Guidelines for the management of a patient with a subarachnoid haemorrhage
|
|
|
- Gervais Collins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Guidelines for the management of a patient with a subarachnoid haemorrhage Item Type Report Authors Health Service Executive (HSE) Citation Health Service Executive. Guidelines for the management of a patient with a subarachnoid haemorrhage. Dublin: Health Service Executive; 2010 Apr. 11p Publisher Health Service Executive (HSE) Download date 27/09/ :31:26 Link to Item Find this and similar works at -
2 !!" #$! #%&%!!" #$! #%&% ' "! (' ) *' ( (!!!" (' +(, ',(! -. #$/%0/&% 1" 2 #$! #%&%! " #$! #%&& 1
3 CONTENTS: Introduction Page 3 Purpose Page 3 Scope Page 3 Definitions & Abbreviations Page 4 Responsibilities Page 4 Procedures Page 4 9 References Page 10 Audit & Evaluation Page 11 2
4 1.0 Introduction SAH accounts for 5% of all strokes with the majority due to ruptured aneurysms. Other causes identified are aterio-venous abnormalities (AVM s), metastases, haemorrhagic primary brain tumours and idiopathic reasons. In 7-10% of confirmed cases of non-traumatic SAH, no cause is found (i.e. idiopathic SAH). The estimated annual rate of aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) ranges between 10 to 28 per 100,000 population. 10% of patients die before reaching hospital. Among patients surviving the initial haemorrhage, without definitive treatment (i.e. surgery or interventional neuroradiology), rebleeding is the major cause of morbidity and mortality (risk of re-haemorrhage is 15-20% in the first two weeks). After definitive treatment, vasospasm is the greatest risk to patients with an approximate 7% mortality and another approximate 7% severe neurological deficit. Risk factors for SAH include hypertension, smoking, excessive alcohol consumption and sympathomimetic drugs (cocaine abuse). These guidelines are based on international guidelines (e.g. American Heart Association/ American Stroke Association) and evidenced based research. These guidelines are not meant to replace or substitute for good clinical judgment and the admitting consultant makes decisions based on his or her professional judgement as to the appropriate course of treatment. Clinical guidelines can still only assist the practitioner; they cannot be used to mandate, authorise or outlaw treatment options. Regardless of the strength of the evidence, it will remain the responsibility of the practising clinicians to interpret their application taking account of local circumstances and the needs and wishes of individual patients. It would be wholly inappropriate for clinical guidelines to be used as a means of coercion of the individual clinician, by managers and senior professionals (NHS Executive, 1996 Clinical Guidelines: using clinical guidelines to improve patient care within the NHS, DOH, London, p, 10). Critical to the successful implementation of these guidelines is the provision of adequate in patient and outpatient resources. 2.0 Purpose The purpose of these guidelines is to advise and guide all staff caring for SAH on the management of patients admitted to National Neurosurgical Centre with a SAH. 3.0 Scope. The scope applies to all medical and nursing practitioners caring for patients with Subarachnoid Haemorrhage. 3
5 4.0 Definitions and Abbreviations 1 Subarachnoid Haemorrhage (SAH). 2 Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). 3 Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) 4 Computerised Tomography (CT). 5 Computerised Tomography Angiography (CTA). 6 Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA). 7 Cerebral Blood Flow (CBF) 8 Lumbar Puncture (LP). 9 Trans Cranial Doppler (TCD). 10 Cerebro Spinal Fluid (CSF). 11 Cerebral Blood Flow (CBF). 12 World Federation of Neurosurgeons (WFNS). 13 Glasgow Coma Score (GCS). 14 Muliti-disciplinary team (MDT). 15 Central venous catheter (CVC). 16 National Neurosurgical Centre Beaumont Hospital or Cork University Hospital 5.0 Responsibilities It is the responsibility of all medical and nursing practitioners to 1 Read and familiarise themselves with this guideline. 2 Refer to the guideline if unfamiliar with any aspect of caring for a patient with an SAH. 6.0 Presentation 6.1 Symptoms: Sudden onset of headache is the classical presentation of SAH and can be accompanied by nausea/vomiting, stiff neck, loss of consciousness and focal neurological deficit. About 20% of SAH patients will have a history of a sentinel or warning bleed Diagnosis: the cornerstone of SAH diagnosis is a non contrast cranial CT scan. The sensitivity of a non contrast CT is >95% in the first 24 hours declining to 57-85% at day 6 post SAH. CT brain scans also assess ventricular size (i.e. hydrocephalus), intra cerebral haematoma, infarction; the amount of blood on the CT may give some indication as to the likelihood of vasospasm. A CT angiogram (CTA) is performed also may identify any aneurysm(s). Misdiagnosis occurs in about 12% of cases and is accompanied by a four-fold increase in mortality and morbidity. The commonest error is failure to obtain a timely non-contrast CT. CTA has a sensitivity of 95% and a specificity of 83% for aneurysms as small as 2.2mm. Diagnostic lumbar puncture (LP) should be performed if the CT scan is negative for patients with suspected SAH. 4
6 Three samples of cerebro spinal fluid (CSF) is analysed for red cell counts (usually >100,000/ml) and white cell counts, xanthochromia and spectroscopy. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is not sensitive acutely in the first hours. Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) is the gold standard to confirm the cause of the SAH and is superior to CTA and MRA. In addition to revealing the source (if there is a source as 7-10% of non-traumatic cases are idiopathic), the DSA can confirm shape, size and number of aneurysm(s) and also vasospasm Grades of SAH World Federation of Neurosurgeons (WFNS) Classification uses Glasgow Coma Score (GCS) and focal neurological deficit to gauge severity of symptoms. Grade GCS Focal Neurological deficit Absent Absent Present Present or Absent 5 <7 Present or Absent Neurosurgery Referral Grades 1 and 2 patients are admitted within 24 hours of referral. Grades 3, 4 and 5 patients are referred if and when they clinically improve Initial Treatment 1 Oxygenation 2 Intubation if necessary depending on level of consciousness. 3 Prevention of reflex cardiac dysrhythmia 4 Prevention of unnecessary blood pressure fluctuation. 5 All patients diagnosed with SAH should be commenced on Nimodipine 60 mgs 4 hourly orally / enterally for 21 days duration. 6 Treat seizures Definitive Treatment Regimes 1 Early referral to National Neurosurgical Centre with experienced neurosurgeons and interventional neuroradiologists is essential. 2 Early treatment is probably indicated in the majority of patients (i.e good WFNS grades). 3 Although there is much debate as to early (i.e. with 72 hours approximately) versus late treatment in cases of aneurysmal SAH, there is strong evidence to support early definitive intervention which is associated with better outcomes. 5
7 4 The decision to either surgically clipping or coil an aneurysm is dependant on the discussion between the neurosurgeons and the neuroradiologists in each instance. The more suitable approach (i.e. in terms of safety and effectiveness) is agreed. Whilst there is a weekly neuro-vascular MDT meeting at Beaumont Hospital, it is not always possible to discuss all emergency SAH patient admissions before definitive treatment as timing of definitive treatment is crucial. Such cases are however discussed after definitive treatment. 5 Where an experienced team determine an aneurysm is suitable for surgical or endovascular coiling, coiling can be beneficial. Surgical clipping or coiling should be performed to reduce the rate of re-bleeding and its associated morbidity and mortality. 6 Occasionally, neither endovascular coiling nor surgical clipping is possible and therefore surgical wrapping of an aneurysm is performed. Complete occlusion is recommended wherever possible Anaesthetic Considerations in Aneurysm Care 1 Minimise the degree and length of hypotension during surgery. 2 Induced hypothermia is not routinely recommended. 7.0 Complications. 7.1 Cerebral Vasospasm Treatment and prevention of vasospasm remains challenging. Symptomatic vasospasm occurs in 20-30% of patients but is present in 30-70% of DSAs. Vasospasm usually starts after day 3 of the ictus and usually resolves around day 12. The precise cause of vasospasm is unknown. Treatment involves; 1 Avoid hypovolaemia. Patients with suspected vasospasm will require a central venous catheter (CVC). 2 Pharmacolical : oral or i.v. calcium channel blockers (i.e. Nimodipine) 3 Triple H therapy i.e. hypervolaemia, hypertension and haemodilution). 4 Interventional neuroradiology : angioplasty or intra-arterial papaverine. Note : Triple H thereapy is not recommended in patients with unsecured aneurysms as it increases the risk of re-haemorrhage. 7.2 Hydrocephalus 1 Acute hydrocephalus happens in 20-30% of SAH patients. Chronic hydrocephalus is seen in 18-26% of survivors. 2 Temporary or permanent CSF diversion is recommended. 7.3 Seizures 6
8 1 Seizures occur in 6-18% of SAH patients. 2 Prophylactic anticonvulsants may be considered in the immediate post SAH period. 3 Long term use is not recommended but may be considered in patients with risk factors. 8.0 Nursing Considerations. 1. Self ventilating: Patient must be nursed in area of close observation. 2. Patient ventilated on arrival transfer to intensive care unit. 8.1 Airway Management. 1 Assess rate, rhythm and depth of respirations Frequency of recording is determined by the patient s condition. 2 Assess oxygen saturations frequently using pulse oximetry. 3 Ensure emergency equipment is in close proximity to the patient. 8.2 Neurological Assessment. 1 Perform baseline assessment of the Glasgow Coma Scale, Vital Signs (temperature, pulse, blood pressure) 2 Frequency of observations is determined by the patient s condition and instruction from the medical practitioner. Observations may be recorded quarter hourly 2 hourly. 3 Report any deterioration or subtle changes noted to the medical practitioner promptly. 8.3 Nutrition and Hydration 1 Administer intravenous therapy (sodium lactate or 0.9% normal saline) as prescribed. 2 The fluid regime for each patient is determined by the patient s condition, age and blood pressure maintenance. 3 Monitor urea and electrolytes closely and report abnormalities promptly to the medical practitioner. 4 Monitor for signs of circulatory overload (tachycardia, breathlessness). 5 Assist patient at meal times and provide hand hygiene facilities prior to and after meals. 6 Investigation and procedures: Patients may be required to fast from 12 midnight as per medical practitioner s instruction. 7 Liaise with the Allied Health Professionals (Speech & Language Therapist and Dietician) to assess swallow and ensure adequate nutritional needs are maintained. 8 If nasogastric feeding required maintain care as per local policies and procedures. 7
9 9 Utilising local oral hygiene assessment tools to assess frequency for oral hygiene. Nausea and vomiting: o Assess for signs of nausea and vomiting. o Administer anti-emetics as prescribed. Commonly used anti-emetics include Ondansetron / Metoclopramide / Cyclizine / IM/PO/IV. 8.4 Maintaining a Safe Environment 1 Continuous close monitoring is essential due to the potential risk of sudden deterioration. 2 Resuscitation equipment should be in close proximity to the clinical area. 3 Nurse patient on bed rest or as directed by medical practitioner in a quiet closely supervised area. 4 Assess patient s need for cot sides. Cot sides should be used to maintain the safety of the confused patient and risk of seizure activity. (Refer to local policy and procedures on the use of side rails. Deep Vein Thrombosis 5 Anti-thrombolytic medications are contraindicated or used only at the Consultants discretion due to the potential risk of re bleeding. 6 Apply TED (trans-embolic deterrent) stockings on admission. 7 Patients heels and behind knees must be checked frequently for potential risk of pressure area development. Pressure Area Management 8 Use a pressure sore Risk Assessment Tool e.g. Waterlow Score to assess if a patient s pressure areas are at risk. 9 Assess patients pressure areas (sacrum, heels, and elbows, back of ears & occipital area and document frequency of assessment in nursing care plan. 10 Assess and document presence of pressure areas prior to admission to hospital. 11 Complete pressure ulcer report and refer to the Tissue Viability Nurse for assessment and management as per local policy and procedure. 12 Specify clearly whether hospital or community acquired ulcer. 8.5 Elimination Bladder: 1 Toilet Facilities (bedpan/urinal) if the patient is not catheterised and on strict bedrest. 2 Privacy maintained and hygiene facilities available. 3 Record output on fluid balance chart. 4 If catheter in situ maintain catheter care as per local policies and Guidelines. 8
10 Bowel: 1 Record last bowel motion on admission. 2 Administer laxatives as prescribed by the medical practitioner. 3 If no bowel motion > 3 days, discuss with medical team. Administer PR laxatives as prescribed and record effectiveness in nursing records. 8.6 Wound Care 1 Procedure is explained to patient and relatives by the Consultant or Registrar outlining associated complications and written consent obtained. Cerebral angiogram +/- coiling of an aneurism 2 Assess groin site for oozing & haematoma formation following neurological assessment. 3 Assess pedal pulses (Dorsalis Pedis, Anterior Tibia & Posterior Tibia) Craniotomy & Clipping of Cerebral Aneurism. 4 Assess wound dressing for indication of bleeding & oozing. 5 If redivac insitu, assess and record amount in the fluid balance chart. 6 Remove redivac as per surgeon s instructions, usually 24 hours post surgery. 7 Prior to removal explain to patient procedure about temporary eye swelling & closure post removal. 8 Day 3 Remove wound dressing and clean wound aseptically. Assess for signs of infection. 9 Day 5 - Remove clips or as per Consultant instruction. 10 Educate patient on the care of craniotomy site, hair washing & signs of infection prior to discharge. 9
11 9.0 Reference List Benderson J.B. Sandar Connoly E. Batjer H. Dacey R.J. Dion E.J. Diringer M.N. Duldner J.E. Harbaugh R.e. Aman B. Ronnwaster P&H (2009) Guidelines for the Management of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Haemorrhage: A Statement of Healthare Professionals from a special writing group of Stroke Council, American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Cook NF (2008) Emergency care of the patient with subarachnoid haemorrhage British Journal of Nursing 17 (10): Fiehler J; Burne JV (2009) Factors affecting outcome after endovascular treatment in intracranial aneurysms. Current Opinion in Neurology 22 (1): Lang e F (2009) Nursing management of subarachnoid haemorrhage: a reflective case study British Journal of Neuroscience Nursing Oct; 5 910): (NHS Executive, 1996 Clinical Guidelines: using clinical guidelines to improve patient care within the NHS, DOH, London, p, 10). Rinkel GJE Klijm CJM (2009) Prevention and treatment of medical and neurological complications in patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage Practical Neurology 9 (4):
12 Population screening is not supported by the medical literature. Screening of asymptomatic members of the familial intracranial syndrome has not been demonstrated to be cost-effective and should be considered on an individual basis. In symptomatic members of such families (who have had an aneurysm treated) late radiological evaluation should be considered. There is no consensus on screening method. MRA and CTA combined may be as accurate as DSA. Others have suggested they are complimentary. Catheter angiography remains the Gold Standard screening method should be individualised. Audit and Evaluation. These guidelines will be monitored and evaluated as follows; The performance of the National Neurosurgical Centres against agreed performance indicators. Feedback to the Quality & Clinical Care Directorate of the HSE. The Guidelines will be reviewed one year from the date of their launch nationally utilising these parameters. 11
Sub-arachnoid haemorrhage
 Sub-arachnoid haemorrhage Dr Mary Newton Consultant Anaesthetist The National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery UCL Hospitals NHS Trust mary.newton@uclh.nhs.uk Kiev, Ukraine September 17 th 2009
Sub-arachnoid haemorrhage Dr Mary Newton Consultant Anaesthetist The National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery UCL Hospitals NHS Trust mary.newton@uclh.nhs.uk Kiev, Ukraine September 17 th 2009
Method Hannah Shotton
 #asah Method Hannah Shotton 2 Introduction SAH Rupturing aneurysm Poor outlook Intervention Secure the aneurysm: clipping or coiling Recommended 48 hours Regional Specialist NSC Conservative management
#asah Method Hannah Shotton 2 Introduction SAH Rupturing aneurysm Poor outlook Intervention Secure the aneurysm: clipping or coiling Recommended 48 hours Regional Specialist NSC Conservative management
WHITE PAPER: A GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE
 WHITE PAPER: A GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE Subarachnoid Hemorrhage is a serious, life-threatening type of hemorrhagic stroke caused by bleeding into the space surrounding the brain,
WHITE PAPER: A GUIDE TO UNDERSTANDING SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE Subarachnoid Hemorrhage is a serious, life-threatening type of hemorrhagic stroke caused by bleeding into the space surrounding the brain,
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) Disclosures/Relationships. Click to edit Master title style. Click to edit Master title style.
 Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) William J. Jones, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology Co-Director, UCH Stroke Program Click to edit Master title style Disclosures/Relationships No conflicts of interest
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) William J. Jones, M.D. Assistant Professor of Neurology Co-Director, UCH Stroke Program Click to edit Master title style Disclosures/Relationships No conflicts of interest
SAH READMISSIONS TO NCCU
 SAH READMISSIONS TO NCCU Are they preventable? João Amaral Rebecca Gorf Critical Care Outreach Team - NHNN 2015 Total admissions to NCCU =862 Total SAH admitted to NCCU= 104 (93e) (12.0%) Total SAH readmissions=
SAH READMISSIONS TO NCCU Are they preventable? João Amaral Rebecca Gorf Critical Care Outreach Team - NHNN 2015 Total admissions to NCCU =862 Total SAH admitted to NCCU= 104 (93e) (12.0%) Total SAH readmissions=
TCD AND VASOSPASM SAH
 CURRENT TREATMENT FOR CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS TCD AND VASOSPASM SAH Michigan Sonographers Society 2 Nd Annual Fall Vascular Conference Larry N. Raber RVT-RDMS Clinical Manager General Ultrasound-Neurovascular
CURRENT TREATMENT FOR CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS TCD AND VASOSPASM SAH Michigan Sonographers Society 2 Nd Annual Fall Vascular Conference Larry N. Raber RVT-RDMS Clinical Manager General Ultrasound-Neurovascular
Epidemiology And Treatment Of Cerebral Aneurysms At An Australian Tertiary Level Hospital
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 Number 2 Epidemiology And Treatment Of Cerebral Aneurysms At An Australian Tertiary Level Hospital A Granger, R Laherty Citation A Granger, R Laherty.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 Number 2 Epidemiology And Treatment Of Cerebral Aneurysms At An Australian Tertiary Level Hospital A Granger, R Laherty Citation A Granger, R Laherty.
Neurointensive Care of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Alejandro A. Rabinstein Department of Neurology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, USA
 Neurointensive Care of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Alejandro A. Rabinstein Department of Neurology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, USA The traditional view: asah is a bad disease Pre-hospital mortality
Neurointensive Care of Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Alejandro A. Rabinstein Department of Neurology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, USA The traditional view: asah is a bad disease Pre-hospital mortality
Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury
 Guideline for North Bristol Trust Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury This guideline describes the following: Initial assessment and management of the patient with head injury Indications for CT
Guideline for North Bristol Trust Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury This guideline describes the following: Initial assessment and management of the patient with head injury Indications for CT
Current State of the Art
 SAH Current State of the Art Thomas C. Steineke, M.D., Ph.D. Director of Neurovascular Surgery NJ Neuroscience Institute JFK Medical Center Introduction Signs and symptoms of a problem What are aneurysms
SAH Current State of the Art Thomas C. Steineke, M.D., Ph.D. Director of Neurovascular Surgery NJ Neuroscience Institute JFK Medical Center Introduction Signs and symptoms of a problem What are aneurysms
Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC PAEDIATRICS Case Report Brain AVM with Accompanying Venous Aneurysm with Intracerebral and Intraventricular Hemorrhage Dimitrios Panagopoulos* Neurosurgical Department, University
Guideline scope Subarachnoid haemorrhage caused by a ruptured aneurysm: diagnosis and management
 0 0 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Subarachnoid haemorrhage caused by a ruptured aneurysm: diagnosis and management The Department of Health and Social Care in England
0 0 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Subarachnoid haemorrhage caused by a ruptured aneurysm: diagnosis and management The Department of Health and Social Care in England
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Brain Aneurysm
 Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Brain Aneurysm DIN Department of Interventional Neurology What is SAH? Subarachnoid Haemorrhage is the sudden leaking (haemorrhage) of blood from the blood vessels of brain.
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage and Brain Aneurysm DIN Department of Interventional Neurology What is SAH? Subarachnoid Haemorrhage is the sudden leaking (haemorrhage) of blood from the blood vessels of brain.
Intra-arterial nimodipine for the treatment of vasospasm due to aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
 Romanian Neurosurgery (2016) XXX 4: 461 466 461 DOI: 10.1515/romneu-2016-0074 Intra-arterial nimodipine for the treatment of vasospasm due to aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage A. Chiriac, Georgiana Ion*,
Romanian Neurosurgery (2016) XXX 4: 461 466 461 DOI: 10.1515/romneu-2016-0074 Intra-arterial nimodipine for the treatment of vasospasm due to aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage A. Chiriac, Georgiana Ion*,
ENDOVASCULAR TREATMENT OF CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS AND MANAGEMENT OF RUPTURED ANEURYSM. Vikram Jadhav MD, PhD. 04/12/2018 CentraCare Health St.
 ENDOVASCULAR TREATMENT OF CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS AND MANAGEMENT OF RUPTURED ANEURYSM Vikram Jadhav MD, PhD 04/12/2018 CentraCare Health St. Cloud, MN OBJECTIVES Understand epidemiology and risk factors for
ENDOVASCULAR TREATMENT OF CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS AND MANAGEMENT OF RUPTURED ANEURYSM Vikram Jadhav MD, PhD 04/12/2018 CentraCare Health St. Cloud, MN OBJECTIVES Understand epidemiology and risk factors for
Nursing Management Pre /Post Thrombolysis in Stroke
 Craigavon Area Hospital Guidelines for Nursing Management Pre /Post Thrombolysis in Stroke 1. A senior nurse in the stroke unit will be required to monitor the patients condition post Thrombolysis on a
Craigavon Area Hospital Guidelines for Nursing Management Pre /Post Thrombolysis in Stroke 1. A senior nurse in the stroke unit will be required to monitor the patients condition post Thrombolysis on a
From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is a Stroke? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is a Stroke? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall T. Higashida, M.D., Chair
Flow-diverting stents (in the Treatment of intracranial aneurysms)
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Flow-diverting stents (in the Treatment of intracranial aneurysms) Lysholm Department of Neuroradiology If you would like this document in another language
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Flow-diverting stents (in the Treatment of intracranial aneurysms) Lysholm Department of Neuroradiology If you would like this document in another language
PRACTICE GUIDELINE. DEFINITIONS: Mild head injury: Glasgow Coma Scale* (GCS) score Moderate head injury: GCS 9-12 Severe head injury: GCS 3-8
 PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
PRACTICE GUIDELINE Effective Date: 9-1-2012 Manual Reference: Deaconess Trauma Services TITLE: TRAUMATIC BRAIN INJURY GUIDELINE OBJECTIVE: To provide practice management guidelines for traumatic brain
What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms
 American Society of Neuroradiology American Society of Interventional & Therapeutic Neuroradiology What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee
American Society of Neuroradiology American Society of Interventional & Therapeutic Neuroradiology What You Should Know About Cerebral Aneurysms From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee
(aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage, 17%~60% :SAH. ,asah , 22%~49% : Willis. :1927 Moniz ;(3) 2. ischemic neurological deficit,dind) SAH) SAH ;(6)
 ,, 2. : ;,, :(1), (delayed ;(2) ischemic neurological deficit,dind) ;(3) 2. :SAH ;(4) 5-10 10 HT -1-1 ;(5), 10 SAH ;(6) - - 27%~50%, ( cerebral vasospasm ) Glasgow (Glasgow Coma Scale,GCS), [1],, (aneurysmal
,, 2. : ;,, :(1), (delayed ;(2) ischemic neurological deficit,dind) ;(3) 2. :SAH ;(4) 5-10 10 HT -1-1 ;(5), 10 SAH ;(6) - - 27%~50%, ( cerebral vasospasm ) Glasgow (Glasgow Coma Scale,GCS), [1],, (aneurysmal
CONCISE GUIDE National Clinical Guidelines for Stroke 2nd Edition
 CONCISE GUIDE 2004 National for Stroke 2nd Edition This concise guide summarises the recommendations, graded according to the evidence, from the National 2nd edition. As critical aspects of care are not
CONCISE GUIDE 2004 National for Stroke 2nd Edition This concise guide summarises the recommendations, graded according to the evidence, from the National 2nd edition. As critical aspects of care are not
Neurosurgical decision making in structural lesions causing stroke. Dr Rakesh Ranjan MS, MCh, Dip NB (Neurosurgery)
 Neurosurgical decision making in structural lesions causing stroke Dr Rakesh Ranjan MS, MCh, Dip NB (Neurosurgery) Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Every year, an estimated 30,000 people in the United States experience
Neurosurgical decision making in structural lesions causing stroke Dr Rakesh Ranjan MS, MCh, Dip NB (Neurosurgery) Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Every year, an estimated 30,000 people in the United States experience
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Venous sinus stents (for the treatment of venous sinus stenosis and idiopathic intracranial hypertension) Lysholm Department of Neuroradiology If you would
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Venous sinus stents (for the treatment of venous sinus stenosis and idiopathic intracranial hypertension) Lysholm Department of Neuroradiology If you would
THE EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF CILOSTAZOL IN SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE. A META- ANALYSIS OF RANDOMIZED AND NON RANDOMIZED STUDIES DR. MUHAMMAD F.
 THE EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF CILOSTAZOL IN SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE. A META- ANALYSIS OF RANDOMIZED AND NON RANDOMIZED STUDIES DR. MUHAMMAD F. ISHFAQ ZEENAT QURESHI STROKE INSTITUTE AND UNIVERSITY OF TENNESSEE,
THE EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF CILOSTAZOL IN SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE. A META- ANALYSIS OF RANDOMIZED AND NON RANDOMIZED STUDIES DR. MUHAMMAD F. ISHFAQ ZEENAT QURESHI STROKE INSTITUTE AND UNIVERSITY OF TENNESSEE,
Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes
 Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes By Sheila Smith, MD Swedish Medical Center 1 Disclosures I have no disclosures 2 Course Objectives Review significance and differential
Diagnosis of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH) and Non- Aneurysmal Causes By Sheila Smith, MD Swedish Medical Center 1 Disclosures I have no disclosures 2 Course Objectives Review significance and differential
Cerebral Aneurysms. U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service National Institutes of Health
 Cerebral Aneurysms U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service National Institutes of Health Cerebral Aneurysms What is a cerebral aneurysm? cerebral aneurysm (also known as an
Cerebral Aneurysms U.S. DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service National Institutes of Health Cerebral Aneurysms What is a cerebral aneurysm? cerebral aneurysm (also known as an
Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care 3.6 Acute Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
 Last Updated: May 21, 2013 Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care 2011-2013 Update Contents Search Strategy... 2 CSN Current Recommendations...Error!
Last Updated: May 21, 2013 Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care 2011-2013 Update Contents Search Strategy... 2 CSN Current Recommendations...Error!
Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts
 Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is the build up of an excess
Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is the build up of an excess
Management of Cerebral Aneurysms in Polycystic Kidney Disease. Dr H Stockley Consultant Neuroradiologist Greater Manchester Neuroscience Centre
 Management of Cerebral Aneurysms in Polycystic Kidney Disease Dr H Stockley Consultant Neuroradiologist Greater Manchester Neuroscience Centre What is a cerebral aneurysm? Developmental degenerative arterial
Management of Cerebral Aneurysms in Polycystic Kidney Disease Dr H Stockley Consultant Neuroradiologist Greater Manchester Neuroscience Centre What is a cerebral aneurysm? Developmental degenerative arterial
TURN IT UP TO 11: LP IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SAH. Matt Greer February 10 th, 2015
 TURN IT UP TO 11: LP IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SAH Matt Greer February 10 th, 2015 IN CASE YOU MISSED THE REFERENCE HEADACHES IN THE ED Account for approximately 2% of ED visits 1% of these are due to SAH Approximately
TURN IT UP TO 11: LP IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SAH Matt Greer February 10 th, 2015 IN CASE YOU MISSED THE REFERENCE HEADACHES IN THE ED Account for approximately 2% of ED visits 1% of these are due to SAH Approximately
FORM ID. Patient's Personal Details. SECTION A : Medical Record of the Patient. Name. Policy Number. NRIC/Old IC/Passport/Birth Cert/Others
 CRITICAL ILLNESS CLAIM - DOCTOR'S STATEMENT Brain and Nerve Related Conditions Note: This form is to be completed at the Patient s expense by the Attending Physician/ Surgeon who treated the patient. Patient's
CRITICAL ILLNESS CLAIM - DOCTOR'S STATEMENT Brain and Nerve Related Conditions Note: This form is to be completed at the Patient s expense by the Attending Physician/ Surgeon who treated the patient. Patient's
Bleeding in the brain: haemorrhagic stroke
 Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Bleeding in the brain: haemorrhagic stroke Some strokes are due to bleeding in or around the brain, and are known as haemorrhagic strokes.
Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Bleeding in the brain: haemorrhagic stroke Some strokes are due to bleeding in or around the brain, and are known as haemorrhagic strokes.
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage & Vasospasm basic level
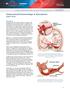 Subarachnoid Hemorrhage & Vasospasm basic level Overview Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is a serious, lifethreatening type of stroke caused by bleeding into the space surrounding the brain. A stroke occurs
Subarachnoid Hemorrhage & Vasospasm basic level Overview Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is a serious, lifethreatening type of stroke caused by bleeding into the space surrounding the brain. A stroke occurs
WEB device for treating brain (intracranial) aneurysms
 WEB device for treating brain (intracranial) aneurysms This leaflet explains more about the WEB device, including the benefits, risks and any alternatives and what you can expect when you come to hospital.
WEB device for treating brain (intracranial) aneurysms This leaflet explains more about the WEB device, including the benefits, risks and any alternatives and what you can expect when you come to hospital.
Summary of some of the landmark articles:
 Summary of some of the landmark articles: The significance of unruptured intracranial saccular aneurysms: Weibers et al Mayo clinic. 1987 1. 131 patients with 161 aneurysms were followed up at until death,
Summary of some of the landmark articles: The significance of unruptured intracranial saccular aneurysms: Weibers et al Mayo clinic. 1987 1. 131 patients with 161 aneurysms were followed up at until death,
LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT. Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT
 LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT OUTLINE Causes Head Injury Clinical Features Complications Rapid Assessment Glasgow Coma Scale Classification
LOSS OF CONSCIOUSNESS & ASSESSMENT Sheba Medical Center Acute Medicine Department MATTHEW WRIGHT OUTLINE Causes Head Injury Clinical Features Complications Rapid Assessment Glasgow Coma Scale Classification
ATTENDING PHYSICIAN'S STATEMENT STROKE / BRAIN ANEURYSM SURGERY OR CEREBRAL SHUNT INSERTION / CAROTID ARTERY SURGERY
 ATTENDING PHYSICIAN'S STATEMENT STROKE / BRAIN ANEURYSM SURGERY OR CEREBRAL SHUNT INSERTION / CAROTID ARTERY SURGERY A) Patient s Particulars Name of Patient Gender NRIC/FIN or Passport No. Date of Birth
ATTENDING PHYSICIAN'S STATEMENT STROKE / BRAIN ANEURYSM SURGERY OR CEREBRAL SHUNT INSERTION / CAROTID ARTERY SURGERY A) Patient s Particulars Name of Patient Gender NRIC/FIN or Passport No. Date of Birth
Clinical manifestations, diagnosis and medical management of
 Clinical manifestations, diagnosis and medical management of aneurysmal SAH David Bervini, MD MAdvSurg Department of Neurosurgery Inselspital University of Bern Switzerland 1 2 3 Aneurysmal SAH Incidence:
Clinical manifestations, diagnosis and medical management of aneurysmal SAH David Bervini, MD MAdvSurg Department of Neurosurgery Inselspital University of Bern Switzerland 1 2 3 Aneurysmal SAH Incidence:
Using Embolization to Treat a Brain Aneurysm
 Using Embolization to Treat a Brain Aneurysm Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: what a brain aneurysm is how embolization treatment helps how to prepare what to expect who
Using Embolization to Treat a Brain Aneurysm Information for patients and families Read this booklet to learn: what a brain aneurysm is how embolization treatment helps how to prepare what to expect who
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG
 Title: Author: Speciality/ Division: Directorate: Date Uploaded: Review Date: September 2019 CG ID TAG CG0423 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Clinical Guideline for Alteplase in intra-arterial thrombolysis
Title: Author: Speciality/ Division: Directorate: Date Uploaded: Review Date: September 2019 CG ID TAG CG0423 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Clinical Guideline for Alteplase in intra-arterial thrombolysis
GUIDELINES FOR THE EARLY MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE
 2018 UPDATE QUICK SHEET 2018 American Heart Association GUIDELINES FOR THE EARLY MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE A Summary for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American
2018 UPDATE QUICK SHEET 2018 American Heart Association GUIDELINES FOR THE EARLY MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS WITH ACUTE ISCHEMIC STROKE A Summary for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American
Guideline for the Acute Management of Stroke in Paediatric Patients with Sickle Cell Disease
 Guideline for the Acute Management of Stroke in Paediatric Patients with Sickle Cell Disease Summary Outline of the presentation of stroke in paediatric patients with sickle cell disease, urgent investigations,
Guideline for the Acute Management of Stroke in Paediatric Patients with Sickle Cell Disease Summary Outline of the presentation of stroke in paediatric patients with sickle cell disease, urgent investigations,
Neurosurgical Management of Stroke
 Overview Hemorrhagic Stroke Ischemic Stroke Aneurysmal Subarachnoid hemorrhage Neurosurgical Management of Stroke Jesse Liu, MD Instructor, Neurological Surgery Initial management In hospital management
Overview Hemorrhagic Stroke Ischemic Stroke Aneurysmal Subarachnoid hemorrhage Neurosurgical Management of Stroke Jesse Liu, MD Instructor, Neurological Surgery Initial management In hospital management
STROKE INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES. When the student has finished this module, he/she will be able to:
 STROKE INTRODUCTION Stroke is the medical term for a specific type of neurological event that causes damage to the brain. There are two types of stroke, but both types of stroke cause the same type of
STROKE INTRODUCTION Stroke is the medical term for a specific type of neurological event that causes damage to the brain. There are two types of stroke, but both types of stroke cause the same type of
Department of Neurological Surgery
 Department of Neurological Surgery CAT 1 A Basic Privileges: Patient management, including H & Ps and diagnostic and therapeutic treatments, procedures and interventions, Requiring a level of training
Department of Neurological Surgery CAT 1 A Basic Privileges: Patient management, including H & Ps and diagnostic and therapeutic treatments, procedures and interventions, Requiring a level of training
Report of the Welsh Neuroscience External Expert Review Group. All Wales Recommendations
 Report of the Welsh Neuroscience External Expert Review Group All Wales Recommendations Main Recommendations 1. The workforce delivering all aspects of care to people with acute and long term neurological
Report of the Welsh Neuroscience External Expert Review Group All Wales Recommendations Main Recommendations 1. The workforce delivering all aspects of care to people with acute and long term neurological
B S PERERA ORATION 2009 ANAESTHETIC MANAGEMENT FOR INTERVENTIONAL NEURORADIOLOGY
 Sri Lankan Journal of Anaesthesiology 18(1) : 10-14 (20) B S PERERA ORATION 2009 ANAESTHETIC MANAGEMENT FOR INTERVENTIONAL NEURORADIOLOGY Dr Shirani Hapuarachchi Interventional neuroradiology dates back
Sri Lankan Journal of Anaesthesiology 18(1) : 10-14 (20) B S PERERA ORATION 2009 ANAESTHETIC MANAGEMENT FOR INTERVENTIONAL NEURORADIOLOGY Dr Shirani Hapuarachchi Interventional neuroradiology dates back
4/10/2018. The Surgical Treatment of Cerebral Aneurysms. Aneurysm Locations. Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Jerone Kennedy, M.D.
 The Surgical Treatment of Cerebral Aneurysms Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Jerone Kennedy, M.D. Medical Director, Vascular Neurosurgery CentraCare Health-Neurosciences St. Cloud Hospital Aneurysm
The Surgical Treatment of Cerebral Aneurysms Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Jerone Kennedy, M.D. Medical Director, Vascular Neurosurgery CentraCare Health-Neurosciences St. Cloud Hospital Aneurysm
If you have any further questions, please speak to a doctor or nurse caring for you.
 Surgical Removal of a Paraganglioma of the Temporal Bone This leaflet explains more about surgery for the removal of a paraganglioma of the temporal bone, including the benefits, risks and any alternatives
Surgical Removal of a Paraganglioma of the Temporal Bone This leaflet explains more about surgery for the removal of a paraganglioma of the temporal bone, including the benefits, risks and any alternatives
Thrombolysis Delivery, Care, and Monitoring. 5 Acute Trusts - 6 Primary Care Trusts Ambulance Trust 4 Local Authorities
 Thrombolysis Delivery, Care, and Monitoring Documentation & Pathways Need to follow locally agreed policies and procedures Follow thrombolysis pathway? Need to complete Sits database Weight Dose matters!
Thrombolysis Delivery, Care, and Monitoring Documentation & Pathways Need to follow locally agreed policies and procedures Follow thrombolysis pathway? Need to complete Sits database Weight Dose matters!
Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury. Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center
 Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center Traumatic Brain Injury is Common 235,000 Americans hospitalized for non-fatal TBI
Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center Traumatic Brain Injury is Common 235,000 Americans hospitalized for non-fatal TBI
Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
Code Stroke Intervention: Endovascular therapy for asah and management J. DIEGO LOZANO MD INTERVENTIONAL NEURORADIOLOGY
 Code Stroke Intervention: Endovascular therapy for asah and management J. DIEGO LOZANO MD INTERVENTIONAL NEURORADIOLOGY Disclosures None Part B. Objectives Epidemiology of asah Concept: What is a brain
Code Stroke Intervention: Endovascular therapy for asah and management J. DIEGO LOZANO MD INTERVENTIONAL NEURORADIOLOGY Disclosures None Part B. Objectives Epidemiology of asah Concept: What is a brain
NEUROSURGICAL EMERGENCY GUIDELINE DEVELOPMENT GROUP P3 NEURO CENTER OF NEUROSCIENCE RESEARCH AND SERVICE USM
 NEUROSURGICAL EMERGENCY GUIDELINE DEVELOPMENT GROUP P3 NEURO CENTER OF NEUROSCIENCE RESEARCH AND SERVICE USM Chairperson Professor Dr Zamzuri Idris Head of Department Members Associate Professor Dato Dr
NEUROSURGICAL EMERGENCY GUIDELINE DEVELOPMENT GROUP P3 NEURO CENTER OF NEUROSCIENCE RESEARCH AND SERVICE USM Chairperson Professor Dr Zamzuri Idris Head of Department Members Associate Professor Dato Dr
Faculty of Clinical Forensic Medicine Committee 1/2018
 Guideline Subject: Clinical Forensic Assessment and Management of Non-Fatal Strangulation Approval Date: January 2018 Review Date: January 2021 Review By: Number: Faculty of Clinical Forensic Medicine
Guideline Subject: Clinical Forensic Assessment and Management of Non-Fatal Strangulation Approval Date: January 2018 Review Date: January 2021 Review By: Number: Faculty of Clinical Forensic Medicine
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery. Cerebral angiogram (Overnight stay) Neurovascular Team
 National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Cerebral angiogram (Overnight stay) Neurovascular Team If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of an
National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Cerebral angiogram (Overnight stay) Neurovascular Team If you would like this document in another language or format or if you require the services of an
11/27/2017. Stroke Management in the Neurocritical Care Unit. Conflict of interest. Karel Fuentes MD Medical Director of Neurocritical Care
 Stroke Management in the Neurocritical Care Unit Karel Fuentes MD Medical Director of Neurocritical Care Conflict of interest None Introduction Reperfusion therapy remains the mainstay in the treatment
Stroke Management in the Neurocritical Care Unit Karel Fuentes MD Medical Director of Neurocritical Care Conflict of interest None Introduction Reperfusion therapy remains the mainstay in the treatment
Interventions in the Management of Acute Stroke. Dr Md Shafiqul Islam Associate Professor Neurosurgery Dhaka Medical College Hospital
 Interventions in the Management of Acute Stroke Dr Md Shafiqul Islam Associate Professor Neurosurgery Dhaka Medical College Hospital Acute stroke intervention Number of stroke patients increasing day by
Interventions in the Management of Acute Stroke Dr Md Shafiqul Islam Associate Professor Neurosurgery Dhaka Medical College Hospital Acute stroke intervention Number of stroke patients increasing day by
Care in the Last Days of Life
 Care in the Last Days of Life Introduction This guideline is an aid to clinical decision making and good practice in person-centred care for patients who are deteriorating and at risk of dying. The patient
Care in the Last Days of Life Introduction This guideline is an aid to clinical decision making and good practice in person-centred care for patients who are deteriorating and at risk of dying. The patient
Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke
 Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Original Contribution Spontaneous Recanalization after Complete Occlusion of the Common Carotid Artery with Subsequent Embolic Ischemic Stroke Abstract Introduction: Acute carotid artery occlusion carries
Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Presentation and Complications
 Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Presentation and Complications Sherry H-Y. Chou MD MMSc FNCS Department of Critical Care Medicine, Neurology and Neurosurgery University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine
Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Presentation and Complications Sherry H-Y. Chou MD MMSc FNCS Department of Critical Care Medicine, Neurology and Neurosurgery University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine
Epilepsy after two different neurosurgical approaches
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 1052-1056 Epilepsy after two different neurosurgical approaches to the treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysm R. J. CABRAL, T. T. KING,
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1976, 39, 1052-1056 Epilepsy after two different neurosurgical approaches to the treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysm R. J. CABRAL, T. T. KING,
Guideline scope Stroke and transient ischaemic attack in over 16s: diagnosis and initial management (update)
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Stroke and transient ischaemic attack in over s: diagnosis and initial management (update) 0 0 This will update the NICE on stroke and
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Guideline scope Stroke and transient ischaemic attack in over s: diagnosis and initial management (update) 0 0 This will update the NICE on stroke and
Extracranial to intracranial bypass for intracranial atherosclerosis
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Extracranial to intracranial bypass for intracranial atherosclerosis In cerebrovascular disease, blood vessels
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Extracranial to intracranial bypass for intracranial atherosclerosis In cerebrovascular disease, blood vessels
Update in Diagnosis and Management of Intracranial Aneurysms for Primary Health Care Providers November 15, 2012 Boston, Massachusetts
 Update in Diagnosis and Management of Intracranial Aneurysms for Primary Health Care Providers November 15, 2012 Boston, Massachusetts Educational Partner: Session 1: Update in Diagnosis and Management
Update in Diagnosis and Management of Intracranial Aneurysms for Primary Health Care Providers November 15, 2012 Boston, Massachusetts Educational Partner: Session 1: Update in Diagnosis and Management
Ischemia cerebrale dopo emorragia subaracnoidea Vasospasmo e altri nemici
 Ischemia cerebrale dopo emorragia subaracnoidea Vasospasmo e altri nemici Nino Stocchetti Milan University Neuroscience ICU Ospedale Policlinico IRCCS Milano stocchet@policlinico.mi.it Macdonald RL et
Ischemia cerebrale dopo emorragia subaracnoidea Vasospasmo e altri nemici Nino Stocchetti Milan University Neuroscience ICU Ospedale Policlinico IRCCS Milano stocchet@policlinico.mi.it Macdonald RL et
Treatment of Acute Hydrocephalus After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage With Serial Lumbar Puncture
 19 Treatment of Acute After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage With Serial Lumbar Puncture Djo Hasan, MD; Kenneth W. Lindsay, PhD, FRCS; and Marinus Vermeulen, MD Downloaded from http://ahajournals.org by on vember,
19 Treatment of Acute After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage With Serial Lumbar Puncture Djo Hasan, MD; Kenneth W. Lindsay, PhD, FRCS; and Marinus Vermeulen, MD Downloaded from http://ahajournals.org by on vember,
Subarachnoid Haemorrhage
 2011 Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Subarachnoid Haemorrhage This pamphlet will briefly describe what may happen to a person who has a subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH). We would like to encourage you to read this
2011 Subarachnoid Haemorrhage Subarachnoid Haemorrhage This pamphlet will briefly describe what may happen to a person who has a subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH). We would like to encourage you to read this
10. Severe traumatic brain injury also see flow chart Appendix 5
 10. Severe traumatic brain injury also see flow chart Appendix 5 Introduction Severe traumatic brain injury (TBI) is the leading cause of death in children in the UK, accounting for 15% of deaths in 1-15
10. Severe traumatic brain injury also see flow chart Appendix 5 Introduction Severe traumatic brain injury (TBI) is the leading cause of death in children in the UK, accounting for 15% of deaths in 1-15
What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)?
 American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
American Society of Neuroradiology What Is an Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)? From the Cerebrovascular Imaging and Intervention Committee of the American Heart Association Cardiovascular Council Randall
Attending Physician Statement- Stroke
 Instruction to doctor: This patient is insured with us against the happening of certain contingent events associated with his health A claim has been submitted in connection with Stroke / Intracranial
Instruction to doctor: This patient is insured with us against the happening of certain contingent events associated with his health A claim has been submitted in connection with Stroke / Intracranial
Protocol for IV rtpa Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke
 Protocol for IV rtpa Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke Acute stroke management is progressing very rapidly. Our team offers several options for acute stroke therapy, including endovascular therapy and
Protocol for IV rtpa Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke Acute stroke management is progressing very rapidly. Our team offers several options for acute stroke therapy, including endovascular therapy and
/ / / / / / Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA. Participant ID: Hospital Code: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
 Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis Participant ID: Hospital Code: Hospital Abstraction: Stroke/TIA History and Hospital Record 1. Was the participant hospitalized as an immediate consequence of this
FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY
 FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY Information for Patients WHAT IS FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY? The foot and the ankle are crucial for human movement. The balanced action of many bones, joints, muscles and tendons
FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY Information for Patients WHAT IS FOOT AND ANKLE ARTHROSCOPY? The foot and the ankle are crucial for human movement. The balanced action of many bones, joints, muscles and tendons
Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care. (Updated 2008) Section # 3 Section # 3 Hyperacute Stroke Management
 Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care (Updated 2008) Section # 3 Section # 3 Hyperacute Stroke Management Reorganization of Recommendations 2008 2006 RECOMMENDATIONS: 2008 RECOMMENDATIONS:
Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care (Updated 2008) Section # 3 Section # 3 Hyperacute Stroke Management Reorganization of Recommendations 2008 2006 RECOMMENDATIONS: 2008 RECOMMENDATIONS:
HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM
 REVIEW DATE REVIEWER'S ID HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM : DISCHARGE DATE: RECORDS FROM: Hospitalization ER Please check all that may apply: Myocardial Infarction Pages 2, 3,
REVIEW DATE REVIEWER'S ID HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM : DISCHARGE DATE: RECORDS FROM: Hospitalization ER Please check all that may apply: Myocardial Infarction Pages 2, 3,
presents the fourth annual HONEY BASH GALA The Cira Centre Atrium
 presents the fourth annual HONEY BASH GALA S a t u r d a y, S e p t e m b e r 1 6, 2 0 1 7 The Cira Centre Atrium P H I L A D E L P H I A, P E N N S Y LVA N I A S P O N S O R S H I P & B E N E FA C T O
presents the fourth annual HONEY BASH GALA S a t u r d a y, S e p t e m b e r 1 6, 2 0 1 7 The Cira Centre Atrium P H I L A D E L P H I A, P E N N S Y LVA N I A S P O N S O R S H I P & B E N E FA C T O
Neurosurgery (Orthopaedic PGY-1) Goals. Objectives
 Neurosurgery (Orthopaedic PGY-1) Length: 1 month of PGY-1 (Orthopaedic Designated Residents) or 1 month of PGY-2, -3, or -4 year Location: The Queen's Medical Center Primary Supervisor: William Obana,
Neurosurgery (Orthopaedic PGY-1) Length: 1 month of PGY-1 (Orthopaedic Designated Residents) or 1 month of PGY-2, -3, or -4 year Location: The Queen's Medical Center Primary Supervisor: William Obana,
Surgical Privileges Form: "Neurosurgery" Clinical Privileges Request. Requested (To be completed by the applicant) Not Recommended (For committee use)
 Surgical Form: Clinical Request "Neurosurgery" Applicant s Name:. License No. (If Any):... Date:... Scope of Practice:. Facility:.. Place of Work:. the applicant) CATEGORY I: Core : 1. Interpretation of
Surgical Form: Clinical Request "Neurosurgery" Applicant s Name:. License No. (If Any):... Date:... Scope of Practice:. Facility:.. Place of Work:. the applicant) CATEGORY I: Core : 1. Interpretation of
Screening and Management of Blunt Cereberovascular Injuries (BCVI)
 Grady Memorial Hospital Trauma Service Guidelines Screening and Management of Blunt Cereberovascular Injuries (BCVI) BACKGROUND Blunt injury to the carotid or vertebral vessels (blunt cerebrovascular injury
Grady Memorial Hospital Trauma Service Guidelines Screening and Management of Blunt Cereberovascular Injuries (BCVI) BACKGROUND Blunt injury to the carotid or vertebral vessels (blunt cerebrovascular injury
Moving from a Primary Stroke Center to a Comprehensive Stroke Center
 Moving from a Primary Stroke Center to a Comprehensive Stroke Center MJ Hampel, MPH, MBA The Joint Commission October 19, 2012 Presenter Disclosure Information MJ Hampel Moving from a Primary Stroke Center
Moving from a Primary Stroke Center to a Comprehensive Stroke Center MJ Hampel, MPH, MBA The Joint Commission October 19, 2012 Presenter Disclosure Information MJ Hampel Moving from a Primary Stroke Center
Long term follow-up of patients with coiled intracranial aneurysms Sprengers, M.E.S.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Long term follow-up of patients with coiled intracranial aneurysms Sprengers, M.E.S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Sprengers, M. E. S.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Long term follow-up of patients with coiled intracranial aneurysms Sprengers, M.E.S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Sprengers, M. E. S.
DOCUMENT CONTROL PAGE
 DOCUMENT CONTROL PAGE Title Title: UNDERGOING SPINAL DEFORMITY SURGERY Version: 2 Reference Number: Supersedes Supersedes: all other versions Description of Amendment(s): Revision of analgesia requirements
DOCUMENT CONTROL PAGE Title Title: UNDERGOING SPINAL DEFORMITY SURGERY Version: 2 Reference Number: Supersedes Supersedes: all other versions Description of Amendment(s): Revision of analgesia requirements
Management of the Endovascular Patient and Acute Emergencies in the Angio Suite
 Management of the Endovascular Patient and Acute Emergencies in the Angio Suite June 9, 2015 Bridget Cantrell, APN, CNP Endovascular Neurosurgery Advocate Medical Group No Disclosures The human brain is
Management of the Endovascular Patient and Acute Emergencies in the Angio Suite June 9, 2015 Bridget Cantrell, APN, CNP Endovascular Neurosurgery Advocate Medical Group No Disclosures The human brain is
WEB intracranial aneurysm device for treating cerebral aneurysms
 WEB intracranial aneurysm device for treating cerebral aneurysms Information for patients This booklet explains how the WEB device is used to treat cerebral (brain) aneurysms, and the benefits and risks
WEB intracranial aneurysm device for treating cerebral aneurysms Information for patients This booklet explains how the WEB device is used to treat cerebral (brain) aneurysms, and the benefits and risks
Guidelines for the Conduct of Epidural Analgesia for Parturients
 Page 1 of 6 Guidelines for the Conduct of Epidural Analgesia for Version Effective Date 1 Feb 1993 (Reviewed Feb 2002) 2 Oct 2012 Document No. HKCA P4 v2 Prepared by College Guidelines Committee Endorsed
Page 1 of 6 Guidelines for the Conduct of Epidural Analgesia for Version Effective Date 1 Feb 1993 (Reviewed Feb 2002) 2 Oct 2012 Document No. HKCA P4 v2 Prepared by College Guidelines Committee Endorsed
STROKE SERVICE STANDARDS. CLINICAL STANDARDS COMMITTEE June 2014
 STROKE SERVICE STANDARDS CLINICAL STANDARDS COMMITTEE June 2014 A Bhalla (Chair), G Subramanian P Gompertz, D Wilson, B Patel, K Harkness, T Hassan, MR Chowdhury, J Korner, F Doubal STROKE SERVICE STANDARDS
STROKE SERVICE STANDARDS CLINICAL STANDARDS COMMITTEE June 2014 A Bhalla (Chair), G Subramanian P Gompertz, D Wilson, B Patel, K Harkness, T Hassan, MR Chowdhury, J Korner, F Doubal STROKE SERVICE STANDARDS
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Procedure (TAVI)
 Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
STROKE PROGRAM PATIENT RESOURCE GUIDE
 STROKE PROGRAM PATIENT RESOURCE GUIDE TABLE OF Contents STROKE Prevention Stroke Prevention............................................ 1 Risk Factors for Stroke.......................................1
STROKE PROGRAM PATIENT RESOURCE GUIDE TABLE OF Contents STROKE Prevention Stroke Prevention............................................ 1 Risk Factors for Stroke.......................................1
Understanding Stroke
 MINTO PREVENTION & REHABILITATION CENTRE CENTRE DE PREVENTION ET DE READAPTATION MINTO Understanding Stroke About This Kit Stroke is the fourth leading cause of death in Canada after heart disease and
MINTO PREVENTION & REHABILITATION CENTRE CENTRE DE PREVENTION ET DE READAPTATION MINTO Understanding Stroke About This Kit Stroke is the fourth leading cause of death in Canada after heart disease and
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Medical technology guidance SCOPE Pipeline embolisation device for the treatment of
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Medical technology guidance SCOPE Pipeline embolisation device for the treatment of 1 Technology complex intracranial aneurysms 1.1 Description of
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Medical technology guidance SCOPE Pipeline embolisation device for the treatment of 1 Technology complex intracranial aneurysms 1.1 Description of
Canadian Stroke Best Practices Initial ED Evaluation of Acute Stroke and Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA) Order Set (Order Set 1)
 Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care: All patients presenting to an emergency department with suspected stroke or transient ischemic attack must have an immediate clinical evaluation
Canadian Best Practice Recommendations for Stroke Care: All patients presenting to an emergency department with suspected stroke or transient ischemic attack must have an immediate clinical evaluation
Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism A pulmonary embolism (PE) is
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism A pulmonary embolism (PE) is
Distal anterior cerebral artery (DACA) aneurysms are. Case Report
 248 Formos J Surg 2010;43:248-252 Distal Anterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysm: an Infrequent Cause of Transient Ischemic Attack Followed by Diffuse Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Report of a Case Che-Chuan Wang
248 Formos J Surg 2010;43:248-252 Distal Anterior Cerebral Artery Aneurysm: an Infrequent Cause of Transient Ischemic Attack Followed by Diffuse Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Report of a Case Che-Chuan Wang
Course Handouts & Post Test
 STROKE/COMA: DISEASE TRAJECTORY AND HOSPICE ELIGIBILITY Terri L. Maxwell PhD, APRN VP, Strategic Initiatives Weatherbee Resources Hospice Education Network Course Handouts & Post Test To download presentation
STROKE/COMA: DISEASE TRAJECTORY AND HOSPICE ELIGIBILITY Terri L. Maxwell PhD, APRN VP, Strategic Initiatives Weatherbee Resources Hospice Education Network Course Handouts & Post Test To download presentation
PSEUDO-SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE AFTER INADVERTENT DURAL PUNCTURE DURING CERVICAL EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION
 PSEUDO-SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE AFTER INADVERTENT DURAL PUNCTURE DURING CERVICAL EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION HAI NGUYEN, DO, MPH Anesthesiology Resident (University of Kansas Wichita) JOEL CAVAZOS, MD Pain
PSEUDO-SUBARACHNOID HEMORRHAGE AFTER INADVERTENT DURAL PUNCTURE DURING CERVICAL EPIDURAL STEROID INJECTION HAI NGUYEN, DO, MPH Anesthesiology Resident (University of Kansas Wichita) JOEL CAVAZOS, MD Pain
Patient Information BRAIN ANEURYSMS (Including screening for familial aneurysms)
 Patient Information BRAIN ANEURYSMS (Including screening for familial aneurysms) 1 What is a cerebral aneurysm? An aneurysm is formed when there is a weakness in the blood vessel causing a ballooning or
Patient Information BRAIN ANEURYSMS (Including screening for familial aneurysms) 1 What is a cerebral aneurysm? An aneurysm is formed when there is a weakness in the blood vessel causing a ballooning or
Referral Criteria for Medical CT Radiation Exposures. Neuro Referrals
 Referral Criteria for Medical CT Radiation Exposures Neuro Referrals CHH & HRI The Ionising Radiation (Medical Exposure) Regulations 2017 Document Control Reference No: 3.2 First published: 2016 Version:
Referral Criteria for Medical CT Radiation Exposures Neuro Referrals CHH & HRI The Ionising Radiation (Medical Exposure) Regulations 2017 Document Control Reference No: 3.2 First published: 2016 Version:
