SUMMARY REPORT. Autonomic Nervous System Function. Valsalva 100
|
|
|
- Robert Stewart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUMMARY REPORT Nervous System Function 8 Heart Rate (red) & Blood Pressure (blue) Parasympathetic Balance Sympathetic hypertonia 4 [bpm] Resting Deep Breathing Valsalva Standing Relaxation Balance Stress. Sympathetic (LFa). Sympathetic (LFa). Sympathetic (LFa). Sympathetic (LFa) Sympathetic Vagal HR BP LFa HFa SpO2 Comment Resting 82 28/ Borderline normal level of sympathetic and parasympathetic tone; Deep 89 7/ Normal Parasympathetic to stimulation; Breathing 7 Valsalva 9 32/ Normal Sympathetic to stimulation; Standing 95 25/ Normal ANS to stimulation; Enhanced cardiovascular adaptation. The autonomic regulation of the functioning of the cardiovascular system provides enormous ability for a long-term adaptation to physical exertions and to adequately tolerate them. Typically this is a sign of the absence of physical exhaustion, overtraining or any cardiovascular health conditions. This is a typical pattern of a physically active healthy individual without any evident signs of physical exhaustion, overtraining or other conditions altering the regulatory functions of the autonomic nervous system or a cardiovascular to it; Activity 68 ms2 4-8 Valsalva Ratio.25 ratio >.5 Balance 2.3 ratio :5 Ratio.26 ratio >. E/I Ratio.5 ratio >. Functional Age 56 years < 53 Score Norms Description Comments MSI -.88 <. MSI is an indicator of accumulative mental stress. Mental stress can be caused by situations one has to cope with daily and the emotional states that result. The way in which a person copes with stressful events is a significant contributing factor to this process When the stress becomes too great the body will show PSI. <. PSI is an indicator of accumulative chronic physical stress. Physical stress can be caused by long-term exposure to negative factors in one`s life or physical illness. The way in which a person copes with physical stressors is a significant contributing factor to this process When the stress becomes too great the body Cardiovascular Function Score Norms Description Comments EEI EEI is an indicator for left ventricle ejection power and elasticity of large arteries. Borderline Normal Blood Circulation DDI DDI indicates the contractility, tension and stiffness in the small arteries. Borderline Normal Blood Circulation DEI DEI represents the reflection of arterial elasticity and blood flow in the venous system. Normal Blood Circulation The score is below average. It indicates low mental stress. Stress in the recent past has had little effect on your mental-health. The negative effects of mental stress are limited. The score is clearly above average. It indicates high physical stress. Stress in the recent past has had a major impact on your physical balance. The negative effects of physical stress are clearly visible. It is possible that you experience physical inconveniences as myalgia, back complaints, palpitations and reduced resistance to illness. AI -.28 < -.7 Augmentation Index (AI) is a useful marker for cardiac risk. AI increases with age and a AI is a measure of arterial stiffness and it provides general information about the arteries. AI is sedentary lifestyle. positively correlated with pulsewave velocity, blood pressure and hypertension. ABI Ankle/Brachial Index Acceptable, Borderline TBI.5 >.75 Toe/Brachial Index Normal range Reflection Index Cardiac Output 5.29 l/min C 2.8 ml/mmhg >. Ventricular Extrasystole < QRS 53 ms 6-2 Stiffness Index 8.55 m/s < 8. Mean Arterial Pressure 88 mmhg 7- C ml/mmhg > 6. Atrial Extrasystole < QTc 355 ms Sudomotor Function Stroke Volume 64.6 ml 55- Blood Volume 5.25 l 3-5 DPTI/SPTI.26 ratio Artifacts < Body Mass Index Score Norms Description Comments Sudomotor Neuropathy 4 < 5 Risk for sudomotor autonomic neuropathy. Sweat Gland C-Fiber density and function Printed: 9 May 28 2:8
2 CARDIAC AUTONOMIC NEUROPATHY ASSESSMENT 5 AUTONOMIC ACTIVITY AUTONOMIC BALANCE - Sympathetic Balance Parasympathetic The sympathetic nervous system activates the fight-or-flight s. It activates the glands and organs that defend the body against attack. The sympathetic nervous system uses up energy and depletes the body.the parasympathetic nervous system controls the rest and digest s. The parasympathetic nervous system, when activated by rest, relaxation and happy thoughts, is essential for balanced living and for all healing Parasympathetic Balance Sympathetic Relaxation Sympathetic hypertonia Balance Stress Vagal E/I RATIO:.5 Expiration/Inspiration Ratio is a marker of cardiovagal VALSALVA RATIO:.25 Marker of baroreceptor sensitivity /5 RATIO:.26 Heart rate change during standing or tilt at 3 and 5 second Systolic Pressure Response to Standing: Marker of sympathetic adrenergic function. 4 mmhg Nervous System Borderline normal level of sympathetic and parasympathetic tone; Parasympathetic Response to Deep Breathing Normal Parasympathetic to stimulation; Sympathetic Response to Valsalva Maneuver Normal Sympathetic to stimulation; Active Standing Normal ANS to stimulation; Enhanced cardiovascular adaptation. The autonomic regulation of the functioning of the cardiovascular system provides enormous ability for a long-term adaptation to physical exertions and to adequately tolerate them. Typically this is a sign of the absence of physical exhaustion, overtraining or any cardiovascular health conditions. This is a typical pattern of a physically active healthy individual without any evident signs of physical exhaustion, overtraining or other conditions altering the regulatory functions of the autonomic nervous system or a cardiovascular to it; Printed: 9 May 28 2:8
3 AUTONOMIC REGULATION ASSESSMENT AUTONOMIC PHYSICAL DYSREGULATION (PSI) =. PSI is an indicator of accumulative chronic physical stress. Physical stress can be caused by long-term exposure to negative factors in one`s life or physical illness. The way in which a person copes with physical stressors is a significant contributing factor to this process. When the stress becomes too great, the body will show signs of distress. ACCUMULATIVE MENTAL STRESS (MSI) = -.88 MSI is an indicator of accumulative mental stress. Mental stress can be caused by situations one has to cope with daily and the emotional states that result. The way in which a person copes with stressful events is a significant contributing factor to this process. When the stress becomes too great, the body will show signs of distress. A A B B C C C C D E F F The score is clearly above average. It indicates high physical stress. Stress in the recent past has had a major impact on your physical balance. The negative effects of physical stress are clearly visible. It is possible that you experience physical inconveniences as myalgia, back complaints, palpitations and reduced resistance to illness. A A B B C C C C D E F F The score is below average. It indicates low mental stress. Stress in the recent past has had little effect on your mental-health. The negative effects of mental stress are limited. Balance: 2.3 Borderline normal level of sympathetic and parasympathetic tone; The sympathetic nervous system activates the fight-or-flight s. The parasympathetic nervous system controls the rest and digest s. Total Activity: 68 Maker of the overall ANS activity at rest Body Mass Index (BMI): 27 Overweight - prone to health risks Body mass index is defined as the individual's body weight divided by the square of his or her height. The body mass index can be used to identify if you are overweight. Parasympathetic Balance Sympathetic LFa.38 ms2.5-4 HFa 2.7 ms2.5-4 Blood Pressure 28/7 mmhg <2 SpO2 97 % >94 BPSys Response to Standing 4 mmhg < Functional Age 56 years < 53 Health Risk Factor 45 % < 5 SDNN 28 ms > 4 HeartRate 82 bpm < 9 Ventricular Extrasystole < Atrial Extrasystole < Artifacts < A - Normal B - Borderline Normal C - Moderate D - Borderline Abnormal E - Abnormal F - Severe Relaxation Sympathetic hypertonia Balance Stress Vagal 8 Heart Rate (red) & Blood Pressure (blue) 4 [bpm] 3 6 [s].79 ECG -.79 [mv] Printed: 9 May 28 2:8
4 PERIPHERAL ARTERY DISEASE ASSESSMENT ANKLE/BRACHIAL INDEX (ABI) =.99 ABI test is a quick, noninvasive way to check your risk of peripheral artery disease (PAD). Peripheral artery disease is a condition in which the arteries in your legs or arms are narrowed or blocked. TOE/BRACHIAL INDEX (TBI) =.5 Determine the severity of peripheral arterial disease present in a lower extremity. F E E E D D C A A A A D Acceptable, Borderline F F D D C A A A A Normal range Ejection Elasticity Index (EEI):.6 EEI is an indicator for left ventricle ejection power and elasticity of large arteries. F E D C B A A B C D E F Borderline Normal Blood Circulation Dicrotic Dilation Index (DDI):.63 DDI indicates the contractility, tension and stiffness in the small arteries. F E D C B A A B C D E F Borderline Normal Blood Circulation Dicrotic Elasticity Index (DEI):.5 DEI represents the reflection of arterial elasticity and blood flow in the venous system. F E D C B A A B C D E F Normal Blood Circulation Coronary Respiratory Response: 2.6 E D C A A A CAD occurs when the blood vessels that transport blood to the heart are narrowed and hardened due to plaque buildup (atherosclerosis) Acceptable, Borderline Augmentation Index -.27 < -.7 Stroke Volume 64.6 ml 55- Blood Volume 5.25 l 3-5 DPTI/SPTI.28 ratio Blood Pressure 28/7 mmhg < 2 Reflection Index Cardiac Output 5.29 l/min C 2.72 ml/ >. mmhg Systemic Vascular Resistance Central Systolic Pressure 22 mmhg 2-24 Stiffness Index 8.55 m/s < 8. Mean Arterial Pressure 88 mmhg 7- C ml/ > 6. mmhg Pulse Oximetry 96.4 > 95 A - Normal B - Borderline Normal C - Moderate D - Borderline Abnormal E - Abnormal F - Severe 6 [s] PPG Printed: 9 May 28 2:8
5 ECG ANALYSIS REPORT Age:52 (DOB: Jan 966 2:) Exam Date: Sep 27 4:45 Recorded time Start Date :45:24 Duration 3 min (248 beats) High Pass Filters 3.4 Hz Heart Rate Average Heart Rate Fastest rate Slowest rate 82 bpm 89 bpm 77 bpm Ventricular Details PVC - Ventricular Ectopy beats (%) Ventricular Couplet episodes Supraventricular Details PAC - Supraventricular Ectopy beats (%) Supraventricular Couplet episodes Pause / Block Irregular / Artifact beat beats (.4%) HRV Analysis SDNN 23 ms QRS Analysis QRS QT / QTc PR int / seg ST int / seg 53 ms 32 ms / 355 ms 8 ms / 63 ms 246 ms / 5 ms PAC - Atrial Extrasystole: % PVC - Ventricular Extrasystole: % Irregular / Artifact beat:.4% Normal: 99.6% Interpretations: 7.6 [s] [mv] [s] [mv] Printed: 9 May 28 2:8
6 Arterial Vascular Assessment - Segmental Analysis Age:52 (DOB: Jan 966 2:) Exam Date: Sep 27 4:45 Resting - Right - Arm Standing - Arm Compare - Arm EEI =.64 DDI =.63 DEI =.5 AI = -.27 RI =.45 SI = 8.55 PTT = 55.4 ms DPTI/SPTI =.28 PWV = 5.8 m/s Systolic = 28 mmhg SpO2 = 96.4 % Diastolic = 7 mmhg CASP = 22 mmhg 4 [s] PVR EEI =.95 DDI =.87 DEI =.93 AI = -.7 RI =.32 SI = 7.79 PTT = 4.96 ms DPTI/SPTI =.8 PWV = 5.88 m/s Systolic = 28 mmhg SpO2 = 94 % Diastolic = 92 mmhg CASP = 22 mmhg 4 [s] PVR deei =.3 dddi =.24 ddei =.44 dai = -.43 dri = -.4 dsi = -.76 dptt = ms ddpti/dspti = -. dpwv =.7 m/s d Systolic = mmhg dspo2 = -2.4 % d Diastolic = 2 mmhg 4 [s] PPG 4 [s] PPG Resting - Right - Ankle Standing - Ankle Compare - Ankle EEI =.55 DDI =.63 DEI =.36 AI = -.4 RI =.4 SI = 6.87 PTT = ms DPTI/SPTI =.25 EEI =.7 DDI =.9 DEI =.7 AI = -.36 RI =.9 SI = 7.97 PTT = 2 ms DPTI/SPTI =. deei =.5 dddi =.28 ddei =.34 dai = -.2 dri = -.2 dsi =.9 PWV = 6.35 m/s SpO2 = 96.2 % Systolic = 6 mmhg Diastolic = 74 mmhg PWV = 3.62 m/s SpO2 = 9.8 % Systolic = 42 mmhg Diastolic = mmhg dptt = ms dpwv = m/s ddpti/dspti = -.4 d Systolic = -8 mmhg.8 [s].8 [s] dspo2 = -4.4 % d Diastolic = 36 mmhg Resting - Right - Compare Standing - Compare deei = -.9 dddi = ddei = -.4 deei = -.25 dddi =.3 ddei = -.23 dai =.3 dri = -.5 dsi = -.68 dai =.35 dri = -.2 dsi =.8 ftptt = 6.88 ms ddpti/dspti = -.3 ftptt = 7 ms ddpti/dspti = -.8 ftpwv = 9.73 m/s d Systolic = 3 mmhg ftpwv = 7.5 m/s d Systolic = 5 mmhg dspo2 = -.2 % d Diastolic = 3 mmhg dspo2 = -2.2 % d Diastolic = mmhg Ankle/Brachial Index (ABI) =.99 Toe/Brachial Index (TBI) =.5 Ankle/Brachial Index (ABI) =.3 Toe/Brachial Index (TBI) =.96 Acceptable, Borderline Printed: 9 May 28 2:8
7 SUDOMOTOR SYMPATHETIC RESPONSE HANDS Asymmetry = 22% (Unfavorable values: higher than 2 %) Bioelectrical Conductivity Response (dbec) = 7 (dbec correlate with Sweat Gland Function) 66 Bioelectrical Conductivity (BEC) = 88.8 µs (BEC correlate with Sweat Gland Nerve Density) Right µs FEET Asymmetry = 8% (Unfavorable values: higher than 2 %) Bioelectrical Conductivity Response (dbec) = 67 (dbec correlate with Sweat Gland Function) 66 Bioelectrical Conductivity (BEC) = µs Possible: Palmar Hyperhidrosis Right µs SUDOMOTOR AUTONOMIC NEUROPATHY Risk for sudomotor autonomic neuropathy = 3.9 (No risk if < 4, Moderate 4-6, Elevated risk if > 6) Sudomotor autonomic neuropathy correlate with Sweat Gland Nerve Density and Sweat Gland Function Right: Foot Left: Foot Printed: 9 May 28 2:8
8 BIOELECTRICAL IMPEDANCE ANALYSIS (BIA) BIOELECTRICAL IMPEDANCE ANALYSIS Parameter Value Norms Weight 83 kg high cell% low water% Fat-Free Mass 79 % 78-9 Body Fat Mass 2 % -22 Intracellular Water 34 % 34-4 Extracellular Water 25 % Total Body Water 59 % OBESITY ANALYSIS high water % R low cell% Parameter Value Norms Body Mass Index 27 kg/m law muscle mass obesity Body Fat-Free Mass Index 2 kg/m Body Fat Mass Index 6 kg/m Hydration Phase Angle (5KHz) 7.79 >6. Basal Metabolic Rate BODY COMPOSITION 75 kcal chronic energy d fi i FFMI high muscle Values Total Body Water Fat-Free Mass Weight Intracellular Water 28kg (34%) 49kg (59%) Extracellular Water 2kg (25%) 66kg (79%) Dry Lean Mass 7kg (2%) 83kg Body Fat Mass 7kg (2%) Body Mass Index (BMI) = 27 D C B A A B C C D D E E F F Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR) = 75 cal Total Daily Energy Expenditure = 2626 cal Risk of Associated Disease According to BMI and Waist Size 8.5 or less: Underweight : Normal - very low risk of associated diseases 23-25: Borderline Normal - Increased Risk 25-3: Overweight - prone to health risks 3-35: Overweight to Obese - high risk of associated diseases 35-4: Obese - very high risk of associated diseases 4 or greater: Extremely Obese - very high risk of associated diseases Printed: 9 May 28 2:8
9 Electro Interstitial Scan - Living Tissue DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Interstitial ph = 64 (>5)(7.9) Na+/K+APTase Activity = 54 (>5)(42.3) Oxygen Delivery = 5 (>5)(.4) Intracellular Water = 33.2% (34-4) Hydration = 74.3% (55-7) Dry Lean Mass = 2.3% (5-3) Overall Score = 54 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Interstitial ph = 7 (>5)(7.7) Na+/K+APTase Activity = 72 (>5)(4.4) Oxygen Delivery = 52 (>5)(.5) Intracellular Water = 4.6% (34-4) Hydration = 72.3% (55-7) Dry Lean Mass = 9.5% (5-3) Overall Score = 64 HORMONAL/THYROID SYSTEM Interstitial ph = 7 (>5)(8.2) Na+/K+APTase Activity = 54 (>5)(4.5) Oxygen Delivery = 52 (>5)(.5) Intracellular Water = 33.4% (34-4) Hydration = 73% (55-7) Dry Lean Mass = 2.3% (5-3) Overall Score = 56 UROGENITAL & RENAL SYSTEM Interstitial ph = 6 (>5)(7) Na+/K+APTase Activity = 6 (>5)(5.2) Oxygen Delivery = 5 (>5)(.4) Intracellular Water = 36.% (34-4) Hydration = 75.% (55-7) Dry Lean Mass = 9.8% (5-3) Overall Score = 55 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Interstitial ph = 74 (>5)(7.4) Na+/K+APTase Activity = 86 (>5)(4.2) Oxygen Delivery = 53 (>5)(.5) Intracellular Water = 37.9% (34-4) Hydration = 84.8% (55-7) Dry Lean Mass = 25% (5-3) Overall Score = 7 BRAIN SYSTEM Interstitial ph = (>5)(25.2) Na+/K+APTase Activity = 58 (>5)(44) Oxygen Delivery = 56 (>5)(.6) Intracellular Water = 26% (34-4) Hydration = 69.% (55-7) Dry Lean Mass = 25% (5-3) Overall Score = 57 Printed: 9 May 28 2:8
ARTERIAL STIFFNESS ASSESSMENT COMMENTS:
 ARTERIAL STIFFNESS ASSESSMENT 10% Low small artery stiffness risk. However, we detect mild vasoconstriction in small artery. No large arterial stiffness has been detected. High Blood Pressure & Arterial
ARTERIAL STIFFNESS ASSESSMENT 10% Low small artery stiffness risk. However, we detect mild vasoconstriction in small artery. No large arterial stiffness has been detected. High Blood Pressure & Arterial
QANS ASSESSMENT SYSTEM
 Comprehensive Non Invasive System Includes: Autonomic Balance Analysis Cardiovascular Pulse Wave Velocity Analysis ECG Analysis Cardiovascular Fitness Analysis Metabolic Report Arterial Vascular Assessment
Comprehensive Non Invasive System Includes: Autonomic Balance Analysis Cardiovascular Pulse Wave Velocity Analysis ECG Analysis Cardiovascular Fitness Analysis Metabolic Report Arterial Vascular Assessment
ESTECK Status Report [Abridged]
![ESTECK Status Report [Abridged] ESTECK Status Report [Abridged]](/thumbs/90/101774171.jpg) Back www.geoffbond.com ESTECK Status Report [Abridged] WARNING! The ES Teck system [] does not replace any existing other medical examinations. The ES Teck system[] is not used for diagnosis. It is intended
Back www.geoffbond.com ESTECK Status Report [Abridged] WARNING! The ES Teck system [] does not replace any existing other medical examinations. The ES Teck system[] is not used for diagnosis. It is intended
QANS ASSESSMENT SYSTEM
 Comprehensive Non Invasive System Includes: Autonomic Balance Analysis Cardiovascular Pulse Wave Velocity Analysis ECG Analysis Cardiovascular Fitness Analysis Metabolic Report Arterial Vascular Assessment
Comprehensive Non Invasive System Includes: Autonomic Balance Analysis Cardiovascular Pulse Wave Velocity Analysis ECG Analysis Cardiovascular Fitness Analysis Metabolic Report Arterial Vascular Assessment
VitalScan ANS. Cardiac Autonomic Function Testing (ANS) VitalScan ANS+ In 15 Minutes Identify Patients at Risk
 VitalScan ANS Medeia Inc Cardiac Autonomic Function Testing (ANS) In 15 Minutes Identify Patients at Risk The VitalScan diagnostic test provides next generation non invasive patient diagnostics within
VitalScan ANS Medeia Inc Cardiac Autonomic Function Testing (ANS) In 15 Minutes Identify Patients at Risk The VitalScan diagnostic test provides next generation non invasive patient diagnostics within
Cardiac Output MCQ. Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology. Cairo University 2007
 Cardiac Output MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 90- Guided by Ohm's law when : a- Cardiac output = 5.6 L/min. b- Systolic and diastolic BP
Cardiac Output MCQ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim Ahmed, MD Professor of Cardiovascular Physiology Cairo University 2007 90- Guided by Ohm's law when : a- Cardiac output = 5.6 L/min. b- Systolic and diastolic BP
LD TECHNOLOGY PRODUCT CATALOG
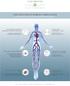 LD TECHNOLOGY M A K I N G A D I F F E R E N C E EARLY DETECTION OF DIABETES COMPLICATIONS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM AND ARTERY ASSESSEMENT BLOOD PRESSURE AND ARTERIAL STIFFNESS ANALYSIS Monitoring and Treatment
LD TECHNOLOGY M A K I N G A D I F F E R E N C E EARLY DETECTION OF DIABETES COMPLICATIONS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM AND ARTERY ASSESSEMENT BLOOD PRESSURE AND ARTERIAL STIFFNESS ANALYSIS Monitoring and Treatment
EARLY DETECTION OF DIABETES COMPLICATIONS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM AND VASCULAR FUNCTION ASSESSMENTS
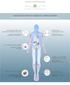 HIGHLY REIMBURSABLE M A K I N G A D I F F E R E N C E EARLY DETECTION OF DIABETES COMPLICATIONS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM AND VASCULAR FUNCTION ASSESSMENTS BLOOD PRESSURE AND ARTERIAL STIFFNESS ANALYSIS
HIGHLY REIMBURSABLE M A K I N G A D I F F E R E N C E EARLY DETECTION OF DIABETES COMPLICATIONS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM AND VASCULAR FUNCTION ASSESSMENTS BLOOD PRESSURE AND ARTERIAL STIFFNESS ANALYSIS
LD TECHNOLOGY PRODUCT CATALOG
 LD TECHNOLOGY M A K I N G A D I F F E R E N C E EARLY DETECTION OF DIABETES COMPLICATIONS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM AND VASCULAR FUNCTION ASSESSMENTS BLOOD PRESSURE AND ARTERIAL STIFFNESS ANALYSIS Monitoring
LD TECHNOLOGY M A K I N G A D I F F E R E N C E EARLY DETECTION OF DIABETES COMPLICATIONS AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM AND VASCULAR FUNCTION ASSESSMENTS BLOOD PRESSURE AND ARTERIAL STIFFNESS ANALYSIS Monitoring
Blood pressure. Formation of the blood pressure: Blood pressure. Formation of the blood pressure 5/1/12
 Blood pressure Blood pressure Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Ø Blood pressure means the force exerted by the blood against the vessel wall Ø ( or the force exerted by the blood against any unit area
Blood pressure Blood pressure Dr Badri Paudel www.badripaudel.com Ø Blood pressure means the force exerted by the blood against the vessel wall Ø ( or the force exerted by the blood against any unit area
Properties of Pressure
 OBJECTIVES Overview Relationship between pressure and flow Understand the differences between series and parallel circuits Cardiac output and its distribution Cardiac function Control of blood pressure
OBJECTIVES Overview Relationship between pressure and flow Understand the differences between series and parallel circuits Cardiac output and its distribution Cardiac function Control of blood pressure
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
ANS1 : Sudopath & TM Oxi
 ANS1 : Sudopath & TM Oxi Assessment of: Autonomic Nervous System Cardiovascular System Sudomotor Function Endothelial (arterial) Function Clinical Applications: Early Detection of risk for Peripheral Small
ANS1 : Sudopath & TM Oxi Assessment of: Autonomic Nervous System Cardiovascular System Sudomotor Function Endothelial (arterial) Function Clinical Applications: Early Detection of risk for Peripheral Small
P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp , , , I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System
 P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp 360-390, 395-404, 410-428 433-438, 441-445 I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Structure of the Heart 1. atria 2. ventricles
P215 SPRING 2019: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Chaps 13, 14 & 15: pp 360-390, 395-404, 410-428 433-438, 441-445 I. Major Functions of the Circulatory System 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Structure of the Heart 1. atria 2. ventricles
Electrical Conduction
 Sinoatrial (SA) node Electrical Conduction Sets the pace of the heartbeat at 70 bpm AV node (50 bpm) and Purkinje fibers (25 40 bpm) can act as pacemakers under some conditions Internodal pathway from
Sinoatrial (SA) node Electrical Conduction Sets the pace of the heartbeat at 70 bpm AV node (50 bpm) and Purkinje fibers (25 40 bpm) can act as pacemakers under some conditions Internodal pathway from
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices. Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont
 Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont Review of Cardiac Anatomy Four chambers Two atria-receive blood from the vena cave and pulmonary veins Two
Principles of Biomedical Systems & Devices Lecture 8: Cardiovascular Dynamics Dr. Maria Tahamont Review of Cardiac Anatomy Four chambers Two atria-receive blood from the vena cave and pulmonary veins Two
BIOL 219 Spring Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System
 1 BIOL 219 Spring 2013 Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System Outline: Components of the CV system Heart anatomy Layers of the heart wall Pericardium Heart chambers, valves, blood vessels, septum Atrioventricular
1 BIOL 219 Spring 2013 Chapters 14&15 Cardiovascular System Outline: Components of the CV system Heart anatomy Layers of the heart wall Pericardium Heart chambers, valves, blood vessels, septum Atrioventricular
POSTURAL ORTHOSTATIC TACHYCARDIA SYNDROME (POTS) IT S NOT THAT SIMPLE
 POSTURAL ORTHOSTATIC TACHYCARDIA SYNDROME (POTS) IT S NOT THAT SIMPLE POTS Irritable heart syndrome. Soldier s heart. Effort syndrome. Vasoregulatory asthenia. Neurocirculatory asthenia. Anxiety neurosis.
POSTURAL ORTHOSTATIC TACHYCARDIA SYNDROME (POTS) IT S NOT THAT SIMPLE POTS Irritable heart syndrome. Soldier s heart. Effort syndrome. Vasoregulatory asthenia. Neurocirculatory asthenia. Anxiety neurosis.
Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives To understand the volume, mechanical, pressure and electrical changes during the cardiac cycle To understand the inter-relationship
Heart Pump and Cardiac Cycle Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives To understand the volume, mechanical, pressure and electrical changes during the cardiac cycle To understand the inter-relationship
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
(D) (E) (F) 6. The extrasystolic beat would produce (A) increased pulse pressure because contractility. is increased. increased
 Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Review Test 1. A 53-year-old woman is found, by arteriography, to have 5% narrowing of her left renal artery. What is the expected change in blood flow through the stenotic artery? Decrease to 1 2 Decrease
Chapter 9, Part 2. Cardiocirculatory Adjustments to Exercise
 Chapter 9, Part 2 Cardiocirculatory Adjustments to Exercise Electrical Activity of the Heart Contraction of the heart depends on electrical stimulation of the myocardium Impulse is initiated in the right
Chapter 9, Part 2 Cardiocirculatory Adjustments to Exercise Electrical Activity of the Heart Contraction of the heart depends on electrical stimulation of the myocardium Impulse is initiated in the right
IP: Regulation of Cardiac Output
 ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chap... Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chapter 18 Signed in as Alex Sokolowski Help Close Resources Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 25, 2013 Note:
ANP 1105D Winter 2013 Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chap... Assignment 9: The Heart, part 2: Chapter 18 Signed in as Alex Sokolowski Help Close Resources Due: 11:59pm on Monday, March 25, 2013 Note:
Cardiac Output 1 Fox Chapter 14 part 1
 Vert Phys PCB3743 Cardiac Output 1 Fox Chapter 14 part 1 T. Houpt, Ph.D. Regulation of Heart & Blood Pressure Keep Blood Pressure constant if too low, not enough blood (oxygen, glucose) reaches tissues
Vert Phys PCB3743 Cardiac Output 1 Fox Chapter 14 part 1 T. Houpt, Ph.D. Regulation of Heart & Blood Pressure Keep Blood Pressure constant if too low, not enough blood (oxygen, glucose) reaches tissues
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function
 Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disorders
 Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disorders Blood Pressure Normal blood pressure is 120/80 mmhg (millimeters of mercury) Hypertension is when the resting blood pressure is too high Systolic BP is 140 mmhg
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disorders Blood Pressure Normal blood pressure is 120/80 mmhg (millimeters of mercury) Hypertension is when the resting blood pressure is too high Systolic BP is 140 mmhg
Cardiovascular System. Heart
 Cardiovascular System Heart Electrocardiogram A device that records the electrical activity of the heart. Measuring the relative electrical activity of one heart cycle. A complete contraction and relaxation.
Cardiovascular System Heart Electrocardiogram A device that records the electrical activity of the heart. Measuring the relative electrical activity of one heart cycle. A complete contraction and relaxation.
During exercise the heart rate is 190 bpm and the stroke volume is 115 ml/beat. What is the cardiac output?
 The Cardiovascular System Part III: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Be able to calculate cardiac output (CO) be able to define heart rate
The Cardiovascular System Part III: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Be able to calculate cardiac output (CO) be able to define heart rate
The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 18 Part A The Cardiovascular System 1/19/16 1 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Similarities of Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle RMP Ion concentration Deploarization Action Potential Repolarization
Chapter 18 Part A The Cardiovascular System 1/19/16 1 Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images Similarities of Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle RMP Ion concentration Deploarization Action Potential Repolarization
Skin supplied by T1-4 (medial upper arm and neck) T5-9- epigastrium Visceral afferents from skin and heart are the same dorsal root ganglio
 Cardio 2 ECG... 3 Cardiac Remodelling... 11 Valvular Diseases... 13 Hypertension... 18 Aortic Coarctation... 24 Erythropoiesis... 27 Haemostasis... 30 Anaemia... 36 Atherosclerosis... 44 Angina... 48 Myocardial
Cardio 2 ECG... 3 Cardiac Remodelling... 11 Valvular Diseases... 13 Hypertension... 18 Aortic Coarctation... 24 Erythropoiesis... 27 Haemostasis... 30 Anaemia... 36 Atherosclerosis... 44 Angina... 48 Myocardial
Cardiovascular Effects of Exercise. Background Cardiac function
 Cardiovascular Effects of Exercise In this experiment, you will record an electrocardiogram, or ECG, and finger pulse from a healthy volunteer. You will then compare the ECG and pulse recordings when the
Cardiovascular Effects of Exercise In this experiment, you will record an electrocardiogram, or ECG, and finger pulse from a healthy volunteer. You will then compare the ECG and pulse recordings when the
INTRODUCTORY TEXT BOX
 INTRODUCTORY TEXT BOX Diagnostic Partners provides a range of onsite, in-office cardiac and vascular diagnostic testing services. From Resting Echocardiograms to Abdominal Aorta scans, each study is performed
INTRODUCTORY TEXT BOX Diagnostic Partners provides a range of onsite, in-office cardiac and vascular diagnostic testing services. From Resting Echocardiograms to Abdominal Aorta scans, each study is performed
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System
 AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System Learning Objectives The link between the Cardiac Cycle and the Conduction system of the heart. The relationship between Stroke volume, Heart rate and Cardiac Output.
AS Level OCR Cardiovascular System Learning Objectives The link between the Cardiac Cycle and the Conduction system of the heart. The relationship between Stroke volume, Heart rate and Cardiac Output.
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
HRV in Diabetes and Other Disorders
 HRV in Diabetes and Other Disorders Roy Freeman, MD Center for Autonomic and Peripheral Nerve Disorders Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Control Propranolol Atropine Wheeler
HRV in Diabetes and Other Disorders Roy Freeman, MD Center for Autonomic and Peripheral Nerve Disorders Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Control Propranolol Atropine Wheeler
Lighten-up your Child s Growth
 Specifications Key Specifications Bioelectrical Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) Impedance (Z) Measurement Items 15 Impedance Measurements by Using 3 Different Frequencies (5kHz, 50kHz, 250kHz) at
Specifications Key Specifications Bioelectrical Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) Impedance (Z) Measurement Items 15 Impedance Measurements by Using 3 Different Frequencies (5kHz, 50kHz, 250kHz) at
Congestive Heart Failure or Heart Failure
 Congestive Heart Failure or Heart Failure Dr Hitesh Patel Ascot Cardiology Group Heart Failure Workshop April, 2014 Question One What is the difference between congestive heart failure and heart failure?
Congestive Heart Failure or Heart Failure Dr Hitesh Patel Ascot Cardiology Group Heart Failure Workshop April, 2014 Question One What is the difference between congestive heart failure and heart failure?
HE 250 PERSONAL HEALTH. Stress
 HE 250 PERSONAL HEALTH Stress Stress Stress General state of the body, mind, and emotions when an environmental stressor has triggered the stress response Stressor Events or agents in the environment that
HE 250 PERSONAL HEALTH Stress Stress Stress General state of the body, mind, and emotions when an environmental stressor has triggered the stress response Stressor Events or agents in the environment that
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide
 Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
MAX PULSE RESULT INTERPRETATION GUIDE PROVE CLINICAL EFFICACY IMPROVE CLINICAL OUTCOMES IMPROVE PATIENT ADHERENCE
 MAX PULSE RESULT INTERPRETATION GUIDE PROVE CLINICAL EFFICACY IMPROVE CLINICAL OUTCOMES IMPROVE PATIENT ADHERENCE PLETHYSMOGRAPHY VOLUME CAPACITY PG ON FINGERTIP VELOCITY PG (1ST DIFFERENTIATION) APG (2ND
MAX PULSE RESULT INTERPRETATION GUIDE PROVE CLINICAL EFFICACY IMPROVE CLINICAL OUTCOMES IMPROVE PATIENT ADHERENCE PLETHYSMOGRAPHY VOLUME CAPACITY PG ON FINGERTIP VELOCITY PG (1ST DIFFERENTIATION) APG (2ND
Outcomes: By the end of this session the student will be able to:
 Outcomes: By the end of this session the student will be able to: Discuss the cardiovascular system Identify the normal changes that occur with ageing Explain the nurses role in the care of residents with
Outcomes: By the end of this session the student will be able to: Discuss the cardiovascular system Identify the normal changes that occur with ageing Explain the nurses role in the care of residents with
Cardiovascular Physiology. Heart Physiology. Introduction. The heart. Electrophysiology of the heart
 Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology Introduction The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and two vascular systems, the systemic and pulmonary circulations. The heart pumps blood through
Cardiovascular Physiology Heart Physiology Introduction The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and two vascular systems, the systemic and pulmonary circulations. The heart pumps blood through
*Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates. *Ensuring one-way blood. *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction
 *Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations *Ensuring one-way blood flow: valves *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction rate and force match blood
*Generating blood pressure *Routing blood: separates pulmonary and systemic circulations *Ensuring one-way blood flow: valves *Regulating blood supply *Changes in contraction rate and force match blood
RM-3A Cardiovascular & ANS Medical Device
 RM-3A Cardiovascular & ANS Medical Device The RM-3A medical device is a powerful analytical tool in managing your patients health. Scientifically validated and FDA cleared, this medical device performs
RM-3A Cardiovascular & ANS Medical Device The RM-3A medical device is a powerful analytical tool in managing your patients health. Scientifically validated and FDA cleared, this medical device performs
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
*(a) Describe the blood clotting process. (4)
 1 There are many venomous (poisonous) snakes in the world. Many of the venoms from these snakes affect the blood clotting process. *(a) Describe the blood clotting process. (4) (b) Factor Xa is a clotting
1 There are many venomous (poisonous) snakes in the world. Many of the venoms from these snakes affect the blood clotting process. *(a) Describe the blood clotting process. (4) (b) Factor Xa is a clotting
Risk Factors for Heart Disease
 Risk Factors for Heart Disease Risk Factors we cannot change (Age, Gender, Family History) Risk Factors we can change (modifiable) Smoking Blood pressure Cholesterol Diabetes Inactivity Overweight Stress
Risk Factors for Heart Disease Risk Factors we cannot change (Age, Gender, Family History) Risk Factors we can change (modifiable) Smoking Blood pressure Cholesterol Diabetes Inactivity Overweight Stress
Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes
 Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Identify the components of the cardiovascular system and the various types of cardiovascular disease Ø Discuss ways of promoting cardiovascular
Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Identify the components of the cardiovascular system and the various types of cardiovascular disease Ø Discuss ways of promoting cardiovascular
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System. The heart. The heart is a double pump. A quick note on arteries vs. veins. = the muscular pump of the CV system
 Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors
 Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia)
 Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Blood Pressure and its Regulation
 Blood Pressure and its Regulation Blood pressure in your blood vessels is closely monitored by baroreceptors; they send messages to the cardio regulatory center of your medulla oblongata to regulate your
Blood Pressure and its Regulation Blood pressure in your blood vessels is closely monitored by baroreceptors; they send messages to the cardio regulatory center of your medulla oblongata to regulate your
Circulation. Sinoatrial (SA) Node. Atrioventricular (AV) Node. Cardiac Conduction System. Cardiac Conduction System. Linked to the nervous system
 Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
Circulation Cardiac Conduction System AHS A H S Your body resembles a large roadmap. There are routes or arteries that take you downtown to the heart of the city and veins that take you to the outskirts
BIOH122 Session 6 Vascular Regulation
 BIOH122 Session 6 Vascular Regulation To complete this worksheet, select: Module: Distribution Title: Vascular Regulation Introduction 1. a. How do Mean Arterial Blood Pressure (MABP) and Systemic Vascular
BIOH122 Session 6 Vascular Regulation To complete this worksheet, select: Module: Distribution Title: Vascular Regulation Introduction 1. a. How do Mean Arterial Blood Pressure (MABP) and Systemic Vascular
Impedance Cardiography (ICG) Method, Technology and Validity
 Method, Technology and Validity Hemodynamic Basics Cardiovascular System Cardiac Output (CO) Mean arterial pressure (MAP) Variable resistance (SVR) Aortic valve Left ventricle Elastic arteries / Aorta
Method, Technology and Validity Hemodynamic Basics Cardiovascular System Cardiac Output (CO) Mean arterial pressure (MAP) Variable resistance (SVR) Aortic valve Left ventricle Elastic arteries / Aorta
Note: At the end of the instructions, you will find a table which must be filled in to complete the exercise.
 Autonomic Nervous System Theoretical foundations and instructions for conducting practical exercises carried out during the course List of practical exercises 1. Deep (controlled) breath test 2. Cold pressor
Autonomic Nervous System Theoretical foundations and instructions for conducting practical exercises carried out during the course List of practical exercises 1. Deep (controlled) breath test 2. Cold pressor
Cardiovascular Diseases in CKD
 1 Cardiovascular Diseases in CKD Hung-Chun Chen, MD, PhD. Kaohsiung Medical University Taiwan Society of Nephrology 1 2 High Prevalence of CVD in CKD & ESRD Foley RN et al, AJKD 1998; 32(suppl 3):S112-9
1 Cardiovascular Diseases in CKD Hung-Chun Chen, MD, PhD. Kaohsiung Medical University Taiwan Society of Nephrology 1 2 High Prevalence of CVD in CKD & ESRD Foley RN et al, AJKD 1998; 32(suppl 3):S112-9
SECONDARY HYPERTENSION
 HYPERTENSION Hypertension is the clinical term used to describe a high blood pressure of 140/90 mmhg or higher (National Institute of Health 1997). It is such a health risk the World Health Organisation
HYPERTENSION Hypertension is the clinical term used to describe a high blood pressure of 140/90 mmhg or higher (National Institute of Health 1997). It is such a health risk the World Health Organisation
3/10/2009 VESSELS PHYSIOLOGY D.HAMMOUDI.MD. Palpated Pulse. Figure 19.11
 VESSELS PHYSIOLOGY D.HAMMOUDI.MD Palpated Pulse Figure 19.11 1 shows the common sites where the pulse is felt. 1. Temporal artery at the temple above and to the outer side of the eye 2. External maxillary
VESSELS PHYSIOLOGY D.HAMMOUDI.MD Palpated Pulse Figure 19.11 1 shows the common sites where the pulse is felt. 1. Temporal artery at the temple above and to the outer side of the eye 2. External maxillary
Cardiovascular System and Health. Chapter 15
 Cardiovascular System and Health Chapter 15 Cardiovascular Disease Leading cause of death in U.S. Claims 1 life every 43 seconds Often, the first sign is a fatal heart attack Death Rates #1 CVD #2 Cancer
Cardiovascular System and Health Chapter 15 Cardiovascular Disease Leading cause of death in U.S. Claims 1 life every 43 seconds Often, the first sign is a fatal heart attack Death Rates #1 CVD #2 Cancer
Circulation. Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications. Venous Return. Arterial flow. Regulation of Cardiac Output.
 Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
Circulation Blood Pressure and Antihypertensive Medications Two systems Pulmonary (low pressure) Systemic (high pressure) Aorta 120 mmhg Large arteries 110 mmhg Arterioles 40 mmhg Arteriolar capillaries
Cardiac Output (C.O.) Regulation of Cardiac Output
 Cardiac Output (C.O.) Is the volume of the blood pumped by each ventricle per minute (5 Litre) Stroke volume: Is the volume of the blood pumped by each ventricle per beat. Stroke volume = End diastolic
Cardiac Output (C.O.) Is the volume of the blood pumped by each ventricle per minute (5 Litre) Stroke volume: Is the volume of the blood pumped by each ventricle per beat. Stroke volume = End diastolic
BUSINESS. Articles? Grades Midterm Review session
 BUSINESS Articles? Grades Midterm Review session REVIEW Cardiac cells Myogenic cells Properties of contractile cells CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART Conduction pathway SA node (pacemaker) atrial depolarization
BUSINESS Articles? Grades Midterm Review session REVIEW Cardiac cells Myogenic cells Properties of contractile cells CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART Conduction pathway SA node (pacemaker) atrial depolarization
Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co.
 Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Anatomy Views Label the diagrams of the heart below: Interactive Physiology Study
Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Anatomy Views Label the diagrams of the heart below: Interactive Physiology Study
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Heart 2
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
Cardiovascular Responses to Exercise
 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY 69 Case 13 Cardiovascular Responses to Exercise Cassandra Farias is a 34-year-old dietician at an academic medical center. She believes in the importance of a healthy lifestyle
CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY 69 Case 13 Cardiovascular Responses to Exercise Cassandra Farias is a 34-year-old dietician at an academic medical center. She believes in the importance of a healthy lifestyle
VitalScan Plus. Autonomic Dysfunction Assessment. VitalScan + In 15 Minutes Identify Patients at Risk. Medeia Inc
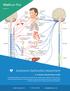 VitalScan Plus Medeia Inc Autonomic Dysfunction Assessment In 15 Minutes Identify Patients at Risk The VitalScan diagnostic test provides next generation non invasive patient diagnostics within minutes.
VitalScan Plus Medeia Inc Autonomic Dysfunction Assessment In 15 Minutes Identify Patients at Risk The VitalScan diagnostic test provides next generation non invasive patient diagnostics within minutes.
Hypertension and Heart Disease. Weldon James, MD, Mercy Clinic Family Medicine, Union
 Hypertension and Heart Disease Weldon James, MD, Mercy Clinic Family Medicine, Union The Silent Killer High blood pressure, also known as HBP or hypertension, is a widely misunderstood medical condition
Hypertension and Heart Disease Weldon James, MD, Mercy Clinic Family Medicine, Union The Silent Killer High blood pressure, also known as HBP or hypertension, is a widely misunderstood medical condition
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology
 d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
Age-related changes in cardiovascular system. Dr. Rehab Gwada
 Age-related changes in cardiovascular system Dr. Rehab Gwada Objectives explain the main structural and functional changes in cardiovascular system associated with normal aging Introduction aging results
Age-related changes in cardiovascular system Dr. Rehab Gwada Objectives explain the main structural and functional changes in cardiovascular system associated with normal aging Introduction aging results
How to Analyze Stress from Heart Rate & Heart Rate Variability: A Review of Physiology
 How to Analyze Stress from Heart Rate & Heart Rate Variability: A Review of Physiology STRESS AFFECTS THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM TERMINOLOGY Heart rate (HR): heartbeat frequency as beats per minute (bpm)
How to Analyze Stress from Heart Rate & Heart Rate Variability: A Review of Physiology STRESS AFFECTS THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM TERMINOLOGY Heart rate (HR): heartbeat frequency as beats per minute (bpm)
C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders
 C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders GENERAL ISSUES REGARDING MEDICAL FITNESS-FOR-DUTY 1. These medical standards apply to Union Pacific Railroad (UPRR) employees
C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders GENERAL ISSUES REGARDING MEDICAL FITNESS-FOR-DUTY 1. These medical standards apply to Union Pacific Railroad (UPRR) employees
BODYSTAT BODY COMPOSITION AND WELLNESS PROFILE FOR. Sample Report
 BODYSTAT BODY COMPOSITION AND WELLNESS PROFILE FOR Sample Report Copyright 1998, 22. Bodystat (Isle of Man) Ltd. BODYSTAT and the BODYSTAT LOGO are the internationally registered trade marks of BODYSTAT
BODYSTAT BODY COMPOSITION AND WELLNESS PROFILE FOR Sample Report Copyright 1998, 22. Bodystat (Isle of Man) Ltd. BODYSTAT and the BODYSTAT LOGO are the internationally registered trade marks of BODYSTAT
A Comparative Study of Physical Fitness among Rural Farmers and Urban Sedentary Group of Gulbarga District
 AJMS Al Ameen J Med Sci (20 1 2 )5 (1 ):3 9-4 4 (A US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal) I S S N 0 9 7 4-1 1 4 3 C O D E N : A A J M B G ORIGI NAL ARTICLE A Comparative Study of Physical Fitness
AJMS Al Ameen J Med Sci (20 1 2 )5 (1 ):3 9-4 4 (A US National Library of Medicine enlisted journal) I S S N 0 9 7 4-1 1 4 3 C O D E N : A A J M B G ORIGI NAL ARTICLE A Comparative Study of Physical Fitness
Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors
 Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors 1 Human Health: What s Killing Us? Health in America Health is the U.S Average life
Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors 1 Human Health: What s Killing Us? Health in America Health is the U.S Average life
BLOOD PRESSURE. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 BLOOD PRESSURE Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration Blood Pressure The force of your blood pushing on the walls of your arteries. How is Blood Pressure Measured? Measured at an artery in the arm and
BLOOD PRESSURE Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration Blood Pressure The force of your blood pushing on the walls of your arteries. How is Blood Pressure Measured? Measured at an artery in the arm and
RESULTS SHEET BREAKDOWN
 SAMPLE RESULTS SHEET This is the body composition results sheet that the InBody 270 prints out. Understand each output secion in the following pages. 6 BODY COMPOSITION ANALYSIS Body Composition Analysis
SAMPLE RESULTS SHEET This is the body composition results sheet that the InBody 270 prints out. Understand each output secion in the following pages. 6 BODY COMPOSITION ANALYSIS Body Composition Analysis
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Blood vessels, heart and blood Functions Transport oxygen, nutrients, waste, hormones White blood cells fighting disease Temperature regulation Blood vessels; Arteries Arteries carry
Cardiovascular System Blood vessels, heart and blood Functions Transport oxygen, nutrients, waste, hormones White blood cells fighting disease Temperature regulation Blood vessels; Arteries Arteries carry
Module 1: Introduction to ECG & Normal ECG
 Module 1: Introduction to ECG & Normal ECG Importance of Correct anatomical positions Measurements & Morphologies ONLY accurate if Precise anatomical positions adhered to Standardised techniques are used
Module 1: Introduction to ECG & Normal ECG Importance of Correct anatomical positions Measurements & Morphologies ONLY accurate if Precise anatomical positions adhered to Standardised techniques are used
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals
 Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 5: Rhythm Strip Interpretation and Sinus Rhythms Learning Outcomes 5.1 Explain the process of evaluating ECG tracings
Electrocardiography for Healthcare Professionals Kathryn A. Booth Thomas O Brien Chapter 5: Rhythm Strip Interpretation and Sinus Rhythms Learning Outcomes 5.1 Explain the process of evaluating ECG tracings
AUTONOMIC FUNCTION IS A HIGH PRIORITY
 AUTONOMIC FUNCTION IS A HIGH PRIORITY 1 Bladder-Bowel-AD Tetraplegia Sexual function Walking Bladder-Bowel-AD Paraplegia Sexual function Walking 0 10 20 30 40 50 Percentage of respondents an ailment not
AUTONOMIC FUNCTION IS A HIGH PRIORITY 1 Bladder-Bowel-AD Tetraplegia Sexual function Walking Bladder-Bowel-AD Paraplegia Sexual function Walking 0 10 20 30 40 50 Percentage of respondents an ailment not
Vital Signs. Vital Signs. Vital Signs
 Vital Signs Vital Signs Why do vital signs? Determine relative status of vital organs Establish baseline Monitor response to Rx, meds Observe trends Determine need for further evaluation, Rx, intervention
Vital Signs Vital Signs Why do vital signs? Determine relative status of vital organs Establish baseline Monitor response to Rx, meds Observe trends Determine need for further evaluation, Rx, intervention
TEACH Lesson Plan Manual for Herlihy s The Human Body in Health and Illness 5 th edition
 TEACH Lesson Plan Manual for Herlihy s The Human Body in Health and Illness 5 th edition Chapter 17 Function of the Heart Lesson 17.1 Function of the Heart 1. Define cardiac cycle with respect to systole
TEACH Lesson Plan Manual for Herlihy s The Human Body in Health and Illness 5 th edition Chapter 17 Function of the Heart Lesson 17.1 Function of the Heart 1. Define cardiac cycle with respect to systole
Chapter 14 Blood Vessels, Blood Flow and Pressure Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 14 Blood Vessels, Blood Flow and Pressure Exam Study Questions 14.1 Physical Law Governing Blood Flow and Blood Pressure 1. How do you calculate flow rate? 2. What is the driving force of blood
Chapter 14 Blood Vessels, Blood Flow and Pressure Exam Study Questions 14.1 Physical Law Governing Blood Flow and Blood Pressure 1. How do you calculate flow rate? 2. What is the driving force of blood
Chapter 1: Exercise Physiology. ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition
 Chapter 1: Exercise Physiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Physiology is the study of the myriad functions in a living organism. Exercise physiology is the study of the ways
Chapter 1: Exercise Physiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Physiology is the study of the myriad functions in a living organism. Exercise physiology is the study of the ways
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1. Resting membrane potential of the ventricular myocardium is: A. -55 to-65mv B. --65 to-75mv C. -75 to-85mv D. -85 to-95 mv E. -95 to-105mv 2. Regarding myocardial contraction:
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM 1. Resting membrane potential of the ventricular myocardium is: A. -55 to-65mv B. --65 to-75mv C. -75 to-85mv D. -85 to-95 mv E. -95 to-105mv 2. Regarding myocardial contraction:
Myocardial Infarction: Left Ventricular Failure
 CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY 93 Case 17 Myocardial Infarction: Left Ventricular Failure Marvin Zimmerman is a 52-year-old construction manager who is significantly overweight. Despite his physician's repeated
CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY 93 Case 17 Myocardial Infarction: Left Ventricular Failure Marvin Zimmerman is a 52-year-old construction manager who is significantly overweight. Despite his physician's repeated
Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR
 Regulation of MAP Flow = pressure gradient resistance CO = MAP TPR Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR TPR is the total peripheral resistance: this is the combined resistance of all blood vessels (remember
Regulation of MAP Flow = pressure gradient resistance CO = MAP TPR Therefore MAP=CO x TPR = HR x SV x TPR TPR is the total peripheral resistance: this is the combined resistance of all blood vessels (remember
Indications and Uses of Testing. Laboratory Testing of Autonomic Function. Generalized Autonomic Failure. Benign Disorders 12/30/2012.
 Indications and Uses of Testing Laboratory Testing of Autonomic Function Conditions of generalized autonomic failure Help define the degree of autonomic dysfunction and distinguish more benign from life
Indications and Uses of Testing Laboratory Testing of Autonomic Function Conditions of generalized autonomic failure Help define the degree of autonomic dysfunction and distinguish more benign from life
Heart Disease. Signs and Symptoms
 Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
AS OCR PHYSICAL EDUCATION The Vascular System
 AS OCR PHYSICAL EDUCATION The Vascular System Learning Objectives: - Distribution of Cardiac output at rest and during exercise - Role of the Vasomotor centre, arterioles and pre-capillary sphincters -
AS OCR PHYSICAL EDUCATION The Vascular System Learning Objectives: - Distribution of Cardiac output at rest and during exercise - Role of the Vasomotor centre, arterioles and pre-capillary sphincters -
Blood Pressure Regulation. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD
 Blood Pressure Regulation Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the short term and long term regulators of BP Know how baroreceptors and chemoreceptors work Know function of the atrial reflex.
Blood Pressure Regulation Faisal I. Mohammed, MD,PhD 1 Objectives Outline the short term and long term regulators of BP Know how baroreceptors and chemoreceptors work Know function of the atrial reflex.
CASE 10. What would the ST segment of this ECG look like? On which leads would you see this ST segment change? What does the T wave represent?
 CASE 10 A 57-year-old man presents to the emergency center with complaints of chest pain with radiation to the left arm and jaw. He reports feeling anxious, diaphoretic, and short of breath. His past history
CASE 10 A 57-year-old man presents to the emergency center with complaints of chest pain with radiation to the left arm and jaw. He reports feeling anxious, diaphoretic, and short of breath. His past history
Blood Pressure. And Natural Strategies for Optimizing C O N T E N T S. What is Blood Pressure?
 Blood Pressure And Natural Strategies for Optimizing Blood Pressure What is Blood Pressure? As the heart beats, it pumps blood throughout the body carrying nutrients and oxygen to the cells and removing
Blood Pressure And Natural Strategies for Optimizing Blood Pressure What is Blood Pressure? As the heart beats, it pumps blood throughout the body carrying nutrients and oxygen to the cells and removing
The circulatory system
 Introduction to Physiology (Course # 72336) 1 הלב עקרונות בסיסיים (הכנה למעבדת לב) Adi Mizrahi mizrahia@cc.huji.ac.il Textbook Chapter 12 2 The circulatory system To the heart Away from the heart 3 L 2.5
Introduction to Physiology (Course # 72336) 1 הלב עקרונות בסיסיים (הכנה למעבדת לב) Adi Mizrahi mizrahia@cc.huji.ac.il Textbook Chapter 12 2 The circulatory system To the heart Away from the heart 3 L 2.5
