor, Illinois College of Optometry lsicks@ico.edu
Ocular Anatomy for the Paraoptometric Minnesota Optometric Association Paraoptometric CE Friday September 30, 2016 Lindsay A. Sicks, OD, FAAO Assistant Professor, Illinois College of Optometry lsicks@ico.edu
Sense of Vision. Chapter 8. The Eye and Vision. The Eye Orbit. Eyebrows, Eyelids, Eyelashes. Accessory Organs 5/3/2016.
 Sense of Vision Chapter 8 Special Senses The Eye and Vision 70 percent of all sensory receptors are in the eyes Each eye has over 1 million nerve fibers Protection for the eye Most of the eye is enclosed
Sense of Vision Chapter 8 Special Senses The Eye and Vision 70 percent of all sensory receptors are in the eyes Each eye has over 1 million nerve fibers Protection for the eye Most of the eye is enclosed
[TRAVOPROST] 40 MICROGRAMS/ML, EYE DROPS, SOLUTION RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN. TRAVOPR-v
![[TRAVOPROST] 40 MICROGRAMS/ML, EYE DROPS, SOLUTION RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN. TRAVOPR-v [TRAVOPROST] 40 MICROGRAMS/ML, EYE DROPS, SOLUTION RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN. TRAVOPR-v](/thumbs/94/119684929.jpg) [TRAVOPROST] 40 MICROGRAMS/ML, EYE DROPS, SOLUTION RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN TRAVOPR-v2-270214 VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Studies estimated that 3-6 million people
[TRAVOPROST] 40 MICROGRAMS/ML, EYE DROPS, SOLUTION RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN TRAVOPR-v2-270214 VI.2 Elements for a public summary VI.2.1 Overview of disease epidemiology Studies estimated that 3-6 million people
CONSUMER INFORMATION. Sandoz Travoprost / Timolol PQ ophthalmic solution travoprost and timolol ophthalmic solution with POLYQUAD * as preservative
 CONSUMER INFORMATION Pr Sandoz Travoprost / Timolol PQ ophthalmic solution travoprost and timolol ophthalmic solution with POLYQUAD * as preservative This leaflet is designed specifically for Consumers.
CONSUMER INFORMATION Pr Sandoz Travoprost / Timolol PQ ophthalmic solution travoprost and timolol ophthalmic solution with POLYQUAD * as preservative This leaflet is designed specifically for Consumers.
THE EYE: RETINA AND GLOBE
 Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas February 24, 2011, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15. Your histology and gross anatomy books should be useful. Reading: Histology of the Eye from any histology book
Neuroanatomy Suzanne Stensaas February 24, 2011, 10:00-12:00 p.m. Reading: Waxman Ch. 15. Your histology and gross anatomy books should be useful. Reading: Histology of the Eye from any histology book
OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA
 OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA Learning outcomes By the end of this lecture the students would be able to Classify occlusive vascular disorders (OVD) of the retina. Correlate the clinical features
OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA Learning outcomes By the end of this lecture the students would be able to Classify occlusive vascular disorders (OVD) of the retina. Correlate the clinical features
