A+Neurological+Assessment+
|
|
|
- Steven Taylor
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The+Neurological+Assessment+ Laurie'Edge+Hughes,'' BScPT,+MAnimSt+(Animal+Physio),+ CAFCI,+CCRT+ Four+Leg+Rehab+Inc+ The+Canine+Fitness+Centre+Ltd+ SubjecJve+History:++ History+of+Present+injury+ Course+of+Progression+ AggravaJon+/+Ease+ AbiliJes+at+present+ Job +of+the+dog+ Veterinary+IntervenJon+ Diagnosis+&+RecommendaJons+/+MedicaJons+ Tests:++X8rays,+U/S,+Myelograms,+MRI,+Blood+Tests+ Always+call+the+aXending+vet+ Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
2 Past+Medical+History:+++ as+per+owner+and+vet+ Other+PerJnent+QuesJons:+ Stairs+ Bowel+&+Bladder+(B+&+B)+ Licking+&+Chewing+ Signs+&+Symptoms+(S+&+S)+AM+vs+PM+&+with+acJvity+ AppeJte,+Hair+Coat,+Depression,+Thirst+ Clumsiness+ Changes+in+Behaviour+/+Likes+&+Dislikes+ Anything+else+the+owner+has+noJced+ ON+EXAMINATION+ General+ObservaJons:+temperament,+ condijon+&+acjvity+level+ Gait+ExaminaJon:+Stance,+Si^ng,+ AmbulaJon+ Walk+&+Trot+ Crossing+Over?+ Lying+/+Sit+to+Stand+and+back+again+ Turns+in+both+direcJon+ Familiarize+before+you+start+to+poke around!+ ++ Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
3 Extremity+Scan:+ Run+your+hands+down+the+limbs+assessing+for+muscle+ tone+and+bulk.+ Check+the+joints+and+muscles+for+any+obvious+signs+of+ heat,+swelling+and+tenderness+ Check+for+other+NEURO+clues+such+as+scuffed+toes+and+ toe+nails+ Check+for+dermaJJs, lick+ granulomas+or+ulcers+ R.O.M.+Scan+ Just+to+make+sure+there+is+no+other+complicaJng+ orthopedic+factors+ Full+Flexion+of+a+limb+ Full+Extension+of+a+limb+ CauJon+with+hip++ +extension+when+looking+ + +at+spinal+problems.+ Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
4 Neurological+TesJng+ Balance+on+displacement+ A+displacement+force+is+ normally+withstood+and+ will+not+cause+an+animal+ to+go+off+balance+ Neurological+TesJng+ Paper+Slide+Test+ In+standing,+place+the+animal s+ foot+on+a+piece+of+paper.++now+ slowly+pull+the+paper+to+slide+ the+foot+out+sideways.++the+ animal+should+nojce+the+ displacement+of+the+limb+and+ replace+the+leg+into+a+normal+ stance+posijon+before+the+foot+ is+an+unnatural+standing+ distance+away+from+the+body.+ Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
5 Neurological+TesJng+ Placing+Reflex+ (should+have+a+less+than+2+ second+return):++flip+the+paw+ over+so+that+the+dorsal+surface+ is+in+contact+with+the+ground.++ A+normal+animal+should+ right + the+posijon+immediately.+ Neurological+Tests+ Crossed+Extensor+Reflex+ PosiJve+(neurological)+ NegaJve+(normal)+ An+abnormal+reflex+where+ the+full+flexion+of+one+leg+ causes+rigid+extension+of+the+ opposite+leg.+ Normal Neurologic Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
6 Pain+PercepJon+vs+Flexor+ Withdrawal+ Pain+percepJon:+Hair+pulling+or+ hard+squeezing+of+a+digit+should+ be+felt+and+acknowledged+by+a+ normal+animal.+ Flexor+withdrawal:++Full+leg+ withdrawal+from+a+noxious+ sjmulus+is+considered+normal.++it+ is+a+spinal+cord+mediated+reflex.+ Tendon+Reflexes+&+Muscle+Reflexes+ Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
7 Perineal+Reflex+ A+noxious+sJmulus+at+the+side+of+the+anus+will+Normally+cause+a+ contracjon+of+the+sphincter+ Hopping+Reflex+ An+animal+should+hop+to+ support+itself+if+made+to+ weight+bear+on+one+leg+ when+displaced+in+an+ oblique+direcjon+ Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
8 Para8Walking+/+Hemi8Walking+ When+two+legs+on+the+same+side+ are+limed+up+and+the+animal+is+ displaced+sideways+(towards+the+ side+with+the+legs+down),+the+ animal+should+ walk +one+leg+ followed+by+the+other+on+the+ same+side+(i.e.+front+leg+steps+ sideways,+then+the+back+leg+ steps+sideways)+ Neurological+TesJng+ Babinski+Reflex+ Clonus+ Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
9 Was+anything+revealed+on+your+orthopedic+scan?+ Do+you+need+to+further+evaluate+the+extremity+ joints+for+specific+orthopedic+problems?+ Spinal+EvaluaJon:+++ For+general+localizaJon+of+ the+lesion+(if+spinal+cord+ based)+ Palpate+muscle+bulk+and+tone+ Palpate+the+spinous+processes+ for+pain+and+adjacent+ paraspinal+muscle+reacjvity+ Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
10 A+Spinal+EvaluaJon+ Dorsal+ +Ventral+Pressures?+ RotaJons?+ Cervical+Spine+Side+Glides?+ Tail+ROM+&+Pulls+ DeducJve+Reasoning+in+the+Neurological+ PaJent+ LMNL+(lower+motor+neuron+lesions):++ (the+grey+maxer+in+the+ventral+horn+of+the+spinal+ cord)+nerve+root+or+peripheral+ SIGNS+OF+A+LMNL+ Muscle+Weakness+ Hyporeflexia+/+Areflexia+ Hypotonia+or+Atonia+ Neurogenic+atrophy+appears+within days+ (up+to+half+of+the+muscle+volume+can+be+lost+in+ this+jme+with+a+severed+nerve+lesion)+ Owner+observaJons+are+very+valuable+for+ assessing+incomplete+lmnls+ Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
11 NERVES+ CUTANEOUS+INNERVATION+ DeducJve+Reasoning+in+the+Neurological+PaJent+ NERVE+ROOT+DISTRIBUTION+ FRONT+LIMB:+C6+ +T2+ WHAT+DO+THE+FOLLOWING+NERVES+DO?+ Radial+Nerve+ Musculocutaneous+Nerve+ Ulnar+and+Median+Nerves+ Suprascapular+/+Axillary+/+Subscapular+Nerves+ Pectoral+Nerve+ Thoracodorsal+Nerve+ Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
12 DeducJve+Reasoning+in+the+Neurological+PaJent+ NERVE+ROOT+DISTRIBUTION+ HIND+LIMB:+L4+ +S1+ WHAT+DO+THE+FOLLOWING+NERVES+DO?+ Femoral+Nerve+ SciaJc+Nerve+ Obturator+Nerve+ Gluteal+Nerves+ DeducJve+Reasoning+in+the+Neurological+PaJent+ NERVE+ROOT+DISTRIBUTION+ BOWEL+AND+BLADDER:+S1+ +S3+ WHAT+DOES+THE+FOLLOWING+NERVE+DO?+ Pudendal+ Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
13 DeducJve+Reasoning+in+the+Neurological+PaJent+ Relevant+Anatomy+as+it+Relates+to+the+LMNL+ The+C/S+has+7+vertebra+and+8+spinal+cord+ segments+&+nerve+roots+ The+spinal+cord+can+end+at+L4+in+large+dogs+or+L6+in+ smaller+dogs+ Relevance:++disc+lesions+below+the+end+of+the+spinal+cord+ will+display+as+lmnls+ Cord+Segments+L5+to+S3+extend+from+the+middle+of+ the+l3+vertebra+down+to+l6+(raise+these+levels+by+ one+segment+for+large+breed+dogs)+ DeducJve+Reasoning+in+the+Neurological+PaJent+ LMNL:++Nerve+Root+Impingement+ EJology+ Compression+or+tracJon+of+nerve+root+due+to+spinal+or+ pelvis+dysfuncjon+/+misalignment+ Bone+Spurs+near+the+facet+joint+encroaching+upon+the+ nerve+roots+ Central+disc+lesions+affecJng+the+cauda+equina (or+compression+of+the+cord+segments+that+correspond+to+ the+limbs)+ Lateralized+disc+lesions+in+the+C/S+or+L/S+ FibrocarJlaginous+embolism+ Nerve+sheath+tumors+ Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
14 DeducJve+Reasoning+in+the+Neurological+PaJent+ Signs+&+Symptoms+of+Nerve+Root+Impingement+ ExtrapolaJon+from+Humans+ 1. Pins+&+Needles:++(animal+might+chew+or+lick+the+limb+ or+off+weight+the+limb+in+a+jppy+toe+kind+of+manner)+ 2. Pain:+(root+signature+stance+or+may+aXack+the+leg+or+ act+as+if+he+was+suddenly+pinched+/+poked)+ 3. Motor+Impairment:++(amer+pain,+where+the+motor+ funcjoning+is+problemajc and+the+animal+may+not+ be+able+to+perform+a+task)+ DeducJve+Reasoning+in+the+Neurological+PaJent+ Signs+&+Symptoms+of+Nerve+Root+Impingement+ Spine+is+tender+on+palpaJon+ Facilitated+muscle+spasm+bilaterally+/+unilaterally+ Joint+Mobility:+ May+have+spinal+or+pelvis+misalignment+/+dysfuncJon+ A+disc+herniaJon+would+not+have+the+above+problems,+the+ pelvis+and+facet+joint+mobility+would+be+equal+bilaterally.++ Spasm+may+impede+tesJng.+ Bone+spurs:+Perhaps+unilateral+sJffness+depending+upon+ where+the+spurs+were+encroaching+ If+Pelvis:++piriformis+muscle+tension+with+compression+or+ tracjon+of+the+nerve+roots+ Off+weighJng+/+root+signature+stance++ Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
15 Which+one+has+a+Root+Signature+stance?++ What+does+the+other+one+have?++ Neurological+Assessments+ DeducJve+Reasoning+in+the+Neurological+PaJent+ Cranial+Nerves+ The+cranial+nerves+are+in+effect+the+nerve+roots+of+the+ brainstem+(medulla,+pons+&+midbrain)+ These+are+good+to+understand+as+a+reference,+but+of+ lixle+clinical+use+in+rehab+pracjce.+ Trigeminal+Nerve+(CN+5)+ Facial+Nerve+(CN+7)+ VesJbulocochlear+(CN+8)+ Accessory+(CN+11)+ Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
16 DeducJve+Reasoning+in+the+Neurological+PaJent+ Clinical+Signs+of+an+UMNL+(upper+motor+neuron+lesion)+ UMN+refers+to+the+spinal+cord+and+brain.+ Paresis+to+Paralysis+ Hyper8reflexia+ Hypertonia+ Disuse+Atrophy+ DeducJve+Reasoning+in+the+Neurological+PaJent+ Spinal+Cord+Anatomy+as+it+relates+to+the+UMNL+ The+Ascending+tract+sends+info+from+the+receptors+to+the+ brain+ The+Descending+tract+sends+info+from+the+brain+to+the+LMN+ The+Sensory+Tract+ 1. The+Fasciculus+Gracilus+&+Cuneatus:+(conscious+percepJon)+ 2. Dorsal+/+Ventral+Spinocerebellar:+(proprio.+in+hind+legs)+ 3. Rostral+Spinal:+(front+leg+conscious+proprio.)+ 4. Spinothalamic:+(pain+percepJon)+ The+Motor+Tract+ Is+deeper+(Rubrospinal,+ReJculospinal,+VesJbulospinal)+ WHY+DO+WE+CARE???+ Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
17 The+Spinal+Cord+ Why+do+we+care???+ LIFO+&+FILO+ Conscious+PercepJon+ Conscious+ PropriocepJon+ Motor+ Deep+Pain+ Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
18 So+it s+a+neuro+case?+++ Assess+FuncJon+ Treat+the+root+of+the+ problem+ Neuro8Rehab+to+ retrain+function+ C/S:+The+Spinal+Nerves+ Table'2.2.''Segmental'Nerve'Roots,'Peripheral'Nerves'and'Thoracic'Limb'Muscle' InnervaBon+ Nerve+ Nerve'Roots+ Muscles+ Suprascapular+N.+ (C5),C6,+C7+ Supraspinatus,+Infraspinatus+ Subscapular+N.+ C6,'C7+ Subscapularis+ Axillary+N.+ (C6),'C7,'C8+ Teres+Major,+Teres+Minor,+Deltoideus,+ (Subscapularis)+ Pectoral+N.+ C7,+C8+ Superficial+and+Deep+Pectorals+ Musculocutaneous+N.+ C6,+C7,+(C8)+ Biceps+Brachii,+Brachialis,+Coracobrachialis+ Radial+N.+ C7,'C8,'T1,+(T2)+ Triceps+brachii,+Extensor+carpi+radialis,+Ulnaris+ lateralis,+common+digital+extensor,+lateral+ digital+extensor+ Median+N.+ C8,'T1,'(T2)+ Flexor+carpi+radialis,+Superficial+digital+flexor,+ (Deep+digital+flexor)+ Ulnar+N.+ C8,'T1,+(T2)+ Flexor+carpi+ulnaris,+Deep+digital+flexor+ Thoracodorsal+N.+ (C7),+C8,+(T1)++ LaJssimus+Dorsi+ Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
19 T/S:+Anatomy+&+Biomechanics+ Table'3.1.''Branches'of'the'Spinal'Nerves+ Meningeal'Branch+ Supplies+the+dura+mater,+the+dorsal+longitudinal+ligament,+the+ vertebral+venous+sinus+and+other+blood+vessels+in+the+canal.++each+ annulus+fibrosis+of+the+disc+is+supplied+by+meningeal+branches+from+ two+or+more+spinal+nerves.+ Dorsal'Branch+ Divided+into+medial+and+lateral+branches.++Supply+the+epaxial+muscles+ and+skin+over+the+dorsal+aspect+of+the+body+wall.+ Ventral'Branch+ The'Visceral' Branch+ Also+called+intercostals+nerves.++These+are+also+divided+into+medial+ and+lateral+branches+except+in+the+region+of+the+brachial+plexus+and+ lumbosacral+plexus+or+the+supply+to+the+tail.++++the+intercostals+nerves+ supply+the+hypaxial+muscles+of+the+body+wall+and+give+off+lateral+and+ ventral+cutaneous+branches+to+supply+the+skin+of+the+lateral+and+ ventral+aspects+of+the+body+wall.+ Carries+only+general+visceral+sympatheJc+fibers+to+and+from+visceral+ structures.+ L/S+Anatomy+&+Biomechanics+ Table'4.3.''Segmental'Nerve'Roots,'Peripheral'Nerves'and'Thoracic'Limb'Muscle'InnervaBon' (Sisson'&'Grossman'1953;'Evans'1993;'Messonnier'2000)+ Nerve+ Nerve'Roots+ Muscles+ Femoral+Nerve+ L4,+L5,+L6+ Iliopsoas,+Quadriceps+complex,+Sartorius+ Obturator+Nerve+ (L4),+L5,'L6+ External+obturator,+PecJneus,+Gracilis,+Adductor+ Cranial+Gluteal+Nerve+ L6,'L7,+S1+ Middle+Gluteal,+Deep+Gluteal,+Tensor+Fascia+ Lata,+Piriformis+ Caudal+Gluteal+Nerve+ L7+(S1,+S2)+ Superficial+gluteal,+(Middle+gluteal),+(Biceps+ Femoris),+(Semitendinosus)+ SciaJc+Nerve+ L6,'L7,'S1+(S2)+ Biceps+Femoris,+Semimembranosus,+ Semitendinosus,+Obturator+internus,+Quadratus+ femoris,+gemelli+ Common+Peroneal+Nerve+ a/a+ Peroneus+longus,+Lateral+digital+extensor,+Long+ digital+extensor,+cranial+jbial+ Tibial+Nerve+ a/a+ Gastrocnemius,+Popliteus,+Superficial+digital+ flexor+ Pudendal+Nerve+ S1,'S2,'S3+ External+anal+sphincter,+the+external+genitalia+ Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
20 Dermatomes+ Cranial iliohypogastric Caudal iliohypogastric Ilio-inguinal Lateral cutaneous femoral Communicating ramus Sympathetic trunk To psoas major Ext. spermatic To iliopsoas Femoral Sciatic Cranial gluteal Obturator Caudal gluteal To quadratus femoris & gemelli To internal obturator Hypogastric Pelvic To medial coccygeus & lateral coccygeus Hemorrhoidal Caudal cutaneous femoral The Lumbosacral Plexus Pudendal Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
21 Phrenic branch To brachiocephalicus Suprascapular Phrenic nerve Subscapular To supf. pectoral To subscapularis & teres major To teres minor & deltoideus Musculocutaneous Axillary Radial Lateral thoracic (to cutaneous trunci) Thoracodorsal To biceps To deep pectoral Median Ulnar Brachial Plexus Radial Nerve C7 T2 Ulnar Nerve C8 - T2 Median & Ulnar Nerves C8 -T2 Cutaneous Innervation of the Forepaw Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
22 Sciatic nerve L6 L7 Femoral nerve (L3), L4 L6 Cutaneous Innervation of the Hind Paw Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
23 CRANIAL NERVES:+ The cranial nerve signs indicate a LMNL in the brainstem (medulla, pons and midbrain) Nerve Dysfunction CN1 Olfactory Loss of sense of smell CN2 Optic Blindness and pupil dilation CN3 Oculomotor outwards) Reduced ability to move the eye Lateral strabismus of the eye (ipsilateral eye looks Ptosis of the eye lid (droopiness) CN4 Trochlear Dorsomedial strabismus of the eye CN5 Trigeminal Asymmetric chewing, bilateral jaw drop (acute) Inability to open jaw (chronic Hypalgesia or hyperesthesia of one side of face CRANIAL+NERVES+ CN6 Abducens CN 7 Facial Medial strabismus of the eye Asymmetry of facial expression, ear droop, Muzzle deviates to contraleteral side, Food collects in cheek Partial dry mouth and dry eye CN 8 Vestibulocochlear Disequilibrium, head tilt, spontaneous nystagmus, Circling, ataxia Weakness of ipsilateral extensor muscles, +/- Deafness CN 9 Glossopharyngeal Partial dysphagia to pharyngeal paralysis Partial dryness of mouth Loss of taste, touch, and pain in caudal 1/3 of tongue Tachycardia, Increased blood pressure Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
24 CRANIAL+NERVES+ CN 10 Vagus Hoarseness, dysphonia, dysphagia Tachycardia, decreased peristalsis Inhalation pneumonia CN 11 Accessory Atrophy of neck muscles, Inability to draw shoulder cranially, Abduction of dorsal part of scapula (trapezius & sternomastoideus) CN 12 Hypoglossal Ipsilateral: Acute: tongue deviates to contralateral side Chronic: tongue deviates to ipsilateral side Bilateral: Paralysis of tongue+ Copyright+Laurie+Edge8Hughes,
Synapse Homework. Back page last question not counted. 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts. 26/34 students answered correctly!
 Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Examination and Diseases of Cranial Nerves
 Cranial nerve evaluation is an important part of a neurologic exam. There are some differences in the assessment of cranial nerves with different species but the general principles are the same. Going
Cranial nerve evaluation is an important part of a neurologic exam. There are some differences in the assessment of cranial nerves with different species but the general principles are the same. Going
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments
 Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
Lab 16: PNS: Nerves and Autonomic NS Hamilton Answers to Pre- Lab Assignments Pre-Lab Activity 1: 1. a. olfactory nerve b. optic nerve c. oculomotor nerve d. abducens nerve e. trochlear nerve f. trigeminal
Peripheral Nervous System
 Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Receptors Motor Endings Cranial Nerves The Four Plexuses Extremities Review of Reflexes Fast, preprogrammed, inborn, automatic responses Occur in the CNS at the spinal
Peripheral Nervous System Sensory Receptors Motor Endings Cranial Nerves The Four Plexuses Extremities Review of Reflexes Fast, preprogrammed, inborn, automatic responses Occur in the CNS at the spinal
Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
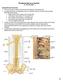 Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Spinal Nerves Overview Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves are connected to the spinal cord No special names; numbered by level of vertebral column at which they
Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Spinal Nerves Overview Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves are connected to the spinal cord No special names; numbered by level of vertebral column at which they
CRANIAL NERVES. Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy
 CRANIAL NERVES Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES Named the cranial nerves Identify the funcunal component of each cranial nerve Identify the effect of each
CRANIAL NERVES Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES Named the cranial nerves Identify the funcunal component of each cranial nerve Identify the effect of each
Chapter 13: The Peripheral Nervous System
 Chapter 13: The Peripheral Nervous System Objectives: 1. Define peripheral nervous system and list its components. 2. Classify general sensory receptors by structure, stimulus detected, and body location.
Chapter 13: The Peripheral Nervous System Objectives: 1. Define peripheral nervous system and list its components. 2. Classify general sensory receptors by structure, stimulus detected, and body location.
Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Structure of Spinal Nerves: Somatic Pathways dorsal root CNS interneuron spinal nerve dorsal ramus somatic sensory
Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Structure of Spinal Nerves: Somatic Pathways dorsal root CNS interneuron spinal nerve dorsal ramus somatic sensory
Brain and spinal nerve. By: shirin Kashfi
 Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
The Neurologic Examination
 The Neurologic Examination Cheryl L. Chrisman, DVM, MS, EdS, DACVIM (Neurology) The neurologic examination is a series of observations and tests done to answer the following four questions: h Is a lesion
The Neurologic Examination Cheryl L. Chrisman, DVM, MS, EdS, DACVIM (Neurology) The neurologic examination is a series of observations and tests done to answer the following four questions: h Is a lesion
Cranial Nerves. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 1: Proximal bones, plexuses and patterns
 213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 1: Proximal bones, plexuses and patterns CLAVICLE Examine an isolated clavicle and compare it with a clavicle on an articulated skeleton. Viewed from above,
213: HUMAN FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY: PRACTICAL CLASS 1: Proximal bones, plexuses and patterns CLAVICLE Examine an isolated clavicle and compare it with a clavicle on an articulated skeleton. Viewed from above,
Course: Physical Assessment II Date: October 17, 2008 Doc: Practice Quiz 1
 Course: Physical Assessment II Date: October 17, 2008 Doc: Practice Quiz 1 This is the practice quiz we did in Class 4. The answers are at the end of the quiz should you wish to test yourself. Complete
Course: Physical Assessment II Date: October 17, 2008 Doc: Practice Quiz 1 This is the practice quiz we did in Class 4. The answers are at the end of the quiz should you wish to test yourself. Complete
Proceedings of the European Veterinary Conference Voorjaarsdagen
 Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the European Veterinary Conference Voorjaarsdagen Apr. 13-15, 2016 Next Meeting: April 1 -, 201 The Hague, The Netherlands Reprinted in IVIS
Close this window to return to IVIS www.ivis.org Proceedings of the European Veterinary Conference Voorjaarsdagen Apr. 13-15, 2016 Next Meeting: April 1 -, 201 The Hague, The Netherlands Reprinted in IVIS
Peripheral Nervous System
 Peripheral Nervous System Nervous system consists of CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves ~10% (10 Bil) of all neurons in body
Peripheral Nervous System Nervous system consists of CNS = brain and spinal cord ~90% (90 Bil) of all neurons in body are in CNS PNS = Cranial nerves and spinal nerves ~10% (10 Bil) of all neurons in body
Nervous System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
BRACHIAL PLEXUS 11/12/2014 كيف تتكون الضفيرة FORMATION ENLARGEMENT (INTUMESCENCE) OF THE SPINAL CORD. Grey matter. Cervical intumescence - C 6 - T 2
 BRACHIAL PLEXUS Prof. Fawzy Elnady ENLARGEMENT (INTUMESCENCE) OF THE SPINAL CORD Grey matter Cervical intumescence - C 6 - T 2 Lumbar intumescence - L 4 S 2 كيف تتكون الضفيرة FORMATION The ventral rami
BRACHIAL PLEXUS Prof. Fawzy Elnady ENLARGEMENT (INTUMESCENCE) OF THE SPINAL CORD Grey matter Cervical intumescence - C 6 - T 2 Lumbar intumescence - L 4 S 2 كيف تتكون الضفيرة FORMATION The ventral rami
The Deconstructed Neurological Examination
 The Deconstructed Neurological Examination Marguerite Knipe, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) I. MENTATION: Normal, Quiet, Obtunded (mild, moderate, severe), Stuporous, Comatose Define stuporous and comatose.
The Deconstructed Neurological Examination Marguerite Knipe, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) I. MENTATION: Normal, Quiet, Obtunded (mild, moderate, severe), Stuporous, Comatose Define stuporous and comatose.
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body
 Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Peripheral Nervous Sytem: Upper Body MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 10 Department of Myotherapy Cervical Plexus Accessory nerve (CN11 + C1-5) Motor: trapezius and sternocleidomastoid Greater auricular
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery. Sem 4 Cranial Nerves Dr. Abbas Garib Alla
 Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Cranial Nerves Dr. Abbas Garib Alla Cranial Nerves I through XII FUNCTIPONAL CLSSIFICATION OF THE CN parasympathetic nerves 1973 PHARYNGEAL ARCHES nerves 1975
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Cranial Nerves Dr. Abbas Garib Alla Cranial Nerves I through XII FUNCTIPONAL CLSSIFICATION OF THE CN parasympathetic nerves 1973 PHARYNGEAL ARCHES nerves 1975
Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves. Spinal Cord. Chapter 12
 Chapter 12 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 Spinal Cord Extends from foramen magnum to second lumbar vertebra Segmented: Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar & Sacral Gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves Not uniform
Chapter 12 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 Spinal Cord Extends from foramen magnum to second lumbar vertebra Segmented: Cervical, Thoracic, Lumbar & Sacral Gives rise to 31 pairs of spinal nerves Not uniform
Lab Activity 19 & 20. Cranial Nerves General Senses. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 19 & 20 Cranial Nerves General Senses Portland Community College BI 232 Cranial Nerves Nerves that originate from the brain rather than the spinal cord Part of the peripheral nervous system
Lab Activity 19 & 20 Cranial Nerves General Senses Portland Community College BI 232 Cranial Nerves Nerves that originate from the brain rather than the spinal cord Part of the peripheral nervous system
Brachial plexuses and axillary lymph nodes
 Brachial plexuses and axillary lymph nodes Introduction about nervous system nervous system central nervous system periphral nervous system brain spinal cord 31 pairs of spinal nerves 12 paris of cranial
Brachial plexuses and axillary lymph nodes Introduction about nervous system nervous system central nervous system periphral nervous system brain spinal cord 31 pairs of spinal nerves 12 paris of cranial
*Our main subject is the brachial plexus but it's important to understand the spinal cord first in order to understand the brachial plexus.
 *Our main subject is the brachial plexus but it's important to understand the spinal cord first in order to understand the brachial plexus. *Vertebral column is formed by the union of 33 sequential vertebrae
*Our main subject is the brachial plexus but it's important to understand the spinal cord first in order to understand the brachial plexus. *Vertebral column is formed by the union of 33 sequential vertebrae
Human Nervous System:
 OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
Nervous System. The Peripheral Nervous System Agenda Review of CNS v. PNS PNS Basics Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Reflexes Pathways
 Nervous System Agenda Review of CNS v. PNS PNS Basics Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Sensory Motor Review of CNS v. PNS Central nervous system (CNS) Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) All
Nervous System Agenda Review of CNS v. PNS PNS Basics Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Sensory Motor Review of CNS v. PNS Central nervous system (CNS) Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) All
Bellringer: The central nervous system is comprised of: What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Brain. b.
 Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
Cranial Nerves Exam. 1. To learn how to examine the functions of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves.
 Cranial Nerves Exam [Purpose] 1. To learn how to examine the functions of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves. 2. To understand the function of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves. [Principle] The cranial nerves
Cranial Nerves Exam [Purpose] 1. To learn how to examine the functions of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves. 2. To understand the function of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves. [Principle] The cranial nerves
Laboratory 08 Peripheral Nervous System
 Laboratory 08 Peripheral Nervous System Goals: Structure and function of the cranial nerves. 1. List the cranial nerves by name and number. 2. Describe the specific functions of each of the cranial nerves
Laboratory 08 Peripheral Nervous System Goals: Structure and function of the cranial nerves. 1. List the cranial nerves by name and number. 2. Describe the specific functions of each of the cranial nerves
Structure, function and assessments of cranial nerves: Part 1 (CN 1-7) MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 12 Department of Myotherapy
 Structure, function and assessments of cranial nerves: Part 1 (CN 1-7) MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 12 Department of Myotherapy Session objectives List the four functions of the cranial nerves (CNs).
Structure, function and assessments of cranial nerves: Part 1 (CN 1-7) MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 12 Department of Myotherapy Session objectives List the four functions of the cranial nerves (CNs).
Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity
 Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity I. Peripheral nervous system A. PNS links CNS to the body B. Sensory: the afferent division C. Motor: the efferent division D. Ganglia: collections of cell bodies in
Chapter 13 PNS and reflex activity I. Peripheral nervous system A. PNS links CNS to the body B. Sensory: the afferent division C. Motor: the efferent division D. Ganglia: collections of cell bodies in
Lab Activity 13. Spinal Cord. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 13 Spinal Cord Portland Community College BI 232 Definitions Tracts: collections of axons in CNS Nerves:collections of axons in PNS Ganglia: collections of neuron cell bodies in PNS Nucleus
Lab Activity 13 Spinal Cord Portland Community College BI 232 Definitions Tracts: collections of axons in CNS Nerves:collections of axons in PNS Ganglia: collections of neuron cell bodies in PNS Nucleus
Cranial nerves.
 Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Spinal Cord Anatomy Protective structures: Vertebral column and the meninges protect the spinal cord and provide physical stability. a. Dura mater, b. Arachnoid,
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Spinal Cord Anatomy Protective structures: Vertebral column and the meninges protect the spinal cord and provide physical stability. a. Dura mater, b. Arachnoid,
Human Anatomy Biology 351
 1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
1 Human Anatomy Biology 351 Upper Limb Exam Please place your name on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average,
Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓
 Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓 1 Arm Lateral intermuscular septum Anterior (flexor) compartment: stronger Medial intermuscular septum Posterior (extensor) compartment 2 Coracobrachialis Origin: coracoid
Upper limb Arm & Cubital region 黃敏銓 1 Arm Lateral intermuscular septum Anterior (flexor) compartment: stronger Medial intermuscular septum Posterior (extensor) compartment 2 Coracobrachialis Origin: coracoid
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart
 Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Muscle Anatomy Review Chart BACK Superficial (5) Trapezius Transverse cervical a. Latissimus dorsi Thoracodorsal a. Rhomboideus major Dorsal scapular a. Rhomboideus minor Levator scapulae Intermediate
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp
 Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Cord Flashcards
 1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
Upper and Lower Motoneurons for the Head Objectives
 Upper and Lower Motoneurons for the Head Objectives Know the locations of cranial nerve motor nuclei Describe the effects of motor cranial nerve lesions Describe how the corticobulbar tract innervates
Upper and Lower Motoneurons for the Head Objectives Know the locations of cranial nerve motor nuclei Describe the effects of motor cranial nerve lesions Describe how the corticobulbar tract innervates
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM
 PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
examination in Companion Animals
 Peer reviewed The Neurologic examination in Companion Animals Part 2: Interpreting Abnormal Findings Helena Rylander, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) In the January/February issue of Today s Veterinary
Peer reviewed The Neurologic examination in Companion Animals Part 2: Interpreting Abnormal Findings Helena Rylander, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Neurology) In the January/February issue of Today s Veterinary
The 12 Cranial Nerves. Edited by Sterling Precision Nelson
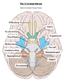 The 12 Cranial Nerves Edited by Sterling Precision Nelson Cranial Nerve I: Olfactory Nerve Type of Nerve: Sensory Function of Nerve: Sense of Smell Brief description: The Olfactory Nerve is the first of
The 12 Cranial Nerves Edited by Sterling Precision Nelson Cranial Nerve I: Olfactory Nerve Type of Nerve: Sensory Function of Nerve: Sense of Smell Brief description: The Olfactory Nerve is the first of
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
Chapter 14. The Nervous System. The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College
 Chapter 14 The Nervous System The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of: The spinal
Chapter 14 The Nervous System The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The Central Nervous System (CNS) consists of: The spinal
Chapter 13 & 14 The Peripheral Nervous System & the Autonomic Nervous System. Nervous System Organization
 Chapter 13 & 14 The Peripheral Nervous System & the Autonomic Nervous System 49 slides 1 Nervous System Organization Figure 13.1 Place of the PNS in the structural organization of the nervous system. 2
Chapter 13 & 14 The Peripheral Nervous System & the Autonomic Nervous System 49 slides 1 Nervous System Organization Figure 13.1 Place of the PNS in the structural organization of the nervous system. 2
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
MUSCLES. Anconeus Muscle
 LAB 7 UPPER LIMBS MUSCLES Anconeus Muscle anconeus origin: distal end of dorsal surface of humerus insertion: lateral surface of ulna from distal margin of the semilunar notch to proximal end of the olecranon
LAB 7 UPPER LIMBS MUSCLES Anconeus Muscle anconeus origin: distal end of dorsal surface of humerus insertion: lateral surface of ulna from distal margin of the semilunar notch to proximal end of the olecranon
Part 1: Communication between CNS & PNS
 Ch. 6: Peripheral Nervous System Objectives: 1. Communication between CNS & PNS: afferent (sensory) pathway versus efferent (motor) pathway of information. 2. Regulation of somatic (voluntary) motor system
Ch. 6: Peripheral Nervous System Objectives: 1. Communication between CNS & PNS: afferent (sensory) pathway versus efferent (motor) pathway of information. 2. Regulation of somatic (voluntary) motor system
Neurological Assessment
 Neurological Assessment Name: Age: Gender: Date: History Review of history related to neurological system YES/NO If YES, provide details: General Neurological Mental Illness Neurological disease Severe
Neurological Assessment Name: Age: Gender: Date: History Review of history related to neurological system YES/NO If YES, provide details: General Neurological Mental Illness Neurological disease Severe
Neurological Assessment Part 1
 Neurological Assessment Part 1 MOTOR EXAMINATION: Look at bulk, contour and symmetry of individual muscles: muscles of face upper arm arm thigh lower leg Look for atrophy--may help to localize the site
Neurological Assessment Part 1 MOTOR EXAMINATION: Look at bulk, contour and symmetry of individual muscles: muscles of face upper arm arm thigh lower leg Look for atrophy--may help to localize the site
Classification of Neurons
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 11b Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: Neurons The neuron is the cell of the nervous system capable of conducting and sending nerve impulses throughout the body. All
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 11b Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: Neurons The neuron is the cell of the nervous system capable of conducting and sending nerve impulses throughout the body. All
Cranial Nerves. Study slides
 Cranial Nerves Study slides What is the name of cranial nerve V? ANSWER What is the name of cranial nerve V? Trigeminal nerve What number is the trigeminal nerve? ANSWER What number is the trigeminal nerve?
Cranial Nerves Study slides What is the name of cranial nerve V? ANSWER What is the name of cranial nerve V? Trigeminal nerve What number is the trigeminal nerve? ANSWER What number is the trigeminal nerve?
Nerve Injury. 1) Upper Lesions of the Brachial Plexus called Erb- Duchene Palsy or syndrome.
 Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Neurological examinations made easy. Dr. H. A. M. Nazmul Ahasan Professor Department of Medicine Dhaka Medical College Hospital
 Neurological examinations made easy Dr. H. A. M. Nazmul Ahasan Professor Department of Medicine Dhaka Medical College Hospital Introduction The aim of the neurological examination is to delineate the patient
Neurological examinations made easy Dr. H. A. M. Nazmul Ahasan Professor Department of Medicine Dhaka Medical College Hospital Introduction The aim of the neurological examination is to delineate the patient
Human Anatomy. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
History & Observation
 History & Observation Examination Algorithm for Trauma/Whiplash or Signs and or Symptoms Ascribable to VBI or Upper Cervical Instability If Noncardinal Syx/Signs continue testing: Blurred vision Severe
History & Observation Examination Algorithm for Trauma/Whiplash or Signs and or Symptoms Ascribable to VBI or Upper Cervical Instability If Noncardinal Syx/Signs continue testing: Blurred vision Severe
Gateway to the upper limb. An area of transition between the neck and the arm.
 Gateway to the upper limb An area of transition between the neck and the arm. Pyramidal space inferior to shoulder @ junction of arm & thorax Distribution center for the neurovascular structures that serve
Gateway to the upper limb An area of transition between the neck and the arm. Pyramidal space inferior to shoulder @ junction of arm & thorax Distribution center for the neurovascular structures that serve
Muscle Action Origin Insertion Nerve Innervation Chapter Page. Deltoid. Trapezius. Latissimus Dorsi
 Muscle Action Origin Insertion Nerve Innervation Chapter Page All Fibers Abduct the shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid Anterior Fibers Flex the shoulder (G/H joint) Horizontally adduct the shoulder
Muscle Action Origin Insertion Nerve Innervation Chapter Page All Fibers Abduct the shoulder (glenohumeral joint) Deltoid Anterior Fibers Flex the shoulder (G/H joint) Horizontally adduct the shoulder
Peripheral Nervous System
 Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University ( https://www.lf2.cuni.cz) Peripheral Nervous System The test on the peripheral nervous system is in written format and follows the general rules
Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University ( https://www.lf2.cuni.cz) Peripheral Nervous System The test on the peripheral nervous system is in written format and follows the general rules
4/5/2015. Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
 Peripheral Nervous System Learn and Understand: Peripheral nerves connect the edges of the body and outside world to the CNS. Most nerves carry specific types of information to/from specific locations.
Peripheral Nervous System Learn and Understand: Peripheral nerves connect the edges of the body and outside world to the CNS. Most nerves carry specific types of information to/from specific locations.
Unit VIII Problem 4 Physiology lab: Brain Stem Lesions
 Unit VIII Problem 4 Physiology lab: Brain Stem Lesions - Motor and sensory somatotopy: Pre-central gyrus: is the motor area. Post-central gyrus: is the sensory area. Somatotopy: there is a map of thee
Unit VIII Problem 4 Physiology lab: Brain Stem Lesions - Motor and sensory somatotopy: Pre-central gyrus: is the motor area. Post-central gyrus: is the sensory area. Somatotopy: there is a map of thee
Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture. caudal = toward the spinal cord)
 Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Acknowledgments Figure Credits List of Clinical Blue Boxes Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p.
 Preface p. ix Acknowledgments p. xi Figure Credits p. xv List of Clinical Blue Boxes p. xix Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p. 2 Regional Anatomy p. 2 Systemic
Preface p. ix Acknowledgments p. xi Figure Credits p. xv List of Clinical Blue Boxes p. xix Introduction to Clinically Oriented Anatomy Approaches to Studying Anatomy p. 2 Regional Anatomy p. 2 Systemic
Al-Balqa Applied University
 Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Al-Balqa Applied University Faculty Of Medicine *You can use this checklist as a guide to you for the lab. the items on this checklist represent the main features of the models that you have to know for
Lower Limb Nerves. Clinical Anatomy
 Lower Limb Nerves Clinical Anatomy Lumbar Plexus Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh Major nerves.. Lumbar Plexus Nerves relation to psoas m. : Obturator n.
Lower Limb Nerves Clinical Anatomy Lumbar Plexus Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh Major nerves.. Lumbar Plexus Nerves relation to psoas m. : Obturator n.
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b
 Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh
 3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh ***Muscles Connecting the Upper Limb to the Vertebral Column 1.Trapezius Muscle ***The first muscle on the back is trapezius muscle, it s called so according
3 Mohammad Al-Mohtasib Areej Mosleh ***Muscles Connecting the Upper Limb to the Vertebral Column 1.Trapezius Muscle ***The first muscle on the back is trapezius muscle, it s called so according
Forelimb Amputation. Indications. Pre operatively 11/12/2008. Technique Preparing for surgery. Bone neoplasia. Severe trauma/paralysis
 Forelimb Amputation January 10, 2007 Amy Bringardner Becky Pentecost Indications Bone neoplasia Osteosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Chondrosarcoma Severe trauma/paralysis Brachial plexus avulsion Infection Congenital
Forelimb Amputation January 10, 2007 Amy Bringardner Becky Pentecost Indications Bone neoplasia Osteosarcoma Fibrosarcoma Chondrosarcoma Severe trauma/paralysis Brachial plexus avulsion Infection Congenital
Lumbar Plexus. Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Major nerves.. Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh
 Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
Lab # 2: Spinal Cord & Nerves, Reflexes and General Senses. A & P II Spring, 2014
 Lab # 2: Spinal Cord & Nerves, Reflexes and General Senses A & P II Spring, 2014 Objectives Be able to identify specified spinal cord structures and spinal nerves on models Be familiar with spinal nerve
Lab # 2: Spinal Cord & Nerves, Reflexes and General Senses A & P II Spring, 2014 Objectives Be able to identify specified spinal cord structures and spinal nerves on models Be familiar with spinal nerve
Neurological Assessment. Lecture 8
 Neurological Assessment Lecture 8 Nervous System Central Nervous System Brain Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Central Nervous System-Brain Central Nervous System-Spinal
Neurological Assessment Lecture 8 Nervous System Central Nervous System Brain Spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Central Nervous System-Brain Central Nervous System-Spinal
Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm
 Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
Axilla and Brachial Region
 L 4 A B O R A T O R Y Axilla and Brachial Region BRACHIAL PLEXUS 5 Roots/Rami (ventral rami C5 T1) 3 Trunks Superior (C5, C6) Middle (C7) Inferior (C8, T1) 3 Cords Lateral Cord (Anterior Superior and Anterior
L 4 A B O R A T O R Y Axilla and Brachial Region BRACHIAL PLEXUS 5 Roots/Rami (ventral rami C5 T1) 3 Trunks Superior (C5, C6) Middle (C7) Inferior (C8, T1) 3 Cords Lateral Cord (Anterior Superior and Anterior
G24: Shoulder and Axilla
 G24: Shoulder and Axilla Syllabus - Pg. 2 ANAT 6010- Medical Gross Anatomy David A. Morton, Ph.D. Objectives Upper limb Systemically: Bones (joints) Muscles Nerves Vessels (arteries/veins) Fascial compartments
G24: Shoulder and Axilla Syllabus - Pg. 2 ANAT 6010- Medical Gross Anatomy David A. Morton, Ph.D. Objectives Upper limb Systemically: Bones (joints) Muscles Nerves Vessels (arteries/veins) Fascial compartments
The Peripheral Nervous
 The Peripheral Nervous System Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The PNS is not as contained as the CNS because it is defined as everything that is not the CNS. Some peripheral structures are incorporated into the other
The Peripheral Nervous System Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The PNS is not as contained as the CNS because it is defined as everything that is not the CNS. Some peripheral structures are incorporated into the other
The Clavicle Right clavicle Deltoid tubercle: Conoid tubercle, conoid ligamen Impression for the
 The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
The Clavicle Muscle Attachment Sites in the Upper Limb Pectoralis major Right clavicle Smooth superior surface of the shaft, under the platysma muscle tubercle: attachment of the deltoid Acromial facet
Neurological examination of the horse
 Neurological examination of the horse Aim of the neurological examination Is there a neurological disease? Anatomical location of the problem? Diagnosis? Are there therapeutic options? What is the prognosis?
Neurological examination of the horse Aim of the neurological examination Is there a neurological disease? Anatomical location of the problem? Diagnosis? Are there therapeutic options? What is the prognosis?
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Forebrain Interprets sensory
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Forebrain Interprets sensory
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System
 Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System Kyle E. Rarey, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy & Cell Biology and Otolaryngology University of Florida College of Medicine Outline of Presentation Vertebral Column Upper
Anatomy of the Musculoskeletal System Kyle E. Rarey, Ph.D. Department of Anatomy & Cell Biology and Otolaryngology University of Florida College of Medicine Outline of Presentation Vertebral Column Upper
Surgery Under Regional Anesthesia
 Surgery Under Regional Anesthesia Jean Daniel Eloy, MD Assistant Professor Residency Program Director Rutgers-New Jersey Medical School Rutgers The State University of New Jersey Peripheral Nerve Block
Surgery Under Regional Anesthesia Jean Daniel Eloy, MD Assistant Professor Residency Program Director Rutgers-New Jersey Medical School Rutgers The State University of New Jersey Peripheral Nerve Block
BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII
 463 Brain stem Case history BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII A 60 year old man with hypertension wakes one morning with trouble walking. He is feeling dizzy and is sick to his stomach. His wife
463 Brain stem Case history BRAIN STEM CASE HISTORIES CASE HISTORY VII A 60 year old man with hypertension wakes one morning with trouble walking. He is feeling dizzy and is sick to his stomach. His wife
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5. September 30, 2011
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
1. Which of the following muscles inserts via the calcaneal tendon'? A. semitendinosus B. sartorius C. tibialis anterior D.
 1. Which of the following muscles inserts via the calcaneal tendon'? A. semitendinosus B. sartorius C. tibialis anterior D. gastrocnemius 2. Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. Cerebrospinal
1. Which of the following muscles inserts via the calcaneal tendon'? A. semitendinosus B. sartorius C. tibialis anterior D. gastrocnemius 2. Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. Cerebrospinal
Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Monday, Nov 6, 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium
Autonomic Nervous System (the visceral motor system) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Monday, Nov 6, 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB. Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Gluteal Region Cutaneous nerve supply of (Gluteal region) 1. Lateral cutaneous
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine THE LOWER LIMB Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Gluteal Region Cutaneous nerve supply of (Gluteal region) 1. Lateral cutaneous
A&P 1 Brain & Cranial Nerves Guide #1 - Pre-Lab Exercises
 A&P 1 Brain & Cranial Nerves Guide #1 - Pre-Lab Exercises In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be looking at the brain & cranial nerves. This should be done before lab, so we don't waste time in lab! This
A&P 1 Brain & Cranial Nerves Guide #1 - Pre-Lab Exercises In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be looking at the brain & cranial nerves. This should be done before lab, so we don't waste time in lab! This
CLASS-X EPISTODE-6 STATE SYLLABUS NERVOUS SYSTEM
 CLASS-X EPISTODE-6 STATE SYLLABUS NERVOUS SYSTEM In the last episode we have seen the structures and function of the components of central nervous system. In this episode we shall examine the peripheral
CLASS-X EPISTODE-6 STATE SYLLABUS NERVOUS SYSTEM In the last episode we have seen the structures and function of the components of central nervous system. In this episode we shall examine the peripheral
Fig Cervical spinal nerves. Cervical enlargement C7. Dural sheath. Subarachnoid space. Thoracic. Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) spinal nerves
 Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
Fig. 13.1 C1 Cervical enlargement C7 Cervical spinal nerves Dural sheath Subarachnoid space Thoracic spinal nerves Spinal cord Vertebra (cut) Lumbar enlargement Medullary cone T12 Spinal nerve Spinal nerve
The Upper Limb III. The Brachial Plexus. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Upper Limb III The Brachial Plexus Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Brachial plexus Network of nerves supplying the upper limb Compression of the plexus results in motor & sensory changes
The Upper Limb III The Brachial Plexus Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 12 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Brachial plexus Network of nerves supplying the upper limb Compression of the plexus results in motor & sensory changes
Anatomy of Nervous System. Neurological Assessment. Brain. Brain. Spinal Cord. Spinal Cord 03/23/2010. Central. Peripheral
 Anatomy of Nervous System Neurological Assessment Central Brain Spinal cord Peripheral Spinal Nerves Brain Cerebral cortex ( rind ) gray matter Frontal Parietal Temporal Occipital Wernicke s area receptive
Anatomy of Nervous System Neurological Assessment Central Brain Spinal cord Peripheral Spinal Nerves Brain Cerebral cortex ( rind ) gray matter Frontal Parietal Temporal Occipital Wernicke s area receptive
Bilateral nerve damage icd 10
 Bilateral nerve damage icd 10 The Borg System is 100 % Bilateral nerve damage icd 10 Anterior interosseous nerve syndrome; Neuropathy (nerve damage), suprascapular; Paralysis of phrenic nerve; Posterior
Bilateral nerve damage icd 10 The Borg System is 100 % Bilateral nerve damage icd 10 Anterior interosseous nerve syndrome; Neuropathy (nerve damage), suprascapular; Paralysis of phrenic nerve; Posterior
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE BRAIN STEM
 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE BRAIN STEM Dr Syed Shahid Habib Professor & Consultant Clinical Neurophysiology Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH King Saud University OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE BRAIN STEM Dr Syed Shahid Habib Professor & Consultant Clinical Neurophysiology Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH King Saud University OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p.
 General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
Physical Assessment Class 3
 Physical Assessment Class 3 Daily Tasks **Spot Test and assessment 1 (Class materials from1 2)** Goals: Understand significant features of a neurological history Know the complete sequence of cranial nerve
Physical Assessment Class 3 Daily Tasks **Spot Test and assessment 1 (Class materials from1 2)** Goals: Understand significant features of a neurological history Know the complete sequence of cranial nerve
Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for
 Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes
 13 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal
13 The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal Reflexes PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal
HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY PRACTICE QUESTIONS
 HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY PRACTICE QUESTIONS 1. A patient complains that he has lost sensation on his face and that the skin of his face feels numb. The physician tests tactile acuity by touching the forehead
HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY PRACTICE QUESTIONS 1. A patient complains that he has lost sensation on his face and that the skin of his face feels numb. The physician tests tactile acuity by touching the forehead
