Neonatal Chest X-Ray Introduction Indications Interpretation
|
|
|
- Lauren Short
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 43 Neonatal Chest X-Ray Introduction The chest X-ray is the most frequently ordered radiological investigation in NICUs. It should ideally be performed in the ICU using a portable X-ray equipment. In most cases, an anteroposterior view of the chest would provide sufficient diagnostic information. Lateral chest and abdomen views should be included only when there is a clinical indication. Indications The indications for ordering a chest X-ray include: 1. For evaluating the initial cause of respiratory distress 2. For suspected cardiac or pericardial disease 3. To check position of endotracheal tube, umbilical venous or arterial lines, peripherally inserted central catheters or chest tubes 4. For evaluating the cause of worsening respiratory distress in a ventilated neonate after ruling out mechanical problems (tube block/secretions/dislodgement) or ventilator dysfunction Some conditions where X-rays are not indicated include: 1. Routine / daily X-rays in ventilated neonates 2. Routine pre/post extubation X-rays 3. After re-intubation in a neonate where the optimal tip-tolip distance is known based on initial X-ray 4. Evaluation of an isolated episode of desaturation/ apnea 5. Routinely before/after giving surfactant 6. Transient / mild respiratory distress (<4 hr) after birth Interpretation While describing an X-ray, the following observations need to be made: - Projection (AP vs PA film) - Exposure (hard vs soft films) 526
2 Neonatal Chest X-ray - Rotation - Soft tissue/bones - Lungs: Expansion Parenchymal appearance lucency, nature of opacities, fissure Cardiac and diaphragmatic margins - Cardiac: Cardio thoracic ratio/ cardiac size Pulmonary vascular markings Specific chamber enlargement Projection The following features distinguish AP from a PA film: In PA films, the scapulae lie postero-laterally and are away from the lung fields, whereas they tend to overlap the lungs in AP films Due to its anterior placement, the heart appears larger in AP rather than a PA film The cervico-thoracic vertebral end plates are tangential to the AP projection beam, making them prominently seen in AP view, while the lamina appear more prominent in PA view The ribs appear to be more horizontally placed in AP view Practical tip: Most neonatal chest X-rays are AP films, unless the baby is made to lie prone Exposure Lucency of soft tissue shadow - darker the soft tissue, more is the exposure Ease of visibility of retrocardiac vertebrae if the retrocardiac vertebrae are easily seen, the film is over exposed Relative lucency of lung fields When long bones appear to disappear, it is over-exposed film 527
3 AIIMS Protocols in Neonatology Rotation The chest X-ray is rotated if The distance of the anterior ends of ribs from the midline of spine are unequal on either side. The film is rotated to that side on which the distance appears greater Medial end of clavicles are not equidistant from the midline The first criterion is usually more helpful as the lower chest tends to be rotated more commonly than the upper chest, as the latter is usually stabilised at the time of taking X-rays. Usually the side to which the chest is rotated appears more hyperlucent than the other and hence should be interpreted with caution. Soft tissue/ bone The importance of carefully looking at the bones cannot be overemphasised, especially for picking up changes of osteopenia and fractures. Thymus - normal and abnormal The thymus may create some challenges in the interpretation of neonatal chest X-rays. One needs to differentiate its normal from abnormal appearance. Normally, thymus appears as a bilateral smoothly outlined superior mediastinal shadow blending with the cardiac silhouette. Some normal variants of thymus: Notch sign - uniform enlargement of thymus on both sides with prominent notch on inferior left border (corresponding to the junction of inferior aspect of normal thymus gland and cardiac silhouette) Sail sign - Characteristic sail like border of normal thymus, more commonly seen on right side Wavy thymus sign -Undulating waviness of the lateral border of thymus due to indentation of ribs Interpretation of lung fields Lung expansion Normal lung expansion: Up to 6 ribs anteriorly and 8 ribs posteriorly. This follows the normal position of the diaphragm 528
4 Neonatal Chest X-ray th th between 5 and 7 anterior ribs The radiological features of hyper-expansion are: 1. Presence of more than 6 ribs anteriorly and 8 ribs posteriorly 2. Flattening of diaphragm 3. Increased lucency of lung fields (blackness) 4. Air under the heart/ herniation of lung to opposite side 5. Ribs more horizontal However, the evaluation of lung expansion by counting the number of ribs (or intercostal spaces) above the diaphragm can be tricky in newborns due to two reasons: 1. This technique represents the expansion in two dimensions only. But newborns, unlike older infants and children, have highly compliant thoracic cage, which can easily expand in the antero-posterior dimension as well. 2. Lesser diaphragmatic excursions occur during inspiration in neonates as compared to older children Characteristic appearance of common disease conditions Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) The condition is caused by the deficiency of surfactant production by type II alveolar cells, which results in alveolar collapse with overinflation of larger alveoli and resultant transudation of proteinaceous fluid into alveoli, creating the classical hyaline membranes. The radiological features of the condition are Under- aerated lungs Reticulo-granularity (presence of air in the distended terminal bronchioles and alveolar ducts against a background of alveolar atelectasis) Air bronchograms-with progress of disease, more and more distal airways collapse, leaving the proximal bronchi standing out as air bronchograms. Note that air bronchograms may be absent in an expiratory film Diffuse granularity In severe cases or in expiratory films, these findings may be replaced by white-out lungs due to diffuse alveolar atelectasis 529
5 AIIMS Protocols in Neonatology The severity of RDS has been classified based on radiological findings as follows: Mild: Normal/ decreased aeration, reticulo-granularity Moderate: Decreased aeration, air bronchograms and indistinct diaphragm and heart borders Severe: Confluent opacification of lungs with loss of mediastinal and diaphragmatic borders ( white-out ) RDS mimickers: A few congenital heart disorders such as total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (TAPVC), pulmonary vein atresia and hypoplastic left heart syndrome by producing interstitial pulmonary edema can mimic the granular pattern seen in RDS. Transient tachypnea of newborn (retained fluid syndrome) This is a condition resulting from the delayed clearance of fetal lung fluid, overloading the interstitium, lymphatics and cardiovascular system. X-ray picture is characterised by Prominent hilum with perivascular streaky shadows Prominent interlobar fissure (horizontal fissure) Small pleural effusion There may be mild cardiomegaly Normal to increased lung volume Radiographic findings usually resolve in hours Pulmonary interstitial emphysema (PIE) It is caused by the dissection of air from alveoli into the parenchyma and interstitium of lungs and perivascular sheaths of vessels, tracking towards the hilum. X-ray appearance is characterised by Radiolucent streaks- linear or irregular, branching/ cystic spaces (honeycomb like) or pneumatoceles; seen radiating from the hilum towards the periphery of the lung PIE may present with linear or cystic changes. Linear lucencies of PIE may be differentiated from air bronchograms in that the latter are generally smooth and branching, in contrast to interstitial air which is coarser and non-branching 530
6 Pneumothorax This results from the dissection of extra-alveolar air to the hilum, followed by rupture into pleural space. Increased radiolucency of the ipsilateral lung and sharpness of mediastinal border are the earliest signs of pneumothorax. The characteristic X-ray findings are: Clear border of collapsed lung Absent lung markings beyond the collapsed lung border (this differentiates pneumothorax from vertical skin folds) May or may not be accompanied by mediastinal shift Herniation of the pneumothorax bounded by parietal pleura into the contralateral side Pneumomediastinum Presence of air adjacent to the heart outlining the thymus and elevating it. The thymus is compressed by pneumothorax, whereas it is elevated by pneumomediastinum. Meconium aspiration syndrome (MAS) The radiological appearance may range from hyperexpansion to collapse: Gross hyperexpansion of lungs Bilateral coarse patchy nodular opacities (this represents areas of focal alveolar atelectasis with focal alveolar overdistension in between) Sometimes, a large piece of meconium can obstruct the bronchus leading to emphysema of one lung/lobe and compression of the other lung Pneumonia The radiological picture is variable and may range from reticulo granularity to lobar or segmental consolidation Asymmetry of reticulogranular pattern with air bronchograms may be seen Coarse granular patchy infiltrates with irregular areas of hyperinflation Pleural effusion Detected by the blunting of lateral costophrenic angle (only 531 Neonatal Chest X-ray
7 AIIMS Protocols in Neonatology in erect film) In supine radiographs, there is decreased transradiancy of the lung with preserved pulmonary vascular markings If enough fluid is present, it is seen as a peripheral band separating the lung and lateral chest wall Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) The radiological appearance is variable and depends on the postnatal age (Northway, et al): Stage I (2-3 days)-air bronchograms, reticulo-granularity (similar to RDS) Stage II (4-10 days)- Opacification; coarse irregular densities Stage III (11-20 days)- Small generalised radiolucent cysts Stage IV (1 month)- Dense fibrotic strands, generalised cystic areas, hyper-inflated lungs Three types of bubbles in chest X-ray Type I bubbles: Seen in RDS Small and uniform, rounded 1-2 mm in diameter More prominent in lung bases Due to overdistension of the terminal airways Become less pronounced on expiration Type II bubbles: Seen in pulmonary interstitial emphysema (PIE) Nodular and tortuous in shape 2-3 mm in diameter Peribronchial and perivascular in location Do not empty on expiration Type III bubbles: Larger than the first two types of bubbles Irregular shaped Seen in focal hyperaeration syndrome, eg. bronchopulmonary dysplasia Also become less pronounced on expiration, like type I bubbles 532
8 Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: Bochdalek defects present with a well defined dome shaped soft tissue opacity usually on the left chest. They are dynamic in nature and may come and go in serial films. Importantly, intestinal loops may be gasless in the first few hours of life with the herniated abdominal contents appearing as an opaque mass with ipsilateral lung hypoplasia and contralateral mediastinal shift. The classical appearance of gas filled loops in the chest may appear only few hours after birth. Morgagni hernias are seen as opacities adjacent to the right costophrenic angle. Tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF) A soft rubber tube is better than an infant feeding tube for the radiological diagnosis of TEF. The X-ray shows coiling of the tube in the upper esophagus. If one desires to delineate the extent of gap between the upper and lower pouch, a lateral X-ray is preferable. Absent stomach gas suggests associated esophageal atresia. Interpretation of the cardiac shadow in X-ray The most important features to be noted are: Cardiac size Pulmonary vasculature Shape and size of different chambers/ cardiac situs Cardiac size This may be assessed simply by measuring the cardiothoracic ratio (CT ratio). CT ratio is the largest transverse diameter of the heart divided by the maximum internal diameter of the chest. A CT ratio of more than 0.6 suggests cardiomegaly in newborns. Pulmonary vasculature Normally it is difficult to appreciate pulmonary vascular markings in the lateral third of the lung fields as well as in the lung apices. Increased pulmonary vascularity is said to be present when the pulmonary vessels are seen in the lateral third of the film, or in 533 Neonatal Chest X-ray
9 AIIMS Protocols in Neonatology the lung apices, or if the right pulmonary artery which is visible in the right hilus appears wider than the trachea. Decreased pulmonary blood flow/pbf (oligemia) is diagnosed by the relative blackness of lung fields with small lung hilum. Causes of decreased PBF Tricuspid atresia Ebstein s anomaly Pulmonary stenosis (PS) Tetralogy of Fallot Pulmonary atresia Persistent truncus (type IV) Eisenmenger syndrome 534 Causes of increased PBF Acyanotic: Ostium primum/ secundum ASD Ventricular septal defect Patent ductus arteriosus Cyanotic: Admixture lesions without PS Transposition of great Total anomalous pulmonary venous drainage Persistent truncus arteriosus Single ventricle Specific chamber enlargement In an AP view, the right heart border is formed from above downwards by superior vena cava (SVC), ascending aorta (AA), right atrial appendage (RAA), and the right atrium (RA). The left heart border is formed by the aortic arch (AoA), main pulmonary artery (PA), left atrial appendage (LAA), and the left ventricle (LV). This forms the basis for diagnosing various chamber enlargements. Note that the right ventricle (RV) does not contribute to either of the borders and usually presents with an upturned apex, when enlarged. Left atrial enlargement results in splaying of the carina, straightening of left heart border and double left heart border appearance. Specific x-ray picture in congenital heart lesions Heart lesion Ventricular septal defect Patent ductus arteriosus Coarctation of aorta X-ray picture Prominent pulmonary vascular markings, left atrial and ventricular enlargement Prominent main pulmonary artery, left atrial and ventricular enlargement Reverse 3 sign along the upper left heart borderhypoplastic aortic knob along with left ventricular prominence; inferior rib border notching contd...
10 Neonatal Chest X-ray Tetrology of fallot Transposition of great arteries Truncus arteriosus Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (supracardiac) Coeur en sabot (boot shaped) heart caused by a small pedicle (atretic PA) with a upturned apex due to RV hypertrophy; pulmonary oligemia Egg on side appearance due to the narrow pedicle created by the parallel orientation of aorta and pulmonary artery Narrow pedicle, frequently accompanied by absent thymus Snowman appearance caused by the dilated vertical vein, innominate vein and SVC, pulmonary plethora Line positions Umbilical arterial line High: Between T6 and T9 thoracic vertebrae Low: Between L3 and L4 vertebrae Umbilical venous line: 0.5 cm to 1 cm above the diaphragm Endotracheal tube tip: T1 or T2; atleast 2 cm above carina (Note: position of the baby s head and neck may alter ETT position) Percutaneous central line (PICC): When inserted from upper limb, the line must have crossed the first rib and passed medially, with the tip lying between T3 and T6 vertebrae. Practical tips While doing an X-ray Follow aseptic precautions. Adequate hand hygiene is a must for all including the radiographer Always make note and discuss the exposure settings with the radiographer in order to optimise image quality. A rough guide is to use kv and 4-10 ma Avoid direct contact of the X-ray plate with the baby to prevent hypothermia. Always place the X-ray plate in the separate tray meant for that purpose In small babies, beware of hypothermia as the radiant warmer is tilted away during the X-ray and provide extra 535
11 AIIMS Protocols in Neonatology heat source if necessary. X-ray can be done through an incubator safely Instruct health care providers to wear lead apron themselves and use gonad shield for the baby. Safe distance for health care professionals when a x-ray is being filmed in order to prevent radiation hazard is not clear Expose only the area of interest and remove chest leads, tubings, etc. from the field Make sure the baby is not rotated As far as possible, quieten the baby to avoid swings in respiratory depth While reading an X-ray Read schematically; jumping to the diagnosis may entail the risk of missing additional details Correlate findings with clinical details Make note of age in hours/ days, serial sequence number and interventions done before (such as surfactant administration) and after the X-ray (pulling out a deeply placed endotracheal tube) Use of a view box and magnifying glass is ideal References 1. Deorari A, Kumar P, Murki S. Workbook on CPAP: Science, nd evidence and practice. 2 ed. New Delhi: Neonatal chest x-ray interpretation; p th 2. Swischuk LE. Imaging of the newborn, infant and young child. 5 ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Respiratory system; p Abdulla R. Heart Diseases in Children: A Pediatrician s Guide. Chicago: Spinger: Chapter 2, Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray; p Northway WH, Rosan RC, Porter DY. Pulmonary disease following respirator therapy of hyaline-membrane disease. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia. N Engl J Med Feb 16;276(7):
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays. Objectives. Indications for X-Rays 5/14/2018
 Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
Neonatal Chest X-Ray Interpretation
 CHAPTER 7 Neonatal Chest X-Ray Interpretation Prof. Praveen Kumar Neonatal unit, Department of Pediatrics, PGIMER, Chandigarh Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you should be able to: 1. Schematically
CHAPTER 7 Neonatal Chest X-Ray Interpretation Prof. Praveen Kumar Neonatal unit, Department of Pediatrics, PGIMER, Chandigarh Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you should be able to: 1. Schematically
Chest X rays and Case Studies. No disclosures. Outline 5/31/2018. Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital
 Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray
 Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
Chapter 2 Cardiac Interpretation of Pediatric Chest X-Ray Ra-id Abdulla and Douglas M. Luxenberg Key Facts The cardiac silhouette occupies 50 55% of the chest width on an anterior posterior chest X-ray
4/16/2017. Learning Objectives. Interpretation of the Chest Radiograph. Components. Production of the Radiograph. Density & Appearance
 Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Chest X-ray Interpretation
 Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Approach to CXR. Terminology. 1.Identification. Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow. Correct patient Correct date and time Correct examination
 Approach to CXR Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow From Rob Posteraro http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_interpret.txt.html ; http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_main.txt.html) Approach to viewing Chest
Approach to CXR Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow From Rob Posteraro http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_interpret.txt.html ; http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_main.txt.html) Approach to viewing Chest
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax. Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem
 Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
UERMMMC Department of Radiology. Basic Chest Radiology
 UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC
 Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC An approach to reviewing a chest x-ray will create a foundation that will facilitate the detection of abnormalities. You should create your own
Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC An approach to reviewing a chest x-ray will create a foundation that will facilitate the detection of abnormalities. You should create your own
10/17/2016. Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology. Objectives. Techniques
 Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
J Somerville and V Grech. The chest x-ray in congenital heart disease 2. Images Paediatr Cardiol Jan-Mar; 12(1): 1 8.
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2010 PMCID: PMC3228330 The chest x-ray in congenital heart disease 2 J Somerville and V Grech Paediatric Department, Mater Dei Hospital, Malta Corresponding
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. 2010 PMCID: PMC3228330 The chest x-ray in congenital heart disease 2 J Somerville and V Grech Paediatric Department, Mater Dei Hospital, Malta Corresponding
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations
 Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013
 Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Disclosure. Clinical Chest Radiography Interpretation Part I
 Clinical Chest Radiography Interpretation Part I Anthony M. Angelow, PhD(c), MSN, ACNPC, AGACNP-BC, CEN Associate Lecturer, Fitzgerald Health Education Associates Clinical practice Division of Trauma Surgery
Clinical Chest Radiography Interpretation Part I Anthony M. Angelow, PhD(c), MSN, ACNPC, AGACNP-BC, CEN Associate Lecturer, Fitzgerald Health Education Associates Clinical practice Division of Trauma Surgery
X-Rays. Prepared by Prof.Dr. Magda Hassab Allah Assist.lecturer Marwa Al Hady
 X-Rays Prepared by Prof.Dr. Magda Hassab Allah Assist.lecturer Marwa Al Hady CHEST X-RAYS Normal Chest X-ray Comments on chest X ray includes examination of 1- Bony cage (ribs,clavicles &vertebral column
X-Rays Prepared by Prof.Dr. Magda Hassab Allah Assist.lecturer Marwa Al Hady CHEST X-RAYS Normal Chest X-ray Comments on chest X ray includes examination of 1- Bony cage (ribs,clavicles &vertebral column
The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists
 Mayo Clinic & British Cardiovascular Society at the Royal College of Physicians, London : 21-23-October 2013 Cases-Controversies-Updates 2013 The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists Michael Rubens Royal Brompton
Mayo Clinic & British Cardiovascular Society at the Royal College of Physicians, London : 21-23-October 2013 Cases-Controversies-Updates 2013 The Chest X-ray for Cardiologists Michael Rubens Royal Brompton
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus
 Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
!"#$%&'%()'*+,-%&&.'+('*/%)+%,#+0' 12/.,'3%)+"4#%52.
 !"#$%&'%()'*+,-%&&.'+('*/%)+%,#+0' 12/.,'3%)+"4#%52.!"#$%&'()$*+&,--#&$.//,0'1232'!-#0'45 *6 '7849!!"#$%&'"(&)*+),$-.*/*01) 2$34/&1)*+)5"-.3.(") 6%.(3")*+)7*(08/$)9(.:"%;.&1)) )?
!"#$%&'%()'*+,-%&&.'+('*/%)+%,#+0' 12/.,'3%)+"4#%52.!"#$%&'()$*+&,--#&$.//,0'1232'!-#0'45 *6 '7849!!"#$%&'"(&)*+),$-.*/*01) 2$34/&1)*+)5"-.3.(") 6%.(3")*+)7*(08/$)9(.:"%;.&1)) )?
B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY
 (YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
(YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
X-Rays. Kunal D Patel Research Fellow IMM
 X-Rays Kunal D Patel Research Fellow IMM The 12-Steps } 1: Name 2: Date 3: Old films 4: What type of view(s) 5: Penetration } Pre-read 6: Inspiration 7: Rotation Quality Control 8: Angulation 9: Soft tissues
X-Rays Kunal D Patel Research Fellow IMM The 12-Steps } 1: Name 2: Date 3: Old films 4: What type of view(s) 5: Penetration } Pre-read 6: Inspiration 7: Rotation Quality Control 8: Angulation 9: Soft tissues
disease, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, pulmonary hypoplasia and congenital diaphragmatic hernia.
 Neonatal Chest Imaging - What the Nurse Should Know Expires Monday, April 30, 2018 Nursing Michael J. Diament, M.D. Objectives 1. Describe a good technique for positioning a neonate for the purpose of
Neonatal Chest Imaging - What the Nurse Should Know Expires Monday, April 30, 2018 Nursing Michael J. Diament, M.D. Objectives 1. Describe a good technique for positioning a neonate for the purpose of
The External Anatomy of the Lungs. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The External Anatomy of the Lungs Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Introduction The lungs are the vital organs of respiration Their main function is to oxygenate the blood by bringing inspired air into
The External Anatomy of the Lungs Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Introduction The lungs are the vital organs of respiration Their main function is to oxygenate the blood by bringing inspired air into
Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis?
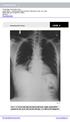 1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
PATIENT DATA EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATION: IMAGING STUDIES
 PATIENT DATA EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATION: IMAGING STUDIES Robert Harwood, MSA, RRT-NPS Objectives At the end of this presentation the student should be able to: Describe the indications of a chest radiograph.
PATIENT DATA EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATION: IMAGING STUDIES Robert Harwood, MSA, RRT-NPS Objectives At the end of this presentation the student should be able to: Describe the indications of a chest radiograph.
Congenital Heart Defects
 Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Normal Heart Congenital Heart Defects 1. Patent Ductus Arteriosus The ductus arteriosus connects the main pulmonary artery to the aorta. In utero, it allows the blood leaving the right ventricle to bypass
Children are not small adults Children are Not Small Adults Anatomic considerations Pliable bony & cartilagenous structures - Significant thoracic inj
 PEDIATRIC CHEST TRAUMA Children are not small adults Role of imaging Spectrum of injury Children are not small adults Children are Not Small Adults Anatomic considerations Pliable bony & cartilagenous
PEDIATRIC CHEST TRAUMA Children are not small adults Role of imaging Spectrum of injury Children are not small adults Children are Not Small Adults Anatomic considerations Pliable bony & cartilagenous
Heart and Lungs. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship of pulmonary parenchyma to heart and chest wall.
 Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Heart and Lungs Normal Sonographic Anatomy THORAX Axial and coronal sections demonstrate integrity of thorax, fetal breathing movements, and overall size and shape. LUNG Coronal section demonstrates relationship
Chest and cardiovascular
 Module 1 Chest and cardiovascular A. Doss and M. J. Bull 1. Regarding the imaging modalities of the chest: High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) uses a slice thickness of 4 6 mm to identify mass lesions
Module 1 Chest and cardiovascular A. Doss and M. J. Bull 1. Regarding the imaging modalities of the chest: High resolution computed tomography (HRCT) uses a slice thickness of 4 6 mm to identify mass lesions
SUMPh N. Testemitanu Radiology and Medical imaging department PEDIATRIC IMAGING. M. Crivceanschii, assistant professor
 SUMPh N. Testemitanu Radiology and Medical imaging department PEDIATRIC IMAGING M. Crivceanschii, assistant professor GOALS AND OBJECTIVES to be aware of the role of modern diagnostic imaging modalities
SUMPh N. Testemitanu Radiology and Medical imaging department PEDIATRIC IMAGING M. Crivceanschii, assistant professor GOALS AND OBJECTIVES to be aware of the role of modern diagnostic imaging modalities
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART
 ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan
 PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan Fetal Cardiology Unit, Harris Birthright Research Centre for Fetal Medicine, King's College Hospital, London, UK IMPORTANCE OF PRENATAL
PRACTICAL GUIDE TO FETAL ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IC Huggon and LD Allan Fetal Cardiology Unit, Harris Birthright Research Centre for Fetal Medicine, King's College Hospital, London, UK IMPORTANCE OF PRENATAL
Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code
 Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code Herring, W ISBN-13: 9780323074445 Table of Contents 1. Recognizing Anything The "colorful" world of radiology A
Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code Herring, W ISBN-13: 9780323074445 Table of Contents 1. Recognizing Anything The "colorful" world of radiology A
Tubes and lines in neonatal chest radiograph
 Tubes and lines in neonatal chest radiograph Poster No.: C-1008 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. TUMMA, N. AHMED, V. Prasad ; Hyderabad/IN, 1 2 1 1 2 HYDERABAD, ANDHRA PRADESH/IN
Tubes and lines in neonatal chest radiograph Poster No.: C-1008 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. TUMMA, N. AHMED, V. Prasad ; Hyderabad/IN, 1 2 1 1 2 HYDERABAD, ANDHRA PRADESH/IN
Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps. Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania None Disclosures Objectives Describe blunt and penetrating traumatic
Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania None Disclosures Objectives Describe blunt and penetrating traumatic
Undergraduate Teaching
 Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
FUNDAMENTALS OF CXR INTERPRETATION THE BASICS
 FUNDAMENTALS OF CXR INTERPRETATION THE BASICS PART I QUALITY ASSESSMENT 1 PATIENT-DEPENDENT FACTORS 3 REVIEW OF IMPORTANT ANATOMY 7 LUNGS AND PLEURA 11 DIAPHRAGMS 13 BONES AND SOFT TISSUES 14 A BRIEF LOOK
FUNDAMENTALS OF CXR INTERPRETATION THE BASICS PART I QUALITY ASSESSMENT 1 PATIENT-DEPENDENT FACTORS 3 REVIEW OF IMPORTANT ANATOMY 7 LUNGS AND PLEURA 11 DIAPHRAGMS 13 BONES AND SOFT TISSUES 14 A BRIEF LOOK
Interpretation of the chest radiograph Elizabeth Puddy MB ChB FCARCSI Catherine Hill MB ChB MRCP FRCR
 Interpretation of the chest radiograph Elizabeth Puddy MB ChB FCARCSI Catherine Hill MB ChB MRCP FRCR The traditional technique used in the acquisition and development of a chest radiograph uses methods
Interpretation of the chest radiograph Elizabeth Puddy MB ChB FCARCSI Catherine Hill MB ChB MRCP FRCR The traditional technique used in the acquisition and development of a chest radiograph uses methods
Dana Alrafaiah. - Moayyad Al-Shafei. -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 - 6 - Dana Alrafaiah - Moayyad Al-Shafei -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb 1 P a g e Quick recap: Both lungs have an apex, base, mediastinal and costal surfaces, anterior and posterior borders. The right lung,
- 6 - Dana Alrafaiah - Moayyad Al-Shafei -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb 1 P a g e Quick recap: Both lungs have an apex, base, mediastinal and costal surfaces, anterior and posterior borders. The right lung,
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart
 Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Heart and Soul Evaluation of the Fetal Heart Ivana M. Vettraino, M.D., M.B.A. Clinical Associate Professor, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine Objectives Review the embryology of the formation
Lung & Pleura. The Topics :
 Lung & Pleura The Topics : The Trachea. The Bronchi. The Brochopulmonary Segments. The Lungs. The Hilum. The Pleura. The Surface Anatomy Of The Lung & Pleura. The Root & Hilum. - first of all, the lung
Lung & Pleura The Topics : The Trachea. The Bronchi. The Brochopulmonary Segments. The Lungs. The Hilum. The Pleura. The Surface Anatomy Of The Lung & Pleura. The Root & Hilum. - first of all, the lung
Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th & 12 th Eds.)
 PLEURAL CAVITY AND LUNGS Dr. Milton M. Sholley SELF STUDY RESOURCES Essential Clinical Anatomy 3 rd ed. (ECA): pp. 70 81 Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th &
PLEURAL CAVITY AND LUNGS Dr. Milton M. Sholley SELF STUDY RESOURCES Essential Clinical Anatomy 3 rd ed. (ECA): pp. 70 81 Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th &
Radiology of the respiratory/cardiac diseases (part 2)
 Cardiology Cycle - Lecture 6 436 Teams Radiology of the respiratory/cardiac diseases (part 2) Objectives Done By Team Leaders: Khalid Alshehri Hanin Bashaikh Team Members: Leena Alwakeel Aroob Alhuthail
Cardiology Cycle - Lecture 6 436 Teams Radiology of the respiratory/cardiac diseases (part 2) Objectives Done By Team Leaders: Khalid Alshehri Hanin Bashaikh Team Members: Leena Alwakeel Aroob Alhuthail
Cardiac Catheterization Cases Primary Cardiac Diagnoses Facility 12 month period from to PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient)
 PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
PRIMARY DIAGNOSES (one per patient) Septal Defects ASD (Atrial Septal Defect) PFO (Patent Foramen Ovale) ASD, Secundum ASD, Sinus venosus ASD, Coronary sinus ASD, Common atrium (single atrium) VSD (Ventricular
Lines and tubes. 1 Nasogastric tubes Endotracheal tubes Central lines Permanent pacemakers Chest drains...
 Lines and tubes 1 Nasogastric tubes... 15 2 Endotracheal tubes.... 19 3 Central lines... 21 4 Permanent pacemakers.... 25 5 Chest drains... 30 This page intentionally left blank 1 Nasogastric tubes Background
Lines and tubes 1 Nasogastric tubes... 15 2 Endotracheal tubes.... 19 3 Central lines... 21 4 Permanent pacemakers.... 25 5 Chest drains... 30 This page intentionally left blank 1 Nasogastric tubes Background
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES
 THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 7. LUNGS Q1. Fill in the blanks: the lung has lobes and fissures. A. Right, three, two. B. Right, two, one. C. Left, three, two. D. Left, two, three. Q2. The base of the lung
THE GOOFY ANATOMIST QUIZZES 7. LUNGS Q1. Fill in the blanks: the lung has lobes and fissures. A. Right, three, two. B. Right, two, one. C. Left, three, two. D. Left, two, three. Q2. The base of the lung
When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영
 When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영 The Korean Society of Cardiology COI Disclosure Eun-Young Choi The author have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose
When is Risky to Apply Oxygen for Congenital Heart Disease 부천세종병원 소아청소년과최은영 The Korean Society of Cardiology COI Disclosure Eun-Young Choi The author have no financial conflicts of interest to disclose
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD)
 CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE (CHD) DEFINITION It is the result of a structural or functional abnormality of the cardiovascular system at birth GENERAL FEATURES OF CHD Structural defects due to specific disturbance
Right lung. -fissures:
 -Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
-Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 51-60, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 51-60, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Congenital Lung Malformations: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments
 Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Bronchioles. Alveoli. Type I alveolar cells are very thin simple squamous epithelial cells and form most of the lining of an alveolus.
 276 Bronchioles Bronchioles continue on to form bronchi. The primary identifying feature is the loss of hyaline cartilage. The epithelium has become simple ciliated columnar, and there is a complete ring
276 Bronchioles Bronchioles continue on to form bronchi. The primary identifying feature is the loss of hyaline cartilage. The epithelium has become simple ciliated columnar, and there is a complete ring
Lecture 3. Inflammatory Processes
 Lecture 3 Inflammatory Processes Process: Increased vascular permeability Water and cellular infiltrations Results: Abscess, ulceration, cavitation Penetration, perforation and fistula formation Scarring,
Lecture 3 Inflammatory Processes Process: Increased vascular permeability Water and cellular infiltrations Results: Abscess, ulceration, cavitation Penetration, perforation and fistula formation Scarring,
Manage TB Dr. A. Chitrakumar Madras Medical College and RGGGH Institute of Thoracic Medicine, Chennai
 Manage TB Dr. A. Chitrakumar Madras Medical College and RGGGH Institute of Thoracic Medicine, Chennai Lecture 16 Radiology in diagnosis of Tuberculosis Session 01 So, welcome to the session Radiology in
Manage TB Dr. A. Chitrakumar Madras Medical College and RGGGH Institute of Thoracic Medicine, Chennai Lecture 16 Radiology in diagnosis of Tuberculosis Session 01 So, welcome to the session Radiology in
Cardiac Radiography. Jared D. Christensen, M.D.
 Cardiac Radiography Jared D. Christensen, M.D. Cardiac radiography Jared D. Christensen, M.D. Overview Basic Concepts Technique Normal anatomy Cases Technique 3 Standard Views Posterior-Anterior (PA) Anterior-Posterior
Cardiac Radiography Jared D. Christensen, M.D. Cardiac radiography Jared D. Christensen, M.D. Overview Basic Concepts Technique Normal anatomy Cases Technique 3 Standard Views Posterior-Anterior (PA) Anterior-Posterior
Radiological conference. Left upper lobe collapse. Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1998, v. 20 n. 9, p
 Title Radiological conference. Left upper lobe collapse Author(s) Wong, LLS; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1998, v. 20 n. 9, p. 513-517 Issued Date 1998 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44672
Title Radiological conference. Left upper lobe collapse Author(s) Wong, LLS; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1998, v. 20 n. 9, p. 513-517 Issued Date 1998 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44672
Imaging of the Lung in Children
 Imaging of the Lung in Children Imaging methods X-Ray of the Lung (Anteroposterior, ) CT, HRCT MRI USG Congenital developmental defects of the lungs Agenesis, aplasia, hypoplasia Tension pulmonary anomalies
Imaging of the Lung in Children Imaging methods X-Ray of the Lung (Anteroposterior, ) CT, HRCT MRI USG Congenital developmental defects of the lungs Agenesis, aplasia, hypoplasia Tension pulmonary anomalies
Radiology of the respiratory disease
 Radiology of the respiratory disease [ Color index: Important Notes Extra ] [ Editing file Feedback Share your notes Shared notes ] Resources: - 435 Slides - 434 Team - 435 Notes Done by: - Mai Alageel
Radiology of the respiratory disease [ Color index: Important Notes Extra ] [ Editing file Feedback Share your notes Shared notes ] Resources: - 435 Slides - 434 Team - 435 Notes Done by: - Mai Alageel
Interactive Lecture. Lecture 7 - Interactive. Radiology of cardiorespiratory disease. Editing File. Done By. Color Coding Important Notes Extra
 Lecture 7 - Interactive 436 Teams Interactive Lecture Radiology of cardiorespiratory disease Done By Team Leaders: Khalid Alshehri Hanin Bashaikh Team Members: Ghaida Alsaeed Maha Alissa Nawwaf AlHarbi
Lecture 7 - Interactive 436 Teams Interactive Lecture Radiology of cardiorespiratory disease Done By Team Leaders: Khalid Alshehri Hanin Bashaikh Team Members: Ghaida Alsaeed Maha Alissa Nawwaf AlHarbi
Elderly Man with Dyspnoea
 Asia Pacific Family Medicine, 2004; 3 (1-2): 46-50 RADIOLOGY SERIES Elderly Man with Dyspnoea Wei-Yang LIM Faculty of Medicine National University of Singapore, Singapore Wilfred CG PEH Singapore Health
Asia Pacific Family Medicine, 2004; 3 (1-2): 46-50 RADIOLOGY SERIES Elderly Man with Dyspnoea Wei-Yang LIM Faculty of Medicine National University of Singapore, Singapore Wilfred CG PEH Singapore Health
Case 47 Clinical Presentation
 93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
93 Case 47 C Clinical Presentation 45-year-old man presents with chest pain and new onset of a murmur. Echocardiography shows severe aortic insufficiency. 94 RadCases Cardiac Imaging Imaging Findings C
Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP. October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18
 Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18 Identifying normal anatomy Identifying various pathologic states Identifying placement of hardware Identifying limitations of portable CXR
Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18 Identifying normal anatomy Identifying various pathologic states Identifying placement of hardware Identifying limitations of portable CXR
Advances in MDCT of Thoracic Trauma
 Baltic Congress of Radiology, Riga 2010 Advances in MDCT of Thoracic Trauma Robert A. Novelline, MD Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical School Director of Emergency Radiology, Massachusetts General
Baltic Congress of Radiology, Riga 2010 Advances in MDCT of Thoracic Trauma Robert A. Novelline, MD Professor of Radiology, Harvard Medical School Director of Emergency Radiology, Massachusetts General
Introduction to Chest Radiography
 Introduction to Chest Radiography RSTH 366: DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES Alan Alipoon BS, RCP, RRT Instructor Department of Cardiopulmonary Sciences 1 Introduction Discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen Terminology
Introduction to Chest Radiography RSTH 366: DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES Alan Alipoon BS, RCP, RRT Instructor Department of Cardiopulmonary Sciences 1 Introduction Discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen Terminology
Anatomy notes-thorax.
 Anatomy notes-thorax. Thorax: the part extending from the root of the neck to the abdomen. Parts of the thorax: - Thoracic cage (bones). - Thoracic wall. - Thoracic cavity. ** The thoracic cavity is covered
Anatomy notes-thorax. Thorax: the part extending from the root of the neck to the abdomen. Parts of the thorax: - Thoracic cage (bones). - Thoracic wall. - Thoracic cavity. ** The thoracic cavity is covered
Interpretation of Neonatal Chest Radiography 신생아흉부촬영의판독
 Review Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.74.5.279 Interpretation of Neonatal Chest Radiography 신생아흉부촬영의판독 Hye-Kyung Yoon, MD* Department of Radiology, Kangwon
Review Article pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.74.5.279 Interpretation of Neonatal Chest Radiography 신생아흉부촬영의판독 Hye-Kyung Yoon, MD* Department of Radiology, Kangwon
Anatomy Lecture 8. In the previous lecture we talked about the lungs, and their surface anatomy:
 Anatomy Lecture 8 In the previous lecture we talked about the lungs, and their surface anatomy: 1-Apex:it lies 1 inch above the medial third of clavicle. 2-Anterior border: it starts from apex to the midpoint
Anatomy Lecture 8 In the previous lecture we talked about the lungs, and their surface anatomy: 1-Apex:it lies 1 inch above the medial third of clavicle. 2-Anterior border: it starts from apex to the midpoint
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome
 Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome Fact sheet on Absent Pulmonary Valve Syndrome In this condition, which has some similarities to Fallot's Tetralogy, there is a VSD with narrowing at the pulmonary valve.
ISUOG Basic Training. Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon
 ISUOG Basic Training Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon Learning objectives 9 & 10 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: recognise the differences between the normal & most common
ISUOG Basic Training Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon Learning objectives 9 & 10 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: recognise the differences between the normal & most common
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES
 PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
Signs in Chest Radiology
 Signs in Chest Radiology Jonathan H. Chung, MD Disclosures No pertinent disclosures Jonathan H. Chung, MD Assistant Professor Institute t of fadvanced d Biomedical Imaging National Jewish Health Denver,
Signs in Chest Radiology Jonathan H. Chung, MD Disclosures No pertinent disclosures Jonathan H. Chung, MD Assistant Professor Institute t of fadvanced d Biomedical Imaging National Jewish Health Denver,
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
9/8/2009 < 1 1,2 3,4 5,6 7,8 9,10 11,12 13,14 15,16 17,18 > 18. Tetralogy of Fallot. Complex Congenital Heart Disease.
 Current Indications for Pediatric CTA S Bruce Greenberg Professor of Radiology Arkansas Children s Hospital University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences greenbergsbruce@uams.edu 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10
Current Indications for Pediatric CTA S Bruce Greenberg Professor of Radiology Arkansas Children s Hospital University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences greenbergsbruce@uams.edu 45 40 35 30 25 20 15 10
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II
 Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY. Guidelines. Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta.
 BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF HUMAN ANATOMY Guidelines Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Topic of the lesson Aorta. Thoracic aorta. Course 1 The number of hours 3 1. The
Thorax Lecture 2 Thoracic cavity.
 Thorax Lecture 2 Thoracic cavity. Spring 2016 Dr. Maher Hadidi, University of Jordan 1 Enclosed by the thoracic wall. Extends between (thoracic inlet) & (thoracic outlet). Thoracic inlet At root of the
Thorax Lecture 2 Thoracic cavity. Spring 2016 Dr. Maher Hadidi, University of Jordan 1 Enclosed by the thoracic wall. Extends between (thoracic inlet) & (thoracic outlet). Thoracic inlet At root of the
CHEST & ABDOMINAL X-RAYS MALIKA IBRAHIM CORE MEDICAL TRAINEE BLACKPOOL VICTORIA HOSPITAL DATA INTERPRETATION COURSE FEB 20, 2017
 CHEST & ABDOMINAL X-RAYS MALIKA IBRAHIM CORE MEDICAL TRAINEE BLACKPOOL VICTORIA HOSPITAL DATA INTERPRETATION COURSE FEB 20, 2017 1. Sample x-rays 2. Basic chest x-ray interpretation skills 3. Chest x-ray
CHEST & ABDOMINAL X-RAYS MALIKA IBRAHIM CORE MEDICAL TRAINEE BLACKPOOL VICTORIA HOSPITAL DATA INTERPRETATION COURSE FEB 20, 2017 1. Sample x-rays 2. Basic chest x-ray interpretation skills 3. Chest x-ray
Anatomy Sheet #5. In the previous lecture, we finished discussion about the larynx; now we continue with trachea, lungs and pleura.
 Anatomy Sheet #5 In the previous lecture, we finished discussion about the larynx; now we continue with trachea, lungs and pleura. Trachea and lungs The knowledge about the pleura and lungs is very important
Anatomy Sheet #5 In the previous lecture, we finished discussion about the larynx; now we continue with trachea, lungs and pleura. Trachea and lungs The knowledge about the pleura and lungs is very important
Sectional Anatomy Quiz - III
 Sectional Anatomy - III Rashid Hashmi * Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales (UNSW), Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 30 Jun 2018
Sectional Anatomy - III Rashid Hashmi * Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales (UNSW), Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 30 Jun 2018
PREMATURITY/ESTIMATED GESTATIONAL AGE
 PREMATURITY/ESTIMATED GESTATIONAL AGE 765.21 < 24 completed weeks of gestation P07.21 Extreme immaturity of newborn, gestational age less than 23 completed weeks P07.22 Extreme immaturity of newborn, gestational
PREMATURITY/ESTIMATED GESTATIONAL AGE 765.21 < 24 completed weeks of gestation P07.21 Extreme immaturity of newborn, gestational age less than 23 completed weeks P07.22 Extreme immaturity of newborn, gestational
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5
 DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
DEVELOPMENT OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM L E C T U R E 5 REVIEW OF CARDIAC ANATOMY Heart 4 chambers Base and apex Valves Pericardial sac 3 layers: epi, myo, endo cardium Major blood vessels Aorta and its
Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!!
 The lateral chest radiograph: Challenging area around the thoracic aorta!!! Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!! Dong Yoon Han 1, So Youn
The lateral chest radiograph: Challenging area around the thoracic aorta!!! Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!! Dong Yoon Han 1, So Youn
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD
 COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
Techniques of examination of the thorax and lungs. Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 24. Sept
 Techniques of examination of the thorax and lungs Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 24. Sept. 2013. Inspection of the thorax Observe: the shape of chest Deformities
Techniques of examination of the thorax and lungs Dr. Szathmári Miklós Semmelweis University First Department of Medicine 24. Sept. 2013. Inspection of the thorax Observe: the shape of chest Deformities
Radiological evaluation of neonatal lesions in 118 neonates
 Original Research Article ISSN: 394-006 (P) Radiological evaluation of neonatal thoracic lesions in 8 neonates Konark Sarvaiya *, Himanshu Singla, Nirav Patel, Jai Inder Dhillon, Babubhai Patel 3 nd year
Original Research Article ISSN: 394-006 (P) Radiological evaluation of neonatal thoracic lesions in 8 neonates Konark Sarvaiya *, Himanshu Singla, Nirav Patel, Jai Inder Dhillon, Babubhai Patel 3 nd year
Cyanosis and Pulmonary Disease in Infancy
 CLINICAL CONFERENCE Cyanosis and Pulmonary Disease in Infancy By Robert A. Miller, M.D. Division of Cardiology, Children s Memorial Hospital, and the Department of Pediatrics, Northwestern University Medical
CLINICAL CONFERENCE Cyanosis and Pulmonary Disease in Infancy By Robert A. Miller, M.D. Division of Cardiology, Children s Memorial Hospital, and the Department of Pediatrics, Northwestern University Medical
Two Lesser Known but Useful Signs of Neonatal Pneumothorax
 Two Lesser Known but Useful Signs of Neonatal Pneumothorax LEONARD E. SWISCHUK1 Two lesser known signs of neonatal pneumothorax are presented : the large, hyperlucent hemithorax sign and the medial stripe
Two Lesser Known but Useful Signs of Neonatal Pneumothorax LEONARD E. SWISCHUK1 Two lesser known signs of neonatal pneumothorax are presented : the large, hyperlucent hemithorax sign and the medial stripe
Notes by Sandra Dankwa 2009 HF- Heart Failure DS- Down Syndrome IE- Infective Endocarditis ET- Exercise Tolerance. Small VSD Symptoms -asymptomatic
 Congenital Heart Disease: Notes. Condition Pathology PC Ix Rx Ventricular septal defect (VSD) L R shuntsdefect anywhere in the ventricle, usually perimembranous (next to the tricuspid valve) 30% 1)small
Congenital Heart Disease: Notes. Condition Pathology PC Ix Rx Ventricular septal defect (VSD) L R shuntsdefect anywhere in the ventricle, usually perimembranous (next to the tricuspid valve) 30% 1)small
CongHeartDis.doc. Андрій Миколайович Лобода
 CongHeartDis.doc Андрій Миколайович Лобода 2015 Зміст 3 Зміст Зміст 4 A child with tetralogy of Fallot is most likely to exhibit: -Increased pulmonary blood flow -Increased pressure in the right ventricle
CongHeartDis.doc Андрій Миколайович Лобода 2015 Зміст 3 Зміст Зміст 4 A child with tetralogy of Fallot is most likely to exhibit: -Increased pulmonary blood flow -Increased pressure in the right ventricle
Pitfalls of the Pediatric Chest and Abdomen SPR 2017
 Pitfalls of the Pediatric Chest and Abdomen SPR 2017 Richard I. Markowitz, MD, FACR Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania No Disclosures Cognitive Perceptual
Pitfalls of the Pediatric Chest and Abdomen SPR 2017 Richard I. Markowitz, MD, FACR Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania No Disclosures Cognitive Perceptual
24. An infant with recurrent pneumonia underwent a frontal chest radiograph (Fig 24-A) followed by
 24. An infant with recurrent pneumonia underwent a frontal chest radiograph (Fig 24-A) followed by diagnosis? ndings, what is the most likely A. Pulmonary sequestration B. Congenital pulmonary airway malformation
24. An infant with recurrent pneumonia underwent a frontal chest radiograph (Fig 24-A) followed by diagnosis? ndings, what is the most likely A. Pulmonary sequestration B. Congenital pulmonary airway malformation
10/14/2018 Dr. Shatarat
 2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
Lab #3. Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb. Jumana Jihad. Ammar Ramadan. 0 P a g e
 Lab #3 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Jumana Jihad Ammar Ramadan 0 P a g e Last anatomy lab: Lungs and structure on the mediastinal surfs: 1-the right lung: How do we know it s the right lung??? -the 3 lobes
Lab #3 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Jumana Jihad Ammar Ramadan 0 P a g e Last anatomy lab: Lungs and structure on the mediastinal surfs: 1-the right lung: How do we know it s the right lung??? -the 3 lobes
Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems
 Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems Respiratory Distress Occurs in about 7% of infants Clinical presentation includes: Apnea Cyanosis Grunting Inspiratory stridor Nasal flaring Poor feeding Tachypnea
Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems Respiratory Distress Occurs in about 7% of infants Clinical presentation includes: Apnea Cyanosis Grunting Inspiratory stridor Nasal flaring Poor feeding Tachypnea
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
List by Region - Visceral Anomalies
 1 List by Region - Visceral Anomalies General Terms 10127 Situs inversus 80,00 10125 Aneurysm 68,42 10126Fluid-filled abdomen -35,00 Brain 10131 Hydrocephaly 10128 Dilated cerebral ventricle 20,00 10132
1 List by Region - Visceral Anomalies General Terms 10127 Situs inversus 80,00 10125 Aneurysm 68,42 10126Fluid-filled abdomen -35,00 Brain 10131 Hydrocephaly 10128 Dilated cerebral ventricle 20,00 10132
Lung sequestration and Scimitar syndrome
 Lung sequestration and Scimitar syndrome Imaging approaches M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Rotterdam, The Netherlands Pulmonary sequestration Pulmonary sequestration (PS)
Lung sequestration and Scimitar syndrome Imaging approaches M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Rotterdam, The Netherlands Pulmonary sequestration Pulmonary sequestration (PS)
