In-Vitro Examination of Clinically Relevant Stent Parameters
|
|
|
- Laureen McCarthy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 May In-Vitro Examination of Clinically Relevant Stent Parameters K.-P. SCHMITZ, W. SCHMIDT, P. BEHRENS, D. BEHREND University of Rostock, Institute for Biomedical Engineering, Rostock, Germany D. LOOTZ Institute for Implant Technology and Biomaterials, Rostock-Warnemünde, Germany B. GRAF Schwerin Med. Center, Clinic for Internal Medicine, Department of Cardiology, Schwerin, Germany Summary For currently available coronary stents, important technical parameters were determined and compared in laboratory measurements. The resulting measured values for changes in length due to expansion, recoil, inner diameter after expansion, X-ray contrast, and the flexural and radial strength of the expanded stent are extremely important for handling the stent and for a treatment of stenosis that is aimed at permanent opening of the lumen. The results are discussed with a view toward clinical practice, the desired acute results, and possible long-term results. Key Words Coronary stent systems, technical parameters Introduction The examination of the structural mechanical characteristics of coronary stents forms the basis for evaluating the influence of individual technical parameters on the success of therapy in cases of coronary dilation with subsequent stent application [1,2]. In this article, the values with a fundamental influence on stent behavior are examined based on standardized measurements taken from nine different stent systems. These results are then compared. Fundamental measured values are recoil, the change in length occurring during stent implantation, the inner diameter, the flexural strength of the expanded stent, and the radial strength. X-ray density measurements are also performed on the expanded stent. In order to ensure that the results are comparable, the stents used in the study generally have the same dimensions (3.5 x 15 mm); the ACS RX Multilink Tristar and the Cordis BX Velocity only have dimensions of 3.5 x 13 mm available. The results serve primarily to characterize the implanted stent without the balloon catheter. Precisely these characteristics have a lasting effect on the success of therapy and the expected rate of restenosis. The likewise important issues of fatigue analysis [3], the surface area of the biomaterial and the influence on local hemodynamics due to the stent cannot be ascertained more closely, at least insofar as they are not determined by the inner diameter achieved and the elastic recoil. A separate study is conducted regarding the interaction between the stent and the PTCA catheter, which is extremely important for the application phase. Materials and Methods Two specimens of each of the industry-standard coronary stent systems documented in Figure 1 and listed below are studied. All types were tested with 3.5 mm balloons so that the measurements would be comparable. The tests were performed with reference to the following points: Stent expansion and determination of recoil. Measurement of the radial strength of the stent. Measurement of the flexural strength of the stent when expanded. Determination of the change in length after stent expansion and determination of the inner diameter of the stent. X-ray density measurement of expanded stent.
2 198 May Figure 1. Identification and portrayal of test objects in expanded state. Stent Expansion and Determination of Recoil The measurements of stent expansion and recoil are conducted without touching the stent, using a laser measurement system specially designed for use in a water bath (Figure 2) [4]. The expansion of the coronary stent was conducted with the balloon catheter. The expansion of the stent was performed stepwise, in pressure steps from 1 bar up to the rated value of the stent system. By scanning the stent range in 0.5 mm steps at the given pressure steps, expansion profiles could be obtained that were able to supply information as to the current stent diameter, and thus served as a basis for calculation of the elastic recoil. The average stent diameter during the individual pressure steps of expansion and after the subsequent release of pressure were calculated by taking the arithmetic average d of the diameters drms(z) resulting from the profile measurements. The following holds: Figure 2. Measurement principle for determination of diameter via 2-axis laser scanner. where dx and dy are the individual measured values for the x- and y-projections, za and ze are the first and last
3 May measured points on the stent, and n is the number of measured points at the stent. Measurement of the Radial Strength of the Stent To test the radial strength of the stent, the stent is used in the test arrangement described more extensively in [4]. The stent, implanted in a thin-walled tube (Pellethane, I.D. = 3.5 mm, wall thickness = mm) is placed in a tempered test basin. The pressure in the test basin is increased to 1.5 bar in steps of 0.1 bar. This pressure creates a radial load on the tube around the stent. Environmental pressures above 1.5 bar are not deemed reasonable with reference to clinical practice. Measurement of the Flexural Strength of the Expanded Stent The measurement setup for determination of the flexural strength of the expanded stent is described extensively in [4] and is depicted schematically in Figure 3. The flexural strength EI of the stent is determined via reconstruction from the relationship between the bending deflection (f) and the point force (F), based on the general bending theory for a cantilever. In order to consider the influence of stent geometry, the measurements of the flexural strength for all stents are performed at 5 measurement points, each shifted by 45 along the perimeter. Three measurements are performed at each measurement point in order to reduce random measurement error, and the results are determined. The resulting flexural strength that is determined for each stent is given with both reference to the measurement points and averaged over the entire range. Figure 3. Test setup for measurement of flexural strength. Figure 4. Measurement setup for determination of the attenuation of X-ray radiation as per DIN V Determination of the Change in Length upon Stent Expansion and of the Inner Diameter of the Stent The stent length before and after expansion is tested with a digital caliper gauge (Mitutoyo). The total length is measured with calipers under a microscope. The values are then rounded to the next 1 mm as per EN The change in length is the difference between the lengths before and after expansion. The inner diameter of the stent after expansion is determined with test rods, which are available for the relevant diameter range in steps of 0.1 mm with a tolerance of ± 0.01 mm. X-Ray Density Measurement of the Expanded Stent The X-ray density of the expanded stent was determined with the analogous device (D800-1, TUR Dresden, with a 7:1 scatter-ray grid) at a high-voltage of 70 kv, with an energy dose of 2.5 µgy and a basic setup as per DIN V : , Section 6 (Figure 4). The distance between the radiation source and the film (Film focal distance) was 1150 mm. The distance between the focus and the test object depends on the device and the scattering body thickness of 150 mm. This came to 850 mm. Film material with a sensitivity class of 200 was used, as per DIN (Kodak Lanex Medium). The quantitative evaluation was performed through
4 200 May 2000 Figure 5. Recoil of stent systems studied after expansion at the nominal pressure. Figure 6. Pressure at collapse for the stent types studied. scanning the film into a transmitted light scanner (HP ScanJet 6100) with fixed settings for brightness, contrast and resolution. Then, the picture pixel values were determined as a measure for the gray tone of the picture and were averaged arithmetically. The researcher determined the tone and position of the evaluated surfaces where at least 5x5 pixels must be evaluated for the stent area. The gray tones were determined for the stent body (Gs), possible stent markers (Gsm), balloon markers (Gbm) and the immediately adjacent film area (Gf) without an object. The characteristic values K the risk of incisions or even ruptures of the vessel wall. The measured recoil values were averaged for the two specimens of each individual stent type, and dis played in Figure 5. Seven types showed a recoil of < 4 %; only two were > 5 %. These good results and development that has been reached for modern stents. Figure 6 shows a graphic display of the pressure at failpcoll one specimen of each. Coil stents showed a special collapsing characteristic are appropriate for comparison as a measure for the X-ray contrast. Results Stent Expansion and Determination of the Recoil The elastic recoil after expansion is always an important characteristic value for balloon-expandable coronary stents. Types with small recoil values guarantee a large acute lumen with minimal strain on the vessel, and thus, reduce Figure 7. Average flexural strengths while expanded for the stents examined (averages over the perimeters of two specimens of each).
5 May completely; instead, the external pressure causes the stent cross-section to collapse partially at individual stent segments. At the failure pressure portrayed in the figure, the stent function is no longer guaranteed, although the stent has not yet collapsed completely. Flexural Strength of the Stent in Expanded Form Figure 7 gives an overview of the average flexural strength for each stent type (averages around perimeter for the two specimens). A high flexibility is a condition of the construction of the coil stents, (Crossflex, S670), closely followed by Tenax XR, RX Tristar and Synthesis Star System, which, as slotted-tube types, are also very flexible. The BX Velocity, the bestent and the NIR Royal are noticeably stiff by contrast. It is expected of flexible stents that they adjust optimally the vessel wall both at bends and during movement over the course of the heart cycle, and thus, cause less vessel irritation. Table 1. Inner stent diameter measured after expansion (rounded as per EN and averaged over two specimens). Change in Length upon Stent Expansion and Internal Diameter of the Stent Figure 8 provides information as to the percent change in the stent length upon stent expansion when drawn as compared to the length of the stent type when contracted. A low change in length due to expansion is desirable for sure positioning. This requirement is fulfilled for most types. Values > 5 % only occur for S670, NIR Royal and BX Velocity. Critical for the evaluation are especially the types with low longitudinal rigidity (e.g., S670), for which a change in length can additionally be influenced by external causes such as the vessel wall. Our expansions took place without a vessel simulation, since these conditions are easier to make objective. Table 1 shows the inner stent diameter measured after expansion. All stents were expanded to the nominal diameter of 3.5 mm. The measured inner diameters are partially a measure of the elastic recoil, which reduces the attainable inner lumen, but also for the partially uneven, not entirely circular cross-sectional geometry after pressure is released. X-Ray Density Measurement of Expanded Stent The X-ray pictures of the coronary stent systems studied are displayed in Figure 9. Figure 10 shows a comparison of the calculated contrast values K. A high value for Kmeans good visibility; K= 0 means that the Figure 8. Percent change in length of stent systems studied after expansion to the nominal value (for each stent type). Figure 9. X-Ray picture of expanded coronary stents - From left to right: Sorin Carbostent; Biotronik Tenax XR; Medtronic bestent Brava; Cordis Bx Velocity; Cordis Crossflex; Scimed NIR Royal; Medtronic AVE S670; ACS RX Multilink Tristar.
6 202 May 2000 Figure 10. X-ray contrast of expanded stent. lightness of the object and film are exactly the same, i.e., the object is not visible. The X-ray visibility of the body of the expanded stent is low for Carbostent, Tenax XR and bestent along the entire stent; however, special markers at the stent ends more than make up for this disadvantage. The X-ray contrast of the stent markers is, at least for Tenax XR and bestent, even higher than that of the stents of types without special X-ray marking. The visibility is not determined only through contrast, but also by the size of the visible surface [14]. Here, the types that are visible over the entire surface, as well as the extensively marked Tenax XR, are at an advantage. Discussion The elastic stent recoil should be small, since the hemodynamic lumen attained remains decisive for the success of therapy. High-grade recoil must otherwise be corrected during implantation by overstretching the balloon-stent system [5]. In the clinic, intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) diagnostics show evidence of recoil problems for some stents that are expanded incompletely. Certainly, stents that are not completely expanded, that have partially collapsed, or that show constrictions not due to focal calcifications or the vessel wall, are especially noticeable with IVUS. The measured recoil values are generally small. Due to the great importance of a hemodynamically effective vessel cross-section, even small increases in recoil above 4 or 5 % are definitely not to be neglected. There are ongoing discussions on this topic for coronary stents, but also with an eye toward peripheral stent implantation [7,9,10]. The percent change in length has a decisive influence on quality in stent expansion, and requires direct evaluation. Especially in central vessel sections with highlumen side-branch apertures, disadvantageous placement can cause the additional problem of side-branch perfusion. However, the consistency, not necessarily the absolute value, of the change in length is decisive for a stent type, since reference relative to the stenosis or to the beginning and end of dissection must be possible during implantation. Good X-ray visibility is necessary for safe placement of the stent and clear assignation to the vessel segment being [13]. Above all, exact marking of the ends is necessary in order to be able to judge whether the location of the implanted stent is appropriate to the vessel morphology. A high X-ray contrast over the entire range of the stent is thus not optimal, especially when overcontrast hinders or falsifies the evaluation of an in-stent restenosis with a contour procedure. With better imaging procedures such as digital coronary angiography (DCA) or IVUS, these problems can only be reduced, but not be remedied entirely [13,14]. A sufficient radial strength constitutes the main function of a vessel stent, although there is no foundational information as to minimum requirements. Clinical cases for the failure of support functions are extremely rare, and usually occur with relation to external influences such as resuscitation and heart massage, or with unclear anamnesis (complete dilatation?); for this reason, one cannot arrive at the general conclusion that requirements should be followed that exceed current practice. Since a high radial strength often means an increased flexural strength [6,9,15], a compromise is necessary depending on the stent design. The flexural strength of expanded stents is of particular clinical importance for very tortuous vessels, e.g., in connection with long-term hypertonia, accordingly mechanical loads are exerted so that there is clearly increased hyperproliferative inflammation at the stent ends. This means that stiff stents have a much higher restenosis rate, especially at the ends [11]. An injury to the endothelium then results, causing increased smooth muscle cell immigration. In this context, the term "compliance mismatch" is coined in [8] for the situation arising between the generally stiff stent and the vessel wall that gives rise to hemodynamically unfavorable relationships. These effects are especially pronounced for lengthto-diameter ratios of > 10 and in connection with the
7 May overstretching of the vessel in the stent segment. As a result, modern coronary stents must fulfill a number of requirements regarding their geometries and mechanical characteristics [12,15,16]. The results of this in-vitro study show how far the development and improvement of structural mechanical characteristics has already come. The results also show that the future in the field of coronary stents lies less in the founding of new principles than in the improvement of known characteristic values. In addition, further new parameters, including the relationship of the stent and delivery system as a unit, are being discussed. In the future, these new parameters would also require evaluation by means of objective measurement. The influence of the stent material or stent coatings on improvements in hemocompatibility and on further reduction in the restenosis rate is also of extreme clinical importance. It is not, however, further examined in this study. References [1] Schmitz K-P, Behrend D, Lootz D, et al. Entwicklung und Testung von Stents aus bioresorbierbaren Materialien - Werkstoffseitige Möglichkeiten und strukturmechanische Grenzen. Proc. 3. Jahrestagung DGBM. Tübingen. 1998: [2] Behrend D, Lootz D, Schmitz K-P, et al. PHB as a Bioresorbable Material for Intravascular Stents. The American Journal of Cardiology. Suppl. 1998: 4S. [3] Schmidt W, Behrens P, Behrend D, et al. Fatigue analysis of coronary stents. Med. and Biolog. Eng. Comput. 1999; 37: [4] Schmidt W, Behrens P, Behrend D, et al. Measurement of mechanical properties of coronary stents according to the European Standard pren Progr Biomed Res. 1999; 1(4): [5] Rogers C, Tseng DY, Squire JS, et al. Balloon-artery interactions during stent placement, Circ. Res. 1999; 84: [6] Schmitz K-P, Behrend D, Behrens P, et al. Comparative studies of different stent designs. Progr Biomed Res. 1999; 1(4): [7] Schmitz K-P, Behrend D, Behrens P, et al. Entwicklung von Koronarstents und experimentelle Untersuchungen der strukturmechanischen Eigenschaften. VDI-Berichte. 1999; 1.463: [8] How TV, Black RA, Harris PL. Hemodynamic consequences of intravascular stent deployment. In: Endoluminal stenting. Sigwart U (Ed.). W.B. Saunders, London, 1996: [9] Dyet JF, Watts WG, Ettles DF, et al. Mechanical properties of metallic stents: How do these properties influence the choice of stent for specific lesions?, Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2000; 23: [10] Carozza JP, Hosley SE, Cohen DJ, et al. In vivo assessment of stent expansion and recoil in normal porcine coronary arteries. Circulation. 1999; 100: [11] Chalmers RTA, Hoballah JJ, Sharp WJ, et al. The effect of an intraluminal stent on neointimal hyperplasia at an end-to-side Polytetrafluoroethylene graft arterial anastomosis. Am. J. Surg. 1994; 168: [12] Eeckhout E, Kappenberger L, Goy JJ. Stents for intracoronary placement: Current status and future directions, JACC. 1996; 27: [13] Haas R. Implantation and imaging of coronary stents. Radiol. Technol. 1996; 67: [14] Schmiedl R, Schaldach M. X-ray imaging of coronary stents. Prog Biomed Res. 2000; 3(5): [15] Ozaki Y, Violaris AG, Serruys PW. New stent technologies, Progr. in Cardiovasc. Diseases. 1996; 2(39): [16] Rankin JM, Penn IM. Coronary stenting: a global perspective. ACC Current J. Rev. 1998; 7(6):
Experimental Study of Peripheral, Balloon-expandable Stent Systems
 246 May 2001 Experimental Study of Peripheral, Balloon-expandable Stent Systems W. SCHMIDT, P. BEHRENS, D. BEHREND, K.-P. SCHMITZ Institute for Biomedical Engineering, University of Rostock, Rostock, Germany
246 May 2001 Experimental Study of Peripheral, Balloon-expandable Stent Systems W. SCHMIDT, P. BEHRENS, D. BEHREND, K.-P. SCHMITZ Institute for Biomedical Engineering, University of Rostock, Rostock, Germany
Measurement of Mechanical Properties of Coronary Stents according to the European Standard pren
 February 1999 45 Measurement of Mechanical Properties of Coronary Stents according to the European Standard pren 12006-3 W. SCHMIDT, P. BEHRENS, D. BEHREND, K.-P. SCHMITZ Institute for Biomedical Engineering,
February 1999 45 Measurement of Mechanical Properties of Coronary Stents according to the European Standard pren 12006-3 W. SCHMIDT, P. BEHRENS, D. BEHREND, K.-P. SCHMITZ Institute for Biomedical Engineering,
Is a Standardized Measurement of the Elastic Recoil of Coronary Stents under Vascular Conditions Necessary and Meaningful?
 204 May 2000 Is a Standardized Measurement of the Elastic Recoil of Coronary Stents under Vascular Conditions Necessary and Meaningful? W. SCHMIDT, K. P. SCHMITZ, P. BEHRENS, D. BEHREND University of Rostock,
204 May 2000 Is a Standardized Measurement of the Elastic Recoil of Coronary Stents under Vascular Conditions Necessary and Meaningful? W. SCHMIDT, K. P. SCHMITZ, P. BEHRENS, D. BEHREND University of Rostock,
TRACKABILITY MEASUREMENT OF CORONARY STENT IN A CORONARY VESSEL MODELL
 TRACKABILITY MEASUREMET OF COROARY STET I A COROARY VESSEL MODELL Péter Szabadíts Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, 1111 Budapest, Goldmann
TRACKABILITY MEASUREMET OF COROARY STET I A COROARY VESSEL MODELL Péter Szabadíts Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, 1111 Budapest, Goldmann
A Highly Flexible Slotted Tube Stent Design Coated with a-sic:h First Clinical Experiences
 40 February 1998 A Highly Flexible Slotted Tube Stent Design Coated with a-sic:h First Clinical Experiences J. KOOLEN, C. HANEKAMP, H. BONNIER 1Catharina Hospital, Eindhoven, Netherlands Summary A new
40 February 1998 A Highly Flexible Slotted Tube Stent Design Coated with a-sic:h First Clinical Experiences J. KOOLEN, C. HANEKAMP, H. BONNIER 1Catharina Hospital, Eindhoven, Netherlands Summary A new
FLEXIBLE, BALOON EXPANDABLE
 EARLY RESULTS OF A CLINICAL TRIAL OF FLEXIBLE, BALOON EXPANDABLE COVERED STENT GRAFT IN ILIAC OCCLUSIVE DISEASE Chris LeCroy Coastal Vascular and Interventional Pensacola, Florida Clinical Trial WL GORE
EARLY RESULTS OF A CLINICAL TRIAL OF FLEXIBLE, BALOON EXPANDABLE COVERED STENT GRAFT IN ILIAC OCCLUSIVE DISEASE Chris LeCroy Coastal Vascular and Interventional Pensacola, Florida Clinical Trial WL GORE
Evaluation of Stent Performances using FEA considering a Realistic Balloon Expansion
 Evaluation of Stent Performances using FEA considering a Realistic Balloon Expansion Won-Pil Park, Seung-Kwan Cho, Jai-Young Ko, Anders Kristensson, S.T.S. Al-Hassani, Han-Sung Kim, and Dohyung Lim Abstract
Evaluation of Stent Performances using FEA considering a Realistic Balloon Expansion Won-Pil Park, Seung-Kwan Cho, Jai-Young Ko, Anders Kristensson, S.T.S. Al-Hassani, Han-Sung Kim, and Dohyung Lim Abstract
Cover Page. Author: Wang, Ancong Title: Automatic quantification of intravascular optical coherence tomography Issue Date:
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29690 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Wang, Ancong Title: Automatic quantification of intravascular optical coherence
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/29690 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Wang, Ancong Title: Automatic quantification of intravascular optical coherence
Radiation Safety Abbott Vascular. All rights reserved.
 Radiation Safety More and more complex cases are performed Complexity Index and Fluoroscopy Time 2 3 Collimators / Distances The intensity of scattered radiation is a function of exposed field size Use
Radiation Safety More and more complex cases are performed Complexity Index and Fluoroscopy Time 2 3 Collimators / Distances The intensity of scattered radiation is a function of exposed field size Use
Investigation of metallic surface area of coronary stents
 Investigation of metallic surface area of coronary stents Dóra KÁROLY 1, Miksa KOVÁCS 1, Andrew Attila TERDIK 1, Eszter BOGNÁR 1,2 1 Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Faculty of Mechanical
Investigation of metallic surface area of coronary stents Dóra KÁROLY 1, Miksa KOVÁCS 1, Andrew Attila TERDIK 1, Eszter BOGNÁR 1,2 1 Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Faculty of Mechanical
For Personal Use. Copyright HMP 2013
 Case Report J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(2):E39-E41 A Case With Successful Retrograde Stent Delivery via AC Branch for Tortuous Right Coronary Artery Yoshiki Uehara, MD, PhD, Mitsuyuki Shimizu, MD, PhD,
Case Report J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(2):E39-E41 A Case With Successful Retrograde Stent Delivery via AC Branch for Tortuous Right Coronary Artery Yoshiki Uehara, MD, PhD, Mitsuyuki Shimizu, MD, PhD,
Technical Characteristics of coronary prostheses(stents)
 Technical Characteristics of coronary prostheses(stents) 4 th Congress of Innovations in Interventional Cardiology and Electrophysiology Thessaloniki 24/25/26/11,2011 Georgios C. Bompotis Cardiologist,
Technical Characteristics of coronary prostheses(stents) 4 th Congress of Innovations in Interventional Cardiology and Electrophysiology Thessaloniki 24/25/26/11,2011 Georgios C. Bompotis Cardiologist,
Rationale and algorithm for below-the-knee acute gain optimization
 Leipzig, 01 Feb. 2018 Rationale and algorithm for below-the-knee acute gain optimization Flavio Airoldi, MD Flavio Airoldi Multimedica IRCCS Milan ITALY flavio.airoldi@multimedica.it Rationale Restenosis
Leipzig, 01 Feb. 2018 Rationale and algorithm for below-the-knee acute gain optimization Flavio Airoldi, MD Flavio Airoldi Multimedica IRCCS Milan ITALY flavio.airoldi@multimedica.it Rationale Restenosis
Angioplasty remains the most common method
 When AVF Angioplasty Fails Defining procedural success and overcoming common problems. By Thomas M. Vesely, MD Angioplasty remains the most common method of treating obstructive vascular stenoses associated
When AVF Angioplasty Fails Defining procedural success and overcoming common problems. By Thomas M. Vesely, MD Angioplasty remains the most common method of treating obstructive vascular stenoses associated
A Novel Low Pressure Self Expanding Nitinol Coronary Stent (vprotect): Device Design and FIH Experience
 A Novel Low Pressure Self Expanding Nitinol Coronary Stent (vprotect): Device Design and FIH Experience Juan F. Granada, MD Medical Director, Skirball Center for Cardiovascular Research The Cardiovascular
A Novel Low Pressure Self Expanding Nitinol Coronary Stent (vprotect): Device Design and FIH Experience Juan F. Granada, MD Medical Director, Skirball Center for Cardiovascular Research The Cardiovascular
PCI for Ostial Lesion
 PCI for Ostial Lesion ii) LAD ostial Osamu Katoh,M.D. kyoto Katsura Hospital Cardiovascular Center PCI for a LAD ostial lesion is well-known to be associated with a high restenosis rate because of excessive
PCI for Ostial Lesion ii) LAD ostial Osamu Katoh,M.D. kyoto Katsura Hospital Cardiovascular Center PCI for a LAD ostial lesion is well-known to be associated with a high restenosis rate because of excessive
Proven Performance Through Innovative Design *
 Proven Performance Through Innovative Design * Deliver Our Next Generation AV Covered Stent Results The COVERA Vascular Covered Stent builds upon proven technologies from the category leader in AV Access.
Proven Performance Through Innovative Design * Deliver Our Next Generation AV Covered Stent Results The COVERA Vascular Covered Stent builds upon proven technologies from the category leader in AV Access.
Magmaris: the impact of scaffold design and materials on reducing thrombogenicity
 : the impact of scaffold design and materials on reducing thrombogenicity Michael Joner, MD Deutsches Herzzentrum München und Deutsches Zentrum für Herz-Kreislaufforschung e.v. Potential conflicts of interest
: the impact of scaffold design and materials on reducing thrombogenicity Michael Joner, MD Deutsches Herzzentrum München und Deutsches Zentrum für Herz-Kreislaufforschung e.v. Potential conflicts of interest
Finally, the Control You Need to Deliver Accurate Treatment
 Finally, the Control You Need to Deliver Accurate Treatment LIFESTREAM Covered Stent. has joined BD When you reach for a balloon expandable stent, you require accuracy. The LIFESTREAM Balloon Expandable
Finally, the Control You Need to Deliver Accurate Treatment LIFESTREAM Covered Stent. has joined BD When you reach for a balloon expandable stent, you require accuracy. The LIFESTREAM Balloon Expandable
NC EMERGE TM PTCA Dilatation Catheter
 LEARN MORE Indications, contraindications, warnings and instructions for use can be found in the product labeling supplied with each device. Information for use only in countries with applicable health
LEARN MORE Indications, contraindications, warnings and instructions for use can be found in the product labeling supplied with each device. Information for use only in countries with applicable health
The Effect of Paclitaxel Drug-coating on the Balloon Performances
 International Conference on Manufacturing Science and Engineering (ICMSE 2015) The Effect of Paclitaxel Drug-coating on the Performances Shi Xiao Man1,2,a, Lu Chun Lan1,b and Li Xin Yue1,2,c* 1 College
International Conference on Manufacturing Science and Engineering (ICMSE 2015) The Effect of Paclitaxel Drug-coating on the Performances Shi Xiao Man1,2,a, Lu Chun Lan1,b and Li Xin Yue1,2,c* 1 College
IVUS Guided Case Review Case Performed by Frank R. Arko III, MD Charlotte, NC
 IVUS Guided Case Review Case Performed by Frank R. Arko III, MD Charlotte, NC The opinions and clinical experiences presented herein are for informational purposes only. Dr. Arko is a paid consultant for
IVUS Guided Case Review Case Performed by Frank R. Arko III, MD Charlotte, NC The opinions and clinical experiences presented herein are for informational purposes only. Dr. Arko is a paid consultant for
Intravascular Ultrasound for Complex Cases
 Intravascular Ultrasound for Complex Cases The Practical Value of IVUS Shigeru Nakamura M.D. Intravascular ultrasound imaging provides short axis information about the vessel. Image quality is not as clear
Intravascular Ultrasound for Complex Cases The Practical Value of IVUS Shigeru Nakamura M.D. Intravascular ultrasound imaging provides short axis information about the vessel. Image quality is not as clear
Mechanical Properties of the GORE TIGRIS Vascular Stent
 Mechanical Properties of the GORE TIGRIS The nitinol frame makes it strong. The fluoropolymers make it flexible. Together, they make it unique. Purpose The association of target vessel restenosis with
Mechanical Properties of the GORE TIGRIS The nitinol frame makes it strong. The fluoropolymers make it flexible. Together, they make it unique. Purpose The association of target vessel restenosis with
MULTIVESSEL PCI. IN DRUG-ELUTING STENT RESTENOSIS DUE TO STENT FRACTURE, TREATED WITH REPEAT DES IMPLANTATION
 MULTIVESSEL PCI. IN DRUG-ELUTING STENT RESTENOSIS DUE TO STENT FRACTURE, TREATED WITH REPEAT DES IMPLANTATION C. Graidis, D. Dimitriadis, A. Ntatsios, V. Karasavvides Euromedica Kyanous Stavros, Thessaloniki.
MULTIVESSEL PCI. IN DRUG-ELUTING STENT RESTENOSIS DUE TO STENT FRACTURE, TREATED WITH REPEAT DES IMPLANTATION C. Graidis, D. Dimitriadis, A. Ntatsios, V. Karasavvides Euromedica Kyanous Stavros, Thessaloniki.
PCI for Left Anterior Descending Artery Ostial Stenosis
 PCI for Left Anterior Descending Artery Ostial Stenosis Why do you hesitate PCI for LAD ostial stenosis? LAD Ostial Lesion Limitations of PCI High elastic recoil Involvement of the distal left main coronary
PCI for Left Anterior Descending Artery Ostial Stenosis Why do you hesitate PCI for LAD ostial stenosis? LAD Ostial Lesion Limitations of PCI High elastic recoil Involvement of the distal left main coronary
Keywords: Angioplasty, Explicit finite elements method, Tube hidroforming, Stents.
 Blucher Mechanical Engineering Proceedings May 2014, vol. 1, num. 1 www.proceedings.blucher.com.br/evento/10wccm AN ANALYSIS OF THE CONTACT BETWEEN THE STENT AND THE ARTERY USING TUBE HIDROFORMING SIMULATION
Blucher Mechanical Engineering Proceedings May 2014, vol. 1, num. 1 www.proceedings.blucher.com.br/evento/10wccm AN ANALYSIS OF THE CONTACT BETWEEN THE STENT AND THE ARTERY USING TUBE HIDROFORMING SIMULATION
Angiographic long-term results after implantation of the paclitaxel-eluting coronary stent coroflex please : Data under real-world conditions
 244 U. Gerk, B. Leithäuser, U. Schäfer, F. Jung, J.-W. Park Applied Cardiopulmonary Pathophysiology 14: 244-249, 2010 Angiographic long-term results after implantation of the paclitaxel-eluting coronary
244 U. Gerk, B. Leithäuser, U. Schäfer, F. Jung, J.-W. Park Applied Cardiopulmonary Pathophysiology 14: 244-249, 2010 Angiographic long-term results after implantation of the paclitaxel-eluting coronary
Nitinol biomedical devices: Design analysis
 Biomedical Engineering Nitinol biomedical devices: Design analysis M. Conti Dipartimento di Meccanica Strutturale, Università degli Studi di Pavia, Italy micheleconti82@gmail.com http://www.unipv.it/dms/auricchio
Biomedical Engineering Nitinol biomedical devices: Design analysis M. Conti Dipartimento di Meccanica Strutturale, Università degli Studi di Pavia, Italy micheleconti82@gmail.com http://www.unipv.it/dms/auricchio
Optical Coherence Tomography
 Optical Coherence Tomography Disclosure Information Demetrius Lopes MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: University Grant/Research Support: Rush University Industry Grant
Optical Coherence Tomography Disclosure Information Demetrius Lopes MD The following relationships exist related to this presentation: University Grant/Research Support: Rush University Industry Grant
Branch Pulmonary Artery Stenosis Long-term Outcomes of Endovascular Stenting
 Branch Pulmonary Artery Stenosis Long-term Outcomes of Endovascular Stenting Lee Benson MD Professor Pediatrics (Cardiology) Director, Cardiac Diagnostic & Interventional Unit The Hospital for Sick Children
Branch Pulmonary Artery Stenosis Long-term Outcomes of Endovascular Stenting Lee Benson MD Professor Pediatrics (Cardiology) Director, Cardiac Diagnostic & Interventional Unit The Hospital for Sick Children
Ruofei Jia, Zening Jin, Hong Li, Jing Han. Introduction
 Case Report Re-crossing the distal cell in bifurcation verified by using an enhanced stent visualization system and optical coherence tomography: a report of two cases Ruofei Jia, Zening Jin, Hong Li,
Case Report Re-crossing the distal cell in bifurcation verified by using an enhanced stent visualization system and optical coherence tomography: a report of two cases Ruofei Jia, Zening Jin, Hong Li,
An Adolescent Patient with Coarctation of Aorta Treated with Self-Expandable Nitinol Stent
 Case Report Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal An Adolescent Patient with Coarctation of Aorta Treated with Self-Expandable Nitinol Stent Woo Sup Shim, MD 1, Jin Young
Case Report Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal An Adolescent Patient with Coarctation of Aorta Treated with Self-Expandable Nitinol Stent Woo Sup Shim, MD 1, Jin Young
Dynamic simulation of stent deployment effects of design, material and coating
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Dynamic simulation of stent deployment effects of design, material and coating To cite this article: A Schiavone et al 2013 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 451 012032
Journal of Physics: Conference Series OPEN ACCESS Dynamic simulation of stent deployment effects of design, material and coating To cite this article: A Schiavone et al 2013 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 451 012032
Refinements in Mathematical Models to Predict Aneurysm Growth and Rupture
 Refinements in Mathematical Models to Predict Aneurysm Growth and Rupture RAMON BERGUER, a,b JOSEPH L. BULL, a,b AND KHALIL KHANAFER a a Vascular Mechanics Laboratory, Department of Biomedical Engineering,
Refinements in Mathematical Models to Predict Aneurysm Growth and Rupture RAMON BERGUER, a,b JOSEPH L. BULL, a,b AND KHALIL KHANAFER a a Vascular Mechanics Laboratory, Department of Biomedical Engineering,
Yukon Chrome PC. Translumina trust is what counts. Sirolimus Eluting CoCr Coronary Stent System. 5-Years Randomized Clinical Follow-Up
 Sirolimus Eluting CoCr Coronary Stent System Yukon Chrome PC 5-Years Randomized Clinical Follow-Up Translumina trust is what counts trust is what counts Yukon Chrome PC DES coating with excellent long-term
Sirolimus Eluting CoCr Coronary Stent System Yukon Chrome PC 5-Years Randomized Clinical Follow-Up Translumina trust is what counts trust is what counts Yukon Chrome PC DES coating with excellent long-term
FLUID MECHANICAL PERTURBATIONS INDUCED BY STENT IMPLANTATION: A NUMERICAL STUDY
 LABORATORY OF BIOLOGICAL STRUCTURE MECHANICS www.labsmech.polimi.it FLUID MECHANICAL PERTURBATIONS INDUCED BY STENT IMPLANTATION: A NUMERICAL STUDY Rossella Balossino, Francesca Gervaso, Francesco Migliavacca,
LABORATORY OF BIOLOGICAL STRUCTURE MECHANICS www.labsmech.polimi.it FLUID MECHANICAL PERTURBATIONS INDUCED BY STENT IMPLANTATION: A NUMERICAL STUDY Rossella Balossino, Francesca Gervaso, Francesco Migliavacca,
Development of Computational Models for Evaluation of Mechanical and Hemodynamic Behavior of an Intravascular Stent
 Development of Computational Models for Evaluation of Mechanical and Hemodynamic Behavior of an Intravascular Stent Kuang-Huei Lee, Hao-Ming Hsiao, Ying-Chih Liao, Yi-Hsiang Chiu, Yu-Seng Tee Dept. of
Development of Computational Models for Evaluation of Mechanical and Hemodynamic Behavior of an Intravascular Stent Kuang-Huei Lee, Hao-Ming Hsiao, Ying-Chih Liao, Yi-Hsiang Chiu, Yu-Seng Tee Dept. of
thoracic stent graft system Smallest delivery profile as from 20 F
 thoracic stent graft system Smallest delivery profile as from 20 F Third-generation thoracic stent graft system effective, precise and safe JOTEC develops stent graft systems in close collaboration with
thoracic stent graft system Smallest delivery profile as from 20 F Third-generation thoracic stent graft system effective, precise and safe JOTEC develops stent graft systems in close collaboration with
3D Printing & Echocardiography
 ASE SOTA Feb 19, 2018 3D Printing & Echocardiography Stephen H. Little, MD John S. Dunn Chair in Cardiovascular Research and Education, Associate professor, Weill Cornell Medicine Disclosures Personal
ASE SOTA Feb 19, 2018 3D Printing & Echocardiography Stephen H. Little, MD John S. Dunn Chair in Cardiovascular Research and Education, Associate professor, Weill Cornell Medicine Disclosures Personal
Vascular V12. Covered Stent. The New Standard of Care
 Vascular V12 Covered Stent The New Standard of Care Innovation Novel Thermo-Conformable Covered Stent 316L stainless steel stent completely encapsulated in a proprietary one piece eptfe film cast covering
Vascular V12 Covered Stent The New Standard of Care Innovation Novel Thermo-Conformable Covered Stent 316L stainless steel stent completely encapsulated in a proprietary one piece eptfe film cast covering
FFR Fundamentals and Measurements
 FFR Fundamentals and Measurements Ghassan S. Kassab Thomas Linnemeier Chair Professor Biomedical Engineering, Indiana University Purdue University Indianapolis Principle of FFR Q S ( P P ) / R P max d
FFR Fundamentals and Measurements Ghassan S. Kassab Thomas Linnemeier Chair Professor Biomedical Engineering, Indiana University Purdue University Indianapolis Principle of FFR Q S ( P P ) / R P max d
Evaluation of Intermediate Coronary lesions: Can You Handle the Pressure? Jeffrey A Southard, MD May 4, 2013
 Evaluation of Intermediate Coronary lesions: Can You Handle the Pressure? Jeffrey A Southard, MD May 4, 2013 Disclosures Consultant- St Jude Medical Boston Scientific Speaker- Volcano Corporation Heart
Evaluation of Intermediate Coronary lesions: Can You Handle the Pressure? Jeffrey A Southard, MD May 4, 2013 Disclosures Consultant- St Jude Medical Boston Scientific Speaker- Volcano Corporation Heart
Introduction What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease? How Do Doctors Treat Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 9
 Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
Document issued on: January 13, 2005
 Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff Non-Clinical Tests and Recommended Labeling for Intravascular Stents and Associated Delivery Systems Document issued on: January 13, 2005 For questions regarding this
Guidance for Industry and FDA Staff Non-Clinical Tests and Recommended Labeling for Intravascular Stents and Associated Delivery Systems Document issued on: January 13, 2005 For questions regarding this
Innovation by design. Technology that sets a new standard
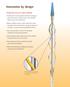 Innovation by design Technology that sets a new standard Flexible nitinol scoring element with three rectangular spiral struts works in tandem with a semi-compliant balloon to score the target lesion Balloon
Innovation by design Technology that sets a new standard Flexible nitinol scoring element with three rectangular spiral struts works in tandem with a semi-compliant balloon to score the target lesion Balloon
Lessons & Perspectives: What is the role of Cryoplasty in SFA Intervention?
 Lessons & Perspectives: What is the role of Cryoplasty in SFA Intervention? Michael Wholey, MD, MBA San Antonio, TX USA 19/06/2009 at 09:35 during 4mn as a Speaker Session: Improving Femoral Artery Recanalization
Lessons & Perspectives: What is the role of Cryoplasty in SFA Intervention? Michael Wholey, MD, MBA San Antonio, TX USA 19/06/2009 at 09:35 during 4mn as a Speaker Session: Improving Femoral Artery Recanalization
Introduction 3. What is Peripheral Vascular Disease? 5. What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease? 6
 Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease? 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease? 6 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease? 7 How
Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease? 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease? 6 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease? 7 How
Pathology of percutaneous interventions (PCI) in coronary arteries. Allard van der Wal, MD.PhD; Pathologie AMC, Amsterdam, NL
 Pathology of percutaneous interventions (PCI) in coronary arteries Allard van der Wal, MD.PhD; Pathologie AMC, Amsterdam, NL Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Definition: transcatheter opening of
Pathology of percutaneous interventions (PCI) in coronary arteries Allard van der Wal, MD.PhD; Pathologie AMC, Amsterdam, NL Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) Definition: transcatheter opening of
Complex Coronary Interventions: Bifurcations. John M. Lasala MD PhD Professor of Medicine Washington University St Louis, Missouri
 Complex Coronary Interventions: Bifurcations John M. Lasala MD PhD Professor of Medicine Washington University St Louis, Missouri Disclosures Advisory Board Boston Scientific, St. Jude Medical Speaker-
Complex Coronary Interventions: Bifurcations John M. Lasala MD PhD Professor of Medicine Washington University St Louis, Missouri Disclosures Advisory Board Boston Scientific, St. Jude Medical Speaker-
Vascular Surgery and Transplant Unit University of Catania. Pierfrancesco Veroux
 Vascular Surgery and Transplant Unit University of Catania Pierfrancesco Veroux Bologna-Palazzo dei Congressi, 23 Ottobre 2017 Disclosure Speaker name: Prof. Pierfrancesco Veroux I have the following potential
Vascular Surgery and Transplant Unit University of Catania Pierfrancesco Veroux Bologna-Palazzo dei Congressi, 23 Ottobre 2017 Disclosure Speaker name: Prof. Pierfrancesco Veroux I have the following potential
Evolution In Interventional Cardiology. Jawed Polad Jeroen Bosch Hospital s-hertogenbosch The Netherlands
 Evolution In Interventional Cardiology Jawed Polad Jeroen Bosch Hospital s-hertogenbosch The Netherlands 25 November 2010 Coronary Atherosclerosis Timeline in interventional cardiology Indications for
Evolution In Interventional Cardiology Jawed Polad Jeroen Bosch Hospital s-hertogenbosch The Netherlands 25 November 2010 Coronary Atherosclerosis Timeline in interventional cardiology Indications for
Biodegradable Stents An update and work-in
 Biodegradable Stents An update and work-in in-progress Department of Cardiology, Hideo Tamai, M.D. Metallic stents... Background induce a varing degree of thrombogenesis eg, subacute thrombosis in complex
Biodegradable Stents An update and work-in in-progress Department of Cardiology, Hideo Tamai, M.D. Metallic stents... Background induce a varing degree of thrombogenesis eg, subacute thrombosis in complex
IN-STENT RESTENOSIS. K.Boerlage-van Dijk CarVasZ 2014
 IN-STENT RESTENOSIS K.Boerlage-van Dijk CarVasZ 2014 Definition ISR Angiographic: recurrent diameter stenosis >50% at the stent segment or edges (5-mm segments adjacent to stent) Mehran system morphological
IN-STENT RESTENOSIS K.Boerlage-van Dijk CarVasZ 2014 Definition ISR Angiographic: recurrent diameter stenosis >50% at the stent segment or edges (5-mm segments adjacent to stent) Mehran system morphological
When Outcomes Matter, Design Matters
 to receive our latest news and key activities. Cordis S.M.A.R.T. Self-Expanding Nitinol Lower Extremity Solutions When Outcomes Matter, Design Matters For superficial femoral artery (SFA) and iliac lesions.
to receive our latest news and key activities. Cordis S.M.A.R.T. Self-Expanding Nitinol Lower Extremity Solutions When Outcomes Matter, Design Matters For superficial femoral artery (SFA) and iliac lesions.
Optimal assessment observation of intravascular ultrasound
 Optimal assessment observation of intravascular ultrasound Katsutoshi Kawamura and Atsunori Okamura Division of Radiology Cardiovascular Center Sakurabashi Watanabe Hospital SAKURABASHI WATANABE Hospital
Optimal assessment observation of intravascular ultrasound Katsutoshi Kawamura and Atsunori Okamura Division of Radiology Cardiovascular Center Sakurabashi Watanabe Hospital SAKURABASHI WATANABE Hospital
KEN-ICHIRO SASAKI, HIDETOSHI CHIBANA, TAKAFUMI UENO, NAOKI ITAYA, MASAHIRO SASAKI AND YOSHIHIRO FUKUMOTO
 Case Report This is Advance Publication Article Kurume Medical Journal, 63, 39-43, 2016 Successful Endovascular Treatment of Aortoiliac Bifurcation Stenosis Using an Empirically Based T and Protrude-Stenting
Case Report This is Advance Publication Article Kurume Medical Journal, 63, 39-43, 2016 Successful Endovascular Treatment of Aortoiliac Bifurcation Stenosis Using an Empirically Based T and Protrude-Stenting
Yukon Choice PC Translumina trust is what counts
 Sirolimus Eluting Coronary Stent System 5-Years Randomized Clinical Follow-Up Translumina trust is what counts trust is what counts DES with excellent long-term clinical outcome The Translumina PC drug-eluting
Sirolimus Eluting Coronary Stent System 5-Years Randomized Clinical Follow-Up Translumina trust is what counts trust is what counts DES with excellent long-term clinical outcome The Translumina PC drug-eluting
A comparison of balloon- and self-expanding stents
 Min Invas Ther & Allied Technol 2002: 11(4) 173 178 A comparison of balloon- and self-expanding stents T.W. Duerig 1 and M. Wholey 2 1 Nitinol Devices and Components, Westinghouse Road, Fremont, CA, USA
Min Invas Ther & Allied Technol 2002: 11(4) 173 178 A comparison of balloon- and self-expanding stents T.W. Duerig 1 and M. Wholey 2 1 Nitinol Devices and Components, Westinghouse Road, Fremont, CA, USA
Is a Stent or Scaffold Necessary in The SFA?
 1 2 3 Is a Stent or Scaffold Necessary in The SFA? Stents were developed to optimize acute results after angioplasty Specifically, stents are universally accepted to manage flow limiting dissections and
1 2 3 Is a Stent or Scaffold Necessary in The SFA? Stents were developed to optimize acute results after angioplasty Specifically, stents are universally accepted to manage flow limiting dissections and
Original paper. Introduction. Material and methods. Aim
 Original paper Relation between coronary plaque calcium deposits as described by computed tomography coronary angiography and acute results of stent deployment as assessed by intravascular ultrasound Jerzy
Original paper Relation between coronary plaque calcium deposits as described by computed tomography coronary angiography and acute results of stent deployment as assessed by intravascular ultrasound Jerzy
Current DES designs and expansion capacity testing
 construction of Sagrada Família basilica had commenced in 1882 anticipated completion date: 2026 Current DES designs and expansion capacity testing N. FOIN, MSc, PhD INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR CIRCULATORY
construction of Sagrada Família basilica had commenced in 1882 anticipated completion date: 2026 Current DES designs and expansion capacity testing N. FOIN, MSc, PhD INTERNATIONAL CENTRE FOR CIRCULATORY
ASX Small to Mid Caps New York Conference. March 1, 2012
 ASX Small to Mid Caps New York Conference March 1, 2012 Important Notice Not an Offer for Securities This presentation has been prepared by REVA Medical, Inc. (REVA or the Company) solely for its use at
ASX Small to Mid Caps New York Conference March 1, 2012 Important Notice Not an Offer for Securities This presentation has been prepared by REVA Medical, Inc. (REVA or the Company) solely for its use at
Access More Patients. Customize Each Seal.
 Access More. Customize Each Seal. The Least Invasive Path Towards Proven Patency ULTRA LOW PROFILE TO EASE ADVANCEMENT The flexible, ultra-low 12F ID Ovation ix delivery system enables you to navigate
Access More. Customize Each Seal. The Least Invasive Path Towards Proven Patency ULTRA LOW PROFILE TO EASE ADVANCEMENT The flexible, ultra-low 12F ID Ovation ix delivery system enables you to navigate
Shockwave Intravascular Lithotripsy System treatment of calcified lesions: Intravascular OCT analysis
 Shockwave Intravascular Lithotripsy System treatment of calcified lesions: Intravascular OCT analysis Andrew Holden, MBChB, FRANZCR, EBIR Director of Interventional Radiology Auckland, New Zealand LINC
Shockwave Intravascular Lithotripsy System treatment of calcified lesions: Intravascular OCT analysis Andrew Holden, MBChB, FRANZCR, EBIR Director of Interventional Radiology Auckland, New Zealand LINC
3D Printing & Echocardiography
 Echo Hawaii Jan 18, 2018 3D Printing & Echocardiography Stephen H. Little, MD John S. Dunn Chair in Cardiovascular Research and Education, Associate professor, Weill Cornell Medicine Rapid Prototyping
Echo Hawaii Jan 18, 2018 3D Printing & Echocardiography Stephen H. Little, MD John S. Dunn Chair in Cardiovascular Research and Education, Associate professor, Weill Cornell Medicine Rapid Prototyping
-vita THORACIC 3G. Stent Graft System SOLUTIONS FOR VASCULAR DISEASE
 Stent Graft SOLUTIONS FOR VASCULAR DISEASE 1 PURE PERFORMANCE AND QUALITY: STENT GRAFT SYSTEMS BY JOTEC JOTEC is an innovation-oriented company with consistent focus on its core competencies: the development
Stent Graft SOLUTIONS FOR VASCULAR DISEASE 1 PURE PERFORMANCE AND QUALITY: STENT GRAFT SYSTEMS BY JOTEC JOTEC is an innovation-oriented company with consistent focus on its core competencies: the development
EXAMINATION OF MECHANICAL AND MEDICAL APPLICATION PROPERTIES OF CORONARY STENTS
 EXAMINATION OF MECHANICAL AND MEDICAL APPLICATION PROPERTIES OF CORONARY STENTS Zsófia Bálint-Pataki Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering János Dobránszky
EXAMINATION OF MECHANICAL AND MEDICAL APPLICATION PROPERTIES OF CORONARY STENTS Zsófia Bálint-Pataki Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering János Dobránszky
PCI for Bifurcation Coronary Lesion
 PCI for Bifurcation Coronary Lesion Bifurcation Lesions PCI is Challenging Higher acute complication Lower success rates Higher restenosis & TLR Restenosis Rate 21 ~ 57% TLR 8 ~ 43% Event Free Survival
PCI for Bifurcation Coronary Lesion Bifurcation Lesions PCI is Challenging Higher acute complication Lower success rates Higher restenosis & TLR Restenosis Rate 21 ~ 57% TLR 8 ~ 43% Event Free Survival
Acute dissections of the descending thoracic aorta (Debakey
 Endovascular Treatment of Acute Descending Thoracic Aortic Dissections Nimesh D. Desai, MD, PhD, and Joseph E. Bavaria, MD Acute dissections of the descending thoracic aorta (Debakey type III or Stanford
Endovascular Treatment of Acute Descending Thoracic Aortic Dissections Nimesh D. Desai, MD, PhD, and Joseph E. Bavaria, MD Acute dissections of the descending thoracic aorta (Debakey type III or Stanford
XIENCE Sierra INTRODUCING
 INTRODUCING Sierra With the safety you ve always relied on and the deliverability you ve always wanted, choosing the right stent is now an easier decision. START 2017 Abbott. All rights reserved. AP2944678-OUS
INTRODUCING Sierra With the safety you ve always relied on and the deliverability you ve always wanted, choosing the right stent is now an easier decision. START 2017 Abbott. All rights reserved. AP2944678-OUS
HCS Working Group Seminars Macedonia Pallas Hotel, Friday 21 st February Drug-eluting stents Are they all equal?
 HCS Working Group Seminars Macedonia Pallas Hotel, Friday 21 st February 2014 Drug-eluting stents Are they all equal? Vassilis Spanos Interventional Cardiologist, As. Director 3 rd Cardiology Clinic Euroclinic
HCS Working Group Seminars Macedonia Pallas Hotel, Friday 21 st February 2014 Drug-eluting stents Are they all equal? Vassilis Spanos Interventional Cardiologist, As. Director 3 rd Cardiology Clinic Euroclinic
Angiographic and Intravascular Ultrasound Predictors of In-Stent Restenosis
 1630 JACC Vol. 32, No. 6 Angiographic and Intravascular Ultrasound Predictors of In-Stent Restenosis SHUNJI KASAOKA, MD, JONATHAN M. TOBIS, MD, FACC, TATSURO AKIYAMA, MD,* BERNHARD REIMERS, MD,* CARLO
1630 JACC Vol. 32, No. 6 Angiographic and Intravascular Ultrasound Predictors of In-Stent Restenosis SHUNJI KASAOKA, MD, JONATHAN M. TOBIS, MD, FACC, TATSURO AKIYAMA, MD,* BERNHARD REIMERS, MD,* CARLO
Intravascular Imaging Insights into the Mechanism of Action of Focal Force Balloon Angioplasty
 LINC 2015 Global Expert Exchange Forum January 28, 2015 Intravascular Imaging Insights into the Mechanism of Action of Focal Force Balloon Angioplasty Sahil A. Parikh, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine
LINC 2015 Global Expert Exchange Forum January 28, 2015 Intravascular Imaging Insights into the Mechanism of Action of Focal Force Balloon Angioplasty Sahil A. Parikh, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine
CYPHER (Polymer-based Sirolimus-eluting DES) New Stent Platforms. Campbell Rogers, M.D. Chief Technology Officer
 Ground breaking, Life changing CYPHER (Polymer-based Sirolimus-eluting DES) New Stent Platforms Campbell Rogers, M.D. Chief Technology Officer Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I am a full-time
Ground breaking, Life changing CYPHER (Polymer-based Sirolimus-eluting DES) New Stent Platforms Campbell Rogers, M.D. Chief Technology Officer Disclosure Statement of Financial Interest I am a full-time
Malperfusion Syndromes Type B Aortic Dissection with Malperfusion
 Malperfusion Syndromes Type B Aortic Dissection with Malperfusion Jade S. Hiramoto, MD, MAS April 27, 2012 Associated with early mortality Occurs when there is end organ ischemia secondary to aortic branch
Malperfusion Syndromes Type B Aortic Dissection with Malperfusion Jade S. Hiramoto, MD, MAS April 27, 2012 Associated with early mortality Occurs when there is end organ ischemia secondary to aortic branch
Complex PCI. Your partner in complex PCI: In-stent restenosis (ISR)
 Comple PCI Your partner in comple PCI: Your partner in comple PCI: Philips provides a portfolio of specialty coronary diagnostic and therapy devices that enable safe and effective treatment of a wide variety
Comple PCI Your partner in comple PCI: Your partner in comple PCI: Philips provides a portfolio of specialty coronary diagnostic and therapy devices that enable safe and effective treatment of a wide variety
An Overview of Post-EVAR Endoleaks: Imaging Findings and Management. Ravi Shergill BSc Sean A. Kennedy MD Mark O. Baerlocher MD FRCPC
 An Overview of Post-EVAR Endoleaks: Imaging Findings and Management Ravi Shergill BSc Sean A. Kennedy MD Mark O. Baerlocher MD FRCPC Disclosure Slide Mark O. Baerlocher: Current: Consultant for Boston
An Overview of Post-EVAR Endoleaks: Imaging Findings and Management Ravi Shergill BSc Sean A. Kennedy MD Mark O. Baerlocher MD FRCPC Disclosure Slide Mark O. Baerlocher: Current: Consultant for Boston
Intravascular Ultrasound
 May 2008 Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Intravascular Ultrasound Matthew Altman, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC Department of Radiology Presentation Overview 1. Patient
May 2008 Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Intravascular Ultrasound Matthew Altman, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC Department of Radiology Presentation Overview 1. Patient
Guide Wires design and selection Abbott Vascular. All rights reserved.
 Guide Wires design and selection the cardiac catheter was...the key in the lock Cournand AF, Nobel lecture December 11, 1956; nowadays, the coronary guidewire is the master key to all locks Colombo et
Guide Wires design and selection the cardiac catheter was...the key in the lock Cournand AF, Nobel lecture December 11, 1956; nowadays, the coronary guidewire is the master key to all locks Colombo et
Balloon Expandable Covered Stents. Suddenly a Crowded Space
 Novel Balloon Expandable Covered Stents for Aorto-iliac Occlusive Disease: New Trial Data makes for an Interesting Balloon Expandable Covered Stents Comparison in Aorto-iliac Occlusive Disease: Andrew
Novel Balloon Expandable Covered Stents for Aorto-iliac Occlusive Disease: New Trial Data makes for an Interesting Balloon Expandable Covered Stents Comparison in Aorto-iliac Occlusive Disease: Andrew
malapposition assessed by OCT
 Stent t coverage and malapposition assessed by OCT Myeong-Ki Hong, M.D. Ph D Professor of Medicine Division of Cardiology, Severance Cardiovascular Hospital Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul,
Stent t coverage and malapposition assessed by OCT Myeong-Ki Hong, M.D. Ph D Professor of Medicine Division of Cardiology, Severance Cardiovascular Hospital Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul,
Drug eluting balloons in CAD
 Drug eluting balloons in CAD Ioannis Iakovou, MD, PhD Interventional Cardiology 1 st Cath Lab Onassis Cardiac Surgery Center Drug-Eluting Balloons (DEB) Technology and Applications 1. Special Features
Drug eluting balloons in CAD Ioannis Iakovou, MD, PhD Interventional Cardiology 1 st Cath Lab Onassis Cardiac Surgery Center Drug-Eluting Balloons (DEB) Technology and Applications 1. Special Features
Making the difference with Live Image Guidance
 Interventional Cardiology AlluraClarity Making the difference with Live Image Guidance Diagnosis and treatment of coronary artery diseases and atherosclerosis Where/who The First Bethune Hospital of Jilin
Interventional Cardiology AlluraClarity Making the difference with Live Image Guidance Diagnosis and treatment of coronary artery diseases and atherosclerosis Where/who The First Bethune Hospital of Jilin
New Cardiac Technologies. Melva Meminger MSN, RN, CCRN
 New Cardiac Technologies Melva Meminger MSN, RN, CCRN What s New in Cardiac Care? Bigger is not always better: the new smaller Loop recorders First we burned and now we freeze (sometimes!): Cryoablation
New Cardiac Technologies Melva Meminger MSN, RN, CCRN What s New in Cardiac Care? Bigger is not always better: the new smaller Loop recorders First we burned and now we freeze (sometimes!): Cryoablation
Numerical Analysis of the Influence of Stent Parameters on the Fatigue Properties
 Numerical Analysis of the Influence of Stent Parameters on the Fatigue Properties Lin Chen, Shen Jingfeng & Chen Bing School of mechanical engineering, University of Shanghai for Science & Technology,
Numerical Analysis of the Influence of Stent Parameters on the Fatigue Properties Lin Chen, Shen Jingfeng & Chen Bing School of mechanical engineering, University of Shanghai for Science & Technology,
Clinical Application of OCT in Stent Evaluation
 Imaging & Physiology Summit 2010 in Soul #1. Basics of Image Interpretation: IVUS/VH/OCT Clinical Application of OCT in Stent Evaluation Mitsuyasu Terashima, MD, PhD, FACC Stent implantation Stent Apposition
Imaging & Physiology Summit 2010 in Soul #1. Basics of Image Interpretation: IVUS/VH/OCT Clinical Application of OCT in Stent Evaluation Mitsuyasu Terashima, MD, PhD, FACC Stent implantation Stent Apposition
BME. Lesson Title. Grade Level. Stent Design 6-8
 BME Lesson Title Stent Design Grade Level 6-8 Authors Dr. Brian Davis, Dr. Carin Helfer Purpose This activity aims at using everyday materials to design and develop stents to unclog blood vessels. Materials
BME Lesson Title Stent Design Grade Level 6-8 Authors Dr. Brian Davis, Dr. Carin Helfer Purpose This activity aims at using everyday materials to design and develop stents to unclog blood vessels. Materials
Next Generation of DCB: Efficacy and tolerance of drug-coated hyper-compliant balloons (DCHCB) in peripheral arteries of swine
 Next Generation of DCB: Efficacy and tolerance of drug-coated hyper-compliant balloons (DCHCB) in peripheral arteries of swine Maciej Kusmierczuk 1 ; Stephanie Bienek, PhD 1 ; Sebastian Schurmann 1 ; Antje
Next Generation of DCB: Efficacy and tolerance of drug-coated hyper-compliant balloons (DCHCB) in peripheral arteries of swine Maciej Kusmierczuk 1 ; Stephanie Bienek, PhD 1 ; Sebastian Schurmann 1 ; Antje
Case Report Successful Implantation of a Coronary Stent Graft in a Peripheral Vessel
 Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 725168, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/725168 Case Report Successful Implantation of a Coronary Stent Graft in a Peripheral Vessel Alexander
Case Reports in Vascular Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 725168, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/725168 Case Report Successful Implantation of a Coronary Stent Graft in a Peripheral Vessel Alexander
What Coronary Specialists Teach The Vascular Community About Vessel Prep? Tony Das, MD Texas Health, Dallas Dallas, Texas
 What Coronary Specialists Teach The Vascular Community About Vessel Prep? Tony Das, MD Texas Health, Dallas Dallas, Texas Stent Era Lessons on Vessel Preparation Under expanded stent consequences Abrupt
What Coronary Specialists Teach The Vascular Community About Vessel Prep? Tony Das, MD Texas Health, Dallas Dallas, Texas Stent Era Lessons on Vessel Preparation Under expanded stent consequences Abrupt
Indications for use. Contraindications within the United States
 Indications for use Indications within the United States The GORE TAG Thoracic Endoprosthesis is intended for endovascular repair of all lesions of the descending thoracic aorta, including: Isolated lesions
Indications for use Indications within the United States The GORE TAG Thoracic Endoprosthesis is intended for endovascular repair of all lesions of the descending thoracic aorta, including: Isolated lesions
Expanding to every demand: The GORE VIABAHN VBX Stent Graft
 Expanding to every demand: The GORE VIABAHN VBX Stent Graft GORE, VIABAHN, and designs are trademarks of W. L. Gore & Associates. 2017 W. L. Gore & Associates, Inc. Program Faculty Martin Austermann, MD
Expanding to every demand: The GORE VIABAHN VBX Stent Graft GORE, VIABAHN, and designs are trademarks of W. L. Gore & Associates. 2017 W. L. Gore & Associates, Inc. Program Faculty Martin Austermann, MD
NON-COMPLIANT PTCA RAPID EXCHANGE DILATATION CATHETER
 Page 1 of 5 NON-COMPLIANT PTCA RAPID EXCHANGE DILATATION CATHETER STERILE. SINGLE USE ONLY. Sterilized with ethylene oxide gas. Non pyrogenic. Do not resterilize. Do not use opened or damaged packages.
Page 1 of 5 NON-COMPLIANT PTCA RAPID EXCHANGE DILATATION CATHETER STERILE. SINGLE USE ONLY. Sterilized with ethylene oxide gas. Non pyrogenic. Do not resterilize. Do not use opened or damaged packages.
Left main coronary artery (LMCA): The proximal segment
 Anatomy and Pathology of Left main coronary artery G Nakazawa Tokai Univ. Kanagawa, Japan 1 Anatomy Difinition Left main coronary artery (LMCA): The proximal segment RCA AV LAD LM LCX of the left coronary
Anatomy and Pathology of Left main coronary artery G Nakazawa Tokai Univ. Kanagawa, Japan 1 Anatomy Difinition Left main coronary artery (LMCA): The proximal segment RCA AV LAD LM LCX of the left coronary
ABDOMINAL XT ABDOMINAL STENT GRAFT SYSTEM
 ABDOMINAL XT ABDOMINAL STENT GRAFT SYSTEM Pure performance and quality: Stent graft systems by JOTEC JOTEC is an innovation-oriented company with consistent focus on its core competencies: the development
ABDOMINAL XT ABDOMINAL STENT GRAFT SYSTEM Pure performance and quality: Stent graft systems by JOTEC JOTEC is an innovation-oriented company with consistent focus on its core competencies: the development
Sirolimus Nanocrystal Balloon Based Delivery for Coronary DES ISR
 Sirolimus Nanocrystal Balloon Based Delivery for Coronary DES ISR DR. SAMEER I DANI Director, Department of Cardiology, Apollo Hospital & Life Care Institute (LIMSAR), Ahmedabad, India. IN STENT RESTENOSIS
Sirolimus Nanocrystal Balloon Based Delivery for Coronary DES ISR DR. SAMEER I DANI Director, Department of Cardiology, Apollo Hospital & Life Care Institute (LIMSAR), Ahmedabad, India. IN STENT RESTENOSIS
Clinical Value of OCT. Guidance for Coronary Stenting. Giulio Guagliumi, MD
 Clinical Value of OCT Guidance for Coronary Stenting Giulio Guagliumi, MD 100 % Endovascular Imaging Indications of use 87.5 % 75 % 57.5 % 50 % 45 % 25 % 15 % 0 Lesion morphology Stent optimization Lesion
Clinical Value of OCT Guidance for Coronary Stenting Giulio Guagliumi, MD 100 % Endovascular Imaging Indications of use 87.5 % 75 % 57.5 % 50 % 45 % 25 % 15 % 0 Lesion morphology Stent optimization Lesion
Imaging, it s central role in planning and guiding intervention. Prof. Luis Izquierdo. MD, PhD, FEBVS
 Imaging, it s central role in planning and guiding intervention Prof. Luis Izquierdo. MD, PhD, FEBVS IMPORTANT INFORMATION: These materials are intended to describe common clinical considerations and procedural
Imaging, it s central role in planning and guiding intervention Prof. Luis Izquierdo. MD, PhD, FEBVS IMPORTANT INFORMATION: These materials are intended to describe common clinical considerations and procedural
RECOMMENDED INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
 Rapid Exchange PTCA Dilatation Catheter RECOMMENDED INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Available in diameters 1.25mm to 4.5mm and in lengths 09mm to 40mm Caution: This device should be used only by physicians trained
Rapid Exchange PTCA Dilatation Catheter RECOMMENDED INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Available in diameters 1.25mm to 4.5mm and in lengths 09mm to 40mm Caution: This device should be used only by physicians trained
