(12) United States Patent
|
|
|
- Christine Harmon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 USOO B2 (12) United States Patent Cage et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9.498,226 B2 Nov. 22, 2016 (54) EMBOLIC COIL DELIVERY SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Logan Michael Cage, Bloomington, IN (US); Sarah Elizabeth Reeves, Bloomington, IN (US) (73) Assignee: Cook Medical Technologies, LLC, Bloomington, IN (US) (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this patent is extended or adjusted under 35 U.S.C. 154(b) by 758 days. (21) Appl. No.: 13/596,599 (22) Filed: Aug. 28, 2012 (65) Prior Publication Data US 2013 FOOT2961 A1 Mar. 21, 2013 Related U.S. Application Data (60) Provisional application No. 61/535,553, filed on Sep. 16, (51) Int. Cl. A6 IF 2/06 ( ) A6B 7/2 ( ) (52) U.S. Cl. CPC. A61B 17/12113 ( ); A61B 17/1214 ( ); A61B 2017/1205 ( ) (58) Field of Classification Search CPC... A61F 2/962: A61F 2/966; A61F 2/97; A61F 2002/9665; A61B 2017/1205; A61B 2017/12054: A61B 17/12022: A61B 17/12113: A61B 17/12118: A61B 17/1214: A61B 17/12145; A61B 17/1215; A61B 17/12154: A61B 2017/12127; A61B 17/1254 USPC /1.11, 1.12: 606/108, 194, 200, 191 See application file for complete search history. (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS 5, A * 5/1994 Palermo... A61B 17, ,108 5,735,859 A * 4/1998 Fischell et al ,108 5,824,041 A * 10/1998 Lenker... A61F 2/91 606, ,342 B2 7, 2011 Gandhi et al. 2002/0O26217 A1 2/2002 Baker et al , fOO32459 A1* 3, 2002 Horzewski... A61B 17, , , A1* 4, 2007 Buiser... A61B 17, , , OO27482 A1 2010, O A1 2011/ A1 1/2008 Sekido et al. 6, 2010 Schrodt 1/2011 Tekulve OTHER PUBLICATIONS Cook Medical, Amplatz Vascular Obstruction Device, 2011, pp * cited by examiner Primary Examiner Jonathan Miles Assistant Examiner Kankindi Rwego (74) Attorney, Agent, or Firm Liell & McNeil (57) ABSTRACT An embolic coil delivery system includes a flexible elongate body having a distal segment. An embolic coil is loaded on the flexible elongate body at the distal segment and contacts an outer surface of the flexible elongate body. The embolic coil delivery system also includes a delivery catheter sized to advance over the flexible elongate body during an embo lic coil delivery procedure, wherein a distal segment of the delivery catheter contacts the embolic coil during the embo lic coil delivery procedure. 16 Claims, 3 Drawing Sheets
2 U.S. Patent US 9.498,226 B2?Inº?I
3 U.S. Patent Nov. 22, 2016 Sheet 2 of 3 US 9.498,226 B2
4 U.S. Patent Nov. 22, 2016 Sheet 3 of 3 US 9.498,226 B2 Œ===========É ZZ
5 1. EMBOLIC COL DELVERY SYSTEM RELATION TO OTHER PATENT APPLICATION This application claims priority to provisional patent application 61/535,553, filed Sep. 16, 2011, with the same title. TECHNICAL FIELD The present disclosure relates generally to an embolic coil delivery system, and more particularly to a system for loading an embolic coil on an outer surface of a flexible elongate body and advancing a delivery catheter over the flexible elongate body to contact and unload the embolic coil. BACKGROUND Embolization procedures are designed to create an artifi cial blockage within a vessel to block blood from flowing downstream from the blockage. These procedures are used to treat several conditions, including, for example, aneu rysms, hemorrhages, and lesions or growths. Specifically, for example, an embolic device may be used to occlude blood flow to an aneurysm and, thus, reduce the risk of the aneurysm rupturing and producing internal hemorrhaging. Embolic devices may include physical barriers, such as coils, balloons, chemicals, and the like. According to one type of embolization procedure, a plurality of embolic coils are delivered to the embolization site. These coils may vary in stiffness, such that a stiffer coil may provide a strong radial force to maintain the position of the artificial block age, while a softer coil may be used as packing material to occupy space at the blockage. During an embolic coil delivery procedure, the one or more embolic coils are typically delivered to the emboliza tion site in the vasculature of a patient through the use of a catheter delivery system. Specifically, the embolic coils are loaded into the lumen of a catheter and the catheter is inserted into the vasculature such that the distal end of the catheter is proximate the embolization site. The embolic coils are then advanced through the lumen of the catheter using a pusher wire or pressurized fluid until the coils exit the distal end of the catheter. Unfortunately, this delivery procedure Suffers drawbacks, including those caused by the resistance created by the one or more coils loaded into the catheter lumen. For example, this resistance to the force created by the pusher wire or pressurized fluid may lead to procedural complications, including imprecise positioning of the embolic coils within the patient vasculature. The present disclosure is directed toward one or more of the problems set forth above. SUMMARY OF THE DISCLOSURE In one aspect, an embolic coil delivery system includes a flexible elongate body having a distal segment. An embolic coil is loaded on the flexible elongate body at the distal segment and contacts an outer Surface of the flexible elon gate body. The embolic coil delivery system also includes a delivery catheter sized to advance over the flexible elongate body during an embolic coil delivery procedure, wherein a distal segment of the delivery catheter contacts the embolic coil during the embolic coil delivery procedure. In another aspect, a preloaded wire guide for an embolic coil delivery system includes a mandril wire guide having a US 9,498,226 B distal segment. An embolic coil is loaded on the mandril wire guide at the distal segment and contacts an outer surface of the flexible elongate body. A delivery sheath is positioned over the embolic coil. In yet another aspect, a method of delivering an embolic coil to a delivery site within a patient vessel includes loading the embolic coil around an outer Surface of a distal segment of a flexible elongate body. The distal segment of the flexible elongate body is advanced through the patient vessel to the delivery site, and the embolic coil is unloaded from the flexible elongate body at least in part by advancing a delivery catheter over the flexible elongate body and con tacting the embolic coil with a distal segment of the delivery catheter. BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS FIG. 1 is a cross sectional schematic of an embolic coil delivery system, according to one embodiment of the pres ent disclosure; FIG. 2 is a cross sectional schematic of a preloaded wire guide of the embolic coil delivery system of FIG. 1, shown inserted into the vasculature of a patient at a first stage of an embolic coil delivery procedure; FIG.3 is a cross sectional schematic of the preloaded wire guide of the previous Figures, shown at a second stage of the embolic coil delivery procedure with a delivery sheath removed; FIG. 4 is a cross sectional schematic of the preloaded wire guide of the previous Figures, shown at a third stage of the embolic coil delivery procedure with a delivery catheter of the embolic coil delivery system advanced over the pre loaded wire guide; and FIG. 5 is a cross sectional schematic of a fourth stage of the embolic coil delivery procedure, wherein the embolic coils are delivered at a delivery site. DETAILED DESCRIPTION Referring to FIG. 1, there is shown an embolic coil delivery system 10 according to one embodiment of the present disclosure. The embolic coil delivery system 10 may include a number of components, which may be provided within a sterile, tear open package 12, as is known in the art. In performing an embolic coil delivery procedure on a patient, some or all of the components of the embolic coil delivery system 10 may be used, depending upon the spe cifics of the procedure to be performed. As should be appreciated, however, the components shown in FIG. 1 might be separately packaged and/or the embolic coil deliv ery system 10 might also include components in addition to those shown, including components routinely used in per cutaneous endovascular procedures. The embolic coil delivery system 10 may generally include a flexible elongate body 14, which may be a solid structure, as shown, or may be hollow, with an outer tube defining an internal lumen. According to the exemplary embodiment, the flexible elongate body 14 may be a mandril wire guide 15 formed from stainless steel, or other com monly selected material, to provide a desired combination of stiffness and flexibility. For example, a certain degree of stiffness may be required for pushability and trackability, while a certain degree of flexibility may be required for improving vasculature navigation. It should be appreciated that the stiffness of the flexible elongate body 14 may be consistent along a longitudinal axis A of the body 14 or may
6 3 vary, depending on the specifics of the procedure to be performed and the performance characteristics desired. As shown, the flexible elongate body 14 may include a distal segment 16 that is tapered. The taper, which may increase flexibility of elongate body 14, may be gradual or abrupt, and may begin at any position along the flexible elongate body 14 from a proximal end 18 to a distal end 20 of the body 14. In addition, a thermoplastic polymer coating 22, Such as a polyester or polyether block amide, may be provided at the distal end 20 of the flexible elongate body 14. Particularly, the polymer coating 22 may provide a desirable lubricity profile that exhibits low friction during introduction of the flexible elongate body 14 through a vessel of the patient. A coating, such as a thermoplastic coating, may also be provided along an entire length of the flexible elongate body 14. For example, an outer surface 24 of the flexible elongate body 14 may be coated with high density polyeth ylene (HDPE), polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), polyethyl ene terephthalate (PET), polyester or polyether block amide (PEBA), polyurethane, polyimide, polyolefin, nylon, or any combination thereof. The coatings, including the polymer coating 22, may be applied by, for example, over-extrusion, dip-coating, melt fusion, heat shrinking, or using other known application means. The embolic coil delivery system 10 may also include a first embolic coil 26 and a second embolic coil 28 loaded on the flexible elongate body 14 at the distal segment 16 of the body 14. Although two embolic coils 26 and 28 are shown, any number of coils, including only one coil, may be loaded on the flexible elongate body 14. The embolic coils 26 and 28 may be helically wound coils, randomly wound coils, coils would within other coils, or may have various other coil configurations. Further, the coils may be made from a radiopaque metallic material. Such as, for example, platinum or stainless steel. According to some embodiments, a first stiffness measurement, or durometer, of the first coil 26 may be different than a second stiffness measurement of the second coil 28. The embolic coils 26 and 28, which may have various configurations, may be frictionally engaged with the outer surface 24 of the flexible elongate body 14 to maintain a loaded, or relatively fixed position of the embolic coils 26 and 28 relative to the body 14. The flexible elongate body 14, with the embolic coils 26 and 28 loaded thereon, may also be referenced as a preloaded wire guide 30. A delivery sheath 32 may be positioned over the embolic coils 26 and 28, as shown in the exemplary embodiment. The delivery sheath 32 may be made from a flexible film, Such as, for example, a medical grade polyethylene film, and may be positioned over a segment of the outer Surface 24 of the flexible elongate body 24, including the segment Sup porting the embolic coils 26 and 28. A distal end 34 or, more specifically, an open distal end of the delivery sheath 32 may be removably attached to the flexible elongate body 14 at an axial position of the body 14 that is distally spaced from the embolic coils 26 and 28. Specifically, according to one embodiment, the delivery sheath 32 may have an attached distal end 34 and an unattached proximal end 36 that is unattached relative to the flexible elongate body 14. The unattached proximal end 36, according to the exemplary embodiment, may extend from the attached distal end 34 toward the proximal end 18 of the flexible elongate body 14. The removable attachment of the delivery sheath 32 to the flexible elongate body 14 at the attached distal end 34 may include any attachment that facilitates removal of the deliv ery sheath 32, or at least the portion that covers the embolic coils 26 and 28, while the flexible elongate body 14 is positioned within the vasculature of the patient. Thus, the US 9,498,226 B removable attachment may be as simple as a perforated tear away section or may be relatively complex. Such as includ ing a repositioning device that may be manipulated exter nally from the vasculature of the patient. Although a delivery sheath 32 is described, it should be appreciated that another component capable of shielding the embolic coils 26 and 28 and/or maintaining a loaded position of the coils 26 and 28 during an embolic coil delivery procedure may be substi tuted for the delivery sheath 32. The embolic coil delivery system 10 may also include a delivery catheter 38 sized to advance over the flexible elongate body 14 during an embolic coil delivery procedure. Specifically, the delivery catheter 38 may include a tube 40 defining an internal lumen 42 extending from a distal segment 44 to a proximal segment 46, wherein the lumen 42 defines an inner diameter d that Substantially matches an outer diameter d of the flexible elongate body 14. As used herein, matches' means that the inner diameter d is slightly greater than the outer diameter d or otherwise sized such that the distal segment 44 of the delivery catheter 38 may advance over the flexible elongate body 14 and contact the embolic coils 26 and 28 during an embolic coil delivery procedure. As such, the distal segment 44 may be suitably shaped to urge the coils 26 and 28 from the flexible elongate body 14. The delivery catheter 38 may comprise a lubricious material such as PTFE and may or may not include a reinforcement material to provide kink resistance and torqueability while retaining a desired level of flexibility. As should be appreciated, the delivery catheter 38 may be a multi-layer tube comprised of various other materials, or may even include single polymeric tubes. It should also be appreciated that the materials and overall construction of the delivery catheter 38 and flexible elongate body 14 may be selected to improve or enhance usability of the embolic coil delivery system 10. INDUSTRIAL APPLICABILITY The present disclosure is generally applicable to embolic coil delivery systems for use in percutaneous endovascular procedures. More specifically, the present disclosure finds application in procedures to deliver an embolic coil to a delivery site within the vascular system of a patient. Further the present disclosure finds specific application in proce dures during which a plurality of embolic coils are delivered to the delivery site within the vasculature of the patient to provide an artificial blockage. Referring to FIGS. 2-5, an embolic coil delivery proce dure using the embolic coil delivery system 10 (FIG. 1) will be described with reference to a vascular structure V of a patient. Although not shown, it should be appreciated that a needle, or introducer, may be used to gain percutaneous access to the vascular structure V, as is known to those skilled in the art. It should also be appreciated that the embolic coils 26 and 28 may be preloaded around the outer surface 24 of the distal segment 16 of the flexible elongate body 14 to define a preloaded wire guide 30. Loading the embolic coils 26 and 28, according to an exemplary embodi ment, may include frictionally engaging the embolic coils 26 and 28 with the outer surface 24 of the flexible elongate body 14. Further, a delivery sheath 32, as described above, may be provided over the embolic coils 26 and 28 to shield the embolic coils 26 and 28 during the embolic coil delivery procedure and, particularly, during advancement of the flexible elongate body 14 through the vasculature structure V.
7 5 At the first stage of the embolic coil delivery procedure, shown in FIG. 2, the distal segment 16 of the flexible elongate body 14, or preloaded wire guide 30, may be advanced through the vascular structure V to a delivery site 50. The delivery site 50 may represent a desired delivery site for the embolic coils 26 and 28, such as, for example, a bulge or aneurysm. The delivery sheath 32 may assist in main taining a loaded position of the embolic coils 26 and 28 while the preloaded wire guide 30 is advanced relative to the delivery site 50. It should be appreciated that any of a number of imaging techniques and/or systems may be used to assist in the positioning of the preloaded wire guide 30 or, more specifically, the distal segment 16 of the flexible elongate body 14 relative to the delivery site 50. A next stage of the embolic coil delivery procedure is shown in FIG. 3. Specifically, FIG. 3 depicts the preloaded wire guide 30 positioned such that the distal segment 16 is proximate the delivery site 50. The delivery sheath 32 is also shown partially removed. Removing the delivery sheath 32 may include separating an unattached proximal segment 36 of the delivery sheath 32 from an attached distal end 34 of the delivery sheath 32. For example, a clinician may sepa rate the unattached proximal segment 36 from the attached distal end 34 at a perforated tear away section by pulling, at a location external from the vasculature V, the proximal segment 36 in a proximal direction. In the present disclo sure, proximal' is used to refer to the end of a component or feature that is closest to a clinician or a direction that is toward the clinician, while distal' is used to refer to a component or feature that is farthest away from the clinician or a direction that is away from the clinician. Such meanings are consistent with conventional use of the terms and, as such, should be understood by those skilled in the art. Turning now to FIG. 4, the preloaded wire guide 30 is shown with the delivery sheath 32 entirely removed from the flexible elongate body 14. After removing or repositioning the delivery sheath 32, a delivery catheter 38 is advanced over the flexible elongate body 14 such that a distal segment 44 of the delivery catheter 38 contacts at least one of the embolic coils 26 and 28. The embolic coils 26 and 28 may then be unloaded by moving the delivery catheter 38 relative to the flexible elongate body 14 such that the delivery catheter 38 pushes the coils 26 and 28 off of the outer surface 24 of the body 14 at the delivery site 50, as shown in FIG. 5. Once the embolic coils 26 and 28 have been delivered, the remaining components of the embolic coil delivery system 10 may be retracted, or withdrawn, from the vasculature V. The embolic coil delivery system of the present disclosure provides a system for placement of embolic coil into the vasculature of a patient that can be done in a precise and controlled manner, while maintaining overall simplicity, reliability, and manufacturability. This alternative means for delivering embolic coils does not suffer from the drawbacks of conventional catheter delivery systems relating to resis tance provided by the coils loaded into the catheter lumen. As such, the present embolic coil delivery system may be particularly useful in procedures for delivering a plurality of embolic coils. It should be understood that the above description is intended for illustrative purposes only, and is not intended to limit the scope of the present disclosure in any way. Thus, those skilled in the art will appreciate that other aspects of the disclosure can be obtained from a study of the drawings, the disclosure and the appended claims. US 9,498,226 B What is claimed is: 1. An embolic coil delivery system, comprising: a flexible elongate body having a distal segment; an embolic coil loaded on the flexible elongate body at the distal segment and contacting an outer Surface of the flexible elongate body; a delivery catheter sized to advance over the flexible elongate body during an embolic coil delivery proce dure, wherein a distal segment of the delivery catheter contacts the embolic coil during the embolic coil deliv ery procedure; a delivery sheath positioned over the embolic coil, and including a distal end attached to the flexible elongate body; and wherein the distal end of the delivery sheath is removably attached to a proximal segment of the delivery sheath at a tear away section located at an axial position of the flexible elongate body distally spaced from the embolic coil; wherein the flexible elongate body, the embolic coil and the delivery sheath move together as a unit to a delivery site; wherein the embolic coil delivery system has a first configuration in which the embolic coil is covered by the delivery sheath, and a second configuration in which the proximal segment is detached from the distal end of the delivery sheath at a tear away section, and the embolic coil is uncovered and out of contact with the proximal segment. 2. The embolic coil delivery system of claim 1, wherein the proximal segment of the delivery sheath is unattached relative to the flexible elongate body. 3. The embolic coil delivery system of claim 1, wherein the flexible elongate body is a mandril wire guide. 4. The embolic coil delivery system of claim 1, wherein the flexible elongate body, the embolic coil and the delivery sheath have the second configuration in which a proximal segment of the delivery sheath is disconnected from the flexible elongate body and moved proximally to uncover the embolic coil; and wherein the embolic coil is frictionally engaged with the outer surface of the flexible elongate body while posi tioned within the delivery sheath to maintain a rela tively fixed position of the embolic coil relative to the flexible elongate body while the flexible elongate body is being maneuvered to the delivery site. 5. The embolic coil delivery system of claim 1, further including a plurality of embolic coils loaded on the flexible elongate body at the distal segment, wherein a first stiffness measurement of a first coil of the plurality of embolic coils is different than a second stiffness measurement of a second coil of the plurality of embolic coils. 6. A preloaded wire guide for an embolic coil delivery System, comprising: a mandril wire guide having a distal segment; an embolic coil loaded on the mandril wire guide at the distal segment and contacting an outer Surface of the mandril wire guide; and a delivery sheath positioned over the embolic coil, and including a distal end attached to the mandril wire guide, and the distal end of the delivery sheath is removably attached to a proximal segment of the delivery sheath at a tear away section located at an axial position of the mandril wire guide distally spaced from the embolic coil; wherein the embolic coil is frictionally engaged with the outer surface of the mandril wire guide while posi
8 7 tioned within the delivery sheath to maintain a rela tively fixed position of the embolic coil relative to the mandril wire guide while the mandril wire guide is being maneuvered to a delivery site: wherein the mandril wire guide, the embolic coil and the delivery sheath move together as a unit to the delivery site; wherein the embolic coil delivery system has a first configuration in which the embolic coil is covered by the delivery sheath, and a second configuration in which the proximal segment is detached from the distal end of the delivery sheath at a tear away section, and the embolic coil is uncovered and out of contact with the proximal segment. 7. The preloaded wire guide of claim 6, wherein a distal end of the delivery sheath is removably attached to the mandril wire guide at an axial position of the flexible elongate body distally spaced from the embolic coil. 8. The preloaded wire guide of claim 7, wherein a proximal segment of the delivery sheath is unattached relative to the mandril wire guide. 9. The loaded wire guide of claim 8, further including a plurality of embolic coils loaded on the mandril wire guide at the distal segment, wherein a first stiffness measurement of a first coil of the plurality of embolic coils is different than a second stiffness measurement of a second coil of the plurality of embolic coils. 10. The loaded wire guide of claim 9, wherein each of the plurality of embolic coils is frictionally engaged with the outer Surface of the mandril wire guide to maintain a relatively fixed position of the embolic coil relative to the mandril wire guide while the mandril wire guide is being maneuvered to the delivery site. 11. A method of delivering an embolic coil to a delivery site within a patient with an embolic coil delivery system that includes a flexible elongate body having a distal seg ment; an embolic coil loaded on the flexible elongate body at the distal segment and contacting an outer surface of the flexible elongate body; a delivery catheter sized to advance over the flexible elongate body during an embolic coil delivery procedure, wherein a distal segment of the delivery catheter contacts the embolic coil during the embolic coil delivery procedure; a delivery sheath positioned over the embolic coil, and including a distal end attached to the flexible elongate body; wherein a distal end of the delivery sheath is removably attached to the flexible elongate body a proximal segment of the delivery sheath at a tear away section located at an axial position of the flexible elongate body distally spaced from the embolic coil; wherein the flexible elongate body, the embolic coil and the delivery sheath move together as a unit to a delivery site wherein the embolic coil delivery system has a first configuration in which the embolic coil is covered by the delivery sheath, and a second configuration in which the proximal segment is US 9,498,226 B detached from the distal end of the delivery sheath at a tear away section, and the embolic coil is uncovered and out of contact with the proximal segment, and the method com prising steps of: loading the embolic coil around an outer surface of a distal segment of a flexible elongate body; advancing the distal segment of the flexible elongate body through the patient vessel to the delivery site with the embolic coil loaded on the distal segment; and unloading the embolic coil from the flexible elongate body at least in part by advancing the delivery catheter over the flexible elongate body and contacting the embolic coil with a distal segment of the delivery catheter; and wherein the embolic coil is frictionally engaged with the outer surface of the flexible elongate body to maintain a relatively fixed position of the embolic coil relative to the flexible elongate body while the distal segment of the flexible elongate body is being maneuvered to the delivery site during the advancing step; and wherein the flexible elongate body, the embolic coil and the- a delivery sheath move together as a unit to the delivery site. 12. The method of claim 11, including shielding the embolic coil with the delivery sheath positioned over the embolic coil prior to and during the advancing step; and wherein the shielding step includes maintaining a loaded position of the embolic coil during the advancing step at least in part by frictionally engaging the embolic coil with the outer surface of the flexible elongate body. 13. The method of claim 11, further including removing at least a proximal segment of the delivery sheath subse quent to the advancing step. 14. The method of claim 13, wherein the removing step includes separating the unat tached proximal segment of the delivery sheath from an attached distal end of the delivery sheath along a tear located distal to the embolic coil. 15. The method of claim 11, wherein the loading step includes frictionally engaging the embolic coil with the outer surface of the flexible elongate body to maintain a loaded position of the embolic coil during the advancing Step. 16. The method of claim 11, wherein the loading step includes loading a plurality of embolic coils of varying stiffnesses around the outer surface of the distal segment of the flexible elongate body, and the unloading step includes unloading the plurality of embolic coils from the flexible elongate body at least in part by advancing the delivery catheter over the flexible elongate body and contacting at least one of the plurality of embolic coils with the distal segment of the delivery catheter. :k k k k k
Sepetka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 3, ) VARIABLE STIFFNESS CATHETER 4,739,768 4/1988 Engelson.
 United States Patent (19) 11 USOO5308342A Patent Number: Sepetka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 3, 1994 54) VARIABLE STIFFNESS CATHETER 4,739,768 4/1988 Engelson. o 4,775,371 10/1988 Mueller, Jr.... 604/280
United States Patent (19) 11 USOO5308342A Patent Number: Sepetka et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 3, 1994 54) VARIABLE STIFFNESS CATHETER 4,739,768 4/1988 Engelson. o 4,775,371 10/1988 Mueller, Jr.... 604/280
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Jones et al. USOO6833003B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 2004 (54) EXPANDABLE STENT AND DELIVERY SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Donald K. Jones, Lauderhill, FL (US);
(12) United States Patent Jones et al. USOO6833003B2 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Dec. 21, 2004 (54) EXPANDABLE STENT AND DELIVERY SYSTEM (75) Inventors: Donald K. Jones, Lauderhill, FL (US);
IIII. United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 11 Patent Number: 5,776,150 45) Date of Patent: Jul. 7, 1998
 United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 54) SUTURE ASSIST DEVICE 75) Inventors: Leo J. Nolan; John P. Measamer, both of Cincinnati; James D. Staley, Jr., Loveland; Robert F. Welch, Maineville, all of Ohio
United States Patent (19) Nolan et al. 54) SUTURE ASSIST DEVICE 75) Inventors: Leo J. Nolan; John P. Measamer, both of Cincinnati; James D. Staley, Jr., Loveland; Robert F. Welch, Maineville, all of Ohio
(12) United States Patent
 US008556757B2 (12) United States Patent Kilshaw (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2013 (54) BICYCLE GEAR MECHANISM (76) Inventor: Richard J. Kilshaw, Lake Oswego, OR (US) *) Notice: Subject
US008556757B2 (12) United States Patent Kilshaw (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 15, 2013 (54) BICYCLE GEAR MECHANISM (76) Inventor: Richard J. Kilshaw, Lake Oswego, OR (US) *) Notice: Subject
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,514,280 B1. Gilson (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 4, 2003
 USOO651428OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,514,280 B1 Gilson (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 4, 2003 (54) DELIVERY CATHETER 5,683,451 A 11/1997 Lenker et al.... 623/1 5,885.258 A * 3/1999
USOO651428OB1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,514,280 B1 Gilson (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 4, 2003 (54) DELIVERY CATHETER 5,683,451 A 11/1997 Lenker et al.... 623/1 5,885.258 A * 3/1999
( 12 ) United States Patent
 ( 12 ) United States Patent Ingwer et al. US009907655B2 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 907, 655 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Mar. 6, 2018 ( 54 ) COMPONENTS FOR ARTIFICIAL JOINTS ( 56 ) References Cited U. S.
( 12 ) United States Patent Ingwer et al. US009907655B2 ( 10 ) Patent No. : US 9, 907, 655 B2 ( 45 ) Date of Patent : Mar. 6, 2018 ( 54 ) COMPONENTS FOR ARTIFICIAL JOINTS ( 56 ) References Cited U. S.
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States US 2012O316632A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0316632 A1 Gao (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2012 (54) RETRIEVABLE COVERED STENT FOR (52) U.S. Cl.... 623A1.2 BFURCATION
(19) United States US 2012O316632A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0316632 A1 Gao (43) Pub. Date: Dec. 13, 2012 (54) RETRIEVABLE COVERED STENT FOR (52) U.S. Cl.... 623A1.2 BFURCATION
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0208302 A1 Webster et al. US 200702083 02A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 6, 2007 (54) DEFLECTION CONTROL CATHETERS, SUPPORT CATHETERS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0208302 A1 Webster et al. US 200702083 02A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 6, 2007 (54) DEFLECTION CONTROL CATHETERS, SUPPORT CATHETERS
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 20160135857A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0135857 A1 Marrero, SR. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CURVEDTIBIOTALARFUSION NAIL AND Publication Classification
US 20160135857A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0135857 A1 Marrero, SR. (43) Pub. Date: May 19, 2016 (54) CURVEDTIBIOTALARFUSION NAIL AND Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,819,889 B2
 patent is extended or adjusted under 35 6,113,622 U.S.C. 154(b) by 1301 days. US007819889B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Healy et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 26, 2010 (54) DETACHABLE INTRODUCER
patent is extended or adjusted under 35 6,113,622 U.S.C. 154(b) by 1301 days. US007819889B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Healy et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Oct. 26, 2010 (54) DETACHABLE INTRODUCER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 US 20070179519A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0179519 A1 Huisun (43) Pub. Date: (54) STENT DELIVERY SYSTEM TO IMPROVE (22) Filed: Jan. 27, 2006 PLACEMENT
US 20070179519A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0179519 A1 Huisun (43) Pub. Date: (54) STENT DELIVERY SYSTEM TO IMPROVE (22) Filed: Jan. 27, 2006 PLACEMENT
58 Field of Search /191,192, wire stent which extends in a path defining a generally
 USOO5882335A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Leone et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar 16, 1999 54 RETRIEVABLE DRUG DELIVERY STENT 5,306,250 4/1994 March et al.... 604/104 5,306,286 4/1994 Stack
USOO5882335A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Leone et al. (45) Date of Patent: Mar 16, 1999 54 RETRIEVABLE DRUG DELIVERY STENT 5,306,250 4/1994 March et al.... 604/104 5,306,286 4/1994 Stack
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Globerman et al. USOO6402777B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,402.777 B1 Jun. 11, 2002 (54) RADIOPAQUE STENT MARKERS (75) Inventors: Oren Globerman, Holon; Mordechay
(12) United States Patent Globerman et al. USOO6402777B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 6,402.777 B1 Jun. 11, 2002 (54) RADIOPAQUE STENT MARKERS (75) Inventors: Oren Globerman, Holon; Mordechay
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States US 20150273 183A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0273183 A1 Foley et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2015 (54) INTERMITTENTURINARY CATHETER ASSEMBLY AND ANADAPTER
(19) United States US 20150273 183A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0273183 A1 Foley et al. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 1, 2015 (54) INTERMITTENTURINARY CATHETER ASSEMBLY AND ANADAPTER
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,461,697 B1
 USOO646.1697B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,461,697 B1 Slat et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) POLYETHYLENE TEREPHTHALATE 4,149,645 A 4/1979 Valyi MULTI-LAYER PREFORM USED
USOO646.1697B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,461,697 B1 Slat et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 8, 2002 (54) POLYETHYLENE TEREPHTHALATE 4,149,645 A 4/1979 Valyi MULTI-LAYER PREFORM USED
III. United States Patent (19) Sheiban 5,226,889. Jul. 13, and at least a pair of inflatable balloons carried on the
 United States Patent (19) Sheiban (54) DOUBLE BALLOON CATHETER FOR STENT IMPLANTATION 76 Inventor: Imad Sheiban, Via Sommavalle No. 9, Verona, 37128, Italy (21) Appl. No.: 734,968 (22 Filed: Jul. 24, 1991
United States Patent (19) Sheiban (54) DOUBLE BALLOON CATHETER FOR STENT IMPLANTATION 76 Inventor: Imad Sheiban, Via Sommavalle No. 9, Verona, 37128, Italy (21) Appl. No.: 734,968 (22 Filed: Jul. 24, 1991
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States US 201701 65099A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0165099 A1 Buddharaju (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 15, 2017 (54) CONDOM CATHETER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A61F 5/453
(19) United States US 201701 65099A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0165099 A1 Buddharaju (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 15, 2017 (54) CONDOM CATHETER (52) U.S. Cl. CPC... A61F 5/453
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0165859 A1 ECKHOUSE et al. US 2012O165859A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) DEVICE AND METHOD INVOLVING
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2012/0165859 A1 ECKHOUSE et al. US 2012O165859A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 28, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (63) DEVICE AND METHOD INVOLVING
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 US 20050209506A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0209506A1 Butler et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2005 (54) DEVICE (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
US 20050209506A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0209506A1 Butler et al. (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 22, 2005 (54) DEVICE (30) Foreign Application Priority Data (75)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/ A1
 (19) United States US 2007019.8075A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0198075A1 Levy (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 23, 2007 (54) BFURCATED ANEURYSM TREATMENT Publication Classification
(19) United States US 2007019.8075A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2007/0198075A1 Levy (43) Pub. Date: Aug. 23, 2007 (54) BFURCATED ANEURYSM TREATMENT Publication Classification
50 3 % % 2. ta. SN & (12) United States Patent US 7, B1. Jun. 10, (45) Date of Patent: (10) Patent No.:
 USOO7384414B1 (1) United States Patent Marshall et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,384.414 B1 Jun., 008 (54) SAFETY PEN NEEDLE WITH (75) (73) (*) (1) () (51) (5) (58) (56) NON-INUECTION END
USOO7384414B1 (1) United States Patent Marshall et al. () Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 7,384.414 B1 Jun., 008 (54) SAFETY PEN NEEDLE WITH (75) (73) (*) (1) () (51) (5) (58) (56) NON-INUECTION END
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Itou et al. US 2005OO15007A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 20, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) CATHETER ASSEMBLY Inventors: Takenari Itou,
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: Itou et al. US 2005OO15007A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 20, 2005 (54) (75) (73) (21) (22) (30) CATHETER ASSEMBLY Inventors: Takenari Itou,
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
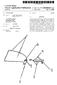 US 20080082047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0082047 A1 Harmon (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2008 (54) VEIN HOLDER (52) U.S. Cl.... 604/115 (76) Inventor: Stoney
US 20080082047A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0082047 A1 Harmon (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 3, 2008 (54) VEIN HOLDER (52) U.S. Cl.... 604/115 (76) Inventor: Stoney
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 9,468,773 B1. Anderson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 18, 2016
 United States Patent US009468773B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: Anderson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 18, 2016 (54) INTERVENTIONAL MEDICAL SYSTEMS 7,647,109 B2 * 1/2010 Hastings... A61N 1/O587 AND IMPLANTABLE
United States Patent US009468773B1 (12) (10) Patent No.: Anderson et al. (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 18, 2016 (54) INTERVENTIONAL MEDICAL SYSTEMS 7,647,109 B2 * 1/2010 Hastings... A61N 1/O587 AND IMPLANTABLE
(12) United States Patent
 US009 138575B2 (12) United States Patent Osypka (54) (71) BALLOON CATHETER Applicant: Peter Osypka Stiftung, Grenzach-Wyhlen (DE) (72) Inventor: Peter Osypka, Grenzach-Wyhlen (DE) (73) Assignee: Peter
US009 138575B2 (12) United States Patent Osypka (54) (71) BALLOON CATHETER Applicant: Peter Osypka Stiftung, Grenzach-Wyhlen (DE) (72) Inventor: Peter Osypka, Grenzach-Wyhlen (DE) (73) Assignee: Peter
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8,500,773 B2. Nardone et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2013
 US008500 773B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nardone et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2013 (54) SPRING DETACH JOINT FOR DELIVERING 4,827,941. A * 5/1989 Taylor et al.... 600,434 A DETACHABLE
US008500 773B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Nardone et al. (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 6, 2013 (54) SPRING DETACH JOINT FOR DELIVERING 4,827,941. A * 5/1989 Taylor et al.... 600,434 A DETACHABLE
US A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,554,114 Wallace et al. (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 10, 1996
 III III III US005.41 14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Wallace et al. () Date of Patent: Sep., 1996 54 INFUSION DEVICE WITH PREFORMED 5,116,9 5/1992 Coll... 4/281 X SHAPE 5,122,136 6/1992
III III III US005.41 14A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Wallace et al. () Date of Patent: Sep., 1996 54 INFUSION DEVICE WITH PREFORMED 5,116,9 5/1992 Coll... 4/281 X SHAPE 5,122,136 6/1992
United States Patent (19) James
 United States Patent (19) James 54 DEVICE FOR DISPENSING MEDICAMENTS (75) Inventor: Michael James, Welwyn Garden City, England Allen & Hanburys Limited, London, 73 Assignee: England (21) Appl. No.: 767,518
United States Patent (19) James 54 DEVICE FOR DISPENSING MEDICAMENTS (75) Inventor: Michael James, Welwyn Garden City, England Allen & Hanburys Limited, London, 73 Assignee: England (21) Appl. No.: 767,518
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,332,914 B2
 USOO9332914B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Langston (45) Date of Patent: *May 10, 2016 (54) COAXIAL DUAL LUMEN PIGTAIL 4,777,951 A * 10/1988 Cribier et al.... 606, 194 CATHETER 4,961,731
USOO9332914B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: Langston (45) Date of Patent: *May 10, 2016 (54) COAXIAL DUAL LUMEN PIGTAIL 4,777,951 A * 10/1988 Cribier et al.... 606, 194 CATHETER 4,961,731
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,039,574 B2
 US0090395.74B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,039,574 B2 Wilson (45) Date of Patent: May 26, 2015 (54) EXERCISE RING USPC... 482/24, 44 50, 79, 91, 92, 121-128, 482/131, 139 (76) Inventor:
US0090395.74B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 9,039,574 B2 Wilson (45) Date of Patent: May 26, 2015 (54) EXERCISE RING USPC... 482/24, 44 50, 79, 91, 92, 121-128, 482/131, 139 (76) Inventor:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0287886 A1 Patti US 20140287886A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PROTECTOR FOR EXERCISE BAR Applicant:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0287886 A1 Patti US 20140287886A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 25, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) PROTECTOR FOR EXERCISE BAR Applicant:
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0071716 A1 Milsom et al. US 2017007 1716A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 16, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) (60) METHOD AND APPARATUS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0071716 A1 Milsom et al. US 2017007 1716A1 (43) Pub. Date: Mar. 16, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) (60) METHOD AND APPARATUS
United States Patent (1s 3,671,979 Moulopoulos (45) June 27, 1972
 United States Patent (1s Moulopoulos (45) June 27, 1972 (54). CATHETER MOUNTED ARTIFICIAL 2,442,573 6/1948 Stafford... 128/245 X HEART WALVE FOR MPLANTING IN 3,266,487 8/1966 Watkins et al... 128/1 R CLOSE
United States Patent (1s Moulopoulos (45) June 27, 1972 (54). CATHETER MOUNTED ARTIFICIAL 2,442,573 6/1948 Stafford... 128/245 X HEART WALVE FOR MPLANTING IN 3,266,487 8/1966 Watkins et al... 128/1 R CLOSE
(12) United States Patent
 US008529521B2 (12) United States Patent Erickson et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,529,521 B2 Sep. 10, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) LOW-DOSAGE SYRINGE
US008529521B2 (12) United States Patent Erickson et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,529,521 B2 Sep. 10, 2013 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) (56) LOW-DOSAGE SYRINGE
USOO A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,829,589 Nguyen et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 3, 1998
 USOO5829589A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Nguyen et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 3, 1998 54 PEN NEEDLE MAGAZINE DISPENSER 5,285,896 2/1994 Salatka et al.... 206/366 75 Inventors: Tuan V.
USOO5829589A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: Nguyen et al. (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 3, 1998 54 PEN NEEDLE MAGAZINE DISPENSER 5,285,896 2/1994 Salatka et al.... 206/366 75 Inventors: Tuan V.
-100 III IIHIIII. United States Patent (19) Fischell et al. 11) Patent Number: 5,492,530 45) Date of Patent: Feb. 20, 1996
 United States Patent (19) Fischell et al. 54 METHOD FOR ACCESSING THE CORONARY ARTERIES FROM THE RADAL OR BRACHIAL ARTERY IN THE ARM 75) Inventors: Robert E. Fischell, Dayton, Md.; David R. Fischell, Fair
United States Patent (19) Fischell et al. 54 METHOD FOR ACCESSING THE CORONARY ARTERIES FROM THE RADAL OR BRACHIAL ARTERY IN THE ARM 75) Inventors: Robert E. Fischell, Dayton, Md.; David R. Fischell, Fair
(12) United States Patent
 USOO951 0624B2 (12) United States Patent Li et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,510,624 B2 Dec. 6, 2016 (54) DISPOSABLE ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (75) Inventors: Yonghai Li, Shenzhen (CN); Zhongli
USOO951 0624B2 (12) United States Patent Li et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,510,624 B2 Dec. 6, 2016 (54) DISPOSABLE ELECTRONIC CIGARETTE (75) Inventors: Yonghai Li, Shenzhen (CN); Zhongli
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent USOO9579453B1 (10) Patent No.: Brasington (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 28, 2017 (54) TWO-STEP AUTO-INJECTION DEVICE (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Chalbourne Brasington, Greenville,
(12) United States Patent USOO9579453B1 (10) Patent No.: Brasington (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 28, 2017 (54) TWO-STEP AUTO-INJECTION DEVICE (56) References Cited (71) Applicant: Chalbourne Brasington, Greenville,
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kimber et al. USOO6565529B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,565,529 B1 (45) Date of Patent: May 20, 2003 (54) TAMPEREVIDENT SYRINGE DESIGN (75) Inventors: Michael Browning Kimber, New South
(12) United States Patent Kimber et al. USOO6565529B1 (10) Patent No.: US 6,565,529 B1 (45) Date of Patent: May 20, 2003 (54) TAMPEREVIDENT SYRINGE DESIGN (75) Inventors: Michael Browning Kimber, New South
Zenith Renu AAA Converter Graft. Device Description Planning and Sizing Deployment Sequence Patient Follow-Up
 Zenith Renu AAA Converter Graft Device Description Planning and Sizing Deployment Sequence Patient Follow-Up Device description: Device indications The Zenith Renu AAA Converter Graft with Z-Trak Introduction
Zenith Renu AAA Converter Graft Device Description Planning and Sizing Deployment Sequence Patient Follow-Up Device description: Device indications The Zenith Renu AAA Converter Graft with Z-Trak Introduction
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0196770 A1 Klintenstedt et al. US 201701.96770A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) (60) (30) CNTAINER
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0196770 A1 Klintenstedt et al. US 201701.96770A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 13, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) (60) (30) CNTAINER
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0143905 A1 Goyal et al. US 20170143905A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) NEEDLE-FREE INUECTION GUIDE
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0143905 A1 Goyal et al. US 20170143905A1 (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2017 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) NEEDLE-FREE INUECTION GUIDE
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/ A1
 (19) United States US 2005O130094A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0130094A1 Graham (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) ORTHODONTIC ACCESSORY ARCH BAR (52) U.S. Cl.... 433/20
(19) United States US 2005O130094A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2005/0130094A1 Graham (43) Pub. Date: Jun. 16, 2005 (54) ORTHODONTIC ACCESSORY ARCH BAR (52) U.S. Cl.... 433/20
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 (19) United States US 20160213850A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0213850 A1 LOOF et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 28, 2016 (54) MEDICAMENT DELIVERY DEVICE Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20160213850A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0213850 A1 LOOF et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 28, 2016 (54) MEDICAMENT DELIVERY DEVICE Publication Classification
US A United States Patent Patent Number: 5,662,621 Lafontaine 45 Date of Patent: Sep. 2, 1997
 US005662621A United States Patent 19 11. Patent Number: Lafontaine Date of Patent: Sep. 2, 1997 54 GUIDE CATHETER WITH SHAPE MEMORY 5,226,899 7/1993 Lee et al.... 604/282 RETENTION 5,236,424 8/1993 Imran......
US005662621A United States Patent 19 11. Patent Number: Lafontaine Date of Patent: Sep. 2, 1997 54 GUIDE CATHETER WITH SHAPE MEMORY 5,226,899 7/1993 Lee et al.... 604/282 RETENTION 5,236,424 8/1993 Imran......
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1
 US 2016O1 OO694A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0100694 A1 PELLETER (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) KNEE PILLOW Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
US 2016O1 OO694A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0100694 A1 PELLETER (43) Pub. Date: Apr. 14, 2016 (54) KNEE PILLOW Publication Classification (71) Applicant:
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Fung (54) DENTAL CROWN 76) Inventor: John Fung, 627 George Street, Sydney, NSW 2000, Australia (21) Appl. No.: 969,186 (22) PCT Filed: Jul. 5, 1991 (86). PCT No.: PCT/AU91/00300
United States Patent (19) Fung (54) DENTAL CROWN 76) Inventor: John Fung, 627 George Street, Sydney, NSW 2000, Australia (21) Appl. No.: 969,186 (22) PCT Filed: Jul. 5, 1991 (86). PCT No.: PCT/AU91/00300
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,334,451 B1
 USOO6334451B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent o.: US 6,334,451 B1 Yang (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2002 (54) TOOTHBRUSH WITH FILLIG OF 1,340,043 A 5/1920 Grace... 132/311 TOOTHPASTE 1,451,941. A
USOO6334451B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent o.: US 6,334,451 B1 Yang (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 1, 2002 (54) TOOTHBRUSH WITH FILLIG OF 1,340,043 A 5/1920 Grace... 132/311 TOOTHPASTE 1,451,941. A
Paper No Filed: October 23, 2017 UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD
 Trials@uspto.gov Paper No. 8 571-272-7822 Filed: October 23, 2017 UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD ABIOMED, INC. and ABIOMED R&D, INC., Petitioner, v.
Trials@uspto.gov Paper No. 8 571-272-7822 Filed: October 23, 2017 UNITED STATES PATENT AND TRADEMARK OFFICE BEFORE THE PATENT TRIAL AND APPEAL BOARD ABIOMED, INC. and ABIOMED R&D, INC., Petitioner, v.
Catheters and Wires. Dr. Vaibhav Jain MD,DNB,MNAMS Senior Consultant, IR Medanta, the Medicity, Gurgaon
 Catheters and Wires Dr. Vaibhav Jain MD,DNB,MNAMS Senior Consultant, IR Medanta, the Medicity, Gurgaon Guidewires: Guidewires (solid wires navigated within the vascular system / extravascular tract) act
Catheters and Wires Dr. Vaibhav Jain MD,DNB,MNAMS Senior Consultant, IR Medanta, the Medicity, Gurgaon Guidewires: Guidewires (solid wires navigated within the vascular system / extravascular tract) act
Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 6,120,471
![Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 6,120,471 Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 6,120,471](/thumbs/72/66899349.jpg) US006120471A Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 6,120,471 Varn [45] Date of Patent: Sep. 19, 2000 [54] DORSAL RESTING HAND ORTHOSIS 5,637,078 6/1997 Varn..... 602/21 5,746,707 5/1998 Eck.....
US006120471A Ulllted States Patent [19] [11] Patent Number: 6,120,471 Varn [45] Date of Patent: Sep. 19, 2000 [54] DORSAL RESTING HAND ORTHOSIS 5,637,078 6/1997 Varn..... 602/21 5,746,707 5/1998 Eck.....
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,108,510 B2
 US00710851 OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,108,510 B2 Niznick (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 19, 2006 (54) ENDOSSEOUS DENTAL IMPLANT 6,733,291 B1* 5/2004 Hurson... 433,173 20O2/O110784 A1*
US00710851 OB2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,108,510 B2 Niznick (45) Date of Patent: Sep. 19, 2006 (54) ENDOSSEOUS DENTAL IMPLANT 6,733,291 B1* 5/2004 Hurson... 433,173 20O2/O110784 A1*
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,744,043 B2
 USOO774.4043B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Otinger (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 29, 20 (54) CPAP HOSETENDER 6,854,694 B1* 2/2005 Van Etten... 248,75 7,040,581 B2 * 5/2006 Noelke et al.... 248,75
USOO774.4043B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Otinger (45) Date of Patent: Jun. 29, 20 (54) CPAP HOSETENDER 6,854,694 B1* 2/2005 Van Etten... 248,75 7,040,581 B2 * 5/2006 Noelke et al.... 248,75
III IIII. United States Patent (19) Albergo. Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Michaelson & Wallace
 United States Patent (19) Albergo (54) (75) 73) 21 22) 51) (52) 58 56 ADJUSTABLE STRETCHING EXERCISE DEVICE Inventor: George N. Albergo, North Hollywood, Calif. Assignee: Phsyical Success, Inc., North
United States Patent (19) Albergo (54) (75) 73) 21 22) 51) (52) 58 56 ADJUSTABLE STRETCHING EXERCISE DEVICE Inventor: George N. Albergo, North Hollywood, Calif. Assignee: Phsyical Success, Inc., North
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) Galloway 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,738,667 Apr. 19, 1988 W 54 PREFORMED CATHETER ASSEMBLY 76 Inventor: Niall T. M. Galloway, 3211 Massdale Ave., Durham, N.C. 27707
United States Patent (19) Galloway 11 Patent Number: 45 Date of Patent: 4,738,667 Apr. 19, 1988 W 54 PREFORMED CATHETER ASSEMBLY 76 Inventor: Niall T. M. Galloway, 3211 Massdale Ave., Durham, N.C. 27707
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.690,305 B2
 US0076903 05B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.690,305 B2 Harjula et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2010 (54) INCREMENT CHARGE FOR 4,408,534 A * 10, 1983 Araki et al.... 102.288 FIN-STABILIZED
US0076903 05B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7.690,305 B2 Harjula et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 6, 2010 (54) INCREMENT CHARGE FOR 4,408,534 A * 10, 1983 Araki et al.... 102.288 FIN-STABILIZED
Guide Wires design and selection Abbott Vascular. All rights reserved.
 Guide Wires design and selection the cardiac catheter was...the key in the lock Cournand AF, Nobel lecture December 11, 1956; nowadays, the coronary guidewire is the master key to all locks Colombo et
Guide Wires design and selection the cardiac catheter was...the key in the lock Cournand AF, Nobel lecture December 11, 1956; nowadays, the coronary guidewire is the master key to all locks Colombo et
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,044,921 B2
 USOO7044921B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 7,044,921 B2 Asmus et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 16, 2006 (54) MEDICAL DEVICE WITH CHANGEABLE 4,846,186 A 7, 1989 Box et al. TPFLEXBILITY 4,895,168
USOO7044921B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: US 7,044,921 B2 Asmus et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 16, 2006 (54) MEDICAL DEVICE WITH CHANGEABLE 4,846,186 A 7, 1989 Box et al. TPFLEXBILITY 4,895,168
U.S.C. 154(b) by 0 days. (21) Appl. No.: 10/064,070 (22) Filed: Jun. 6, 2002 (51) Int. Cl... A61F 2/06 623/1.11, 902, 903, 909 XXX .. 2.
 (12) United States Patent Weiss USOO6676694B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 13, 2004 (54) METHOD FOR INSTALLING ASTENT GRAFT (76) Inventor: Mitchell Weiss, 300 Pinellas St. Radiology Dept.
(12) United States Patent Weiss USOO6676694B1 (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Jan. 13, 2004 (54) METHOD FOR INSTALLING ASTENT GRAFT (76) Inventor: Mitchell Weiss, 300 Pinellas St. Radiology Dept.
I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll
 (12) United States Patent Masini I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US006558426Bl (10) Patent No.: US 6,558,426 Bl (45) Date of Patent: May 6, 2003 (54)
(12) United States Patent Masini I lllll llllllll Ill lllll lllll lllll lllll lllll 111111111111111111111111111111111 US006558426Bl (10) Patent No.: US 6,558,426 Bl (45) Date of Patent: May 6, 2003 (54)
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0039210 A1 Yates et al. US 20090039210A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 12, 2009 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) CPAP HOSE SUPPORT SYSTEM Inventors:
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2009/0039210 A1 Yates et al. US 20090039210A1 (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 12, 2009 (54) (76) (21) (22) (60) CPAP HOSE SUPPORT SYSTEM Inventors:
( ) -- (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/ A1. (19) United States. (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2016.
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0310302 A1 NEGLEN et al. US 201603103O2A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2016/0310302 A1 NEGLEN et al. US 201603103O2A1 (43) Pub. Date: Oct. 27, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (60) SYSTEMIS AND METHODS
(12) (10) Patent No.: US 7,122,052 B2. Greenhalgh (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 17, 2006
 United States Patent US007122052B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Greenhalgh (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 17, 2006 (54) INTEGRAL SUPPORT STENT GRAFT 5,824,040 A * 10/1998 Cox et al.... 623, 135 ASSEMBLY 6,159,239
United States Patent US007122052B2 (12) (10) Patent No.: Greenhalgh (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 17, 2006 (54) INTEGRAL SUPPORT STENT GRAFT 5,824,040 A * 10/1998 Cox et al.... 623, 135 ASSEMBLY 6,159,239
United States Patent (19) Annoni
 United States Patent (19) Annoni (54. TOOTH TRANSILLUMINATING LIGHT HOLDER 76) Inventor: Jerry D. Annoni, 450 Maple Ave., Vallejo, Calif. 94591 (21) Appl. No.: 427,850 22 Filed: Sep. 29, 1982 51) Int.
United States Patent (19) Annoni (54. TOOTH TRANSILLUMINATING LIGHT HOLDER 76) Inventor: Jerry D. Annoni, 450 Maple Ave., Vallejo, Calif. 94591 (21) Appl. No.: 427,850 22 Filed: Sep. 29, 1982 51) Int.
1 Description. 2 Indications. 3 Warnings ASPIRATION CATHETER
 Page 1 of 5 ASPIRATION CATHETER Carefully read all instructions prior to use, observe all warnings and precautions noted throughout these instructions. Failure to do so may result in complications. STERILE.
Page 1 of 5 ASPIRATION CATHETER Carefully read all instructions prior to use, observe all warnings and precautions noted throughout these instructions. Failure to do so may result in complications. STERILE.
CLARIVEIN INFUSION CATHETER
 CLARIVEIN INFUSION CATHETER General Product Description Overview The ClariVein Infusion Catheter (ClariVein -IC) is an infusion catheter system designed to introduce physician-specified medicaments into
CLARIVEIN INFUSION CATHETER General Product Description Overview The ClariVein Infusion Catheter (ClariVein -IC) is an infusion catheter system designed to introduce physician-specified medicaments into
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0276586 A1 Swaney et al. US 20140276586A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) STEERABLE SURGICAL
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0276586 A1 Swaney et al. US 20140276586A1 (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 18, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (60) STEERABLE SURGICAL
(12) United States Patent
 US007094007B2 (12) United States Patent Satran et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 22, 2006 (54) TANGENTIAL CUTTING INSERT AND MILLING CUTTER (75) Inventors: Amir Satran, Kfar Vradim (IL);
US007094007B2 (12) United States Patent Satran et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 22, 2006 (54) TANGENTIAL CUTTING INSERT AND MILLING CUTTER (75) Inventors: Amir Satran, Kfar Vradim (IL);
Bifurcated system Proximal suprarenal stent Modular (aortic main body and two iliac legs) Full thickness woven polyester graft material Fully
 Physician Training Bifurcated system Proximal suprarenal stent Modular (aortic main body and two iliac legs) Full thickness woven polyester graft material Fully supported by self-expanding z-stents H&L-B
Physician Training Bifurcated system Proximal suprarenal stent Modular (aortic main body and two iliac legs) Full thickness woven polyester graft material Fully supported by self-expanding z-stents H&L-B
(12) United States Patent
 US0093.20587B2 (12) United States Patent Milsom et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,320,587 B2 Apr. 26, 2016 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52) METHOD AND APPARATUS
US0093.20587B2 (12) United States Patent Milsom et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 9,320,587 B2 Apr. 26, 2016 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (86) (87) (65) (63) (60) (51) (52) METHOD AND APPARATUS
y 2. (12) United States Patent VbOt W N 35 (10) Patent No.: US 8,855,348 B2 HAD CIRCUIT ACTIVE TELECOIL (45) Date of Patent: Oct.
 USOO8855348B2 (12) United States Patent Johnson (54) TELECOIL INA DETACHABLE DIRECT AUDIO INPUT ACCESSORY (75) Inventor: Andrew Joseph Johnson, Edina, MN (US) (73) Assignee: Starkey Laboratories, Inc.,
USOO8855348B2 (12) United States Patent Johnson (54) TELECOIL INA DETACHABLE DIRECT AUDIO INPUT ACCESSORY (75) Inventor: Andrew Joseph Johnson, Edina, MN (US) (73) Assignee: Starkey Laboratories, Inc.,
(12) United States Patent
 USOO948.0458B2 (12) United States Patent Chiang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 1, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (62) (30) ULTRASONIC POSITONING DEVICE FOR EPIDURAL SPACE
USOO948.0458B2 (12) United States Patent Chiang et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: Nov. 1, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (62) (30) ULTRASONIC POSITONING DEVICE FOR EPIDURAL SPACE
United States Patent (19) Hensel
 United States Patent (19) Hensel - 54 75 73 1 51 5 58 56) FLUID BEARNG CONSTRUCTION EMPLOYING THRUST PLATE WITH PRESSURE COMPENSATION PORTS Inventor: Robert J. Hensel, Gaston, Oreg. Assignee: Synektron
United States Patent (19) Hensel - 54 75 73 1 51 5 58 56) FLUID BEARNG CONSTRUCTION EMPLOYING THRUST PLATE WITH PRESSURE COMPENSATION PORTS Inventor: Robert J. Hensel, Gaston, Oreg. Assignee: Synektron
Access More Patients. Customize Each Seal.
 Access More. Customize Each Seal. The Least Invasive Path Towards Proven Patency ULTRA LOW PROFILE TO EASE ADVANCEMENT The flexible, ultra-low 12F ID Ovation ix delivery system enables you to navigate
Access More. Customize Each Seal. The Least Invasive Path Towards Proven Patency ULTRA LOW PROFILE TO EASE ADVANCEMENT The flexible, ultra-low 12F ID Ovation ix delivery system enables you to navigate
Penumbra INTRACRANIAL ACCESS REDEFINED
 Penumbra INTRACRANIAL ACCESS REDEFINED BENCHMARK Case Examples Stability & Compatibility Atraumatic Navigation Flow Diverter Delivery Pipeline BENCHMARK Stability Without Surpass Full distal shaft radiopacity
Penumbra INTRACRANIAL ACCESS REDEFINED BENCHMARK Case Examples Stability & Compatibility Atraumatic Navigation Flow Diverter Delivery Pipeline BENCHMARK Stability Without Surpass Full distal shaft radiopacity
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/ A1
 (19) United States US 20080040891A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0040891 A1 Tyler (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 21, 2008 (54) EXERCISE EQUIPMENT HANDLE GRIPS Publication Classification
(19) United States US 20080040891A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2008/0040891 A1 Tyler (43) Pub. Date: Feb. 21, 2008 (54) EXERCISE EQUIPMENT HANDLE GRIPS Publication Classification
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,210,432 B1
 USOO6210432B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,210,432 B1 Solem et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD FOR TREATMENT 5,980,552 * 11/1999 Pinchasik et al.... 623/1.16
USOO6210432B1 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,210,432 B1 Solem et al. (45) Date of Patent: Apr. 3, 2001 (54) DEVICE AND METHOD FOR TREATMENT 5,980,552 * 11/1999 Pinchasik et al.... 623/1.16
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8246574B2 (12) United States Patent Jacobs et al. () Patent No.: US 8.246,574 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 21, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) SUPPORT CATHETER Inventors:
USOO8246574B2 (12) United States Patent Jacobs et al. () Patent No.: US 8.246,574 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 21, 2012 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (60) (51) (52) (58) SUPPORT CATHETER Inventors:
United States Patent Patent Number: 5,582,598 Chanoch 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 10, 1996
 I I US005582598A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: Chanoch 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 10, 1996 54 MEDICATIN DELIVERY PEN WITH 5,114,406 5/1992 Gabriel et al.... 604/232 WARIABLE INCREMENT DSE SCALE
I I US005582598A United States Patent 19 11 Patent Number: Chanoch 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 10, 1996 54 MEDICATIN DELIVERY PEN WITH 5,114,406 5/1992 Gabriel et al.... 604/232 WARIABLE INCREMENT DSE SCALE
United States Patent (19)
 United States Patent (19) US005611782A 11 Patent Number: Haedt (45) Date of Patent: Mar 18, 1997 (54) METHOD OF DELIVERING A BLOOD 57) ABSTRACT SAMPLE TO AN EVACUATED RECEPTACLE A method of delivering
United States Patent (19) US005611782A 11 Patent Number: Haedt (45) Date of Patent: Mar 18, 1997 (54) METHOD OF DELIVERING A BLOOD 57) ABSTRACT SAMPLE TO AN EVACUATED RECEPTACLE A method of delivering
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,900,634 B2
 USOO790.0634B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Tjong Joe Wai (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2011 (54) BRONCHUS BLOCKER AND ARTIFICIAL RESPRATION SYSTEM (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
USOO790.0634B2 (12) United States Patent () Patent No.: Tjong Joe Wai (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 8, 2011 (54) BRONCHUS BLOCKER AND ARTIFICIAL RESPRATION SYSTEM (56) References Cited U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS
(12) United States Patent Garman
 (12) United States Patent Garman US006299445B1 (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 9, 2001 (54) ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENT, INSTRUMENT BLANK AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURE (75) Inventor: Gary T. Garman, La
(12) United States Patent Garman US006299445B1 (10) Patent N0.: (45) Date of Patent: Oct. 9, 2001 (54) ENDODONTIC INSTRUMENT, INSTRUMENT BLANK AND METHOD OF MANUFACTURE (75) Inventor: Gary T. Garman, La
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7, B2
 US007052479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,052.479 B2 Drennan (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 2006 (54) TRACTION DEVICE 3,762.405 A * 10/1973 De George... 602/23 3,771,519 A * 11/1973 Haake......
US007052479B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 7,052.479 B2 Drennan (45) Date of Patent: May 30, 2006 (54) TRACTION DEVICE 3,762.405 A * 10/1973 De George... 602/23 3,771,519 A * 11/1973 Haake......
AXS Catalyst Distal Access Catheter
 AXS Catalyst Distal Access Catheter Directions for Use 2 AXS Catalyst Distal Access Catheter ONLY Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. warning Contents
AXS Catalyst Distal Access Catheter Directions for Use 2 AXS Catalyst Distal Access Catheter ONLY Caution: Federal Law (USA) restricts this device to sale by or on the order of a physician. warning Contents
-vita THORACIC 3G. Stent Graft System SOLUTIONS FOR VASCULAR DISEASE
 Stent Graft SOLUTIONS FOR VASCULAR DISEASE 1 PURE PERFORMANCE AND QUALITY: STENT GRAFT SYSTEMS BY JOTEC JOTEC is an innovation-oriented company with consistent focus on its core competencies: the development
Stent Graft SOLUTIONS FOR VASCULAR DISEASE 1 PURE PERFORMANCE AND QUALITY: STENT GRAFT SYSTEMS BY JOTEC JOTEC is an innovation-oriented company with consistent focus on its core competencies: the development
United States Patent (19) Dobben
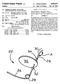 United States Patent (19) Dobben 54 ARTIFICIAL HEART VALVE FOR MPLANTATION IN A BLOOD WESSEL (76 Inventor: Richard L. Dobben, 6355 N. 600 West, Michigan City, Ind. 46360 21 Appl. No.: 342,2 (22 Filed:
United States Patent (19) Dobben 54 ARTIFICIAL HEART VALVE FOR MPLANTATION IN A BLOOD WESSEL (76 Inventor: Richard L. Dobben, 6355 N. 600 West, Michigan City, Ind. 46360 21 Appl. No.: 342,2 (22 Filed:
(12) United States Patent
 USOO8622925B2 (12) United States Patent Dunn (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,622,925 B2 Jan. 7, 2014 (54) DERMAL PUNCH DEVICE (75) Inventor: Raymond Dunn, Shrewsbury, MA (US) (73) Assignee:
USOO8622925B2 (12) United States Patent Dunn (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: US 8,622,925 B2 Jan. 7, 2014 (54) DERMAL PUNCH DEVICE (75) Inventor: Raymond Dunn, Shrewsbury, MA (US) (73) Assignee:
RECOMMENDED INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
 Rapid Exchange PTCA Dilatation Catheter RECOMMENDED INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Available in diameters 1.25mm to 4.5mm and in lengths 09mm to 40mm Caution: This device should be used only by physicians trained
Rapid Exchange PTCA Dilatation Catheter RECOMMENDED INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Available in diameters 1.25mm to 4.5mm and in lengths 09mm to 40mm Caution: This device should be used only by physicians trained
s 3. S. E. E. t 3. guide another balloon catheter to the Stenosis for treatment
 USOO5876375A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,876,375 Penny (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 2, 1999 54 GUIDE CATHETER SYSTEM FOR AN OTHER PUBLICATIONS ANGOPLASTY BALLOON CATHETER Replacing the Occluded
USOO5876375A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,876,375 Penny (45) Date of Patent: Mar. 2, 1999 54 GUIDE CATHETER SYSTEM FOR AN OTHER PUBLICATIONS ANGOPLASTY BALLOON CATHETER Replacing the Occluded
MAXIMIZE RADIAL SOLUTIONS TO PERIPHERAL CHALLENGES
 MAXIMIZE RADIAL SOLUTIONS TO PERIPHERAL CHALLENGES PUSHING BOUNDARIES Terumo Interventional Systems is committed to your success with innovative procedural solutions and ongoing support for your most challenging
MAXIMIZE RADIAL SOLUTIONS TO PERIPHERAL CHALLENGES PUSHING BOUNDARIES Terumo Interventional Systems is committed to your success with innovative procedural solutions and ongoing support for your most challenging
(12) United States Patent
 (12) United States Patent Kupiecki et al. USOO634.4041B1 (10) Patent o.: US 6,344,041 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 5, 2002 (54) AEURYSM CLOSURE DEVICE ASSEMBLY (76) Inventors: David Kupiecki, 10384 Alpine
(12) United States Patent Kupiecki et al. USOO634.4041B1 (10) Patent o.: US 6,344,041 B1 (45) Date of Patent: Feb. 5, 2002 (54) AEURYSM CLOSURE DEVICE ASSEMBLY (76) Inventors: David Kupiecki, 10384 Alpine
(12) United States Patent
 USOO9381093B1 (12) United States Patent Morris et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Jul. 5, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (63) (51) (52) (58) LOCKING DEVICE FOR FXATION MECHANISM OF MEDICAL
USOO9381093B1 (12) United States Patent Morris et al. (10) Patent No.: (45) Date of Patent: *Jul. 5, 2016 (54) (71) (72) (73) (*) (21) (22) (63) (51) (52) (58) LOCKING DEVICE FOR FXATION MECHANISM OF MEDICAL
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/ A1
 (19) United States US 2014001 1160A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0011160 A1 JOrneus et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ABUTMENT SYSTEMAND
(19) United States US 2014001 1160A1 (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2014/0011160 A1 JOrneus et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jan. 9, 2014 (54) (71) (72) (73) (21) (22) (30) ABUTMENT SYSTEMAND
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/ A1
 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0190141 A1 Cragg et al. US 2015O1901.41A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) (60) ENDOVASCULAR OCCLUSION
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0190141 A1 Cragg et al. US 2015O1901.41A1 (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 9, 2015 (54) (71) (72) (21) (22) (63) (60) ENDOVASCULAR OCCLUSION
NAVIGATE DISTAL AND TORTUOUS ANATOMY
 PROGREAT ALPHA PUSHINGBOUNDARIES Terumo Interventional Systems is committed to your success with innovative procedural solutions and ongoing support for your most challenging cases. We are relentlessly
PROGREAT ALPHA PUSHINGBOUNDARIES Terumo Interventional Systems is committed to your success with innovative procedural solutions and ongoing support for your most challenging cases. We are relentlessly
(12) United States Patent
 USOO879424.4B2 (12) United States Patent Hammel et al. (10) Patent No.: US 8,794,244 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) ELECTRONIC RECHARGEABLESMOKING
USOO879424.4B2 (12) United States Patent Hammel et al. (10) Patent No.: US 8,794,244 B2 (45) Date of Patent: Aug. 5, 2014 (54) (75) (73) (*) (21) (22) (65) (51) (52) (58) ELECTRONIC RECHARGEABLESMOKING
75 Inventors: Ulrik Nosted, Lyngby; Jan Torstensen, 55. o1. Rho 206/364
 US006059107A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,059,107 Nosted et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2000 54). URINARY CATHETER ASSEMBLY WITH A 3,967,728 7/1976 Gordon et al.. READY-TO-USE CATHETER
US006059107A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 6,059,107 Nosted et al. (45) Date of Patent: May 9, 2000 54). URINARY CATHETER ASSEMBLY WITH A 3,967,728 7/1976 Gordon et al.. READY-TO-USE CATHETER
Berry (43) Pub. Date: May 6, (76) Inventor: Bret Berry, Cordova, TN (US) (57) ABSTRACT
 US 20040O88054A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0088054A1 Berry (43) Pub. Date: (54) LATERALLY EXPANDABLE CAGE (52) U.S. Cl.... 623/17.11 (76) Inventor: Bret
US 20040O88054A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2004/0088054A1 Berry (43) Pub. Date: (54) LATERALLY EXPANDABLE CAGE (52) U.S. Cl.... 623/17.11 (76) Inventor: Bret
thoracic stent graft system Smallest delivery profile as from 20 F
 thoracic stent graft system Smallest delivery profile as from 20 F Third-generation thoracic stent graft system effective, precise and safe JOTEC develops stent graft systems in close collaboration with
thoracic stent graft system Smallest delivery profile as from 20 F Third-generation thoracic stent graft system effective, precise and safe JOTEC develops stent graft systems in close collaboration with
ABDOMINAL XT ABDOMINAL STENT GRAFT SYSTEM
 ABDOMINAL XT ABDOMINAL STENT GRAFT SYSTEM Pure performance and quality: Stent graft systems by JOTEC JOTEC is an innovation-oriented company with consistent focus on its core competencies: the development
ABDOMINAL XT ABDOMINAL STENT GRAFT SYSTEM Pure performance and quality: Stent graft systems by JOTEC JOTEC is an innovation-oriented company with consistent focus on its core competencies: the development
