Saluki heart pathology study
|
|
|
- Sabrina Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Heart conditions by MaryDee Sist, DVM Originally published in Baraka Book, Autumn-Winter 2001 For the last decade I have been involved in Saluki heart research. Ouroriginalgoalwastoexaminethe incidence of cardiomyopathy. When characterizing Saluki hearts through physical examinations, electrocardiograms and ultrasonography, we discovered that there were differences from what was accepted as normal in mixed-breed populations. To know if these changes were significant or were just unique to Salukis we had to continue to examine these dogs as they aged and after death to see if any of these changes resulted in heart disease. Saluki fanciers want to know what heart diseases occur and if any of the conditions could be inherited or genetic. Our pathology study is documenting what heart conditions occur in Salukis. But determining if these are significant diseases that could be inherited or geneticisverydifficult.someheart conditions are thought to be inherited in certain breeds because the condition occurs at a greater incidence than in mixed breed populations. And some conditions seem to be prevalent in certain families. However, is it fair to generalize from what is found in other breeds to salukis? Pedigree studies need to be done on affected dogs andtheirrelativestodeterminethe possible inheritance. Heart conditions can be classified in two major groups, congenital or acquired. Congenital conditions, or defects that the dog was born with, are abnormalities in the structure of the heart, heart valves, or the major vessels. These might or might not be genetic. They typically cause problems or symptoms early in the dog s life, such as inactivity or poor growth and a heart murmur. Congenital heart diseases that are known to have a polygenic mode of inheritance in the following breeds are: Patent ductus arteriosis (PDA) in poodles, Aortic stenosis (AS) or narrowing of the valve in Newfoundlands, and Pulmonic stenosis (PS) in beagles. Acquired heart conditions develop due to disease states or degenerative conditions that occur as the dog ages. The dog is born with a normal functioning heart, but changes occur with time and affect either the fibrous sac enclosing the heart, the pericardium (PERICARDIAL DISEASE) or the heart muscle itself, (PRIMARY MYOCARDIAL DISEASE) or the heart valves (VALVULAR DISEASE). PERICARDIAL DISEASE is the least commonly encountered. It generally involves the accumulation of fluid in the sac around the heart. Heart sounds are often muffled due to the fluid accumulation. The heart looks huge on a radiograph and an echocardiogram is needed to determine of it is fluid around the heart or if the heart is enlarged. This fluid or pericardial effusion impairs the ability of the heart to fill properly with blood. As a result fluid builds up in the lungs or abdominal cavity causing signs of heart failure since the heart can t pump the blood through the body properly. Usually a mass on the surface of the heart or, much less commonly, thickening in the pericardium due to infection causes the fluid build up. In older dogs, cancer (usually hemangiosarcoma) in the heart is the most common cause and rupture of the mass causes bleeding into the sac and the dog collapses. PRIMARY MYOCARDIAL DISEASE occurs when the heart muscle weakens and fails as a pump. Early on there are no symptoms as the heart compensates for its loss of contractility by enlarging. But eventually, the failure of the heart to pump enough blood results in accumulation of fluid in the body and signs of heart failure. Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), where the heart muscle wall thins out, is more commonly seen than where the muscle wall thickens (hypertrophic cardiomyopathy). A hereditary nature is suspected since DCM affects certain, generally large breeds of dogs, and expresses itself differently in different breeds. Giant breeds most often show congestive heart failure signs with fluid accumulation in the lungs. While in Boxers, the major abnormality is in the electrical conduction system of the heart. This causes an irregular heart rhythm and can result in fainting or syncopal episodes which makes the dog prone to sudden death. The condition is diagnosed on an echocardiograph by finding enlargement of the chambers of the heart and poor contractility. HOWEVER, other heart conditions can cause some secondary enlargement of the chambers and alteration of contractility, but these are not primary diseases of the heart muscle like DCM. VALVULAR DISEASE occurs when any of the four valves that regulate the direction and amount of blood flow through and out of the heart don t function properly. The AV valves separate the upper chambers (atri) from the lower pumping chanbers (ventricles) on the right (mitral) and left (tricuspid) sides of the heart. The pulmonary valve regulates the blood flowing in the artery to the lungs and the aortic valve, blood flowingtothebody.sincethevalve doesn t close completely, blood spills back (regurgitation) across the leaky (insufficient) valve and a murmur from turbulent blood flow is heard. Over time this back flow of blood causes the heart 20 ASA newsletter, Summer 2010
2 muscle to have to work harder to move thesamevolumeofblood.themuscle thickens and the heart enlarges. Eventually, signs of heart failure will develop as fluid builds up in the lungs or body (volume overload). This is the most common group of heart conditions and can occur from a variety of causes. Valvular disease can be a congenital condition, generally termed dysplasia, because there is some defect that makes the valves not fit and close properly. There can be infectious causes where bacteria colonize on the valve causing vegetations or nodules to form (termed itis ). With age, degeneration (termed osis ) of the valves can also occur where the leaflets thicken and develop nodular swellings that coalesce. With time this resultsinmoreleakagewhichcauses more changes in the valves. In some dogs, this volume overload is well tolerated, whereas in other dogs there is a rapid progression to congestive heart failure. Bacterial infections usually affect the aortic and mitral valves causing valvular endocarditis. Degenerative changes commonly affect the AV valves causing valvular endocardiosis. The left AV or mitralvalveismorefrequentlyinvolved and as the insufficiency progresses, eventually fluid will build up in the lungs. Less commonly, regurgitation of the tricuspid or right AV valve will result in fluid building up in the abdomen (ascites). Early on, dogs with valvular endocardiosis have no outward signs, but a murmur can be heard by a veterinarian. The point of maximum intensity (PMI) or location of the murmur can indicate what valve is leaking. The loudness of the murmur (graded on a scale of I to VI) doesn t necessarily indicate the severity of the leak of blood across the valve. The definitive identification of valvular conditions requires a cardiac ultrasound with a Doppler exam to quantify the direction, volume, and velocity or severity of the regurgitant blood flow. Mitral degeneration, or valvular endocardiosis (also termed verrucous or myxomatous degeneration of the valvular endocardium) is common in smallbreedsofdogsastheyage.itis not thought to routinely occur in large breeds. However, a large number of the Salukis examined had varying degrees ofmitralvalvedisease.insomedogs, this insufficiency was well tolerated. In others, it progressed to congestive heart failure. Pedigree analyses of affected and related dogs need to be conducted to help determine if this could have a heritable component. Congenital heart defects generally cause clinical signs in young dogs. However acquired heart conditions develop as a dog ages. Without routine physical examinations, these will not be detected unless the dog has progressed to a severity of disease where signs of heart failure become apparent. Murmurs detected on physical examination are often early indicators of heart problems and necessitate further evaluation. Often, this requires repeated examinations as the dog ages to see if the heart condition progresses. Saluki heart pathology study by MaryDee Sist, DVM Originally published in Baraka Book, 2002 There has been debate regarding the incidence, importance and types of cardiac disease found in Salukis. Dr. Cathy Gaber, a board certified cardiologist, has evaluated 100 Salukis from one to six times over a 6 year period in the Saluki Heart Study that I initiated in The goal was to characterize the normal Saluki heart through auscultation, electrocardiogram and ultrasonographic evaluation. However, many Salukis when compared to mixed breeds, had changes that could be associated with heart disease. Over a third of the Salukis examined had a heart murmur on auscultation, due to abnormal blood flow across a heartvalve.mostweresoftmurmursand the dogs remained free of signs of heart disease. Some had arrhythmias, or an irregular heart rhythm and/or rate on the ECG recording. Many of the Salukis had enlarged hearts, especially the left ventricles, when compared with other breeds of similar body size. Also, some had decreased contractility (%FS) of the heart muscle during the echo examination. Each of these are changes that can be associated with significant heart diseases as well as dilated cardiomyopathy. Asaresult,apost-mortemstudy of the hearts was begun in 1997 to try to determine if the changes seen in the cardiovascular examinations of the salukis were significant to their health, especially as the dogs aged. Dr. Thomas Bell, a pathologist at the Animal Health Diagnostic Laboratory at Michigan State University was recruited to perform gross, macro and microscopic evaluations of Saluki hearts. He found a surprising array of pathological changes in the Salukis while very few had developed clinical signs of heart disease. This led to further investigations of Salukis that died suddenly or had various forms of cancer. To date 96 (40 males, 8 castrated males, 24 females and24spayedfemalesrangingfrom 7 months to nearly 16 years of age) Saluki hearts have been examined. ASA newsletter, Summer
3 The most prevalent finding was myxomatous degeneration of the valvular endocardium, also known as verrucous endocardiosis of the left AV or mitral valve (Fig. 1). These nodular thickenings stop the valve from closing properly and the valve becomes insufficient or leaks. This change was found in 52% (50/96) of the hearts, but the lesions were of sufficient severity to cause the demise of only half of the dogs with mitral insufficiency. Five Salukis died of congenital heart valve defects. Fig. 2 shows a hole in the tricuspid valve where there is only a single cusp instead of three. Only twodiedofprimarydilated Cardiomyopathy, which was definatively diagnosed by microscopically finding the characteristic wavy cardiac myofibers (Fig. 3) and large heart size. The next most common cause of death was a rare type of vascular cancer, Hemangiosarcoma, which was found in 25% (24/96) of the Salukis. Fig. 4 shows a ruptured hemangiosarcoma tumor in the atrial appendage and a small metastasis growing out of the epicardial surface of the ventricle. The right atrial appendage of the heart was the most common primary site. However, the most disconcerting finding was that 52% (50/96) of the Salukis had one or more forms of cancer contributing to their demise. Another unexpected finding was the incidence in 47% (45/96) of some form of acquired heart vessel changes, most commonly arteriolosclerosis or a narrowing of the small arteries due to connective tissue deposition in the wall (Fig. 5). Less commonly arterio- and atherosclerotic (fatty) changes were also found. As is the case in most dogs, only a small number of Salukis had infarcts or ischemic areas in the heart muscle (Fig. 6) due to these vessel changes. Any of these vascular changes that affect the blood supply to the heart muscle canleadtoheartattacksinhumans. Fig. 2 Fig ASA newsletter, Summer 2010
4 Fig. 3 normal heart muscle Fig. 3 abnormal heart muscle However, in dogs, due to their abundant collateral circulation, this rarely causes symptoms and only one dog had significant myocardial degeneration due to the blockage of the small arteries. The pathology study was initiated to examine the hearts of normal Salukis however, some dogs did develop heart-related signs. Chronic or long term heart failure signs developed in 13 dogs and they died at an average age of 8.6 years. These chronic heart disease signs included difficulty breathing, coughing, inappetence and weakness. Over half of these dogs died as a result of verrucous endocardiosis of the mitral (left AV) valve. Their hearts had failed to pump adequate amounts of blood due to leakage across the mitral valve and compensated by becoming quite large (average heart weight was 334 grams, about a third larger than hearts without any pathology) (Fig. 7). Seven additional dogs had acute (less than two days) signs of heart failure and died at an average age of10.6years.halfofthesediedof hemangiosarcoma in the right atrial appendage of the heart. A second group included dogs euthanized for reasons that were unrelatedtosymptomsofheart conditions. Most of the hearts examined were from older dogs showing signs of failing health. These dogs averaged years of age at death and 50% had verrucous endocardial changes of the left AV valve or mitral insufficiency. Their hearts, however, were not as large as the chronic heart failure group discussed above. 80% had some formofcancer.fig.8shows hemangiosarcoma tumors in the heart, spleen, liver and seeded throughout the abdominal cavity. Of the dogs euthanized at an average of 11 years without signs of failing health, most had mild verrucous endocardiosis, but their heartswerejudgedtobenormal for their age and were not enlarged (average heart weight 230 grams). The last group consisted of 24 dogs that died suddenly at an average age of 7.5 years. The hearts of two of these dogs showed no pathology. 50% (12/24) died of hemangiosarcoma and 25% (6/24) died of a suspected arrhythmia due to Purkinje fiber degeneration. Fig. 9 shows degeneration and vacuoles or holes where Purkinje fibers should be. This degeneration caused an electrical conduction disturbance in the heart. Two died from Fig. 5 normal arteriole Fig. 5 arteriosclerosis (narrowed arteriole) Fig. 6 arteriolosclerosis resulting in ischemia (lack of normal blood flow) and infarction (atrophy, necrosis, fibrosis and vacuolization of the heart muscle fibers
5 myocarditis or an infection affecting the heart, and two from congenital valvular heart defects. Fig. 7 In conclusion, the examination of Saluki hearts in this study showed that: - A surprising array of heart pathology was found in symptom-free dogs. - Myxomatous degeneration of the valvular endocardium of the left AV (mitral) valve or MITRAL INSUFFICIENCY was the most common heart problem and the heart showed compensatory enlargement or dilation as the condition progressed over time. Clinically in these dogs, a heart murmur should be heard when examined prior to death. - A dilated heart does not necessarily mean a diagnosis Fig 8 of cardiomyopathy. - Arteriolosclerosis was commonly found. It caused no obvious symptoms and no heart attacks or sudden death, butcouldaccountforsome decreased heart contractility. - The presence of an arrhythmia does not mean the dog has or will develop cardiomyopathy, but it may cause sudden death. - There was a high incidence of cancer in the Salukis examined. A rare form, hemangiosarcoma, was found in 25% of the hearts. Clearly this incidence of cancer needs further investigation. -Suddendeathcanoften, but not always, be attributed to an arrhythmia or rupture of a hemangiosarcoma. - Because congenital heart defects may cause death at an early age, the incidence in this group was low. - Heart conditions can progress in severity with time. Without the support of the generous individuals who have either allowed their dogs to be examined or offered their financial support, this would not have been possible. Thank you for your contributions. Fig. 9 Purkinje fiber necrosis, swelling and vacuolization; causes a conduction disturbance in the heart and the resulting arrhythmia can lead to sudden death 26 ASA newsletter, Summer 2010
Saluki Studies supported by Saluki Health Research, Inc.
 Saluki Studies supported by Saluki Health Research, Inc. prepared by MaryDee Sist, DVM for the Saluki World Congress in Helsinki, Finland, June 2008 MaryDee Sist, DVM is the President and Director of Saluki
Saluki Studies supported by Saluki Health Research, Inc. prepared by MaryDee Sist, DVM for the Saluki World Congress in Helsinki, Finland, June 2008 MaryDee Sist, DVM is the President and Director of Saluki
Heart Disease in Dogs: An Overview
 Heart Disease in Dogs: An Overview Heart disease in dogs is a commonly diagnosed condition. A dog s heart, lungs, and blood vessels combine to form his circulatory system. The heart is the central player
Heart Disease in Dogs: An Overview Heart disease in dogs is a commonly diagnosed condition. A dog s heart, lungs, and blood vessels combine to form his circulatory system. The heart is the central player
BOXER CARDIOMYOPATHY
 BOXER CARDIOMYOPATHY by: Wendy Wallner, DVM What is Boxer cardiomyopathy? Boxer cardiomyopathy as we know it consists primarily of an electrical conduction disorder which causes the heart to beat erratically
BOXER CARDIOMYOPATHY by: Wendy Wallner, DVM What is Boxer cardiomyopathy? Boxer cardiomyopathy as we know it consists primarily of an electrical conduction disorder which causes the heart to beat erratically
Degenerative Valve Disease (DVD)
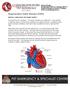 Degenerative Valve Disease (DVD) BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART WORK? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles.
Degenerative Valve Disease (DVD) BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART WORK? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles.
Pulmonic Stenosis BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART WORK?
 Pulmonic Stenosis BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART WORK? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In addition
Pulmonic Stenosis BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART WORK? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles. In addition
Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics
 Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics OVERVIEW Failure of the right side of the heart to pump blood at a sufficient rate to meet the needs of the body or to prevent blood from pooling within the
Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics OVERVIEW Failure of the right side of the heart to pump blood at a sufficient rate to meet the needs of the body or to prevent blood from pooling within the
Auscultation screening (listening with a stethoscope) at shows for murmurs which could be associated with aortic stenosis has been underway for some
 A report on cardiac examinations performed at the Saluki or Gazelle Hound Club Championship show on 1/11/2009 S.E. Brownlie PhD BVM&S MRCVS Cert SAC Kileeekie, Crosshill, Maybole, Ayrshire KA19 7PY My
A report on cardiac examinations performed at the Saluki or Gazelle Hound Club Championship show on 1/11/2009 S.E. Brownlie PhD BVM&S MRCVS Cert SAC Kileeekie, Crosshill, Maybole, Ayrshire KA19 7PY My
Heart Disorders. Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8. Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders
 Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders Susie Turner, MD 1/7/13 Heart Disorders Coronary Artery Disease Cardiac Arrhythmias Congestive Heart
Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders Susie Turner, MD 1/7/13 Heart Disorders Coronary Artery Disease Cardiac Arrhythmias Congestive Heart
Pulmonic Stenosis. How does the heart work?
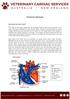 Pulmonic Stenosis How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Pulmonic Stenosis How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Presenter: Steven Brust, HCS-D, HCS-H Product Manager, Home Health Coding Center
 Presenter: Steven Brust, HCS-D, HCS-H Product Manager, Home Health Coding Center Pinpoint & properly assign the appropriate heart failure codes Left- vs. Right-sided Left ventricular failure (LVF) may
Presenter: Steven Brust, HCS-D, HCS-H Product Manager, Home Health Coding Center Pinpoint & properly assign the appropriate heart failure codes Left- vs. Right-sided Left ventricular failure (LVF) may
Sarah J. Miller, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Cardiology) Degenerative Valvular Disease What s New?
 Sarah J. Miller, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Cardiology) Degenerative Valvular Disease What s New? Chronic degenerative valvular disease is the most common cardiovascular disease in small animals, and is also
Sarah J. Miller, DVM, Diplomate ACVIM (Cardiology) Degenerative Valvular Disease What s New? Chronic degenerative valvular disease is the most common cardiovascular disease in small animals, and is also
2
 1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
Atrioventricular Valve Dysplasia
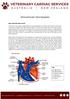 Atrioventricular Valve Dysplasia How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job
Atrioventricular Valve Dysplasia How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job
Atrioventricular Valve Endocardiosis Basics
 Atrioventricular Valve Endocardiosis Basics OVERVIEW Atrioventricular valve refers to the heart valves between the top chamber (known as the atrium ) and the bottom chamber (known as the ventricle ) of
Atrioventricular Valve Endocardiosis Basics OVERVIEW Atrioventricular valve refers to the heart valves between the top chamber (known as the atrium ) and the bottom chamber (known as the ventricle ) of
Cardiomyopathy Consequences. function of the myocardium for any reason. This is a serious disease in which the heart muscle
 Becki Simmons Cardiomyopathy Consequences Cardiomyopathy, which literally means "heart muscle disease," is the deterioration of the function of the myocardium for any reason. This is a serious disease
Becki Simmons Cardiomyopathy Consequences Cardiomyopathy, which literally means "heart muscle disease," is the deterioration of the function of the myocardium for any reason. This is a serious disease
Mitral Valve Disease (MVD)
 Mitral Valve Disease (MVD) What is the mitral valve? The heart contains 4 valves within it. Each valve is present to allow unidirectional flow and to prevent flow backwards. The mitral valve is the valve
Mitral Valve Disease (MVD) What is the mitral valve? The heart contains 4 valves within it. Each valve is present to allow unidirectional flow and to prevent flow backwards. The mitral valve is the valve
Alfonso López. Cardiac Hypertrophy and Dilation
 Cardiac Hypertrophy and Dilation Alfonso López Professor of Anatomic Pathology Dept. Pathology and Microbiology Atlantic Veterinary College University of Prince Edward Island Canada Jan 23, 2012 Compensatory
Cardiac Hypertrophy and Dilation Alfonso López Professor of Anatomic Pathology Dept. Pathology and Microbiology Atlantic Veterinary College University of Prince Edward Island Canada Jan 23, 2012 Compensatory
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to:
 The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
Ventricular Tachycardia Basics
 Ventricular Tachycardia Basics OVERVIEW Ventricular refers to the ventricles of the heart; tachycardia is the medical term for rapid heart rate The heart of the dog or cat is composed of four chambers;
Ventricular Tachycardia Basics OVERVIEW Ventricular refers to the ventricles of the heart; tachycardia is the medical term for rapid heart rate The heart of the dog or cat is composed of four chambers;
Pericardial Effusion
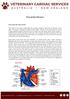 Pericardial Effusion How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Pericardial Effusion How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Atrial Fibrillaton. Key: RA: right atrium RV: right ventricle PA: pulmonic artery LA: left atrium LV: left ventricle AO: aorta
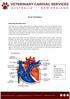 Atrial Fibrillaton How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Atrial Fibrillaton How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right
Myocardial Infarction
 Myocardial Infarction MI = heart attack Defined as necrosis of heart muscle resulting from ischemia. A very significant cause of death worldwide. of these deaths, 33% -50% die before they can reach the
Myocardial Infarction MI = heart attack Defined as necrosis of heart muscle resulting from ischemia. A very significant cause of death worldwide. of these deaths, 33% -50% die before they can reach the
Convulsive Disorder and Cardiac Disease. Running Rachael, Active Ashlee, Sassy Savannah
 Convulsive Disorder and Cardiac Disease Running Rachael, Active Ashlee, Sassy Savannah Convulsive Disorder Seizure is over. Pay attention to how long the seizure lasts. Stay calm. Make the person as comfortable
Convulsive Disorder and Cardiac Disease Running Rachael, Active Ashlee, Sassy Savannah Convulsive Disorder Seizure is over. Pay attention to how long the seizure lasts. Stay calm. Make the person as comfortable
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System The heart The heart is a four chambered muscular organ that pumps the blood around the body The heart lies in the mediastinum within the thoracic cavity It is conical in shape and
The Circulatory System The heart The heart is a four chambered muscular organ that pumps the blood around the body The heart lies in the mediastinum within the thoracic cavity It is conical in shape and
MITRAL VALVE DISEASE IN CAVALIER KING CHARLES SPANIELS. Carroll Loyer, DVM, DACVIM
 MITRAL VALVE DISEASE IN CAVALIER KING CHARLES SPANIELS Carroll Loyer, DVM, DACVIM CAVIEPALOOZA!! MITRAL INSUFFICIENCY mitral regurgitation (MR) chronic degenerative mitral valve disease (CVD) myxomatous
MITRAL VALVE DISEASE IN CAVALIER KING CHARLES SPANIELS Carroll Loyer, DVM, DACVIM CAVIEPALOOZA!! MITRAL INSUFFICIENCY mitral regurgitation (MR) chronic degenerative mitral valve disease (CVD) myxomatous
Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
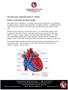 Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART WORK? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles.
Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) BRIEFLY, HOW DOES THE HEART WORK? The heart has four chambers. The upper chambers are called atria. One chamber is called an atrium, and the lower chambers are called ventricles.
Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes
 Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Identify the components of the cardiovascular system and the various types of cardiovascular disease Ø Discuss ways of promoting cardiovascular
Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Identify the components of the cardiovascular system and the various types of cardiovascular disease Ø Discuss ways of promoting cardiovascular
Do Now. Get out work from last class to be checked
 Do Now Get out work from last class to be checked Heart Actions Cardiac Cycle: One complete heartbeat. The contraction of a heart chamber is called systole and the relaxation of a chamber is called diastole.
Do Now Get out work from last class to be checked Heart Actions Cardiac Cycle: One complete heartbeat. The contraction of a heart chamber is called systole and the relaxation of a chamber is called diastole.
10/8/2018. Lecture 9. Cardiovascular Health. Lecture Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor
 Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
Adult Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 Anatomy and Physiology Pathology Clinical Care and Safety Measurement Techniques, Maneuvers,
HISTORY. Question: How do you interpret the patient s history? CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: 45-year-old man.
 HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
HISTORY 45-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Dyspnea of two days duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: His dyspnea began suddenly and has been associated with orthopnea, but no chest pain. For two months he has felt
Case # 1. Page: 8. DUKE: Adams
 Case # 1 Page: 8 1. The cardiac output in this patient is reduced because of: O a) tamponade physiology O b) restrictive physiology O c) coronary artery disease O d) left bundle branch block Page: 8 1.
Case # 1 Page: 8 1. The cardiac output in this patient is reduced because of: O a) tamponade physiology O b) restrictive physiology O c) coronary artery disease O d) left bundle branch block Page: 8 1.
Septal Defects. How does the heart work?
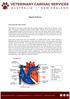 Septal Defects How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right side
Septal Defects How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job of the right side
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors
 Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors 1 Human Health: What s Killing Us? Health in America Health is the U.S Average life
Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors 1 Human Health: What s Killing Us? Health in America Health is the U.S Average life
Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm!
 Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm! Prof. dr. Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Ass Member ECVDI, Dip ECEIM Dept. of Large Animal Internal Medicine Ghent University, Belgium Murmurs
Clinical significance of cardiac murmurs: Get the sound and rhythm! Prof. dr. Gunther van Loon, DVM, PhD, Ass Member ECVDI, Dip ECEIM Dept. of Large Animal Internal Medicine Ghent University, Belgium Murmurs
1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI).
 1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI). 5- cardiogenic shock (massive MIs >40% of the left ventricle)
1) Severe, crushing substernal chest pain 2) radiate to the neck, jaw, epigastrium, or left arm. 3- rapid and weak pulse 4- nausea (posterior MI). 5- cardiogenic shock (massive MIs >40% of the left ventricle)
Chapter 14. Circulatory System Images. VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II
 Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
Chapter 14 Circulatory System Images VT-122 Anatomy & Physiology II The mediastinum Dog heart Dog heart Cat heart Dog heart ultrasound Can see pericardium as distinct bright line Pericardial effusion Fluid
HEART DISEASE HEART CONDITIONS, RISKS AND PROTECTION
 Spotlight on Health 2017 HEART DISEASE HEART CONDITIONS, RISKS AND PROTECTION Heart disease is the leading cause of death for both men and women worldwide, accounting for over 17 million deaths per year.
Spotlight on Health 2017 HEART DISEASE HEART CONDITIONS, RISKS AND PROTECTION Heart disease is the leading cause of death for both men and women worldwide, accounting for over 17 million deaths per year.
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition
 Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Practical Echocardiography: ECHOES in the REAL WORLD Know When to Hold Em and When to Fold Em
 Practical Echocardiography: ECHOES in the REAL WORLD Know When to Hold Em and When to Fold Em Introduction The use of ultrasound in private veterinary practice is continuing to grow. The popularity of
Practical Echocardiography: ECHOES in the REAL WORLD Know When to Hold Em and When to Fold Em Introduction The use of ultrasound in private veterinary practice is continuing to grow. The popularity of
Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Dogs
 Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Dogs (a Type of Heart-Muscle Disease) Basics OVERVIEW The heart of the dog is composed of four chambers; the top two chambers are the left and right atria and the bottom two chambers
Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Dogs (a Type of Heart-Muscle Disease) Basics OVERVIEW The heart of the dog is composed of four chambers; the top two chambers are the left and right atria and the bottom two chambers
By the end of this session, the student should be able to:
 Valvular Heart disease HVD By Dr. Ashraf Abdelfatah Deyab VHD- Objectives By the end of this session, the student should be able to: Define and classify valvular heart disease. Enlist the causes of acquired
Valvular Heart disease HVD By Dr. Ashraf Abdelfatah Deyab VHD- Objectives By the end of this session, the student should be able to: Define and classify valvular heart disease. Enlist the causes of acquired
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
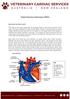 Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) How does the heart work? The heart is the organ responsible for pumping blood to and from all tissues of the body. The heart is divided into right and left sides. The job
Circulation. Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body
 Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
Cardiovascular System angio BELLWORK Day One: Define using technology hemo/hema cardio Medical Therapeutics Standards 11) Outline the gross normal structure and function of all body systems and summarize
Detection Of Heart. By Dr Gary Mo
 Detection Of Heart Disease By Dr Gary Mo Types Of Heart Disease A. Coronary Heart Disease B. Valvular Heart Disease C. Cardiac Arrhythmia ( Rhythm disturbance ) D. Heart Blocks ( Conduction Abnormalities
Detection Of Heart Disease By Dr Gary Mo Types Of Heart Disease A. Coronary Heart Disease B. Valvular Heart Disease C. Cardiac Arrhythmia ( Rhythm disturbance ) D. Heart Blocks ( Conduction Abnormalities
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy in Cats (a Type of Heart-Muscle Disease) Basics
 Restrictive Cardiomyopathy in Cats (a Type of Heart-Muscle Disease) Basics OVERVIEW The heart of the cat is composed of four chambers; the top two chambers are the left and right atria and the bottom two
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy in Cats (a Type of Heart-Muscle Disease) Basics OVERVIEW The heart of the cat is composed of four chambers; the top two chambers are the left and right atria and the bottom two
MI Acute occlusion of the proximal left anterior descending (LAD) artery is the cause of 40% to 50% of all MIs. *
 MI *33% -50% die before hospital lethal arrhythmia Sudden Cardiac Death. * Arrhythmias are caused by electrical abnormalities of the ischemic myocardium and conduction system. *Acute occlusion of the proximal
MI *33% -50% die before hospital lethal arrhythmia Sudden Cardiac Death. * Arrhythmias are caused by electrical abnormalities of the ischemic myocardium and conduction system. *Acute occlusion of the proximal
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders
 C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders GENERAL ISSUES REGARDING MEDICAL FITNESS-FOR-DUTY 1. These medical standards apply to Union Pacific Railroad (UPRR) employees
C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders GENERAL ISSUES REGARDING MEDICAL FITNESS-FOR-DUTY 1. These medical standards apply to Union Pacific Railroad (UPRR) employees
Unit 6: Circulatory System. 6.2 Heart
 Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
ADVANCES IN MITRAL VALVE DISEASE
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk ADVANCES IN MITRAL VALVE DISEASE Author : Gemma Hopkins Categories : Vets Date : June 1, 2009 Gemma Hopkins relates an informative
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk ADVANCES IN MITRAL VALVE DISEASE Author : Gemma Hopkins Categories : Vets Date : June 1, 2009 Gemma Hopkins relates an informative
results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both.
 results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both. The outcome of valvular disease depends on : 1-the valve involved 2-the degree of impairment 3-the cause of its development
results in stenosis or insufficiency (regurgitation or incompetence), or both. The outcome of valvular disease depends on : 1-the valve involved 2-the degree of impairment 3-the cause of its development
Abstract Clinical and paraclinical studies on myocardial and endocardial diseases in dog
 Abstract The doctoral thesis entitled Clinical and paraclinical studies on myocardial and endocardial diseases in dog was motivated by the study of the most frequent cardiopathies in dogs, which involves
Abstract The doctoral thesis entitled Clinical and paraclinical studies on myocardial and endocardial diseases in dog was motivated by the study of the most frequent cardiopathies in dogs, which involves
What Is Valvular Heart Disease? Heart valve disease occurs when your heart's valves do not work the way they should.
 What Is Valvular Heart Disease? Heart valve disease occurs when your heart's valves do not work the way they should. How Do Heart Valves Work? MAINTAIN ONE-WAY BLOOD FLOW THROUGH YOUR HEART The four heart
What Is Valvular Heart Disease? Heart valve disease occurs when your heart's valves do not work the way they should. How Do Heart Valves Work? MAINTAIN ONE-WAY BLOOD FLOW THROUGH YOUR HEART The four heart
Cardiovascular Pathology Lab. Shannon Martinson,
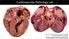 Cardiovascular Pathology Lab Shannon Martinson, 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 10 year old MC DSH Cat History Heart murmur detected on PE recommended cardiac US Blood work was
Cardiovascular Pathology Lab Shannon Martinson, 2017 http://people.upei.ca/smartinson/ Case 1 Signalment: 10 year old MC DSH Cat History Heart murmur detected on PE recommended cardiac US Blood work was
Presented at the ANTA fall Festival, Oct 15, 2005 by Lori Pelletier and Carol Falk
 Mitral Valve Disease in Norfolk Terriers Presented at the ANTA fall Festival, Oct 15, 2005 by Lori Pelletier and Carol Falk What is Mitral Valve Disease (MVD) The heart has two chambers. The upper middle
Mitral Valve Disease in Norfolk Terriers Presented at the ANTA fall Festival, Oct 15, 2005 by Lori Pelletier and Carol Falk What is Mitral Valve Disease (MVD) The heart has two chambers. The upper middle
Heart Disease. Signs and Symptoms
 Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Blood Functions. Blood and the Cardiovascular System. Blood. Plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) Erythrocytes (RBCs) 4/7/2017
 Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
PATIENT BOOKLET MEDTRONIC SURGICAL VALVE REPLACEMENT. Tissue Valve for Aortic and Mitral Valve Replacement
 PATIENT BOOKLET MEDTRONIC SURGICAL VALVE REPLACEMENT Tissue Valve for Aortic and Mitral Valve Replacement ARE MEDTRONIC SURGICAL TISSUE HEART VALVES RIGHT FOR YOU? Medtronic surgical heart valves are for
PATIENT BOOKLET MEDTRONIC SURGICAL VALVE REPLACEMENT Tissue Valve for Aortic and Mitral Valve Replacement ARE MEDTRONIC SURGICAL TISSUE HEART VALVES RIGHT FOR YOU? Medtronic surgical heart valves are for
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by the fact that a murmur was heard at birth?
 HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
CARDIOVASCULAR PATHOLOGY LABORATORY CASES AND SLIDES. VPM Lisa Miller CARDIOVASCULAR LAB
 CARDIOVASCULAR PATHOLOGY LABORATORY CASES AND SLIDES VPM 222 2009 Lisa Miller CARDIOVASCULAR LAB Case 1 Heart - Echoplane section from a 7-month-old Labrador retriever Give two morphologic diagnoses 1.
CARDIOVASCULAR PATHOLOGY LABORATORY CASES AND SLIDES VPM 222 2009 Lisa Miller CARDIOVASCULAR LAB Case 1 Heart - Echoplane section from a 7-month-old Labrador retriever Give two morphologic diagnoses 1.
HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY
 HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY Most often diagnosed during infancy or adolescence, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is the second most common form of heart muscle disease, is usually genetically transmitted,
HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY Most often diagnosed during infancy or adolescence, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is the second most common form of heart muscle disease, is usually genetically transmitted,
Murmur diagnosis in cats. Your pet has a murmur! Meg Sleeper VMD, DACVIM (cardiology) Gainesville, FL. Reasons to work up the murmur in a cat
 Murmur diagnosis in cats Your pet has a murmur! Meg Sleeper VMD, DACVIM (cardiology) Gainesville, FL Heart disease diagnosis in cats and kittens in general is challenging because: Approximately ½ of systolic
Murmur diagnosis in cats Your pet has a murmur! Meg Sleeper VMD, DACVIM (cardiology) Gainesville, FL Heart disease diagnosis in cats and kittens in general is challenging because: Approximately ½ of systolic
Rotation: Echocardiography: Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE)
 Rotation: Echocardiography: Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE) Rotation Format and Responsibilities: Fellows rotate in the echocardiography laboratory in each clinical year. Rotations during the first
Rotation: Echocardiography: Transthoracic Echocardiography (TTE) Rotation Format and Responsibilities: Fellows rotate in the echocardiography laboratory in each clinical year. Rotations during the first
Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease
 Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease Jessi Smith, MD Cardiothoracic imaging, Indiana University Slides courtesy of Stacy Rissing, MD Outline Imaging planes Disease findings Pulse sequences used
Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease Jessi Smith, MD Cardiothoracic imaging, Indiana University Slides courtesy of Stacy Rissing, MD Outline Imaging planes Disease findings Pulse sequences used
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12
 A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
Learning About Mitral Regurgitation (MR) Causes Symptoms Treatment Options
 Learning About Mitral Regurgitation (MR) Causes Symptoms Treatment Options How Your Heart Works Your heart pumps blood through your lungs to replenish it with oxygen, and then pumps the oxygen-rich blood
Learning About Mitral Regurgitation (MR) Causes Symptoms Treatment Options How Your Heart Works Your heart pumps blood through your lungs to replenish it with oxygen, and then pumps the oxygen-rich blood
Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Cardiomyopathies. Stephanie Coulter, MD, FACC, FASE April, 2016
 Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Cardiomyopathies Stephanie Coulter, MD, FACC, FASE April, 2016 Cardiomyopathies (CMP) primary disease intrinsic to cardiac muscle Dilated CMP Hypertrophic CMP Infiltrative
Echocardiographic Evaluation of the Cardiomyopathies Stephanie Coulter, MD, FACC, FASE April, 2016 Cardiomyopathies (CMP) primary disease intrinsic to cardiac muscle Dilated CMP Hypertrophic CMP Infiltrative
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia PSVT.
 Atrial Tachycardia; is the name for an arrhythmia caused by a disorder of the impulse generation in the atrium or the AV node. An area in the atrium sends out rapid signals, which are faster than those
Atrial Tachycardia; is the name for an arrhythmia caused by a disorder of the impulse generation in the atrium or the AV node. An area in the atrium sends out rapid signals, which are faster than those
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline
 Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Pediatric Echocardiography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 Anatomy and Physiology Normal Anatomy and Physiology 10% 2 Abnormal Pathology and Pathophysiology
Biomedical Terminology. Cardiovascular and Lymphatic System
 Biomedical Terminology Cardiovascular and Lymphatic System Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular system is composed of the Heart (cardi/o) Blood vessels (angi/o) Arteries (arteri/o) blood vessels which
Biomedical Terminology Cardiovascular and Lymphatic System Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular system is composed of the Heart (cardi/o) Blood vessels (angi/o) Arteries (arteri/o) blood vessels which
0 P a g e NEIL E STRICKMAN MD
 0 P a g e NEIL E STRICKMAN MD T ranscatheter Aortic Valve Replacement INTRODUCTION The heart is a muscular organ located in your chest between your lungs which is designed to pump blood throughout the
0 P a g e NEIL E STRICKMAN MD T ranscatheter Aortic Valve Replacement INTRODUCTION The heart is a muscular organ located in your chest between your lungs which is designed to pump blood throughout the
Rheumatic heart disease
 Rheumatic heart disease What will we discuss today? Etiology and epidemiology of rheumatic heart disease Pathogenesis of rheumatic heart disease Morphological changes in rheumatic heart disease Clinical
Rheumatic heart disease What will we discuss today? Etiology and epidemiology of rheumatic heart disease Pathogenesis of rheumatic heart disease Morphological changes in rheumatic heart disease Clinical
My dog has heart problems... what do I do now?
 Supporting dietary food for dogs with heart problems My dog has heart problems... what do I do now? reliable and affordable dietary pet food In the veterinary practice, patients with heart problems are
Supporting dietary food for dogs with heart problems My dog has heart problems... what do I do now? reliable and affordable dietary pet food In the veterinary practice, patients with heart problems are
HEART MURMURS: DECIPHERING THEIR CAUSE AND SIGNIFICANCE
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk HEART MURMURS: DECIPHERING THEIR CAUSE AND SIGNIFICANCE Author : Pedro Oliveira Categories : Vets Date : May 27, 2013 PEDRO
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk HEART MURMURS: DECIPHERING THEIR CAUSE AND SIGNIFICANCE Author : Pedro Oliveira Categories : Vets Date : May 27, 2013 PEDRO
Heart failure congestive heart failure, or CHF
 Heart failure Heart failure (also called congestive heart failure, or CHF) is a frequent end point of many of the conditions In the United States alone, CHF affects nearly 5 million individuals annually,
Heart failure Heart failure (also called congestive heart failure, or CHF) is a frequent end point of many of the conditions In the United States alone, CHF affects nearly 5 million individuals annually,
Structural Heart Disease Patient Guide. Guide contents: 2 What Is Structural Heart Disease? 2 What Happens During Structural Heart Disease?
 Guide contents: 2 What Is Structural Heart Disease? 2 What Happens During Structural Heart Disease? 3 Diagnosis 3 Treatment Options 4 Managing the Condition 5 Surgery and Insurance 6 Symptom Tracker Form
Guide contents: 2 What Is Structural Heart Disease? 2 What Happens During Structural Heart Disease? 3 Diagnosis 3 Treatment Options 4 Managing the Condition 5 Surgery and Insurance 6 Symptom Tracker Form
Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease
 Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease Stacy Rissing, MD! Cardiothoracic imaging, Indiana University! Outline Imaging planes Disease findings Pulse sequences used for each indication Pathophysiology
Cardiac MRI: Clinical Application to Disease Stacy Rissing, MD! Cardiothoracic imaging, Indiana University! Outline Imaging planes Disease findings Pulse sequences used for each indication Pathophysiology
Mitral Valve Disease. Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna
 Mitral Valve Disease Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna Fall 2008 Mitral Valve Stenosis Lecture Outline Mitral Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical features Diagnostic testing
Mitral Valve Disease Prof. Sirchak Yelizaveta Stepanovna Fall 2008 Mitral Valve Stenosis Lecture Outline Mitral Stenosis Mitral Regurgitation Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical features Diagnostic testing
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery. George L. Hicks, Jr., MD
 TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, 2018 Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery George L. Hicks, Jr., MD Aortic Valve Pathology and Treatment Valvular Aortic Stenosis in Adults Average Course (Post mortem data)
TSDA Boot Camp September 13-16, 2018 Introduction to Aortic Valve Surgery George L. Hicks, Jr., MD Aortic Valve Pathology and Treatment Valvular Aortic Stenosis in Adults Average Course (Post mortem data)
Patent Ductus Arteriosus
 Patent Ductus Arteriosus (Type of Heart Birth Defect) Basics OVERVIEW Patent refers to open ; ductus arteriosus is a blood vessel between the aorta (main artery of the body) and the pulmonary artery (main
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (Type of Heart Birth Defect) Basics OVERVIEW Patent refers to open ; ductus arteriosus is a blood vessel between the aorta (main artery of the body) and the pulmonary artery (main
Index of subjects. effect on ventricular tachycardia 30 treatment with 101, 116 boosterpump 80 Brockenbrough phenomenon 55, 125
 145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
145 Index of subjects A accessory pathways 3 amiodarone 4, 5, 6, 23, 30, 97, 102 angina pectoris 4, 24, 1l0, 137, 139, 140 angulation, of cavity 73, 74 aorta aortic flow velocity 2 aortic insufficiency
4. The two inferior chambers of the heart are known as the atria. the superior and inferior vena cava, which empty into the left atrium.
 Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
cardiomyopathy. INTRODUCTION NONISCHEMIC CARDIOMYOPATHY
 FACTS ABOUT Cardiomyopathy INTRODUCTION Ischemic cardiomyopathy typically refers to heart muscle damage that results from coronary artery disease, such as heart attack, Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the
FACTS ABOUT Cardiomyopathy INTRODUCTION Ischemic cardiomyopathy typically refers to heart muscle damage that results from coronary artery disease, such as heart attack, Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the
AORTIC STENOSIS HENRY FORD HOSPITAL CENTER FOR STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE
 AORTIC STENOSIS HENRY FORD HOSPITAL CENTER FOR STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE WHAT IS AORTIC STENOSIS? THE AORTIC VALVE The aorta is the major vessel that carries oxygenated blood out of the left side of the
AORTIC STENOSIS HENRY FORD HOSPITAL CENTER FOR STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE WHAT IS AORTIC STENOSIS? THE AORTIC VALVE The aorta is the major vessel that carries oxygenated blood out of the left side of the
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart -
 Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Mitral Regurgitation
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Mitral Regurgitation Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes mitral regurgitation, a disease of the mitral valve. It explains how this disease is
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Mitral Regurgitation Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes mitral regurgitation, a disease of the mitral valve. It explains how this disease is
Cardiovascular Disease
 Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 15 Introduction Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the U.S. One American dies from CVD every 33 seconds Nearly half of all Americans will die from
Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 15 Introduction Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the U.S. One American dies from CVD every 33 seconds Nearly half of all Americans will die from
Consequences of Cardiomyopathy. thickened and stiff, the left ventricle is most often affected. This results in a lack of pumping
 Roseanne Baird March 30, 2010 BI 104 Dr. Hammoudi Consequences of Cardiomyopathy Cardiomyopathy is a disease in which the myocardium of the heart becomes enlarged, thickened and stiff, the left ventricle
Roseanne Baird March 30, 2010 BI 104 Dr. Hammoudi Consequences of Cardiomyopathy Cardiomyopathy is a disease in which the myocardium of the heart becomes enlarged, thickened and stiff, the left ventricle
PDA in Pets There s Nothing Affectionate About Patent Ductus Arteriosus
 PDA in Pets There s Nothing Affectionate About Patent Ductus Arteriosus People are frequently born with heart defects. They often require intricate and specialized surgeries to help correct them. So too
PDA in Pets There s Nothing Affectionate About Patent Ductus Arteriosus People are frequently born with heart defects. They often require intricate and specialized surgeries to help correct them. So too
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 6, 2016,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 6, 2016, 4612 4617 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) STUDY ON PATHOMORPHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN 21 CASES OF CANINE DILATED CARDIOMYOPATHY
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 5, No 6, 2016, 4612 4617 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) STUDY ON PATHOMORPHOLOGICAL CHANGES IN 21 CASES OF CANINE DILATED CARDIOMYOPATHY
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE
 VALVULAR HEART DISEASE Stenosis: failure of a valve to open completely, obstructing forward flow. - almost always due to a chronic process (e.g., calcification or valve scarring). Insufficiency : failure
VALVULAR HEART DISEASE Stenosis: failure of a valve to open completely, obstructing forward flow. - almost always due to a chronic process (e.g., calcification or valve scarring). Insufficiency : failure
I (312) Mitral Regurgitation What Should You Know?
 Mitral Regurgitation What Should You Know? Table of Contents What is Mitral Regurgitation? 3 What are the Symptoms? 4 What are the risks? 5 Who Gets Mitral Regurgitation? 6 Diagnosing Mitral Regurgitation
Mitral Regurgitation What Should You Know? Table of Contents What is Mitral Regurgitation? 3 What are the Symptoms? 4 What are the risks? 5 Who Gets Mitral Regurgitation? 6 Diagnosing Mitral Regurgitation
