10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
|
|
|
- Edith Baker
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis D. hypertension 3. Blood returning to the heart from the lungs enters the, and blood is pumped from the heart to the lungs by the. A. left atrium; left ventricle B. left atrium; right ventricle C. right atrium; right ventricle D. right atrium; left ventricle 4. From which section of a capillary does water and small dissolved solutes move into the capillary? A. arterial end B. midsection C. venous end 5. What valve is found between the left atrium and left ventricle? A. pulmonary semilunar valve B. tricuspid valve C. bicuspid valve D. aortic semilunar valve 6. During the ventricular systole, the AV valves and the semilunar valves. A. close; open B. close; close C. open; close D. open; open 7. An increase in the frequency of sympathetic impulses to arteries and arterioles, produces, which blood pressure and velocity. A. vasoconstriction; increases B. vasoconstriction; decreases C. vasodilation; increases D. vasodilation; decreases 8. During atrial systole, the AV valves are and the semilunar valves are. A. closed; open B. closed; closed C. open; closed D. open; open 9. The correct sequence in the conduction system of the heart is A. Purkinje fibers, AV bundle, bundle branches. B. AV node, SA node, Purkinje fibers. C. SA node, AV node, AV bundle, bundle branches, Purkinje fibers. D. AV node, bundle branches, SA node, Purkinje fibers.
2 10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C. hemorrhoids D. congestive heart failure 11. Constriction and dilation of smooth muscle in is used to control blood pressure. A. capillaries B. venules C. arteries D. arterioles 12. The hepatic portal system is an unusual vein in that it is transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich blood 13. Blood pressure normally allows plasma substances to leak out of so as to nourish body tissues. A. arteries B. arterioles C. capillaries D. venules 14. Heart rate regulation is primarily controlled by the cardiac control center located in the A. hypothalamus. B. cerebrum. C. medulla oblongata. D. pons. 15. In an ECG, the T wave represents A. depolarization of the atria. B. depolarization of the ventricles. C. repolarization of the atria. D. repolarization of the ventricles. 16. What vessels carry oxygen poor blood from the right ventricle to the lungs for gas exchange? A. pulmonary arteries B. pulmonary veins C. aorta and coronary arteries D. superior and inferior vena cavas 17. What vein returns blood from the lower part of the body to the heart? A. inferior mesenteric vein B. hepatic portal vein C. brachiocephalic vein D. inferior vena cava 18. The left atrium A. receives oxygen rich blood from lungs. B. pumps oxygen rich blood toward the body tissues. C. receives oxygen poor blood from the body tissues. D. pumps oxygen poor blood to the lungs.
3 19. Small vessels that are involved in the control of blood pressure and distribution of blood are A. capillaries. B. venules. C. arterioles. 20. The valve prevents the backflow of blood from the left ventricle into the left atrium. A. bicuspid atrioventricular B. aortic semilunar C. tricuspid atrioventricular D. pulmonary semilunar 21. The cardiac output is dependent on A. heart rate. B. respiration rate. C. stroke volume D. Both heart rate and stroke volume are correct. 22. The p wave of an ECG represents A. atrial depolarization. B. atrial repolarization. C. ventricular depolarization. D. ventricular repolarization. 23. Cardiac output is equal to A. heart rate stroke volume. B. heart rate / stroke volume. C. stroke volume + heart rate. D. stroke volume - heart rate 24. The visceral pericardium also forms the of the heart wall. A. epicardium B. myocardium C. endocardium 25. When is the second sound of the heartbeat produced? A. beginning of atrial systole B. beginning of atrial diastole C. beginning of ventricular systole D. beginning of ventricular diastole 26. The pulmonary veins are unusual as veins because they are transporting. A. oxygenated blood B. de-oxygenated blood C. high fat blood D. nutrient-rich blood 27. The hepatic portal vein goes from the A. liver to vena cava. B. abdominal organs to the liver. C. kidney to vena cava. D. intestine to kidney. 28. Parasympathetic stimulation of the heart causes the heart rate to A. increase. B. decrease. C. stay the same. D. increase, then decrease.
4 29. The membranous covering of the heart is the, which includes a loosely fitting sac composed of an inner and an outer. A. epicardium; parietal pericardium; fibrous pericardium B. endocardium; parietal pericardium; epicardium C. epicardium; fibrous pericardium; parietal pericardium D. pericardium; parietal pericardium; fibrous pericardium 30. A precapillary sphincter muscle controls the flow of blood from A. capillary to venule. B. arteriole to capillary. C. artery to arteriole. D. capillary to arteriole. 31. What is the function of the heart valves? A. to push blood B. to prevent the backflow of blood C. to stimulate the heart D. to give support to the heart 32. handle tissue exchange. A. Veins B. Arteries C. Capillaries 33. A heart rate above 100 beats per minute is called A. tachycardia. B. fibrillation. C. bradycardia. D. ectopic. 34. The first heart sound "lub" is made by A. closure of the AV valves. B. closure of the semilunar valves. C. contraction of the ventricles. D. contraction of the atria. 35. Why does the left ventricle have a thicker myocardial wall? A. It has to pump blood to the lungs. B. It has to pump blood to the body. C. It has to pump blood to the left atrium. D. It has to pump blood to the liver. 36. The cardioregulatory center is located in the A. cerebrum. B. cerebellum. C. medulla oblongata. D. pons. 37. As blood leaves the right atrium, it passes through the valve to the right ventricle. A. tricuspid B. pulmonary semilunar C. mitral D. bicuspid 38. Systole refers to A. relaxation. B. contraction. C. stimulation.
5 39. An increase in blood pressure will cause reflex of the heart rate. A. increase B. decrease C. no change D. increase, then decrease 40. Which chambers contract simultaneously? A. two atria B. right atrium and right ventricle C. all chambers contract simultaneously D. all chambers contract separately 41. Which pressure is greater on the arteriole side of a capillary? A. blood pressure B. osmotic pressure C. blood pressure and osmotic pressure are the same 42. In an ECG, the QRS complex represents A. depolarization of the atria. B. depolarization of the ventricles. C. repolarization of the atria. D. repolarization of the ventricles. 43. In an ECG, the P wave represents A. depolarization of the atria. B. depolarization of the ventricles. C. repolarization of the atria. D. repolarization of the ventricles. 44. The acts to receive blood from all of the veins of the heart. A. coronary sinus B. great cardiac vein C. anterior interventricular vein D. posterior interventricular vein 45. Which of the following is NOT a vessel that empties into the right atrium? A. inferior vena cava B. superior vena cava C. coronary sinus D. pulmonary veins 46. The sound of a heart murmur is created from A. acid reflux in the esophagus. B. fluid in the lungs. C. leaky heart valves. D. a hiccup. 47. Heart attacks are most likely to be caused by blockage of which vessel? A. The aorta B. The pulmonary veins C. The coronary arteries D. The cardiac veins 48. A heart rate below 60 beats per minute is called A. tachycardia. B. fibrillation. C. bradycardia. D. ectopic.
6 49. Which chamber pumps the blood to the body through the systemic circuit? A. right atrium B. left atrium C. right ventricle D. left ventricle 50. The aortic semilunar valve prevents blood from flowing backwards into the A. right atrium. B. left atrium. C. right ventricle. D. left ventricle. 51. What vessels carry oxygen rich blood to the left atrium? A. superior and inferior vena cavas B. pulmonary veins C. pulmonary arteries D. Both superior and inferior vena cavas and pulmonary veins 52. Why is it important that blood move very slowly through the capillaries? A. to allow for molecular exchange between the blood and the tissues B. to allow for normal heart functioning C. blood moves very quickly through the capillaries 53. The QRS complex of an ECG represents A. atrial depolarization. B. atrial repolarization. C. ventricular depolarization. D. ventricular repolarization. 54. have valves to prevent backflow. A. Veins B. Arteries C. Capillaries 55. The rhythmically forms impulses initiating each heartbeat and transmits these inpulses to the. A. A-V node; A-V bundle B. S-A node; A-V node C. A-V node; S-A node D. S-A node; A-V bundle 56. What initiates the heartbeat and is called the pacemaker? A. nerves B. AV node C. SA node D. brain 57. The atrioventricular valve is located on the right side of the heart, while the valve is on the left. A. bicuspid; tricuspid B. bicuspid; mitral C. mitral; bicuspid D. tricupid; bicuspid 58. Which are the strongest pumping chambers? A. atria B. ventricles
7 59. Blood pressure is lowest in the A. aorta. B. capillaries. C. superior and inferior vena cavas. D. venules. 60. carry blood to the heart. A. Veins B. Arteries C. Capillaries 61. At any given time, more than half the total blood volume is found in A. capillaries. B. arteries and arterioles. C. venules and veins. D. arterioles and venules. 62. When is the first sound of the heartbeat produced? A. beginning of atrial systole B. beginning of atrial diastole C. beginning of ventricular systole D. beginning of ventricular diastole 63. The act to receive blood from veins, while the pump blood away from the heart. A. ventricles; capillaries B. ventricles; atria C. atria; ventricles D. atria; capillaries 64. The right atrium A. receives oxygen rich blood from lungs. B. pumps oxygen rich blood toward the body tissues. C. receives oxygen poor blood from the body tissues. D. pumps oxygen poor blood to the lungs. 65. The amount of blood pumped out of a ventricle in one minute is the A. stroke volume. B. heart rate. C. cardiac output. D. cardiac cycle. 66. The pathway from the lungs, through the left side of the heart and out the aorta to the body tissues is called the A. pulmonary circuit. B. coronary circulation. C. systemic circuit. D. hepatic-portal system. 67. If excessive fluid retention increases blood volume, blood pressure is likely to A. decrease. B. be unaffected. C. increase. D. alter the heart rate.
8 68. Which of the following states do not normally occur in the heart? A. atrial systole and ventricular systole together. B. atrial systole and ventricular diastole together. C. atrial diastole and ventricular diastole together. D. atrial diastole and ventricular diastole together. 69. The pulmonary vein A. carries oxygen rich blood from lungs to the left atrium. B. carries oxygen rich blood toward the body tissues. C. receives oxygen poor blood from the body tissues. D. carries oxygen poor blood to the lungs. 70. An area other than the SA node can become the pacemaker. This area is called a(an) A. heart block. B. intrinsic conduction system. C. ec D. interventricular septum. 71. The heart sounds are due to the A. valves closing. B. heart contraction. C. heart relaxing. D. blood flowing. 72. Sympathetic stimulation of the heart causes the heart rate to A. increase. B. decrease. C. stay the same. D. increase, then decrease. 73. The acts to slow action potentials, while the transmits these signals very quickly. A. A-V node; A-V bundle B. S-A node; A-V bundle C. A-V bundle; Purkinje fibers D. A-V node; Purkinje fibers 74. Diastole refers to A. relaxation. B. contraction. C. stimulation. 75. Constriction of the smooth muscles of an arteriole will blood pressure and blood flow into an area. A. increase; increase B. increase; decrease C. decrease; increase D. decrease; decrease 76. The is referred to as the pacemaker of the heart. A. A-V node B. S-A node C. Purkinje fibers D. A-V bundle
9 77. What type of receptors, found in the aorta and common carotids arteries, send information to the cardioregulatory center to control heart rate? A. proprioceptors B. nociceptors C. baroreceptors D. photoreceptors 78. During, the atrioventricular valves are closed and the semilunar valves are open. A. atrial systole B. ventricular diastole C. ventricular systole D. atrial and ventricular diastole 79. Which of the following vessels would have a high oxygen content? A. aorta B. pulmonary veins C. pulmonary arteries D. Both the aorta and pulmonary veins. 80. The second heart sound "dup" is caused by the A. closing of the AV valves. B. closing of the mitral valve. C. closing of the semilunar valves. D. contraction of the ventricles. 81. If blood pressure increases above normal, the response from the medulla oblongata will be to A. increase heart rate and dilate the arterioles. B. increase heart rate and constrict the arterioles. C. decrease heart rate and dilate the arterioles. D. decrease heart rate and constrict the arterioles. 82. The tissue layer found in major blood vessels and the heart is the. A. smooth muscle layer B. endothelial layer C. tunica externa D. parietal pericardium 83. As the total cross-sectional area of the vessels increases, the velocity of blood flow A. increases. B. decreases. C. does not change. 84. A systolic pressure consistently above 140 or a diastolic pressure above 90 is called A. hypertension. B. fibrillation. C. hypotension. D. tachycardia. 85. The pathway from the superior and inferior vena cavas, through the right side of the heart to the lungs is called the A. pulmonary circuit. B. coronary circulation. C. systemic circuit. D. hepatic-portal system.
10 86. Which of the following does NOT affect the stroke volume of the heart? A. oxygen concentration of the blood B. strength of contraction of the ventricles C. blood electrolyte concentration D. venous return to the right atrium 87. What accounts for blood flow in the arteries? A. blood pressure B. skeletal muscle contraction C. blood pressure and skeletal muscle contraction 88. In which type of vessel is blood velocity the greatest? A. capillaries B. arterioles C. veins D. arteries 89. What structures control blood flow into capillary beds? A. adhesion junctions B. precapillary sphincters C. arteriovenous shunt D. semilunar valve 90. Which pressure is greater on the venous end of a capillary? A. blood pressure B. osmotic pressure C. blood pressure and osmotic pressure are the same 91. Which type of vessel consists of one layer of endothelial cells? A. arteries B. veins C. capillaries 92. Osmotic pressure is created from A. the pumping of the heart. B. movement of substances from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. C. a difference in solute concentration on either side of a semipermeable membrane. D. blood volume. 93. Which type of vessel have very thick, muscular walls? A. veins B. arteries C. arterioles D. capillaries 94. How is the heart muscle nourished? A. by blood in the left ventricle B. by the coronary arteries C. by the cardiac vein D. by the carotid artery 95. The pumps blood into the aorta, and the receives blood from the vena cavae. A. right ventricle; right atrium B. right ventricle; left atrium C. left ventricle; left atrium D. left ventricle; right atrium
11 96. The aorta A. receives oxygen rich blood from lungs. B. carries oxygen rich blood toward the body tissues. C. receives oxygen poor blood from the body tissues. D. carries oxygen poor blood to the lungs. 97. The heart rate is increased by impulses from neurons and decreased by impulses from neurons. A. sympathetic; parasympathetic B. parasympathetic; sympathetic C. afferent; efferent D. motor; sensory 98. Which of the following represents the correct sequence when tracing the path of blood from the superior or inferior vena cava to the lungs? A. left atrium, pulmonary semilunar valve, left ventricle, mitral valve, pulmonary arteries B. right atrium, tricuspid valve, right ventricle, pulmonary semilunar valve, pulmonary arteries C. tricuspid valve, right atrium, aortic semilunar valve, right ventricle, pulmonary veins D. pulmonary semilunar valve, right atrium, mitral valve, right ventricle, pulmonary veins 99. An abnormal heartbeat that has a rate exceeding 100 beats per minute is. A. bradycardia B. tachycardia C. atrial fibrillation D. ventricular fibrillation 100.Vasoconstriction in blood vessels is controlled by the vasomotor center in the A. pons. B. cerebellum. C. hypothalamus. D. medulla oblongata.
4. The two inferior chambers of the heart are known as the atria. the superior and inferior vena cava, which empty into the left atrium.
 Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Figure ) The specific chamber of the heart that is indicated by letter A is called the. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
Chapter 12 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 12 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 12 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
The Heart. Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet
 The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
The Heart Happy Friday! #takeoutyournotes #testnotgradedyet Introduction Cardiovascular system distributes blood Pump (heart) Distribution areas (capillaries) Heart has 4 compartments 2 receive blood (atria)
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Function: Transportation of. Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases
 Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes
 Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
The Heart. Size, Form, and Location of the Heart. 1. Blunt, rounded point; most inferior part of the heart.
 12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
The ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Indians and Chinese believed the heart was the centre of thinking and emotions
 The Concept of Mind The ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Indians and Chinese believed the heart was the centre of thinking and emotions Hippocrates 460 BC 370 BC - Thoughts, ideas, and feelings come from
The Concept of Mind The ancient Babylonians, Egyptians, Indians and Chinese believed the heart was the centre of thinking and emotions Hippocrates 460 BC 370 BC - Thoughts, ideas, and feelings come from
The Cardiovascular System. Chapter 15. Cardiovascular System FYI. Cardiology Closed systemof the heart & blood vessels. Functions
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular System FYI The heart pumps 7,000 liters (4000 gallons) of blood through the body each day The heart contracts 2.5 billion times in an avg. lifetime The heart & all blood vessels
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
CIRCULATION. Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions. Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis
 CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
CIRCULATION CIRCULATION Cardiovascular & lymphatic systems Functions Transport Defense / immunity Homeostasis 2 Types of Circulatory Systems Open circulatory system Contains vascular elements Mixing of
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Cardiovascular System
 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
11 PART A The Cardiovascular System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Cardiovascular
Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system. What are the function of the cardiovascular system? Arteries and arterioles:
 5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
The HEART. What is it???? Pericardium. Heart Facts. This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep
 This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
Cardiovascular. Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Nutrients Waste Hormones Immune cells Oxygen
 Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Circulatory System Notes
 Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
Circulatory System Notes Functions of Circulatory System A. Transports B. Transports C. Transports D. Transports E. of fluids F. G. Regulate temperature H. Blood clotting Characteristics of various blood
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
11/10/2014. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM BLOOD VESSELS
 Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
Name: Block: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Multicellular organisms (above the level of roundworms) rely on a circulatory system to bring nutrients to, and take wastes away from, cells. In higher organisms such as
The Heart. The Heart A muscular double pump. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits
 C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
The Cardiovascular System. Preview of Heart Action. The CV system provides oxygen & nutrients to tissues-removes wastes.
 The Cardiovascular System BIO 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Preview of Heart Action http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d3zdj gfddk0&nr=1 The CV system provides oxygen & nutrients to tissues-removes wastes.
The Cardiovascular System BIO 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Preview of Heart Action http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d3zdj gfddk0&nr=1 The CV system provides oxygen & nutrients to tissues-removes wastes.
Chapter 13. Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 13 Cardiovascular System 1 Introduction A. The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and vessels (arteries, capillaries and veins.) B. A functional cardiovascular system is vital for supplying
Chapter 13 Cardiovascular System 1 Introduction A. The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and vessels (arteries, capillaries and veins.) B. A functional cardiovascular system is vital for supplying
The Mammalian Circulatory System
 The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
The Mammalian Heart The Mammalian Circulatory System Recall: What are the 3 cycles of the mammalian circulatory system? What are their functions? What are the three main vessel types in the mammalian circulatory
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart -
 Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 1: Overview of the Cardiovascular System Lesson Objectives Upon
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Slides 11.1 11.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Cardiovascular System
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Slides 11.1 11.19 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Cardiovascular System
The Cardiovascular System (Heart)
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System (Heart) A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Test Review Circulatory System Chapters
 Test Review Circulatory System Chapters 13-2010 1. The tissue that forms the tight fitting sac around the heart is the a. parietal pericardium c. myocardium b. visceral pericardium d. endocardium 2. Which
Test Review Circulatory System Chapters 13-2010 1. The tissue that forms the tight fitting sac around the heart is the a. parietal pericardium c. myocardium b. visceral pericardium d. endocardium 2. Which
10/23/2017. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Also called the circulatory system Consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries Main function is to pump/circulate oxygenated blood
STRUCTURES OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Also called the circulatory system Consists of the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries Main function is to pump/circulate oxygenated blood
Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co.
 Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Anatomy Views Label the diagrams of the heart below: Interactive Physiology Study
Anatomy Review: The Heart Graphics are used with permission of A.D.A.M. Software, Inc. and Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Co. Anatomy Views Label the diagrams of the heart below: Interactive Physiology Study
Chapter 18 - Heart. I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity)
 Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein THE BLOOD SYSTEM 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
Cardiovascular System
 Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 13
Hole s Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki Lewis Created by Dr. Melissa Eisenhauer Head Athletic Trainer/Assistant Professor Trevecca Nazarene University Chapter 13
BIOL 4350 Cardiovascular Physiology Dr. Hamilton. Using the figure above, match the following: 1. Purkinje fibers. 2. SA node. 3. AV node.
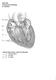 BIOL 4350 Cardiovascular Physiology Dr. Hamilton Using the figure above, match the following: 1. Purkinje fibers. 2. SA node. 3. AV node. 1 Using the figure above, match the following: 4. Atrial depolarization.
BIOL 4350 Cardiovascular Physiology Dr. Hamilton Using the figure above, match the following: 1. Purkinje fibers. 2. SA node. 3. AV node. 1 Using the figure above, match the following: 4. Atrial depolarization.
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11 PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
Chapter 05 Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 05 Cardiovascular System 1 Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels 2 Points to ponder What are the functions of the cardiovascular system? What is the anatomy of the heart? Of blood vessels,
Chapter 05 Cardiovascular System 1 Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels 2 Points to ponder What are the functions of the cardiovascular system? What is the anatomy of the heart? Of blood vessels,
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM
 IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
IB TOPIC 6.2 THE BLOOD SYSTEM THE BLOOD SYSTEM TERMS TO KNOW circulation ventricle artery vein 6.2.U1 - Arteries convey blood at high pressure from the ventricles to the tissues of the body Circulation
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System. The heart. The heart is a double pump. A quick note on arteries vs. veins. = the muscular pump of the CV system
 Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
The Cardiovascular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Slides 11.1 11.19 Seventh Edition Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Functions of the Cardiovascular system Function of the heart: to pump blood
Functions of Blood. Blood Vessels. Lymphatic System. Components of the Cardiovascular System. Unit 5 Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels
 Unit 5 Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels Components of the Cardiovascular System Heart pumps blood Blood vessels the tubes through which the blood flows Functions of Blood Blood removes wastes
Unit 5 Cardiovascular System: Heart and Blood Vessels Components of the Cardiovascular System Heart pumps blood Blood vessels the tubes through which the blood flows Functions of Blood Blood removes wastes
Chapter 05 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 05 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
2. right heart = pulmonary pump takes blood to lungs to pick up oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide
 A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
1. Label the Diagram using the following terms: artery, arterioles, vein, venules, capillaries, valve, inner wall, middle wall, outer wall
 Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
Bio 20 Ms. Nyboer Arteries, Veins, Capillaries, and the Heart Structure and Function Workbook Use your textbook (Ch. 10) and notes to fill in this workbook Part A: Arteries, Veins, Capillaries 1. Label
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
Do Now. Get out work from last class to be checked
 Do Now Get out work from last class to be checked Heart Actions Cardiac Cycle: One complete heartbeat. The contraction of a heart chamber is called systole and the relaxation of a chamber is called diastole.
Do Now Get out work from last class to be checked Heart Actions Cardiac Cycle: One complete heartbeat. The contraction of a heart chamber is called systole and the relaxation of a chamber is called diastole.
Heart. Structure Physiology of blood pressure and heartbeat
 Heart Structure Physiology of blood pressure and heartbeat Location and Anatomy Location and Anatomy Pericardial cavity: surrounds, isolates, and anchors heart Parietal pericardium lined with serous membrane
Heart Structure Physiology of blood pressure and heartbeat Location and Anatomy Location and Anatomy Pericardial cavity: surrounds, isolates, and anchors heart Parietal pericardium lined with serous membrane
Approximately the size of your fist Location. Pericardial physiology
 Heart Anatomy Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Wednesday, March 28, 2012 Muscle
Heart Anatomy Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Wednesday, March 28, 2012 Muscle
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1
 Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
Anatomy & Physiology of Cardiovascular System. Chapter 18 & 19
 Anatomy & Physiology of Cardiovascular System Chapter 18 & 19 Objectives..cont 1. Discuss the physiological stages of cardiac muscle contraction. 2. Trace a typical ECG and label each wave or complex 3.
Anatomy & Physiology of Cardiovascular System Chapter 18 & 19 Objectives..cont 1. Discuss the physiological stages of cardiac muscle contraction. 2. Trace a typical ECG and label each wave or complex 3.
Cardiac Conduction System
 Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
Anatomy of the Heart. Figure 20 2c
 Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Anatomy of the Heart Figure 20 2c Pericardium & Myocardium Remember, the heart sits in it s own cavity, known as the mediastinum. The heart is surrounded by the Pericardium, a double lining of the pericardial
Cardiac Cycle. Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time.
 The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
Biology Unit 3 The Human Heart P
 Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
Biology 2201 Unit 3 The Human Heart P 314-321 Structure and Function of the Human Heart Structure of the Human Heart Has four Chambers (2 Atria and 2 Ventricles) Made of Cardiac Muscle Found in Chest Cavity
CV Anatomy Quiz. Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green
 CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
CV Anatomy Quiz Dr Ella Kim Dr Pip Green Q1 The location of the heart is correctly described as A) lateral to the lungs. B) medial to the sternum. C) superior to the diaphragm. D) posterior to the spinal
Circulation. Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body
 Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Circulation Circulation = is a process used for the transport of oxygen, carbon! dioxide, nutrients and wastes through-out the body Heart = muscular organ about the size of your fist which pumps blood.
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
Human Anatomy, First Edition
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
(2) (1) (3) (4) BLOOD PATHWAY ASSESSMENT RUBRIC
 BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(4) BLOOD%PATHWAY%ASSESSMENT%(3)% BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(3) (4) (3) (2) (1) Using a completely blank diagram of the heart, all valves, chambers, great vessels, and direction of blood
BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(4) BLOOD%PATHWAY%ASSESSMENT%(3)% BLOODPATHWAYASSESSMENT(3) (4) (3) (2) (1) Using a completely blank diagram of the heart, all valves, chambers, great vessels, and direction of blood
Cardiovascular system
 BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
The cardiovascular system is composed of the heart and blood vessels that carry blood to and from the body s organs. There are 2 major circuits:
 1 The cardiovascular system is composed of the heart and blood vessels that carry blood to and from the body s organs. There are 2 major circuits: pulmonary and systemic. The pulmonary goes out to the
1 The cardiovascular system is composed of the heart and blood vessels that carry blood to and from the body s organs. There are 2 major circuits: pulmonary and systemic. The pulmonary goes out to the
AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
Student Name CHAPTER 18 AN ATOMY OF THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM T he heart is actually two pumps one moves blood to the lungs, the other pushes it out into the body. These two functions seem rather elementary
THE HEART. A. The Pericardium - a double sac of serous membrane surrounding the heart
 THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
THE HEART I. Size and Location: A. Fist-size weighing less than a pound (250 to 350 grams). B. Located in the mediastinum between the 2 nd rib and the 5 th intercostal space. 1. Tipped to the left, resting
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Part 1
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
Unit 6: Circulatory System. 6.2 Heart
 Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Unit 6: Circulatory System 6.2 Heart Functions of Circulatory System 1. The heart is the pump necessary to circulate blood to all parts of the body 2. Arteries, veins and capillaries are the structures
Circulatory System 10.1
 1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
1 Circulatory System 10.1 2 ARTERIES Arteries-blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Thick walls Inner & Outer layers: connective tissue Middle layers are muscle and elastic connective tissue
Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column,
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12
 A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
A DAYS CARDIOVASCULAR UNIT GUIDE DUE WEDNESDAY 4/12 MONDAY TUESDAY WEDNESDAY THURSDAY FRIDAY 3/20 - B 3/21 - A 3/22 - B 3/23 - A 3/24 - B 3/27 - A Dissection Ethics Debate 3/28 - B 3/29 - A Intro to Cardiovascular
Heart. Heart 2-Tunica media: middle layer (media ='middle') muscle fibers (smooth or cardiac).
 t. innermost lumenal General Circulatory system heart and blood vessels walls have 3 layers (inside to outside) 1-Tunica interna: aka tunica intima layer--lumenal layer epithelium--endothelium simple squamous
t. innermost lumenal General Circulatory system heart and blood vessels walls have 3 layers (inside to outside) 1-Tunica interna: aka tunica intima layer--lumenal layer epithelium--endothelium simple squamous
Blood Functions. Blood and the Cardiovascular System. Blood. Plasma. Erythrocytes (RBCs) Erythrocytes (RBCs) 4/7/2017
 Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Blood Functions Blood and the Cardiovascular System Distribution Delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all body cells; Transport of wastes to lungs and excretory organs; Transport of hormones Regulation
Cardiovascular System- Heart. Miss Wheeler Unit 8
 Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
Cardiovascular System- Heart Miss Wheeler Unit 8 Overview CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM heart vessels Made up of heart, blood vessels, and blood Functions Heart- pump blood Vessels- (veins, arteries, capillaries)
THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions is of the heart & blood vessels 1. The heart is an essential pumping organ in the cardiovascular system where the right heart pumps deoxygenated blood (returned
THE HEART Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions is of the heart & blood vessels 1. The heart is an essential pumping organ in the cardiovascular system where the right heart pumps deoxygenated blood (returned
The Heart and Cardiovascular System
 The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
The Heart and Cardiovascular System What you will learn The location of the heart 3 layers and covering of the heart Explain the function of the heart as 2 separate pumps Identify the 4 chambers of the
INTRODUCTORY REMARKS:
 INTRODUCTORY REMARKS: The circulatory system provides a way for the blood to be transported throughout the body. This provides nutrients to the cells and allows wastes to be removed. Open vs. Closed Circulatory
INTRODUCTORY REMARKS: The circulatory system provides a way for the blood to be transported throughout the body. This provides nutrients to the cells and allows wastes to be removed. Open vs. Closed Circulatory
Happy One Week before Spring Break!
 Happy One Week before Spring Break! Essential Question Today How does the structure of the heart ensure its functions? Objectives Identify the major parts of the heart. Describe the pathway of circulation,
Happy One Week before Spring Break! Essential Question Today How does the structure of the heart ensure its functions? Objectives Identify the major parts of the heart. Describe the pathway of circulation,
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS
 Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Heart and Heart Disease
 The Heart and Heart Disease Illustration of the heart by Leonardo DaVinci heart-surgeon.com/ history.html 2/14/2010 1 I. Location, Size and Position of the Heart A. Triangular organ located 1. of mass
The Heart and Heart Disease Illustration of the heart by Leonardo DaVinci heart-surgeon.com/ history.html 2/14/2010 1 I. Location, Size and Position of the Heart A. Triangular organ located 1. of mass
Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System
 Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System I. The Cardiovascular System A. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels 1. The heart pumps blood 2. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the
Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System I. The Cardiovascular System A. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels 1. The heart pumps blood 2. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the
Blood must move! 4/15/2014. Heart Basics
 What is the CARDIOVASCULAR system? The cardiovascular system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from different places in the body. The Heart has the job of pumping these things around the body.
What is the CARDIOVASCULAR system? The cardiovascular system carries blood and dissolved substances to and from different places in the body. The Heart has the job of pumping these things around the body.
Collin County Community College. ! BIOL Anatomy & Physiology! WEEK 5. The Heart
 Collin County Community College! BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology! WEEK 5 The Heart 1 (1578-1657) A groundbreaking work in the history of medicine, English physician William Harvey s Anatomical Essay on
Collin County Community College! BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology! WEEK 5 The Heart 1 (1578-1657) A groundbreaking work in the history of medicine, English physician William Harvey s Anatomical Essay on
