JKSS. Pinch-off syndrome INTRODUCTION CASE REPORTS
|
|
|
- Marshall Nash
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CASE REPORT pissn eissn Journal of the Korean Surgical Society Pinch-off syndrome Jin-Beom Cho, Il-Young Park, Ki-Young Sung, Jong-Min Baek, Jun-Hyun Lee, Do-Sang Lee Department of Surgery, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea Subclavian venous catheterization was previously frequently performed, but because of life-threatening complications such as hemothorax, pneumothorax, mediastinal hematoma, and myocardial injury, its use has become less common. However, this practice has some advantages in patient mobility, secured dressing, and rapidity and adequacy of vascular access. In some situations where patient comfort is an especially important consideration, such as with totally implantable venous port insertion for chemotherapy, the subclavian route can be a good choice if an experienced and well-trained faculty is available. The authors have had recent experience with pinch-off syndrome in other words, spontaneous catheter fracture in 3 patients who had undergone venous port implantation through the right subclavian route. Through these cases, we intend to review the dangers of subclavian venous catheterization, the causes of pinch-off syndrome, and its clinical presentation, progress, treatments, and prevention. Corresponding Author Do-Sang Lee Department of Surgery, Bucheon St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, 327 Sosa-ro 327beon-gil, Wonmi-gu, Bucheon , Korea Tel: Fax: dosangs@catholic.ac.kr Key Words Pinch off syndrome, Subclavian venous catheterization, Spontaneous catheter fracture, Implantable venous port INTRODUCTION Central vein catheterization is a common practice for volume resuscitation, emergency venous access, parenteral nutrition, hemodialysis, and central venous pressure monitoring; especially for stable and long-term administration of chemotherapeutic agents, implantable central venous devices are placed through the internal jugular venous route or subclavian venous route. As research on internal jugular venous access using real-time ultrasound has been conducted and widely accepted, the frequency of subclavian venous access has been reduced because of life-threatening complications such as hemothorax, pneumothorax, mediastinal hematoma, vascular perforation, and myocardial injury [1,2]. Therefore, reports on pinch-off syndrome that occurred occasionally in the past have recently become rare. The authors encountered pinch-off syndrome in 3 patients who had undergone totally implantable venous device insertion through the right subclavian route. We report on this rare but critical complication. CASE REPORTS Case 1 A 42-year-old woman with cancer of the left breast had undergone breast conservative surgery on January 4, An implantable venous port was inserted through the right subclavian vein for adjuvant chemotherapy, and the location was confirmed by chest radiography (Fig. 1). There was no problem with the catheter Received December 6, 2012 Revieweed February 19, 2013 Accepted February 22, 2013 J Korean Surg Soc 2013;85: Copyright 2013, the Korean Surgical Society cc Journal of the Korean Surgical Society is an Open Access Journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Journal of the Korean Surgical Society 139
2 Fig. 1. (A) Chest X-ray showed deviated central venous catheter between clavicle and first rib repre senting pinchoff sign grade 1. (B) Close up view. Fig. 2. Chest X-ray showed fractured central venous catheter and embolization of distal portion of the catheter. location, but a pinch-off sign showed as a catheter deviation between the clavicle and the first rib. After the initial injection of chemotherapeutic agent, the patient did not experience pain or swelling, and because there was no problem with blood aspiration or flushing, chemotherapy was administered 3 times under close observation. Three months after the port insertion, the patient was hospitalized for the fourth adjuvant chemotherapy. A chest radiograph showed that the transected catheter had embolized to the right atrium (Fig. 2). The patient was referred to an interventional radiologist, and the embolized catheter was successfully removed via the percutaneous approach through the right internal jugular vein under fluoroscopic guidance (Fig. 3). The remaining implantable venous port was removed surgically. Case 2 A 56-year-old woman with stomach cancer had undergone Fig. 3. Flouroscopic guided foreign body removal. gastrectomy on December 31, After the operation, an implantable venous port was inserted through the right subclavian vein, and adjuvant chemotherapy was administered 6 times without any unusual complications. The patient had follow-ups on a regular basis, and the port was removed 18 months after its insertion. Part of the catheter was fractured and had embolized the right atrium and inferior vena cava, which was confirmed by chest radiography after the procedure (Fig. 4). In a retrospective review of the patient s chest radiographs, a pinch-off sign was noted in the chest radiograph taken immediately after the port insertion and the catheter s course was deviated by the clavicle (Fig. 5). During the adjuvant chemotherapy and outpatient followup observations, the patient did not complain of any pain or swelling, and there was no unusual problem with drug administration through the port. Transection of the catheter is assumed to have occurred at the end of the adjuvant chemotherapy, which was 6 months after the port insertion, 140 thesurgery.or.kr
3 but the exact time was impossible to confirm. The patient was referred to an interventional radiologist, and the embolized catheter was successfully removed by a percutaneous approach through the right internal jugular vein under fluoroscopic guidance (Fig. 6). Case 3 A 48-year-old man with rectosigmoid colon cancer had undergone low anterior resection on July 15, For adjuvant chemotherapy, an implantable venous port was inserted through the right subclavian vein, and its location was confirmed by chest radiography (Fig. 7). No associated com plication with the location of the catheter, and no pinchoff sign was suspected. The patient had undergone adjuvant chemotherapy 4 times without any unusual problems, ended the therapy of his own accord, and was lost to follow-up. Six months after he terminated the therapy, the patient returned to the outpatient clinic. His test results indicated that his disease had aggravated; therefore, chemotherapy was initiated again with different medications. He had chemotherapy twice during 2 months without any unusual complications but the port became dysfunctional after he was hospitalized for the third cycle; therefore, the removal of the original venous catheter and reinsertion through the left subclavian route were conducted. In the chest radiograph taken immediately after the second cannulation, some parts of the catheter of the removed right subclavian venous port remained (Fig. 8). In a retrospective review of the patient s chest radiographs, we observed catheter s luminal narrowing, that was not present on the initial chest X-ray, in the chest radiograph that was taken 4 months after the insertion of the right subclavian venous port (Fig. 9). It is assumed that the weakened catheter was fractured by the force used during the removal. To find out the exact location of the catheter, pulmonary arteriography Fig. 4. Chest X-ray showed remnant catheter. Fig. 6. Flouroscopic guided foreign body removal. Fig. 5. (A) Chest X ray showed deviated central venous catheter between clavicle and first rib representing pinchoff sign grade 1. (B) Close up view. Journal of the Korean Surgical Society 141
4 Fig. 7. Chest X-ray showed no deviation or luminal narrowing of central venous catheter representing pinch-off sign grade 0. Fig. 8. Chest X-ray showed inserted left subclavian venous port and foreign body on left lung field. Fig. 9. (A) Chest X-ray showed luminal narrowing of central venous catheter representing pinch-off sign grade 2. (B) Close up view. was performed (Fig. 10). The patient was referred to an interventional radiologist, and the embolized catheter was successfully removed by the percutaneous approach through the right common femoral artery (Fig. 11). DISCUSSION When a subclavian venous catheter is compressed between the clavicle and the first rib, it can cause permanent or intermittent obstruction, and as a result, tearing, transection, and catheter embolization can occur. In 1990, Hinke et al. [3] first described this phenomenon as pinch-off syndrome. Before this, Aitken and Minton [4] named the chest X-ray findings that indicated impending subclavian catheter problems as pinch-off signs. Hinke et al. [3] distinguished pinch-off signs on the following scale when introducing pinch-off syndrome: grade 0, no narrowing in the catheter s course; grade 1, no luminal catheter narrowing, but deviation; grade 2, luminal narrowing as the catheter passes under the clavicle (true pinch-off sign); grade 3, catheter transection between the clavicle and the first rib that is accompanied by embolization of the distal catheter. According to the research by Mirza et al. [5], the most common clinical presentation in patients with pinch-off syndrome was pain with or without swelling at the catheter insertion site, and the next most common was dysfunctional catheter, in other words, problems with blood aspiration or flushing, and the lesser common clinical presentation were accidental discovery of catheter embolization on routine chest X-ray, cardiac palpitation, bilateral chest pain, abdominal pain and nausea, new S3 heart sound, paresis of the ipsilateral arm, etc. The median interval from the time of catheter insertion to pinch-off 142 thesurgery.or.kr
5 Fig. 10. Pulmonary arteriography showed transected catheter located inside pulmonary artery. syndrome was 5.3 months, the average time interval was 5 months, and the longest interval was 60 months from the time of insertion. According to the collective review by Fisher and Ferreyro [6], the rate of serious complications related to embolized catheters including death was 71% in patients who had pinch-off syndrome, and they asserted that the central venous catheter should be removed as soon as possible. Mirza et al. [5] suggested the use of the internal jugular venous route to fundamentally prevent pinch-off syndrome. In fact, the subclavian venous route is being used less frequently because of pinch-off syndrome and other associated complications such as hemothorax, pneumothorax, mediastinal hematoma, vascular perforation, and myocardial injury. However, this practice has some advantages of patient mobility, secured dressing, and rapid and adequate vascular access [7]. A subclavian venous port can be a good choice if an welltrained, experienced faculty is available, especially in the case of totally implantable venous port insertion for chemotherapy because patient comfort is an important consideration in this case. As shown in the aforementioned cases, pinchoff syndrome can occur without any unusual symptoms; therefore, it is necessary to closely observe with repeated chest X-rays of those patients who undergo subclavian venous port insertion; if problems occur with blood aspiration and heparin flushing, the possibility of pinch-off syndrome should be suspected. In the first and second cases, a grade 1 pinch-off sign was observed in the chest radiograph taken immediately after port insertion, and in the third case, pinch-off signs were not observed immediately after port insertion, but grade 2 pinch-off sign was newly observed eventually. Therefore, chest radiographs should be taken after subclavian venous Fig. 11. Flouroscopic guided foreign body removal. catheterization, and pinch-off signs as well as mechanical complications such as hemothorax and pneumothorax should be checked. In the second and third cases, the authors were unable to predict pinch-off syndrome and only discovered the pinch-off signs by retrospective review. In addition, in the second case, pinch-off syndrome was detected after the venous port was removed, 12 months after the termination of chemotherapy. Therefore, if the venous port is not required, then the catheter should be immediately removed to avoid pinch-off syndrome. Rubenstein et al. [8] and Zieren et al. [9] reported that, while gaining subclavian venous access, cannulation on the lateral side of the mid clavicular line may reduce pinch-off syndrome. Therefore, we conclude that, the basic principles are important for preventing this syndrome. These principles include performing the procedure accurately, observing the patients closely, and removing the venous port immediately, if no longer required. CONFLICTS OF INTEREST No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported. REFERENCES 1. Slama M, Novara A, Safavian A, Ossart M, Safar M, Fagon JY. Improvement of internal jugular vein cannulation using an ultrasound-guided technique. Intensive Care Med 1997;23: Karakitsos D, Labropoulos N, De Groot E, Patrianakos AP, Kouraklis G, Poularas J, et al. Real-time ultrasound-guided catheterisation of the internal jugular vein: a prospective comparison with the landmark technique in critical care patients. Journal of the Korean Surgical Society 143
6 Crit Care 2006;10:R Hinke DH, Zandt-Stastny DA, Goodman LR, Quebbeman EJ, Krzywda EA, Andris DA. Pinch-off syndrome: a complication of implantable subclavian venous access devices. Radiology 1990;177: Aitken DR, Minton JP. The "pinch-off sign": a warning of impending problems with permanent subclavian catheters. Am J Surg 1984;148: Mirza B, Vanek VW, Kupensky DT. Pinch-off syndrome: case report and collective review of the literature. Am Surg 2004;70: Fisher RG, Ferreyro R. Evaluation of current techniques for nonsurgical removal of intravascular iatrogenic foreign bodies. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1978;130: De Moor B, Vanholder R, Ringoir S. Subclavian vein hemodialysis catheters: advantages and disadvantages. Artif Organs 1994;18: Rubenstein RB, Alberty RE, Michels LG, Pederson RW, Rosenthal D. Hickman catheter separation. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr 1985;9: Zieren J, Thul P, Romaniuk P, Muller JM. Intravascular disruption of central venous ports. Clin Nutr 1998;17: thesurgery.or.kr
Catheter Fracture of a Totally Implantable Venous Device Due to Pinch Off Syndrome in Breast Cancer: A Case Report
 Kosin Medical Journal 2016;31:167-172. https://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2016.31.2.167 KMJ Case Report Catheter Fracture of a Totally Implantable Venous Device Due to Pinch Off Syndrome in Breast Cancer: A Case
Kosin Medical Journal 2016;31:167-172. https://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2016.31.2.167 KMJ Case Report Catheter Fracture of a Totally Implantable Venous Device Due to Pinch Off Syndrome in Breast Cancer: A Case
Peel-Apart Percutaneous Introducer Kits for
 Bard Access Systems Peel-Apart Percutaneous Introducer Kits for Table of Contents Contents Page Bard Implanted Ports Hickman*, Leonard*, Broviac*, Tenckhoff*, and Groshong* Catheters Introduction....................................
Bard Access Systems Peel-Apart Percutaneous Introducer Kits for Table of Contents Contents Page Bard Implanted Ports Hickman*, Leonard*, Broviac*, Tenckhoff*, and Groshong* Catheters Introduction....................................
Totally implantable venous devices (TIVDs) significantly
 Case Report 425 Catheter Fracture and Cardiac Migration - An Unusual Fracture Site of Totally Implantable Venous Devices: Report of Two Cases Chia-Lo Chang, MD; Hong-Hwa Chen, MD; Shung-Eing Lin, MD Totally
Case Report 425 Catheter Fracture and Cardiac Migration - An Unusual Fracture Site of Totally Implantable Venous Devices: Report of Two Cases Chia-Lo Chang, MD; Hong-Hwa Chen, MD; Shung-Eing Lin, MD Totally
Dr. prakruthi Dept. of anaesthesiology, Rrmch, bangalore
 CENTRAL VENOUS CATHETERIZATION Dr. prakruthi Dept. of anaesthesiology, Rrmch, bangalore OBJECTIVES Introduction Indications and Contraindications Complications Technique Basic principles Specifics by Site
CENTRAL VENOUS CATHETERIZATION Dr. prakruthi Dept. of anaesthesiology, Rrmch, bangalore OBJECTIVES Introduction Indications and Contraindications Complications Technique Basic principles Specifics by Site
Spontaneous Migration of a Central Line Catheter into the Heart. Saeed Al Hindi, MD, CABS, FRCSI* Khulood Al-Saad, MD**
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 29, No. 3, September 2007 Spontaneous Migration of a Central Line Catheter into the Heart Saeed Al Hindi, MD, CABS, FRCSI* Khulood Al-Saad, MD** Background: Spontaneous migration
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 29, No. 3, September 2007 Spontaneous Migration of a Central Line Catheter into the Heart Saeed Al Hindi, MD, CABS, FRCSI* Khulood Al-Saad, MD** Background: Spontaneous migration
Case Report The Sheared Central Venous Catheter?
 Case Reports in Anesthesiology Volume 2011, Article ID 379827, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/379827 Case Report The Sheared Central Venous Catheter? Harihar V. Hegde, 1 Vijay G. Yaliwal, 1 Shyamsundar K. Joshi,
Case Reports in Anesthesiology Volume 2011, Article ID 379827, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/379827 Case Report The Sheared Central Venous Catheter? Harihar V. Hegde, 1 Vijay G. Yaliwal, 1 Shyamsundar K. Joshi,
Central Venous Access Devices. Stephanie Cunningham Amy Waters
 Central Venous Access Devices Stephanie Cunningham Amy Waters 5 Must Know Facts About CVAD s 1) What are CVAD s? 2) What are CVAD s used for? 3) How are these devices put in? 4) What are the complications
Central Venous Access Devices Stephanie Cunningham Amy Waters 5 Must Know Facts About CVAD s 1) What are CVAD s? 2) What are CVAD s used for? 3) How are these devices put in? 4) What are the complications
Mary Lou Garey MSN EMT-P MedFlight of Ohio
 Mary Lou Garey MSN EMT-P MedFlight of Ohio Function Prolonged and frequent access to venous circulation Allows for patient to carry on normal life; decrease number of needle sticks Medications, parenteral
Mary Lou Garey MSN EMT-P MedFlight of Ohio Function Prolonged and frequent access to venous circulation Allows for patient to carry on normal life; decrease number of needle sticks Medications, parenteral
Overview of CVADs. Type of device commonly used. Dwell time Flushing requirement Associated complications. lumens
 Source: Clinical Skills Management of Vascular Access Devices Pre-course handbook. Adapted with permission from NHS Lothian Employee and Education Development Team. Overview of CVADs Type of device Veins
Source: Clinical Skills Management of Vascular Access Devices Pre-course handbook. Adapted with permission from NHS Lothian Employee and Education Development Team. Overview of CVADs Type of device Veins
Central Line Care and Management
 Central Line Care and Management What is a Central Line/ CVAD? (central venous access device) A vascular infusion device that terminates at or close to the heart or in one of the great vessels (aorta,
Central Line Care and Management What is a Central Line/ CVAD? (central venous access device) A vascular infusion device that terminates at or close to the heart or in one of the great vessels (aorta,
이동된중심정맥도관으로인한간헐적심계항진환자의경피적도관제거
 대한내과학회지 : 제 85 권제 2 호 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.3904/kjm.2013.85.2.194 이동된중심정맥도관으로인한간헐적심계항진환자의경피적도관제거 연세대학교의과대학강남세브란스병원내과 정혜문 이광원 하지윤 김승규 윤지영 권혁문 이병권 Successful Percutaneous Transcatheter Retrieval of
대한내과학회지 : 제 85 권제 2 호 2013 http://dx.doi.org/10.3904/kjm.2013.85.2.194 이동된중심정맥도관으로인한간헐적심계항진환자의경피적도관제거 연세대학교의과대학강남세브란스병원내과 정혜문 이광원 하지윤 김승규 윤지영 권혁문 이병권 Successful Percutaneous Transcatheter Retrieval of
Appendix E: Overview of Vascular
 Appendix E: Overview of Vascular 56 Peripheral Short Catheter, less than 3 inches (7.5 cm) in length; over-the-needle catheter is most common. Inserted by percutaneous venipuncture, generally into a hand
Appendix E: Overview of Vascular 56 Peripheral Short Catheter, less than 3 inches (7.5 cm) in length; over-the-needle catheter is most common. Inserted by percutaneous venipuncture, generally into a hand
Research Article Can we predict the Position of Central Venous Catheter Tip Following Cannulation of Internal Jugular Vein?
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ANAESTHESIA Research Article Can we predict the Position of Central Venous Catheter Tip Following Cannulation of Internal Jugular Vein? Pradeep Marur Venkategowda 1, Surath Manimala
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS ANAESTHESIA Research Article Can we predict the Position of Central Venous Catheter Tip Following Cannulation of Internal Jugular Vein? Pradeep Marur Venkategowda 1, Surath Manimala
2013 Coding Changes. Diagnostic Radiology. Nuclear Medicine
 2013 Coding Changes The principal coding changes affecting Radiologists in 2013 occur in the Interventional Radiology Section of the AMA/CPT Manual. As in the past, we continue to see the Relative Update
2013 Coding Changes The principal coding changes affecting Radiologists in 2013 occur in the Interventional Radiology Section of the AMA/CPT Manual. As in the past, we continue to see the Relative Update
AV ACESS COMPLICATIONS. Ass. Prof. Dr. Habas
 AV ACESS COMPLICATIONS Ass. Prof. Dr. Habas COMPLICATION AVF IS CONSIDERED A MINOR PROCEDURE INCIDENCE OF COMPLICATION- 20-27% MANY A COMPLICATION LEADS TO FAILURE OF FISTULA LOSS OF SITE AND VEIN FOR
AV ACESS COMPLICATIONS Ass. Prof. Dr. Habas COMPLICATION AVF IS CONSIDERED A MINOR PROCEDURE INCIDENCE OF COMPLICATION- 20-27% MANY A COMPLICATION LEADS TO FAILURE OF FISTULA LOSS OF SITE AND VEIN FOR
Port-A Catheter Fracture: A Potential Lethal Iatrogenic Complication Identified on PET-CT
 Port-A Catheter Fracture: A Potential Lethal Iatrogenic Complication Identified on PET-CT Hung-Jen Hsieh 1, Kun-Han Lue 1, Bee-Song Chang 2, Chih-Hao K. Kao 1, Shu-Hsin Liu 1, Pan-Fu Kao 1 1 Department
Port-A Catheter Fracture: A Potential Lethal Iatrogenic Complication Identified on PET-CT Hung-Jen Hsieh 1, Kun-Han Lue 1, Bee-Song Chang 2, Chih-Hao K. Kao 1, Shu-Hsin Liu 1, Pan-Fu Kao 1 1 Department
Lines and tubes. 1 Nasogastric tubes Endotracheal tubes Central lines Permanent pacemakers Chest drains...
 Lines and tubes 1 Nasogastric tubes... 15 2 Endotracheal tubes.... 19 3 Central lines... 21 4 Permanent pacemakers.... 25 5 Chest drains... 30 This page intentionally left blank 1 Nasogastric tubes Background
Lines and tubes 1 Nasogastric tubes... 15 2 Endotracheal tubes.... 19 3 Central lines... 21 4 Permanent pacemakers.... 25 5 Chest drains... 30 This page intentionally left blank 1 Nasogastric tubes Background
Totally implantable venous access system (TIVAS) Complicated by Tracheo-Venous Fistula
 Totally implantable venous access system (TIVAS) Complicated by Tracheo-Venous Fistula Samer Khaled, M.D., Vladimir Gotlieb, M.D., and Arunbai Patel, M.D. Citation: Khaled S, Gotlieb V, Patel A. Totally
Totally implantable venous access system (TIVAS) Complicated by Tracheo-Venous Fistula Samer Khaled, M.D., Vladimir Gotlieb, M.D., and Arunbai Patel, M.D. Citation: Khaled S, Gotlieb V, Patel A. Totally
Transhepatic placement of haemodialysis catheter: A solution for vascular access exhaustion. Yap, DYH; Tso, WK; Chu, FSK; Chan, TM; Lai, KN; Tang, SCW
 Title Transhepatic placement of haemodialysis catheter: A solution for vascular access exhaustion Author(s) Yap, DYH; Tso, WK; Chu, FSK; Chan, TM; Lai, KN; Tang, SCW Citation Nephrology, 2010, v. 15 n.
Title Transhepatic placement of haemodialysis catheter: A solution for vascular access exhaustion Author(s) Yap, DYH; Tso, WK; Chu, FSK; Chan, TM; Lai, KN; Tang, SCW Citation Nephrology, 2010, v. 15 n.
Advocate Christ Medical Center CVC Placement Certification Course
 Advocate Christ Medical Center CVC Placement Certification Course July 12th, 2012 Hannah Watts, MD Medical Simulation Director Modified August 10, 2017 Taajwar Khan, MD Chief Resident of Internal Medicine
Advocate Christ Medical Center CVC Placement Certification Course July 12th, 2012 Hannah Watts, MD Medical Simulation Director Modified August 10, 2017 Taajwar Khan, MD Chief Resident of Internal Medicine
You have a what, inside you?
 Costal Emergency Medicine Conference You have a what, inside you? Less than mainstream medical devices encountered in the ED. Eric Ossmann, MD, FACEP Associate Professor Duke University Medical Center
Costal Emergency Medicine Conference You have a what, inside you? Less than mainstream medical devices encountered in the ED. Eric Ossmann, MD, FACEP Associate Professor Duke University Medical Center
Kristin Wise, MD, FHM Division of General Internal Medicine and Geriatrics Hospital Medicine 2013
 Kristin Wise, MD, FHM Division of General Internal Medicine and Geriatrics Hospital Medicine 2013 Objectives for CVC Placement Understand the indications and contraindications Determine appropriate CVC
Kristin Wise, MD, FHM Division of General Internal Medicine and Geriatrics Hospital Medicine 2013 Objectives for CVC Placement Understand the indications and contraindications Determine appropriate CVC
10/14/2018 Dr. Shatarat
 2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
Polyurethane Catheter
 References 1. Aitken, D.R. and Minton, J.P. The Pinch-Off Sign: A Subclavian Catheters, American Journal of Surgery, Vol. 148, Nov. 1984, pp. 633-636. 2. Rubenstein, R.B., Alberty, R.E., et al. Hickman
References 1. Aitken, D.R. and Minton, J.P. The Pinch-Off Sign: A Subclavian Catheters, American Journal of Surgery, Vol. 148, Nov. 1984, pp. 633-636. 2. Rubenstein, R.B., Alberty, R.E., et al. Hickman
Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement
 Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement of Severe Segmental Coronary Artery Occlusion Operative Technique Rene G. Favaloro, M.D. D irect operation on the coronary artery has been performed in 180 patients
Saphenous Vein Autograft Replacement of Severe Segmental Coronary Artery Occlusion Operative Technique Rene G. Favaloro, M.D. D irect operation on the coronary artery has been performed in 180 patients
Bard Meridian Filter Fracture
 Bard Meridian Filter Fracture The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published Publisher Wu, Alex et al. Bard
Bard Meridian Filter Fracture The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published Publisher Wu, Alex et al. Bard
Instructions For Use. Implantable Ports. with Open-Ended and Groshong Catheters
 Instructions For Use Implantable Ports with Open-Ended and Groshong Catheters 3 Implantable Ports with Open-Ended and Groshong Catheters 1 Description The BardPort, SlimPort, and X-Port implantable ports
Instructions For Use Implantable Ports with Open-Ended and Groshong Catheters 3 Implantable Ports with Open-Ended and Groshong Catheters 1 Description The BardPort, SlimPort, and X-Port implantable ports
A Primer on Central Venous Access: Peripherally-Inserted Central Catheters, Tunneled Catheters, and Subcutaneous Ports
 Disclosures A Primer on Central Venous Access: Peripherally-Inserted Central Catheters, Tunneled Catheters, and Subcutaneous Ports No conflicts of interest relevant to this presentation Jason W. Pinchot,
Disclosures A Primer on Central Venous Access: Peripherally-Inserted Central Catheters, Tunneled Catheters, and Subcutaneous Ports No conflicts of interest relevant to this presentation Jason W. Pinchot,
Intro: Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Basic understanding of interventional radiology. Gain knowledge of key terms and phrases
 Slide 1 Intro: PRESENTED BY: Selena M. Moore, AAS, CCS, CPC HIMS Physician Liaison Coder This is a modified/updated presentation that was originally written by: Rosemary Waligorski, RHIT, CCS, RCC and
Slide 1 Intro: PRESENTED BY: Selena M. Moore, AAS, CCS, CPC HIMS Physician Liaison Coder This is a modified/updated presentation that was originally written by: Rosemary Waligorski, RHIT, CCS, RCC and
Patient guide: pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system. Catheter occlusion of. Patent Ductus Arteriosus. with the
 Patient guide: Catheter occlusion of Patent Ductus Arteriosus with the pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system pfm Produkte für die Medizin - AG Wankelstr. 60 D - 50996 Cologne Phone: +49 (0) 2236 96
Patient guide: Catheter occlusion of Patent Ductus Arteriosus with the pfm Nit-Occlud PDA coil occlusion system pfm Produkte für die Medizin - AG Wankelstr. 60 D - 50996 Cologne Phone: +49 (0) 2236 96
Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information
 Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information A Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and a Pulmonary Embolism (PE) are both disorders of unwanted blood clotting. Unwanted blood clots can occur
Deep Vein Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism: Patient Information A Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and a Pulmonary Embolism (PE) are both disorders of unwanted blood clotting. Unwanted blood clots can occur
Individual Pulmonary Vein Atresia in Adults: Report of Two Cases
 Case Report DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.3.395 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(3):395-399 Individual Pulmonary Vein Atresia in Adults: Report of Two Cases Hyoung Nam Lee, MD, Young
Case Report DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.3.395 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(3):395-399 Individual Pulmonary Vein Atresia in Adults: Report of Two Cases Hyoung Nam Lee, MD, Young
Victoria Chapman BS, RN, HP (ASCP)
 Victoria Chapman BS, RN, HP (ASCP) Considerations: Age Sex Body Composition Hydration Status Chemotherapy Use Access History Considerations: Immunosuppression Use Chemotherapy Frequency of plasma exchanges
Victoria Chapman BS, RN, HP (ASCP) Considerations: Age Sex Body Composition Hydration Status Chemotherapy Use Access History Considerations: Immunosuppression Use Chemotherapy Frequency of plasma exchanges
Advancing Lives and the Delivery of Health Care. The High-Flow Port Designed for Apheresis
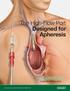 Advancing Lives and the Delivery of Health Care The High-Flow Port Designed for Apheresis Optimized for Long Device Life Bench Tested up to 1,000 Accesses 1 Bard is proud to introduce the first and only
Advancing Lives and the Delivery of Health Care The High-Flow Port Designed for Apheresis Optimized for Long Device Life Bench Tested up to 1,000 Accesses 1 Bard is proud to introduce the first and only
Fluoroscopy-Guided Endoscopic Removal of Foreign Bodies
 CASE REPORT Clin Endosc 2017;50:197-201 https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.085 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Fluoroscopy-Guided Endoscopic Removal of Foreign odies Junhwan Kim
CASE REPORT Clin Endosc 2017;50:197-201 https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.085 Print ISSN 2234-2400 / On-line ISSN 2234-2443 Open Access Fluoroscopy-Guided Endoscopic Removal of Foreign odies Junhwan Kim
2018 HEMODIALYSIS CATHETERS CODING AND REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE
 2018 HEMODIALYSIS CATHETERS CODING AND REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE Contents Overview of Central Venous Access s for Hemodialysis 2 Procedures Using Hemodialysis s 2 Physician Reimbursement for Hemodialysis s 3
2018 HEMODIALYSIS CATHETERS CODING AND REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE Contents Overview of Central Venous Access s for Hemodialysis 2 Procedures Using Hemodialysis s 2 Physician Reimbursement for Hemodialysis s 3
You have a what, inside you?
 Costal Emergency Medicine Conference You have a what, inside you? Less than mainstream medical devices encountered in the ED. Eric Ossmann, MD, FACEP Associate Professor Duke University Medical Center
Costal Emergency Medicine Conference You have a what, inside you? Less than mainstream medical devices encountered in the ED. Eric Ossmann, MD, FACEP Associate Professor Duke University Medical Center
External Ref: Andres, D.A., et al. Catheter Pinch-Off Syndrome: Recognition and Management.
 Department Policy Code: D: PC-5530 Entity: Fairview Pharmacy Services Department: Fairview Home Infusion Manual: Policy and Procedure Manual Category: Home Infusion Subject: Complications With Intravenous
Department Policy Code: D: PC-5530 Entity: Fairview Pharmacy Services Department: Fairview Home Infusion Manual: Policy and Procedure Manual Category: Home Infusion Subject: Complications With Intravenous
An Adolescent Patient with Coarctation of Aorta Treated with Self-Expandable Nitinol Stent
 Case Report Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal An Adolescent Patient with Coarctation of Aorta Treated with Self-Expandable Nitinol Stent Woo Sup Shim, MD 1, Jin Young
Case Report Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal An Adolescent Patient with Coarctation of Aorta Treated with Self-Expandable Nitinol Stent Woo Sup Shim, MD 1, Jin Young
Ultrasound-guided infraclavicular axillary vein cannulation for central venous access {
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 93 (2): 188 92 DOI: 10.1093/bja/aeh187 Advance Access publication June 25, 2004 Ultrasound-guided infraclavicular axillary vein cannulation for central venous access { A.
British Journal of Anaesthesia 93 (2): 188 92 DOI: 10.1093/bja/aeh187 Advance Access publication June 25, 2004 Ultrasound-guided infraclavicular axillary vein cannulation for central venous access { A.
Methods of Counting Ribs on Chest CT: The Modified Sternomanubrial Approach 1
 Methods of Counting Ribs on Chest CT: The Modified Sternomanubrial Approach 1 Kyung Sik Yi, M.D., Sung Jin Kim, M.D., Min Hee Jeon, M.D., Seung Young Lee, M.D., Il Hun Bae, M.D. Purpose: The purpose of
Methods of Counting Ribs on Chest CT: The Modified Sternomanubrial Approach 1 Kyung Sik Yi, M.D., Sung Jin Kim, M.D., Min Hee Jeon, M.D., Seung Young Lee, M.D., Il Hun Bae, M.D. Purpose: The purpose of
IV Drug Delivery Systems used in Cancer Care
 IV Drug Delivery Systems used in Cancer Care Cheri Constantino-Shor, RN, MSN, CRNI Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Nursing Staff Development Coordinator Presentation Objective Describe drug delivery devices
IV Drug Delivery Systems used in Cancer Care Cheri Constantino-Shor, RN, MSN, CRNI Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Nursing Staff Development Coordinator Presentation Objective Describe drug delivery devices
Estimation of Stellate Ganglion Block Injection Point Using the Cricoid Cartilage as Landmark Through X-ray Review
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2011 September; Vol. 24, No. 3: 141-145 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.3.141 Estimation of Stellate Ganglion Block Injection Point
Original Article Korean J Pain 2011 September; Vol. 24, No. 3: 141-145 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.3.141 Estimation of Stellate Ganglion Block Injection Point
Dignity Dual Power Injectable Implantable Infusion Port INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
 DESCRIPTION: Dignity Dual Power Injectable Implantable Infusion Port INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE The Dignity Dual power injectable implantable infusion port is an implantable access device designed to provide
DESCRIPTION: Dignity Dual Power Injectable Implantable Infusion Port INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE The Dignity Dual power injectable implantable infusion port is an implantable access device designed to provide
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
The Lost Guide Wire. Ghazi Y Ismael, MBBS* Dhafer M Kamal, MD, MSc, FRCS (Canada)**
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 32, No. 2, June 2010 The Lost Guide Wire Ghazi Y Ismael, MBBS* Dhafer M Kamal, MD, MSc, FRCS (Canada)** A guide wire was lost during insertion of a femoral arterial line
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 32, No. 2, June 2010 The Lost Guide Wire Ghazi Y Ismael, MBBS* Dhafer M Kamal, MD, MSc, FRCS (Canada)** A guide wire was lost during insertion of a femoral arterial line
Carry this card with you at all times. Show this card to any medical professional treating you. Patient Implant Card. Option ELITE Vena Cava Filter.
 Patient Guide A Safe Option for a Healthier You! P/N: P-2017-0175-00 Rev B 1. Static magnetic field of 3 Tesla or less. 2. Spatial gradient magnetic field of 720 Gauss/cm or less. 3. Maximum whole body
Patient Guide A Safe Option for a Healthier You! P/N: P-2017-0175-00 Rev B 1. Static magnetic field of 3 Tesla or less. 2. Spatial gradient magnetic field of 720 Gauss/cm or less. 3. Maximum whole body
Stenting of the Superior Vena Cava and Left Brachiocephalic Vein with Preserving the Central Venous Catheter in Situ
 Case Report http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2011.12.5.629 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(5):629-633 Stenting of the Superior Vena Cava and Left Brachiocephalic Vein with Preserving
Case Report http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2011.12.5.629 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(5):629-633 Stenting of the Superior Vena Cava and Left Brachiocephalic Vein with Preserving
Sample page. POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your trusted coding partner for 32 years. Visit optum360coding.com.
 2018 Complete Guide for Interventional Radiology An in-depth guide to interventional radiology coding, billing, and reimbursement for facilities and physicians POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your
2018 Complete Guide for Interventional Radiology An in-depth guide to interventional radiology coding, billing, and reimbursement for facilities and physicians POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your
Interruption of Chest Compression for Central Venous Catheterization during Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation
 Korean J Crit Care Med 2014 August 29(3):172-176 / http://dx.doi.org/10.4266/kjccm.2014.29.3.172 ISSN 2383-4870 (Print) ㆍ ISSN 2383-4889 (Online) Original Article Interruption of Chest Compression for
Korean J Crit Care Med 2014 August 29(3):172-176 / http://dx.doi.org/10.4266/kjccm.2014.29.3.172 ISSN 2383-4870 (Print) ㆍ ISSN 2383-4889 (Online) Original Article Interruption of Chest Compression for
Intravenous Catheter Complications
 Vascular Access Device-Related Infection Inadequate skin antisepsis prior to VAD insertion Acute onset of fever, chills, and hypotension. No other apparent source of Notify Prescriber immediately Obtain
Vascular Access Device-Related Infection Inadequate skin antisepsis prior to VAD insertion Acute onset of fever, chills, and hypotension. No other apparent source of Notify Prescriber immediately Obtain
Case Report Thoracic Imaging. Eun Kyung Khil, MD 1, Heon Lee, MD, PhD 1, Keun Her, MD 2 INTRODUCTION CASE REPORT
 Case Report Thoracic Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.173 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(1):173-177 Spontaneous Intramural Full-Length Dissection of Esophagus Treated
Case Report Thoracic Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.1.173 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(1):173-177 Spontaneous Intramural Full-Length Dissection of Esophagus Treated
Permanent central venous catheters: complications and strategies using different accesses.
 Permanent central venous catheters: complications and strategies using different accesses. Poster No.: C-1038 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. D. Ferrer-Puchol, R. Ramiro, E. Garcia-Oliver,
Permanent central venous catheters: complications and strategies using different accesses. Poster No.: C-1038 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. D. Ferrer-Puchol, R. Ramiro, E. Garcia-Oliver,
Groshong Central Venous Catheters
 Bard Access Systems Groshong Central Venous Catheters Long Term Instructions For Use Table of Contents Contents Page Introduction... 1 Description Placement Schematics Groshong Valve Function Indications
Bard Access Systems Groshong Central Venous Catheters Long Term Instructions For Use Table of Contents Contents Page Introduction... 1 Description Placement Schematics Groshong Valve Function Indications
If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to to view current policies.
 If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to www.fairview.org/fhipolicies to view current policies. Department Policy Code: D: PC-5530 Entity: Fairview Pharmacy Services
If viewing a printed copy of this policy, please note it could be expired. Got to www.fairview.org/fhipolicies to view current policies. Department Policy Code: D: PC-5530 Entity: Fairview Pharmacy Services
Aorto-Innominate Venous Fistula after Percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation of the Sternoclavivular Joint Anterior Dislocation - A case report -
 The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol11, No4, October, 1998 = Abstract = Aorto-Innominate Venous Fistula after Percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation of the Sternoclavivular Joint Anterior Dislocation
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol11, No4, October, 1998 = Abstract = Aorto-Innominate Venous Fistula after Percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation of the Sternoclavivular Joint Anterior Dislocation
IV Fluids Nursing B23 Objectives Serum Osmolality 275 to 295 Isotonic
 1 IV Fluids Nursing B23 2 Objectives 3 Serum Osmolality Serum osmolality solute concentration of a solution Higher osmolality means greater pulling power for water Normal serum osmolality is 275 to 295
1 IV Fluids Nursing B23 2 Objectives 3 Serum Osmolality Serum osmolality solute concentration of a solution Higher osmolality means greater pulling power for water Normal serum osmolality is 275 to 295
Deep Vein Thrombosis
 Deep Vein Thrombosis from NHS (UK) guidelines Introduction Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in one of the deep veins in the body. Blood clots that develop in a vein are also known as venous thrombosis.
Deep Vein Thrombosis from NHS (UK) guidelines Introduction Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a blood clot in one of the deep veins in the body. Blood clots that develop in a vein are also known as venous thrombosis.
The Comparison of the Result of Epiduroscopic Laser Neural Decompression between FBSS or Not
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2014 January; Vol. 27, No. 1: 63-67 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.63 The Comparison of the Result of Epiduroscopic Laser Neural
Original Article Korean J Pain 2014 January; Vol. 27, No. 1: 63-67 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2014.27.1.63 The Comparison of the Result of Epiduroscopic Laser Neural
IV Fluids. Nursing B23. Objectives. Serum Osmolality
 IV Fluids Nursing B23 Objectives Discuss the purpose of IV Discuss nursing interventions in IV therapy Identify complications of IV therapy Differentiate between peripheral line, central line, and PICC
IV Fluids Nursing B23 Objectives Discuss the purpose of IV Discuss nursing interventions in IV therapy Identify complications of IV therapy Differentiate between peripheral line, central line, and PICC
Comparative Study for the Efficacy of Small Bore Catheter in the Patients with Iatrogenic Pneumothorax
 Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 20;44:48-422 ISSN: 2233-60X (Print) ISSN: 2093-656 (Online) Clinical Research http://dx.doi.org/0.5090/kjtcs.20.44.6.48 Comparative Study for the Efficacy of Small Bore
Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 20;44:48-422 ISSN: 2233-60X (Print) ISSN: 2093-656 (Online) Clinical Research http://dx.doi.org/0.5090/kjtcs.20.44.6.48 Comparative Study for the Efficacy of Small Bore
Unit 11. Objectives. Indications for IV Therapy. Intravenous Access Devices & Common IV Fluids. 3 categories. Maintenance Replacement Restoration
 Unit 11 Fluids, Electrolytes and Acid Base Imbalances Intravenous Access Devices & Common IV Fluids Objectives Review the purpose and types of intravenous (IV) therapy. Recall the nursing care related
Unit 11 Fluids, Electrolytes and Acid Base Imbalances Intravenous Access Devices & Common IV Fluids Objectives Review the purpose and types of intravenous (IV) therapy. Recall the nursing care related
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 10 Page October 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i10.79 Original Article Bedside Prediction of
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i10.79 Original Article Bedside Prediction of
Case #1. Case #1- Possible codes. Unraveling the -59 modifier. Principles of Interventional. CASE 1: Simple angioplasty
 Unraveling the -59 modifier Principles of Interventional Coding Donald Schon, MD, FACP Debra Lawson, CPC, PCS Distinct or independent from other services performed on the same day Normally not reported
Unraveling the -59 modifier Principles of Interventional Coding Donald Schon, MD, FACP Debra Lawson, CPC, PCS Distinct or independent from other services performed on the same day Normally not reported
Primary to non-coronary IVUS
 codes 2018 2018 codes Primary to non-coronary IVUS Page 2 All coding, coverage, billing and payment information provided herein by Philips is gathered from third-party sources and is subject to change.
codes 2018 2018 codes Primary to non-coronary IVUS Page 2 All coding, coverage, billing and payment information provided herein by Philips is gathered from third-party sources and is subject to change.
Thrombin injection vs Conventional Surgical Repair in Treatment of Iatrogenic Post-cath Femoral Artery Pseudoaneurysm (IFAP)
 Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 11, NO 3 September 2010 31 Thrombin injection vs Conventional Surgical Repair in Treatment of Iatrogenic Post-cath Femoral Artery Pseudoaneurysm (IFAP) Farghaly A,
Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 11, NO 3 September 2010 31 Thrombin injection vs Conventional Surgical Repair in Treatment of Iatrogenic Post-cath Femoral Artery Pseudoaneurysm (IFAP) Farghaly A,
Endo- aneurysmorrhaphy of a giant aneurysm of the subclavian vein
 Endo- aneurysmorrhaphy of a giant aneurysm of the subclavian vein Ahmed Afifi, Ahmed ElGuindy, Mahmoud Farouk, Magdi H Yacoub* * m.yacoub@imperial.ac.uk DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5339/gcsp.2012.13 ISSN:
Endo- aneurysmorrhaphy of a giant aneurysm of the subclavian vein Ahmed Afifi, Ahmed ElGuindy, Mahmoud Farouk, Magdi H Yacoub* * m.yacoub@imperial.ac.uk DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.5339/gcsp.2012.13 ISSN:
Exceptional Performance and Ease of Placement
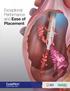 Exceptional Performance and Ease of Placement S IMU LATED FLO W PERFO RMANC E Higher Flow Rates Higher is Better GLIDEPATH catheters demonstrated on average in forward Precision catheters Lower Pressures
Exceptional Performance and Ease of Placement S IMU LATED FLO W PERFO RMANC E Higher Flow Rates Higher is Better GLIDEPATH catheters demonstrated on average in forward Precision catheters Lower Pressures
PEMSS PROTOCOLS INVASIVE PROCEDURES
 PEMSS PROTOCOLS INVASIVE PROCEDURES Panhandle Emergency Medical Services System SURGICAL AND NEEDLE CRICOTHYROTOMY Inability to intubate is the primary indication for creating an artificial airway. Care
PEMSS PROTOCOLS INVASIVE PROCEDURES Panhandle Emergency Medical Services System SURGICAL AND NEEDLE CRICOTHYROTOMY Inability to intubate is the primary indication for creating an artificial airway. Care
The University of Toledo Medical Center and its Medical Staff
 Name of Policy: Policy Number: Department: 3364-109-GEN-705 Infection Control Medical Staff Hospital Administration Approving Officer: Responsible Agent: Scope: Chair, Infection Control Committee Chief
Name of Policy: Policy Number: Department: 3364-109-GEN-705 Infection Control Medical Staff Hospital Administration Approving Officer: Responsible Agent: Scope: Chair, Infection Control Committee Chief
CEU Final Exam for Code It! Sixth Edition
 CEU Final Exam for 3-2-1 Code It! Sixth Edition Note to CEU applicant In order to receive CEU credit for taking this exam, the following criteria must be met: You must be certified by AAPC prior to purchasing
CEU Final Exam for 3-2-1 Code It! Sixth Edition Note to CEU applicant In order to receive CEU credit for taking this exam, the following criteria must be met: You must be certified by AAPC prior to purchasing
Sectional Anatomy Quiz - III
 Sectional Anatomy - III Rashid Hashmi * Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales (UNSW), Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 30 Jun 2018
Sectional Anatomy - III Rashid Hashmi * Rural Clinical School, University of New South Wales (UNSW), Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia A R T I C L E I N F O Article type: Article history: Received: 30 Jun 2018
Looking Outside the Box: Incidental Extracardiac Finding in Echo
 Looking Outside the Box: Incidental Extracardiac Finding in Echo Dr. Aijaz Shah Head of Division, Adult Echocardiography Laboratory Prince Sultan Cardiac Centre Riyadh Case 1 17 year old boy presented
Looking Outside the Box: Incidental Extracardiac Finding in Echo Dr. Aijaz Shah Head of Division, Adult Echocardiography Laboratory Prince Sultan Cardiac Centre Riyadh Case 1 17 year old boy presented
IV therapy. By: Susan Mberenga, RN, MSN. Copyright 2016, 2013, 2010, 2006, 2002 by Saunders, an imprint of Elsevier Inc.
 IV therapy By: Susan Mberenga, RN, MSN 1 IV Therapy Types of solutions Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic Caution: Too rapid or excessive infusion of any IV fluid has the potential to cause serious problems
IV therapy By: Susan Mberenga, RN, MSN 1 IV Therapy Types of solutions Isotonic Hypotonic Hypertonic Caution: Too rapid or excessive infusion of any IV fluid has the potential to cause serious problems
The Effects of Nursing Intervention on Pain Control during Chemoport Needle Insertion
 Vol.128 (Healthcare and Nursing 2016), pp.169-173 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016. The Effects of Nursing Intervention on Pain Control during Chemoport Needle Insertion Jin Hee Shin 1, Mee Lan Park²,
Vol.128 (Healthcare and Nursing 2016), pp.169-173 http://dx.doi.org/10.14257/astl.2016. The Effects of Nursing Intervention on Pain Control during Chemoport Needle Insertion Jin Hee Shin 1, Mee Lan Park²,
A Comparative Study Of Internal Jugular Vein Cannulation- Central Approach Versus Subclavian Vein Cannulation Infraclavicular Approach.
 DOI:.76/aimdr.6..3. Original Article ISSN (O):395-8; ISSN (P):395-84 A Comparative Study Of Internal Jugular Vein Cannulation- Central Approach Versus Subclavian Vein Cannulation Infraclavicular Approach.
DOI:.76/aimdr.6..3. Original Article ISSN (O):395-8; ISSN (P):395-84 A Comparative Study Of Internal Jugular Vein Cannulation- Central Approach Versus Subclavian Vein Cannulation Infraclavicular Approach.
The use of ultrasound during and after central venous catheter insertion versus conventional chest X-ray after insertion of a central venous catheter
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The use of ultrasound during and after central venous catheter insertion versus conventional chest X-ray after insertion of a central venous catheter M.J. Blans 1 *, H. Endeman 2, F.H.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE The use of ultrasound during and after central venous catheter insertion versus conventional chest X-ray after insertion of a central venous catheter M.J. Blans 1 *, H. Endeman 2, F.H.
Two Consecutive Levels of Unilateral Cervical Spondylolysis on Opposite Sides 두개의연속된척추에서반대쪽편측에발생한경추척추분리증
 Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.73.3.181 Two Consecutive Levels of Unilateral Cervical Spondylolysis on Opposite Sides 두개의연속된척추에서반대쪽편측에발생한경추척추분리증 Kyeong
Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.73.3.181 Two Consecutive Levels of Unilateral Cervical Spondylolysis on Opposite Sides 두개의연속된척추에서반대쪽편측에발생한경추척추분리증 Kyeong
Introduction to IV Therapy. BY Terry White, MBA, BSN
 Introduction to IV Therapy BY Terry White, MBA, BSN Important It is West Virginia State Law that nursing students (LPN and RN) are forbidden to start IVs or draw blood samples on patients Taking this class
Introduction to IV Therapy BY Terry White, MBA, BSN Important It is West Virginia State Law that nursing students (LPN and RN) are forbidden to start IVs or draw blood samples on patients Taking this class
Thrombectomy, open, arteriovenous fistula without revision, autogenous or nonautogenous dialysis graft (separate procedure)
 Dialysis Vascular Access Coverage, Coding and Reimbursement Overview Hospital Outpatient 2019 Edition All Reimbursement Amounts are Listed at ational Unadjusted Medicare Rates and Do ot Include the 2%
Dialysis Vascular Access Coverage, Coding and Reimbursement Overview Hospital Outpatient 2019 Edition All Reimbursement Amounts are Listed at ational Unadjusted Medicare Rates and Do ot Include the 2%
2012 CPT Changes Affecting Radiology REVISIONS
 2012 CPT Changes Affecting Radiology REVISIONS 22520 Percutaneous vertebroplasty (bone biopsy included when performed), 1 vertebral body, unilateral or bilateral injection; thoracic 22521 lumbar 22522
2012 CPT Changes Affecting Radiology REVISIONS 22520 Percutaneous vertebroplasty (bone biopsy included when performed), 1 vertebral body, unilateral or bilateral injection; thoracic 22521 lumbar 22522
Per-Q-Cath* PICC Catheters with Excalibur Introducer* System
 Bard Access Systems Per-Q-Cath* PICC and Catheters with Excalibur Introducer* System Instructions For Use Table of Contents Table of Contents Page Contents 1 Product Description, Indications & Contraindications
Bard Access Systems Per-Q-Cath* PICC and Catheters with Excalibur Introducer* System Instructions For Use Table of Contents Table of Contents Page Contents 1 Product Description, Indications & Contraindications
Min Hur, Eun-Hee Kim, In-Kyung Song, Ji-Hyun Lee, Hee-Soo Kim, and Jin Tae Kim INTRODUCTION. Clinical Research
 Anesth Pain Med 2016; 11: 375-379 https://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375 Clinical Research http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-10-25 pissn
Anesth Pain Med 2016; 11: 375-379 https://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375 Clinical Research http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-10-25 pissn
1 Description. 2 Indications. 3 Warnings ASPIRATION CATHETER
 Page 1 of 5 ASPIRATION CATHETER Carefully read all instructions prior to use, observe all warnings and precautions noted throughout these instructions. Failure to do so may result in complications. STERILE.
Page 1 of 5 ASPIRATION CATHETER Carefully read all instructions prior to use, observe all warnings and precautions noted throughout these instructions. Failure to do so may result in complications. STERILE.
Introduction What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease? How Do Doctors Treat Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 9
 Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
Document No. BMB/IFU/40 Rev No. & Date 00 & 15/11/2017 Issue No & Date 01 & 15/11/2017
 Central Venous Catheter Device Description Multi-lumen catheters incorporate separate, non-communicating vascular access lumens within a single catheter body. Minipunctur Access Sets And Trays: Used for
Central Venous Catheter Device Description Multi-lumen catheters incorporate separate, non-communicating vascular access lumens within a single catheter body. Minipunctur Access Sets And Trays: Used for
Expanding Horizons: AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy at UTHealth
 Expanding Horizons: AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy at UTHealth Naveed Saqib, MD Assistant Professor Department of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery McGovern Medical School The University of Texas Science
Expanding Horizons: AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy at UTHealth Naveed Saqib, MD Assistant Professor Department of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery McGovern Medical School The University of Texas Science
Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC
 Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC An approach to reviewing a chest x-ray will create a foundation that will facilitate the detection of abnormalities. You should create your own
Chest X-ray (CXR) Interpretation Brent Burbridge, MD, FRCPC An approach to reviewing a chest x-ray will create a foundation that will facilitate the detection of abnormalities. You should create your own
Acute abdominal venous thromboses- the hyperdense noncontrast CT sign
 Acute abdominal venous thromboses- the hyperdense noncontrast CT sign Poster No.: C-1095 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Goldstein, K. Jhaveri; Toronto, ON/CA Keywords: Abdomen,
Acute abdominal venous thromboses- the hyperdense noncontrast CT sign Poster No.: C-1095 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Goldstein, K. Jhaveri; Toronto, ON/CA Keywords: Abdomen,
Children's (Pediatric) PICC Line Placement
 Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) PICC Line Placement A peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC line) is most often used to deliver medication over a long period. The doctor or nurse inserts
Scan for mobile link. Children's (Pediatric) PICC Line Placement A peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC line) is most often used to deliver medication over a long period. The doctor or nurse inserts
Percutaneously Inserted AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy for the Treatment of Filter-Related. Iliocaval Thrombosis
 Percutaneously Inserted AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy for the Treatment of Filter-Related Iliocaval Thrombosis Faiz D. Francis, DO; Gianvito Salerno, MD; Sabbah D. Butty, MD Abstract In the setting of
Percutaneously Inserted AngioVac Suction Thrombectomy for the Treatment of Filter-Related Iliocaval Thrombosis Faiz D. Francis, DO; Gianvito Salerno, MD; Sabbah D. Butty, MD Abstract In the setting of
2019 ABBOTT REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE CMS Physician Fee Schedule
 ABBOTT REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE CMS Physician Fee Schedule This document and the information contained herein is for general information purposes only and is not intended and does not constitute legal, reimbursement,
ABBOTT REIMBURSEMENT GUIDE CMS Physician Fee Schedule This document and the information contained herein is for general information purposes only and is not intended and does not constitute legal, reimbursement,
Procedures/Risks:central venous catheter
 Procedures/Risks:central venous catheter Central Venous Catheter Placement Procedure: Placement of the central venous catheter will take place in the Interventional Radiology Department (IRD) at The Ohio
Procedures/Risks:central venous catheter Central Venous Catheter Placement Procedure: Placement of the central venous catheter will take place in the Interventional Radiology Department (IRD) at The Ohio
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis 2017 Edition
 Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
Arterial Map of the Thorax, Abdomen and Pelvis Angiography 75605 (-26) Aortography, thoracic 75625 (-26) Aortography, abdominal by serialography 75630 (-26) Aortography, abdominal + bilat iliofemoral 75705
SAMPLE CHAPTERS UNESCO-EOLSS MANAGEMENT OF SUBCLAVIAN VEIN THROMBOSIS KNOWN AS PAGET-SCHROETTER SYNDROME
 MANAGEMENT OF SUBCLAVIAN VEIN THROMBOSIS KNOWN AS PAGETSCHROETTER SYNDROME J. Ernesto Molina University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota, U.S.A. Keywords: Thoracic outlet, Venous disease Contents 1.
MANAGEMENT OF SUBCLAVIAN VEIN THROMBOSIS KNOWN AS PAGETSCHROETTER SYNDROME J. Ernesto Molina University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, Minnesota, U.S.A. Keywords: Thoracic outlet, Venous disease Contents 1.
CATHETER MALPOSITION FOLLOWING SUPRACLAVICULAR APPROACH FOR SUBCLAVIAN VEIN CATHETERISATION
 CATHETER MALPOSITION FOLLOWING SUPRACLAVICULAR APPROACH FOR SUBCLAVIAN VEIN CATHETERISATION - Case Reports - Prem K Singh *, Zulfiquar Ali *, Girija P Rath ** and Hemanshu Prabhakar *** Abstract The supraclavicular
CATHETER MALPOSITION FOLLOWING SUPRACLAVICULAR APPROACH FOR SUBCLAVIAN VEIN CATHETERISATION - Case Reports - Prem K Singh *, Zulfiquar Ali *, Girija P Rath ** and Hemanshu Prabhakar *** Abstract The supraclavicular
Vascular Devices Pre-Existing. Jamla Bergman, MSN, RN, EMT Christopher J. Fullagar, MD, EMT-P, FACEP Stan Goettel, MS, EMT-P
 Vascular Devices Pre-Existing Jamla Bergman, MSN, RN, EMT Christopher J. Fullagar, MD, EMT-P, FACEP Stan Goettel, MS, EMT-P Author credits / conflict declaration No financial conflicts of interest 2 Content
Vascular Devices Pre-Existing Jamla Bergman, MSN, RN, EMT Christopher J. Fullagar, MD, EMT-P, FACEP Stan Goettel, MS, EMT-P Author credits / conflict declaration No financial conflicts of interest 2 Content
INTRAVENOUS CATHETER FRAGMENTS: ENDOVASCULAR RETRIEVAL*
 Original Article INTRAVENOUS CATHETER RAGENTS: ENDOVASCULAR RETRIEVAL* Gustavo Andrade 1, Romero arques 1, Norma Brito 1, Ângelo Bomfim 1, Douglas Cavalcanti 2, Carlos Abath 1 * Study developed at Angiorad
Original Article INTRAVENOUS CATHETER RAGENTS: ENDOVASCULAR RETRIEVAL* Gustavo Andrade 1, Romero arques 1, Norma Brito 1, Ângelo Bomfim 1, Douglas Cavalcanti 2, Carlos Abath 1 * Study developed at Angiorad
Port Design. Page 1. Port Placement, Removal, and Management. Selecting a Vascular Access Device. Thomas M. Vesely, MD
 Non-Dialysis Procedures Port Placement, Removal, and Management Thomas M. Vesely, MD Saint Louis, Missouri Selecting a Vascular Access Device Duration of use Number of lumens Frequency used Blood flow
Non-Dialysis Procedures Port Placement, Removal, and Management Thomas M. Vesely, MD Saint Louis, Missouri Selecting a Vascular Access Device Duration of use Number of lumens Frequency used Blood flow
