Clinical Cardiac A & P Dr. Gary Mumaugh
|
|
|
- Eustace Walker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Clinical Cardiac A & P Dr. Gary Mumaugh Coronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology o Atherosclerotic disease and coronary artery disease accounts for 45% of all USA deaths o 50% of female deaths are cardiovascular o Etiology includes the presence of plaques lining the coronary arteries with plaque rupture and coronary artery spasm o Result is ischemia, angina or MI, cell death and or electrical dysfunction o 3 Elements of atherogenesis is plaque formation, plaque rupture, vasoregulation creating atherosclerotic disease CAD risk factors o Older age o Family history o Socioeconomic factors o Overweight with trunk fat depostition o Blood pressure o Smoking o Personality and psychological factors o Glycemic control o Increased LDL and triglycerides o Poor dental hygeine o Chronic infections o With several risk factors the risk could be up to 20X Preventative therapy to reduce heart attacks o Specific therapy for those with pre-clinical CAD Lovastatin and strict diet control Proper diabetic control Antihypertensives Folic acid for high homocysteine Temporary antibiotics Maintenance of good oral hygiene o General therapy for all adults Low dose ASA Smoking cessation & stress management Folic acid, Vitamin C and E, omega-3 fatty acids Increasing aerobic exercise 1
2 Coronary Artery Occlusion with MI Incidence o 1,100,000 American had MI, with 650,000 being the first attack and 450,000 instant deaths S & S o Crushing chest pain with diaphoresis, dyspnea, weakness, palpitations, vomiting Diagnosis o Patient presentation with ECG and blood tests Treatment o Admission to CCU has best survival o Oxygen, beta blockers, heparin, tpa o Pacemaker insertion or CABG surgery Famous Cardiac Caveats o In all men or older women with acute physical distress of any kind, always think, Is this a myocardial infarction? o When a young man complains of pain in his heart, it is usually his stomach. When an old man complains of pain in his stomach, it is usually his heart. o Such thought has saved thousands of lives Hypertension Up to 50 million in the USA 95% diagnosed as essential o Essential means preventable or likely due to diet, obesity, inactivity, stress and alcohol Conventional treatment with lifestyle modifications work well with integrative care o According to the 6 th Joints Commission of Hypertension, even with a BP of 140/90, the main intervention is lifestyle intervention before starting medication. o This includes weight loss, decrease sodium and alcohol and moderate exercise for one year before starting medication. Causes of essential hypertension o Heredity o Obesity o Salt intake o Stress o Alcohol 2
3 Three diagnostic components of essential HTN o Careful history, family history, organ system review, lifestyle evaluation o Thorough physical examination o Lab studies Treatment of essential HTN o Lifestyle changes Weight, exercise, smoking, salt restriction, stress reduction, DASH diet o Medication (only after lifestyle modification) Diuretics Calcium channel blockers ACE inhibitors Alpha blockers Beta-blockers Angiotensin II receptor blockers Causes of secondary hypertension o white coat hypertension o Medical noncompliance o Exogenous drug usage Oral contraceptives, weight control drugs, NSAIDs, steroids, sympathomimetic cold remedies o Renal disease o Aldosteronism o Endocrine diseases o Sleep apnea o Congenital stenosis of the aorta Treatment of secondary HTN o Remove the cause and the HTN is gone Congestive Heart Failure CHF Incidence o In the USA, 3 million hospitalizations per year o 30-40% are readmitted with six months o 4-5 millions current cases o 500, ,000 new cases per year o 250,000 deaths per year o Half of all CHF diagnosis die within 5 years 10% die in year one o Twice as common in African-Americans o USA yearly treatment cost - $21 billion 3
4 Causes of CHF o Coronary artery disease o Hypertension o Aortic stenosis and insufficiency o Mitral regurgitation o Atrial fibrillation, flutter or tachycardia o Viral myocarditis o Septicemia o Hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism o Alcohol abuse o Chemotherapy o Congenital or rheumatic heart disease o Chagas disease parasitic heart infection Pathophysiology of CHF o The pumping action of the heart becomes less and less powerful o Despite its misleading name, in heart failure the heart doesn't suddenly stop working o Heart failure develops slowly as the heart muscle gradually weakens o The "failure" refers to the heart's inability to pump enough blood. o Blood and fluid do not move efficiently through the circulatory system, and starts to "back up o Eventually, parts of your body (lungs, abdomen, and lower limbs) hold blood and fluid that your heart isn't circulating very well o This is called "becoming congested," and is why this condition is called "congestive heart failure" Left sided vs. Right sided Heart Failure o Can involve the heart's left side, right side or both sides, though CHF much more affects the left heart o Left-sided heart failure Fluid collects in the lungs - this extra fluid in the lungs ("congestion") makes it more difficult for the airways to expand as you inhale Presents with dyspnea, pulmonary edema, and orthopnea o Right-sided heart failure Due to failure of the right ventricle Fluid collects in other body tissues especially the lower extremities pitting edema, liver enlargement 4
5 CHF Symptoms o Three cardinal symptoms are dyspnea, fatigue and fluid retention o Sudden weight gain, despite loss of appetite o Swelling in legs, ankles, feet, or abdomen o Tired and short of breath when doing things that are normally easy, such as walking o Breathing difficulty when lying flat in bed or may wake up with a choking feeling May need to sleep with your head raised up on several pillows o Persistent cough, more at night o Less frequent urination during the day o Irregular heartbeats, feeling of heart pounding o Chest pain, pressure or chest discomfort o Loss of appetite o Dizziness or lightheadedness, inability to concentrate 5
6 Four Stages of CHF - New York Heart Association Guidelines o Class I (Mild) 35% No limitation of physical activity Ordinary physical activity does not cause symptoms fatigue o Class II (Mild) 35% Slight limitation of physical activity Comfortable at rest, but ordinary physical activity results in fatigue, palpitation, or dyspnea o Class III (Moderate) 25% Marked limitation of physical activity Comfortable at rest, but less than any activity causes fatigue, palpitation, or dyspnea o Class IV (Severe) 5% Unable to carry out any physical activity without discomfort Symptoms of cardiac insufficiency at rest If any physical activity is undertaken, discomfort is increased CHF Diagnosis o Family history o Medical history o HTN, angina, diabetes, high cholesterol, valve disease, PVD, rheumatic disease, chest radiation o Life style o Health habits o Physical exam o Peripheral edema, hepatomegaly, ascites, pallor, tachycardia, jugular venous distension o Chest x-ray o EKG o Echocardiogram o Blood work 6
7 CHF treatment o Aldosterone antagonists Reduce the stress to the heart Weak diuretic effect o Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors Help reduce the stress on your heart o Beta blockers Help decrease the heart s need for blood and oxygen by reducing its workload Help the heart to beat more regularly o Digoxin (Lanoxin ) Help increases the strength of the pumping action o Diuretics (water pills) Help reduce the amount of fluid in your body Extrinsic Innervation of the Heart Heart is stimulated by the sympathetic cardioaccelerator center Heart is inhibited by the parasympathetic cardioinhibitory center Heart Physiology: Sequence of Excitation o Sinoatrial (SA) node generates impulses about 75 times/minute o Atrioventricular (AV) node delays the impulse approximately 0.1 second o Impulse passes from atria to ventricles via the atrioventricular bundle (bundle of His) o Heart Block - the only route for impulse transmission from the atria to the ventricles is through the AV node, and damage to the AV node is called heart block 7
8 Cardiac Arrhythmias Premature atrial contractions (PAC) o Seen in normal people with to much caffeine, anxiety, alcohol, electrolytes, vomiting or diarrhea Premature ventricular contractions (PVC) o Often seen in middle age and of no concern o Can also occur with MI, CHF, hypoxia Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT) o Usually in women o May be congenital and start in first year of life Called Wolf Parkinson White Syndrome which requires a catheter radio-ablation 8
9 Cardiac Arrhythmias - continued Atrial fibrillation and flutter (AF) o Not life-threatening, yet it is a common cause of hospitilization o Causes the heart to be sporadically with no rhythmic pattern o May be caused by COPD, alcohol, cardiac surgery, hyperthyroidism, or idiopathic o The inefficiency of the atrial contraction leads to a potential buildup of clots in the wall of the atria o Treated with electrical cardioversion with anticoagulation meds o Some are resistant to cardioversion which puts them at risk for strokes, ventricular fibrillation and sudden death Ventricular tachycardia (VT) o A normal response to exercise, stress reactions and sexual activity causing the heart to elevate up to 200/minute o In patient s with structural heart disease, VT can occur without provocation o S & S pounding heart and lightheadedness o Treated with electrical cardioversion and beta blockers Bradycardia o Pulse less than 60/min or 46/min for athletes o Extrinsic causes by drugs, hypothyroidism, CNS disorders o Intrinsic causes by SA or AV node dysfunction o Treat the cause, such as a pacemaker Heart block o Often caused by ischemia due to CAD or may be idiopathic o Three degrees possible 1 st degree impulses reach the ventricles and slow in the AV node no treatment needed 2 nd degree impulse slows so that not all beats get through the ventricle, causing bradycardia may or may not need a pacemaker 3 rd degree (complete) all impulses from the atria to the ventricles are blocked at the AV node all need external pacemaker o Sick sinus syndrome - a wide variety of alternate bradycardia and tachycardia 9
10 Cardiac Valve Disease Heart valve malfunction comes in two forms: o Valves that do not open well This constricts the flow and is called stenosis o Valves that do not close well This causes backwards leakage and is called regurgitation or insufficiency Four most common valve problems o Mitral regurgitation (insufficiency) In the past, was caused by rheumatic fever o Mitral stenosis Caused by rheumatic fever, congenital abnormalities, lupus, or tumor o Aortic regurgitation (insufficiency) The 3 cusps leak after contraction Caused by rheumatic heart disease, congenital defects, endocarditis or degeneration Causes ventricular enlargement o Aortic stenosis Most common valve problem in adults Most caused by arteriosclerosis of flaps normal aging 10
11 11
12 Pericarditis Has a triad of chest pain, ECG changes and pericardial friction rub the patient must have 2 of the 3 to make the diagnosis Major causes o Viral infections, myocardial infarction, drug side effect, connective tissue disorders, blunt or penetrating trauma S & S o Chest pain radiating to back or left shoulder o Fatigue or dyspnea Diagnosis o High intensity friction rub and ECHO Treatment o NSAIDs and steroids o Pericardiocentesis to avoid cardiac tamponade from effusion Tamponade is fatal it not relieved Prognosis o Most resolve in four weeks o Some cases become chronic which require surgery to remove the thickened constrictive heart layer 12
13 Endocarditis Infection of inner heart lining, usually bacterial o Can be acute or subacute o Usually occur on damaged valves in which the bacteria accumulates and forms blood clots on the valves Bacteria in the bloodstream comes from mouth, dental work, gingivitis, skin infections, medical procedures (Streptococcus, staphlococcus, enterococcus) o Heart valve vegetations can and easily embolize throughout the body causing satellite abscesses o Diagnosis with ECHO and blood culture Consider in any patient with fever heart murmur o Treatment IV antibiotics and possible valve replacement Aortic Artery Disease Ruptured aortic aneurysms are responsible for 15,000 deaths per year (half die in surgery) o (> 4 cm diameter with normal at 2.5 to 3 cm) S & S o Often no symptoms when they are small o When they enlarge, they cause low back pain and powerful abdominal pulse sensation Diagnosis o Pulsating aneurysm palpated and seen on ultrasound Treatment o Surgical resection > 5 cm diameter 13
14 Peripheral Artery Disease Arteriosclerosis o Generalized narrowing and stiffening of arteries occurring over 65 years old Atherosclerosis o The process of plaque formations over the age of 35 o Plaques build up where vessels split and can lead to strokes, gangrene and heart attacks o Very common in diabetes o Risk factors Tobacco (3-4X), age, HTN, diabetes, cholesterol, sedentary lifestyle, high homocysteine Aortic Artery Disease Ruptured aortic aneurysms are responsible for 15,000 deaths per year (half die in surgery) o (> 4 cm diameter with normal at 2.5 to 3 cm) S & S o Blood flow restricted to lower extremities o Severe claudication o Sharp pain with exercise that stops with lack of movement Diagnosis o Diminished or absent peripheral pulses o Doppler flowmeter changes o Ischemic limbs have purple-red color o Glove-like distribution of nerve loss Treatment o Vasodilators o Vascular surgery 14
15 15
Clinical Cardiology A & P. Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Clinical Cardiology A & P Dr. Gary Mumaugh Films on Demand Video Coronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology Atherosclerotic disease and coronary artery disease accounts for 45% of all USA deaths 50% of female
Clinical Cardiology A & P Dr. Gary Mumaugh Films on Demand Video Coronary Artery Disease Pathophysiology Atherosclerotic disease and coronary artery disease accounts for 45% of all USA deaths 50% of female
Heart Disorders. Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8. Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders
 Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders Susie Turner, MD 1/7/13 Heart Disorders Coronary Artery Disease Cardiac Arrhythmias Congestive Heart
Cardiovascular Disorders (Part B-1) Module 5 -Chapter 8 Overview Heart Disorders Vascular Disorders Susie Turner, MD 1/7/13 Heart Disorders Coronary Artery Disease Cardiac Arrhythmias Congestive Heart
Cardiovascular Disorders. Heart Disorders. Diagnostic Tests for CV Function. Bio 375. Pathophysiology
 Cardiovascular Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology Heart Disorders Heart disease is ranked as a major cause of death in the U.S. Common heart diseases include: Congenital heart defects Hypertensive heart
Cardiovascular Disorders Bio 375 Pathophysiology Heart Disorders Heart disease is ranked as a major cause of death in the U.S. Common heart diseases include: Congenital heart defects Hypertensive heart
Diseases. Cardiovascular System
 Diseases Cardiovascular System Angina Pectoris A condition marked by severe pain in the chest, often spreading to the shoulder or neck. Caused by inadequate blood supply to the heart. Cardiomyopathy Refers
Diseases Cardiovascular System Angina Pectoris A condition marked by severe pain in the chest, often spreading to the shoulder or neck. Caused by inadequate blood supply to the heart. Cardiomyopathy Refers
Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation
 Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation Which of the following best describes the physical activity performed in my leisure time? A. I perform vigorous physical activity 3X/week for 20 minutes each time B.
Cardiac Pathology & Rehabilitation Which of the following best describes the physical activity performed in my leisure time? A. I perform vigorous physical activity 3X/week for 20 minutes each time B.
Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors
 Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors 1 Human Health: What s Killing Us? Health in America Health is the U.S Average life
Lecture 8 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 8 1. Introduction 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factors 1 Human Health: What s Killing Us? Health in America Health is the U.S Average life
Heart Disease. Signs and Symptoms
 Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition
 Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
Cardiovascular Nursing Practice: A Comprehensive Resource Manual and Study Guide for Clinical Nurses 2 nd Edition Table of Contents Volume 1 Chapter 1: Cardiovascular Anatomy and Physiology Basic Cardiac
10/8/2018. Lecture 9. Cardiovascular Health. Lecture Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor
 Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
Lecture 9 Cardiovascular Health 1 Lecture 9 1. Heart 2. Cardiovascular Health 3. Stroke 4. Contributing Factor 1 The Heart Muscular Pump The Heart Receives blood low pressure then increases the pressure
Topic Page: congestive heart failure
 Topic Page: congestive heart failure Definition: congestive heart f ailure from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary (1930) : heart failure in which the heart is unable to maintain an adequate circulation
Topic Page: congestive heart failure Definition: congestive heart f ailure from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary (1930) : heart failure in which the heart is unable to maintain an adequate circulation
HEART DISEASE HEART CONDITIONS, RISKS AND PROTECTION
 Spotlight on Health 2017 HEART DISEASE HEART CONDITIONS, RISKS AND PROTECTION Heart disease is the leading cause of death for both men and women worldwide, accounting for over 17 million deaths per year.
Spotlight on Health 2017 HEART DISEASE HEART CONDITIONS, RISKS AND PROTECTION Heart disease is the leading cause of death for both men and women worldwide, accounting for over 17 million deaths per year.
Heart Failure. Symptoms and Treatments. FloridaHospital.com
 Heart Failure Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Understanding Heart Failure According to the American Heart Association, one in five people over age 40 will develop heart failure. Right now,
Heart Failure Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Understanding Heart Failure According to the American Heart Association, one in five people over age 40 will develop heart failure. Right now,
Cardiomyopathy Consequences. function of the myocardium for any reason. This is a serious disease in which the heart muscle
 Becki Simmons Cardiomyopathy Consequences Cardiomyopathy, which literally means "heart muscle disease," is the deterioration of the function of the myocardium for any reason. This is a serious disease
Becki Simmons Cardiomyopathy Consequences Cardiomyopathy, which literally means "heart muscle disease," is the deterioration of the function of the myocardium for any reason. This is a serious disease
2
 1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes
 Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Identify the components of the cardiovascular system and the various types of cardiovascular disease Ø Discuss ways of promoting cardiovascular
Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes LEARNING OBJECTIVES Ø Identify the components of the cardiovascular system and the various types of cardiovascular disease Ø Discuss ways of promoting cardiovascular
Cardiovascular disease
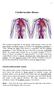 1 Cardiovascular disease The essential components of the human cardiovascular system are the heart, blood, and blood vessels. It includes: the pulmonary circulation, a "loop" through the lungs where blood
1 Cardiovascular disease The essential components of the human cardiovascular system are the heart, blood, and blood vessels. It includes: the pulmonary circulation, a "loop" through the lungs where blood
Cardiovascular Disease
 Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 15 Introduction Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the U.S. One American dies from CVD every 33 seconds Nearly half of all Americans will die from
Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 15 Introduction Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the U.S. One American dies from CVD every 33 seconds Nearly half of all Americans will die from
Unit 6: Circulatory System. 6.2 Heart
 Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Chapter 14 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since.
 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 14 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since. Accounts for 1 of every 2.8 deaths Cardiovascular disease (CVD)
1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 14 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since. Accounts for 1 of every 2.8 deaths Cardiovascular disease (CVD)
Cardiovascular System and Health. Chapter 15
 Cardiovascular System and Health Chapter 15 Cardiovascular Disease Leading cause of death in U.S. Claims 1 life every 43 seconds Often, the first sign is a fatal heart attack Death Rates #1 CVD #2 Cancer
Cardiovascular System and Health Chapter 15 Cardiovascular Disease Leading cause of death in U.S. Claims 1 life every 43 seconds Often, the first sign is a fatal heart attack Death Rates #1 CVD #2 Cancer
Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps
 Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps Cardiology is the word in health care associated with heart, but the body s vascular system is also an important part of heart care. Your body has more than 60,000 miles
Guide to Cardiology Care at Scripps Cardiology is the word in health care associated with heart, but the body s vascular system is also an important part of heart care. Your body has more than 60,000 miles
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy in Cats (a Type of Heart-Muscle Disease) Basics
 Restrictive Cardiomyopathy in Cats (a Type of Heart-Muscle Disease) Basics OVERVIEW The heart of the cat is composed of four chambers; the top two chambers are the left and right atria and the bottom two
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy in Cats (a Type of Heart-Muscle Disease) Basics OVERVIEW The heart of the cat is composed of four chambers; the top two chambers are the left and right atria and the bottom two
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
Arrhythmias. Pulmonary Artery
 Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
Arrhythmias Introduction Cardiac arrhythmia is an irregularity of the heart beat that causes the heart to beat too slowly, too fast, or irregularly. There are different types of arrhythmias. Most arrhythmias
Congestive Heart Failure
 Congestive Heart Failure GENERAL INFORMATION: What is congestive heart failure? Congestive heart failure is a life-threatening disease that occurs when your heart becomes too weak to pump blood properly.
Congestive Heart Failure GENERAL INFORMATION: What is congestive heart failure? Congestive heart failure is a life-threatening disease that occurs when your heart becomes too weak to pump blood properly.
Chest Pain. Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal. Department of Medicine
 Chest Pain Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine BACKGROUND Approx 5% of all ED visits 15 % - AMI 25-30 % - Unstable angina 50-55 % - Other conditions Atypical presentations common 2% of patients
Chest Pain Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine BACKGROUND Approx 5% of all ED visits 15 % - AMI 25-30 % - Unstable angina 50-55 % - Other conditions Atypical presentations common 2% of patients
Heart Problems and Treatments
 Heart Problems and Treatments A healthy heart Your heart s main functions are to receive used blood from your body and pump fresh oxygen rich blood to nourish your body. To do this well: The heart muscle
Heart Problems and Treatments A healthy heart Your heart s main functions are to receive used blood from your body and pump fresh oxygen rich blood to nourish your body. To do this well: The heart muscle
Presenter: Steven Brust, HCS-D, HCS-H Product Manager, Home Health Coding Center
 Presenter: Steven Brust, HCS-D, HCS-H Product Manager, Home Health Coding Center Pinpoint & properly assign the appropriate heart failure codes Left- vs. Right-sided Left ventricular failure (LVF) may
Presenter: Steven Brust, HCS-D, HCS-H Product Manager, Home Health Coding Center Pinpoint & properly assign the appropriate heart failure codes Left- vs. Right-sided Left ventricular failure (LVF) may
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to:
 The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
The Cardiovascular System Part I: Heart Outline of class lecture After studying part I of this chapter you should be able to: 1. Describe the functions of the heart 2. Describe the location of the heart,
Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics
 Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics OVERVIEW Failure of the right side of the heart to pump blood at a sufficient rate to meet the needs of the body or to prevent blood from pooling within the
Right-Sided Congestive Heart Failure Basics OVERVIEW Failure of the right side of the heart to pump blood at a sufficient rate to meet the needs of the body or to prevent blood from pooling within the
Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias
 Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Atrial Fibrillation According to the American Heart Association, Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects an estimated 2.7 million
Atrial Fibrillation & Arrhythmias Symptoms and Treatments FloridaHospital.com Atrial Fibrillation According to the American Heart Association, Atrial fibrillation (AF) affects an estimated 2.7 million
About atrial fibrillation (AFib) Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) What is AFib? What s the danger? Who gets AFib?
 Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
Understanding AFib Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) About AFib 3 How Your Heart Works 4 Types of AFib 5 Symptoms 5 Risk Factors 5 How is AFib Diagnosed? 6 Treatment 6 What to Ask Your Doctor 7 A normal heartbeat
Can be felt where an artery passes near the skin surface and over a
 1 Chapter 14 Cardiovascular Emergencies 2 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since. Accounts for 1 of every 2.8 deaths Cardiovascular disease (CVD) claimed
1 Chapter 14 Cardiovascular Emergencies 2 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since. Accounts for 1 of every 2.8 deaths Cardiovascular disease (CVD) claimed
When the heart job fails ~HEART FAILURE~
 HEART FAILURE Dr. BALINT, HAJNALKA Research/ Clinical Fellow Congenital Cardiac Centre for Adults University Health Network Peter Munk Cardiac Centre / Toronto General Hospital Toronto, ON, Canada Heart
HEART FAILURE Dr. BALINT, HAJNALKA Research/ Clinical Fellow Congenital Cardiac Centre for Adults University Health Network Peter Munk Cardiac Centre / Toronto General Hospital Toronto, ON, Canada Heart
C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders
 C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders GENERAL ISSUES REGARDING MEDICAL FITNESS-FOR-DUTY 1. These medical standards apply to Union Pacific Railroad (UPRR) employees
C1: Medical Standards for Safety Critical Workers with Cardiovascular Disorders GENERAL ISSUES REGARDING MEDICAL FITNESS-FOR-DUTY 1. These medical standards apply to Union Pacific Railroad (UPRR) employees
A C P S P E C I A L R E P O R T. Understanding and Living With. Heart Failure
 SM A C P S P E C I A L R E P O R T Understanding and Living With Heart Failure What Is Heart Failure? Heart failure (sometimes called congestive heart failure) is a condition in which the heart isn t pumping
SM A C P S P E C I A L R E P O R T Understanding and Living With Heart Failure What Is Heart Failure? Heart failure (sometimes called congestive heart failure) is a condition in which the heart isn t pumping
Heart disease remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in industrialized nations. It accounts for nearly 40% of all deaths in the United
 Heart disease remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in industrialized nations. It accounts for nearly 40% of all deaths in the United States, totaling about 750,000 individuals annually
Heart disease remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in industrialized nations. It accounts for nearly 40% of all deaths in the United States, totaling about 750,000 individuals annually
Results of Ischemic Heart Disease
 Ischemic Heart Disease: Angina and Myocardial Infarction Ischemic heart disease; syndromes causing an imbalance between myocardial oxygen demand and supply (inadequate myocardial blood flow) related to
Ischemic Heart Disease: Angina and Myocardial Infarction Ischemic heart disease; syndromes causing an imbalance between myocardial oxygen demand and supply (inadequate myocardial blood flow) related to
INTRODUCTORY TEXT BOX
 INTRODUCTORY TEXT BOX Diagnostic Partners provides a range of onsite, in-office cardiac and vascular diagnostic testing services. From Resting Echocardiograms to Abdominal Aorta scans, each study is performed
INTRODUCTORY TEXT BOX Diagnostic Partners provides a range of onsite, in-office cardiac and vascular diagnostic testing services. From Resting Echocardiograms to Abdominal Aorta scans, each study is performed
Cardiac Arrhythmias. Cathy Percival, RN, FALU, FLMI VP, Medical Director AIG Life and Retirement Company
 Cardiac Arrhythmias Cathy Percival, RN, FALU, FLMI VP, Medical Director AIG Life and Retirement Company The Cardiovascular System Three primary functions Transport of oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to
Cardiac Arrhythmias Cathy Percival, RN, FALU, FLMI VP, Medical Director AIG Life and Retirement Company The Cardiovascular System Three primary functions Transport of oxygen, nutrients, and hormones to
Heart Failure. Cardiac Anatomy. Functions of the Heart. Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics. Determinants of Cardiac Output. Cardiac Output
 Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
Pediatrics. Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment. Overview
 Pediatrics Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment See online here The most common form of cardiac arrhythmia in children is sinus tachycardia which can be caused by
Pediatrics Arrhythmias in Children: Bradycardia and Tachycardia Diagnosis and Treatment See online here The most common form of cardiac arrhythmia in children is sinus tachycardia which can be caused by
Paroxysmal Supraventricular Tachycardia PSVT.
 Atrial Tachycardia; is the name for an arrhythmia caused by a disorder of the impulse generation in the atrium or the AV node. An area in the atrium sends out rapid signals, which are faster than those
Atrial Tachycardia; is the name for an arrhythmia caused by a disorder of the impulse generation in the atrium or the AV node. An area in the atrium sends out rapid signals, which are faster than those
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disorders
 Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disorders Blood Pressure Normal blood pressure is 120/80 mmhg (millimeters of mercury) Hypertension is when the resting blood pressure is too high Systolic BP is 140 mmhg
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Disorders Blood Pressure Normal blood pressure is 120/80 mmhg (millimeters of mercury) Hypertension is when the resting blood pressure is too high Systolic BP is 140 mmhg
Presentation, symptoms and signs of heart failure
 3 Presentation, symptoms and signs of heart failure What will I learn? In this section you will learn: Who is at risk of heart failure The symptoms of heart failure The signs of heart failure The importance
3 Presentation, symptoms and signs of heart failure What will I learn? In this section you will learn: Who is at risk of heart failure The symptoms of heart failure The signs of heart failure The importance
Hypertension and Heart Disease. Weldon James, MD, Mercy Clinic Family Medicine, Union
 Hypertension and Heart Disease Weldon James, MD, Mercy Clinic Family Medicine, Union The Silent Killer High blood pressure, also known as HBP or hypertension, is a widely misunderstood medical condition
Hypertension and Heart Disease Weldon James, MD, Mercy Clinic Family Medicine, Union The Silent Killer High blood pressure, also known as HBP or hypertension, is a widely misunderstood medical condition
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acute coronary syndrome(s), anticoagulant therapy in, 706, 707 antiplatelet therapy in, 702 ß-blockers in, 703 cardiac biomarkers in,
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Chapter 16 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since 1900.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 Chapter 16 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since 1900. Accounts for of every 3 deaths Cardiovascular disease
1 2 3 4 5 6 Chapter 16 Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular Emergencies Cardiovascular disease has been leading killer of Americans since 1900. Accounts for of every 3 deaths Cardiovascular disease
Unit 4 Problems of Cardiac Output and Tissue Perfusion
 Unit 4 Problems of Cardiac Output and Tissue Perfusion Lemone and Burke Ch 30-32 Objectives Review the anatomy and physiology of the cardiovascular system. Identify normal heart sounds and relate them
Unit 4 Problems of Cardiac Output and Tissue Perfusion Lemone and Burke Ch 30-32 Objectives Review the anatomy and physiology of the cardiovascular system. Identify normal heart sounds and relate them
Cardiac Pathophysiology
 Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12
 A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
Care of the Patient with a Cardiovascular or a Peripheral Vascular Disorder
 Care of the Patient with a Cardiovascular or a Peripheral Vascular Disorder 1 Slide 1 human heart Slide 2 MECHANICAL: PUSHES BLOOD FROM HEAD TO TOES AND BACK Slide 3 1 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM: TRIGGERS THE MECHANICAL
Care of the Patient with a Cardiovascular or a Peripheral Vascular Disorder 1 Slide 1 human heart Slide 2 MECHANICAL: PUSHES BLOOD FROM HEAD TO TOES AND BACK Slide 3 1 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM: TRIGGERS THE MECHANICAL
Your Heart Anatomy and Procedures
 Your heart is a muscular organ about the size of your fist. It is located behind the lower part of your sternum (breast bone). With each beat of the heart, the heart muscle pumps and circulates blood through
Your heart is a muscular organ about the size of your fist. It is located behind the lower part of your sternum (breast bone). With each beat of the heart, the heart muscle pumps and circulates blood through
Heart Disease and Congestive Heart Failure
 Heart Disease and Congestive Heart Failure Heart failure affects nearly 5 million Americans. Roughly 550,000 people are diagnosed with heart failure each year. It is the leading cause of hospitalization
Heart Disease and Congestive Heart Failure Heart failure affects nearly 5 million Americans. Roughly 550,000 people are diagnosed with heart failure each year. It is the leading cause of hospitalization
Atrial Fibrillation. Damage to your heart caused by a heart attack or rheumatic heart disease
 Atrial Fibrillation GENERAL INFORMATION: What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a condition that causes the atria (top chambers of the heart) to shake or quiver. Normally, there is 1 contraction
Atrial Fibrillation GENERAL INFORMATION: What is atrial fibrillation? Atrial fibrillation is a condition that causes the atria (top chambers of the heart) to shake or quiver. Normally, there is 1 contraction
Management strategies for atrial fibrillation Thursday, 20 October :27
 ALTHOUGH anyone who has had to run up a flight of steps or has had a frightening experience is quite familiar with a racing heartbeat, for the more than 2 million Americans who suffer from atrial fibrillation
ALTHOUGH anyone who has had to run up a flight of steps or has had a frightening experience is quite familiar with a racing heartbeat, for the more than 2 million Americans who suffer from atrial fibrillation
AORTIC STENOSIS HENRY FORD HOSPITAL CENTER FOR STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE
 AORTIC STENOSIS HENRY FORD HOSPITAL CENTER FOR STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE WHAT IS AORTIC STENOSIS? THE AORTIC VALVE The aorta is the major vessel that carries oxygenated blood out of the left side of the
AORTIC STENOSIS HENRY FORD HOSPITAL CENTER FOR STRUCTURAL HEART DISEASE WHAT IS AORTIC STENOSIS? THE AORTIC VALVE The aorta is the major vessel that carries oxygenated blood out of the left side of the
HEART FAILURE. Study day November 2017 Sarah Briggs and Janet Laing
 HEART FAILURE Study day November 2017 Sarah Briggs and Janet Laing Overview and Introduction This course is an introduction and overview of heart failure. Normal heart function and basic pathophysiology
HEART FAILURE Study day November 2017 Sarah Briggs and Janet Laing Overview and Introduction This course is an introduction and overview of heart failure. Normal heart function and basic pathophysiology
This information explains heart failure, including causes and signs of heart failure, how heart failure is diagnosed, and how it s treated.
 PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Heart Failure This information explains heart failure, including causes and signs of heart failure, how heart failure is diagnosed, and how it s treated. About Heart Failure
PATIENT & CAREGIVER EDUCATION Heart Failure This information explains heart failure, including causes and signs of heart failure, how heart failure is diagnosed, and how it s treated. About Heart Failure
LET S GET EDUCATED! Men s Health. By: Dr. Alfred Sparman
 HAPPY FATHER S DAY! LET S GET EDUCATED! Men s Health By: Dr. Alfred Sparman About me. Cardiology Fellowship 1995-1998 University of Florida, College of Medicine Medical Residency 1993-1995 St. Luke s Roosevelt
HAPPY FATHER S DAY! LET S GET EDUCATED! Men s Health By: Dr. Alfred Sparman About me. Cardiology Fellowship 1995-1998 University of Florida, College of Medicine Medical Residency 1993-1995 St. Luke s Roosevelt
Cardiac Drugs: Chapter 9 Worksheet Cardiac Agents. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate.
 Complete the following. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate. 2. drugs affect the force of contraction and can be either positive or negative. 3.
Complete the following. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate. 2. drugs affect the force of contraction and can be either positive or negative. 3.
Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Causes of Cardiac Arrythmias Abnormal rhythmicity of the pacemaker Shift of pacemaker from sinus node Blocks at different
Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Causes of Cardiac Arrythmias Abnormal rhythmicity of the pacemaker Shift of pacemaker from sinus node Blocks at different
2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif
 2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif Rhythms from the Sinus Node Sinus Tachycardia: HR > 100 b/m Causes: o Withdrawal of vagal tone & Sympathetic stimulation (exercise, fight or flight) o Fever
2) Heart Arrhythmias 2 - Dr. Abdullah Sharif Rhythms from the Sinus Node Sinus Tachycardia: HR > 100 b/m Causes: o Withdrawal of vagal tone & Sympathetic stimulation (exercise, fight or flight) o Fever
BUSINESS. Articles? Grades Midterm Review session
 BUSINESS Articles? Grades Midterm Review session REVIEW Cardiac cells Myogenic cells Properties of contractile cells CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART Conduction pathway SA node (pacemaker) atrial depolarization
BUSINESS Articles? Grades Midterm Review session REVIEW Cardiac cells Myogenic cells Properties of contractile cells CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART Conduction pathway SA node (pacemaker) atrial depolarization
LeMone & Burke Ch 30-32
 LeMone & Burke Ch 30-32 2 Right side- Low oxygenation Low pressure Light workload Goes toward the lungs Left side High oxygenation Thick walled high pressure Heavier workload Carries oxygenation blood
LeMone & Burke Ch 30-32 2 Right side- Low oxygenation Low pressure Light workload Goes toward the lungs Left side High oxygenation Thick walled high pressure Heavier workload Carries oxygenation blood
Cardiovascular Disease
 Cardiovascular Disease Session Guidelines This is a 15 minute webinar session for CNC physicians and staff CNC holds webinars on the 3 rd Wednesday of each month to address topics related to risk adjustment
Cardiovascular Disease Session Guidelines This is a 15 minute webinar session for CNC physicians and staff CNC holds webinars on the 3 rd Wednesday of each month to address topics related to risk adjustment
10/16/2014. CCRN Review - Cardiovascular. CCRN Review - Cardiovascular. CCRN Review - Cardiovascular
 Hypertrophic (IHSS) Diagnosis Chest x ray cardiomegaly Electrocardiography LV hypertrophy, ST segment T was changes, Q waves in inferior & precordial leads Atrial & ventricular dysrhythmias Hypertrophic
Hypertrophic (IHSS) Diagnosis Chest x ray cardiomegaly Electrocardiography LV hypertrophy, ST segment T was changes, Q waves in inferior & precordial leads Atrial & ventricular dysrhythmias Hypertrophic
Introduction. What atrial fibrillation (AF) is Warning signs & symptoms, and risk factors for developing AFrelated
 Got FIB? Introduction FAST, IRREGULAR heartbeats = FIB FIB is short for fibrillation fibrillation, or quivering of the top two chambers of the heart (the atria) Important that you understand: What atrial
Got FIB? Introduction FAST, IRREGULAR heartbeats = FIB FIB is short for fibrillation fibrillation, or quivering of the top two chambers of the heart (the atria) Important that you understand: What atrial
Cardiac arrhythmias. Janusz Witowski. Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences. J. Witowski
 Cardiac arrhythmias Janusz Witowski Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences A 68-year old man presents to the emergency department late one evening complaining of increasing
Cardiac arrhythmias Janusz Witowski Department of Pathophysiology Poznan University of Medical Sciences A 68-year old man presents to the emergency department late one evening complaining of increasing
X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary
 X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary Introduction Atrial fibrillation is a common heart condition that affects approximately 2.5 million Americans every year. Atrial fibrillation requires immediate
X-Plain Atrial Fibrillation Reference Summary Introduction Atrial fibrillation is a common heart condition that affects approximately 2.5 million Americans every year. Atrial fibrillation requires immediate
Rhythm Disorders 2017 TazKai LLC and NRSNG.com
 Rhythm Disorders 1. Outline the conduction system of the heart. 2. What do the different portions of the EKG represent? 3. Define the following terms: a. Automaticity b. Conductivity c. Excitability d.
Rhythm Disorders 1. Outline the conduction system of the heart. 2. What do the different portions of the EKG represent? 3. Define the following terms: a. Automaticity b. Conductivity c. Excitability d.
FAMILIAR CHRONIC CASES:
 CHAPTER 1 FAMILIAR CHRONIC CASES: CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES AND STROKE (12 CONTACT HOURS) Learning objectives Define cardiovascular disease. Identify the prevalence of cardiovascular disease in the United
CHAPTER 1 FAMILIAR CHRONIC CASES: CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES AND STROKE (12 CONTACT HOURS) Learning objectives Define cardiovascular disease. Identify the prevalence of cardiovascular disease in the United
CHAPTER 1 FAMILIAR CHRONIC CASES: CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES AND STROKE (7 CONTACT HOURS) Learning objectives!! Define cardiovascular disease.
 CHAPTER 1 FAMILIAR CHRONIC CASES: CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES AND STROKE (7 CONTACT HOURS) Learning objectives!! Define cardiovascular disease.!! Identify the prevalence of cardiovascular disease in the United
CHAPTER 1 FAMILIAR CHRONIC CASES: CARDIOVASCULAR DISEASES AND STROKE (7 CONTACT HOURS) Learning objectives!! Define cardiovascular disease.!! Identify the prevalence of cardiovascular disease in the United
Heart Failure Dr ahmed almutairi Assistant professor internal medicin dept
 Heart Failure Dr ahmed almutairi Assistant professor internal medicin dept (MBBS)(SBMD) Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology diastolic/systolic Risk factors Signs and symptoms Classification of HF
Heart Failure Dr ahmed almutairi Assistant professor internal medicin dept (MBBS)(SBMD) Introduction Epidemiology Pathophysiology diastolic/systolic Risk factors Signs and symptoms Classification of HF
PLEASE LET US KNOW YOUR REASON FOR TODAY S VISIT : CURRENT MEDICATIONS (WITH DOSAGE) PLEASE INCLUDE VITAMINS AND HERBAL MEDICATIONS:
 1 NAME: DATE OF BIRTH PLEASE LET US KNOW YOUR REASON FOR TODAY S VISIT : CURRENT MEDICATIONS (WITH DOSAGE) PLEASE INCLUDE VITAMINS AND HERBAL MEDICATIONS: PAST MEDICAL HISTORY (YOUR MEDICAL HISTORY) :
1 NAME: DATE OF BIRTH PLEASE LET US KNOW YOUR REASON FOR TODAY S VISIT : CURRENT MEDICATIONS (WITH DOSAGE) PLEASE INCLUDE VITAMINS AND HERBAL MEDICATIONS: PAST MEDICAL HISTORY (YOUR MEDICAL HISTORY) :
Dysrhythmias 11/7/2017. Disclosures. 3 reasons to evaluate and treat dysrhythmias. None. Eliminate symptoms and improve hemodynamics
 Dysrhythmias CYDNEY STEWART MD, FACC NOVEMBER 3, 2017 Disclosures None 3 reasons to evaluate and treat dysrhythmias Eliminate symptoms and improve hemodynamics Prevent imminent death/hemodynamic compromise
Dysrhythmias CYDNEY STEWART MD, FACC NOVEMBER 3, 2017 Disclosures None 3 reasons to evaluate and treat dysrhythmias Eliminate symptoms and improve hemodynamics Prevent imminent death/hemodynamic compromise
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 3: The Pathology of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 3: The Pathology of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives
Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis happens when the blood vessels
 Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis happens when the blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients from your heart to the rest of your body (arteries) become thick and stiff sometimes restricting blood flow
Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis happens when the blood vessels that carry oxygen and nutrients from your heart to the rest of your body (arteries) become thick and stiff sometimes restricting blood flow
Cardiac Emergencies. A Review of Cardiac Compromise. Lawrence L. Lambert
 Cardiac Emergencies A Review of Cardiac Compromise Lawrence L. Lambert 1 Cardiac Emergencies Objectives: Following successful completion of this training session, the student should be able to: 1. Describe
Cardiac Emergencies A Review of Cardiac Compromise Lawrence L. Lambert 1 Cardiac Emergencies Objectives: Following successful completion of this training session, the student should be able to: 1. Describe
cardiomyopathy. INTRODUCTION NONISCHEMIC CARDIOMYOPATHY
 FACTS ABOUT Cardiomyopathy INTRODUCTION Ischemic cardiomyopathy typically refers to heart muscle damage that results from coronary artery disease, such as heart attack, Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the
FACTS ABOUT Cardiomyopathy INTRODUCTION Ischemic cardiomyopathy typically refers to heart muscle damage that results from coronary artery disease, such as heart attack, Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the
Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Dogs
 Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Dogs (a Type of Heart-Muscle Disease) Basics OVERVIEW The heart of the dog is composed of four chambers; the top two chambers are the left and right atria and the bottom two chambers
Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Dogs (a Type of Heart-Muscle Disease) Basics OVERVIEW The heart of the dog is composed of four chambers; the top two chambers are the left and right atria and the bottom two chambers
Heart Failure. Dr. William Vosik. January, 2012
 Heart Failure Dr. William Vosik January, 2012 Questions for clinicians to ask Is this heart failure? What is the underlying cause? What are the associated disease processes? Which evidence-based treatment
Heart Failure Dr. William Vosik January, 2012 Questions for clinicians to ask Is this heart failure? What is the underlying cause? What are the associated disease processes? Which evidence-based treatment
Anatomy of the Heart and the. ICD-10 Codes
 Anatomy of the Heart and the Diseases ICD-10 Codes Sharon J. Oliver CPC, CPMA, CPC-I All Rights Reserved 1 Anatomy of the Heart Pulmonary Tricuspid (AV) Valve Mitral Aortic Semilunar Valve Chordae Tendineae
Anatomy of the Heart and the Diseases ICD-10 Codes Sharon J. Oliver CPC, CPMA, CPC-I All Rights Reserved 1 Anatomy of the Heart Pulmonary Tricuspid (AV) Valve Mitral Aortic Semilunar Valve Chordae Tendineae
Cardiology/Cardiothoracic
 Cardiology/Cardiothoracic ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Code Mapper 800-334-5724 www.contexomedia.com 2013 ICD-9-CM 272.0 Pure hypercholesterolemia 272.2 Mixed hyperlipidemia 272.4 Other and hyperlipidemia 278.00
Cardiology/Cardiothoracic ICD-9-CM to ICD-10-CM Code Mapper 800-334-5724 www.contexomedia.com 2013 ICD-9-CM 272.0 Pure hypercholesterolemia 272.2 Mixed hyperlipidemia 272.4 Other and hyperlipidemia 278.00
A C P S P E C I A L R E P O R T. African Americans Living With. Heart Failure
 SM A C P S P E C I A L R E P O R T African Americans Living With Heart Failure What Is Heart Failure? Heart failure doesn t mean that your heart has stopped beating. Rather, it s a term used to describe
SM A C P S P E C I A L R E P O R T African Americans Living With Heart Failure What Is Heart Failure? Heart failure doesn t mean that your heart has stopped beating. Rather, it s a term used to describe
10/17/2015. Chapter 47. Care of the Patient with a Cardiovascular or a Peripheral Vascular Disorder. The Heart. Chambers of the Heart
 Chapter 47 Care of the Patient with a Cardiovascular or a Peripheral Vascular Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. The
Chapter 47 Care of the Patient with a Cardiovascular or a Peripheral Vascular Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. The
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Objectives. Identify early signs and symptoms of Acute Coronary Syndrome Initiate proper protocol for ACS patient 10/2013 2
 10/2013 1 Objectives Identify early signs and symptoms of Acute Coronary Syndrome Initiate proper protocol for ACS patient 10/2013 2 Purpose of this Education Module: Chest Pain Center Accreditation involves
10/2013 1 Objectives Identify early signs and symptoms of Acute Coronary Syndrome Initiate proper protocol for ACS patient 10/2013 2 Purpose of this Education Module: Chest Pain Center Accreditation involves
Circulation and Cardiac Emergencies. Emergency Medical Response
 Circulation and Cardiac Emergencies Lesson 19: The Circulatory System and Cardiac Emergencies You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are called to the home of a 50-year-old man whose wife called 9-1-1
Circulation and Cardiac Emergencies Lesson 19: The Circulatory System and Cardiac Emergencies You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are called to the home of a 50-year-old man whose wife called 9-1-1
Which blood type is the universal donor? Which structure of the blood serves as the body s natural defense against injury and disease:
 Scrub In: Which blood type is the universal donor? a. A b. B c. AB d. O Which structure of the blood serves as the body s natural defense against injury and disease: a. Plasma b. Erythrocytes c. Leukocytes
Scrub In: Which blood type is the universal donor? a. A b. B c. AB d. O Which structure of the blood serves as the body s natural defense against injury and disease: a. Plasma b. Erythrocytes c. Leukocytes
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 26 Caring for Clients with Coronary Heart Disease and Dysrhythmias Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Leading
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 26 Caring for Clients with Coronary Heart Disease and Dysrhythmias Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) Leading
HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM
 REVIEW DATE REVIEWER'S ID HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM : DISCHARGE DATE: RECORDS FROM: Hospitalization ER Please check all that may apply: Myocardial Infarction Pages 2, 3,
REVIEW DATE REVIEWER'S ID HEART AND SOUL STUDY OUTCOME EVENT - MORBIDITY REVIEW FORM : DISCHARGE DATE: RECORDS FROM: Hospitalization ER Please check all that may apply: Myocardial Infarction Pages 2, 3,
Review Packet EKG Competency This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test.
 Review Packet EKG Competency 2015 This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test. Normal Sinus Rhythm Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: 60-100 bpm
Review Packet EKG Competency 2015 This packet is a review of the information you will need to know for the proctored EKG competency test. Normal Sinus Rhythm Rhythm: Regular Ventricular Rate: 60-100 bpm
Wellness: Concepts and Applications 8 th Edition Anspaugh, Hamrick, Rosato
 Wellness: Concepts and Applications 8 th Edition Anspaugh, Hamrick, Rosato Preventing Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 2 Cardiovascular Disease the leading cause of death in the U.S. 35.3% of all deaths
Wellness: Concepts and Applications 8 th Edition Anspaugh, Hamrick, Rosato Preventing Cardiovascular Disease Chapter 2 Cardiovascular Disease the leading cause of death in the U.S. 35.3% of all deaths
Catheter Ablation. Patient Education
 Catheter Ablation Patient Education Allina Health System Your heart has four chambers. Two upper chambers (atria) pump blood to the two lower chambers (ventricles). In order for the heart to pump, it requires
Catheter Ablation Patient Education Allina Health System Your heart has four chambers. Two upper chambers (atria) pump blood to the two lower chambers (ventricles). In order for the heart to pump, it requires
Arrhythmia 341. Ahmad Hersi Professor of Cardiology KSU
 Arrhythmia 341 Ahmad Hersi Professor of Cardiology KSU Objectives Epidemiology and Mechanisms of AF Evaluation of AF patients Classification of AF Treatment and Risk stratification of AF Identify other
Arrhythmia 341 Ahmad Hersi Professor of Cardiology KSU Objectives Epidemiology and Mechanisms of AF Evaluation of AF patients Classification of AF Treatment and Risk stratification of AF Identify other
Chapter 2: An Overview of Cardiovascular Nursing. 10 Contact Hours. Learning objectives. Introduction. By: Adrianne E. Avillion, D.Ed.
 Chapter 2: An Overview of Cardiovascular Nursing 10 Contact Hours By: Adrianne E. Avillion, D.Ed., RN Learning objectives Define cardiovascular disease. Identify the prevalence of cardiovascular disease
Chapter 2: An Overview of Cardiovascular Nursing 10 Contact Hours By: Adrianne E. Avillion, D.Ed., RN Learning objectives Define cardiovascular disease. Identify the prevalence of cardiovascular disease
Heart Disease (Coronary Artery Disease)
 Heart Disease (Coronary Artery Disease) Understanding how the heart works To understand heart disease, you must first know how the heart works. The heart is like any other muscle, requiring blood to supply
Heart Disease (Coronary Artery Disease) Understanding how the heart works To understand heart disease, you must first know how the heart works. The heart is like any other muscle, requiring blood to supply
