ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION ON DHAMANI IN AYURVEDA WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO SUSRUTA SAMHITA
|
|
|
- Joseph Collins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Article ANATOMICAL CONSIDERATION ON DHAMANI IN AYURVEDA WITH SPECIAL REFERENCE TO SUSRUTA SAMHITA Bhan Pratap Yadaw 1*, Awasthi HH 2 1. Senior Resident & Ph.D. Scholar, Dept. of Rachana Sharira, Faculty of Ayurveda, IMS, BHU, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, India. 2. Professor & Head, Dept. of Rachana Sharira, Faculty of Ayurveda, IMS, BHU, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, India. Received: ; Revised: ; Accepted: Abstract The term siras and dhamanis are as old as vedas. They have been generally used in the same sense. But these are not synonymous. In general, siras and dhamanis means blood vessels. But on the basis of interpretation of commentators dhamani is a channel connected to the heart which is thick whereas sira is a thin blood vessel. Sira and dhamani both are related to heart, but their relations are different. In relation to dhamani, hridaya is ashraya (abode). Ashraya is those structures which provide base, nutrition and protection to their ashrayi (shelters). Heart is place of ojus, so dhamani which carry ojus are called as ojovaha dhamani. Heart is also place of prana, so dhamani are also pranavaha. Due to place of rasa, dhamanis are rasavahini. Heart is the place of contraction and relaxation, so contraction and relaxation also received by dhamani. Thus dhamanis are ashrita (depends) on heart for ojus, prana, rasa, spandana etc. although siras are also related to heart but they do not receive any significant things from heart, sira only drain their blood into the heart. Keywords: Dhamani; Sira; Srotas; Urdhwaga: Adhoga, Tiryaga; Ayurveda *Address for correspondence: Dr. Bhan Pratap Yadaw, Senior Resident & Ph.D. Scholar, Dept. of Rachana Sharira, Faculty of Ayurveda, IMS, BHU, Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, India bhanpratapyadaw@gmail.com Cite This Article Bhan Pratap Yadaw, Awasthi HH. Anatomical consideration on dhamani in Ayurveda with special reference to Susruta samhita. Ayurpharm Int J Ayur Alli Sci. 2014;3(10): Ayurpharm - International Journal of Ayurveda and Allied Sciences 299
2 INTRODUCTION Ayurveda is that science, which imports all the knowledge of life. Life is the combination of four factors sharira, indriya, satva and atma. [1] Thorough structural scientific knowledge of the life was recommended by ancient acharyas. The knowledge of Rachana Sharira is mandatory for the students of any system of medicine. It is a vital subject in pre-clinical studies. The Atharva veda refers to dhamaniswhich are ducts with thick walls equivalent to arteries; siras- which are ducts with thin walls equivalent to veins and still finer ducts are referred to as snavas similar to capillaries. However some misconceptions existed and the vedic scholars considered nerves also as hollow tubes or ducts which are quite far from reality. Originally, the ancient Greeks believed that arteries only held air. This was because, in the absence of a heartbeat, the arteries of the dead were empty. In the middle ages it was believed that arteries carried vital spirits, separate and different from blood. It wasn't until the seventeenth century that William Harvey described the circulatory system as we know it. Acharya sushruta has said to be the father of surgery because of description available in sushruta samhita regarding methodology for learning of the anatomy, dissection on cadaver, dhamani, sira, marma, management of fractures, different surgical procedures etc. He has given more emphasis on the practical knowledge. A surgeon who desires to obtain thorough knowledge of the body must dissect a dead body properly and see each and every structure and organ in it. [2] Ayurvedic acharyas has used an anatomical term dhamani, which is one of the controversial terms (structure), used to represents tubular structure, to carry sabda, sparsa, rupa, rasa and gandha and it is one of the synonyms of srotas. Modern science describes blood vessels of three types' viz-artery, vein & capillaries. The other two important channels for the maintenance of the body are lymphatics & nerves. The relevant terms in ayurvedic language are sira, dhamani and srotas and in these three terms the modern five structures namely artery, vein, capillary lymphatic and nerve are incorporated. Many times controversies or differences in opinions had been raised due to the two types of commentators. One who had performed the dissection and seen the structures and having profound knowledge then commented the terms, they had not left any chance for controversies. Others who had not performed the dissection but commented the terms on the basis of knowledge of Sanskrita and other literature and using the synonyms of the terms like sira, dhamani and srotas. They had left many chances for controversies. The terms sira, dhamani and srotas are as old as the Vedas. They have been used loosely in common parlance through ignorance of their specific meanings. The statement of Amarkosh Nadi tu dhamanih sira stands on this wrong basis. Unfortunately this has been followed by many commentators, the words dhamani and sira are synonym, [3] it has been admitted by some ayurvedic acharyas, but sushruta has differentiated them on anatomical basis. Sushruta s concept of dhamani is specifically unique. Concept of dhamani The Atharvaveda refers to dhamanis- which are ducts with thick walls equivalent to arteries; siras- which are ducts with thin walls equivalent to veins and still finer ducts are referred to as snavas similar to capillaries. Acharya charak starts from the root meaning of dhamani. Dhamani term is derived from the root 'Dhma' (Dhamani + Va Digha). Dhamani is pipe or tubular vessels or canal of the human body starting from heart or from the naval on supported to carry the rasa. According to charak 'Dhamanadhamanyah' hence dhamani is that tract which produces sound. [4] According to sushruta, sira & dhamani are the channels other than srotas. [5] Ayurpharm - International Journal of Ayurveda and Allied Sciences 300
3 Origin & division of Dhamani According sushruta nabhi is the site of origin of both dhamani and sira. [6] Even in charak, astanga sangraha and astanga hridaya, nabhi word has been used in reference to fetal life. Sushruta has himself shifted from his own view in relation to the origin of dhamanis from nabhi to hridaya in sutrasthan 'sonitavarniya adhyaya. [7] Charaka has also mentioned in 30th chapter of sutrasthan that the dhamanis arise from the hridaya. [8] According to sushruta, among the dhamani arising from the nabhi, ten spread upward, ten downward and four sideward (transverse). [9] Charak said that 10 dhamani arises from hridaya. [10] In astang sangraha sharira 6/9, it is said that dhamani are twenty four; by them the entire body gets supplied with nourishment similar to a vast plot of land by canals carrying water; from them (dhamani) the nabhi is surrounded just as a axle hole is surrounded by the spokes (of wheel); at that umbilicus (centre) life is designed to dwell; hence it is seat of internal fire. [11] Bhavprakash also said that dhamanis are originated from nabhi and are twenty four in number (24). From among them, ten spread upwards, ten downwards and four in different directions. These vessels have got minute outlets, through which rasa (nutrients) move in entirely similar to the flower stalk of lotus where pores are present naturally. Urdhvaga dhamani Those dhamanis spreading upward, support (maintain) the body by attending to functions such as receiving sensation of sound, touch, sight, taste and smell; inspiration, expiration, yawning, sneezing, laughing, talking g, shouting and such other functions. These dhamanis, after reaching the hridaya each one divides into three, thus becoming thirty. Out of these, two each carry vata, pitta, kapha, sonita and rasa- thus ten; two each carry sensations sound, sight, taste and smell thus eight; two attend to speaking (in words), two attend to shouting (loud sound without words), two attend to sleep, and two to waking, two carry tears (in the eyes), two carry breast milk in the breasts of women, these only carry sukra from the breast in men thus thirty (dhamani) are described by their divisions. By these dhamanis parts of the body above the umbilicus, such as the abdomen, flanks, back, chest, shoulders, neck, arms etc. are supported and maintained. The upward dhamani perform all these functions always (throughout life). [12] Adhoga dhamani Dhamanis spreading downward purvey flatus, faces, semen, and menstrual blood etc downward. These, on reaching the pittashaya acting upon the essence of foods and drinks produce by the heat separates it into sara (essence) and kitta (waste); purveys it throughout the body and nourish the body supplying nutrient materials present in the essence of food supply it (the essence of food) to the dhamani spreading in upward and transverse direction, fill the seat of rasa (hridaya) and separate urine, faeces and sweat (from the rasa). In between the amashaya and pakvashaya, each one of these divides into three branches thus becoming thirty; out of these, two each carry vata, pitta, kapha, sonita and rasa thus ten; two present in the intestine purvey anna, two carry toya (water produce during digestion), two present in the bladder carry urine, two are meant for production of sukra in the testes, and two meant for its elimination, these only purvey the blood known as artava in women and eliminate it; two attached to the large intestine are for expelling the faces; another eight dhamani supply sweat to those (dhamani) spreading transversely; thus the thirty branches are described. By these dhamanis, the parts of the body below the umbilicus such as large intestines, pelvis, organs of urine (bladder), faeces (rectum), anus, bladder, penis and legs are supported and maintained. Dhamani Ayurpharm - International Journal of Ayurveda and Allied Sciences 301
4 spreading downward perform these functions all the time (throughout life). [13] Tiryagga dhamani Each one of the four dhamani spreading sideward/transversely divide into hundred and thousand of branches further and so becomes innumerable; by these, the entire body appears to be full of windows; these knit together broadly, their mouths (openings) are attached to the hair follicles; these purvey sweda and rasa both inside and outside; through these only the potency (effect) of materials (medicines) used in the form of anointing, pouring liquids on the body and application of pastes, get cooked (processed by heat) in the skin, enter into the interior of the body. The sensation of touch both comfortable and uncomfortable, are perceived (understood) by these only. Thus were described the four dhamani along with their branches, spread throughout the body. [14] MATERIAL AND METHODS The present study depends on the data collected from the ayurveda samhitas and modern books, national and international journals, magazines, conferences, internet materials, previous work done, presented papers etc, critically evaluated and important information will be sought to approach the objectives scientifically. DISCUSSION Ayurveda, a hidden abode of basic concepts and treatment aspects had suffered with many hurdles in its progress and not communicated properly since few centuries. An extensive description about dhamani is available in ayurvedic literature but the correlative interpretation and applied aspect of dhamani with latest up to date modern parameters is not available. The advancing age of information technology demands the classical ancient Ayurveda to be communicated, interpreted and correlated in term of exciting knowledge for international debate. The basic ideology of Ayurvedic treatment with the recent and sophisticated improvements in contemporary science like investigative methods may answer the unsolved question in neurology and angiology. The term dhamani, in one place reflects a meaning of blood vessels while at other place, it means nerve. In such condition it is very difficult to know doubtlessly about it like modern anatomy. Therefore, it requires great research work to establish a clear concept of dhamani in ayurveda. It has been started earlier (in chap. 14. of sutra sthana) that there are twenty-four dhamani, arising from the hridaya. [15] On that, some scholars say sira, dhamani and srotas are not different, and dhamani and srotas are the vikara (modifications) of sira only. [16] This view is not correct, dhamani and srotas are different from sira. How? It is so because of vyanajananyatva (difference in their features), mulasanniyama (difference in number at their place of origin), karma vaisesya (function special to each) and agama (description in scriptures treatises of Ayurveda). [17] Dalhana explains these reasons as follows; Reasons of difference 1. Difference in features sira (veins) carrying vata, pitta, kapha and rakta are described as light red, blue, white and (deep) red in color respectively, whereas, dhamani are described as having no color and srotas as having the same color of the dhatu (tissues) in which they are present. 2. Number at origin At their site of origin (the umbilicus) sira are described as forty in number, whereas dhamani are twenty four and srotas are twenty two. Ayurpharm - International Journal of Ayurveda and Allied Sciences 302
5 3. Special functions Performing all the functions of the body, mind and intellect without any hindrance (interruption) is the function of the sira, whereas functions of dhamani are perception of object of senses (such as sound, light, taste, smell and touch) and those of srotas are purveying air, water, food, rasa etc. 4. Description in texts Treatises of Ayurveda have mentioned sira, dhamani and srotas separately at many places. Hence dhamani and srotas are different from sira. Reasons for confusion Identifying these as one and the same are due to sannikarsa (nearness), sadrisagamatva (similarity of description in texts), sadrisa karmatva (similarity of functions) and sauksmya (minuteness)-these though actually performing different functions yet appear to be not different (in other words appear to be one and the same). 1. Nearness - as for e.g., burning of blades of grass placed nearer to one another though burning separately, yet appear as though all are burning together. 2. Similarity of description in texts- as for example the statement that vacant places, sira, dhamani, srotas, marga etc. all belong to akashabhuta group since there is space inside them. 3. Similarity of functions- for examplemelody of each member of an orchestra though different individually, still appears to be one when combined together. 4. Minuteness- though each one of the innumerable atoms of mud present in a pot are supporting the water in the pot, still they are not recognized separately. The examples given by Dalhana above are of a general nature and not very scientific. These four reasons can be explained better as- veins and arteries along with their branches are found side by side closely, in all the parts of the body; the statements of authorities that veins, arteries, channels are identical is because all these are hollow tubes; similarity of function- veins and arteries are passages of circulation of rasa-rakta (blood) while tissue channels divide themselves into minute branches, some of which are invisible and are present side by side. By these reasons these structures may not be distinguished easily. Sushruta has used the word ''nabhiprabhava'' only because during intra uterine life the vessels like umbilical arteries and umbilical veins start from the fetal umbilicus. Therefore, one can accept this statement in relation to fetal life. Even in charak, astanga sangraha and astanga hridaya, nabhi word has been used in reference to fetal life. Apparent similarity between the functions of dhamani (arteries) and nerves is because these functions are interdependent and supplementary to one another. Functions of nerves will not be effective in any part of the body if that part is not supplied with blood by the arteries. For example when the eye, (specially its retina) is not supplied with blood, then vision will be hampered or lost though nerve impulse is present; similarly so with all sense organs, viscera such as larynx, stomach, intestines, urinary bladder, rectum, uterus etc and tissues likes muscles etc. for every function of the body arteries supplying blood and nerves supplying the stimulation to act, both are equally important and any one only will be useless. Sushruta has given greater emphasis to dhamanis (arteries) and attributed all the functions to these purvey the three doshas also, along with rasa dhatu. Ayurpharm - International Journal of Ayurveda and Allied Sciences 303
6 CONCLUSION The dhamani have throbbing that indicates the presence of life, it also indicates health and ill health. When, throbbing stops we judge that the heart has stopped functioning and body is declared dead. The nervous tissue, more than any other tissue of the body, depends for its normal functioning on the continuous supply of arterial blood. Whenever, the volume of blood circulating in the brain is reduced for even a short time unconsciousness results. The nerve cells suffer irreversible damage if the blood flow remains insufficient for too long, the time measured \in minutes. Consequently disturbance in the blood supply of brain tissue and the lesions resulting there from constitute a large part of the pathology of the brain. In a tissue whose activity depends so much upon its blood supply, the micro-anatomical relations between the cells and the blood vessels are of particular interest. The materials used in the form of liquid or pastes on the surface of body enter into the interior of the body through these dhamani. Comfortable and uncomfortable touches are perceived by dhamani. The dhamani are panchabhoutika, which help establish, contact between the sense organs and their respective objects throughout the life. Such contact happens in each sense organ separately. This contact ceases at the time of death of body. With these features contrary to those of those arteries, equating dhamani with nerve is untenable. Apparent similarity between the functions of dhamanis (arteries) and nerves is because these functions are interdependent and supplementary to one another. Functions of nerves will not be effective in any part of the body if that part is not supplied with blood by the arteries. REFERENCES 1. Caraka. Charaka samhita (Chakrapani dutta Sutrasthana, 1.p Susruta. Susruta samhita (English), Vol. I. sthana, 5. p Caraka. Charaka samhita (Chakrapani dutta Ayurveda dipika Commentary), Vol. II. Sharma Vimanasthana, 5. p Caraka. Charaka samhita (Chakrapani dutta Sutrasthana, 30. p Susruta. Susruta samhita (English), Vol. I. sthana, 9. p Susruta. Susruta samhita (English), Vol. I. sthana, 9. p Susruta. Susruta samhita (English), Vol. I. Chowkhambha Orientalia; Sutrasthana, 14. p Caraka. Charaka samhita (Chakrapani dutta Sutrasthana, 30. p Susruta. Susruta samhita (English), Vol. I. sthana, 9. p Caraka. Charaka samhita (Chakrapani dutta Sutrasthana, 30. p Vagbhata. Astanga Samgraha (English), Vol. II. Srikantha Murthy KR, editor. 1 st ed. Varanasi: Chowkhambha Orientalia; Sharirasthana, 6. p Susruta. Susruta samhita (English), Vol. I. sthana, 9. p Susruta. Susruta samhita (English), Vol. I. sthana, 9. p Susruta. Susruta samhita (English), Vol. I. sthana, 9. p.145. Ayurpharm - International Journal of Ayurveda and Allied Sciences 304
7 15. Susruta. Susruta samhita (English), Vol. I. Chowkhambha Orientalia; Sutrasthana, 14. p Susruta. Susruta samhita (English), Vol. I. sthana, 9. p Susruta. Susruta samhita (English), Vol. I. sthana, 9. p.140. Source of Support: Nil Conflict of Interest: None Declared Ayurpharm - International Journal of Ayurveda and Allied Sciences 305
ANVESHANA CONCEPT OF SROTAS AN AYURVEDIC REVIEW
 www.aamj.in ANVESHANA Review Article AYURVEDA MEDICAL JOURNAL ISSN: 2395-4159 CONCEPT OF SROTAS AN AYURVEDIC REVIEW Burde Priyanka Gajananrao Assistant Professor, Department of Rachana Sharira, Rural Institute
www.aamj.in ANVESHANA Review Article AYURVEDA MEDICAL JOURNAL ISSN: 2395-4159 CONCEPT OF SROTAS AN AYURVEDIC REVIEW Burde Priyanka Gajananrao Assistant Professor, Department of Rachana Sharira, Rural Institute
Ijapc /3/2018. Volume 8 Issue 2. Greentree Group Received 08/02/18 Accepted 26/02/18 Published 10/03/18
 Ijapc 2018 Volume 8 Issue 2 www.ijapc.com 10/3/2018 Greentree Group Received 08/02/18 Accepted 26/02/18 Published 10/03/18 2018 Greentree IJAPC 2018 Vol. 8 Issue 2 Greentree www.ijapc.com Group 145 REVIEW
Ijapc 2018 Volume 8 Issue 2 www.ijapc.com 10/3/2018 Greentree Group Received 08/02/18 Accepted 26/02/18 Published 10/03/18 2018 Greentree IJAPC 2018 Vol. 8 Issue 2 Greentree www.ijapc.com Group 145 REVIEW
Ayurved, Pune-43.India. 2 Assistant professor (Kriya Sharir) 2. Bharati Vidyapeeth (Deemed to be University), College of
 International Journal of Applied Ayurved Research ISSN: 2347-6362 INTERPRETATION OF PESHI ON THE BASIS OF LITERARY AND CADAVERIC STUDY 1 Kadam Rupaji J. 2 Kadam Manisha R. 1 Associate professor(rachana
International Journal of Applied Ayurved Research ISSN: 2347-6362 INTERPRETATION OF PESHI ON THE BASIS OF LITERARY AND CADAVERIC STUDY 1 Kadam Rupaji J. 2 Kadam Manisha R. 1 Associate professor(rachana
A LITERATURE REVIEW OF SIRA AND VEIN
 INTERNATIONAL AYURVEDIC MEDICAL JOURNAL International Ayurvedic Medical Journal, (ISSN: 2320 5091) (May, 2017) 5 (5) A LITERATURE REVIEW OF SIRA AND VEIN Khan Rohee WadoodKhan Assistant professor, Kriya
INTERNATIONAL AYURVEDIC MEDICAL JOURNAL International Ayurvedic Medical Journal, (ISSN: 2320 5091) (May, 2017) 5 (5) A LITERATURE REVIEW OF SIRA AND VEIN Khan Rohee WadoodKhan Assistant professor, Kriya
A REVIEW ON SUTRASTHANA OF VAGBHATA S SAMHITA IS BEST AMONG AYURVEDIC CLASSICS (Sutrasthane tu Vagbhate)
 Review Article A REVIEW ON SUTRASTHANA OF VAGBHATA S SAMHITA IS BEST AMONG AYURVEDIC CLASSICS (Sutrasthane tu Vagbhate) Sudama Singh Yadav 1*, Goswami PK 2 1. Assistant Professor, Dept. of Samhita & Sanskrit,
Review Article A REVIEW ON SUTRASTHANA OF VAGBHATA S SAMHITA IS BEST AMONG AYURVEDIC CLASSICS (Sutrasthane tu Vagbhate) Sudama Singh Yadav 1*, Goswami PK 2 1. Assistant Professor, Dept. of Samhita & Sanskrit,
Nervous System. Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body
 Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
A NIDANATMAKA (EPIDEMIOLOGICAL) STUDY ON MUTRASHMARI
 Review Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 A NIDANATMAKA (EPIDEMIOLOGICAL) STUDY ON MUTRASHMARI Kumar Hemant 1, Tiwari Manisha 2 1 Lecturer, Dept. of Roga Nidana Evam Vikriti
Review Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 A NIDANATMAKA (EPIDEMIOLOGICAL) STUDY ON MUTRASHMARI Kumar Hemant 1, Tiwari Manisha 2 1 Lecturer, Dept. of Roga Nidana Evam Vikriti
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII BIOLOGY
 HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
A CONCEPTUAL STUDY OF TRAYA-AVARTH YONI
 INTERNATIONAL AYURVEDIC MEDICAL JOURNAL International Ayurvedic Medical Journal, (ISSN: 2320 5091) (September, 2017) 5(9) A CONCEPTUAL STUDY OF TRAYA-AVARTH YONI INTRODUCTION Anatomy of Female Reproductive
INTERNATIONAL AYURVEDIC MEDICAL JOURNAL International Ayurvedic Medical Journal, (ISSN: 2320 5091) (September, 2017) 5(9) A CONCEPTUAL STUDY OF TRAYA-AVARTH YONI INTRODUCTION Anatomy of Female Reproductive
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
HUMAN BODY. Contents:
 HUMAN BODY HUMAN BODY Contents: 1. Main objectives. 2. Useful websites. 3. Word wall cards. 4. Vocabulary cards. 5. Glossary. 6. Key question cards. 7. Prior learning diagram. 8. Hands on activity. 9.
HUMAN BODY HUMAN BODY Contents: 1. Main objectives. 2. Useful websites. 3. Word wall cards. 4. Vocabulary cards. 5. Glossary. 6. Key question cards. 7. Prior learning diagram. 8. Hands on activity. 9.
UNDERSTANDING THE CONCEPT SAMAYOGVAHI WITH THE HELP OF HO- MEOSTATIC FEEDBACK MECHANISM
 Review Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 UNDERSTANDING THE CONCEPT SAMAYOGVAHI WITH THE HELP OF HO- MEOSTATIC FEEDBACK MECHANISM Deshpande Anil Chandrakant Assistant Professor,
Review Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 UNDERSTANDING THE CONCEPT SAMAYOGVAHI WITH THE HELP OF HO- MEOSTATIC FEEDBACK MECHANISM Deshpande Anil Chandrakant Assistant Professor,
Study of mutrakrichchra in ayurveda
 Study of mutrakrichchra in ayurveda Bishnu kumar*, Jyoti singh *Assistant professor, Dept.of shalya r k ayurvedic medical college, Azamgarh,UP Assistant professor,dept.of pharmacology, Ashoka institute
Study of mutrakrichchra in ayurveda Bishnu kumar*, Jyoti singh *Assistant professor, Dept.of shalya r k ayurvedic medical college, Azamgarh,UP Assistant professor,dept.of pharmacology, Ashoka institute
UNIT 2. THE VITAL FUNCTIONS OF HUMAN BEINGS. PRIMARY 3 / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández
 UNIT 2. THE VITAL FUNCTIONS OF HUMAN BEINGS PRIMARY 3 / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández VITAL FUNCTIONS Nutrition It is the process of transforming NUTRIENTS into ENERGY. When we eat, we
UNIT 2. THE VITAL FUNCTIONS OF HUMAN BEINGS PRIMARY 3 / Natural Science Pedro Antonio López Hernández VITAL FUNCTIONS Nutrition It is the process of transforming NUTRIENTS into ENERGY. When we eat, we
Leucorrhoea in ayurvedic review
 Leucorrhoea in ayurvedic review Snehal Pol 1, Deepali Rajput 2, Manda Ghorpade 3 1.PG Scholar, Department of Prasutitantra and Streerog, S.S.A.M College,Hadapsar, Pune. 2.Guide, department of Prasutitantra
Leucorrhoea in ayurvedic review Snehal Pol 1, Deepali Rajput 2, Manda Ghorpade 3 1.PG Scholar, Department of Prasutitantra and Streerog, S.S.A.M College,Hadapsar, Pune. 2.Guide, department of Prasutitantra
By Helen and Mark Warner
 By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
Contents. 1. The Spiritual Aspect of Ayurveda - Body, Mind and Spirit The Human Universe The Disease Process and Healing in Ayurveda 39
 Contents 1. The Spiritual Aspect of Ayurveda - Body, Mind and Spirit 19 2. The Human Universe 29 3. The Disease Process and Healing in Ayurveda 39 4. Ayurvedic Diagnosis 61 5. The Types of Body Constitutions
Contents 1. The Spiritual Aspect of Ayurveda - Body, Mind and Spirit 19 2. The Human Universe 29 3. The Disease Process and Healing in Ayurveda 39 4. Ayurvedic Diagnosis 61 5. The Types of Body Constitutions
Ayurvedic Application of Asana :: Structure and Dosha
 Ayurvedic Application of Asana :: Structure and Dosha Ayurvedic Application of Asana :: Structure and Dosha Module 1 :: Lesson 10 Yoga Veda Institute Ayurvedic Application of Asana :: Sattva Guna :: Module
Ayurvedic Application of Asana :: Structure and Dosha Ayurvedic Application of Asana :: Structure and Dosha Module 1 :: Lesson 10 Yoga Veda Institute Ayurvedic Application of Asana :: Sattva Guna :: Module
1. INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM: skin is the largest system.
 Chapter 7 Body Structure and Function Cell: Tissue: Examples: lining of the nose, mouth, stomach, muscle tissue Organs: Example: heart, brain, liver, lungs, kidneys Systems: organs that work together to
Chapter 7 Body Structure and Function Cell: Tissue: Examples: lining of the nose, mouth, stomach, muscle tissue Organs: Example: heart, brain, liver, lungs, kidneys Systems: organs that work together to
The common and general meaning of the term 'Udaka Vaha Srotas' means the chanel or the path by which water (Udaka) i9s carried
 The common and general meaning of the term 'Udaka Vaha Srotas' means the chanel or the path by which water (Udaka) i9s carried from opne place to other. It is also said that t.he 'Udaka Vaha Srotas' cannot
The common and general meaning of the term 'Udaka Vaha Srotas' means the chanel or the path by which water (Udaka) i9s carried from opne place to other. It is also said that t.he 'Udaka Vaha Srotas' cannot
AYUSHDHARA. An International Journal of Research in AYUSH and Allied Systems. Research Article
 AYUSHDHARA An International Journal of Research in AYUSH and Allied Systems ISSN: 233-83 (P)/ 233-1 (O) Research Article A STUDY ON THE ROLE OF RASA-VAHA SROTAS IN PANDU ROGA Sharma Giriraj 1, Sharma Pooja
AYUSHDHARA An International Journal of Research in AYUSH and Allied Systems ISSN: 233-83 (P)/ 233-1 (O) Research Article A STUDY ON THE ROLE OF RASA-VAHA SROTAS IN PANDU ROGA Sharma Giriraj 1, Sharma Pooja
Pre-operative Management in Ayurveda
 Pre-operative Management in Ayurveda Review article Vijay Lakshmi 1*, Ramesh Chandra 2, Ramesh Kumar Gupta 3 1. Lecturer, Department of Prasuti Tantra, Government Ayurvedic College, Varanasi (U.P.) 2.
Pre-operative Management in Ayurveda Review article Vijay Lakshmi 1*, Ramesh Chandra 2, Ramesh Kumar Gupta 3 1. Lecturer, Department of Prasuti Tantra, Government Ayurvedic College, Varanasi (U.P.) 2.
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
International Journal of Applied Ayurved Research ISSN: A REVIEW ON UNDERSTANDING OF DHAMANI
 International Journal of Applied Ayurved Research ISSN: 2347-6362 A REVIEW ON UNDERSTANDING OF DHAMANI Swapna H N 1, Uma B Gopal 2, Swati S Bedeker 3 PG Scholar 1, HOD 2, Professor 3, Department of Shreera
International Journal of Applied Ayurved Research ISSN: 2347-6362 A REVIEW ON UNDERSTANDING OF DHAMANI Swapna H N 1, Uma B Gopal 2, Swati S Bedeker 3 PG Scholar 1, HOD 2, Professor 3, Department of Shreera
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology
 Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
Bi100 Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy and Physiology A. Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts; in other words, what are things called? B.
World Journal of Pharmaceutical and Life Sciences WJPLS
 wjpls, 2016, Vol. 2, Issue 5, 348-353. Research Article ISSN 2454-2229 WJPLS www.wjpls.org SJIF Impact Factor: 3.347 KALA SHARIR TESTIMONY INSIGHT FROM AYURVEDA Ravindra Dhimdhime 1, Tawalare Kiran* 2
wjpls, 2016, Vol. 2, Issue 5, 348-353. Research Article ISSN 2454-2229 WJPLS www.wjpls.org SJIF Impact Factor: 3.347 KALA SHARIR TESTIMONY INSIGHT FROM AYURVEDA Ravindra Dhimdhime 1, Tawalare Kiran* 2
CHAPTER 1 THE HUMAN BODY
 HPTER 1 THE HUMN OY TRUE/FLSE 1. midsagittal plane vertically divides the body through the midline into two equal left and right portions or halves. NS: T NOT: midsagittal plane vertically divides the
HPTER 1 THE HUMN OY TRUE/FLSE 1. midsagittal plane vertically divides the body through the midline into two equal left and right portions or halves. NS: T NOT: midsagittal plane vertically divides the
CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SURFACE ANATOMY Surface anatomy is the identification of landmarks on the surface of the skin which allows us to compare our knowledge of our own surface anatomy
CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SURFACE ANATOMY Surface anatomy is the identification of landmarks on the surface of the skin which allows us to compare our knowledge of our own surface anatomy
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide
 Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Dissection: The Fetal Pig
 Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
disease Yogahealer.com copyright 2012 Yogahealer, llc all rights reserved with Cate Stillman
 6 stages of disease Yogahealer.com with Cate Stillman 1 What is health? Health consists of a balanced state of the 3 doshas (energies), the 7 dhatus (tissues), the 3 wastes (malas) and agni (digestive
6 stages of disease Yogahealer.com with Cate Stillman 1 What is health? Health consists of a balanced state of the 3 doshas (energies), the 7 dhatus (tissues), the 3 wastes (malas) and agni (digestive
International Journal of Applied Ayurved Research ISSN: ROLE OF PURISHADHARA KALA CALCIUM & BILIRUBIN METABOLISM
 International Journal of Applied Ayurved Research ISSN: 2347-6362 ROLE OF PURISHADHARA KALA CALCIUM & BILIRUBIN METABOLISM 1 Christy jose cherian, 2 Manjeet singh 1,2 MD Scholars, Y.M.T Ayurvedic Medical
International Journal of Applied Ayurved Research ISSN: 2347-6362 ROLE OF PURISHADHARA KALA CALCIUM & BILIRUBIN METABOLISM 1 Christy jose cherian, 2 Manjeet singh 1,2 MD Scholars, Y.M.T Ayurvedic Medical
System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) (Lysosomes) Main Organs: Main Organs: SKIN HAIR NAILS KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA
 URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
URINARY System Name: (Lysosomes) KIDNEYS URETERS BLADDER URETHRA LUNGS SKIN EXCRETORY System Name: INTEGUMENTARY (cell wall) SKIN HAIR NAILS Skin is the largest Organ. The excretory system collects and
BIOLOGY 30S: Fetal Pig Dissection Worksheet
 BIOLOGY 30S: Fetal Pig Dissection Worksheet Name: Part A: External Anatomy & Oral Cavity 1. How long (metric) is your fetal pig? 2. What is the age of your fetal pig? 3. What sense organs are located on
BIOLOGY 30S: Fetal Pig Dissection Worksheet Name: Part A: External Anatomy & Oral Cavity 1. How long (metric) is your fetal pig? 2. What is the age of your fetal pig? 3. What sense organs are located on
Lecture Overview. Chapter 4 Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues. Epithelial Tissues. Glandular Epithelium
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
A B S T R A C T INTRODUCTION. ISSN: ORIGINAL ARTICLE July-Aug Institute of Ayurvedic Medical Sciences, Manipal, Karnataka, INDIA.
 A comparative clinical study on the efficacy of Siravyadha and Agnikarma in the management of Snayugata Vata affecting Kurpara Sandhi vis-à-vis Tennis Elbow Dr. Saiprasad S. Shettigar, 1 Dr. D. Gururaja
A comparative clinical study on the efficacy of Siravyadha and Agnikarma in the management of Snayugata Vata affecting Kurpara Sandhi vis-à-vis Tennis Elbow Dr. Saiprasad S. Shettigar, 1 Dr. D. Gururaja
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
A CONCEPTUAL ANALYSIS OF BHRAJAKA PITTA
 Research Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 A CONCEPTUAL ANALYSIS OF BHRAJAKA PITTA Amrutha B L 1, Elgeena Varghese 2, Prathibha Kulkarni 3 1,2 P.G. Scholar, 3 Associate Professor
Research Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 A CONCEPTUAL ANALYSIS OF BHRAJAKA PITTA Amrutha B L 1, Elgeena Varghese 2, Prathibha Kulkarni 3 1,2 P.G. Scholar, 3 Associate Professor
Frog Dissection-Skin Vista Murrieta High School-- Biomedical Science. Mr. Diaz
 Frog Dissection-Skin Vista Murrieta High School-- Biomedical Science Mr. Diaz Background: Please read entire lab As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but
Frog Dissection-Skin Vista Murrieta High School-- Biomedical Science Mr. Diaz Background: Please read entire lab As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but
CHAPTER 3. The Human Body National Safety Council
 CHAPTER 3 The Human Body The Human Body Composed of many different organs and tissues All parts work together: To sustain life Allow activity Injury or illness impairs functions 3-3 Cranial located in
CHAPTER 3 The Human Body The Human Body Composed of many different organs and tissues All parts work together: To sustain life Allow activity Injury or illness impairs functions 3-3 Cranial located in
AN ANATOMICAL STUDY OF INDRABASTI MARMA; ON BASIS OF CADAVERIC DISSECTION Dr. Nitin Kumar 1 Dr. Harish Chandra Gupta 2 Dr.
 Review Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 AN ANATOMICAL STUDY OF INDRABASTI MARMA; ON BASIS OF CADAVERIC DISSECTION Dr. Nitin Kumar 1 Dr. Harish Chandra Gupta 2 Dr.Vikash Bhatnagar
Review Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 AN ANATOMICAL STUDY OF INDRABASTI MARMA; ON BASIS OF CADAVERIC DISSECTION Dr. Nitin Kumar 1 Dr. Harish Chandra Gupta 2 Dr.Vikash Bhatnagar
REVIEW ON CONCEPT OF SMRITHI (MEMORY) IN AYURVEDA
 Review Article REVIEW ON CONCEPT OF SMRITHI (MEMORY) IN AYURVEDA Kuber Sankh 1*, Ashalatha M 2 1. Ph.D Scholar, Dept. of Dravyaguna, Government Ayurveda Medical College, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India. 2.
Review Article REVIEW ON CONCEPT OF SMRITHI (MEMORY) IN AYURVEDA Kuber Sankh 1*, Ashalatha M 2 1. Ph.D Scholar, Dept. of Dravyaguna, Government Ayurveda Medical College, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India. 2.
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
Colon Cancer Surgery
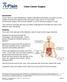 Colon Cancer Surgery Introduction Colon cancer is a life-threatening condition that affects thousands of people. Doctors usually recommend surgery for the removal of colon cancer. If your doctor recommends
Colon Cancer Surgery Introduction Colon cancer is a life-threatening condition that affects thousands of people. Doctors usually recommend surgery for the removal of colon cancer. If your doctor recommends
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body
 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
They need to transport all these to various parts of their body. Further, animal need to transport wastes to parts from where they can be removed.
 They need to transport all these to various parts of their body. Further, animal need to transport wastes to parts from where they can be removed. PLASMA Carry various substances. Blood is a liquid, which
They need to transport all these to various parts of their body. Further, animal need to transport wastes to parts from where they can be removed. PLASMA Carry various substances. Blood is a liquid, which
CHAPTER 3. The Human Body National Safety Council
 CHAPTER 3 The Human Body Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the primary areas of the body. 2. List the 10 body systems and explain a key function of each. 3. For each body system, describe at least 1 injury
CHAPTER 3 The Human Body Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the primary areas of the body. 2. List the 10 body systems and explain a key function of each. 3. For each body system, describe at least 1 injury
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
THE STRUCTURAL STUDY AND PROGNOSTIC ASSESSMENT OF KURPARA MARMA Pande Prasad Prabhakharrao1. Deshpande Pradnya Ravindra2 1
 Research Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 THE STRUCTURAL STUDY AND PROGNOSTIC ASSESSMENT OF KURPARA MARMA Pande Prasad Prabhakharrao1 Deshpande Pradnya Ravindra2 1 Associate
Research Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 THE STRUCTURAL STUDY AND PROGNOSTIC ASSESSMENT OF KURPARA MARMA Pande Prasad Prabhakharrao1 Deshpande Pradnya Ravindra2 1 Associate
International Journal of Applied Ayurved Research ISSN: STANDARD OPERATING PROTOCOL OF GANDOOSHA & KAVALA
 International Journal of Applied Ayurved Research ISSN: 2347-6362 STANDARD OPERATING PROTOCOL OF GANDOOSHA & KAVALA Chhaya Bhakti 1 Bhogayata Kamlesh 2 Mer Raksha 3 1 Associate Professor, Dept. of Shalakyatantra,
International Journal of Applied Ayurved Research ISSN: 2347-6362 STANDARD OPERATING PROTOCOL OF GANDOOSHA & KAVALA Chhaya Bhakti 1 Bhogayata Kamlesh 2 Mer Raksha 3 1 Associate Professor, Dept. of Shalakyatantra,
Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Formation and validation of questionnaire to assess Jāṭharāgni
 Original Article Formation and validation of questionnaire to assess Jāṭharāgni H. T. Eswaran, M. B. Kavita, T. B. Tripaty, Shivakumar Department of Swasthavritta, Sri Dharmasthala Manjunatheshwara College
Original Article Formation and validation of questionnaire to assess Jāṭharāgni H. T. Eswaran, M. B. Kavita, T. B. Tripaty, Shivakumar Department of Swasthavritta, Sri Dharmasthala Manjunatheshwara College
Microscopic Anatomy Cytology study of the cell Histology study of tissues
 Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology Dr. Gary Mumaugh Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another o Gross or macroscopic
Human Body Systems. Human Body Project Notes
 Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology: Page 1 of 31 Differing Abilities Anatomy and Physiology Supplementary Resources Handout 1: Male Reproductive System Handout 2: Male Anatomy Diagram Handout 3: Female Reproductive
Anatomy and Physiology: Page 1 of 31 Differing Abilities Anatomy and Physiology Supplementary Resources Handout 1: Male Reproductive System Handout 2: Male Anatomy Diagram Handout 3: Female Reproductive
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
Biology Anatomy and Physiology I. Learn and Understand. What is Biology? bios = life -ology = study of
 Biology 2331 Anatomy and Physiology I "If you want something you've never had, then you've got to do something you've never done." Learn and Understand A new language At this stage, science drives the
Biology 2331 Anatomy and Physiology I "If you want something you've never had, then you've got to do something you've never done." Learn and Understand A new language At this stage, science drives the
VEDA ONE: SELF CARE. Ayurveda is an ancient system of health that takes into account your unique body, mind and circumstances.
 : SELF CARE The purpose of this course is for you to light up your own path of inner knowledge. As human beings, we have all been gifted with the birthright of higher consciousness. Ayurveda is simply
: SELF CARE The purpose of this course is for you to light up your own path of inner knowledge. As human beings, we have all been gifted with the birthright of higher consciousness. Ayurveda is simply
What is the function of the urinary system? How do the kidneys filter the blood? What are common problems with the urinary system?
 CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
Urinary System Chapter 16
 Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Research Article
 Research Article www.ijrap.net Arun Bhaskaran et al / IJRAP 3(1), Jan Feb 2012 CLINICAL EVALUATION OF AMRAGANDHA HARIDRA (CURCUMA AMADA ROXB) IN PRATISYAYA W.S.R TO ALLERGIC RHINITIS: A FOLKLORE CLAIM
Research Article www.ijrap.net Arun Bhaskaran et al / IJRAP 3(1), Jan Feb 2012 CLINICAL EVALUATION OF AMRAGANDHA HARIDRA (CURCUMA AMADA ROXB) IN PRATISYAYA W.S.R TO ALLERGIC RHINITIS: A FOLKLORE CLAIM
Ayurveda Returning to Wholeness. Sheila Patel, MD Medical Director, Chopra Center for Wellbeing Mind-Body Medical Group Carlsbad, CA
 Ayurveda Returning to Wholeness Sheila Patel, MD Medical Director, Chopra Center for Wellbeing Mind-Body Medical Group Carlsbad, CA WHAT IS HEALING? Experiencing self-regulation A process of self-organization
Ayurveda Returning to Wholeness Sheila Patel, MD Medical Director, Chopra Center for Wellbeing Mind-Body Medical Group Carlsbad, CA WHAT IS HEALING? Experiencing self-regulation A process of self-organization
IMPROVEMENT OF MEDHA AN IMPERATIVE NEED OF THE ERA
 Research Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 IMPROVEMENT OF MEDHA AN IMPERATIVE NEED OF THE ERA Mungath Girija Devi Kekuda Prashanth Chiplunkar Shivprasad Dept. of Kriya Shareera,
Research Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 IMPROVEMENT OF MEDHA AN IMPERATIVE NEED OF THE ERA Mungath Girija Devi Kekuda Prashanth Chiplunkar Shivprasad Dept. of Kriya Shareera,
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology
 Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
Overview of Anatomy & Physiology Anatomy the study of the structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Gross or macroscopic Microscopic Developmental Physiology the study of the function
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
S2 Biology. Topic 2: THE HUMAN BODY
 S2 Biology. Topic 2: THE HUMAN BODY SCN 3-12a: I have explored the structure and function of organs and organ systems and can relate this to the basic biological processes required to sustain life SCN
S2 Biology. Topic 2: THE HUMAN BODY SCN 3-12a: I have explored the structure and function of organs and organ systems and can relate this to the basic biological processes required to sustain life SCN
AN AYURVEDIC PERSPECTIVE OF FATIGUE AFTER STROKE (PAKSHAGHATA)
 ISSN 2347-2375 UNIQUE JOURNAL OF AYURVEDIC AND HERBAL MEDICINES Available online: www.ujconline.net Research Article AN AYURVEDIC PERSPECTIVE OF FATIGUE AFTER STROKE (PAKSHAGHATA) De Silva DPPS 1*,Ediriweera
ISSN 2347-2375 UNIQUE JOURNAL OF AYURVEDIC AND HERBAL MEDICINES Available online: www.ujconline.net Research Article AN AYURVEDIC PERSPECTIVE OF FATIGUE AFTER STROKE (PAKSHAGHATA) De Silva DPPS 1*,Ediriweera
Body systems WORKSHEET 2.1
 Body systems WORKSHEET 2.1 1. Unscramble the body systems in the box then write below the correct picture. osnreuv peodctuievrr otorolmoc gitdeevsi teyrocxer 2. Draw and label the organs. A. Kidneys B.
Body systems WORKSHEET 2.1 1. Unscramble the body systems in the box then write below the correct picture. osnreuv peodctuievrr otorolmoc gitdeevsi teyrocxer 2. Draw and label the organs. A. Kidneys B.
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Review Article Influence of Doshic Variation in the Genesis of Vyadhis Dr. Pushpa Kumari 1, Dr. P. S. Byadgi 2 1 Junior
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Review Article Influence of Doshic Variation in the Genesis of Vyadhis Dr. Pushpa Kumari 1, Dr. P. S. Byadgi 2 1 Junior
Ayurveda- A Complete Science of Life, Health & Longevity
 Ayurveda- A Complete Science of Life, Health & Longevity Welcome to read about the most ancient and traditional science on one of the most modern systems the internet. How can this ancient system of health
Ayurveda- A Complete Science of Life, Health & Longevity Welcome to read about the most ancient and traditional science on one of the most modern systems the internet. How can this ancient system of health
A comprehensive review on Vrishan Karma (aphrodisiac action) by Piyush (cow colostrum) Bhavin Dhanavade, 1 Anil Pandya. 2
 A comprehensive review on Vrishan Karma (aphrodisiac action) by Piyush (cow colostrum) Bhavin Dhanavade, 1 Anil Pandya. 2 1 Final Year M.D. Scholar, 2 HOD, Department of Dravya Guna, Parul Institute of
A comprehensive review on Vrishan Karma (aphrodisiac action) by Piyush (cow colostrum) Bhavin Dhanavade, 1 Anil Pandya. 2 1 Final Year M.D. Scholar, 2 HOD, Department of Dravya Guna, Parul Institute of
Body Systems Unit End Project
 Body Systems Unit End Project Digestive System Your Assignment Create a model of the digestive system using the top diagram on p 130 in your text book. Use Pipe Cleaners and paper to label the following
Body Systems Unit End Project Digestive System Your Assignment Create a model of the digestive system using the top diagram on p 130 in your text book. Use Pipe Cleaners and paper to label the following
CYSTOSCOPY PATIENT INFORMATION
 CYSTOSCOPY PATIENT INFORMATION ADHB Urology Department; Reviewed FEB 2005 Ubix code UPEB3 1 The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery; some
CYSTOSCOPY PATIENT INFORMATION ADHB Urology Department; Reviewed FEB 2005 Ubix code UPEB3 1 The information contained in this booklet is intended to assist you in understanding your proposed surgery; some
NEO 111 Melanie Jorgenson, RN, BSN
 NEO 111 Melanie Jorgenson, RN, BSN Inspection: performing deliberate, purposeful observations in a systematic manner Palpation: using the sense of touch Percussion: striking one object against another
NEO 111 Melanie Jorgenson, RN, BSN Inspection: performing deliberate, purposeful observations in a systematic manner Palpation: using the sense of touch Percussion: striking one object against another
A B S T R A C T INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVE OF THE STUDY. ISSN: ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mar-Apr Limbda, Vadodara.
 A controlled clinical study on the efficacy of Khadira Churna Pratisarana with Madhu in management of Mukhapaka (Stomatitis) in Children Mohsin P. Tamboli, 1 Sunil Changle, 2 Purnima Hope. 3 1 Post Graduate
A controlled clinical study on the efficacy of Khadira Churna Pratisarana with Madhu in management of Mukhapaka (Stomatitis) in Children Mohsin P. Tamboli, 1 Sunil Changle, 2 Purnima Hope. 3 1 Post Graduate
Chapter One Study Guide Answers
 Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
Chapter One Study Guide Answers I. Aids to Understanding Words Append to hang something Cardi heart Cran helmet pertaining to the part of the skull that surrounds the brain. Dors back Homeo same -logy
Key words: Migraine, Nasya, Mig 17, Shirahshoola, Nasal Drop, Quick Relief
 TO EVALUATE THE FASTER ACTION OF MIG-17 NASAL DROPS IN THE MANAGEMENT OF ARDHAVABHEDAKA W.S.R. TO MIGRAINE IN COMPARISION WITH OTHER POPULAR MODERN PAINKILLERS Dr. Tushar Trivedi a, Dr. Prerak Shah b a
TO EVALUATE THE FASTER ACTION OF MIG-17 NASAL DROPS IN THE MANAGEMENT OF ARDHAVABHEDAKA W.S.R. TO MIGRAINE IN COMPARISION WITH OTHER POPULAR MODERN PAINKILLERS Dr. Tushar Trivedi a, Dr. Prerak Shah b a
Body Systems Notes. Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive
 Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
THE CLINICAL UTILITY OF BASIC PRINCIPLES OF AYURVEDA
 Review Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 THE CLINICAL UTILITY OF BASIC PRINCIPLES OF AYURVEDA Dewan Shweta Kumar Baldev P.G. Department of Basic Principles, National Institute
Review Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 THE CLINICAL UTILITY OF BASIC PRINCIPLES OF AYURVEDA Dewan Shweta Kumar Baldev P.G. Department of Basic Principles, National Institute
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
Internal Structures of Animals
 SCIENCE GRADE 5 Below Level California Content Standards Life Sciences: 2.A Life Sciences: 2.B Life Sciences: 2.C Life Sciences: 2.D Internal Structures LOOK INSIDE FOR: of Animals FOCUScurriculum Curriculum
SCIENCE GRADE 5 Below Level California Content Standards Life Sciences: 2.A Life Sciences: 2.B Life Sciences: 2.C Life Sciences: 2.D Internal Structures LOOK INSIDE FOR: of Animals FOCUScurriculum Curriculum
It s Natural to Be Health: Introduction to Maharishi Ayurveda. Course Syllabus
 Course Overview: It s Natural to Be Health: Introduction to Maharishi Ayurveda Course Syllabus Lesson 1: Locating your body s own inner intelligence to help create balance in your physiology Lesson 2:
Course Overview: It s Natural to Be Health: Introduction to Maharishi Ayurveda Course Syllabus Lesson 1: Locating your body s own inner intelligence to help create balance in your physiology Lesson 2:
By Semih. The first system is about the respiratory system. It provides our body with the oxygen it needs and gets rid of carbon dioxide.
 By Semih Exercise is very important to our body. Exercise is an everyday activity and it keeps your body fit and healthy. There are 3 main systems involved are the respiratory system, the circulatory system
By Semih Exercise is very important to our body. Exercise is an everyday activity and it keeps your body fit and healthy. There are 3 main systems involved are the respiratory system, the circulatory system
ANATOMICAL CHANGES OCCURING IN TWACHA SHARIR DUE TO DADRU W.S.R. TO RINGWORM
 INTERNATIONAL AYURVEDIC MEDICAL JOURNAL International Ayurvedic Medical Journal, (ISSN: 2320 5091) (July, 2017) 5(7) ANATOMICAL CHANGES OCCURING IN TWACHA SHARIR DUE TO DADRU W.S.R. TO RINGWORM Suhas S.
INTERNATIONAL AYURVEDIC MEDICAL JOURNAL International Ayurvedic Medical Journal, (ISSN: 2320 5091) (July, 2017) 5(7) ANATOMICAL CHANGES OCCURING IN TWACHA SHARIR DUE TO DADRU W.S.R. TO RINGWORM Suhas S.
A CONCEPTUAL NOTE ON VISHAGHNA LEPA
 Review Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 A CONCEPTUAL NOTE ON VISHAGHNA LEPA Kalyanimath Gurusiddeshwar.J. H.T Chaitra Dept. of Agada Tantra and vyavahara Ayurveda. SDM College
Review Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN:2320 5091 A CONCEPTUAL NOTE ON VISHAGHNA LEPA Kalyanimath Gurusiddeshwar.J. H.T Chaitra Dept. of Agada Tantra and vyavahara Ayurveda. SDM College
Human Body Systems Study Guide Answers
 Human Body Systems Study Guide Answers 1. What are the five levels of structural organization in order from largest to smallest? Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems - Organism 2. What are the phases of
Human Body Systems Study Guide Answers 1. What are the five levels of structural organization in order from largest to smallest? Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems - Organism 2. What are the phases of
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS 1. NUTRITION The process of nutrition allows living organisms to obtain the matter and energy they need for making their own matter and for carrying out their
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS 1. NUTRITION The process of nutrition allows living organisms to obtain the matter and energy they need for making their own matter and for carrying out their
The Circulatory System. Lesson 4. Quick Check. Trace the path of blood after it is pumped from the heart. 22. First
 Lesson 4 The Circulatory System How does blood transport materials? Your circulatory system is a delivery system. Red blood cells travel in the blood, bringing things to and from your body cells. The main
Lesson 4 The Circulatory System How does blood transport materials? Your circulatory system is a delivery system. Red blood cells travel in the blood, bringing things to and from your body cells. The main
Understanding Essential Hypertension through Ayurveda A Review
 ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2013; 4(4): 591-595 REVIEW ARTICLE Understanding Essential Hypertension through Ayurveda
ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2013; 4(4): 591-595 REVIEW ARTICLE Understanding Essential Hypertension through Ayurveda
The Cardiovascular System
 CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
CHAPTER 16 1 SECTION Circulation and Respiration The Cardiovascular System California Science Standards 7.5.a, 7.5.b, 7.6.j BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these
After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 17 1 The Nervous System SECTION Communication and Control 7.5.a, 7.5.b California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What
CHAPTER 17 1 The Nervous System SECTION Communication and Control 7.5.a, 7.5.b California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Introduction in human anatomy
 Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Introduction in human anatomy Overview of Anatomy Anatomy is the study of the body structure and the relationships of the various parts of the body Gross or macroscopic (visible structures) Microscopic
Chapter 1. Introduction to Human. Anatomy and Physiology 8/16/2012. believe are the major requirements
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts, in other words, what things are called. Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts, in other words, what things are called. Physiology
Impact factor: 3.958/ICV: 4.10 ISSN:
 Impact factor: 3.958/ICV: 4.10 ISSN: 0978-7908 21 Pharma Science Monitor 7(3), Jul-Sep 2016 PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Journal home page: http://www.pharmasm.com
Impact factor: 3.958/ICV: 4.10 ISSN: 0978-7908 21 Pharma Science Monitor 7(3), Jul-Sep 2016 PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES Journal home page: http://www.pharmasm.com
 The human body is amazing! Like a machine, the human body is made of smaller parts that all work together. The human body is always working. Think about this: while you read this, your heart is pumping
The human body is amazing! Like a machine, the human body is made of smaller parts that all work together. The human body is always working. Think about this: while you read this, your heart is pumping
Chapter: Interactions of Human Systems
 Table of Contents Chapter: Interactions of Human Systems Section 1: The Human Organism Section 2: How Your Body Works The Human Organism Organization in the Human Body Although your body is not made of
Table of Contents Chapter: Interactions of Human Systems Section 1: The Human Organism Section 2: How Your Body Works The Human Organism Organization in the Human Body Although your body is not made of
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS:
 BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
BODY SYSTEMS UNIT ANCHOR CHARTS: LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION smallest unit Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems largest unit Body TISSUES IN THE HUMAN BODY Tissue Function Example Muscle makes parts of the body
1. In Oriental medicine, what two organs are related to the earth element? 2. In Oriental medicine what two organs are related to the wood element?
 THIS SECTION IS ON ORIENTAL MODALITIES. SOME EXAMS HAVE SEVERAL QUESTIONS ON ORIENTAL MODALITIES HOWEVER THE MBLEx DOES NOT FOCUS ON THE SPECIFICS OF ORIENTAL MODALITIES 1. In Oriental medicine, what two
THIS SECTION IS ON ORIENTAL MODALITIES. SOME EXAMS HAVE SEVERAL QUESTIONS ON ORIENTAL MODALITIES HOWEVER THE MBLEx DOES NOT FOCUS ON THE SPECIFICS OF ORIENTAL MODALITIES 1. In Oriental medicine, what two
