Feasibility of real-time three-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiography for guidance of percutaneous atrial septal defect closure
|
|
|
- Allen Bryant
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 European Journal of Echocardiography (2009) 10, doi: /ejechocard/jen337 Feasibility of real-time three-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiography for guidance of percutaneous atrial septal defect closure Joseph A. Lodato 1 *, Qi Ling Cao 2, Lynn Weinert 1, Lissa Sugeng 1, John Lopez 1, Roberto M. Lang 1, and Ziyad M. Hijazi 2 1 University of Chicago Medical Center, 5841 South Maryland Ave. MC 5084, Chicago, IL 60637, USA; and 2 Rush University Medical Center, Chicago, IL, USA Received 21 August 2008; accepted after revision 29 December 2008; online publish-ahead-of-print 29 January 2009 KEYWORDS Atrial septal defect; Three-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiography; Intracardiac echocardiography; Amplatzer septal occluder Aims Intracardiac echocardiography (ICE) and two-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiography (2D TEE) are used in most centres for guiding transcatheter atrial septal defect (ASD) closure. ASDs have complex shapes that are not well characterized with 2D imaging. Real-time 3D TEE (RT3D TEE) provides en-face visualization of the ASD, allowing precise assessment of ASD dimensions. Accordingly, our aims were (i) to determine the feasibility of RT3D TEE to guide ASD closure and (ii) to compare ASD and balloon dimensions (BDs) using RT3D TEE vs. ICE and 2D TEE. Methods and Results Thirteen patients with ostium secundum ASD underwent transcatheter ASD closure. 2D TEE, RT3D TEE, and ICE images were acquired sequentially. RT3D TEE was feasible in all patients. Comparing RT3D TEE and 2D imaging, the mean difference in long-axis dimension was þ0.5 mm (P ¼ NS for both), and 21.4 mm in short-axis (2D TEE, P, 0.05; ICE, P ¼ 0.06). BD was greater with 3D TEE vs. ICE (þ0.9 mm). Conclusion RT3D TEE can be used to guide transcatheter ASD closure with the advantages of lower cost than ICE, and ability to visualize en-face views of the ASD. ASD and BD as measured by RT3D TEE differ when compared with 2D imaging. Introduction Successful transcatheter closure of secundum atrial septal defect (ASD) is dependent on accurate assessment of ASD size, rim architecture and length, and relationship of the defect to adjacent cardiac structures. These ASD features are of paramount importance in determining the appropriateness of transcatheter closure, device selection, and guidance of device deployment. Historically, guidance of ASD closure device selection and placement was performed with fluoroscopy together with two-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiography (2D TEE). Intracardiac echocardiography (ICE) has emerged as a preferred method for guiding deployment of transcatheter septal occluder devices in some centres because its use has resulted in (i) shorter procedural times and (ii) ability to guide device deployment without the need for general endotracheal anaesthesia. 1,2 * Corresponding author. Tel: þ ; fax: þ address: jlodato@medicine.bsd.uchicago.edu Atrial septal defects are known to have complex geometry that may be elliptical, oblong, or fenestrated in shape. 3 6 These unique shapes are not adequately characterized by 2D imaging. Previous studies have investigated the utility of 3D TEE in the assessment of ASDs, 7 9 providing unprecedented en-face dynamic views of ASDs. However, this older method of rendering 3D reconstructions from multiple 2D images was cumbersome, time-consuming, and not applicable to on-line, point of care analysis. To overcome these limitations, a transducer was recently developed to allow real-time acquisition and on-line display of 3D images. We previously showed the ability to obtain highquality, 3D, anatomically detailed views of the interatrial septum (IAS) 85% of the time in more than 200 consecutive patients referred for transoesophageal echocardiography. 10,11 Acar et al. 12 and Martin-Reyes et al. 13 separately recently described the application of this probe in the guidance of transcatheter closure of an ASD and a patent foramen ovale, respectively. We hypothesized that real-time 3D TEE (RT3D TEE) could provide a suitable alternative to ICE for guidance of Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. & The Author For permissions please journals.permissions@oxfordjournals.org.
2 544 J.A. Lodato et al. percutaneous ASD closure. In this study, we evaluated the feasibility of RT3D TEE in guiding transcatheter device closure of ostium secundum ASD. Secondly, we compared ASD dimensions as assessed by RT3D TEE, ICE, and biplane 2D TEE. Methods Thirteen consecutive patients with ostium secundum ASD meeting clinical criteria for closure were prospectively identified as appropriate for transcatheter approach based on prior 2D imaging (TEE). Informed consent was obtained from all patients. The study was approved by our centre s Institutional Review Board. Real-time 3D TEE images were acquired using the 3D matrix-array TEE (3D MTEE) probe and ie33 ultrasound machine (Philips Medical Systems, Andover, MA, USA). Similar to the transthoracic echocardiographic matrix array probe (x4; Philips Medical Systems), this probe combines novel electronic circuitry with miniaturized beamforming technology that accommodates thousands of fully sampled elements into the tip of an otherwise conventional TEE probe affording the capability of RT3D, biplane 2D, and Doppler imaging. The new 3D MTEE probe can be used in three imaging modes: narrow and wide angle acquisitions as well as the zoom mode. 3D MTEE data sets of the IAS were acquired by first obtaining a biplane view of the IAS from a mid-oesophageal transducer position. Initially, gain settings were optimized using the narrow-angled acquisition mode, which allows RT3D imaging without the need for ECG gating. This mode displays a pyramidal volume of The 3D zoom mode, which displays a smaller, magnified pyramidal volume, was then used to capture 3D data sets of the IAS for on-line quantitative analysis. Three-dimensional data sets were analysed on-line using ultrasound machine equipped, dedicated 3D software (QLab, Philips). ASD dimensions were measured in the multi-planar reconstruction mode available in the 3DQ plugin for QLab. This tool displays two orthogonal 2D cut planes perpendicular to the IAS. A third orthogonal cut plane provides the en-face view of the ASD from where the long- and short-axis dimensions were measured with the electronic callipers available in the software package (Figure 1). Intracardiac echocardiography imaging was performed using the 8 Fr AccuNav catheter (Biosense Webster Inc., Diamond Bar, CA, USA) connected to a Sequoia ultrasound machine (Acuson, a Siemens company, Mountain View, CA, USA). Biplane 2D TEE imaging was performed with the 3D MTEE probe and ie33 ultrasound machine. Long- and short-axis ASD dimensions for both 2D TEE and ICE were obtained by identifying the plane that visually appeared to be the greatest and smallest rim to rim distance, and measured from a still frame acquisition (Figure 1). All measurements from the three different ultrasound modalities were made at the point of care, in real time. The ICE operator was at the foot of the patient and the TEE operator at the patients head. The operators made measurements independently of one another and then recorded them. Those measurements were then reported to the interventionalist. The interventionalist chose the largest of the measurements for initial device sizing. ICE measurements were determined by the physician sonographer operating the ICE system. RT3D TEE and biplane 2D TEE measurements were acquired independently of ICE measurements by a separate physician operating the transoesophageal ultrasound system. All measurements were made at end-systole, when the ASD is known to be at its greatest dimension. Measurements for each modality were recorded on a still frame and reported independently to the interventional cardiologist in an effort to avoid measurement bias from a priori knowledge of ASD dimensions from another modality. Guide wire and sheath placement across the ASD were visualized with both ICE and RT3D TEE in narrow angle and zoom modes. The sizing balloon was expanded with diluted contrast until cessation of flow was achieved as demonstrated by colour Doppler echocardiography ( Stop-Flow Diameter ). The balloon diameter (BD) when the flow was abolished was measured by ICE and RT3D TEE. The BDs for the two echocardiographic techniques were measured as described above. Not all ASDs were sized with a balloon prior to device deployment. This decision was determined by the interventional cardiologist performing the procedure. When balloon sizing was performed, the BD was measured by RT3D TEE and ICE only. 2D TEE and fluoroscopic measurements of BD were not a part of the research protocol, and therefore were not measured or recorded (Figure 2). The appropriate size closure device was subsequently selected based on the largest dimensions acquired among any of the modalities so as not to undersize the device. In the event that there was a large discrepancy in dimensions, the interventional cardiologist used the stop-flow diameter to select device size. All stages of device deployment could be successfully observed in the Live 3D mode. The left atrial disc was expanded first, followed by the connecting waist and finally the right atrial disc. Gentle push/pull (The Minnesota Wiggle) to assure stability and appropriate apposition to the rims was performed prior to device release. ICE and RT3D TEE images were acquired during each phase of deployment. Final post deployment images were acquired with particular attention to colour Doppler assessment for residual shunt flow (2D TEE and ICE), and demonstration of appropriate ASD rim impingement between the apposing discs of the septal occluder device with RT3D TEE imaging (Figure 3). Statistics Results are reported as mean + SD. Long- and short-axis ASD dimensions were compared among RT3D TEE, 2D TEE, and ICE. Balloon dimensions were compared among RT3D TEE and ICE only. Student s t-test was used for continuous variables using a two-tailed P-value of,0.05 for statistical significance. A Bland Altman analysis was additionally performed to compare inter-modality differences. Figure 1 Long- and short-axis dimensions of an intermediate-sized atrial septal defect (ASD) from the three echocardiographic modalities. In this example, ASD dimensions are fairly similar among the three imaging modalities. However, with the 3D cut-plane technique, the dimensions of the ASD can be measured from one acquisition. No trial and error imaging is required to find the true long- and short-axis dimensions as is often necessary in 2D imaging. Results The study group consisted of 13 patients, mean age years (range: 9 52). All defects were closed with the Amplatzer Septal Occluder (AGA Medical Corp., Plymouth, MN, USA). Mean device size was 28 mm (range: 15 38). Mean fluoroscopy time was 8.1 min (range: min) and mean total procedure time was 49 min (range: 9 80 min). ASD closure was successful in all 13 patients.
3 Feasibility of real-time 3D transoesophageal echocardiography 545 Figure 2 Balloon dimension (BD) as measured by 2D TEE, ICE, and RT3D TEE. The arrows indicate the expanded balloon in the left atrium on this still frame from a narrow angle acquisition. The bottom panels show three orthogonal cut planes from a multi-planar reconstruction view. BD can be measured from the en-face view of the balloon as it traverses the atrial septal defect as seen in the bottom right panel. Figure 3 Real-time three-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiography acquisition post deployment of an Amplatzer Septal Occluder. The left (A) and right (B) atrial discs can be visualized with exquisite detail. Also demonstrated in (C), (D), and (E), as indicated by the arrows, the rims of the ASD are well apposed between the discs. Assessment of residual shunt with colour Doppler can be performed with the 3D multi-array TEE probe (not depicted here).
4 546 J.A. Lodato et al. RT3D TEE imaging was feasible in all 13 patients, providing high-quality images suitable for analysis. RT3D TEE was capable of providing diagnostic quality imaging for all phases of ASD assessment and closure. Qualititatively, 3D imaging was superb in all patients. There was no dropout or reconstruction artifact present in the 3D acquisitions. With Live 3D imaging, the interventionalist and echocardiographer were afforded not only en-face views of the ASD, but also of the spatial orientation, anatomic position and relationship of adjacent cardiac structures, the delivery catheter, and the closure device itself; available from one angle and a stationary oesophageal position in most cases. 2D imaging, whether it was ICE or 2D TEE, required frequent probe manipulation and angle adjustment to capture the anatomy or structure of interest. Long-axis dimensions in millimetres by RT3D TEE, 2D TEE, and ICE were , , and mm, respectively (Table 1). There were no statistically significant differences in mean long-axis dimension among the three imaging modalities. However, the mean of the differences in long-axis dimension across modalities would suggest that 2D imaging in general yields a smaller long-axis dimension (mean difference ¼ 0.5 mm) when compared with RT3D TEE. Furthermore, there was considerable variation in measurements. In 6 of 13 cases, the difference between 3D and ICE was.1 mm, and in two cases in particular that difference was 9 and 11 mm, respectively. The Bland Altman analysis of long-axis dimension showed a similar bias but narrower limits of agreement with 2D TEE (+5.87 mm) as opposed to ICE (+8.66 mm) when compared with RT3D TEE (Figure 4). Short-axis dimensions were , , and for RT3D TEE, 2D TEE, and ICE, respectively. When Compared with 3D TEE, ICE, and 2D TEE tended to yield larger short-axis dimensions of the ASD. There was a statistically significant difference in the mean difference in short-axis dimension as measured by RT3D TEE and 2D TEE (21.4 mm, P ¼ 0.001). The mean difference in short-axis dimension as measured by 3D TEE and ICE was not statistically significant; however, there was a trend towards a difference in this small group of patients (21.4 mm, P ¼ 0.06). Short-axis dimensions as measured by RT-3D TEE differed by.1 mm in seven and five patients compared with 2D TEE and ICE, respectively, including two patients with differences of 6 mm by ICE compared with 3D TEE. The Bland Altman analysis again confirmed a similar bias, but narrower limits of agreement with 2D TEE (+2.39 mm) compared with ICE (+4.87 mm) as depicted in Figure 4. Balloon dimensions measured by RT3D TEE were available for only 7 of 13 patients (Table 1). BDs were not acquired in Table 1 Long-axis, short-axis, and balloon dimensions (n ¼ 7) in mm (mean + SD), for the echocardiographic techniques 3D TEE ICE 2D TEE 3D ICE 3D 2D 2D ICE LAX (mm) range (29 to 11) 0.5 (27 to 5) 0.07 (26 to6) SAX (mm) range (26 to2) 21.4* (23 to 0) 0.0 (24 to2) BD (mm) range (21 to2) The three right-sided columns represent the mean difference in dimensions and the range of differences comparing RT3D TEE with ICE and 2D TEE, and 2D TEE with ICE. Only the difference of short-axis dimension as measured by RT3D TEE and 2D TEE was statistically significant; however, there was a trend towards a statistically significant difference comparing short-axis dimension by RT3D TEE and ICE. There is considerable range of measurement differences comparing 3D and 2D imaging techniques. (LAX, long axis; SAX, short axis; BD, balloon dimension). *P, P ¼ P ¼ Figure 4 The Bland Altman analysis comparing long-axis dimensions (upper panels), with short-axis dimensions (lower panels) of atrial septal defect size as measured by real-time three-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiography (RT3D TEE), intracardiac echocardiography (ICE), and 2D TEE. 2D TEE and ICE showed similar bias, but 2D TEE had narrow limits of agreement when compared with RT3D TEE.
5 Feasibility of real-time 3D transoesophageal echocardiography 547 the six remaining patients because balloon occlusion of the ASD was not performed in those patients as per the discretion of the interventionalist performing the procedure. In the seven patients in whom measurements were possible, BD by RT3D TEE was slightly larger than ICE-derived dimensions ( vs mm). The mean difference was þ0.9 mm (range: 21 toþ2 mm). Discussion Percutaneous closure of secundum ASD is becoming more commonplace in academic medical centres worldwide. ICE is a preferred method for guiding transcatheter closure of ASDs where it is available. Due to the high cost of the ICE catheters ($2500 USD per non-reusable catheter) and the need for a specific ultrasound machine (Acuson, Siemens) and technical expertise, 2D TEE continues to be used in most centres worldwide. In this study, we demonstrated the feasibility of a new transoesophageal probe that delivers RT3D rendered images of the ASD. This novel probe was capable of guiding each phase of ASD closure, from preclosure assessment to guide wire and sheath placement to balloon occlusion, and finally device delivery, release and post-closure assessment. Compared with its 2D counterparts, there are distinct advantages of RT3D TEE imaging deserving mention. For one, the images afforded by the 3D MTEE probe are unique and extraordinary. It allows the operator a dynamic en-face view of the ASD in real time. The entire rim and adjacent cardiac structures can be visualized from one acquisition. Further, with appropriate system equipped software, the operator can manipulate the 3D data set for advanced analysis at the point of care. Accurate dimensions of the ASD or related cardiac structures are accessible from one acquisition rather than through a trial and error process of micro manipulations of standard 2D probes, be it conventional TEE or ICE. Imaging in two dimensions limits the operator s ability to adequately characterize the 3D shape of the ASD, leaving too much to mental reconstruction and imagination. While ASDs are usually single and sometimes elliptical, they are known to have complex ovoid or egg-like shapes, or possibly contain multiple defects or fenestrations. Accordingly, dimensions measured by RT3D TEE will differ when compared with those measured with 2D TEE or ICE. This study showed that 2D TEE and ICE are more likely to provide a smaller long-axis dimension, and larger short-axis dimension when compared with RT3D TEE. Figure 5 demonstrates how 2D imaging might misrepresent ASD size. While this difference is frequently small and inconsequential, there were two patients in this study with a difference in long-axis dimension of 10 mm. It is unclear if such measurement differences would impact device selection. In the two cases referenced here, it did not, because the balloon dimension or stop flow diameter was similar among the three ultrasound modalities. However, these measurement differences may help to determine whether the patient is appropriate for percutaneous closure at all. Balloon dimensions as measured by RT3D TEE and ICE were less divergent although the mean difference in dimension was slightly higher with RT3D TEE (þ0.9 mm, range 21 to þ2). With balloon distention, the irregularly shaped ASD assumes a more circular geometry. The balloon dimension, regardless of 2D cut plane, would therefore be similar. The slightly larger measurement with 3D TEE may be attributable to the choice of 2D imaging plane, as described previously; it may not be the longest dimension of the balloon as it passes through the ASD, as is demonstrated in Figure 5. Limitations Although these patients were consecutive and unselected, this is a small study. A larger trial with a greater number of patients will better define the utility of this new probe in all patients referred for percutaneous closure of secundum ASDs. Also, we did not assess the feasibility of the RT3D TEE probe in patients,60 kg. If there is not sufficient depth between the probe and the ASD as might be the case in patients of smaller size or those with a small left atrium, the ASD may only partially lie in the field of the pyramidal 3D data set. Figure 5 This figure illustrates the pitfalls of two dimensional assessment of atrial septal defects (ASDs). If the operator does not choose the appropriate angle and probe location, the ASD dimensions will not be accurately characterized. This example demonstrates the underestimation of long-axis and overestimation of short-axis dimensions with 2D imaging. (SVC, superior vena cava; AO, aortic root; TV, tricuspid valve; IVC, inferior vena cava; LAX, long axis; SAX, short axis).
6 548 J.A. Lodato et al. Conclusion Real-time 3D TEE provides unique, dynamic en-face views of ASDs not possible with 2D imaging. ASD dimensions as measured by 3D TEE differ slightly when compared with 2D imaging which is likely related to operator selection of 2D imaging plane. Finally, while ICE will likely remain the preferred method due to faster procedure times, and independence from general anaesthesia, 3D TEE is a feasible alternative to imaging guidance during transcatheter closure of ASDs. Conflict of interest: Dr. Roberto Lang is the recipient of an equipment grant from Philips Medical Systems. Drs. Roberto Lang and Lissa Sugeng are members of the Philips Speakers Bureau. References 1. Mullen MJ, Dias BF, Walker F, Siu SC, Benson LN, McLaughlin PR. Intracardiac echocardiography guided device closure of atrial septal defects. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003;41: Zanchetta M, Onorato E, Rigatelli G, Pedon L, Zennaro M, Carrozza A et al. Intracardiac echocardiography-guided transcatheter closure of secundum atrial septal defect: a new efficient device selection method. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003;42: Acar P, Saliba Z, Bonhoeffer P, Aggoun Y, Bonnet D, Sidi D et al. Influence of atrial septal defect anatomy in patient selection and assessment of closure with the Cardioseal device. A three-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiographic reconstruction. Eur Heart J 2000;21: Franke A, Kuhl HP, Rulands D, Jansen C, Erena C, Grabitz RG et al. Quantitative analysis of the morphology of secundum-type atrial septal defects and their dynamic change using transesophageal threedimensional echocardiography. Circulation 1997;96:II Maeno YV, Benson LN, McLaughlin PR, Boutin C. Dynamic morphology of the secundum atrial septal defect evaluated by three dimensional transoesophageal echocardiography. Heart 2000;83: Rigatelli G, Zanchetta M, Onorato E, Pedon L, Zennaro M, Visentin E et al. A fenestrated fossa ovalis aneurysm mimicking an atrial septal defect: correct diagnosis and treatment by intracardiac echocardiography. Ital Heart J 2002;3: Cao QL, Radtke W, Berger F, Zhu W, Hijazi ZM. Transcatheter closure of multiple atrial septal defects. Initial results and value of two- and threedimensional transoesophageal echocardiography. Eur Heart J 2000;21: Magni G, Hijazi ZM, Pandian NG, Delabays A, Sugeng L, Laskari C et al. Two- and three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography in patient selection and assessment of atrial septal defect closure by the new DAS-Angel Wings Device: initial clinical experience. Circulation 1997;96: Marx GR, Fulton DR, Pandian NG, Vogel M, Cao QL, Ludomirsky A et al. Delineation of site, relative size and dynamic geometry of atrial septal defects by real-time three-dimensional echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol 1995;25: Sugeng L, Shernan SK, Salgo IS, Weinert L, Shook D, Raman J et al. Live 3-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography initial experience using the fully-sampled matrix array probe. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008;52: Sugeng L, Shernan SK, Salgo IS, Weinert L, Shook D, Raman J et al. First experience with a new real-time three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiographic transducer. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007;49: 103A. Ref Type: Abstract. 12. Acar P, Massabuau P, Elbaz M. Real-time 3D transoesophageal echocardiography for guiding Amplatzer septal occluder device deployment in an adult patient with atrial septal defect. Eur J Echocardiogr 2008;9: Martin-Reyes R, Lopez-Fernandez T, Moreno-Yanguela M, Moreno R, Navas-Lobato MA, Refoyo E et al. Role of real-time three-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiography for guiding transcatheter patent foramen ovale closure. Eur J Echocardiogr 2008;10:
2D/3D in Evaluation of Atrial Septum
 2D/3D in Evaluation of Atrial Septum Roberto M Lang, MD OSTIUM SECUNDUM ASD: 2D AND 3D TNSESOPHAGEAL ECHO 1 Biplane views 90 0 3D Acquisi on Acquire 3D volume Lang RM et al. JASE 2012;25:3 46. Right atrial
2D/3D in Evaluation of Atrial Septum Roberto M Lang, MD OSTIUM SECUNDUM ASD: 2D AND 3D TNSESOPHAGEAL ECHO 1 Biplane views 90 0 3D Acquisi on Acquire 3D volume Lang RM et al. JASE 2012;25:3 46. Right atrial
Assessment of Atrial Septal Defect Role of Real-Time 3D Color Doppler Echocardiography for Interventional Catheterization
 Original Article Chung-Hsien Su et al. Acta Cardiol Sin 2005;21:146 52 Pediatric Cardiology Assessment of Atrial Septal Defect Role of Real-Time 3D Color Doppler Echocardiography for Interventional Catheterization
Original Article Chung-Hsien Su et al. Acta Cardiol Sin 2005;21:146 52 Pediatric Cardiology Assessment of Atrial Septal Defect Role of Real-Time 3D Color Doppler Echocardiography for Interventional Catheterization
Intracardiac echocardiography: an ideal guiding tool for device closure of interatrial communications
 Eur J Echocardiography (2005) 6, 92e96 Intracardiac echocardiography: an ideal guiding tool for device closure of interatrial communications Thomas Bartel a, *, Thomas Konorza a, Ulrich Neudorf b, Tiko
Eur J Echocardiography (2005) 6, 92e96 Intracardiac echocardiography: an ideal guiding tool for device closure of interatrial communications Thomas Bartel a, *, Thomas Konorza a, Ulrich Neudorf b, Tiko
Contemporary echocardiographic guiding tools for device closure of interatrial communications
 Review Article Contemporary echocardiographic guiding tools for device closure of interatrial communications Thomas Bartel, Silvana Müller Department of Medicine, Cardiology Division (Cardiology), Innsbruck
Review Article Contemporary echocardiographic guiding tools for device closure of interatrial communications Thomas Bartel, Silvana Müller Department of Medicine, Cardiology Division (Cardiology), Innsbruck
The earliest application of intracardiac imaging
 Intracardiac Echocardiography for Structural Heart Defects A review of ICE innovations, devices, and techniques. BY ZAHID AMIN, MD; QI-LING CAO, MD; AND ZIYAD M. HIJAZI, MD The earliest application of
Intracardiac Echocardiography for Structural Heart Defects A review of ICE innovations, devices, and techniques. BY ZAHID AMIN, MD; QI-LING CAO, MD; AND ZIYAD M. HIJAZI, MD The earliest application of
Atrial Septal Defect Closure. Stephen Brecker Director, Cardiac Catheterisation Labs
 Stephen Brecker Director, Cardiac Catheterisation Labs ADVANCED ANGIOPLASTY Incorporating The Left Main 5 Plus Course Conflicts of Interest The following companies have supported educational courses held
Stephen Brecker Director, Cardiac Catheterisation Labs ADVANCED ANGIOPLASTY Incorporating The Left Main 5 Plus Course Conflicts of Interest The following companies have supported educational courses held
Original Article Safe and effective guidance by intracardiac echocardiography for transcatheter closure in atrial septal defects
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(6):9815-9819 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0006687 Original Article Safe and effective guidance by intracardiac echocardiography for transcatheter closure in atrial septal
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(6):9815-9819 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0006687 Original Article Safe and effective guidance by intracardiac echocardiography for transcatheter closure in atrial septal
ATRIAL SEPTAL CLOSURE AND LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE OCCLUSION: INDICATIONS AND GUIDANCE ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN INTERVENTIONAL CARDIOLOGY
 ATRIAL SEPTAL CLOSURE AND LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE OCCLUSION: INDICATIONS AND GUIDANCE Aristides G. Panlilio, MD, FPCP, FPCC,FPSE, FASE Philippine Heart Center Chinese General Hospital and Medical Center
ATRIAL SEPTAL CLOSURE AND LEFT ATRIAL APPENDAGE OCCLUSION: INDICATIONS AND GUIDANCE Aristides G. Panlilio, MD, FPCP, FPCC,FPSE, FASE Philippine Heart Center Chinese General Hospital and Medical Center
Assessing ASDs prior to device closure using 3D echocardiography. Just pretty pictures or a useful clinical tool?
 European Journal of Echocardiography (2008) 9, 478 482 doi:10.1016/j.euje.2007.07.001 Assessing ASDs prior to device closure using 3D echocardiography. Just pretty pictures or a useful clinical tool? G.J.
European Journal of Echocardiography (2008) 9, 478 482 doi:10.1016/j.euje.2007.07.001 Assessing ASDs prior to device closure using 3D echocardiography. Just pretty pictures or a useful clinical tool? G.J.
INTEGRATING ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY WITH CATHETER INTERVENTIONS FOR CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE. Krishna Kumar SevenHills Hospital, Mumbai, India
 INTEGRATING ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY WITH CATHETER INTERVENTIONS FOR CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Krishna Kumar SevenHills Hospital, Mumbai, India Why talk about it? What is the big deal? Are we not stating the obvious?
INTEGRATING ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY WITH CATHETER INTERVENTIONS FOR CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE Krishna Kumar SevenHills Hospital, Mumbai, India Why talk about it? What is the big deal? Are we not stating the obvious?
Original Article Safe and efectivef guidance by intracardiac echocardiography for transcatheter closure in atrial septal defects
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(5):8015-8019 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0007568 Original Article Safe and efectivef guidance by intracardiac echocardiography for transcatheter closure in atrial septal
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(5):8015-8019 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0007568 Original Article Safe and efectivef guidance by intracardiac echocardiography for transcatheter closure in atrial septal
Atrial Septal Defects
 Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
Supplementary ACHD Echo Acquisition Protocol for Atrial Septal Defects The following protocol for echo in adult patients with atrial septal defects (ASDs) is a guide for performing a comprehensive assessment
When Does 3D Echo Make A Difference?
 When Does 3D Echo Make A Difference? Wendy Tsang, MD, SM Assistant Professor, University of Toronto Toronto General Hospital, University Health Network 1 Practical Applications of 3D Echocardiography Recommended
When Does 3D Echo Make A Difference? Wendy Tsang, MD, SM Assistant Professor, University of Toronto Toronto General Hospital, University Health Network 1 Practical Applications of 3D Echocardiography Recommended
Echocardiographic Guidance During Placement of the Buttoned Double-Disk Device for Atrial Septa1 Defect Closure
 Echocardiographic Guidance During Placement of the Buttoned Double-Disk Device for Atrial Septa1 Defect Closure L. LUANN MINICH, M.D., and A. REBECCA SNIDER, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, C.S. Mott Children
Echocardiographic Guidance During Placement of the Buttoned Double-Disk Device for Atrial Septa1 Defect Closure L. LUANN MINICH, M.D., and A. REBECCA SNIDER, M.D. Department of Pediatrics, C.S. Mott Children
Experience with Intracardiac Echocardiography for Guiding Transcatheter Device Closure of Atrial Septal Defects
 Original ORIGINAL Article ARTICLE Korean Circulation J 2006;36:612-616 ISSN 1738-5520 c 2006, The Korean Society of Circulation Experience with Intracardiac Echocardiography for Guiding Transcatheter Device
Original ORIGINAL Article ARTICLE Korean Circulation J 2006;36:612-616 ISSN 1738-5520 c 2006, The Korean Society of Circulation Experience with Intracardiac Echocardiography for Guiding Transcatheter Device
Outcome of Transcatheter Closure of Oval Shaped Atrial Septal Defect with Amplatzer Septal Occluder
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.5.1104 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 54(5):1104-1109, 2013 Outcome of Transcatheter Closure of Oval Shaped Atrial Septal Defect
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2013.54.5.1104 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 54(5):1104-1109, 2013 Outcome of Transcatheter Closure of Oval Shaped Atrial Septal Defect
Role of Intracardiac Echocardiography (ICE) in Transcatheter Occlusion of Atrial Septal Defects
 Role of Intracardiac Echocardiography (ICE) in Transcatheter Occlusion of Atrial Septal Defects 7 Ismael Gonzalez, Qi-Ling Cao and Ziyad M. Hijazi * Rush Center for Congenital & Structural Heart Disease,
Role of Intracardiac Echocardiography (ICE) in Transcatheter Occlusion of Atrial Septal Defects 7 Ismael Gonzalez, Qi-Ling Cao and Ziyad M. Hijazi * Rush Center for Congenital & Structural Heart Disease,
Intracardiac Echocardiography-Guided Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defect A New Efficient Device Selection Method
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 42, No. 9, 2003 2003 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/03/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(03)01231-2
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 42, No. 9, 2003 2003 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/03/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/s0735-1097(03)01231-2
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
IMAGES. in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY
 IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. PMCID: PMC3232598 Three-dimensional trans-esophageal Echocardiographic Evaluation of Atrial Septal Defects: A Pictorial Essay Vinay K Sharma, S
IMAGES in PAEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Images Paediatr Cardiol. PMCID: PMC3232598 Three-dimensional trans-esophageal Echocardiographic Evaluation of Atrial Septal Defects: A Pictorial Essay Vinay K Sharma, S
Fabien Praz, Andreas Wahl, Sophie Beney, Stephan Windecker, Heinrich P. Mattle*, Bernhard Meier
 Procedural Outcome after Percutaneous Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale using the Amplatzer PFO Occluder Without Intra-Procedural Echocardiography in 1,000 Patients Fabien Praz, Andreas Wahl, Sophie Beney,
Procedural Outcome after Percutaneous Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale using the Amplatzer PFO Occluder Without Intra-Procedural Echocardiography in 1,000 Patients Fabien Praz, Andreas Wahl, Sophie Beney,
Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects with transthoracic echocardiography
 Cardiology in the Young (2011), 21, 204 208 doi:10.1017/s1047951110001782 r Cambridge University Press, 2010 Original Article Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects with transthoracic echocardiography
Cardiology in the Young (2011), 21, 204 208 doi:10.1017/s1047951110001782 r Cambridge University Press, 2010 Original Article Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects with transthoracic echocardiography
Imaging Evaluation of the Ventricular Septum
 Imaging Evaluation of the Ventricular Septum Craig E Fleishman, MD FACC FASE The Heart Center at Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children, Orlando SCAI Fall Fellows Course 2013 Las Vegas Disclosure Information
Imaging Evaluation of the Ventricular Septum Craig E Fleishman, MD FACC FASE The Heart Center at Arnold Palmer Hospital for Children, Orlando SCAI Fall Fellows Course 2013 Las Vegas Disclosure Information
A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Method for
 Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 1(1), 59-64 (1999) INVITED PAPER Use of MRI in ASD Asessment A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Method for Evaluating Atrial Septa1 Defects Godtfred Holmvang Cardiac
Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 1(1), 59-64 (1999) INVITED PAPER Use of MRI in ASD Asessment A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Method for Evaluating Atrial Septa1 Defects Godtfred Holmvang Cardiac
Hybrid Muscular VSD Closure in Small Weight Children
 Hybrid Muscular VSD Closure in Small Weight Children Shakeel A Qureshi, on behalf of: John P. Cheatham, MD George H. Dunlap Endowed Chair in Interventional Cardiology Director Cardiac Catheterization &
Hybrid Muscular VSD Closure in Small Weight Children Shakeel A Qureshi, on behalf of: John P. Cheatham, MD George H. Dunlap Endowed Chair in Interventional Cardiology Director Cardiac Catheterization &
Eight-French Intracardiac Echocardiography
 Circulation Journal Official Journal of the Japanese Circulation Society http://www.j-circ.or.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiovascular Intervention Eight-French Intracardiac Echocardiography Safe and Effective
Circulation Journal Official Journal of the Japanese Circulation Society http://www.j-circ.or.jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cardiovascular Intervention Eight-French Intracardiac Echocardiography Safe and Effective
Revealing new insights. irotate electronic rotation and xplane adjustable biplane imaging. Ultrasound cardiology. irotate and xplane
 Ultrasound cardiology irotate and xplane Revealing new insights irotate electronic rotation and xplane adjustable biplane imaging Annemien van den Bosch and Jackie McGhie Department of Cardiology, Erasmus
Ultrasound cardiology irotate and xplane Revealing new insights irotate electronic rotation and xplane adjustable biplane imaging Annemien van den Bosch and Jackie McGhie Department of Cardiology, Erasmus
Multidetector computed tomography in the evaluation of atrial septal defects
 Multidetector computed tomography in the evaluation of atrial septal defects Poster No.: C-0502 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: S. Espejo, R. Ysamat, B. Cajal, M. Pan,
Multidetector computed tomography in the evaluation of atrial septal defects Poster No.: C-0502 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: S. Espejo, R. Ysamat, B. Cajal, M. Pan,
Introduction. Sébastien Hascoet 1,2 *, Khaled Hadeed 1, Pauline Marchal 1, Yves Dulac 1, Xavier Alacoque 3, Francois Heitz 4, and Philippe Acar 1
 European Heart Journal Cardiovascular Imaging (2015) 16, 747 755 doi:10.1093/ehjci/jeu316 The relation between atrial septal defect shape, diameter, and area using three-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiography
European Heart Journal Cardiovascular Imaging (2015) 16, 747 755 doi:10.1093/ehjci/jeu316 The relation between atrial septal defect shape, diameter, and area using three-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiography
A case of mislabeled textbooks: misnomer of the traditional "bicaval" view.
 Providence St. Joseph Health Providence St. Joseph Health Digital Commons Journal Articles and Abstracts 8-1-2018 A case of mislabeled textbooks: misnomer of the traditional "bicaval" view. Laura Vaskelyte
Providence St. Joseph Health Providence St. Joseph Health Digital Commons Journal Articles and Abstracts 8-1-2018 A case of mislabeled textbooks: misnomer of the traditional "bicaval" view. Laura Vaskelyte
Part II: Fundamentals of 3D Echocardiography: Acquisition and Application
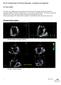 Part II: Fundamentals of 3D Echocardiography: Acquisition and Application Dr. Bruce Bollen 3D matrix array TEE probes provide options for both 2D and 3D imaging. Indeed, their utility in obtaining multiple
Part II: Fundamentals of 3D Echocardiography: Acquisition and Application Dr. Bruce Bollen 3D matrix array TEE probes provide options for both 2D and 3D imaging. Indeed, their utility in obtaining multiple
The Role of Echocardiography in the Percutaneous Treatment of Septal Defects
 Update The Role of Echocardiography in the Percutaneous Treatment of Septal Defects Simone Rolim F. Fontes Pedra, Sérgio Cunha Pontes Jr, Renata de Sá Cassar, Carlos Augusto Cardoso Pedra, Sérgio Luiz
Update The Role of Echocardiography in the Percutaneous Treatment of Septal Defects Simone Rolim F. Fontes Pedra, Sérgio Cunha Pontes Jr, Renata de Sá Cassar, Carlos Augusto Cardoso Pedra, Sérgio Luiz
Percutaneous VSD closure
 Percutaneous VSD closure Gianfranco Butera San Donato Milanese - Italy Patients selection Pts having hemodynamically significant VSD Left ventricular enlargement (left ventricular overload),defined as
Percutaneous VSD closure Gianfranco Butera San Donato Milanese - Italy Patients selection Pts having hemodynamically significant VSD Left ventricular enlargement (left ventricular overload),defined as
Patent Foramen Ovale Closure Without Echocardiographic Control: Use of Standby Intracardiac Ultrasound
 JACC: CARDIOVASCULAR INTERVENTIONS VOL. 1, NO. 4, 2008 2008 BY THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY FOUNDATION ISSN 1936-8798/08/$34.00 PUBLISHED BY ELSEVIER INC. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcin.2008.05.006 Patent Foramen
JACC: CARDIOVASCULAR INTERVENTIONS VOL. 1, NO. 4, 2008 2008 BY THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY FOUNDATION ISSN 1936-8798/08/$34.00 PUBLISHED BY ELSEVIER INC. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcin.2008.05.006 Patent Foramen
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING
 PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
PART II ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY LABORATORY OPERATIONS ADULT TRANSTHORACIC ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY TESTING STANDARD - Primary Instrumentation 1.1 Cardiac Ultrasound Systems SECTION 1 Instrumentation Ultrasound instruments
Conflict of Interests
 Introduction to Interventional Echocardiography Roberto M Lang, MD Tomtec Conflict of Interests Research Grants Philips Medical Imaging Research Grants Speakers bureau Advisory bureau 1 Structural Heart
Introduction to Interventional Echocardiography Roberto M Lang, MD Tomtec Conflict of Interests Research Grants Philips Medical Imaging Research Grants Speakers bureau Advisory bureau 1 Structural Heart
Echocardiography Conference
 Echocardiography Conference David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY-6 September 20, 2005 Atrial Septal Aneurysm Bulging of Fossa Ovalis Associated commonly with Atrial septal defect or small perforations
Echocardiography Conference David Stultz, MD Cardiology Fellow, PGY-6 September 20, 2005 Atrial Septal Aneurysm Bulging of Fossa Ovalis Associated commonly with Atrial septal defect or small perforations
Jian Fang 1, Shaobo Xie 2, Lunchao Ma 2, Chao Yang 2. Original Article
 Original Article Anatomic and surgical factors affecting the switch from minimally invasive transthoracic occlusion to open surgery during ventricular septal defect repair Jian Fang 1, Shaobo Xie 2, Lunchao
Original Article Anatomic and surgical factors affecting the switch from minimally invasive transthoracic occlusion to open surgery during ventricular septal defect repair Jian Fang 1, Shaobo Xie 2, Lunchao
Real-Time Three-Dimensional Transesophageal Echocardiography in Transcutaneous, Catheter-Based Procedures for Repair of Structural Heart Diseases
 Real-Time Three-Dimensional Transesophageal Echocardiography in Transcutaneous, Catheter-Based Procedures for Repair of Structural Heart Diseases Gila Perk, MD, Carlos Ruiz, MD, PhD, Muhamed Saric, MD,
Real-Time Three-Dimensional Transesophageal Echocardiography in Transcutaneous, Catheter-Based Procedures for Repair of Structural Heart Diseases Gila Perk, MD, Carlos Ruiz, MD, PhD, Muhamed Saric, MD,
Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale using the internal jugular venous approach
 New methods in diagnosis and therapy Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale using the internal jugular venous approach Przemysław Węglarz 1,2, Ewa Konarska-Kuszewska 2, Tadeusz Zębik 2, Piotr Kuszewski
New methods in diagnosis and therapy Transcatheter closure of patent foramen ovale using the internal jugular venous approach Przemysław Węglarz 1,2, Ewa Konarska-Kuszewska 2, Tadeusz Zębik 2, Piotr Kuszewski
Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defects with Superior-anterior Rim Deficiency Using Amplatzer Septal Occluder
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defects with Superior-anterior Rim Deficiency Using Amplatzer Septal Occluder Chien-Fu Huang, 1 Chih-Yuan Fang, 2 Sheung-Fat Ko, 3 Shao-Ju Chien,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Transcatheter Closure of Atrial Septal Defects with Superior-anterior Rim Deficiency Using Amplatzer Septal Occluder Chien-Fu Huang, 1 Chih-Yuan Fang, 2 Sheung-Fat Ko, 3 Shao-Ju Chien,
Case Report Hemostasis of Left Atrial Appendage Bleed With Lariat Device
 273 Case Report Hemostasis of Left Atrial Appendage Bleed With Lariat Device Amena Hussain MD, Muhamed Saric MD, Scott Bernstein MD, Douglas Holmes MD, Larry Chinitz MD NYU Langone Medical Center, United
273 Case Report Hemostasis of Left Atrial Appendage Bleed With Lariat Device Amena Hussain MD, Muhamed Saric MD, Scott Bernstein MD, Douglas Holmes MD, Larry Chinitz MD NYU Langone Medical Center, United
Transcatheter closure of interatrial
 372 Br HeartJf 1994;72:372-377 PRACTICE REVIEWED Department of Paediatric Cardiology, Royal Brompton Hospital, London A N Redington M L Rigby Correspondence to: Dr A N Redington, Department of Paediatric
372 Br HeartJf 1994;72:372-377 PRACTICE REVIEWED Department of Paediatric Cardiology, Royal Brompton Hospital, London A N Redington M L Rigby Correspondence to: Dr A N Redington, Department of Paediatric
The variety and complexity of percutaneous
 Hellenic J Cardiol 2012; 53: 1-5 Editorial Real-Time 3-Dimensional Transoesophageal Echocardiography: n Indispensable Resident in the Catheter Laboratory Constantina ggeli 1, Michael ellamy 1, Nilesh Sutaria
Hellenic J Cardiol 2012; 53: 1-5 Editorial Real-Time 3-Dimensional Transoesophageal Echocardiography: n Indispensable Resident in the Catheter Laboratory Constantina ggeli 1, Michael ellamy 1, Nilesh Sutaria
JOINT MEETING 2 Tricuspid club Chairpersons: G. Athanassopoulos, A. Avgeropoulou, M. Khoury, G. Stavridis
 JOINT MEETING 2 Tricuspid club Chairpersons: G. Athanassopoulos, A. Avgeropoulou, M. Khoury, G. Stavridis Similarities and differences in Tricuspid vs. Mitral Valve Anatomy and Imaging. Echo evaluation
JOINT MEETING 2 Tricuspid club Chairpersons: G. Athanassopoulos, A. Avgeropoulou, M. Khoury, G. Stavridis Similarities and differences in Tricuspid vs. Mitral Valve Anatomy and Imaging. Echo evaluation
Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defect in Patients Over 60 Years Old
 Original Article Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defect in Patients Over 60 Years Old Saet Byul Woo, MD 1, So-Ick
Original Article Print ISSN 1738-5520 On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Korean Circulation Journal Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defect in Patients Over 60 Years Old Saet Byul Woo, MD 1, So-Ick
Percutaneous occluder device closure through femoral vein guidance by transthoracic echocardiography in adult atrial septal defect patients
 Original Article Percutaneous occluder device closure through femoral vein guidance by transthoracic echocardiography in adult atrial septal defect patients Yixin Jia, Xu Meng, Yan Li, Chunlei Xu, Wen
Original Article Percutaneous occluder device closure through femoral vein guidance by transthoracic echocardiography in adult atrial septal defect patients Yixin Jia, Xu Meng, Yan Li, Chunlei Xu, Wen
6). However, for cases in which an ASO cannot
 Hiroshima J. Med. Sci. Vol. 64, No. 1 2, 1~7, June, 1 HIJM 64 1 1 A Logical Method of Selecting an Approach for Amplatzer Septal Occluder Implantation: Using Transesophageal Echocardiography to Reduce
Hiroshima J. Med. Sci. Vol. 64, No. 1 2, 1~7, June, 1 HIJM 64 1 1 A Logical Method of Selecting an Approach for Amplatzer Septal Occluder Implantation: Using Transesophageal Echocardiography to Reduce
Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defects: Results in Patients with Large and Extreme Defects
 Heart, Lung and Circulation (2014) 23, 127 131 1443-9506/04/$36.00 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.hlc.2013.07.020 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defects: Results in Patients
Heart, Lung and Circulation (2014) 23, 127 131 1443-9506/04/$36.00 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.hlc.2013.07.020 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defects: Results in Patients
Percutaneous atrial septal defect closure with the Occlutech Figulla Flex ASD Occluder.
 Percutaneous atrial septal defect closure with the Occlutech Figulla Flex ASD Occluder. First case with a novel delivery system. Werner Budts, Md, PhD, FESC Congenital and Structural Cardiology University
Percutaneous atrial septal defect closure with the Occlutech Figulla Flex ASD Occluder. First case with a novel delivery system. Werner Budts, Md, PhD, FESC Congenital and Structural Cardiology University
Breakout Session: Transesophageal Echocardiography
 Breakout Session: Transesophageal Echocardiography Doris Ockert, MD Andrew Schroeder, MD University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health Jutta Novalija, MD, PhD Medical College of Wisconsin
Breakout Session: Transesophageal Echocardiography Doris Ockert, MD Andrew Schroeder, MD University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health Jutta Novalija, MD, PhD Medical College of Wisconsin
Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defects in the Elderly
 REVIEW DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.2.47 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defects in the Elderly
REVIEW DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.2.47 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Transcatheter Closure of Secundum Atrial Septal Defects in the Elderly
Transseptal catheterization is an established
 Site-Specific Transseptal Puncture for Emerging Structural Heart Interventions Imaging-assisted techniques for accurate access. By Michael J. Rinaldi, MD, FACC, FSCAI; Markus Scherer, MD, FACC, FSCCT;
Site-Specific Transseptal Puncture for Emerging Structural Heart Interventions Imaging-assisted techniques for accurate access. By Michael J. Rinaldi, MD, FACC, FSCAI; Markus Scherer, MD, FACC, FSCCT;
Type Size AP/PS RP/RS Qp/Qs. Ia Resistive <0.3 < Ib Resistive <0.3 < IIa Resistive <0.5 >2
 Transcatheter closure of VSD using Duct Occluder device Nguyen Lan Hieu, MD, PhD Hanoi Medical University Vietnam Heart Institute Anatomy of VSD 1. Perimembranous VSD: Aneurysm septal membranous(tv or
Transcatheter closure of VSD using Duct Occluder device Nguyen Lan Hieu, MD, PhD Hanoi Medical University Vietnam Heart Institute Anatomy of VSD 1. Perimembranous VSD: Aneurysm septal membranous(tv or
Treatment of Inter-MitraClip Regurgitation Due to Posterior Leaflet Cleft by Use of The Amplatzer Vascular Plug II device
 Volume 1, Issue 3 Case Report ISSN: 2572-9292 Treatment of Inter-MitraClip Regurgitation Due to Posterior Leaflet Cleft by Use of The Amplatzer Vascular Plug II device Neha M. Mantri, Gagan D. Singh, Thomas
Volume 1, Issue 3 Case Report ISSN: 2572-9292 Treatment of Inter-MitraClip Regurgitation Due to Posterior Leaflet Cleft by Use of The Amplatzer Vascular Plug II device Neha M. Mantri, Gagan D. Singh, Thomas
Transcatheter Atrial Septal Defect Closure with Right Aortic Arch Is it really difficult? M Tokue, H Hara, K Sugi, M Nakamura
 5th Asia Pacific Congenital & Structural Heart Intervention Symposium 2014 10 12 October 2014, Hong Kong Convention and Exhibition Centre Organizer: Hong Kong Society of Congenital & Structural Heart Disease
5th Asia Pacific Congenital & Structural Heart Intervention Symposium 2014 10 12 October 2014, Hong Kong Convention and Exhibition Centre Organizer: Hong Kong Society of Congenital & Structural Heart Disease
For Personal Use. Copyright HMP 2013
 Case Report With Brief Review J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(4):E78-E80 Percutaneous Transjugular Device Closure of Postoperative Residual Atrial Septal Defect Saktheeswaran Mahesh Kumar, MD, DM, Sasidharan
Case Report With Brief Review J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(4):E78-E80 Percutaneous Transjugular Device Closure of Postoperative Residual Atrial Septal Defect Saktheeswaran Mahesh Kumar, MD, DM, Sasidharan
Diagnostic approach to heart disease
 Diagnostic approach to heart disease Initial work up History Physical exam Chest radiographs ECG Special studies Echocardiography Cardiac catheterization Echocardiography principles Technique of producing
Diagnostic approach to heart disease Initial work up History Physical exam Chest radiographs ECG Special studies Echocardiography Cardiac catheterization Echocardiography principles Technique of producing
Transcatheter closure of the patent ductus arteriosus using the new Amplatzer duct occluder: Initial clinical applications in children
 Transcatheter closure of the patent ductus arteriosus using the new Amplatzer duct occluder: Initial clinical applications in children Basil Thanopoulos, MD, PhD, a Nikolaos Eleftherakis, MD, a Konstantinos
Transcatheter closure of the patent ductus arteriosus using the new Amplatzer duct occluder: Initial clinical applications in children Basil Thanopoulos, MD, PhD, a Nikolaos Eleftherakis, MD, a Konstantinos
Real-Time 3D: Theory, Knobology and Data Acquisition
 Madhav Swaminathan, MD, FASE, FAHA Associate Professor of Anesthesiology Director, Perioperative Echocardiography Duke University Health System Real-Time 3D: Theory, Knobology and Data Acquisition Learning
Madhav Swaminathan, MD, FASE, FAHA Associate Professor of Anesthesiology Director, Perioperative Echocardiography Duke University Health System Real-Time 3D: Theory, Knobology and Data Acquisition Learning
Welcome Number 6. The background of the Cardiac Sonographer Network News masthead is a diagnostic image:
 Number 6 Welcome Number 6 Welcome to the newsletter created just for you: sonographers who perform pediatric echocardiograms in primarily adult echo labs. Each issue features tips on echocardiography of
Number 6 Welcome Number 6 Welcome to the newsletter created just for you: sonographers who perform pediatric echocardiograms in primarily adult echo labs. Each issue features tips on echocardiography of
Secundum atrial septal defect (ASD) is a common congenital heart disease and
 Device closure of atrial septal defects with the Amplatzer septal occluder: Safety and outcome in infants Karim A. Diab, MD, a Qi-Ling Cao, MD, a Emile A. Bacha, MD, b and Ziyad M. Hijazi, MD, MPH a Objective:
Device closure of atrial septal defects with the Amplatzer septal occluder: Safety and outcome in infants Karim A. Diab, MD, a Qi-Ling Cao, MD, a Emile A. Bacha, MD, b and Ziyad M. Hijazi, MD, MPH a Objective:
BASIL D. THANOPOULOS MD, PhD Associate Professor Honorary Consultant, RBH, London, UK
 TRANSCATHETER CLOSURE OF ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT AND PFO BASIL D. THANOPOULOS MD, PhD Associate Professor Honorary Consultant, RBH, London, UK TRANSCATHETER CLOSURE OF ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT AND PFO BASIL D.
TRANSCATHETER CLOSURE OF ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT AND PFO BASIL D. THANOPOULOS MD, PhD Associate Professor Honorary Consultant, RBH, London, UK TRANSCATHETER CLOSURE OF ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT AND PFO BASIL D.
Course Learning Objectives Sunday, February 17 Friday, February 22
 Course Learning Objectives Sunday, February 17 Friday, February 22 1. Define the physical principles of ultrasound technology and its applications for two and threedimensional (2D, 3D) imaging and use
Course Learning Objectives Sunday, February 17 Friday, February 22 1. Define the physical principles of ultrasound technology and its applications for two and threedimensional (2D, 3D) imaging and use
What I Have Learned from 3D Imaging of Heart Valve Disease
 What I Have Learned from 3D Imaging of Heart Valve Disease Rebecca T. Hahn, MD Director of Interventional Echocardiography Columbia University Core Lab Director for multiple tricuspid device trials for
What I Have Learned from 3D Imaging of Heart Valve Disease Rebecca T. Hahn, MD Director of Interventional Echocardiography Columbia University Core Lab Director for multiple tricuspid device trials for
Conflict of Interests
 New Approaches to Systolic Function: 4D Roberto M Lang, MD Conflict of Interests Philips Medical Imaging Research Grants Speakers bureau Advisory bureau Tomtec Research Grants Epsilon Research Grants 1
New Approaches to Systolic Function: 4D Roberto M Lang, MD Conflict of Interests Philips Medical Imaging Research Grants Speakers bureau Advisory bureau Tomtec Research Grants Epsilon Research Grants 1
Anaesthesia for percutaneous closure of atrial septal defects Patrick A Calvert BCh MA MRCP Andrew A Klein MBBS FRCA
 Anaesthesia for percutaneous closure of atrial septal defects Patrick A Calvert BCh MA MRCP Andrew A Klein MBBS FRCA Key points Percutaneous closure is the procedure of choice for the majority of patients
Anaesthesia for percutaneous closure of atrial septal defects Patrick A Calvert BCh MA MRCP Andrew A Klein MBBS FRCA Key points Percutaneous closure is the procedure of choice for the majority of patients
Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia
 Marshall University Marshall Digital Scholar Internal Medicine Faculty Research Spring 5-2004 Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia Ellen A. Thompson
Marshall University Marshall Digital Scholar Internal Medicine Faculty Research Spring 5-2004 Diversion of the inferior vena cava following repair of atrial septal defect causing hypoxemia Ellen A. Thompson
Transcatheter aortic valve replacement with intracardiac echocardiography from the right internal jugular vein
 Case Report Transcatheter aortic valve replacement with intracardiac echocardiography from the right internal jugular vein Hiroto Yagasaki 1, Yoshiaki Goto 1, Yoshio Mori 2, Toshiyuki Noda 1 1 Department
Case Report Transcatheter aortic valve replacement with intracardiac echocardiography from the right internal jugular vein Hiroto Yagasaki 1, Yoshiaki Goto 1, Yoshio Mori 2, Toshiyuki Noda 1 1 Department
Transesophageal Echocardiography in Children: An Interactive Session on Common Congenital Cardiac Defects
 Transesophageal Echocardiography in Children: An Interactive Session on Common Congenital Cardiac Defects Wanda C. Miller-Hance, M.D. Objective: At the conclusion of this workshop the participant should
Transesophageal Echocardiography in Children: An Interactive Session on Common Congenital Cardiac Defects Wanda C. Miller-Hance, M.D. Objective: At the conclusion of this workshop the participant should
Competency Training Requirements for the Area of Focused Competence in Adult Echocardiography
 Competency Training Requirements for the Area of Focused Competence in Adult Echocardiography 2013 VERSION 1.0 These training requirements apply to those who begin training on or after July 1 st, 2013.
Competency Training Requirements for the Area of Focused Competence in Adult Echocardiography 2013 VERSION 1.0 These training requirements apply to those who begin training on or after July 1 st, 2013.
Concomitant procedures using minimally access
 Surgical Technique on Cardiac Surgery Concomitant procedures using minimally access Nelson Santos Paulo Cardiothoracic Surgery, Centro Hospitalar de Vila Nova de Gaia, Oporto, Portugal Correspondence to:
Surgical Technique on Cardiac Surgery Concomitant procedures using minimally access Nelson Santos Paulo Cardiothoracic Surgery, Centro Hospitalar de Vila Nova de Gaia, Oporto, Portugal Correspondence to:
Multifenestrated Septal Occluder Cribriform
 Multifenestrated Septal Occluder Cribriform Instructions for Use Device Description The AMPLATZER Multifenestrated Septal Occluder Cribriform (Cribriform Occluder) is a self-expanding double-disc nitinol
Multifenestrated Septal Occluder Cribriform Instructions for Use Device Description The AMPLATZER Multifenestrated Septal Occluder Cribriform (Cribriform Occluder) is a self-expanding double-disc nitinol
Real-time imaging for transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects
 Review Real-time imaging for transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects Nowadays transcatheter closure has become the standard treatment for an atrial septal defect (ASD). Since morphologic variation
Review Real-time imaging for transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects Nowadays transcatheter closure has become the standard treatment for an atrial septal defect (ASD). Since morphologic variation
Perventricular Closure of Muscular VSD
 Perventricular Closure of Muscular VSD John P. Cheatham, MD, MSCAI George H. Dunlap Endowed Chair in Interventional Cardiology Co-Director, The Heart Center, Nationwide Children s Hospital Professor, Pediatrics
Perventricular Closure of Muscular VSD John P. Cheatham, MD, MSCAI George H. Dunlap Endowed Chair in Interventional Cardiology Co-Director, The Heart Center, Nationwide Children s Hospital Professor, Pediatrics
Device Closure of ASD in Children Using the Amplatzer Devices: Indications and catheter preparations, technique, and outcome [15]
![Device Closure of ASD in Children Using the Amplatzer Devices: Indications and catheter preparations, technique, and outcome [15] Device Closure of ASD in Children Using the Amplatzer Devices: Indications and catheter preparations, technique, and outcome [15]](/thumbs/73/69533656.jpg) Device Closure of ASD in Children Using the Amplatzer Devices: Indications and catheter preparations, technique, and outcome [15] SCAI Fellow Course Fall 2014 Ralf J Holzer MD MSc FSCAI Medical Director
Device Closure of ASD in Children Using the Amplatzer Devices: Indications and catheter preparations, technique, and outcome [15] SCAI Fellow Course Fall 2014 Ralf J Holzer MD MSc FSCAI Medical Director
Closure of Atrial Septal Defects With the Amplatzer Occlusion Device: Preliminary Results
 1110 JACC Vol. 31, No. 5 PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Closure of Atrial Septal Defects With the Amplatzer Occlusion Device: Preliminary Results BASIL (VASILIOS) D. THANOPOULOS, MD, CLEO V. LASKARI, MD, GEORGE
1110 JACC Vol. 31, No. 5 PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY Closure of Atrial Septal Defects With the Amplatzer Occlusion Device: Preliminary Results BASIL (VASILIOS) D. THANOPOULOS, MD, CLEO V. LASKARI, MD, GEORGE
An intensive interactive course for 3D echocardiography: is crop till you drop an effective learning strategy?
 European Journal of Echocardiography (2008) 9, 373 380 doi:10.1016/j.euje.2007.06.011 An intensive interactive course for 3D echocardiography: is crop till you drop an effective learning strategy? Carly
European Journal of Echocardiography (2008) 9, 373 380 doi:10.1016/j.euje.2007.06.011 An intensive interactive course for 3D echocardiography: is crop till you drop an effective learning strategy? Carly
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus. Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE)
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
For Personal Use. Copyright HMP 2013
 Case Report J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(2):E42-E44 Percutaneous Closure of Iatrogenic Ventricular Septal Defect Following Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement Using Two Different Approaches Takashi Matsumoto,
Case Report J INVASIVE CARDIOL 2013;25(2):E42-E44 Percutaneous Closure of Iatrogenic Ventricular Septal Defect Following Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement Using Two Different Approaches Takashi Matsumoto,
Image Assistance in TAVI Why CT? Won-Jang Kim, MD, PhD Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine, Heart Institute, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
 Image Assistance in TAVI Why CT? Won-Jang Kim, MD, PhD Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine, Heart Institute, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea Major Uses of CT in TAVI Ileofemoral Patient Arterial
Image Assistance in TAVI Why CT? Won-Jang Kim, MD, PhD Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine, Heart Institute, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea Major Uses of CT in TAVI Ileofemoral Patient Arterial
Transcatheter closure of atrial septal defects using the Cardio-Seal implant
 320 Department of Pediatrics, Division of Cardiology, The Variety Club Catheterization Laboratories, The Hospital for Sick Children, 555 University Avenue, Toronto, Ontario M5G 1X8, Canada CACPedra J Pihkala
320 Department of Pediatrics, Division of Cardiology, The Variety Club Catheterization Laboratories, The Hospital for Sick Children, 555 University Avenue, Toronto, Ontario M5G 1X8, Canada CACPedra J Pihkala
Assessment of Atrial Septal Defect Area Changes During Cardiac Cycle by Live Three-Dimensional Echocardiography
 J Cardiol 2006 Apr; 47 4 : 181 187 Assessment of Atrial Septal Defect Area Changes During Cardiac Cycle by Live Three-Dimensional Echocardiography Ming-Xing Ling-Yun Xin-Fang Qing Xiao-Fang Ya-Li Jing
J Cardiol 2006 Apr; 47 4 : 181 187 Assessment of Atrial Septal Defect Area Changes During Cardiac Cycle by Live Three-Dimensional Echocardiography Ming-Xing Ling-Yun Xin-Fang Qing Xiao-Fang Ya-Li Jing
AMPLATZER Septal Occluder Structural Heart Therapy. Over 15 years of. Demonstrated. Clinical Experience. We ll show you our data. Ask to see theirs.
 AMPLATZER Septal Occluder Structural Heart Therapy Over 15 years of Demonstrated Clinical Experience We ll show you our data. Ask to see theirs. Leading the Standard of Care 1,2 The AMPLATZER Septal Occluder
AMPLATZER Septal Occluder Structural Heart Therapy Over 15 years of Demonstrated Clinical Experience We ll show you our data. Ask to see theirs. Leading the Standard of Care 1,2 The AMPLATZER Septal Occluder
Rahul Jhaveri, M.D. The Heart Group of Lancaster General Health
 Rahul Jhaveri, M.D. The Heart Group of Lancaster General Health INTRODUCTION Three recently published randomized controlled trials in The New England Journal of Medicine provide new information about closure
Rahul Jhaveri, M.D. The Heart Group of Lancaster General Health INTRODUCTION Three recently published randomized controlled trials in The New England Journal of Medicine provide new information about closure
A challenging case of successful ASD closure without echocardiographic guidance in an 86-year old with severe kyphoscoliosis and platypnoeaorthodeoxia
 A challenging case of successful ASD closure without echocardiographic guidance in an 86-year old with severe kyphoscoliosis and platypnoeaorthodeoxia syndrome. Dr Anvesha Singh, Dr James Ogle, Dr Derek
A challenging case of successful ASD closure without echocardiographic guidance in an 86-year old with severe kyphoscoliosis and platypnoeaorthodeoxia syndrome. Dr Anvesha Singh, Dr James Ogle, Dr Derek
A novel approach to the diagnosis of left atrial appendage thrombus using contrast echocardiography and power Doppler imaging
 European Journal of Echocardiography (2008) 9, 329 333 doi:10.1093/ejechocard/jen068 A novel approach to the diagnosis of left atrial appendage thrombus using contrast echocardiography and power Doppler
European Journal of Echocardiography (2008) 9, 329 333 doi:10.1093/ejechocard/jen068 A novel approach to the diagnosis of left atrial appendage thrombus using contrast echocardiography and power Doppler
Catheter-based left atrial appendage occlusion procedure: role of echocardiography
 European Heart Journal Cardiovascular Imaging (2012) 13, 132 138 doi:10.1093/ejechocard/jer158 REVIEWS Catheter-based left atrial appendage occlusion procedure: role of echocardiography Gila Perk 1 *,
European Heart Journal Cardiovascular Imaging (2012) 13, 132 138 doi:10.1093/ejechocard/jer158 REVIEWS Catheter-based left atrial appendage occlusion procedure: role of echocardiography Gila Perk 1 *,
ACUSON Sequoia C512 Echocardiography System The ultimate in imaging
 ACUSON Sequoia C512 Echocardiography System The ultimate in imaging Optimum imaging for every patient ACUSON Sequoia C512 Patient Specific Imaging Programmable Waveform Generator Coherent Pulse Formation
ACUSON Sequoia C512 Echocardiography System The ultimate in imaging Optimum imaging for every patient ACUSON Sequoia C512 Patient Specific Imaging Programmable Waveform Generator Coherent Pulse Formation
TRANSCATHETER CLOSURE OF MULTI- FENESTRATED ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECTS U SING THE NEW AMPLATZER CRIBRIFORM D EVICE
 P E D I A T R I C C A R D I O L O G Y T O D A Y RELIABLE INFORMATION IN PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 PREMIER ISSUE SEPTEMBER 2003 INSIDE THIS ISSUE Transcatheter Closure of Multifenestrated Atrial
P E D I A T R I C C A R D I O L O G Y T O D A Y RELIABLE INFORMATION IN PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY VOLUME 1, ISSUE 1 PREMIER ISSUE SEPTEMBER 2003 INSIDE THIS ISSUE Transcatheter Closure of Multifenestrated Atrial
Surgical Approach To An Unsuccessful Device Closure of Atrial Septal Defect. U Yetkin, B Özpak,? Yürekli, K Ergüne?, N Eren, O Ergene, A Gürbüz
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Surgical Approach To An Unsuccessful Device Closure of Atrial Septal Defect U Yetkin, B Özpak,? Yürekli, K Ergüne?,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Surgical Approach To An Unsuccessful Device Closure of Atrial Septal Defect U Yetkin, B Özpak,? Yürekli, K Ergüne?,
Real-Time 3-Dimensional Echocardiography Evaluation of Congenital Heart Disease
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Real-Time 3-Dimensional Echocardiography Evaluation of Congenital Heart Disease Lorena Balestrini, MD, Craig Fleishman, MD, Laura Lanzoni, MD, Joseph Kisslo, MD, A. Resai Bengur, MD,
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Real-Time 3-Dimensional Echocardiography Evaluation of Congenital Heart Disease Lorena Balestrini, MD, Craig Fleishman, MD, Laura Lanzoni, MD, Joseph Kisslo, MD, A. Resai Bengur, MD,
In Vitro Two-Dimensional Echocardiographic Imaging of a Stented Porcine Bioprosthetic Valve: The Bent Strut Artifact
 C 2008, the Author Journal compilation C 2008, Wiley Periodicals, Inc. DOI: 10.1111/j.1540-8175.2008.00753.x In Vitro Two-Dimensional Echocardiographic Imaging of a Stented Porcine Bioprosthetic Valve:
C 2008, the Author Journal compilation C 2008, Wiley Periodicals, Inc. DOI: 10.1111/j.1540-8175.2008.00753.x In Vitro Two-Dimensional Echocardiographic Imaging of a Stented Porcine Bioprosthetic Valve:
Automated Volumetric Cardiac Ultrasound Analysis
 Whitepaper Automated Volumetric Cardiac Ultrasound Analysis ACUSON SC2000 Volume Imaging Ultrasound System Bogdan Georgescu, Ph.D. Siemens Corporate Research Princeton, New Jersey USA Answers for life.
Whitepaper Automated Volumetric Cardiac Ultrasound Analysis ACUSON SC2000 Volume Imaging Ultrasound System Bogdan Georgescu, Ph.D. Siemens Corporate Research Princeton, New Jersey USA Answers for life.
The role of intraoperative TOE in congenital cardiac surgery
 The role of intraoperative TOE in congenital cardiac surgery Justiaan Swanevelder Dept of Anaesthesia Groote Schuur and Red Cross War Memorial Children s Hospitals University of Cape Town, South Africa
The role of intraoperative TOE in congenital cardiac surgery Justiaan Swanevelder Dept of Anaesthesia Groote Schuur and Red Cross War Memorial Children s Hospitals University of Cape Town, South Africa
British Society of Echocardiography
 British Society of Echocardiography Affiliated to the British Cardiac Society A Minimum Dataset for a Standard Adult Transthoracic Echocardiogram From the British Society of Echocardiography Education
British Society of Echocardiography Affiliated to the British Cardiac Society A Minimum Dataset for a Standard Adult Transthoracic Echocardiogram From the British Society of Echocardiography Education
Among the congenital defects of the heart diagnosed
 Atrial Septal Defect: Anatomoechocardiographic Correlation Luis Muñóz-Castellanos, MD, Nilda Espinola-Zavaleta, MD, PhD, Magdalena Kuri-Nivón, MD, José Francisco Ruíz, MD, and Candace Keirns, MD, Mexico
Atrial Septal Defect: Anatomoechocardiographic Correlation Luis Muñóz-Castellanos, MD, Nilda Espinola-Zavaleta, MD, PhD, Magdalena Kuri-Nivón, MD, José Francisco Ruíz, MD, and Candace Keirns, MD, Mexico
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE FOR:
 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE FOR: en English bg INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE FOR: GORE CARDIOFORM SEPTAL OCCLUDER Carefully read all instructions prior to use. Observe all warnings and precautions noted throughout these
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE FOR: en English bg INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE FOR: GORE CARDIOFORM SEPTAL OCCLUDER Carefully read all instructions prior to use. Observe all warnings and precautions noted throughout these
