Historical Perspectives
|
|
|
- Howard Anthony
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Clinical Chest Radiography Interpretation Part 1 Theresa M Campo DNP, FNP-C, ENP-BC, FAANP tersa16@comcast.net Historical Perspectives Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen Dutch Physicist Discovered form of radiation roentgen ray First diagnostic radiograph 1896 Roentgen Won Nobel Prize for Physics 1901 Through the years.. 1
2 Image Production Strahlung Ray (X-Ray) from cathode tube Attenuation of the ray Radiant energy short wave greater ability to penetrate objects Cassette Image Radiolucent, Radiopaque, Radiodense Radiolucent Blackening of the film (-1000 HU) Permits passage of rays, low absorbency Radiopague and Radiodense Less blackening of the film Doesn t allow passage of rays, high absorbency (1000 HU) Gas (air) Black Fat Gray-Black Soft tissue (water) Gray Bone (metal) White Radiographic Densities 2
3 Radiographic Contrast Image Quality Motion Scatter Magnification Thickness Distortion The Basics Foundational Concepts Anatomy and Physiology Pathophysiology Shades of Gray 2 dimensional image of 3 dimensional body 3
4 Plain Radiographs Air Fluid Levels Visualize stones Identify gross abnormalities that may lead to further testing Foreign body identification Diagnosis or Finding Right Middle Lobe Infiltrate Pneumonia Radiopague Foreign Body Gangrene THE RULES Obtain a thorough history and physical examination Order when necessary Evaluate the entire radiograph Re-examine the patient and the radiograph Rule of 2s Failsafe measures 4
5 High energy ionizing radiation Atom loses electron ionized Photon with >15 electron volts is capable of ionization Radiation exposure has been researched since the atomic bomb exposure. However, it has been observed since the early 1900s Increased use of plain radiographs, nuclear medicine and CT scans has increased population exposure rates Interrupts cell DNA causing mutations Organs and tissues varying sensitivities Three measures to describe radiation dose Absorbed Amount of energy absorbed/unit mass Effective All irradiated tissue and organ risk of exposure Organ Organ risk of exposure X-Ray Equivalent Chest X-ray = 3 days of background radiation C-spine = 1.5 days of background radiation Pelvis = 14 days of background radiation Abdomen = 16 days of background radiation Thoracic spine = 24 days of background radiation Lumbar spine = 60 days of background radiation 5
6 Plain Radiographs 0.02 msv Chest X-Ray CT scan 2.0 msv Head msv Chest, Abdomen and Pelvis Nuclear Medicine msv (sestamibi scan dual isotope scanning) Ionizing Radiation Medical Imaging Classified as carcinogenic Patients get multiple tests Statistically significant increases in cancer with doses over 50mSv Chest Anatomy 6
7 Positioning Posterior Anterior (PA) Facing the cartridge Supine Anterior Posterior (AP) Only in the critical patient Lateral Position Lateral Decubitus Normal PA and Lateral 7
8 Lung markings more distinct Heart is smaller Clavicles are superimposed over upper lungs Cervical and thoracic vertebrae more clearly visible PA vs AP Heart appears larger than normal Lung volumes are shallow Clavicles usually higher Lateral Decubitus Position Assess volume, mobility or loculation of pleural effusion Dependent lung should have increased density d/t atelectasis from mediastinal pressure Airtrapping if not present ABC s of Interpretation Adequacy, Airway Breathing Circulation Diaphragm Edges Skeleton, Soft Tissue 8
9 Trachea midline or deviated, caliber, mass Lungs abnormal shadowing or lucency Pulmonary vessels artery or vein enlargement Hila masses, lymphadenopathy Heart thorax: heart width > 2:1? Cardiac configuration? Interpretation Mediastinal contour width? mass? Pleura effusion, thickening, calcification Bones lesions or fractures Soft tissues don t miss a mastectomy ICU Films identify tubes first and look for pneumothorax Adequacy Normal Inspiration Penetration Rotation Normal Inspiration Diaphragm at the level of the 8-10 th posterior rib or 5-6 th anterior rib 9
10 Poor Inspiration Expiration Desirable to evaluate a patient with: Suspected pneumothorax Suspected foreign body in bronchus Foreign Body A Normal Full Inspiration There is no volume change on the left B Expiration mediastinum and heart shift to the right Obstruction left main stem bronchus Daffner & Hartman
11 Pneumothorax A Normal Inspiration Left Pneumothorax B Expiration Enlargement of left pneumothorax Daffner & Hartman 2014 PA Thoracic disc spaces should be barely visible through the heart with vertebral bodies not visible Over-penetration = Dark Under-penetration = Light Penetration Lateral Should see 2 sets of ribs Sternal edge may be visible Vertebrae appear darker as you move caudally Over and Penetrated Penetration 11
12 Rotation May result in distortion of normal anatomic structures Clavicle heads and spinal processes should be symmetrical Airway Trachea midline and seen to the carina (bifurcation T4-T5) Slowly angles downward to the thoracic inlet (retrotracheal line 3mm) Bronchogram may be normal or abnormal Air filled tube surrounded by soft tissue The Rest of the A, B, Cs Breathing (Bird cages) Cardiac/circulation Diaphragm Edges Skeleton and Soft Tissue 12
13 What do you see???? Okay now for the Lateral 13
14 Mediastinum Central chest between lungs and heart Divided into three regions Anterior area between sternum and front of heart and great vessels Middle area between anterior and posterior pericardium Includes: pericardium, heart, aortic arch, proximal brachialcephalic vessels, pulmonary veins/arteries, trachea, main bronchus, and lymph nodes Posterior area behind the heart and trachea including vertebral bodies Mediastinum 14
15 Pediatric Considerations Can be challenging Look different in children Different diseases Change with age Limited patient cooperation Thymus can cause confusion Adult versus Child Differences Heart Newborn hearts can be more than ½ the width of the chest Good inspiration needed to judge heart size Poor inspiration can significantly change the look and position of the heart Thymus Increases in size fro birth through puberty BUT child grows so it appears smaller with age Can be variable in size and appearance (i.e. shrink rapidly due to illness or grow due to chemotherapy) 15
16 Look for a Bronchogram Outline of airway that is made visible by surrounding alveoli with fluid or exudate When visualized diagnostic for air space disease 6 causes normal expiration lung consolidation pulmonary edema Non-obstructive pulmonary atelectasis severe interstitial disease Neoplasm Bronchogram Atelectasis Condition of volume loss in some portion of lung May involve sub-segment, segment, lobe or entire lung Increased density usually linear Collapse or incomplete expansion of the lung or part of the lung Segmental and sub-segmental collapse may show linear, curvilinear, wedge shaped opacities 16
17 Atelectasis Causes Obstructive Most common Bronchus obstructed by mucous plug, neoplasm, or foreign body Compressive Normal lung compressed by tumor, emphysematous bulla or heart enlargement Cicatrization Organizing scar tissue Most often after healing granulomatous disease (i.e. TB), pulmonary infarct or trauma Adhesive Inactivation of surfactant (example: hyaline membrane disease) Passive Normal compliance of the lung with pneumothorax or pleural effusion Airway remains patent Linear Atelectasis Plate-like Partial collapse Dense line 1 or more lobes Pulmonary Edema Two basic types Cardiogenic increased hydrostatic pulmonary capillary pressure Non-cardiogenic altered capillary membrane permeability or decreased plasma oncotic pressure NOT CARDIAC (Pneumonic) Near-drowning, Oxygen therapy, Transfusion or Trauma, CNS disorder, ARDS, Aspiration, or Altitude sickness, Renal disorder or Resuscitation, Drugs, Inhaled toxins, Allergic Alveolitis, Contrast or Contusion 17
18 Cardiogenic Cephalization of the pulmonary vessels Kerley A lines thin linear opacities in mid and upper zones radiating to hila Kerley B lines linear opacities 1-2cm long and 1-2mm thick perpendicular to pleural surface caused by interstitial fluid (septal lines) Peribronchial cuffing "bat wing" pattern perihilar and medullary consolidation of both lungs Patchy shadowing with air bronchograms Heart enlargement Pleural effusions Pulmonary Edema Cephalization of Vessels Bat Wing Pattern 18
19 Pulmonary Edema Diffuse Pulmonary Edema Congestive Heart Failure 19
20 Pleural Effusion Causes CHF Infection (parapneumonic) Trauma PE Tumor Autoimmune disease Renal failure Pleural Effusion 88 year old Female Presents with complaints of shortness of breath PMH arthritis, hypercholesterolemia, HTN, CAD, pulmonary HTN, PSH CABG, Cataracts, Aortic Valve Repair Allergy codeine, PCN PE lungs decreased with bibasilar crackles Vital signs BP 146/85, HR 85, RR 16, T 97F, pulse Ox 95% RA 20
21 21
22 78 year old Male Presents with shortness of breath for 1 day progressively getting worse. PMH CAD, HTN, Hypercholesterolemia PSH CABG, pacemaker or AICD patient and family not sure Allergies none PE pale, diaphoretic, in mild respiratory distress. Mild JVD. Lungs with course diffuse rhonchi. S1 S2 no M/G/C Vital signs BP148/90, HR 102, RR 28, T 97.9F pulse Ox 94% RA 52 Year Old Male Complaints of not feeling well, chest tightness, and racing heart. Denied SOB or fever PMH alcohol abuse, depression PSH none Allergies none Social alcohol use daily 1 bottle of scotch; tobacco 1-2 PPD PE unremarkable Vital signs BP 154/103, HR 138, RR 27, T 100.8, pulse Ox 97% RA 22
23 23
24 Chest X-Ray BASICS AND BEYOND Part 2 Theresa M Campo DNP, FNP-C, ENP-BC, FAANP tersa16@comcast.net 3 year old female Fever 102F, sinus congestion and drainage, cough PMH/PSH negative Medications None Allergy whole milk PE erythema to pharynx, Vital signs HR 126; RR 24; T 102.8F, pulse Ox 98% RA 24
25 Types of Pneumonia Lobar Classically Pneumococcal pneumonia Entire lobe consolidated Air bronchogram Lobular Often Staphylococcus Multifocal, patchy, sometimes No air bronchogram Interstitial Viral or Mycoplasma Latter starts perihilar and can become confluent and/or patchy as disease progresses No air bronchogram Aspiration Pneumonia Follows gravitational flow of aspirated contents Anaerobic Bacteroides Fusobacterium Diffuse Infection Community acquired Mycoplasma resolves spontaneously nosocomial Pseudomonas high mortality rate patchy opacities, cavitation, ill-defined nodular immunocompromised host Bacterial, fungal, PCP 25
26 32 Year Old Male Aortic Valve Replacement Post-op 5 days Chest tube removed C/O mild SOB 26
27 Pneumomediastinum Streaky lucencies over the mediastinum that may extend into the neck, and elevation of the parietal pleura along the mediastinal borders Causes Asthma Surgery Traumatic tracheobronchial rupture Abrupt changes in intrathoracic pressure (vomiting, coughing, exercise, parturition) Ruptured esophagus Barotrauma Smoking crack cocaine 27
28 32 yr old Post-op Day 8 28
29 Causes Idiopathic Asthma COPD Pulmonary infection Neoplasm Marfan syndrome Smoking cocaine Trauma Provider Pneumothorax Pneumothorax Traumatic Injuries 29
30 30
31 What Do You Think???? Thoughts?? 31
32 Sternum Fracture 32
33 Radiographic Findings Pruned vascularity most reliable sign Decreased vascularity Hyperlucency Increased retrosternal clear space Increased lung volume Depression/flattening Diaphramatic curve Diaphramatic excursion Prominent central pulmonary artery with rapid tapering 49 year old female Arrived to ED via ambulance swallowed foreign body. Attempted to vomit at home but unsuccessful. PMH hypertension takes no medications No complaints offered but afraid could cause harm PE unremarkable Vital signs BP 156/96; HR 85, RR 18, T 96.7F, pulse Ox 98% RA 33
34 Masses and Tumors Lung and Mediastinal masses are common Solitary pulmonary nodules Tumors Granulomas 34
35 Common and Uncommon Solitary Pulmonary Nodules Common Bronchial adenoma Primary carcinoma Granuloma (fungus, TB) Hematoma Metastases Simulated nodule (nipple, bone lesion, skin tumor, etc) Uncommon Abscess Hematoma Infarct Loculated pleural fluid Vascular lesion 35
36 Cavitary Masses Pulmonary nodules which may cavitate Most Common Carcinoma Necrotizing infections (abscesses) Metastatic lesions (usually squamous cell) Others Causes Fungal or TB infection Hematoma Pneumatoceles Cavitary Masses Wall Thickness >15 mm more likely to be malignant <4 mm more likely to be benign Not specific enough further testing needs to be done (i.e. biopsy) 36
37 37
38 Evaluating Pulmonary Nodules Need to find the epicenter of the pulmonary mass (nodule) Allows for identification of where the mass began (i.e. lung, mediastinum, pleura, chest wall) Spiculated margins Lesions doubling in diameter actually increase 8-fold in volume Utilize old studies Chest radiograph CT MRI PET imaging Spiculated Margins Mediastinal Masses Can be difficult to differentiate from pulmonary parenchymal masses Majority of primary mediastinal masses Occur anterior compartment 1/3 middle compartment Remainder posterior compartment Majority show extrapulmonary signs Obtuse margins with pleura Centered outside the lung 38
39 Mediastinal Masses Anterior compartment Lymphoma, thymomas, teratomas most common Hernias and cysts other abnormalities Middle mediastinum Lymph nodes, metastatic disease, sarcoidosis, infection/inflammation Behind the heart Hiatel/paraesophageal hernia Posterior compartment Neurogenic tumor (paraspinous mass) Teratoma Anterior Compartment 39
40 Sarcoidosis Lymphoma Hiatel Hernia Air/fluid levels Posterior to heart 40
41 Tuberculosis Primary Healthy individuals may have no chest x-ray findings even with a positive PPD Inflammatory response Primary inflammatory complex or Ranke complex calcified nodules and thoracic lymph nodes Not reliable sign (i.e. fungal infections, histoplasmosis) Immunocompromised/chronically ill Nonspecific consolidation Cavity nodule/mass with air/fluid levels ominous sign for transmissible disease Small miliary nodules Necrotizing adenopathy Pleural effusions Tuberculosis Secondary Reactivation of dormant infection Infection thrives on oxygen Particularly upper lobes Consolidation with or without cavitation and adenopathy End Stage Fibrosis Scarring with volume loss Shift of fissures and/or vessels Calcification Tuberculosis Pediatrics Commonly present with thoracic and neck lymphadenopathy Disseminated Can occur anywhere in the body 41
42 Primary Inflammatory Complex Ranke Complex Tuberculosis Cavitary abscess Miliary Tuberculosis 42
43 Chronic/Old Tuberculosis Thank you!! Theresa M Campo DNP, APN, NP-C, ENP-BC, FAANP Drexel University Co-Director FNP Track Associate Clinical Professor tersa16@comcast.net References Collins & Stern. (2008). Chest Radiology: The Essentials. Wolters Kluwer/LWW: Phila, PA. Daffner & Hartman (2014). Clinical Radiology: The Essentials 4 th ed. Wolters Kluwer/LWW: Phila, PA. Hermann et al. (2012). Best practices in digital radiography: White paper. American Society of Radiologic Technologies accessed from cdigradwhp_final.pdf 43
Clinical Chest Radiography Interpretation Part 1. Theresa M Campo DNP, FNP-C, ENP-BC, FAANP
 Clinical Chest Radiography Interpretation Part 1 Theresa M Campo DNP, FNP-C, ENP-BC, FAANP tersa16@comcast.net Historical Perspectives Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen Dutch Physicist Discovered form of radiation
Clinical Chest Radiography Interpretation Part 1 Theresa M Campo DNP, FNP-C, ENP-BC, FAANP tersa16@comcast.net Historical Perspectives Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen Dutch Physicist Discovered form of radiation
Disclosure. Clinical Chest Radiography Interpretation Part I
 Clinical Chest Radiography Interpretation Part I Anthony M. Angelow, PhD(c), MSN, ACNPC, AGACNP-BC, CEN Associate Lecturer, Fitzgerald Health Education Associates Clinical practice Division of Trauma Surgery
Clinical Chest Radiography Interpretation Part I Anthony M. Angelow, PhD(c), MSN, ACNPC, AGACNP-BC, CEN Associate Lecturer, Fitzgerald Health Education Associates Clinical practice Division of Trauma Surgery
Disclosure. Clinical Chest Radiography Interpretation Part II
 Clinical Chest Radiography Interpretation Part II Anthony M. Angelow, PhD(c), MSN, ACNPC, AGACNP-BC, CEN Associate Lecturer, Fitzgerald Health Education Associates Clinical practice Division of Trauma
Clinical Chest Radiography Interpretation Part II Anthony M. Angelow, PhD(c), MSN, ACNPC, AGACNP-BC, CEN Associate Lecturer, Fitzgerald Health Education Associates Clinical practice Division of Trauma
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis
 Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
4/16/2017. Learning Objectives. Interpretation of the Chest Radiograph. Components. Production of the Radiograph. Density & Appearance
 Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Chest X rays and Case Studies. No disclosures. Outline 5/31/2018. Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital
 Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations
 Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
Chest X-ray Interpretation
 Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays. Objectives. Indications for X-Rays 5/14/2018
 Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
Shedding Light on Neonatal X-rays Barbara C. Mordue, MSN, NNP-BC Neonatal Nurse Practitioner LLUH Children s Hospital, NICU Objectives Utilize a systematic approach to neonatal x-ray interpretation Identify
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus
 Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC
 Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC An approach to reviewing a chest x-ray will create a foundation that will facilitate the detection of abnormalities. You should create your own
Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC An approach to reviewing a chest x-ray will create a foundation that will facilitate the detection of abnormalities. You should create your own
10/17/2016. Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology. Objectives. Techniques
 Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Undergraduate Teaching
 Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
Prof. James F Meaney Undergraduate Teaching Chest X-Ray Understanding the normal anatomical by reference to cross sectional imaging Radiology? It s FUN! Cryptic puzzle Sudoku (Minecraft?) It s completely
Introduction to Chest Radiography
 Introduction to Chest Radiography RSTH 366: DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES Alan Alipoon BS, RCP, RRT Instructor Department of Cardiopulmonary Sciences 1 Introduction Discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen Terminology
Introduction to Chest Radiography RSTH 366: DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES Alan Alipoon BS, RCP, RRT Instructor Department of Cardiopulmonary Sciences 1 Introduction Discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen Terminology
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax. Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem
 Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
Radiological Anatomy of Thorax Dr. Jamila Elmedany & Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem Indications for Chest x - A chest x-ray may be used to diagnose and plan treatment for various conditions, including: Diseases/Fractures
Signs in Chest Radiology
 Signs in Chest Radiology Jonathan H. Chung, MD Disclosures No pertinent disclosures Jonathan H. Chung, MD Assistant Professor Institute t of fadvanced d Biomedical Imaging National Jewish Health Denver,
Signs in Chest Radiology Jonathan H. Chung, MD Disclosures No pertinent disclosures Jonathan H. Chung, MD Assistant Professor Institute t of fadvanced d Biomedical Imaging National Jewish Health Denver,
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code
 Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code Herring, W ISBN-13: 9780323074445 Table of Contents 1. Recognizing Anything The "colorful" world of radiology A
Learning Radiology: Recognizing the Basics. Text with Student Consult Online Access Code Herring, W ISBN-13: 9780323074445 Table of Contents 1. Recognizing Anything The "colorful" world of radiology A
UERMMMC Department of Radiology. Basic Chest Radiology
 UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
Objectives. What is a Chest X Ray? CXR Workshop. Definition (diagnostic tool/internal PE) Types. Cost
 Objectives CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson, PA C Georgia Lung Associates Identify the radiographic landmarks on a chest radiograph Recognize identifiers of poor quality on the chest radiograph Outline an approach
Objectives CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson, PA C Georgia Lung Associates Identify the radiographic landmarks on a chest radiograph Recognize identifiers of poor quality on the chest radiograph Outline an approach
Approach to CXR. Terminology. 1.Identification. Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow. Correct patient Correct date and time Correct examination
 Approach to CXR Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow From Rob Posteraro http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_interpret.txt.html ; http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_main.txt.html) Approach to viewing Chest
Approach to CXR Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow From Rob Posteraro http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_interpret.txt.html ; http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_main.txt.html) Approach to viewing Chest
CHEST & ABDOMINAL X-RAYS MALIKA IBRAHIM CORE MEDICAL TRAINEE BLACKPOOL VICTORIA HOSPITAL DATA INTERPRETATION COURSE FEB 20, 2017
 CHEST & ABDOMINAL X-RAYS MALIKA IBRAHIM CORE MEDICAL TRAINEE BLACKPOOL VICTORIA HOSPITAL DATA INTERPRETATION COURSE FEB 20, 2017 1. Sample x-rays 2. Basic chest x-ray interpretation skills 3. Chest x-ray
CHEST & ABDOMINAL X-RAYS MALIKA IBRAHIM CORE MEDICAL TRAINEE BLACKPOOL VICTORIA HOSPITAL DATA INTERPRETATION COURSE FEB 20, 2017 1. Sample x-rays 2. Basic chest x-ray interpretation skills 3. Chest x-ray
Interesting Cases. Pulmonary
 Interesting Cases Pulmonary 54M with prior history of COPD, hep B/C, and possible history of TB presented with acute on chronic dyspnea, and productive cough Hazy opacity overlying the left hemithorax
Interesting Cases Pulmonary 54M with prior history of COPD, hep B/C, and possible history of TB presented with acute on chronic dyspnea, and productive cough Hazy opacity overlying the left hemithorax
Lung Cancer - Suspected
 Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY
 (YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
(YEARS 1 3) CURRICULUM FOR RADIOLOGY 13 B-I-2 CARDIAC AND VASCULAR RADIOLOGY KNOWLEDGE To describe the normal anatomy of the heart and vessels including the lymphatic system as demonstrated by radiographs,
Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis?
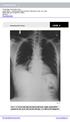 1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
Chest imaging (Case-based teaching) 胸腔病例教學 謝叔強 財團法人恩主公醫院主治醫師萬芳醫院放射科兼任主治醫師.
 Chest imaging (Case-based teaching) 胸腔病例教學 謝叔強 財團法人恩主公醫院主治醫師萬芳醫院放射科兼任主治醫師 e510019@gmail.com Check List(1) 1. Check patient data, position, technical quality and normal anatomy. 2. Review systematically
Chest imaging (Case-based teaching) 胸腔病例教學 謝叔強 財團法人恩主公醫院主治醫師萬芳醫院放射科兼任主治醫師 e510019@gmail.com Check List(1) 1. Check patient data, position, technical quality and normal anatomy. 2. Review systematically
X-Rays. Prepared by Prof.Dr. Magda Hassab Allah Assist.lecturer Marwa Al Hady
 X-Rays Prepared by Prof.Dr. Magda Hassab Allah Assist.lecturer Marwa Al Hady CHEST X-RAYS Normal Chest X-ray Comments on chest X ray includes examination of 1- Bony cage (ribs,clavicles &vertebral column
X-Rays Prepared by Prof.Dr. Magda Hassab Allah Assist.lecturer Marwa Al Hady CHEST X-RAYS Normal Chest X-ray Comments on chest X ray includes examination of 1- Bony cage (ribs,clavicles &vertebral column
Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
 Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
1/13/2014. Proper Radiographs. Proper Radiographs. A Review of Pulmonary Patterns
 Live Webinar A Review of Pulmonary Patterns Sofija R. Liles, DVM, DACVR Proper Radiographs Which views? One lateral plus ventrodorsal (at least) Left lateral is best for thorax Three views for full metastatic
Live Webinar A Review of Pulmonary Patterns Sofija R. Liles, DVM, DACVR Proper Radiographs Which views? One lateral plus ventrodorsal (at least) Left lateral is best for thorax Three views for full metastatic
Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order. Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital
 Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital BASIC ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS Lobes of Lung 3 lobes on the Right lung 2 lobes on the Left Blood
Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital BASIC ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS Lobes of Lung 3 lobes on the Right lung 2 lobes on the Left Blood
Sectional Anatomy Quiz - III
 Sectional Anatomy - III Rashid Hashmi * Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales (UNSW), Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 30 Jun 2018
Sectional Anatomy - III Rashid Hashmi * Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales (UNSW), Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 30 Jun 2018
Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps. Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania None Disclosures Objectives Describe blunt and penetrating traumatic
Imaging of Thoracic Trauma: Tips and Traps Arun C. Nachiappan, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania None Disclosures Objectives Describe blunt and penetrating traumatic
Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD
 TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!!
 The lateral chest radiograph: Challenging area around the thoracic aorta!!! Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!! Dong Yoon Han 1, So Youn
The lateral chest radiograph: Challenging area around the thoracic aorta!!! Do you want to be an excellent Radiologist? - Focus on the thoracic aorta on lateral chest image!!! Dong Yoon Han 1, So Youn
100 Chest X Rays for Study Group. by Dr. Suneet Khurana
 100 Chest X Rays for Study Group by Dr. Suneet Khurana Approach to - Chest X Ray (shadow of the viscera on a photographic plate) Gas appears Black Fat appears Dark Grey Water Appears as Light Grey Bone
100 Chest X Rays for Study Group by Dr. Suneet Khurana Approach to - Chest X Ray (shadow of the viscera on a photographic plate) Gas appears Black Fat appears Dark Grey Water Appears as Light Grey Bone
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT
 How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
Children are not small adults Children are Not Small Adults Anatomic considerations Pliable bony & cartilagenous structures - Significant thoracic inj
 PEDIATRIC CHEST TRAUMA Children are not small adults Role of imaging Spectrum of injury Children are not small adults Children are Not Small Adults Anatomic considerations Pliable bony & cartilagenous
PEDIATRIC CHEST TRAUMA Children are not small adults Role of imaging Spectrum of injury Children are not small adults Children are Not Small Adults Anatomic considerations Pliable bony & cartilagenous
Sectional Anatomy Quiz II
 Sectional Anatomy II Rashid Hashmi Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales, Wagga Wagga, New South Wales, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 3 Aug 2017
Sectional Anatomy II Rashid Hashmi Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales, Wagga Wagga, New South Wales, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 3 Aug 2017
ARDS - a must know. Page 1 of 14
 ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 14, 2013
 Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 14, 2013 Radiologic Presentation of Childhood TB Susan D. John, MD, FACR October 14, 2013 Disclosures I have no disclosures or conflicts of interest to report
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 14, 2013 Radiologic Presentation of Childhood TB Susan D. John, MD, FACR October 14, 2013 Disclosures I have no disclosures or conflicts of interest to report
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas November 13, 2009 Radiographic Manifestations of Pediatric TB Susan D. John, MD, FACR November 13, 2009 Radiologic Presentation of Childhood TB Susan D. John, MD,
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas November 13, 2009 Radiographic Manifestations of Pediatric TB Susan D. John, MD, FACR November 13, 2009 Radiologic Presentation of Childhood TB Susan D. John, MD,
Manage TB Dr. A. Chitrakumar Madras Medical College and RGGGH Institute of Thoracic Medicine, Chennai
 Manage TB Dr. A. Chitrakumar Madras Medical College and RGGGH Institute of Thoracic Medicine, Chennai Lecture 16 Radiology in diagnosis of Tuberculosis Session 01 So, welcome to the session Radiology in
Manage TB Dr. A. Chitrakumar Madras Medical College and RGGGH Institute of Thoracic Medicine, Chennai Lecture 16 Radiology in diagnosis of Tuberculosis Session 01 So, welcome to the session Radiology in
Radiology of the respiratory disease
 Radiology of the respiratory disease [ Color index: Important Notes Extra ] [ Editing file Feedback Share your notes Shared notes ] Resources: - 435 Slides - 434 Team - 435 Notes Done by: - Mai Alageel
Radiology of the respiratory disease [ Color index: Important Notes Extra ] [ Editing file Feedback Share your notes Shared notes ] Resources: - 435 Slides - 434 Team - 435 Notes Done by: - Mai Alageel
Anatomy notes-thorax.
 Anatomy notes-thorax. Thorax: the part extending from the root of the neck to the abdomen. Parts of the thorax: - Thoracic cage (bones). - Thoracic wall. - Thoracic cavity. ** The thoracic cavity is covered
Anatomy notes-thorax. Thorax: the part extending from the root of the neck to the abdomen. Parts of the thorax: - Thoracic cage (bones). - Thoracic wall. - Thoracic cavity. ** The thoracic cavity is covered
Chief Complain. For chemotherapy
 Chief Complain For chemotherapy Present Illness 93.12 Progressive weakness of R t arm for 1 year X-ray: peneative lesion over right proximal humorous Bone scan: multiple increased intake Biopsy of distal
Chief Complain For chemotherapy Present Illness 93.12 Progressive weakness of R t arm for 1 year X-ray: peneative lesion over right proximal humorous Bone scan: multiple increased intake Biopsy of distal
Lecture 3. Inflammatory Processes
 Lecture 3 Inflammatory Processes Process: Increased vascular permeability Water and cellular infiltrations Results: Abscess, ulceration, cavitation Penetration, perforation and fistula formation Scarring,
Lecture 3 Inflammatory Processes Process: Increased vascular permeability Water and cellular infiltrations Results: Abscess, ulceration, cavitation Penetration, perforation and fistula formation Scarring,
Radiological conference. Left upper lobe collapse. Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1998, v. 20 n. 9, p
 Title Radiological conference. Left upper lobe collapse Author(s) Wong, LLS; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1998, v. 20 n. 9, p. 513-517 Issued Date 1998 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44672
Title Radiological conference. Left upper lobe collapse Author(s) Wong, LLS; Peh, WCG Citation Hong Kong Practitioner, 1998, v. 20 n. 9, p. 513-517 Issued Date 1998 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/44672
PATIENT DATA EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATION: IMAGING STUDIES
 PATIENT DATA EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATION: IMAGING STUDIES Robert Harwood, MSA, RRT-NPS Objectives At the end of this presentation the student should be able to: Describe the indications of a chest radiograph.
PATIENT DATA EVALUATION AND RECOMMENDATION: IMAGING STUDIES Robert Harwood, MSA, RRT-NPS Objectives At the end of this presentation the student should be able to: Describe the indications of a chest radiograph.
Neonatal Chest X-Ray Interpretation
 CHAPTER 7 Neonatal Chest X-Ray Interpretation Prof. Praveen Kumar Neonatal unit, Department of Pediatrics, PGIMER, Chandigarh Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you should be able to: 1. Schematically
CHAPTER 7 Neonatal Chest X-Ray Interpretation Prof. Praveen Kumar Neonatal unit, Department of Pediatrics, PGIMER, Chandigarh Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you should be able to: 1. Schematically
X-Rays. Kunal D Patel Research Fellow IMM
 X-Rays Kunal D Patel Research Fellow IMM The 12-Steps } 1: Name 2: Date 3: Old films 4: What type of view(s) 5: Penetration } Pre-read 6: Inspiration 7: Rotation Quality Control 8: Angulation 9: Soft tissues
X-Rays Kunal D Patel Research Fellow IMM The 12-Steps } 1: Name 2: Date 3: Old films 4: What type of view(s) 5: Penetration } Pre-read 6: Inspiration 7: Rotation Quality Control 8: Angulation 9: Soft tissues
Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts
 Nov 2003 Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts Josh Rempell, Harvard Medical School Year III Tuberculosis: the captain of all (wo)men of death Overall, one third of the
Nov 2003 Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts Josh Rempell, Harvard Medical School Year III Tuberculosis: the captain of all (wo)men of death Overall, one third of the
Case Study #2. Case Study #1 cont 9/28/2011. CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C. LH is 78 yowf with PMHx of metz breast CA presents
 Case Study #1 CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C 46 yo female presents with community acquired PNA (CAP). Her condition worsened and she was transferred to the ICU and placed on mechanical ventilation. Describe
Case Study #1 CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C 46 yo female presents with community acquired PNA (CAP). Her condition worsened and she was transferred to the ICU and placed on mechanical ventilation. Describe
8/14/2017. Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual lung pathologic features
 What is that lung disease? Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Dr. Russell Tucker, DACVR Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual lung pathologic features Improved
What is that lung disease? Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Dr. Russell Tucker, DACVR Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual lung pathologic features Improved
Interactive Lecture. Lecture 7 - Interactive. Radiology of cardiorespiratory disease. Editing File. Done By. Color Coding Important Notes Extra
 Lecture 7 - Interactive 436 Teams Interactive Lecture Radiology of cardiorespiratory disease Done By Team Leaders: Khalid Alshehri Hanin Bashaikh Team Members: Ghaida Alsaeed Maha Alissa Nawwaf AlHarbi
Lecture 7 - Interactive 436 Teams Interactive Lecture Radiology of cardiorespiratory disease Done By Team Leaders: Khalid Alshehri Hanin Bashaikh Team Members: Ghaida Alsaeed Maha Alissa Nawwaf AlHarbi
Interpretation of Chest Radiographs Paul Christensen, MD 10/21/09. Diagnostic Evaluation. Medical Evaluation & CXR Interpretation.
 Diagnostic Evaluation Medical Evaluation & CXR Interpretation University of Michigan TB Consultant Washtenaw County Medical history Physical examination Testing for TB exposure (previously covered) Radiologic
Diagnostic Evaluation Medical Evaluation & CXR Interpretation University of Michigan TB Consultant Washtenaw County Medical history Physical examination Testing for TB exposure (previously covered) Radiologic
ACUTE PULMNARY INFECTIONS: UNDERSTANDING THE CHEST RADIOGRAPH. Leonard E. Swischuk, M.D. University of Texas Medical Branch
 ACUTE PULMNARY INFECTIONS: UNDERSTANDING THE CHEST RADIOGRAPH Leonard E. Swischuk, M.D. University of Texas Medical Branch AUTHOR HAS NOTHING TO DECLARE LEARNING OBJETIVES Understand the pathophysiology
ACUTE PULMNARY INFECTIONS: UNDERSTANDING THE CHEST RADIOGRAPH Leonard E. Swischuk, M.D. University of Texas Medical Branch AUTHOR HAS NOTHING TO DECLARE LEARNING OBJETIVES Understand the pathophysiology
Long Case Set 02. Dr Raviraj Uppoor. Dr Sameer Shamshuddin. Consultant Radiologist Cumberland Infirmary, Carlisle, UK
 Long Case Set 02 www.frcrtutorials.com Dr Raviraj Uppoor MBBS, DMRD, DNB, FRCR Consultant Radiologist Cumberland Infirmary, Carlisle, UK Dr Sameer Shamshuddin MBBS, DMRD, FRCR Consultant Radiologist Royal
Long Case Set 02 www.frcrtutorials.com Dr Raviraj Uppoor MBBS, DMRD, DNB, FRCR Consultant Radiologist Cumberland Infirmary, Carlisle, UK Dr Sameer Shamshuddin MBBS, DMRD, FRCR Consultant Radiologist Royal
Use of Integrated PET CT in the Clinical Staging of Non Small Cell Lung Cancer
 November 2010 Use of Integrated PET CT in the Clinical Staging of Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Laura Myers, Harvard Medical School, Year III Clinical Presentation 79yo woman with cough productive of green
November 2010 Use of Integrated PET CT in the Clinical Staging of Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Laura Myers, Harvard Medical School, Year III Clinical Presentation 79yo woman with cough productive of green
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress THE LAST GASP II: LUNGS AND THORAX David Holt, BVSc, Diplomate ACVS University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress THE LAST GASP II: LUNGS AND THORAX David Holt, BVSc, Diplomate ACVS University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary
Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th & 12 th Eds.)
 PLEURAL CAVITY AND LUNGS Dr. Milton M. Sholley SELF STUDY RESOURCES Essential Clinical Anatomy 3 rd ed. (ECA): pp. 70 81 Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th &
PLEURAL CAVITY AND LUNGS Dr. Milton M. Sholley SELF STUDY RESOURCES Essential Clinical Anatomy 3 rd ed. (ECA): pp. 70 81 Syllabus: 6 pages (Page 6 lists corresponding figures for Grant's Atlas 11 th &
Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology
 Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Russell Tucker, DVM, DACVR Washington State University College of Veterinary Medicine Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual
Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Russell Tucker, DVM, DACVR Washington State University College of Veterinary Medicine Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual
CHEST INJURY PULMONARY CONTUSION
 CHEST INJURY PULMONARY CONTUSION Introduction Pulmonary contusion refers to blunt traumatic lung parenchymal injury which results in oedema and haemorrhaging into alveolar spaces. It may also result in
CHEST INJURY PULMONARY CONTUSION Introduction Pulmonary contusion refers to blunt traumatic lung parenchymal injury which results in oedema and haemorrhaging into alveolar spaces. It may also result in
X-rays. Dr Will Dooley
 X-rays Dr Will Dooley Plan Chest X-Rays Abdominal X-Rays Exam approach Presentation skills EMQ EMQ- answers Chest X-Ray - Systematic Approach D R Details RIP Image Quality +/- OBVIOUS ABNORMALITY A B C
X-rays Dr Will Dooley Plan Chest X-Rays Abdominal X-Rays Exam approach Presentation skills EMQ EMQ- answers Chest X-Ray - Systematic Approach D R Details RIP Image Quality +/- OBVIOUS ABNORMALITY A B C
Introduction to Chest CT Interpretation. Objectives 8/28/2017
 Introduction to Chest CT Interpretation Deborah Stein ACNP BC, CCRN NP Education Specialist Department of Anesthesia and Critical Care Medicine August 28, 2017 Objectives Basic Principles Thoracic Anatomy
Introduction to Chest CT Interpretation Deborah Stein ACNP BC, CCRN NP Education Specialist Department of Anesthesia and Critical Care Medicine August 28, 2017 Objectives Basic Principles Thoracic Anatomy
BIOE221. Session 5. Examination of Thorax- Respiratory system. Bioscience Department. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.
 BIOE221 Session 5 Examination of Thorax- Respiratory system Bioscience Department Session Objectives Understand the structure of the thorax and the organs contained in this cavity Understand the importance
BIOE221 Session 5 Examination of Thorax- Respiratory system Bioscience Department Session Objectives Understand the structure of the thorax and the organs contained in this cavity Understand the importance
Bronchial syndrome. Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis
 Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
The Thorax The Ever Challenging Pulmonary Patterns
 The Thorax The Ever Challenging Pulmonary Patterns Lisa G. Britt, DVM, MS, Diplomate American College of Veterinary Radiology, Clinical Assistant Professor @ University of Missouri s College of Veterinary
The Thorax The Ever Challenging Pulmonary Patterns Lisa G. Britt, DVM, MS, Diplomate American College of Veterinary Radiology, Clinical Assistant Professor @ University of Missouri s College of Veterinary
Evaluation of the chest Part II.
 Evaluation of the chest Part II. Nagy Endre SZEGEDI TUDOMÁNYEGYETEM ÁOK, RADIOLÓGIAI KLINIKA, SZEGED ANATOMY parenchyma: alveoloacinar system, pulmonary arteries and veins interstitium: connective tissues
Evaluation of the chest Part II. Nagy Endre SZEGEDI TUDOMÁNYEGYETEM ÁOK, RADIOLÓGIAI KLINIKA, SZEGED ANATOMY parenchyma: alveoloacinar system, pulmonary arteries and veins interstitium: connective tissues
Radiology Pathology Conference
 Radiology Pathology Conference Sharlin Johnykutty,, MD, Cytopathology Fellow Sara Majewski, MD, Radiology Resident Friday, August 28, 2009 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights
Radiology Pathology Conference Sharlin Johnykutty,, MD, Cytopathology Fellow Sara Majewski, MD, Radiology Resident Friday, August 28, 2009 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights
Right lung. -fissures:
 -Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
-Right lung is shorter and wider because it is compressed by the right copula of the diaphragm by the live.. 2 fissure, 3 lobes.. hilum : 2 bronchi ( ep-arterial, hyp-arterial ), one artery mediastinal
TIPS AND PITFALLS IN PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION
 TIPS AND PITFALLS IN PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION Dr Philip Touska MBBS, BMedSci(Hons), MRCS, DO-HNS, FRCR Radiology Fellow Guy s & St Thomas Hospitals LEARNING OBJECTIVES Where do we go wrong? Common pitfalls
TIPS AND PITFALLS IN PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION Dr Philip Touska MBBS, BMedSci(Hons), MRCS, DO-HNS, FRCR Radiology Fellow Guy s & St Thomas Hospitals LEARNING OBJECTIVES Where do we go wrong? Common pitfalls
Pulmonary Pathophysiology
 Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma
 August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
An Image Repository for Chest CT
 An Image Repository for Chest CT Francesco Frajoli for the Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group An Image Repository for Chest CT he Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group is an international and interdisciplinary
An Image Repository for Chest CT Francesco Frajoli for the Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group An Image Repository for Chest CT he Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group is an international and interdisciplinary
Concepts in Small Animal Thoracic Radiology Thoracic Radiology
 Concepts in Small Animal Thoracic Radiology + Radiology of the Pleural Space VMB 960 2/21/2011 Optimizing Image Quality Inherent subject contrast Thorax has high inherent subject contrast c/f abdomen Primarily
Concepts in Small Animal Thoracic Radiology + Radiology of the Pleural Space VMB 960 2/21/2011 Optimizing Image Quality Inherent subject contrast Thorax has high inherent subject contrast c/f abdomen Primarily
Thorax Lecture 2 Thoracic cavity.
 Thorax Lecture 2 Thoracic cavity. Spring 2016 Dr. Maher Hadidi, University of Jordan 1 Enclosed by the thoracic wall. Extends between (thoracic inlet) & (thoracic outlet). Thoracic inlet At root of the
Thorax Lecture 2 Thoracic cavity. Spring 2016 Dr. Maher Hadidi, University of Jordan 1 Enclosed by the thoracic wall. Extends between (thoracic inlet) & (thoracic outlet). Thoracic inlet At root of the
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES
 PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases
 Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Causes: Acute alveolo-capillary sysfunction Interstitial disease Pleural disorders Chest wall disorders Neuromuscular disease Resistance Pathophysiology Reduced compliance
Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases Causes: Acute alveolo-capillary sysfunction Interstitial disease Pleural disorders Chest wall disorders Neuromuscular disease Resistance Pathophysiology Reduced compliance
ANATOMY OF THE PLEURA. Dr Oluwadiya KS
 ANATOMY OF THE PLEURA Dr Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Introduction The thoracic cavity is divided mainly into: Right pleural cavity Mediastinum Left Pleural cavity Pleural cavity The pleural
ANATOMY OF THE PLEURA Dr Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Introduction The thoracic cavity is divided mainly into: Right pleural cavity Mediastinum Left Pleural cavity Pleural cavity The pleural
AJCC-NCRA Education Needs Assessment Results
 AJCC-NCRA Education Needs Assessment Results Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Survey Tool 1 Survey Development, Delivery, Analysis THANKS to NCRA for the following work Developed survey with input from partners
AJCC-NCRA Education Needs Assessment Results Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR Survey Tool 1 Survey Development, Delivery, Analysis THANKS to NCRA for the following work Developed survey with input from partners
GUIDELINES FOR CANCER IMAGING Lung Cancer
 GUIDELINES FOR CANCER IMAGING Lung Cancer Greater Manchester and Cheshire Cancer Network Cancer Imaging Cross-Cutting Group April 2010 1 INTRODUCTION This document is intended as a ready reference for
GUIDELINES FOR CANCER IMAGING Lung Cancer Greater Manchester and Cheshire Cancer Network Cancer Imaging Cross-Cutting Group April 2010 1 INTRODUCTION This document is intended as a ready reference for
!"#$%&'%()'*+,-%&&.'+('*/%)+%,#+0' 12/.,'3%)+"4#%52.
 !"#$%&'%()'*+,-%&&.'+('*/%)+%,#+0' 12/.,'3%)+"4#%52.!"#$%&'()$*+&,--#&$.//,0'1232'!-#0'45 *6 '7849!!"#$%&'"(&)*+),$-.*/*01) 2$34/&1)*+)5"-.3.(") 6%.(3")*+)7*(08/$)9(.:"%;.&1)) )?
!"#$%&'%()'*+,-%&&.'+('*/%)+%,#+0' 12/.,'3%)+"4#%52.!"#$%&'()$*+&,--#&$.//,0'1232'!-#0'45 *6 '7849!!"#$%&'"(&)*+),$-.*/*01) 2$34/&1)*+)5"-.3.(") 6%.(3")*+)7*(08/$)9(.:"%;.&1)) )?
CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS
 CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine Tuberculosis Captain of all the Men of Death Great White Plague devastating effect on society 100 years ago one in
CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine Tuberculosis Captain of all the Men of Death Great White Plague devastating effect on society 100 years ago one in
David E. Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make:
 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David E. Griffith, MD March 13, 2015 TB for Pulmonologist March 13, 2015 Phoenix, AZ EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION David E. Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make:
Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David E. Griffith, MD March 13, 2015 TB for Pulmonologist March 13, 2015 Phoenix, AZ EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION David E. Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make:
Management of Pleural Effusion
 Management of Pleural Effusion Development of Pleural Effusion pulmonary capillary pressure (CHF) capillary permeability (Pneumonia) intrapleural pressure (atelectasis) plasma oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia)
Management of Pleural Effusion Development of Pleural Effusion pulmonary capillary pressure (CHF) capillary permeability (Pneumonia) intrapleural pressure (atelectasis) plasma oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia)
Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Juzar Ali, MD; FRCP(C); FCCP May 4, 2018 Essential Skills for the TB Nurse Case Manager Little Rock, AR May 3 4, 2017 Juzar Ali, MD; FRCP(C); FCCP has the following
Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Juzar Ali, MD; FRCP(C); FCCP May 4, 2018 Essential Skills for the TB Nurse Case Manager Little Rock, AR May 3 4, 2017 Juzar Ali, MD; FRCP(C); FCCP has the following
LUNG PATTERNS IN THE DOG NORMAL AND PATHOLOGICAL
 TRADITION AND MODERNITY IN VETERINARY MEDICINE, 2018, vol. 3, No 1(4): 7 14 LUNG PATTERNS IN THE DOG NORMAL AND PATHOLOGICAL Kalin Spasov 1, Michaela Kunovska 2, Dimo Dimov 3 1 University of Forestry,
TRADITION AND MODERNITY IN VETERINARY MEDICINE, 2018, vol. 3, No 1(4): 7 14 LUNG PATTERNS IN THE DOG NORMAL AND PATHOLOGICAL Kalin Spasov 1, Michaela Kunovska 2, Dimo Dimov 3 1 University of Forestry,
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations
 08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month. Michael B. Gotway, MD. Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ
 September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
Eun-Young Kang, M.D., Jae Wook Lee, M.D., Ji Yung Choo, M.D., Hwan Seok Yong, M.D., Ki Yeol Lee, M.D., Yu-Whan Oh, M.D.
 Eun-Young Kang, M.D., Jae Wook Lee, M.D., Ji Yung Choo, M.D., Hwan Seok Yong, M.D., Ki Yeol Lee, M.D., Yu-Whan Oh, M.D. Department of Radiology, Korea University Guro Hospital, College of Medicine, Korea
Eun-Young Kang, M.D., Jae Wook Lee, M.D., Ji Yung Choo, M.D., Hwan Seok Yong, M.D., Ki Yeol Lee, M.D., Yu-Whan Oh, M.D. Department of Radiology, Korea University Guro Hospital, College of Medicine, Korea
Paramedic Rounds. Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP)
 Paramedic Rounds Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Morgan Hillier MD Class of 2011 Dr. Mike Peddle Assistant Medical Director SWORBHP Objectives Outline evidence for pre-hospital
Paramedic Rounds Pre-Hospital Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) Morgan Hillier MD Class of 2011 Dr. Mike Peddle Assistant Medical Director SWORBHP Objectives Outline evidence for pre-hospital
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II
 Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
Lecture 2: Clinical anatomy of thoracic cage and cavity II Dr. Rehan Asad At the end of this session, the student should be able to: Identify and discuss clinical anatomy of mediastinum such as its deflection,
FUNDAMENTALS OF CXR INTERPRETATION THE BASICS
 FUNDAMENTALS OF CXR INTERPRETATION THE BASICS PART I QUALITY ASSESSMENT 1 PATIENT-DEPENDENT FACTORS 3 REVIEW OF IMPORTANT ANATOMY 7 LUNGS AND PLEURA 11 DIAPHRAGMS 13 BONES AND SOFT TISSUES 14 A BRIEF LOOK
FUNDAMENTALS OF CXR INTERPRETATION THE BASICS PART I QUALITY ASSESSMENT 1 PATIENT-DEPENDENT FACTORS 3 REVIEW OF IMPORTANT ANATOMY 7 LUNGS AND PLEURA 11 DIAPHRAGMS 13 BONES AND SOFT TISSUES 14 A BRIEF LOOK
CT Chest. Verification of an opacity seen on the straight chest X ray
 CT Chest Indications: To assess equivocal plain x-ray findings Staging of lung neoplasm Merastatic workup of extra thoraces malignancies Diagnosis of diffuse lung diseases with HRCT Assessment of bronchietasis
CT Chest Indications: To assess equivocal plain x-ray findings Staging of lung neoplasm Merastatic workup of extra thoraces malignancies Diagnosis of diffuse lung diseases with HRCT Assessment of bronchietasis
BELLWORK page 343. Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary Remember the structures of the respiratory system 1
 BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary respiratory system 1 STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with respiratory disorders, diseases, or syndromes. Citing information
BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary respiratory system 1 STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with respiratory disorders, diseases, or syndromes. Citing information
