Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation
|
|
|
- Dominic Wheeler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation Registered Charity No Copyright 2011
2 Contents Glossary What is Atrial Fibrillation? Why do people with AF have their blood thinned? What blood thinning options are available for doctors to use? Anticoagulants Anti-platelets Which drug is best for me? How long do I need to take the drug? Glossary Anti-arrhythmic drugs Anticoagulant Arrhythmia Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Cardiologist Catheter ablation Drugs used to restore the normal heart rhythm Drugs which help to thin the blood Heart rhythm disorder Irregular heart rhythm A doctor who has specialised in the diagnosis and treatment of patients with a heart condition A treatment which destroys a very small area inside the heart causing the AF Electrophysiologist (EP) A cardiologist who has specialised in heart rhythm disorders Sinus rhythm TIAs Normal rhythm of the heart Transient Ischemic Attacks
3 What is Atrial Fibrillation? Atrial Fibrillation is the most common heart rhythm disturbance. It is a condition that is more common with advancing age and if untreated can lead to serious complications such as heart failure and stroke. Atrial Fibrillation results from a disturbance in the normal electrical conduction pathways in the heart (Figure 1). The normal, sequential electrical pathway is interrupted by a disorganised re-entrant circuit, causing a fast and irregular heart rate. This may contribute to symptoms of palpitations, shortness of breath, chest discomfort, light headedness, fainting or fatigue, although some patients have no symptoms. The goal of treatment in AF is to restore the heart s normal rhythm and if this is not possible then to slow the irregular heart rate to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications of AF related to stroke and heart failure. Sinus Node Pulmonary Veins Atrium AV Node Ventricle Conducting pathways 2010 Figure 1: Electrical system of the heart
4 Why do people with AF need to have their blood thinned? In AF the top chambers of the heart (the atria) develop chaotic electrical activity which completely dominates the natural pacemaker of the heart, the sino-atrial node. This chaotic electrical activity means that the atria no longer contract in together but instead the muscle quivers like a bag of worms. A lack of effi cient contraction means the blood within the atria becomes stagnant and can form clots. These clots can travel anywhere in the body but most worryingly they can travel to the brain and cause a stroke. Indeed the risk of stroke in AF is fi ve times greater than in the normal sinus rhythm (regular heart rhythm). This is why people with AF need to have their blood thinned to reduce the risk of clots forming and thus reduce the risk of strokes. What blood thinning options are available for doctors to use? Clots are made up of two main components from the blood. These are: (i) fi brin, a long protein that binds together to form a mesh and (ii) platelets, small cell particles that stick to the mesh and help to hold it together once they become active. The blood can be thinned to different degrees by attacking each of these components. Drugs like Warfarin and Heparin act to stop the formation of fi brin and are known as anticoagulants, whilst Aspirin and Clopidogrel are drugs that stop the activation of platelets and are known as anti-platelet agents. Anticoagulants By inhibiting the formation of the fi brin network, Warfarin and Heparin act to thin the blood very effi ciently and can reduce the risk of stroke by about two thirds. Warfarin At present only Warfarin is available in tablet form and thus useful for long-term blood thinning. Warfarin acts on the liver to prevent the formation of the proteins that go on to create fi brin. As our bodies have stores of these proteins that last a few days Warfarin will only start to thin
5 the blood effi ciently after a few days. In the same way when you stop Warfarin it takes the body a couple of days to replace these proteins and so the blood thinning effect will remain for a few days after you stop. As well as acting on the liver, Warfarin is removed from our bodies by the liver. We are all slightly different in how effi ciently our liver removes Warfarin as we are all slightly different in age, size and sex, and we all eat different foods, take different medications and drink different amounts of alcohol. This is why the dose of Warfarin needs to be tailored to each individual and is also why the dose of Warfarin needed can change from time to time, for instance drinking more alcohol when on holiday or taking a course of antibiotics for an infection. The effectiveness of Warfarin is measured by the INR (international ratio) which compares how fast blood clots compared to an international standard. Normal blood clots at fast as the international standard, so has an INR of 1. To prevent the risk of stroke in AF the blood needs to be 2-3 times thinner, so that it takes two to three times longer to clot than the standard i.e. has an INR of 2-3. By measuring the INR, anticoagulant clinics ensure that your blood is thinned to just the right amount. Too little Warfarin (INR<2) won t have the full benefi t of preventing strokes, whereas too much Warfarin (INR>3) thins the blood too much and can put you at risk of bleeding heavily when you cut yourself and of bruising badly when you fall. When you fi rst start taking Warfarin you will attend the anticoagulant clinic weekly as they adjust your dose to suit you. Most people fi nd once they are established on Warfarin their INR is pretty stable and they need only attend the clinic every 6-8 weeks. However you have to watch out for things that can affect your Warfarin level to keep it stable. One of these is alcohol. Taking alcohol in itself is not a large problem, but changing your average intake will alter the affect of the Warfarin and thus your INR level. Another thing you have to watch out for is medications including cough remedies, herbal cures and many other over-the-counter medications. In short you are fi ne to have a couple of paracetamol for a headache but anything else you should seek advice from your doctor or chemist. As your Warfarin level can change without you realising it, you should take care to avoid cuts and bruises; for instance use a thimble if you are sewing,
6 use an electric razor when shaving, etc. This all can sound a bit daunting but the vast majority of people who take Warfarin do so without any problems. Heparin At present Heparin-based products can only be given by injection either into the skin or veins, so are not useful for long-term blood thinning. Heparin thins the blood by blocking the proteins that form fi brin, i.e. it does not affect the production of these proteins but blocks them immediately. This gives Heparin the great advantage of being quick to act (i.e. effective immediately) and quick to stop (hours to half a day dependant on the type). Therefore Heparin is very useful when the level of blood thinning needs to be changed quickly. For example some people when they fi rst develop AF are very much at risk of a stroke and will be started on Heparin to protect them immediately. Another example is in preparation for surgery or other invasive procedures; Warfarin will be stopped and Heparin given instead until the day of the procedure. Anti-platelets Aspirin and Clopidogrel act in slightly different ways to prevent the activation of platelets. As they affect the platelets that are circulating in the blood they are effective almost immediately. However, as platelets are not so vital for clot formation in the atria they are less effective than anticoagulants at preventing strokes thus only reducing the stroke risk in AF by 20%. In some people who are at very low risk of stroke this is suffi cient. There are not the same problems with dose changes with Aspirin and Clopidogrel so there is not the need to attend regular clinics and not the same worries about taking other medications or injury risks. Although both Aspirin and Clopidogrel do prolong bleeding and thus increase the risk of bruising this is much less than the risks with Warfarin. The main problem with anti-platelet medication is gastric ulcers. This is only a risk with Aspirin and can be signifi cantly reduced by taking medications that reduce stomach acid like Omeprazole.
7 Table 1 Patients, with paroxysmal, persistent, permanent AF Determine stroke/ thromboembolic risk 1 1. Note that risk factors are not mutually exclusive, and are additive to each other producing a composite risk. High risk: previous ischaemic stroke/tia or thromboembolic event age 75 with hypertension, diabetes or vascular disease clinical evidence of valve disease or heart failure, or impaired left ventricular function on echocardiography. Moderate risk: age 65 with no high risk factors age < 75 with hypertension, diabetes or vascular disease. Low risk: age < 65 with no moderate or high risk factors. Anticoagulation with Warfarin Contraindications to Warfarin? Warfarin, target INR 2.5 (range 2.0 to 3.0) Consider anticoagulation or Aspirin 2 Aspirin 75 to 300 mg/ day if no contraindications Reassess risk stratifi cation whenever individual risk factors are reviewed 2. Owing to lack of sufficient clear-cut evidence, treatment may be decided on an individual basis, and the physician must balance the risk and benefi ts of Warfarin versus Aspirin. As stroke risk factors are cumulative, Warfarin may, for example, be used in the presence of two or more moderate stroke risk factors. Referral and echocardiography may help in cases of uncertainty. Figure 2 Stroke risk stratifi cation algorithm taken from current NICE guidelines on AF management. This fl ow-chart shows the steps in deciding whether a patient should be on Aspirin or Warfarin. Decision as to which medication needs to be discussed with your doctor.
8 Which drug is best for me? The choice of which drug is best for you depends on:- (i) your personal risk of stroke and (ii) if any interventions such as cardioversion or ablation are planned. Personal stroke risk By looking at large groups of people with AF and seeing who develops stroke it has become possible to identify which things put patients at risk of strokes. These have been made into scoring systems such as the stroke risk stratifi cation algorithm in the current NICE guidelines (Table 1). In this system patients are determined to be at high, moderate or low risk of stroke dependant on their age, clinical risk factors and fi ndings on cardiac ultrasound echocardiography. Assess your personal risk score Question Points Your Score Are you over 75? 1 Do you have high blood pressure? 1 Do you have Diabetes? 1 Do you have heart failure? 1 Have you suffered a stroke (even a mild stroke)? 2 Total Your annual risk of stroke rises from under 2% a year with no risk factors to over 10% a year for fi ve or six. Most experts who have looked at this scoring scheme (the CHADS score) would suggest that the tipping point for your benefi ts on taking anticoagulation medication (Warfarin) over its risks, is at a score of 2 or above. However, there are situations where, using the more detailed clinician assessment already shown, that even with a score of below 2, anticoagulation may be recommended. _
9 How long do I need to take the drug? As the decision of which blood thinning medication is determined by things other than the presence of AF, patients will usually stay on their blood thinning medication for life. There are a few situations where a patient s blood thinning medication will be changed for a short-period of time, for example if you develop problems with bleeding from somewhere such as an active ulcer, you may well switch onto Clopidogrel whilst your ulcer is cured. If you have a stroke whilst on aspirin you will most likely be switched to Warfarin. Another exception to the rule is interventions that try to return the heart to normal sinus rhythm such as cardioversion or AF ablation. By returning the heart to sinus rhythm these interventions will allow the atria to start contracting properly. In this situation any clots within the atria are at risk of being dislodged allowing them to travel to the brain and cause a stroke. It is for this reason that patients who are normally at low risk of stroke, and can have their blood suffi ciently thinned by anti-platelets, will have to temporarily be switched to Warfarin for cardioversion or AF ablation, and for a while after these procedures have been carried out.
10 Further information For further information on Atrial Fibrillation, please contact the Atrial Fibrillation Association. Helpline : +44 (0) Info@afa.org.uk Website:
11 Atrial Fibrillation Association MEMBERSHIP APPLICATION FORM Membership is free, however donations are gratefully received. Cheques should be made payable to AFA. If you are interested in receiving further information, becoming a volunteer or fundraiser, please do not hesitate to contact us. PLEASE PRINT - Patient Title: Mr / Mrs / Miss / Ms / Dr Full Name: Address: Postcode: Daytime Telephone no: Evening Telephone no: Date of Birth: Carer Name: Tel: Address: Tick box if happy to receive newsletters and updates from AFA Patient Diagnosed: Yes No Diagnosis: If Diagnosed by whom: GP Geriatrician Cardiologist Paediatrician Name: Hospital/Medical Centre: Registered Charity No: GIFT AID DECLARATION Name of taxpayer: Address: Postcode: Please tick to allow AFA to claim an extra 28p for every 1 you donate, at no cost to you. I want AFA to treat all donations I make from the date of this declaration until I notify you otherwise, as Gift Aid donations. I currently pay an amount of income tax and/or capital gains tax at least equal to the tax that AFA reclaims on my donations in the tax year (currently 28p for each ). I may cancel this declaration at any time by notifying AFA. I will notify AFA if I change my name or address. Please note full details of Gift Aid tax relief are available from your local tax office in leaflet IR 65. If you pay tax at the higher rate you can claim further tax relief in your Self-Assessment tax return. PLEASE RETURN TO: AFA, PO Box 1219, Chew Magna, BRISTOL BS40 8WB Telephone: info@afa.org.uk Registered Charity No:
12 Acknowledgements: The Atrial Fibrillation Association (AFA) would like to thank the GPs, cardiologists and nurses who helped develop these booklets. Particular thanks is given to Professor Gregory Y H Lip, Professor Clifford Garratt, Dr Jane Caldwell and Dr Matthew Fay for their work on this booklet. Trustees: Professor A John Camm Mrs Jayne Mudd Professor Richard Schilling Patron: Baroness Smith of Gilmorehill Baron Maples of Stratford upon Avon AFA Medical Advisory Committee: Dr Campbell Cowan Dr Matthew Fay Dr Adam Fitzpatrick Dr Andrew Grace Professor Gregory Y H Lip Dr Andreas Wolff Director & Chief Executive: Mrs Trudie Lobban Assistant Director: Mrs Jo Jerrome PO Box 1219, Chew Magna, Bristol, BS40 8WB, UK Tel: +44 (0) info@afa.org.uk Please remember these are general guidelines and individuals should always discuss The Heart Rhythm Charity their condition with their own doctor. Affiliated to Arrhythmia Alliance endorsed by Published May 2008 Reviewed December 2009 Re-printed September 2010
Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
 AF A Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Antiarrhythmic
AF A Blood Thinning in Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Antiarrhythmic
Patient & Primary Care Checklist
 established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Patient & Primary Care Checklist Tel: +44 (0)1789 451 837 Registered Charity Number: 1122442 2011 INTRODUCTION If you have been recently
established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Patient & Primary Care Checklist Tel: +44 (0)1789 451 837 Registered Charity Number: 1122442 2011 INTRODUCTION If you have been recently
Blood thinning (anticoagulation) in atrial fibrillation (AF)
 AF A Blood thinning (anticoagulation) in atrial fibrillation (AF) Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for atrial fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered
AF A Blood thinning (anticoagulation) in atrial fibrillation (AF) Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for atrial fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered
Living with Atrial Fibrillation: RELATIONSHIPS
 www.afa.org.uk Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Living with Atrial Fibrillation: RELATIONSHIPS Registered Charity No. 1122442
www.afa.org.uk Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Living with Atrial Fibrillation: RELATIONSHIPS Registered Charity No. 1122442
Patient and primary care checklist
 AF A www.afa.org.uk Patient and primary care checklist Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity No.
AF A www.afa.org.uk Patient and primary care checklist Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity No.
THE HEART, THE PULSE and THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAPH
 www.afa.org.uk Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation THE HEART, THE PULSE and THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAPH Registered Charity No. 1122442
www.afa.org.uk Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation THE HEART, THE PULSE and THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAPH Registered Charity No. 1122442
Patient & Primary Care Checklist
 www.afa-us.org established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Patient & Primary Care Checklist www.afa-us.org Tel: (843) 785 4101 Non-profit organization 501(C)(3) AFA 2011 AFA - US
www.afa-us.org established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Patient & Primary Care Checklist www.afa-us.org Tel: (843) 785 4101 Non-profit organization 501(C)(3) AFA 2011 AFA - US
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Patient Information
 Australia www.atrialfibrillation-au.org www.afa-international.org Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
Australia www.atrialfibrillation-au.org www.afa-international.org Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
Atrial Flutter Patient Information
 AF A Atrial Flutter Patient Information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Anti-arrhythmic
AF A Atrial Flutter Patient Information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Anti-arrhythmic
Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Patient Information
 AF A Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Patient Information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity No. 1122442
AF A Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Patient Information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity No. 1122442
Atrial fibrillation (AF) patient information
 AF A www.afa.org.uk Atrial fibrillation (AF) patient information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for atrial fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered
AF A www.afa.org.uk Atrial fibrillation (AF) patient information Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for atrial fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered
The heart, the pulse and the electrocardiograph
 AF A www.afa.org.uk The heart, the pulse and the electrocardiograph Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for atrial fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered
AF A www.afa.org.uk The heart, the pulse and the electrocardiograph Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for atrial fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered
Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulation- Challenges and Considerations
 Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulation- Challenges and Considerations Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation The development of
Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulation- Challenges and Considerations Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation The development of
Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation
 AF A Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation COMPLICATIONS OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION ABLATION Is catheter ablation safe? Registered Charity
AF A Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation COMPLICATIONS OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION ABLATION Is catheter ablation safe? Registered Charity
Electrophysiology Studies (EPS) The Heart Rhythm Charity
 Electrophysiology Studies (EPS) The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Electrophysiology Studies (EPS)
Electrophysiology Studies (EPS) The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Electrophysiology Studies (EPS)
How does the heart work? The heart is muscle whose main function is a pump; to push blood the rest of your body.
 1 You have a condition called atrial fibrillation. I would like you to learn more about this condition. You should read about it below, and can also watch an Internet program about it. After reading about
1 You have a condition called atrial fibrillation. I would like you to learn more about this condition. You should read about it below, and can also watch an Internet program about it. After reading about
Implantable Loop Recorder
 Implantable Loop Recorder Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity No. 1107496 Glossary
Implantable Loop Recorder Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity No. 1107496 Glossary
Fibrillation. Living. withatrial. Further information
 Further information Anticoagulation UK is committed to the prevention of thrombosis and to providing information and support to help people maintain their quality of life whilst on anticoagulant or antiplatelet
Further information Anticoagulation UK is committed to the prevention of thrombosis and to providing information and support to help people maintain their quality of life whilst on anticoagulant or antiplatelet
Genetic testing for inherited cardiac conditions
 Genetic testing for inherited cardiac conditions Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity
Genetic testing for inherited cardiac conditions Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity
Management strategies for atrial fibrillation Thursday, 20 October :27
 ALTHOUGH anyone who has had to run up a flight of steps or has had a frightening experience is quite familiar with a racing heartbeat, for the more than 2 million Americans who suffer from atrial fibrillation
ALTHOUGH anyone who has had to run up a flight of steps or has had a frightening experience is quite familiar with a racing heartbeat, for the more than 2 million Americans who suffer from atrial fibrillation
Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation
 AF A Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Anti-arrhythmic
AF A Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary Anti-arrhythmic
Direct Current (DC) Cardioversion
 Page 1 of 10 Direct Current (DC) Cardioversion Introduction This leaflet is to inform you about your planned Direct Current (DC) electrical cardioversion. A cardioversion is an electrical treatment which
Page 1 of 10 Direct Current (DC) Cardioversion Introduction This leaflet is to inform you about your planned Direct Current (DC) electrical cardioversion. A cardioversion is an electrical treatment which
Catheter Ablation. Patient Education
 Catheter Ablation Patient Education Allina Health System Your heart has four chambers. Two upper chambers (atria) pump blood to the two lower chambers (ventricles). In order for the heart to pump, it requires
Catheter Ablation Patient Education Allina Health System Your heart has four chambers. Two upper chambers (atria) pump blood to the two lower chambers (ventricles). In order for the heart to pump, it requires
The Heart, The Pulse and The Electrocardiograph
 AF A The Heart, The Pulse and The Electrocardiograph Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary
AF A The Heart, The Pulse and The Electrocardiograph Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.atrialfibrillation-au.org Glossary
Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants
 Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants A guide to your diagnosis and treatment Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: York Anticoagulant Clinic Tel: 01904
Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulants A guide to your diagnosis and treatment Information for patients, relatives and carers For more information, please contact: York Anticoagulant Clinic Tel: 01904
INFORMATION. Atrial Fibrillation. Summary. Information from the
 1. Information from the For more information contact Heartline 1300 362 787 or www.heartfoundation.com.au Atrial Fibrillation INFORMATION Summary What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is
1. Information from the For more information contact Heartline 1300 362 787 or www.heartfoundation.com.au Atrial Fibrillation INFORMATION Summary What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is
X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary
 X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary Introduction Atrial fibrillation is a common heart condition that affects approximately 2.5 million Americans every year. Atrial fibrillation requires immediate
X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary Introduction Atrial fibrillation is a common heart condition that affects approximately 2.5 million Americans every year. Atrial fibrillation requires immediate
Special health. guide. Hugh Calkins, M.D., and Ronald Berger, M.D., Ph.D. Guide to Understanding. Atrial Fibrillation WITH
 Hugh Calkins, M.D., and Ronald Berger, M.D., Ph.D. Guide to Understanding Atrial Fibrillation WITH Table of Contents Atrial Fibrillation: An Introduction... 1 How AF Affects the Heart... 2 Who Gets AF?...
Hugh Calkins, M.D., and Ronald Berger, M.D., Ph.D. Guide to Understanding Atrial Fibrillation WITH Table of Contents Atrial Fibrillation: An Introduction... 1 How AF Affects the Heart... 2 Who Gets AF?...
Information for patients, parents and guardians. Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation.
 Having an ablation Information for patients, parents and guardians Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation. An ablation is a treatment for an abnormal heartbeat.
Having an ablation Information for patients, parents and guardians Your child s doctor has recommended that your child has a procedure called an ablation. An ablation is a treatment for an abnormal heartbeat.
Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation
 AF A Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity No. 1122442
AF A Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity No. 1122442
Tachycardia (Fast Heart Rhythm)
 Tachycardia The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Tachycardia (Fast Heart Rhythm) www.heartrhythmcharity.org.uk
Tachycardia The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Tachycardia (Fast Heart Rhythm) www.heartrhythmcharity.org.uk
Atrial fibrillation. Understanding NICE guidance
 Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Atrial fibrillation NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases and the treatments
Understanding NICE guidance Information for people who use NHS services Atrial fibrillation NICE clinical guidelines advise the NHS on caring for people with specific conditions or diseases and the treatments
Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Definition of atrial fibrillation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Atrial fibrillation is a heart rhythm disturbance that causes an irregular (and often
Definition of atrial fibrillation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Atrial Fibrillation Ablation Atrial fibrillation is a heart rhythm disturbance that causes an irregular (and often
Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide
 Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
Atrial Fibrillation Your quick guide Coronary heart disease is the UK s single biggest killer. For over 50 years we ve pioneered research that s transformed the lives of people living with heart and circulatory
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES
 UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
UNDERSTANDING ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY STUDIES Testing and Treating Your Heart s Electrical System A Problem with Your Heart Rhythm The speed and pattern of a heartbeat is called the heart rhythm. The rhythm
Helping to prevent stroke caused by non-valvular atrial fibrillation Information booklet
 Helping to prevent stroke caused by non-valvular atrial fibrillation Information booklet IF FOUND, PLEASE RETURN TO: Name Address Phone number Contents ALERT CARD...2 BOOKLET INFORMATION...3 What is atrial
Helping to prevent stroke caused by non-valvular atrial fibrillation Information booklet IF FOUND, PLEASE RETURN TO: Name Address Phone number Contents ALERT CARD...2 BOOKLET INFORMATION...3 What is atrial
Arrhythmias. Pulmonary Artery
 Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
About atrial fibrillation (AFib) Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) What is AFib? What s the danger? Who gets AFib?
 Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation
 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation Todd J. Florin, M.D. Table of Contents The Normal Heart...1 What is Atrial Fibrillation...3 Risks of Afib: Stroke...5 Treatment Options...7 Radiofrequency Ablation...9
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation Todd J. Florin, M.D. Table of Contents The Normal Heart...1 What is Atrial Fibrillation...3 Risks of Afib: Stroke...5 Treatment Options...7 Radiofrequency Ablation...9
Blood-thinning medication after stroke
 Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent clots forming in your blood. They are often prescribed
Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 Website: stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent clots forming in your blood. They are often prescribed
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) patient information
 Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) patient information Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) patient information Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered
CATHETER ABLATION for ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 CATHETER ABLATION for ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation Clinic Dr. Richard Leather, Dr. Larry Sterns, Dr Paul Novak, Dr. Chris Lane and Dr. Sikkel Royal Jubilee Hospital Block 3 rd floor, Rm 343
CATHETER ABLATION for ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation Clinic Dr. Richard Leather, Dr. Larry Sterns, Dr Paul Novak, Dr. Chris Lane and Dr. Sikkel Royal Jubilee Hospital Block 3 rd floor, Rm 343
Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information
 Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
Melbourne Heart Rhythm Pacemaker and AV Node Ablation Patient Information The Heart The heart is a pump responsible for maintaining blood supply to the body. It has four chambers. The two upper chambers
Blood-thinning medication after stroke
 Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent clots forming in your blood. They are
Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Blood-thinning medication after stroke Blood-thinning medicines are drugs that help to prevent clots forming in your blood. They are
stroke.org.uk Atrial Fibrillation Reducing your risk of stroke
 stroke.org.uk Atrial Fibrillation Reducing your risk of stroke What is AF? Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is the most common type of irregular heartbeat. Over 1 million people in the UK are living with the condition,
stroke.org.uk Atrial Fibrillation Reducing your risk of stroke What is AF? Atrial Fibrillation (AF) is the most common type of irregular heartbeat. Over 1 million people in the UK are living with the condition,
Catheter Ablation for Atrial Flutter
 Additional Notes Our mission Providing the excellent care we would expect for our own families. The Royal Bournemouth Hospital, Castle Lane East, Bournemouth, Dorset, BH7 7DW The Bournemouth Hospital Charity
Additional Notes Our mission Providing the excellent care we would expect for our own families. The Royal Bournemouth Hospital, Castle Lane East, Bournemouth, Dorset, BH7 7DW The Bournemouth Hospital Charity
Atrial fibrillation (AF) and stroke
 Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Atrial fibrillation (AF) and stroke Atrial fibrillation is a type of irregular heartbeat. It means that your heart may not be pumping
Call the Stroke Helpline: 0303 3033 100 or email: info@stroke.org.uk Atrial fibrillation (AF) and stroke Atrial fibrillation is a type of irregular heartbeat. It means that your heart may not be pumping
GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
PATIENT INFORMATION GUIDE TO ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Atrial Fibrillation (AF) Atrial Flutter (AFL) Rate and Rhythm Control Stroke Prevention This document is endorsed by: A Comprehensive Resource from the
HEART SERIES H9 UNDERSTANDING ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 HEART SERIES H9 UNDERSTANDING ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland improves the quality of life for people in Scotland affected by chest, heart and stroke illness, through medical research,
HEART SERIES H9 UNDERSTANDING ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland improves the quality of life for people in Scotland affected by chest, heart and stroke illness, through medical research,
requesting information regarding atrial fibrillation in NHS Ashford Clinical Commissioning Group
 October 2015 Our Ref: FOI.15.ASH0149 requesting information regarding atrial fibrillation in NHS Ashford Clinical Commissioning Group Original Request Survey attached. Question 1: Between 1 July 2014 and
October 2015 Our Ref: FOI.15.ASH0149 requesting information regarding atrial fibrillation in NHS Ashford Clinical Commissioning Group Original Request Survey attached. Question 1: Between 1 July 2014 and
Warfarin. Living. with. Further information
 Further information Anticoagulation UK is committed to the prevention of thrombosis and to providing information and support to help people maintain their quality of life whilst on anticoagulant or antiplatelet
Further information Anticoagulation UK is committed to the prevention of thrombosis and to providing information and support to help people maintain their quality of life whilst on anticoagulant or antiplatelet
Question 1: Between 1 July 2014 and 30 June 2015, in the area covered by your CCG:
 Atrial Fibrillation in Your Area Question 1: Between 1 July 2014 and 30 June 2015, in the area covered by your CCG: a) What was the prevalence of atrial fibrillation (AF)? 6636 (as of 22/10/2015) 2.1%
Atrial Fibrillation in Your Area Question 1: Between 1 July 2014 and 30 June 2015, in the area covered by your CCG: a) What was the prevalence of atrial fibrillation (AF)? 6636 (as of 22/10/2015) 2.1%
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation A guide for patients
 Understanding Atrial Fibrillation A guide for patients Your doctor has determined that you have atrial fibrillation (AF), a common disturbance of the heart s rhythm. This pamphlet will answer many of your
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation A guide for patients Your doctor has determined that you have atrial fibrillation (AF), a common disturbance of the heart s rhythm. This pamphlet will answer many of your
What can I do about sudden cardiac arrest?
 The Heart Rhythm Charity What can I do about sudden cardiac arrest? Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for those affected by heart rhythm disorders (cardiac arrhythmias)
The Heart Rhythm Charity What can I do about sudden cardiac arrest? Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for those affected by heart rhythm disorders (cardiac arrhythmias)
AF AND YOU AN INFORMATION BOOKLET FOR PEOPLE LIVING WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
 www.irishheart.ie AF AND YOU AN INFORMATION BOOKLET FOR PEOPLE LIVING WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Registered charity number CHY 5507 Produced by the Irish Heart Foundation This booklet is one of the publications
www.irishheart.ie AF AND YOU AN INFORMATION BOOKLET FOR PEOPLE LIVING WITH ATRIAL FIBRILLATION Registered charity number CHY 5507 Produced by the Irish Heart Foundation This booklet is one of the publications
Frequently Asked Questions
 AF A Frequently Asked Questions Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity No. 1122442 Glossary Aortic
AF A Frequently Asked Questions Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for Atrial Fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity No. 1122442 Glossary Aortic
Atrial fibrillation and anticoagulation therapy
 Atrial fibrillation and anticoagulation therapy This leaflet offers more information about atrial fibrillation for patients who have been advised that they need anticoagulation therapy. If you have any
Atrial fibrillation and anticoagulation therapy This leaflet offers more information about atrial fibrillation for patients who have been advised that they need anticoagulation therapy. If you have any
Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias
 Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Atrial Fibrillation According to the American Heart Association, Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects an estimated 2.7 million
Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Atrial Fibrillation According to the American Heart Association, Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects an estimated 2.7 million
Frequently asked questions
 AF A Frequently asked questions Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for atrial fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity No. 1122442 Glossary Abdominal
AF A Frequently asked questions Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for atrial fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity No. 1122442 Glossary Abdominal
Atrial Fibrillation Ablation
 Patient Information Atrial Fibrillation Ablation This leaflet is designed to give you more information about atrial fibrillation and catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. It will hopefully cover any
Patient Information Atrial Fibrillation Ablation This leaflet is designed to give you more information about atrial fibrillation and catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. It will hopefully cover any
Electrophysiology Studies and Catheter Ablation. Electrophysiology Studies and Catheter Ablation
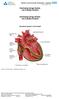 Electrophysiology Studies Cardiac Conduction System. Mdmedicine.wordpress.com Patient Information Leaflet for: Electrophysiology Studies Available via Trust Docs Version: 6 Trust Docs ID: 10 Page 1 of
Electrophysiology Studies Cardiac Conduction System. Mdmedicine.wordpress.com Patient Information Leaflet for: Electrophysiology Studies Available via Trust Docs Version: 6 Trust Docs ID: 10 Page 1 of
National Service Framework
 National Service Framework The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias National Requirments - Local Implementation
National Service Framework The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias National Requirments - Local Implementation
Catheter Ablation for Supra-ventricular Tachycardia
 Additional Notes Our mission To provide the excellent care we would expect for our families. The Royal Bournemouth Hospital, Castle Lane East, Bournemouth, Dorset, BH7 7DW The Bournemouth Hospital Charity
Additional Notes Our mission To provide the excellent care we would expect for our families. The Royal Bournemouth Hospital, Castle Lane East, Bournemouth, Dorset, BH7 7DW The Bournemouth Hospital Charity
Treatment strategy decision tree
 strategy decision tree strategy decision tree Confirmed diagnosis of AF Further investigations and clinical assessment including risk stratification for stroke/thromboembolism Paroxysmal AF Persistent
strategy decision tree strategy decision tree Confirmed diagnosis of AF Further investigations and clinical assessment including risk stratification for stroke/thromboembolism Paroxysmal AF Persistent
Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology
 Definition of electrophysiology study and ablation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Electrophysiology Study and Ablation An electrophysiology, or EP, study is a test of the heart
Definition of electrophysiology study and ablation Kadlec Regional Medical Center Cardiac Electrophysiology Electrophysiology Study and Ablation An electrophysiology, or EP, study is a test of the heart
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO THE LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE CLOSURE. Reducing the risk of stroke in atrial fibrillation
 A PATIENT S GUIDE TO THE LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE CLOSURE Reducing the risk of stroke in atrial fibrillation TABLE OF CONTENTS IMPORTANT Please Note: Information provided by Boston Scientific Corporation
A PATIENT S GUIDE TO THE LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE CLOSURE Reducing the risk of stroke in atrial fibrillation TABLE OF CONTENTS IMPORTANT Please Note: Information provided by Boston Scientific Corporation
What is an. arrhythmia?
 What is an arrhythmia? What is an arrhythmia? Arrhythmia is an umbrella term used to describe a number of conditions where the muscle contraction of the heart is too slow, too fast or irregular because
What is an arrhythmia? What is an arrhythmia? Arrhythmia is an umbrella term used to describe a number of conditions where the muscle contraction of the heart is too slow, too fast or irregular because
Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
 Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Normally blood moves freely throughout the body without any problems. However, if a blood clot forms in a vein it can block the vein and stop the blood from flowing properly. Sometimes
Pulmonary Embolism (PE) Normally blood moves freely throughout the body without any problems. However, if a blood clot forms in a vein it can block the vein and stop the blood from flowing properly. Sometimes
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION ANSWERS. A Patient Education Handbook on Electrophysiology
 ATRIAL FIBRILLATION ANSWERS A Patient Education Handbook on Electrophysiology MY LIFE HAS TAKEN A TURN FOR THE BETTER. -Emie Bishop ARRHYTHMIAANSWERS.COM AF ANSWERS. A PATIENT EDUCATION HANDBOOK ON ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY
ATRIAL FIBRILLATION ANSWERS A Patient Education Handbook on Electrophysiology MY LIFE HAS TAKEN A TURN FOR THE BETTER. -Emie Bishop ARRHYTHMIAANSWERS.COM AF ANSWERS. A PATIENT EDUCATION HANDBOOK ON ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY
Listen to Your Heart. What Everyone Needs To Know About Atrial Fibrillation & Stroke. The S-ICD System. The protection you need
 Listen to Your Heart The S-ICD System What Everyone Needs To Know About Atrial Fibrillation & Stroke The protection you need without Stroke. touching Are you your at heart risk? Increase your knowledge.
Listen to Your Heart The S-ICD System What Everyone Needs To Know About Atrial Fibrillation & Stroke The protection you need without Stroke. touching Are you your at heart risk? Increase your knowledge.
Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION. in general practice. 22 BPJ Issue 39
 Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION in general practice 22 BPJ Issue 39 What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia encountered in primary care. It is often
Management of ATRIAL FIBRILLATION in general practice 22 BPJ Issue 39 What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia encountered in primary care. It is often
Direct Current Cardioversion (DCCV)
 PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is a This is a procedure carried out under a brief anaesthetic, which uses a
PLEASE PRINT WHOLE FORM DOUBLE SIDED ON YELLOW PAPER Patient Information to be retained by patient affix patient label What is a This is a procedure carried out under a brief anaesthetic, which uses a
Drug Treatment for Heart Rhythm Disorders (Arrhythmia)
 Drug Treatment for Heart Rhythm Disorders (Arrhythmia) The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Drug Treatment
Drug Treatment for Heart Rhythm Disorders (Arrhythmia) The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Drug Treatment
AF Today: W. For the majority of patients with atrial. are the Options? Chris Case
 AF Today: W hat are the Options? Management strategies for patients with atrial fibrillation should depend on the individual patient. Treatment with medications seems adequate for most patients with atrial
AF Today: W hat are the Options? Management strategies for patients with atrial fibrillation should depend on the individual patient. Treatment with medications seems adequate for most patients with atrial
I know my value. Be an active part of your anticoagulation therapy with INR self-monitoring
 I know my value Be an active part of your anticoagulation therapy with INR self-monitoring INR* self-monitoring needs only a drop of blood, is easy, fast and decreases the possibility Be involved in your
I know my value Be an active part of your anticoagulation therapy with INR self-monitoring INR* self-monitoring needs only a drop of blood, is easy, fast and decreases the possibility Be involved in your
Pacemaker Patient Information
 Pacemaker Patient Information The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Pacemaker Patient Information www.heartrhythmcharity.org.uk
Pacemaker Patient Information The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Pacemaker Patient Information www.heartrhythmcharity.org.uk
Abnormal Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias)
 Abnormal Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias) Page 1 of 5 The heart needs a small electrical current to pass through the heart in a very set pattern. This is called the heart's conduction system. This leaflet explains
Abnormal Heart Rhythms (Arrhythmias) Page 1 of 5 The heart needs a small electrical current to pass through the heart in a very set pattern. This is called the heart's conduction system. This leaflet explains
Cardioversion of atrial fibrillation
 AF A www.afa.org.uk Cardioversion of atrial fibrillation Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for atrial fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity
AF A www.afa.org.uk Cardioversion of atrial fibrillation Providing information, support and access to established, new or innovative treatments for atrial fibrillation www.afa.org.uk Registered Charity
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease
 Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
Patient Resources: Arrhythmias and Congenital Heart Disease Overview Arrhythmias (abnormal heart rhythms) can develop in patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) due to thickening/weakening of their
Warfarin. Information for patients taking warfarin
 Warfarin Information for patients taking warfarin Read this booklet to learn: what warfarin is and why you are taking it what blood tests you need to use warfarin safely how other medicines and diet can
Warfarin Information for patients taking warfarin Read this booklet to learn: what warfarin is and why you are taking it what blood tests you need to use warfarin safely how other medicines and diet can
Atrial Fibrillation Information for patients
 be informed about... Atrial Fibrillation Information for patients Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an abnormal heart rhythm. This pamphlet answers some questions you may have about AF, and gives an overview
be informed about... Atrial Fibrillation Information for patients Atrial fibrillation (AF) is an abnormal heart rhythm. This pamphlet answers some questions you may have about AF, and gives an overview
Closing your atrial septal defect without surgery
 Patient information service Bristol Heart Institute Closing your atrial septal defect without surgery Respecting everyone Embracing change Recognising success Working together Our hospitals. What is an
Patient information service Bristol Heart Institute Closing your atrial septal defect without surgery Respecting everyone Embracing change Recognising success Working together Our hospitals. What is an
Some useful websites
 MonashHeart, Monash Health is committed to providing outstanding cardiac services for cardiac patients of all ages Some useful websites MonashHealth Every 10 minutes, an Australian dies from cardiovascular
MonashHeart, Monash Health is committed to providing outstanding cardiac services for cardiac patients of all ages Some useful websites MonashHealth Every 10 minutes, an Australian dies from cardiovascular
What can I do about sudden cardiac arrest?
 What can I do about sudden cardiac arrest? Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity
What can I do about sudden cardiac arrest? Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias www.heartrhythmalliance.org Registered Charity
The Heart Rhythm Charity
 The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Registered Charity No. 1107496 2007 CRT / Pacemaker Patient Information
The Heart Rhythm Charity Promoting better understanding, diagnosis, treatment and quality of life for individuals with cardiac arrhythmias Registered Charity No. 1107496 2007 CRT / Pacemaker Patient Information
Sudden Cardiac Arrest. How you can make a difference. Restart The Heart. Arrhythmia Alliance. The Heart Rhythm Charity
 Restart The Heart Arrhythmia Alliance The Heart Rhythm Charity www.heartrhythmcharity.org.uk Registered Charity No. 1107496 2011 Sudden Cardiac Arrest How you can make a difference Everyday, someone like
Restart The Heart Arrhythmia Alliance The Heart Rhythm Charity www.heartrhythmcharity.org.uk Registered Charity No. 1107496 2011 Sudden Cardiac Arrest How you can make a difference Everyday, someone like
Pharmaceutical Care of People with Atrial Fibrillation. Course information
 Pharmaceutical Care of People with Atrial Fibrillation Course information Pharmaceutical Care of People with Atrial Fibrillation Course information page 3 Introduction 5 Teaching plan 6 Needs Assessment
Pharmaceutical Care of People with Atrial Fibrillation Course information Pharmaceutical Care of People with Atrial Fibrillation Course information page 3 Introduction 5 Teaching plan 6 Needs Assessment
Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast. Information for patients Pharmacy
 Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast Information for patients Pharmacy Your doctor has prescribed a tablet called rivaroxaban. This leaflet tells you about
Rivaroxaban to prevent blood clots for patients who have a lower limb plaster cast Information for patients Pharmacy Your doctor has prescribed a tablet called rivaroxaban. This leaflet tells you about
Radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery
 Issue date: May 2005 Radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery Understanding NICE guidance information for people considering the procedure, and for the
Issue date: May 2005 Radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery Understanding NICE guidance information for people considering the procedure, and for the
Cryoablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery. Issue date: May 2005
 Issue date: May 2005 Cryoablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery Understanding NICE guidance information for people considering the procedure, and for the public Information
Issue date: May 2005 Cryoablation for atrial fibrillation in association with other cardiac surgery Understanding NICE guidance information for people considering the procedure, and for the public Information
Banner Health Center
 Banner Health Center Coumadin Education Class Anticoagulation Clinic Please turn cell phones off. Thank you! The History of Coumadin 1920s: cattle deaths due to anti-clotting agent found in clover Mid-1940s:
Banner Health Center Coumadin Education Class Anticoagulation Clinic Please turn cell phones off. Thank you! The History of Coumadin 1920s: cattle deaths due to anti-clotting agent found in clover Mid-1940s:
Information about TIA
 Information about TIA Transient Ischemic Attack (mini-stroke) Did I have a TIA? Did you have stroke-like symptoms such as slurred speech or weakness in one arm that seemed to go away after a few minutes
Information about TIA Transient Ischemic Attack (mini-stroke) Did I have a TIA? Did you have stroke-like symptoms such as slurred speech or weakness in one arm that seemed to go away after a few minutes
Treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism with low molecular weight heparin
 Treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism with low molecular weight heparin You have been given this leaflet because you have a blood clot. Normally blood flows freely around the body without
Treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism with low molecular weight heparin You have been given this leaflet because you have a blood clot. Normally blood flows freely around the body without
Palpitation Checklist
 Palpitation Checklist Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias Palpitation Checklist Registered Charity No. 1107496 2016 Introduction When
Palpitation Checklist Working together to improve the diagnosis, treatment quality of life for all those affected by arrhythmias Palpitation Checklist Registered Charity No. 1107496 2016 Introduction When
ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT INDIGESTION FUNDING RESEARCH INTO DISEASES OF THE GUT, LIVER & PANCREAS
 ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT INDIGESTION FUNDING RESEARCH INTO DISEASES OF THE GUT, LIVER & PANCREAS THIS FACTSHEET IS ABOUT INDIGESTION Indigestion (also known as dyspepsia) is a term used to describe unpleasant
ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW ABOUT INDIGESTION FUNDING RESEARCH INTO DISEASES OF THE GUT, LIVER & PANCREAS THIS FACTSHEET IS ABOUT INDIGESTION Indigestion (also known as dyspepsia) is a term used to describe unpleasant
Working together with individuals, families, and medical professionals to offer support and information on Syncope. Do you suffer from unexplained...
 Working together with individuals, families, and medical professionals to offer support and information on Syncope Do you suffer from unexplained... Affiliated to Arrhythmia Alliance BMA Patient Information
Working together with individuals, families, and medical professionals to offer support and information on Syncope Do you suffer from unexplained... Affiliated to Arrhythmia Alliance BMA Patient Information
Medicines for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation. Choosing the right one for you
 Medicines for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation Choosing the right one for you Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a condition that affects the heart, causing it to beat irregularly and too fast. When this
Medicines for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation Choosing the right one for you Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a condition that affects the heart, causing it to beat irregularly and too fast. When this
Atrial Fibrillation Implementation challenges. Lesley Edgar Ross Maconachie
 Atrial Fibrillation Implementation challenges Lesley Edgar Ross Maconachie Atrial Fibrillation Most common heart rhythm disturbance Rapid and irregular electrical signals Reduced efficiency of blood flow
Atrial Fibrillation Implementation challenges Lesley Edgar Ross Maconachie Atrial Fibrillation Most common heart rhythm disturbance Rapid and irregular electrical signals Reduced efficiency of blood flow
Initial assessment of patient with AF in primary care DR BRUCE TAYLOR GPwSI Cardiology SCN Merseyside and Cheshire Clinical Lead Primary care
 Initial assessment of patient with AF in primary care DR BRUCE TAYLOR GPwSI Cardiology SCN Merseyside and Cheshire Clinical Lead Primary care 11 th and 25 th September 2014 3 KEY OBJECTIVES OF TALK 1.
Initial assessment of patient with AF in primary care DR BRUCE TAYLOR GPwSI Cardiology SCN Merseyside and Cheshire Clinical Lead Primary care 11 th and 25 th September 2014 3 KEY OBJECTIVES OF TALK 1.
Atrial Fibrillation. Damage to your heart caused by a heart attack or rheumatic heart disease
 Atrial Fibrillation GENERAL INFORMATION: What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a condition that causes the atria (top chambers of the heart) to shake or quiver. Normally, there is 1 contraction
Atrial Fibrillation GENERAL INFORMATION: What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a condition that causes the atria (top chambers of the heart) to shake or quiver. Normally, there is 1 contraction
