ischaemia during infusions lasting for up to six hours. Subsequently these workers and others in America used this technique in man for the rapid
|
|
|
- Emerald Hopkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Treatment of bleeding oesophageal varices by infusion of vasopressin into the superior mesenteric artery Gut, 1973, 14, IAIN M. MURRAY-LYON, R. N. H. PUGH, H. B. NUNNERLEY, J. W. LAWS, J. L. DAWSON, AND ROGER WILLIAMS From the Liver Unit and Department of Radiology, King's College Hospital and Medical School, London SUMMARY Seventeen patients bleeding from oesophageal varices were treated by continuous infusion of vasopressin through a catheter inserted percutaneously and positioned in the superior mesenteric artery and in two other patients catheterization proved technically impossible. Bleeding was completely controlled on only four out of 18 occasions in the 17 patients treated. In seven patients, bleeding was controlled for two or more days but then recurred although the infusion was continued with an increased dose of vasopressin. There was a high incidence of complications, including bleeding from the site of catheter insertion in the groin and septicaemias. Sengstaken balloon tamponade and oesophageal transection had to be used to control bleeding in some patients but only six out of 17 survived to leave hospital. The treatment of bleeding oesophageal varices represents a continuing challenge as the mortality during the first hospital admission has remained at around 50% for the past 30 years (Ratnoff and Patek, 1942; Nachlas, O'Neil, and Campbell, 1955; Hislop, Waters, Kellock, and Swynnerton, 1966). Unless haemorrhage can be quickly controlled, the consequent fall in liver blood flow leads to deteriorating liver function and coagulation tests, making the bleeding even more difficult to control. Various forms of balloon tamponade (Bertrand and Michel, 1969; Pitcher, 1971) are effective ins the short term but aspiration pneumonia and other serious complications are common, and haemorrhage subsequently recurs in many patients. Likewise, systemic vasopressin is usually only temporarily effective (Shaldon and Sherlock, 1960) and its use is limited by coronary artery constriction leading sometimes to myocardial infarction or serious arrythmia (Beller, Trevino, and Urban, 1971). In 1967, Nusbaum, Baum, Sakiyalek, and Blakemore showed in dogs that the infusion of a small dose of vasopressin into the superior mesenteric artery reduced arterial flow and portal venous pressure without altering systemic arterial pressure or cardiac output and with no evidence of bowel Received for publication 7 November ischaemia during infusions lasting for up to six hours. Subsequently these workers and others in America used this technique in man for the rapid control of variceal haemorrhage with encouraging results (Nusbaum, Baum, Kuroda, and Blakemore, 1968; Nusbaum, Baum, and Blakemore, 1969; Baum and Nusbaum, 1971; Rosch, Dotter, and Rose, 1971; Stahl, 1971; Conn, Ramsby, and Storer, 1972). Our experience has been somewhat different and in this paper we describe the results obtained in the treatment of 19 patients admitted as an emergency with massive bleeding from oesophageal varices. Patients and Methods Eighteen patients had cirrhosis (10 alcoholic, four cryptogenic, two primary biliary, and two active chronic hepatitis), the remaining patient having an extrahepatic portal vein block. The majority of the cirrhotic patients had evidence of liver failure, with ascites in 14 and encephalopathy in 13. The serum bilirubin at the time of admission was more than 2 mg/100 ml in 12 patients and the prothrombin time was prolonged by more than three seconds in 12 patients (Table I). Oesophageal varices were demonstrated in each patient either on barium meal
2 60 Iain M. Murray-Lyon, R. N. H. Pugh, H. B. Nunnerley, J. W. Laws, J. L. Dawson, and Roger Williams Case Age Sex Aetiology Serum Prothrombin Duration of Sengstaken Control of Complications and Clinical -Time (sec Vasopressin Tube Bleeding Outcome Bilirubin Albumin prolonged) Infusion (day) (days) (mg/ (gl (days) 100 m) 100 ml) I 55 M Alcoholic Complete Died 2 months bleeding 2 56 M Alcoholic Complete Died 6 months hepatic failure 3 58 M Alcoholic 35S Died day 7 bleeding 4 40 M Alcoholic Transection of oesophagus day 11; cardiac arrest day 20 5 (Ist S0 M Cryptogenic Nil Transection of oesophagus admission) day 9; discharged 5 (2nd Died day 5 bleeding admission) 6 S0 M Cryptogenic & Died day 35 bleeding 7 25 M Extra Nil Transection of oesophagus hepatic day 2; discharged portal vein block 8 51 M Alcoholic Died day 10 bleeding 9 48 F Primary Died day 7 bleeding biliary M Cryptogenic Nil Died day 11 bleeding F Alcoholic & 6 Nil Died day 8 bleeding M Alcoholic Died day 10 live, failure M Active Complete Died day 2 ruptured chronic valve cusp F Primary Complete Mesenteric-caval shunt biliary day 2; discharged IS S0 F Alcoholic Nil Transection of oesophagus day 5; discharged M Active Nil Died day 2 bleeding chronic F Alcoholic 1l Nil Transection of oesophagus day 4; died day 6 meningitis Table Relevant clinical data in the 17 patients who had a superior mesenteric artery infusion of vasopressin or at oesophagoscopy and no other source for the bleeding was found. Using the Seldinger technique under local anaesthesia, a reverse curved red Kifa catheter with a single hole was inserted into the femoral artery and manipulated into the superior mesenteric artery. Twenty ml Conray 420 was then injected at 10 ml/second and serial films were taken at one film/ second starting after the first 10 ml of contrast medium had been injected. Aqueous vasopressin was then infused at 0-2 units/minute for 10 minutes and after flushing the catheter with saline a further series of films was taken. In some of the later patients, the timed films were omitted and only a single film was taken to confirm the position of the catheter which was then fixed to the skin of the groin by sutures. Subsequently in the ward, films were taken at regular intervals to check that the catheter remained in position. An Ivac 501 continuous infusion pump (Tekmar Medical Limited, Harrow) was used to give the vasopressin which was contained in 5% dextrose in closed polythene bags (Steriflex) to obviate the risk of air embolism. Initially 0-2 units/ml/min were given but if bleeding was doubled or trebled and creased to 0-8 units/minute. Results continued the dose on one occasion in- In one patient it was not possible to catheterize the superior mesenteric artery because of extreme tortuosity of the vessels and in another the hepatic artery arose from the superior mesenteric artery making selective infusion impossible. The remaining 17 patients received 18 trials of treatment (Table) as case 5, who was discharged home after the first, had a further bleed requiring treatment some months later. On 10 occasions the patients were treated by superior mesenteric artery infusion alone (Fig. 1), but bleeding was completely controlled in only two of these (cases 1 and 2). In four patients (cases 3, 4, 8, and 9) bleeding stopped for two or more days but then recurred even though the infusion was being continued. In each case the catheter was correctly positioned, and increasing the dose of vasopressin had no effect. In four patients (cases 5, first admission, 7, 11, 15) the initial bleeding was
3 Treatment of bleeding oesophageal varices by infusion of vasopressin into the superior mesenteric artery TREATMENT TRIALS C OMPLETE INITIAL NONE COMPLETE INITIAL NONE CONTROL never satisfactorily controlled. One of these in whom there was arteriographic evidence of superior mesenteric artery vasoconstriction when the infusion was started (Fig. 2), required a Sengstaken tube and then a transection of the oesophagus to stop the haemorrhage (Fig. 3). Indeed, no correlation could be observed between vasoconstriction demonstrated on the arteriogram at the beginning of the infusion, and subsequent control of the bleeding. Because of the failure to control the bleeding consistently, it was decided to use a Sengstaken tube for the first one to two days in conjunction with superior mesenteric artery infusion. This was done on eight occasions but without improvement CONTROL Fig. 1 Results of treatment using superior mesenteric artery infusion alone or with a Sengstaken tube concurrently. in the results. Bleeding was completely controlled in two patients (cases 13, 14) but one of them died on the second day with a ruptured aortic valve cusp due to acute bacterial endocarditis. In three patients (cases 5, second admission, 6, 12) bleeding was controlled initially but recurred some time after the balloons were deflated although the infusion was continued. COMPLICATIONS Six patients developed either a large haematoma in the groin or persistent arterial bleeding and in three of these the artery had to be repaired surgically. The infusion catheter became occluded by thrombus ac h Fig. 2 Superior mesenteric arteriograms in case S (first admission) before (a) andfollowing (b) 10 min infusion with vasopressin 0-2 units/min. Note the constriction of the superior mesenteric artery and its branches and reflux of contrast into the aorta.
4 62 Iain M. Murray-Lyon, R. N. H. Pugh, H. B. Nunnerley, J. W. Laws, J. L. Dawson, and Roger Williams VASOPRESSIN 0.6 UNITS/MIN 0.4 BLEEDING FROM MAJOR MINOR VARICES MODERATE l l2r SENGSTAKEN TUBE DAYS TRANSECTION OF OESOPHAGUS -- Cotheter positior ---1 on 1 Checked --_- Fig. 3 The clinical course in case S (first admission) showing the increasing dose of vasopressin infused, recurrence of bleeding, and the use of other procedures. on two occasions and in two other patients nonocclusive thrombus was found at necropsy in the aorta or femoral artery in proximity to the catheter. In one patient severe femoral artery spasm necessitated removal of the catheter. The catheter became dislodged from the superior mesenteric artery on six occasions in five patients and because of the risk of infection with repositioning a new catheter was inserted in the opposite groin. Nevertheless, in the complete series three patients developed pyrexia and leucocytosis, and in one E. coli was subsequently grown from the catheter tip. SURVIVAL AND OVERALL RESULTS Only six (35%) of the 17 patients treated survived to leave hospital, these including three of the five patients (see Table), who because of continuing bleeding underwent transthoracic transection of the oesophagus and ligation of varices, and another who had a mesenteric-caval shunt performed. She remains well at three months, and two (cases 7 and 15) of those who had interruption of varices have not bled again after nine and two months respectively. The other three patients died within six months from further haemorrhage or hepatic failure. Of the 12 patients dying in hospital the causes of death were haemorrhage (8), hepatic failure (1), bacterial endocarditis (1), pneumococcal meningitis (1), and unexplained cardiac arrest (1). Discussion In this series we achieved complete control of variceal haemorrhage by vasopressin infusion on only four out of 18 occasions and the two patients in whom catheterization of the superior mesenteric artery was not technically possible must also be considered as failures of treatment. This is to be contrasted with the results reported by Baum and Nusbaum (1971) with control of bleeding in 27 of 28 patients. These workers never found it necessary to use more than 04 units of vasopressin per minute, and, whenever arteriographic films showed arterial narrowing or delay in clearing the dye from the mesenteric circulation, they found a significant drop in the portal venous pressure as measured by catheterization of the umbilical vein or by hepatic venous wedge pressure. Rosch et al (1971) reported control of acute bleeding in all five patients treated for up to four hours and Stahl (1971) had been able to control haemorrhage in each of the 24 cirrhotic patients so treated. However, none of these series is reported in sufficient detail to make comparison with ourpatientspossible, and it is noteworthythat the period of infusion in many cases was limited to only a few hours. Furthermore the criteria for control of bleedingare not always clearly defined. We haveaimed to control variceal haemorrhage for at least a week in order to allow time for improvement in the patient's general condition and liver function, so
5 Treatment of bleeding oesophageal varices by infusion of vasopressin into the superior mesenteric artery 63 that oesophageal transection or portal systemic shunting in selected cases may then be undertaken under more favourable conditions. Although verification by oesophagoscopy that the varices were the site of bleeding was not obtained in every patient, no other source of haemorrhage was discovered in those coming to necropsy, and in others bleeding stopped promptly following transection of the oesophagus or a shunt procedure. In the seven patients in whom bleeding was controlled initially but recurred subsequently despite continuation of the infusion, resistance to vasopressin (tachyphlaxis) may have developed. Aqueous vasopressin contains an unknown and variable mixture of beef and pork pituitary hormone and it is of course possible that the preparations available in different countries vary. The only serious complication mentioned in the early series was femoral artery spasm in one case which required removal of the catheter (R6sch et al, 1971), although more recently Conn et al (1972) in reporting control of bleeding for at least 24 hours in 10 of 11 patients did observe infected ascites, bacteraemia, intestinal necrosis, and cardiac arrythmias, and Renert, Button, Fuld, and Casarella (1972) described the development of mesenteric venous thrombosis and small intestinal infarction. The complications in our patients were both numerous and serious. The high incidence of local bleeding in the groin was almost certainly related to the marked prolongation of the prothrombin time present in so many of them. Cirrhotic patients are particularly prone to develop septicaemias (Tisdale, 1961) and the presence of an indwelling arterial catheter must further increase this risk. Indeed with this high complication rate and poor overall results we do not feel justified in continuing to use vasopressin infusion in this way. We are grateful to Drs M. 0. Rake, C. 0. Record, A. R. Davidson, and our house physicians for help with the care of these patients. The support of the Medical Research Council is also gratefully acknowledged. References Baum, S., and Nusbaum, M. (1971). The control of gastrointestinal hemorrhage by selective mesenteric arterial infusion of vasopressin. Radiology, 98, Beller, B. M., Trevino, A., and Urban, E. (1971). Pitressin-induced myocardial injury and depression in a young woman. Amer. J. Med., 51, Bertrand, L., and Michel, H. (1969). La sonde de Linton-Nachlas: sa superiorit6 sur celle de Sengstaken-Blakemore pour le tamponnement des varices oeso-gastriques chez le cirrhotique. Arch. Mal. Appar. dig., 58, Conn, H. O., Ramsby, G. R., and Storer, E. H. (1972). Intra-arterial vasopressin in the treatment of upper gastrointestinal hemorrhage. Gastroenterology, 62, 868. Hislop, I. G., Waters, T. E., Kellock, T. D., and Swynnerton, B. (1966). The natural history of haemorrhage from oesophageal varices. Lancet, 1, Nachlas, M. M., O'Neil, J. E., and Campbell, A. J. A. (1955). The life history of patients with cirrhosis of the liver and bleeding esophageal varices. Ann. Surg., 141, Nusbaum, M., Baum, S., and Blakemore, W. S. (1969). Clinical experience with the diagnosis and management of gastrointestinal hemorrhage by selective mesenteric catheterization. Ann. Surg., 170, Nusbaum, M., Baum, S., Kuroda, K., and Blakemore, W. S. (1968). Control of portal hypertension by selective mesenteric arterial drug infusion. Arch. Surg., 97, Nusbaum, M. Baum, S., Sakiyalek, P., and Blakemore, W. S. (1967). Pharmacologic control of portal hypertension. Surgery, 62, Pitcher, J. L. (1971). Safety and effectiveness of the modified Sengstaken-Blakemore tube: a prospective study. Gastroenterology, 61, Ratnoff, 0. D., and Patek, A. J., Jr. (1942). The natural history of Laennec's cirrhosis of the liver. An analysis of 386 cases. Medicine (Baltimore), 21, Renert, W. A., Button, K. F., Fuld, S. L., and Casarella, W. J. (1972). Mesenteric venous thrombosis and small-bowel infarction following infusion of vasopressin into the superior mesenteric artery. Radiology, 102, Rosch, J., Dotter, C. T., and Rose, R. W. (1971). Selective arterial infusions of vasoconstrictors in acute gastro-intestinal bleeding. Radiology, 99, Shaldon, S., and Sherlock, S. (1960). The use ofvasopressin (Pitressin) in the control of bleeding from oesophageal varices. Lancet, 2, Stahl, W. M. (1971). In discussion. Amer. J. Surg., 121, 117. Tisdale, W. A. (1961). Spontaneous colon bacillus bacteremnia in Laennec's cirrhosis. Gastroenterology, 40,
THE BLEEDING MARGINAL ULCER*
 DECEMBER, 1975 THE BLEEDING MARGINAL ULCER* ABSTRACT: CATHETERIZATION DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY By ALFRED ROSENBAUM, M.D.,t STANLEY S. SIEGELMAN, M.D.4 and SEYMOUR SPRAYREGEN, M.D. Superior mesenteric arteriography
DECEMBER, 1975 THE BLEEDING MARGINAL ULCER* ABSTRACT: CATHETERIZATION DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY By ALFRED ROSENBAUM, M.D.,t STANLEY S. SIEGELMAN, M.D.4 and SEYMOUR SPRAYREGEN, M.D. Superior mesenteric arteriography
Portogram shows opacification of gastroesophageal varices.
 Portogram shows opacification of gastroesophageal varices. http://clinicalgate.com/radiologic-hepatobiliary-interventions/ courtesyhttp://emedicine.medscape.com/article/372708-overview DR.Thulfiqar Baiae
Portogram shows opacification of gastroesophageal varices. http://clinicalgate.com/radiologic-hepatobiliary-interventions/ courtesyhttp://emedicine.medscape.com/article/372708-overview DR.Thulfiqar Baiae
Michele Bettinelli RN CCRN Lahey Health and Medical Center
 Michele Bettinelli RN CCRN Lahey Health and Medical Center Differentiate the types of varices Identify glue preparations utilized when treating gastric varices Review the process of glue administration
Michele Bettinelli RN CCRN Lahey Health and Medical Center Differentiate the types of varices Identify glue preparations utilized when treating gastric varices Review the process of glue administration
Haemodynamic response to intravenous vasopressin and nitroglycerin in portal hypertension
 Gut, 1988, 29, 372-377 Haemodynamic response to intravenous vasopressin and nitroglycerin in portal hypertension D WSTABY, A GIMSON, P C HAYS, AND ROGR WILLIAMS From the Liver Unit, King's College School
Gut, 1988, 29, 372-377 Haemodynamic response to intravenous vasopressin and nitroglycerin in portal hypertension D WSTABY, A GIMSON, P C HAYS, AND ROGR WILLIAMS From the Liver Unit, King's College School
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
 - 100 - SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION The problem of portal hypertension and its alarming complications is still attracting the attentions of surgeons and physicians all over the world. Portal hypertension usually
- 100 - SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION The problem of portal hypertension and its alarming complications is still attracting the attentions of surgeons and physicians all over the world. Portal hypertension usually
Staging & Current treatment of HCC
 Staging & Current treatment of HCC Dr.: Adel El Badrawy Badrawy; ; M.D. Staging & Current ttt of HCC Early stage HCC is typically silent. HCC is often advanced at first manifestation. The selective ttt
Staging & Current treatment of HCC Dr.: Adel El Badrawy Badrawy; ; M.D. Staging & Current ttt of HCC Early stage HCC is typically silent. HCC is often advanced at first manifestation. The selective ttt
GI bleeding in chronic liver disease
 GI bleeding in chronic liver disease Stuart McPherson Consultant Hepatologist Liver Unit, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne and Institute of Cellular Medicine, Newcastle University. Case 54 year old
GI bleeding in chronic liver disease Stuart McPherson Consultant Hepatologist Liver Unit, Freeman Hospital, Newcastle upon Tyne and Institute of Cellular Medicine, Newcastle University. Case 54 year old
Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension Gastroenterology Teaching Project American Gastroenterological Association
 CIRRHOSIS AND PORTAL HYPERTENSION Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension Gastroenterology Teaching Project American Gastroenterological Association WHAT IS CIRRHOSIS? What is Cirrhosis? DEFINITION OF CIRRHOSIS
CIRRHOSIS AND PORTAL HYPERTENSION Cirrhosis and Portal Hypertension Gastroenterology Teaching Project American Gastroenterological Association WHAT IS CIRRHOSIS? What is Cirrhosis? DEFINITION OF CIRRHOSIS
Evidence-Base Management of Esophageal and Gastric Varices
 Evidence-Base Management of Esophageal and Gastric Varices Rino Alvani Gani Hepatobiliary Division Department of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine Universitas Indonesia Cipto Mangunkusumo National
Evidence-Base Management of Esophageal and Gastric Varices Rino Alvani Gani Hepatobiliary Division Department of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine Universitas Indonesia Cipto Mangunkusumo National
Trans-catheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) work up
 Trans-catheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) work up You have been referred for an assessment known as a TAVI work up because you have been diagnosed with aortic stenosis. This factsheet explains the
Trans-catheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) work up You have been referred for an assessment known as a TAVI work up because you have been diagnosed with aortic stenosis. This factsheet explains the
1 Description. 2 Indications. 3 Warnings ASPIRATION CATHETER
 Page 1 of 5 ASPIRATION CATHETER Carefully read all instructions prior to use, observe all warnings and precautions noted throughout these instructions. Failure to do so may result in complications. STERILE.
Page 1 of 5 ASPIRATION CATHETER Carefully read all instructions prior to use, observe all warnings and precautions noted throughout these instructions. Failure to do so may result in complications. STERILE.
Case 37 Clinical Presentation
 Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism A pulmonary embolism (PE) is
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism A pulmonary embolism (PE) is
Supplemental Appendix. 1. Protocol Definition of Sustained Virologic Response. A patient has a sustained virologic response if:
 Supplemental Appendix 1. Protocol Definition of Sustained Virologic Response A patient has a sustained virologic response if: 1. The patient is a responder at the end of treatment and all subsequent planned
Supplemental Appendix 1. Protocol Definition of Sustained Virologic Response A patient has a sustained virologic response if: 1. The patient is a responder at the end of treatment and all subsequent planned
Clinical Indications for Echocardiography
 Clinical Indications for Echocardiography Echocardiography is widely utilised and potential applications are increasing with advances in technology. The aim of this document is two-fold: 1) To define clinical
Clinical Indications for Echocardiography Echocardiography is widely utilised and potential applications are increasing with advances in technology. The aim of this document is two-fold: 1) To define clinical
Hemodynamic Monitoring and Circulatory Assist Devices
 Hemodynamic Monitoring and Circulatory Assist Devices Speaker: Jana Ogden Learning Unit 2: Hemodynamic Monitoring and Circulatory Assist Devices Hemodynamic monitoring refers to the measurement of pressure,
Hemodynamic Monitoring and Circulatory Assist Devices Speaker: Jana Ogden Learning Unit 2: Hemodynamic Monitoring and Circulatory Assist Devices Hemodynamic monitoring refers to the measurement of pressure,
Intro: Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Basic understanding of interventional radiology. Gain knowledge of key terms and phrases
 Slide 1 Intro: PRESENTED BY: Selena M. Moore, AAS, CCS, CPC HIMS Physician Liaison Coder This is a modified/updated presentation that was originally written by: Rosemary Waligorski, RHIT, CCS, RCC and
Slide 1 Intro: PRESENTED BY: Selena M. Moore, AAS, CCS, CPC HIMS Physician Liaison Coder This is a modified/updated presentation that was originally written by: Rosemary Waligorski, RHIT, CCS, RCC and
CY2015 Hospital Outpatient: Endovascular Procedure APCs and Complexity Adjustments
 CY2015 Hospital Outpatient: Endovascular Procedure APCs Complexity Adjustments Comprehensive Ambulatory Payment Classifications (c-apcs) CMS finalized the implementation of 25 Comprehensive APC to further
CY2015 Hospital Outpatient: Endovascular Procedure APCs Complexity Adjustments Comprehensive Ambulatory Payment Classifications (c-apcs) CMS finalized the implementation of 25 Comprehensive APC to further
Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement
 Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement of Severe Segmental Coronary Artery Occlusion Operative Technique Rene G. Favaloro, M.D. D irect operation on the coronary artery has been performed in 180 patients
Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement of Severe Segmental Coronary Artery Occlusion Operative Technique Rene G. Favaloro, M.D. D irect operation on the coronary artery has been performed in 180 patients
DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service
 M AY. 6. 2011 10:37 A M F D A - C D R H - O D E - P M O N O. 4147 P. 1 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue Document Control
M AY. 6. 2011 10:37 A M F D A - C D R H - O D E - P M O N O. 4147 P. 1 DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES Public Health Service Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue Document Control
PORTAL HYPERTENSION. Tianjin Medical University LIU JIAN
 PORTAL HYPERTENSION Tianjin Medical University LIU JIAN DEFINITION Portal hypertension is present if portal venous pressure exceeds 10mmHg (1.3kPa). Normal portal venous pressure is 5 10mmHg (0.7 1.3kPa),
PORTAL HYPERTENSION Tianjin Medical University LIU JIAN DEFINITION Portal hypertension is present if portal venous pressure exceeds 10mmHg (1.3kPa). Normal portal venous pressure is 5 10mmHg (0.7 1.3kPa),
Etiology of liver cirrhosis
 Liver cirrhosis 1 Liver cirrhosis Liver cirrhosis is the progressive replacement of normal hepatic cells by fibrous scar tissue, This scarring is accompanied by the loss of viable hepatocytes, which are
Liver cirrhosis 1 Liver cirrhosis Liver cirrhosis is the progressive replacement of normal hepatic cells by fibrous scar tissue, This scarring is accompanied by the loss of viable hepatocytes, which are
MASSIVE GASTROINTESTINAL HAEMORRHAGE: THE RADIOLOGIST'S ROLE IN DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 MASSIVE GASTROINTESTINAL HAEMORRHAGE: THE RADIOLOGIST'S ROLE IN DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT K.P. Tan H.K. Boey SYNOPSIS Massive gastrointestinal haemorrhage is a life -threatening condition. Angiography can
MASSIVE GASTROINTESTINAL HAEMORRHAGE: THE RADIOLOGIST'S ROLE IN DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT K.P. Tan H.K. Boey SYNOPSIS Massive gastrointestinal haemorrhage is a life -threatening condition. Angiography can
Key words : hemoperitoneum, intra-abdominal varices, liver cirrhosis
 Key words : hemoperitoneum, intra-abdominal varices, liver cirrhosis protsin (-) 1. Hematological oxamination r-ctp gg U/l Ht 37-7 % Tp 6.9 s/dl Plt. 2. Urinalysis glucose ( - ) bili.ubinl ( -) urobilin(&en
Key words : hemoperitoneum, intra-abdominal varices, liver cirrhosis protsin (-) 1. Hematological oxamination r-ctp gg U/l Ht 37-7 % Tp 6.9 s/dl Plt. 2. Urinalysis glucose ( - ) bili.ubinl ( -) urobilin(&en
Management of Cirrhotic Complications Uncontrolled Ascites. Siwaporn Chainuvati, MD Siriraj Hospital Mahidol University
 Management of Cirrhotic Complications Uncontrolled Ascites Siwaporn Chainuvati, MD Siriraj Hospital Mahidol University Topic Definition, pathogenesis Current therapeutic options Experimental treatments
Management of Cirrhotic Complications Uncontrolled Ascites Siwaporn Chainuvati, MD Siriraj Hospital Mahidol University Topic Definition, pathogenesis Current therapeutic options Experimental treatments
MESENTERIC ISCHEMIA THE FORGOTTEN DIAGNOSIS. Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, Illinois
 MESENTERIC ISCHEMIA THE FORGOTTEN DIAGNOSIS Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, Illinois SCBT/MR 2010 San Diego, California March 8, 2010 16:00-16:10
MESENTERIC ISCHEMIA THE FORGOTTEN DIAGNOSIS Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, Illinois SCBT/MR 2010 San Diego, California March 8, 2010 16:00-16:10
PROBLEM SET 2. Assigned: February 10, 2004 Due: February 19, 2004
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.542J: Quantitative Physiology: Organ Transport Systems Instructors: Roger Mark and Jose Venegas MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY Departments
ACG & AASLD Joint Clinical Guideline: Prevention and Management of Gastroesophageal Varices and Variceal Hemorrhage in Cirrhosis
 ACG & AASLD Joint Clinical Guideline: Prevention and Management of Gastroesophageal Varices and Variceal Hemorrhage in Cirrhosis Guadalupe Garcia-Tsao, M.D., 1 Arun J. Sanyal, M.D., 2 Norman D. Grace,
ACG & AASLD Joint Clinical Guideline: Prevention and Management of Gastroesophageal Varices and Variceal Hemorrhage in Cirrhosis Guadalupe Garcia-Tsao, M.D., 1 Arun J. Sanyal, M.D., 2 Norman D. Grace,
Ascites Management. Atif Zaman, MD MPH Oregon Health & Science University Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
 Ascites Management Atif Zaman, MD MPH Oregon Health & Science University Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Disclosure 1. The speaker Atif Zaman, MD MPH have no relevant
Ascites Management Atif Zaman, MD MPH Oregon Health & Science University Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Disclosure 1. The speaker Atif Zaman, MD MPH have no relevant
King Abdul-Aziz University Hospital (KAUH) is a tertiary
 Modelling Factors Causing Mortality in Oesophageal Varices Patients in King Abdul Aziz University Hospital Sami Bahlas Abstract Objectives: The objective of this study is to reach a model defining factors
Modelling Factors Causing Mortality in Oesophageal Varices Patients in King Abdul Aziz University Hospital Sami Bahlas Abstract Objectives: The objective of this study is to reach a model defining factors
Tranjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt
 Tranjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Christopher Selhorst July 25, 2005 BIDMC Radiology Overview Portal Hypertension Indications, Contraindications The Procedure Case Review Complications Outcomes
Tranjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Christopher Selhorst July 25, 2005 BIDMC Radiology Overview Portal Hypertension Indications, Contraindications The Procedure Case Review Complications Outcomes
VARICEAL BLEEDING. Ram Subramanian MD Hepatology & Critical Care Medical Director of Liver Transplant Emory University, Atlanta.
 VARICEAL BLEEDING Ram Subramanian MD Hepatology & Critical Care Medical Director of Liver Transplant Emory University, Atlanta Disclosures: None OUTLINE Pathophysiology of portal hypertension Splanchnic
VARICEAL BLEEDING Ram Subramanian MD Hepatology & Critical Care Medical Director of Liver Transplant Emory University, Atlanta Disclosures: None OUTLINE Pathophysiology of portal hypertension Splanchnic
NYU School of Medicine Department of Radiology Rotation-Specific House Staff Evaluation
 Vascular & Interventional Radiology Rotation 1 Core competency in vascular and interventional radiology during the first resident rotation consists of clinical objectives, technical objectives and image
Vascular & Interventional Radiology Rotation 1 Core competency in vascular and interventional radiology during the first resident rotation consists of clinical objectives, technical objectives and image
Page 1 of 6. Low 1 (score 0-3) Monitor platelets and signs and symptoms of thrombosis and continue heparin
 Page 1 of 6 Estimate probability of HIT using the Four T s 1 Low 1 (score 0-3) Intermediate 1 (score 4-5) or High 1 (score 6-8) Monitor platelets and signs and symptoms of thrombosis and continue heparin
Page 1 of 6 Estimate probability of HIT using the Four T s 1 Low 1 (score 0-3) Intermediate 1 (score 4-5) or High 1 (score 6-8) Monitor platelets and signs and symptoms of thrombosis and continue heparin
open-heart surgery patients
 Thorax (1975), 30, 26. Analysis of results of catheter tip cultures in open-heart surgery patients R. FREEMAN and B. KING Department of Microbiology, University of Leeds Freeman, R. and King, B. (1975).
Thorax (1975), 30, 26. Analysis of results of catheter tip cultures in open-heart surgery patients R. FREEMAN and B. KING Department of Microbiology, University of Leeds Freeman, R. and King, B. (1975).
British Society of Gastroenterology. St. Elsewhere's Hospital. National Comparative Audit of Blood Transfusion
 British Society of Gastroenterology UK Com parat ive Audit of Upper Gast roint est inal Bleeding and t he Use of Blood Transfusion Extract December 2007 St. Elsewhere's Hospital National Comparative Audit
British Society of Gastroenterology UK Com parat ive Audit of Upper Gast roint est inal Bleeding and t he Use of Blood Transfusion Extract December 2007 St. Elsewhere's Hospital National Comparative Audit
Liver failure &portal hypertension
 Liver failure &portal hypertension Objectives: by the end of this lecture each student should be able to : Diagnose liver failure (acute or chronic) List the causes of acute liver failure Diagnose and
Liver failure &portal hypertension Objectives: by the end of this lecture each student should be able to : Diagnose liver failure (acute or chronic) List the causes of acute liver failure Diagnose and
DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY CARDIOVASCULAR-THORACIC SECTION
 DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY CARDIOVASCULAR-THORACIC SECTION DIRECTIONS: This must accompany all initial applications for appointment to the Cardiovascular-Thoracic Section, Department of Surgery. Please indicate
DEPARTMENT OF SURGERY CARDIOVASCULAR-THORACIC SECTION DIRECTIONS: This must accompany all initial applications for appointment to the Cardiovascular-Thoracic Section, Department of Surgery. Please indicate
AORTIC GRAFT INFECTION
 NURSING CARE Theresa O Keefe NUM Vascular Unit PAH Vascular infections are serious They are associated with high morbidity and mortality The primary cause of surgical wound infections is contamination
NURSING CARE Theresa O Keefe NUM Vascular Unit PAH Vascular infections are serious They are associated with high morbidity and mortality The primary cause of surgical wound infections is contamination
pitfall Table 1 4 disorientation pitfall pitfall Table 1 Tel:
 11 687 692 2002 pitfall 1078 29 17 9 1 2 3 dislocation outflow block 11 1 2 3 9 1 2 3 4 disorientation pitfall 11 687 692 2002 Tel: 075-751-3606 606-8507 54 2001 8 27 2002 10 31 29 4 pitfall 16 1078 Table
11 687 692 2002 pitfall 1078 29 17 9 1 2 3 dislocation outflow block 11 1 2 3 9 1 2 3 4 disorientation pitfall 11 687 692 2002 Tel: 075-751-3606 606-8507 54 2001 8 27 2002 10 31 29 4 pitfall 16 1078 Table
Complications of Cirrhosis
 Complications of Cirrhosis Causes of Cirrhosis Alcohol Chronic Viral Hepatitis (B/C) Haemochromatosis Autoimmune Hepatitis NAFLD/NASH Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis 1-AT deficiency
Complications of Cirrhosis Causes of Cirrhosis Alcohol Chronic Viral Hepatitis (B/C) Haemochromatosis Autoimmune Hepatitis NAFLD/NASH Primary Biliary Cirrhosis Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis 1-AT deficiency
TIPS. D Patch Royal Free Hospital London UK
 TIPS D Patch Royal Free Hospital London UK TIPS Technique Ascites Budd Chiari Variceal Bleeding Historical Experimental Development 1967 Piccone Shunt between recanalized umbilical vein and saphenous
TIPS D Patch Royal Free Hospital London UK TIPS Technique Ascites Budd Chiari Variceal Bleeding Historical Experimental Development 1967 Piccone Shunt between recanalized umbilical vein and saphenous
M-AFRAKHTEH. MD OCT.2017 SHOHADA HOSPITAL TAJRISH
 Unrestricted M-AFRAKHTEH. MD OCT.2017 SHOHADA HOSPITAL TAJRISH Patients at imminent risk of exsanguination Manual aortic compression Resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta Uterine tourniquet
Unrestricted M-AFRAKHTEH. MD OCT.2017 SHOHADA HOSPITAL TAJRISH Patients at imminent risk of exsanguination Manual aortic compression Resuscitative endovascular balloon occlusion of the aorta Uterine tourniquet
Gastro-Intestinal Bleeding- Interventional Radiology turning off the tap. Simon McPherson, Vascular Interventional Radiologist, Leeds
 Gastro-Intestinal Bleeding- Interventional Radiology turning off the tap Simon McPherson, Vascular Interventional Radiologist, Leeds Scale UK 100,000 /year Commonest Vascular IR on-call 75% UGIB 65% NVUGIB
Gastro-Intestinal Bleeding- Interventional Radiology turning off the tap Simon McPherson, Vascular Interventional Radiologist, Leeds Scale UK 100,000 /year Commonest Vascular IR on-call 75% UGIB 65% NVUGIB
Update in abdominal Surgery in cirrhotic patients
 Update in abdominal Surgery in cirrhotic patients Safi Dokmak HBP department and liver transplantation Beaujon Hospital, Clichy, France Cairo, 5 April 2016 Cirrhosis Prevalence in France (1%)* Patients
Update in abdominal Surgery in cirrhotic patients Safi Dokmak HBP department and liver transplantation Beaujon Hospital, Clichy, France Cairo, 5 April 2016 Cirrhosis Prevalence in France (1%)* Patients
Patient guide: pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system. Catheter occlusion of. Patent Ductus Arteriosus. with the
 Patient guide: Catheter occlusion of Patent Ductus Arteriosus with the pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system pfm Produkte für die Medizin - AG Wankelstr. 60 D - 50996 Cologne Phone: +49 (0) 2236 96
Patient guide: Catheter occlusion of Patent Ductus Arteriosus with the pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system pfm Produkte für die Medizin - AG Wankelstr. 60 D - 50996 Cologne Phone: +49 (0) 2236 96
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. 1 Approach to the patient with gross gastrointestinal bleeding. Grace H. Elta, Mimi Takami
 1 Approach to the patient with gross gastrointestinal bleeding Grace H. Elta, Mimi Takami Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding is a common clinical problem that requires more than 300 000 hospitalizations annually
1 Approach to the patient with gross gastrointestinal bleeding Grace H. Elta, Mimi Takami Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding is a common clinical problem that requires more than 300 000 hospitalizations annually
following the last documented transfusion; thereafter, evaluate the residual impairment(s).
 Adult Listings 5.01 Category of Impairments, Digestive System 5.02 Gastrointestinal hemorrhaging from any cause, requiring blood transfusion (with or without hospitalization) of at least 2 units of blood
Adult Listings 5.01 Category of Impairments, Digestive System 5.02 Gastrointestinal hemorrhaging from any cause, requiring blood transfusion (with or without hospitalization) of at least 2 units of blood
The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS)
 n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) Information for patients Your liver doctor has recommended that you have a Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic
n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) Information for patients Your liver doctor has recommended that you have a Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic
Review Article Self-Expandable Metal Stents in the Treatment of Acute Esophageal Variceal Bleeding
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2011, Article ID 910986, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2011/910986 Review Article Self-Expandable Metal Stents in the Treatment of Acute
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Gastroenterology Research and Practice Volume 2011, Article ID 910986, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2011/910986 Review Article Self-Expandable Metal Stents in the Treatment of Acute
ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE. T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar
 ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar LEARNING OBJECTIVES q Through a series of cases illustrate the updated Atlanta symposium
ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar LEARNING OBJECTIVES q Through a series of cases illustrate the updated Atlanta symposium
Esophageal Varices Beta-Blockers or Band Ligation. Cesar Yaghi MD Hotel-Dieu de France University Hospital Universite Saint Joseph
 Esophageal Varices Beta-Blockers or Band Ligation Cesar Yaghi MD Hotel-Dieu de France University Hospital Universite Saint Joseph Esophageal Varices Beta-Blockers or Band Ligation? Risk of esophageal variceal
Esophageal Varices Beta-Blockers or Band Ligation Cesar Yaghi MD Hotel-Dieu de France University Hospital Universite Saint Joseph Esophageal Varices Beta-Blockers or Band Ligation? Risk of esophageal variceal
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute variceal bleeding management of, 251 262 balloon tamponade of esophagus in, 257 258 endoscopic therapies in, 255 257. See also Endoscopy,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute variceal bleeding management of, 251 262 balloon tamponade of esophagus in, 257 258 endoscopic therapies in, 255 257. See also Endoscopy,
Liver Transplantation
 1 Liver Transplantation Department of Surgery Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine Kim Myoung Soo M.D. ysms91@wonju.yonsei.ac.kr http://gs.yonsei.ac.kr History Development of Liver transplantation
1 Liver Transplantation Department of Surgery Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine Kim Myoung Soo M.D. ysms91@wonju.yonsei.ac.kr http://gs.yonsei.ac.kr History Development of Liver transplantation
RadRx Your Prescription for Accurate Coding & Reimbursement Copyright All Rights Reserved.
 Interventional Radiology Coding Case Studies Prepared by Stacie L. Buck, RHIA, CCS-P, RCC, CIRCC, AAPC Fellow President & Senior Consultant Week of October 29, 2018 Mesenteric Arteriogram & Thrombectomy/Thrombolysis
Interventional Radiology Coding Case Studies Prepared by Stacie L. Buck, RHIA, CCS-P, RCC, CIRCC, AAPC Fellow President & Senior Consultant Week of October 29, 2018 Mesenteric Arteriogram & Thrombectomy/Thrombolysis
Transjugular Intrahepatic
 Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS): A Clinical and Procedural Review Mark R. Werley, M.D. and John Briguglio, M.D. Lancaster Radiology Associates, Ltd. INTRODUCTION This article reviews
Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS): A Clinical and Procedural Review Mark R. Werley, M.D. and John Briguglio, M.D. Lancaster Radiology Associates, Ltd. INTRODUCTION This article reviews
CATCH A WAVE.. INTRODUCTION NONINVASIVE HEMODYNAMIC MONITORING 4/12/2018
 WAVES CATCH A WAVE.. W I S C O N S I N P A R A M E D I C S E M I N A R A P R I L 2 0 1 8 K E R I W Y D N E R K R A U S E R N, C C R N, E M T - P Have you considered that if you don't make waves, nobody
WAVES CATCH A WAVE.. W I S C O N S I N P A R A M E D I C S E M I N A R A P R I L 2 0 1 8 K E R I W Y D N E R K R A U S E R N, C C R N, E M T - P Have you considered that if you don't make waves, nobody
Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located
 How Your Heart Works Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located slightly to the left and behind your breastbone. Its function is to pump blood throughout your body. As your heart
How Your Heart Works Your heart is a muscular pump about the size of your fist, located slightly to the left and behind your breastbone. Its function is to pump blood throughout your body. As your heart
Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies. V.Stoynova
 Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies V.Stoynova Abdominal vessels V. Stoynova 2 Acute liver bleeding trauma anticoagulant therapy liver disease : HCC, adenoma, meta, FNH, Hemangioma Diagnosis :CT angiography
Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies V.Stoynova Abdominal vessels V. Stoynova 2 Acute liver bleeding trauma anticoagulant therapy liver disease : HCC, adenoma, meta, FNH, Hemangioma Diagnosis :CT angiography
RadRx Your Prescription for Accurate Coding & Reimbursement Copyright All Rights Reserved.
 Interventional Radiology Coding Case Studies Prepared by Stacie L. Buck, RHIA, CCS-P, RCC, CIRCC, AAPC Fellow President & Senior Consultant Week of June 4, 2018 Thrombolysis, Thrombectomy & Angioplasty
Interventional Radiology Coding Case Studies Prepared by Stacie L. Buck, RHIA, CCS-P, RCC, CIRCC, AAPC Fellow President & Senior Consultant Week of June 4, 2018 Thrombolysis, Thrombectomy & Angioplasty
CY2017 Hospital Outpatient: Vascular Procedure APCs and Complexity Adjustments
 CY2017 Hospital Outpatient: Vascular Procedure APCs and Complexity Adjustments Comprehensive Ambulatory Payment Classifications (c-apcs) In CY2015 and in an effort to help pay providers for quality, not
CY2017 Hospital Outpatient: Vascular Procedure APCs and Complexity Adjustments Comprehensive Ambulatory Payment Classifications (c-apcs) In CY2015 and in an effort to help pay providers for quality, not
INCREASED resistance to blood flow in the liver or portal venous system results
 EFFECTIVE SPONTANEOUS PORTACAVAL VENOUS SHUNT Report of Two Cases B. H. SULLIVAN, JR., M.D., CHARLES H. BROWN, M.D., Department of Gastroenterology THOMAS F. MEANEY, M.D., Division of Radiology and EARL
EFFECTIVE SPONTANEOUS PORTACAVAL VENOUS SHUNT Report of Two Cases B. H. SULLIVAN, JR., M.D., CHARLES H. BROWN, M.D., Department of Gastroenterology THOMAS F. MEANEY, M.D., Division of Radiology and EARL
CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG
 Title: Author: Speciality/ Division: Directorate: Date Uploaded: Review Date: September 2019 CG ID TAG CG0423 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Clinical Guideline for Alteplase in intra-arterial thrombolysis
Title: Author: Speciality/ Division: Directorate: Date Uploaded: Review Date: September 2019 CG ID TAG CG0423 CLINICAL GUIDELINES ID TAG Clinical Guideline for Alteplase in intra-arterial thrombolysis
Nitroglycerin and Heparin Drip Interfacility Protocols
 Nitroglycerin and Heparin Drip Interfacility Protocols EMS Protocol This protocol applies to nitroglycerin and Heparin drips that are initiated at the transferring facility prior to transport and are not
Nitroglycerin and Heparin Drip Interfacility Protocols EMS Protocol This protocol applies to nitroglycerin and Heparin drips that are initiated at the transferring facility prior to transport and are not
Contraindications. Indications. Complications. Currently TIPS is considered second or third line therapy for:
 Contraindications Absolute Relative Primary prevention variceal bleeding HCC if centrally located Active congestive heart failure Obstruction all hepatic veins Thomas D. Boyer, M.D. University of Arizona
Contraindications Absolute Relative Primary prevention variceal bleeding HCC if centrally located Active congestive heart failure Obstruction all hepatic veins Thomas D. Boyer, M.D. University of Arizona
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Diagnosis and Management
 Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Diagnosis and Management Nizar A. Mukhtar, MD Co-director, SMC Liver Tumor Board April 30, 2016 1 Objectives Review screening/surveillance guidelines Discuss diagnostic algorithm
Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Diagnosis and Management Nizar A. Mukhtar, MD Co-director, SMC Liver Tumor Board April 30, 2016 1 Objectives Review screening/surveillance guidelines Discuss diagnostic algorithm
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) Information for patients Sheffield Vascular Institute
 Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) Information for patients Sheffield Vascular Institute You have been given this leaflet because you need a procedure called a transjugular intrahepatic
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) Information for patients Sheffield Vascular Institute You have been given this leaflet because you need a procedure called a transjugular intrahepatic
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Accelerated intravascular coagulation and fibrinolysis (AICF) in liver disease, 390 391 Acid suppression in liver disease, 403 404 ACLF.
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Accelerated intravascular coagulation and fibrinolysis (AICF) in liver disease, 390 391 Acid suppression in liver disease, 403 404 ACLF.
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم أوتيتم من العلم إال قليال وما
 بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم أوتيتم من العلم إال قليال وما 1 2 Goals of the Lecture: What is the portal vein? How common is PVT? What conditions are associated with PVT? How does patient with PVT present? How
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم أوتيتم من العلم إال قليال وما 1 2 Goals of the Lecture: What is the portal vein? How common is PVT? What conditions are associated with PVT? How does patient with PVT present? How
Mechanical Bleeding Complications During Heart Surgery
 Mechanical Bleeding Complications During Heart Surgery Arthur C. Beall, Jr., M.D., Kenneth L. Mattox, M.D., Mary Martin, R.N., C.C.P., Bonnie Cromack, C.C.P., and Gary Cornelius, C.C.P. * Potential for
Mechanical Bleeding Complications During Heart Surgery Arthur C. Beall, Jr., M.D., Kenneth L. Mattox, M.D., Mary Martin, R.N., C.C.P., Bonnie Cromack, C.C.P., and Gary Cornelius, C.C.P. * Potential for
Information for patients (and their families) waiting for liver transplantation
 Information for patients (and their families) waiting for liver transplantation Waiting list? What is liver transplant? Postoperative conditions? Ver.: 5/2017 1 What is a liver transplant? Liver transplantation
Information for patients (and their families) waiting for liver transplantation Waiting list? What is liver transplant? Postoperative conditions? Ver.: 5/2017 1 What is a liver transplant? Liver transplantation
SHOCK AETIOLOGY OF SHOCK (1) Inadequate circulating blood volume ) Loss of Autonomic control of the vasculature (3) Impaired cardiac function
 SHOCK Shock is a condition in which the metabolic needs of the body are not met because of an inadequate cardiac output. If tissue perfusion can be restored in an expeditious fashion, cellular injury may
SHOCK Shock is a condition in which the metabolic needs of the body are not met because of an inadequate cardiac output. If tissue perfusion can be restored in an expeditious fashion, cellular injury may
Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management
 Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management Mary Finn Gillian Lieberman, MD Primary Care Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School April 2014 Outline I. Definition and Epidemiology
Gastroschisis Sequelae and Management Mary Finn Gillian Lieberman, MD Primary Care Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School April 2014 Outline I. Definition and Epidemiology
6. Endovascular aneurysm repair
 Introduction The standard treatment for aortic aneurysm, open repair, involves a large abdominal incision and cross-clamping of the aorta. In recent years, a minimally invasive technique, endovascular
Introduction The standard treatment for aortic aneurysm, open repair, involves a large abdominal incision and cross-clamping of the aorta. In recent years, a minimally invasive technique, endovascular
BILLING BULLETIN. Re: Interventional Cardiology. Bulletin #: 1. Date Issued: November 10, Background
 BILLING BULLETIN Re: Interventional Cardiology Bulletin #: 1 Date Issued: November 10, 2016 Background This Billing Bulletin provides billing guidance when submitting claims to Manitoba Health, Seniors
BILLING BULLETIN Re: Interventional Cardiology Bulletin #: 1 Date Issued: November 10, 2016 Background This Billing Bulletin provides billing guidance when submitting claims to Manitoba Health, Seniors
Emergency Medical Retrieval Service (EMRS) Standard Operating Procedure
 Emergency Medical Retrieval Service (EMRS) www.emrs.scot.nhs.uk Standard Operating Procedure Title Oesophagogastric Tamponade Tube Version 4 Related Documents SOP-Upper GI Haemorrhage Author G Cowan, C
Emergency Medical Retrieval Service (EMRS) www.emrs.scot.nhs.uk Standard Operating Procedure Title Oesophagogastric Tamponade Tube Version 4 Related Documents SOP-Upper GI Haemorrhage Author G Cowan, C
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/23/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 78 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/23/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 78 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis 2017 Edition
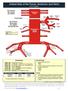 Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION IN DOGS
 CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION IN DOGS WILLIAM H. NOBLE, B.A., IVLD., DIP.ANAES., F.R.C.P.(C) AND J. COLIN KAY, A.I.IX~.L.T. (ENG.) INTRODUCTION MANY INVESTIGATORS require cardiac catheterization data as a part
CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION IN DOGS WILLIAM H. NOBLE, B.A., IVLD., DIP.ANAES., F.R.C.P.(C) AND J. COLIN KAY, A.I.IX~.L.T. (ENG.) INTRODUCTION MANY INVESTIGATORS require cardiac catheterization data as a part
Original article Correlation between serum-ascites albumin concentration gradient and endoscopic parameters of portal hypertension
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (005), Vol. 3, No., Issue, 37-333 Original article Correlation between serum-ascites albumin concentration gradient and endoscopic parameters of portal hypertension
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (005), Vol. 3, No., Issue, 37-333 Original article Correlation between serum-ascites albumin concentration gradient and endoscopic parameters of portal hypertension
Proper Completion of a Death Certificate"
 Proper Completion of a Death Certificate" Pennsylvania Department of Health Bureau of Health Statistics and Research Division of Statistical Registries Division of Vital Records Why should you care? 1.
Proper Completion of a Death Certificate" Pennsylvania Department of Health Bureau of Health Statistics and Research Division of Statistical Registries Division of Vital Records Why should you care? 1.
ATHEROSCLEROSIS. Secondary changes are found in other coats of the vessel wall.
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a disease process affecting the intima of the aorta and large and medium arteries, taking the form of focal thickening or plaques of fibrous tissue and
AN UNUSUAL CAUSE OF HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY
 Originally Posted: June 01, 2014 AN UNUSUAL CAUSE OF HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY Resident(s): Rajesh Bhavsar, MD Program/Dept(s): Montefiore Medical Center, Albert Einstein College of Medicine CHIEF COMPLAINT
Originally Posted: June 01, 2014 AN UNUSUAL CAUSE OF HEPATIC ENCEPHALOPATHY Resident(s): Rajesh Bhavsar, MD Program/Dept(s): Montefiore Medical Center, Albert Einstein College of Medicine CHIEF COMPLAINT
CVICU EXAM. Mrs. Jennings is a 71-year-old post-op CABG x5 with an IABP in her left femoral artery
 CVICU EXAM 1111 North 3rd Street Mrs. Jennings is a 71-year-old post-op CABG x5 with an IABP in her left femoral artery 1. Nursing standards for a patient on an IABP device include: a. Know results of
CVICU EXAM 1111 North 3rd Street Mrs. Jennings is a 71-year-old post-op CABG x5 with an IABP in her left femoral artery 1. Nursing standards for a patient on an IABP device include: a. Know results of
Endovascular Techniques for Symptomatic Portal Hypertension. Michael Meuse, M.D. Vascular and Interventional Radiology
 Endovascular Techniques for Symptomatic Portal Hypertension Michael Meuse, M.D. Vascular and Interventional Radiology Objectives Review indications and contraindications for TIPS Define a treatment algorithm
Endovascular Techniques for Symptomatic Portal Hypertension Michael Meuse, M.D. Vascular and Interventional Radiology Objectives Review indications and contraindications for TIPS Define a treatment algorithm
Complications of Acute Myocardial Infarction
 Acute Myocardial Infarction Complications of Acute Myocardial Infarction Diagnosis and Treatment JMAJ 45(4): 149 154, 2002 Hiroshi NONOGI Director, Division of Cardiology and Emergency Medicine, National
Acute Myocardial Infarction Complications of Acute Myocardial Infarction Diagnosis and Treatment JMAJ 45(4): 149 154, 2002 Hiroshi NONOGI Director, Division of Cardiology and Emergency Medicine, National
INFLUENCE OF VASOPRESSIN ON COLON BLOOD FLOW IN MONKEYS
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 72:474-478, 1977 Copyright 1977 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 72, No.3 Printed in U.S A. INFLUENCE OF VASOPRESSIN ON COLON BLOOD FLOW IN MONKEYS JOHN C. KERR, B.A., ROBERT W. HOBSON,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 72:474-478, 1977 Copyright 1977 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 72, No.3 Printed in U.S A. INFLUENCE OF VASOPRESSIN ON COLON BLOOD FLOW IN MONKEYS JOHN C. KERR, B.A., ROBERT W. HOBSON,
Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock. Richard A. McPherson, M.D.
 Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock Richard A. McPherson, M.D. Edema The accumulation of abnormal amounts of fluid in intercellular spaces of body cavities. Inflammation and release of mediators
Hemodynamic Disorders, Thrombosis, and Shock Richard A. McPherson, M.D. Edema The accumulation of abnormal amounts of fluid in intercellular spaces of body cavities. Inflammation and release of mediators
Primary to non-coronary IVUS
 codes 2018 2018 codes Primary to non-coronary IVUS Page 2 All coding, coverage, billing and payment information provided herein by Philips is gathered from third-party sources and is subject to change.
codes 2018 2018 codes Primary to non-coronary IVUS Page 2 All coding, coverage, billing and payment information provided herein by Philips is gathered from third-party sources and is subject to change.
THE goal of treatment of portal hypertension and bleeding esophageal
 MANAGEMENT OF BLEEDING FROM ESOPHAGEAL VARICES RICHARD C. BRITTON, M.D. Department General Surgery THE goal treatment portal hypertension and bleeding esophageal varices is the control hemorrhage and the
MANAGEMENT OF BLEEDING FROM ESOPHAGEAL VARICES RICHARD C. BRITTON, M.D. Department General Surgery THE goal treatment portal hypertension and bleeding esophageal varices is the control hemorrhage and the
Cardiac anaesthesia. Simon May
 Cardiac anaesthesia Simon May Contents Cardiac: Principles of peri-operative management for cardiac surgery Cardiopulmonary bypass, cardioplegia and off pump cardiac surgery Cardiac disease and its implications
Cardiac anaesthesia Simon May Contents Cardiac: Principles of peri-operative management for cardiac surgery Cardiopulmonary bypass, cardioplegia and off pump cardiac surgery Cardiac disease and its implications
Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014
 Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014 Indications for cardiac catheterization Before a decision to perform an invasive procedure such
Indications of Coronary Angiography Dr. Shaheer K. George, M.D Faculty of Medicine, Mansoura University 2014 Indications for cardiac catheterization Before a decision to perform an invasive procedure such
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR)
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR) Treatment for aortic stenosis This handout explains when your doctor may advise TAVR to treat aortic stenosis. It includes the
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR) Treatment for aortic stenosis This handout explains when your doctor may advise TAVR to treat aortic stenosis. It includes the
Management of Ascites and Hepatorenal Syndrome. Florence Wong University of Toronto. June 4, /16/ Gore & Associates: Consultancy
 Management of Ascites and Hepatorenal Syndrome Florence Wong University of Toronto June 4, 2016 6/16/2016 1 Disclosures Gore & Associates: Consultancy Sequana Medical: Research Funding Mallinckrodt Pharmaceutical:
Management of Ascites and Hepatorenal Syndrome Florence Wong University of Toronto June 4, 2016 6/16/2016 1 Disclosures Gore & Associates: Consultancy Sequana Medical: Research Funding Mallinckrodt Pharmaceutical:
caused by chronic pancreatitis
 Gut, 1983, 24, 1094-1098 Case report Embolisation of gastroduodenal artery aneurysm caused by chronic pancreatitis R V THAKKER, B GAJJAR, R A WILKINS, AND A J LEVI From Northwick Park Hospital and Clinical
Gut, 1983, 24, 1094-1098 Case report Embolisation of gastroduodenal artery aneurysm caused by chronic pancreatitis R V THAKKER, B GAJJAR, R A WILKINS, AND A J LEVI From Northwick Park Hospital and Clinical
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Procedure (TAVI)
 Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
Thrombin injection vs Conventional Surgical Repair in Treatment of Iatrogenic Post-cath Femoral Artery Pseudoaneurysm (IFAP)
 Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 11, NO 3 September 2010 31 Thrombin injection vs Conventional Surgical Repair in Treatment of Iatrogenic Post-cath Femoral Artery Pseudoaneurysm (IFAP) Farghaly A,
Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 11, NO 3 September 2010 31 Thrombin injection vs Conventional Surgical Repair in Treatment of Iatrogenic Post-cath Femoral Artery Pseudoaneurysm (IFAP) Farghaly A,
Arterial Line Insertion Pre Reading
 PROCEDURE ACCREDITATION THE CANBERRA HOSPITAL EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT Arterial Line Insertion Pre Reading Indications Requirement for continuous blood pressure monitoring (all patients on pressors, inotropes,
PROCEDURE ACCREDITATION THE CANBERRA HOSPITAL EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT Arterial Line Insertion Pre Reading Indications Requirement for continuous blood pressure monitoring (all patients on pressors, inotropes,
Albumin (serum, plasma)
 Albumin (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Albumin (plasma or serum) 1.2 Alternative names None (note that albumen is a protein found in avian eggs) 1.3 NLMC code 1.4
Albumin (serum, plasma) 1 Name and description of analyte 1.1 Name of analyte Albumin (plasma or serum) 1.2 Alternative names None (note that albumen is a protein found in avian eggs) 1.3 NLMC code 1.4
