α 1 receptor smooth muscle activation
|
|
|
- Howard Tyler
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Drugs in Hypertension Dr. Yuri Clement Pharmacology Unit, FMS Objectives Revision of physiological control of BP. What is hypertension? Associated risks of uncontrolled hypertension ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS: 1. Sympathetic Nervous System inhibition β-blockers, α 1 blockers, mixed α, β blockers, central α agonists, peripheral adrenergic blockers. 2. Sodium/Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone System balance Diuretics, ACE inhibitors, AT11 receptors blockers 3. Vasodilators Ca 2+ -channel blockers, oral and parenteral vasodilators Mechanisms of action, other indications, contraindications and adverse effects 1
2 Hemodynamic factors affecting BP Arterial Blood Pressure Cardiac Output (CO) x Total Peripheral Resistance (TPR) Arteriolar volume Heart rate Contractility Filling pressure Blood volume Venous tone sympathetic ti activity BP Regulation: SNS and RAAS Baroreceptor reflex system mediated β 1 receptor cardiac activation α 1 receptor smooth muscle activation CO TPR BP BP Renal blood volume-pressure system Renal flow renin Angiotensin II Aldosterone GFR Na +, H 2 O retention Blood volume 2
3 What is hypertension? JNC 6 Category JNC 7 Category (2004) SBP/DBP (mmhg) Optimal <120/80 NORMAL Normal /80 129/ Borderline / PREHYPERTENSION Hypertension >140/90 HYPERTENSION Stage /90 159/ STAGE 1 Stage 2 (moderate) / Stage 3 (severe) 180/110 STAGE 2 A chronic disease of persistent elevated arterial blood pressure. Classification 1 o or essential hypertension (> 95%) Genetic Ethnic Lifestyle Gender and age 2 o hypertension (~5%) Chronic renal disease Pheochromocytoma Cushing s syndrome and glucocorticoid excess states 1 o aldosteronism and other mineralocorticoid excess states Coarctation of the aorta Drug-induced 3
4 Associated risks Chronic arterial BP likelihood of morbidity and mortality. 1. CAD 2. LVH 3. CHF 4. MI 5. Arrhythmias 6. Angina 7. Stroke 8. Dementia 9. Renal disease CVD risk doubles for each increment of 20/10 mmhg Why treat? LVH Treating hypertension: stroke by 40% - 45% CHF by 40% - 50% CAD by 16% - 25% >30% unaware Educational intervention BP. In UK, only ~6% adequately treated. 4
5 Drug classification β antagonists SNS inhibition Mixed α, β antagonists t Central α 2 agonists α 1 antagonists Sodium/RAAS balance Peripheral adrenergic antagonists Diuretics Ca 2+ channel blockers ACE Inhibitors Vasodilators ATII antagonists Others β antagonists Generic name Propranolol Nadolol Pindolol Acebutolol (*) Metoprolol (*) Atenolol (*) Betaxolol (*) Bisoprolol (*) Trade name(s) Inderal Corgard Visken Sectral Toprol, Lopressor Tenormin Kerlone Zebeta Doses available Oral: 10, 20, 40, 60, 80, 90mg; 4, 8mg/mL oral soln; Inderal LA: 60, 80, 120, 160mg Parenteral: 1mg/mL soln Oral: 20, 40, 80, 120, 160mg Oral: 5, 10mg Oral: 200, 400mg Oral: 50, 100mg; XL: 25, 50, 100, 200mg Parenteral: 1mg/mL soln Oral: 25, 50, 100mg; Parenteral: 0.5mg/mL soln Oral: 10, 20mg Oral:5, 10mg (*) cardioselective 5
6 Mechanism of Action Acute effect β 1 blockade in myocardial cells -ve inotropic -ve chronotropic CO Long term effect β 1 blockade in juxtaglomerular cells aldosterone Renin release Na + retention Shift in whole body autoregulation Blood volume TPR [Angiotensin II] plasma arterial vasoconstriction Change in arterial remodelling BP Other Indications Angina pectoris Arrhythmias Glaucoma (applied topically) Migraine IHD and prevention of 2 nd MI. Useful as monotherapy in Stage 1 HTN or with vasodilators (and diuretics) in stage 2. 6
7 Contraindications CHF and nodal conduction diseases. But, carvedilol (Coreg ), misoprolol and metoprolol mortality in CHF Non-selective β blockers in asthma. Cardio-selective drugs lose selectivity at higher doses. Use with caution in insulin-dependent diabetic patients. Glycogenolysis is adrenergically mediated. β blockers antagonize sympathetic response to hypoglycemia and blunt recovery. Adverse Effects CNS: Sedation, depression, lethargy, sleep disturbances CV: CHF in LV dysfunction, heart block, bradyarrhythmias Bronchospasms (non-selective blockers) in asthma and COPD. HDL and plasma l triacylglycerol l l Abrupt cessation may induce unstable angina, MI or death in patients predisposed to ischemic myocardial events. Taper over 14 days. 7
8 α 1 antagonists Generic name Prazosin Terazosin Doxazosin Tamsulosin Trade name(s) Minipress Hytrin Cardura Flomax Doses available Oral: 1, 2, 5mg Oral: 1, 2, 5, 10mg Oral:1,2,4,8mg Oral: 0.4mg α 1 antagonists Mechanism of Action: Arterial and venous relaxation - TPR ; BP. Minimal CO, renal blood flow or GFR. No long-term tachycardia and renin release. Indication: Benign prostatic hypertrophy and hypertension (prostate capsule relaxation decreases resistance to urinary flow) Adverse Effects: 1. 1 st dose dizziness or syncope give at bedtime (caution in elderly). 2. Initial reflex tachycardia (propranolol to counteract) 3. Postural hypotension 4. Infrequent and mild CNS: vivid dreams, lassitude and depression. 8
9 Mixed α, β antagonists Generic name Labetalol Carvedilol Trade name(s) Normodyne Coreg Doses available Oral:100, 200, 300mg Parenteral: 5mg/mL soln Oral: 3.125, 6.25, 12.5, 25mg Labetalol Equimolar mixture of 4 stereoisomers: 2i inactive, 1 α 1 -blocker, other non-selective β-blocker k and β 2 - partial agonist. Useful in hypertensive emergencies (as iv) Similar efficacy and side-effects effects as β- and α 1 -antagonists when given orally. Mechanism of action: 1. α 1 blockade and β 2 stimulation cause rapid vasodilatation, TPR leading to BP Contraindications same as non-selective β blockers 9
10 Peripheral adrenergic antagonists Generic name Trade name(s) Doses available Reserpine - Oral: 0.1, 0.25mg Guanethidine Guanadrel Ismelin Hylorel Oral: 10, 25mg Oral: 10, 25mg Reserpine: Mechanism of action 1. Binds avidly to NE and 5-HT storage vesicles in central and peripheral adrenergic neurons inducing catecholamine leakage. 2. Overall Effect: Minimal active transmitter discharged from depolarized nerve endings. 3. Neurotransmitter depletion in brain and myocardium leads to sedation, depression and CO. Rauwolfia serpentina root used in Ayuvedic medicine, isolated in 1950 s and used in Western medicine 10
11 Reserpine CO, TPR HR, (Na + and dho 2 retention) ti Low doses + diuretic diuretic + propranolol or methyldopa Adverse Effects 1. CNS: Sedation, inability to concentrate, nightmares, dose- related psychotic depression contraindicated in pre- existing gdep depression. ess 2. Unabated parasympathetic activity - nasal stuffiness, gastric acid secretion (contraindicated in peptic ulcer), diarrhea and bradycardia Central α 2 agonists Generic name Clonidine Trade name(s) Catapress Doses available Methyldopa - Oral:250, 500mg Guanabenz Guanfacine Wytensin Tenex Oral: 0.1, 0.2, 0.3mg Transdermal patch: 0.1, 0.2, 0.3mg/24hrs Oral: 4, 8mg Oral:1, 2mg 11
12 Mechanism of action Selective α 2 agonists in the CNS: CNS sympathetic outflow enhanced parasympathetic activity - vagal tone - BP HR, CO, TPR, plasma renin, blunted baroreceptor reflexes. NE plasma levels directly TPR with BP. Clonidine useful in pheochromocytoma diagnosis -Methyldopa Drug of choice in this class; usefulness limited it by adverse effects. Chronic use results in Na + and fluid retention (diuretic). Metabolized to its active form (α- methylnorepinephrine) in the brain 12
13 -Methyldopa t 1/2 : 2hrs; peak effect: ~6-8hrs; Duration of action: ~24hr In elderly: HR and stroke volume resulting in CO, in young uncomplicated patient no such effect. Adverse effects: Sedation, lassitude, nightmares, depression, vertigo, galactorrhea (men & women). Clonidine CO and TPR cardiac sympathetic tone leads to iontropy, chronotropy Adverse Effects: 1. CNS Sedation; avoid in depression 2. Dry mouth Not 1 st line therapy 13
14 Clonidine Caution: Dose-related withdrawal syndrome within hrs; sympathetic discharge leading to rebound hypertension or overshoot hypertension. Symptoms: headache, apprehension, tremors, abdominal pain, sweating, and tachycardia. ACE Inhibitors Generic name Enalapril Captopil Lisinopril Fosinopril Benazepril Quinapril Trade name(s) Vasotec Capoten Zestril, Prinivil Monopril Lotensin Accupril Doses available Oral: 2.5, 5, 10, 20mg Oral: 12.5, 25, 50, 100mg Oral: 2.5, 5, 10, 20, 40mg Oral:10, 20, 40mg Oral: 5, 10, 20, 40mg Oral: 5, 10, 20, 40mg 14
15 Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Angiotensinogen Renin Angiotensin I Angiotensin II Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Na +, H 2 O retention Aldosterone Vasoconstriction Blood volume Facilitates NE transmission CO X TPR BP ACE inhibitors block bradykinin degradation, stimulate PE 2 & prostacyclin ACE Inhibitors As effective as diuretics and β-blockers Supervise 1 st dose TPR without reflex CO, HR or inotrophy Fetotoxic (absolutely contraindicated in pregnacy) Initiate with very low dose with slow titration. 15
16 Other Indicators CHF ( nonfatal and fatal events). LVH (may prevent or partial regression). Type 1 diabetic nephropathy Adverse Effects Acute hypotension (at onset, esp in severe Na Skin rash (sometimes transient) t) Cough (10% - 20%) (at onset, esp in severe Na + & volume depletion) To a lesser extent (<1%): Hematologic toxicity: neutropenia, agranulocytosis Angioedema more in Africans Acute renal failure esp. in unilateral/bilateral renal artery stenosis Glomerulonephritis Proteinuria (captopril) Hyperkalemia esp. in renal disease, DM, on NSAIDs, K + supp. or K+- sparing diuretics Fever 16
17 Angiotensin II receptor antagonists Generic name Losartan Valsartan Candesartan Olmesartan Telmisartan Irbesartan Trade name(s) Cozaar Diovan Atacand Benicar Micardis Avapro Doses available Oral: 25, 50, 100mg Oral: 40, 80, 160, 320mg Oral: 4, 8, 16, 32mg Oral: 5, 10, 20, 40mg Oral: 20, 40, 80mg Oral: 75, 150, 300mg Mechanism of Action Blockade of AgII receptors vasocontriction TPR BP Na + retention Blood volume CO Acute effect Ag II Ag I Stimulation of arterial wall growth wall to lumen ratio (remodelling) Long term effect vasoconstriction No effect on bradykinin breakdown 17
18 Angiotensin II receptor subtypes AT 1 (site of action of ATII antagonists) Vasoconstriction Aldosterone release Sympathetic activation ADH release Constriction of efferent glomerular arterioles AT 2 (beneficial effect not blocked) Vasodilation AgII also produced by enzymic reactions of chymases Other Indications ACE inhibitor without the cough Heart failure Intolerance to other hypertensive drugs All have similar antihypertensive efficacy with flat dose-response curve 18
19 Adverse Effects Renal insufficiency ( glomerular perfusion pressure) Hyperkalemia Caution: History of ACE inhibitor-induced induced angioedema Generic name Chlorothiazide Diuretics Trade name(s) Diuril Available doses Oral: 250, 500; 250mg/mL oral suspension Hydrochlorothiazide Chlorthalidone Indapamide Metolazone Furosemide Bumetamide Torsemide Hydrodiuril Thalitone Lozol, others Zaroxolyn Lasix Bumex Demadex Oral: 25, 50, 100mg tabs; 12.5mg capsules Parenteral: 10mg/mLsoln Oral: 250, 500 mg; 250 mg/5ml oral suspension Oral: 1.25, 2.5mg Oral: 0.5mg Oral: 20, 40, 80 mg; Parenteral: 10mg/mL Oral: 0.5, 1, 2 mg; Parenteral: 0.5mg/2mL Oral: 5, 10, 15, 20mg; Parenteral: 10mg/mL Ethacrynic Acid Spironolactone Eplerenone Edecrin Aldactone Inspra Amiloride Midamor Triamterene Dyrenium Oral: 25, 50mg; Parenteral: 50mg/mL Oral: 25, 50, 100mg Oral: 25, 50mg Oral: 5mg Oral: 50, 100mg 19
20 Diuretics Thiazides (1 (1 st st line) Acute effect Block renal tubule Na + -Cl - reabsorption angiotensin II -ve effect urinary loss of Na + and H 2 O renin release Long term effect CO returns to normal Slight in body Na + Opening of K + channels (hyperpolarization) BP TPR extracellular volume CO BP [Ca 2+ ] in vascular smooth muscle cells affinity of vascular smooth muscle cells for vasoconstrictor hormones Contractility of vascular smooth muscle cells Diuretics Furosemide (not 1 (not 1 st line) Acute effect Binds to Cl - binding site of Na + -K + -2 Cl - cotransporter in thick ascending loop of Henle Angiotensin II loss of Na + and H 2 O Extracellular fluid volume Renin release Long term effect CO returns to normal Slight in body Na + CO BP Contractility of VSMC? BP? TPR 20
21 Loop Diuretic Furosemide Indications: Resistant hypertension (not 1 st line) Edema (renal impairment or volume overload) Hypercalcemia Hyperkalemia Generic name Benzothiazepine Diltiazem Diphenylalkylamine Verapamil Dihydropyridine Nifedipine Amlodipine Felodipine Isradipine Nicardipine Nisoldipine Ca 2+ channel blockers Trade name(s) Doses available Cardizem Oral: 30, 60, 90, 120mg; sustained release: 60, 90, 120, 180, 240, 300, 360, 420mg. Parenteral: 5mg/mL soln Calan, Isoptin Adalat CC, Procardia XL Norvasc Plendil DynaCirc Cardene Sular Oral: 40, 80, 120mg; sustained release: 120, 180, 240mg Parenteral: 2.5mg/mL soln Oral: 10, 20mg. Extended release: 30, 60, 90mg Oral: 2.5, 5, 10mg Oral extended release: 2.5, 5, 10mg Oral:2.5, 5mg; controlled release: 5, 10mg Oral:20, 30mg; sustained release: 30, 45, 60mg Parenteral: 2.5mg/mL soln Oral extended release: 10, 20, 30, 40mg 21
22 Mechanism of Action Dihydropyridines Nifedipine, Amlodipine Block L-type Ca 2+ channels in arterial smooth muscle Verapamil, Diltiazem Block L-type Ca 2+ channels in SA and AV node TPR or abolishes reflex tachycardia BP Baroreceptor-mediated reflex tachycardia Inhibit influx of Ca ++ ions thru voltage-gated gated channels Relative efficacy Drug Vasodilation (coronary flow) -ve inotropy Automaticity (SA node) suppression AV conduction suppression Diltiazem Nifedipine Verapamil Relative cardiovascular effect: 0=no effect, 5=maximum effect 22
23 Indications Mild to moderate HTN associated with exerciseinduced, variant and unstable angina. MI (ACE inhibitors>protective than dihydropyridines) Antiarrhythmic (diltiazem and verapamil for (supraventricular tachycardia, atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter). Not clinically superior to diuretics or β-blockers, usually 2 nd & 3 rd line therapy. Adverse Effects Vasodilatory-related (more with dihydropyridines): dizziness, flushing, headache, peripheral edema Gingival hyperplasia Mood swings & fatigue Verapamil causes constipation (7%) and contraindicated in CHF 23
24 Oral and parenteral vasodilators Generic name Hydralazine Nitroprusside Trade name(s) Apresoline Nitropress Doses available Oral: 10, 25, 50, 100mg Parenteral: 20mg/mL soln Parenteral: 50mg/vial Minoxidil Diazoxide Fenoldopam Loniten Hyperstat IV Corlopam Oral: 2.5, 10mg Topical (Rogaine, etc): 2% soln Oral: 50mg capsule Parenteral: 15mg/mL Parenteral: 10mg/mL soln Hydralazine Well absorbed orally, short t 1/2 (1 hr), peak effect (1/2 hr to 2 hrs) & duration of action (12hr). Bioavailability determined by acetylator status: 16% in fast and 35% in slow acetylators. Adverse effects limit use. Reserved for refractory severe hypertension used concomitantly with diuretics and β- blockers (never as monotherapy). Used occasionally with isosorbide dinitrate in CHF. Contraindicated in CAD and > 40years 24
25 Hydralazine Direct relaxation at of arteries es (not veins), camp mediated. Vasodilatation causes baroreceptor-mediated reflex, sympathetic stimulation tachycardia CO; renin release Na + and H 2 O retention. CO and fluid retention cause tachyphylaxis, unless used in combination with β-blockers ( reflex tachycardia) and diuretics ( fluid retention). Hydralazine: Adverse Effects Direct extension of pharmacological activity: headache, nausea, flushing, dizziness, hypotension, palpitation, tachycardia, angina pectoris, MI Immunological reactions (unknown mechanism): Serum sickness, hemolytic anemia, vasculitis, rapidly progressing glomerulonephritis 10-20%incidence of reversible dose-related lupus erythematosus-like syndrome high dose or after >6mth chronic use. (Use <200mg daily) Effect > in females and slow acetylators. Limited usefulness in hypertension 25
26 Minoxidil Direct relaxation of arteries (not veins). blood flow to skin, skeletal muscles, GI tract, heart. Reflex CO, renal vasodilatation and renin secretion. Minoxidil > potency than hydralazine Well absorbed orally, short t 1/2 :3-4 hrs, duration of action: 12hr. NEVER as monotherapy, use with β-blockers and diuretics (loop diuretic). Reserved for refractory severe hypertension. 26
27 Minoxidil Adverse Effects More dramatic fluid retention than hydralazine (not renin and aldosterone secretion related). renal perfusion pressure and reflex stimulation of renal tubular α-receptors. Headache, sweating Hypertrichosis: Used topically to treat of male-pattern baldness. Sodium nitroprusside Given by iv continuous infusion. Onset: 30sec; peak effect: 2 mins. Metabolized to NO and cyanide. 1. NO causes vasodilatation. 2. Cyanide is poisonous, and further metabolized to thiocyanate. Very potent vasodilator of both arteries and veins Drug of choice in hypertension emergencies (BP>210/150mmHg). 27
28 Sodium nitroprusside Modest HR and myocardial l O 2 demand d Other indications: Acute aortic dissection (propranolol given first to prevent reflex sympathetic activation). In CHF to CO In acute MI to myocardial O 2 demand Sodium Nitroprusside: Adverse Effects Cyanide and thiocyanate poisoning: Anorexia, nausea, fatigue, disorientation, toxic psychosis. Closely monitor BP and plasma thiocyanate (<0.1μg/mL). Antidote: Infusion of sodium thiosulphate thiocyanate risk of poisoning in impaired renal function Worsens arterial hypoxemia in COPD Abrupt cessation after short-term term use causes rebound HTN. 28
29 Prescribed Antihypertensive Drugs in Trinidad (n=442) Drug Class/Generic Drug name All HTN N (%) HTN alone N (%) HTN with DM N (%) ACE Inhibitors (ACEI) Enalapril Lisinopril Fosinopril Captopril β-blockers (BB) Atenolol Propranolol Bisoprolol Diuretics Thiazide (bendrofluazide) Furosemide Calcium channel blockers (CCB) Nifedipine Amlodipine Verapamil α-blockers Terazosin Doxasosin Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) Valsartan Presartan Other drugs Methydopa Reserpine 281 (63.6) (29.2) (25.8) (12.0) (0.7) (2.3) (6.1) (58.9) (33.9) (34.4) (12.0) (0.5) (2.6) (9.4) (67.2) (25.6) (19.2) (12.0) (0.8) (2.0) (3.6) 7 2 Antihypertensive drug therapy in Trinidadian patients with complete accessible drug records (n=442) Antihypertensive drug therapy All HTN patients N (%) HTN alone N (%) HTN with DM N (%) No drug therapy 26 (5.9) 8 (4.2) 18 (7.2) Monotherapy 242 (54.8) 86 (44.8) 156 (62.4) Dual drug therapy 121 (27.3) 62 (32.3) 59 (23.6) Triple drug therapy 45 (10.2) 30 (15.6) 15 (6.0) Quadruple drug therapy 8 (1.8) 6 (3.1) 2 (0.8) TOTAL
30 β-blockers α 1 -blockers sympathetic activity BP β 1 receptor cardiac activation α 1 receptor smooth muscle activation Ca 2+ -channel blockers Vasodilators CO TPR BP ACE inhibitors Renal flow renin Angiotensin II AgII receptor Aldosterone blockers GFR Na +, H 2 O retention Blood volume Diuretics 30
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat
 Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Antihypertensive drugs SUMMARY Made by: Lama Shatat Diuretic Thiazide diuretics The loop diuretics Potassium-sparing Diuretics *Hydrochlorothiazide *Chlorthalidone *Furosemide *Torsemide *Bumetanide Aldosterone
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs
 Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
7/7/ CHD/MI LVH and LV dysfunction Dysrrhythmias Stroke PVD Renal insufficiency and failure Retinopathy. Normal <120 Prehypertension
 Prevalence of Hypertension Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management T. Villela, M.D. Program Director University of California, San Francisco-San Francisco General Hospital Family and Community Medicine
Prevalence of Hypertension Hypertension: Diagnosis and Management T. Villela, M.D. Program Director University of California, San Francisco-San Francisco General Hospital Family and Community Medicine
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Antihypertensive Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Agents that block production or action of angiotensin Angiotensin-converting
Antihypertensives. Antihypertensive Classes. RAAS Inhibitors. Renin-Angiotensin Cascade. Angiotensin Receptors. Approaches to Hypertension Treatment
 Approaches to Hypertension Treatment Antihypertensives Inhibit Sympathetic impulses Inhibit contractility Inhibit heart rate Inhibit vasoconstriction Inhibit smooth muscle function Inhibit RAAS Inhibit
Approaches to Hypertension Treatment Antihypertensives Inhibit Sympathetic impulses Inhibit contractility Inhibit heart rate Inhibit vasoconstriction Inhibit smooth muscle function Inhibit RAAS Inhibit
Hypertension is also an important risk factor in the development of chronic kidney disease and heart failure.
 Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension is defined as either a sustained systolic blood pressure of greater than 140 mm Hg or a sustained diastolic blood pressure of greater than 90 mm Hg. Hypertension
Hypertension Hypertension Hypertension is defined as either a sustained systolic blood pressure of greater than 140 mm Hg or a sustained diastolic blood pressure of greater than 90 mm Hg. Hypertension
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson you will be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT SUBCOURSE MD0806 LESSON 7 Therapeutics III. Antihypertensive Agents. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 7-1--7-12. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson you will be able to: 7-1. From
LESSON ASSIGNMENT SUBCOURSE MD0806 LESSON 7 Therapeutics III. Antihypertensive Agents. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 7-1--7-12. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson you will be able to: 7-1. From
Section 3, Lecture 2
 59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
59-291 Section 3, Lecture 2 Diuretics: -increase in Na + excretion (naturesis) Thiazide and Related diuretics -decreased PVR due to decreases muscle contraction -an economical and effective treatment -protect
Hypertension (JNC-8)
 Hypertension (JNC-8) Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 17, 2018, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D.! The 8 th Joint
Hypertension (JNC-8) Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 17, 2018, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D.! The 8 th Joint
Cardiac Medications At A Glance
 Cardiac Medications At A Glance 1) Anticoagulants (Also known as Blood Thinners.) Dalteparin (Fragmin), Danaparoid (Orgaran) Enoxaparin (Lovenox) Heparin (various) Tinzaparin (Innohep) Warfarin (Coumadin)
Cardiac Medications At A Glance 1) Anticoagulants (Also known as Blood Thinners.) Dalteparin (Fragmin), Danaparoid (Orgaran) Enoxaparin (Lovenox) Heparin (various) Tinzaparin (Innohep) Warfarin (Coumadin)
sympatholytics sympatholytics sympatholytics
 sympatholytics sympatholytics sympatholytics CNS-ACTING SYMPATHOPLEGICS Sympathetic brain signals Doesn t affect baroreceptor reflex (no orthostatic hypotension) Methyldopa α-methylne crosses BBB (+) α-adrenoreceptors
sympatholytics sympatholytics sympatholytics CNS-ACTING SYMPATHOPLEGICS Sympathetic brain signals Doesn t affect baroreceptor reflex (no orthostatic hypotension) Methyldopa α-methylne crosses BBB (+) α-adrenoreceptors
12.5mg, 25mg, 50mg. 25mg, 50mg. 250mg, 500mg, 250mg/5ml. 2.5mg, 5mg, 10mg. 5mg, 10mg, 20mg, 100mg. 25mg
 MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Blood Pressure P&T DATE: 9/11/2018 THERAPEUTIC CLASS: Cardiovascular Disorders REVIEW HISTORY: 5/17, 9/15, 2/13, 2/08, LOB
MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Blood Pressure P&T DATE: 9/11/2018 THERAPEUTIC CLASS: Cardiovascular Disorders REVIEW HISTORY: 5/17, 9/15, 2/13, 2/08, LOB
12.5mg, 25mg, 50mg. 25mg, 50mg. 2.5mg, 5mg, 10mg. 5mg, 10mg, 20mg, 100mg. 25mg. -- $2.81 Acetazolamide (IR, 125mg, 250mg, 500mg (ER)
 MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Blood Pressure P&T DATE: 5/9/2017 THERAPEUTIC CLASS: Cardiovascular Disorders REVIEW HISTORY: 9/15, 2/13, 2/08, 5/07 LOB
MEDICATION COVERAGE POLICY PHARMACY AND THERAPEUTICS ADVISORY COMMITTEE POLICY: Blood Pressure P&T DATE: 5/9/2017 THERAPEUTIC CLASS: Cardiovascular Disorders REVIEW HISTORY: 9/15, 2/13, 2/08, 5/07 LOB
HYPERTENSION IN EMERGENCY MEDICINE Michael Jay Bresler, M.D., FACEP
 HYPERTENSION IN EMERGENCY MEDICINE Michael Jay Bresler, M.D., FACEP What is normal blood pressure? Prehypertension 130-139/80-90 Compared with normal BP Double the risk for developing hypertension. Lifestyle
HYPERTENSION IN EMERGENCY MEDICINE Michael Jay Bresler, M.D., FACEP What is normal blood pressure? Prehypertension 130-139/80-90 Compared with normal BP Double the risk for developing hypertension. Lifestyle
Preventing and Managing High Blood Pressure
 MINTO PREVENTION & REHABILITATION CENTRE CENTRE DE PREVENTION ET DE READAPTATION MINTO Preventing and Managing High Blood Pressure About This Kit Fortunately, high blood pressure is easily detected and
MINTO PREVENTION & REHABILITATION CENTRE CENTRE DE PREVENTION ET DE READAPTATION MINTO Preventing and Managing High Blood Pressure About This Kit Fortunately, high blood pressure is easily detected and
Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood:
 Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood: Cardiac Output (CO) CO=SVxHR (stroke volume x heart rate) Cardiac output: The amount of blood
Towards a Greater Understanding of Cardiac Medications Foundational Cardiac Concepts That Must Be Understood: Cardiac Output (CO) CO=SVxHR (stroke volume x heart rate) Cardiac output: The amount of blood
HYPERTENSION: Sustained elevation of arterial blood pressure above normal o Systolic 140 mm Hg and/or o Diastolic 90 mm Hg
 Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
Lecture 39 Anti-Hypertensives B-Rod BLOOD PRESSURE: Systolic / Diastolic NORMAL: 120/80 Systolic = measure of pressure as heart is beating Diastolic = measure of pressure while heart is at rest between
ANTIHYPERTENSIVES. Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut
 ANTIHYPERTENSIVES Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut Hypertension Hypertension is a condition in which the blood pressure is persistently higher than normal Hypertension > 140 mmhg > 90 mmhg Systolic Blood Pressure
ANTIHYPERTENSIVES Assoc. Prof. Bilgen Başgut Hypertension Hypertension is a condition in which the blood pressure is persistently higher than normal Hypertension > 140 mmhg > 90 mmhg Systolic Blood Pressure
Antihypertensive Agents
 Antihypertensive Agents Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 7, 08, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D! Usual Dose,
Antihypertensive Agents Southern California University of Health Sciences Physician Assistant Program Management and Treatment of Hypertension April 7, 08, presented by Ezra Levy, Pharm.D! Usual Dose,
Antihypertensive Agents
 Antihypertensive Agents Öner Süzer www.onersuzer.com osuzer@istanbul.edu.tr Last update: 13.11.2009 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 2 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 3 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005
Antihypertensive Agents Öner Süzer www.onersuzer.com osuzer@istanbul.edu.tr Last update: 13.11.2009 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 2 1 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005 3 Süzer Farmakoloji 3. Baskı 2005
Treatment of Essential Hypertension
 2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
8/19/2016. No Conflicts. I struggled with everything cardiac in nursing school.
 Cindy Weston, DNP, RN, CCRN, CNS CC, FNP BC Assistant Professor, Texas A&M Health Science Center College of Nursing Describe and define epidemiology and pathophysiology of hypertension Differentiate JNC8
Cindy Weston, DNP, RN, CCRN, CNS CC, FNP BC Assistant Professor, Texas A&M Health Science Center College of Nursing Describe and define epidemiology and pathophysiology of hypertension Differentiate JNC8
Beta 1 Beta blockers A - Propranolol,
 Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Pharma Lecture 3 Beta blockers that we are most interested in are the ones that target Beta 1 receptors. Beta blockers A - Propranolol, it s a non-selective competitive antagonist of beta 1 and beta 2
Management of Hypertension
 Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of Hypertension Definition and classification of blood pressure levels (mmhg) Category Systolic Diastolic Normal
Chapter 23. Media Directory. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Hypertension: Classified into Three Categories
 Chapter 23 Drugs for Hypertension Slide 37 Slide 41 Media Directory Nifedipine Animation Doxazosin Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Includes
Chapter 23 Drugs for Hypertension Slide 37 Slide 41 Media Directory Nifedipine Animation Doxazosin Animation Upper Saddle River, New Jersey 07458 All rights reserved. Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) Includes
University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D
 University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1. Antihypertensives 2. Antianginal 3. Drugs for HF 4. Antiarrythemics 5. Drugs for Hyperlipoproteniemia
University of Al Qadisiyah College of Pharmacy Dr. Bassim I Mohammad, MBChB, MSc, Ph.D Cardiovascular Pharmacology 1. Antihypertensives 2. Antianginal 3. Drugs for HF 4. Antiarrythemics 5. Drugs for Hyperlipoproteniemia
Treatment of Essential Hypertension
 2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
2016 edition by Mark A. Simmons, PhD Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences School of Pharmacy University of Maryland Eastern Shore Originally developed by Hugh J. Burford, PhD, FCP Department of Pharmacology
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS AND VASODILATORS. Lecture 5
 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS AND VASODILATORS Lecture 5 Hypertension Blood pressure BP = CO x PVR n Interaction between autonomic nervous system, cardiovascular system and renal system Normal: 110/70 Prehypertension
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE AGENTS AND VASODILATORS Lecture 5 Hypertension Blood pressure BP = CO x PVR n Interaction between autonomic nervous system, cardiovascular system and renal system Normal: 110/70 Prehypertension
Diabetes and a Healthy Heart. Meeting 6. Welcome! Glucose. Balance Makes a Difference! Medicine Helps with. Glucose. Balance!
 6-1 Welcome! Welcome to the lesson! It s good to see you again! Before we visit with Uncle Tommy and Kaipo, let s take a few minutes to review the last five meetings. Glucose Balance Makes a Difference!
6-1 Welcome! Welcome to the lesson! It s good to see you again! Before we visit with Uncle Tommy and Kaipo, let s take a few minutes to review the last five meetings. Glucose Balance Makes a Difference!
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS
 ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: September 28, 2010 Materials on: Exam #3 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 11 1 1 in 3 adults HYPERTENSION 64% of
ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUGS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: September 28, 2010 Materials on: Exam #3 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 11 1 1 in 3 adults HYPERTENSION 64% of
TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION
 TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION Aim of treatment BP Goals Main items of treatment Lifestyle modification When to start drug Rx Pharmacological therapy 1. Relief of symptoms 2. Prevention of complications and
TREATMENT OF HYPERTENSION Aim of treatment BP Goals Main items of treatment Lifestyle modification When to start drug Rx Pharmacological therapy 1. Relief of symptoms 2. Prevention of complications and
Medications and Falls Part 1
 Medications and Falls Part 1 Introduction with General Principles and Risk Evaluation for Cardiovascular Medications Dennis J Chapron Medication Safety Pharmacist Saint Francis Hospital and Medical Center
Medications and Falls Part 1 Introduction with General Principles and Risk Evaluation for Cardiovascular Medications Dennis J Chapron Medication Safety Pharmacist Saint Francis Hospital and Medical Center
Some Facts. Medications and Falls Part 1. Centers for Disease Control (CDC) Falls Statistics for Older Adults ( 65yrs) 11/27/2018
 Medications and Falls Part 1 Introduction with General Principles and Risk Evaluation for Cardiovascular Medications Dennis J Chapron reports no real or potential conflicts of interest relevant to this
Medications and Falls Part 1 Introduction with General Principles and Risk Evaluation for Cardiovascular Medications Dennis J Chapron reports no real or potential conflicts of interest relevant to this
What in the World is Functional Medicine?
 What in the World is Functional Medicine? An Introduction to a Systems Based Approach of Chronic Disease Meneah R Haworth, FNP-C Disclosure v I am a student of the Institute for Functional Medicine. They
What in the World is Functional Medicine? An Introduction to a Systems Based Approach of Chronic Disease Meneah R Haworth, FNP-C Disclosure v I am a student of the Institute for Functional Medicine. They
Antihypertensives. Diagnostic category
 Measurement of blood pressure At first assessment, take both arms then choose the one with the higher reading. Beware of orthostatic hypotension. Measure BP in sitting position, and repeat after patient
Measurement of blood pressure At first assessment, take both arms then choose the one with the higher reading. Beware of orthostatic hypotension. Measure BP in sitting position, and repeat after patient
Antihypertensive Drugs. Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2014
 Antihypertensive Drugs Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2014 Antihypertensive Drugs What is Hypertension: A common, incurable, persistent, but usually
Antihypertensive Drugs Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE Faculty of Medicine, The University of Jordan November, 2014 Antihypertensive Drugs What is Hypertension: A common, incurable, persistent, but usually
New classification of HT Systolic Diastolic Normal <120 <80 Prehypertension Stage1HT Stage 2 HT >160 or >100
 Hypertension 1 Definition Hypertension can be defined as a condition where blood pressure is elevated to an extent that clinical benefit is obtained from blood pressure lowering. it is an important risk
Hypertension 1 Definition Hypertension can be defined as a condition where blood pressure is elevated to an extent that clinical benefit is obtained from blood pressure lowering. it is an important risk
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS)
 DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
Antihypertensive Agents
 1. Blood Pressure Regulation Antihypertensive Agents - 2007 Edward JN Ishac. Ph.D. Associate Professor, Dept. Pharmacology & Toxicology Office: Smith 742; Tel: 828 2127 eishac@hsc.vcu.edu Frank's formula,
1. Blood Pressure Regulation Antihypertensive Agents - 2007 Edward JN Ishac. Ph.D. Associate Professor, Dept. Pharmacology & Toxicology Office: Smith 742; Tel: 828 2127 eishac@hsc.vcu.edu Frank's formula,
DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI
 DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI 3. Vasodilators Drugs which dilate blood vessels ( decrease peripheral vascular resistance) by acting on smooth muscle cells through non-autonomic mechanisms:
DRUGS USED TO TREAT HYPERTENSION BY ALI ALALAWI 3. Vasodilators Drugs which dilate blood vessels ( decrease peripheral vascular resistance) by acting on smooth muscle cells through non-autonomic mechanisms:
1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias
 1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias Only need to know drugs discussed in class At the end of this section you should
1. Antihypertensive agents 2. Vasodilators & treatment of angina 3. Drugs used in heart failure 4. Drugs used in arrhythmias Only need to know drugs discussed in class At the end of this section you should
PassAssured's Pharmacy Technician Training Systems. Medication Review. Cardiovascular Drugs. Pharmacy Technician Training Systems Passassured, LLC
 Medication Review Cardiovascular Drugs Pharmacy Technician Training Systems Passassured, LLC p1 Medication Review, Cardiovascular Drugs Click Here for Glossary Index! Click Here to Print Topic Help File
Medication Review Cardiovascular Drugs Pharmacy Technician Training Systems Passassured, LLC p1 Medication Review, Cardiovascular Drugs Click Here for Glossary Index! Click Here to Print Topic Help File
Antihypertensive Drugs. Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan October, 2017
 Antihypertensive Drugs Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan October, 2017 Antihypertensive Drugs What is Hypertension? A common, incurable, persistent, but usually
Antihypertensive Drugs Munir Gharaibeh, MD, PhD, MHPE School of Medicine, The University of Jordan October, 2017 Antihypertensive Drugs What is Hypertension? A common, incurable, persistent, but usually
Introduction. Factors affecting blood pressure: 1-COP = HR X SV mainly affect SBP. 2-TPR = diameter of arterioles X viscosity of blood affect DBP
 Introduction Hypertension is a persistent elevation of blood pressure above 140 / 90 mmhg for more than three sitting. (0ptimal level
Introduction Hypertension is a persistent elevation of blood pressure above 140 / 90 mmhg for more than three sitting. (0ptimal level
Antihypertensive drugs: I. Thiazide and other diuretics:
 Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
Clinical assessment of hypertensive patient: You have to take history regarding the presence of other risk factors for CAb like diabetes mellitus, smoking, etc. Take history whether the patient takes medications
Managing Hypertension in Diabetes Sean Stewart, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Internal Medicine Park Nicollet Clinic St Louis Park.
 Managing Hypertension in Diabetes 2015 Sean Stewart, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Internal Medicine Park Nicollet Clinic St Louis Park Case Scenario Mike M is a 59 year old man with type 2 diabetes managed
Managing Hypertension in Diabetes 2015 Sean Stewart, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP, CLS Internal Medicine Park Nicollet Clinic St Louis Park Case Scenario Mike M is a 59 year old man with type 2 diabetes managed
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment
 Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Heart Failure (HF) Treatment Heart Failure (HF) Complex, progressive disorder. The heart is unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the needs of the body. Its cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue, and
Prof dr Aleksandar Raskovic DIRECT VASODILATORS
 Prof dr Aleksandar Raskovic DIRECT VASODILATORS Direct vasodilators Minoxidil (one of the most powerful peripheral arterial dilators) Opening of KATP channels, efflux of K, lose of Ca and smooth muscle
Prof dr Aleksandar Raskovic DIRECT VASODILATORS Direct vasodilators Minoxidil (one of the most powerful peripheral arterial dilators) Opening of KATP channels, efflux of K, lose of Ca and smooth muscle
DROGAS PARA HIPERTENSION ARTERIAL JONATHAN POVEDA FERNANDEZ HSJD / 2013 FACC/FSCAI/FESC
 DROGAS PARA HIPERTENSION ARTERIAL JONATHAN POVEDA FERNANDEZ HSJD / 2013 FACC/FSCAI/FESC Pharmacotherapy of HTN Rationale for reducing arterial pressure Reduce cardiac output Reduce heart rate Reduce stroke
DROGAS PARA HIPERTENSION ARTERIAL JONATHAN POVEDA FERNANDEZ HSJD / 2013 FACC/FSCAI/FESC Pharmacotherapy of HTN Rationale for reducing arterial pressure Reduce cardiac output Reduce heart rate Reduce stroke
ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG TABLET GENERIC BETA BLOCKERS ALISKIREN 150MG TABLET RASILAZ RENIN INHIBITOR
 S/N ME OF MEDICATIONS BRANDED/GENERIC DRUG CLASS * UNIT PRICE RANGE (SGD$) 1 ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG CAPSULE SECTRAL BETA BLOCKERS 0.50 2 ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG TABLET GENERIC BETA BLOCKERS 0.33 3 ALISKIREN
S/N ME OF MEDICATIONS BRANDED/GENERIC DRUG CLASS * UNIT PRICE RANGE (SGD$) 1 ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG CAPSULE SECTRAL BETA BLOCKERS 0.50 2 ACEBUTOLOL HCL 100MG TABLET GENERIC BETA BLOCKERS 0.33 3 ALISKIREN
HypertensionTreatment Guidelines. Michaelene Urban APRN, MSN, ACNS-BC, ANP-BC
 HypertensionTreatment Guidelines Michaelene Urban APRN, MSN, ACNS-BC, ANP-BC Objectives: Review the definition of the different stages of HTN. Review the current guidelines for treatment of HTN. Provided
HypertensionTreatment Guidelines Michaelene Urban APRN, MSN, ACNS-BC, ANP-BC Objectives: Review the definition of the different stages of HTN. Review the current guidelines for treatment of HTN. Provided
Top 200 Section 4. Cardiovascular Drugs
 Top 200 Section 4 Cardiovascular Drugs Objectives After finishing this presentation the audience should be able to: Describe conditions/disease states that would make a person a candidate for drug therapy.
Top 200 Section 4 Cardiovascular Drugs Objectives After finishing this presentation the audience should be able to: Describe conditions/disease states that would make a person a candidate for drug therapy.
Hypertension Clinical Pearls: We re treating more than a number
 Hypertension Clinical Pearls: We re treating more than a number Emily Ashjian, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP February 2017 Learning Objectives Review blood pressure goals and differences between treatment guidelines
Hypertension Clinical Pearls: We re treating more than a number Emily Ashjian, PharmD, BCPS, BCACP February 2017 Learning Objectives Review blood pressure goals and differences between treatment guidelines
4/3/2014 OBJECTIVES BLOOD PRESSURE BASICS. Discuss the new blood pressure guidelines (JNC 8) and recognize the changes from JNC 7
 1 OBJECTIVES Discuss the new blood pressure guidelines (JNC 8) and recognize the changes from JNC 7 Review mechanisms for the main drug classes used to treat hypertension Describe the dosing strategies
1 OBJECTIVES Discuss the new blood pressure guidelines (JNC 8) and recognize the changes from JNC 7 Review mechanisms for the main drug classes used to treat hypertension Describe the dosing strategies
Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2018
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2018 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2018 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2018 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2018 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Fundamentals of Pharmacology for Veterinary Technicians Chapter 8
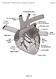 Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
Hypertension Management - Summary
 Who should have blood pressure assessed? Hypertension Management - Summary All patients over the age of 40 years, every 1-3 years in order to determine their cardiovascular risk (ie. Framingham Risk Score)
Who should have blood pressure assessed? Hypertension Management - Summary All patients over the age of 40 years, every 1-3 years in order to determine their cardiovascular risk (ie. Framingham Risk Score)
Antihypertensive Drugs. Nafrialdi
 Antihypertensive Drugs Nafrialdi 1 Mechanisms of Blood Pressure Regulation Blood Presure Cardiac Output Peripheral Resistance Heart Rate Stroke volume Vascular tone Vessel elasticity Myocardial contractility
Antihypertensive Drugs Nafrialdi 1 Mechanisms of Blood Pressure Regulation Blood Presure Cardiac Output Peripheral Resistance Heart Rate Stroke volume Vascular tone Vessel elasticity Myocardial contractility
Annual Review of Antihypertensives - Fiscal Year 2009
 Annual Review of Antihypertensives - Fiscal Year 2009 Oklahoma HealthCare Authority April 2010 Current Prior Authorization Criteria There are 7 categories of antihypertensive medications currently included
Annual Review of Antihypertensives - Fiscal Year 2009 Oklahoma HealthCare Authority April 2010 Current Prior Authorization Criteria There are 7 categories of antihypertensive medications currently included
MEDICATION FACT SHEET
 ACE Inhibitors Names of ACE Inhibitors: quinapril (Accupril ), enalapril (Vasotec ), ramipril (Altace ), captopril (Capoten ), fosinopril (Monopril ), benazepril (Lotensin ), lisinopril (Zestril, Prinivil
ACE Inhibitors Names of ACE Inhibitors: quinapril (Accupril ), enalapril (Vasotec ), ramipril (Altace ), captopril (Capoten ), fosinopril (Monopril ), benazepril (Lotensin ), lisinopril (Zestril, Prinivil
Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Diabetic Mellitus. Presenter: Dr. Martin N. Wanyoike MB.CHB., M. Med.(internal med) Physician / Cardiologist
 Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Diabetic Mellitus Presenter: Dr. Martin N. Wanyoike MB.CHB., M. Med.(internal med) Physician / Cardiologist Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Diabetic Mellitus Disclosures
Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Diabetic Mellitus Presenter: Dr. Martin N. Wanyoike MB.CHB., M. Med.(internal med) Physician / Cardiologist Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Diabetic Mellitus Disclosures
Value-Based Drug List for ABCs of Diabetes
 Effective January 1, 2019 Value-Based Drug List for ABCs of Diabetes PCPS provides a Value-Based Benefit Design (VBD) to qualified participants in the ABCs of Diabetes. This means you will have lower out-of-pocket
Effective January 1, 2019 Value-Based Drug List for ABCs of Diabetes PCPS provides a Value-Based Benefit Design (VBD) to qualified participants in the ABCs of Diabetes. This means you will have lower out-of-pocket
Categories of HTN. Overview of Hypertension. Types of Hypertension
 Categories of HTN Overview of Hypertension Normal SBP 100 Quick review of the Basics: What is
Categories of HTN Overview of Hypertension Normal SBP 100 Quick review of the Basics: What is
Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2016
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2016 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2016 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Heart Failure Clinician Guide JANUARY 2016 Introduction This evidence-based guideline summary is based on the 2016 National Heart Failure Guideline.
Blood pressure (BP) control. Hypertension
 Blood pressure (BP) control Normal heart function Blood pressure (BP) control blood pressure (BP) cardiac output (CO) = total peripheral resistance (TPR) heart rate (HR) filling pressure arteriolar volume
Blood pressure (BP) control Normal heart function Blood pressure (BP) control blood pressure (BP) cardiac output (CO) = total peripheral resistance (TPR) heart rate (HR) filling pressure arteriolar volume
Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018
 Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018 Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018 Introduction This Clinician Guide is based on the 2018
Kaiser Permanente National CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018 Adult Blood Pressure Clinician Guide June 2018 Introduction This Clinician Guide is based on the 2018
Evaluation and Management of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (HF) with Reduced Ejection Fraction Systolic Heart Failure (HFrEF)(EF<40%
 Evaluation and Management of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (HF) with Reduced Ejection Fraction Systolic Heart Failure (HFrEF)(EF
Evaluation and Management of Acute Decompensated Heart Failure (HF) with Reduced Ejection Fraction Systolic Heart Failure (HFrEF)(EF
1/4/18. Heart Failure Guideline Review and Update. Disclosure. Pharmacist Objectives. Pharmacy Technician Objectives. What is Heart Failure?
 Disclosure Heart Failure Guideline Review and Update I have had no financial relationship over the past 12 months with any commercial sponsor with a vested interest in this presentation. Natalie Beiter,
Disclosure Heart Failure Guideline Review and Update I have had no financial relationship over the past 12 months with any commercial sponsor with a vested interest in this presentation. Natalie Beiter,
8/20/2018. Objectives. What is hypertension? cont. What is hypertension? Epidemiology cont. Epidemiology
 Objectives Hypertension (high blood pressure): Clinical Pearls for the Pharmacy Technician Tanya Schmidt PharmD, RPh Director of Central Operations at Thrifty White Pharmacy North Dakota Board of Pharmacy
Objectives Hypertension (high blood pressure): Clinical Pearls for the Pharmacy Technician Tanya Schmidt PharmD, RPh Director of Central Operations at Thrifty White Pharmacy North Dakota Board of Pharmacy
Heart failure. Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs. CHF = congestive heart failure. increased blood volume, interstitial fluid
 Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs CHF = congestive heart failure increased blood volume, interstitial fluid Underlying causes/risk factors Ischemic heart disease (CAD) 70% hypertension
Failure? blood supply insufficient for body needs CHF = congestive heart failure increased blood volume, interstitial fluid Underlying causes/risk factors Ischemic heart disease (CAD) 70% hypertension
Heart Failure. Dr. Alia Shatanawi
 Heart Failure Dr. Alia Shatanawi Left systolic dysfunction secondary to coronary artery disease is the most common cause, account to 70% of all cases. Heart Failure Heart is unable to pump sufficient blood
Heart Failure Dr. Alia Shatanawi Left systolic dysfunction secondary to coronary artery disease is the most common cause, account to 70% of all cases. Heart Failure Heart is unable to pump sufficient blood
Hypertension (HTN) Lecture Note
 Hypertension (HTN) Lecture Note October, 2009 Chuang-Ye Hong, MD, PhD, FACP Wan-Fang Hospital Taipei Medical University Outline Definition Epidemiology Measurement of BP Secondary cause Target organ damage
Hypertension (HTN) Lecture Note October, 2009 Chuang-Ye Hong, MD, PhD, FACP Wan-Fang Hospital Taipei Medical University Outline Definition Epidemiology Measurement of BP Secondary cause Target organ damage
Pharmacology of the Sympathetic Nervous System II
 Pharmacology of the Sympathetic Nervous System II Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Professor Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia
Pharmacology of the Sympathetic Nervous System II Edward JN Ishac, Ph.D. Professor Smith Building, Room 742 eishac@vcu.edu 828-2127 Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia
Antihypertensives. Alia Shatanawi Associate Professor Department of Pharmacology School of Medicine University of Jordan
 Antihypertensives Alia Shatanawi Associate Professor Department of Pharmacology School of Medicine University of Jordan shatanawi79@gmail.com Blood Pressure Blood pressure is the force that circulating
Antihypertensives Alia Shatanawi Associate Professor Department of Pharmacology School of Medicine University of Jordan shatanawi79@gmail.com Blood Pressure Blood pressure is the force that circulating
CARDIAC IMAGING QUESTIONNAIRE
 Date of test: / / Month day year Last name First name Middle initial Street address City State Zip code Home phone ( ) - Work phone ( ) - Cell Phone ( ) - Email: Age: Demographics: What is your ethnicity?
Date of test: / / Month day year Last name First name Middle initial Street address City State Zip code Home phone ( ) - Work phone ( ) - Cell Phone ( ) - Email: Age: Demographics: What is your ethnicity?
Cardiovascular Clinical Practice Guideline Pilot Implementation
 Cardiovascular Clinical Practice Guideline Pilot Implementation Pharmacologic Management of Chronic Heart Failure Sept 15, 2004 Angela Allerman, PharmD, BCPS DoD Pharmacoeconomic Center Promoting high
Cardiovascular Clinical Practice Guideline Pilot Implementation Pharmacologic Management of Chronic Heart Failure Sept 15, 2004 Angela Allerman, PharmD, BCPS DoD Pharmacoeconomic Center Promoting high
HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY. University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D
 HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the effects of heart failure in the body
HEART FAILURE PHARMACOLOGY University of Hawai i Hilo Pre- Nursing Program NURS 203 General Pharmacology Danita Narciso Pharm D 1 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understand the effects of heart failure in the body
Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists
 Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists (CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS) Classification Mechanism of Anti-ischemic Actions Indications Drug Interaction with Verapamil Contraindications Adverse Effects Treatment of Drug
Chapter (9) Calcium Antagonists (CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS) Classification Mechanism of Anti-ischemic Actions Indications Drug Interaction with Verapamil Contraindications Adverse Effects Treatment of Drug
Adapted d from Federation of Health Regulatory Colleges of Ontario Template Last Updated September 18, 2017
 Insert Logo or Org Name Here Primary Care Medical Directive for Hypertension Management Adapted d from Federation of Health Regulatory Colleges of Ontario Template Last Updated September 18, 2017 Title:
Insert Logo or Org Name Here Primary Care Medical Directive for Hypertension Management Adapted d from Federation of Health Regulatory Colleges of Ontario Template Last Updated September 18, 2017 Title:
Cardiovascular drugs
 chapter 13 Cardiovascular drugs Cardiovascular drugs act on the heart or blood vessels to control the cardiovascular system. They are used to treat a variety of conditions from hypertension to chronic
chapter 13 Cardiovascular drugs Cardiovascular drugs act on the heart or blood vessels to control the cardiovascular system. They are used to treat a variety of conditions from hypertension to chronic
Byvalson. (nebivolol, valsartan) New Product Slideshow
 Byvalson (nebivolol, valsartan) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Byvalson Generic name: Nebivolol, valsartan Pharmacological class: Beta-blocker + angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) Strength
Byvalson (nebivolol, valsartan) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Byvalson Generic name: Nebivolol, valsartan Pharmacological class: Beta-blocker + angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) Strength
PHARM 504: Pharmacy Practice Winter 2009 MCP DRUGS #3: CARDIOVASCULAR PRODUCTS January 22th, 2010 Laura Knutzen
 PHARM 504: Pharmacy Practice Winter 2009 MCP DRUGS #3: CARDIOVASCULAR PRODUCTS January 22th, 2010 Laura Knutzen General Tips and Information: 1. Types of Cardiovascular Disorders: Myocardial infarction
PHARM 504: Pharmacy Practice Winter 2009 MCP DRUGS #3: CARDIOVASCULAR PRODUCTS January 22th, 2010 Laura Knutzen General Tips and Information: 1. Types of Cardiovascular Disorders: Myocardial infarction
M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY
 M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY USING CVS SYSTEM AS AN EXAMPLE NIGEL FONG 2 JAN 2014 TODAY S OBJECTIVE Pharmacology often seems like an endless list of mechanisms and side effects to memorize. To
M2 TEACHING UNDERSTANDING PHARMACOLOGY USING CVS SYSTEM AS AN EXAMPLE NIGEL FONG 2 JAN 2014 TODAY S OBJECTIVE Pharmacology often seems like an endless list of mechanisms and side effects to memorize. To
Heart Disease and Prevention PRESENTED BY: DOTTIE CRAIG NP- C, JANE ARCHER NP-C, KATHY DAPPER RN, NICCI FRAVEL RN
 Heart Disease and Prevention PRESENTED BY: DOTTIE CRAIG NP- C, JANE ARCHER NP-C, KATHY DAPPER RN, NICCI FRAVEL RN Objectives Identify Normal Systolic and Diastolic Blood pressures Recognize common Antihypertensive
Heart Disease and Prevention PRESENTED BY: DOTTIE CRAIG NP- C, JANE ARCHER NP-C, KATHY DAPPER RN, NICCI FRAVEL RN Objectives Identify Normal Systolic and Diastolic Blood pressures Recognize common Antihypertensive
Adrenergic Receptor as part of ANS
 Adrenergic Receptor as part of ANS Actions of Adrenoceptors Beta-1 adrenergic receptor Located on the myocytes of the heart Specific actions of the β1 receptor include: 0 Increase cardiac output, by 0
Adrenergic Receptor as part of ANS Actions of Adrenoceptors Beta-1 adrenergic receptor Located on the myocytes of the heart Specific actions of the β1 receptor include: 0 Increase cardiac output, by 0
Autonomic Pharmacology
 Autonomic Pharmacology ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR BLOCKERS Adrenergic-receptor antagonists block the effects of sympathetic stimulation and adrenergic agonists mediated through - and -receptors. Adrenergic receptor
Autonomic Pharmacology ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR BLOCKERS Adrenergic-receptor antagonists block the effects of sympathetic stimulation and adrenergic agonists mediated through - and -receptors. Adrenergic receptor
Hypertension Update. Objectives 4/28/2015. Beverly J. Mathis, D.O. OOA May 2015
 Hypertension Update Beverly J. Mathis, D.O. OOA May 2015 Objectives Learn new recommendations for BP treatment goals Approach to hypertension in the office Use of hypertensive drugs, and how to tailor
Hypertension Update Beverly J. Mathis, D.O. OOA May 2015 Objectives Learn new recommendations for BP treatment goals Approach to hypertension in the office Use of hypertensive drugs, and how to tailor
Dr Narender Goel MD (Internal Medicine and Nephrology) Financial Disclosure: None, Conflict of Interest: None
 Dr Narender Goel MD (Internal Medicine and Nephrology) drnarendergoel@gmail.com Financial Disclosure: None, Conflict of Interest: None 12 th December 2013, New York Visit us at: http://kidneyscience.info/
Dr Narender Goel MD (Internal Medicine and Nephrology) drnarendergoel@gmail.com Financial Disclosure: None, Conflict of Interest: None 12 th December 2013, New York Visit us at: http://kidneyscience.info/
By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat
 What is The Optimum? By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat Professor of Cardiology - Benha Faculty of Medicine HT. Introduction Despite major worldwide efforts over recent decades directed at diagnosing and treating
What is The Optimum? By Prof. Khaled El-Rabat Professor of Cardiology - Benha Faculty of Medicine HT. Introduction Despite major worldwide efforts over recent decades directed at diagnosing and treating
Beta-blockers. Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol.
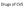 Drugs of CVS Beta-blockers Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol. Atenolol.cardioselective Propranolol, nonselective Bisoprolol, cardioselective Metoprolol Carvedilol, alpha
Drugs of CVS Beta-blockers Atenolol. Propranolol. Bisoprolol. Metoprolol. Labetalol. Carvedilol. Atenolol.cardioselective Propranolol, nonselective Bisoprolol, cardioselective Metoprolol Carvedilol, alpha
Hypertension: Update
 Hypertension: Update Meenakshi A Bhalla MD,FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Director Preventive Cardiology Advanced Heart Failure and Transplant Cardiology University of Kentucky Faculty Disclosure
Hypertension: Update Meenakshi A Bhalla MD,FACC Associate Professor of Medicine Director Preventive Cardiology Advanced Heart Failure and Transplant Cardiology University of Kentucky Faculty Disclosure
Heart Failure. Subjective SOB (shortness of breath) Peripheral edema. Orthopnea (2-3 pillows) PND (paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea)
 Pharmacology I. Definitions A. Heart Failure (HF) Heart Failure Ezra Levy, Pharm.D. HF Results when one or both ventricles are unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the body s needs There are 2 types
Pharmacology I. Definitions A. Heart Failure (HF) Heart Failure Ezra Levy, Pharm.D. HF Results when one or both ventricles are unable to pump sufficient blood to meet the body s needs There are 2 types
Table 1. Diuretics. Drugs Mechanisms of Action Indications Adverse Drug Effects. Table 2. Electrolyte Modifiers.
 Table 1. Diuretics. hydrochlorothiazide 23 furosemide 23 triamterene 23 Inhibits sodium reabsorption at the distal convoluted tubule Inhibits sodium reabsorption at the loop of Henle Competitive inhibitor
Table 1. Diuretics. hydrochlorothiazide 23 furosemide 23 triamterene 23 Inhibits sodium reabsorption at the distal convoluted tubule Inhibits sodium reabsorption at the loop of Henle Competitive inhibitor
Difficult to Control HTN: It is not all the same. Structured approach to evaluation and treatment
 Difficult to Control HTN: It is not all the same. Structured approach to evaluation and treatment Dmitri Vasin M.D. Nephrologist and ASH certified clinical hypertension specialist Bremerton, WA, USA Johnson
Difficult to Control HTN: It is not all the same. Structured approach to evaluation and treatment Dmitri Vasin M.D. Nephrologist and ASH certified clinical hypertension specialist Bremerton, WA, USA Johnson
Dr. Vishaal Bhat. anti-adrenergic drugs
 Dr. Vishaal Bhat anti-adrenergic drugs Divisions of human nervous system Human Nervous system Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system Includes neurons and
Dr. Vishaal Bhat anti-adrenergic drugs Divisions of human nervous system Human Nervous system Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system Includes neurons and
Living with Congestive Heart Failure: A Guide to a Healthy Heart
 Living with Congestive Heart Failure: A Guide to a Healthy Heart Things to Know, Before You Go Dear Patient/Caregiver These are the things you NEED TO KNOW, BEFORE YOU GO. It is very important that you
Living with Congestive Heart Failure: A Guide to a Healthy Heart Things to Know, Before You Go Dear Patient/Caregiver These are the things you NEED TO KNOW, BEFORE YOU GO. It is very important that you
Chapter 9. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Cardiac Arrhythmias. Define electrical therapy
 Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Network Hypertension Algorithm
 Network Hypertension Algorithm Content Review and Approval: This document is subject to review, revision, and (re)approval by the Clinical Integration and Oversight Committee (CIOC) annually and following
Network Hypertension Algorithm Content Review and Approval: This document is subject to review, revision, and (re)approval by the Clinical Integration and Oversight Committee (CIOC) annually and following
Physician/Clinic Collaborative Practice Agreement
 Physician/Clinic Collaborative Practice Agreement Effective October 1, 2010, Connecticut Senate Bill 428 (PA 10-117) extends to all settings and medical conditions the opportunity for licensed pharmacists
Physician/Clinic Collaborative Practice Agreement Effective October 1, 2010, Connecticut Senate Bill 428 (PA 10-117) extends to all settings and medical conditions the opportunity for licensed pharmacists
LESSON ASSIGNMENT Given the trade and/or generic name of an adrenergic blocking agent, classify that agent as either an alpha or beta blocker.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 8 Adrenergic Blocking Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 8-1 through 8-5. LESSON OBJECTIVES 8-1. Given a group of statements, select the statement that best describes one of the
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 8 Adrenergic Blocking Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 8-1 through 8-5. LESSON OBJECTIVES 8-1. Given a group of statements, select the statement that best describes one of the
