Use of muscle flap to cover infections of the carotid artery after carotid endarterectomy
|
|
|
- Cameron Fitzgerald
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Use of muscle flap to cover infections of the carotid artery after carotid endarterectomy Dimitrios C. Zacharoulis, MD, Sushil K. Gupta, MD, Patricia Seymour, BA, and Raul A. Landa, MD, Framingham, Mass. Wound infection after carotid endarterectomy is an extremely uncommon complication. This complication occurred in two of our patients in a series of 170 consecutive carotid endarterectomies over the last 3 years. There has been an increased use of prosthetic patch grafts to close carotid endarterectomy sites. However, the presence of infection in the setting of prosthetic graft material poses difficulties in management and may lead to life-threatening complications. Recent strategies for the management of wound infections (in cases where the artery/graft interface is intact) include the use of appropriate antibiotics, repeated wound debridement, and covering the tissue defect or the perigraft area with well-vascularized muscle flap. In this case report the use of sternodeidomastoid muscle flap as a coverage for the infected area is described. The use of sternocleidomastoid muscle flap helped control the infective process and secured the viability of the patched carotid arteries. (J Vasc Surg 1997;25: ) Wound infection after carotid endarterectomy (CEA) is an extremely uncommon complication. 1 When it does occur, it is usually superficial, causing little discomfort or prolongation of hospital stay. However, wound infection in this area may have potentially devastating results if it leads to exposure of underlying artery or the patched artery. Management of deep infection is not well documented in the literature. Traditional management of graft/artery wound infections includes the use of culture-specific antibiotics and wide debridement of the necrotic soft tissue. Current recommendations for protection of graft/artery interface and the perigraft area include coverage with a viable, well-vascularized tissue such as healthy and properly mobilized muscle flap or free tissue transfers. These flaps have been widely used in vascular surgery to achieve graft survival and to avoid spread of the infection. 2-9 In the cases described herein, the sternal head of the sternocleidomastoid muscle was mobilized with its blood supply intact to preserve the patched carotid artery. From the MetroWest Medical Center. Reprint requests: Sushil K. Gupta, MD, MetroWest Medical Center, 115 Lincoln St., Framingham, MA Copyright 1997 by The Society for Vascular Surgery and International Society for Cardiovascular Surgery, North American Chapter /97/$ /4/76173 CASE REPORTS Case 1. A 55-year-old white woman who was a onepack-a-year smoker was found to have bilateral carotid stenosis on workup for migraines and ocular symptoms. Physical examination revealed diminished left radial pulse with a left supraclavicular bruit. The femoral, popliteal, and pedal pulses were normal. The carotid duplex study indicated greater than 80% stenosis of the left internal carotid artery and 60% to 80% stenosis of the tight carotid artery. There was also stenosis of the left subclavian artery distal to the carotid origin. The carotid angiogram revealed a 70% narrowing of the left internal carotid artery and confirmed the subclavian disease. The tight internal carotid artery had a 60% narrowing. Other significant medical history included insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus for 10 years, degenerative lower back disk disease, hypothyroidism, and hypercholesterolemia. Cancer of the left breast had been diagnosed 2 years previously and was managed with a lumpectomy and radiation therapy. A left carotid endarterectomy was recommended. Because of the small size of the patient's internal carotid artery, a polytetrafluoroethylene patch of the bulb and internal carotid artery was performed. Preoperative prophylactic antibiotics were not used. The patient tolerated the procedure well without neurologic deficits after surgery. She was discharged from the hospital on the second postoperative day. One week later the patient returned to the office with reports of increasing pain, swelling, and drainage from her left neck. She had no fever or chills and denied any neurologic symptoms. Physical examination revealed a tempera- 769
2 770 Zacharoulis et al. April 1997 \ Fig. 1. Direction of rotation ofsternocleidomastoid head to cover patched carotid artery. ture of 97.8 orally and stable vital signs. The left transverse cervical incision had erythema along the edges with moderate swelling and purulent drainage expressible deep to the platysmal closure layer, which indicated a deeper infection. The patient was initially treated with intravenous vancomycin, ceftazidime, and metronidazole. When the patient was brought to the operating room, the wound was found to have purulent fluid deep to the platysma and a small amount deep to the sternocleidomastoid muscle and cervical fascia. However, the patch was intact. The surgical procedure consisted of drainage of the collections and copious irrigation with antibiotic solution, which contained Kanamycin and Bacitracin. The decision to use sternocleidomastoid rotated muscle flap was made to control the spread of infection and to preserve the patch. The sternal head of the sternocleidomastoid muscle was mobilized, divided, and rotated up while its blood supply was preserved, and it was used to cover the carotid patch, providing well-vascularized tissue to cover the patch and the carotid artery (Fig. 1). The remainder of the wound was left open. Tissue cultures taken from the operative wound revealed Streptococcus A as the causative organism. After surgery the patient was treated with intravenous vancomycin, ceftazidime, and metronidazole and remained \ afebrile. The wound was managed with twice-daily dressing changes with antibiotic-soaked gauze. The patient was discharged with no signs of infection on the eleventh postoperative day with a prescription for penicillin V-Q 500 mg four times a day. Color duplex studies of the left internal carotid artery after 1 month revealed 30% residual stenosis of the distal left internal artery with a widely patent left internal carotid endarterectomy site. The wound completely healed after 3 months and remains healed more than 1 year after surgery. Case 2. A 64-year-old woman came to the emergency department with an acute anterior wall myocardial infarction. She was treated with thrombolytic therapy, and her initial hospital course was complicated by congestive heart failure and hypotension. Other significant history included hypertension, insulin-dependent diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and peripheral vascular disease. Workup after myocardial infarction revealed an ejection fraction of 45% to 50%. Coronary arteriography showed significant three-vessel coronary artery disease. A coronary artery bypass procedure was scheduled. Before the date of the coronary artery surgery she had an acute occlusion of her right iliac artery requiting urgent iliac thrombolysis and angioplasty followed by four-compartment fasciotomy because of prolonged ischemia. The fasciotomy site later became infected and was managed with local wound care and systemic antibiotics. During the same hospitalization the patient had multiple transient ischemic attacks in the right carotid distribution. A duplex scan of the extracranial carotid system revealed 70% stenosis of the right internal carotid artery with findings within normal limits for the vertebrobasilar system. A right carotid endarterectomy was performed. Ceflazidime was used for I day before the procedure for prophylaxis. Six days later the patient had an episode ofamaurosis fugax on the side of the carotid endarterectomy. A duplex study revealed a patent internal carotid artery with 40% to 50% stenosis. The angiogram revealed a flap causing stenosis at the site of endarterectomy. The patient was brought to the operating room, where a large hematoma was evacuated from the subfascial plane. The carotid artery was reopened, and in the area of the upper end of the endarterectomy limit, on the internal carotid artery, a small flap was seen between two tacking sutures, an additional tacking suture was placed, and the arteriotomy was closed with polytetrafluoroethylene patch. The wound was closed after thorough irrigation was performed with antibiotic solution containing Kanamycin and Bacitracin. After 5 days erythema and wound drainage were noted. Culture of the wound confirmed a diagnosis of infection by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, the same organism that infected the fasciotomy wound. Vancomycin and aztreonam were administered intravenously. The patient's wound was opened, and infected areas were debrided with the patients under sedation and local anesthesia with 1% lidocaine hydrochloride infiltration. To fill in the area and to cover the graft with healthy
3 Volume 25, Number 4 Zacharoulis et al. 771 Occipital a. -- Sup. thyroid a Thyrocervical trunk Fig. 2. Normal blood supply to sternocleidomastoid muscle. tissue, a sternocleidomastoid muscle rotated flap was prepared after the incision was extended at the lower part of the wound. The sternal head was mobilized and divided while its blood supply was preserved. The flap was rotated up and placed to cover the carotid patch. The sternocleidomastoid was tacked down with interrupted Vicryl sutures. The wound was irrigated again with antibiotic solution containing kanamycin and bacitracin and was left open. Antibiotic-soaked gauze was used to dress the wound. Aztreonam was discontinued 1 day after the surgery, and Vancomycin was discontinued 3 days after the surgery. At this time the patient was given ciprofloxacin and rifampin orally. The wound completely healed after 1 month. A follow-up duplex scan at 1 month showed a patent tight CEA with a small smooth plaque without hemodynamic significance. DISCUSSION The preoperative use of antibiotics in CEA is not a common practice. Infections in this area are rare and usually superficial. However, factors such as previous head and neck surgery, radiation of the head and neck, preoperative arteriogram, or technically poor soft-tissue closures leading to tension or hematoma can predispose patients to wound infection) Previous radiation to the left neck in the first patient and multiple procedures with the development of a hematoma in the second patient contributed to the likelihood of infection. Obviously, other comorbidities such as diabetes or an immunologically incompetent patient make the use of prophylactic antibiotics advisable in CEA.I,ll Although the value of prophylactic antibiotics in carotid surgery has not been conclusively proven, prophylactic antibiotics should have been used in the first case. We are now using prophylactic antibiotics in all our carotid cases. If a deep wound infection becomes established and involves a vascular graft in any area of the body, management should include the use of culture-specific antibiotics, debridement of the infected soft tissue, and excision of the infected graft. The graft can be preserved if it is patent, the anastomosis is intact, and the patient is not septic.i Graft excision is
4 772 Zacharoulis et al. April 1997 Fig. 3. Line of incision and dissection of sternocleidomastoid head before rotation. Blood supply from thyrocervical trunk (inferior portion of muscle) is sacrificed while preserving vessels from occipital and superior thyroid arteries, thus ensuring adequate blood supply to SCM flap. mandatory when the patient presents with anastomotic or graft hemorrhage or pseudoaneurysm, or if there is significant systemic sepsis} ~ However, this option, when the infection is in the carotid area, presents the danger of causing a stroke in some patients. In both these cases after infection was discovered, one option would have been to excise the polytetrafluoroethylene graft and replace it with a vein graft. This obviously would have been necessary if the suture line had been involved. Because the suture line was intact, we decided to preserve the patch by covering it with a well-vascularized muscle flap. The use of culture-specific antibiotics after the infection has been diagnosed is a critical first step. We recommend a bacterial specific antibiotic course of at least 6 weeks (intravenous and oral). However, longterm or lifelong antibiotic suppression should be taken under consideration depending on the organism and clinical situation. The extent of the infection, the presence of gross purulent material, and the pa- tient's response to the infection also should be taken into account when deciding the duration of intravenous and then oral antibiotics. The last step in the local management of wound infections is coveting the soft-tissue defect and especially the perigraft tissue with healthy, wefl-vascularized tissue. The use of rotational muscle flap in the management of acute wound infections has become commonplace. The pectoralis major muscle 2 and the serratus anterior muscle 3 have been transposed for the treatment of intrathoracic and sternal wound infections. Rectus abdominis muscle flap 4 has also been used in lower chest wall infections. Gracilis muscle flap has been used in the groin and perineal area. s Gastrocnemius 6 and soleus muscles are used in the management of lower hmb wound infections, osteomyelitis, 6 and infected orthopedic hardware. Trapezius and latissimus dorsi muscles have been used for closure of complex back wounds, s In vascular surgery the use of muscle flaps has mainly been used for covering grafts in the peripheral vessels. 9,1 Sartorius, rectus femoris, and rectus abdominis muscles have been used to cover vascular grafts in the groin. 9 The use of muscle flap has been shown experimentally and clinically to improve healing time, lower bacterial counts, and finally, bring well-vascularized tissue to clinically infected areas} 1 The muscle used for rotational coverage depends on the anatomic region involved and the integrity of a muscle's vascular supply. Precise knowledge of a muscle's blood supply is essential to prevent ischemic damage. In this case report the infected wound is covered by rotational muscle flap devised from the sternocleidomastoid muscle. The sternocleidomastoid muscle attaches inferiorly as two distinct heads into the sternum and medial third of the clavicle. The two heads then ascend posteriorly and vertically to insert superiorly into the mastoid process. The blood supply to the superior portion of the sternocleidomastoid is from a branch originating in the occipital artery that enters the muscle just below the mastoid region. The blood supply to the inferior portion is from a branch of the thyrocervical trunk. Midway between its origin and insertion the sternocleidomastoid is supplied by a branch of the superior thyroid artery and a smaller vessel from the adjacent muscles 12 (Fig. 2). With our technique the incision is extended to the sternal end. The platysma and the anterior sheet of the cervical fascia was dissected. The sternal head of the sternocleidomastoid muscle was then mobilized as low as necessary to allow rotation of the muscle pedicle and to reach the area of the surgical
5 Volume 25, Number 4 Zacharoulis et al. 773 need (Figs. 1, 3). The muscle's pedicle's blood supply was based at the branch of the superior thyroid artery, which as we mentioned previously supplies the mid portion of the muscle. The inferior blood supply from the thyrocervical trunk may be sacrificed. The sternal head of the muscle was rotated up so that the blood vessels would not be compromised. The wound was covered successfully with this flap and left open until healed. CONCLUSION Graft preservation and wound healing after an infection after CEA can be achieved through a multimodal approach of appropriate antibiotics, local debridement, and the use ofwell-vascularized muscle flap for coverage of the infected area. REFERENCES 1. Mora W, Hunter G, Malone J. Wound infection following carotid endarterectomy. 5 Cardiovasc Surg 1981 ;22: Hugo NE, Sultan MR, Asherman JA, et al. Single-stage management of 74 consecutive sternal wound complications with pectoralis major myocutaneous advancement flaps. Plast Reconstr Surg 1994;93: Arnold PG, Pairolero PC. The serratus anterior muscle in thoracic and extrathoracic utilization. Plast Reconstr Surg 1984;73: Coleman J, Bostwick J. Rectus abdominis muscle-musculocutaneous flap in chest wall reconstruction. Surg Clin North Am 1989;69: Ryan JA. Gracilis muscle flap for the purulent perineal sinus of inflammatoq' bowel disease. Am J Surg 1984;148: Hemphil ES, Ebert FR, Muench AG. Medial gastrocnemius muscle flap in the treatment of wound complications following total knee arthroplas~. Orthopedics 1992;15: Weiland AJ, Moore JA, Dowd RK. The efficacy of free tissue transfer in the treatment of osteomyelitis. Br J Surg 1991 ;78: Klink BK, Thruman RT, Wittgen GP, et al. Muscle flap closure for salvage of complex back wounds. Spine 1994;19: Peter BA, Vander Kolk CA, Dufrense CR, William GM. Can Infected prosthetic grafts be salvaged with rotation muscle flaps? Surgery 1991;110: Calligaro K, Veith F, editors. Management of infected arterial grafts. St Louis: Quality Medical Publishing, Inc, Piano G. Infections in lower extremity vascular grafts. Surg Clin North Am 1995;75: Gray's anatomy. 38th ed. New York: Churchill Livingstone, 1995: Submitted Apr. 18, 1996; accepted July 1, 1996.
Interesting Case Series. Omental Flap for Thoracic Aortic Graft Infection
 Interesting Case Series Omental Flap for Thoracic Aortic Graft Infection Andrew A. Marano, BA, Adam M. Feintisch, MD, and Mark S. Granick, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Rutgers
Interesting Case Series Omental Flap for Thoracic Aortic Graft Infection Andrew A. Marano, BA, Adam M. Feintisch, MD, and Mark S. Granick, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, Department of Surgery, Rutgers
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty
 CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
CASE REPORT An Innovative Solution to Complex Inguinal Defect: Deepithelialized SIEA Flap With Mini Abdominoplasty Augustine Reid Wilson, MS, Justin Daggett, MD, Michael Harrington, MD, MPH, and Deniz
Combat Extremity Vascular Trauma
 Combat Extremity Vascular Trauma Training teams to be a TEAM Chatt A. Johnson LTC, MC, USA 08 March 2010 US Army Trauma Training Center Core Discussion Series Outline: Combat Vascular Injury Physiologic
Combat Extremity Vascular Trauma Training teams to be a TEAM Chatt A. Johnson LTC, MC, USA 08 March 2010 US Army Trauma Training Center Core Discussion Series Outline: Combat Vascular Injury Physiologic
CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY. Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS
 CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS The plastic and reconstructive surgeon is often called upon to treat many wound problems of the lower extremity. These include
CHAPTER 16 LOWER EXTREMITY Amanda K Silva, MD and Warren Ellsworth, MD, FACS The plastic and reconstructive surgeon is often called upon to treat many wound problems of the lower extremity. These include
Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida
 Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida Appearance: oearly < 3 mo. olate > 3 mo.. Extent: Szilagyi Classification: Grade I: infection
Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida Appearance: oearly < 3 mo. olate > 3 mo.. Extent: Szilagyi Classification: Grade I: infection
PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD
 PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD Bala Ramanan, MBBS 1 st year vascular surgery fellow Introduction The epidemic of diabetes and ageing of our population ensures critical limb ischemia will continue to grow.
PUT YOUR BEST FOOT FORWARD Bala Ramanan, MBBS 1 st year vascular surgery fellow Introduction The epidemic of diabetes and ageing of our population ensures critical limb ischemia will continue to grow.
Pathologic abnormality of the sternoclavicular joint (SCJ)
 Surgical Management of the Infected Sternoclavicular Joint Rubie Sue Jackson, MD, Yvonne M. Carter, MD, and M. Blair Marshall, MD Pathologic abnormality of the sternoclavicular joint (SCJ) is rare. The
Surgical Management of the Infected Sternoclavicular Joint Rubie Sue Jackson, MD, Yvonne M. Carter, MD, and M. Blair Marshall, MD Pathologic abnormality of the sternoclavicular joint (SCJ) is rare. The
Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 170 174 Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap Arif Turkmen*, A. Graeme B. Perks Plastic Surgery Department, Nottingham City
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 170 174 Endoscopic assisted harvest of the pedicled pectoralis major muscle flap Arif Turkmen*, A. Graeme B. Perks Plastic Surgery Department, Nottingham City
Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida
 Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida Appearance: oearly < 3 mo. olate > 3 mo.. Extent: Szilagyi Classification: Grade I: infection
Division of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery University of South Florida School of Medicine Tampa, Florida Appearance: oearly < 3 mo. olate > 3 mo.. Extent: Szilagyi Classification: Grade I: infection
Nanogen Aktiv. Naz Wahab MD, FAAFP, FAPWCA Nexderma
 Nanogen Aktiv Naz Wahab MD, FAAFP, FAPWCA Nexderma Patient BM 75 y.o female with a history of Type 2 Diabetes, HTN, Hypercholesterolemia, Renal insufficiency, Chronic back Pain, who had undergone a L3-L4
Nanogen Aktiv Naz Wahab MD, FAAFP, FAPWCA Nexderma Patient BM 75 y.o female with a history of Type 2 Diabetes, HTN, Hypercholesterolemia, Renal insufficiency, Chronic back Pain, who had undergone a L3-L4
Pedicled Fillet of Leg Flap for Extensive Pressure Sore Coverage
 Pedicled Fillet of Leg Flap for Extensive Pressure Sore Coverage Shareef Jandali, MD, and David W. Low, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, University of Pennsylvania Health System, Philadelphia Correspondence:
Pedicled Fillet of Leg Flap for Extensive Pressure Sore Coverage Shareef Jandali, MD, and David W. Low, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, University of Pennsylvania Health System, Philadelphia Correspondence:
Axillary-to-carotid artery bypass grafting for symptomatic severe common carotid artery occlusive disease
 Axillary-to-carotid artery bypass grafting for symptomatic severe common carotid artery occlusive disease Joseph P. Archie, Jr, PhD, MD, Raleigh, NC Purpose: Revascularization of the internal or external
Axillary-to-carotid artery bypass grafting for symptomatic severe common carotid artery occlusive disease Joseph P. Archie, Jr, PhD, MD, Raleigh, NC Purpose: Revascularization of the internal or external
Anatomical study. Clinical study. R. Ogawa, H. Hyakusoku, M. Murakami, R. Aoki, K. Tanuma* and D. G. Pennington?
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2002) 55, 396-40 I 9 2002 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 10.1054/bjps.2002.3877 PLASTIC SURGERY An anatomical and clinical study of the dorsal intercostal
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2002) 55, 396-40 I 9 2002 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons doi: 10.1054/bjps.2002.3877 PLASTIC SURGERY An anatomical and clinical study of the dorsal intercostal
How to manage the left subclavian and left vertebral artery during TEVAR
 How to manage the left subclavian and left vertebral artery during TEVAR Jürg Schmidli Chief of Vascular Surgery Inselspital Hamburg 2017 Dept Cardiovascular Surgery, Bern, Switzerland Disclosure No Disclosures
How to manage the left subclavian and left vertebral artery during TEVAR Jürg Schmidli Chief of Vascular Surgery Inselspital Hamburg 2017 Dept Cardiovascular Surgery, Bern, Switzerland Disclosure No Disclosures
Flaps vs Grafts. Ronen Avram, MD MSc FRCSC
 Flaps vs Grafts Ronen Avram, MD MSc FRCSC POS Keratoacanthoma is not a malignant tumor! Methods of Reconstruction Reconstructive Ladder Primary closure Primary Delayed Secondary Intention Skin Graft Pedicled
Flaps vs Grafts Ronen Avram, MD MSc FRCSC POS Keratoacanthoma is not a malignant tumor! Methods of Reconstruction Reconstructive Ladder Primary closure Primary Delayed Secondary Intention Skin Graft Pedicled
Guidelines for Ultrasound Surveillance
 Guidelines for Ultrasound Surveillance Carotid & Lower Extremity by Ian Hamilton, Jr, MD, MBA, RPVI, FACS Corporate Medical Director BlueCross BlueShield of Tennessee guidelines for ultrasound surveillance
Guidelines for Ultrasound Surveillance Carotid & Lower Extremity by Ian Hamilton, Jr, MD, MBA, RPVI, FACS Corporate Medical Director BlueCross BlueShield of Tennessee guidelines for ultrasound surveillance
Exposure of the anterior tibial artery by medial popliteal extension
 Exposure of the anterior tibial artery by medial popliteal extension J. G. Sladen, FRCS(C), G. Kougeer, FRCS(C), and J. D. S. Reid, FRCS(C), Vancouver) British Columbia) Canada This report describes exploration
Exposure of the anterior tibial artery by medial popliteal extension J. G. Sladen, FRCS(C), G. Kougeer, FRCS(C), and J. D. S. Reid, FRCS(C), Vancouver) British Columbia) Canada This report describes exploration
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps
 Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
Breast Reconstruction with Superficial Inferior Epigastric Artery Flaps: A Prospective Comparison with TRAM and DIEP Flaps Pierre M. Chevray, M.D., Ph.D. Houston, Texas Breast reconstruction using the
Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer
 Original Article Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer K. Murali Mohan Reddy, D. Mukunda Reddy Department of Plastic Surgery, Nizams Institute of Medical Sciences, India. Address
Original Article Role of free tissue transfer in management of chronic venous ulcer K. Murali Mohan Reddy, D. Mukunda Reddy Department of Plastic Surgery, Nizams Institute of Medical Sciences, India. Address
2 Aortic Arch Debranching UCSF Vascular Symposium /14/16. J Endovasc Ther 2002;9:suppl 2; II98 105
 How I Do It: Aortic Arch Debranching Exposures, Tunnels and Techniques Warren Gasper MD Assistant Professor of Surgery UCSF Vascular Surgery No disclosures 2 Aortic Arch Debranching UCSF Vascular Symposium
How I Do It: Aortic Arch Debranching Exposures, Tunnels and Techniques Warren Gasper MD Assistant Professor of Surgery UCSF Vascular Surgery No disclosures 2 Aortic Arch Debranching UCSF Vascular Symposium
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5. Contents lists available at ScienceDirect. JPRAS Open. journal homepage:
 JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
JPRAS Open 3 (2015) 1e5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect JPRAS Open journal homepage: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/ jpras-open Case report The pedicled transverse partial latissimus dorsi
FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION
 FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION CPT/HCPCS Codes 93875 Non-invasive physiologic studies of extracranial arteries, complete bilateral study (eg, periorbital
FIRST COAST SERVICE OPTIONS FLORIDA MEDICARE PART B LOCAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION CPT/HCPCS Codes 93875 Non-invasive physiologic studies of extracranial arteries, complete bilateral study (eg, periorbital
Interesting Case Series. Fournier s Gangrene and the Reconstructive Challenges for the Plastic Surgeon
 Interesting Case Series Fournier s Gangrene and the Reconstructive Challenges for the Plastic Surgeon David Izadi, MB, BChir, MA(Oxon), MA(Cantab), MRCS, James Coelho, BMBS, MSc, MRCS, Sameer Gurjal, MBBCh,
Interesting Case Series Fournier s Gangrene and the Reconstructive Challenges for the Plastic Surgeon David Izadi, MB, BChir, MA(Oxon), MA(Cantab), MRCS, James Coelho, BMBS, MSc, MRCS, Sameer Gurjal, MBBCh,
Interesting Case Series. Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle
 Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
Interesting Case Series Scalp Reconstruction With Free Latissimus Dorsi Muscle Danielle H. Rochlin, BA, Justin M. Broyles, MD, and Justin M. Sacks, MD Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery,
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Tracheo-innominate artery fistula (TIF) is an uncommon
 Technique for Managing Tracheo-Innominate Artery Fistula Gorav Ailawadi, MD Tracheo-innominate artery fistula (TIF) is an uncommon complication (0.1-1%) following both open and percutaneous tracheostomy.
Technique for Managing Tracheo-Innominate Artery Fistula Gorav Ailawadi, MD Tracheo-innominate artery fistula (TIF) is an uncommon complication (0.1-1%) following both open and percutaneous tracheostomy.
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
FASCIAL PLANE BLOCKS TOM BARIBEAULT MSN, CRNA
 FASCIAL PLANE BLOCKS TOM BARIBEAULT MSN, CRNA TECHNIQUES Abdominal Wall TAP Rectus Sheath Quadratus Lumborum Erector Spinae Chest PECS I & II Erector Spinae TECHNIQUES Knee Ipack/LIA Hip Fascia Iliaca
FASCIAL PLANE BLOCKS TOM BARIBEAULT MSN, CRNA TECHNIQUES Abdominal Wall TAP Rectus Sheath Quadratus Lumborum Erector Spinae Chest PECS I & II Erector Spinae TECHNIQUES Knee Ipack/LIA Hip Fascia Iliaca
Tor Chiu. Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161
 18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
Evaluation & Management of Penetrating Wounds to the NECK
 Evaluation & Management of Penetrating Wounds to the NECK Goal Effectively identify patients with a high probability of injury requiring surgical intervention Define the role of diagnostic tests in assessing
Evaluation & Management of Penetrating Wounds to the NECK Goal Effectively identify patients with a high probability of injury requiring surgical intervention Define the role of diagnostic tests in assessing
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFTING (CABG) (Part 1) Mark Shikhman, MD, Ph.D., CSA Andrea Scott, CST
 CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFTING (CABG) (Part 1) Mark Shikhman, MD, Ph.D., CSA Andrea Scott, CST I have constructed this lecture based on publications by leading cardiothoracic American surgeons: Timothy
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFTING (CABG) (Part 1) Mark Shikhman, MD, Ph.D., CSA Andrea Scott, CST I have constructed this lecture based on publications by leading cardiothoracic American surgeons: Timothy
GUIDELINE FOR RECOVERY ROOM MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS AFTER CAROTID ENDARTERECTOMY
 GUIDELINE FOR RECOVERY ROOM MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS AFTER CAROTID ENDARTERECTOMY Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Guideline for Recovery Room Management of Patients after Carotid
GUIDELINE FOR RECOVERY ROOM MANAGEMENT OF PATIENTS AFTER CAROTID ENDARTERECTOMY Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Guideline for Recovery Room Management of Patients after Carotid
Gross Anatomy Faculty: Gross Anatomy Faculty: Gross Anatomy Faculty: Dr. Melissa McGinn. Welcome to Gross and Developmental Anatomy
 Welcome to Gross and Developmental Anatomy M1 Anatomy Gross Anatomy Faculty: Dr. Richard Krieg Dr. Milton Sholley Dr. David Simpson 1 2 Gross Anatomy Faculty: Gross Anatomy Faculty: Dr. Steve Gudas Dr.
Welcome to Gross and Developmental Anatomy M1 Anatomy Gross Anatomy Faculty: Dr. Richard Krieg Dr. Milton Sholley Dr. David Simpson 1 2 Gross Anatomy Faculty: Gross Anatomy Faculty: Dr. Steve Gudas Dr.
Acute arterial complications associated with total hip and knee arthroplasty
 From the Eastern Vascular Society Acute arterial complications associated with total hip and knee arthroplasty Keith D. Calligaro, MD, a Matthew J. Dougherty, MD, a Sean Ryan, MD, a and Robert E. Booth,
From the Eastern Vascular Society Acute arterial complications associated with total hip and knee arthroplasty Keith D. Calligaro, MD, a Matthew J. Dougherty, MD, a Sean Ryan, MD, a and Robert E. Booth,
Gastrocnemius Muscle Flap Coverage of Chronically= Infected Knee Joints
 Gastrocnemius Muscle Flap Coverage of Chronically= Infected Knee Joints ABSTRACT Chronically infected open knee joints present dif cult problem. Aggressive debridement of chronically infected soft tissue
Gastrocnemius Muscle Flap Coverage of Chronically= Infected Knee Joints ABSTRACT Chronically infected open knee joints present dif cult problem. Aggressive debridement of chronically infected soft tissue
Reconstruction of the Chest Wall
 HOW TO DO IT Reconstruction of the Chest Wall Reed 0. Dingman, M.D., and Louis C. Argenta, M.D. ABSTRACT Reconstruction of the chest wall can now be accomplished reliably and expeditiously. Past experience
HOW TO DO IT Reconstruction of the Chest Wall Reed 0. Dingman, M.D., and Louis C. Argenta, M.D. ABSTRACT Reconstruction of the chest wall can now be accomplished reliably and expeditiously. Past experience
The Waist Coat Flap: a new technique for closure of infected median sternotomy wounds
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 728 732 The Waist Coat Flap: a new technique for closure of infected median sternotomy wounds Adel Wagdi Morsi, Frank Kimble*, Craig Quarmby, Alicia
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 728 732 The Waist Coat Flap: a new technique for closure of infected median sternotomy wounds Adel Wagdi Morsi, Frank Kimble*, Craig Quarmby, Alicia
Anatomical Study of Pectoral Nerves and its Implications in Surgery
 DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/8631.4545 Anatomy Section Original Article Anatomical Study of Pectoral Nerves and its Implications in Surgery Prakash KG 1, Saniya K 2 ABSTRACT Introduction: This anatomical study
DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/8631.4545 Anatomy Section Original Article Anatomical Study of Pectoral Nerves and its Implications in Surgery Prakash KG 1, Saniya K 2 ABSTRACT Introduction: This anatomical study
Due in Lab weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10. Homework #8. Both sides! Both sides!
 Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Lab 8 MUSCLES Due in Lab 10 2 weeks because of Thanksgiving Prelab #10 Both sides! Homework #8 Both sides! Refer to Muscles 22-23 Naming of muscles Origin Site of muscle attachment that doesn t move during
Alexander C Vlantis. Selective Neck Dissection 33
 05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
Case 37 Clinical Presentation
 Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
Case 37 73 Clinical Presentation The patient is a 62-year-old woman with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding. 74 RadCases Interventional Radiology Imaging Findings () Image from a selective digital subtraction
National Vascular Registry
 National Vascular Registry Bypass Patient Details Patient Consent* 2 Not Required If patient not consented: Date consent recorded / / (DD/MM/YYYY) Do not record NHS number, NHS number* name(s) or postcode.
National Vascular Registry Bypass Patient Details Patient Consent* 2 Not Required If patient not consented: Date consent recorded / / (DD/MM/YYYY) Do not record NHS number, NHS number* name(s) or postcode.
1TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE
 TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE SURFACE ANATOMY SKELETON JOINTS & LIGAMENTS MUSCLES VASCULATURE NERVES SPINAL CORD & VERTEBRAL CANAL ANTERIOR BODY WALL & MAMMARY GLAND LATERAL BODY WALL INGUINAL REGION SUPERFICIAL
TRUNK: BODY WALL AND SPINE SURFACE ANATOMY SKELETON JOINTS & LIGAMENTS MUSCLES VASCULATURE NERVES SPINAL CORD & VERTEBRAL CANAL ANTERIOR BODY WALL & MAMMARY GLAND LATERAL BODY WALL INGUINAL REGION SUPERFICIAL
Breast Reconstruction Options
 Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
Breast Reconstruction Options Natural reconstruction using your ABDOMINAL tissue: TRAM Flap (Transverse Rectus Abdominis Myocutaneous) There are various forms of TRAM flap reconstruction that are commonly
Amputations. Chapter 23
 Amputations Chapter 23 Amputations Introduction Battle casualties who sustain amputations have the most severe extremity injuries. Historically, 1 in 3 patients with a major amputation (proximal to the
Amputations Chapter 23 Amputations Introduction Battle casualties who sustain amputations have the most severe extremity injuries. Historically, 1 in 3 patients with a major amputation (proximal to the
Surgical Options for revascularisation P E T E R S U B R A M A N I A M
 Surgical Options for revascularisation P E T E R S U B R A M A N I A M The goal Treat pain Heal ulcer Preserve limb Preserve life The options Conservative Endovascular Surgical bypass Primary amputation
Surgical Options for revascularisation P E T E R S U B R A M A N I A M The goal Treat pain Heal ulcer Preserve limb Preserve life The options Conservative Endovascular Surgical bypass Primary amputation
A 10-year experience of infection following carotid endarterectomy with patch angioplasty
 From the Eastern Vascular Society A 10-year experience of infection following carotid endarterectomy with patch angioplasty Patrick A. Stone, MD, Mohit Srivastava, MD, John E. Campbell, MD, Albeir Y. Mousa,
From the Eastern Vascular Society A 10-year experience of infection following carotid endarterectomy with patch angioplasty Patrick A. Stone, MD, Mohit Srivastava, MD, John E. Campbell, MD, Albeir Y. Mousa,
EARLY AND LONG-TERM RESULTS OF PROSTHETIC CHEST WALL RECONSTRUCTION
 EARLY AND LONG-TERM RESULTS OF PROSTHETIC CHEST WALL RECONSTRUCTION Claude Deschamps, MD Bulent Mehmit Tirnaksiz, MD Ramin Darbandi Victor F. Trastek, MD Mark S. Allen, MD Daniel L. Miller, MD Phillip
EARLY AND LONG-TERM RESULTS OF PROSTHETIC CHEST WALL RECONSTRUCTION Claude Deschamps, MD Bulent Mehmit Tirnaksiz, MD Ramin Darbandi Victor F. Trastek, MD Mark S. Allen, MD Daniel L. Miller, MD Phillip
Neck-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
The gastrocnemius with soleus bi-muscle flap
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 77 82 The gastrocnemius with soleus bi-muscle flap Ikuo Hyodo a, *, Bin Nakayama b, Mitsuru Takahashi c, Kazuhiro Toriyama d, Yuzuru Kamei d, Shuhei
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 77 82 The gastrocnemius with soleus bi-muscle flap Ikuo Hyodo a, *, Bin Nakayama b, Mitsuru Takahashi c, Kazuhiro Toriyama d, Yuzuru Kamei d, Shuhei
Coral Reef Aorta- Treatment Options?
 Chronic mesenteric ischemia (CMI) Coral Reef Aorta- Treatment Options? Bala Ramanan Vascular Fellow, UCSF CMI is a life-threatening problem that can result in death from inanition or bowel infarction Incidence
Chronic mesenteric ischemia (CMI) Coral Reef Aorta- Treatment Options? Bala Ramanan Vascular Fellow, UCSF CMI is a life-threatening problem that can result in death from inanition or bowel infarction Incidence
Schedule of Benefits. for Professional Fees Vascular Procedures
 Schedule of Benefits for Professional Fees 2018 Vascular Procedures ANASTOMOSIS RULES 820 Arteriovenous anastomosis in arm 1453 Arteriovenous anastomosis, open by basilic vein transposition 1465 Splenorenal
Schedule of Benefits for Professional Fees 2018 Vascular Procedures ANASTOMOSIS RULES 820 Arteriovenous anastomosis in arm 1453 Arteriovenous anastomosis, open by basilic vein transposition 1465 Splenorenal
Abscess. A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body.
 Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
Abscess A abscess is a localized collection of pus in the skin and may occur on any skin surface and be formed in any part of body. Ethyology Bacteria causing cutaneous abscesses are typically indigenous
Chest Wall Tumors and Reconstruction: Lateral Chest Wall. Dr. Robert Kelly
 Chest Wall Tumors and Reconstruction: Lateral Chest Wall Dr. Robert Kelly THORACIC PROGRAMME: ADVANCES IN CHEST WALL SURGERY AND OSTEOSYNTHESIS Dr. José Ribas Milanez de Campos Assistant, Professor, Department
Chest Wall Tumors and Reconstruction: Lateral Chest Wall Dr. Robert Kelly THORACIC PROGRAMME: ADVANCES IN CHEST WALL SURGERY AND OSTEOSYNTHESIS Dr. José Ribas Milanez de Campos Assistant, Professor, Department
Scapular & Parascapular flap FLAP TERRITORY ANATOMY. is normally accompanied by two venae comitantes.
 Scapular & Parascapular flap FLAP TERRITORY This is a composite flap that is situated over the scapula with various incisional arrangements. It can be harvested as a skin and subcutaneous tissue flap,
Scapular & Parascapular flap FLAP TERRITORY This is a composite flap that is situated over the scapula with various incisional arrangements. It can be harvested as a skin and subcutaneous tissue flap,
Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery. Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University
 Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University Introduction Rationale for anatomical basis for OPS Anatomical considerations: 1. Surface
Essential Anatomy for oncoplastic surgery Omar Z. Youssef M.D Professor of surgical oncology NCI- Cairo University Introduction Rationale for anatomical basis for OPS Anatomical considerations: 1. Surface
Versatility of Reverse Sural Artery Flap for Heel Reconstruction
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
be very thin and variable. Facial nerve branches that exit the parotid gland are deep to the SMAS.
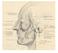 The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect of Upper and Middle Third Leg
 Downloaded from wjps.ir at 22:25 +0330 on Sunday November 18th 28 314 Gastrocnemius flap for coverage of leg defects Original Article Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect
Downloaded from wjps.ir at 22:25 +0330 on Sunday November 18th 28 314 Gastrocnemius flap for coverage of leg defects Original Article Gastrocnemius Myocutaneous Flap: A Versatile Option to Cover the Defect
Distal Femoral Resection
 Distal Femoral Resection Annie Arteau, Bruno Fuchs Introduction This text is a general description of a distal femoral resection. Focus is on anatomical structures and muscle resection. Each femoral resection
Distal Femoral Resection Annie Arteau, Bruno Fuchs Introduction This text is a general description of a distal femoral resection. Focus is on anatomical structures and muscle resection. Each femoral resection
Modified Radical Mastectomy
 Modified Radical Mastectomy Valerie L. Staradub, MD, and Monica Morrow, MD S urgical management options for breast cancer include modified radical mastectomy (MRM), MRM with immediate reconstruction, and
Modified Radical Mastectomy Valerie L. Staradub, MD, and Monica Morrow, MD S urgical management options for breast cancer include modified radical mastectomy (MRM), MRM with immediate reconstruction, and
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report
 Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report BY JIRI J. VITEK, M.D., JAMES H. HALSEY, JR., M.D., AND HOLT A. McDOWELL, M.D. Abstract: Occlusion of All Four
Occlusion of All Four Extracranial Vessels With Minimal Clinical Symptomatology. Case Report BY JIRI J. VITEK, M.D., JAMES H. HALSEY, JR., M.D., AND HOLT A. McDOWELL, M.D. Abstract: Occlusion of All Four
National Vascular Registry
 National Vascular Registry Angioplasty Patient Details Patient Consent* 2 Not Required If patient not consented: Date consent recorded / / (DD/MM/YYYY) Do not record NHS number, NHS number* name(s) or
National Vascular Registry Angioplasty Patient Details Patient Consent* 2 Not Required If patient not consented: Date consent recorded / / (DD/MM/YYYY) Do not record NHS number, NHS number* name(s) or
The posterolateral thoracotomy is still probably the
 Posterolateral Thoracotomy Jean Deslauriers and Reza John Mehran The posterolateral thoracotomy is still probably the most commonly used incision in general thoracic surgery. It provides not only excellent
Posterolateral Thoracotomy Jean Deslauriers and Reza John Mehran The posterolateral thoracotomy is still probably the most commonly used incision in general thoracic surgery. It provides not only excellent
Subclavian artery Stenting
 Subclavian artery Stenting Etiology Atherosclerosis Takayasu s arteritis Fibromuscular dysplasia Giant Cell Arteritis Radiation-induced Vascular Injury Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Neurofibromatosis Incidence
Subclavian artery Stenting Etiology Atherosclerosis Takayasu s arteritis Fibromuscular dysplasia Giant Cell Arteritis Radiation-induced Vascular Injury Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Neurofibromatosis Incidence
Indications: following: embolization. artery that has diseases 5. The evaluation. of suspected. such entities. a cold hand. biopsy
 Peripheral Arterial Ultrasound Protocol Using Color and Spectral Doppler Reviewed by: Mark Yuhasz, MD Last Review Date: January 2015 Contact: (866) 761 4200, Option 1 Indications: The indications for peripheral
Peripheral Arterial Ultrasound Protocol Using Color and Spectral Doppler Reviewed by: Mark Yuhasz, MD Last Review Date: January 2015 Contact: (866) 761 4200, Option 1 Indications: The indications for peripheral
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman
 Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Recommendations for Follow-up After Vascular Surgery Arterial Procedures SVS Practice Guidelines
 Recommendations for Follow-up After Vascular Surgery Arterial Procedures 2018 SVS Practice Guidelines vsweb.org/svsguidelines About the guidelines Published in the July 2018 issue of Journal of Vascular
Recommendations for Follow-up After Vascular Surgery Arterial Procedures 2018 SVS Practice Guidelines vsweb.org/svsguidelines About the guidelines Published in the July 2018 issue of Journal of Vascular
Infected Lower Extremity Aneurysms C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD
 Infected Lower Extremity Aneurysms C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD University Hospital of Brooklyn Department of Surgery History 52F c PMHx of HTN, asthma p/w fever, malaise s/p one week of ABx for presumed
Infected Lower Extremity Aneurysms C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD University Hospital of Brooklyn Department of Surgery History 52F c PMHx of HTN, asthma p/w fever, malaise s/p one week of ABx for presumed
Critical Limb Ischemia A Collaborative Approach to Patient Care. Christopher LeSar, MD Vascular Institute of Chattanooga July 28, 2017
 Critical Limb Ischemia A Collaborative Approach to Patient Care Christopher LeSar, MD Vascular Institute of Chattanooga July 28, 2017 Surgeons idea Surgeons idea represents the final stage of peripheral
Critical Limb Ischemia A Collaborative Approach to Patient Care Christopher LeSar, MD Vascular Institute of Chattanooga July 28, 2017 Surgeons idea Surgeons idea represents the final stage of peripheral
Alexander C Vlantis. Total Laryngectomy 57
 07 Total Laryngectomy Alexander C Vlantis Total Laryngectomy 57 Total Laryngectomy STEP 1 INCISION AND POSITION OF STOMA A superiorly based apron flap incision is marked with the horizontal limb placed
07 Total Laryngectomy Alexander C Vlantis Total Laryngectomy 57 Total Laryngectomy STEP 1 INCISION AND POSITION OF STOMA A superiorly based apron flap incision is marked with the horizontal limb placed
AORTIC GRAFT INFECTION
 NURSING CARE Theresa O Keefe NUM Vascular Unit PAH Vascular infections are serious They are associated with high morbidity and mortality The primary cause of surgical wound infections is contamination
NURSING CARE Theresa O Keefe NUM Vascular Unit PAH Vascular infections are serious They are associated with high morbidity and mortality The primary cause of surgical wound infections is contamination
Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC
 Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
Downloaded from Reconstruction of the Breast after Cancer An Overview of Procedures and Options by Karen M. Horton, MD, MSc, FRCSC What is Breast Reconstruction? Reconstruction of the breast involves recreating
-primarily by apposition of the anterior rectus
 2 Component separation Cop HARVEY CHIM, KAREN KIM EVANS, AND SAMIR MARDINI Mater al Introduction 7 Preoperative markings 7 Intraoperative details 9 Technique modification: Component separation with preservation
2 Component separation Cop HARVEY CHIM, KAREN KIM EVANS, AND SAMIR MARDINI Mater al Introduction 7 Preoperative markings 7 Intraoperative details 9 Technique modification: Component separation with preservation
Medical Journal of the Volume 20 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 1385 November Original Articles
 Medical Journal of the Volume 0 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 38 November 00 Original Articles ANATOMY OF THE SUPERFICIAL INFERIOR EPIGASTRIC ARTERY FLAP MAHDI FATHI, M.D., EBRAHIM HATAMIPOUR,
Medical Journal of the Volume 0 Islamic Republic of Iran Number 3 Fall 38 November 00 Original Articles ANATOMY OF THE SUPERFICIAL INFERIOR EPIGASTRIC ARTERY FLAP MAHDI FATHI, M.D., EBRAHIM HATAMIPOUR,
Lateral approach to the popliteal artery
 Lateral approach to the popliteal artery Frank J. Veith, M.D., Enrico Ascer, M.D., Sushil K. Gupta, M.D., and Kurt R. Wengerter, M.D., New York, N.Y. Techniques for exposure of the popliteal artery via
Lateral approach to the popliteal artery Frank J. Veith, M.D., Enrico Ascer, M.D., Sushil K. Gupta, M.D., and Kurt R. Wengerter, M.D., New York, N.Y. Techniques for exposure of the popliteal artery via
Neck Ultrasound. Faculty Info: Amy Kule, MD
 Neck Ultrasound Date: Friday, October 19, 2018 Time: 11:00 AM Location: SMALL GROUP LABORATORY SSOM L71 Watch: Ø Neck Ultrasound Scanning Protocol (4:00): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zozd2x2ll4q Faculty
Neck Ultrasound Date: Friday, October 19, 2018 Time: 11:00 AM Location: SMALL GROUP LABORATORY SSOM L71 Watch: Ø Neck Ultrasound Scanning Protocol (4:00): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zozd2x2ll4q Faculty
AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION
 CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
CHAPTER 18 AESTHETIC SURGERY OF THE BREAST: MASTOPEXY, AUGMENTATION & REDUCTION Ali A. Qureshi, MD and Smita R. Ramanadham, MD Aesthetic surgery of the breast aims to either correct ptosis with a mastopexy,
2016 Physician Quality Reporting System Data Collection Form: Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) (for patients aged 18 years and older)
 2016 Physician Quality Reporting System Data Collection Form: Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) (for patients aged 18 years and older) IMPORTANT: Any measure with a 0% performance rate (100% for inverse
2016 Physician Quality Reporting System Data Collection Form: Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) (for patients aged 18 years and older) IMPORTANT: Any measure with a 0% performance rate (100% for inverse
4/30/2010. Options for abdominal wall reconstruction. Scott L. Hansen, MD
 Components Separation Scott L. Hansen, MD University of California, San Francisco Chief, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery San Francisco General Hospital Overview Options for abdominal wall reconstruction
Components Separation Scott L. Hansen, MD University of California, San Francisco Chief, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery San Francisco General Hospital Overview Options for abdominal wall reconstruction
Date of Admission: [DATE]. Date of Discharge:
![Date of Admission: [DATE]. Date of Discharge: Date of Admission: [DATE]. Date of Discharge:](/thumbs/74/71277118.jpg) Date of Admission: [DATE]. Date of Discharge: History of Present Illness: Mr. [NAME] AKA [NAME] is a 31-year-old male who presents to the [PLACE] Trauma Surgery Service as a moderate trauma on [DATE] following
Date of Admission: [DATE]. Date of Discharge: History of Present Illness: Mr. [NAME] AKA [NAME] is a 31-year-old male who presents to the [PLACE] Trauma Surgery Service as a moderate trauma on [DATE] following
17 FibulA FlAP Tor Chiu fibula flap 153
 17 Fibula Flap Tor Chiu Fibula Flap 153 Fibula Flap FLAP TERRITORY This flap includes a segment of the fibular bone with or without the overlying skin island on the peroneal/ lateral aspect of the calf.
17 Fibula Flap Tor Chiu Fibula Flap 153 Fibula Flap FLAP TERRITORY This flap includes a segment of the fibular bone with or without the overlying skin island on the peroneal/ lateral aspect of the calf.
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT (CABG) MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW
 CONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT (CABG) MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2015 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: 2015 PQRS MEASURES IN CONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT (CABG) MEASURES GROUP: #43 Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG):
CONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT (CABG) MEASURES GROUP OVERVIEW 2015 PQRS OPTIONS F MEASURES GROUPS: 2015 PQRS MEASURES IN CONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT (CABG) MEASURES GROUP: #43 Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG):
Physician s Vascular Interpretation Examination Content Outline
 Physician s Vascular Interpretation Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 6 Cerebrovascular Abdominal Peripheral Arterial - Duplex Imaging Peripheral Arterial
Physician s Vascular Interpretation Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 4 5 6 Cerebrovascular Abdominal Peripheral Arterial - Duplex Imaging Peripheral Arterial
Carotid Stenosis 1/24/2019. Review of Primary Studies. NASCET- Moderate stenosis. ACAS (Asymptomatic Carotid Atherosclerosis Study) NASCET
 Review of Primary Studies Carotid Stenosis NINDS National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke 2 large studies to determine who would benefit from surgery NASCET North American Symptomatic Carotid
Review of Primary Studies Carotid Stenosis NINDS National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke 2 large studies to determine who would benefit from surgery NASCET North American Symptomatic Carotid
Surgical Procedures for. Symptomatic Post-CAS Carotid. Restenosis: Experiences and. Mid-Term Outcomes. Lefeng Qu M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Surgery
 Surgical Procedures for Symptomatic Post-CAS Carotid Restenosis: Experiences and Mid-Term Outcomes Lefeng Qu M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Surgery Department of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Changzheng
Surgical Procedures for Symptomatic Post-CAS Carotid Restenosis: Experiences and Mid-Term Outcomes Lefeng Qu M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Surgery Department of Vascular and Endovascular Surgery, Changzheng
Vascular Surgery Rotation Objectives for Junior Residents (PGY-1 and 2)
 Vascular Surgery Rotation Objectives for Junior Residents (PGY-1 and 2) Definition Vascular surgery is the specialty concerned with the diagnosis and management of congenital and acquired diseases of the
Vascular Surgery Rotation Objectives for Junior Residents (PGY-1 and 2) Definition Vascular surgery is the specialty concerned with the diagnosis and management of congenital and acquired diseases of the
Research Article Immediate versus Delayed Sarcoma Reconstruction: Impact on Outcomes
 Sarcoma Volume 2016, Article ID 7972318, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7972318 Research Article Immediate versus Delayed Sarcoma Reconstruction: Impact on Outcomes Kyle J. Sanniec, 1 Cristine
Sarcoma Volume 2016, Article ID 7972318, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7972318 Research Article Immediate versus Delayed Sarcoma Reconstruction: Impact on Outcomes Kyle J. Sanniec, 1 Cristine
Selected Operative Procedure Categories for KNHSS SSI Surveillance
 Selected Operative Procedure Categories for KNHSS SSI Surveillance Breast Surgery Excision of lesion or tissue of breast including radical, modified, or quadrant resection, lumpectomy, incisional biopsy,
Selected Operative Procedure Categories for KNHSS SSI Surveillance Breast Surgery Excision of lesion or tissue of breast including radical, modified, or quadrant resection, lumpectomy, incisional biopsy,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. The Thoracoacromial/Cephalic Vascular System for Microvascular Anastomoses in the Vessel-Depleted Neck
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Thoracoacromial/Cephalic Vascular System for Microvascular Anastomoses in the Vessel-Depleted Neck Jeffrey R. Harris, MD; E. Lueg, MD; E. Genden, MD; M. L. Urken, MD Objective: To
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Thoracoacromial/Cephalic Vascular System for Microvascular Anastomoses in the Vessel-Depleted Neck Jeffrey R. Harris, MD; E. Lueg, MD; E. Genden, MD; M. L. Urken, MD Objective: To
Morbidity Audit and Logbook Tool SNOMED Board Reporting Terms for SET and IMG Vascular Surgery AMPUTATION AORTA
 SNOMED s for SET and IMG Vascular Surgery AMPUTATION Amputation above-knee Amputation of leg through tibia and fibula Amputation of the foot Amputation of toe Through knee amputation Ray amputation of
SNOMED s for SET and IMG Vascular Surgery AMPUTATION Amputation above-knee Amputation of leg through tibia and fibula Amputation of the foot Amputation of toe Through knee amputation Ray amputation of
2013 Coding Changes. Diagnostic Radiology. Nuclear Medicine
 2013 Coding Changes The principal coding changes affecting Radiologists in 2013 occur in the Interventional Radiology Section of the AMA/CPT Manual. As in the past, we continue to see the Relative Update
2013 Coding Changes The principal coding changes affecting Radiologists in 2013 occur in the Interventional Radiology Section of the AMA/CPT Manual. As in the past, we continue to see the Relative Update
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi
 Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
Osteosynthesis involving a joint Thomas P Rüedi How to use this handout? The left column contains the information given during the lecture. The column at the right gives you space to make personal notes.
The earlier clinic experience of the reverse-flow anterolateral thigh island flap
 British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 160 164 The earlier clinic experience of the reverse-flow anterolateral thigh island flap Gang Zhou, Qi-Xu Zhang*, Guang-Yu Chen Scar Multiple Treatment Centre,
British Journal of Plastic Surgery (2005) 58, 160 164 The earlier clinic experience of the reverse-flow anterolateral thigh island flap Gang Zhou, Qi-Xu Zhang*, Guang-Yu Chen Scar Multiple Treatment Centre,
Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles. Muscles of the Head and Neck. Masseter. Orbicularis occuli. Orbicularis oris. Sternocleidomastoid
 Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles Muscles of the Head and Neck Masseter Orbicularis occuli Orbicularis oris Sternocleidomastoid Temporalis BIO 113 Fall 2011 Muscles Page 1 of 5 Muscles of the
Bio 113 Anatomy and Physiology The Muscles Muscles of the Head and Neck Masseter Orbicularis occuli Orbicularis oris Sternocleidomastoid Temporalis BIO 113 Fall 2011 Muscles Page 1 of 5 Muscles of the
REINFORCED BIOSCAFFOLDS
 REINFORCED BIOSCAFFOLDS Midline Incisional Open OviTex 1S Resorbable Clinical Case Study: Open Abdomen Incisional Herniorrhaphy in Contaminated (CDC Class IV) Operative Field Performed by Dr. Michael Sawyer,
REINFORCED BIOSCAFFOLDS Midline Incisional Open OviTex 1S Resorbable Clinical Case Study: Open Abdomen Incisional Herniorrhaphy in Contaminated (CDC Class IV) Operative Field Performed by Dr. Michael Sawyer,
Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1714-7 RESEARCH Open Access Selective salvage of zones 2 and 4 in the pedicled TRAM flap: a focus on reducing fat necrosis and improving aesthetic outcomes Chi Sun Yoon and Kyu Nam
