"Spontaneous" and Traumatic Rupture of the Diaphragm:
|
|
|
- Andrew Cole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 "Spontaneous" and Traumatic Rupture of the Diaphragm: Long-Term Results SZABOLCS M. BEKASSY, M.D., KAMAL S. DAVE, M.D., GEOFFREY H. WOOLER, M.D., MARIAN 1. IONESCU, M.D. TRAUMATIC RUPTURE of the diaphragm is usually caused by stab wounds or crush injuries to the chest and abdomen. It is becoming more common due to an increase in road accidents and violent trauma. On the other hand "spontaneous" rupture of the diaphragm is extremely rare. Only two cases, to our knowledge, have been reported so far, and one is from this department.8'23 Long-term results of the surgical repair of ruptured diaghragm have been published by only a few authors.'2,19 The purpose of this paper is to report our experience with 14 patients with traumatic and five with "spontaneous" rupture of the diaphragm, and to discuss the important diagnostic aspects, the surgical management and the long-term results. Clinical Material Nineteen patients with ruptured diaphragms have been seen in this hospital between 1940 and There were 17 males and two females. Their ages ranged from seven to 66 years with an average of 41 years. All had rupture of the left side of the diaphragm. Fourteen patients had a history of trauma (four had bullet wounds and ten crush injuries). Five other patients were considered to have sustained "spontaneous" rupture. In four rupture occurred after sudden severe exertion without direct or indirect trauma to the chest or abdomen (in one while lifting a wardrobe, in another after a severe twisting movement, and in two others during heavy physical work in a mine). In the fifth patient, rupture of the Submitted for publication January 25, Reprint requests: M. I. Ionescu, Department of Cardio-thoracic Surgery, The General Infirmary, Leeds, Great Britain. From the Department of Cardio-thoracic Surgery, The General Infirmary at Leeds and Leeds University, Leeds, Great Britain diaphragm occurred after a severe bout of coughing 6 days after left pneumonectomy. Of the 14 patients with traumatic rupture, the diagnosis was made in three immediately following injury, while in 11 there was a delay of from 1 to 36 years. In half of the patients with traumatic rupture the correct diagnosis was made more than 5 years after injury. Of the five patients with "spontaneous" rupture of the diaphragm, only one was diagnosed within 3 days of the onset of symptoms. In the remainder, although the onset of symptoms was sudden, they subsided and a long symptom-free period followed. The diagnosis in these patients was established between 9 months and 4 years after the onset of symptoms. Clinical Findings In the traumatic group, dyspnea, epigastric and/or subcostal pain and dyspepsia were the most common presenting symptoms, while in the "spontaneous" group nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain and left-sided shoulder pain were more often encountered (Table 1). In the traumatic group, five patients had diminished air entry over the left hemithorax, one had audible intestinal sounds in the chest, and another had surgical emphysema following fractured ribs. Nine patients of the traumatic group had associated injuries which are summarized in Table 2. In the "spontaneous" group physical examination had revealed no abnormal findings attributable to the ruptured diaphragm in three patients. Signs of upper intestinal obstruction were found in one patient and in 320
2 Vol * No. 3 TABLE 1. Presenting Symptoms in 14 Patients with Traumatic and Five with "Spontaneous" Rutpture of the Diaphragm. Traumatic Rupture TRAUMATIC RUPTURE OF THE DIAPHRAGM 321 "Spontaneous" Rupture Epigastric pain 10 3 Dyspnoea 10 1 Left sided subcostal pain 9 Dyspepsia 7 Loss of weight 4 1 Nausea and vomiting 2 4 Respiratory distress 3 1 Left sided shoulder pain 2 3 Acute intestinal obstruction 1 2 Cardio-circulatory shock 2 Dysphagia 2 Melena 1 Gurgling noises in the chest 1 TABLE 3. Radiological Findings in 14 Patients with Traumatic and Five with "Spontaneous" Rupture of the Diaphragm Plain Chest Radiographs-19 Traumatic "Spontaneous" patients Rupture Rupture Displacement of the heart and mediastinum to the right 6 2 Elevated diaphragm on the left side 3 Bowel shadows in the left hemithorax 2 1 Atelectasis of the left lower lobe 3 1 Left pleural effusion 4 1 Right pleural effusion 1 Left pneumothorax 3 Right pneumothorax 3 Opacity suggesting tumour of the left lower lobe 1 Contrast Radiologic Examination-14 patients Stomach in the left hemithorax 9 2 Colon in the left hemithorax 6 another one there had been signs of struction and fluid in the left pleural large bowel obcavity. Radiological Findings Plain X-rays of the chest showed some abnormality in all 19 patients but only in two was a definite diagnosis made by this examination. Suspicion of the lesion was confirmed in 14 cases by contrast radiographic studies (Table 3). In three patients the correct diagnosis was not made until operation (one patient with spontaneous rupture of the diaphragm following pneumonectomy had been first diagnosed as volvulus of the stomach; another was thought to have a volvulus of the stomach also; and in the third patient the lesion was mistaken for a left lower lobe tumor. Operative Findings Eighteen patients have had operative repair of the ruptured diaphragm. One patient, who is now 76 years old, refused operation. She is being followed regularly in the outpatient clinic. A left thoracotomy was used in 16 patients and a left thoracoabdominal approach in two. All 18 patients had rupture of the left diaphragm. In the traumatic group three had lesions in the muscular portion and ten in the tendinous portion, while in the "spontaneous" group all five had tears in the tendinous part of the diaphragm. In one of the traumatic cases the tear extended from the central tendon into the pericardial sac, opening it TABLE 2. Associated Lesions in Nine Patients with Traumatic Rupture of the Diaphragm Fracture of the skull, cerebral commotion 1 Fractured ribs on one or both sides and pneumothorax 3 Multiple fractures of extremities 5 Fractured pelvis 3 widely. The left lobe of the liver had herniated and had adhered to the epicardium. At operation 9 months after injury the diaphragm had been repaired but the pericardial sac had to be left open due to its retraction. The length of the tears varied from 2.5 to 8 cm. Three patients in each group had circular tears with irregular margins, while the remainder had linear tears. Two of the three patients with "spontaneous" rupture and small circular tears in the diaphragm showed symptoms of intestinal obstruction. The organs which herniated into the pleural cavity are shown in Table 4. In one patient the herniated colon, and in another the jejunum, became gangrenous and required resection. A herniated spleen was removed in one patient. The diaphragmatic rupture was closed with multiple interrupted silk sutures in 15 patients, three of whom also had second layers of continuous catgut suture. Catgut sutures alone were used in three patients. Hospital Mortality There were two postoperative deaths. One patient aspirated gastric contents at the end of the operation and died 6 hours later of bronchopneumonia. The second patient died 3 weeks after resection of the gangrenous colon as a result of empyema and septicemia. TABLE 4. Abdominal Viscera Herniated in the Left Hemithorax Across the Ruptured Diaphragm in 18 Patients Operated Upon Stomach Colon Greater Omentum Ileum Spleen Liver Jej unum
3 322 Followc-up) Seventeen patients who were discharged from the hospital have been followed for 3 to 26 years (average 14 years). One patient had not been operated upon. There have been three late deaths, at 9, 12 and 15 years postoperatively. The cause of these late deaths was myocardial infarction in one patient, carcinoma of the lung in the second and old age in the third. In the patient who died from coronary thrombosis the diaphragm was found to be normal at post-mortem examination. Fourteen patients are alive to date. One who wvas symptom-free 3 years followving repair, cannot be traced. Of the remaining 13 patients BEKASSY, DAVE, WOOLER AND IONESCU 12 are asvmptomatic and one has abdominal pain with no obvious cause. The patient wnho has not been operated upon is alive and well 11 years after injury. Expeerimental Rupture of the Diaplhragm In order to elucidate the cause of the left sided prevalence of diaphragmatic rupture the following experiment was carried out. Diaphragms were taken from the autopsy room, within the first 24 hours of death. The age at time of death of the ten patients varied from 18 to 68 years. Both the right and left leaves of each diaphragm were mounted in turn into a pressure chamber connected to a manometer and a pump. The pressure inside the chamber was progressively increased until rupture of the diaphragm occurred. The results of this artificial rupture of the diaphragm are showvn in Table 5. Discussion The historical aspects of traumatic rupture of the diaphragm have been well documented.,1"620 Most of the war time injuries causing traumatic rupture of the diaphragm are associated with penetrating bullet TABLE 5. Comparison of Pressuires (kp/cm'il) Required to Ruipture the Diaphragm Age at Time of Death Sex Left Leaf Right Leaf Years I 1.26 I 1.12 F 1.19 \ 1.33 W\I W\I AI F A1I \I 0.46 Mean: Standard deviatioin: t: P > 0.3 injuries. However, in one of our patients the rupture of the diaphragm was caused by a crushing injury from a tank. The majority of civilian injuries are abdominal and/or thoracic crushing injurics usually resulting from road traffic accidents. In one of the patients the rupture was caused by a fall from a height. In our series no relationship wnzas found between the site of rupture and the embryologically weak part of the diaphragm in either the trautiatic or the "spontaneous" groups. Blunt and indirect trauma producing a sudden increase in abdominal pressure relative to the intrathoracic pressure results in a gradient across the diaphragm sufficient to rupture it. This theory is supported by the fact that the rupture is more common on the left side than on the right, presumably because the right hemidiaphragm is protected by the liver. In other published works a leftsided rupture is reported to be about eight times as common as a rightsided rupture.6(9, ,13,17. 1 ),.!2a,26,2 Aiiii. Surg. * MIarch 1973 It seems logical to consider the protective role of the liver which may create an even distribution of the pressure forces over the entire hemidiaphragm.24'6 However, our experiments indicate that the left hemidiaphragm is less resistant to pressure than the right. In eight of ten cases the pressure required to rupture the left diaphragm wvas less as compared with the right. However, the difference was not statistically significant. All the "spontaneous" ruptures occurred on the left side. This finding again supports the contention that the left leaf of the diaphragm is weaker than the right. "Spontaneous" rupture of the diaphragm may result from increased transdiaphragmatic pressures. Unequal mechanical stretching of the diaphragm should also be considered as a contributory factor. The diagnosis of traumatic rupture of the diaphragm is difficult because the clinical picture immediately after trauma is masked by other associated injuries.'9"4 In our series these have been fractures of the skull, ribs, extremities or pelvis, some of them resulting in shock and unconsciousness. After an initial period, the clinical features involving the respiratory, circulatory, or alimentary systems may become apparent.1"'26'7"13,'8'22 Some patients later had symptoms resembling chronic pulmonary disease, coronary artery disease, or chronic gastrointestinal lesions. A relatively high proportion of patients had symptoms of acute gastrointestinal obstruction. The time lapse between trauma and the onset of symptoms is probably related to the size of the tear.4 The defect in the diaphragm possibly enlarges with the passage of time as a result of changing pressures in the abdominal and thoracic cavities. This results in progressive herniation of abdominal viscera into the chest.24
4 Vol. 177 * No. 3 TRAUMATIC RUPTURE OF THE DIAPHRAGM 323 It seems to be more difficult to establish the correct diagnosis in the cases of "spontaneous" rupture as compared with the traumatic ones. The symptoms in patients with "spontaneous" rupture are frequently vague, intermittent, and spread over a long period of time with intervals of excellent health. The patient has to be interrogated carefully as to the association of sudden severe exertion with the onset of symptoms. Symptoms of acute upper intestinal obstruction were seen more often in patients with "spontaneous" rupture as compared with traumatic diaphragmatic rupture. This is probably related to the small size of the tear in these cases. Two out of the three patients who had a small tear were in the "spontaneous" group. Plain chest radiographs were abnormal in all the patients and confirmed the diagnosis in three. In 14 patients the diagnosis was suspected on plain radiographs and confirmed by contrast radiography. Barium swallow X-ray was found to be the most useful diagnostic procedure in both groups. In one patient, however, barium swallow was suggestive of a volvulus of the stomach and the diagnosis of ruptured diaphragm was made at operation. The diagnostic value of radiologic examination is of equal importance in both traumatic and spontaneous rupture of the diaphragm. The differential diagnosis of ruptured diaphragm may be difficult. The diagnosis of pneumothorax is often made first, as it is a common finding after chest injuries.22'25'28 Breathlessness, absence of breath sounds, decreased air entry on the affected side, and in some cases an elevation of the diaphragm may occur in both pneumothorax and rupture of the diaphragm.23 The paralyzed diaphragm of traumatic origin caused by damage to the phrenic nerve is rare but should be excluded. Diagnostic chest aspiration carries the risk of injury to the herniated viscera. Stacker and Korner25 reported two patients in whom gastric contents were aspirated through the thoracic wall. Salomon, Feller and Levy23 reported one case in which the spleen was injured during chest aspiration. In doubtful cases exploration should be performed preferably through thoracotomy. In one of our patients the lesion was missed at laparotomy and the patient returned 3 months later with an incarcerated stomach. Operative repair of the ruptured diaphragm should be carried out in all patients because of the ever present danger of incarceration and its complications. '7"10,21'22'27 However, one patient in this series refused operation and at the present time is 76 years old and asymptomatic. The lower thoracic incision gives an excellent view of the diaphragm and can easily be extended into the abdomen if necessary. Stomach, colon and omentum herniated most commonly. In four patients the liver was also found to have herniated into the chest. In one the left lobe of the liver was found in the pericardial cavity. Associated pericardial rupture is rare. 3,11,17,18,22 In our series it was encountered only once. The patient complained of abdominal pain and shortness of breath on exertion. The use of non-absorbable material is the safest means of repairing the diaphragm. There were two hospital deaths (10.5%). One was due to aspiration of gastric contents into the trachea and bronchial tree; the other death occurred in a severely ill patient with a gangrenous colon in the chest requiring resection. The three late deaths were not related to the diaphragmatic rupture per se. Recurrence after repair is rare.'12'14"5 In our series there has been no recurrence on long-term follow-up study. Except for one patient who had persistent abdominal pain, all the others are asymptomatic three to 26 years after repair of the diapbragmatic rupture. Summary Fourteen patients with traumatic and five with "spontaneous" rupture of the diaphragm are reported. Eighteen had been operated upon. There were two hospital deaths and three late deaths; the latter were not related to the diaphragmatic rupture. The clinical and radiologic features are described. The diagnostic aspects, surgical management, probable mechanism of rupture and some experimental evidence regarding its location are discussed. The long-term results three to 26 years postoperatively are presented. "Spontaneous" rupture of the diaphragm should be suspected in patients with sudden onset of respiratory, circulatory or abdominal symptoms following severe instantaneous effort. Traumatic rupture should be suspected in patients with similar symptoms following injury to the chest or abdomen. The diagnosis depends on adequate radiological examination with accurate selection of the procedure and correct interpretation of the X-ray findings. Acknowledgments We wish to thank Mr. L. A. Catchpole, Mr. R. W. Catchpole and Mr. V. Taide for technical assistance and Mrs. J. Ladley for secretarial help. References 1. Arbulu, A., Read, R. C. and Berkas, E. M.: Delayed Symptomatology in Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia with a Note on Eventration. Dis. Chest, 47:527, Balas, A., Drexler, M. and Ratkai, I.: Ober Zwerchfellruptur und Nachfolgende Incarceration. Chirurg, 38:416, Beddingfield, G. W.: Cardiac Tamponade Due to Traumatic Hernia of the Diaphragm and Pericardium. Ann. Thorac. Surg., 6:178, Blades, B.: Ruptured Diaphragm. Am. J. Surg., 105:501, 1963.
5 324 BEKASSY, DAVE, WOOLER AND IONESCU Ann. Surg. MMarch Bowditch, H.: Diaphragmatic Hernia. Buffalo Med. J., 9: 1, Carter, B. N., Giuseffi, J. and Felson, B.: Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia. Am. J. Roentgenol., Radium Ther. Nucl. Med.,65:56, Carter, R. and Brewer, L. A.: Strangulating Diaphragmatic Hernia. Ann. Thorac. Surg., 12:281, Dave, K. S., Bekassy, S. M., Wooler, G. H. and Ionescu, M. I.: "Spontaneous" Rupture of the Diaghragm During Delivery. Accepted for publication, Grage, T. B., MacLean, L. D. and Campbell, G. S.: Traumatic Rupture of the Diaphragm. Surgery, 46:669, Hardy, K. J., Hughes, E. S. R. and Cuthbertson, A. M.: Largebowel Obstruction and Rupture of the Diaphragm. Med. J. Aust., 1:684, Heberer, G., Senno, A. and Laur, A.: Traumatische Intraperikardiale Zwerchfellrisse mit Baucheingeweideprolaps. Chirurg., 38:410, Hedblom, C. A.: Diaphragmatic Hernia. J. A. M. A., 85:947, Hollander, A. G. and Dugan, D. J.: Herniation of the Liver. J. Thorac. Surg., 29:357, Hood, R. M.: Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia. Ann. Thorac. Surg., 12:311, Lewis, E. A. and Lagundoye, S. B.: Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia. West Afr. Med. J., 19:145, Lindskog, G. E.: Some Historical Aspects of Thoracic Trauma. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg., 42:1, Lucido, J. L. and Wall, C. A.: Rupture of the Diaphragm Due to Blunt Trauma. Arch. Surg., 86:989, Moore, T. C.: Traumatic Pericardial Diaphragnmatic Hernia. Arch. Surg., 79:827, Noon, G. P., Beall, A. C. Jr. and De Bakey, M. E.: Surgical Management of Traumatic Rupture of the Diaphlragm. J. Trauma, 6:344, Riolfi, cited by Hedblom, C. A.: Diaphragmatic Hernia. JAMA, 85:947, Rosolleck, H.: Traumatische Zwerchfellruptur. Med. Welt, 2:141, Samaan, H. A.: Undiagnosed Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia. Br. J. Surg., 58:257, Salomon, J., Feller, N. and Levy, MI. J.: A Case of Spontaneous Rupture of the Diaphragmii. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg., 58:221, Schneider, C. F.: Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia. Am. J. Surg., 91:290, Stacker, A. D. and K6rner, K.: Diagnose, Differentialdiagnose und Therapie der Stumpfen Traumatischen Zwerchfellruptur. Hefte Unffallheilkd. 94:230, Sutherland, H. D.: Indirect Traumatic Rupture of the Diaphragm. Postgrad. Med. J. 34:210, Sutton, J. P., Carlisle, R. B. and Stephenson, S. E. Jr.: Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia. Ann. Thorac. Surg., 3:136, Wren, H. B., Texada, P. J. and Krementz, E. T.: Traumatic Rupture of the Diaphragm. J. Trauma, 2:117, 1962.
INTRA-THORACIC AND INTRA-ABDO-MINAL PERFORATION OF THE COLON IN TRAUMATIC DIAPHRAGMATIC
 INTRA-THORACIC AND INTRA-ABDO-MINAL PERFORATION OF THE COLON IN TRAUMATIC DIAPHRAGMATIC Pages with reference to book, From 14 To 16 S. Amjad Hussain, Chinda Suriyapa, Karl Grubaugh ( Depts. of Surger and
INTRA-THORACIC AND INTRA-ABDO-MINAL PERFORATION OF THE COLON IN TRAUMATIC DIAPHRAGMATIC Pages with reference to book, From 14 To 16 S. Amjad Hussain, Chinda Suriyapa, Karl Grubaugh ( Depts. of Surger and
Missed And Delayed Diagnosis Of Diaphragmatic Hernia: A Case Report
 Missed And Delayed Diagnosis Of Diaphragmatic Hernia: A Case Report Mohammed Tafash Dagash M.B.Ch.B, FICMS Instructor Department of Surgery College of Medicine Anbar University Iraq- Al-Anbar-Fallujah
Missed And Delayed Diagnosis Of Diaphragmatic Hernia: A Case Report Mohammed Tafash Dagash M.B.Ch.B, FICMS Instructor Department of Surgery College of Medicine Anbar University Iraq- Al-Anbar-Fallujah
Diaphragmatic Rupture with Pericardial Involvement
 Diaphragmatic Rupture with Pericardial Involvement Report of Two Cases Raymond M. Wetrich, M.D., Thomas M. Sawyers, M.D., and Chester A. Haug, M.D. D iaphragmatic rupture with pericardial involvement is
Diaphragmatic Rupture with Pericardial Involvement Report of Two Cases Raymond M. Wetrich, M.D., Thomas M. Sawyers, M.D., and Chester A. Haug, M.D. D iaphragmatic rupture with pericardial involvement is
Diaphragmatic Hernia Presenting With Intrathoracic Perforation
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 2 Number 1 Diaphragmatic Hernia Presenting With Intrathoracic Perforation A ERDOGAN Citation A ERDOGAN.. The Internet Journal of Surgery. 2000 Volume 2
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 2 Number 1 Diaphragmatic Hernia Presenting With Intrathoracic Perforation A ERDOGAN Citation A ERDOGAN.. The Internet Journal of Surgery. 2000 Volume 2
Title: Post traumatic Diaphragmatic hernia in children: Diagnostic Dilemmas and lessons learned. Type: Original article
 Title: Post traumatic Diaphragmatic hernia in children: Diagnostic Dilemmas and lessons learned. Type: Original article Authors: Dr Vaibhav Pandey 1*, Dr. Pranay Panigrahi 2 Srivastav 4 & Dr Rakesh Kumar
Title: Post traumatic Diaphragmatic hernia in children: Diagnostic Dilemmas and lessons learned. Type: Original article Authors: Dr Vaibhav Pandey 1*, Dr. Pranay Panigrahi 2 Srivastav 4 & Dr Rakesh Kumar
Right Diaphragm Spontaneous Rupture: A Surgical Approach
 Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2011) 11, 1036 1040 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2011.91 Right Diaphragm Spontaneous Rupture: A Surgical Approach Duilio Divisi*, Giovanna Imbriglio, Andrea De
Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2011) 11, 1036 1040 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2011.91 Right Diaphragm Spontaneous Rupture: A Surgical Approach Duilio Divisi*, Giovanna Imbriglio, Andrea De
Enter modality here Enter modality here, enter none if none. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: April 2015
![Enter modality here Enter modality here, enter none if none. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: April 2015 Enter modality here Enter modality here, enter none if none. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: April 2015](/thumbs/83/87309292.jpg) Radiological Category: Enter category here Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): Enter modality here Enter modality here, enter none if none Case Report # [] Submitted by: Varun Rachakonda, M.D.
Radiological Category: Enter category here Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): Enter modality here Enter modality here, enter none if none Case Report # [] Submitted by: Varun Rachakonda, M.D.
Calvin 9 year old NM DLH. Dr. Norman Ackerman Memorial Radiography Case Challenge
 September 2014 Dr. Norman Ackerman served the University of Florida, College of Veterinary Medicine with distinction as Professor of Radiology from 1979 to 1994. A concerned teacher of veterinary students
September 2014 Dr. Norman Ackerman served the University of Florida, College of Veterinary Medicine with distinction as Professor of Radiology from 1979 to 1994. A concerned teacher of veterinary students
Acute Diaphragmatic Injuries
 .. Acute Diaphragmatic Injuries John A. Drews, M.D., Elliott C. Mercer, M.D., and John R. Benfield, M.D. ABSTRACT A 5-year experience with 43 patients with acute diaphragmatic injuries is reviewed. Thirty-three
.. Acute Diaphragmatic Injuries John A. Drews, M.D., Elliott C. Mercer, M.D., and John R. Benfield, M.D. ABSTRACT A 5-year experience with 43 patients with acute diaphragmatic injuries is reviewed. Thirty-three
Bull Emerg Trauma 2013;1(2): The Etiology, Associated Injuries and Clinical Presentation of Post Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia
 Bull Emerg Trauma 2013;1(2):76-80. Original Article The Etiology, Associated Injuries and Clinical Presentation of Post Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia Farooq Ahmad Gaine *, Ghulam Nabi Lone, Mushtaq Ahmad
Bull Emerg Trauma 2013;1(2):76-80. Original Article The Etiology, Associated Injuries and Clinical Presentation of Post Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia Farooq Ahmad Gaine *, Ghulam Nabi Lone, Mushtaq Ahmad
Bull Emerg Trauma 2013;1(2): The Etiology, Associated Injuries and Clinical Presentation of Post Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia
 Bull Emerg Trauma 2013;1(2):76-80. Original Article The Etiology, Associated Injuries and Clinical Presentation of Post Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia Farooq Ahmad Gaine *, Ghulam Nabi Lone, Mushtaq Ahmad
Bull Emerg Trauma 2013;1(2):76-80. Original Article The Etiology, Associated Injuries and Clinical Presentation of Post Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia Farooq Ahmad Gaine *, Ghulam Nabi Lone, Mushtaq Ahmad
Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps. Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania None Disclosures Objectives Describe blunt and penetrating traumatic
Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania None Disclosures Objectives Describe blunt and penetrating traumatic
Case Report. Abstract
 Nigerian journal of surgical research Vol 7 No 3 4 2005: 323-324 Case Report Delayed presentation of blunt traumatic diaphragmatic hernia: A case report A T Kidmas, D Iya, 1 E S Isamade 2 and E Ekedigwe,
Nigerian journal of surgical research Vol 7 No 3 4 2005: 323-324 Case Report Delayed presentation of blunt traumatic diaphragmatic hernia: A case report A T Kidmas, D Iya, 1 E S Isamade 2 and E Ekedigwe,
Congenital diaphragmatic anomalies: Case review
 Case Report: Congenital diaphragmatic anomalies: Case review 1Dr. Shivali Srivastava, 2 Dr. S. S. Rajasekar, 3 Dr. Deepa Somanath 1Post graduate, Department of Anatomy, SMVMCH, Pondicherry- 605107 2Professor
Case Report: Congenital diaphragmatic anomalies: Case review 1Dr. Shivali Srivastava, 2 Dr. S. S. Rajasekar, 3 Dr. Deepa Somanath 1Post graduate, Department of Anatomy, SMVMCH, Pondicherry- 605107 2Professor
Acquired hernias of the diaphragm
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (1988) 64, 317-321 Acquired hernias of the diaphragm C.D. Johnson and H. Ellis Department of Surgery, Westminster Hospital, Page Street Wing, London SWIP 2AP, U.K. Summary:
Postgraduate Medical Journal (1988) 64, 317-321 Acquired hernias of the diaphragm C.D. Johnson and H. Ellis Department of Surgery, Westminster Hospital, Page Street Wing, London SWIP 2AP, U.K. Summary:
Case Report Fractured Ribs and the CT Funky Fat Sign of Diaphragmatic Rupture
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6723632, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6723632 Case Report Fractured Ribs and the CT Funky Fat Sign of Diaphragmatic Rupture Iclal Ocak 1 and
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 6723632, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6723632 Case Report Fractured Ribs and the CT Funky Fat Sign of Diaphragmatic Rupture Iclal Ocak 1 and
CHEST INJURIES. Jacek Piątkowski M.D., Ph. D.
 CHEST INJURIES Jacek Piątkowski M.D., Ph. D. CHEST INJURIES 3-4% of all injuries 8% of patients hospitalized due to injuries 65% of patients who died at the accident place CLASSIFICATION OF THE CHEST INJURIES
CHEST INJURIES Jacek Piątkowski M.D., Ph. D. CHEST INJURIES 3-4% of all injuries 8% of patients hospitalized due to injuries 65% of patients who died at the accident place CLASSIFICATION OF THE CHEST INJURIES
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress THE LAST GASP II: LUNGS AND THORAX David Holt, BVSc, Diplomate ACVS University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress THE LAST GASP II: LUNGS AND THORAX David Holt, BVSc, Diplomate ACVS University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays. Objectives. Indications for X-Rays 5/14/2018
 Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
Traumatic Diaphragmatic Rupture
 Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School December 2009 Traumatic Diaphragmatic Rupture Kapil Verma, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD Agenda Background Menu of Tests
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School December 2009 Traumatic Diaphragmatic Rupture Kapil Verma, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD Agenda Background Menu of Tests
Bochdalek s Hernia in Adults a Report of 4 Cases
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 18 Number 2 Bochdalek s Hernia in Adults a Report of 4 Cases S Pai, L Ramachandra, R Shenoy, G Kamath Citation S Pai, L Ramachandra, R Shenoy, G Kamath.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 18 Number 2 Bochdalek s Hernia in Adults a Report of 4 Cases S Pai, L Ramachandra, R Shenoy, G Kamath Citation S Pai, L Ramachandra, R Shenoy, G Kamath.
Morgagni hernia repair in adult obese patient by hybrid robotic thoracic surgery
 Case Report Morgagni hernia repair in adult obese patient by hybrid robotic thoracic surgery Dario more, Carlo ergaminelli, Davide Di Natale, Dino Casazza, Roberto Scaramuzzi, Carlo Curcio Division of
Case Report Morgagni hernia repair in adult obese patient by hybrid robotic thoracic surgery Dario more, Carlo ergaminelli, Davide Di Natale, Dino Casazza, Roberto Scaramuzzi, Carlo Curcio Division of
Esophageal Perforation
 Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Esophageal Perforation Dr. Carmine Simone Thoracic Surgeon, Division of General Surgery Head, Division of Critical Care May 15, 2006 Overview Case presentation Radiology Pre-operative management Operative
Diaphragmatic Hernias in Trauma
 Diaphragmatic Hernias in Trauma ONAONA GURNEY, PGY4 SUNY DOWNSTATE DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY AUGUST 28 TH 2015 Case Presentation 61M restrained driver in MVA, transferred from Brookdale Hospital Airbag deployment,
Diaphragmatic Hernias in Trauma ONAONA GURNEY, PGY4 SUNY DOWNSTATE DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY AUGUST 28 TH 2015 Case Presentation 61M restrained driver in MVA, transferred from Brookdale Hospital Airbag deployment,
Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia
 Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia A Review of 25 Cases John P. Sutton, M.D., Robert Byron Carlisle, M.D., and Sam E. Stephenson, Jr., M.D. I n 579 Ambrose Part [9] reported the result of a necropsy performed
Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia A Review of 25 Cases John P. Sutton, M.D., Robert Byron Carlisle, M.D., and Sam E. Stephenson, Jr., M.D. I n 579 Ambrose Part [9] reported the result of a necropsy performed
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II
 Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
Left diaphragmmatic eventration with gastric volvulus: Laparoscopic mesh repair of left diaphragmatic eventration
 JMSR Dr. Lakshmikanth T Case Report Left diaphragmmatic eventration with gastric volvulus: Laparoscopic mesh repair of left diaphragmatic eventration Lakshmikanth T 1 and Sanjeeva Rao K 1 1 Department
JMSR Dr. Lakshmikanth T Case Report Left diaphragmmatic eventration with gastric volvulus: Laparoscopic mesh repair of left diaphragmatic eventration Lakshmikanth T 1 and Sanjeeva Rao K 1 1 Department
Chapter 29 - Chest_and_Abdominal_Trauma
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 29.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11, 15, 18, 27 29.2 Describe mechanisms of injury commonly associated with chest injuries. Slides
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 29.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11, 15, 18, 27 29.2 Describe mechanisms of injury commonly associated with chest injuries. Slides
PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS AND PREOPERATIVE DATA (ecrf 1).
 PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS AND PREOPERATIVE DATA (ecrf 1). 1 Inform Consent Date: / / dd / Mmm / yyyy 2 Patient identifier: Please enter the 6 digit Patient identification number from your site patient log
PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS AND PREOPERATIVE DATA (ecrf 1). 1 Inform Consent Date: / / dd / Mmm / yyyy 2 Patient identifier: Please enter the 6 digit Patient identification number from your site patient log
In ESH we usually see blunt chest trauma but penetrating injuries also treated here (usually as single injuries, like stab wound)
 Chest Trauma Dr Csaba Dioszeghy MD PhD FRCEM FFICM FERC East Surrey Hospital Emergency Department Scope Thoracic injuries are common and can be life threatening In ESH we usually see blunt chest trauma
Chest Trauma Dr Csaba Dioszeghy MD PhD FRCEM FFICM FERC East Surrey Hospital Emergency Department Scope Thoracic injuries are common and can be life threatening In ESH we usually see blunt chest trauma
Hernia. emoryhealthcare.org
 Hernia Have you noticed a bulge or pain in your abdominal wall or groin? If so you may have a hernia. You may be in the process of confirming this diagnosis with your Primary Care Physician or already
Hernia Have you noticed a bulge or pain in your abdominal wall or groin? If so you may have a hernia. You may be in the process of confirming this diagnosis with your Primary Care Physician or already
Case Report A Case of Spontaneous Transdiaphragmatic Intercostal Hernia with Contralateral Injury, and Review of the Literature
 Hindawi Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2017, Article ID 7416092, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7416092 Case Report A Case of Spontaneous Transdiaphragmatic Intercostal Hernia with Contralateral
Hindawi Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2017, Article ID 7416092, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7416092 Case Report A Case of Spontaneous Transdiaphragmatic Intercostal Hernia with Contralateral
Unusual presentations of late onset diaphragmatic hernia: a six year study
 International Surgery Journal Aggarwal S et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Apr;4(4):1180-1184 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20170895
International Surgery Journal Aggarwal S et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Apr;4(4):1180-1184 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20170895
JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 05 Page May 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Blunt Traumatic Diaphragmatic Injuries - An Experience of 5 Years Authors Priya Goyal 1, Shekhar Gogna 2, Prateek Thakur 3, Sonia Goyal
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Blunt Traumatic Diaphragmatic Injuries - An Experience of 5 Years Authors Priya Goyal 1, Shekhar Gogna 2, Prateek Thakur 3, Sonia Goyal
CHEST TRAUMA. Dr Naeem Zia FCPS,FACS,FRCS
 CHEST TRAUMA Dr Naeem Zia FCPS,FACS,FRCS Learning objectives Anatomy of chest wall and thoracic viscera Physiology of respiration and nerve pathways for pain Enumerate different thoracic conditions requiring
CHEST TRAUMA Dr Naeem Zia FCPS,FACS,FRCS Learning objectives Anatomy of chest wall and thoracic viscera Physiology of respiration and nerve pathways for pain Enumerate different thoracic conditions requiring
Pericardial rupture from blunt chest trauma
 Thorax (1974), 29, 329. Pericardial rupture from blunt chest trauma J. BORRIE and I. LICHTER Department of Thoracic Surgery, Otago Medical School, Dunedin, New Zealand Borme, J. and Lichter, I. (1974).
Thorax (1974), 29, 329. Pericardial rupture from blunt chest trauma J. BORRIE and I. LICHTER Department of Thoracic Surgery, Otago Medical School, Dunedin, New Zealand Borme, J. and Lichter, I. (1974).
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
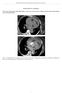 SUPPLEMENTL MTERIL Marie erna, Martin Kocher, Rohit Philip Thomas. cute aorta, overview of acute T findings and endovascular treatment options (doi: 10.5507/bp.2016.060) Fig. 1. : Non-enhanced T, hemopericardium
SUPPLEMENTL MTERIL Marie erna, Martin Kocher, Rohit Philip Thomas. cute aorta, overview of acute T findings and endovascular treatment options (doi: 10.5507/bp.2016.060) Fig. 1. : Non-enhanced T, hemopericardium
Paraoesophageal Hernia
 Paraoesophageal Hernia Grand Round Adam Cichowitz Surgical Registrar Paraoesophageal Hernia Type of hiatal hernia Transdiaphragmatic migration of abdominal content gastric fundus gastric body pylorus colon
Paraoesophageal Hernia Grand Round Adam Cichowitz Surgical Registrar Paraoesophageal Hernia Type of hiatal hernia Transdiaphragmatic migration of abdominal content gastric fundus gastric body pylorus colon
INJURIES CHEST, ABDOMEN, LIMBS. FN Brno November 2011
 INJURIES CHEST, ABDOMEN, LIMBS FN Brno November 2011 Injury Chest Abdomen Limbs Injury to the rib cage Fractured one or more ribs Sharp pain at the site of fracture Pain on taking a deep breath Shallow
INJURIES CHEST, ABDOMEN, LIMBS FN Brno November 2011 Injury Chest Abdomen Limbs Injury to the rib cage Fractured one or more ribs Sharp pain at the site of fracture Pain on taking a deep breath Shallow
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations
 Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
GEOFFREY H. Leeds WOOLER. The coronary ligament surrounds the bare area of
 Thorax (1956), 11, 21 1. SUBPHRENIC ABSCESS BY GEOFFREY H. Leeds The term subphrenic abscess denotes infection occurring in the region bounded by the diaphragm above, and by the transverse meso-colon,
Thorax (1956), 11, 21 1. SUBPHRENIC ABSCESS BY GEOFFREY H. Leeds The term subphrenic abscess denotes infection occurring in the region bounded by the diaphragm above, and by the transverse meso-colon,
Laparoscopic Repair of a Traumatic Intrapericardial Diaphragmatic Hernia
 CASE REPORT Laparoscopic Repair of a Traumatic Intrapericardial Diaphragmatic Hernia SreyRam Kuy, MD, MHS, Jeremy Juern, MD, John A. Weigelt, DVM, MD ABSTRA Introduction: Intrapericardial diaphragmatic
CASE REPORT Laparoscopic Repair of a Traumatic Intrapericardial Diaphragmatic Hernia SreyRam Kuy, MD, MHS, Jeremy Juern, MD, John A. Weigelt, DVM, MD ABSTRA Introduction: Intrapericardial diaphragmatic
Morbidity and mortality of oesophageal perforation
 Thorax (1972), 27, 353. Morbidity and mortality of oesophageal perforation M. R. B. KEIGHLEY, R. W. GIRDWOOD, G. H. WOOLER, and M. I. IONESCU Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, The General Infirmary
Thorax (1972), 27, 353. Morbidity and mortality of oesophageal perforation M. R. B. KEIGHLEY, R. W. GIRDWOOD, G. H. WOOLER, and M. I. IONESCU Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, The General Infirmary
LIVER INJURIES PROFF. S.FLORET
 LIVER INJURIES PROFF. S.FLORET Abdominal injuries For anatomical consideration: Abdomen can be divided in four areas Intra thoracic abdomen True abdomen Pelvic abdomen Retroperitoneal abdomen ETIOLOGY
LIVER INJURIES PROFF. S.FLORET Abdominal injuries For anatomical consideration: Abdomen can be divided in four areas Intra thoracic abdomen True abdomen Pelvic abdomen Retroperitoneal abdomen ETIOLOGY
Science & Technologies
 A GIANT LIVER HYDATIDE CYST SIMULTANEOUSLY PERFORATED TO PERITONEAL AND PLEURAL CAVITIES A RARE CASE REPORT. Ivan P. Novakov Department of Special Surgery; Medical University - Plovdiv Abstract. Background.
A GIANT LIVER HYDATIDE CYST SIMULTANEOUSLY PERFORATED TO PERITONEAL AND PLEURAL CAVITIES A RARE CASE REPORT. Ivan P. Novakov Department of Special Surgery; Medical University - Plovdiv Abstract. Background.
Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code
 Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code Herring, W ISBN-13: 9780323074445 Table of Contents 1. Recognizing Anything The "colorful" world of radiology A
Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code Herring, W ISBN-13: 9780323074445 Table of Contents 1. Recognizing Anything The "colorful" world of radiology A
Trauma. Neck trauma zones. Neck Injuries 1/3/2018. Basic principles A ; Airway B ; Breathing C ; Circulation D ; Disability E ; Exposure
 Trauma 45 minutes highest points Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Basic principles A ; Airway B ; Breathing C ; Circulation D ; Disability E ; Exposure Neck trauma zones Airway ;Rapid sequence intubation Breathing ;Needle
Trauma 45 minutes highest points Ahmed Mahmoud, MD Basic principles A ; Airway B ; Breathing C ; Circulation D ; Disability E ; Exposure Neck trauma zones Airway ;Rapid sequence intubation Breathing ;Needle
Correspondence should be addressed to Saptarshi Biswas;
 Hindawi Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2017, Article ID 8412927, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8412927 Case Report Jejunal Diverticular Perforation Causing Small Bowel Obstruction in a Type 4 Hiatal
Hindawi Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2017, Article ID 8412927, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8412927 Case Report Jejunal Diverticular Perforation Causing Small Bowel Obstruction in a Type 4 Hiatal
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal injuries clinical presentation of, 23 24 Abdominal trauma evaluation for pediatric surgeon, 59 74 background of, 60 colon and
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abdominal injuries clinical presentation of, 23 24 Abdominal trauma evaluation for pediatric surgeon, 59 74 background of, 60 colon and
SETTING Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center. RESPONSIBLE PARTY Haiquan Chen MD.
 OFFICIAL TITLE A Phase Ⅲ Study of Left Side Thoracotomy Approach (SweetProcedure) Versus Right Side Thoracotomy Plus Midline Laparotomy Approach (Ivor-Lewis Procedure) Esophagectomy in Middle or Lower
OFFICIAL TITLE A Phase Ⅲ Study of Left Side Thoracotomy Approach (SweetProcedure) Versus Right Side Thoracotomy Plus Midline Laparotomy Approach (Ivor-Lewis Procedure) Esophagectomy in Middle or Lower
The ABC s of Chest Trauma
 The ABC s of Chest Trauma J Bradley Pickhardt MD, FACS Providence St Patrick Hospital What s the Problem? 2/3 of trauma patients have chest trauma Responsible for 25% of all trauma deaths Most injuries
The ABC s of Chest Trauma J Bradley Pickhardt MD, FACS Providence St Patrick Hospital What s the Problem? 2/3 of trauma patients have chest trauma Responsible for 25% of all trauma deaths Most injuries
Case Report Incarcerated Thoracic Gastric Herniation after Nephrectomy: A Report of Two Cases
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 896452, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/896452 Case Report Incarcerated Thoracic Gastric Herniation after Nephrectomy: A Report of Two Cases Conall
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 896452, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/896452 Case Report Incarcerated Thoracic Gastric Herniation after Nephrectomy: A Report of Two Cases Conall
Strangulated diaphragmatic hernia
 Strangulated diaphragmatic hernia EUGENE HOFFMAN From the Thoracic Surgery Unzit, Poole Hospital, Middlesbroughl Thorax (1968), 23, 541. Seventy-six cases of strangulated diaphragmatic hernia were reported
Strangulated diaphragmatic hernia EUGENE HOFFMAN From the Thoracic Surgery Unzit, Poole Hospital, Middlesbroughl Thorax (1968), 23, 541. Seventy-six cases of strangulated diaphragmatic hernia were reported
Penetrating Neck Injuries. Jason Levine MD Lutheran Medical Center July 22, 2010
 Penetrating Neck Injuries Jason Levine MD Lutheran Medical Center July 22, 2010 CASE PRESENTATION 19 YO M 3 Stab Wounds Right zone I neck SW 2 SW anterior abdomen Left epigastrium anterior axillary line
Penetrating Neck Injuries Jason Levine MD Lutheran Medical Center July 22, 2010 CASE PRESENTATION 19 YO M 3 Stab Wounds Right zone I neck SW 2 SW anterior abdomen Left epigastrium anterior axillary line
Chest x-ray in Trauma Pearls and pitfalls. Mats O. Beckman. Stockholm
 Chest x-ray in Trauma Pearls and pitfalls Mats O. Beckman Radiology Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm 3 chestmb08 4 chestmb08 5 chestmb08 6 chestmb08 7 chestmb08 Traumaroom 8 chestmb08 When to do
Chest x-ray in Trauma Pearls and pitfalls Mats O. Beckman Radiology Karolinska University Hospital Stockholm 3 chestmb08 4 chestmb08 5 chestmb08 6 chestmb08 7 chestmb08 Traumaroom 8 chestmb08 When to do
Discussing feline tracheal disease
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Discussing feline tracheal disease Author : ANDREW SPARKES Categories : Vets Date : March 24, 2008 ANDREW SPARKES aims to
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Discussing feline tracheal disease Author : ANDREW SPARKES Categories : Vets Date : March 24, 2008 ANDREW SPARKES aims to
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia in the older child
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1981, 56, 253-257 Congenital diaphragmatic hernia in the older child P D BOOKER, P W D MEERSTADT, AND G H BUSH Alder Hey Childrens Hospital, Liverpool SUMMARY Five children
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1981, 56, 253-257 Congenital diaphragmatic hernia in the older child P D BOOKER, P W D MEERSTADT, AND G H BUSH Alder Hey Childrens Hospital, Liverpool SUMMARY Five children
Esophageal injuries. Pre-test /11/10. 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119. O What is the most common cause of esophageal injuries?
 Esophageal injuries 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119 Pre-test 1 O What is the most common cause of esophageal injuries? A. Traffic accidents B. Gunshot wounds C. Iatrogenic 1 Pre-test 2 O Which contrast
Esophageal injuries 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119 Pre-test 1 O What is the most common cause of esophageal injuries? A. Traffic accidents B. Gunshot wounds C. Iatrogenic 1 Pre-test 2 O Which contrast
Congenital Morgagni-Larrey's hernia (CMLH) is
 Bilateral congenital Morgagni-Larrey's hernia Ahmed Hassan Al-Salem Dammam, Saudi Arabia 76 Background: Congenital Morgagni-Larrey's hernia (CMLH) is rare and known to be associated with a high incidence
Bilateral congenital Morgagni-Larrey's hernia Ahmed Hassan Al-Salem Dammam, Saudi Arabia 76 Background: Congenital Morgagni-Larrey's hernia (CMLH) is rare and known to be associated with a high incidence
Different Sonographic Pictures of Traumatic Hepatic Herniation and Reasons for Their Differences
 C S E R E P O R T Different Sonographic Pictures of Traumatic Hepatic Herniation and Reasons for Their Differences Chih-Shun Wu*, Wei-Jen Yao 1, Yen-Hua Huang 2 Sonographic features used in the diagnosis
C S E R E P O R T Different Sonographic Pictures of Traumatic Hepatic Herniation and Reasons for Their Differences Chih-Shun Wu*, Wei-Jen Yao 1, Yen-Hua Huang 2 Sonographic features used in the diagnosis
Chest X rays and Case Studies. No disclosures. Outline 5/31/2018. Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital
 Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Post-Traumatic Diaphragmatic Hernia Late Diagnosed: A Case Report
 Received: 02 Sept 2017 Revised: 20 September 2017 Accepted: 14 Oct 2017 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15520/.v5i10.75. Manuscript Central Journal of Medical Biomedical and Applied Sciences Post-Traumatic Diaphragmatic
Received: 02 Sept 2017 Revised: 20 September 2017 Accepted: 14 Oct 2017 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.15520/.v5i10.75. Manuscript Central Journal of Medical Biomedical and Applied Sciences Post-Traumatic Diaphragmatic
Chest X-ray Interpretation
 Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
A DEATH DUE TRANS-DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIA YEARS AFTER FIREARM INJURIES. Dayapala A. District General Hospital, Negombo
 A DEATH DUE TRANS-DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIA YEARS AFTER FIREARM INJURIES Dayapala A. District General Hospital, Negombo INTRODUCTION Effects of penetrating injuries including firearm injuries can be very variable.
A DEATH DUE TRANS-DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIA YEARS AFTER FIREARM INJURIES Dayapala A. District General Hospital, Negombo INTRODUCTION Effects of penetrating injuries including firearm injuries can be very variable.
Case Report Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia with Delayed Presentation
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2016, Article ID 7284914, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7284914 Case Report Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia with Delayed Presentation Alireza Malekzadegan 1 and
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2016, Article ID 7284914, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7284914 Case Report Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia with Delayed Presentation Alireza Malekzadegan 1 and
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.132 Hiatal Hernia: A Rare Cause of Dyspnea
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.132 Hiatal Hernia: A Rare Cause of Dyspnea
X-Rays. Prepared by Prof.Dr. Magda Hassab Allah Assist.lecturer Marwa Al Hady
 X-Rays Prepared by Prof.Dr. Magda Hassab Allah Assist.lecturer Marwa Al Hady CHEST X-RAYS Normal Chest X-ray Comments on chest X ray includes examination of 1- Bony cage (ribs,clavicles &vertebral column
X-Rays Prepared by Prof.Dr. Magda Hassab Allah Assist.lecturer Marwa Al Hady CHEST X-RAYS Normal Chest X-ray Comments on chest X ray includes examination of 1- Bony cage (ribs,clavicles &vertebral column
Case Report Transdiaphragmatic Intercostal Herniation following Blunt Trauma
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2012, Article ID 502765, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/502765 Case Report Transdiaphragmatic Intercostal Herniation following Blunt Trauma Debkumar Sarkar, Melissa Warta, and
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2012, Article ID 502765, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/502765 Case Report Transdiaphragmatic Intercostal Herniation following Blunt Trauma Debkumar Sarkar, Melissa Warta, and
Thirteen Years Experience of Diaphragmatic Injury in Children from the Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences (PGIMS), Rohtak, India
 Original Article Thirteen Years Experience of Diaphragmatic Injury in Children from the Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences (PGIMS), Rohtak, India Kamal Nain Rattan 1, Rajat Narang 1, Seema Rohilla
Original Article Thirteen Years Experience of Diaphragmatic Injury in Children from the Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences (PGIMS), Rohtak, India Kamal Nain Rattan 1, Rajat Narang 1, Seema Rohilla
The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax
 Respiratory 131 The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a relatively common presentation in patients under the age of 40 years (approximately, 85% of patients are younger than 40 years).
Respiratory 131 The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a relatively common presentation in patients under the age of 40 years (approximately, 85% of patients are younger than 40 years).
Gastro-pleural fistula a rare complication of chronic traumatic diaphragmatic hernia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 19 Number 1 Gastro-pleural fistula a rare complication of chronic traumatic diaphragmatic hernia P Leake, S Cawich, M McFarlane Citation P Leake, S Cawich,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 19 Number 1 Gastro-pleural fistula a rare complication of chronic traumatic diaphragmatic hernia P Leake, S Cawich, M McFarlane Citation P Leake, S Cawich,
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
Pneumothorax. Defined as air in the pleural space which can occur through a number of mechanisms
 Pneumothorax Defined as air in the pleural space which can occur through a number of mechanisms Traumatic pneumothorax Penetrating chest trauma Common secondary to bullet or knife penetration Chest tube
Pneumothorax Defined as air in the pleural space which can occur through a number of mechanisms Traumatic pneumothorax Penetrating chest trauma Common secondary to bullet or knife penetration Chest tube
CONGENITAL RIGHT-SIDED DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIA
 CONGENTAL RGHT-SDED DAPHRAGMATC HERNA SOME DFFCULTES N DFFERENTAL DAGNOSS AND OPERATVE REPAR BY diaphragmatic hernia are described; in neither was the diagnosis established until several other tentative
CONGENTAL RGHT-SDED DAPHRAGMATC HERNA SOME DFFCULTES N DFFERENTAL DAGNOSS AND OPERATVE REPAR BY diaphragmatic hernia are described; in neither was the diagnosis established until several other tentative
BODY SYSTEMS BODY CAVITIES THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. Movements BODY CAVITIES. Pediatric Considerations In Respiratory System
 BODY SYSTEMS A body system is a group of organs and other structures work together to carry out specific functions. The following systems work together to carry out a function needed for life: Respiratory
BODY SYSTEMS A body system is a group of organs and other structures work together to carry out specific functions. The following systems work together to carry out a function needed for life: Respiratory
Auscultation of the lung
 Auscultation of the lung Auscultation of the lung by the stethoscope. *Compositions of the stethoscope: 1-chest piece 2-Ear piece 3-Rubber tubs *Auscultation area of the lung(triangle of auscultation).
Auscultation of the lung Auscultation of the lung by the stethoscope. *Compositions of the stethoscope: 1-chest piece 2-Ear piece 3-Rubber tubs *Auscultation area of the lung(triangle of auscultation).
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN
 UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
Thoracostomy: An Update on Imaging Features and Current Surgical Practice
 Thoracostomy: An Update on Imaging Features and Current Surgical Practice Robert D. Ambrosini, MD, PhD, Christopher Gange, MD, Katherine Kaproth-Joslin, MD, PhD, Susan Hobbs, MD, PhD Department of Imaging
Thoracostomy: An Update on Imaging Features and Current Surgical Practice Robert D. Ambrosini, MD, PhD, Christopher Gange, MD, Katherine Kaproth-Joslin, MD, PhD, Susan Hobbs, MD, PhD Department of Imaging
Radiographic signs of pulmonary embolism and pulmonary infarction
 Thlorax (1973), 28, 198. Radiographic signs of pulmonary embolism and pulmonary infarction S. TALBOT, B. S. WORTHINGTON, and E. J. ROEBUCK General Hospital, Nottingham A comparative analysis of the radiographic
Thlorax (1973), 28, 198. Radiographic signs of pulmonary embolism and pulmonary infarction S. TALBOT, B. S. WORTHINGTON, and E. J. ROEBUCK General Hospital, Nottingham A comparative analysis of the radiographic
Approach to CXR. Terminology. 1.Identification. Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow. Correct patient Correct date and time Correct examination
 Approach to CXR Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow From Rob Posteraro http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_interpret.txt.html ; http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_main.txt.html) Approach to viewing Chest
Approach to CXR Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow From Rob Posteraro http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_interpret.txt.html ; http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_main.txt.html) Approach to viewing Chest
OSAMA A. ABDULMAJID, ABDELMOMEN M. EBEID, MOHAMED M. MOTAWEH, and IBRAHIM S. KLEIBO
 Aspirated foreign bodies in the tracheobronchial tree: report of 250 cases Thorax (1976), 31, 635. OSAMA A. ABDULMAJID, ABDELMOMEN M. EBEID, MOHAMED M. MOTAWEH, and IBRAHIM S. KLEIBO Thoracic Surgical
Aspirated foreign bodies in the tracheobronchial tree: report of 250 cases Thorax (1976), 31, 635. OSAMA A. ABDULMAJID, ABDELMOMEN M. EBEID, MOHAMED M. MOTAWEH, and IBRAHIM S. KLEIBO Thoracic Surgical
X-rays. Dr Will Dooley
 X-rays Dr Will Dooley Plan Chest X-Rays Abdominal X-Rays Exam approach Presentation skills EMQ EMQ- answers Chest X-Ray - Systematic Approach D R Details RIP Image Quality +/- OBVIOUS ABNORMALITY A B C
X-rays Dr Will Dooley Plan Chest X-Rays Abdominal X-Rays Exam approach Presentation skills EMQ EMQ- answers Chest X-Ray - Systematic Approach D R Details RIP Image Quality +/- OBVIOUS ABNORMALITY A B C
Acute Penetrating Tracheal Trauma
 Acute Penetrating Tracheal Trauma Panagiotis N. Symbas, M.D., Charles R. Hatcher, Jr., M.D., and Gerhard A. W. Boehm, M.D. ABSTRACT During the past ten years, 20 patients with acute penetrating tracheal
Acute Penetrating Tracheal Trauma Panagiotis N. Symbas, M.D., Charles R. Hatcher, Jr., M.D., and Gerhard A. W. Boehm, M.D. ABSTRACT During the past ten years, 20 patients with acute penetrating tracheal
The Importance of Chiliaditi s Sign- Syndrome
 October, 2017 2017; Vol1; Issue9 http://iamresearcher.online The Importance of Chiliaditi s Sign- Syndrome Yanik Fazli 1, Karamustafaoglu Yekta Altemur 1, Tarladacalisir Taner 2, Yoruk Y. 1 1 Trakya University,
October, 2017 2017; Vol1; Issue9 http://iamresearcher.online The Importance of Chiliaditi s Sign- Syndrome Yanik Fazli 1, Karamustafaoglu Yekta Altemur 1, Tarladacalisir Taner 2, Yoruk Y. 1 1 Trakya University,
Muscle spasm Diminished bowel sounds Nausea/vomiting
 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Chapter 8: Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Abdominal Injuries Abdomen is major body cavity extending from to pelvis. Contains organs that make up digestive, urinary, and genitourinary systems.
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Chapter 8: Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Abdominal Injuries Abdomen is major body cavity extending from to pelvis. Contains organs that make up digestive, urinary, and genitourinary systems.
Advances in MDCT of Thoracic Trauma
 Baltic Congress of Radiology, Riga 2010 Advances in MDCT of Thoracic Trauma Robert A. Novelline, MD Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical School Director of Emergency Radiology, Massachusetts General
Baltic Congress of Radiology, Riga 2010 Advances in MDCT of Thoracic Trauma Robert A. Novelline, MD Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical School Director of Emergency Radiology, Massachusetts General
Hiatal hernias may be classified. hiatal hernia DESCRIPTION AND IDENTIFICATION. This article is the first in a twopart series about these somewhat
 paraesophagealh hiatal hernia Leslie K Browder, MD, and Alex G Little, MD DESCRIPTION AND IDENTIFICATION Hiatal hernias may be classified as four types. The most common, Type I, may present as gastroesophageal
paraesophagealh hiatal hernia Leslie K Browder, MD, and Alex G Little, MD DESCRIPTION AND IDENTIFICATION Hiatal hernias may be classified as four types. The most common, Type I, may present as gastroesophageal
Chapter 29 - Chest Injuries
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 National EMS Education Standard Competencies (1 of 5) Trauma Applies fundamental knowledge to provide basic emergency care and transportation based on assessment findings for an acutely
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 National EMS Education Standard Competencies (1 of 5) Trauma Applies fundamental knowledge to provide basic emergency care and transportation based on assessment findings for an acutely
HERNIA AND EVENTRATION
 Thorax (1950), 5, 343. FIFTY-SEVEN CASES OF DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIA AND EVENTRATION BY C. J. EVANS AND J. A. SIMPSON Froml the Regional Thoracic Surgery Centre, Shotley Bridge Hospital, Newcastle-upon-Tyne
Thorax (1950), 5, 343. FIFTY-SEVEN CASES OF DIAPHRAGMATIC HERNIA AND EVENTRATION BY C. J. EVANS AND J. A. SIMPSON Froml the Regional Thoracic Surgery Centre, Shotley Bridge Hospital, Newcastle-upon-Tyne
Esophageal injuries. 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119
 Esophageal injuries 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119 Pre-test 1 What is the most common cause of esophageal injuries? A. Traffic accidents B. Gunshot wounds C. Iatrogenic Pre-test 2 Which contrast agent
Esophageal injuries 新光急診張志華醫師 Facebook.com/jack119 Pre-test 1 What is the most common cause of esophageal injuries? A. Traffic accidents B. Gunshot wounds C. Iatrogenic Pre-test 2 Which contrast agent
Nasty surprise of traumatic Diaphragmatic Rupture.
 Nasty surprise of traumatic Diaphragmatic Rupture Rifaat kamar 1, Emad Sarawy 1, Mohamed Ahmed Osman 1 and Reham M Khalil 2 1 Cardiac Surgery department, National Heart Institute (NHI) 2 Radiodiagnosis
Nasty surprise of traumatic Diaphragmatic Rupture Rifaat kamar 1, Emad Sarawy 1, Mohamed Ahmed Osman 1 and Reham M Khalil 2 1 Cardiac Surgery department, National Heart Institute (NHI) 2 Radiodiagnosis
CHAPTER 3. The Human Body National Safety Council
 CHAPTER 3 The Human Body The Human Body Composed of many different organs and tissues All parts work together: To sustain life Allow activity Injury or illness impairs functions 3-3 Cranial located in
CHAPTER 3 The Human Body The Human Body Composed of many different organs and tissues All parts work together: To sustain life Allow activity Injury or illness impairs functions 3-3 Cranial located in
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen
 PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/23566
PDF hosted at the Radboud Repository of the Radboud University Nijmegen The following full text is a publisher's version. For additional information about this publication click this link. http://hdl.handle.net/2066/23566
Introduction and Definitions
 Bowel obstruction Introduction and Definitions Accounts for 5% of all acute surgical admissions Patients are often extremely ill requiring prompt assessment, resuscitation and intensive monitoring Obstruction
Bowel obstruction Introduction and Definitions Accounts for 5% of all acute surgical admissions Patients are often extremely ill requiring prompt assessment, resuscitation and intensive monitoring Obstruction
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax. Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem
 Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
Thoracic trauma. 1 The majority of deaths occur after the. FEBRUARY 2001 The Surgical Technologist
 Thoracic trauma Richard Wills, MD, MBA, ACSM, Michael Norton, DC, and Kathryn DeLaney Approximately 25% of nonmilitary trauma-related deaths are due to thoracic trauma. 1 The majority of deaths occur after
Thoracic trauma Richard Wills, MD, MBA, ACSM, Michael Norton, DC, and Kathryn DeLaney Approximately 25% of nonmilitary trauma-related deaths are due to thoracic trauma. 1 The majority of deaths occur after
Chest Trauma.
 Chest Trauma www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Objectives Anatomy of Thorax Main Causes of Chest Injuries S/S of Chest Injuries Different Types of Chest Injuries Treatments of Chest Injuries Anatomy of the chest
Chest Trauma www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Objectives Anatomy of Thorax Main Causes of Chest Injuries S/S of Chest Injuries Different Types of Chest Injuries Treatments of Chest Injuries Anatomy of the chest
Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials
 Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials 1 1. A high-risk bodily fluid for spreading infection is blood. 2. Items that can reduce the spread of infection include masks, gloves, and
Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials 1 1. A high-risk bodily fluid for spreading infection is blood. 2. Items that can reduce the spread of infection include masks, gloves, and
APHN. Shortness of breath. Ednin Hamzah CEO, Hospis Malaysia.
 APHN Shortness of breath Ednin Hamzah CEO, Hospis Malaysia ednin@hospismalaysia.org What is it? a subjective experience of difficult and uncomfortable breathing American Thoracic Society What do the patients
APHN Shortness of breath Ednin Hamzah CEO, Hospis Malaysia ednin@hospismalaysia.org What is it? a subjective experience of difficult and uncomfortable breathing American Thoracic Society What do the patients
Right lung. -fissures:
 -Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
-Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
