doi: /j.ultrasmedbio
|
|
|
- Annabelle Marsh
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 doi: /j.ultrasmedbio Ultrasound in Med. & Biol., Vol. 37, No. 1, pp , 2011 Copyright Ó 2011 World Federation for Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology Printed in the USA. All rights reserved /$ - see front matter d Original Contribution CHANGES IN FETAL AND MATERNAL DOPPLER PARAMETERS OBSERVED DURING ACUTE SEVERE HYPERTENSION TREATMENT WITH HYDRALAZINE OR LABETALOL: A RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL MARIA RITA F. BAGGIO,* WELLINGTON P. MARTINS,* y ANA CAROLINA S. CALDERON,* ADERSON T. BEREZOWSKI,* ALESSANDRA CRISTINA MARCOLIN,* GERALDO DUARTE,* and RICARDO C. CAVALLI* * Departamento de Ginecologia e Obstetrıcia, Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeir~ao Preto, Universidade de S~ao Paulo (DGO-FMRP-USP), Ribeir~ao Preto, S~ao Paulo, Brazil; and y Escola de Ultra-sonografia e Reciclagem Medica de Ribeir~ao Preto (EURP), Ribeir~ao Preto, S~ao Paulo, Brazil (Received 22 July 2010; revised 29 September 2010; in final form 7 October 2010) Abstract We evaluated 16 pregnant women with gestational age between 20 and 32 weeks in acute severe hypertension which were randomly allocated to receive either hydralazine or labetalol. Blood pressure and Doppler ultrasound parameters from maternal uterine and fetal middle cerebral and umbilical arteries were assessed during acute severe hypertension and after treatment. A significant reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure was observed in both groups. A significant change in Doppler parameters was observed only in pregnant women who received hydralazine: an increase in uterine arteries resistance index. We concluded that both drugs were highly effective in reducing blood pressure in these women. Despite the observed increase in resistance index of uterine arteries associated with hydralazine, the use of hydralazine and labetalol were not related to any significant changes in fetal Doppler, which is reassuring about the safety of these drugs when treating acute severe hypertension in pregnancy. ( wpmartins@gmail.com) Ó 2011 World Federation for Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology. Key Words: Hydralazine, Labetalol, Hypertension, Pregnancy-induced, Ultrasonography, Doppler. INTRODUCTION The hypertensive disorders affect approximately 6% of pregnant women (Povoa et al. 2008) and is one of the three leading causes of pregnancy-related deaths (Chang et al. 2003), which are embolism (20%), hemorrhage (17%) and pregnancy-induced hypertension (16%). Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy are also associated with impaired uteroplacental circulation and consequent intrauterine growth restriction (Miller et al. 2008). Hydralazine and labetalol are the most recommended drugs to control acute hypertension in pregnant women (ACOG 2002; NHBPEP 2000). Labetalol is a b-adrenergic blocker and nonselective a1 receptor blocker (Louis et al. 1984; Lund-Johansen 1984), which Address correspondence to: Wellington P. Martins, Departamento de Ginecologia e Obstetrıcia do Hospital das Clınicas - 8 andar, Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeir~ao Preto, Universidade de S~ao Paulo, Av Bandeirantes Campus da USP, Ribeir~ao Preto, S~ao Paulo, Brazil. wpmartins@gmail.com reduces the systemic vascular resistance without reducing cerebral, renal and coronary blood flow (Pearce and Wallin 1994). This drug has been used in pregnancyinduced hypertension because reduced placental transfer occurs, mainly due to low lipid solubility (Varon and Marik 2003). Hydralazine acts directly on smooth muscle, predominantly on the high resistance vessels (small arteries and arterioles) preserving the oxygenation of vital areas, such as the spleen, heart, brain and kidneys (Sato et al. 2003). However, the use of hydralazine was associated with higher rate of maternal hypotension, cesarean section, placental detachment, maternal oliguria and lower values for the 1 min Apgar compared with the use of oral nifedipine and labetalol (Magee et al. 2003) but the evidence was not sufficiently robust for clinical recommendation. The objective of treating severe hypertension is to avoid vascular damage (encephalopathy and hemorrhage) and congestive heart failure due to blood pressure elevation without causing excessive reduction in blood pressure that would critically affect uteroplacental 53
2 54 Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology Volume 37, Number 1, 2011 perfusion (Bolte et al. 2001; Vigil-De Gracia et al. 2006). In situations when uteroplacental perfusion is impaired, changes in uterine artery blood flow and subsequent adaptive changes in fetal circulation one should expect, what probably could be detected by Doppler ultrasound (Hoffman and Galan 2009). In this study we evaluate maternal blood pressure and Doppler ultrasound parameters of uterine, umbilical and middle cerebral arteries before and after acute severe hypertension treatment using either hydralazine or labetalol. METHODS Subjects Pregnant women in acute severe hypertension with gestational age between 20 and 32 weeks and body mass index #40 kg/m 2 were enrolled in this study. Acute severe hypertension was defined according to the guidelines of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program (NHBPEP): sustained high blood pressure: $160 mm Hg systolic, $105 mm Hg diastolic or both (NHBPEP 2000). We considered as sustained high blood pressure when high values were observed in two consecutive measurements at least 30 min apart. A total of 17 pregnant women who agreed to participate were randomly assigned to receive either labetalol or hydralazine but one was excluded from the study because both drugs were necessary to control blood pressure. Therefore, 16 patients were fully evaluated: eight were assigned to use hydralazine and the other eight to use labetalol. This study was approved by the local institutional review board and all subjects signed informed consent. Hypertension was classified according to the guidelines of the NHBPEP as chronic hypertension, pre-eclampsia-eclampsia, preeclampsia superimposed on chronic hypertension and gestational hypertension (NHBPEP 2000). In the labetalol group, there were four pre-eclampsia, one pre-eclampsia superimposed on chronic hypertension and three gestational hypertension; in the hydralazine group there were five pre-eclampsia, two gestational hypertension and one chronic hypertension. Sample size Considering described values for middle cerebral artery pulsatility index in women with pregnancy-induce hypertension: (Piazze et al. 2005), we need to evaluate eight women per group to have an 80% power to detect a 20% relative change in this parameter, considering a Blood pressure evaluation The maternal blood pressure was evaluated by using a standard mercury sphygmomanometer in the nondominant arm. Blood pressure was evaluated during acute severe hypertension and after labetalol or hydralazine. Treatment of acute severe hypertension Labetalol or hydralazine was used according to the American Congress of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) guidelines (2002): Hydralazine: 5 10-mg doses intravenously every min until blood pressure lower than 150/100 mm Hg Labetalol: 20-mg intravenous bolus dose followed by 40 mg if not effective within 10 min; then, 80 mg every 10 min until blood pressure lower than 150/100 mmhg or maximum total dose of 220 mg. The fetuses were monitored by Doppler assessment of fetal heart rate each 10 min after treatment until Doppler evaluation. Ultrasonography Maternal and fetal Doppler ultrasound (US) examinations were performed in a room with controlled temperature of about 23 C and moderate lighting. Before the US examination, the pregnant women rested for 10 min with their back supported in a 45 degree position to prevent compression of the inferior vena cava (Ryo et al. 1998). Doppler US was performed using an HDI 3500 ATL (Advanced Technologies Laboratories, Bothell, WA, USA), using a 2 5 MHz broadband probe. For evaluation by Doppler US, a low filter (100 Hz) was used to prevent loss of the diastolic flow component (Gallarreta et al. 2010; Maulik 1989) and the insonation angle was always less than 60 to avoid artifacts in the spectral Doppler (Gallarreta et al. 2010). Doppler US of the maternal uterine arteries was performed with the women breathing spontaneously. After identification of the vessel on the oblique plane, the sample was positioned 1 cm distal to the point of anatomical crossing with the external iliac artery and the angle was corrected until five similar consecutive waves were obtained. Doppler analysis of the fetal umbilical artery and middle cerebral arteries was performed during periods of fetal rest in the presence of a fetal heart rate of 120 to 160 bpm. For the acquisition of the tracing of the umbilical artery, the artery was identified with color Doppler of a free loop and the 3 mm samples was positioned in such a way as to permit evaluation of both the artery and vein, with the Doppler spectrum being evaluated until five similar consecutive waves were obtained by free loop color Doppler. For the identification of the fetal middle cerebral artery, an axial section of the fetal head was obtained at the level of the thalamus and of the cavum septum pellucidum. The transducer was then moved up to the Willis polygon and the pulsation of the two middle cerebral arteries was observed. With the aid of the amplitude
3 Hypertension treatment with hydralazine or labetalol d M. R. F. BAGGIO et al. 55 Doppler it was possible to identify the artery to be studied, with the spectral Doppler being then activated. The dial was calibrated for a sample volume of 1 mm and placed on the middle cerebral artery as close as possible to the skull cap, before its bifurcation (Luzi et al. 1996). The resistance index (RI) of these waves was calculated as systolic velocity diastolic velocity/ systolic velocity using the manual mode for the middle cerebral and umbilical arteries, while the pulsatility index (PI) was determined for the uterine arteries as (systolic velocity diastolic velocity)/mean velocity. Laboratory evaluation Serum concentrations of hemoglobin, platelets, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), creatinine, total bilirubin and urea were determined in blood samples collected from pregnant women during the acute severe hypertension. Statistical analysis Statistical analysis used the software PASW 18.0 for Windows (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Kolmogorov- Smirnov test was used to assess normality of the evaluated parameters. We compared the values obtained for the age of pregnant women, gestational age and laboratory tests, among pregnant women who used hydralazine or labetalol, by unpaired t-test. Concerning uterine artery PI and RI, we compare the values using paired t-test. Since no significant differences were observed between right and left uterine artery PI and RI, we used the average value for all other comparisons (Manetta et al. 2008). In both groups the blood pressure, heart rate and Doppler parameters values observed during acute severe hypertension were compared with values observed after labetalol or hydralazine by using the paired t-test. The observed changes in these parameters [(value observed after labetalol or hydralazine) (value observed during acute severe hypertension)] were compared between the groups by using the unpaired t-test. Significance level was considered as p,.05. RESULTS No significant difference was observed when comparing age, gestational age and laboratory tests between pregnant women randomized to receive either hydralazine or labetalol (Table 1). When comparing blood pressure and Doppler parameters values observed during acute severe hypertension and after treatment with hydralazine or labetalol until blood pressure lower than 150/100 mm Hg we observed a significant reduction in systolic and diastolic blood pressure in both groups (Table 2). When evaluating uterine artery Doppler parameters, a significant increase in RI was observed in pregnant women who received hydralazine, while a trend to decrease in both RI and PI of uterine arteries was observed in those who received labetatol (Table 2). When comparing maternal and fetal heart rate before and after treatment no significant differences were observed in both hydralazine (maternal heart rate: bpm vs bpm, p ; fetal heart rate: bpm vs bpm, p ; pre- vs. post treatment values, respectively) and labetalol groups (maternal heart rate: bpm vs bpm, p ; fetal heart rate: bpm vs bpm, p ; pre- vs. post treatment values, respectively). When comparing changes in the evaluated parameters between pregnant women who received hydralazine or labetalol, a significant difference was observed only in uterine artery RI (p ) (Table 3). DISCUSSION Acute severe hypertension is associated with generalized arteriolar vasoconstriction and reduced flow uteroplacental and consequent deficit of oxygen supply in the areas of maternal fetal exchange, submitting the fetus to Table 1. Comparison of age, gestational age and laboratory tests between pregnant women randomized to receive either hydralazine or labetalol Hydralazine Labetalol Mean SD Mean SD p Age (years) Gestational age (weeks) Hemoglobin (g/dl) Platelets (1.000/mm 3 ) AST (IU/L) Creatinine (mg/dl) Total bilirubin (mg/dl) Urea (mg/dl) p values obtained by unpaired t-test. AST 5 aspartate aminotransferase.
4 56 Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology Volume 37, Number 1, 2011 Table 2. Comparison of blood pressure and Doppler parameters from maternal uterine arteries and fetal middle cerebral and umbilical arteries observed during acute severe hypertension (pre) with values observed after labetalol or hydralazine (post) Pre Post Hydralazine Mean SD Mean SD p Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) ,0.01 Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) ,0.01 Umbilical artery PI Umbilical artery RI Middle cerebral artery PI Middle cerebral artery RI Uterine artery PI Uterine artery RI Pre Post Labetalol Mean SD Mean SD p Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) ,0.01 Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) ,0.01 Umbilical artery PI Umbilical artery RI Middle cerebral artery PI Middle cerebral artery RI Uterine artery PI Uterine artery RI p values were obtained by using paired t-test. PI 5 pulsatility index; RI 5 resistance index. hypoxia (Williams and Wilson 1999). The administration of antihypertensive drugs may increase the uteroplacental flow, due to the reduction of uterine vascular resistance; however, blood pressure reduction may cause a reverse effect, reducing uteroplacental flow and worsening the intra-uterine conditions. A recent meta-analysis suggested that intravenous labetalol is as effective as and has fewer side effects than intravenous hydralazine (Magee et al. 2003). In this meta-analysis authors evaluated five trials that compared hydralazine with labetalol: hydralazine was associated with significantly higher maternal side effects and worse maternal and perinatal outcomes than labetalol. On the other hand, a more recent randomized controlled clinical trial evaluating 200 pregnant women with severe hypertension in pregnancy receiving either hydralazine or labetalol found similar maternal and neonatal outcomes between the two groups (Vigil-De Gracia et al. 2006): palpitations and tachycardia were more common in women using hydralazine, while neonatal bradycardia and hypotension were more common with labetalol; and exactly two neonatal and no maternal deaths occurred in each group. Additionally, the authors from another recent meta-analysis evaluating hypertensive drugs for very high blood pressure during pregnancy concluded that until better evidence is available, the choice of antihypertensive should depend on the clinician s experience and familiarity with a particular drug because until now there is insufficient data proving superiority of one drug over others (Duley et al. 2006). Table 3. Comparison of the observed changes in the blood pressure and Doppler parameters from maternal uterine arteries and fetal middle cerebral and umbilical arteries between pregnant women who use hydralazine or labetalol Hydralazine Labetalol Mean SD Mean SD p Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) Umbilical artery PI Umbilical artery RI Middle cerebral artery PI Middle cerebral artery RI Uterine artery PI Uterine artery RI p values were obtained by using paired t-test. Change 5 [(value observed after labetalol or hydralazine) (value observed during acute severe hypertension)]. PI 5 pulsatility index; RI 5 resistance index.
5 Hypertension treatment with hydralazine or labetalol d M. R. F. BAGGIO et al. 57 In our study, both drugs were very effective in reducing blood pressure and in only one pregnant woman we needed to use both drugs to reduce blood pressure to more desirable levels. Both hydralazine and labetalol are now considered as first-line drugs in the treatment of severe hypertension (Vigil-De Gracia et al. 2006): hydralazine has been used safely in pregnant women for several decades and is, therefore, considered the treatment as the first alternative by some guidelines (ACOG 2002; NHBPEP 2000). Labetalol, an a- and b-adrenergic blocker with both immediate and prolonged effect, also proved to be very safe and is being frequently used (Caetano et al. 2004) and recommended to treat severe hypertension in pregnancy (Frias and Belfort 2003; Leeman and Fontaine 2008). Concerning Doppler evaluation, an increase in uterine arteries RI was observed in pregnant women who received hydralazine, while the use of labetalol was associated with a trend of decrease in uterine arteries PI and RI. Therefore, one should conclude that these results favor labetalol, since this drug was associated with improvement in uteroplacental blood flow, while hydralazine worsened the resistance index. The significant difference in the change of uterine artery resistance observed in pregnant women who received hydralazine might be a consequence of greater (but not significant) reduction in blood pressure observed in women using hydralazine (Table 3): the observed change in systolic blood pressure was vs , with p (hydralazine vs. labetalol, respectively) and the observed change in diastolic blood pressure was vs , with p This observation is in accordance with higher rates of maternal hypotension observed with hydralazine compared to labetalol (Magee et al. 2003) and greater reductions in blood pressure are not desirable because low blood pressure can impair uteroplacental circulation. On the other hand, in situations where fetal oxygenation is reduced, several changes in fetal hemodynamics occur in an attempt to preserve vital organs, such as central nervous system, which would be noticed by Doppler ultrasound, e.g., a resistance reduction in middle cerebral arteries (Hoffman and Galan 2009). Since the use of both drugs were not associated with significant changes in fetal Doppler ultrasound parameters, further conclusions about negative effect of hydralazine on uteroplacental circulation would be still premature. A criticism to this evidence is the small sample evaluated by this study, which does not have the sufficient power to evaluate more subtle changes (e.g.,,20% of relative change). Another interesting point was to consider that women with chronic hypertension (and longer-standing disease) may respond differently from those with hypertension occurring only during the current pregnancy; however, our sample was not sufficiently big enough to permit such stratification. In conclusion, we observed that both drugs were highly effective in reducing blood pressure of pregnant women with very high blood pressure. Although the use of hydralazine has caused worse changes in uterine arteries resistance index, the use of both drugs were not related to any significant changes in Doppler evaluation of fetal hemodynamic and this information is reassuring about the safety of these drugs in the treatment of severe acute hypertension during pregnancy. Therefore, the choice between these two drugs should be based in other criteria such as respective contraindications, costs, availability and clinician s experience. REFERENCES ACOG. ACOG practice bulletin. Diagnosis and management of preeclampsia and eclampsia. Number 33, January Obstet Gynecol 2002;99: Bolte AC, van Geijn HP, Dekker GA. Management and monitoring of severe preeclampsia. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2001;96: Caetano M, Ornstein MP, Von Dadelszen P, Hannah ME, Logan AG, Gruslin A, Willan A, Magee LA. A survey of Canadian practitioners regarding the management of the hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Hypertens Pregnancy 2004;23: Chang J, Elam-Evans LD, Berg CJ, Herndon J, Flowers L, Seed KA, Syverson CJ. Pregnancy-related mortality surveillance United States, MMWR Surveill Summ 2003;52:1 8. Duley L, Henderson-Smart DJ, Meher S. Drugs for treatment of very high blood pressure during pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2006;3: CD Frias AE Jr, Belfort MA. Post Magpie: How should we be managing severe preeclampsia? Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 2003;15: Gallarreta FM, Martins WP, Nastri CO, Mauad Filho F, Nicolau LG, Barra DA, Morais EN, Crott GC. Evaluation of ductus venosus and inferior vena cava by using multiple Doppler ultrasound parameters in healthy fetuses. Arch Gynecol Obstet Hoffman C, Galan HL. Assessing the at-risk fetus: Doppler ultrasound. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 2009;21: Leeman L, Fontaine P. Hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Am Fam Physician 2008;78: Louis WJ, McNeil JJ, Drummer OH. Pharmacology of combined alpha-beta-blockade. I. Drugs 1984;28(Suppl 2): Lund-Johansen P. Pharmacology of combined alpha-beta-blockade. II. Haemodynamic effects of labetalol. Drugs 1984;28(Suppl 2): Luzi G, Coata G, Caserta G, Cosmi EV, Di Renzo GC. Doppler velocimetry of different sections of the fetal middle cerebral artery in relation to perinatal outcome. J Perinat Med 1996;24: Magee LA, Cham C, Waterman EJ, Ohlsson A, von Dadelszen P. Hydralazine for treatment of severe hypertension in pregnancy: Meta-analysis. BMJ 2003;327: Manetta LA, de Paula Martins W, Rosa e Silva JC, de Sa Rosa e Silva AC, Nogueira AA, Ferriani RA. Uterine ultrasonographic changes during endometriosis treatment: A comparison between levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine devices and a gonadotropinreleasing hormone agonist. Ultrasound Med Biol 2008;34: Maulik D. Basic principles of Doppler ultrasound as applied in obstetrics. Clin Obstet Gynecol 1989;32: Miller J, Turan S, Baschat AA. Fetal growth restriction. Semin Perinatol 2008;32: NHBPEP. Report of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program Working Group on High Blood Pressure in Pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2000;183:S1 S22.
6 58 Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology Volume 37, Number 1, 2011 Pearce CJ, Wallin JD. Labetalol and other agents that block both alphaand beta-adrenergic receptors. Cleve Clin J Med 1994;61:59 69: quiz Piazze J, Padula F, Cerekja A, Cosmi EV, Anceschi MM. Prognostic value of umbilical-middle cerebral artery pulsatility index ratio in fetuses with growth restriction. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2005;91: Povoa AM, Costa F, Rodrigues T, Patricio B, Cardoso F. Prevalence of hypertension during pregnancy in Portugal. Hypertens Pregnancy 2008;27: Ryo E, Okai T, Takagi K, Okuno S, Sadatsuki M, Kaneko M, Taketani Y. Comparison of umbilical artery Doppler velocimetry between maternal supine position and complete left lateral position in predicting obstetric complications. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1998;11: Sato N, Tanaka KA, Szlam F, Tsuda A, Arias ME, Levy JH. The vasodilatory effects of hydralazine, nicardipine, nitroglycerin, and fenoldopam in the human umbilical artery. Anesth Analg 2003;96: Varon J, Marik PE. Clinical review: The management of hypertensive crises. Crit Care 2003;7: Vigil-De Gracia P, Lasso M, Ruiz E, Vega-Malek JC, de Mena FT, Lopez JC. Severe hypertension in pregnancy: Hydralazine or labetalol. A randomized clinical trial. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2006;128: Williams KP, Wilson S. Antepartum middle mean cerebral blood flow velocity correlation with maternal hemodynamics. Hypertens Pregnancy 1999;18:
Comparison of Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Labetalol Versus Hydralazine for Management of Severe Hypertension in Pregnancy
 https://doi.org/10.1007/s13224-017-1053-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Labetalol Versus Hydralazine for Management of Severe Hypertension in Pregnancy Purvi Patel 1
https://doi.org/10.1007/s13224-017-1053-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Efficacy and Safety of Intravenous Labetalol Versus Hydralazine for Management of Severe Hypertension in Pregnancy Purvi Patel 1
CMQCC Preeclampsia Tool Kit: Hypertensive Disorders Across the Lifespan
 CMQCC Preeclampsia Tool Kit: Hypertensive Disorders Across the Lifespan Carol J Harvey, MS, BSN, RNC-OB, C-EFM, CS Northside Hospital Atlanta Cherokee - Forsyth New! Improving Health Care Response to Preeclampsia:
CMQCC Preeclampsia Tool Kit: Hypertensive Disorders Across the Lifespan Carol J Harvey, MS, BSN, RNC-OB, C-EFM, CS Northside Hospital Atlanta Cherokee - Forsyth New! Improving Health Care Response to Preeclampsia:
AWHONN Oregon Section 2014
 AWHONN Oregon Section 2014 Carol J Harvey, MS, BSN, RNC-OB, C-EFM, CS Northside Hospital Atlanta Cherokee - Forsyth Hypertensive in Pregnancy Carol J Harvey, MS, RNC-OB, C-EFM Clinical Specialist Northside
AWHONN Oregon Section 2014 Carol J Harvey, MS, BSN, RNC-OB, C-EFM, CS Northside Hospital Atlanta Cherokee - Forsyth Hypertensive in Pregnancy Carol J Harvey, MS, RNC-OB, C-EFM Clinical Specialist Northside
The Fetus: Five Top Do Not Miss Diagnoses. Doppler Ultrasound
 The Fetus: Five Top Do Not Miss Diagnoses Doppler Ultrasound Giancarlo Mari, MD, MBA Professor and Chair Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, TN
The Fetus: Five Top Do Not Miss Diagnoses Doppler Ultrasound Giancarlo Mari, MD, MBA Professor and Chair Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Tennessee Health Science Center Memphis, TN
Policy REVISED: 6/30/2016 3:30 PM. Applies To: ObGyn Responsible Department: ObGyn Revised: June 30, 2016
 Title: Antihypertensive Treatment for Severe Hypertension During Pregnancy Applies To: ObGyn Responsible Department: ObGyn Revised: June 30, 2016 Policy POLICY STATEMENT: Pregnant or postpartum patients
Title: Antihypertensive Treatment for Severe Hypertension During Pregnancy Applies To: ObGyn Responsible Department: ObGyn Revised: June 30, 2016 Policy POLICY STATEMENT: Pregnant or postpartum patients
39 th Annual Perinatal Conference Vanderbilt University December 6, 2013 IUGR. Diagnosis and Management
 39 th Annual Perinatal Conference Vanderbilt University December 6, 2013 IUGR Diagnosis and Management Giancarlo Mari, M.D., M.B.A. Professor and Chair Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University
39 th Annual Perinatal Conference Vanderbilt University December 6, 2013 IUGR Diagnosis and Management Giancarlo Mari, M.D., M.B.A. Professor and Chair Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University
You admitted a previously healthy nullipara at 36 weeks gestation who presented with new-onset periorbital edema and is found to have blood pressure
 Preeclampsia Case report You admitted a previously healthy nullipara at 36 weeks gestation who presented with new-onset periorbital edema and is found to have blood pressure readings of 150/100 to 155/105
Preeclampsia Case report You admitted a previously healthy nullipara at 36 weeks gestation who presented with new-onset periorbital edema and is found to have blood pressure readings of 150/100 to 155/105
Stroke in Pregnancy. Stroke in Pregnancy 6/23/13
 G5#$#Preven*ng#Maternal#Morbidity#and#Mortality#Via# Expanded#Scope#of#Nursing#Prac*ce#As#First#Responder# in#hypertensive#crisis#of#preeclampsia# The$presenter$reports$no$relevant,$influencing$financial$rela5onships.$
G5#$#Preven*ng#Maternal#Morbidity#and#Mortality#Via# Expanded#Scope#of#Nursing#Prac*ce#As#First#Responder# in#hypertensive#crisis#of#preeclampsia# The$presenter$reports$no$relevant,$influencing$financial$rela5onships.$
Mercy San Juan Medical Center. Preeclampsia and Other Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy
 SUBJECT: Preeclampsia and Other Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy DEPARTMENTS: FBC, Emergency Department PURPOSE: To outline the nursing management of inpatients who have preeclampsia or other hypertensive
SUBJECT: Preeclampsia and Other Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy DEPARTMENTS: FBC, Emergency Department PURPOSE: To outline the nursing management of inpatients who have preeclampsia or other hypertensive
Declaration of conflict of interest
 Declaration of conflict of interest Claudio Borghi Lectures fees: Menarini International, Servier International, Recordati International, Ely-Lilly USA, BMS, Boheringer Ingelheim, Novartis Pharma Research
Declaration of conflict of interest Claudio Borghi Lectures fees: Menarini International, Servier International, Recordati International, Ely-Lilly USA, BMS, Boheringer Ingelheim, Novartis Pharma Research
Optimising your Doppler settings for an accurate PI. Alison McGuinness Mid Yorks Hospitals
 Optimising your Doppler settings for an accurate PI Alison McGuinness Mid Yorks Hospitals Applications Both maternal uterine and fetal circulations can be studied with doppler sonography Uterine arteries
Optimising your Doppler settings for an accurate PI Alison McGuinness Mid Yorks Hospitals Applications Both maternal uterine and fetal circulations can be studied with doppler sonography Uterine arteries
MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY, THE ALGORHITHM
 MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY, THE ALGORHITHM Are Particular Anti-hypertensives More Effective or Harmful Than Others in Hypertension in Pregnancy? Existing data is inadequate Methyldopa and
MANAGEMENT OF HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY, THE ALGORHITHM Are Particular Anti-hypertensives More Effective or Harmful Than Others in Hypertension in Pregnancy? Existing data is inadequate Methyldopa and
INTRAVENOUS HYDRALAZINE POLICY
 PURPOSE INTRAVENOUS HYDRALAZINE POLICY The purpose of this policy is to: provide safe and effective care for women establish a local approach to care that is evidence based and consistent inform good decision
PURPOSE INTRAVENOUS HYDRALAZINE POLICY The purpose of this policy is to: provide safe and effective care for women establish a local approach to care that is evidence based and consistent inform good decision
Diagnosis and Management of the Early Growth Restricted Fetus
 11 th Congress of Maternal Fetal Medicine and Perinatology Society of Turkey Diagnosis and Management of the Early Growth Restricted Fetus Giancarlo Mari, MD, MBA, FACOG, FAIUM Professor and Chair Department
11 th Congress of Maternal Fetal Medicine and Perinatology Society of Turkey Diagnosis and Management of the Early Growth Restricted Fetus Giancarlo Mari, MD, MBA, FACOG, FAIUM Professor and Chair Department
Magnesium sulfate has an antihypertensive effect on severe pregnancy induced hypertension
 Hypertension Research In Pregnancy 11 S. Takenaka et al. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Magnesium sulfate has an antihypertensive effect on severe pregnancy induced hypertension Shin Takenaka 1, Ryu Matsuoka 2, Daisuke
Hypertension Research In Pregnancy 11 S. Takenaka et al. ORIGINAL ARTICLE Magnesium sulfate has an antihypertensive effect on severe pregnancy induced hypertension Shin Takenaka 1, Ryu Matsuoka 2, Daisuke
CHAPTER 12 HYPERTENSION IN SPECIAL GROUPS HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY
 CHAPTER 12 HYPERTENSION IN SPECIAL GROUPS HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY v Mild preeclampsia is managed by close observation of the mother and fetus preferably in hospital. If the diastolic blood pressure remains
CHAPTER 12 HYPERTENSION IN SPECIAL GROUPS HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY v Mild preeclampsia is managed by close observation of the mother and fetus preferably in hospital. If the diastolic blood pressure remains
Clinical features. Abnormal vasculogenesis and angiogenesis and releasing of antiangiogenic
 Clinical features Abnormal vasculogenesis and angiogenesis and releasing of antiangiogenic factors results in Vasospasm Endothelial dysfunction Etiology of various clinical signs and symptoms So, Preeclampsia
Clinical features Abnormal vasculogenesis and angiogenesis and releasing of antiangiogenic factors results in Vasospasm Endothelial dysfunction Etiology of various clinical signs and symptoms So, Preeclampsia
Hypertensives Emergency and Urgency
 Hypertensives Emergency and Urgency Budi Yuli Setianto Cardiology Divisision Department of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine UGM Sardjito Hospital Yogyakarta Background USA: Hypertension is 30% of
Hypertensives Emergency and Urgency Budi Yuli Setianto Cardiology Divisision Department of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine UGM Sardjito Hospital Yogyakarta Background USA: Hypertension is 30% of
Based on 2014 SOGC Guidelines
 Based on 2014 SOGC Guidelines 22nd Edition 2015 1 ICH + gestational hypertension by far the biggest cause of direct maternal deaths New stats coming in 2013 OCR 22nd Edition 2015 2 Diastolic 90 mmhg is
Based on 2014 SOGC Guidelines 22nd Edition 2015 1 ICH + gestational hypertension by far the biggest cause of direct maternal deaths New stats coming in 2013 OCR 22nd Edition 2015 2 Diastolic 90 mmhg is
PIAF study: Placental insufficiency and aortic isthmus flow Jean-Claude Fouron, MD
 Dear colleagues, I would like to thank you very sincerely for agreeing to participate in our multicentre study on the clinical significance of recording fetal aortic isthmus flow during placental circulatory
Dear colleagues, I would like to thank you very sincerely for agreeing to participate in our multicentre study on the clinical significance of recording fetal aortic isthmus flow during placental circulatory
PREGNANCY INDUCED HYPERTENSION; TO COMPARE EFFICACY OF METHYLDOPA AND LABETALOL IN MANAGEMENT
 The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.17957/TPMJ/16.3489 ORIGINAL PROF-3489 PREGNANCY INDUCED HYPERTENSION; TO COMPARE EFFICACY OF METHYLDOPA AND LABETALOL IN MANAGEMENT naadiasharif@hotmail.com 1.
The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.17957/TPMJ/16.3489 ORIGINAL PROF-3489 PREGNANCY INDUCED HYPERTENSION; TO COMPARE EFFICACY OF METHYLDOPA AND LABETALOL IN MANAGEMENT naadiasharif@hotmail.com 1.
4/19/2018. St. Cloud Hospital Perinatology Kristin Olson, RDMS, RVT
 St. Cloud Hospital Perinatology Kristin Olson, RDMS, RVT Review Fetal Circulation Provide Indications for Umbilical Artery, Middle Cerebral Artery, and Ductus Venosus Doppler studies. Demonstrate normal
St. Cloud Hospital Perinatology Kristin Olson, RDMS, RVT Review Fetal Circulation Provide Indications for Umbilical Artery, Middle Cerebral Artery, and Ductus Venosus Doppler studies. Demonstrate normal
Int J Adv Pharm Biol Sci Vol.2, Issue 3, COMPARISON BETWEEN NIFEDIPINE AND METHYLDOPA ON BLOOD PRESSURE AND FETAL OUTCOME IN PRE-ECLAMPSIA
 Int J Adv Pharm Biol Sci Vol.2, Issue 3, 191-198 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCE PHARMACEUTICAL AND BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES Vol. 2, Issue. 3, July-September 2012 ISSN 2249 8966 Research Article Available
Int J Adv Pharm Biol Sci Vol.2, Issue 3, 191-198 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCE PHARMACEUTICAL AND BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES Vol. 2, Issue. 3, July-September 2012 ISSN 2249 8966 Research Article Available
Key issues in (early and late) IUGR
 Key issues in (early and late) IUGR Eduard Gratacós Maternal-Fetal Medicine Department, Hospital Clínic, University of Barcelona www.fetalmedicinebarcelona.org (early-onset) IUGR vs SGA: the era of UA
Key issues in (early and late) IUGR Eduard Gratacós Maternal-Fetal Medicine Department, Hospital Clínic, University of Barcelona www.fetalmedicinebarcelona.org (early-onset) IUGR vs SGA: the era of UA
Shock is defined as a state of cellular and tissue hypoxia due to : reduced oxygen delivery and/or increased oxygen consumption or inadequate oxygen
 Shock is defined as a state of cellular and tissue hypoxia due to : reduced oxygen delivery and/or increased oxygen consumption or inadequate oxygen utilization The effects of shock are initially reversible
Shock is defined as a state of cellular and tissue hypoxia due to : reduced oxygen delivery and/or increased oxygen consumption or inadequate oxygen utilization The effects of shock are initially reversible
Basic Doppler Assessment of Fetal Distress
 Basic Doppler Assessment of Fetal William J. Polzin, M.D. Co-Director, Fetal Care Center of Cincinnati Director, Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Good Samaritan Hospital Cincinnati, OH No Relevant Disclosures
Basic Doppler Assessment of Fetal William J. Polzin, M.D. Co-Director, Fetal Care Center of Cincinnati Director, Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Good Samaritan Hospital Cincinnati, OH No Relevant Disclosures
DRUG GUIDELINE. HYDRALAZINE (Intravenous severe hypertension in pregnancy)
 DRUG GUIDELINE HYDRALAZINE (Intravenous severe hypertension SCOPE (Area): FOR USE IN: Labour Ward, HDU, Theatre and ED EXCLUSIONS: Paediatrics (seek Paediatrician advice) and other general wards. SCOPE
DRUG GUIDELINE HYDRALAZINE (Intravenous severe hypertension SCOPE (Area): FOR USE IN: Labour Ward, HDU, Theatre and ED EXCLUSIONS: Paediatrics (seek Paediatrician advice) and other general wards. SCOPE
Outcomes of Pregnancies at Risk for Hypertensive Complications Managed Using Impedance Cardiography
 Outcomes of Pregnancies at Risk for Hypertensive Complications Managed Using Impedance Cardiography David G. Chaffin, M.D., 1 and Denise G. Webb, RNC, BSN 2 ABSTRACT We assessed the effect of antihypertensive
Outcomes of Pregnancies at Risk for Hypertensive Complications Managed Using Impedance Cardiography David G. Chaffin, M.D., 1 and Denise G. Webb, RNC, BSN 2 ABSTRACT We assessed the effect of antihypertensive
C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet. C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart
 Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
Name: Date: C3, 4, 5, 6, & 7 Worksheet C3 Describe the inter-relationships of the structures of the heart 1. Label and give the functions of the following: a. left and right atrium: b. left and right ventricle:
The short-term effect of nifedipine tocolysis on placental, fetal cerebral and atrioventricular Doppler waveforms
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 004; 4: 761 765 Published online 6 October 004 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.100/uog.1770 The short-term effect of nifedipine tocolysis on placental,
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 004; 4: 761 765 Published online 6 October 004 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.100/uog.1770 The short-term effect of nifedipine tocolysis on placental,
Research Article ISSN Vol 2/Issue 1/Jan-Mar 2012
 A COMPARATIVE RANDOMISED CONTROLLED PARALLEL GROUP STUDY OF EFFICACY AND TOLERABILITY OF LABETALOL VERSUS METHYLDOPA IN THE TREATMENT OF NEW ONSET HYPERTENSION DURING PREGNANCY REENA VERMA 1, *KINGSHUK
A COMPARATIVE RANDOMISED CONTROLLED PARALLEL GROUP STUDY OF EFFICACY AND TOLERABILITY OF LABETALOL VERSUS METHYLDOPA IN THE TREATMENT OF NEW ONSET HYPERTENSION DURING PREGNANCY REENA VERMA 1, *KINGSHUK
The Role of the Anaesthesiologist in the Perioperative Management of Preeclampsia. RA Dyer Interlaken 2017
 The Role of the Anaesthesiologist in the Perioperative Management of Preeclampsia RA Dyer Interlaken 2017 6 In preeclampsia - Understanding of pathophysiology Assessment of disease severity Prediction
The Role of the Anaesthesiologist in the Perioperative Management of Preeclampsia RA Dyer Interlaken 2017 6 In preeclampsia - Understanding of pathophysiology Assessment of disease severity Prediction
Tocolytics. Tocolytics (terbutaline, magnesium sulfate injection) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.30.06 Subject: Tocolytics Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 15, 2016 Tocolytics Description Tocolytics
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.30.06 Subject: Tocolytics Page: 1 of 5 Last Review Date: September 15, 2016 Tocolytics Description Tocolytics
What effects will proximal or distal disease have on a waveform?
 Spectral Doppler Interpretation Director of Ultrasound Education & Quality Assurance Baylor College of Medicine Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Maternal Fetal Center Imaging Manager Texas Children
Spectral Doppler Interpretation Director of Ultrasound Education & Quality Assurance Baylor College of Medicine Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Maternal Fetal Center Imaging Manager Texas Children
Hemodynamic Changes in Obstetric Anesthesia. Sonia Vaida PANA, Hershey, April 2009
 Hemodynamic Changes in Obstetric Anesthesia Sonia Vaida PANA, Hershey, April 2009 Pregnancy is a normal healthy condition and is simultaneously the most common altered physiologic state to which human
Hemodynamic Changes in Obstetric Anesthesia Sonia Vaida PANA, Hershey, April 2009 Pregnancy is a normal healthy condition and is simultaneously the most common altered physiologic state to which human
Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients
 Article Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients Zeev Weiner, MD, Abraham Lorber, MD, Eliezer Shalev, MD Objective. To examine the feasibility of
Article Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients Zeev Weiner, MD, Abraham Lorber, MD, Eliezer Shalev, MD Objective. To examine the feasibility of
Agonistic Autoantibodies to Angiotensin II Type I Receptor Contributes Partly to Placental Ischemia-Induced Cerebrovascular Abnormalities
 Agonistic Autoantibodies to Angiotensin II Type I Receptor Contributes Partly to Placental Ischemia-Induced Cerebrovascular Abnormalities Junie Paula Warrington 1, Fan Fan 1, Babbette B. LaMarca 1, Ralf
Agonistic Autoantibodies to Angiotensin II Type I Receptor Contributes Partly to Placental Ischemia-Induced Cerebrovascular Abnormalities Junie Paula Warrington 1, Fan Fan 1, Babbette B. LaMarca 1, Ralf
LEARNING OBJECTIVES 2/20/2017
 HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY: PREVENTING SEVERE MATERNAL MORBIDITY & MORTALITY THROUGH THE IMPLEMENTATION OF EVIDENCED BASED PROTOCOLS Laura Senn, RN, PhD, CNS Sutter Medical Center, Sacramento LEARNING OBJECTIVES
HYPERTENSION IN PREGNANCY: PREVENTING SEVERE MATERNAL MORBIDITY & MORTALITY THROUGH THE IMPLEMENTATION OF EVIDENCED BASED PROTOCOLS Laura Senn, RN, PhD, CNS Sutter Medical Center, Sacramento LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Research Article Relation of Hyperuricemia with Maternal and Perinatal Complications in Severe Preeclampsia
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC GYNAECOLOGY Research Article Relation of Hyperuricemia with Maternal and Perinatal Complications in Severe Preeclampsia Armando Alberto Moreno Santillan 1, Daniela Yesenia Paz Cervantes
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC GYNAECOLOGY Research Article Relation of Hyperuricemia with Maternal and Perinatal Complications in Severe Preeclampsia Armando Alberto Moreno Santillan 1, Daniela Yesenia Paz Cervantes
From Head to Toe Use of Advanced Dynamic Flow in prenatal ultrasound
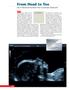 From Head to Toe Use of Advanced Dynamic Flow in prenatal ultrasound Without doubt, the B- Schwerdtfeger, R. tant diagnostic instrument. Furthermore, we use colour in feto- mode imaging is the most important
From Head to Toe Use of Advanced Dynamic Flow in prenatal ultrasound Without doubt, the B- Schwerdtfeger, R. tant diagnostic instrument. Furthermore, we use colour in feto- mode imaging is the most important
Preeclampsia: What s old is new again. Gene Chang, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine
 Preeclampsia: What s old is new again Gene Chang, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Objectives Define Preeclampsia Review current guidelines Role of proteinuria Timing of delivery Seizure prevention Severe Hypertension
Preeclampsia: What s old is new again Gene Chang, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Objectives Define Preeclampsia Review current guidelines Role of proteinuria Timing of delivery Seizure prevention Severe Hypertension
Disclosure Information : No conflict of interest
 Intravenous nicorandil improves symptoms and left ventricular diastolic function immediately in patients with acute heart failure : a randomized, controlled trial M. Shigekiyo, K. Harada, A. Okada, N.
Intravenous nicorandil improves symptoms and left ventricular diastolic function immediately in patients with acute heart failure : a randomized, controlled trial M. Shigekiyo, K. Harada, A. Okada, N.
Management of Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
 Background and Prevalence Management of Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Pregestational Diabetes - 8 million women in the US are affected, complicating 1% of all pregnancies. Type II is
Background and Prevalence Management of Pregestational and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Pregestational Diabetes - 8 million women in the US are affected, complicating 1% of all pregnancies. Type II is
Hypertension - Management of Acute
 1. Purpose Severe hypertensive disorders of pregnancy are associated with high rates of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality. It is imperative in this clinical situation that severe blood pressure
1. Purpose Severe hypertensive disorders of pregnancy are associated with high rates of maternal and fetal morbidity and mortality. It is imperative in this clinical situation that severe blood pressure
Management of IUGR Prof. Dr. Acar KOÇ
 Management of IUGR Prof. Dr. Acar KOÇ Ankara University School of Medicine Department of OB&GYN Department of Perinatology Definition and Diagnosis: SGA IUGR EFW: < 10th percentile EFW: < 10th percentile
Management of IUGR Prof. Dr. Acar KOÇ Ankara University School of Medicine Department of OB&GYN Department of Perinatology Definition and Diagnosis: SGA IUGR EFW: < 10th percentile EFW: < 10th percentile
Nifedipine Tocolysis Regime Policy
 Document ID: MATY072 Version: 1.0 Facilitated by: Karen Wakelin, ACMM Issue Date: August 2010 Approved by: Maternity Quality Committee Review date: October 2017 Nifedipine Tocolysis Regime Policy Policy
Document ID: MATY072 Version: 1.0 Facilitated by: Karen Wakelin, ACMM Issue Date: August 2010 Approved by: Maternity Quality Committee Review date: October 2017 Nifedipine Tocolysis Regime Policy Policy
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Questionnaire-based study of cerebrovascular complications during pregnancy in Aichi Prefecture, Japan
 Hypertension Research Eclampsia and stroke In Pregnancy during pregnancy 40 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Questionnaire-based study of cerebrovascular complications during pregnancy in Aichi Prefecture, Japan Yasumasa
Hypertension Research Eclampsia and stroke In Pregnancy during pregnancy 40 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Questionnaire-based study of cerebrovascular complications during pregnancy in Aichi Prefecture, Japan Yasumasa
Venous Doppler Evaluation of the Growth-Restricted Fetus
 Venous Doppler Evaluation of the Growth-Restricted Fetus Ahmet Alexander Baschat, MD KEYWORDS Fetal growth restriction Doppler Ductus venosus Venous circulation Fetal surveillance Integrated testing The
Venous Doppler Evaluation of the Growth-Restricted Fetus Ahmet Alexander Baschat, MD KEYWORDS Fetal growth restriction Doppler Ductus venosus Venous circulation Fetal surveillance Integrated testing The
Counseling and Long-term Follow up After Gestational Disorders
 Counseling and Long-term Follow up After Gestational Disorders Tanya Melnik, MD Assistant Professor, University of Minnesota Sarina Martini, MD Ob/Gyn Resident, PGY4 University of Minnesota Counseling
Counseling and Long-term Follow up After Gestational Disorders Tanya Melnik, MD Assistant Professor, University of Minnesota Sarina Martini, MD Ob/Gyn Resident, PGY4 University of Minnesota Counseling
Kofinas Perinatal Providing Care to the Unborn
 Alexander D. Kofinas, MD Director, Kofinas Perinatal Associate Professor, Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology Cornell University, College of Medicine Patient instructions for the use of Indomethacin and
Alexander D. Kofinas, MD Director, Kofinas Perinatal Associate Professor, Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology Cornell University, College of Medicine Patient instructions for the use of Indomethacin and
Evaluation of normal fetal pulmonary veins from the early second trimester by enhanced-flow (e-flow) echocardiography
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 211; 38: 652 657 Published online 1 November 211 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.8965 Evaluation of normal fetal pulmonary veins from the early
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 211; 38: 652 657 Published online 1 November 211 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com). DOI: 1.12/uog.8965 Evaluation of normal fetal pulmonary veins from the early
RETIRED: REVIEWED/Revised: 12/14; 10/15; 1/16; 9/16, 10/16, 5/17, 5/18, 9/18
 PAGE: 1 of 9 Scope Louisiana Healthcare Connections (LHCC) Medical Department Purpose To provide medical necessity criteria for obstetrical Home Health programs offered by vendors such as Optum Obstetrical
PAGE: 1 of 9 Scope Louisiana Healthcare Connections (LHCC) Medical Department Purpose To provide medical necessity criteria for obstetrical Home Health programs offered by vendors such as Optum Obstetrical
Isolated proteinuria in Chinese pregnant women with pre-eclampsia: Results of retrospective observational study
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (11): 5162-5166 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Isolated proteinuria in Chinese pregnant women with pre-eclampsia: Results of retrospective observational study Jing Cai 1,
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (11): 5162-5166 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Isolated proteinuria in Chinese pregnant women with pre-eclampsia: Results of retrospective observational study Jing Cai 1,
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
First-Trimester Fetal Cardiac Function
 CME Article First-Trimester Fetal Cardiac Function Noirin E. Russell, MRCPI, Fionnuala M. McAuliffe, MD, FRCPI, MRCOG Objective. The purpose of this study was to establish normal values for fetal heart
CME Article First-Trimester Fetal Cardiac Function Noirin E. Russell, MRCPI, Fionnuala M. McAuliffe, MD, FRCPI, MRCOG Objective. The purpose of this study was to establish normal values for fetal heart
Preeclampsia. &Eclampsia. Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy. What we need to know about. Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy.
 Preeclampsia &Eclampsia Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy Barbara Koop MS, RNC-OB What we need to know about Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy Define clinical criteria for: Gestational hypertension,
Preeclampsia &Eclampsia Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy Barbara Koop MS, RNC-OB What we need to know about Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy Define clinical criteria for: Gestational hypertension,
Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy Guideline
 Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy Guideline Approved by: Senior Director of Operations, Women s & Child Health, GNCH/MCH Facility Chief, Obstetrics/Gynecology, GNCH Facility Chief, Obstetrics/Gynecology,
Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy Guideline Approved by: Senior Director of Operations, Women s & Child Health, GNCH/MCH Facility Chief, Obstetrics/Gynecology, GNCH Facility Chief, Obstetrics/Gynecology,
FHR Monitoring: Maternal Fetal Physiology
 FHR Monitoring: Maternal Fetal Physiology M. Sean Esplin, MD and Alexandra Eller, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Intermountain Healthcare University of Utah Health Sciences Center Disclosures I have no financial
FHR Monitoring: Maternal Fetal Physiology M. Sean Esplin, MD and Alexandra Eller, MD Maternal Fetal Medicine Intermountain Healthcare University of Utah Health Sciences Center Disclosures I have no financial
Figure removed due to copyright restrictions.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY HST 071 An Example of a Fetal Heart Rate Tracing Figure removed
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY HST 071 An Example of a Fetal Heart Rate Tracing Figure removed
Impact of Nicorandil on Renal Function in Patients With Acute Heart Failure and Pre-Existing Renal Dysfunction
 Impact of Nicorandil on Renal Function in Patients With Acute Heart Failure and Pre-Existing Renal Dysfunction Masahito Shigekiyo, Kenji Harada, Ayumi Okada, Naho Terada, Hiroyoshi Yoshikawa, Akira Hirono,
Impact of Nicorandil on Renal Function in Patients With Acute Heart Failure and Pre-Existing Renal Dysfunction Masahito Shigekiyo, Kenji Harada, Ayumi Okada, Naho Terada, Hiroyoshi Yoshikawa, Akira Hirono,
Maternal and Fetal Physiology
 Background Maternal and Fetal Physiology Anderson Lo, DO Fellow, Maternal-Fetal Medicine Wayne State University School of Medicine SEMCME Fetal Assessment Course July 20, 2018 Oxygen pathway Mother Placenta
Background Maternal and Fetal Physiology Anderson Lo, DO Fellow, Maternal-Fetal Medicine Wayne State University School of Medicine SEMCME Fetal Assessment Course July 20, 2018 Oxygen pathway Mother Placenta
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
Serum β-hcg levels between 12 to 20 weeks of gestation in prediction of. hypertensive disorders of pregnancy.
 International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Muthulakshmi D et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2017 Aug;6(8):3347-3351 www.ijrcog.org DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-1770.ijrcog20173263
International Journal of Reproduction, Contraception, Obstetrics and Gynecology Muthulakshmi D et al. Int J Reprod Contracept Obstet Gynecol. 2017 Aug;6(8):3347-3351 www.ijrcog.org DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-1770.ijrcog20173263
Is massive proteinuria associated with maternal and fetal morbidities in preeclampsia?
 Original Article Obstet Gynecol Sci 2017;60(3):260-265 https://doi.org/10.5468/ogs.2017.60.3.260 pissn 2287-8572 eissn 2287-8580 Is massive proteinuria associated with maternal and fetal morbidities in
Original Article Obstet Gynecol Sci 2017;60(3):260-265 https://doi.org/10.5468/ogs.2017.60.3.260 pissn 2287-8572 eissn 2287-8580 Is massive proteinuria associated with maternal and fetal morbidities in
Sri Lankan Journal of Anaesthesiology 17(2) : (2009)
 Sri Lankan Journal of Anaesthesiology 17(2) : 55-60 (2009) COMPARISON OF PROPHYLACTIC INTRAMUSCULAR EPHEDRINE WITH PRELOADING VERSUS PRELOADING ALONE IN PREVENTION OF HYPOTENSION DURING ELECTIVE CAESAREAN
Sri Lankan Journal of Anaesthesiology 17(2) : 55-60 (2009) COMPARISON OF PROPHYLACTIC INTRAMUSCULAR EPHEDRINE WITH PRELOADING VERSUS PRELOADING ALONE IN PREVENTION OF HYPOTENSION DURING ELECTIVE CAESAREAN
Agenda. Management of Accelerated Hypertension (Updated in 2017) Salwa Roshdy Prof. of Cardiology Assiut University CardioEgypt 23/2/2017 2/27/2017
 Management of Accelerated Hypertension (Updated in 2017) By Salwa Roshdy Prof. of Cardiology Assiut University CardioEgypt 23/2/2017 Agenda Definition of Accelerated HTN Pathophysiology & Etiology Prognosis
Management of Accelerated Hypertension (Updated in 2017) By Salwa Roshdy Prof. of Cardiology Assiut University CardioEgypt 23/2/2017 Agenda Definition of Accelerated HTN Pathophysiology & Etiology Prognosis
Effects of pregnancy-related hemodynamic and hormonal changes
 Information extracted from WWW.HEARTDISEASEANDPREGNANCY.COM CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the leading cause of death worldwide in women. It has already been noted
Information extracted from WWW.HEARTDISEASEANDPREGNANCY.COM CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) is the leading cause of death worldwide in women. It has already been noted
Importance of Pulse Repetition Frequency Adjustment for 3- and 4-Dimensional Power Doppler Quantification
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Importance of Pulse Repetition Frequency Adjustment for 3- and 4-Dimensional Power Doppler Quantification Andre H. Miyague, PhD, Theo Z. Pavan, PhD, Carlos A. Soares, MD, Luc De Catte,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Importance of Pulse Repetition Frequency Adjustment for 3- and 4-Dimensional Power Doppler Quantification Andre H. Miyague, PhD, Theo Z. Pavan, PhD, Carlos A. Soares, MD, Luc De Catte,
Guideline for Management of Severe or Fulminating Pre-Eclampsia
 Guideline for Management of Severe or Fulminating Pre-Eclampsia Originator: Labour Ward Forum, Maternity Services Date Approved: September 2011 Approved by: W&CH Quality & Safety Group Reviewed and ratified
Guideline for Management of Severe or Fulminating Pre-Eclampsia Originator: Labour Ward Forum, Maternity Services Date Approved: September 2011 Approved by: W&CH Quality & Safety Group Reviewed and ratified
SEVERE PRE-ECLAMPSIA
 DEFINITIONS SEVERE PRE-ECLAMPSIA Pre-eclampsia: pregnancy induced hypertension with significant proteinuria +/- oedema affecting virtually any organ system in the body Severe pre-eclampsia: Diastolic blood
DEFINITIONS SEVERE PRE-ECLAMPSIA Pre-eclampsia: pregnancy induced hypertension with significant proteinuria +/- oedema affecting virtually any organ system in the body Severe pre-eclampsia: Diastolic blood
Hypothermia in Neonates with HIE TARA JENDZIO, DNP(C), RN, RNC-NIC
 Hypothermia in Neonates with HIE TARA JENDZIO, DNP(C), RN, RNC-NIC Objectives 1. Define Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) 2. Identify the criteria used to determine if an infant qualifies for therapeutic
Hypothermia in Neonates with HIE TARA JENDZIO, DNP(C), RN, RNC-NIC Objectives 1. Define Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) 2. Identify the criteria used to determine if an infant qualifies for therapeutic
Subhankar Dasgupta, Debdutta Ghosh, Subrata Lall Seal, Gourisankar Kamilya, Madan Karmakar and Debdas Saha
 bs_bs_banner doi:10.1111/j.1447-0756.2011.01806.x J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. Vol. 38, No. 5: 763 771, May 2012 Randomized controlled study comparing effect of magnesium sulfate with placebo on fetal umbilical
bs_bs_banner doi:10.1111/j.1447-0756.2011.01806.x J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. Vol. 38, No. 5: 763 771, May 2012 Randomized controlled study comparing effect of magnesium sulfate with placebo on fetal umbilical
Sympathetic Vasomotor Response Of The Radial Artery In Patients With End Stage Renal Disease
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nephrology Volume 2 Number 1 Sympathetic Vasomotor Response Of The Radial Artery In Patients With End Stage Renal Disease L Galea, M Schembri, M Debono Citation L Galea,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nephrology Volume 2 Number 1 Sympathetic Vasomotor Response Of The Radial Artery In Patients With End Stage Renal Disease L Galea, M Schembri, M Debono Citation L Galea,
Hydralazine for treatment of severe hypertension in pregnancy: meta-analysis
 Hydralazine for treatment of severe in pregnancy: meta-analysis Laura A Magee, Chris Cham, Elizabeth J Waterman, Arne Ohlsson, Peter von Dadelszen Abstract Objective To review outcomes in randomised controlled
Hydralazine for treatment of severe in pregnancy: meta-analysis Laura A Magee, Chris Cham, Elizabeth J Waterman, Arne Ohlsson, Peter von Dadelszen Abstract Objective To review outcomes in randomised controlled
Tailoring treatment to risk
 OBG MANAGEMENT COVER ARTICLE Hypertension in pregnancy Tailoring treatment to risk BY BAHA M. SIBAI, MD, and MARK CHAMES, MD Not all hypertensive gravidas should receive drug therapy. In fact, antihypertensive
OBG MANAGEMENT COVER ARTICLE Hypertension in pregnancy Tailoring treatment to risk BY BAHA M. SIBAI, MD, and MARK CHAMES, MD Not all hypertensive gravidas should receive drug therapy. In fact, antihypertensive
Circulatory System MARE HEIFER. aorta cvc. iia eia ipa. aorta. dca. (uov) oa. uboa. uma. ubva va. bua. iia. uma. ubva. eia. ua bua. cvc.
 Circulatory System 13 MARE aorta cvc ov (uov) oa dca uboa iia eia ipa ua uma bua ubva va HEIFER iia aorta cvc eia oa uma ua bua ubva va ov (uov) uboa 18 Chapter 1 Hemodynamics Plug flow Natural disturbed
Circulatory System 13 MARE aorta cvc ov (uov) oa dca uboa iia eia ipa ua uma bua ubva va HEIFER iia aorta cvc eia oa uma ua bua ubva va ov (uov) uboa 18 Chapter 1 Hemodynamics Plug flow Natural disturbed
What effects will proximal or distal disease have on an waveform?
 Spectral Doppler Interpretation Director Director of of Ultrasound Ultrasound Education Education & & Quality Quality Assurance Assurance Baylor Baylor College College of of Medicine Medicine Division
Spectral Doppler Interpretation Director Director of of Ultrasound Ultrasound Education Education & & Quality Quality Assurance Assurance Baylor Baylor College College of of Medicine Medicine Division
Ductus Venosus Doppler Ultrasound in Diabetic Pregnancies
 International Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences. Vol. 5 No. 2. 2016. Copyright by. All Rights Reserved Full Length Research Paper Ductus Venosus Doppler Ultrasound in Diabetic Pregnancies Alaa Ibrahim
International Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences. Vol. 5 No. 2. 2016. Copyright by. All Rights Reserved Full Length Research Paper Ductus Venosus Doppler Ultrasound in Diabetic Pregnancies Alaa Ibrahim
CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY
 CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY LAS VEGAS, NEVADA, USA 27 February 1 March 2016 SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT WITH RECOMBINANT TISSUE PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR OF MASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN THE 16 TH WEEK OF PREGNANCY
CARDIAC PROBLEMS IN PREGNANCY LAS VEGAS, NEVADA, USA 27 February 1 March 2016 SUCCESSFUL TREATMENT WITH RECOMBINANT TISSUE PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR OF MASSIVE PULMONARY EMBOLISM IN THE 16 TH WEEK OF PREGNANCY
Comparision of Intravenous Bolus Phenylephrine and Ephedrine for Prevention of Post Spinal Hypotension in Cesarean Sections
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. II (July. 2015), PP 99-103 www.iosrjournals.org Comparision of Intravenous Bolus Phenylephrine
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. II (July. 2015), PP 99-103 www.iosrjournals.org Comparision of Intravenous Bolus Phenylephrine
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs
 Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Introductory Clinical Pharmacology Chapter 41 Antihypertensive Drugs Blood Pressure Normal = sys
Magnesium Sulfate Prophylaxis in Preeclampsia: Evidence From Randomized Trials
 CLINICAL OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY Volume 48, Number 2, 478 488 Ó 2005, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Magnesium Sulfate Prophylaxis in Preeclampsia: Evidence From Randomized Trials BAHA M. SIBAI, MD Department
CLINICAL OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY Volume 48, Number 2, 478 488 Ó 2005, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Magnesium Sulfate Prophylaxis in Preeclampsia: Evidence From Randomized Trials BAHA M. SIBAI, MD Department
Pre-eclampsia: key issues. Robin Russell Nuffield Department of Anaesthetics John Radcliffe Hospital Oxford
 Robin Russell Nuffield Department of Anaesthetics John Radcliffe Hospital Oxford Antenatal Issues Labour Analgesia Anaesthesia for Delivery High Dependency Care Hypertension systolic >140 mmhg or diastolic
Robin Russell Nuffield Department of Anaesthetics John Radcliffe Hospital Oxford Antenatal Issues Labour Analgesia Anaesthesia for Delivery High Dependency Care Hypertension systolic >140 mmhg or diastolic
https://www.lucidoc.com/cgi/doc-gw.pl?ref=overlake_p:53602
 Page 1 of 6 Protocol : Severe Hypertension in Obstetrics: Emergent Treatment DocID: 53602 Revision: 7 Status: Official Department: Women's and Infants' Admin Manual(s): Labor and Delivery Mother Baby Unit
Page 1 of 6 Protocol : Severe Hypertension in Obstetrics: Emergent Treatment DocID: 53602 Revision: 7 Status: Official Department: Women's and Infants' Admin Manual(s): Labor and Delivery Mother Baby Unit
Doppler assessment of fetal aortic isthmus blood flow in two different sonographic planes during the second half of gestation
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 26: 170 174 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1955 Doppler assessment of fetal aortic isthmus blood flow in two different
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 26: 170 174 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1955 Doppler assessment of fetal aortic isthmus blood flow in two different
Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring Myths and Misperceptions s: Electronic Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring (EFM): Baseline Assumptions.
 Can FHR Monitoring Prevent Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy in the Newborn? Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring Myths and Misperceptions 1. Yes 2. No 72% Tekoa L. King CNM, MPH June 6, 2008 28% Yes No Objectives
Can FHR Monitoring Prevent Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy in the Newborn? Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring Myths and Misperceptions 1. Yes 2. No 72% Tekoa L. King CNM, MPH June 6, 2008 28% Yes No Objectives
First Trimester Fetal Echocardiography: Insight Into the Fetal Circulation
 First Trimester Fetal Echocardiography: Insight Into the Fetal Circulation Lisa K. Hornberger, MD Fetal & Neonatal Cardiology Program Department of Pediatrics, Division of Cardiology Department of Obstetrics
First Trimester Fetal Echocardiography: Insight Into the Fetal Circulation Lisa K. Hornberger, MD Fetal & Neonatal Cardiology Program Department of Pediatrics, Division of Cardiology Department of Obstetrics
Scholars Research Library
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Archives of Applied Science Research, 2010, 2 (1) 383-389 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Archives of Applied Science Research, 2010, 2 (1) 383-389 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-508X
Background: Bedside ultrasound is emerging as a useful tool in the assessment of
 Abstract: Background: Bedside ultrasound is emerging as a useful tool in the assessment of intravascular volume status by examining measurements of the inferior vena cava (IVC). Many previous studies do
Abstract: Background: Bedside ultrasound is emerging as a useful tool in the assessment of intravascular volume status by examining measurements of the inferior vena cava (IVC). Many previous studies do
Original Research Article
 A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF INTRAVENOUS LABETALOL WITH ORAL ANTIHYPERTENSIVE COMBINATION NIFEDIPINE AND ALPHA-METHYLDOPA IN THE ACUTE MANAGEMENT OF HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE IN SEVERE PREGNANCY-INDUCED HYPERTENSION
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF INTRAVENOUS LABETALOL WITH ORAL ANTIHYPERTENSIVE COMBINATION NIFEDIPINE AND ALPHA-METHYLDOPA IN THE ACUTE MANAGEMENT OF HIGH BLOOD PRESSURE IN SEVERE PREGNANCY-INDUCED HYPERTENSION
HST 071. IN SUMMARY PREGNANCY INDUCED HYPERTENSION Classification of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY Classification of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy HST
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.071: Human Reproductive Biology Course Director: Professor Henry Klapholz IN SUMMARY Classification of Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy HST
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers PROTEINURIA
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers PROTEINURIA
Opinion. Technical aspects of aortic isthmus Doppler velocimetry in human fetuses
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009; 33: 628 633 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.6406 Opinion Technical aspects of aortic isthmus Doppler velocimetry in
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2009; 33: 628 633 Published online in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.6406 Opinion Technical aspects of aortic isthmus Doppler velocimetry in
A (quasi)evidence-based approach to the management of early-onset IUGR
 A (quasi)evidence-based approach to the management of early-onset IUGR Eduard Gratacós Barcelona Center for Maternal-Fetal and Neonatal Medicine Hospital Clínic and Hospital Sant Joan de Deu, University
A (quasi)evidence-based approach to the management of early-onset IUGR Eduard Gratacós Barcelona Center for Maternal-Fetal and Neonatal Medicine Hospital Clínic and Hospital Sant Joan de Deu, University
By Dr.Asmaa Al sanjary
 By Dr.Asmaa Al sanjary Preterm delivery is defined by a birth occurring before 37 completed weeks of gestation. Prematurity is multifactorial and its incidence has increased during the last decade in most
By Dr.Asmaa Al sanjary Preterm delivery is defined by a birth occurring before 37 completed weeks of gestation. Prematurity is multifactorial and its incidence has increased during the last decade in most
What is the mechanism of the audible carotid bruit? How does one calculate the velocity of blood flow?
 CASE 8 A 65-year-old man with a history of hypertension and coronary artery disease presents to the emergency center with complaints of left-sided facial numbness and weakness. His blood pressure is normal,
CASE 8 A 65-year-old man with a history of hypertension and coronary artery disease presents to the emergency center with complaints of left-sided facial numbness and weakness. His blood pressure is normal,
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD
 COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
COMPREHENSIVE EVALUATION OF FETAL HEART R. GOWDAMARAJAN MD Disclosure No Relevant Financial Relationships with Commercial Interests Fetal Echo: How to do it? Timing of Study -optimally between 22-24 weeks
Normal pericardial fluid in the fetus: color and spectral Doppler analysis
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001; 18: 248 252 Normal pericardial fluid in the fetus: color and spectral Blackwell ORIGINAL Science, PAPERLtd Doppler analysis S.-J. YOO*, J.-Y. MIN and Y.-H. LEE *Department
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001; 18: 248 252 Normal pericardial fluid in the fetus: color and spectral Blackwell ORIGINAL Science, PAPERLtd Doppler analysis S.-J. YOO*, J.-Y. MIN and Y.-H. LEE *Department
Medical Policy An Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association
 Acute and Maintenance Page 1 of 11 Medical Policy An Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association Title: Acute and Maintenance Subcutaneous and Intravenous Tocolysis Professional
Acute and Maintenance Page 1 of 11 Medical Policy An Independent Licensee of the Blue Cross and Blue Shield Association Title: Acute and Maintenance Subcutaneous and Intravenous Tocolysis Professional
CONTROL OF BLOOD PRESSURE IN PREGNANCY: HOW HIGH IS TOO HIGH? EVELYNE REY, CHU Ste-Justine, Montreal
 CONTROL OF BLOOD PRESSURE IN PREGNANCY: HOW HIGH IS TOO HIGH? EVELYNE REY, CHU Ste-Justine, Montreal CONFLICTS OF INTEREST $: None Others: Canadian guidelines, CHIPS CSIM2015 2 LEARNING OBJECTIVES New
CONTROL OF BLOOD PRESSURE IN PREGNANCY: HOW HIGH IS TOO HIGH? EVELYNE REY, CHU Ste-Justine, Montreal CONFLICTS OF INTEREST $: None Others: Canadian guidelines, CHIPS CSIM2015 2 LEARNING OBJECTIVES New
