Anterior Segment Cataract Surgery
|
|
|
- Ambrose Berry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Current Use of Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs in the Treatment of Ocular Inflammation Related to Cataract Surgery Eric Donnenfeld Clinical Professor of Ophthalmology, New York University, New York, US Abstract Ocular inflammation and pain are a common consequence of cataract surgery, and if left untreated, may lead to extensive ocular damage, resulting in impaired vision as well as decreased satisfaction with the procedure. Effective management of ophthalmic inflammation after surgery is therefore vital. Topical ophthalmic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have become a mainstay of management of ocular pain and inflammation as a result of their anti-inflammatory activity, analgesic property and established safety record. Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of topical NSAIDs in post-operative prevention of ocular inflammation, inhibition of intra-operative miosis, reduction of pain associated with cataract surgery and pre-operative use to prevent cystoid macular oedema. Studies have also indicated that NSAIDs and steroids act synergistically when administered together, and that a combination of steroid and NSAID therapy is recommended to achieve successful outcomes. With appropriate administration, NSAIDs are safe and effective therapeutic agents, which rarely result in serious local and systemic responses. Keywords Cataract surgery, cystoid macula oedema, miosis, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Disclosure: The author has no conflicts of interest to declare. Acknowledgement: Writing support was provided by Touch Briefings. Received: 1 June 212 Accepted: 23 July 212 Citation: European Ophthalmic Review, 212;6(3):173 7 DOI: /EOR Correspondence: Eric Donnenfeld, Ophthalmic Consultants of Long Island, 2 North Village Avenue, Suite 42, Rockville Centre, NY 1157, US. E: eddoph@aol.com Support: The publication of this article was funded by Alcon. The views and opinions expressed are those of the author and not necessarily those of Alcon. Cataract surgery is an invasive procedure involving an incision and manipulation of ocular tissue, leading to intraocular inflammation. The latter is characterised by redness, swelling, and/or pain. Inflammation arises from the release of prostaglandins (PGs). Activation of phospholipase A 2, following tissue injury during surgery, breaks down cell membrane phospholipids to arachidonic acid. This is then converted to PGs by activation of cyclo-oxygenase (COX) enzymes via the COX-1 and COX-2 pathways. Production of PGs causes local vasodilation and increased vascular permeability resulting in a number of symptoms including hyperaemia, miosis, pain, photophobia and diminished visual acuity secondary to cystoid macular oedema (CMO) the most common complication of cataract surgery and potentially the most adverse ocular outcome of PG production. 1 Two agents are primarily employed for the reduction of intraocular inflammation: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids. NSAIDs are potent inhibitors of cyclo-oxygenase enzymes and hence of PG synthesis. Together with corticosteroids, they act on the COX-1 and COX-2 pathways. While corticosteroids inhibit phospholipase A 2, preventing arachidonic acid release from phospholipids, NSAIDs act downstream and more specifically in the cascade by direct inhibition of COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes (see Figure 1). 2 Post-operative ocular inflammation is a complex condition owing to the diverse types of tissues that may be affected, including the conjunctiva, retina, sclera, aqueous and vitreous humour, cornea, iris, ciliary body, choroid and retina. 3 Corticosteroids have a long history of use in the management of ocular inflammation but their efficacy is tempered by serious adverse effects including impairment of wound healing, elevation of intraocular pressure (IOP), progression of cataracts, increased susceptibility to microbial infections owing to a suppressed host immune response, delayed corneal epithelial and stromal wound healing, and safety issues associated with long-term use including glaucoma. 1 The use of NSAIDs for ocular applications began in the 197s, when it was found that topical formulations were more effective in intraocular penetration than systemic formulations. Topical NSAIDs have a number of important roles in the treatment of inflammation following ophthalmic cataract surgery. These include prevention of intra-operative miosis during cataract surgery; management of post-operative inflammation; reduction of pain and discomfort following cataract surgery; and prevention and treatment of CMO following cataract surgery. 3 Advantages of NSAIDs over corticosteroids include a reduction in post-operative pain and photophobia, decreased itching in allergic conjunctivitis, decrease in ocular pressure and reduction of intra-operative miosis. 4 However, the development of topical formulations of NSAIDs has been difficult. Most NSAIDs are weakly acidic and ionise at the ph of lachrymal fluid and have limited corneal permeability. Reducing the ph enhances permeability but increases the potential for ocular irritation TOUCH BRIEFINGS 212
2 Current Use of Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs in the Treatment of Ocular Inflammation Figure 1: Mechanism of Action of Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs Phospholipase A2 Membrane phospholipids Cyclo-oxygenase Arachidonic acid Lipoxygenase PGG2 5-HPETE Hydroperoxidase Lipoxygenase PGH2 Leukotriene A4 (LTA4) PGE PGF PGI PGD TXA LTA 4 Hydrolase Glutathione S-transferase PGE2 PGE 9- ketoreductase PGI2 PGD2 TXA2 LTB4 Y-glutamyl transpeptidase LTC4 Y-glutamyl leukotrienase PGF-2α LTD4 Dipeptidase LTE 4 5-HPETE = 5-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid; LT = leukotriene; PG = prostaglandin; TX = thromboxane. Source: Reddy, Kim, NSAIDs with proven efficacy in the treatment and prevention of ocular inflammation include, indomethacin.1 % and 1. %, flurbiprofen.3 %, suprofen 1. %, ketorolac tromethamine.4 %,.45 % and.5 %, diclofenac.1 % and bromfenac.9 %. Among the most recently developed is nepafenac.1 %, an amide prodrug that is converted to its active form, amfenac, by intraocular hydrolases. 6 A multicentre double-masked study (n=75) aiming to evaluate the aqueous humour concentrations and COX inhibitory activities of nepafenac, amfenac, ketorolac and bromfenac after topical ocular administration demonstrated that, for example, nepafenac has significantly greater ocular bioavailability than ketorolac tromethamine (see Figure 2). 7 Being less polar than other NSAIDs, nepafenac is able to easily penetrate the cornea, enhancing corneal epithelial absorption. 8 As a result, nepafenac is optimally distributed in the cornea, iris, ciliary body and retina/choroid and has longer duration of action at these sites. In terms of safety, the prodrug structure minimises surface accumulation, as it is rapidly distributed through the cornea to the anterior and posterior chambers. As a result, ocular surface complications associated with conventional NSAID therapies may be reduced. 6,8 Figure 2: Aqueous Humour Drug Concentration Following Dosing with Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs Aqueous humour concentration (ng/ml) Time posting-dosing (hours) Bromfenac Amfenac Amfenac and Ketorolac Source: Walters, et al., Efficacy Studies Involving Topical Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs Considerable evidence exists to support the use of topical NSAIDs in place of or in addition to topical corticosteroids after cataract surgery, to avoid excessive inflammation and aid in visual recovery. Flurbiprofen.3 %, suprofen 1. % diclofenac.1 %, ketorolac.4 %, bromfenac.9 % and nepafenac.1 % are approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and in Europe for topical ocular applications. 3 Diclofenac was approved in the US following a clinical trial in which it was found to have equivalent efficacy to prednisolone in reducing inflammation following cataract surgery. 9 Ketorolac tromethamine has been found to give a comparable reduction to prednisolone acetate in intraocular inflammation and pain following cataract surgery. 1 A comparison of two topical steroids (prednisolone 1. % and rimexolone 1. %) with ketorolac tromethamine.5 % after extracapsular cataract extraction concluded that ketorolac tromethamine controlled intraocular inflammation after cataract extraction without the risk of IOP increase associated with steroid use. 11 A prospective randomised double-masked study to compare the efficacy of ketorolac tromethamine.5 % and loteprednol etabonate.5 %, reported that ketorolac tromethamine was as effective as loteprednol etabonate in reducing inflammation after routine phacoemulsification and intraocular lens (IOL) implantation. 12 In a randomised, prospective multicentre study, ketorolac tromethamine.5 % was found to be as effective as rimexolone 1 % in reducing inflammation after cataract surgery. 13 EUROPEAN OPHTHALMIC REVIEW 174
3 Figure 3: Cumulative Percentage Cures (Defined as 5 Cells and Absence of Flare) by Visit Using in the Treatment of Ocular Inflammation Following Cataract Surgery Percent Source: Lane, et al., Day 1 Day 3 Day 7 Day 14 Visit Vehicle p.5 The most recently developed topical NSAIDs are bromfenac and nepafenac. The efficacy of bromfenac was established in four randomised, double-masked, vehicle or active-controlled, clinical trials. 14 In a randomised double-masked study evaluating the safety and effectiveness of nepafenac in preventing and treating inflammation and pain following cataract surgery, a higher percentage of patients in the nepafenac group were pain-free at all visits ( %) compared with patients treated with vehicle ( %) (p<.1). Furthermore, the nepafenac-treated group had clinical cure rates (defined as cells plus flare equal to zero) of 62.6 % compared with 17.2 % for vehicle (see Figures 3 and 4). 6 Effect of Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs on Intra-operative Miosis The maintenance of mydriasis is critical during cataract surgery to allow adequate access to the extraction of the crystalline lens and implantation of the IOL without causing trauma to the iris. However, surgically induced miosis is a common complication of cataract surgery as a result of the release of PGs. Miosis may obstruct the surgeon s view during cataract surgery, complicating the procedure and increasing the risk of post-operative inflammation, vitreous loss and capsule rupture. 15,16 NSAIDs inhibit PG synthesis, subsequently inhibiting intra-operative miosis, as several studies have demonstrated. Topical ketorolac was Figure 4: Percentage of Pain-free Patients by Visit Using in the Treatment of Ocular Inflammation Following Cataract Surgery Per cent Day 1 Day 3 Day 7 Day 14 Visit Source: Lane, et al., Vehicle p< found to inhibit miosis more effectively than topical diclofenac during extracapsular cataract extraction and intraocular implantation, and gave a more stable mydriatic effect during surgery. 17 NSAIDs also increase the cost-effectiveness of the procedure; the use of ketorolac eliminated the need for the combination of a pre-operative NSAID (flurbiprofen) and post-operative corticosteroid for the prevention of intra-operative miosis and post-operative inflammation in cataract surgery. 18 A study comparing the effects of topical ketorolac.5 % with topical.3 % flurbiprofen on the inhibition of surgically induced miosis during phacoemulsification cataract surgery concluded that topical ketorolac is an effective inhibitor of miosis during phacoemulsification cataract surgery and confers a stable mydriatic effect throughout surgery. 15 In a prospective, randomised, single-masked comparative study (n=6) of nepafenac, the difference in mean pupil size following phacoemulsification cataract surgery between the control group (6.84±.93 mm) and the nepafenac group (7.91±.74 mm) was statistically significant (p<.1). 16 Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs in the Prevention of Cystoid Macular Oedema While NSAIDs inhibit the production of PGs, they do not affect PGs that have already been formed. It is important to begin NSAID treatment sufficiently in advance of surgery to inhibit the formation of PGs in response to surgical insult. While post-operative NSAID use is important to control pain and inflammation, pre-operative treatment is essential to improve the results of surgery. However, the pre-operative use of NSAIDs to prevent CMO has been the subject of considerable debate. CMO is caused by inflammation resulting from trauma associated with cataract surgery and is the most common cause of visual decline following uncomplicated cataract surgery. 19 Increased inflammation post-operatively is associated with an increased risk of developing CMO. 2 CMO is defined as angiographic or clinically significant. Angiographic CMO is detected by fluorescein angiogram and it is often not seen on clinical examination of the eye. Clinically significant CMO is observed on biomicroscopic examination and detected on fluorescein angiography. A study found that patients who had angiographic CMO at day 6 were more likely to have had more post-operative inflammation than patients who did not develop CMO. 21 The exact incidence of overt CMO varies widely but studies suggest that the rate of clinical CMO following modern cataract surgical techniques ranges from 1 to 2 %. 22 The incidence of angiographic CMO may be as high as 19 %. 21 CMO frequently has a late onset, occurring 4 6 weeks post-operatively. CMO is the result of a variety of processes that cause fluid to accumulate in the central retina. The condition is often asymptomatic. Symptoms include blurred or reduced central vision and painless inflammation of the retina. Visual impairment, though usually temporary, can in rare cases lead to permanent loss of vision. 1 Loss of contrast sensitivity is common in patients who have experienced CMO. Several studies have demonstrated the efficacy of topical NSAIDs in the prevention of CMO. In a multicentre, prospective clinical trial to compare diclofenac and fluorometholone in preventing CMO after small incision cataract surgery, it was found that five weeks after surgery CMO was present in significantly fewer (5.7 %) of the eyes receiving diclofenac than in those receiving fluorometholone (54.7 %) (p<.1). 23 In a retrospective study, a 2.4 % incidence of CMO was reported with use of prophylactic NSAIDs in 1,659 consecutive 175 EUROPEAN OPHTHALMIC REVIEW
4 Current Use of Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs in the Treatment of Ocular Inflammation cases of cataract surgery performed by residents over a five-year period. When patients with diabetes were excluded, the rate of CMO was 2.1 %. 24 In a prospective study to compare the efficacy of several prophylactic regimens with ketorolac tromethamine.4 %, pre-treatment with NSAID improved visual acuity outcomes significantly in the immediate post-operative period (at one day and two weeks) compared with pre-treatment for one hour or placebo (p<.5 for all). 25 Bromfenac has also been found to have efficacy in preventing CMO after cataract surgery in patients with diabetes. 26 More recently, a randomised study was conducted for comparing nepafenac.1 % (approved in the EU for reduction in the risk of post-operative macular oedema associated with cataract surgery in diabetic patients) with fluorometholone.1 % in preventing CMO after small-incision cataract extraction with IOL implantation. Five weeks after surgery, the incidence of fluorescein angiographic CMO was significantly lower in the nepafenac group (14.3 %) than in the fluorometholone group (81.5 %) (P<.1). 27 Clinical data show that topical NSAIDs can prevent CMO, but no consensus for their therapeutic usage has been published. It has been recommended that the dosing schedule varies according to risk factors which include pre-existing ocular inflammation, epiretinal or vitreoretinal interface membrane problems, diabetic retinopathy, patients suffering from ocular vascular or cardiovascular disease and patients with history of retinitis pigmentosa. Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs and Pain Relief NSAIDs provide effective reduction of pain associated with cataract procedures. In a single-centre, double-masked, randomised, placebo-controlled study of 25 patients undergoing cataract surgery, patients reported significantly less ocular pain during the 24 hours following surgery when treated with ketorolac.4 % than with placebo (p=.2). Ocular pain was reported for only a single ketorolac.4 %-treated eye (4 %) during that period, compared with 39 % of placebo-treated eyes (p=.4). 28 In a larger study (n=1), patients treated with ketorolac tromethamine experienced less intra-operative and post-operative pain compared with a placebo group and did not require additional anaesthesia. 25 In a large trial of bromfenac (n=872), the proportion of patients that were pain-free at one, three and 15 days were significantly higher in the treatment group than in the placebo group. 14 In a multicentre, randomised, placebo- and active-controlled, double-masked clinical trial (n=227), more patients were pain-free at each time-point from day three post-operatively with nepafenac than with placebo, (p<.5) (see Figure 5). 29 Pain reduction is an important consideration because patient expectations of outcomes are high in modern cataract surgery and ocular pain or discomfort is a common cause of patient dissatisfaction. Safety Issues Associated with the Use of Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs Many topical NSAIDs in ophthalmic use can cause a range of adverse events including conjunctival hyperaemia, burning, stinging and corneal anaesthesia. 3,31 A more serious complication is the risk of indolent corneal ulceration and full-thickness corneal melts. Scleral wound melting may arise with any ophthalmic NSAID in patients who have undergone cataract surgery. Moreover, a study found that cases of corneal melt following use of NSAIDs found inconsistent and variable dose/toxicity relationships suggesting that Figure 5: Analgesic Effect of Percent pain-free p=.3 p= p= p<.1 p= p= Day 1 Day 3 Day 7 Day 14 Day 21 Day 28 Ketorolac Placebo nepafenac.1 % versus placebo, chi-square test. nepafenac.1 % versus ketorolac.5 %, chi square test. The numbers at the bottom of the day one bar represents the number of evaluable patients in each arm. The number of evaluable patients did not vary across time points. Source: Nardi, et al., factors other than simple drug toxicity are involved. Corneal melts were found to be more commonly associated with the use of generic NSAIDs. 32 The use of nepafenac in accordance with its approved indications and posology has not been associated with high levels of ocular irritation. 29 Combined Therapies While NSAIDs have been shown to reduce inflammation and improve post-operative comfort, they are not successful in all cases. In most of the studies detailed above, patients were not free of inflammation at two weeks. The inflammatory response is complex, involving numerous cells and cytokines, not all of which are inhibited by NSAIDs. Corticosteroids and NSAIDs work at different levels of the arachidonic acid cascade and may provide synergistic effects. The adjunctive use of NSAIDs with steroids optimises surgical outcomes as numerous studies have demonstrated that the combination of an NSAID and steroid is more effective for the treatment of post-operative inflammation, 33 CMO 34 and improving visual acuity than either NSAID or steroid monotherapy. By combining NSAIDs and steroids, the doses of each may be lessened, minimising adverse effects while maintaining efficacy. The concomitant use of topical NSAIDs and corticosteroids should be carefully monitored, particularly among patients at high-risk for corneal injury, such as those with rheumatoid arthritis or fulminate collagen vascular disorders, as such combined therapy has been identified as a risk factor for the development of corneal erosion and possible perforation. 35 Conclusion NSAIDs are effective treatment options for a broad range of inflammatory eye disorders, which rarely result in serious local and systemic responses. Furthermore, they are valuable in the treatment of intraocular inflammation, prevention of pain and inhibition of miosis during cataract surgery, and for the prevention of CMO. As our understanding of the pathogenesis of inflammatory eye disorders increases and new, more potent topical formulations of NSAIDs are developed, the clinical indications of NSAIDs are likely to expand. However, given the complexity of the inflammatory response, synergistic effects may be achieved by the concurrent use of NSAIDs and corticosteroids, allowing the dosages of each to be minimised. With appropriate administration, NSAIDs are valuable prophylactic and therapeutic agents in cataract surgery. n 63.2 EUROPEAN OPHTHALMIC REVIEW 176
5 1. Cho H, Wolf KJ, Wolf EJ, Management of ocular inflammation and pain following cataract surgery: focus on bromfenac ophthalmic solution, Clin Ophthalmol, 29;3: Reddy R, Kim SJ, Critical appraisal of ophthalmic ketorolac in treatment of pain and inflammation following cataract surgery, Clin Ophthalmol, 211;5: Colin J, The role of NSAIDs in the management of postoperative ophthalmic inflammation, Drugs, 27;67: Flach AJ, Topical nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs in ophthalmology, Int Ophthalmol Clin, 22;42: Ahuja M, Dhake AS, Sharma SK, et al., Topical ocular delivery of NSAIDs, AAPS J, 28;1: Lane SS, Modi SS, Lehmann RP, et al., ophthalmic suspension.1% for the prevention and treatment of ocular inflammation associated with cataract surgery, J Cataract Refract Surg, 27;33: Walters T, Raizman M, Ernest P, et al., In vivo pharmacokinetics and in vitro pharmacodynamics of nepafenac, amfenac, ketorolac, and bromfenac, J Cataract Refract Surg, 27;33: Gaynes BI, Onyekwuluje A, Topical ophthalmic NSAIDs: a discussion with focus on nepafenac ophthalmic suspension, Clin Ophthalmol, 28;2: Roberts CW, Brennan KM, A comparison of topical diclofenac with prednisolone for postcataract inflammation, Arch Ophthalmol, 1995;113: Simone JN, Pendelton RA, Jenkins JE, Comparison of the efficacy and safety of ketorolac tromethamine.5% and prednisolone acetate 1% after cataract surgery, J Cataract Refract Surg, 1999;25: Hirneiss C, Neubauer AS, Kampik A, et al., Comparison of prednisolone 1%, rimexolone 1% and ketorolac tromethamine.5% after cataract extraction: a prospective, randomized, double-masked study, Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol, 25;243: Holzer MP, Solomon KD, Sandoval HP, et al., Comparison of ketorolac tromethamine.5% and loteprednol etabonate.5% for inflammation after phacoemulsification: prospective randomized double-masked study, J Cataract Refract Surg, 22;28: Solomon KD, Vroman DT, Barker D, et al., Comparison of ketorolac tromethamine.5% and rimexolone 1% to control inflammation after cataract extraction. Prospective randomized double-masked study, J Cataract Refract Surg, 21;27: Henderson BA, Gayton JL, Chandler SP, et al., Safety and efficacy of bromfenac ophthalmic solution (Bromday) dosed once daily for postoperative ocular inflammation and pain, Ophthalmology, 211;118: Solomon KD, Turkalj JW, Whiteside SB, et al., Topical.5% ketorolac vs.3% flurbiprofen for inhibition of miosis during cataract surgery, Arch Ophthalmol, 1997;115: Cervantes-Coste G, Sanchez-Castro YG, Orozco-Carroll M, et al., Inhibition of surgically induced miosis and prevention of postoperative macular edema with nepafenac, Clin Ophthalmol, 29;3: Srinivasan R, Madhavaranga MS, Topical ketorolac tromethamine.5% versus diclofenac sodium.1% to inhibit miosis during cataract surgery, J Cataract Refract Surg, 22;28: Snyder RW, Siekert RW, Schwiegerling J, et al., Acular as a single agent for use as an antimiotic and anti-inflammatory in cataract surgery, J Cataract Refract Surg, 2;26: O'Brien TP, Emerging guidelines for use of NSAID therapy to optimize cataract surgery patient care, Curr Med Res Opin, 25;21: Flach AJ, The incidence, pathogenesis and treatment of cystoid macular edema following cataract surgery, Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc, 1998;96: Ursell PG, Spalton DJ, Whitcup SM, et al., Cystoid macular edema after phacoemulsification: relationship to bloodaqueous barrier damage and visual acuity, J Cataract Refract Surg, 1999;25: Ray S, D'Amico DJ, Pseudophakic cystoid macular edema, Semin Ophthalmol, 22;17: Miyake K, Masuda K, Shirato S, et al., Comparison of diclofenac and fluorometholone in preventing cystoid macular edema after small incision cataract surgery: a multicentered prospective trial, Jpn J Ophthalmol, 2;44: Henderson BA, Kim JY, Ament CS, et al., Clinical pseudophakic cystoid macular edema. Risk factors for development and duration after treatment, J Cataract Refract Surg, 27;33: Donnenfeld ED, Perry HD, Wittpenn JR, et al., Preoperative ketorolac tromethamine.4% in phacoemulsification outcomes: pharmacokinetic-response curve, J Cataract Refract Surg, 26;32: Endo N, Kato S, Haruyama K, et al., Efficacy of bromfenac sodium ophthalmic solution in preventing cystoid macular oedema after cataract surgery in patients with diabetes, Acta Ophthalmol, 21;88: Miyake K, Ota I, Miyake G, et al.,.1% versus fluorometholone.1% for preventing cystoid macular edema after cataract surgery, J Cataract Refract Surg, 211;37: Price MO, Price FW, Efficacy of topical ketorolac tromethamine.4% for control of pain or discomfort associated with cataract surgery, Curr Med Res Opin, 24;2: Nardi M, Lobo C, Bereczki A, et al., Analgesic and antiinflammatory effectiveness of nepafenac.1% for cataract surgery, Clin Ophthalmol, 27;1: Aragona P, Tripodi G, Spinella R, et al., The effects of the topical administration of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on corneal epithelium and corneal sensitivity in normal subjects, Eye (Lond), 2;14( Pt 2): Flach AJ, Topical nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs for ophthalmic use, Int Ophthalmol Clin, 1996;36: Flach AJ, Corneal melts associated with topically applied nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc, 21;99: Wittpenn JR, Silverstein S, Heier J, et al., A randomized, masked comparison of topical ketorolac.4% plus steroid vs steroid alone in low-risk cataract surgery patients, Am J Ophthalmol, 28;146: Heier JS, Topping TM, Baumann W, et al., Ketorolac versus prednisolone versus combination therapy in the treatment of acute pseudophakic cystoid macular edema, Ophthalmology, 2;17: Gaynes BI, Fiscella R, Topical nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for ophthalmic use: a safety review, Drug Saf, 22;25: EUROPEAN OPHTHALMIC REVIEW
Better ophthalmic surgery outcomes in recent years have created more Demanding Patients.
 By Alaa EL Zawawi Prof. of Ophthalmology Alexandria - Egypt Launch Better ophthalmic surgery outcomes in recent years have created more Demanding Patients. 1 NSAIDs can play a pivotal role in facilitating
By Alaa EL Zawawi Prof. of Ophthalmology Alexandria - Egypt Launch Better ophthalmic surgery outcomes in recent years have created more Demanding Patients. 1 NSAIDs can play a pivotal role in facilitating
Medical Science. Research Paper. 2nd yr post graduate, Dept. Of Ophthalmology, SVS Medical College
 Dr. A.Narasimha Rao Dr. N.Deepika Dr. D.Chandrakanth Reddy Dr. M. Vijaya Ramaraju ABSTRACT KEYWORDS Research Paper Medical Science Comparative Evaluation of the Anti- Inflammatory Effect of Topical 1 %
Dr. A.Narasimha Rao Dr. N.Deepika Dr. D.Chandrakanth Reddy Dr. M. Vijaya Ramaraju ABSTRACT KEYWORDS Research Paper Medical Science Comparative Evaluation of the Anti- Inflammatory Effect of Topical 1 %
Rama Vadapalli * 1, Vankadara Naga Suresh 2. Online Access and Article Informtaion. Original Research Article
 Original Research Article An Interventional Follow up Study to Determine the Effect of Nepafenac 0.1% in Macular thickness in Patients who had Undergone Cataract Surgery as Determined By OCT Rama Vadapalli
Original Research Article An Interventional Follow up Study to Determine the Effect of Nepafenac 0.1% in Macular thickness in Patients who had Undergone Cataract Surgery as Determined By OCT Rama Vadapalli
nepafenac 1mg/mL eye drops, suspension (Nevanac ) SMC No. (813/12) Alcon Laboratories (UK) Ltd
 nepafenac 1mg/mL eye drops, suspension (Nevanac ) SMC No. (813/12) Alcon Laboratories (UK) Ltd 05 October 2012 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
nepafenac 1mg/mL eye drops, suspension (Nevanac ) SMC No. (813/12) Alcon Laboratories (UK) Ltd 05 October 2012 The Scottish Medicines Consortium (SMC) has completed its assessment of the above product
Surgery Post-operative
 Surgery Post-operative Redefining the Treatment Paradigm for Post-operative Inflammation Control The Role of Topical Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs Oliver Findl Associate Professor of Ophthalmology
Surgery Post-operative Redefining the Treatment Paradigm for Post-operative Inflammation Control The Role of Topical Non-steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs Oliver Findl Associate Professor of Ophthalmology
A New Paradigm in NSAID Treatment
 V 5/6 pg Contents Common Uses of Ophthalmic NSAIDs A New Paradigm in NSAID History of (bromfenac ophthalmic solution).9% Efficacy of Phase III trials Pain data Post-Approval trials Pharmacokinetics, Penetration,
V 5/6 pg Contents Common Uses of Ophthalmic NSAIDs A New Paradigm in NSAID History of (bromfenac ophthalmic solution).9% Efficacy of Phase III trials Pain data Post-Approval trials Pharmacokinetics, Penetration,
BARRY A. SCHECHTER ABSTRACT
 JOURNAL OF OCULAR PHARMACOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS Volume 22, Number 2, 2006 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. The Evaluation of Ketorolac (Acular LS ) to Improve Patient Comfort During the Induction Phase of Cyclosporin-A
JOURNAL OF OCULAR PHARMACOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS Volume 22, Number 2, 2006 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. The Evaluation of Ketorolac (Acular LS ) to Improve Patient Comfort During the Induction Phase of Cyclosporin-A
INDICATIONS ACULAR 0,4% ophthalmic solution is indicated for the reduction of ocular pain and burning/stinging following corneal refractive surgery.
 Page 1 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME (and dosage form) ACULAR 0,4% COMPOSITION ACULAR 0,4% ophthalmic solution contains: Ketorolac tromethamine: 4 mg/ml Preservative: Benzalkonium chloride
Page 1 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME (and dosage form) ACULAR 0,4% COMPOSITION ACULAR 0,4% ophthalmic solution contains: Ketorolac tromethamine: 4 mg/ml Preservative: Benzalkonium chloride
WARNING LETTER. According to the Indications and Usage section of the FDA approved product labeling (PI):
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration Rockville, MD 20857 TRANSMITTED BY FACSIMILE David E.I. Pyott President and Chief Executive Officer PO Box 19534
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration Rockville, MD 20857 TRANSMITTED BY FACSIMILE David E.I. Pyott President and Chief Executive Officer PO Box 19534
PHARMACOLOGY Class: Ketorolac trometamol is a member of the pyrrolo-pyrolle group of non-steroidal antiinflammatory
 ACULAR Eye Drops NAME OF THE DRUG Non-proprietary name: ketorolac trometamol. Chemical Structure: Chemical Name: ( )-5-Benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid compound with 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediol
ACULAR Eye Drops NAME OF THE DRUG Non-proprietary name: ketorolac trometamol. Chemical Structure: Chemical Name: ( )-5-Benzoyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrrolizine-1-carboxylic acid compound with 2-amino-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1,3-propanediol
The Effects of Two Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs, Bromfenac 0.1% and Ketorolac 0.45%, on Cataract Surgery
 Original Article Yonsei Med J 215 Nov;56(6):1671-1677 pissn: 513-5796 eissn: 1976-2437 The Effects of Two Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs, and, on Cataract Surgery Ji Won Jung 1,2, Byung Hoon Chung
Original Article Yonsei Med J 215 Nov;56(6):1671-1677 pissn: 513-5796 eissn: 1976-2437 The Effects of Two Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs, and, on Cataract Surgery Ji Won Jung 1,2, Byung Hoon Chung
INDICATIONS ACULAR 0,5 % is indicated for the relief of inflammation following ocular surgery.
 Page 1 of 5 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 3 PROPRIETARY NAME (AND DOSAGE FORM) ACULAR 0,5 % COMPOSITION ACULAR 0,5 % contains: Preservatives: Benzalkonium chloride 0,01 % m/v Disodium edetate 0,1 % m/v PHARMACOLOGICAL
Page 1 of 5 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 3 PROPRIETARY NAME (AND DOSAGE FORM) ACULAR 0,5 % COMPOSITION ACULAR 0,5 % contains: Preservatives: Benzalkonium chloride 0,01 % m/v Disodium edetate 0,1 % m/v PHARMACOLOGICAL
Vankadara Naga Suresh * 1, Rama Vadapalli 2. Online Access and Article Informtaion. Original Research Article
 Original Research Article Effect of Prophylactic Bromfenac 0.07% on Cystoid Macular Edema Assessed using Optical Coherence Tomography Quantification of Total Macular Volume after Cataract Surgery Vankadara
Original Research Article Effect of Prophylactic Bromfenac 0.07% on Cystoid Macular Edema Assessed using Optical Coherence Tomography Quantification of Total Macular Volume after Cataract Surgery Vankadara
AUSTRALIAN PRODUCT INFORMATION ACULAR (ketorolac trometamol) Eye Drops
 AUSTRALIAN PRODUCT INFORMATION ACULAR (ketorolac trometamol) Eye Drops 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINE Ketorolac trometamol 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION ACULAR contains ketorolac trometamol 5 mg/ml.
AUSTRALIAN PRODUCT INFORMATION ACULAR (ketorolac trometamol) Eye Drops 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINE Ketorolac trometamol 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION ACULAR contains ketorolac trometamol 5 mg/ml.
84 Year Old with Rosacea
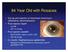 84 Year Old with Rosacea S/p tap and injection of intravitreal vancomycin, ceftazidime, dexamethasone Post-injection day#1 Va HM IOP 14 mmhg Post-injection week#3 BCVA 20/20-3 (plano +0.50 x 180) IOP 23
84 Year Old with Rosacea S/p tap and injection of intravitreal vancomycin, ceftazidime, dexamethasone Post-injection day#1 Va HM IOP 14 mmhg Post-injection week#3 BCVA 20/20-3 (plano +0.50 x 180) IOP 23
For last half century corticosteroids are used for ocular inflammation. They are used to suppress ocular inflammation in trauma, uveitis as well as
 The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.17957/TPMJ/17.3940 1. MBBS, DO, FCPS (Ophthalmology) Eye Specialist PAF Base Hospital Rafiqui Shorkot. 2. MBBS, DO, MCPS, FCPS (Ophthalmology) Classified Eye Specialist,
The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.17957/TPMJ/17.3940 1. MBBS, DO, FCPS (Ophthalmology) Eye Specialist PAF Base Hospital Rafiqui Shorkot. 2. MBBS, DO, MCPS, FCPS (Ophthalmology) Classified Eye Specialist,
Cataract surgery is a hugely important means of preventing poor-quality vision or vision loss, especially in the elderly and people
 Nepafenac in the Treatment of Ocular Inflammation Following Cataract Surgery (Pseudophakic Macular Oedema) an Update Hadi Kjærbo Scandinavian Eye Center, Hellerup, Denmark; Department of Ophthalmology,
Nepafenac in the Treatment of Ocular Inflammation Following Cataract Surgery (Pseudophakic Macular Oedema) an Update Hadi Kjærbo Scandinavian Eye Center, Hellerup, Denmark; Department of Ophthalmology,
The role of perioperative nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs use in cataract surgery
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 18, Issue 1 Ser. 15 (January. 2019), PP 23-27 www.iosrjournals.org The role of perioperative nonsteroidal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 18, Issue 1 Ser. 15 (January. 2019), PP 23-27 www.iosrjournals.org The role of perioperative nonsteroidal
Topical Corticosteroid and NSAID Therapies for Ocular Inflammation A concise overview for clinical practice.
 Section Editor: Sumit Sam Garg, MD Topical Corticosteroid and NSAID Therapies for Ocular Inflammation A concise overview for clinical practice. BY GARRICK CHAK, MD; AMANDA E. KIELY, MD; AND PRATAP CHALLA,
Section Editor: Sumit Sam Garg, MD Topical Corticosteroid and NSAID Therapies for Ocular Inflammation A concise overview for clinical practice. BY GARRICK CHAK, MD; AMANDA E. KIELY, MD; AND PRATAP CHALLA,
INVELTYS (loteprednol etabonate ophthalmic suspension) 1%, for topical ophthalmic use Initial U.S. Approval: 1998
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use INVELTYS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for INVELTYS. INVELTYS (loteprednol
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use INVELTYS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for INVELTYS. INVELTYS (loteprednol
Ocular NSAIDs: A New Option
 Insert to March 2006 Ocular NSAIDs: A New Option Evaluating performance parameters to optimize therapy. Potency and Penetration Efficacy Safety Clinical Experience to Date This continuing medical education
Insert to March 2006 Ocular NSAIDs: A New Option Evaluating performance parameters to optimize therapy. Potency and Penetration Efficacy Safety Clinical Experience to Date This continuing medical education
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use NEVANAC* safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for NEVANAC. NEVANAC (nepafenac
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use NEVANAC* safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for NEVANAC. NEVANAC (nepafenac
Phase II Results of an Intraocular Steroid Delivery System for Cataract Surgery
 Phase II Results of an Intraocular Steroid Delivery System for Cataract Surgery David F. Chang, MD, 1 Ivan H. Garcia, MD, 2 John D. Hunkeler, MD, 3 Thomas Minas, MD 4 Objective: To evaluate the safety
Phase II Results of an Intraocular Steroid Delivery System for Cataract Surgery David F. Chang, MD, 1 Ivan H. Garcia, MD, 2 John D. Hunkeler, MD, 3 Thomas Minas, MD 4 Objective: To evaluate the safety
WARNING LETTER DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES TRANSMITTED BY FACSIMILE
 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration Rockville, MD 20857 TRANSMITTED BY FACSIMILE Cary Rayment President and Chief Executive Officer Alcon, Inc. C/O
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration Rockville, MD 20857 TRANSMITTED BY FACSIMILE Cary Rayment President and Chief Executive Officer Alcon, Inc. C/O
CME. Clinical Uses of NSAIDs in Ophthalmic Surgery. Learning Objectives. September 1, Earn 1.0 hour CME credit
 September 1, 2005 Clinical Uses of NSAIDs in Ophthalmic Surgery CME Earn 1.0 hour CME credit Learning Objectives After reviewing the material, the participant should be able to: Discuss the use of NSAIDs
September 1, 2005 Clinical Uses of NSAIDs in Ophthalmic Surgery CME Earn 1.0 hour CME credit Learning Objectives After reviewing the material, the participant should be able to: Discuss the use of NSAIDs
TOBAFLAM Eye Drops (Loteprednol etabonate 0.5% + Tobramycin 0.3%)
 Published on: 23 Sep 2014 TOBAFLAM Eye Drops (Loteprednol etabonate 0.5% + Tobramycin 0.3%) Composition Loteprednol Etabonate 5 mg (0.5% w/v) Tobramycin...3 mg (0.3% w/v) Benzalkonium Chloride.. 0.01%
Published on: 23 Sep 2014 TOBAFLAM Eye Drops (Loteprednol etabonate 0.5% + Tobramycin 0.3%) Composition Loteprednol Etabonate 5 mg (0.5% w/v) Tobramycin...3 mg (0.3% w/v) Benzalkonium Chloride.. 0.01%
William F. Mieler, MD University of Illinois at Chicago Chicago, IL
 William F. Mieler, MD University of Illinois at Chicago Chicago, IL Advisory Board Genentech Data and Safety Monitoring Committee ThromboGenics (in the past) Acucela Corticosteroids and NSAIDs are the
William F. Mieler, MD University of Illinois at Chicago Chicago, IL Advisory Board Genentech Data and Safety Monitoring Committee ThromboGenics (in the past) Acucela Corticosteroids and NSAIDs are the
sodium [2-(2,6-dichloroanilino)phenyl] acetate, a phenylacetic acid derivative CH 2 COONa
![sodium [2-(2,6-dichloroanilino)phenyl] acetate, a phenylacetic acid derivative CH 2 COONa sodium [2-(2,6-dichloroanilino)phenyl] acetate, a phenylacetic acid derivative CH 2 COONa](/thumbs/78/77533900.jpg) PRODUCT INFORMATION VOLTAREN * OPHTHA Eye Drop (diclofenac sodium) NAME OF THE MEDICINE Active ingredient: Chemical name: Molecular formula: C 14 H 10 Cl 2 NNaO 2 CAS number: 15307-79-6 Molecular weight:
PRODUCT INFORMATION VOLTAREN * OPHTHA Eye Drop (diclofenac sodium) NAME OF THE MEDICINE Active ingredient: Chemical name: Molecular formula: C 14 H 10 Cl 2 NNaO 2 CAS number: 15307-79-6 Molecular weight:
CME in the Phaco era Myth or Reality. Nicholas Lee Hillingdon & Western Eye
 CME in the Phaco era Myth or Reality Nicholas Lee Hillingdon & Western Eye Scope History Incidence Pathogenesis Treatments None Steroids Acular Yellox Diamox Anti-vegf Prevention Audit Irvine Gass Syndrome
CME in the Phaco era Myth or Reality Nicholas Lee Hillingdon & Western Eye Scope History Incidence Pathogenesis Treatments None Steroids Acular Yellox Diamox Anti-vegf Prevention Audit Irvine Gass Syndrome
DAFTAR PUSTAKA. American Academy of Ophthalmology Basic and clinical. science course: Section 11 Lens and cataract.
 DAFTAR PUSTAKA American Academy of Ophthalmology. 2011-2012. Basic and clinical science course: Section 11 Lens and cataract. San Fransisco: American Academy Opthalmology. p 193-5. American Academy of
DAFTAR PUSTAKA American Academy of Ophthalmology. 2011-2012. Basic and clinical science course: Section 11 Lens and cataract. San Fransisco: American Academy Opthalmology. p 193-5. American Academy of
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY 5.1 Increased Bleeding Time Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of 5.2 Delayed Healing
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ILEVRO* (nepafenac ophthalmic suspension), 0.3% safely and effectively. See full prescribing information
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ILEVRO* (nepafenac ophthalmic suspension), 0.3% safely and effectively. See full prescribing information
INDICATIONS For steroid responsive inflammation of the palpebral and bulbar conjunctiva, cornea, and anterior segment of the eye globe.
 Page 1 of 5 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM PRED FORTE Sterile Eye Suspension COMPOSITION PRED FORTE Sterile Eye Suspension contains: Prednisolone acetate 10 mg/ml Preservative:
Page 1 of 5 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM PRED FORTE Sterile Eye Suspension COMPOSITION PRED FORTE Sterile Eye Suspension contains: Prednisolone acetate 10 mg/ml Preservative:
Pseudophakic cystoid macular edema prevention and risk factors; prospective study with adjunctive once daily topical nepafenac 0.
 McCafferty et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:16 DOI 10.1186/s12886-017-0405-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Pseudophakic cystoid macular edema prevention and risk factors; prospective study with adjunctive
McCafferty et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2017) 17:16 DOI 10.1186/s12886-017-0405-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Pseudophakic cystoid macular edema prevention and risk factors; prospective study with adjunctive
AWMSG SECRETARIAT ASSESSMENT REPORT. Nepafenac (Nevanac ) 1 mg/ml eye drops, suspension. Reference number: 1509 FULL SUBMISSION
 AWMSG SECRETARIAT ASSESSMENT REPORT Nepafenac (Nevanac ) 1 mg/ml eye drops, suspension Reference number: 1509 FULL SUBMISSION This report has been prepared by the All Wales Therapeutics and Toxicology
AWMSG SECRETARIAT ASSESSMENT REPORT Nepafenac (Nevanac ) 1 mg/ml eye drops, suspension Reference number: 1509 FULL SUBMISSION This report has been prepared by the All Wales Therapeutics and Toxicology
ASCRS 2016 Instructional Course Mastering Femtosecond Laser Assisted Phacoemulsification. An Evidence-Based Review
 ASCRS 2016 Instructional Course 07-410 Mastering Femtosecond Laser Assisted Phacoemulsification An Evidence-Based Review TIMOTHY V ROBERTS MBBS (NSW), MMed (Syd), FRANZCO, FRACS, GAICD Vision Eye Institute,
ASCRS 2016 Instructional Course 07-410 Mastering Femtosecond Laser Assisted Phacoemulsification An Evidence-Based Review TIMOTHY V ROBERTS MBBS (NSW), MMed (Syd), FRANZCO, FRACS, GAICD Vision Eye Institute,
Comparison of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Dexamethasone and Diclofenac Sodium Eye Drops in Phacoemulsification
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Dexamethasone and Diclofenac Sodium Eye Drops in Phacoemulsification Muhammad Waseem and Sadia Humayun ABSTRACT Objective: To compare the effectiveness
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Dexamethasone and Diclofenac Sodium Eye Drops in Phacoemulsification Muhammad Waseem and Sadia Humayun ABSTRACT Objective: To compare the effectiveness
Management of ocular infl ammation and pain following cataract surgery: focus on bromfenac ophthalmic solution
 REVIEW Management of ocular infl ammation and pain following cataract surgery: focus on bromfenac ophthalmic solution Hyung Cho 1 Kenneth J Wolf 1 Eric J Wolf 2 1 Department of Ophthalmology, Albert Einstein
REVIEW Management of ocular infl ammation and pain following cataract surgery: focus on bromfenac ophthalmic solution Hyung Cho 1 Kenneth J Wolf 1 Eric J Wolf 2 1 Department of Ophthalmology, Albert Einstein
Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Omidria (phenylephrine / ketorolac)
 EMA/368070/2015 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Omidria (phenylephrine / ketorolac) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Omidria, which details the measures to be taken
EMA/368070/2015 Summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Omidria (phenylephrine / ketorolac) This is a summary of the risk management plan (RMP) for Omidria, which details the measures to be taken
NSAIDs in Treatment of Retinal Disorders
 NSAIDs in Treatment of Retinal Disorders These drugs are playing new roles beyond their established use in cataract and refractive surgery. NON-STEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMm a t o r y drugs are approved for the
NSAIDs in Treatment of Retinal Disorders These drugs are playing new roles beyond their established use in cataract and refractive surgery. NON-STEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMm a t o r y drugs are approved for the
D90 (27/10/2005) Final SmPC NL/H/653/01
 1/6 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MONOFREE DEXAMETHASON 1 mg/ml, eye drops, solution 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 ml solution contains 1 mg of dexamethasone phosphate as dexamethasone
1/6 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT MONOFREE DEXAMETHASON 1 mg/ml, eye drops, solution 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 ml solution contains 1 mg of dexamethasone phosphate as dexamethasone
New Zealand Data Sheet
 New Zealand Data Sheet Prednisolone-AFT 1% Prednisolone acetate (Ph Eur) 1% w/v ophthalmic suspension Presentation Prednisolone-AFT 1% is a milky white suspension in an eyedropper bottle for ophthalmic
New Zealand Data Sheet Prednisolone-AFT 1% Prednisolone acetate (Ph Eur) 1% w/v ophthalmic suspension Presentation Prednisolone-AFT 1% is a milky white suspension in an eyedropper bottle for ophthalmic
2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Dexafree 1 mg/ml, eye drops, solution in single-dose container 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 ml solution contains 1 mg
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Dexafree 1 mg/ml, eye drops, solution in single-dose container 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 ml solution contains 1 mg
Optometric Postoperative Cataract Surgery Management
 Financial Disclosures Optometric Postoperative Cataract Surgery Management David Dinh, OD Oak Cliff Eye Clinic Dallas Eye Consultants March 10, 2015 Comanagement Joint cooperation between two or more specialists
Financial Disclosures Optometric Postoperative Cataract Surgery Management David Dinh, OD Oak Cliff Eye Clinic Dallas Eye Consultants March 10, 2015 Comanagement Joint cooperation between two or more specialists
SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4. PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM OZURDEX intravitreal implant
 Page 1 of 10 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM intravitreal implant COMPOSITION One intravitreal implant contains: Dexamethasone 700 μg Excipients: Ester terminated 50:50 poly
Page 1 of 10 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM intravitreal implant COMPOSITION One intravitreal implant contains: Dexamethasone 700 μg Excipients: Ester terminated 50:50 poly
Department of Ophthalmology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea 2
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2017;31(5):394-401 https://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2016.0109 Original Article Additive Effect of Oral Steroid with Topical Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2017;31(5):394-401 https://doi.org/10.3341/kjo.2016.0109 Original Article Additive Effect of Oral Steroid with Topical Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatory
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT ENFLUAT 0.4 % Sterile Eye Drops 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Drug substance: Ketorolac Tromethamine 0,4 % Each bottle
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT ENFLUAT 0.4 % Sterile Eye Drops 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Drug substance: Ketorolac Tromethamine 0,4 % Each bottle
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
The Biomedical Ocular Coil Drug delivery Comfort (OCDC) project
 The Biomedical Ocular Coil Drug delivery Comfort (OCDC) project Prof.dr. R.M.M.A. Nuijts (MUMC+) Dr. A. Dias (Eyegle BV) Prof.dr. R. Tuinier (TU/e) I. Schefman, BA (Eyegle BV) Dr. H. Theunissen (MVC, Part.
The Biomedical Ocular Coil Drug delivery Comfort (OCDC) project Prof.dr. R.M.M.A. Nuijts (MUMC+) Dr. A. Dias (Eyegle BV) Prof.dr. R. Tuinier (TU/e) I. Schefman, BA (Eyegle BV) Dr. H. Theunissen (MVC, Part.
World Journal of Pharmaceutical and Life Sciences WJPLS
 wjpls, 2017, Vol. 3, Issue 9, 192-197 Research Article ISSN 2454-2229 Arafath et al. WJPLS www.wjpls.org SJIF Impact Factor: 4.223 EFFICACY OF BROMFENAC IN PREVENTION OF MACULAR EDEMA FOLLOWING CATARACT
wjpls, 2017, Vol. 3, Issue 9, 192-197 Research Article ISSN 2454-2229 Arafath et al. WJPLS www.wjpls.org SJIF Impact Factor: 4.223 EFFICACY OF BROMFENAC IN PREVENTION OF MACULAR EDEMA FOLLOWING CATARACT
PRECISION PROGRAM. Injection Technique Quick-Reference Guide. Companion booklet for the Video Guide to Injection Technique
 Injection Technique Quick-Reference Guide PRECISION PROGRAM Companion booklet for the Video Guide to Injection Technique Available at www.ozurdexprecisionprogram.com Provides step-by-step directions with
Injection Technique Quick-Reference Guide PRECISION PROGRAM Companion booklet for the Video Guide to Injection Technique Available at www.ozurdexprecisionprogram.com Provides step-by-step directions with
Loteprednol etabonate ophthalmic suspension 0.5 %: efficacy and safety for postoperative anti-inflammatory use
 Int Ophthalmol (2012) 32:507 517 DOI 10.1007/s10792-012-9589-2 REVIEW Loteprednol etabonate ophthalmic suspension 0.5 %: efficacy and safety for postoperative anti-inflammatory use Michael Amon Massimo
Int Ophthalmol (2012) 32:507 517 DOI 10.1007/s10792-012-9589-2 REVIEW Loteprednol etabonate ophthalmic suspension 0.5 %: efficacy and safety for postoperative anti-inflammatory use Michael Amon Massimo
CONTRAINDICATIONS Hypersensitivity to any component of this product (4)
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use OMIDRIA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for OMIDRIA. OMIDRIA (phenylephrine
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use OMIDRIA safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for OMIDRIA. OMIDRIA (phenylephrine
Innovation In Ophthalmology
 Innovation In Ophthalmology INVELTYS TM Approval August 2018 Disclaimers and Notices This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform
Innovation In Ophthalmology INVELTYS TM Approval August 2018 Disclaimers and Notices This presentation contains forward-looking statements within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform
Downloaded from:
 Lim, BX; Lim, CH; Lim, DK; Evans, JR; Bunce, C; Wormald, R (2016) Prophylactic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the prevention of macular oedema after cataract surgery. The Cochrane database of
Lim, BX; Lim, CH; Lim, DK; Evans, JR; Bunce, C; Wormald, R (2016) Prophylactic non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the prevention of macular oedema after cataract surgery. The Cochrane database of
CORNEAL CONDITIONS CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION
 GENERAL INFORMATION CORNEAL CONDITIONS CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION WHAT ARE CORNEAL CONDITIONS? The cornea is the clear outer layer of the eye. Shaped like a dome, it helps to protect the eye from foreign
GENERAL INFORMATION CORNEAL CONDITIONS CORNEAL TRANSPLANTATION WHAT ARE CORNEAL CONDITIONS? The cornea is the clear outer layer of the eye. Shaped like a dome, it helps to protect the eye from foreign
Postoperative follow up and treatment after refractive surgery
 Postoperative follow up and treatment after refractive surgery George Kontadakis, MD, MSc, PhD Institute of Vision and Optics and Department of Ophthalmology University of Crete Target of postoperative
Postoperative follow up and treatment after refractive surgery George Kontadakis, MD, MSc, PhD Institute of Vision and Optics and Department of Ophthalmology University of Crete Target of postoperative
Provided as a service by CiplaMed
 Allergy Reaction of the body tissues to an allergen which leads to production of antibodies finally culminating in an antigen-antibody antibody reaction. Normal Individual Entry of allergen Allergen-Antibody
Allergy Reaction of the body tissues to an allergen which leads to production of antibodies finally culminating in an antigen-antibody antibody reaction. Normal Individual Entry of allergen Allergen-Antibody
SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM
 Page 1 of 5 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM FML Liquifilm Sterile Eye Suspension COMPOSITION FML Liquifilm Sterile Eye Suspension contains: Fluorometholone 1,0 mg/ml Liquifilm
Page 1 of 5 SCHEDULING STATUS Schedule 4 PROPRIETARY NAME AND DOSAGE FORM FML Liquifilm Sterile Eye Suspension COMPOSITION FML Liquifilm Sterile Eye Suspension contains: Fluorometholone 1,0 mg/ml Liquifilm
Department of Ophthalmology
 Department of Ophthalmology Period : 02/July/18 to 30/August/18 Semester : 7 th Semester Lecture Lesson Plan Sr. Date Topic Lesson plan Name of Faculty No. 1 02.07.18 Lens- Lens-Anatomy, Classification
Department of Ophthalmology Period : 02/July/18 to 30/August/18 Semester : 7 th Semester Lecture Lesson Plan Sr. Date Topic Lesson plan Name of Faculty No. 1 02.07.18 Lens- Lens-Anatomy, Classification
NSAIDs. The Evolving Role of. in Cataract Surgery
 Supplement to April 2011 The Evolving Role of NSAIDs in Cataract Surgery Strategies for ocular surface management with the newly approved q.d. formulation of bromfenac 0.09%. Featuring: Johnny Gayton,
Supplement to April 2011 The Evolving Role of NSAIDs in Cataract Surgery Strategies for ocular surface management with the newly approved q.d. formulation of bromfenac 0.09%. Featuring: Johnny Gayton,
AUSTRALIAN PRODUCT INFORMATION FLAREX (FLUOROMETHOLONE ACETATE) EYE DROPS SUSPENSION
 AUSTRALIAN PRODUCT INFORMATION FLAREX (FLUOROMETHOLONE ACETATE) EYE DROPS SUSPENSION 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINE Fluorometholone acetate. 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION The active ingredient in
AUSTRALIAN PRODUCT INFORMATION FLAREX (FLUOROMETHOLONE ACETATE) EYE DROPS SUSPENSION 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINE Fluorometholone acetate. 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION The active ingredient in
Update on management of Anterior Uveitis
 Update on management of Anterior Uveitis Parthopratim Dutta Majumder Senior Consultant, Department of Uvea & Intraocular Inflammation Medical Research Foundation, Sankara Nethralaya ABCD of Treating a
Update on management of Anterior Uveitis Parthopratim Dutta Majumder Senior Consultant, Department of Uvea & Intraocular Inflammation Medical Research Foundation, Sankara Nethralaya ABCD of Treating a
Disorders of the. blood-aqueous barrier after. phacoemulsification in diabetic patients CLINICAL STUDY. Y Liu, L Luo, M He and X Liu
 (2004) 18, 900 904 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/04 $30.00 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY Disorders of the blood-aqueous barrier after phacoemulsification in diabetic
(2004) 18, 900 904 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/04 $30.00 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY Disorders of the blood-aqueous barrier after phacoemulsification in diabetic
Subnormal Vision in Uneventful Cataract Surgery after 6 Weeks Hospital Based Study
 ISSN 2231-4261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Subnormal Vision in Uneventful Cataract Surgery after 6 Weeks Hospital Based Study 1* 1 1 V. H. Karambelkar, Ankit Sharma, Viraj Pradhan 1 Department of Ophthalmology, Krishna
ISSN 2231-4261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Subnormal Vision in Uneventful Cataract Surgery after 6 Weeks Hospital Based Study 1* 1 1 V. H. Karambelkar, Ankit Sharma, Viraj Pradhan 1 Department of Ophthalmology, Krishna
Effect of Preoperative Use of Nepafenac and Flurbiprofen Eye Drops In Maintaining My driasis during Small Incision Cataract Surgery
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 18, Issue 2 Ser. 1 (February. 2019), PP 26-33 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Preoperative Use of Nepafenac
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 18, Issue 2 Ser. 1 (February. 2019), PP 26-33 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Preoperative Use of Nepafenac
ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT NEVANAC 1 mg/ml eye drops, suspension 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 ml of suspension contains 1 mg nepafenac.
ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT NEVANAC 1 mg/ml eye drops, suspension 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 ml of suspension contains 1 mg nepafenac.
You can C-ME after Uveitis
 You can C-ME after Uveitis Abstract: Approximately 50% of uveitis patients will present with vision loss secondary to cystoid macular edema[1]. Two patients with uveitis present with a constant decrease
You can C-ME after Uveitis Abstract: Approximately 50% of uveitis patients will present with vision loss secondary to cystoid macular edema[1]. Two patients with uveitis present with a constant decrease
How Do Ocular Corticosteroids and NSAIDs Work?
 DICAL EDU G ME CA UIN TIO TIN CON CME N A CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION PUBLICATION ISSUE 6 How Do Ocular Corticosteroids and NSAIDs Work? Membrane Phospholipids Corticosteroids Daniel r. saban, PHD Corticosteroids
DICAL EDU G ME CA UIN TIO TIN CON CME N A CONTINUING MEDICAL EDUCATION PUBLICATION ISSUE 6 How Do Ocular Corticosteroids and NSAIDs Work? Membrane Phospholipids Corticosteroids Daniel r. saban, PHD Corticosteroids
Measure #192: Cataracts: Complications within 30 Days Following Cataract Surgery Requiring Additional Surgical Procedures
 Measure #192: Cataracts: Complications within 30 Days Following Cataract Surgery Requiring Additional Surgical Procedures 2012 PHYSICIAN QUALITY REPORTING OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY
Measure #192: Cataracts: Complications within 30 Days Following Cataract Surgery Requiring Additional Surgical Procedures 2012 PHYSICIAN QUALITY REPORTING OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY
Endo Optiks. Clinical Publication Summaries
 Endo Optiks Clinical Publication Summaries Effective. Safe. Simple. Four scientific studies demonstrating the proven clinical benefits of combined ECP and cataract surgery. ECP is an Effective, Safe, and
Endo Optiks Clinical Publication Summaries Effective. Safe. Simple. Four scientific studies demonstrating the proven clinical benefits of combined ECP and cataract surgery. ECP is an Effective, Safe, and
Slide 4. Slide 5. Slide 6
 Slide 1 Slide 4 Allergic Response Mechanisms of Type 1 hypersensitivity allergic reaction, IgE-mediated mast cell degranulation, and release of inflammatory mediators Antigen Derek N. Cunningham, O.D.,
Slide 1 Slide 4 Allergic Response Mechanisms of Type 1 hypersensitivity allergic reaction, IgE-mediated mast cell degranulation, and release of inflammatory mediators Antigen Derek N. Cunningham, O.D.,
Role of Initial Preoperative Medical Management in Controlling Post-Operative Anterior Uveitis in Patients of Phacomorphic Glaucoma
 Original Article Role of Initial Preoperative Medical Management in Controlling Post-Operative Anterior Uveitis in Patients of Phacomorphic Glaucoma Irfan Qayyum Malik, M. Moin, A. Rehman, Mumtaz Hussain
Original Article Role of Initial Preoperative Medical Management in Controlling Post-Operative Anterior Uveitis in Patients of Phacomorphic Glaucoma Irfan Qayyum Malik, M. Moin, A. Rehman, Mumtaz Hussain
CLINICAL SCIENCES. Intravitreal Ketorolac for Chronic Uveitis and Macular Edema. Trial Registration: clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT
 CLINICL SCIENCES Intravitreal Ketorolac for Chronic Uveitis and Macular Edema Pilot Study Stephen J. Kim, MD; Terrence J. Doherty, MD; Edward F. Cherney, MD Objective: To investigate the adverse ocular
CLINICL SCIENCES Intravitreal Ketorolac for Chronic Uveitis and Macular Edema Pilot Study Stephen J. Kim, MD; Terrence J. Doherty, MD; Edward F. Cherney, MD Objective: To investigate the adverse ocular
psivida Transforms into Commercial Stage Specialty BioPharmaceutical Company AAO October 25, 2018 NASDAQ: EYPT
 psivida Transforms into Commercial Stage Specialty BioPharmaceutical Company OIS @ AAO October 25, 2018 NASDAQ: EYPT Forward Looking SAFE HARBOR STATEMENTS UNDER THE PRIVATE SECURITIES LITIGATION REFORM
psivida Transforms into Commercial Stage Specialty BioPharmaceutical Company OIS @ AAO October 25, 2018 NASDAQ: EYPT Forward Looking SAFE HARBOR STATEMENTS UNDER THE PRIVATE SECURITIES LITIGATION REFORM
The Visian ICL Advantages
 The Visian ICL Advantages Many vision correction procedures promise an improved level of vision, but few vision correction alternatives offer the quality and features found with the Visian ICL. These include:
The Visian ICL Advantages Many vision correction procedures promise an improved level of vision, but few vision correction alternatives offer the quality and features found with the Visian ICL. These include:
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1. PRODUCT NAME
 NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1. PRODUCT NAME Flucon fluorometholone 0.1% Eye Drops Suspension 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each ml of Flucon contains 1.0 mg of fluorometholone (0.1% w/v). Excipient
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1. PRODUCT NAME Flucon fluorometholone 0.1% Eye Drops Suspension 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each ml of Flucon contains 1.0 mg of fluorometholone (0.1% w/v). Excipient
Recurrent intraocular hemorrhage secondary to cataract wound neovascularization (Swan Syndrome)
 Recurrent intraocular hemorrhage secondary to cataract wound neovascularization (Swan Syndrome) John J. Chen MD, PhD; Young H. Kwon MD, PhD August 6, 2012 Chief complaint: Recurrent vitreous hemorrhage,
Recurrent intraocular hemorrhage secondary to cataract wound neovascularization (Swan Syndrome) John J. Chen MD, PhD; Young H. Kwon MD, PhD August 6, 2012 Chief complaint: Recurrent vitreous hemorrhage,
Management of Angle Closure Glaucoma Hospital Authority Convention 18 May 2015
 Management of Angle Closure Glaucoma Hospital Authority Convention 18 May 2015 Jimmy Lai Clinical Professor Department of Ophthalmology The University of Hong Kong 1 Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma PACG
Management of Angle Closure Glaucoma Hospital Authority Convention 18 May 2015 Jimmy Lai Clinical Professor Department of Ophthalmology The University of Hong Kong 1 Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma PACG
Department of Ophthalmology
 Period : 03/July/17 to 07/September/17 Semester : 7 th Semester Department of Ophthalmology Lecture Lesson Plan Sr 1 03.07.17 Uvea-Anatomy, Uvea-Anatomy, Classification of Uveitis Dr R Paranjpe Classification
Period : 03/July/17 to 07/September/17 Semester : 7 th Semester Department of Ophthalmology Lecture Lesson Plan Sr 1 03.07.17 Uvea-Anatomy, Uvea-Anatomy, Classification of Uveitis Dr R Paranjpe Classification
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Contents METHODS... 2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria... 2 Supplementary table S1... 2 Assessment of abnormal ocular signs and symptoms... 3 Supplementary table S2... 3 Ocular
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Contents METHODS... 2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria... 2 Supplementary table S1... 2 Assessment of abnormal ocular signs and symptoms... 3 Supplementary table S2... 3 Ocular
Issue 15 The following key clinical peer reviewed journals will be reviewed: MONTHLY RESEARCH UPDATE 151(3) American Journal of Ophthalmology 129(5)
 Welcome to Bausch and Lomb s monthly research update. With our background in clinical ophthalmic research, mainly of the anterior eye, Bausch and Lomb have asked us to produce an independent report of
Welcome to Bausch and Lomb s monthly research update. With our background in clinical ophthalmic research, mainly of the anterior eye, Bausch and Lomb have asked us to produce an independent report of
Evaluation of Changes of Macular Thickness in Diabetic Retinopathy after Cataract Surgery
 pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2011;25(4):238-242 DOI: 10.3341/kjo.2011.25.4.238 Evaluation of Changes of Macular Thickness in Diabetic Retinopathy after Cataract Surgery Original
pissn: 1011-8942 eissn: 2092-9382 Korean J Ophthalmol 2011;25(4):238-242 DOI: 10.3341/kjo.2011.25.4.238 Evaluation of Changes of Macular Thickness in Diabetic Retinopathy after Cataract Surgery Original
PRED-G (gentamicin and prednisolone acetate ophthalmic ointment, USP) 0.3%/0.6% sterile
 PRED-G (gentamicin and prednisolone acetate ophthalmic ointment, USP) 0.3%/0.6% sterile PRED-G sterile ophthalmic ointment is a topical anti-inflammatory/anti-infective combination product for ophthalmic
PRED-G (gentamicin and prednisolone acetate ophthalmic ointment, USP) 0.3%/0.6% sterile PRED-G sterile ophthalmic ointment is a topical anti-inflammatory/anti-infective combination product for ophthalmic
SCIENTIFIC PROGRAM. Pediatric ophthalmology- Optometry challenges (max 20 attendees)
 FRIDAY, 22 SEPTEMBER 2017 WORKSHOPS (OPHTHALMICA Eye Institute) 08:30-09:00 Registration-Welcome 09:00-11:30 Workshops SCIENTIFIC PROGRAM I. Cornea & Refractive surgery (max 30 attendees) - Clinical examination
FRIDAY, 22 SEPTEMBER 2017 WORKSHOPS (OPHTHALMICA Eye Institute) 08:30-09:00 Registration-Welcome 09:00-11:30 Workshops SCIENTIFIC PROGRAM I. Cornea & Refractive surgery (max 30 attendees) - Clinical examination
An Injector s Guide to OZURDEX (dexamethasone intravitreal implant) 0.7 mg
 An Injector s Guide to OZURDEX (dexamethasone intravitreal implant) 0.7 mg This guide is intended to provide injectors with information on the recommended injection technique and the important risks related
An Injector s Guide to OZURDEX (dexamethasone intravitreal implant) 0.7 mg This guide is intended to provide injectors with information on the recommended injection technique and the important risks related
CONSENT FOR CATARACT SURGERY REQUEST FOR SURGICAL OPERATION / PROCEDURE AND ANAESTHETIC
 CONSENT FOR CATARACT SURGERY REQUEST FOR SURGICAL OPERATION / PROCEDURE AND ANAESTHETIC Your doctor has indicated that the condition of your eye appears stable and your cataract surgery and/or implantation
CONSENT FOR CATARACT SURGERY REQUEST FOR SURGICAL OPERATION / PROCEDURE AND ANAESTHETIC Your doctor has indicated that the condition of your eye appears stable and your cataract surgery and/or implantation
Abela-Formanek, C., M. Amon, et al. (2011). "Biocompatibility of hydrophilic acrylic, hydrophobic acrylic, and silicone intraocular lenses in eyes wit
 Abela-Formanek, C., M. Amon, et al. (2011). "Biocompatibility of hydrophilic acrylic, hydrophobic acrylic, and silicone intraocular lenses in eyes with uveitis having cataract surgery: Long-term follow-up."
Abela-Formanek, C., M. Amon, et al. (2011). "Biocompatibility of hydrophilic acrylic, hydrophobic acrylic, and silicone intraocular lenses in eyes with uveitis having cataract surgery: Long-term follow-up."
Implantation of a corneal graft keratoprosthesis for severe corneal opacity in wet blinking eyes
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Implantation of a corneal graft keratoprosthesis for severe corneal opacity in wet blinking eyes The cornea
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Implantation of a corneal graft keratoprosthesis for severe corneal opacity in wet blinking eyes The cornea
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH. (Fluorometholone 0.1% Ophthalmic Suspension), USP. Corticosteroid
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH Pr Sandoz Fluorometholone (Fluorometholone 0.1% Ophthalmic Suspension), USP Corticosteroid Sandoz Canada Inc., Date of Revision: June 21, 2012 145 Jules-Léger Boucherville, QC, Canada
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH Pr Sandoz Fluorometholone (Fluorometholone 0.1% Ophthalmic Suspension), USP Corticosteroid Sandoz Canada Inc., Date of Revision: June 21, 2012 145 Jules-Léger Boucherville, QC, Canada
Internal document code 1 Nev061117iNZ
 NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1. PRODUCT NAME NEVANAC TM (nepafenac) Eye Drops 0.1% 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Nevanac contains 1 mg in 1 ml of nepafenac. Excipient with known effect Benzalkonium
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET 1. PRODUCT NAME NEVANAC TM (nepafenac) Eye Drops 0.1% 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Nevanac contains 1 mg in 1 ml of nepafenac. Excipient with known effect Benzalkonium
Anterior Segment Disease and the Systemic Link Mile Brujic, OD, FAAO
 Anterior Segment Disease and the Systemic Link Mile Brujic, OD, FAAO brujic@prodigy.net Summary As optometry s role in health care increases, so does our responsibility to appropriately diagnose and appropriately
Anterior Segment Disease and the Systemic Link Mile Brujic, OD, FAAO brujic@prodigy.net Summary As optometry s role in health care increases, so does our responsibility to appropriately diagnose and appropriately
Cost-utility analysis of cataract surgery in the second eye Busbee B G, Brown M M, Brown G C, Sharma S
 Cost-utility analysis of cataract surgery in the second eye Busbee B G, Brown M M, Brown G C, Sharma S Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria for inclusion
Cost-utility analysis of cataract surgery in the second eye Busbee B G, Brown M M, Brown G C, Sharma S Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria for inclusion
What you can expect with OZURDEX
 Important Information About Macular Edema Following Branch or Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO) and Treatment For patients with RVO What you can expect with OZURDEX Approved Use OZURDEX (dexamethasone
Important Information About Macular Edema Following Branch or Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (RVO) and Treatment For patients with RVO What you can expect with OZURDEX Approved Use OZURDEX (dexamethasone
Cataract and Diabetic macular edema: What should I do?
 Cataract and Diabetic macular edema: What should I do? Irini Chatziralli Ophthalmic Surgeon, University Scholar 2 nd Department of Ophthalmology, University of Athens (Director: Prof P. Theodossiadis)
Cataract and Diabetic macular edema: What should I do? Irini Chatziralli Ophthalmic Surgeon, University Scholar 2 nd Department of Ophthalmology, University of Athens (Director: Prof P. Theodossiadis)
2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR INDIVIDUAL MEASURES: REGISTRY ONLY
 Measure #192 (NQF 0564): Cataracts: Complications within 30 Days Following Cataract Surgery Requiring Additional Surgical Procedures National Quality Strategy Domain: Patient Safety 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR
Measure #192 (NQF 0564): Cataracts: Complications within 30 Days Following Cataract Surgery Requiring Additional Surgical Procedures National Quality Strategy Domain: Patient Safety 2016 PQRS OPTIONS FOR
ISSN: (Paper) eissn: (Online) JOURNAL OF ADVANCED ACADEMIC RESEARCH (JAAR) April 2017
 Topical proparacaine vs combined topical-intracameral lidocaine anesthesia in phacoemulsification surgery with preoperative counseling about intraoperative visual fear Kiran Shakya 1, Sangita Shakya 2,
Topical proparacaine vs combined topical-intracameral lidocaine anesthesia in phacoemulsification surgery with preoperative counseling about intraoperative visual fear Kiran Shakya 1, Sangita Shakya 2,
Intracameral Mydriasis: The New Standard Route for Cataract Surgery
 Supplement February 2016 Intracameral Mydriasis: The New Standard Route for Cataract Surgery Laboratoires Théa Satellite Symposium XXXIII Congress of the ESCRS 6 September 2015 Barcelona, Spain Chairperson
Supplement February 2016 Intracameral Mydriasis: The New Standard Route for Cataract Surgery Laboratoires Théa Satellite Symposium XXXIII Congress of the ESCRS 6 September 2015 Barcelona, Spain Chairperson
Ophthalmology. Cataract Surgery and IOL Implants
 Ophthalmology Cataract Surgery and IOL Implants APOLLO_Krames_Cataract surgery and IOL implants_print.indd 1 5/9/2016 5:38:55 PM What is a cataract? Sclera A cataract is an eye disease in which Ciliary
Ophthalmology Cataract Surgery and IOL Implants APOLLO_Krames_Cataract surgery and IOL implants_print.indd 1 5/9/2016 5:38:55 PM What is a cataract? Sclera A cataract is an eye disease in which Ciliary
Author's response to reviews
 Author's response to reviews Title:Efficacy of 1% carboxymethylcellulose sodium for treating dry eye after phacoemulsification: results from a multicenter, open-label, randomized, controlled study Authors:
Author's response to reviews Title:Efficacy of 1% carboxymethylcellulose sodium for treating dry eye after phacoemulsification: results from a multicenter, open-label, randomized, controlled study Authors:
Ophthalmology. Ophthalmology Services
 Ophthalmology Ophthalmology Services The Ophthalmology service offers the latest and most comprehensive eye care for patients. With a dedicated team of eye surgeons and consultants, we treat vision problems
Ophthalmology Ophthalmology Services The Ophthalmology service offers the latest and most comprehensive eye care for patients. With a dedicated team of eye surgeons and consultants, we treat vision problems
