European Urology 47 (2005)
|
|
|
- Cody Morgan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 European Urology European Urology 47 (2005) The Comparison of Artificial Urinary Sphincter Implantation and Endourethral Macroplastique Injection for thetreatment of Postprostatectomy Incontinence M. Abdurrahim Imamoglu*, Can Tuygun, Hasan Bakirtas, Orhan Yiğitbasi, Ahmet Kiper Department of Urology, SSK Ankara Education Hospital, Ankara, Turkey Accepted 24 August 2004 Available online 11 September 2004 Abstract Objectives: To compare the effectiveness of macroplastique injection with artificial urinary sphincter implantation (AUS) for treatment of postprostatectomy incontinence (PPI). Methods: A prospective randomized clinical trial including 45 patients with PPI was performed secondary to radical retropubic prostatectomy (RRP), transvesical prostatectomy (TVP), transurethral prostatectomy (TURP), and TURP with TVP, in 12, 16, 16, 1 patients respectively. Patients were divided into two groups as minimal (group I) and total incontinence (group II) according to the severity of incontinence. Respectively, Group I (n = 21) and group II (n = 24) patients were randomized as AUS implantation (n = 11, n = 11) and macroplastique injection (n = 10, n = 13). Follow-up period was 48 (6 84) months in patients with macroplastique injection and 60 (8 120) months in AUS implantation. The success of the treatment was evaluated by calculating the average number of pads used by the patient per day, the weight of the pads and score of quality of life survey scale for each group both in the preoperative and in the postoperative period. Results: There were statistically significant differences between preoperative and postoperative average pad weight, average number of pads and quality of life scores, both in patients with minimal and total incontinence. In group I there was no statistically significant difference between the two techniques. However, in group II there was a significant difference favoring AUS implantation. Conclusions: Endourethral injection should be the treatment of choice for patients with minimal incontinence, whereas AUS implantation as the first choice for patients with total incontinence. # 2004 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. Keywords: Postprostatectomy incontinence; Macroplastique; Artificial urinary sphincter 1. Introduction After transurethral prostatectomy (TURP) or transvesical prostatectomy (TVP), the risk of incontinence is reported to be 0.4 1%. This might increase up to 20 40% following radical retropubic prostatectomy (RRP) [1,2]. After being cured from some major problems such as voiding difficulties and malignancy, these * Corresponding author. Present address: Mesrutiyet Caddesi, Bayindir- 2 sok. 58/5, Kizilay, Ankara, Turkey. Tel address: mai2603@superonline.com (M.A. Imamoglu). patients are confronted with the social and hygienic problems brought forward by incontinence. Currently, problems secondary to postprostatectomy incontinence (PPI) are solved with these popular approaches; injection of urethral bulking agents, implantation of artificial urethral sphincter (AUS) and male sling operations. To the best of our knowledge, there is not any randomized prospective trial comparing the success rate of injection of urethral bulking agents and implantation of AUS reported in the English literature. In this article, we report a comparative study between the implantation of AUS and macroplastique /$ see front matter # 2004 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved. doi: /j.eururo
2 210 M.A. Imamoglu et al. / European Urology 47 (2005) injection to the urethral sphincter region with regards to their therapeutic efficacies, effects on the quality of life, morbidity and costs in patients with PPI (of both benign and malignant causes). 2. Methods The patients who have complaints of incontinence despite conservative treatment (Kegel exercises, imipramine) following RRP or TURP/TVP lasting a year or six months respectively were included in the study. The selected patients needed more than one pad/day in the last month diary and did not receive any prior surgical treatment for PPI. None of the patients were given radiotherapy for prostate carcinoma. The patients were diagnosed with urodynamic studies, sphincteric EMG and cytoscopic examinations. All patients had a minimum bladder capacity of 150 cc, they did not have detrussor instability or hyperreflexia. They had urethral pressure profiles (UPP) below 20 cmh 2 O and leak point pressures (LPP) below 40 cmh 2 O. Most of these patients had decreased sphincteric activity in EMG and some did not have any activity. The cases were divided into two groups as minimal incontinence (group I) and total incontinence (group II) depending on the symptom scores and weight and average number of pads used per day. Minimal incontinence was defined as total number of pads, total weight of pads and score of quality of life scale less than/equal to 2, 100 g, 30 respectively. The values above these numbers were accepted as total incontinence. The distribution of etiologic factors and treatment modalities between the two groups were given in Table 1. In group I patients (n = 21) were randomized as artificial urethral sphincter implantation (n = 11) and macroplastique injection (n = 10). In group II patients (n = 24) were also randomized as AUS implantation (n = 9) and macroplastique injection (n = 13). Two patients with total incontinence who had urethral strictures including the sphincter were treated with permanent urethral wall stent (Memotherm 1 ANGIOMED). After a follow-up period of 12 months there was not any tissue ingrowth into the lumen. Then, these patients underwent AUS implantation (nonrandomized) and followed for another 12 months. Macroplastique is an injection material composed of polydimethylslioxane elastomer implants as the solute component and hydrogel as the carrier. Macroplastique was injected under general or spinal anesthesia by having the patient in lithotomy position and using 24 Fr, 0 degree cystoscope. An average volume of cc was applied above or around the striated sphincter region of the urethra at 3, 6 and 9 o clock positions submucosally with a special Table 1 The distribution of treatment modalities according to severity and etiology of incontinence Etiologic factor Group I Group II Injection AUS Total Injection AUS Total TUR TVP RRP TUR + TVP 1 1 Total Group I: minimal incontinence, Group II: total incontinence. needle following RRP or TURP/TVP. If the patient was not free of his complaints by the end of the first month, a second application was made. The patients who did not improve after the second attempt were directed to AUS implantation. AUS implantation was performed under general anesthesia and in lithotomy position in all cases. The cuff of the AMS 800 sphincter was placed to the bulbar urethra, the pump to the scrotum and the reservoir balloon with cmh 2 O pressure to the space of Retzius. The urethral catheter that was placed during the operation was taken out on the first postoperative day. The patients were discharged from the hospital within 4 8 (average 6) days. Following 4 6 weeks of deactivation, the system was activated. The patients came to control visits on postoperative 1, 6 and 12 months. For evaluating the success of the treatment, the average number of pads used by the patient per day and the weight of the pads were calculated for each group both in the preoperative and in the postoperative period. Patients who do not need to use pads were regarded as dry. The ones using less than one pad were accepted as socially continent, and who were using more than one pad classified as incontinent. Average pad weight was calculated by adding the weights of the pads the patient had changed when he felt himself uncomfortable while performing daily activities. Quality of life survey scale was utilized in order to evaluate the satisfaction of the patients [4]. The statistical evaluation of the parameters were performed by t-test and p significance test in both groups. 3.Results Mean age of the patients who underwent AUS implantation was 64 (52 76) and mean age of the patients who underwent Macroplastique injection was 62 (55 75) years. The patients with macroplastique injection were followed up for a period of 48 months (6 84), while the patients with AUS implantation were followed up for 60 months (8 120). There was no statistically significant difference between patients with AUS implantation and the ones with macroplastique injection considering UPP (5 15 cmh 2 O) or LPP (0 20 cmh 2 O). Success rates after the treatment were calculated separately for two groups (Table 2). When we made a comparison between the preoperative and postoperative values of the criteria used to evaluate success such Table 2 The distribution of patients according to the severity of incontinence and success rate of treatment modalities Group I Group II Injection AUS Injection AUS Patients (n) Dry 8 (80%) 10 (90.9%) 3 (23.1%) 8 (72.7%) Socially continent 1 (10%) 1 (9.1%) 5 (38.5%) 2 (18.2%) Incontinent 1 (10%) 5 (38.5%) 1 (9.1%) Group I: minimal incontinence, Group II: total incontinence.
3 M.A. Imamoglu et al. / European Urology 47 (2005) Table 3 The comparison of treatment modalities according to success criteria in group I Macroplastique injection Preop Postop p AUS implantation Preop Postop p Average number of pads < <0.001 Average pad weight (g) < <0.001 Quality of life scale < <0.001 Preop: preoperative, postop: postoperative. Table 4 The comparison of treatment modalities according to success criteria in group II Macroplastique injection AUS implantation Preop Postop p Preop Postop p Average number of pads < <0.001 Average pad weight (g) < <0.001 Quality of life scale < <0.001 Preop: preoperative, postop: postoperative. as average pad weight, average number of pads and quality of life scores, both in patients with minimal and total incontinence there were differences of statistically significance (p < 0.05) (Tables 3 and 4). There was no statistically significant difference in the group I between two techniques (p < 0.2). However, when this comparison was made for the group II there was a significant difference favoring AUS implantation (p < 0.01). Of 11 patients who remained incontinent after injection, 5 were selected for AUS implantation. In order to identify whether etiological factors were important for the success of selected treatment techniques, success rates were calculated separately for each and every etiological factor. As a result of such an approach, we have identified that for patients developing incontinence after TURP, submucosal injection therapy was of considerable success, whereas it was less successful in cases that developed incontinence due to open surgical procedures (Tables 5 and 6). Although the complication rates were significantly higher in the AUS group, we could not make a statistical comparison between the two groups, as the types of complications were different for each group. AUS implantation was complicated in five patients with different causes. Implants were taken out in one patient because of infection and in another patient due to the erosion of the cuff. These patients underwent new AUS implantations six months after the removal of older ones. One patient experienced scrotal erosion so the pump was transferred to the contralateral side. In one patient, the pump that was not functional due to mechanical reasons was changed. In another patient, there was migration to the intraperitoneal region, which was corrected with reservoir operation and brought back to the extraperitoneal field. One patient Table 5 The success rate of treatment modalities according to etiology in group I Etiology Patient (n) Dry Socially continent Incontinent Inj. AUS Total Inj. AUS Total Inj. AUS Total Inj. AUS Total TURP TVP RRP TURP + TVP Total Table 6 The success rate of treatment modalities according to etiology in group II Etiology Patient (n) Dry Socially continent Incontinent Inj. AUS Tot. Inj. AUS Tot. Inj. AUS Tot. Inj. AUS Tot. TURP TVP RRP Total
4 212 M.A. Imamoglu et al. / European Urology 47 (2005) treated with macroplastique injection had to be catheterized because of urinary retention and two other patients developed urinary infections. Considering the costs of these procedures, 18 patients had only one injection, and 5 patients were injected twice resulting in a total macroplastique injection volume of cc. Per capita cost for the patient was $2264, taking into account the cost of the injection material, treatment of complications and hospitalization charge. Considering the AUS implantation, per capita cost for the patient was $6142 including the cost of the implant, treatment of complications and hospitalization charge. 4. Discussion Several techniques have been developed with the aim of preserving bladder capacity and compliance and achieving continence in incontinent patients with intact bladder and urethral function. Currently, the popular surgical techniques are the injection of endourethral bulking agents, the implantation of artificial sphincters and male sling operations [5 9]. However, the number of studies evaluating the success rate of these techniques separately for patients with minimal and total incontinence is quite limited if not existent. There are studies reporting success rates of 90% for artificial sphincter implantations [6,7]. In our study total cure rate was 90.9% in group I and 72.7% in group II. When we include the patients who were socially continent and the ones with improved quality of life scores to these, the figures are 100% and 91% respectively. Success rate has been reported to be around 60% for injections [8,9]. In our study, in group I dryness was achieved in 80%, whereas this figure fell down to 23.1% for group II. When socially continent patients with improved quality of life scores were included, these figures were 90% and 62% respectively. One of the most striking findings of our study was that, when success was evaluated by taking into consideration the etiological risk factors, the patients who were incontinent after TURP had considerable success rates with macroplastique injection. Although the number of patients were limited and did not allow for statistical comparison, we have seen that submucosal injection had lower success rates in cases of incontinence due to open surgical procedures. When compared with injection agents, AUS implantation carries morbidity of significant degree [6,7,10,11]. Infection surrounding the prosthesis, erosion of the cuff, and mechanical insufficiency of the device are the main disadvantages of this procedure. Due to such reasons, we had to perform revisions in 5 patients (22.7%) in our study. One of the most important reasons behind the hesitations of the urologists concerning the implantation of AUS is the high rate of complications. There are studies reporting revision rates of 32% and 90% of the revisions were required within the first 3 years [12].It is also reported that prostheses had to be taken out in 37% of the cases within 10 years [13]. Pump problems secondary to mechanical problems seen in long-term follow-ups should also be considered [10,14]. Morbidity rates were quite low in our injection group. The most important considerations for injections are, low success rates and requirement for repetitive injections. Some researchers report definitive results after 4 5 injections, however, a consensus has been reached for not proceeding further in patients who have not experienced any symptomatic improvement despite receiving the second injection [3,15 17]. The authors think that repetitive injections should only be tried in patients with minimal incontinence. Our study was different from the similar studies in the literature in the sense that, preoperative indications were shown to be influential factors on the final success rates. In patients with minimal incontinence similar success rates were obtained from the two techniques with a randomized approach, however in total incontinence AUS implantation had statistically significant success over endourethral injection. Another point to be emphasized is that, in patients who have received macroplastique injection despite having total incontinence, there were significant improvements in the number of pads used, the weight of the pads and quality of life scores, yet they remained mostly incontinent when evaluated with our success criteria. Furthermore, as we had to implant stents to two patients who had recurrent strictures of the urethra, these patients had to be implanted with AUS as well. 5. Conclusions The main message of this article is that degree of PPI is the most important parameter determining the success of the treatment modality chosen. Endourethral injection should be the treatment of choice for patients with minimal incontinence, whereas AUS implantation should be considered as the first choice for patients with total incontinence. Furthermore, the authors conclude that endourethral injection should be the first choice in patients with incontinence after TURP and AUS implantation should be offered to patients experiencing incontinence after open surgical procedures.
5 M.A. Imamoglu et al. / European Urology 47 (2005) References [1] Fowler Jr FJ, Barry MJ, Lu-Yao G, Roman A, Wasson J, Wennberg JE. Patient reported complications and follow-up treatment after radical prostatectomy. The National Medicare Experience: Urology 1993;42(6):622. [2] Murphy GP, Mettlin C, Menck H, Winchester DP, Davidson AM. National patterns of prostate cancer treatment by radical prostatectomy: result of a survey by the American Collage of Surgeons Committee on Cancer. J Urol 1994;152(5 Pt 2):1817. [3] Kuznetsov DD, Kim HL, Patel RV, Steinberg GD, Bales GT. Comparison of artificial urinary sphincter and collagen for the treatment of postprostatectomy incontinence. Urology 2000;56(4):600. [4] Raz S, Ericsa DR. SEAPI QMM incontinence classification system. Neurol Urodyn 1992;11:192. [5] Dikranian AH, Chang JH, Rhee EY, Aboseif SR. The male perineal sling: comparison of sling materials. J Urol 2004;172(2): [6] Litwiller SE, Kim KB, Fone PD, White RW, Stone AR. Post-prostatectomy incontinence and the artificial urinary sphincter: a long term study of patient satisfaction and criteria for success. J Urol 1975; 156(6). [7] Kowalczyk JJ, Snabsigh R, Scott FB. Experience with the artificial urinary sphincter model AMS800 in 148 patients. J Urol 1989;141 :307. [8] Politano VA. Transurethral polytef injection for post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence. Br J Urol 1992;69(1):26. [9] Dahms SE, Eggersmann C, Hohenfellner M, Lampel A, Thuroff JW. Stellenwert der Injektionstherapie bei Harninkontinenz. Akt Urol 1996;27:185. [10] Bartoletti R, Gacci M, Travaglini F, Sarti E, Selli C. Intravesical migration of AMS 800 artificial urinary sphincter and stone formation in a patient who underwent radical prostatectomy. Urol Int 2000; 64(3):167. [11] Peyromaure M, Ravery V, Boccon-Gibod L. The management of stress urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy. BJU Int 2002;90(2): [12] Hajivassiliou CA. A review of the complications and results of implantation of the artificial urinary sphincter. Eur Urol 1999; 35(1):36. [13] Venn SN, Greenwell TJ, Mundy AR. The long-term outcome of artificial urinary sphincters. J Urol 2000;164(3 Pt 1):702. [14] De Stefani S, Liguori G, Ciampalini S, Belgrano E. AMS 800 artificial sphincter: an unusual case of circumscribed peritonitis due to prosthetic reservoir infection. Arch Esp Urol 1999;52(4):412. [15] Smith DN, Appell RA, Rackley RR, Winters JC. Collagen injection therapy for post-prostatectomy incontinence. J Urol 1998;160(2):364. [16] Cespedes RD, Cross CA, McGuire EJ. Collagen injection therapy for the treatment of male urinary incontinence. J Urol 1996;155(Suppl):458A. [17] Kylmala T, Tainio H, Raitanen M, Tammela TL. Treatment of postoperative male urinary incontinence using transurethral macroplastique injections. J Endourol 2003;17(2):113 5.
Comparison of bone-anchored male sling and collagen implant for the treatment of male incontinence
 Blackwell Publishing AsiaMelbourne, AustraliaIJUInternational Journal of Urology0919-81722006 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty Ltd???2006130012071211Original ArticleComparison of male sling and collagen implant
Blackwell Publishing AsiaMelbourne, AustraliaIJUInternational Journal of Urology0919-81722006 Blackwell Publishing Asia Pty Ltd???2006130012071211Original ArticleComparison of male sling and collagen implant
Four-year follow-up on a Zephyr Surgical Implants 375 artificial urinary sphincter for male urinary incontinence from one urological centre in Poland
 320 O R I G I N A L P A P E R FUNCTIONAL UROLOGY Four-year follow-up on a Zephyr Surgical Implants 375 artificial urinary sphincter for male urinary incontinence from one urological centre in Poland Ireneusz
320 O R I G I N A L P A P E R FUNCTIONAL UROLOGY Four-year follow-up on a Zephyr Surgical Implants 375 artificial urinary sphincter for male urinary incontinence from one urological centre in Poland Ireneusz
A New Artificial Urinary Sphincter with Conditional Occlusion for Stress Urinary Incontinence: Preliminary Clinical Results
 european urology xxx (2006) xxx xxx available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Ageing Male A New Artificial Urinary Sphincter with Conditional Occlusion for Stress Urinary
european urology xxx (2006) xxx xxx available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Ageing Male A New Artificial Urinary Sphincter with Conditional Occlusion for Stress Urinary
Deirdre M. Bochove-Overgaauw* and Bart Ph. Schrier
 An Adjustable Sling for the Treatment of All Degrees of Male Stress Urinary Incontinence: Retrospective Evaluation of Efficacy and Complications After a Minimal Followup of 14 Months Deirdre M. Bochove-Overgaauw*
An Adjustable Sling for the Treatment of All Degrees of Male Stress Urinary Incontinence: Retrospective Evaluation of Efficacy and Complications After a Minimal Followup of 14 Months Deirdre M. Bochove-Overgaauw*
Management of Post-Prostatectomy Urinary Incontinence and Sexual Dysfunction
 Management of Post-Prostatectomy Urinary Incontinence and Sexual Dysfunction Robert C. Eyre, MD, FACS Associate Clinical Professor of Surgery (Urology) Harvard Medical School Post-prostatectomy Incontinence
Management of Post-Prostatectomy Urinary Incontinence and Sexual Dysfunction Robert C. Eyre, MD, FACS Associate Clinical Professor of Surgery (Urology) Harvard Medical School Post-prostatectomy Incontinence
Urodynamic study before and after radical porstatectomy 가톨릭의대성바오로병원김현우
 Urodynamic study before and after radical porstatectomy 가톨릭의대성바오로병원김현우 Introduction Radical prostatectomy - treatment of choice for patients with localized prostate cancer. Urinary incontinence and/or
Urodynamic study before and after radical porstatectomy 가톨릭의대성바오로병원김현우 Introduction Radical prostatectomy - treatment of choice for patients with localized prostate cancer. Urinary incontinence and/or
Since the first published article, in 1974 by Scott et al on
 Perineal Approach for Artificial Urinary Sphincter Implantation Appears to Control Male Stress Incontinence Better Than the Transscrotal Approach Gerard D. Henry,* Stephen M. Graham, Mario A. Cleves, Caroline
Perineal Approach for Artificial Urinary Sphincter Implantation Appears to Control Male Stress Incontinence Better Than the Transscrotal Approach Gerard D. Henry,* Stephen M. Graham, Mario A. Cleves, Caroline
I-STOP TOMS Transobturator Male Sling
 I-STOP TOMS Transobturator Male Sling The CL Medical I-STOP TOMS sling for male stress urinary incontinence was developed in France where it is widely used and is the market leader. It is constructed with
I-STOP TOMS Transobturator Male Sling The CL Medical I-STOP TOMS sling for male stress urinary incontinence was developed in France where it is widely used and is the market leader. It is constructed with
Artificial urinary sphincter for urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy: a historical cohort from 2004 to 2015
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 43 (1): 150-154, January - February, 2017 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0244 Artificial urinary sphincter for urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy: a historical cohort
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 43 (1): 150-154, January - February, 2017 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0244 Artificial urinary sphincter for urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy: a historical cohort
Post- prostatectomy Incontinence - PPI
 Post- prostatectomy Incontinence - PPI Dr. Kolombo Ivan, MD, FEBU Assoc.Prof. Popken Gralf MD, PhD, Assoc.Prof. Otčenášek Michal MD, PhD, Dr. Klézl Petr MD, MBA, Dr. Kolombová Jitka MD, MBA, Assoc.Prof.
Post- prostatectomy Incontinence - PPI Dr. Kolombo Ivan, MD, FEBU Assoc.Prof. Popken Gralf MD, PhD, Assoc.Prof. Otčenášek Michal MD, PhD, Dr. Klézl Petr MD, MBA, Dr. Kolombová Jitka MD, MBA, Assoc.Prof.
Long-term results of permanent memotherm urethral stent in the treatment of recurrent bulbar urethral strictures
 ORIGINAL Article Vol. 40 (1): 80-86, January - February, 2014 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.01.12 Long-term results of permanent memotherm urethral stent in the treatment of recurrent bulbar urethral
ORIGINAL Article Vol. 40 (1): 80-86, January - February, 2014 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.01.12 Long-term results of permanent memotherm urethral stent in the treatment of recurrent bulbar urethral
Periurethral constrictor: late results of the treatment of post prostatectomy urinary incontinence
 Clinical Urology International Braz J Urol Vol 37 (4): 483-487, July - August, 2011 Periurethral constrictor: late results of the treatment of post prostatectomy urinary incontinence Roberto S. Lima, Evandilson
Clinical Urology International Braz J Urol Vol 37 (4): 483-487, July - August, 2011 Periurethral constrictor: late results of the treatment of post prostatectomy urinary incontinence Roberto S. Lima, Evandilson
Management of LUTS after TURP and MIT
 Management of LUTS after TURP and MIT Hong Sup Kim Konkuk University TURP & MIT TURP : Gold standard MIT TUIP TUNA TUMT HIFU LASER Nd:YAG, ILC, HoLRP, KTP LUTS after TURP and MIT Improved : about 70% Persistent
Management of LUTS after TURP and MIT Hong Sup Kim Konkuk University TURP & MIT TURP : Gold standard MIT TUIP TUNA TUMT HIFU LASER Nd:YAG, ILC, HoLRP, KTP LUTS after TURP and MIT Improved : about 70% Persistent
Conclusions. Keywords
 Functional Urology Outcomes of single- vs double-cuff artificial urinary sphincter insertion in low- and high-risk profile male patients with severe stress urinary incontinence Sascha A. Ahyai*, Tim A.
Functional Urology Outcomes of single- vs double-cuff artificial urinary sphincter insertion in low- and high-risk profile male patients with severe stress urinary incontinence Sascha A. Ahyai*, Tim A.
The role of synthetic slings in male stress incontinence
 Arab Journal of Urology (2011) 9, 129 134 Arab Journal of Urology (Official Journal of the Arab Association of Urology) www.sciencedirect.com URODYNAMICS/FEMALE UROLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE The role of synthetic
Arab Journal of Urology (2011) 9, 129 134 Arab Journal of Urology (Official Journal of the Arab Association of Urology) www.sciencedirect.com URODYNAMICS/FEMALE UROLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE The role of synthetic
Department of Urology, Cochin hospital Paris Descartes University
 Technical advances in the treatment of localized prostate cancer Pr Michaël Peyromaure Department of Urology, Cochin hospital Paris Descartes University Introduction Curative treatments of localized prostate
Technical advances in the treatment of localized prostate cancer Pr Michaël Peyromaure Department of Urology, Cochin hospital Paris Descartes University Introduction Curative treatments of localized prostate
Department of Urology, University Hospital Ulm, Prittwitzstrasse 43, D Ulm, Germany
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 304205, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/304205 Clinical Study The Retrourethral Transobturator Sling Suspension in the Treatment of
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 304205, 5 pages doi:10.5402/2012/304205 Clinical Study The Retrourethral Transobturator Sling Suspension in the Treatment of
Management of Artificial Urinary Sphincter Dysfunction
 European Urology European Urology 46 (2004) 241 246 Management of Artificial Urinary Sphincter Dysfunction Frédéric Maillet, Jean-Marie Buzelin, Olivier Bouchot, Georges Karam * Clinique Urologique, CHU
European Urology European Urology 46 (2004) 241 246 Management of Artificial Urinary Sphincter Dysfunction Frédéric Maillet, Jean-Marie Buzelin, Olivier Bouchot, Georges Karam * Clinique Urologique, CHU
Outcome and complications of adjustable continence therapy (ProACT ) after radical prostatectomy: 10 years experience in 143 patients
 Received: 16 August 2017 Accepted: 13 November 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23463 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Outcome and complications of adjustable continence therapy (ProACT ) after radical prostatectomy: 10
Received: 16 August 2017 Accepted: 13 November 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23463 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Outcome and complications of adjustable continence therapy (ProACT ) after radical prostatectomy: 10
Introduction. Keywords Male urinary incontinence Artificial urinary sphincter Compressive adjustable slings
 https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2523-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of adjustable male slings and artificial urinary sphincter in the treatment of male urinary incontinence: a retrospective analysis
https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2523-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of adjustable male slings and artificial urinary sphincter in the treatment of male urinary incontinence: a retrospective analysis
Male urinary incontinence: Artificial sphincter
 GUIDELINES IN FOCUS Truzzi JC et al. Male urinary incontinence: Artificial sphincter Incontinência urinária masculina: Esfíncter artificial Authorship: Brazilian Society of Urology (SBU) Participants:
GUIDELINES IN FOCUS Truzzi JC et al. Male urinary incontinence: Artificial sphincter Incontinência urinária masculina: Esfíncter artificial Authorship: Brazilian Society of Urology (SBU) Participants:
Life after prostate cancer End your frustration. Restore your normalcy. Renew your confidence. Take the next step
 Take the next step Visit EDCure.org to: Take the online ED quiz and get your customized treatment results Find an ED specialist in your area Register for free educational seminars to learn more about treatment
Take the next step Visit EDCure.org to: Take the online ED quiz and get your customized treatment results Find an ED specialist in your area Register for free educational seminars to learn more about treatment
6 Page Male Incontinence Booklet 10/09/ :44 Page 1. The Natural Non-Surgical Option for Male Urinary Incontinence
 6 Page Male Incontinence Booklet /9/ :44 Page The Natural Non-Surgical Option for Male Urinary Incontinence 6 Page Male Incontinence Booklet /9/ :44 Page Stress Urinary Incontinence - A Stressful Prospect
6 Page Male Incontinence Booklet /9/ :44 Page The Natural Non-Surgical Option for Male Urinary Incontinence 6 Page Male Incontinence Booklet /9/ :44 Page Stress Urinary Incontinence - A Stressful Prospect
Artificial urinary sphincter revision for urethral atrophy: comparing single cuff downsizing and tandem cuff placement
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 43 (2): 264-270, March - April, 2017 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0240 Artificial urinary sphincter revision for urethral atrophy: comparing single cuff downsizing and tandem
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 43 (2): 264-270, March - April, 2017 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2016.0240 Artificial urinary sphincter revision for urethral atrophy: comparing single cuff downsizing and tandem
INJINTERNATIONAL. Original Article INTRODUCTION. Int Neurourol J 2017;21: pissn eissn
 Official Journal of Korean Continence Society / Korean Society of Urological Research / The Korean Children s Continence and Enuresis Society / The Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and
Official Journal of Korean Continence Society / Korean Society of Urological Research / The Korean Children s Continence and Enuresis Society / The Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and
Managing urinary morbidity after brachytherapy. Kieran O Flynn Department of Urology, Salford Royal Foundation Trust, Manchester
 Managing urinary morbidity after brachytherapy Kieran O Flynn Department of Urology, Salford Royal Foundation Trust, Manchester Themes Can we predict urinary morbidity? Prevention of urinary morbidity
Managing urinary morbidity after brachytherapy Kieran O Flynn Department of Urology, Salford Royal Foundation Trust, Manchester Themes Can we predict urinary morbidity? Prevention of urinary morbidity
AdVance Male Sling System
 AdVance Male Sling System Clinical study summary This document is a compilation and summary of several AdVance Male Sling System peer-reviewed journal articles. The information presented here is taken
AdVance Male Sling System Clinical study summary This document is a compilation and summary of several AdVance Male Sling System peer-reviewed journal articles. The information presented here is taken
A New Postoperative Predictor of Time to Urinary Continence after Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy: The Urine Loss Ratio
 european urology 52 (2007) 178 185 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Laparoscopy A New Postoperative Predictor of Time to Urinary Continence after Laparoscopic
european urology 52 (2007) 178 185 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Laparoscopy A New Postoperative Predictor of Time to Urinary Continence after Laparoscopic
Introduction/Learning Objectives. Incontinence: Natural History. Course Outline 10/14/2016. Urinary Incontinence: Conservative Measures
 Management of Urinary Complications after Prostatectomy Course Faculty: Introduction/Learning Objectives Jaspreet S. Sandhu, MD Associate Attending Urologist Department of Surgery/Urology Memorial Sloan
Management of Urinary Complications after Prostatectomy Course Faculty: Introduction/Learning Objectives Jaspreet S. Sandhu, MD Associate Attending Urologist Department of Surgery/Urology Memorial Sloan
Hong Kong College of Surgical Nursing
 Hong Kong College of Surgical Nursing Higher Surgical Nursing Training: Part B Specialty - Urological Nursing Curriculum TABLE OF CONTENTS No. Contents Page. Introduction. Aims. Learning Objectives 4.
Hong Kong College of Surgical Nursing Higher Surgical Nursing Training: Part B Specialty - Urological Nursing Curriculum TABLE OF CONTENTS No. Contents Page. Introduction. Aims. Learning Objectives 4.
Short-term evaluation of the adjustable bulbourethral male sling for post-prostatectomy urinary incontinence
 Received: 26 September 2017 Revised: 9 March 2018 Accepted: 23 April 2018 DOI: 10.1111/luts.12227 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Short-term evaluation of the adjustable bulbourethral male sling for post-prostatectomy
Received: 26 September 2017 Revised: 9 March 2018 Accepted: 23 April 2018 DOI: 10.1111/luts.12227 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Short-term evaluation of the adjustable bulbourethral male sling for post-prostatectomy
Urinary Incontinence. Biopolymer GmbH & Co.KG - Germany
 Urinary Incontinence Treatment Options: 1. Physical Therapy: a conservative early stage treatment for UI, including pelvic floor muscles training known as Kegel exercise. 2. Medications: by means of pharmaceutical
Urinary Incontinence Treatment Options: 1. Physical Therapy: a conservative early stage treatment for UI, including pelvic floor muscles training known as Kegel exercise. 2. Medications: by means of pharmaceutical
Combination therapy for male erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence
 sian J ndrol 2008; 10 (1): 149 154 DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-7262.2008.00364.x www.asiaandro.com. Clinical Experience. Combination therapy for male erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence Helen Zafirakis
sian J ndrol 2008; 10 (1): 149 154 DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-7262.2008.00364.x www.asiaandro.com. Clinical Experience. Combination therapy for male erectile dysfunction and urinary incontinence Helen Zafirakis
Surgery for stress urinary incontinence due to presumed sphincter deficiency after prostate surgery (Review)
 Surgery for stress urinary incontinence due to presumed sphincter deficiency after prostate surgery (Review) Silva LA, Andriolo RB, Atallah ÁN, da Silva EMK This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared
Surgery for stress urinary incontinence due to presumed sphincter deficiency after prostate surgery (Review) Silva LA, Andriolo RB, Atallah ÁN, da Silva EMK This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared
Original Policy Date
 MP 7.01.39 Transurethral Microwave Thermotherapy Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical
MP 7.01.39 Transurethral Microwave Thermotherapy Medical Policy Section Surgery Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical
Medical Policy Title: Periurethral Bulking ARBenefits Approval: <Date>
 Medical Policy Title: Periurethral Bulking ARBenefits Approval: Agents for the Treatment of Incontinence Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0279 Revision Date: Code(s): 51715 Endoscopic injection
Medical Policy Title: Periurethral Bulking ARBenefits Approval: Agents for the Treatment of Incontinence Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0279 Revision Date: Code(s): 51715 Endoscopic injection
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 57 (2010)
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 57 (2010) 430 436 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Surgery in Motion Transrectal Ultrasound Guided Implantation of Adjustable Continence Therapy
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 57 (2010) 430 436 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Surgery in Motion Transrectal Ultrasound Guided Implantation of Adjustable Continence Therapy
Jennifer Locke UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Resident Year 3 October 12, Learning Objectives
 Artificial Urinary Sphincter after 40 Years of Use: Indications, Techniques and Outcomes Jennifer Locke UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Resident Year 3 October 12, 2016 Learning Objectives 1. Identify
Artificial Urinary Sphincter after 40 Years of Use: Indications, Techniques and Outcomes Jennifer Locke UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Resident Year 3 October 12, 2016 Learning Objectives 1. Identify
Long-term results of the implantation of the AMS 800 artificial sphincter for post-prostatectomy incontinence: a single-center experience
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 44 (1): 114-120, January - February, 2018 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2017.0165 Long-term results of the implantation of the AMS 800 artificial sphincter for post-prostatectomy incontinence:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 44 (1): 114-120, January - February, 2018 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2017.0165 Long-term results of the implantation of the AMS 800 artificial sphincter for post-prostatectomy incontinence:
Stress Incontinence. Susannah Elvy Urogynaecology CNS
 Stress Incontinence Susannah Elvy Urogynaecology CNS Definitions Prevalence Assessment Investigation Treatment Surgery Men International Continence Society define as the complaint of any involuntary leakage
Stress Incontinence Susannah Elvy Urogynaecology CNS Definitions Prevalence Assessment Investigation Treatment Surgery Men International Continence Society define as the complaint of any involuntary leakage
Fan Zhang 1,2 and Limin Liao 1,2*
 Zhang and Liao BMC Urology (018) 18:3 DOI 10.1186/s1894-018-0314-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Artificial urinary sphincter implantation: an important component of complex surgery for urinary tract reconstruction
Zhang and Liao BMC Urology (018) 18:3 DOI 10.1186/s1894-018-0314-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Artificial urinary sphincter implantation: an important component of complex surgery for urinary tract reconstruction
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF POST-PROSTATECTOMY INCONTINENCE
 SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF POST-PROSTATECTOMY INCONTINENCE Arthi Satyanarayan, Ryan Mooney, *Nirmish Singla Department of Urology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, Texas, USA *Correspondence
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF POST-PROSTATECTOMY INCONTINENCE Arthi Satyanarayan, Ryan Mooney, *Nirmish Singla Department of Urology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, Texas, USA *Correspondence
The Prognostic Importance of Prostate-Specific Antigen in Monitoring Patients Undergoing Maximum Androgen Blockage for Metastatic Prostate Cancer
 Research Article TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (005) 5, 8 4 ISSN 57-744X; DOI 0.00/tsw.005.9 The Prognostic Importance of Prostate-Specific Antigen in Monitoring Patients Undergoing Maximum Androgen Blockage
Research Article TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (005) 5, 8 4 ISSN 57-744X; DOI 0.00/tsw.005.9 The Prognostic Importance of Prostate-Specific Antigen in Monitoring Patients Undergoing Maximum Androgen Blockage
Urethral catheter removal 3 days after radical retropubic prostatectomy is feasible and desirable
 Urethral catheter 3 days after radical retropubic prostatectomy is feasible and desirable (2002) 5, 291 295 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1365 7852/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/pcan JM
Urethral catheter 3 days after radical retropubic prostatectomy is feasible and desirable (2002) 5, 291 295 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1365 7852/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/pcan JM
Early-Stage Clinical Experiences of Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP)
 JRural Med 2007 ; 2 : 93 97 Original article Early-Stage Clinical Experiences of Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP) Shuzo Hamamoto 1,TakehikoOkamura 1,HideyukiKamisawa 1,KentaroMizuno 1,
JRural Med 2007 ; 2 : 93 97 Original article Early-Stage Clinical Experiences of Holmium Laser Enucleation of the Prostate (HoLEP) Shuzo Hamamoto 1,TakehikoOkamura 1,HideyukiKamisawa 1,KentaroMizuno 1,
Efficacy of High-frequency Magnetic Stimulation of the Sacral Root in Patients with Urinary Incontinence Following a Radical Prostatectomy
 LUTS (2011) 3, 10 14 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficacy of High-frequency Magnetic Stimulation of the Sacral Root in Patients with Urinary Incontinence Following a Radical Prostatectomy Nobuyuki KAI, 1 Masakazu
LUTS (2011) 3, 10 14 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficacy of High-frequency Magnetic Stimulation of the Sacral Root in Patients with Urinary Incontinence Following a Radical Prostatectomy Nobuyuki KAI, 1 Masakazu
Evaluating the impact of radiation therapy on patient quality of life following primary artificial urinary sphincter placement
 Original Article Evaluating the impact of radiation therapy on patient quality of life following primary artificial urinary sphincter placement Jason P. Joseph, Marcelino E. Rivera, Brian J. Linder, Boyd
Original Article Evaluating the impact of radiation therapy on patient quality of life following primary artificial urinary sphincter placement Jason P. Joseph, Marcelino E. Rivera, Brian J. Linder, Boyd
Medical Policy Title: Radiofrequency ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011
 Medical Policy Title: Radiofrequency ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011 Treatment, Urinary Stress Incontinence, Transurethral Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0359 Revision Date: Code(s): 53860 Transurethral
Medical Policy Title: Radiofrequency ARBenefits Approval: 10/19/2011 Treatment, Urinary Stress Incontinence, Transurethral Effective Date: 01/01/2012 Document: ARB0359 Revision Date: Code(s): 53860 Transurethral
Medical Review Criteria Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence
 Medical Review Criteria Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Effective Date: December 21, 2016 Subject: Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Background: Urinary incontinence (the involuntary
Medical Review Criteria Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Effective Date: December 21, 2016 Subject: Invasive Treatment for Urinary Incontinence Background: Urinary incontinence (the involuntary
Long-term functional outcomes after artificial urinary sphincter implantation in men with stress urinary. incontinence
 Long-term functional outcomes after artificial urinary sphincter implantation in men with stress urinary incontinence Priscilla Léon, Emmanuel Chartier-Kastler, Morgan Rouprêt, Vanina Ambrogi, Pierre Mozer,
Long-term functional outcomes after artificial urinary sphincter implantation in men with stress urinary incontinence Priscilla Léon, Emmanuel Chartier-Kastler, Morgan Rouprêt, Vanina Ambrogi, Pierre Mozer,
Efficacy of the InVance TM Male Sling in Men with Stress Urinary Incontinence
 european urology 51 (2007) 498 503 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Reconstructive Urology Efficacy of the InVance TM Male Sling in Men with Stress Urinary Incontinence
european urology 51 (2007) 498 503 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Reconstructive Urology Efficacy of the InVance TM Male Sling in Men with Stress Urinary Incontinence
Can Bipolar Vaporization be Considered an Alternative Energy Source in the Endoscopic Treatment of Urethral Strictures and Bladder Neck Contracture?
 Clinical Urology Bipolar Energy for Treating Urethral Strictures International Braz J Urol Vol. 34 (5): 577-586, September - October, 2008 Can Bipolar Vaporization be Considered an Alternative Energy Source
Clinical Urology Bipolar Energy for Treating Urethral Strictures International Braz J Urol Vol. 34 (5): 577-586, September - October, 2008 Can Bipolar Vaporization be Considered an Alternative Energy Source
Holmium:YAG Laser for Treatment of Strictures of Vesicourethral Anastomosis after Radical Prostatectomy
 JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 19, Number 4, May 2005 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Holmium:YAG Laser for Treatment of Strictures of Vesicourethral Anastomosis after Radical Prostatectomy BRUNOLF W. LAGERVELD,
JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY Volume 19, Number 4, May 2005 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Holmium:YAG Laser for Treatment of Strictures of Vesicourethral Anastomosis after Radical Prostatectomy BRUNOLF W. LAGERVELD,
Complication of long indwelling urinary catheter and stent COMPLICATION OF LONG INDWELLING URINARY CATHETER AND STENT
 151 COMPLICATION OF LONG INDWELLING URINARY CATHETER AND STENT Jain A 1 *, Srivastava R 1, Prasad A 1, Marwah K 1 1. Department of surgery, Subharti medical college, Meerut U.P. India Correspondence: Dr.
151 COMPLICATION OF LONG INDWELLING URINARY CATHETER AND STENT Jain A 1 *, Srivastava R 1, Prasad A 1, Marwah K 1 1. Department of surgery, Subharti medical college, Meerut U.P. India Correspondence: Dr.
THE ARTIFICIAL URINARY SPHINCTER:
 THE ARTIFICIAL URINARY SPHINCTER: A TREATMENT FOR POST- PROSTATECTOMY URINARY INCONTINENCE Andrew L. Siegel, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon Director: Center for Continence Care An
THE ARTIFICIAL URINARY SPHINCTER: A TREATMENT FOR POST- PROSTATECTOMY URINARY INCONTINENCE Andrew L. Siegel, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon Director: Center for Continence Care An
Transcorporal artificial urinary sphincter in radiated and non - radiated compromised urethra. Assessment with a minimum 2 year follow-up
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 42 (3): 494-500, May - June, 2016 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2015.0329 Transcorporal artificial urinary sphincter in radiated and non - radiated compromised urethra. Assessment
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 42 (3): 494-500, May - June, 2016 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2015.0329 Transcorporal artificial urinary sphincter in radiated and non - radiated compromised urethra. Assessment
ORIGINAL PAPER. Summary
 ORIGINAL PAPER DOI: 10.4081/aiua.2015.3.233 A two staged treatment procedure for the difficult to treat bladder neck contractures with concomitant incontinence. In the search of a solution to a complex
ORIGINAL PAPER DOI: 10.4081/aiua.2015.3.233 A two staged treatment procedure for the difficult to treat bladder neck contractures with concomitant incontinence. In the search of a solution to a complex
A.M.I. ATOMS System. Hydraulic system substitutes urinary sphincter function in incontinent males
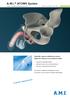 A.M.I. ATOMS System Product Group Urology Issue 11/2016 ATOMS = Adjustable TransObturator Male System Hydraulic system substitutes urinary sphincter function in incontinent males Long-term, adjustable
A.M.I. ATOMS System Product Group Urology Issue 11/2016 ATOMS = Adjustable TransObturator Male System Hydraulic system substitutes urinary sphincter function in incontinent males Long-term, adjustable
Title risk patients with urinary retentio. Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (2005), 51(4):
 Title Urethral stent (Angiomed-Memotherm) risk patients with urinary retentio Uchikoba, Takushi; Horiuchi, Kazuta Author(s) Oka, Fumiatsu; Saitoh, Yuka; Tsuboi Taiji Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (2005), 51(4): 235-239
Title Urethral stent (Angiomed-Memotherm) risk patients with urinary retentio Uchikoba, Takushi; Horiuchi, Kazuta Author(s) Oka, Fumiatsu; Saitoh, Yuka; Tsuboi Taiji Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (2005), 51(4): 235-239
Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566
 Single-incision short sling mesh insertion for stress urinary incontinence in women Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566 Your responsibility This guidance
Single-incision short sling mesh insertion for stress urinary incontinence in women Interventional procedures guidance Published: 12 October 2016 nice.org.uk/guidance/ipg566 Your responsibility This guidance
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control SURGERY TO TREAT URINARY INCONTINENCE AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is Urinary Incontinence? Urinary incontinence
BLADDER HEALTH Loss of Bladder Control SURGERY TO TREAT URINARY INCONTINENCE AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION What Is Urinary Incontinence? Urinary incontinence
TURP Complications & Treatments. G. Testa
 TURP Complications & Treatments G. Testa Statistics Operative mortality 0.2 per cent Most common cause of death was sepsis which occurred >1 month after surgery 77% of patients had significant pre-existing
TURP Complications & Treatments G. Testa Statistics Operative mortality 0.2 per cent Most common cause of death was sepsis which occurred >1 month after surgery 77% of patients had significant pre-existing
PERINEAL PROSTATECTOMY
 Abstract PERINEAL PROSTATECTOMY Pages with reference to book, From 204 To 206 Altaf Hussain Rathore ( Dept. of Surgery, Punjab Medical College, Faisalabad. ) A series of twenty-five medically high risk
Abstract PERINEAL PROSTATECTOMY Pages with reference to book, From 204 To 206 Altaf Hussain Rathore ( Dept. of Surgery, Punjab Medical College, Faisalabad. ) A series of twenty-five medically high risk
Life after prostate cancer. End your frustration. Restore your normalcy. Renew your confidence. Erectile dysfunction and male incontinence
 Life after prostate cancer End your frustration. Restore your normalcy. Renew your confidence. Erectile dysfunction and male incontinence Welcome This brochure is designed to help you learn more about
Life after prostate cancer End your frustration. Restore your normalcy. Renew your confidence. Erectile dysfunction and male incontinence Welcome This brochure is designed to help you learn more about
A. Simonato, 1 M. Ennas, 1 A. Benelli, 1 A. Gregori, 2 F. Oneto, 1 E. Daglio, 1 P. Traverso, 1 and G. Carmignani 1. 1.
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 481943, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/481943 Clinical Study Comparison between Two Different Two-Stage Transperineal Approaches to
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Advances in Urology Volume 2012, Article ID 481943, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/481943 Clinical Study Comparison between Two Different Two-Stage Transperineal Approaches to
Controversies in the Management of Post Prostatectomy Incontinence Workshop 17 Monday 23 August 2010, 14:00 17:00
 Controversies in the Management of Post Prostatectomy Incontinence Workshop 17 Monday 23 August 2010, 14:00 17:00 Time Time Topic Speaker 14.00 14.00 Introduction Ajay Singla 14.00 14.30 Pathophysiology
Controversies in the Management of Post Prostatectomy Incontinence Workshop 17 Monday 23 August 2010, 14:00 17:00 Time Time Topic Speaker 14.00 14.00 Introduction Ajay Singla 14.00 14.30 Pathophysiology
Urinary Incontinence Following Surgery for bph: the Role of Aging on the Incidence of Bladder Dysfunction
 Neurology International Braz J Urol Vol 37 (3): 380-387, May - June, 2011 doi: 10.1590/S1677-55382011000300012 Urinary Incontinence Following Surgery for bph: the Role of Aging on the Incidence of Bladder
Neurology International Braz J Urol Vol 37 (3): 380-387, May - June, 2011 doi: 10.1590/S1677-55382011000300012 Urinary Incontinence Following Surgery for bph: the Role of Aging on the Incidence of Bladder
Suburethral sling at the time of radical prostatectomy in patients at high risk of postoperative incontinence
 Original Article IMMEDIATE SLING DURING RP IN HIGH-RISK PATIENTS WESTNEY et al. Suburethral sling at the time of radical prostatectomy in patients at high risk of postoperative incontinence O. LENAINE
Original Article IMMEDIATE SLING DURING RP IN HIGH-RISK PATIENTS WESTNEY et al. Suburethral sling at the time of radical prostatectomy in patients at high risk of postoperative incontinence O. LENAINE
Loss of Bladder Control
 BLADDER HEALTH: Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Loss of Bladder Control Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Don t Let Urinary Incontinence Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is Urinary Incontinence? What
BLADDER HEALTH: Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Loss of Bladder Control Surgery for Urinary Incontinence Don t Let Urinary Incontinence Keep You from Enjoying Life. What is Urinary Incontinence? What
Presentation, management, and outcomes of complications following prostate cancer therapy
 Original Article Presentation, management, and outcomes of complications following prostate cancer therapy Uwais B. Zaid, Jack W. McAninch, Allison S. Glass, Nadya M. Cinman, Benjamin N. Breyer Department
Original Article Presentation, management, and outcomes of complications following prostate cancer therapy Uwais B. Zaid, Jack W. McAninch, Allison S. Glass, Nadya M. Cinman, Benjamin N. Breyer Department
The Surgical Learning Curve for Artificial Urinary Sphincter Procedures Compared to Typical Surgeon Experience
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 60 (2011) 1285 1290 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Reconstructive Urology The Surgical Learning Curve for Artificial Urinary Sphincter Procedures
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 60 (2011) 1285 1290 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Reconstructive Urology The Surgical Learning Curve for Artificial Urinary Sphincter Procedures
urethral stricture recurrence after internal urethrotomy.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 9-, p-issn: 9-.Volume, Issue Ver. II (Nov. ), PP - www.iosrjournals.org Effects of Intralesional Triamcinalone injection following Internal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 9-, p-issn: 9-.Volume, Issue Ver. II (Nov. ), PP - www.iosrjournals.org Effects of Intralesional Triamcinalone injection following Internal
Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas The artificial genitourinary sphincter
 BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas The artificial genitourinary sphincter John T. Stoffel and David M. Barrett Department of Urology, Lahey Clinic Medical Center, Burlington, USA
BJUI BJU INTERNATIONAL Surgery Illustrated Surgical Atlas The artificial genitourinary sphincter John T. Stoffel and David M. Barrett Department of Urology, Lahey Clinic Medical Center, Burlington, USA
Information for men considering a male sling procedure UHB is a no smoking Trust
 Information for men considering a male sling procedure UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
Information for men considering a male sling procedure UHB is a no smoking Trust To see all of our current patient information leaflets please visit www.uhb.nhs.uk/patient-information-leaflets.htm Introduction
Single institution experience with the transobturator sling suspension system AdVance in the treatment of male urinary incontinence: mid-term results
 Clinical Urology International Braz J Urol Vol 37 (4): 488-494, July - August, 2011 Single institution experience with the transobturator sling suspension system AdVance in the treatment of male urinary
Clinical Urology International Braz J Urol Vol 37 (4): 488-494, July - August, 2011 Single institution experience with the transobturator sling suspension system AdVance in the treatment of male urinary
THE BULKING AGENT WITH LONG-LASTING EFFECT!
 THE BULKING AGENT WITH LONG-LASTING EFFECT! Urogyn BV Transistorweg 5a 6534 AT Nijmegen The Netherlands t +31(0) 24 711 41 30 info@urogynbv.com www.urogynbv.com THE FIRST INJECTABLE IMPLANT THAT CAN COMPETE
THE BULKING AGENT WITH LONG-LASTING EFFECT! Urogyn BV Transistorweg 5a 6534 AT Nijmegen The Netherlands t +31(0) 24 711 41 30 info@urogynbv.com www.urogynbv.com THE FIRST INJECTABLE IMPLANT THAT CAN COMPETE
A Simplified Urinary Incontinence Score for the Evaluation of Treatment Outcomes
 Neurourology and Urodynamics 19:127 135 (2000) A Simplified Urinary Incontinence Score for the Evaluation of Treatment Outcomes Asnat Groutz, Jerry G. Blaivas,* and Jarrod E. Rosenthal Weill Medical College,
Neurourology and Urodynamics 19:127 135 (2000) A Simplified Urinary Incontinence Score for the Evaluation of Treatment Outcomes Asnat Groutz, Jerry G. Blaivas,* and Jarrod E. Rosenthal Weill Medical College,
BJU International (2002), 89,
 BJU International (22), 89, 714 719 Biofeedback vs verbal feedback as learning tools for pelvic muscle exercises in the early management of urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy D.L. FLORATOS*,
BJU International (22), 89, 714 719 Biofeedback vs verbal feedback as learning tools for pelvic muscle exercises in the early management of urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy D.L. FLORATOS*,
Urethral Carcinoma Recurrence in Ileal Orthotopic Neobladder: Urethrectomy and Conversion in a Continent Pouch with Abdominal Stoma
 Case Report Urol Int 1999;62:213 216 Received: June 19, 1998 Accepted after revision: March 8, 1999 Urethral Carcinoma Recurrence in Ileal Orthotopic Neobladder: Urethrectomy and Conversion in a Continent
Case Report Urol Int 1999;62:213 216 Received: June 19, 1998 Accepted after revision: March 8, 1999 Urethral Carcinoma Recurrence in Ileal Orthotopic Neobladder: Urethrectomy and Conversion in a Continent
Fix your incontinence Find your happiness. Restore your normalcy. Renew your confidence. Male stress urinary incontinence
 Fix your incontinence Find your happiness. Restore your normalcy. Renew your confidence. Male stress urinary incontinence Understanding your condition What is incontinence? Incontinence is defined as any
Fix your incontinence Find your happiness. Restore your normalcy. Renew your confidence. Male stress urinary incontinence Understanding your condition What is incontinence? Incontinence is defined as any
Blue Ridge Urogynecology
 Surgery for Stress Urinary Incontinence Surgery has proved to be a very effective treatment for stress incontinence. The best surgical procedures improve or cure the incontinence in 85 to 90 percent of
Surgery for Stress Urinary Incontinence Surgery has proved to be a very effective treatment for stress incontinence. The best surgical procedures improve or cure the incontinence in 85 to 90 percent of
Pelvic floor muscle training to improve urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy: a systematic review of effectiveness
 Urological Oncology PELVIC-FLOOR MUSCLE TRAINING AND INCONTINENCE AFTER RP MACDONALD et al. Pelvic floor muscle training to improve urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy: a systematic review
Urological Oncology PELVIC-FLOOR MUSCLE TRAINING AND INCONTINENCE AFTER RP MACDONALD et al. Pelvic floor muscle training to improve urinary incontinence after radical prostatectomy: a systematic review
Early Recovery of Urinary Continence After Radical Prostatectomy Using Early Pelvic Floor Electrical Stimulation and Biofeedback Associated Treatment
 Early Recovery of Urinary Continence After Radical Prostatectomy Using Early Pelvic Floor Electrical Stimulation and Biofeedback Associated Treatment Gianna Mariotti, Alessandro Sciarra,* Alessandro Gentilucci,
Early Recovery of Urinary Continence After Radical Prostatectomy Using Early Pelvic Floor Electrical Stimulation and Biofeedback Associated Treatment Gianna Mariotti, Alessandro Sciarra,* Alessandro Gentilucci,
POTENCY, CONTINENCE AND COMPLICATIONS IN 3,477 CONSECUTIVE RADICAL RETROPUBIC PROSTATECTOMIES
 0022-5347/04/1726-2227/0 Vol. 172, 2227 2231, December 2004 THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION DOI: 10.1097/01.ju.0000145222.94455.73 POTENCY, CONTINENCE
0022-5347/04/1726-2227/0 Vol. 172, 2227 2231, December 2004 THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION DOI: 10.1097/01.ju.0000145222.94455.73 POTENCY, CONTINENCE
The impact of androgen deprivation on artificial urinary sphincter outcomes
 Original Article The impact of androgen deprivation on artificial urinary sphincter outcomes George C. Bailey 1, Brian J. Linder 1, Marcelino E. Rivera 1, Matthew J. Ziegelmann 1, Laureano J. Rangel 2,
Original Article The impact of androgen deprivation on artificial urinary sphincter outcomes George C. Bailey 1, Brian J. Linder 1, Marcelino E. Rivera 1, Matthew J. Ziegelmann 1, Laureano J. Rangel 2,
Policy #: 213 Latest Review Date: September 2012
 Name of Policy: Temporary Prostatic Stent Policy #: 213 Latest Review Date: September 2012 Category: Medicine Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and updates.
Name of Policy: Temporary Prostatic Stent Policy #: 213 Latest Review Date: September 2012 Category: Medicine Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and updates.
ELUTS Meeting 2018 Programme EAU Section of Genito-Urinary Reconstructive Surgeons (ESGURS)
 Friday, 21 September ELUTS Meeting 2018 Programme EAU Section of Genito-Urinary Reconstructive Surgeons (ESGURS) 08.15 08.30 Opening and welcome Room Brown 3 08.30 10.00 Urethral surgery standards of care
Friday, 21 September ELUTS Meeting 2018 Programme EAU Section of Genito-Urinary Reconstructive Surgeons (ESGURS) 08.15 08.30 Opening and welcome Room Brown 3 08.30 10.00 Urethral surgery standards of care
Urethral pressure measurement in stress incontinence: does it help?
 Int Urol Nephrol (2009) 41:491 495 DOI 10.1007/s11255-008-9506-9 UROLOGY - ORIGINAL PAPER Urethral pressure measurement in stress incontinence: does it help? Bassem S. Wadie Æ Ahmed S. El-Hefnawy Received:
Int Urol Nephrol (2009) 41:491 495 DOI 10.1007/s11255-008-9506-9 UROLOGY - ORIGINAL PAPER Urethral pressure measurement in stress incontinence: does it help? Bassem S. Wadie Æ Ahmed S. El-Hefnawy Received:
THE LONG-TERM SOLUTION FOR MALE INCONTINENCE
 THE LONG-TERM SOLUTION FOR MALE INCONTINENCE Urogyn BV Transistorweg 5a 6534 AT Nijmegen The Netherlands t +31(0) 24 711 41 30 info@urogynbv.com www.urogynbv.com THE FIRST INJECTABLE IMPLANT THAT CAN COMPETE
THE LONG-TERM SOLUTION FOR MALE INCONTINENCE Urogyn BV Transistorweg 5a 6534 AT Nijmegen The Netherlands t +31(0) 24 711 41 30 info@urogynbv.com www.urogynbv.com THE FIRST INJECTABLE IMPLANT THAT CAN COMPETE
Effectiveness of Early Pelvic Floor RehabilitationTreatment for Post-Prostatectomy Incontinence
 European Urology European Urology 48 (2005) 734 738 Effectiveness of Early Pelvic Floor RehabilitationTreatment for Post-Prostatectomy Incontinence Maria Teresa Filocamo, Vincenzo Li Marzi*, Giulio Del
European Urology European Urology 48 (2005) 734 738 Effectiveness of Early Pelvic Floor RehabilitationTreatment for Post-Prostatectomy Incontinence Maria Teresa Filocamo, Vincenzo Li Marzi*, Giulio Del
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 56 (2009)
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 56 (2009) 923 927 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Platinum Priority Incontinence Editorial by Drogo K. Montague on pp. 934 935 of this issue
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 56 (2009) 923 927 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Platinum Priority Incontinence Editorial by Drogo K. Montague on pp. 934 935 of this issue
Morbidity Audit and Logbook Tool SNOMED Board Reporting Terms for SET and IMG Urology ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT
 ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT Cystolitholapaxy Cystoscopic removal of foreign body from bladder Cystoscopic removal of ureteric stent Cystoscopy and cystodiathermy Cystoscopy and transurethral biopsy
ENDOSCOPIC LOWER URINARY TRACT Cystolitholapaxy Cystoscopic removal of foreign body from bladder Cystoscopic removal of ureteric stent Cystoscopy and cystodiathermy Cystoscopy and transurethral biopsy
Title:Transurethral Cystolitholapaxy with the AH -1 Stone Removal System for the Treatment of Bladder Stones of Variable Size
 Author's response to reviews Title:Transurethral Cystolitholapaxy with the AH -1 Stone Removal System for the Treatment of Bladder Stones of Variable Size Authors: Aihua Li (Li121288@aliyun.com) Chengdong
Author's response to reviews Title:Transurethral Cystolitholapaxy with the AH -1 Stone Removal System for the Treatment of Bladder Stones of Variable Size Authors: Aihua Li (Li121288@aliyun.com) Chengdong
Understanding your treatment options for male stress urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction
 Understanding your treatment options for male stress urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction Male Stress Urinary Incontinence and Erectile Dysfunction What causes male stress urinary incontinence
Understanding your treatment options for male stress urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction Male Stress Urinary Incontinence and Erectile Dysfunction What causes male stress urinary incontinence
Current Indications for the Use of The Artificial Genitourinary Sphincter and Management of It s Complications
 Article TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2004) 4 (S1), 114 127 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2004.57 Current Indications for the Use of The Artificial Genitourinary Sphincter and Management of It s Complications
Article TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2004) 4 (S1), 114 127 ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2004.57 Current Indications for the Use of The Artificial Genitourinary Sphincter and Management of It s Complications
CASES FOR TRAINING OF THE INTERNATIONAL SPINAL CORD INJURY LOWER URINARY TRACT FUNCTION BASIC DATA SET CASE 1
 1 CASES FOR TRAINING OF THE INTERNATIONAL SPINAL CORD INJURY LOWER URINARY TRACT FUNCTION BASIC DATA SET CASE 1 35 years old man, who previously has been completely healthy, was shot twice in the neck
1 CASES FOR TRAINING OF THE INTERNATIONAL SPINAL CORD INJURY LOWER URINARY TRACT FUNCTION BASIC DATA SET CASE 1 35 years old man, who previously has been completely healthy, was shot twice in the neck
Index. urologic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Ablative therapies, transurethral needle ablation, Adverse events, sexual side effects of BPH Aging, and incidence of BPH associated with
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Ablative therapies, transurethral needle ablation, Adverse events, sexual side effects of BPH Aging, and incidence of BPH associated with
