Clinical Ophthalmology
|
|
|
- Daniella Sharp
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Clinical Ophthalmology By : Saif S. Zaina Diagnosis: Entropion: Malposition (inward turning) of eyelid toward the eyeball with trichiasis (misdirection of the eyelashes toward the eyeball). Causes of entropion: 1) Congenital (rare). 2) Acute spastic conditions such as infections, inflammatory & traumatic. 3) Cicatricial (scaring of the palpebral conjunctiva). Causes of trichiasis: 1) Infections (trachoma, herpes). 2) Auto-immune (ocular cicatricial pemphigoid). 3) Inflammatory (Stevens-Johnson syndrome, vernal keratoconjunctivitis). 4) Trauma. Complications (entropion & trichiasis): 1) Infections.
2 2) Corneal ulceration. Treatment of entropion: 1) Eyelid hygiene. 2) Antibiotics to treat the causative microorganism. 3) Steroids. 4) Lubrication. 5) Small amount of botulinum toxin (BOTOX). 6) Surgical repair (Lateral canthotomy, lateral canthoplasty). Treatment of trichiasis: 1) Treatment of the underlying disease (Stevens-Johnson syndrome & ocular cicatritial pemphigoid). 2) Lubrication. 3) Treatment of infection. 4) Surgery (follicle destroying or lash/follicle repositioning). Diagnosis: Ectropion: Abnormal eversion (outward turning) of the lower eyelid margin away from the globe. Patient complaint: Lacrimation. Causes:
3 1) Congenital. 2) Acquired: a) Senile. b) Paralytic (facial nerve palsy). c) Cicatricial (due to scar) such as burns, glaucoma drops and chronic dermatitis.etc. d) Mechanical (tumour) such as neurofibromas. Complications: 1) Conjunctival keratinization. 2) Corneal breakdown (ulceration) 3) Epiphoria (watery eye : tears flow onto the cheek). 4) Pain. Treatment: 1) Treatment of infection (Chlamydia, herpes). 2) Lubrication. 3) Steroid. 4) Surgical repair (V to Y plasty or Z plasty). Diagnosis: Entropion with trichiasis & corneal ulceration.
4 Diagnosis: Stye : red swollening of the upper eyelid due to inflammation of eyelash follicles. Causes: Bacterial infection staph. Aureus infection. Treatment: 1) Local antibiotics & eye drops. 2) Bathing in warm water. 3) Removal of the eyelash involved.
5 Diagnosis: Ophthalmia neonatorum (neonatal conjunctivitis). Causes: 1) Chemical (silver nitrate). 2) Bacterial (1 st 3 days=staph.aureus, after the 3 rd day= Strept.peumonia, after the 1 st week=neisseria gonorrhea, after 12 days=chlamydia). 3) after 15 days=viral (H. influenza & herpes simplex virus). Treatment: 1) Gonococcal infection treated by cefotaxime for 7 days. 2) Chlamydial infection by systemic erythromycin. 3) Herpes by I.V acyclovir. 4) Topical antibiotic for staph.
6 Diagnosis: Phlyctenular conjunctivitis: Small pinkish-yellow nodule surrounded by a zone of dilated blood vessels at corneoscleral junction. Causes: Hypersensitivity reaction (type 4) to endogenous antigens e.g. bacterial antigens as T.B & Chlamydia. Diagnosis: Bulbar spring catarrhal: Treatment: Avoiding exposure to the causative allergen, topical steroids, mast cell stabilizers, anti histaminic dark glasses & cold compresses.
7 Diagnosis: Ulcerative blepharitis: erythema & crusting of the lashes and lid margins & adherence of the lashes with each other by oily debris. Causes: 1) Herpes simplex & Varicella zoster dermatitis. 2) Allergic or contact dermatitis. 3) Bacterial infection (Staph.) is the usual pathogen. 4) Exposure to smoke, fumes & other irritants. 5) Sjogren syndrome may be present as blepharitis. Complications: Chronic conjunctivitis, Madarosis, trichiasis, Poliosis, epiphora, Ectropion, corneal ulcer. Treatment: 1) Eyelid margin hygiene (warming, washing & application of antibiotic ointment to the lid margins). 2) Antibiotic corticosteroid solutions to reduce inflammation if the cause is bacterial. 3) Antivirals. 4) Avoiding exposure to irritant materials.
8 Diagnosis: Mucopurulent conjunctivitis: Diffuse redness of the sclera with yellowish mucopurulent discharge & eyelid edema. Cause: Trachoma. Complications: 1) Membrane formation. 2) Subsequent scarring of the punctum. 3) Corneal ulcer. Treatment: 1) Eye lotions. 2) Antibiotics ointments e.g. tobramycin at night. 3) Antibiotic eye drops (tetracycline). 4) Hot foments.
9 Diagnosis: Pterygium : Localized redness located at the nasal corner of the eye, triangular in shape with the apex extended to involve the cornea & it is a fibrovascular ingrowths. Causes: 1) Direct ultra violet exposure. 2) Exposure to irritant materials (dust, smoke ). Treatment: Surgical removal with conjunctival graft. Surgical indications: 1) Functional abnormalities of vision. 2) Foreign body sensation. 3) Cosmetic reasons.
10 Diagnosis: Posterior Synechiae. Cause: Anterior uveitis (iritis). Complications: 1) Band keratopathy. 2) Bulus keratopathy. 3) Cataract. 4) Glaucoma. Treatment: 1) Atropine & corticosteroid drops. 2) Surgical separation (synechialysis).
11 Diagnosis: Rubeosis iridis (Growth of blood vessels onto the iris) & Peripheral iridectomy. Causes: 1) Diabetic retinopathy. 2) Central retinal vein occlusion(crvo). 3) Long standing retinal detachment. 4) Ocular ischemic syndrome. 5) Hyoptonus eye. 6) Long standing uveitis. 7) Uveal melanoma. 8) Retinoblastoma. Complication: Rubeotic glaucoma & prognosis is very bad. Diagnosis: Iridodialysis: A dark crescentic gap at the edge of the iris where the tear has occurred. Causes 1) Trauma. 2) Tumour excision.
12 Patient complaint: Uniocular diplopia. Treatment: Surgical reduction and suturing of the iris. Diagnosis: Left partial ptosis: drooping of the left upper eyelid. Causes: 1) Oculomotor nerve palsy. 2) Horner syndrome. 3) Birth trauma. 4) Congenital. Factors affecting prognosis & treatment: 1) Is the pupil covered by the ptotic lid or not? 2) Are there significant refractive errors between the eyes? The significance is developing of ambylopia (causes): 1) Strabismus ambylopia due to squint. 2) Anisometropic ambylopia due to deferent refractive errors. 3) Deprivational ambylopia.
13 Diagnosis: Central retinal vein occlusion(congested dilated blood vessels). Causes: 1) Extaluminal causes: hypertension & tumour. 2) In the wall: vasculitis. 3) Intraluminal: thrombus. Complications: 1) Neovascular glaucoma. 2) Chronic macular edema. Diagnosis: Dendritic ulcer. Cause:
14 Herpes simplex virus. Treatment: Acyclovir, trifluridine & idoxuridine. Diagnosis: Keratoconus : Munson`s sign. Significance: It is one of the common causes of reduction in visual acuity(myopia & Astigmatism). Treatment: 1) Rigid contact lenses. 2) Shaving the corneal surface. 3) Corneal graft.
15 Diagnosis: Central retinal artery occlusion:(attenuation & constriction of the arteries cattle track appearance), the whole retina is pale except the fovea (cherry red spot) due to double blood supply. Causes: Usually embolic. Diagnosis: Abnormal cupping of the optic disc(cup-disc ratio > 0.3). Criteria for abnormal cupping of optic nerve: 1) Cup-disc ratio ) Progressively enlarging. 3) Asymmetrical between the two eyes. Causes: Primary open angle glaucoma. Criteria to diagnose glaucoma: 1) Increased IOP. Normally 15±6 mmhg. 2) Abnormal cupping. 3) Changes in visual field.
16 Diagnosis: Retinitis pigmentosa: bone spicules, waxy disc & attenuated blood vessels. Patient complaints: 1) Night blindness(nyctalopia). 2) Visual loss. 3) Seeing flashes of light(photopsia). Causes: 1) Autosomal dominant / recessive. 2) Bardet - biedl syndrome. 3) Refsum s disease.
17 Diagnosis: Hypermetropia. Correction is by: Convex lenses (+) & refractive eye surgery. Significance: Angle closure glaucoma as a complication. Diagnosis: Myopia. Correction is by: Concave lenses (-) & refractive eye surgery. Retinal detachment, macular hole & open angle glaucoma as complications.
18 Name the device & what is it used for? Goldmann applanation tonometer for measuring IOP. Diagnosis: Congenital failure of canalization of nasolacrimal duct. Procedure\management: 1) Reassurance of the parents. 2) Topical antibiotic with massage & waiting till the end of first year. 3) If not opened, probing and irrigation with antiseptic solution. Child presentation: Lacrimation.
19 Diagnosis: Subconjunctival hemorrhage(sectoral redness). What do you want to ask the patient in your history taking? 1) Trauma. 2) Hypertension. 3) Straining conditions(valsalva). 4) Bleeding disorders. 5) Anticoagulants & non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Diagnosis: Membranous conjunctivitis. Causes:
20 True membrane: diphtheria. Pseudo-membrane: most of bacterial infections like staph. Corneal topography. Used for studying the shape & refractive power of cornea in every point with details. Diagnosis: Leukocoria & pseudosquint. Causes of Leukocoria: 1) Retinoblastoma. 2) congenital cataract.
21 3) Retinopathy of prematurity. Cause of pseudosquint: Epicanthal fold. Is it a concomitant or incomitant squint? It is incomitant squint(being maximal in the direction of the action of the affected muscle). Top photo: Patient looking to the right. Which muscle is affected? Right lateral rectus. What is the nerve supply? Right abducent nerve.
22 Diagnosis: Left complete ptosis. Causes: 1) Oculomotor nerve palsy. 2) Horner syndrome. 3) Birth trauma. 4) Congenital. Describe this facies: Staring facies & periorbital swelling(thyroid eye disease). Enumerate four ocular features of this disease:
23 1) Lid lag. 2) Lid retraction. 3) Exophthalmoses. 4) Chemosis. 5) Periorbital soft tissue changes as chemosis & lid swelling. 6) Exposure keratopathy. 7) Ophthalmoplegia. Enumerate four systemic features of this disease: 1) Tachycardia. 2) Tremor. 3) Increased appetite with loss of weight. 4) Goitre. Description of skin lesion: Crusty lesion on erythematous base involving the left forehead & the nose. Describe the ocular lesion: Yellow discharge(fluorescenein stain): corneal ulcer. Diagnosis: Herpes zoster ophthalmicus
24 Casue: Herpes zoster(varicella zoster virus). Diagnosis: Right lower motor facial palsy with lagophalmus & Bull's phenomenon. Significance: Exposure keratopathy. Treatment: 1) Artificial tear drops. 2) Surgery (Lid shorting procedure: lateral tarsorrhaphy). Diagnosis:
25 Papillae of right upper eyelid(gobble stone appearance). Causes: Allergic conjunctivitis: atopic, seasonal, giant papillary conjunctivitis. Treatment: Avoiding exposure to the causative allergen, topical steroids, mast cell stabilizers, anti histaminic, dark glasses & cold compresses. By using which test we can get this view? Viewing the angle of anterior chamber by using gonioscope with goniolens for detecting glaucoma. Describe the aqueous circulation: It is produced by the ciliary process of ciliary body posterior chamber through pupil anterior chamber trabecular meshwork Canal of Schlemm collecting channels episcleral venous plexus.
26 Comment on the anterior chamber depth: 1) Eclipse sign: we shine a light on the temporal aspect of the patient anterior chamber & watching the iris, if the AC is deep the whole iris is illuminated, if the AC is shallow, only the temporal part is illuminated. 2) Important in angle closure glaucoma. If this patient is asymptomatic, how would you treat him? Miotic agents, alpha agonist, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and prostaglandin analogs.
27 What is this & give diagnosis? Perimetry graph showing paracentral scotoma in open angle glaucoma. Patient complaint: no complaint, it is diagnosed by chance. What is this? Laser Iridotomy. Indication: Shallow anterior chamber(angle closure glaucoma).
28 What is he doing?! Measuring corneal diameter by a caliber. Why? To detect & follow up the congenital glaucoma ( buphthalmos). What is this lesion? Arcus lipidis. What is the clinical significance? It indicates hyper lipidemia in young people. What is the visual prognosis?
29 It never affect vision. Diagnosis: Ameboid ulcer. Causes: Mistreatment of dendritic ulcer by steroid. Diagnosis:
30 Hypopyon: pus in the anterior chamber. Causes: Infected: endophthalmitis(pneumococcus). Sterile: severe iritis. Description: Nodulo-ulcerative lesion. DDx: Squamous cell carcinoma, malignant melanoma & sebaceous cell carcinoma. Describe this lesion:
31 Localized swelling in the left upper eyelid. What is the most likely diagnosis? Chalazion. Enumerate four possible causes: 1) blockage of tarsal glands. 2) Seborrhea. 3) Chronic blepharitis. 4) Acne rosacea. Treatment: Antibiotic ointment or surgical incision and curettage of the gland. What is this procedure? Eversion of upper eyelid. What are its benefits? 1) Entrapment of foreign body. 2) Arlet line of trachoma. 3) Giant papillary conjunctivitis. 4) Follicular reaction. 5) Adrenochrome deposits. 6) Melanoma.
32 7) Conjunctival concretion. What is this procedure? Cover / uncover test. In which disease you want to use it in your examination? It is used to diagnose inapparent squint(phoria). Diagnosis: Hyphema. Cause: Trauma is the major cause, surgery (during & after), intraocular tumours anticoagulant treatment.
33 Diagnosis: Corneal foreign body. Treatment: Surgical removal. Diagnosis: Symblepharon Causes: 1) Post-trachomatous. 2) Post-operative ( Pterygium excision). 3) Ocular cicatricial pemphigoid.
34 Error of refraction : High myopia. Complications: 1) Chorio-retinal degenerations. 2) retinal tears. 3) retinal detachment. Field defect: Bitemporal hemianopia. Cause:
35 Optic chiasma lesions (nasal fibers damage) e.g. Pituitary gland tumor. Examination of neonates (4) buphthalmos arapaho.nsuok.edu/~fulk/ Images/Img0055.JPG Diagnosis : Buphthalmos. Surgical procedures: 1) Goniotomy. 2) Trabeculotomy. Esotropia: convergent Exotropia: divergent
36 Description: Red congested eye. Common Causes: 1- Conjunctivitis. 2- Acute iritis (ant. Uveitis). 3- Keratitis (Corneal Ulcer ). 4- Angle closure glaucoma. 5- Episcleritis (& scleritis). 6- Subconjunctival hemorrhage. 7- Dry eye.
37 Describe: Upper eyelid eversion, follicular formation. Causes: Trachoma & viral conjunctivitis. Describe: Chemosis: edema of the conjunctiva. Causes: 1) Conjunctivitis. 2) If drainage of blood & lymph from around the eye is obstructed.
38 Diagnosis: Astigmatism. Treatment: Cylindrical lenses & refractive eye surgery. Sign:
39 Marcus Gunn phenomenon Pathogenesis: Faulty Innervation (motor fibers from 5 th nerve reach levator instead of the 3 rd nerve). Describe: Red congested eye (acute angle closure glaucoma). Features: 1) Painful red eye. 2) Achy, abdominal pain. 3) Misty vision. 4) Go from light into dark. 5) Small eye, shallow anterior chamber, pupil mid dilated. 6) Iris lens contact. 7) Push the iris forward. 8) Eye feels hard.
40 Diagnosis: Subhaloid hemorrhage(hemorrhage between retina & vitreous.
OPHTHALMOLOGY REFERRAL GUIDE FOR GPS
 OPHTHALMOLOGY REFERRAL GUIDE FOR GPS A guidebook to support general practitioners in the management and referral of a range of common eye problems. Contents 3 Introduction 4 Ophthalmic Workup 6 Acute Visual
OPHTHALMOLOGY REFERRAL GUIDE FOR GPS A guidebook to support general practitioners in the management and referral of a range of common eye problems. Contents 3 Introduction 4 Ophthalmic Workup 6 Acute Visual
PAINFUL PAINLESS Contact lens user BOV
 Common Causes Allergies Infections Ocular Cornea, uveitis, endophthalmitis Orbital Orbital cellulitis Inflammation Uveitis Scleritis / episcleritis Glaucomas Trauma Foreign bodies Chemical injuries History
Common Causes Allergies Infections Ocular Cornea, uveitis, endophthalmitis Orbital Orbital cellulitis Inflammation Uveitis Scleritis / episcleritis Glaucomas Trauma Foreign bodies Chemical injuries History
Lower Eyelid Malposition
 Oculoplastic Surgeon s DDX for the Red Eye Geeta Belsare Been,MD The Center for Facial Plastic Surgery Barrington, IL Lower Eyelid Malposition Ectropion Involutional Cicatricial Paralytic Entropion Involutional
Oculoplastic Surgeon s DDX for the Red Eye Geeta Belsare Been,MD The Center for Facial Plastic Surgery Barrington, IL Lower Eyelid Malposition Ectropion Involutional Cicatricial Paralytic Entropion Involutional
KPA PFIZER EDUCATION GRANT
 KPA PFIZER EDUCATION GRANT What every Paediatrician needs to know in Paediatric Ophthalmology Dr. Njambi Ombaba Paediatricians knowledge in ophthalmology Outline Visual development in a child Amblyopia
KPA PFIZER EDUCATION GRANT What every Paediatrician needs to know in Paediatric Ophthalmology Dr. Njambi Ombaba Paediatricians knowledge in ophthalmology Outline Visual development in a child Amblyopia
Paediatric acute ophthalmology. Harry Bradshaw
 Paediatric acute ophthalmology Harry Bradshaw Approach Red eye Leukocoria Neurological Trauma Visual loss Red eye Orbital Eyelid Conjunctiva Cornea Uvea Orbital Orbit fixed volume Contiguous with sinuses,
Paediatric acute ophthalmology Harry Bradshaw Approach Red eye Leukocoria Neurological Trauma Visual loss Red eye Orbital Eyelid Conjunctiva Cornea Uvea Orbital Orbit fixed volume Contiguous with sinuses,
Nasolacrimal Duct Blockage
 The eyelids play a key role in protecting the eyes. They help spread moisture (tears) over the surface of the eyes when they close (for example, while blinking); thus, they help prevent the eyes from becoming
The eyelids play a key role in protecting the eyes. They help spread moisture (tears) over the surface of the eyes when they close (for example, while blinking); thus, they help prevent the eyes from becoming
Ocular Allergy. Phil Lieberman, MD
 Ocular Allergy Phil Lieberman, MD Disclosure Consultant/Advisory Board: Genentech, Meda, Mylan, Teva Speaker: Genentech, Meda, Merck, Mylan, Teva Learning Objectives Upon completion of this session, participants
Ocular Allergy Phil Lieberman, MD Disclosure Consultant/Advisory Board: Genentech, Meda, Mylan, Teva Speaker: Genentech, Meda, Merck, Mylan, Teva Learning Objectives Upon completion of this session, participants
By Darlene Jones, Nurse. May 2017
 By Darlene Jones, Nurse May 2017 Disclosure of potential conflict of interest Darlene Jones, Nurse I have no conflict of interest Course objectives Become familiar with the different pathologies in ophthalmology
By Darlene Jones, Nurse May 2017 Disclosure of potential conflict of interest Darlene Jones, Nurse I have no conflict of interest Course objectives Become familiar with the different pathologies in ophthalmology
Table of Contents 1 Orbit 3 2 Eyelids 7
 Table of Contents Preface, x List of abbreviations xi Glossary xii Section I Atlas 1 1 Orbit 3 Clinical signs associated with orbital neoplasia 3 Clinical signs associated with orbital cellulitis 3 Enophthalmos
Table of Contents Preface, x List of abbreviations xi Glossary xii Section I Atlas 1 1 Orbit 3 Clinical signs associated with orbital neoplasia 3 Clinical signs associated with orbital cellulitis 3 Enophthalmos
ASSESSING THE EYES. Structures. Eyelids Extraocularmuscles Eyelashes Lacrimal glands: Lacrimal ducts Cornea Conjunctiva Sclera Pupils Iris.
 ASSESSING THE EYES Structures External Eyelids Extraocularmuscles Eyelashes Lacrimal glands: Lacrimal ducts Cornea Conjunctiva Sclera Pupils Iris 1 2 Structures Internal Optic disc Physiological cup Retinal
ASSESSING THE EYES Structures External Eyelids Extraocularmuscles Eyelashes Lacrimal glands: Lacrimal ducts Cornea Conjunctiva Sclera Pupils Iris 1 2 Structures Internal Optic disc Physiological cup Retinal
Mom, There s Something Wrong With My Eye
 Mom, There s Something Wrong With My Eye Veeral Shah MD, PHD Texas Children's Hospital Most Common Issues Seen by the Pediatrician Emergent Ocular Issues Seen by the Pediatrician 1 What does this baby
Mom, There s Something Wrong With My Eye Veeral Shah MD, PHD Texas Children's Hospital Most Common Issues Seen by the Pediatrician Emergent Ocular Issues Seen by the Pediatrician 1 What does this baby
JINNAH SINDH MEDICAL UNIVERSITY STUDY GUIDE- OPHTHALMOLOGY YEAR 4,
 INTRODUCTION Pakistan, the 7th most populous country in the world, has an urban population of 38.8% and rural dwellers of 61.2%. The country has faced challenges with vision impairment and blindness as
INTRODUCTION Pakistan, the 7th most populous country in the world, has an urban population of 38.8% and rural dwellers of 61.2%. The country has faced challenges with vision impairment and blindness as
Sepideh Tara Rousta, MD FAAO Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital Saint Peter s University Hospital Wills Eye Hospital
 Sepideh Tara Rousta, MD FAAO Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital Saint Peter s University Hospital Wills Eye Hospital 14 mo old w R eye cross (parents) 9 mo old R eye crossing getting worse for past
Sepideh Tara Rousta, MD FAAO Robert Wood Johnson University Hospital Saint Peter s University Hospital Wills Eye Hospital 14 mo old w R eye cross (parents) 9 mo old R eye crossing getting worse for past
Ophthalmology Quick Reference Card
 Purpose: Provide guidance for documentation required to assign the most appropriate and detailed codes in the new coding system (ICD-10 CM/PCS). Laterality Status of disease Origin of disease Left Right
Purpose: Provide guidance for documentation required to assign the most appropriate and detailed codes in the new coding system (ICD-10 CM/PCS). Laterality Status of disease Origin of disease Left Right
ICD 10 CM OPHTHALMOLOGY 2017 Quick Reference Guide SYMPTOMS CATARACT/LENS. with status migrainosus... G43.801
 ICD 10 CM OPHTHALMOLOGY 2017 Quick Reference Guide SYMPTOMS Blurred vision (368.8)... H53.8 Contusion of eyeball and orbital tissues (921.3) eye initial encounter... S05.11XA subsequent encounter... S05.11XD
ICD 10 CM OPHTHALMOLOGY 2017 Quick Reference Guide SYMPTOMS Blurred vision (368.8)... H53.8 Contusion of eyeball and orbital tissues (921.3) eye initial encounter... S05.11XA subsequent encounter... S05.11XD
Page 1 RED EYES. conjunctivitis keratitis episcleritis / scleritis. Frank Larkin Moorfields Eye Hospital. acute glaucoma anterior uveitis
 The RED EYE and ALLERGIC EYE DISEASE DIAGNOSIS & MANAGEMENT Frank Larkin Moorfields Eye Hospital RED EYES conjunctivitis keratitis episcleritis / scleritis acute glaucoma anterior uveitis post-op. / trauma
The RED EYE and ALLERGIC EYE DISEASE DIAGNOSIS & MANAGEMENT Frank Larkin Moorfields Eye Hospital RED EYES conjunctivitis keratitis episcleritis / scleritis acute glaucoma anterior uveitis post-op. / trauma
OOGZIEKTEN VOOR DE HUISARTS F. GOES, JR.
 OOGZIEKTEN VOOR DE HUISARTS F. GOES, JR. HET RODE OOG F. GOES, JR. Condition Signs Symptoms Causes Conjunctivitis Viral Normal vision, normal pupil size Mild to no pain, diffuse Adenovirus (most common),
OOGZIEKTEN VOOR DE HUISARTS F. GOES, JR. HET RODE OOG F. GOES, JR. Condition Signs Symptoms Causes Conjunctivitis Viral Normal vision, normal pupil size Mild to no pain, diffuse Adenovirus (most common),
THE 35 GOLDEN EYE RULES
 THE 35 GOLDEN EYE RULES The Sense of Sight, from La Dame a la Licorne, The Lady and the Unicorn Tapestries, Late 15th Century Flemish Tapestry in wool and silk, Musée Nationale du Moyen Age, Paris. 1.
THE 35 GOLDEN EYE RULES The Sense of Sight, from La Dame a la Licorne, The Lady and the Unicorn Tapestries, Late 15th Century Flemish Tapestry in wool and silk, Musée Nationale du Moyen Age, Paris. 1.
Aristotle University Thessaloniki Medical School I. & II. Departments of Ophthalmology 90 DIAGNOSTIC & THERAPEUTIC APPROACHES IN OPHTHALMOLOGY
 Aristotle University Thessaloniki Medical School I. & II. Departments of Ophthalmology 90 DIAGNOSTIC & THERAPEUTIC APPROACHES IN OPHTHALMOLOGY The medical student should be able to... I. Pathophysiology
Aristotle University Thessaloniki Medical School I. & II. Departments of Ophthalmology 90 DIAGNOSTIC & THERAPEUTIC APPROACHES IN OPHTHALMOLOGY The medical student should be able to... I. Pathophysiology
THE RED EYE Cynthia McNamara, MD Week 25
 THE RED EYE Cynthia McNamara, MD Week 25 Educational Objectives: 1. Know the differential diagnosis and presentation of specific etiologies of the red eye 2. Be able to evaluate patients presenting with
THE RED EYE Cynthia McNamara, MD Week 25 Educational Objectives: 1. Know the differential diagnosis and presentation of specific etiologies of the red eye 2. Be able to evaluate patients presenting with
The Red Eye: Conjunctivitis, Iritis, or Worse? Sean P. Donahue, MD, PhD
 The Red Eye: Conjunctivitis, Iritis, or Worse? Sean P. Donahue, MD, PhD Sam and Darthea Coleman Chair Vice Chair of Clinical Affairs, Department of Ophthalmology Professor of Pediatrics, Ophthalmology,
The Red Eye: Conjunctivitis, Iritis, or Worse? Sean P. Donahue, MD, PhD Sam and Darthea Coleman Chair Vice Chair of Clinical Affairs, Department of Ophthalmology Professor of Pediatrics, Ophthalmology,
Acute Eyes for ED. Enis Kocak. The Alfred Ophthalmology
 Acute Eyes for ED Enis Kocak The Alfred Ophthalmology The problem with eyes Things to cover Ocular anatomy Basic assessment Common presentations Eye first aid and procedures Ophthalmic emergencies What
Acute Eyes for ED Enis Kocak The Alfred Ophthalmology The problem with eyes Things to cover Ocular anatomy Basic assessment Common presentations Eye first aid and procedures Ophthalmic emergencies What
Conjunctivitis in Cats
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Conjunctivitis in Cats (Inflammation of the Moist Tissues of the Eye) Basics OVERVIEW
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Conjunctivitis in Cats (Inflammation of the Moist Tissues of the Eye) Basics OVERVIEW
Dr Jo-Anne Pon. Dr Sean Every. 8:30-9:25 WS #70: Eye Essentials for GPs 9:35-10:30 WS #80: Eye Essentials for GPs (Repeated)
 Dr Sean Every Ophthalmologist Southern Eye Specialists Christchurch Dr Jo-Anne Pon Ophthalmologist Southern Eye Specialists, Christchurch Hospital, Christchurch 8:30-9:25 WS #70: Eye Essentials for GPs
Dr Sean Every Ophthalmologist Southern Eye Specialists Christchurch Dr Jo-Anne Pon Ophthalmologist Southern Eye Specialists, Christchurch Hospital, Christchurch 8:30-9:25 WS #70: Eye Essentials for GPs
Index. C Canalicular system, 4 Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, 29 30
 A Acanthamoeba keratitis (AK), 82, 83 Acute angle-closure crisis, 156 Acute angle-closure glaucoma (AACG), 121, 141, 284 causes of, 122 clinical presentation, 153 evaluation, 156 157 management/treatment,
A Acanthamoeba keratitis (AK), 82, 83 Acute angle-closure crisis, 156 Acute angle-closure glaucoma (AACG), 121, 141, 284 causes of, 122 clinical presentation, 153 evaluation, 156 157 management/treatment,
a.superficial (adenoid layer).contain lymphoid tissue.
 Conjunctiva Dr. saifalshamarti Anatomy Microscopic: 1.Epithelium (non keratinized,includes goblet cell). 2.Epithelial basement membrane. 3.Stroma : a.superficial (adenoid layer).contain lymphoid tissue.
Conjunctiva Dr. saifalshamarti Anatomy Microscopic: 1.Epithelium (non keratinized,includes goblet cell). 2.Epithelial basement membrane. 3.Stroma : a.superficial (adenoid layer).contain lymphoid tissue.
Conjunctivitis in Dogs
 Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Conjunctivitis in Dogs (Inflammation of the Moist Tissues of the Eye) Basics OVERVIEW
Customer Name, Street Address, City, State, Zip code Phone number, Alt. phone number, Fax number, e-mail address, web site Conjunctivitis in Dogs (Inflammation of the Moist Tissues of the Eye) Basics OVERVIEW
Eye infections. Hossain Jabbari, MD, MPH, ID & TM Infectious Diseases Dept., Digestive Diseases Research Institute (DDRI) TUMS
 Eye infections Hossain Jabbari, MD, MPH, ID & TM Infectious Diseases Dept., Digestive Diseases Research Institute (DDRI) TUMS Eye: An overview Eye: An overview The eye is one of the most complex parts
Eye infections Hossain Jabbari, MD, MPH, ID & TM Infectious Diseases Dept., Digestive Diseases Research Institute (DDRI) TUMS Eye: An overview Eye: An overview The eye is one of the most complex parts
OPHTHALMOLOGIC PEARLS FOR THE NON- OPHTHALMOLOGIST. David G. Gross D.O. Deen-Gross Eye Centers Merrillville-Hobart Deengrosseye.
 OPHTHALMOLOGIC PEARLS FOR THE NON- OPHTHALMOLOGIST David G. Gross D.O. Deen-Gross Eye Centers Merrillville-Hobart Deengrosseye.com A FEW OF THE AREAS WE WILL DISCUSS Red Eye Glaucoma Neuro ophthalmic tid
OPHTHALMOLOGIC PEARLS FOR THE NON- OPHTHALMOLOGIST David G. Gross D.O. Deen-Gross Eye Centers Merrillville-Hobart Deengrosseye.com A FEW OF THE AREAS WE WILL DISCUSS Red Eye Glaucoma Neuro ophthalmic tid
Scrub In. What is the function of vitreous humor? What does the pupil do when exposed to bright light? a. Maintain eye shape and provide color vision
 Scrub In What is the function of vitreous humor? a. Maintain eye shape and provide color vision b. Maintain eye shape and refract light rays c. Provide night vision and color vision d. Provide night vision
Scrub In What is the function of vitreous humor? a. Maintain eye shape and provide color vision b. Maintain eye shape and refract light rays c. Provide night vision and color vision d. Provide night vision
Quick Reference Guide
 ICD-1O-CM Quick Reference Guide SYMPTOMS Blurred vision (368.8)... H53.8 Contusion of eyeball and orbital tissues (921.3) eye initial encounter... S05.11XA eye subsequent encounter... S05.11XD sequela...
ICD-1O-CM Quick Reference Guide SYMPTOMS Blurred vision (368.8)... H53.8 Contusion of eyeball and orbital tissues (921.3) eye initial encounter... S05.11XA eye subsequent encounter... S05.11XD sequela...
OPHTHALMOLOGY MCQS. 4. The commonest painless lid swelling is a. stye b. cyst of moll c. cyst of Zeis d. internal hordeolum e.
 OPHTHALMOLOGY MCQS Following are important MCQs from Ophthalmology for 4 th Year MBBS students for their 3 rd Professional Examination. 1. The first line of treatment in chemical injury is a. admission
OPHTHALMOLOGY MCQS Following are important MCQs from Ophthalmology for 4 th Year MBBS students for their 3 rd Professional Examination. 1. The first line of treatment in chemical injury is a. admission
Patient Symptoms- What They Might Mean. Sarah Dougherty Wood, OD, MS, FAAO Heart of America, February 2011 Paraoptometric Lecture
 Patient Symptoms- What They Might Mean Sarah Dougherty Wood, OD, MS, FAAO Heart of America, February 2011 Paraoptometric Lecture Basic ocular anatomy and physiology Movie projector analogy Blur at near/eye
Patient Symptoms- What They Might Mean Sarah Dougherty Wood, OD, MS, FAAO Heart of America, February 2011 Paraoptometric Lecture Basic ocular anatomy and physiology Movie projector analogy Blur at near/eye
Test Bank for Medical Surgical Nursing An Integrated Approach 3rd Edition by White
 Test Bank for Medical Surgical Nursing An Integrated Approach 3rd Edition by White Link full download : http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-medical-surgical-nursing-anintegrated-approach-3rd-edition-by-white/
Test Bank for Medical Surgical Nursing An Integrated Approach 3rd Edition by White Link full download : http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-medical-surgical-nursing-anintegrated-approach-3rd-edition-by-white/
Ophthalmology. Juliette Stenz, MD
 Ophthalmology Juliette Stenz, MD Required Slide Disclosures NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT Required Slide At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1.
Ophthalmology Juliette Stenz, MD Required Slide Disclosures NO SIGNIFICANT FINANCIAL, GENERAL, OR OBLIGATION INTERESTS TO REPORT Required Slide At the end of this session, students will be able to: 1.
Clinical Practice Guide for the Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Anterior Eye Conditions. April 2018
 Clinical Practice Guide for the Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Anterior Eye Conditions This Clinical Practice Guide provides evidence-based information about current best practice in the management
Clinical Practice Guide for the Diagnosis, Treatment and Management of Anterior Eye Conditions This Clinical Practice Guide provides evidence-based information about current best practice in the management
Dry Eye Assessment and Management Study ELIGIBILITY OCULAR EVALUATION FORM
 Page 1 of 13 BEFORE COMPLETING THE OCULAR EXAMINATION, YOU MUST BE ABLE TO ANSWER YES TO THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS: Have you done MMP9? (SVonly) The Following are done at Baseline: Have you done Tear Osmolarity?
Page 1 of 13 BEFORE COMPLETING THE OCULAR EXAMINATION, YOU MUST BE ABLE TO ANSWER YES TO THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS: Have you done MMP9? (SVonly) The Following are done at Baseline: Have you done Tear Osmolarity?
Ocular Pathology. I. Congenital and/or developmental. A. Trisomy 21. Hypertelorism (widely spaced eyes) Keratoconus (cone shaped cornea)
 I. Congenital and/or developmental Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6 th Ed. A. Trisomy 21 Hypertelorism (widely spaced eyes) Keratoconus (cone shaped cornea) Focal hypoplasia of iris Cataracts frequently
I. Congenital and/or developmental Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease, 6 th Ed. A. Trisomy 21 Hypertelorism (widely spaced eyes) Keratoconus (cone shaped cornea) Focal hypoplasia of iris Cataracts frequently
ICD-10 and Opthalmology
 ICD-10 and Opthalmology Steven M. Verno, CEMCS ICD-10 and Opthalmology Steven M. Verno, CEMCS September 25, 2008 Note: ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 are owned and copyrighted by the World Health Organization. The
ICD-10 and Opthalmology Steven M. Verno, CEMCS ICD-10 and Opthalmology Steven M. Verno, CEMCS September 25, 2008 Note: ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 are owned and copyrighted by the World Health Organization. The
10/4/2013. Bruce K.Williams, MSN, RN,ACNP-BC Sisters of Charity Providence Hospitals. What is the worst thing that can go wrong with an eye?
 Red Eyes, Red Alert! Bruce K.Williams, MSN, RN,ACNP-BC Sisters of Charity Providence Hospitals Red Eyes, Red Alert! Red Eyes, Red Alert! What is the worst thing that can go wrong with an eye? 1 Red Eyes,
Red Eyes, Red Alert! Bruce K.Williams, MSN, RN,ACNP-BC Sisters of Charity Providence Hospitals Red Eyes, Red Alert! Red Eyes, Red Alert! What is the worst thing that can go wrong with an eye? 1 Red Eyes,
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS
 THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA? People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA? People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
Differential diagnosis of the red eye. Carol Slight Nurse Practitioner Ophthalmology
 Differential diagnosis of the red eye Carol Slight Nurse Practitioner Ophthalmology The red eye Conjunctivitis HSV Keratitis Acute angle closure glaucoma Anterior Uveitis Red eye Scleritis Subconjunctival
Differential diagnosis of the red eye Carol Slight Nurse Practitioner Ophthalmology The red eye Conjunctivitis HSV Keratitis Acute angle closure glaucoma Anterior Uveitis Red eye Scleritis Subconjunctival
Disclosure Ocular Anatomy and Motility
 Disclosure Ocular Anatomy and Motility Jenean Carlton BA, ABOC, NCLC President, Carlton & Associates, LLC Carlton and Associates, LLC provides communications and educational materials for the optical industry
Disclosure Ocular Anatomy and Motility Jenean Carlton BA, ABOC, NCLC President, Carlton & Associates, LLC Carlton and Associates, LLC provides communications and educational materials for the optical industry
Examining Children s Eyes
 Paediatric Ophthalmology What to refer & when? Aims Tips for assessing a child s eyes in general practice Common paediatric ophthalmology symptoms and signs What needs to be referred and when? MISS FARIHA
Paediatric Ophthalmology What to refer & when? Aims Tips for assessing a child s eyes in general practice Common paediatric ophthalmology symptoms and signs What needs to be referred and when? MISS FARIHA
Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 5. The Eye Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The most common type of eye disorder is: A. Refractive errors B. Macular conditions
Chapter 5. The Eye Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The most common type of eye disorder is: A. Refractive errors B. Macular conditions
NEW YORK UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES AND GOALS
 NEW YORK UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES AND GOALS Revision Date: 6/30/06 Distribution Date: 7/6/06 The Department of Ophthalmology at the NYU Medical Center
NEW YORK UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY EDUCATIONAL OBJECTIVES AND GOALS Revision Date: 6/30/06 Distribution Date: 7/6/06 The Department of Ophthalmology at the NYU Medical Center
Ophthalmology PANRE Review. Brock Phillips, PA-C
 Ophthalmology PANRE Review Brock Phillips, PA-C I am not an ophthalmologist, optometrist or certified eye guy of any sort - I am a practicing UC/EM PA-C who frequently evaluates eye/vision complaints,
Ophthalmology PANRE Review Brock Phillips, PA-C I am not an ophthalmologist, optometrist or certified eye guy of any sort - I am a practicing UC/EM PA-C who frequently evaluates eye/vision complaints,
Ophthalmology Unit Referral Guidelines
 Ophthalmology Unit Referral Guidelines Austin Health Ophthalmology Unit holds sub-specialty sessions to discuss and plan the treatment of patients with specific ocular conditions. General including cataract
Ophthalmology Unit Referral Guidelines Austin Health Ophthalmology Unit holds sub-specialty sessions to discuss and plan the treatment of patients with specific ocular conditions. General including cataract
Aging & Ophthalmology
 Aging & Ophthalmology Pr Jean-Marie Rakic Dr Denis Malaise January 2018 Major ocular diseases 1. Cataract 2. Age-related macular degeneration 3. Ischemic optic neuropathy 4. Horton arteritis 5. Glaucoma
Aging & Ophthalmology Pr Jean-Marie Rakic Dr Denis Malaise January 2018 Major ocular diseases 1. Cataract 2. Age-related macular degeneration 3. Ischemic optic neuropathy 4. Horton arteritis 5. Glaucoma
Written by Administrator Wednesday, 13 January :27 - Last Updated Thursday, 21 January :34
 angle closure glaucoma A type of glaucoma caused by a sudden and severe rise in eye pressure. Occurs when the pupil enlarges too much or too quickly, and the outer edge of the iris blocks the eye s drainage
angle closure glaucoma A type of glaucoma caused by a sudden and severe rise in eye pressure. Occurs when the pupil enlarges too much or too quickly, and the outer edge of the iris blocks the eye s drainage
Case Study: Fuzz April 18th
 Case Study: Fuzz April 18th 33 year old Quarter Horse Had been battling corneal ulcer for several weeks before seeing us No foreign debris found Culture and cytology were taken. Started on topical antibiotics,
Case Study: Fuzz April 18th 33 year old Quarter Horse Had been battling corneal ulcer for several weeks before seeing us No foreign debris found Culture and cytology were taken. Started on topical antibiotics,
DELINEATION OF PRIVILEGES - OPHTHALMOLOGY
 KALEIDA HEALTH Name Date DELINEATION OF PRIVILEGES - OPHTHALMOLOGY PLEASE NOTE: Please check the box for each privilege requested. Do not use an arrow or line to make selections. We will return applications
KALEIDA HEALTH Name Date DELINEATION OF PRIVILEGES - OPHTHALMOLOGY PLEASE NOTE: Please check the box for each privilege requested. Do not use an arrow or line to make selections. We will return applications
OPHTHALMOLOGY DEPARTMENT Primary care referral guidelines
 OPHTHALMOLOGY DEPARTMENT Primary care referral guidelines Contents REFERRAL CATEGIES... 2 Emergency... 2 Urgent... 2 Semi urgent/routine... 2 Not accepted... 2 OPHTHALMOLOGY CONDITIONS NOT ACCEPTED...
OPHTHALMOLOGY DEPARTMENT Primary care referral guidelines Contents REFERRAL CATEGIES... 2 Emergency... 2 Urgent... 2 Semi urgent/routine... 2 Not accepted... 2 OPHTHALMOLOGY CONDITIONS NOT ACCEPTED...
ICD -10 -CM Pediatric/Strabismus
 ICD -10 -CM Pediatric/Strabismus Amblyopia Deprivation H53.011 H53.012 H53.013 H53.019 Refractive H53.021 H53.022 H53.023 H53.029 Strabismic H53.031 H53.032 H53.033 H53.039 Suspect H53.041 H53.042 H43.043
ICD -10 -CM Pediatric/Strabismus Amblyopia Deprivation H53.011 H53.012 H53.013 H53.019 Refractive H53.021 H53.022 H53.023 H53.029 Strabismic H53.031 H53.032 H53.033 H53.039 Suspect H53.041 H53.042 H43.043
PedsCases Podcast Scripts
 PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Approach to Childhood Glaucoma. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics.
PedsCases Podcast Scripts This is a text version of a podcast from Pedscases.com on Approach to Childhood Glaucoma. These podcasts are designed to give medical students an overview of key topics in pediatrics.
Ocular Anatomy for the Paraoptometric
 Ocular Anatomy for the Paraoptometric Minnesota Optometric Association Paraoptometric CE Friday September 30, 2016 Lindsay A. Sicks, OD, FAAO Assistant Professor, Illinois College of Optometry lsicks@ico.edu
Ocular Anatomy for the Paraoptometric Minnesota Optometric Association Paraoptometric CE Friday September 30, 2016 Lindsay A. Sicks, OD, FAAO Assistant Professor, Illinois College of Optometry lsicks@ico.edu
Basic ophthalmology for the health practitioner: the red eye
 Basic ophthalmology for the health practitioner: the red eye N Mohamed, MBChB, DipOphth(SA), FCOphth(SA), Clinical Registrar DP Smit, MBChB, MMed(Ophth), FC Ophth(SA), Consultant Department of Ophthalmology,
Basic ophthalmology for the health practitioner: the red eye N Mohamed, MBChB, DipOphth(SA), FCOphth(SA), Clinical Registrar DP Smit, MBChB, MMed(Ophth), FC Ophth(SA), Consultant Department of Ophthalmology,
Vision Health: Conditions, Disorders & Treatments EYELID DISORDERS
 Vision Health: Conditions, Disorders & Treatments EYELID DISORDERS There are a number of disorders that can affect the eyelid. Entropion Entropion is an inward turning of the eyelid and lashes toward the
Vision Health: Conditions, Disorders & Treatments EYELID DISORDERS There are a number of disorders that can affect the eyelid. Entropion Entropion is an inward turning of the eyelid and lashes toward the
Ocular Lecture. Sue Bednar NP Ali Atwater PA-C
 Ocular Lecture Sue Bednar NP Ali Atwater PA-C Triaging Ocular Complaints Painful Eye/Red eye +/-blurry vision +/-visual loss +/-floaters +/-fevers If any of the above findings exist, pt is likely to have
Ocular Lecture Sue Bednar NP Ali Atwater PA-C Triaging Ocular Complaints Painful Eye/Red eye +/-blurry vision +/-visual loss +/-floaters +/-fevers If any of the above findings exist, pt is likely to have
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS
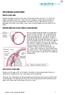 THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
THE CHRONIC GLAUCOMAS WHAT IS GLAUCOMA People with glaucoma have lost some of their field of all round vision. It is often the edge or periphery that is lost. That is why the condition can be missed until
02/03/2014. Average Length: 23mm (Infant ~16mm) Approximately the size of a quarter Volume: ~5mL
 Identify the anatomy of the eye. Explain the basic physiology of the parts of the eye. Briefly discuss various surgeries related to different parts of the anatomy. Average Length: 23mm (Infant ~16mm) Approximately
Identify the anatomy of the eye. Explain the basic physiology of the parts of the eye. Briefly discuss various surgeries related to different parts of the anatomy. Average Length: 23mm (Infant ~16mm) Approximately
ICD-10-CM Are You Prepared? Part III Lids to Lens
 ICD-10-CM Are You Prepared? Part III Lids to Lens Rebecca H. Wartman OD March 2014 With contributions from Doug Morrow OD & Harvey Richman OD Overview This webinar will provide an introduction to ICD-10-CM
ICD-10-CM Are You Prepared? Part III Lids to Lens Rebecca H. Wartman OD March 2014 With contributions from Doug Morrow OD & Harvey Richman OD Overview This webinar will provide an introduction to ICD-10-CM
CURRICULUM FOR THE 2nd SEMESTER
 CURRICULUM FOR THE 2nd SEMESTER SEMESTER- 2 S.No Subject Credits 1 Anatomy of the Eye 2 Physiology of the Eye 3 Islamiyat 4 English 1: ANTOMY OF THE EYE 1. Anatomy of the orbit and the ocular adnexa 1.1
CURRICULUM FOR THE 2nd SEMESTER SEMESTER- 2 S.No Subject Credits 1 Anatomy of the Eye 2 Physiology of the Eye 3 Islamiyat 4 English 1: ANTOMY OF THE EYE 1. Anatomy of the orbit and the ocular adnexa 1.1
The Emergent Eye in the Acute Setting
 The Emergent Eye in the Acute Setting Todd P. Margolis MD, PhD Professor of Ophthalmology & Director of the F.I. Proctor Foundation UCSF Physical Exam-- Visual Acuity Essential Corrected visual acuity
The Emergent Eye in the Acute Setting Todd P. Margolis MD, PhD Professor of Ophthalmology & Director of the F.I. Proctor Foundation UCSF Physical Exam-- Visual Acuity Essential Corrected visual acuity
DNB Question Paper. December
 DNB Question Paper December PAPER - I 1. Discuss clinical features, pathogenesis and management of normal tension glaucoma. (3+3+4) 2. Describe clinical manifestations, pathology, differential diagnosis
DNB Question Paper December PAPER - I 1. Discuss clinical features, pathogenesis and management of normal tension glaucoma. (3+3+4) 2. Describe clinical manifestations, pathology, differential diagnosis
Around The Globe in 60 Minutes
 Around The Globe in 60 Minutes Around the GLOBE in Sixty Minutes Basic Ocular Anatomy, Examination, and Diagnostic Techniques Introduction Focusing on canine and feline ocular anatomy and basic examination
Around The Globe in 60 Minutes Around the GLOBE in Sixty Minutes Basic Ocular Anatomy, Examination, and Diagnostic Techniques Introduction Focusing on canine and feline ocular anatomy and basic examination
Ocular warning signs in GP practice: Paediatric Eye Pointers
 Ocular warning signs in GP practice: Paediatric Eye Pointers Dr Benjamin Chang MB, BCh, BAO, MMedSci, FRCS(Irel), FRCS(Edin), FRCOphth(Lond) Senior Consultant Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences Khoo Teck
Ocular warning signs in GP practice: Paediatric Eye Pointers Dr Benjamin Chang MB, BCh, BAO, MMedSci, FRCS(Irel), FRCS(Edin), FRCOphth(Lond) Senior Consultant Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences Khoo Teck
Ophthalmology. Dr.R.Arulnanthy GP 25/08/09
 Ophthalmology Dr.R.Arulnanthy GP 25/08/09 EYE Red Eye Red eye Pain with/ with out visual problems Acute glaucoma Corneal infections iritis No pain, no visual problems Episcleritis Scleritis Conjunctivitis
Ophthalmology Dr.R.Arulnanthy GP 25/08/09 EYE Red Eye Red eye Pain with/ with out visual problems Acute glaucoma Corneal infections iritis No pain, no visual problems Episcleritis Scleritis Conjunctivitis
Ocular Urgencies and Emergencies
 Ocular Urgencies and Emergencies Pam Boyce, O.D., F.A.A.O. Boyce Family Eye Care, Ltd. 528 Devon Ave. Park Ridge, IL 60068 847-518-0303 Somebody s going to lose an eye Epidemiology 2.4 million ocular and
Ocular Urgencies and Emergencies Pam Boyce, O.D., F.A.A.O. Boyce Family Eye Care, Ltd. 528 Devon Ave. Park Ridge, IL 60068 847-518-0303 Somebody s going to lose an eye Epidemiology 2.4 million ocular and
CENTRAL MERSEY LOCAL OPTICAL COMMITTEE
 CENTRAL MERSEY LOCAL OPTICAL COMMITTEE OPTOMETRIC REFERRAL GUIDELINES The ocular conditions listed in this document are intended to reflect those that might be encountered in optometric practice and this
CENTRAL MERSEY LOCAL OPTICAL COMMITTEE OPTOMETRIC REFERRAL GUIDELINES The ocular conditions listed in this document are intended to reflect those that might be encountered in optometric practice and this
Ophthalmology. Common Eyelid Problems
 Ophthalmology Common Eyelid Problems The Ophthalmology service offers the latest and most comprehensive eye care for patients. With a dedicated team of eye surgeons and consultants, we treat vision problems
Ophthalmology Common Eyelid Problems The Ophthalmology service offers the latest and most comprehensive eye care for patients. With a dedicated team of eye surgeons and consultants, we treat vision problems
Work Sheet And Course Hand Out
 Work Sheet And Course Hand Out This course provides the primary care health professional with a basic understanding of the eye, its function and the assessment of common sight- and non-sight threatening
Work Sheet And Course Hand Out This course provides the primary care health professional with a basic understanding of the eye, its function and the assessment of common sight- and non-sight threatening
Quick Reference Guide
 ICD-10-CM OPHTHALMOLOGY 2015 Quick Reference Guide SYMPTOMS Blurred Vision (368.8)..........H53.8 Contusion of eyeball and orbital tissues (921.3) eye initial encounter..........s05.11xa subsequent encounter.........s05.11xd
ICD-10-CM OPHTHALMOLOGY 2015 Quick Reference Guide SYMPTOMS Blurred Vision (368.8)..........H53.8 Contusion of eyeball and orbital tissues (921.3) eye initial encounter..........s05.11xa subsequent encounter.........s05.11xd
EYE TRAUMA: INCIDENCE
 Introduction EYE TRAUMA: INCIDENCE 2.5 million eye injuries per year in U.S. 40,000 60,000 of eye injuries lead to visual loss Introduction Final visual outcome of many ocular emergencies depends on prompt,
Introduction EYE TRAUMA: INCIDENCE 2.5 million eye injuries per year in U.S. 40,000 60,000 of eye injuries lead to visual loss Introduction Final visual outcome of many ocular emergencies depends on prompt,
OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA
 OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA Learning outcomes By the end of this lecture the students would be able to Classify occlusive vascular disorders (OVD) of the retina. Correlate the clinical features
OCCLUSIVE VASCULAR DISORDERS OF THE RETINA Learning outcomes By the end of this lecture the students would be able to Classify occlusive vascular disorders (OVD) of the retina. Correlate the clinical features
THE PROTECTIVE SYSTEM OF THE EYE
 THE PROTECTIVE SYSTEM OF THE EYE Introduction The eye is offered the same type of protection as the brain being enclosed in a cavity in the skull called the bony orbit (figs1, 2). Fig 1: the bony orbit.
THE PROTECTIVE SYSTEM OF THE EYE Introduction The eye is offered the same type of protection as the brain being enclosed in a cavity in the skull called the bony orbit (figs1, 2). Fig 1: the bony orbit.
DISCLOSURES. PEDIATRIC RED EYES Rachel M. Smith, OD, FCOVD HISTORY, HISTORY, HISTORY WHY RED EYES? EXAMINE THE EYE RED FLAGS TO REFER 3/25/2019
 DISCLOSURES Consultant/Speakers bureaus Research funding PEDIATRIC RED EYES Rachel M. Smith, OD, FCOVD Pediatric Optometrist Children s Hospital & Medical Center Stock ownership/corporate boards employment
DISCLOSURES Consultant/Speakers bureaus Research funding PEDIATRIC RED EYES Rachel M. Smith, OD, FCOVD Pediatric Optometrist Children s Hospital & Medical Center Stock ownership/corporate boards employment
monitored anesthesia care (MAC)
 Entropion Entropion Entropion is an inward turning of the eyelid and lashes toward the eye, usually caused by relaxation of the eye muscles and tissue due to aging. Entropion usually affects the lower
Entropion Entropion Entropion is an inward turning of the eyelid and lashes toward the eye, usually caused by relaxation of the eye muscles and tissue due to aging. Entropion usually affects the lower
The Red Eye GP Update Mr Vaughan Tanner
 The Red Eye GP Update 2010 - Mr Vaughan Tanner Reading Royal Berkshire Hospital Dunedin Hospital www.tanner-eyes.co.uk Windsor Prince Charles Eye Unit Princess Margaret Hospital Lids Conjunctiva Sclera
The Red Eye GP Update 2010 - Mr Vaughan Tanner Reading Royal Berkshire Hospital Dunedin Hospital www.tanner-eyes.co.uk Windsor Prince Charles Eye Unit Princess Margaret Hospital Lids Conjunctiva Sclera
Eye and Ocular Adnexa, Auditory Systems
 Eye and Ocular Adnexa, Auditory Systems CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned
Eye and Ocular Adnexa, Auditory Systems CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned
The Anterior Segment & Glaucoma Visual Recognition & Interpretation of Clinical Signs
 The Anterior Segment & Glaucoma Visual Recognition & Interpretation of Clinical Signs Quiz created by Jane Macnaughton MCOptom & Peter Chapman BSc MCOptom FBDO CET Accreditation C19095 2 CET Points (General)
The Anterior Segment & Glaucoma Visual Recognition & Interpretation of Clinical Signs Quiz created by Jane Macnaughton MCOptom & Peter Chapman BSc MCOptom FBDO CET Accreditation C19095 2 CET Points (General)
Fitting Keratoconus and Other Complicated Corneas
 Fitting Keratoconus and Other Complicated Corneas Christine W Sindt OD FAAO Professor, Clinical Ophthalmology Director, Contact Lens Service University of Iowa Disclosure Consultant: ALCON Vision Care
Fitting Keratoconus and Other Complicated Corneas Christine W Sindt OD FAAO Professor, Clinical Ophthalmology Director, Contact Lens Service University of Iowa Disclosure Consultant: ALCON Vision Care
Ophthalmology Block The Red Eye
 Ophthalmology Block The Red Eye MBChB IV 2012 Prof Polla Roux ETIOLOGY Conjunctivitis Blepharitis Pterygium Keratoconjunc- tivitis sicca Abrasion & FB Subconjunctival haemorrhage Thyroid Eye Disease Herpes
Ophthalmology Block The Red Eye MBChB IV 2012 Prof Polla Roux ETIOLOGY Conjunctivitis Blepharitis Pterygium Keratoconjunc- tivitis sicca Abrasion & FB Subconjunctival haemorrhage Thyroid Eye Disease Herpes
Chapter 7, Section 1 Review Questions. Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. Name PER Date
 Name PER Date Chapter 7, Section 1 Review Questions Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. A. the middle layer of the wall of the eye B. the structure between the choroid
Name PER Date Chapter 7, Section 1 Review Questions Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. A. the middle layer of the wall of the eye B. the structure between the choroid
CORNEAL CONDITIONS CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION
 GENERAL INFORMATION CORNEAL CONDITIONS CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION WHAT ARE CORNEAL CONDITIONS? The cornea is the clear outer layer of the eye. Shaped like a dome, it helps to protect the eye from foreign
GENERAL INFORMATION CORNEAL CONDITIONS CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION WHAT ARE CORNEAL CONDITIONS? The cornea is the clear outer layer of the eye. Shaped like a dome, it helps to protect the eye from foreign
Dr Rachael Neiderer. Ophthalmologist Auckland. 8:35-8:50 Managing Allergic Conjunctivitis & Why Sodium Chromoglycate is Out
 Dr Rachael Neiderer Ophthalmologist Auckland 8:35-8:50 Managing Allergic Conjunctivitis & Why Sodium Chromoglycate is Out Allergic conjunctivitis Rachael Niederer Greenlane Clinical Centre, Auckland Case
Dr Rachael Neiderer Ophthalmologist Auckland 8:35-8:50 Managing Allergic Conjunctivitis & Why Sodium Chromoglycate is Out Allergic conjunctivitis Rachael Niederer Greenlane Clinical Centre, Auckland Case
VN 122 MODULE F EYE AND VISION DISORDERS OCULAR HISTORY 1. PATIENT PERCEPTION OF PROBLEM 2. DECREASED VISION? 3. BLURRED, DOUBLE, DISTORTED?
 VN 122 MODULE F EYE AND VISION DISORDERS OCULAR HISTORY 1. PATIENT PERCEPTION OF PROBLEM 2. DECREASED VISION? 3. BLURRED, DOUBLE, DISTORTED? 4. PAIN? QUALITY OF PAIN? 5. ITCHING, DRY? 6. BOTH EYES? 7.
VN 122 MODULE F EYE AND VISION DISORDERS OCULAR HISTORY 1. PATIENT PERCEPTION OF PROBLEM 2. DECREASED VISION? 3. BLURRED, DOUBLE, DISTORTED? 4. PAIN? QUALITY OF PAIN? 5. ITCHING, DRY? 6. BOTH EYES? 7.
Affections of eyelids in animals
 Affections of eyelids in animals Anatomy and physiology; Consists of movable folds of skin, loose connective tissue, muscular tissue, tarsus and conjunctiva. Dorsal and ventral folds form palpebral fissure.
Affections of eyelids in animals Anatomy and physiology; Consists of movable folds of skin, loose connective tissue, muscular tissue, tarsus and conjunctiva. Dorsal and ventral folds form palpebral fissure.
Ophthalmic Trauma Update
 Ophthalmic Trauma Update Richard S. Davidson, M.D. Professor of Ophthalmology Vice Chair for Quality and Clinical Affairs UCHealth Eye Center University of Colorado School of Medicine August 5, 2017 Financial
Ophthalmic Trauma Update Richard S. Davidson, M.D. Professor of Ophthalmology Vice Chair for Quality and Clinical Affairs UCHealth Eye Center University of Colorado School of Medicine August 5, 2017 Financial
OPHTHALMOLOGY - FIFTH YEAR
 Syllabus OPHTHALMOLOGY - FIFTH YEAR - 96809 Last update 04-11-2015 HU Credits: 3 Degree/Cycle: 2nd degree (Master) Responsible Department: medicine Academic year: 0 Semester: Yearly Teaching Languages:
Syllabus OPHTHALMOLOGY - FIFTH YEAR - 96809 Last update 04-11-2015 HU Credits: 3 Degree/Cycle: 2nd degree (Master) Responsible Department: medicine Academic year: 0 Semester: Yearly Teaching Languages:
People with eye allergies typically have symptoms that include: Eye Anatomy: What Do Eye Allergies Actually Effect?
 Eye Allergies Eye Allergies People with eye allergies typically have symptoms that include: Itchy watery eyes Eyelid problems Dark circles around eyes Dry eyes Reactions to Contacts Let us help allow you
Eye Allergies Eye Allergies People with eye allergies typically have symptoms that include: Itchy watery eyes Eyelid problems Dark circles around eyes Dry eyes Reactions to Contacts Let us help allow you
Handbook for Medical Students Learning Ophthalmology
 International Council of Ophthalmology Handbook for Medical Students Learning Ophthalmology 2009 Compiled by the Task Force on Undergraduate Teaching in Ophthalmology of the International Council of Ophthalmology
International Council of Ophthalmology Handbook for Medical Students Learning Ophthalmology 2009 Compiled by the Task Force on Undergraduate Teaching in Ophthalmology of the International Council of Ophthalmology
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Ophthalmoscopy. Reviewed & ratified by: Mr M Batterbury Consultant Ophthalmologist
 Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Ophthalmoscopy Reviewed & ratified by: o Mr M Batterbury Consultant Ophthalmologist Learning objectives o To understand the anatomy and physiology of the external and
Year 2 MBChB Clinical Skills Session Ophthalmoscopy Reviewed & ratified by: o Mr M Batterbury Consultant Ophthalmologist Learning objectives o To understand the anatomy and physiology of the external and
1 Eyelids. Lacrimal Apparatus. Orbital Region. 3 The Orbit. The Eye
 1 1 Eyelids Orbital Region 2 Lacrimal Apparatus 3 The Orbit 4 The Eye 2 Eyelids The eyelids protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure. The upper eyelid is larger and more mobile
1 1 Eyelids Orbital Region 2 Lacrimal Apparatus 3 The Orbit 4 The Eye 2 Eyelids The eyelids protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure. The upper eyelid is larger and more mobile
GNK485 The eye and related structures. Prof MC Bosman 2012
 GNK485 The eye and related structures Prof MC Bosman 2012 Surface anatomy Bony orbit Eyeball and Lacrimal apparatus Extra-ocular muscles Movements of the eye Innervation Arterial supply and venous drainage
GNK485 The eye and related structures Prof MC Bosman 2012 Surface anatomy Bony orbit Eyeball and Lacrimal apparatus Extra-ocular muscles Movements of the eye Innervation Arterial supply and venous drainage
GLAUCOMA. An Overview
 GLAUCOMA An Overview Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com --()-- IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your
GLAUCOMA An Overview Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2004) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com --()-- IMPORTANT The health information contained herein is not meant as a substitute for advice from your
4/22/16. Eye. External Anatomy of Eye. Accessory Structures. Bio 40B Dr. Kandula
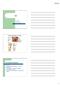 Eye Bio 40B Dr. Kandula External Anatomy of Eye Accessory Structures l Eyebrows l Levator Palpebrae Superioris - opens eye l Eyelashes l Ciliary glands modified sweat glands l Small sebaceous glands l
Eye Bio 40B Dr. Kandula External Anatomy of Eye Accessory Structures l Eyebrows l Levator Palpebrae Superioris - opens eye l Eyelashes l Ciliary glands modified sweat glands l Small sebaceous glands l
Herpes Zoster Ophtalmicus in a HIV positive patient: A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurology Volume 9 Number 2 Herpes Zoster Ophtalmicus in a HIV positive patient: A Case Report G Lopez Bejerano, Y Graza Fernandez Citation G Lopez Bejerano, Y Graza Fernandez..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurology Volume 9 Number 2 Herpes Zoster Ophtalmicus in a HIV positive patient: A Case Report G Lopez Bejerano, Y Graza Fernandez Citation G Lopez Bejerano, Y Graza Fernandez..
Mild NPDR. Moderate NPDR. Severe NPDR
 Diabetic retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of blindness in adults aged 35-65 years-old. Hyperglycaemia is thought to cause increased retinal blood flow and abnormal metabolism in
Diabetic retinopathy Diabetic retinopathy is the most common cause of blindness in adults aged 35-65 years-old. Hyperglycaemia is thought to cause increased retinal blood flow and abnormal metabolism in
