Research Article Ultrasound Thickness of Bladder Wall in Continent and Incontinent Women and Its Correlation with Cystometry
|
|
|
- Hilary Cameron
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 e Scientific World Journal, Article ID , 5 pages Research Article Ultrasound Thickness of Bladder Wall in Continent and Incontinent Women and Its Correlation with Cystometry Edney Norio Otsuki, 1 Edward Araujo Júnior, 2 Emerson Oliveira, 3 Marair Gracio Ferreira Sartori, 1 Manoel João Batista Castelo Girão, 1 and Zsuzsanna Ilona Katalin Jármy-Di Bella 1 1 DepartmentofGynecology,EscolaPaulistadeMedicina-FederalUniversityofSão Paulo (EPM-UNIFESP), São Paulo, SP, Brazil 2 Department of Obstetrics, Escola Paulista de Medicina-Federal University of São Paulo (EPM-UNIFESP), São Paulo, SP, Brazil 3 Department of Gynecology and Obstetrics, Faculty of Medicine of ABC, Santo André, SP, Brazil Correspondence should be addressed to Edward Araujo Júnior; araujojred@terra.com.br Received 16 July 2014; Revised 27 September 2014; Accepted 7 October 2014; Published 4 November 2014 Academic Editor: Antonio Macciò Copyright 2014 Edney Norio Otsuki et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Objective. To compare bladder wall thickness in two kinds of urinary incontinent women stress urinary incontinence (SUI) and overactive bladder (OAB) with urodynamic detrusor overactivity (DO), and to compare them with continent patients by ultrasound, also, correlate with cystometric results in incontinent women. Methods. 91 women were divided into the following groups: continent (n = 31),SUI(n = 30),andDO(n = 30) groups after clinical evaluation and urodynamic test (only in incontinent women). Transvaginal ultrasound was performed to the bladder wall thickness (BWT) measurement. The mean of BWT was calculated and data were analyzed with ANOVA and Turkey s multiple comparison tests. Pearson s correlation coefficient (r)was used to compare two variables. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was performed to study BWT as a diagnostic parameter. Results. BWT in DO group was significantly higher than that in the other groups (P < 0.005). A moderate positive correlation was found between BWT and maximum bladder pressure during involuntary bladder contraction. There was no difference in BWT between SUI and continent groups. DO group had lower first desire to void and cystometric capacity. Maximum bladder pressure at detrusor contraction had a moderate positive correlation with BWT. The ROC revealed an area under the curve of (95% CI, ). Conclusions. DO patients have increased bladder wall thickness, lower first desire to void, and lower cystometric capacity. There was a moderate correlation between BWT and maximum bladder pressure during involuntary bladder contraction. 1. Introduction Urinary incontinence is a common health problem associated with poor perception of personal health, impairment of quality of life, social isolation, and symptoms of depression [1]. The most common subtypes of urinary incontinence are stress urinary incontinence (SUI), with leakage of urine during effort or physical exertion, and urgency urinary incontinence with the complaint of involuntary loss of urine associated with urgency (OAB) [2]. The diagnosis in primary care can be done just based on patient s complaints, or exams may be requested to further investigate the symptoms. Urodynamic test tries to reproduce the situation in which patients complaints occur and therefore is considered an extension of patient history and physical examination in a controlled setting; however, it is not a mandatory exam for incontinence diagnosis [3]. Detrusor overactivity (DO) is an urodynamic observation defined by involuntary detrusor contractions during the filling phase, which may be spontaneous or may be provoked. It is detectable in about half of the patients with OAB submitted to urodynamic test [4]. Ultrasound is a diagnostic method that is very much a part of general practice in obstetrics and gynecology and its role in urogynecology has increasing importance [5, 6].
2 2 The Scientific World Journal 1 Bladder 1 2 (a) (b) Figure1:Two-dimensional transvaginalultrasound. (a) Measurement of anterior wall thickness of bladder (1). (b) Measurement of thickness wall in trigone bladder (1); measurement of thickness wall in dome bladder. When compared to other imaging exams, it is less invasive, nonradioactive, inexpensive, and widely available. In addition, ultrasound is the gold standard for measuring bladder volume and postvoiding residue, and it allows dynamic assessment of pelvic structures [7, 8]. Bladder wall thickness (BWT) has been studied in incontinent patients and those with OAB especially those with DO who show higher values [9]. Farag and Heesakkers [10], in a literature review, compared the various pathways of ultrasound to measure the BWT and they concluded that the study of BWT by transvaginal transducer is more appropriate. Oelke et al. [11] compared the measurement of BWT obtained by conventional ultrasound with the automatic measurement performed by the BVM 6500 device. Although both show good reproducibility, the conventional measurement showed the smallest variation and it was more reliable. Kuhn et al. [12], comparing different ways to perform ultrasound to measure the BWT, found that vaginal measurement was more reliable than abdominal or perineal assessment. The objective of this study was to compare the BWT in two kinds of urinary incontinent women, SUI and OAB with DO, and compare them with continent patients by transvaginal ultrasound, also, correlate with cystometric results in incontinent women. 2. Material and Methods In a tertiary referral ambulatory, we selected women who were continent or with SUI or OAB. The study was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Federal University of São Paulo (UNIFESP), and the volunteer women who agreed to participate gave consent form. We included continent women with gynecological diseases or conditions other than urinary incontinence like miomas or adnexial cists. Patients with mixed urinary incontinence, lower urinary tract diseases, bladder outlet obstruction, previous surgery for urinary incontinence, and current or recurrent urinary tract infection were not included. All patients were examined and pelvic organ prolapse quantification (POP-Q) was determined. Urodynamic test was performed before inclusion in this study and it followed the International Continence Society (ICS) recommendations using Dynapack MPX 816 four-channel urodynamic system (Dynamed, Sao Paulo, Brazil). The clinical diagnosis had to match the urodynamic test result. Women were asked to void. Then, in supine position, ultrasound exam was performed using a SA-9900 (Samsung, Seoul, Korea) ultrasound machine equipped with a multifrequential transvaginal transducer (4 9 MHz). Using the method described by Haylen et al. [13], the residual volume wascalculatedtoensurethatitwas<50 ml. The bladder wasvisualizedinthesagittalplaneandthentheprobewas laterally moved 1 cm to achieve a clear view of the bladder and directed cranially to image the bladder in the parasagittal plane. At maximal magnification, the measurements were made perpendicular to the luminal surface of the bladder in the thickest part of trigone, dome of the bladder, and anterior wall of the bladder (Figure 1). BWT was considered the mean value of these three measurements. All exams were performed by the same physician (ENO, urogynecologist) who was also blinded to the incontinence diagnosis. The data were transferred to the spreadsheet program Excel 2007 (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, USA) and the statistical analysis was performed with GraphPad Prism version 5.0 for Windows (GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA). Analysis of variance (ANOVA) or Student s t-test was used to compare continuous variables. Post hoc multiple comparisons were performed using the Tukey s multiple comparison tests. Pearson s chi-squared test (χ 2 )wasused to compare categorical variables. Mann-Whitney U test was applied to compare two independent random samples. Pearson s correlation coefficient (r) was used to compare linear dependence between two variables. In all analyses, we used a significance level of P < Results A total of 91 patients with age between 18 and 81 were included in this study. Of these, 31 were continent, 30 had SUI, and 30 had urgency urinary incontinence (OAB with DO). Clinical characteristics of the groups are listed in Table 1. There was no difference in age (P = 0.258), hormonal status (P = 0.412), body mass index (P = 0.474), parity (P = 0.492),
3 The Scientific World Journal 3 Table 1: Clinical characteristics of the patients. Variable N =91 Age 50.5 ± Menopause 51 (56) BMI ± 5.63 Parity 3.29 ± 2.88 Data presented as mean ± SD; data in parenthesis are percentages. BMI: body mass index. BWT (mm) BWT (mm) Maximum vesical pressure at IDC (cmh 2 O) Figure 3: Scatter plot of correlation between bladder wall thickness (BWT) and maximum vesical pressure at involuntary detrusor contraction (IDC). 0 Continent SUI DO P = Figure 2: Boxplot of the bladder wall thickness (BWT) according to the groups. SUI: stress urinary incontinence; DO: detrusor overactivity. or POP-Q (P = 0.738) among the groups. Postvoid residual ranged from 0 to 40 ml. BWT was higher in detrusor overactivity group and significantly different compared to SUI and continent groups (P = 0.005). There was no difference between SUI and continent groups (Figure 2). In Table 2, urodynamic findings are listed. In SUI group, 3 patients had intrinsic sphincter deficiency. In DO group, first desire to void and maximum cystometric capacity were significantly lower compared to SUI results. The linear dependence in SUI group between BWT and first desire to void (r = 0.16, P = 0.216), volume at leakage (r = 0.10, P = 0.304), and maximum cystometric capacity (r = 0.01, P = 0.462) was not significant. Concerning OAB group, there was a moderate positive correlation between BWT and maximum vesical pressure at involuntary detrusor contraction (r = 0.39, P = 0.017) (Figure 3). There was no significant correlation between BWT andfirstdesiretovoid(r = 0.14, P = 0.242) andmaximum cystometric capacity (r = 0.10, P = 0.308). 4. Discussion The diagnosis of the type of incontinence only with the clinical assessment of patients can mislead to the right treatment. It is not uncommon that patients with OAB have involuntary detrusor contractions triggered by stress maneuver such as coughing or sneezing. In these cases, particularly, Giarenis et al. [14] observed worse efficacy with tolterodine than women with involuntary detrusor contractions during cystometric filling phase of urodynamic test. It takes a good amount of self-perception to tell if the urinary loss is caused by sudden increase in intraabdominal pressure or by a detrusor contraction. Also, different diseases share common lower urinary tract symptoms and many times a consistent diagnosis is not reached [3, 15, 16]. Questionnaires of quality of life, bladder diaries, and visual analog scales are valuable to expand the understanding and bothersome of the symptoms but provide only subjective data. Currently, when clinical assessment of urinary incontinence is compared to urodynamic test, there is lack of a gold standard [17]. Clarke [18] considered the urodynamic test inappropriate to diagnose and introduced treatment based only in symptoms, as he found DO in 64% of the patients with SUI. Urodynamic test can provide valuable information of the underlying pathophysiology, but its intra- and interobserver reproducibility is not good [19, 20]. Healthy patients have BWT measurement ranging from 3 to 5 mm [21]. Conditions such as infection, pelvic radiation, pelvic surgery, neurological disease, cancer, and bladder outlet obstruction can cause thickening of the bladder wall associated to other sonographic signals [22]. The study of BWT has brought the question if it is possible to diagnose OAB by a cut-off value measured by ultrasound. Khullar and Cardozo [23] proposed 5mm as a cut-off value to discriminate detrusor overactivity, while Robinson et al. [5] considered 6 mm to the diagnose of OAB in patients without evidence of SUI. Kuhn et al. [24] withacut-offvalueof 5.6 mm found sensitivity of 83.3% and specificity of 87.5% in distinguishing between OAB and bladder obstruction. Serati et al. [25] compared BWT in different forms of incontinence and concluded that a cut-off value of 6.5 mm could distinguish patients with detrusor overactivity, pure or associatedwithsui,butitcouldnotreplaceurodynamictest.
4 4 The Scientific World Journal Table 2: Urodynamic findings in women with stress urinary incontinence (SUI) or overactive bladder (OAB) with detrusor overactivity (DO). Variable SUI (n =31) DO(n =30) P value Volume at first desire to void (ml) ± ± Maximum cystometric capacity (ml) ± ± <0.001 Valsalva leak point pressure (cmh 2 O) 87.7 ± Volume at leakage (ml) ± Cystometric volume at first IDC (ml) ± Maximum vesical pressure at IDC (cmh 2 O) ± 19.8 Data presented as mean ± SD; data in parenthesis are percentages. IDC: involuntary detrusor contraction. Student s t-test. An important question is if we are looking to the right point. The diagnosis of DO is controversy. DO is present in only 40 60% of the OAB patients [26]. Although urodynamic test is the only method to its diagnosis, the interobserver variation in evaluation of the same exam is high [27]. DO is not exclusive of OAB patients; asymptomatic patients may present DO during urodynamic test when the saline solution is instilled very fast or too cold. It is unknown if involuntary detrusor contraction is the cause of urgency at storage phase or that other types of lower urinary tract dysfunction can cause OAB complaints [28]. Normal bladder physiology includes phasic contractions of low magnitude with frequency of dozens per minute, thus promoting a better adjustment of the bladder surface to urine filling [29]. The detrusor of OAB patients presents biochemical changes, which have different cellular ultrastructure and tissue macrostructure leading to more contractility and resulting in hypertrophy of the detrusor muscle [30]. Using ICS s definition of OAB syndrome, based only on symptoms, can lead to a heterogeneous group, as women with different physiopathologies present with the core complaint of urinary urgency. In a different approach, we aimed to study a homogeneous group only including women who not only complained of urgency, but were also incontinent and with presence of DO at urodynamic test. Women with DO experience more significant impairment to their quality of life and have a greater degree of bladder dysfunction [31]. Our finding of higher values of BWT associated with higher vesical pressure at involuntary detrusor contraction concurs with the background of OAB. Also, there was a moderate positive relation between intensity of OAB and BWT. We decided not to include patients with mixed urinary incontinence because of the difficulty to determine the amount of troublesome of each component of this group. The time lapse necessary to increase the BWT from normal values is a question that remains without response. To our knowledge, it is not demonstrated yet. According to the definition of OAB suggested by the ICS, the need to detect DO loses importance. On the other hand, it seems that increased BWT, as a result of repeated DO, is linked to clinical symptoms, as Panayi et al. [32] observed that women with BWT greater than 5 mm had a visual analog scale of urgency significantly higher when compared to controls. In a recent article, Abou-Gamrah et al. [33] found 4.78 mm of BWT the best cut-off value for prediction of OAB in patients with lower urinary tract symptoms. As a diagnostic tool of urinary incontinence, we agree that BWT cannot replace urodynamic test. Nonetheless, our findings encouraged us to consider it as an index of detrusor activity. One of the strengths of this paper is the observation that the BWT of the SUI patients and that of normal women are similar and significantly thinner than that of the DO patients, the most severe form of OAB. For our knowledge this is the first study that observed the BWT in SUI. The urodynamic evaluation in incontinent women and correlation with ultrasound findings are also the strengths of this paper. On the otherhand,theweaknessofthispaperwasthatwedidnot investigate BWT of mixed urinary incontinence patients. In summary, we believe that the thickening of the bladder wall is itself an important hallmark in OAB patients mainly when the clinic is not compatible with urodynamic test or in women not responsive to anticholinergics. Conflict of Interests The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this paper. References [1]P.Abrams,L.Cardozo,M.Falletal., Thestandardisationof terminology of lower urinary tract function: report from the standardisation sub-committee of the international continence society, Neurourology and Urodynamics,vol.21,no.2,pp , [2] P. L. Dwyer, Differentiating stress urinary incontinence from urge urinary incontinence, International Gynecology &Obstetrics,vol.86,pp.S17 S24,2004. [3] J. P. Heesakkers and J. L. Vriesema, The role of urodynamics in the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms in women, Current Opinion in Urology,vol.15,no.4,pp ,2005. [4] G.A.Digesu,V.Khullar,L.Cardozo,andS.Salvatore, Overactive bladder symptoms: do we need urodynamics? Neurourology and Urodynamics,vol.22,pp ,2003. [5] D. Robinson, K. Anders, L. Cardozo, J. Bidmead, P. Toozs- Hobson, and V. Khullar, Can ultrasound replace ambulatory urodynamics when investigating women with irritative urinary symptoms? British Obstetrics and Gynaecology, vol. 109, no. 2, pp , [6] H. P. Dietz, Pelvic floor ultrasound: a review, The American Obstetrics and Gynecology,vol.202,no.4,pp , 2010.
5 The Scientific World Journal 5 [7]S.Athanasiou,C.Chaliha,P.Toozs-Hobson,S.Salvatore,V. Khullar, and L. Cardozo, Direct imaging of the pelvic floor muscles using two-dimensional ultrasound: a comparison of women with urogenital prolapse versus controls, BJOG: An International Obstetrics & Gynaecology, vol.114,no. 7, pp , [8] M. Serati, S. Salvatore, S. Uccella et al., Urinary incontinence at orgasm: relation to detrusor overactivity and treatment efficacy, European Urology,vol.54,no.4,pp ,2008. [9] V. Khullar, S. Salvatore, L. Cardozo et al., A novel technique for measuring bladder wall thickness in women using transvaginal ultrasound, Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology, vol.4,pp , [10] F. F. Farag and J. P. Heesakkers, Non-invasive techniques in the diagnosis of bladder storage disorders, Neurourology and Urodynamics,vol.30,no.8,pp ,2011. [11] M. Oelke, C. Mamoulakis, D. T. Ubbink, J. J. de La Rosette, and H. Wijkstra, Manual versus automatic bladder wall thickness measurements: a method comparison study, World Urology,vol.27,no.6,pp ,2009. [12] A. Kuhn, S. Bank, D. Robinson, M. Klimek, P. Kuhn, and L. Raio, How should bladder wall thickness be measured? A comparison of vaginal, perineal and abdominal ultrasound, Neurourology and Urodynamics, vol.29,no.8,pp , [13] B. T. Haylen, D. de Ridder, R. M. Freeman et al., An International Urogynecological Association (IUGA)/International Continence Society (ICS) joint report on the terminology for female pelvic floor dysfunction, Neurourology and Urodynamics,vol.29,pp.4 20,2010. [14] I.Giarenis,H.Mastoroudes,S.Srikrishna,D.Robinson,andL. Cardozo, Is there a difference between women with or without detrusor overactivity complaining of symptoms of overactive bladder? BJU International, vol. 112, no. 4, pp , [15] J.G.Blaivas, Thebladderisanunreliablewitness, Neurourology and Urodynamics, vol. 15, no. 5, pp , [16] G. Matharu, M. M. K. Donaldson, C. W. McGrother, and R. J. Matthews, Relationship between urinary symptoms reported in a postal questionnaire and urodynamic diagnosis, Neurourology and Urodynamics,vol.24,no.2,pp ,2005. [17] E. Colli, W. Artibani, J. Goka, F. Parazzini, and A. J. Wein, Are urodynamic tests useful tools for the initial conservative management of non-neurogenic urinary incontinence? A review of the literature, European Urology, vol. 43, no. 1, pp , [18] B. Clarke, The role of urodynamic assessment in the diagnosis of lower urinary tract disorders, International Urogynecology Journal and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, vol.8,no.4,pp , [19] J. P. Theofrastous, J. Whiteside, and M. F. R. Paraiso, The utility of urodynamic testing, the American Association of Gynecologic Laparoscopists,vol.10,no.4,pp ,2003. [20] A. Gupta, G. Defreitas, and G. E. Lemack, The reproducibility of urodynamic findings in healthy female volunteers: results of repeated studies in the same setting and after short-term followup, Neurourology and Urodynamics, vol. 23, no. 4, pp , [21] S. H. Kim, J. Y. Cho, H. J. Lee, C. K. Sung, and S. H. Kim, Ultrasound of the urinary bladder, revisited, Medical Ultrasound,vol.15,no.2,pp.77 90,2007. [22] L. H. Tseng, Ultrasound in urogynecology: an update on clinical application, Medical Ultrasound, vol.15,no. 1, pp , [23] V. Khullar and L. Cardozo, Imaging in urogynaecology, British Obstetrics and Gynaecology,vol.103,no.11,pp , [24] A. Kuhn, S. Genoud, D. Robinson et al., Sonographic transvaginal bladder wall thickness: does the measurement discriminate between urodynamic diagnoses? Neurourology and Urodynamics,vol.30,no.3,pp ,2011. [25] M.Serati,S.Salvatore,E.Cattoni,M.Soligo,A.Cromi,andF. Ghezzi, Ultrasound measurement of bladder wall thickness in different forms of detrusor overactivity, International Urogynecology Journal and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction, vol. 21, no. 11, pp , [26] J.-J. Wyndaele, T. D. van Meel, and S. de Wachter, Detrusor overactivity. Does it represent a difference if patients feel the involuntary contractions? The Urology, vol.172,no. 5, pp , [27] A. Renganathan, R. Cartwright, L. Cardozo, D. Robinson, and S. Srikrishna, Quality control in urodynamics: analysis of an international multi-center study, Neurourology and Urodynamics, vol. 28, no. 5, pp , [28] A. J. Wein, E. S. Rovner, D. R. Staskin, K.-E. Andersson, and J. G. Ouslander, Definition and epidemiology of overactive bladder, Urology,vol.60,no.5,pp.7 12,2002. [29] G. N. A. Sibley, A comparison of spontaneous and nervemediated activity in bladder muscle from man, pig and rabbit, Physiology,vol.354,pp ,1984. [30] A. F. Brading, Spontaneous activity of lower urinary tract smooth muscles: correlation between ion channels and tissue function, The Physiology, vol.570,no.1,pp.13 22, [31] S.Salvatore,M.Serati,G.A.Digesuetal., Efficacyoftolterodine in relation to different urodynamic findings of detrusor overactivity, International Urogynecology Journal and Pelvic Floor Dysfunction,vol.19,no.5,pp ,2008. [32] D. C. Panayi, P. Tekkis, R. Fernando, C. Hendricken, and V. Khullar, Ultrasound measurement of bladder wall thickness is associated with the overactive bladder syndrome, Neurourology and Urodynamics,vol.29,no.7,pp ,2010. [33] A. Abou-Gamrah, M. Fawzy, H. Sammour, and S. Tadros, Ultrasound assessment of bladder wall thickness as a screening test for detrusor instability, Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics,vol.289,no.5,pp ,2014.
6 MEDIATORS of INFLAMMATION The Scientific World Journal Gastroenterology Research and Practice Diabetes Research International Endocrinology Immunology Research Disease Markers Submit your manuscripts at BioMed Research International PPAR Research Obesity Ophthalmology Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Stem Cells International Oncology Parkinson s Disease Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine AIDS Behavioural Neurology Research and Treatment Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity
Clinical Study Predictors of Response to Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin-A Injections in Patients with Idiopathic Overactive Bladder
 Advances in Urology Volume 2009, Article ID 328364, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/328364 Clinical Study Predictors of Response to Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin-A Injections in Patients with Idiopathic Overactive
Advances in Urology Volume 2009, Article ID 328364, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/328364 Clinical Study Predictors of Response to Intradetrusor Botulinum Toxin-A Injections in Patients with Idiopathic Overactive
PRE-OPERATIVE URODYNAMIC
 PRE-OPERATIVE URODYNAMIC STUDIES: IS THERE VALUE IN PREDICTING POST-OPERATIVE STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN UNDERGOING PROLAPSE SURGERY? Dr K Janse van Rensburg Dr JA van Rensburg INTRODUCTION POP
PRE-OPERATIVE URODYNAMIC STUDIES: IS THERE VALUE IN PREDICTING POST-OPERATIVE STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE IN WOMEN UNDERGOING PROLAPSE SURGERY? Dr K Janse van Rensburg Dr JA van Rensburg INTRODUCTION POP
OAB score: A clinical model that predicts the probability of presenting overactive detrusor in the urodynamic study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 44 (2): 348-354, March - Abril, 2018 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2017.0213 OAB score: A clinical model that predicts the probability of presenting overactive detrusor in the urodynamic
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 44 (2): 348-354, March - Abril, 2018 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2017.0213 OAB score: A clinical model that predicts the probability of presenting overactive detrusor in the urodynamic
Management of Female Stress Incontinence
 Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
Management of Female Stress Incontinence Dr. Arvind Goyal Associate Professor (Urology& Renal Transplant) Dayanand Medical College & Hospital, Ludhiana, Punjab, India Stress Incontinence Involuntary loss
Urodynamic findings in women with insensible incontinence
 bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2013) 20, 429 433 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03146.x Original Article: Clinical Investigation Urodynamic findings in women with insensible Benjamin M Brucker,
bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2013) 20, 429 433 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2012.03146.x Original Article: Clinical Investigation Urodynamic findings in women with insensible Benjamin M Brucker,
Clinical Study Cough Test during Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Preventing Postoperative Urinary Retention
 Advances in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 797854, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/797854 Clinical Study Cough Test during Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Preventing Postoperative Urinary
Advances in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 797854, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/797854 Clinical Study Cough Test during Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure in Preventing Postoperative Urinary
CommonKnowledge. Pacific University. Gina Clark Pacific University. Lauren Murphy Pacific University. Recommended Citation.
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge PT Critically Appraised Topics School of Physical Therapy 2012 The diagnostic accuracy of patient subjective history compared to the gold standard of urodynamic testing
Pacific University CommonKnowledge PT Critically Appraised Topics School of Physical Therapy 2012 The diagnostic accuracy of patient subjective history compared to the gold standard of urodynamic testing
URINARY INCONTINENCE. Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 URINARY INCONTINENCE Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition The involuntary loss of urine May denote a symptom, a sign or a condition Symptom the
URINARY INCONTINENCE Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Definition The involuntary loss of urine May denote a symptom, a sign or a condition Symptom the
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence. Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations
 The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
The Management of Female Urinary Incontinence Part 1: Aetiology and Investigations Dr Oseka Onuma Gynaecologist and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgeon 4 Robe Terrace Medindie SA 5081 Urinary incontinence has
Research Article Urinary Catheterization May Not Adversely Impact Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
 ISRN Neurology, Article ID 167030, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/167030 Research Article Urinary Catheterization May Not Adversely Impact Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Rebecca
ISRN Neurology, Article ID 167030, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/167030 Research Article Urinary Catheterization May Not Adversely Impact Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Rebecca
Urodynamics in women. Aims of Urodynamics in women. Why do Urodynamics?
 Urodynamics in women Chendrimada Madhu MD, MA, MRCOG Subspecialty Trainee in Urogynaecology Southmead Hospital 2013 Aims of Urodynamics in women n Confirmation of incontinence and its cause n Definition
Urodynamics in women Chendrimada Madhu MD, MA, MRCOG Subspecialty Trainee in Urogynaecology Southmead Hospital 2013 Aims of Urodynamics in women n Confirmation of incontinence and its cause n Definition
Urogynecology in EDS. Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018
 Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment
 Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
The new International Continence Society
 ROLE OF CYSTOMETRY IN EVALUATING PATIENTS WITH OVERACTIVE BLADDER ADAM J. FLISSER AND JERRY G. BLAIVAS ABSTRACT Overactive bladder (OAB) can be caused by a variety of conditions. We believe that cystometrography
ROLE OF CYSTOMETRY IN EVALUATING PATIENTS WITH OVERACTIVE BLADDER ADAM J. FLISSER AND JERRY G. BLAIVAS ABSTRACT Overactive bladder (OAB) can be caused by a variety of conditions. We believe that cystometrography
Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh Repair: A Prospective Study of 105 Cases
 International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
BJUI. Validity and reliability of the patient s perception of intensity of urgency scale in overactive bladder
 ; 2010 Lower Urinary Tract PATIENT S PERCEPTION OF INTENSITY OF URGENCY SCALE IN OAB CARTWRIGHT ET AL. BJUI Validity and reliability of the patient s perception of intensity of urgency scale in overactive
; 2010 Lower Urinary Tract PATIENT S PERCEPTION OF INTENSITY OF URGENCY SCALE IN OAB CARTWRIGHT ET AL. BJUI Validity and reliability of the patient s perception of intensity of urgency scale in overactive
Objectives. Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS
 URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
This Special Report supplement
 ...INTRODUCTION... Overactive Bladder: Defining the Disease Alan J. Wein, MD This Special Report supplement to The American Journal of Managed Care features proceedings from the workshop, Overactive Bladder:
...INTRODUCTION... Overactive Bladder: Defining the Disease Alan J. Wein, MD This Special Report supplement to The American Journal of Managed Care features proceedings from the workshop, Overactive Bladder:
Practical urodynamics What PA s need to know. Gary E. Lemack, MD Professor of Urology and Neurology
 Practical urodynamics What PA s need to know Gary E. Lemack, MD Professor of Urology and Neurology Urodynamics essential elements Urethral catheter Fill rate Catheter size Intravesical pressure measurements
Practical urodynamics What PA s need to know Gary E. Lemack, MD Professor of Urology and Neurology Urodynamics essential elements Urethral catheter Fill rate Catheter size Intravesical pressure measurements
Urinary Incontinence. Lora Keeling and Byron Neale
 Urinary Incontinence Lora Keeling and Byron Neale Not life threatening. Introduction But can have a huge impact on quality of life. Two main types of urinary incontinence (UI). Stress UI leakage on effort,
Urinary Incontinence Lora Keeling and Byron Neale Not life threatening. Introduction But can have a huge impact on quality of life. Two main types of urinary incontinence (UI). Stress UI leakage on effort,
INCONTINENCE. Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation TYPES OF INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE STRESS INCONTINENCE 11/08/2015
 INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
INCONTINENCE Continence and Pelvic Floor Rehabilitation Dr Irmina Nahon PhD Pelvic Floor Physiotherapist www.nahonpfed.com.au Defined as the accidental and inappropriate passage of urine or faeces (ICI
Urodynamics in Neurological Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction. Mr Chris Harding Consultant Urologist Freeman Hospital Newcastle-upon-Tyne
 Urodynamics in Neurological Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Mr Chris Harding Consultant Urologist Freeman Hospital Newcastle-upon-Tyne Learning Objectives Review functional neurology relevant to lower
Urodynamics in Neurological Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Mr Chris Harding Consultant Urologist Freeman Hospital Newcastle-upon-Tyne Learning Objectives Review functional neurology relevant to lower
Original Article. Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine INTRODUCTION
 Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(3):342-346 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.3.342 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Phasic Changes in Bladder Compliance
Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(3):342-346 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.3.342 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Phasic Changes in Bladder Compliance
Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence. Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes
 Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes 66 year old woman with incontinence PC: 7 year Hx of urgency, frequency, nocturia (incl. incontinence at night), and stress incontinence
Prolapse and Urogynae Incontinence Lucy Tiffin and Hannah Wheldon-Holmes 66 year old woman with incontinence PC: 7 year Hx of urgency, frequency, nocturia (incl. incontinence at night), and stress incontinence
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence in women: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence in women
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence in women: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence in women
Mr. GIT KAH ANN. Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur.
 Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
The Evidence for Antimuscarinic Agents in Female Mixed Urinary Incontinence
 european urology supplements 5 (2006) 849 853 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com The Evidence for Antimuscarinic Agents in Female Mixed Urinary Incontinence Stefano
european urology supplements 5 (2006) 849 853 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com The Evidence for Antimuscarinic Agents in Female Mixed Urinary Incontinence Stefano
Frequency of urinary incontinence with Pelvic organ prolapse and associated factors
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Frequency of urinary incontinence with Pelvic organ prolapse and associated factors Dr. Raheela Mohsin 1, Dr.Ayesha Saba 2, Humera Ismail 3 1 Dr. Raheela Mohsin, Aga Khan University Hospital,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Frequency of urinary incontinence with Pelvic organ prolapse and associated factors Dr. Raheela Mohsin 1, Dr.Ayesha Saba 2, Humera Ismail 3 1 Dr. Raheela Mohsin, Aga Khan University Hospital,
The relationship between urinary symptom questionnaires and urodynamic diagnoses: an analysis of two methods of questionnaire administration
 BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology May 2004, Vol. 111, pp. 468 474 DOI: 1 0. 1111/j.1471-0528.2004.00126.x The relationship between urinary symptom questionnaires and urodynamic
BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology May 2004, Vol. 111, pp. 468 474 DOI: 1 0. 1111/j.1471-0528.2004.00126.x The relationship between urinary symptom questionnaires and urodynamic
Original paper Med Ultrason 2016, Vol. 18, no. 3,
 Original paper Med Ultrason 2016, Vol. 18, no. 3, 345-350 DOI: 10.11152/mu.2013.2066.183.zsu Reproducibility in pelvic floor biometric parameters of nulliparous women assessed by translabial three-dimensional
Original paper Med Ultrason 2016, Vol. 18, no. 3, 345-350 DOI: 10.11152/mu.2013.2066.183.zsu Reproducibility in pelvic floor biometric parameters of nulliparous women assessed by translabial three-dimensional
Various Types. Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG
 Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Various Types Ralph Boling, DO, FACOG The goal of this lecture is to increase assessment and treatment abilities for physicians managing urinary incontinence (UI) patients. 1. Effectively communicate with
Dr. Aso Urinary Symptoms
 Haematuria The presence of blood in the urine (haematuria) is always abnormal and may be the only indication of pathology in the urinary tract. False positive stick tests and the discolored urine caused
Haematuria The presence of blood in the urine (haematuria) is always abnormal and may be the only indication of pathology in the urinary tract. False positive stick tests and the discolored urine caused
Research Article Comparison of Colour Duplex Ultrasound with Computed Tomography to Measure the Maximum Abdominal Aortic Aneurysmal Diameter
 International Vascular Medicine, Article ID 574762, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/574762 Research Article Comparison of Colour Duplex Ultrasound with Computed Tomography to Measure the Maximum
International Vascular Medicine, Article ID 574762, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/574762 Research Article Comparison of Colour Duplex Ultrasound with Computed Tomography to Measure the Maximum
Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion
 Are the Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion the Same for Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence with or without Intrinsic Sphincter Deficiency? A Retrospective Study in Hong Kong
Are the Treatment Outcomes of Tension-free Vaginal Tape Insertion the Same for Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence with or without Intrinsic Sphincter Deficiency? A Retrospective Study in Hong Kong
Involuntary Detrusor Contractions: Correlation of Urodynamic Data to Clinical Categories
 Neurourology and Urodynamics 20:249±257 (2001) Involuntary Detrusor Contractions: Correlation of Urodynamic Data to Clinical Categories Lauri J. Romanzi, Asnat Groutz, Dianne M. Heritz, and Jerry G. Blaivas*
Neurourology and Urodynamics 20:249±257 (2001) Involuntary Detrusor Contractions: Correlation of Urodynamic Data to Clinical Categories Lauri J. Romanzi, Asnat Groutz, Dianne M. Heritz, and Jerry G. Blaivas*
Neurogenic bladder. Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder.
 Definition: Neurogenic bladder Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder. Types: Nervous system diseases: Congenital: like myelodysplasia like meningocele.
Definition: Neurogenic bladder Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder. Types: Nervous system diseases: Congenital: like myelodysplasia like meningocele.
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline
 Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Decidable (Y or N) Inclusion
Adult Urodynamics: American Urological Association (AUA)/Society of Urodynamics, Female Pelvic Medicine & Urogenital Reconstruction (SUFU) Guideline TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Decidable (Y or N) Inclusion
Clinical Study Treatment Strategy According to Findings on Pressure-Flow Study for Women with Decreased Urinary Flow Rate
 Advances in Urology Volume 2009, Article ID 782985, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2009/782985 Clinical Study Treatment Strategy According to Findings on Pressure-Flow Study for Women with Decreased Urinary Flow
Advances in Urology Volume 2009, Article ID 782985, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2009/782985 Clinical Study Treatment Strategy According to Findings on Pressure-Flow Study for Women with Decreased Urinary Flow
Tools for Evaluation. Urodynamics Case Studies. Case 1. Evaluation. Case 1. Bladder Diary SUI 19/01/2018
 Urodynamics Case Studies Christopher K. Payne, MD Vista Urology & Pelvic Pain Partners Emeritus Professor of Urology, Stanford University Tools for Evaluation Ears, Eyes, and Brain Bladder diary Stress
Urodynamics Case Studies Christopher K. Payne, MD Vista Urology & Pelvic Pain Partners Emeritus Professor of Urology, Stanford University Tools for Evaluation Ears, Eyes, and Brain Bladder diary Stress
Urodynamic study before and after radical porstatectomy 가톨릭의대성바오로병원김현우
 Urodynamic study before and after radical porstatectomy 가톨릭의대성바오로병원김현우 Introduction Radical prostatectomy - treatment of choice for patients with localized prostate cancer. Urinary incontinence and/or
Urodynamic study before and after radical porstatectomy 가톨릭의대성바오로병원김현우 Introduction Radical prostatectomy - treatment of choice for patients with localized prostate cancer. Urinary incontinence and/or
What should we consider before surgery? BPH with bladder dysfunction. Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Sung Luck Hee
 What should we consider before surgery? BPH with bladder dysfunction Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Sung Luck Hee Diagnostic tests in three categories Recommendation: there is evidence to support
What should we consider before surgery? BPH with bladder dysfunction Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Sung Luck Hee Diagnostic tests in three categories Recommendation: there is evidence to support
Normal micturition involves complex
 NEW TARGET FOR INTERVENTION: THE NEUROUROLOGY CONNECTION * Donald R. Ostergard, MD, FACOG ABSTRACT Urine storage and release are under the control of the parasympathetic, sympathetic, and somatic nervous
NEW TARGET FOR INTERVENTION: THE NEUROUROLOGY CONNECTION * Donald R. Ostergard, MD, FACOG ABSTRACT Urine storage and release are under the control of the parasympathetic, sympathetic, and somatic nervous
Module 3 Causes Of Urinary Incontinence
 Causes Of Urinary Incontinence V4: Last Reviewed September 2017 Learning Outcomes Appreciate the numerous requirements and skills necessary for the person to achieve and maintain urinary continence Discuss
Causes Of Urinary Incontinence V4: Last Reviewed September 2017 Learning Outcomes Appreciate the numerous requirements and skills necessary for the person to achieve and maintain urinary continence Discuss
Incontinence: Risks, Causes and Care
 Welcome To Incontinence: Risks, Causes and Care Presented by Kamal Masaki, MD Professor and Chair Department of Geriatric Medicine John A. Burns School of Medicine, UH Manoa September 5, 2018 10:00 11:00
Welcome To Incontinence: Risks, Causes and Care Presented by Kamal Masaki, MD Professor and Chair Department of Geriatric Medicine John A. Burns School of Medicine, UH Manoa September 5, 2018 10:00 11:00
Influence of Obesity on Short-term Surgical Outcome of the Transobturator Tape Procedure in Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence
 Urinary Incontinence INJ 2010;14:13-19 Influence of Obesity on Short-term Surgical Outcome of the Transobturator Tape Procedure in Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence Dong-Un Tchey, Won-Tae Kim,
Urinary Incontinence INJ 2010;14:13-19 Influence of Obesity on Short-term Surgical Outcome of the Transobturator Tape Procedure in Patients with Stress Urinary Incontinence Dong-Un Tchey, Won-Tae Kim,
Research Article Predictions of the Length of Lumbar Puncture Needles
 Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, Article ID 732694, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/732694 Research Article Predictions of the Length of Lumbar Puncture Needles Hon-Ping Ma, 1,2
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, Article ID 732694, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/732694 Research Article Predictions of the Length of Lumbar Puncture Needles Hon-Ping Ma, 1,2
Incontinence; Lets talk about it. Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery
 Incontinence; Lets talk about it Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Select the most appropriate subtitle for this talk A: Bladders gone wild! B: There s no such thing
Incontinence; Lets talk about it Karanvir Virk M.D. Minimally Invasive and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Select the most appropriate subtitle for this talk A: Bladders gone wild! B: There s no such thing
Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice
 Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Alan J. Wein Christopher Chapple Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Authors Alan J. Wein Division of Urology University of Pennsylvania Health System Philadelphia
Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Alan J. Wein Christopher Chapple Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Authors Alan J. Wein Division of Urology University of Pennsylvania Health System Philadelphia
Video-urodynamics. P J R Shah Institute of Urology and UCH
 Video-urodynamics P J R Shah Institute of Urology and UCH Bladder Function Storage Capacity and Pressure Emptying Pressure/flow/emptying URODYNAMIC INVESTIGATIONS Free urine flow rate Urethral pressure
Video-urodynamics P J R Shah Institute of Urology and UCH Bladder Function Storage Capacity and Pressure Emptying Pressure/flow/emptying URODYNAMIC INVESTIGATIONS Free urine flow rate Urethral pressure
Urodynamics Mismatch - Should We Listen to the Study, or the Patient?
 Urodynamics Mismatch - Should We Listen to the Study, or the Patient? A Practical Approach to the Diagnosis and Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Victor W. Nitti MD Professor of Urology and
Urodynamics Mismatch - Should We Listen to the Study, or the Patient? A Practical Approach to the Diagnosis and Treatment of Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Victor W. Nitti MD Professor of Urology and
April Clinical Focus Topic URINARY FREQUENCY
 April Clinical Focus Topic URINARY FREQUENCY This month I am focusing on a topic that may seem a little boring. But I would like to look at it from a less common perspective.urinary Frequency and its relationship
April Clinical Focus Topic URINARY FREQUENCY This month I am focusing on a topic that may seem a little boring. But I would like to look at it from a less common perspective.urinary Frequency and its relationship
Content. Terminology Anatomy Aetiology Presentation Classification Management
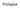 Prolapse Content Terminology Anatomy Aetiology Presentation Classification Management Terminology Prolapse Descent of pelvic organs into the vagina Cystocele ant. vaginal wall involving bladder Uterine
Prolapse Content Terminology Anatomy Aetiology Presentation Classification Management Terminology Prolapse Descent of pelvic organs into the vagina Cystocele ant. vaginal wall involving bladder Uterine
John Laughlin 4 th year Cardiff University Medical Student
 John Laughlin 4 th year Cardiff University Medical Student Prolapse/incontinence You need to know: Pelvic floor anatomy in relation to uterovaginal support and continence The classification of uterovaginal
John Laughlin 4 th year Cardiff University Medical Student Prolapse/incontinence You need to know: Pelvic floor anatomy in relation to uterovaginal support and continence The classification of uterovaginal
General introduction
 General introduction http://hdl.handle.net/1765/103217 General introduction General introduction 1 2 Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam General introduction 3 Functional pelvic floor disorders Symptoms related
General introduction http://hdl.handle.net/1765/103217 General introduction General introduction 1 2 Erasmus Medical Center Rotterdam General introduction 3 Functional pelvic floor disorders Symptoms related
Clinical Study Changing Trends in Use of Laparoscopy: A Clinical Audit
 Minimally Invasive Surgery, Article ID 562785, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/562785 Clinical Study Changing Trends in Use of Laparoscopy: A Clinical Audit Ritu Khatuja, 1 Geetika Jain, 1 Sumita
Minimally Invasive Surgery, Article ID 562785, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/562785 Clinical Study Changing Trends in Use of Laparoscopy: A Clinical Audit Ritu Khatuja, 1 Geetika Jain, 1 Sumita
Comparison of Side Effects of Tolterodine and Solifenacinsucinate in Patients with Urinary Incontinence
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Side Effects of Tolterodine and Solifenacinsucinate in Patients with Urinary Incontinence MARYAM RANA, IRAM MOBUSHER ABSTRACT Background: Overactive bladder syndrome is a
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Side Effects of Tolterodine and Solifenacinsucinate in Patients with Urinary Incontinence MARYAM RANA, IRAM MOBUSHER ABSTRACT Background: Overactive bladder syndrome is a
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist
 Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms K Kuruvilla Zachariah Associate Specialist Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Storage Symptoms Frequency, urgency, incontinence, Nocturia Voiding Symptoms Hesitancy, poor flow, intermittency,
Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery
 Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery APPLICATION FOR NEW FELLOWSHIP Name of Institution: McGill University Location: Royal Victoria Hospital (Glen Site), St Mary s Hospital Centre Type of Fellowship:
Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery APPLICATION FOR NEW FELLOWSHIP Name of Institution: McGill University Location: Royal Victoria Hospital (Glen Site), St Mary s Hospital Centre Type of Fellowship:
Day 1. ICS EDUCATIONAL COURSE São Paulo 28 th - 29 th July 2006 Coordinators: Linda Cardozo & Carlos Arturo Levi D Ancona.
 Day 1 AM Arrive Register 9:00-12:00 Nurses Workshop Urodynamic Course Workshop Physiotherapy Workshop 12:00 Buffet Lunch 13:00 Welcome & & Bary Berghmans & Nelson Rodrigues Netto Jr. Brazilian Urological
Day 1 AM Arrive Register 9:00-12:00 Nurses Workshop Urodynamic Course Workshop Physiotherapy Workshop 12:00 Buffet Lunch 13:00 Welcome & & Bary Berghmans & Nelson Rodrigues Netto Jr. Brazilian Urological
Compassionate and effective management
 IMPACT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE ON QUALITY OF LIFE * Paul Abrams, MD, FRCS ABSTRACT Evaluating the impact of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) on quality of life (QOL) is of paramount importance,
IMPACT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE ON QUALITY OF LIFE * Paul Abrams, MD, FRCS ABSTRACT Evaluating the impact of stress urinary incontinence (SUI) on quality of life (QOL) is of paramount importance,
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Treating Neurologic Bladder in Women: a Randomized Clinical Trial
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Treating Neurologic Bladder in Women: a Randomized Clinical Trial Tahereh Eftekhar 1, Nastaran Teimoory 1, Elahe Miri 1, Abolghasem Nikfallah 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Treating Neurologic Bladder in Women: a Randomized Clinical Trial Tahereh Eftekhar 1, Nastaran Teimoory 1, Elahe Miri 1, Abolghasem Nikfallah 2,
Research Article A Structured Assessment to Decrease the Amount of Inconclusive Endometrial Biopsies in Women with Postmenopausal Bleeding
 International Surgical Oncology Volume 2016, Article ID 3039261, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3039261 Research Article A Structured Assessment to Decrease the Amount of Inconclusive Endometrial
International Surgical Oncology Volume 2016, Article ID 3039261, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3039261 Research Article A Structured Assessment to Decrease the Amount of Inconclusive Endometrial
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN
 Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Bladder dysfunction in ALD and AMN Sara Simeoni, MD Department of Uro-Neurology National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery Queen Square, London 10:15 Dr Sara Simeoni- Bladder issues for AMN patients
Updates in the nonpharmacological. treatment on overactive bladder
 Updates in the nonpharmacological treatment on overactive bladder Overactive Bladder Also known as urgency-frequency syndrome Symptoms Urgency Daytime frequency Nocturia Urge urinary incontinence Sudden
Updates in the nonpharmacological treatment on overactive bladder Overactive Bladder Also known as urgency-frequency syndrome Symptoms Urgency Daytime frequency Nocturia Urge urinary incontinence Sudden
Urinary Incontinence for the Primary Care Provider
 Urinary Incontinence for the Primary Care Provider Diana J Scott FNP-BC https://youtu.be/gmzaue1ojn4 1 Assessment of Urinary Incontinence Urge Stress Mixed Other overflow, postural, continuous, insensible,
Urinary Incontinence for the Primary Care Provider Diana J Scott FNP-BC https://youtu.be/gmzaue1ojn4 1 Assessment of Urinary Incontinence Urge Stress Mixed Other overflow, postural, continuous, insensible,
Role of urodynamics in stress urinary incontinence: A critical appraisal
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Role of urodynamics in stress urinary incontinence: A critical appraisal Shirish Dattatraya Yande 1,2,Omkar Vinay Joglekar 1, Maya Joshi 2 1 Department of Urology, Ruby Hall Clinic, 2
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Role of urodynamics in stress urinary incontinence: A critical appraisal Shirish Dattatraya Yande 1,2,Omkar Vinay Joglekar 1, Maya Joshi 2 1 Department of Urology, Ruby Hall Clinic, 2
Training a Wayward Bladder
 D. James Ballard, PT, DPT, GCS The University of Utah, Dept. of Physical Therapy Training a Wayward Bladder Agenda 1. Discuss urinary incontinence 2. Review pelvic floor and lower urinary tract functional
D. James Ballard, PT, DPT, GCS The University of Utah, Dept. of Physical Therapy Training a Wayward Bladder Agenda 1. Discuss urinary incontinence 2. Review pelvic floor and lower urinary tract functional
Urodynamic Patterns of the Idiopathic Overactive Bladder
 Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 6(5): 74-79 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjcm doi: 10.11648/j.sjcm.20170605.12 ISSN: 2327-2724 (Print); ISSN: 2327-2732 (Online) Urodynamic Patterns
Science Journal of Clinical Medicine 2017; 6(5): 74-79 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/sjcm doi: 10.11648/j.sjcm.20170605.12 ISSN: 2327-2724 (Print); ISSN: 2327-2732 (Online) Urodynamic Patterns
Bristol Urological Institute, Bristol, UK. The Warrell Unit, St Mary s Hospital, Manchester. UK.
 Disclosures Basic Principles of Urodynamics Andrew Gammie Bristol Urological Institute, Bristol, UK Albyn, Andromeda, Laborie, Mediwatch, MMS Project sponsorship T-Doc LLC Trial sponsorship with grateful
Disclosures Basic Principles of Urodynamics Andrew Gammie Bristol Urological Institute, Bristol, UK Albyn, Andromeda, Laborie, Mediwatch, MMS Project sponsorship T-Doc LLC Trial sponsorship with grateful
Case Report Three-Dimensional Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Enhancing Stone/Stent Contrasting and Stone Visualization in Urolithiasis
 Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 646087, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/646087 Case Report Three-Dimensional Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Enhancing Stone/Stent Contrasting
Case Reports in Urology Volume 2013, Article ID 646087, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/646087 Case Report Three-Dimensional Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for Enhancing Stone/Stent Contrasting
Bladder Wall Thickness is Associated with Responsiveness of Storage Symptoms to Alpha-Blockers in Men with Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2012.53.7.487 Voiding Dysfunction Bladder Wall Thickness is Associated with Responsiveness of Storage Symptoms to Alpha-Blockers in Men with Lower Urinary
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2012.53.7.487 Voiding Dysfunction Bladder Wall Thickness is Associated with Responsiveness of Storage Symptoms to Alpha-Blockers in Men with Lower Urinary
Ben Herbert Alex Wojtowicz
 Ben Herbert Alex Wojtowicz 54 year old female presenting with: Dragging sensation Urinary incontinence Some faecal incontinence HPC Since May 14 had noticed a mass protruding from the vagina when going
Ben Herbert Alex Wojtowicz 54 year old female presenting with: Dragging sensation Urinary incontinence Some faecal incontinence HPC Since May 14 had noticed a mass protruding from the vagina when going
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine
 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS The Place of the Ice Water Test (IWT) in the Evaluation of the Patients with Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury Ion Dragomiri STEANU a ; Simona Elena ALBU
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS The Place of the Ice Water Test (IWT) in the Evaluation of the Patients with Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury Ion Dragomiri STEANU a ; Simona Elena ALBU
Urodynamic outcome of parasacral transcutaneous electrical neural stimulation for overactive bladder in children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 41 (4): 739-743, July - August, 2015 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.0303 Urodynamic outcome of parasacral transcutaneous electrical neural stimulation for overactive bladder in
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 41 (4): 739-743, July - August, 2015 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.0303 Urodynamic outcome of parasacral transcutaneous electrical neural stimulation for overactive bladder in
Daofang Zhu, Xianming Dou, Liang Tang, Dongdong Tang, Guiyi Liao, Weihua Fang, and Xiansheng Zhang
 Hindawi BioMed Research International Volume 2017, Article ID 3473796, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3473796 Clinical Study Prevalence of Prostatitis-Like Symptoms and Outcomes of NIH-CPSI in Outpatients
Hindawi BioMed Research International Volume 2017, Article ID 3473796, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3473796 Clinical Study Prevalence of Prostatitis-Like Symptoms and Outcomes of NIH-CPSI in Outpatients
GUIDELINES ON URINARY INCONTINENCE
 GUIDELINES ON URINARY INCONTINENCE 9 J. Thüroff, (chairman), P. Abrams, J-T. Andersen, W. Artibani, E. Chartier-Kastler, C. Hampel, M. Hohenfellner, T. Tammela, Ph. van Kerrebroeck Introduction The condition
GUIDELINES ON URINARY INCONTINENCE 9 J. Thüroff, (chairman), P. Abrams, J-T. Andersen, W. Artibani, E. Chartier-Kastler, C. Hampel, M. Hohenfellner, T. Tammela, Ph. van Kerrebroeck Introduction The condition
REVIEW OF CAUSES, EVALUATION, AND TREATMENTS URINARY INCONTINENCE 101
 REVIEW OF CAUSES, EVALUATION, AND TREATMENTS URINARY INCONTINENCE 101 March 5, 2014 Kevin E Miller, MD Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Kansas School of Medicine- Wichita URINARY INCONTINENCE
REVIEW OF CAUSES, EVALUATION, AND TREATMENTS URINARY INCONTINENCE 101 March 5, 2014 Kevin E Miller, MD Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Kansas School of Medicine- Wichita URINARY INCONTINENCE
Urogynaecology. Colm McAlinden
 Urogynaecology Colm McAlinden Definitions Urinary incontinence compliant of any involuntary leakage of urine with many different causes Two main types: Stress Urge Definitions Nocturia: More than a single
Urogynaecology Colm McAlinden Definitions Urinary incontinence compliant of any involuntary leakage of urine with many different causes Two main types: Stress Urge Definitions Nocturia: More than a single
Incontinence: The silent scourge of the young and old. The International Continence Society has. In this article:
 Focus on CME at the University of Toronto Incontinence: The silent scourge of the young and old By Sender Herschorn, BSc, MDCM, FRCSC In this article: 1. What is the workup for urinary incontinence? 2.
Focus on CME at the University of Toronto Incontinence: The silent scourge of the young and old By Sender Herschorn, BSc, MDCM, FRCSC In this article: 1. What is the workup for urinary incontinence? 2.
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE SCOPE. Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence 2 Background a) The National
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR CLINICAL EXCELLENCE 1 Guideline title SCOPE Urinary incontinence: the management of urinary incontinence in women 1.1 Short title Urinary incontinence 2 Background a) The National
Ralph & Berryl Goldman Fellowship in Neuro urology, voiding dysfunction and bladder reconstruction
 Ralph & Berryl Goldman Fellowship in Neuro urology, voiding dysfunction and bladder reconstruction Length of fellowship: A 1 year Fellowship: This fellowship has been designed for Urology or Gynecology
Ralph & Berryl Goldman Fellowship in Neuro urology, voiding dysfunction and bladder reconstruction Length of fellowship: A 1 year Fellowship: This fellowship has been designed for Urology or Gynecology
GUIDELINES ON URINARY INCONTINENCE
 12 GUIDELINES ON URINARY INCONTINENCE (Text updated March 2005) J. Thüroff, (chairman), P. Abrams, K.E. Andersson, W. Artibani, E. Chartier-Kastler, C. Hampel, Ph. van Kerrebroeck Introduction The condition
12 GUIDELINES ON URINARY INCONTINENCE (Text updated March 2005) J. Thüroff, (chairman), P. Abrams, K.E. Andersson, W. Artibani, E. Chartier-Kastler, C. Hampel, Ph. van Kerrebroeck Introduction The condition
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics
 International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics COMMITTEE FOR UROGYNAECOLOGY AND PELVIC FLOOR MEMBER: TSUNG-HSIEN (CHARLES) SU, CHAIR (TAIWAN) DAVID RICHMOND, CO-CHAIR (UK) CHITTARANJAN PURANDARE,
International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics COMMITTEE FOR UROGYNAECOLOGY AND PELVIC FLOOR MEMBER: TSUNG-HSIEN (CHARLES) SU, CHAIR (TAIWAN) DAVID RICHMOND, CO-CHAIR (UK) CHITTARANJAN PURANDARE,
Overactive bladder can result from one or more of the following causes:
 Overactive bladder can affect people of any age; however, it is more common in older people. Effective treatments are available and seeing your doctor for symptoms of overactive bladder often results in
Overactive bladder can affect people of any age; however, it is more common in older people. Effective treatments are available and seeing your doctor for symptoms of overactive bladder often results in
New York Science Journal 2017;10(9)
 Ul Trasound Assessment of Bladder Wall Thickness as a Screening Test for Detrusor Instability Ahmed Wafaey MSc, Abdelmoniem Zakaria MD, Sameh Saied MD, Ahmed Abdelalem MD Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Ul Trasound Assessment of Bladder Wall Thickness as a Screening Test for Detrusor Instability Ahmed Wafaey MSc, Abdelmoniem Zakaria MD, Sameh Saied MD, Ahmed Abdelalem MD Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Flowmetry/ pelvic floor electromyographic findings in patients with detrusor overactivity
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 41 (3): 521-526, May - June, 2015 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.0204 Flowmetry/ pelvic floor electromyographic findings in patients with detrusor overactivity Farshid Alizadeh
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 41 (3): 521-526, May - June, 2015 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.0204 Flowmetry/ pelvic floor electromyographic findings in patients with detrusor overactivity Farshid Alizadeh
Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI Family Physiotherapy Centre of London
 Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI blandry@fpclondon.com Family Physiotherapy Centre of London Objectives To describe the scope of post-prostatectomy incontinence To describe what s been done To provide
Bill Landry BScPT, BScH, MCPA, CAFCI blandry@fpclondon.com Family Physiotherapy Centre of London Objectives To describe the scope of post-prostatectomy incontinence To describe what s been done To provide
Urogynecology Associates of Philadelphia URODYNAMIC TESTING
 URODYNAMIC TESTING Urogynecology Associates of Philadelphia Most women with urinary incontinence will need to complete a few simple tests, performed in the office, to help your doctor assess your symptoms
URODYNAMIC TESTING Urogynecology Associates of Philadelphia Most women with urinary incontinence will need to complete a few simple tests, performed in the office, to help your doctor assess your symptoms
Clinical Study Perineal Ultrasound as a Complement to POP-Q in the Assessment of Cystoceles
 BioMed Research International, Article ID 740925, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/740925 Clinical Study Perineal Ultrasound as a Complement to POP-Q in the Assessment of Cystoceles Laila Najjari,
BioMed Research International, Article ID 740925, 7 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/740925 Clinical Study Perineal Ultrasound as a Complement to POP-Q in the Assessment of Cystoceles Laila Najjari,
UP DATE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN ADULT
 UP DATE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN ADULT Yunizaf, MD Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology School of Medicine, University of Indonesia/ Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital
UP DATE MANAGEMENT OF URINARY INCONTINENCE IN ADULT Yunizaf, MD Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology School of Medicine, University of Indonesia/ Dr. Cipto Mangunkusumo Hospital
The new ICCS terminology J Urol 176, , 2006
 The new ICCS terminology J Urol 176, 314-324, 2006 The Standardization of Terminology of Lower Urinary Tract Function in Children and Adolescents: Report from the Standardisation Committee of the International
The new ICCS terminology J Urol 176, 314-324, 2006 The Standardization of Terminology of Lower Urinary Tract Function in Children and Adolescents: Report from the Standardisation Committee of the International
PUBOVAGINAL SLING IN THE TREATMENT OF STRESS URINARY INCONTINENCE FOR URETHRAL HYPERMOBILITY AND INTRINSIC SPHINCTERIC DEFICIENCY
 Urological Neurology International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology PUBOVAGINAL SLING IN SUI Vol. 29 (6): 540-544, November - December, 2003 PUBOVAGINAL SLING IN THE TREATMENT
Urological Neurology International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology PUBOVAGINAL SLING IN SUI Vol. 29 (6): 540-544, November - December, 2003 PUBOVAGINAL SLING IN THE TREATMENT
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 4: , 2012
 1112 Usefulness of total bladder capacity and post void residual urine volume as a predictor of detrusor overactivity with impaired contractility in stroke patients SANG HYUB LEE, JOONG GEUN LEE, GYEONG
1112 Usefulness of total bladder capacity and post void residual urine volume as a predictor of detrusor overactivity with impaired contractility in stroke patients SANG HYUB LEE, JOONG GEUN LEE, GYEONG
Effect of Desmopressin with Anticholinergics in Female Patients with Overactive Bladder
 www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2011.52.6.396 Voiding Dysfunction Effect of Desmopressin with Anticholinergics in Female Patients with Overactive Bladder Young Kook Han, Won Ki Lee, Seong Ho Lee, Dae
www.kjurology.org DOI:10.4111/kju.2011.52.6.396 Voiding Dysfunction Effect of Desmopressin with Anticholinergics in Female Patients with Overactive Bladder Young Kook Han, Won Ki Lee, Seong Ho Lee, Dae
Stress Incontinence. Susannah Elvy Urogynaecology CNS
 Stress Incontinence Susannah Elvy Urogynaecology CNS Definitions Prevalence Assessment Investigation Treatment Surgery Men International Continence Society define as the complaint of any involuntary leakage
Stress Incontinence Susannah Elvy Urogynaecology CNS Definitions Prevalence Assessment Investigation Treatment Surgery Men International Continence Society define as the complaint of any involuntary leakage
The Functional Role of Transperineal Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Females with Urinary Incontinence Compared to Urodynamic Studies
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, March: 231-23 7, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net The Functional Role of Transperineal Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Females with Urinary Incontinence
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 82, No. 2, March: 231-23 7, 2014 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net The Functional Role of Transperineal Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Females with Urinary Incontinence
Urinary Incontinence in Women: Never an Acceptable Consequence of Aging
 Urinary Incontinence in Women: Never an Acceptable Consequence of Aging Catherine A. Matthews, MD Associate Professor Chief, Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery University of North Carolina,
Urinary Incontinence in Women: Never an Acceptable Consequence of Aging Catherine A. Matthews, MD Associate Professor Chief, Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery University of North Carolina,
Overactive bladder. Information for patients from Urogynaecology
 Overactive bladder Information for patients from Urogynaecology An overactive bladder (OAB) is a very common problem. It can cause distressing symptoms that are difficult to control. These can include
Overactive bladder Information for patients from Urogynaecology An overactive bladder (OAB) is a very common problem. It can cause distressing symptoms that are difficult to control. These can include
2. Surgeons considering invasive therapy in patients with SUI should assess postvoid residual (PVR) urine volume. (Expert Opinion)
 1 ADULT URODYNAMICS: AUA/SUFU GUIDELINE Approved by the AUA Board of Directors April 2012 Authors disclosure of potential conflicts of interest and author/staff contributions appear at the end of the article.
1 ADULT URODYNAMICS: AUA/SUFU GUIDELINE Approved by the AUA Board of Directors April 2012 Authors disclosure of potential conflicts of interest and author/staff contributions appear at the end of the article.
Five-Year Outcomes of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure for Treatment of Female Stress Urinary Incontinence
 european urology 50 (2006) 333 338 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Female Urology Incontinence Five-Year Outcomes of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure
european urology 50 (2006) 333 338 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Female Urology Incontinence Five-Year Outcomes of the Tension-Free Vaginal Tape Procedure
