Metachronous renal vein and artery injure after percutaneous nephrostolithotomy
|
|
|
- Gerald Sims
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Wang et al. BMC Urology 2013, 13:69 CASE REPORT Open Access Metachronous renal vein and artery injure after percutaneous nephrostolithotomy Chaojun Wang, Shanwen Chen *, Fuqing Tang and Baihua Shen Abstract Background: Percutaneous nephrostolithotomy is important approach for kidney stones removal. A percutaneous nephrostomy drainage tube placement is an effective method to stop venous bleeding. Occasionally, the catheter can pierce into the renal parenchyma, and migrate into the renal vein even to the vena cava. Case presentation: A 66-year-old woman underwent a percutaneous nephrostolithotomy for kidney staghorn stone complicating severe bleeding. A computed tomography angiography showed the percutaneous nephrostomy drainage tube inside the renal vein. The percutaneous nephrostomy drainage tube was withdrawn 3 cm back to the renal parenchyma/sinus/pelvis in stages with the surgical team on standby. Seven days later, the patient developed severe hematuria. Computed tomography angiography demonstrated the pseudoaneurysm located near the percutaneous nephrostomy drainage tube. Pseudoaneurysm is embolized successfully. Conclusion: Our case shows intravenous misplacement of the nephrostomy tube and subsequent pseudoaneurysm after percutaneous nephrostolithotomy. To our knowledge, this seems to be the first documentation of major bleeding from the injury to both renal vein and artery. The percutaneous nephrostomy drainage tube can be withdrawn back to the renal parenchyma/sinus/pelvis in stages with the surgical team on standby, and the withdrawn distance may vary according to patient and catheter position. Keywords: Percutaneous nephrostolithotomy, Misplacement, Pseudoaneurysm, Computed tomography angiography Background Percutaneous nephrostolithotomy (PCNL) was introduced by Fernström and Johansson in 1976 [1], and it has remained as important approach for kidney stones removal since its inception. Venous bleeding during percutaneous procedures is mild and resolves spontaneously or responds to simple maneuvers such as placement a large caliber nephrostomy tube into the tract [2]. Severe bleeding-complications of percutaneous renal surgery are commonly arterial in nature [3,4]. Hemorrhage caused by pseudoaneurysms usually occurs in the postoperative period and can be managed best by selective angiographic embolization. Occasionally nephrectomy is required for refractory bleeding. To our knowledge, major bleeding from injury to both the renal vein and artery has not been reported. We report one case of intravenous misplacement of the nephrostomy tube and subsequent pseudoaneurysms following percutaneous nephrostolithotomy. * Correspondence: chensw123@126.com Department of Urology, the First Affiliated Hospital, Medical of College, Zhejiang University, No. 79 Qing Chun road, Hangzhou , China Case presentation A 66-year-old woman underwent a PCNL for a staghorn stone in the left kidney. Access to the excretory system was achieved by fascial dilators, and a safety guide wire was used during the procedure. An ultrasonic energy source was used to shatter the stone. Severe venous bleeding was noted during the fragmentation process. The procedure was interrupted; a percutaneous nephrostomy drainage tube (PNDT) was inserted and closed in order to control bleeding within the excretory system. PNDT was reopened on the second postoperative day, and intense bleeding was observed through the drainage tube, which was immediately closed. The patient presented with normal blood pressure (128/79 mmhg) and a decreased hemoglobin (7.3 g/dl). The patient was transfused with four units of blood, and she remained hemodinamically stable. On the second post-operative day, a computed tomography angiography showed the PNDT in the left renal vein (Figure 1). Vascular flow was monitored through regular Doppler ultrasonography. Doppler ultrasound 2013 Wang et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
2 Wang et al. BMC Urology 2013, 13:69 Page 2 of 5 Figure 1 Axial contrast enhanced CT and volume rendering image of CT angiography. A-B) Axial contrast enhanced CT and volume rendering image of CT angiography demonstrate percutaneous nephrostomy drainage tube inside the left renal vein; C-D) Axial contrast enhanced CT and volume rendering image of CT angiography reveal percutaneous nephrostomy drainage tube inside the left renal pelvis after the percutaneous nephrostomy drainage tube was withdrawn in stages. showed that there was no renal vein or vena cava thrombosis. The patient was taken to the operating room, and the PNDT was withdrawn 3 cm back to the renal sinus/ parenchyma under fluoroscopy control (the contrast material through the catheter when we withdrew the catheter) with the surgical team on standby ready to intervene. 24 hours later the PNDT was repositioned in the collecting system under fluoroscopy through the same way. Bleeding of the PNDT immediately slowed down and the urine became clear during the next day. The patient was discharged on the sixth post-operative day with a hemoglobin level of 9.3 g/dl. On the eighth post-operative day, the patient developed gross hematuria and severe pain of the left loin. A significant drop of the hemoglobin level was noted (from 9.3 g/dl to 6.8 g/dl) but she remained hemodynamically stable and the coagulation parameters were within normal limits. An abdominal computed tomography scan revealed a large left perinephric hematoma. She was initially treated conservatively with bed rest and transfusions but gross hematuria persisted. After failed resuscitation, a computed tomography angiography was arranged, which revealed a pseudoaneurysm in the left renal artery (Figure 2). A selective left renal angiogram was arranged in order to achieve endovascular control of the bleeding vessel. Active bleeding from the pseudoaneurysm at a branch of the left renal artery with contrast extravasation was shown (Figure 3). The bleeding was embolized selectively with two 2 mm*2 cm metal coils. Twenty-four hours later, hematuria ceased and the patient remained hemodynamically stable. Following above procedure, there was no further gross hematuria. On the thirtieth post-operative day, a nephrostogram revealed the tract had sealed completely, and the PNDT was removed uneventfully. After an 18-month follow up, her post-operative hemoglobin and serum creatinine remained normal. Discussion A PNDT placement in the collecting system following PCNL is a routine practice. It is an effective method to stop venous bleeding [5]. Occasionally, the catheter can pierce into the renal parenchyma, and migrate into the renal vein even to the vena cava [5]. The proximity of the renal vein to the renal pelvis and major posterior calices predisposes them to injury during PCNL [6]. Our patient had complex staghorn renal calculi involving the renal pelvis. Concomitant infection and inflammation
3 Wang et al. BMC Urology 2013, 13:69 Page 3 of 5 Figure 2 Imaging of CT. A) Axial contrast enhanced CT demonstrates the pseudoaneurysm (an oval structure) arising from the lower pole of the left kidney, the pseudoaneurysm was located near the percutaneous nephrostomy tract. B-D) Coronal reformatted (B), maximum intensity projection (C) and volume rendering (D) images of CT angiography reveal the pseudoaneurysm (arrow) arising from the lower polar segmental artery. Figure 3 Angiographic evidence of renal artery pseudoaneurysm before and after angioembolization with coils. A) Arteriography demonstrates one classic pseudaneursym (arrow) blush arising from the lower polar segmental artery of left renal artery. B) Pseudoaneurysm is embolized selectively with two metal coils (arrow). No further contrast medium leakage can be seen following embolisation.
4 Wang et al. BMC Urology 2013, 13:69 Page 4 of 5 may have made the renal pelvic wall more friable and susceptible to the injury. The mechanism of injury was different in resulting from dilating too medially, overzealous tract dilation, injury to a caliceal infundibulum, and pushing too hard on a renal pelvic stone with the ultrasound lithotrite probe as in our patient. Understanding since the renal pelvis is a delicate structure with a thin muscular layer and there is no structural support for it, special care should be taken to stones in the pelvis or lodged at the ureteropelvic junction. By using the ultrasound probe gingerly with firm but gentle intermittent pressure against the stone and without jerky to and fro motions can prevent the stone or the instrument from perforating the collecting system. Abdallah Geara presented a case of visualization of the renal vein during pyelography after nephrostomy, and examination by microscopy showed the presence of tears in the fornix of the pelvic cavity that extend into the kidney parenchyma [7]. However, significant venous injuries during percutaneous renal surgery probably are under diagnosed [8]. Since contrast material generally is not injected during percutaneous procedures to prevent extravasation from obscuring the fluoroscopic image, major injuries may be missed. Clotting of these venous injuries may occur during the operation and, therefore, the injury may not be evident on nephrostograms performed at the conclusion of the procedure or at follow-up. In cases where misplacement of the tube is detected, depending on the postoperative time elapsed, relocation of the nephrostomy tube under fluoroscopy is strongly recommended, and the surgical team must stand ready to operate in case an open emergency procedure is required [9]. Our case illustrates that control on the hemorrhage could be achieved with the catheter being withdrawn in stages, and laparotomy could be avoided despite of the perforation into the major renal vein. If the hemorrhage could not be controlled, in Gupta M experience, the tamponading nephrostomy catheter is optimally suited for this purpose [8]. Holding mild tension on the catheter against the site of injury, the balloon can be further inflated if necessary until extravasation into the vein ceases. However, those cases involved prolonged balloon inflation and risked pressure necrosis. Our case highlights the importance of prompt diagnosis of renal-vein perforation and demonstrates that this can be managed conservatively by the catheter being withdrawn in stages or a tamponading nephrostomy catheter. This study is the fifth report in the literature regarding misplacement of a nephrostomy tube into the vascular system [8-10], yet, it is the first report under the guide of ultrasound, and is also the first report with such a complication of vein and artery following PCNL. It is an uncommon case of renal artery pseudoaneurysm because of its delayed occurrence after invasive procedure. The percutaneous tract disrupts the normal vessel wall and a pseudoaneurysm is formed from the tissues surrounding the high-pressure arterial system, resulting in recanalisation between the intravascular and extravascular space that produces a pulsating, encapsulated hematoma. The vascular compromise is initially controlled by a combination of decreased blood flow, artery spasm, coagulation, and a tamponading effect of the surrounding tissue, which initially prevents hemorrhage and leads to its nonrecognition in the operating room. As these temporizing measures begin to degrade, the patient becomes more active, the blood flow to this vessel increases and the pseudoaneurysm may eventually grow and becomes unstable. With erosion into the pelvicaliceal system, gross hematuria thus occurs. Post-PCNL pseudoaneurysm is usually located in the peripheral arteries. This might explain the absence of significant bleeding intraoperatively and postoperatively. This is supported by the fact that our patient angiography identified that the pseudoaneurysm was located near the punctured cavity. The natural history of pseudoaneurysm ranges from spontaneous resolution to acute rupture. By far, the most common presentation is gross hematuria. Patients are often clinically stable and can present with nonspecific symptoms including flank pain, hypertension, arterial bruits, deterioration of renal function and worsening lower urinary tract symptoms. Patients usually present in the first few weeks (ranging from 1 day to 5 months) postoperatively. The diagnosis of intrarenal pseudoaneurysm is challenging. Clinical diagnosis can be done through invasive (angiography) and non-invasive (angio CT or Doppler ultrasonography) methods. Arteriography remains the gold standard diagnostic tool, although multiplanar contrast enhanced computed tomography is suitable alternatives. The advantages of angiography in this setting include high sensitivity in identifying the pseudoaneurysm (which usually appears as a round or oval structure arising from the main renal artery or one of its branches) and the potential to achieve simultaneous endovascular management of these lesions, with success rates exceeding 90%.10 Superselective embolisation is highly efficient in achieving pseudoaneurysm occlusion through the injection of a permanent agent at the fistulous point. Materials such as ethanol, metal coil, gel foam particles and N-butyl-2- cyanoacrylate have been successfully used for embolisation [11,12]. No significant difference was found between the preangioembolization and postangioembolization serum creatinine, similar to that reported by Martin et al. [11]. Pseudoaneurysm appears as a focal area of high attenuation with a similar enhancement to the adjacent vessels. The advantage of computed tomography imaging is that these modalities not only can diagnose pseudoaneurysms but can also detect other possible intra-abdominal
5 Wang et al. BMC Urology 2013, 13:69 Page 5 of 5 pathologies that may be responsible for the presenting symptoms. A three-dimensional reconstruction can be useful for differentiating a pseudoaneurysm from urinoma, which may, at times, be difficult to distinguish from each other. Conclusions Our case shows intravenous misplacement of the nephrostomy tube and subsequent pseudoaneurysm after percutaneous nephrostolithotomy. To our knowledge, this seems to be the first documentation of major bleeding from the injury to both renal vein and artery. The percutaneous nephrostomy drainage tube can be withdrawn 3 cm back to the renal parenchyma/sinus/pelvis in stages with the surgical team on standby, and the withdrawn distance may vary according to patient and catheter position. 8. Gupta M, Bellman GC, Smith AD: Massive hemorrhage from renal vein injury during percutaneous renal surgery: endourological management. J Urol 1997, 157: Mazzucchi E, Mitre A, Brito A, Arap M, Murta C, Srougi M: Intravenous misplacement of the nephrostomy catheter following percutaneous nephrostolithotomy: two case reports. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 2009, 64: Shaw G, Wah TM, Kellett MJ, Choong SK: Management of renal-vein perforation during a challenging percutaneous nephrolithotomy. J Endourol 2005, 19: Martin X, Murat FJ, Feitosa LC, et al: Severe bleeding after nephrolithotomy: results of hyperselective embolization. Eur Urol 2000, 37: Lee KL, Stoller ML: Minimizing and managing bleeding after percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Curr Opin Urol 2007, 17: doi: / Cite this article as: Wang et al.: Metachronous renal vein and artery injure after percutaneous nephrostolithotomy. BMC Urology :69. Consent Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this manuscript and accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the Editor-in-Chief of this journal. Abbreviations PCNL: Percutaneous nephrostolithotomy; PNDT: Percutaneous nephrostomy drainage tube. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Authors contributions CW and FT cared for the patient and drafted the report. BS cared for the patient. SC revised and approved the final version of the manuscript. All authors reviewed the report and approved the final version of the manuscript. Acknowledgements Language editor Shuo Wang edited our manuscript. Received: 29 July 2013 Accepted: 27 November 2013 Published: 5 December 2013 References 1. Ferström I, Johansson B: Percutaneous pyelolithotomy: a new extraction technique. Scand J Urol Nephrol 1976, 10: Galek L, Darewicz B, Werel T, Darewicz J: Hemorrhagic complications of percutaneous lithotripsy: original methods of treatment. Int Urol Nephrol 2000, 32: Clayman RV, Surya V, Hunter D, et al: Renal vascular complications associated with the percutaneous removal of renal calculi. J Urol 1984, 132: Ugras M, Gunes A, Baydinc C: Severe renal bleeding caused by a ruptured renal sheath: case report of a rare complication of percutaneous nephrolithotomy. BMC Urol 2002, 2: Winfield HN, Weyman P, Clayman RV: Percutaneous nephrostolithotomy: complications of premature nephrostomy tube removal. J Urol 1986, 136: Sampaio FJ: The dilemma of the crossing vessel at the ureteropelvic junction: precise anatomic study. J Endourol 1996, 10: Geara A, Kamal L, El-Imad B, El-Sayegh S: Visualization of the renal vein during pyelography after nephrostomy: a case report. J Med Case Rep 2010, 23:93. Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Intrarenal Pseudoaneurysm after Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy. Angiotomographic Assessment and Endovascular Management
 Case Report Endovascular Management of Intrarenal Pseudoaneurysm after PCNL International Braz J Urol Vol. 32 (4): 440-444, July - August, 2006 Intrarenal Pseudoaneurysm after Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy.
Case Report Endovascular Management of Intrarenal Pseudoaneurysm after PCNL International Braz J Urol Vol. 32 (4): 440-444, July - August, 2006 Intrarenal Pseudoaneurysm after Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. TJ Tan, HS Teh, U Pua, SH Ho
 J HK Coll Radiol. 2008;11:103-107 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endovascular Management of Iatrogenic Renal Vascular Injuries Complicating Percutaneous Nephrolithotripsy: Role of Renal Angiography and Superselective
J HK Coll Radiol. 2008;11:103-107 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endovascular Management of Iatrogenic Renal Vascular Injuries Complicating Percutaneous Nephrolithotripsy: Role of Renal Angiography and Superselective
Diagnosis & Management of Kidney Trauma. LAU - Urology Residency Program LOP Urology Residents Meeting
 Diagnosis & Management of Kidney Trauma LAU - Urology Residency Program LOP Urology Residents Meeting Outline Introduction Investigation Staging Treatment Introduction The kidneys are the most common genitourinary
Diagnosis & Management of Kidney Trauma LAU - Urology Residency Program LOP Urology Residents Meeting Outline Introduction Investigation Staging Treatment Introduction The kidneys are the most common genitourinary
Does Bleeding During Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy Necessitate keeping the Nephrostomy Tube? A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
 Endourology and Stone Disease Does Bleeding During Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy Necessitate keeping the Nephrostomy Tube? A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Masoud Etemadian, 1 Mohammad Javad Soleimani,
Endourology and Stone Disease Does Bleeding During Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy Necessitate keeping the Nephrostomy Tube? A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Masoud Etemadian, 1 Mohammad Javad Soleimani,
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL), as primary. Subcapsular Kidney Urinoma After Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy. Case Report
 JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY CASE REPORTS Volume 3.1, 2017 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 52 56 DOI: 10.1089/cren.2017.0011 Case Report Subcapsular Kidney Urinoma After Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy Eugenio Di Grazia,
JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY CASE REPORTS Volume 3.1, 2017 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 52 56 DOI: 10.1089/cren.2017.0011 Case Report Subcapsular Kidney Urinoma After Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy Eugenio Di Grazia,
A novel endoscopic treatment for renal arteriopelvic fistula post-percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
 Challenging Clinical Cases Vol. 40 (4): 568-573, July. August, 2014 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.04.18 A novel endoscopic treatment for renal arteriopelvic fistula post-percutaneous nephrolithotomy
Challenging Clinical Cases Vol. 40 (4): 568-573, July. August, 2014 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.04.18 A novel endoscopic treatment for renal arteriopelvic fistula post-percutaneous nephrolithotomy
TECHNIQUE OF ENDOPYELOTOMY WITH THE ACUCISE CUTTING BALLOON
 Surgical Technique Brazilian Journal of Urology Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 26 (1): 71-75, January - February, 2000 TECHNIQUE OF ENDOPYELOTOMY WITH THE ACUCISE CUTTING BALLOON
Surgical Technique Brazilian Journal of Urology Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 26 (1): 71-75, January - February, 2000 TECHNIQUE OF ENDOPYELOTOMY WITH THE ACUCISE CUTTING BALLOON
Renal Artery Embolization in Post Traumatic Vascular Lesions
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., VoL 81, No. 2, March: 69-73, 2013 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Renal Artery Embolization in Post Traumatic Vascular Lesions IHAB I. ALI, M.D.*; HESHAM BADAWY, M.D.**; AMR
Med. J. Cairo Univ., VoL 81, No. 2, March: 69-73, 2013 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.com Renal Artery Embolization in Post Traumatic Vascular Lesions IHAB I. ALI, M.D.*; HESHAM BADAWY, M.D.**; AMR
AN UNCOMMON CAUSE OF MASSIVE HEMATURIA
 Originally Posted: August, 01, 2014 AN UNCOMMON CAUSE OF MASSIVE HEMATURIA Resident(s): Monzer Chehab, MD, Alexander Copelan MD Attending(s): Purushottam Dixit, MD Program/Dept(s): Oakland University William
Originally Posted: August, 01, 2014 AN UNCOMMON CAUSE OF MASSIVE HEMATURIA Resident(s): Monzer Chehab, MD, Alexander Copelan MD Attending(s): Purushottam Dixit, MD Program/Dept(s): Oakland University William
Renal Artery Embolization for the Treatment of Renal Artery Pseudoaneurysm Following Partial Nephrectomy
 The Ochsner Journal 13:259 263, 2013 Ó Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation Renal Artery Embolization for the Treatment of Renal Artery Pseudoaneurysm Following Partial Nephrectomy Cara Irwine,
The Ochsner Journal 13:259 263, 2013 Ó Academic Division of Ochsner Clinic Foundation Renal Artery Embolization for the Treatment of Renal Artery Pseudoaneurysm Following Partial Nephrectomy Cara Irwine,
Arvind P Ganpule, Darshan H Shah, Sanika A Ganpule, Ravindra B Sabnis, Mohan M Rajapurkar 3, Mahesh R Desai 1
 CLINICAL PRACTICE ARTICLE Role of multi-detector computed tomography (MDCT) in management of post percutaneous nephrolithotomy () bleeding [version 1; referees: 2 approved] 1 1 2 1 Arvind P Ganpule, Darshan
CLINICAL PRACTICE ARTICLE Role of multi-detector computed tomography (MDCT) in management of post percutaneous nephrolithotomy () bleeding [version 1; referees: 2 approved] 1 1 2 1 Arvind P Ganpule, Darshan
A Giant Hydronephrotic Kidney with Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction with Blunt Renal Trauma in a Boy
 A Giant Hydronephrotic Kidney with Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction with Blunt Renal Trauma in a Boy BY JUNYA TSURUKIRI, HIDEFUMI SANO, YOSUKE TANAKA, TAKAO SATO, HIROKAZU TAGUCHI Abstract An 18-year-old
A Giant Hydronephrotic Kidney with Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction with Blunt Renal Trauma in a Boy BY JUNYA TSURUKIRI, HIDEFUMI SANO, YOSUKE TANAKA, TAKAO SATO, HIROKAZU TAGUCHI Abstract An 18-year-old
Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies. V.Stoynova
 Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies V.Stoynova Abdominal vessels V. Stoynova 2 Acute liver bleeding trauma anticoagulant therapy liver disease : HCC, adenoma, meta, FNH, Hemangioma Diagnosis :CT angiography
Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies V.Stoynova Abdominal vessels V. Stoynova 2 Acute liver bleeding trauma anticoagulant therapy liver disease : HCC, adenoma, meta, FNH, Hemangioma Diagnosis :CT angiography
EVALUATION OF FACTORS AFFECTING DELAYED RENAL BLEEDING AFTER PCNL AND THE ROLE OF CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT FOR THAT BLEEDING
 Basrah Journal Of Surgery EVALUATION OF FACTORS AFFECTING DELAYED RENAL BLEEDING AFTER PCNL AND THE ROLE OF CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT FOR THAT BLEEDING Assistant professor, Urology division, Surgery Department,
Basrah Journal Of Surgery EVALUATION OF FACTORS AFFECTING DELAYED RENAL BLEEDING AFTER PCNL AND THE ROLE OF CONSERVATIVE MANAGEMENT FOR THAT BLEEDING Assistant professor, Urology division, Surgery Department,
Outpatient percutaneous nephrolithotomy in a renal transplant patient: World s first case
 Original case report research Outpatient percutaneous nephrolithotomy in a renal transplant patient: World s first case Kristen McAlpine; Michael J. Leveridge, MD, FRCSC; Darren Beiko, MD, MBA, FRCSC Department
Original case report research Outpatient percutaneous nephrolithotomy in a renal transplant patient: World s first case Kristen McAlpine; Michael J. Leveridge, MD, FRCSC; Darren Beiko, MD, MBA, FRCSC Department
Percutaneous nephrolithotomy for staghorn kidney stones in elderly patients
 Int Urol Nephrol (2011) 43:639 643 DOI 10.1007/s11255-010-9885-6 UROLOGY ORIGINAL PAPER Percutaneous nephrolithotomy for staghorn kidney stones in elderly patients Baris Kuzgunbay Tahsin Turunc Ozgur Yaycioglu
Int Urol Nephrol (2011) 43:639 643 DOI 10.1007/s11255-010-9885-6 UROLOGY ORIGINAL PAPER Percutaneous nephrolithotomy for staghorn kidney stones in elderly patients Baris Kuzgunbay Tahsin Turunc Ozgur Yaycioglu
Traumatic Renocaval Fistula With Pseudoaneurysm Leading To Renal Atrophy
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 6 Number 2 Traumatic Renocaval Fistula With Pseudoaneurysm Leading To Renal Atrophy M Kukkady, A Deena, S Raj, Ramachandra Citation M Kukkady, A Deena,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 6 Number 2 Traumatic Renocaval Fistula With Pseudoaneurysm Leading To Renal Atrophy M Kukkady, A Deena, S Raj, Ramachandra Citation M Kukkady, A Deena,
Comparison of the results of percutaneous nephrolithotomy in different age groups
 International Surgery Journal Borekoglu A et al. Int Surg J. 2018 Dec;5(12):3888-3892 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20185013
International Surgery Journal Borekoglu A et al. Int Surg J. 2018 Dec;5(12):3888-3892 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20185013
West Yorkshire Major Trauma Network Clinical Guidelines 2015
 WYMTN: Pelvic fracture with urogenital trauma KEY RECOMMENDATIONS 1. During the initial exploratory survey / secondary survey, a. The external urethral meatus and the transurethral bladder catheter (if
WYMTN: Pelvic fracture with urogenital trauma KEY RECOMMENDATIONS 1. During the initial exploratory survey / secondary survey, a. The external urethral meatus and the transurethral bladder catheter (if
Endourology and Stones Management of Non-neoplastic Renal Hemorrhage by Transarterial Embolization
 Endourology and Stones Management of Non-neoplastic Renal Hemorrhage by Transarterial Embolization Vikas Jain, Arvind Ganpule, Jigish Vyas, V. Muthu, R. B. Sabnis, Mohan M. Rajapurkar, and Mahesh R. Desai
Endourology and Stones Management of Non-neoplastic Renal Hemorrhage by Transarterial Embolization Vikas Jain, Arvind Ganpule, Jigish Vyas, V. Muthu, R. B. Sabnis, Mohan M. Rajapurkar, and Mahesh R. Desai
Keywords: laparatomy, pyelolithotomy, laparoscopic.
 bü z ÇtÄ TÜà väx Large calculi within malpositioned and malformed kidneys, is percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) feasible? A Single Center s Experience over 10 Years. Awad Ka`abneh and Firas Al-Hammouri
bü z ÇtÄ TÜà väx Large calculi within malpositioned and malformed kidneys, is percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) feasible? A Single Center s Experience over 10 Years. Awad Ka`abneh and Firas Al-Hammouri
Aid to percutaneous renal access by virtual projection of the ultrasound puncture tract onto fluoroscopic images
 Aid to percutaneous renal access by virtual projection of the ultrasound puncture tract onto fluoroscopic images Mozer P., Conort P., Leroy A., Baumann M., Payan Y., Troccaz J., Chartier-Kastler E. & Richard
Aid to percutaneous renal access by virtual projection of the ultrasound puncture tract onto fluoroscopic images Mozer P., Conort P., Leroy A., Baumann M., Payan Y., Troccaz J., Chartier-Kastler E. & Richard
Role of imaging in evaluation of genitourinary i trauma Spectrum of GU injuries Relevance of imaging findings in determining management Focus on MDCT
 Genitourinary Tract Injuries 6 th Nordic Course Scott D. Steenburg, MD Assistant Professor University of Maryland Department of Radiology Division of Trauma and Emergency Radiology R Adams Cowley Shock
Genitourinary Tract Injuries 6 th Nordic Course Scott D. Steenburg, MD Assistant Professor University of Maryland Department of Radiology Division of Trauma and Emergency Radiology R Adams Cowley Shock
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging
 Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
How to manage TAVI related vascular complications. Paul TL Chiam MBBS, FRCP, FESC, FACC, FSCAI
 How to manage TAVI related vascular complications Paul TL Chiam MBBS, FRCP, FESC, FACC, FSCAI Definition VARC-2 consensus statement Complications caused by: Wire Catheter Anything related to vascular access
How to manage TAVI related vascular complications Paul TL Chiam MBBS, FRCP, FESC, FACC, FSCAI Definition VARC-2 consensus statement Complications caused by: Wire Catheter Anything related to vascular access
Question 2. What percentage of abdominal trauma involve the kidney? a) 5 % b) 10% c) 15 % d) 20 %
 Quiz Question 1 After injecting 2ml/kg of contrast for a patient needing a single-shot IVP before kidney exploration, What is the best turnaround time to take the X-ray? a) 3 minutes b) 5 minutes c) 10
Quiz Question 1 After injecting 2ml/kg of contrast for a patient needing a single-shot IVP before kidney exploration, What is the best turnaround time to take the X-ray? a) 3 minutes b) 5 minutes c) 10
Corresponding Author : Dr.P.Gunaseelan
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 5 Ver. 10 (May. 2018), PP 68-72 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of outcomes of Percutaneous
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 5 Ver. 10 (May. 2018), PP 68-72 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of outcomes of Percutaneous
Surgically Discovered Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis Invading Inferior Vena Cava with Coexisting Renal Cell Carcinoma
 Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 5 9 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.6 Surgically Discovered Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis Invading Inferior Vena Cava with Coexisting
Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 5 9 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.6 Surgically Discovered Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis Invading Inferior Vena Cava with Coexisting
Uroradiology For Medical Students
 Uroradiology For Medical Students Lesson 8 Computerized Tomography 2 American Urological Association Objectives In this lesson you will: Gain more experience reading CT images Learn how computer generated
Uroradiology For Medical Students Lesson 8 Computerized Tomography 2 American Urological Association Objectives In this lesson you will: Gain more experience reading CT images Learn how computer generated
Case Report 1. CTA head. (c) Tele3D Advantage, LLC
 Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Case Report 1 CTA head 1 History 82 YEAR OLD woman with signs and symptoms of increased intra cranial pressure in setting of SAH. CT Brain was performed followed by CT Angiography of head. 2 CT brain Extensive
Patient guide: pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system. Catheter occlusion of. Patent Ductus Arteriosus. with the
 Patient guide: Catheter occlusion of Patent Ductus Arteriosus with the pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system pfm Produkte für die Medizin - AG Wankelstr. 60 D - 50996 Cologne Phone: +49 (0) 2236 96
Patient guide: Catheter occlusion of Patent Ductus Arteriosus with the pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system pfm Produkte für die Medizin - AG Wankelstr. 60 D - 50996 Cologne Phone: +49 (0) 2236 96
Interventional Radiology in Trauma. Vikash Prasad, MD, FRCPC Vascular and Interventional Radiology The Moncton Hospital
 Interventional Radiology in Trauma Vikash Prasad, MD, FRCPC Vascular and Interventional Radiology The Moncton Hospital Disclosures None relevant to this presentation Shareholder Johnson and Johnson Goal
Interventional Radiology in Trauma Vikash Prasad, MD, FRCPC Vascular and Interventional Radiology The Moncton Hospital Disclosures None relevant to this presentation Shareholder Johnson and Johnson Goal
NYU School of Medicine Department of Radiology Rotation-Specific House Staff Evaluation
 Vascular & Interventional Radiology Rotation 1 Core competency in vascular and interventional radiology during the first resident rotation consists of clinical objectives, technical objectives and image
Vascular & Interventional Radiology Rotation 1 Core competency in vascular and interventional radiology during the first resident rotation consists of clinical objectives, technical objectives and image
The Management and Treatment of Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (RAAA)
 The Management and Treatment of Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (RAAA) Disclosure Speaker name: Ren Wei, Li Zhui, Li Fenghe, Zhao Yu Department of Vascular Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of
The Management and Treatment of Ruptured Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (RAAA) Disclosure Speaker name: Ren Wei, Li Zhui, Li Fenghe, Zhao Yu Department of Vascular Surgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of
LOWER POLE STONE DR.NOOR ASHANI MD YUSOFF DEPT. OF UROLOGY HOSP.KUALA LUMPUR
 DR.NOOR ASHANI MD YUSOFF DEPT. OF UROLOGY HOSP.KUALA LUMPUR ! The appropriate treatment of lower pole calculi is controversial:! Shock wave lithotripsy! Retrograde ureteroscopy! Percutaneous lithotripsy
DR.NOOR ASHANI MD YUSOFF DEPT. OF UROLOGY HOSP.KUALA LUMPUR ! The appropriate treatment of lower pole calculi is controversial:! Shock wave lithotripsy! Retrograde ureteroscopy! Percutaneous lithotripsy
Case Report Three-Dimensional Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Enhancing Stone/Stent Contrasting and Stone Visualization in Urolithiasis
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 646087, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/646087 Case Report Three-Dimensional Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Enhancing Stone/Stent Contrasting
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 646087, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/646087 Case Report Three-Dimensional Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Enhancing Stone/Stent Contrasting
An Overview of Post-EVAR Endoleaks: Imaging Findings and Management. Ravi Shergill BSc Sean A. Kennedy MD Mark O. Baerlocher MD FRCPC
 An Overview of Post-EVAR Endoleaks: Imaging Findings and Management Ravi Shergill BSc Sean A. Kennedy MD Mark O. Baerlocher MD FRCPC Disclosure Slide Mark O. Baerlocher: Current: Consultant for Boston
An Overview of Post-EVAR Endoleaks: Imaging Findings and Management Ravi Shergill BSc Sean A. Kennedy MD Mark O. Baerlocher MD FRCPC Disclosure Slide Mark O. Baerlocher: Current: Consultant for Boston
ISSN X (Print) Original Research Article. *Corresponding author Avinash Barfa
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2016; 4(5D):1706-1710 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2016; 4(5D):1706-1710 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/23/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 78 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/23/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 78 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Cone-beam CT findings during prostate artery embolization for benign prostatic hyperplasia-induced lower urinary tract symptoms: a case report
 Chen et al. BMC Urology (2017) 17:120 DOI 10.1186/s12894-017-0311-6 CASE REPORT Cone-beam CT findings during prostate artery embolization for benign prostatic hyperplasia-induced lower urinary tract symptoms:
Chen et al. BMC Urology (2017) 17:120 DOI 10.1186/s12894-017-0311-6 CASE REPORT Cone-beam CT findings during prostate artery embolization for benign prostatic hyperplasia-induced lower urinary tract symptoms:
Embolotherapy for salvaging renal allografts with post biopsy complications
 Embolotherapy for salvaging renal allografts with post biopsy complications Poster No.: C-2634 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Gaharwar, R. V. PHADKE ; Lucknow/IN, LUCKNOW, UTTAR
Embolotherapy for salvaging renal allografts with post biopsy complications Poster No.: C-2634 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Gaharwar, R. V. PHADKE ; Lucknow/IN, LUCKNOW, UTTAR
Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy in a Patient with Mainz Pouch II Urinary Diversion: A Case Report
 198) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 117 (2016) No. 4, p. 198 203 Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy in a Patient with Mainz Pouch II Urinary Diversion: A Case Report Stavros Sfoungaristos 1, Ioannis Mykoniatis
198) Prague Medical Report / Vol. 117 (2016) No. 4, p. 198 203 Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy in a Patient with Mainz Pouch II Urinary Diversion: A Case Report Stavros Sfoungaristos 1, Ioannis Mykoniatis
Angioplasty remains the most common method
 When AVF Angioplasty Fails Defining procedural success and overcoming common problems. By Thomas M. Vesely, MD Angioplasty remains the most common method of treating obstructive vascular stenoses associated
When AVF Angioplasty Fails Defining procedural success and overcoming common problems. By Thomas M. Vesely, MD Angioplasty remains the most common method of treating obstructive vascular stenoses associated
Recommendations. Management of Renal Calculi PCNL. Complications of PCNL: How to avoid and manage them 2/8/2008
 Complications of PCNL: How to avoid and manage them Recommendations An exhaustive meta-analysis completed by the panel revealed a lower complication rate and higher stone free rate when PCNL was used as
Complications of PCNL: How to avoid and manage them Recommendations An exhaustive meta-analysis completed by the panel revealed a lower complication rate and higher stone free rate when PCNL was used as
Treatment of pediatric renal calculi between 1990 and 2006 in Henan province
 Treatment of pediatric renal calculi between 1990 and 2006 in Henan province Bingqian Liu *, Yudong Wu, Jinxing Wei, Jianguang Gao Department of Urology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University,
Treatment of pediatric renal calculi between 1990 and 2006 in Henan province Bingqian Liu *, Yudong Wu, Jinxing Wei, Jianguang Gao Department of Urology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University,
Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE)
 Service: Imaging Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions The team delivering your healthcare want to encourage you to become as involved as possible
Service: Imaging Prostate Artery Embolisation (PAE) Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ask 3 Questions The team delivering your healthcare want to encourage you to become as involved as possible
General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]
![General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ] General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]](/thumbs/76/74079340.jpg) General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
Different successful management strategies for obstructing renal parapelvic cysts
 Title Page Different successful management strategies for obstructing renal parapelvic cysts Sabrina H Rossi 1, Brendan Koo 2, Antony Riddick 1, Nimish Shah 1, Grant D Stewart 1 1 Urology Department, Addenbrooke's
Title Page Different successful management strategies for obstructing renal parapelvic cysts Sabrina H Rossi 1, Brendan Koo 2, Antony Riddick 1, Nimish Shah 1, Grant D Stewart 1 1 Urology Department, Addenbrooke's
KNIFED IN THE ABDOMEN
 Originally Posted: November 01, 2014 KNIFED IN THE ABDOMEN Resident(s): Andrew Duarte, MD Attending(s): Ryan Scott, MD & David Kay, MD Program/Dept(s): St. Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix,
Originally Posted: November 01, 2014 KNIFED IN THE ABDOMEN Resident(s): Andrew Duarte, MD Attending(s): Ryan Scott, MD & David Kay, MD Program/Dept(s): St. Joseph s Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix,
MDCT Findings of Renal Trauma
 MDT of Renal Trauma Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/06/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights
MDT of Renal Trauma Genitourinary Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/06/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights
Nonoperative Management of Grade 5 Renal Injury in Children: Does It Have a Place?
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 57 (2010) 154 163 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Pediatric Urology Nonoperative Management of Grade 5 Renal Injury in Children: Does It Have
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 57 (2010) 154 163 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Pediatric Urology Nonoperative Management of Grade 5 Renal Injury in Children: Does It Have
Thrombin injection vs Conventional Surgical Repair in Treatment of Iatrogenic Post-cath Femoral Artery Pseudoaneurysm (IFAP)
 Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 11, NO 3 September 2010 31 Thrombin injection vs Conventional Surgical Repair in Treatment of Iatrogenic Post-cath Femoral Artery Pseudoaneurysm (IFAP) Farghaly A,
Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 11, NO 3 September 2010 31 Thrombin injection vs Conventional Surgical Repair in Treatment of Iatrogenic Post-cath Femoral Artery Pseudoaneurysm (IFAP) Farghaly A,
Renal vascular evaluation with 64 Multislice Computerized Tomography Daniela Stoisa, Fabrizzio E. Galiano, Andrés Quaranta, Roberto L.
 Renal vascular evaluation with 64 Multislice Computerized Tomography Daniela Stoisa, Fabrizzio E. Galiano, Andrés Quaranta, Roberto L. Villavicencio Footnote Diagnóstico Médico Oroño. Bv. Oroño 1515. 2000.
Renal vascular evaluation with 64 Multislice Computerized Tomography Daniela Stoisa, Fabrizzio E. Galiano, Andrés Quaranta, Roberto L. Villavicencio Footnote Diagnóstico Médico Oroño. Bv. Oroño 1515. 2000.
Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet
 Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet If there was no traumatic injury with PENETRATION of the bladder DO NOT proceed Date of injury: / / Time of injury: Date of hospital arrival: / / Time of hospital arrival:
Bladder Trauma Data Collection Sheet If there was no traumatic injury with PENETRATION of the bladder DO NOT proceed Date of injury: / / Time of injury: Date of hospital arrival: / / Time of hospital arrival:
Chan, IHY; Lam, WWM; Wong, KKY; Tam, PKH
 Title Letters to the editor Author(s) Chan, IHY; Lam, WWM; Wong, KKY; Tam, PKH Citation Journal Of Paediatrics And Child Health, 2010, v. 46 n. 6, p. 361-362 Issued Date 2010 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/92175
Title Letters to the editor Author(s) Chan, IHY; Lam, WWM; Wong, KKY; Tam, PKH Citation Journal Of Paediatrics And Child Health, 2010, v. 46 n. 6, p. 361-362 Issued Date 2010 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/92175
Dehiscence of detached internal limiting membrane in eyes with myopic traction maculopathy with spontaneous resolution
 Hirota et al. BMC Ophthalmology 2014, 14:39 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Dehiscence of detached internal limiting membrane in eyes with myopic traction maculopathy with spontaneous resolution Kazunari
Hirota et al. BMC Ophthalmology 2014, 14:39 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Dehiscence of detached internal limiting membrane in eyes with myopic traction maculopathy with spontaneous resolution Kazunari
UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Lecture Series. Urological Trauma
 UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Lecture Series Urological Trauma Disclaimer: This is a lot of information to cover and we are unlikely to cover it all today These slides are to be utilized for your
UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Lecture Series Urological Trauma Disclaimer: This is a lot of information to cover and we are unlikely to cover it all today These slides are to be utilized for your
Nonurographic evaluation of renal calculous disease 1
 Contributions Nonurographic evaluation of renal calculous disease 1 Gregory P. Borkowski, M.D. Craig R. George, M.D. Peter B. O'Donovan, M.D. While excretory urography has been useful in the evaluation
Contributions Nonurographic evaluation of renal calculous disease 1 Gregory P. Borkowski, M.D. Craig R. George, M.D. Peter B. O'Donovan, M.D. While excretory urography has been useful in the evaluation
Researcher 2017;9(4) Outcome of Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy for Staghorn Stones: Al-Azhar 5-Years Experience
 Outcome of Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy for Staghorn Stones: Al-Azhar 5-Years Experience Ibrahim Ahmed El Sotohi Department of Urology, Faculty of Medicine, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt ibrahimelsotohi@gmail.com
Outcome of Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy for Staghorn Stones: Al-Azhar 5-Years Experience Ibrahim Ahmed El Sotohi Department of Urology, Faculty of Medicine, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt ibrahimelsotohi@gmail.com
ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE. T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar
 ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar LEARNING OBJECTIVES q Through a series of cases illustrate the updated Atlanta symposium
ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar LEARNING OBJECTIVES q Through a series of cases illustrate the updated Atlanta symposium
Introduction What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease? How Do Doctors Treat Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 9
 Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
Safe surgical treatment of peripelvic renal cyst combined with renal calculi by percutaneous nephroscopy
 CASE REPORT Safe surgical treatment of peripelvic renal cyst combined with renal calculi by percutaneous nephroscopy Bowei Yang 1, Jiongming Li 1, Jianhe Liu 1, Yuepan Bao 2, Prashant Mishra 1, Haixiang
CASE REPORT Safe surgical treatment of peripelvic renal cyst combined with renal calculi by percutaneous nephroscopy Bowei Yang 1, Jiongming Li 1, Jianhe Liu 1, Yuepan Bao 2, Prashant Mishra 1, Haixiang
The optimal minimally invasive percutaneous nephrolithotomy strategy for the treatment of staghorn stones in a solitary kidney
 Urolithiasis (2016) 44:149 154 DOI 10.1007/s00240-015-0803-3 ORIGINAL PAPER The optimal minimally invasive percutaneous nephrolithotomy strategy for the treatment of staghorn stones in a solitary kidney
Urolithiasis (2016) 44:149 154 DOI 10.1007/s00240-015-0803-3 ORIGINAL PAPER The optimal minimally invasive percutaneous nephrolithotomy strategy for the treatment of staghorn stones in a solitary kidney
Case Report Spontaneous Pelvic Rupture as a Result of Renal Colic in a Patient with Klinefelter Syndrome
 Volume 2013, Article ID 374973, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/374973 Case Report Spontaneous Pelvic Rupture as a Result of Renal Colic in a Patient with Klinefelter Syndrome Sergey Reva and Yuri
Volume 2013, Article ID 374973, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/374973 Case Report Spontaneous Pelvic Rupture as a Result of Renal Colic in a Patient with Klinefelter Syndrome Sergey Reva and Yuri
2. Blunt abdominal Trauma
 Abdominal Trauma 1. Evaluation and management depends on: a. Mechanism (Blunt versus Penetrating) b. Injury complex in addition to abdomen c. Haemodynamic stability assessment: i. Classically patient s
Abdominal Trauma 1. Evaluation and management depends on: a. Mechanism (Blunt versus Penetrating) b. Injury complex in addition to abdomen c. Haemodynamic stability assessment: i. Classically patient s
Treatment of choice for end stage renal disease Imaging to establish baseline and diagnosis of potential complications Review common surgical
 Treatment of choice for end stage renal disease Imaging to establish baseline and diagnosis of potential complications Review common surgical techniques Review normal appearance Discuss US diagnosis of
Treatment of choice for end stage renal disease Imaging to establish baseline and diagnosis of potential complications Review common surgical techniques Review normal appearance Discuss US diagnosis of
TitleRadiographic evaluation of blunt re. TSUJI, Akira; MATSUZAKI, Shouji; TA. Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1989), 35(7):
 TitleRadiographic evaluation of blunt re TSUJI, Akira; MATSUZAKI, Shouji; TA Author(s) NAGAKURA, Kazuhiko; MURAI, Masaru; Hiroshi Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1989), 35(7): 1119-1123 Issue Date 1989-07 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/116611
TitleRadiographic evaluation of blunt re TSUJI, Akira; MATSUZAKI, Shouji; TA Author(s) NAGAKURA, Kazuhiko; MURAI, Masaru; Hiroshi Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1989), 35(7): 1119-1123 Issue Date 1989-07 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/116611
Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation
 Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation Chris Freise, MD Professor of Surgery UCSF Transplant Division Urologic Complications Review of Bladder Anastomosis Complications and Management
Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation Chris Freise, MD Professor of Surgery UCSF Transplant Division Urologic Complications Review of Bladder Anastomosis Complications and Management
Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy: a case report
 Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
Long-term results of percutaneous nephrolithotomy for treatment of staghorn stones
 ; 2010 Laparoscopic and Robotic Urology LONG-TERM RESULTS OF PNL FOR STAGHORN STONES EL-NAHAS et al. BJUI Long-term results of percutaneous nephrolithotomy for treatment of staghorn stones Ahmed R. EL-Nahas,
; 2010 Laparoscopic and Robotic Urology LONG-TERM RESULTS OF PNL FOR STAGHORN STONES EL-NAHAS et al. BJUI Long-term results of percutaneous nephrolithotomy for treatment of staghorn stones Ahmed R. EL-Nahas,
Tubeless Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: Spinal versus General Anesthesia
 Tubeless Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: Spinal versus General Anesthesia Murat Gonen, 1 Betul Basaran 2 ENDOUROLOGY AND STONE DISEASE 1 Department of Urology, Baskent University, Konya, Turkey. 2 Department
Tubeless Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: Spinal versus General Anesthesia Murat Gonen, 1 Betul Basaran 2 ENDOUROLOGY AND STONE DISEASE 1 Department of Urology, Baskent University, Konya, Turkey. 2 Department
Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism A pulmonary embolism (PE) is
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Ultrasound-enhanced, catheter-directed thrombolysis for pulmonary embolism A pulmonary embolism (PE) is
Vascular complications in percutaneous biliary interventions: A series of 111 procedures
 Vascular complications in percutaneous biliary interventions: A series of 111 procedures Poster No.: C-0744 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. BHARADWAZ; AARHUS, Re/DK Keywords: Obstruction
Vascular complications in percutaneous biliary interventions: A series of 111 procedures Poster No.: C-0744 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. BHARADWAZ; AARHUS, Re/DK Keywords: Obstruction
Case Report Formation of a Tunnel under the Major Hepatic Vein Mouths during Removal of IVC Tumor Thrombus
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 129632, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/129632 Case Report Formation of a Tunnel under the Major Hepatic Vein Mouths during Removal of IVC Tumor Thrombus
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 129632, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/129632 Case Report Formation of a Tunnel under the Major Hepatic Vein Mouths during Removal of IVC Tumor Thrombus
Multi-tract percutaneous nephrolithotomy combined with EMS lithotripsy for bilateral complex renal stones: our experience
 Liang et al. BMC Urology (2017) 17:15 DOI 10.1186/s12894-017-0205-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Multi-tract percutaneous nephrolithotomy combined with EMS lithotripsy for bilateral complex renal stones:
Liang et al. BMC Urology (2017) 17:15 DOI 10.1186/s12894-017-0205-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Multi-tract percutaneous nephrolithotomy combined with EMS lithotripsy for bilateral complex renal stones:
Genitourinary. Common Clinical Scenarios Protocoling Module. Patty Ojeda & Mariam Shehata
 The following training module was developed as a quality improvement project to serve as an educational tool for junior radiology residents. The following diagnostic radiology protocoling modules were
The following training module was developed as a quality improvement project to serve as an educational tool for junior radiology residents. The following diagnostic radiology protocoling modules were
Complex multiple renal calculi: stone distribution, pelvicalyceal anatomy and site of puncture as predictors of PCNL outcome
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3017-4 RESEARCH Open Access Complex multiple renal calculi: stone distribution, pelvicalyceal anatomy and site of puncture as predictors of PCNL outcome Amit Verma *, Vinay Tomar
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-3017-4 RESEARCH Open Access Complex multiple renal calculi: stone distribution, pelvicalyceal anatomy and site of puncture as predictors of PCNL outcome Amit Verma *, Vinay Tomar
MINIMALLY INVASIVE MANAGEMENT OF RENOVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS AFTER RENAL GRAFT TRANSPLANTATION
 MINIMALLY INVASIVE MANAGEMENT OF RENOVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS AFTER RENAL GRAFT TRANSPLANTATION Gortes, Francisco Javier B.S; Salsamendi, Jason Thomas M.D LEARNING OBJECTIVES Educate physicians on the prompt
MINIMALLY INVASIVE MANAGEMENT OF RENOVASCULAR COMPLICATIONS AFTER RENAL GRAFT TRANSPLANTATION Gortes, Francisco Javier B.S; Salsamendi, Jason Thomas M.D LEARNING OBJECTIVES Educate physicians on the prompt
Nephrolithiasis Associated with Renal Insufficiency: Factors Predicting Outcome
 JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 17, Number 10, December 2003 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Nephrolithiasis Associated with Renal Insufficiency: Factors Predicting Outcome RAJESH KUKREJA, M.S., DNB, MIHIR DESAI,
JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 17, Number 10, December 2003 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Nephrolithiasis Associated with Renal Insufficiency: Factors Predicting Outcome RAJESH KUKREJA, M.S., DNB, MIHIR DESAI,
Urology Department Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL)
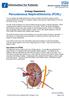 Urology Department Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) Your consultant has diagnosed that you have a problem with kidney stones and has recommended that you have an operation called a percutaneous nephrolithotomy
Urology Department Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy (PCNL) Your consultant has diagnosed that you have a problem with kidney stones and has recommended that you have an operation called a percutaneous nephrolithotomy
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Renal Arteriovenous Malformation: a case report
 Chin J Radiol 2007; 32: 51-55 51 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Renal Arteriovenous Malformation: a case report YU-CHENG HONG CHEN-TE CHOU KWA-WHEI LEE Department of Medical Imaging, Changhua Christian
Chin J Radiol 2007; 32: 51-55 51 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Renal Arteriovenous Malformation: a case report YU-CHENG HONG CHEN-TE CHOU KWA-WHEI LEE Department of Medical Imaging, Changhua Christian
CASE REPORT RENAL TUBERCULOSIS CAUSE OF RENAL REPLACEMENT LIPOMATOSIS : A RARE ASSOCIATION
 CASE REPORT RENAL TUBERCULOSIS CAUSE OF RENAL REPLACEMENT LIPOMATOSIS : A RARE ASSOCIATION DR ANAND AARTI 1, DR CHANDAK PRIYA 2,DR SURESH PARVATHY 3 1. PROF AND HOD, DEPARTMENT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS, GOVERNMENT
CASE REPORT RENAL TUBERCULOSIS CAUSE OF RENAL REPLACEMENT LIPOMATOSIS : A RARE ASSOCIATION DR ANAND AARTI 1, DR CHANDAK PRIYA 2,DR SURESH PARVATHY 3 1. PROF AND HOD, DEPARTMENT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS, GOVERNMENT
Radiological Investigations of Abdominal Trauma
 76 77 Investigations of Abdominal Trauma Introduction: Trauma to abdominal organs is a common cause of patient morbidity and mortality among trauma patients. Causes of abdominal trauma include blunt injuries,
76 77 Investigations of Abdominal Trauma Introduction: Trauma to abdominal organs is a common cause of patient morbidity and mortality among trauma patients. Causes of abdominal trauma include blunt injuries,
Case Report Hemostasis of Left Atrial Appendage Bleed With Lariat Device
 273 Case Report Hemostasis of Left Atrial Appendage Bleed With Lariat Device Amena Hussain MD, Muhamed Saric MD, Scott Bernstein MD, Douglas Holmes MD, Larry Chinitz MD NYU Langone Medical Center, United
273 Case Report Hemostasis of Left Atrial Appendage Bleed With Lariat Device Amena Hussain MD, Muhamed Saric MD, Scott Bernstein MD, Douglas Holmes MD, Larry Chinitz MD NYU Langone Medical Center, United
Ultrasonography Combined with Fluoroscopy for Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: Seven Years Single Center Experiences ENDOUROLOGY AND STONE DISEASE
 ENDOUROLOGY AND STONE DISEASE Ultrasonography Combined with Fluoroscopy for Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: An Analysis Based on Seven Years Single Center Experiences Qinglong Chi, Yan Wang, Ji Lu, Xiaoqing
ENDOUROLOGY AND STONE DISEASE Ultrasonography Combined with Fluoroscopy for Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: An Analysis Based on Seven Years Single Center Experiences Qinglong Chi, Yan Wang, Ji Lu, Xiaoqing
Fall down stairs. Left rib fractures. John A Cieslak III, MD, PhD Charan Singh, MD
 Fall down stairs. Left rib fractures. John A Cieslak III, MD, PhD Charan Singh, MD ? Splenic lacerations, hemoperitoneum, and traumatic pseudoaneurysm formation. High attenuation extraluminal contrast
Fall down stairs. Left rib fractures. John A Cieslak III, MD, PhD Charan Singh, MD ? Splenic lacerations, hemoperitoneum, and traumatic pseudoaneurysm formation. High attenuation extraluminal contrast
Case 37 Clinical Presentation
 Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
The ruptured dissecting aneurysm of the renal artery is a
 Case Report A Ruptured Dissecting Aneurysm of the Renal Artery into the Perinephric Region: A Case Report Abstract A case report of a ruptured dissecting aneurysm of the renal artery into the perinephric
Case Report A Ruptured Dissecting Aneurysm of the Renal Artery into the Perinephric Region: A Case Report Abstract A case report of a ruptured dissecting aneurysm of the renal artery into the perinephric
Urinary tract embolization
 Beograd, 14.10.2012 Urinary tract embolization asist. Peter Popovič, MD, MSc Head of abdominal radiology department, Institute of Radiology, UMC Ljubljana Embolization Who and when procedure: local/general
Beograd, 14.10.2012 Urinary tract embolization asist. Peter Popovič, MD, MSc Head of abdominal radiology department, Institute of Radiology, UMC Ljubljana Embolization Who and when procedure: local/general
ENDOPYELOTOMY WITH THE ACUCISE CATHETER
 Clinical Urology International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 28 (4): 302-310, July - August, 2002 ENDOPYELOTOMY WITH THE ACUCISE CATHETER ARTUR H. BRITO, ANUAR I.
Clinical Urology International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 28 (4): 302-310, July - August, 2002 ENDOPYELOTOMY WITH THE ACUCISE CATHETER ARTUR H. BRITO, ANUAR I.
CASE REVIEW. Risk Factor Analysis and Management of Ureteral Double-J Stent Complications
 CASE REVIEW Risk Factor Analysis and Management of Ureteral Double-J Stent Complications Youness Ahallal, MD, Abdelhak Khallouk, PhD, Mohammed Jamal El Fassi, PhD, Moulay Hassan Farih, PhD Department of
CASE REVIEW Risk Factor Analysis and Management of Ureteral Double-J Stent Complications Youness Ahallal, MD, Abdelhak Khallouk, PhD, Mohammed Jamal El Fassi, PhD, Moulay Hassan Farih, PhD Department of
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY. THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel
 PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
 Title Post-traumatic arterial priapism ev ultrasonography: a case report Author(s) SUZUKI, Noriyoshi; SATO, Yoshikazu; KOITO, Kazumitsu; MARUTA, Hiroshi; Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1999), 45(1): 65-68 Issue Date
Title Post-traumatic arterial priapism ev ultrasonography: a case report Author(s) SUZUKI, Noriyoshi; SATO, Yoshikazu; KOITO, Kazumitsu; MARUTA, Hiroshi; Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1999), 45(1): 65-68 Issue Date
Experimental Model of Upper-Pole Nephrectomy Using Human Tridimensional Endocasts: Analysis of Vascular Injuries
 JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 25, Number 1, January 2011 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 113 118 DOI: 10.1089=end.2010.0214 Experimental Model of Upper-Pole Nephrectomy Using Human Tridimensional Endocasts:
JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 25, Number 1, January 2011 ª Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 113 118 DOI: 10.1089=end.2010.0214 Experimental Model of Upper-Pole Nephrectomy Using Human Tridimensional Endocasts:
Case Report Endovascular Treatment of a Right-Sided Ureteroiliac Fistula in a Patient with a Simultaneous Left-Sided Ureteroileal Fistula
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Urology Volume 20, Article ID 284505, 5 pages doi:0.55/20/284505 Case Report Endovascular Treatment of a Right-Sided Ureteroiliac Fistula in a Patient with
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Urology Volume 20, Article ID 284505, 5 pages doi:0.55/20/284505 Case Report Endovascular Treatment of a Right-Sided Ureteroiliac Fistula in a Patient with
Gas-producing renal infection presenting as pneumaturia: a case report
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2013 Gas-producing renal infection presenting as pneumaturia: a case report Youssef S. Tanagho Jonathan M. Mobley
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2013 Gas-producing renal infection presenting as pneumaturia: a case report Youssef S. Tanagho Jonathan M. Mobley
Efficacy and Safety of Tubeless Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy versus Standard Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy
 Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2395-1893 DOI: 10.17354/SUR/2016/31 Original Article Efficacy and Safety of Tubeless Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy versus Standard Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy Sreedhar
Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2395-1893 DOI: 10.17354/SUR/2016/31 Original Article Efficacy and Safety of Tubeless Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy versus Standard Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy Sreedhar
Abdominal & retroperitoneal endovascular intervention, Bo Kalin, Karolinska Hospital
 Abdominal & retroperitoneal endovascular intervention, Bo Kalin, Karolinska Hospital What is endovascular therapy. Diagnosing Traumatic Arterial Injury Clinical signs CT / CT-angiography To diminish a
Abdominal & retroperitoneal endovascular intervention, Bo Kalin, Karolinska Hospital What is endovascular therapy. Diagnosing Traumatic Arterial Injury Clinical signs CT / CT-angiography To diminish a
Medical - Clinical Research & Reviews
 Research Article Research Article Medical - Clinical Research & Reviews ISSN 2575-6087 Management of Kidney in Saiful Anwar General Hospital Malang Indonesia Besut Daryanto, I Made Udiyana Indradiputra,
Research Article Research Article Medical - Clinical Research & Reviews ISSN 2575-6087 Management of Kidney in Saiful Anwar General Hospital Malang Indonesia Besut Daryanto, I Made Udiyana Indradiputra,
2013 Coding Changes. Diagnostic Radiology. Nuclear Medicine
 2013 Coding Changes The principal coding changes affecting Radiologists in 2013 occur in the Interventional Radiology Section of the AMA/CPT Manual. As in the past, we continue to see the Relative Update
2013 Coding Changes The principal coding changes affecting Radiologists in 2013 occur in the Interventional Radiology Section of the AMA/CPT Manual. As in the past, we continue to see the Relative Update
