JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 10 Page October 2017
|
|
|
- Betty Shepherd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: ISSN (e) x ISSN (p) DOI: Original Article Bedside Prediction of Correct Length of Right Internal Jugular Venous Catheters Based on Anatomical Land Marks Authors Joshi VS 1, Pawar HS 2, Hasnain S 3 1 Associate Professor, Dept of Cardiac Anaesthesiology, Military Hospital CTC, (AFMC), Pune, India 2 Post Graduate Trainee in Anaesthesiology, Armed Forces Medical College, Pune, India 3 Professor, Dept of Anaesthesiology and Critical Care, Armed Forces Medical College, Pune, India Corresponding Author Col V S Joshi Sr Adv, Cardiac Anaesthesiology, Dept of Anaesthesiology and Critical Care Command Hospital Air Force, Bangalore, India, vs_joshi2003@yahoo.com Abstract Background: Correct positioning of the central venous catheter tip near or at the junction of the superior vena cava and right atrium is necessary for better monitoring and avoid complications.the anatomical landmark method is a simpler, cost effective, and performed at bedside, thereby facilitating safe positioning of the CVC tip. Therefore this study was conducted to compare the accuracy of the two method of central venous catheter positioning based on anatomical landmarks and Trans Eosophageal Echography. Methods: After obtaining approval of hospital ethical committee and informed written consent 200 adult patients of either sex scheduled to undergo cardiac surgery were randomly allocated to Group 1,(Anatomical landmark) and Group 2 (Trans-esophageal echo-cardiography group). The right internal jugular vein was cannulated to a depth calculated from apex of the sternocleidomastoid triangle and the junction of superior and middle one third of the manubrium and under the guidance of trans-esophageal echo-cardiography till SVC-RA junction respectively. The catheter was identified on TEE by Saline flush test. Catheter tip was considered acceptable up to 10mm to SVC RA junction in both the groups on TEE. Results: The power of study was 80% and level of significance as 0.05.The two groups were matched. The average length of catheter inserted in anatomical landmark group was 10.36± 1.34 cm and in TEE group was at 10.90± 0.96 cm (p-value < 0.05).65% of catheter had correct placement of tip by anatomical landmark as assessed by TEE (p value <0.001). Out of 65, 40 had tip placed above SVC-RA junction with the mean distance ± 1.78 mm and 4 had tip placed below the SVC-RA junction with the mean distance 7.75 ±2.87 mm and 21 tip was positioned at the SVC-RA junction on TEE.TEE guided catheter insertion resulted in 100% correct placement. Conclusion: In our study we found that the anatomical landmark method is 65% accurate compared to TEE guided central venous catheter insertion. At the bedside, in an emergency situation where vascular access takes priority, anatomical landmark method can be safely practiced to insert central venous catheter to an appropriate depth. Keywords: Internal jugular venous catheters, anatomical landmarks. Joshi VS et al JMSCR Volume 05 Issue 10 October 2017 Page 28942
2 Introduction Cannulation of a large central vein is the standard clinical practice, done usually through the internal jugular vein (IJV), the subclavian vein, and the femoral vein for the administration of vasoactive drugs, rapid fluid resuscitation, blood products and parenteral nutrition. In addition, the pressure in the central veins serve as a useful monitor of the hemodynamic status of critically ill patients (1,2,3). There are various method for correct placement of the CVC catheter tip at the junction of SVC and Rt atrium viz. landmark techniques, Chest X-ray, ECG and USG guided. The anatomical guided method is most widely used especially in emergency settings. The aim of the study is to compare insertion depth of the central venous catheter (CVC) through the Right Internal Jugular Vein based on aqnatomical landmarks and Trans Esophageal Echocardiography (TEE) guided CVC insertion technique, so as to assess the accuracy of the method of CVC positioning based on anatomical landmarks,which is also simpler, cost effective and can easily be performed at bedside without much aids. Methods and material After approval of hospital ethical committee and informed written consent, 200 adults of either sex scheduled for cardiac surgery were randomly allocated to Group1 (anatomical landmark group) and Group2 (Trans-esophageal echo-cardiography group) with 100 patients in each group. The random allocation was done using concealed envelope technique. After attaching all monitors,induction and intubation, under strict asepsis the Right Internal Jugular Vein was cannulated in both the groups using 7.5Fr double lumen /triple lumen (16 and 18 G) 15 cm long central venous catheter. The method of insertion in group 1 and group 2 were to a depth calculated from the external topographic landmarks and under the guidance of trans-esophageal echo-cardiography respectively. In the Group 1(Anatomical landmarkgroup)the patients were positioned for landmark marking by giving the head tilt of degree to left in the preoperative room. Two topographic points were marked on the patient s skin, using surgical skin marker. The first point (A) was located at the apex of the triangle formed by a sternal and clavicular head of sternocleidomastoid muscle. The second point (B) was drawn at the manubrium-coastal joint on a transverse line situated at the junction between the middle third and superior third of sternal manubrium. The distance between point (A) and point (B) was measured using ruler. The distance represents the final CVC length insertion in cm in this group. Fig. 1 Figure showing surface anatomical landmarks for Right IJV cannulation In the Group 2. (Trans-Esophageal Echo- Cardiography Group) technique of RIJV was same as in Group1 but the CVC catheter was inserted under TEE guidance in SVC till SVC-RA junction. TEE was performed by trained anaesthesiologist and the catheter tip was identified on TEE by saline flush test. The catheter tip was considered acceptable up to 10mm to SVC RA junction in both the groups on TEE. Fig. 2 Figure showing TEE image ME Bicaval view showing SVC-RA junction and catheter tip Joshi VS et al JMSCR Volume 05 Issue 10 October 2017 Page 28943
3 Catheter tip position was considered acceptable up to 2 cm above and 1cm below the carina in both the groups on Chest X-ray. The TEE machine used in study was ie33 Philips Diagnostic Ultrasound System with S73t port. After surgery, an anterior-posterior chest x ray was performed with patient lying in supine position with his/her head in neutral position in Intensive Care Unit. The chest x-ray was analysed by a radiologist, who was blinded to the study population groups. The data was tabulated and statistically analysed using SPSS version 21. Results As CVC cannulation cannot be done by both the techniques in same patient, the study population was randomly divided into two groups (Group1 & Group2). The two groups were matched based on demographic variables. Table1.Demographic Variables Variables Group1(n=100) Group2(n=100) P value Sex(M/F) 84/16 73/ Age(Years) 53.28± ± Height(CM) ± ± Weight(Kg) 62.79± ± BMI 23.40± ± Thyroidmanubrium distance(cm) 5.93± ± The average length of central venous catheter inserted and fixed in anatomical landmark group was at 10.36± 1.34 cm and in TEE group was at 10.90± 0.96 cm and by using 2 independent sample t-test, p-value obtained was< 0.05, therefore there was significant difference between mean distance between the groups. Out of 100 patients in group 1, 65% of patients had correct placement of catheter tip by anatomical landmark as assessed by TEE. On the other hand, TEE guided catheter insertion resulted in 100% correct placement. The difference between two groups obtained was statistically significant in our study. Out of 65 patients, 40 patient had tip placed above SVC-RA junction with the mean distance 6.785± 1.78 mm and 4 patients had tip placed below the SVC-RA junction with the mean distance 7.75± 2.87 mm. There were 21 patients in anatomical landmark group in whom catheter tip was positioned at the SVC-RA junction on TEE. In group 1, out of 100 catheters, 54 catheter tips were at carina on post-op chest x-ray. In group 2, out of 100 catheters placed correctly on TEE, 77 catheter tips were at carina on post-op chest x-ray. In total 200 patients, Out of 165 catheters that are correctly placed at SVC RA junction on TEE only 113 catheters were found to be corroborating radiologically on CXR. The inference drawn is the x ray can detect % (P value 0.077) of correctly placed catheter on TEE as shown in fig3. Fig.3 Correlation between correct placement of catheter tip on TEE and X-ray Joshi VS et al JMSCR Volume 05 Issue 10 October 2017 Page 28944
4 There was poor correlation between the height of the patient and the depth of catheter insertion as shown in fig 4 Fig. 4 Correlation between height of the patients and depth of central venous catheter insertion Discussion Correct placement of central venous catheter is of prime importance for proper functioning of central venous access devices and avoiding complications. There is no gold standard in estimation of correct length of central venous catheter insertion. The present study included a total of 100 cases in each group who were demographically similar. Out of 100patients in group 1, 65% of patients had correct placement of catheter tip by anatomical landmark method as assessed by TEE. Dean B. Andropoulos et al. In their study involving 145 pediatric patients, studied the comparison of two techniques (TEE guided and Anatomical landmark) of CVC (right IJV or Subclavian) insertion and observed that 86.3% of patients have correct placement of catheter tip by anatomical landmark as assessed by TEE. (P=0.01) (4) In a prospective randomized study by Ezri T et al. on 100 patients, for the comparison of CVC insertion by topographic landmark technique and predetermined length (15 cm) insertion, 98% of patients in landmark technique were found to have catheter tip positioned at right place on chest X- ray. In this the author did not use TEE to check the position of catheter tip as in our study (5) Lee JH et al. compared the accuracy of CVC tip localization between ECG- and landmark-guided catheterization and concluded that central venous catheterization via the right IJV, landmark guidance was comparable with ECG guidance with regard to CVC tip positioning in the superior vena cava (6) In a study by Myung-Chun Kim et al. to determine whether the topographical measurement along the course of the central veins can estimate the approximate insertion depths of central venous catheters (CVC). The CVC locations could be predicted with a margin of error between 2.2 cm below the carina and 2.3 cm above the carina in 95% of patients (7) The above studies have done the IJV cannulation using different landmark techniques. These studies have not used the TEE to confirm the placement of the catheter. The present study used both TEE and CXR to confirm the placement of the catheter tip. Hence, in all the studies mentioned above, no studies have technique of catheter placement and confirmation comparable with this study. Joshi VS et al JMSCR Volume 05 Issue 10 October 2017 Page 28945
5 In anatomical landmark inserted catheter group, we found 27 catheter tips above and 8 catheter tips below the SVC-RA junction when assessed on TEE. However, we did not find complications due to malpositioning of catheters. TEE guided catheter insertion resulted in 100% correct placement. This finding is similar to a study by Dean B. Andropoulos et al. in pediatric population, which showed that 100% of patients have correct placement of catheter tip by TEE (4). The average length of central venous catheter inserted and fixed in anatomical landmark group is at / cm and fixed in TEE group is at / cm. Rash Kujur et al determined the length of the catheter insertion through Rt IJV by central approach in Indian population and concluded that the catheter can be fixed at a length of cm in males and cm in females in the right IJV (8). Out of 165 catheters that are correctly placed at SVC RA junction on TEE, 113 catheter were only found to be corroborating radiologically on CXR. The inference drawn is the X ray can detect % (P value 0.77) of correctly placed catheter on TEE. In a study bydean B. Andropoulos, Stephen A. Stayer et al. found 84.4% catheter tips were in correct position on chest X-ray when compared with TEE. (4) The Food and Drug Administration guidelines suggest that the tip of central venous catheter should not be positioned in the right atrium (9). Koung-Shing Chu et al. have done a study for accurate central venous catheter placement, comparing Intravenous Electrocardiography and Surface Landmark Techniques using Transesophageal Echocardiography. 81.3% of catheters in IV-ECG Group and 76.7% of Catheters in Surface Landmark (P = 0.52) were in the radiographically defined proper position. The remainder 20% of the catheters appeared in the mid portion of the atrial cavity. (10) Joshi AM et al. compared the electrocardiography guided technique to Peres' formula for Right IJV central venous insertion. They showed that 48% patients had over-insertion of the catheter in to the right atrium when catheter was inserted blindly using Peres' formula of height (in cm)/10 (11). Eagle et al. had shown the lack of correlation between patient s height, length of neck on CT scan study of the neck (12). The routine airway assessment of the patient in preoperative period reveals different proportions among the height and thorax and the neck of the patients. Similarly, our study showed poor correlation between length of catheter placement and height of the patient. This emphasis the need to develop alternative techniques to determine the length of catheter placement rather than using generalized crude formulae. Conclusion Confirmation of the correct placement of the CVC catheter can be done by a number of techniques like USG, ECG, fluoroscopy and TEE guided but for emergency vascular access where we can t find immediate resources, anatomical landmark technique remains a method of choice to determine approximate length of central venous catheter to be inserted and fixed. This method should decrease serious complications of CVC insertion such as vascular perforation, arrhythmias, and cardiac tamponade to a greater extent as compared to blind predetermined length insertion technique. In our study we found that anatomical landmark technique is 65% accurate compared to TEE guided central venous catheter insertion. In cardiac operating rooms, TEE is available inevitably, but at bedside, especially in an emergency situation where vascular access takes priority, anatomical landmark method can be safely practiced to insert central venous catheter to an appropriate depth of about cm in an adult. Conflicts of interest The authors have no conflicts of interest. References 1. Mer M. Intravascular catheter sepsis. S Afr J Crit Care. 1999:15(2): Joshi VS et al JMSCR Volume 05 Issue 10 October 2017 Page 28946
6 2. Mer M. Vascular catheter related infection. Clinical Intensive Care. 2001;12(2): Mer M. Intravascular catheter related infection: current concepts. S Afr J Crit Care.2006;22(1): Dean B. Andropoulos et al. A Controlled Study of Trans esophageal Echocardiography to Guide Central Venous Catheter Placement in Congenital Heart Surgery Patients. AnesthAnalg. 1999;89: Ezri T et al Correct depth of insertion of right internal jugular central venous catheters based on external landmarks: avoiding the right atrium. J Cardiothorac Vas canesth. 2007;21(4): Lee JH et al. Comparision of the bedside central venous catheter placement techniques: Landmark versus electrocardiogram guidance. Br J Anaesth. 2009;102(5): Myung-Chun Kim et al. An estimation of right and left sided central venous catheter insertion depth using measurement of surface landmarks along the course the of central veins. AnesthAnalg. 2011;122: Rash Kujur, S. Manimala Rao, and M. Mrinal How correct is the correct length for central venous catheter insertion. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2009;13(3): Food and Drug administration: precaution necessary with central venous catheter.fda Task Force. FDA drug BULL. July Koung-Shing Chu et al. Accurate Central Venous Port-A Catheter Placement: Intravenous Electrocardiography and Surface Landmark Techniques Compared by Using Transesophageal Echocardiography. Anesth Analg.2004;98: Anish M. Joshi. Guruprasad P. Bhosale, Veena R. Shah.Optimal positioning of right-sided internal jugular venous catheters: Comparison of intra-atrialelectro cardiography versus Peres' formula. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2008;12(1): Eagle CC. The relationship between a person s height and appropriate endotracheal tube length. Anaesth intensive care. 1992;20: Joshi VS et al JMSCR Volume 05 Issue 10 October 2017 Page 28947
Research Article Can we predict the Position of Central Venous Catheter Tip Following Cannulation of Internal Jugular Vein?
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ANAESTHESIA Research Article Can we predict the Position of Central Venous Catheter Tip Following Cannulation of Internal Jugular Vein? Pradeep Marur Venkategowda 1, Surath Manimala
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ANAESTHESIA Research Article Can we predict the Position of Central Venous Catheter Tip Following Cannulation of Internal Jugular Vein? Pradeep Marur Venkategowda 1, Surath Manimala
Depth of Central Venous Catheterization by Intracardiac ECG in Paediatric Patients
 Original Article Elmer Press Depth of Central Venous Catheterization by Intracardiac ECG in Paediatric Patients Prerana N. Shah a, b, Jithesh Appukutty a, Deepa Kane a Abstract Background: Central venous
Original Article Elmer Press Depth of Central Venous Catheterization by Intracardiac ECG in Paediatric Patients Prerana N. Shah a, b, Jithesh Appukutty a, Deepa Kane a Abstract Background: Central venous
Comparison of the bedside central venous catheter placement techniques: landmark vs electrocardiogram guidance
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 102 (5): 662 6 (09) doi:10.1093/bja/aep046 Advance Access publication March 26, 09 Comparison of the bedside central venous catheter placement techniques: landmark vs electrocardiogram
British Journal of Anaesthesia 102 (5): 662 6 (09) doi:10.1093/bja/aep046 Advance Access publication March 26, 09 Comparison of the bedside central venous catheter placement techniques: landmark vs electrocardiogram
Optimal positioning of right-sided internal jugular venous catheters: Comparison of intra-atrial electrocardiography versus Peres formula
 Review Article Optimal positioning of right-sided internal jugular venous catheters: Comparison of intra-atrial electrocardiography versus Peres formula Anish M. Joshi, Guruprasad P. Bhosale, Geeta P.
Review Article Optimal positioning of right-sided internal jugular venous catheters: Comparison of intra-atrial electrocardiography versus Peres formula Anish M. Joshi, Guruprasad P. Bhosale, Geeta P.
Simple Formula to Place Central Venous Catheter Tip at T6 After Surgical Cutdown in Neonates
 Int Surg 2015;100:1424 1428 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-15-00032.1 Simple Formula to Place Central Venous Catheter Tip at T6 After Surgical Cutdown in Neonates Eunhye Lee 1, Suk-Bae Moon 2 Departments of 1
Int Surg 2015;100:1424 1428 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-15-00032.1 Simple Formula to Place Central Venous Catheter Tip at T6 After Surgical Cutdown in Neonates Eunhye Lee 1, Suk-Bae Moon 2 Departments of 1
Correlation of Surface Landmarks Based Insertion Length of Right Subclavian Central Venous Catheter with Post Insertion Location of Catheter Tip
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/50 Correlation of Surface Landmarks Based Insertion Length of Right Subclavian Central Venous Catheter with Post Insertion
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/50 Correlation of Surface Landmarks Based Insertion Length of Right Subclavian Central Venous Catheter with Post Insertion
Comparison Between Novel Tip Positioning Technology using ECG and Doppler and 2-D Echocardiography for the Placement of Central Catheters
 Comparison Between Novel Tip Positioning Technology using ECG and Doppler and 2-D Echocardiography for the Placement of Central Catheters Robert Wagner, MD, PhD 1, Petr Pokorny, MD 1, Jiri Cernosek, Dr.
Comparison Between Novel Tip Positioning Technology using ECG and Doppler and 2-D Echocardiography for the Placement of Central Catheters Robert Wagner, MD, PhD 1, Petr Pokorny, MD 1, Jiri Cernosek, Dr.
Caroline Polley, BSN, RN, VA-BC Clinical Specialist BD
 Caroline Polley, BSN, RN, VA-BC Clinical Specialist BD Disclosures The speaker is a employee of BD. (Please consult BD product for any indications, contraindications, hazards, warnings, cautions and instructions
Caroline Polley, BSN, RN, VA-BC Clinical Specialist BD Disclosures The speaker is a employee of BD. (Please consult BD product for any indications, contraindications, hazards, warnings, cautions and instructions
Lines and tubes. 1 Nasogastric tubes Endotracheal tubes Central lines Permanent pacemakers Chest drains...
 Lines and tubes 1 Nasogastric tubes... 15 2 Endotracheal tubes.... 19 3 Central lines... 21 4 Permanent pacemakers.... 25 5 Chest drains... 30 This page intentionally left blank 1 Nasogastric tubes Background
Lines and tubes 1 Nasogastric tubes... 15 2 Endotracheal tubes.... 19 3 Central lines... 21 4 Permanent pacemakers.... 25 5 Chest drains... 30 This page intentionally left blank 1 Nasogastric tubes Background
Dr. prakruthi Dept. of anaesthesiology, Rrmch, bangalore
 CENTRAL VENOUS CATHETERIZATION Dr. prakruthi Dept. of anaesthesiology, Rrmch, bangalore OBJECTIVES Introduction Indications and Contraindications Complications Technique Basic principles Specifics by Site
CENTRAL VENOUS CATHETERIZATION Dr. prakruthi Dept. of anaesthesiology, Rrmch, bangalore OBJECTIVES Introduction Indications and Contraindications Complications Technique Basic principles Specifics by Site
Mary Lou Garey MSN EMT-P MedFlight of Ohio
 Mary Lou Garey MSN EMT-P MedFlight of Ohio Function Prolonged and frequent access to venous circulation Allows for patient to carry on normal life; decrease number of needle sticks Medications, parenteral
Mary Lou Garey MSN EMT-P MedFlight of Ohio Function Prolonged and frequent access to venous circulation Allows for patient to carry on normal life; decrease number of needle sticks Medications, parenteral
Interesting Cases - A Case Report: Renal Cell Carcinoma With Tumor Mass In IVC And Heart. O Wenker, L Chaloupka, R Joswiak, D Thakar, C Wood, G Walsh
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 3 Number 2 Interesting Cases - A Case Report: Renal Cell Carcinoma With Tumor Mass In IVC And Heart O Wenker, L Chaloupka, R
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 3 Number 2 Interesting Cases - A Case Report: Renal Cell Carcinoma With Tumor Mass In IVC And Heart O Wenker, L Chaloupka, R
Advocate Christ Medical Center CVC Placement Certification Course
 Advocate Christ Medical Center CVC Placement Certification Course July 12th, 2012 Hannah Watts, MD Medical Simulation Director Modified August 10, 2017 Taajwar Khan, MD Chief Resident of Internal Medicine
Advocate Christ Medical Center CVC Placement Certification Course July 12th, 2012 Hannah Watts, MD Medical Simulation Director Modified August 10, 2017 Taajwar Khan, MD Chief Resident of Internal Medicine
Original Article Bedside prediction of peripherally inserted central catheter length: based on patient height combined with surface landmark
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(8):15928-15934 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0022838 Original Article Bedside prediction of peripherally inserted central catheter length: based on patient height combined
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(8):15928-15934 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0022838 Original Article Bedside prediction of peripherally inserted central catheter length: based on patient height combined
Central Vascular Catheter Placement Evaluation Using Saline Flush and Bedside Echocardiography
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH CONTRIBUTION Central Vascular Catheter Placement Evaluation Using Saline Flush and Bedside Echocardiography Anthony J. Weekes, MD, David A. Johnson, MD, Stephen M. Keller, MD, Bradley
ORIGINAL RESEARCH CONTRIBUTION Central Vascular Catheter Placement Evaluation Using Saline Flush and Bedside Echocardiography Anthony J. Weekes, MD, David A. Johnson, MD, Stephen M. Keller, MD, Bradley
Ultrasound Guided Vascular Access. 7/25/2016
 Ultrasound Guided Vascular Access 7/25/2016 www.ezono.com 1 Objectives Indications for insertion of central and peripheral lines Complications associated with procedures Role of ultrasound in vascular
Ultrasound Guided Vascular Access 7/25/2016 www.ezono.com 1 Objectives Indications for insertion of central and peripheral lines Complications associated with procedures Role of ultrasound in vascular
The use of ultrasound during and after central venous catheter insertion versus conventional chest X-ray after insertion of a central venous catheter
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The use of ultrasound during and after central venous catheter insertion versus conventional chest X-ray after insertion of a central venous catheter M.J. Blans 1 *, H. Endeman 2, F.H.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The use of ultrasound during and after central venous catheter insertion versus conventional chest X-ray after insertion of a central venous catheter M.J. Blans 1 *, H. Endeman 2, F.H.
CATHETER MALPOSITION FOLLOWING SUPRACLAVICULAR APPROACH FOR SUBCLAVIAN VEIN CATHETERISATION
 CATHETER MALPOSITION FOLLOWING SUPRACLAVICULAR APPROACH FOR SUBCLAVIAN VEIN CATHETERISATION - Case Reports - Prem K Singh *, Zulfiquar Ali *, Girija P Rath ** and Hemanshu Prabhakar *** Abstract The supraclavicular
CATHETER MALPOSITION FOLLOWING SUPRACLAVICULAR APPROACH FOR SUBCLAVIAN VEIN CATHETERISATION - Case Reports - Prem K Singh *, Zulfiquar Ali *, Girija P Rath ** and Hemanshu Prabhakar *** Abstract The supraclavicular
Children s Acute Transport Service
 Children s Acute Transport Service Vascular Access Document Control Information Author Ramnarayan Author Position Consultant, CATS Document Owner Polke Document Owner Position CATS Co-ordinator Document
Children s Acute Transport Service Vascular Access Document Control Information Author Ramnarayan Author Position Consultant, CATS Document Owner Polke Document Owner Position CATS Co-ordinator Document
Min Hur, Eun-Hee Kim, In-Kyung Song, Ji-Hyun Lee, Hee-Soo Kim, and Jin Tae Kim INTRODUCTION. Clinical Research
 Anesth Pain Med 2016; 11: 375-379 https://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375 Clinical Research http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-10-25 pissn
Anesth Pain Med 2016; 11: 375-379 https://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375 Clinical Research http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-10-25 pissn
Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter & Midline Placement with ECG Confirmation of Tip Placement
 Title/Description: Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter & Midline Placement with ECG Confirmation of Tip Placement Department: Patient Care Services Personnel: Nursing Services Effective Date: April
Title/Description: Peripherally Inserted Central Catheter & Midline Placement with ECG Confirmation of Tip Placement Department: Patient Care Services Personnel: Nursing Services Effective Date: April
Document No. BMB/IFU/40 Rev No. & Date 00 & 15/11/2017 Issue No & Date 01 & 15/11/2017
 Central Venous Catheter Device Description Multi-lumen catheters incorporate separate, non-communicating vascular access lumens within a single catheter body. Minipunctur Access Sets And Trays: Used for
Central Venous Catheter Device Description Multi-lumen catheters incorporate separate, non-communicating vascular access lumens within a single catheter body. Minipunctur Access Sets And Trays: Used for
Appendix E: Overview of Vascular
 Appendix E: Overview of Vascular 56 Peripheral Short Catheter, less than 3 inches (7.5 cm) in length; over-the-needle catheter is most common. Inserted by percutaneous venipuncture, generally into a hand
Appendix E: Overview of Vascular 56 Peripheral Short Catheter, less than 3 inches (7.5 cm) in length; over-the-needle catheter is most common. Inserted by percutaneous venipuncture, generally into a hand
Persistent left superior vena cava with absent right superior vena cava detected during emergent coronary artery bypass grafting surgery
 Kusaka et al. JA Clinical Reports (2015) 1:2 DOI 10.1186/s40981-015-0004-7 CASE REPORT Persistent left superior vena cava with absent right superior vena cava detected during emergent coronary artery bypass
Kusaka et al. JA Clinical Reports (2015) 1:2 DOI 10.1186/s40981-015-0004-7 CASE REPORT Persistent left superior vena cava with absent right superior vena cava detected during emergent coronary artery bypass
Optimal Placement of a Superior Vena Cava Cannula in Minimally Invasive Robot-Assisted Cardiac Surgery
 Circulation Journal Official Journal of the Japanese Circulation Society http://www.j-circ.or.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiovascular Surgery Optimal Placement of a Superior Vena Cava Cannula in Minimally Invasive
Circulation Journal Official Journal of the Japanese Circulation Society http://www.j-circ.or.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiovascular Surgery Optimal Placement of a Superior Vena Cava Cannula in Minimally Invasive
Troubleshooting Technique for Hemodialysis Catheter Insertion
 Troubleshooting Technique for Hemodialysis Catheter Insertion Withoon Ungkitphaiboon Assistant Professor, Department of Surgery, Maha Chakri Sirindhorn Medical Center Srinakharinwirot University Present
Troubleshooting Technique for Hemodialysis Catheter Insertion Withoon Ungkitphaiboon Assistant Professor, Department of Surgery, Maha Chakri Sirindhorn Medical Center Srinakharinwirot University Present
TITLE: Electrocardiograms versus X-rays for Guided Placement of Central Venous Catheter Tips: A Review of Clinical and Cost-effectiveness
 TITLE: Electrocardiograms versus X-rays for Guided Placement of Central Venous Catheter Tips: A Review of Clinical and Cost-effectiveness DATE: 18 July 2012 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES Central venous catheters
TITLE: Electrocardiograms versus X-rays for Guided Placement of Central Venous Catheter Tips: A Review of Clinical and Cost-effectiveness DATE: 18 July 2012 CONTEXT AND POLICY ISSUES Central venous catheters
Ultrasound-guided infraclavicular axillary vein cannulation for central venous access {
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 93 (2): 188 92 DOI: 10.1093/bja/aeh187 Advance Access publication June 25, 2004 Ultrasound-guided infraclavicular axillary vein cannulation for central venous access { A.
British Journal of Anaesthesia 93 (2): 188 92 DOI: 10.1093/bja/aeh187 Advance Access publication June 25, 2004 Ultrasound-guided infraclavicular axillary vein cannulation for central venous access { A.
A Comparative Study Of Internal Jugular Vein Cannulation- Central Approach Versus Subclavian Vein Cannulation Infraclavicular Approach.
 DOI:.76/aimdr.6..3. Original Article ISSN (O):395-8; ISSN (P):395-84 A Comparative Study Of Internal Jugular Vein Cannulation- Central Approach Versus Subclavian Vein Cannulation Infraclavicular Approach.
DOI:.76/aimdr.6..3. Original Article ISSN (O):395-8; ISSN (P):395-84 A Comparative Study Of Internal Jugular Vein Cannulation- Central Approach Versus Subclavian Vein Cannulation Infraclavicular Approach.
Efficacy of the CathRite system to guide bedside placement of peripherally inserted central venous catheters in critically ill patients: a pilot study
 Efficacy of the CathRite system to guide bedside placement of peripherally inserted central venous catheters in critically ill patients: a pilot study Simon J G Hockley, Vida Hamilton, Robert J Young,
Efficacy of the CathRite system to guide bedside placement of peripherally inserted central venous catheters in critically ill patients: a pilot study Simon J G Hockley, Vida Hamilton, Robert J Young,
Ji-Hyun Chin, Eun-Ho Lee * , Jong-Il Kim and In-Cheol Choi
 Chin et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2017) 17:56 DOI 10.1186/s12871-017-0347-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Prediction of the optimal depth for superior vena cava cannulae with cardiac computed tomography during
Chin et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2017) 17:56 DOI 10.1186/s12871-017-0347-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Prediction of the optimal depth for superior vena cava cannulae with cardiac computed tomography during
PEMSS PROTOCOLS INVASIVE PROCEDURES
 PEMSS PROTOCOLS INVASIVE PROCEDURES Panhandle Emergency Medical Services System SURGICAL AND NEEDLE CRICOTHYROTOMY Inability to intubate is the primary indication for creating an artificial airway. Care
PEMSS PROTOCOLS INVASIVE PROCEDURES Panhandle Emergency Medical Services System SURGICAL AND NEEDLE CRICOTHYROTOMY Inability to intubate is the primary indication for creating an artificial airway. Care
Ahsan Mustafa, Khaja Ali Hassan and Syed Abdur Rahman. Department of Anaesthesiology, Deccan College of Medical Sciences, Hyderabad, India
 International Journal of Advances in Health Sciences (IJHS) ISSN 2349-7033 Vol-3, Issue-1, 2016, pp54-59 http://www.ijhsonline.com Research Article Comparison of the rate of success and incidence of complications
International Journal of Advances in Health Sciences (IJHS) ISSN 2349-7033 Vol-3, Issue-1, 2016, pp54-59 http://www.ijhsonline.com Research Article Comparison of the rate of success and incidence of complications
External Jugular Vein Catheterization Using Intra-Atrial Electrocardiogram
 Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.2.222 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 50(2):222-226, 2009 External Jugular Vein Catheterization Using Intra-Atrial Electrocardiogram Dilek Karaaslan,
Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.2.222 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 50(2):222-226, 2009 External Jugular Vein Catheterization Using Intra-Atrial Electrocardiogram Dilek Karaaslan,
Prevention of thrombosis
 Prevention of thrombosis Massimo Lamperti MD, MBA Chief of General Anaesthesia Department Anaesthesiology Institute Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Clinical Professor of Anaesthesiology Cleveland Clinic Lerner
Prevention of thrombosis Massimo Lamperti MD, MBA Chief of General Anaesthesia Department Anaesthesiology Institute Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Clinical Professor of Anaesthesiology Cleveland Clinic Lerner
Comparing the conventional 15 cm and the C-length approaches for central venous catheter placement
 doi: 10.15171/jcvtr.2018.38 http://jcvtr.tbzmed.ac.ir TUOMS Publishing Group Original Article Comparing the conventional 15 cm and the C-length approaches for central venous catheter placement Hashem Jarineshin,
doi: 10.15171/jcvtr.2018.38 http://jcvtr.tbzmed.ac.ir TUOMS Publishing Group Original Article Comparing the conventional 15 cm and the C-length approaches for central venous catheter placement Hashem Jarineshin,
Central Line Care and Management
 Central Line Care and Management What is a Central Line/ CVAD? (central venous access device) A vascular infusion device that terminates at or close to the heart or in one of the great vessels (aorta,
Central Line Care and Management What is a Central Line/ CVAD? (central venous access device) A vascular infusion device that terminates at or close to the heart or in one of the great vessels (aorta,
The carina as a radiological landmark for central venous catheter tip position
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 96 (3): 335 40 (2006) doi:10.1093/bja/aei310 Advance Access publication January 16, 2006 The carina as a radiological landmark for central venous catheter tip position P.
British Journal of Anaesthesia 96 (3): 335 40 (2006) doi:10.1093/bja/aei310 Advance Access publication January 16, 2006 The carina as a radiological landmark for central venous catheter tip position P.
IV therapy. By: Susan Mberenga, RN, MSN. Copyright 2016, 2013, 2010, 2006, 2002 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
 IV therapy By: Susan Mberenga, RN, MSN 1 IV Therapy Types of solutions Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic Caution: Too rapid or excessive infusion of any IV fluid has the potential to cause serious problems
IV therapy By: Susan Mberenga, RN, MSN 1 IV Therapy Types of solutions Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic Caution: Too rapid or excessive infusion of any IV fluid has the potential to cause serious problems
Materials and Methods
 AN INTERNATIONAL QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCES 4(4):687-692 ISSN (online): 2320-4257 www.biolifejournal.com B I O L I F E R E S E A R C H A R T I C L E Validity of ultrasonography in detection
AN INTERNATIONAL QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCES 4(4):687-692 ISSN (online): 2320-4257 www.biolifejournal.com B I O L I F E R E S E A R C H A R T I C L E Validity of ultrasonography in detection
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Potentially fatal complications of peripherally inserted central venous catheters (PICCs)
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Potentially fatal complications of peripherally inserted central venous catheters (PICCs) October 2001 2 Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Children s Hospital
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Potentially fatal complications of peripherally inserted central venous catheters (PICCs) October 2001 2 Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit, Children s Hospital
The C.L.O.T. Tool for Identifying Strategies to Prevent PICC Catheter Occlusions
 The C.L.O.T. Tool for Identifying Strategies to Prevent PICC Catheter Occlusions page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Part 1: Definition and Scope of Catheter Occlusion Part 2: Predictors of Catheter Occlusion Part
The C.L.O.T. Tool for Identifying Strategies to Prevent PICC Catheter Occlusions page 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS Part 1: Definition and Scope of Catheter Occlusion Part 2: Predictors of Catheter Occlusion Part
The University of Toledo Medical Center and its Medical Staff
 Name of Policy: Policy Number: Department: 3364-109-GEN-705 Infection Control Medical Staff Hospital Administration Approving Officer: Responsible Agent: Scope: Chair, Infection Control Committee Chief
Name of Policy: Policy Number: Department: 3364-109-GEN-705 Infection Control Medical Staff Hospital Administration Approving Officer: Responsible Agent: Scope: Chair, Infection Control Committee Chief
Tip navigation and tip location for PICCs. Mauro Pittiruti Catholic University, Rome - Italy
 Tip navigation and tip location for PICCs Mauro Pittiruti Catholic University, Rome - Italy What are we talking about? Tip navigation and tip location are two different aspects of central line insertion:
Tip navigation and tip location for PICCs Mauro Pittiruti Catholic University, Rome - Italy What are we talking about? Tip navigation and tip location are two different aspects of central line insertion:
Kristin Wise, MD, FHM Division of General Internal Medicine and Geriatrics Hospital Medicine 2013
 Kristin Wise, MD, FHM Division of General Internal Medicine and Geriatrics Hospital Medicine 2013 Objectives for CVC Placement Understand the indications and contraindications Determine appropriate CVC
Kristin Wise, MD, FHM Division of General Internal Medicine and Geriatrics Hospital Medicine 2013 Objectives for CVC Placement Understand the indications and contraindications Determine appropriate CVC
Case #1. Case #1- Possible codes. Unraveling the -59 modifier. Principles of Interventional. CASE 1: Simple angioplasty
 Unraveling the -59 modifier Principles of Interventional Coding Donald Schon, MD, FACP Debra Lawson, CPC, PCS Distinct or independent from other services performed on the same day Normally not reported
Unraveling the -59 modifier Principles of Interventional Coding Donald Schon, MD, FACP Debra Lawson, CPC, PCS Distinct or independent from other services performed on the same day Normally not reported
Jefferson Tower Task Trainer List
 Jefferson Tower Task Trainer List Table of Contents Blue Phantom Ultrasound Central Line Training Model 2 Blue Phantom Femoral Vascular Access Training Model 3 Blue Phantom Thoracentesis Ultrasound Training
Jefferson Tower Task Trainer List Table of Contents Blue Phantom Ultrasound Central Line Training Model 2 Blue Phantom Femoral Vascular Access Training Model 3 Blue Phantom Thoracentesis Ultrasound Training
PROTOCOL FOR THE INSERTION OF NON TUNNELLED DIALYSIS CENTRAL VENOUS CATHETERS
 PROTOCOL FOR THE INSERTION OF NON TUNNELLED DIALYSIS CENTRAL VENOUS CATHETERS Version 1.0 Author Vinod Mathrani, Kieron Donovan, Steve Riley, Soma Meran, Gareth Roberts, Vinod Ravindran Agreed 06/11/2015
PROTOCOL FOR THE INSERTION OF NON TUNNELLED DIALYSIS CENTRAL VENOUS CATHETERS Version 1.0 Author Vinod Mathrani, Kieron Donovan, Steve Riley, Soma Meran, Gareth Roberts, Vinod Ravindran Agreed 06/11/2015
Perioperative Ultrasonography Ehab Farag, MD, FRCA Hesham Elsharkawy David G. Anthony, M.D.
 Perioperative Ultrasonography Ehab Farag, MD, FRCA Hesham Elsharkawy David G. Anthony, M.D. Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland OH 1 Complications during central venous catheterization (CVC) occur 2% -15% of the
Perioperative Ultrasonography Ehab Farag, MD, FRCA Hesham Elsharkawy David G. Anthony, M.D. Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland OH 1 Complications during central venous catheterization (CVC) occur 2% -15% of the
Case Report The Sheared Central Venous Catheter?
 Case Reports in Anesthesiology Volume 2011, Article ID 379827, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/379827 Case Report The Sheared Central Venous Catheter? Harihar V. Hegde, 1 Vijay G. Yaliwal, 1 Shyamsundar K. Joshi,
Case Reports in Anesthesiology Volume 2011, Article ID 379827, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/379827 Case Report The Sheared Central Venous Catheter? Harihar V. Hegde, 1 Vijay G. Yaliwal, 1 Shyamsundar K. Joshi,
You have a what, inside you?
 Costal Emergency Medicine Conference You have a what, inside you? Less than mainstream medical devices encountered in the ED. Eric Ossmann, MD, FACEP Associate Professor Duke University Medical Center
Costal Emergency Medicine Conference You have a what, inside you? Less than mainstream medical devices encountered in the ED. Eric Ossmann, MD, FACEP Associate Professor Duke University Medical Center
You have a what, inside you?
 Costal Emergency Medicine Conference You have a what, inside you? Less than mainstream medical devices encountered in the ED. Eric Ossmann, MD, FACEP Associate Professor Duke University Medical Center
Costal Emergency Medicine Conference You have a what, inside you? Less than mainstream medical devices encountered in the ED. Eric Ossmann, MD, FACEP Associate Professor Duke University Medical Center
A case of mislabeled textbooks: misnomer of the traditional "bicaval" view.
 Providence St. Joseph Health Providence St. Joseph Health Digital Commons Journal Articles and Abstracts 8-1-2018 A case of mislabeled textbooks: misnomer of the traditional "bicaval" view. Laura Vaskelyte
Providence St. Joseph Health Providence St. Joseph Health Digital Commons Journal Articles and Abstracts 8-1-2018 A case of mislabeled textbooks: misnomer of the traditional "bicaval" view. Laura Vaskelyte
PICC, port e trombosi cateterecorrelata: la prevenzione è legata alla tecnica di impianto!
 PICC, port e trombosi cateterecorrelata: la prevenzione è legata alla tecnica di impianto! Massimo Lamperti MD, MBA! Clinical Professor of Anesthesiology! Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine! Chief
PICC, port e trombosi cateterecorrelata: la prevenzione è legata alla tecnica di impianto! Massimo Lamperti MD, MBA! Clinical Professor of Anesthesiology! Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine! Chief
Over the Wire Technique vs. Modified Seldinger Technique in Insertion of PICC
 Over the Wire Technique vs. Modified Seldinger Technique in Insertion of PICC Deniz Kasikci Department of Radiology, Jena University Hospital Friedrich-Schiller-University, Jena, Germany Disclosure Speaker
Over the Wire Technique vs. Modified Seldinger Technique in Insertion of PICC Deniz Kasikci Department of Radiology, Jena University Hospital Friedrich-Schiller-University, Jena, Germany Disclosure Speaker
Breakout Session: Transesophageal Echocardiography
 Breakout Session: Transesophageal Echocardiography Doris Ockert, MD Andrew Schroeder, MD University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health Jutta Novalija, MD, PhD Medical College of Wisconsin
Breakout Session: Transesophageal Echocardiography Doris Ockert, MD Andrew Schroeder, MD University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health Jutta Novalija, MD, PhD Medical College of Wisconsin
Spontaneous Migration of a Central Line Catheter into the Heart. Saeed Al Hindi, MD, CABS, FRCSI* Khulood Al-Saad, MD**
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 29, No. 3, September 2007 Spontaneous Migration of a Central Line Catheter into the Heart Saeed Al Hindi, MD, CABS, FRCSI* Khulood Al-Saad, MD** Background: Spontaneous migration
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 29, No. 3, September 2007 Spontaneous Migration of a Central Line Catheter into the Heart Saeed Al Hindi, MD, CABS, FRCSI* Khulood Al-Saad, MD** Background: Spontaneous migration
Double Superior Vena Cava; A Benign Cause of Widened Mediastenum and Implication on Venous Central Access
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Endovascular Medicine Volume 2 Number 1 Double Superior Vena Cava; A Benign Cause of Widened Mediastenum and Implication on Venous H Enuh, A Patel, A Chaudry, K Diaz,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Endovascular Medicine Volume 2 Number 1 Double Superior Vena Cava; A Benign Cause of Widened Mediastenum and Implication on Venous H Enuh, A Patel, A Chaudry, K Diaz,
Catheter Fracture of a Totally Implantable Venous Device Due to Pinch Off Syndrome in Breast Cancer: A Case Report
 Kosin Medical Journal 2016;31:167-172. https://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2016.31.2.167 KMJ Case Report Catheter Fracture of a Totally Implantable Venous Device Due to Pinch Off Syndrome in Breast Cancer: A Case
Kosin Medical Journal 2016;31:167-172. https://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2016.31.2.167 KMJ Case Report Catheter Fracture of a Totally Implantable Venous Device Due to Pinch Off Syndrome in Breast Cancer: A Case
Influence of arm position during infraclavicular subclavian vein catheterization in coronary artery bypass graft surgery
 doi: 10.15171/jcvtr.2018.33 http://jcvtr.tbzmed.ac.ir TUOMS Publishing Group Original Article Influence of arm position during infraclavicular subclavian vein catheterization in coronary artery bypass
doi: 10.15171/jcvtr.2018.33 http://jcvtr.tbzmed.ac.ir TUOMS Publishing Group Original Article Influence of arm position during infraclavicular subclavian vein catheterization in coronary artery bypass
PARENTERAL NUTRITION: VASCUAR ACCESS DEVICE SELECTION
 PARENTERAL NUTRITION: VASCUAR ACCESS DEVICE SELECTION Winifred Magambo-Gasana Vascular Access Nurse Practitioner Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Aim An overview of the range of Vascular
PARENTERAL NUTRITION: VASCUAR ACCESS DEVICE SELECTION Winifred Magambo-Gasana Vascular Access Nurse Practitioner Oxford University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Aim An overview of the range of Vascular
Pneumomediastinitis Following Right Subclavian Vein Central Line Insertion
 318 CAES REPORT Pneumomediastinitis Following Right Subclavian Vein Central Line Insertion Wael Abdulla Sadaqa Department of Anesthesia and Intensive Care, Faculty of Medicine, Al-Najah National University
318 CAES REPORT Pneumomediastinitis Following Right Subclavian Vein Central Line Insertion Wael Abdulla Sadaqa Department of Anesthesia and Intensive Care, Faculty of Medicine, Al-Najah National University
Central Venous Line Insertion
 Central Venous Line Insertion Understand the indications and risks of CVC insertion Understand and troubleshoot the seldinger technique Understand available sites and select the appropriate site for clinical
Central Venous Line Insertion Understand the indications and risks of CVC insertion Understand and troubleshoot the seldinger technique Understand available sites and select the appropriate site for clinical
Case Report Central Venous Line Insertion Revealing Partial Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return: Diagnosis and Management
 Hindawi Case Reports in Critical Care Volume 2017, Article ID 3218063, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3218063 Case Report Central Venous Line Insertion Revealing Partial Anomalous Venous Return:
Hindawi Case Reports in Critical Care Volume 2017, Article ID 3218063, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3218063 Case Report Central Venous Line Insertion Revealing Partial Anomalous Venous Return:
Original Article. Evaluation of the Sherlock 3CG Tip Confirmation System on peripherally inserted central catheter malposition rates.
 Original Article doi:10.1111/anae.12785 Evaluation of the Sherlock 3CG Tip Confirmation System on peripherally inserted central catheter malposition rates A. J. Johnston, 1 A. Holder, 2 S. M. Bishop, 2
Original Article doi:10.1111/anae.12785 Evaluation of the Sherlock 3CG Tip Confirmation System on peripherally inserted central catheter malposition rates A. J. Johnston, 1 A. Holder, 2 S. M. Bishop, 2
MODULE 9 ARTERIAL AND VENOUS CATHETERIZATION. Robert B. McLafferty M.D. Southern Illinois University
 MODULE 9 ARTERIAL AND VENOUS CATHETERIZATION Robert B. McLafferty M.D. Southern Illinois University I. OBJECTIVES By the end of this laboratory session the residents should be able to A. Identify the anatomic
MODULE 9 ARTERIAL AND VENOUS CATHETERIZATION Robert B. McLafferty M.D. Southern Illinois University I. OBJECTIVES By the end of this laboratory session the residents should be able to A. Identify the anatomic
1. CARDIOLOGY. These listings cannot be correctly interpreted without reference to the Preamble. Anes. $ Level
 1. CARDIOLOGY These listings cannot be correctly interpreted without reference to the Preamble. Anes. Referred Cases 33010 Consultation: To consist of examination, review of history, laboratory, X-ray
1. CARDIOLOGY These listings cannot be correctly interpreted without reference to the Preamble. Anes. Referred Cases 33010 Consultation: To consist of examination, review of history, laboratory, X-ray
Navigating Vascular Access Issues
 Navigating Vascular Access Issues The Oley Foundation 27 th Annual Consumer/Clinician Conference Redondo Beach, CA June, 27 2012 Anita Piano, BS, RN, VA-BC Administrative Nurse, PICC Service UCLA Health
Navigating Vascular Access Issues The Oley Foundation 27 th Annual Consumer/Clinician Conference Redondo Beach, CA June, 27 2012 Anita Piano, BS, RN, VA-BC Administrative Nurse, PICC Service UCLA Health
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Pacing in patients with congenital heart disease: part 1
 Pacing in patients with congenital heart disease: part 1 September 2013 Br J Cardiol 2013;20:117 20 doi: 10.5837/bjc/2013.028 Authors: Khaled Albouaini, Archana Rao, David Ramsdale View details Only a
Pacing in patients with congenital heart disease: part 1 September 2013 Br J Cardiol 2013;20:117 20 doi: 10.5837/bjc/2013.028 Authors: Khaled Albouaini, Archana Rao, David Ramsdale View details Only a
Implications of Precise PICC Tip Location: The New Gold Standard in Clinical Practice?
 Implications of Precise PICC Tip Location: The New Gold Standard in Clinical Practice? Nancy Moureau, BSN, CRNI, CPUI, PICC Excellence, Inc. About the Speaker Nancy Moureau is an educator, legal consultant
Implications of Precise PICC Tip Location: The New Gold Standard in Clinical Practice? Nancy Moureau, BSN, CRNI, CPUI, PICC Excellence, Inc. About the Speaker Nancy Moureau is an educator, legal consultant
EMS Subspecialty Certification Review Course. Conflict of Interest Disclosure. Learning Objectives
 EMS Subspecialty Certification Review Course Cardiovascular 1.4.2.2 Placement of peripheral IV lines 1.4.2.2.1 Access or Placement of Central Venous Lines in the field 1.4.2.2.2 Intraosseous lines 1.4.2.2.3.
EMS Subspecialty Certification Review Course Cardiovascular 1.4.2.2 Placement of peripheral IV lines 1.4.2.2.1 Access or Placement of Central Venous Lines in the field 1.4.2.2.2 Intraosseous lines 1.4.2.2.3.
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Procedure (TAVI)
 Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP. October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18
 Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18 Identifying normal anatomy Identifying various pathologic states Identifying placement of hardware Identifying limitations of portable CXR
Alexander A Schult, M.D., FCCP October 21, 2017 Revised 1/10/18 Identifying normal anatomy Identifying various pathologic states Identifying placement of hardware Identifying limitations of portable CXR
Ultrasound in the ICU
 Ultrasound in the ICU Kristine E. W. Breyer, MD Assistant Professor Anesthesia & Critical Care Medicine UCSF DISCLOSURES: NONE Definition The Ultrasound Exam Types & Uses Training Clinical Examples Objectives
Ultrasound in the ICU Kristine E. W. Breyer, MD Assistant Professor Anesthesia & Critical Care Medicine UCSF DISCLOSURES: NONE Definition The Ultrasound Exam Types & Uses Training Clinical Examples Objectives
SCOPE OF PRACTICE PGY-4 PGY-6 (or PGY-5 PGY-7 if Medicine/Pediatrics resident)
 (or PGY-5 PGY-7 if Medicine/Pediatrics Resident) The Pediatric Cardiology Training Program at MUSC does not make distinctions in the Scope of Practice between PGY-4, -5, and -6 Resident Physicians. As
(or PGY-5 PGY-7 if Medicine/Pediatrics Resident) The Pediatric Cardiology Training Program at MUSC does not make distinctions in the Scope of Practice between PGY-4, -5, and -6 Resident Physicians. As
Hemodynamic Monitoring and Circulatory Assist Devices
 Hemodynamic Monitoring and Circulatory Assist Devices Speaker: Jana Ogden Learning Unit 2: Hemodynamic Monitoring and Circulatory Assist Devices Hemodynamic monitoring refers to the measurement of pressure,
Hemodynamic Monitoring and Circulatory Assist Devices Speaker: Jana Ogden Learning Unit 2: Hemodynamic Monitoring and Circulatory Assist Devices Hemodynamic monitoring refers to the measurement of pressure,
Background & Indications Probe Selection
 Teresa S. Wu, MD, FACEP Director, EM Ultrasound Program & Fellowship Co-Director, Simulation Based Training Program & Fellowship Associate Program Director, EM Residency Program Maricopa Medical Center
Teresa S. Wu, MD, FACEP Director, EM Ultrasound Program & Fellowship Co-Director, Simulation Based Training Program & Fellowship Associate Program Director, EM Residency Program Maricopa Medical Center
W J C C M. World Journal of Critical Care Medicine. Focus on peripherally inserted central catheters in critically ill patients.
 W J C C M World Journal of Critical Care Medicine Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.5492/wjccm.v3.i4.80 World J Crit Care Med
W J C C M World Journal of Critical Care Medicine Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.5492/wjccm.v3.i4.80 World J Crit Care Med
A Primer on Central Venous Access: Peripherally-Inserted Central Catheters, Tunneled Catheters, and Subcutaneous Ports
 Disclosures A Primer on Central Venous Access: Peripherally-Inserted Central Catheters, Tunneled Catheters, and Subcutaneous Ports No conflicts of interest relevant to this presentation Jason W. Pinchot,
Disclosures A Primer on Central Venous Access: Peripherally-Inserted Central Catheters, Tunneled Catheters, and Subcutaneous Ports No conflicts of interest relevant to this presentation Jason W. Pinchot,
CSC Standardized Procedure Curriculum
 CSC Standardized Procedure Curriculum USpecialty:U Internal Medicine USimulation:U Ultrasound Guided Central Venous Catheter (CVC) Insertion UContributed by:u LTC Alex Niven, MD UTarget Audience:U Resident
CSC Standardized Procedure Curriculum USpecialty:U Internal Medicine USimulation:U Ultrasound Guided Central Venous Catheter (CVC) Insertion UContributed by:u LTC Alex Niven, MD UTarget Audience:U Resident
Proper insertion depth of endotracheal tubes in adults by topographic landmarks measurements
 Journal of Clinical Anesthesia (2007) 19, 15 19 Original contribution Proper insertion depth of endotracheal tubes in adults by topographic landmarks measurements Shmuel Evron MD a,c, Marian Weisenberg
Journal of Clinical Anesthesia (2007) 19, 15 19 Original contribution Proper insertion depth of endotracheal tubes in adults by topographic landmarks measurements Shmuel Evron MD a,c, Marian Weisenberg
A novel suture-traction method for right internal jugular vein catheterization in left-lateral position in anesthetized patients.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (12): 5628-5632 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A novel suture-traction method for right internal jugular vein catheterization in left-lateral position in anesthetized patients.
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (12): 5628-5632 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info A novel suture-traction method for right internal jugular vein catheterization in left-lateral position in anesthetized patients.
J. H. Ahn 1, I. S. Kim 2, *, J. H. Yang 2, I. G. Lee 2, D. H. Seo 2 and S. P. Kim 3. Abstract NEUROSCIENCES AND NEUROANESTHESIA
 British Journal of Anaesthesia, 118 (2): 215 22 (2017) doi: 10.1093/bja/aew430 Neurosciences and Neuroanesthesia NEUROSCIENCES AND NEUROANESTHESIA Transoesophageal echocardiographic evaluation of central
British Journal of Anaesthesia, 118 (2): 215 22 (2017) doi: 10.1093/bja/aew430 Neurosciences and Neuroanesthesia NEUROSCIENCES AND NEUROANESTHESIA Transoesophageal echocardiographic evaluation of central
PRODUCTS FOR THE DIFFICULT AIRWAY. Courtesy of Cook Critical Care
 PRODUCTS FOR THE DIFFICULT AIRWAY Courtesy of Cook Critical Care EMERGENCY CRICOTHYROTOMY Thyroid Cartilage Access Site Cricoid Cartilage Identify the cricothyroid membrane between the cricoid and thyroid
PRODUCTS FOR THE DIFFICULT AIRWAY Courtesy of Cook Critical Care EMERGENCY CRICOTHYROTOMY Thyroid Cartilage Access Site Cricoid Cartilage Identify the cricothyroid membrane between the cricoid and thyroid
Peel-Apart Percutaneous Introducer Kits for
 Bard Access Systems Peel-Apart Percutaneous Introducer Kits for Table of Contents Contents Page Bard Implanted Ports Hickman*, Leonard*, Broviac*, Tenckhoff*, and Groshong* Catheters Introduction....................................
Bard Access Systems Peel-Apart Percutaneous Introducer Kits for Table of Contents Contents Page Bard Implanted Ports Hickman*, Leonard*, Broviac*, Tenckhoff*, and Groshong* Catheters Introduction....................................
A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress
 A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress Yanick Beaulieu, MD, FRCPC Director, Bedside Ultrasound Curriculum Division of Cardiology and Critical Care Hôpital du Sacré-Coeur
A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress Yanick Beaulieu, MD, FRCPC Director, Bedside Ultrasound Curriculum Division of Cardiology and Critical Care Hôpital du Sacré-Coeur
Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis?
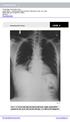 1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
Stuck dialysis catheters. ANZSIN 2013 Michael Lam & Kendal Redmond
 Stuck dialysis catheters ANZSIN 2013 Michael Lam & Kendal Redmond NT 39 yr old CI Maori - ESKD 2 o to cortical necrosis HD August 2002 R IJ tunneled Tesio catheter Oct 2002 Failed L RC AVF Feb 2004 Failed
Stuck dialysis catheters ANZSIN 2013 Michael Lam & Kendal Redmond NT 39 yr old CI Maori - ESKD 2 o to cortical necrosis HD August 2002 R IJ tunneled Tesio catheter Oct 2002 Failed L RC AVF Feb 2004 Failed
Hydrocephalus: Electrocardiographic Localization of
 Arch. Dis. Childh., 1967, 42, 166. Hydrocephalus: Electrocardiographic Localization of the Catheter in Ventriculo-atrial Shunts G. BROCKLEHURST, J. R. W. GLEAVE, R. A. MILLAR, and AILEEN K. ADAMS From
Arch. Dis. Childh., 1967, 42, 166. Hydrocephalus: Electrocardiographic Localization of the Catheter in Ventriculo-atrial Shunts G. BROCKLEHURST, J. R. W. GLEAVE, R. A. MILLAR, and AILEEN K. ADAMS From
10/14/2018 Dr. Shatarat
 2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
Background & Indications Probe Selection
 Teresa S. Wu, MD, FACEP Director, EM Ultrasound Program & Fellowship Co-Director, Simulation Based Training Program & Fellowship Associate Program Director, EM Residency Program Maricopa Medical Center
Teresa S. Wu, MD, FACEP Director, EM Ultrasound Program & Fellowship Co-Director, Simulation Based Training Program & Fellowship Associate Program Director, EM Residency Program Maricopa Medical Center
INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS
 INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS PROVIDER CODE TABLES Note: Due to possible changes in Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP) policy or national coding updates, inclusion of a code on the code tables
INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS PROVIDER CODE TABLES Note: Due to possible changes in Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP) policy or national coding updates, inclusion of a code on the code tables
Imminent Cardiac Collapse: The Catastrophe You Cannot Afford To Miss
 Imminent Cardiac Collapse: The Catastrophe You Cannot Afford To Miss Presenting Authors Ameya J Baxi, MD (baxi@uthscsa.edu) Carlos Restrepo, MD Disclaimer: We do not have any conflict of interest or financial
Imminent Cardiac Collapse: The Catastrophe You Cannot Afford To Miss Presenting Authors Ameya J Baxi, MD (baxi@uthscsa.edu) Carlos Restrepo, MD Disclaimer: We do not have any conflict of interest or financial
Port Design. Page 1. Port Placement, Removal, and Management. Selecting a Vascular Access Device. Thomas M. Vesely, MD
 Non-Dialysis Procedures Port Placement, Removal, and Management Thomas M. Vesely, MD Saint Louis, Missouri Selecting a Vascular Access Device Duration of use Number of lumens Frequency used Blood flow
Non-Dialysis Procedures Port Placement, Removal, and Management Thomas M. Vesely, MD Saint Louis, Missouri Selecting a Vascular Access Device Duration of use Number of lumens Frequency used Blood flow
Incidence of Infectious Complications in Central Venous Catheterization: Internal Jugular versus Subclavian Route
 Original Article DOI: 0.7354/ijss/206/60 Incidence of Infectious Complications in Central Venous Catheterization: Internal Jugular versus Ashita Mowar, H S Nanda 2, R K Goyal 3 Post-graduate Student, Department
Original Article DOI: 0.7354/ijss/206/60 Incidence of Infectious Complications in Central Venous Catheterization: Internal Jugular versus Ashita Mowar, H S Nanda 2, R K Goyal 3 Post-graduate Student, Department
Vascular Access Service Dott.ssa Alessandra Palo Direttore AAT Pavia - SAV Dipartimento Medicina Intensiva Fondazione IRCCS San Matteo Pavia
 Vascular Access Service Dott.ssa Alessandra Palo Direttore AAT Pavia - SAV Dipartimento Medicina Intensiva Fondazione IRCCS San Matteo Pavia Our story so far More and more patients with chronic illness
Vascular Access Service Dott.ssa Alessandra Palo Direttore AAT Pavia - SAV Dipartimento Medicina Intensiva Fondazione IRCCS San Matteo Pavia Our story so far More and more patients with chronic illness
