Fruit fly management practices on tropical fruit in Africa
|
|
|
- Britney Garrett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Fruit fly management practices on tropical fruit in Africa Prepared by Prof. Dr. Talal S. El-Abbassi Plant Protection Research Institute Cairo,EGYPT
2 INTRODUCTION Fruit flies belonging to Family Tephritidae are considered the most important insect pests that cause enormous damage for a wide host range of horticultures allover the world.. More than 950 species are of economic significance in Africa. Some of these species are accidentally introduced from other regions, in particular from Asia. So far, four Asian species belonging to the genus Bactrocera invaded Africa, two of these were introduced in recent years and the risk for other introductions is great.
3 Fruit flies of major importance in Africa Indigenous Species - Ceratitis ( Capitata) capitata Mediterranean fruit fly - Ceratitis (Pardalaspis)ditissima - Ceratitis (Prdalaspis) punctata Cocoa fruit fly - Ceratitis (Pardalaspis) bremi - Ceratitis (Pardalaspis) rosa Natal fruit fly - Ceratitis (Pardalaspis) fasciventris - Ceratitis (Pardalaspis) colae - Ceratitis (Ceratolaspis) cosyra Marula fruit fly - Ceratitis (Ceratolaspis) quinaria Five spotted fruit fly - Ceratitis (Ceratoplaspis) silvestrii
4 - Dacus (Dacus) bivittatus Pumpkin fruit fly - Dacus (Dacus) punctatifrons - Dacus ( Didacus) ciliates Lesser pumpkin fruit fly - Dacus ( Didacus) vertebratus Jointed pumpkin fly - Dacus ( Dedacus )frontalis - Dacus (Dedacus) lounsburyii - Trithithrum nigerrimum - Trithithrum coffeae Coffee fly - Bactrocera ( Daculus) oleae Olive fruit fly Invasive Species - Bactrocera ( Zeugodacus) cucurbitae Melon fly - Bactrocera ( Bactrocera) invadens - Bactrocera (Bactrocera) latifrons Malaysian fruit fly - Bactrocera (Bactrocera) zonata Peach fruit fly
5 The Geographical distribution and presence of these four invasive Bactrocera species in Africa have been studied and illustrated in the following figs.
6 West Africa Benin Burkina Faso Cameroon Gambia Guinea Ivory Coast Mali Niger Distribution of B.cucurbitae (Melon Fly) East Africa Sudan Kenya Tanzania Uganda Congo Mauritius Réunion Seychelles Nigeria Senegal Togo
7 Distribution of B.invadens Senegal Mali Guinea Liberia Cote D'Ivoire Ghana Togo Benin Burkina Faso Niger Nigeria Cameroon Rep.Of Congo Chad Dem.Rep.Congo Sudan Kenya Tanzania Loanda Burundi Ethiopia Comoro Islands Mozambique Zambia Namibia
8 Distribution of B.latifrons (Malaysian Fruit Fly) Kenya Tanzania
9 Distribution of B.zonata (Peach Fruit Fly) Libya Egypt SaudiArabia Oman UAE Yemen Mauritius Réunion
10 C.Capitata Distribution Map
11 In Africa horticulture is recognized to become a major source of income for smallholders and various national development. However, the expansion of fruit production and export is greatly increasing the risk of transferring African fruit flies both within Africa and to other regions of the world; heavy fruit fly infestation seriously reduces the quantity of marketable fruit and increases production costs
12 Many fruit fly species are serious pests of agriculture throughout Africa and represent a threat to the agriculture and ecology of many countries. Because of the threats the pests would constitute to the agricultural systems of foreign countries, certain countries would restrict or prohibit the entry of host produce from the African countries, thereby eliminating many current (and potential future) African export markets.
13 In the absence of government efforts to control exotic fruit fly pests, losses and damage to private and commercial crops would provoke independent control efforts. Lacking the resources or capability to use sophisticated program techniques, such as detection trapping, sterile insect technique, and regulatory controls, the growers or homeowners could be expected to rely predominantly on chemical pesticides. Those efforts could result in continually increasing, uncoordinated, and less controlled use of pesticides.
14 A proposal of an international program ( a broad strategy) among African countries should be prepared to respond to the threat of these invasive pest species. Such program must include a range of alternatives (exclusion, detection and prevention, and control
15 Bactrocera invadens and Ceratitis cosyra are of the major constraints that in general limit tropical fruit production in Africa and mango fruits in particular. They cause up to 40 80% direct damage to mango fruits and also restrict export to large lucrative markets in Europe, the Middle East, Japan and USA.
16 Chemical pesticides have been extensively used for controlling these insect pests for a long time which caused many environmental problems like ( high pesticide residues in edible fruits developing resistant strains of pests against pesticides disturbing the natural balance and the environmental pollution).
17 Developing and implementing an integrated pest management (IPM) programmes is highly requested to minimize the use of chemical pesticides to overcome these abovementioned problems and produce fruit fly-free and residue-free fruits to facilitate compliance with standards required for export markets.
18 To achieve these goals Understanding and extensive studies on the biology and ecology of any insect pest is considered the corner stone to establish effective control measures that might enable us to win the battle against such pest.
19 - Distinguishing between the different fruit fly species in larval stage - The biological studies include the following points - Knowledge of population cycles - Studies on various developmental stages of subjected insect species - The length of time required for the Tephritidae fruit flies to complete their life cycles in relation to weather conditions
20 B- Ecological Studies include the following points: 1) Geographical distribution of economic fruit flies allover the country through : - Finding the relationship between weather factors represented in ( Maximum and minimum day temp. and daily relative humidity. - Survey for all favorite,wild and alternative hosts. 2) Diagnosing symptoms of infestation by fruit flies at various plant hosts.
21 B- Ecological Studies include the following points: (continued) C) Detecting and monitoring system:- 1-Trap catch for fruit flies: - Selecting appropriate and effective trap for catching flies - Using effective attractants ( sex attractants, food attractants,lures and dispensers). 2-Collecting infested fruits from various locations and hosts to be incubated under laboratory conditions
22 B- Ecological Studies include the following points: 1) Geographical distribution of economic fruit flies allover the country through : - Finding the relationship between weather factors represented in ( Maximum and minimum day temp. and daily relative humidity. - Survey for all favorite,wild and alternative hosts. 2) Diagnosing symptoms of infestation by fruit flies at various plant hosts.
23 B- Ecological Studies include the following points: (continued) C) Detecting and monitoring system:- 1-Trap catch for fruit flies: - Selecting appropriate and effective trap for catching flies - Using effective attractants ( sex attractants, food attractants,lures and dispensers). 2-Collecting infested fruits from various locations and hosts to be incubated under laboratory conditions
24 Parapheromone Traps Food Bait Traps Jackson trap Yellow Panel McPhail trap Steiner Trap Adhesive sheet Oben bottom dry Plastic McPhail Champ trap Cook &Cunningham Tephri trap Multilure trap
25 B- Ecological Studies include the following points: (continued) 3- Identification of captured flies into traps or flies emerging from infested fruits. N.B. identification of various fruit fly species by Inspecting larvae in infested fruit needs well trained and experienced staff. D) Determination of hot spots,seasonal peaks and No. of generations per year.
26 Cephalopharyngeal Skeleton Anterior Spiracles Posterior Spiracle C.capitata B. cucurbitae B.Oleae B.zonata B.latifrons
27 Developmental Goal To increase the level of production and quality of fresh fruit and fleshy vegetables, leading to enhanced availability for local consumption, increased exports and higher farmer's incomes. To upgrade the technical knowledge and understanding of the impact of fruit flies on production and export of fresh fruits and fleshy vegetables by plant protection, quarantine, extension services staff and the private sector.
28 The program should focuses on effects of both chemical and nonchemical control methods on the physical environment, human health and safety,socioeconomics, cultural and visual resources, and biological resources. An integrated program would offer the greatest.flexibility for responding to fruit fly pest outbreaks
29 It would be characterized by cooperative integrated efforts to control (suppress, eradicate, or otherwise manage) invasive exotic fruit fly pests. It would utilize principles of integrated pest management (IPM) The integrated program appears to offer the best combination of short-term risk and long-term benefit to agricultural resources and the environment, when compared to no action or a nonchemical program
30 IPM STRATEGY The strategy of IPM programme is based on usage of all means of control procedures in a complementary way ( legislative control, physical control, cultural control, biological control, Biotechnological Control sterile insect technique, wise use of pesticides and postharvest treatments )
31 1- Legislative control -Apply restricted quarantine laws at all country borders to avoid entrance of fruits infested with fruit flies into territories. - Avoid transfer of infested fruits from area to another within the country ( internal quarantine procedures) especially free areas. - Issuance of pronouncements to growers to apply proper sanitary procedures which safe the environment and protect fruit hosts from insect infestation like getting rid of infested, cracked and fallen fruits
32 1- Legislative control ( continued) - Prohibit total coverage spray using chemical pesticides - Prohibit usage of pesticides not recommended by Ministry of Agriculture. - Growers are committed to participate in conducting collective control at the level of a province or a district in case of pest outbreak.
33 2. Physical Control Physical control involves physical actions taken to eliminate fruit fly hosts or host produce. Fruit stripping and host elimination are two principal physical control methods. Fruit stripping is employed when fruit fly larvae are found. The physical elimination of fruit fly hosts, when possible and appropriate, may be especially helpful in the elimination of small, isolated infestations Except in very limited circumstances,host elimination is unacceptable because of environmental considerations, time and resource constraints
34 Fruits can be easily protected against fruit flies by bagging them in paper bags. The bag provides a physical protection to the fruit by preventing adult female flies from laying eggs. This technique has been successfully practiced in Malaysia for exporting Carambola and also widely practiced to protect mangoes in Thailand and Philippines Bagging is inexpensive and easy to apply and guarantees nearly complete protection from fruit flies. It is ideal for small. scale growers who do not use pesticides
35 3. Cultural Control Cultural control reduces pest populations through manipulation of agricultural practices. In general, agricultural practices are modified to make the crop environment as unfavorable as possible for the insect pest. Cultural control methods frequently include: clean culture, special timing, trap cropping, use of resistant varieties, crop rotation, varying plant locations, and manipulation of alternate hosts. Collecting and burying host fruit left after harvest, destroying damaged fruit, and removing unwanted or wild alternate hosts in and around fields are often recommended for suppressing fruit fly infestations.
36 Getting rid of infested, cracked and fallen fruits
37 - Over flooding soil after harvesting may kill larvae and pupae by suffocation and prevent invasion of newly emerged flies to successive fruit hosts - Avoiding cultivating many fruit fly hosts in the same field ( mixed host orchards are severely infested). - Good and balanced nourishing regimes result in strong trees more tolerable to infestation
38 Harvesting the fruit before it reaches a stage of ripeness highly susceptible to fruit fly attack. Although this technique theoretically could reduce fruit fly populations, it is not likely to do so for a variety of reasons. First, some fruits lose flavor when harvested too early,. as they will not ripen fully. Second, the development of most fruit flies generally coincides with the development (growth) of their host crops. Third, it is doubtful that enough control could be exercised over commercial agricultural practices to make the technique effective or worthwhile
39 Finally, the presence of multiple hosts in many areas that are susceptible to fruit fly infestations limits the applicability of this method. Trap cropping involves the planting of a crop that is favored by the pest in order to attract and concentrate the pest in a limited area where the pest can be destroyed by chemical or cultural methods. It is unlikely that this method could be applicable to most fruit fly programs because of the perennial nature of many host species, the availability of multiple host species in the program areas, and the lack of data on effectiveness of trap crops in attracting fruit flies from distant areas.
40 Reduce populations : If fruit flies are present in your field prior to crop ripening, you can try to reduce their population by attracting the adults to a poisoned bait. This can be done by spraying a protein-bait insecticide mixture onto nearby non-crop plants, windbreaks, or a border of corn plants.
41 4. Biological Control Biological control (or biocontrol) is a pest control strategy making use of living natural enemies, antagonists or competitors, and other self replicating biotic entities. In spite of its advantages, biological control has major limitations which influence its suitability for control programs, including: lack of immediate results; potential lack of effectiveness; logistical difficulties; and incomplete or unavailable information about rearing techniques.
42 5. Biotechnological Control Biotechnological control would involve the use of genetic engineering techniques to control fruit fly pests. Currently, there are four primary areas of genetic engineering that show promise for control of insect pests: (1) bio-engineering of crop plants (insertion of specific genes into the plants to improve plant characteristics such as pest resistance), (2) improvement of insect-infecting viruses, (3) production of genetic mutations of the pest (thereby affecting its reproductive capabilities) by radiation or other means, and (4) gene probe techniques to screen for insecticidal properties in microorganisms.
43 Biotechnology is being developed for use against fruit flies, but has not been used extensively because of a number of constraints: (1) the technology is still relatively undeveloped; (2) some control mechanisms have not been developed. (3) Insectinfecting viruses have not been proven effective, nor are they available commercially for fruit fly control; (4) screening done for new strains of bacteria against fruit flies is only the first step in basic research and development of insect-infecting microorganisms; and (5) the information relative to the environmental impacts of bioengineered organisms is incomplete and unavailable..
44 6. Sterile Insect Technique Sterile insect technique (SIT) involves the release of sterilized fruit flies into infested areas where they mate with the feral fruit flies, producing only infertile eggs. SIT has been used successfully and/or developed as a control method for the Medfly, Mexican fruit fly, Caribbean fruit fly (Carib fly), and the melon fly. SIT may be used as a component of an overall detection and prevention strategy, or it may be used as a component of suppression or eradication programs
45 7. Chemical Control Methods A- Male Annihilation Technique ( MAT ) This technique is being used successfully for suppressing population of the peach fruit fly in Egypt ( National area wide program for extermination of peach fruit fly in Egypt ) 1- This technique is used to reduce the No. of males to the least level.
46 2- Fiber blocks ( cm) are saturated with a mixture of the male sex attractant (Methyl eugenol) and a technical insecticide ( fenetrothion) at a rate of 4:1. Each block is loaded with 10 ml of this mixture. 3- Blocks are distributed at a rate of 1 block per acre( i.e. the distance between each two successive blocks is Ca. 65 meters.
47 Fiber blocks
48 Fiber blocks Saturation room
49 Fiber blocks Saturation room 49
50
51 B-Bait spray Application Technique (BAT) 1-This technique is currently used for controlling most species of fruit flies b- In this technique, a food attractant material is mixed with an insecticide. Concentration of the attractant material depends on the type of this material. For instance, in case of Buminal ( a protein hydrolysate ) the efficient concentration is 10%.
52 - Several materials with insecticidal properties inconjunction with an improved bait attractant have been tested against several species of economic tephritid fruit flies. - Phloxine B is a photoactive dye which is toxic to certain insect species added to an attractant bait evoked a high degree of mortality in Medfly and other fruit fly species
53 - Recently new safer insecticides (Spinosad) has been developed for area-wide control of fruit flies. -These latter treatments offer environmentally friendly alternatives to present organophosphate formulations for eradication or suppression of fruit flies without adverse effect on non-target organisms ( honey bees,predators and parasites).
54 Partial Bait Spray
55 Trees are sprayed with a quantity ml of bait mixture. Only trunks near from trees canopy are sprayed.be sure that the spray solution will not contact fruits. Tree are treated by spraying a tree row and leaving a row without treatment, or spraying a row and leaving two rows without treatment depending on level of infestation.
56 C. Soil Treatments - Soil treatment with certain chemical insecticides (such as Diazinon, Chlorpyrifos and Fenthion) directly to the soil within the drip line of host plants immediately after fruit fly larval detection induces significant control against fruit flies. - Because of the nature of the chemicals and /or the method of delivery, there is no potential for drift, runoff, or leaching. - Generally, no more than three applications are made
57 D- Mass trapping Ceratitis spp. can not be controlled using MAT due to many technical and scientific concerns. Therefore Mass trapping is being used in some areas.this technique depends on distributing traps loaded with female attractant lure mounted in sachets in fruit orchards at a rate of 21 traps per acre.these traps are supposed to be effective for a period of approximately 4 months
58 Comparison between Medfly and Peach Fruit Fly Seria l No. Item Of Comparison Medfly Peach Fruit Fly 1 Mean Larval duration 6-8 Days 9-10 Days 2 Flight Range Up to five Mile Up to 20 Miles 3 Pre- Oviposition period 4-7 days days 4 Range of required temperatures C C 5 Mean Adult longevity 55.2 days ( Males ) 61.8 days ( Females) 41.0 days ( Males ) 48.0 days ( Females )
59 No Item Name Distrib. Hosts Life cycle: Duration Larval duration Pupal duration Preovp.period Flight Range Sex B.cucurbitae Melon fly West Africa Some East Africa (19 countries) >100 hosts days 6-11 days 6-9 days days 2 Km Cuelure B.Invadens Most west,east &few south (27 countries) 46 hosts 31 days 11.1 days 12.4 days Not studied Methyl Eugenol B.latifrons Malaysian f.fly Kenya & Tanzania 2 countries 15 Hosts 12 solanacae 3 cucurbits 46 days 8.5 days 10.2 days Days 200 meters Alpha-ionol B.zonata Peach fruit fly Egypt,Libya, Reunion & Mauritius 4 countries >50 hosts days 9-10 days 9-10 days days Up to 30 Km Methyl
60 8. postharvest treatments Export of fresh fruits and vegetables to various countries require conducting certain post harvest treatment to ensure that the consignments are free from infestation. More attention has been paid to apply natural control techniques for controlling insect pests and diseases in fruits and vegetable as safe alternatives to chemical treatments. Type of applicable natural method technique and time of application is dependant on host and pest. These natural techniques could be summarized as follows:-
61 A- Immersion of fruits in warm water path at a temperature C for an hour. This technique is recommended for mango fruits and sufficient to kill all immature stage of Bactrocera zonata inside fruits of present. B- Expose fruits to hot water vapor until temperature of fruit pulp reaches 46.2 C, then keeping temperature at this level for 30 minutes. This method is recommended for treating mango and guava fruits against. Bactrocera zonata.
62 Warm water Immersion
63 Hot water vapor chamber Water boiler
64 Hot water vapour control room
65 C- Cold treatment : This technique is recommended for treating citrus and pomegranate fruits. Fruits should be kept at constant temperature at 1.7 C for continuously 14 days. This technique is sufficient to kill all immature stage of Bactrocera zonata inside treated fruits.
66 Cold treatment Champer
67 THANK YOU
Area-wide integrated pest management of tephritid fruit flies using the sterile insect technique
 Area-wide integrated pest management of tephritid fruit flies using the sterile insect technique Rui Pereira, Jorge Hendrichs, Jesus Reyes and Marc Vreysen Insect Pest Control Section (Joint FAO/IAEA Division)
Area-wide integrated pest management of tephritid fruit flies using the sterile insect technique Rui Pereira, Jorge Hendrichs, Jesus Reyes and Marc Vreysen Insect Pest Control Section (Joint FAO/IAEA Division)
The Mediterranean Fruit Fly in Central America
 The Mediterranean Fruit Fly in Central America P.V. Vail, I. Moore and D. Nadel Dr. Vail is Section Head, Joint FAO/IAEA Division of Atomic Energy in Food and Agriculture. Dr. Moore is Assistant to the
The Mediterranean Fruit Fly in Central America P.V. Vail, I. Moore and D. Nadel Dr. Vail is Section Head, Joint FAO/IAEA Division of Atomic Energy in Food and Agriculture. Dr. Moore is Assistant to the
Bactrocera dorsalis : Current status JH VENTER NPPOZA MAY 2017
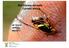 Bactrocera dorsalis : Current status JH VENTER NPPOZA MAY 2017 Photo: JH Venter National exotic fruit fly surveillance program Since 2006 Forms part of the Strategic plan of DAFF An early warning system
Bactrocera dorsalis : Current status JH VENTER NPPOZA MAY 2017 Photo: JH Venter National exotic fruit fly surveillance program Since 2006 Forms part of the Strategic plan of DAFF An early warning system
[Attachment] Survey guidelines for major fruit flies
![[Attachment] Survey guidelines for major fruit flies [Attachment] Survey guidelines for major fruit flies](/thumbs/80/81306935.jpg) [Attachment] Survey guidelines for major fruit flies A. Terms 1) Detection and outbreak Detection Outbreak pre-outbreak phase considered as pest free but emergency measure is implemented Target fruit fly
[Attachment] Survey guidelines for major fruit flies A. Terms 1) Detection and outbreak Detection Outbreak pre-outbreak phase considered as pest free but emergency measure is implemented Target fruit fly
Pheromone Based Mating Disruption
 TM Thaumatotibia leucotreta Reg No: L10320, Act 36 of 1947 Pheromone Based Mating Disruption Pest specific Easy to apply Season long control Manufactured by Hinders chemical resistance Rain fast and no
TM Thaumatotibia leucotreta Reg No: L10320, Act 36 of 1947 Pheromone Based Mating Disruption Pest specific Easy to apply Season long control Manufactured by Hinders chemical resistance Rain fast and no
NAPPO Regional Standards for Phytosanitary Measures (RSPM)
 NAPPO Regional Standards for Phytosanitary Measures (RSPM) RSPM # 10 SURVEILLANCE FOR QUARANTINE FRUIT FLIES (IN A PORTION OF A GENERALLY INFESTED AREA) The Secretariat of the North American Plant Protection
NAPPO Regional Standards for Phytosanitary Measures (RSPM) RSPM # 10 SURVEILLANCE FOR QUARANTINE FRUIT FLIES (IN A PORTION OF A GENERALLY INFESTED AREA) The Secretariat of the North American Plant Protection
Curre nt Status of the Solanaceous Fruit Fly Control Project in Yonaguni Island. Abstract
 Curre nt Status of the Solanaceous Fruit Fly Control Project in Yonaguni Island Hiroyuki Kuba 1, Takashi Matsuyama 2, and Noriaki Mougi 2 1 Research Institute for Subtropics, 1 Asahimachi, Naha, Okinawa
Curre nt Status of the Solanaceous Fruit Fly Control Project in Yonaguni Island Hiroyuki Kuba 1, Takashi Matsuyama 2, and Noriaki Mougi 2 1 Research Institute for Subtropics, 1 Asahimachi, Naha, Okinawa
Population Dynamics of Three Species of Genus Bactrocera (Diptera: Tephritidae: Dacinae) in BARI, Chakwal (Punjab)
 Pakistan J. Zool., vol. 39(2), pp. 123-126, 2007. Population Dynamics of Three Species of Genus Bactrocera (Diptera: Tephritidae: Dacinae) in BARI, Chakwal (Punjab) KHALID MAHMOOD AND MISHKATULLAH Pakistan
Pakistan J. Zool., vol. 39(2), pp. 123-126, 2007. Population Dynamics of Three Species of Genus Bactrocera (Diptera: Tephritidae: Dacinae) in BARI, Chakwal (Punjab) KHALID MAHMOOD AND MISHKATULLAH Pakistan
The Threat of the Mediterranean Fruit Fly1 to American Agriculture and Efforts Being Made to Counter This Threat2 3
 Vol. XXII, No. 3, December, 1977 475 The Threat of the Mediterranean Fruit Fly1 to American Agriculture and Efforts Being Made to Counter This Threat2 3 Ernest J. Harris HAWAIIAN FRUIT FLIES LABORATORY,
Vol. XXII, No. 3, December, 1977 475 The Threat of the Mediterranean Fruit Fly1 to American Agriculture and Efforts Being Made to Counter This Threat2 3 Ernest J. Harris HAWAIIAN FRUIT FLIES LABORATORY,
HIBA ABDALRAHIM Capsca Focal Point Public Health Authority
 HIBA ABDALRAHIM Capsca Focal Point Public Health Authority Introduction Definition Symptom Transmission Global situation Local situation Control Content Introduction Yellow fever (YF) is a mosquito-borne
HIBA ABDALRAHIM Capsca Focal Point Public Health Authority Introduction Definition Symptom Transmission Global situation Local situation Control Content Introduction Yellow fever (YF) is a mosquito-borne
Melon Fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) Genetic Sexing: All-male Sterile Fly Releases in Hawaii
 Melon Proc. Hawaiian Fly Genetic Entomol. Sexing: Soc. All-male (2007) 39:105 110 Sterile Releases in Hawaii 105 Melon Fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) Genetic Sexing: All-male Sterile Fly Releases in Hawaii
Melon Proc. Hawaiian Fly Genetic Entomol. Sexing: Soc. All-male (2007) 39:105 110 Sterile Releases in Hawaii 105 Melon Fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) Genetic Sexing: All-male Sterile Fly Releases in Hawaii
Demographic parameters and biotic factors of two Dacini species, Bactrocera cucurbitae and Dacus ciliatus, on Réunion Island
 Proceedings of 6th International Fruit Fly Symposium 6 10 May 2002, Stellenbosch, South Africa pp. 91 95 Demographic parameters and biotic factors of two Dacini species, Bactrocera cucurbitae and Dacus
Proceedings of 6th International Fruit Fly Symposium 6 10 May 2002, Stellenbosch, South Africa pp. 91 95 Demographic parameters and biotic factors of two Dacini species, Bactrocera cucurbitae and Dacus
[fll ~ft:
 t 1 l\'1/j Primary NSW 1 d GOVERNMENT n ustnes cd1 ~~[fllcd]~ [fll ~@[fllcd]1flrru] ~ft: Understanding Queensland fruit fly A brief overview of the life, ecology and behaviour of the Queensland fruit fly
t 1 l\'1/j Primary NSW 1 d GOVERNMENT n ustnes cd1 ~~[fllcd]~ [fll ~@[fllcd]1flrru] ~ft: Understanding Queensland fruit fly A brief overview of the life, ecology and behaviour of the Queensland fruit fly
Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa
 Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa 355 million people at risk for malaria in 215 297 million at high risk A. Parasite prevalence, 215 Funding for malaria increased from US$ 233 million to US$ 262
Annex 2 A. Regional profile: West Africa 355 million people at risk for malaria in 215 297 million at high risk A. Parasite prevalence, 215 Funding for malaria increased from US$ 233 million to US$ 262
AIDS in Africa. An Update. Basil Reekie
 AIDS in Africa An Update Basil Reekie Contents General Statistics The trend of HIV in Africa Ugandan experience UNAIDS 2006 Latest African Statistics by Country HIV Intervention Light at the end of the
AIDS in Africa An Update Basil Reekie Contents General Statistics The trend of HIV in Africa Ugandan experience UNAIDS 2006 Latest African Statistics by Country HIV Intervention Light at the end of the
Volume 1 Issue 2 April-June,2012 DOSE OF CUE- LURE FOR SUPPRESSION OF MELON FLY POPULATION IN PUMPKIN CHAUDHARY*, F. K. AND PATEL, G. M.
 DOSE OF CUE- LURE FOR SUPPRESSION OF MELON FLY POPULATION IN PUMPKIN CHAUDHARY*, F. K. AND PATEL, G. M. KRUSHI VIGYAN KENDRA, SARDARKRUSHINAGAR DANTIWADA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY DEESA - 385 535 DIST.:
DOSE OF CUE- LURE FOR SUPPRESSION OF MELON FLY POPULATION IN PUMPKIN CHAUDHARY*, F. K. AND PATEL, G. M. KRUSHI VIGYAN KENDRA, SARDARKRUSHINAGAR DANTIWADA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY DEESA - 385 535 DIST.:
Bactrocera invadens: Current status and control
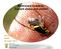 Bactrocera invadens: Current status and control JH VENTER DAFF OCTOBER 2014 Photo:. JH Venter National exotic fruit fly surveillance program Since 2006 Focus on early detection of exotic fruit flies Consists
Bactrocera invadens: Current status and control JH VENTER DAFF OCTOBER 2014 Photo:. JH Venter National exotic fruit fly surveillance program Since 2006 Focus on early detection of exotic fruit flies Consists
The Hawaii Fruit Fly Area-Wide Pest Management Program: Accomplishments and Future Directions
 Hawaii Proc. Hawaiian AWPM Accomplishments Entomol. Soc. (2007) and 39:99 104 Future Directions 99 The Hawaii Fruit Fly Area-Wide Pest Management Program: Accomplishments and Future Directions Roger I.
Hawaii Proc. Hawaiian AWPM Accomplishments Entomol. Soc. (2007) and 39:99 104 Future Directions 99 The Hawaii Fruit Fly Area-Wide Pest Management Program: Accomplishments and Future Directions Roger I.
Ecology and Sustainable Management of Major Bactrocera Fruit Flies in Goa, India
 Ecology and Sustainable Management of Major Bactrocera Fruit Flies in Goa, India V. R. Satarkar, S. V. Krishnamurthy, J.R. Faleiro, A. Verghese, R. Ramesh and J. Ashok Kumar Email: vved20@yahoo.co.in jrfaleiro@yahoo.co.in
Ecology and Sustainable Management of Major Bactrocera Fruit Flies in Goa, India V. R. Satarkar, S. V. Krishnamurthy, J.R. Faleiro, A. Verghese, R. Ramesh and J. Ashok Kumar Email: vved20@yahoo.co.in jrfaleiro@yahoo.co.in
Comparative Analyses of Adolescent Nutrition Indicators
 Comparative Analyses of Adolescent Nutrition Indicators Rukundo K. Benedict, PhD The DHS Program Stakeholders Consultation on Adolescent Girls Nutrition: Evidence, Guidance, and Gaps October 30 31, 2017
Comparative Analyses of Adolescent Nutrition Indicators Rukundo K. Benedict, PhD The DHS Program Stakeholders Consultation on Adolescent Girls Nutrition: Evidence, Guidance, and Gaps October 30 31, 2017
ACTION PLAN. for. CUELURE ATTRACTED FRUIT FLIES including the Melon Fly Bactrocera cucurbitae (Coquillett)
 ACTION PLAN for CUELURE ATTRACTED FRUIT FLIES including the Melon Fly Bactrocera cucurbitae (Coquillett) California Department of Food and Agriculture Plant Health and Pest Prevention Services Pest Detection/Emergency
ACTION PLAN for CUELURE ATTRACTED FRUIT FLIES including the Melon Fly Bactrocera cucurbitae (Coquillett) California Department of Food and Agriculture Plant Health and Pest Prevention Services Pest Detection/Emergency
The Changing Face of Agriculture: fruit flies, innovation and global trade
 The Changing Face of Agriculture: fruit flies, innovation and global trade Eric Jang, Fruit Fly Systems Applied Technologies (FFSATECH), Hilo, HI Dan Ryan, Horticulture Innovation Australia (HIA), Sydney,
The Changing Face of Agriculture: fruit flies, innovation and global trade Eric Jang, Fruit Fly Systems Applied Technologies (FFSATECH), Hilo, HI Dan Ryan, Horticulture Innovation Australia (HIA), Sydney,
Malaria Funding. Richard W. Steketee MACEPA, PATH. April World Malaria Day 2010, Seattle WA
 Malaria Funding Richard W. Steketee MACEPA, PATH April World Malaria Day 2010, Seattle WA Malaria Funding Is there a plan? Is there money? Where does the money come from? Is the money moving efficiently?
Malaria Funding Richard W. Steketee MACEPA, PATH April World Malaria Day 2010, Seattle WA Malaria Funding Is there a plan? Is there money? Where does the money come from? Is the money moving efficiently?
ISPM No. 30 ESTABLISHMENT OF AREAS OF LOW PEST PREVALENCE FOR FRUIT FLIES (TEPHRITIDAE) (2008)
 Establishment of areas of low pest prevalence for fruit flies (Tephritidae) ISPM No. 30 ISPM No. 30 INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR PHYTOSANITARY MEASURES ISPM No. 30 ESTABLISHMENT OF AREAS OF LOW PEST PREVALENCE
Establishment of areas of low pest prevalence for fruit flies (Tephritidae) ISPM No. 30 ISPM No. 30 INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR PHYTOSANITARY MEASURES ISPM No. 30 ESTABLISHMENT OF AREAS OF LOW PEST PREVALENCE
PROGRESS REPORT ON DECADE OF TRADITIONAL MEDICINE IN THE AFRICAN REGION. Progress Report. CONTENTS Paragraphs BACKGROUND PROGRESS MADE...
 5 July 2011 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-first session Yamoussoukro, Côte d Ivoire, 29 August 2 September 2011 Provisional agenda item 17.2 PROGRESS REPORT ON DECADE OF TRADITIONAL
5 July 2011 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-first session Yamoussoukro, Côte d Ivoire, 29 August 2 September 2011 Provisional agenda item 17.2 PROGRESS REPORT ON DECADE OF TRADITIONAL
J. Bio.Env. Sci. 2018
 Journal of Biodiversity and Environmental Sciences (JBES) ISSN: 2220-6663 (Print) 2222-3045 (Online) Vol. 12, No. 6, p. 96-101, 2018 http://www.innspub.net RESEARCH PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effect of type trap,
Journal of Biodiversity and Environmental Sciences (JBES) ISSN: 2220-6663 (Print) 2222-3045 (Online) Vol. 12, No. 6, p. 96-101, 2018 http://www.innspub.net RESEARCH PAPER OPEN ACCESS Effect of type trap,
Comparative Toxicity of Certain Pesticides to Peach Fruit Fly, Bactrocera zonata Saunders (Diptera: Tephritidae) under Laboratory Conditions
 Plant Protect. Sci. Vol. 7,, No. 3: 5 Comparative Toxicity of Certain Pesticides to Peach Fruit Fly, Bactrocera zonata Saunders (Diptera: Tephritidae) under Laboratory Conditions Yahia Youssef Mosleh,
Plant Protect. Sci. Vol. 7,, No. 3: 5 Comparative Toxicity of Certain Pesticides to Peach Fruit Fly, Bactrocera zonata Saunders (Diptera: Tephritidae) under Laboratory Conditions Yahia Youssef Mosleh,
Queensland fruit fly responses (2014)
 Queensland fruit fly responses (2014) George Gill, Principal Adviser, Plant and Environment Response, Operations Branch Barney Stephenson, Principal Adviser, Surveillance and Incursion Investigation, Operations
Queensland fruit fly responses (2014) George Gill, Principal Adviser, Plant and Environment Response, Operations Branch Barney Stephenson, Principal Adviser, Surveillance and Incursion Investigation, Operations
NAPPO Regional Standards for Phytosanitary Measures (RSPM)
 NAPPO Regional Standards for Phytosanitary Measures (RSPM) Guidelines for the Establishment, Maintenance and Verification of Fruit Fly Pest Free Areas in North America The Secretariat of the North American
NAPPO Regional Standards for Phytosanitary Measures (RSPM) Guidelines for the Establishment, Maintenance and Verification of Fruit Fly Pest Free Areas in North America The Secretariat of the North American
Population dynamics of fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) species associated with mango in the Guinea Savanna Agro-Ecological zone of Ghana
 International Journal of Agricultural Sciences ISSN: 2167-0447 Vol. 3 (3), pp. 450-454, March, 2013. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International Scholars Journals Full Length
International Journal of Agricultural Sciences ISSN: 2167-0447 Vol. 3 (3), pp. 450-454, March, 2013. Available online at www.internationalscholarsjournals.org International Scholars Journals Full Length
POLIOMYELITIS ERADICATION: PROGRESS REPORT. Information Document CONTENTS BACKGROUND PROGRESS MADE NEXT STEPS... 12
 5 August 9 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-ninth session Kigali, Republic of Rwanda, August 4 September 9 POLIOMYELITIS ERADICATION: PROGRESS REPORT Information Document CONTENTS
5 August 9 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Fifty-ninth session Kigali, Republic of Rwanda, August 4 September 9 POLIOMYELITIS ERADICATION: PROGRESS REPORT Information Document CONTENTS
Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005
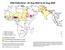 Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005 Wild virus type 1 Wild virus type 3 Wild virus type 1 & 3 Endemic countries Re-established transmission countries Case or outbreak following importation *Excludes
Wild Poliovirus*, 03 Aug 2004 to 02 Aug 2005 Wild virus type 1 Wild virus type 3 Wild virus type 1 & 3 Endemic countries Re-established transmission countries Case or outbreak following importation *Excludes
What is this document and who is it for?
 Measles and Rubella Initiative s Standard Operating Procedures for Accessing Support for Measles and Rubella Supplementary Immunization Activities During 2016 In the context of measles and rubella elimination
Measles and Rubella Initiative s Standard Operating Procedures for Accessing Support for Measles and Rubella Supplementary Immunization Activities During 2016 In the context of measles and rubella elimination
Name change of the invasive fruit fly and update on its pest status in South Africa
 Name change of the invasive fruit fly and update on its pest status in South Africa Fruit flies are the bane of many fruit growers existence, but in this case it s better the devil you know, than the one
Name change of the invasive fruit fly and update on its pest status in South Africa Fruit flies are the bane of many fruit growers existence, but in this case it s better the devil you know, than the one
The suppression of the False Codling Moth, Thaumatotibia leucotreta in South Africa using an AW-IPM approach with a SIT component
 The suppression of the False Codling Moth, Thaumatotibia leucotreta in South Africa using an AW-IPM approach with a SIT component Nevill Boersma Program Manager XSIT South Africa Background FCM sub-saharan
The suppression of the False Codling Moth, Thaumatotibia leucotreta in South Africa using an AW-IPM approach with a SIT component Nevill Boersma Program Manager XSIT South Africa Background FCM sub-saharan
THEMATIC PLAN FOR FRUIT FLY CONTROL USING THE STERILE INSECT TECHNIQUE
 TP-NA-D4-02 Limited Distribution International Atomic Energy Agency THEMATIC PLAN FOR FRUIT FLY CONTROL USING THE STERILE INSECT TECHNIQUE VIENNA, AUSTRIA 15-19 NOVEMBER 1999 Table of Contents I. EXECUTIVE
TP-NA-D4-02 Limited Distribution International Atomic Energy Agency THEMATIC PLAN FOR FRUIT FLY CONTROL USING THE STERILE INSECT TECHNIQUE VIENNA, AUSTRIA 15-19 NOVEMBER 1999 Table of Contents I. EXECUTIVE
The IPM based on mass trapping : Ceratitis capitata (Diptera, Tephritidae)?
 Regional Symposium on the Management of Fruit Flies in Near East Countries, 6 8 Nov. 2012, Hammamet, Tunisia The IPM based on mass trapping : is it an efficient method to control the Medfly Ceratitis capitata
Regional Symposium on the Management of Fruit Flies in Near East Countries, 6 8 Nov. 2012, Hammamet, Tunisia The IPM based on mass trapping : is it an efficient method to control the Medfly Ceratitis capitata
AN ATTEMPT AT THE ERADICATION OF THE ORIENTAL FRUIT FLY, Bactrocera dorsalis (HENDEL) FROM MAURITIUS
 AN ATTEMPT AT THE ERADICATION OF THE ORIENTAL FRUIT FLY, Bactrocera dorsalis (HENDEL) FROM MAURITIUS S I Seewooruthun, P Sookar, S Permalloo, A Joomaye, M Alleck, B Gungah and A R Soonnoo Ministry of Agriculture,
AN ATTEMPT AT THE ERADICATION OF THE ORIENTAL FRUIT FLY, Bactrocera dorsalis (HENDEL) FROM MAURITIUS S I Seewooruthun, P Sookar, S Permalloo, A Joomaye, M Alleck, B Gungah and A R Soonnoo Ministry of Agriculture,
GABON. Neglected tropical disease treatment report profile for mass treatment of NTDs
 GABON Neglected tropical disease treatment report 2017 1 2017 profile for mass treatment of NTDs NEGLECTED TROPICAL DISEASES Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a group of preventable and treatable
GABON Neglected tropical disease treatment report 2017 1 2017 profile for mass treatment of NTDs NEGLECTED TROPICAL DISEASES Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a group of preventable and treatable
Genetic Control Tactic Against Fruit Flies (Diptera: Tephritidae) Insect to Escape Destruction of Perishable Horticulture Crops
 International Journal of Animal Biology Vol. 1, No. 5, 2015, pp. 209-214 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/ijab Genetic Control Tactic Against Fruit Flies (Diptera: Tephritidae) Insect to Escape Destruction
International Journal of Animal Biology Vol. 1, No. 5, 2015, pp. 209-214 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/ijab Genetic Control Tactic Against Fruit Flies (Diptera: Tephritidae) Insect to Escape Destruction
( A JICA-IRRI-PhilRice Initiative) Presented by Noel Magor, Head Unit Impact Acceleration and Training Center, IRRI
 ( A JICA-IRRI-PhilRice Initiative) Presented by Noel Magor, Head Unit Impact Acceleration and Training Center, IRRI Long partnership between; IRRI & PhilRice IRRI & JICA PhilRice & JICA The Season Long
( A JICA-IRRI-PhilRice Initiative) Presented by Noel Magor, Head Unit Impact Acceleration and Training Center, IRRI Long partnership between; IRRI & PhilRice IRRI & JICA PhilRice & JICA The Season Long
ISPM No. 9 GUIDELINES FOR PEST ERADICATION PROGRAMMES (1998)
 ISPM No. 9 INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR PHYTOSANITARY MEASURES ISPM No. 9 GUIDELINES FOR PEST ERADICATION PROGRAMMES (1998) Produced by the Secretariat of the International Plant Protection Convention FAO
ISPM No. 9 INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR PHYTOSANITARY MEASURES ISPM No. 9 GUIDELINES FOR PEST ERADICATION PROGRAMMES (1998) Produced by the Secretariat of the International Plant Protection Convention FAO
Aboubacar Kampo Chief of Health UNICEF Nigeria
 Aboubacar Kampo Chief of Health UNICEF Nigeria Many thanks to UNICEF colleagues in Supply Division-Copenhagen and NY for contributing to this presentation Thirty-five countries are responsible for 98%
Aboubacar Kampo Chief of Health UNICEF Nigeria Many thanks to UNICEF colleagues in Supply Division-Copenhagen and NY for contributing to this presentation Thirty-five countries are responsible for 98%
VAPOUR HEAT TREATMENT AGAINST THREE SPECIES OF FRUIT FLIES IN MANGO DEDONG
 International Plant Protection Convention 13_ECBD_2014_Dec Vapour Heat treatment against three species of fruit flies in Mango Dedong Agenda item: 5.4 VAPOUR HEAT TREATMENT AGAINST THREE SPECIES OF FRUIT
International Plant Protection Convention 13_ECBD_2014_Dec Vapour Heat treatment against three species of fruit flies in Mango Dedong Agenda item: 5.4 VAPOUR HEAT TREATMENT AGAINST THREE SPECIES OF FRUIT
How does California deal with invasive species? Plant Health and Pest Prevention Services California Department of Food and Agriculture
 How does California deal with invasive species? Plant Health and Pest Prevention Services California Department of Food and Agriculture Early Days Junipero Serra (1713-1784) William Wolfskill (1798-1866)
How does California deal with invasive species? Plant Health and Pest Prevention Services California Department of Food and Agriculture Early Days Junipero Serra (1713-1784) William Wolfskill (1798-1866)
Gender, Poverty, and Health in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Framework for Analysis
 Gender, Poverty, and Health in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Framework for Analysis Pathways to Improved Health Outcomes Health outcomes Households/ Communities Household behaviors & risk factors Community factors
Gender, Poverty, and Health in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Framework for Analysis Pathways to Improved Health Outcomes Health outcomes Households/ Communities Household behaviors & risk factors Community factors
Fruit Fly Surveillance in Nepal
 Agricultural and Biological Sciences Journal Vol. 1, No. 3, 2015, pp. 121-125 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/absj Fruit Fly Surveillance in Nepal D. R. Sharma 1, D. Adhikari 2, *, D. B. Tiwari 3 1 National
Agricultural and Biological Sciences Journal Vol. 1, No. 3, 2015, pp. 121-125 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/absj Fruit Fly Surveillance in Nepal D. R. Sharma 1, D. Adhikari 2, *, D. B. Tiwari 3 1 National
Brian N. Barnes 1 & Jan-Hendrik Venter 2
 Fruit Flies of Economic Importance: From Basic to Applied Knowledge Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Fruit Flies of Economic Importance 10-15 September 2006, Salvador, Brazil pp. 271-283
Fruit Flies of Economic Importance: From Basic to Applied Knowledge Proceedings of the 7th International Symposium on Fruit Flies of Economic Importance 10-15 September 2006, Salvador, Brazil pp. 271-283
Expert Group Meeting on the Regional Report for the African Gender and Development Index
 Expert Group Meeting on the Regional Report for the African Gender and Development Index 9-10 October 2017 United Nations Conference Centre, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia Aide Memoire July 2017 I. Background and
Expert Group Meeting on the Regional Report for the African Gender and Development Index 9-10 October 2017 United Nations Conference Centre, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia Aide Memoire July 2017 I. Background and
ASSESSMENT OF FRUIT FLY BACTROCERA INVADENS (DIPTERA: TEPHRITIDAE) PRESENCE IN EASTERN PROVINCE OF RWANDA. M.Olivier & 2 Hance Thierry,
 ASSESSMENT OF FRUIT FLY BACTROCERA INVADENS (DIPTERA: TEPHRITIDAE) PRESENCE IN EASTERN PROVINCE OF RWANDA 1* Harelimana Anastase, 2 Le Goff Guillaume Jean, 3 Rukazambuga Daniel, 4 Ngamata M.Olivier & 2
ASSESSMENT OF FRUIT FLY BACTROCERA INVADENS (DIPTERA: TEPHRITIDAE) PRESENCE IN EASTERN PROVINCE OF RWANDA 1* Harelimana Anastase, 2 Le Goff Guillaume Jean, 3 Rukazambuga Daniel, 4 Ngamata M.Olivier & 2
Lessons learned from the IeDEA West Africa Collaboration
 Lessons learned from the IeDEA West Africa Collaboration François DABIS with the contribution of Didier Koumavi EKOUEVI INSERM U-897, Bordeaux, France, Programme PACCI, ANRS site, Abidjan, Côte d Ivoire
Lessons learned from the IeDEA West Africa Collaboration François DABIS with the contribution of Didier Koumavi EKOUEVI INSERM U-897, Bordeaux, France, Programme PACCI, ANRS site, Abidjan, Côte d Ivoire
Making codling moth mating disruption work in Michigan: Adopting an area-wide approach to managing codling moth in Michigan apple production
 Fruit Crop Advisory Team Alert Vol. 20, No. 17, September 6, 2005 Making codling moth mating disruption work in Michigan: Adopting an area-wide approach to managing codling moth in Michigan apple production
Fruit Crop Advisory Team Alert Vol. 20, No. 17, September 6, 2005 Making codling moth mating disruption work in Michigan: Adopting an area-wide approach to managing codling moth in Michigan apple production
ISPM 26. Establishment of pest free areas for fruit flies (Tephritidae)
 INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR PHYTOSANITARY MEASURES ISPM 26 Establishment of pest free areas for fruit flies (Tephritidae) Produced by the Secretariat of the International Plant Protection Convention Adopted
INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR PHYTOSANITARY MEASURES ISPM 26 Establishment of pest free areas for fruit flies (Tephritidae) Produced by the Secretariat of the International Plant Protection Convention Adopted
PROGRESS REPORT ON THE ROAD MAP FOR ACCELERATING THE ATTAINMENT OF THE MILLENNIUM DEVELOPMENT GOALS RELATED TO MATERNAL AND NEWBORN HEALTH IN AFRICA
 5 July 2011 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-first session Yamoussoukro, Côte d Ivoire, 29 August 2 September 2011 Provisional agenda item 17.1 PROGRESS REPORT ON THE ROAD MAP FOR
5 July 2011 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-first session Yamoussoukro, Côte d Ivoire, 29 August 2 September 2011 Provisional agenda item 17.1 PROGRESS REPORT ON THE ROAD MAP FOR
INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR PHYTOSANITARY MEASURES GUIDELINES FOR PEST ERADICATION PROGRAMMES
 Publication No. 9 November 1998 INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR PHYTOSANITARY MEASURES GUIDELINES FOR PEST ERADICATION PROGRAMMES Secretariat of the International Plant Protection Convention Food and Agriculture
Publication No. 9 November 1998 INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR PHYTOSANITARY MEASURES GUIDELINES FOR PEST ERADICATION PROGRAMMES Secretariat of the International Plant Protection Convention Food and Agriculture
World Toilet Day: Eradicating open defecation still a challenge in Ghana
 Dispatch No. 60 19 November 2015 World Toilet Day: Eradicating open defecation still a challenge in Ghana Afrobarometer Dispatch No. 60 Daniel Armah-Attoh Summary Ghana has been observing Toilet Day since
Dispatch No. 60 19 November 2015 World Toilet Day: Eradicating open defecation still a challenge in Ghana Afrobarometer Dispatch No. 60 Daniel Armah-Attoh Summary Ghana has been observing Toilet Day since
whereas the fourth inhibitor was extracted and semi purified from cabbage (Brassica oleracae) in the Insect Physiology Laboratory of the Department of
 6. SUMMARY Due to long co-evolution of plants and herbivores a vast repertoire of unique bioactive compounds have appeared in plants, some of which have found use in medicines, drugs, antibiotics, insecticides,
6. SUMMARY Due to long co-evolution of plants and herbivores a vast repertoire of unique bioactive compounds have appeared in plants, some of which have found use in medicines, drugs, antibiotics, insecticides,
PPR VACCINE, VACCINATION AND VACCINE QUALITY CONTROL
 Dr DIALLO ADAMA CONSULTANT FAO PPR VACCINE, VACCINATION AND VACCINE QUALITY CONTROL Lessons from rinderpest eradication 2011 was the official recognition of the world freedom from rinderpest Lessons from
Dr DIALLO ADAMA CONSULTANT FAO PPR VACCINE, VACCINATION AND VACCINE QUALITY CONTROL Lessons from rinderpest eradication 2011 was the official recognition of the world freedom from rinderpest Lessons from
Review of Long-Term Containment Strategy for Exotic Fruit Flies in Torres Strait. Andrew Tomkins Chair
 Review of Long-Term Containment Strategy for Exotic Fruit Flies in Torres Strait Andrew Tomkins Chair The Torres Strait Zones protect biosecurity while enabling traditional movement of people and goods.
Review of Long-Term Containment Strategy for Exotic Fruit Flies in Torres Strait Andrew Tomkins Chair The Torres Strait Zones protect biosecurity while enabling traditional movement of people and goods.
IMMUNIZATION VACCINES & EMERGENCIES
 No report No data No data IMMUNIZATION VACCINES & EMERGENCIES ROUTINE IMMUNIZATION PERFORMANCE IN THE AFRICAN REGION October 2013 issue Number of children vaccinated with the 3 rd dose of DTPcontaining
No report No data No data IMMUNIZATION VACCINES & EMERGENCIES ROUTINE IMMUNIZATION PERFORMANCE IN THE AFRICAN REGION October 2013 issue Number of children vaccinated with the 3 rd dose of DTPcontaining
Population Density and Percentage of Infestation with Mediterranean fruit fly Ceratitis capitata (Wiedemann) in Two Iraqi Provinces
 EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. VI, Issue 3/ June 2018 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Population Density and Percentage of Infestation with Mediterranean
EUROPEAN ACADEMIC RESEARCH Vol. VI, Issue 3/ June 2018 ISSN 2286-4822 www.euacademic.org Impact Factor: 3.4546 (UIF) DRJI Value: 5.9 (B+) Population Density and Percentage of Infestation with Mediterranean
Tel: ; Fax: URL: Cohen, E., Ph.D. (Head of Department) Shafir, S., Ph.D.
 ENTOMOLOGY Tel: 972-8-948-9223; Fax: 972-8-946-6768 URL: http://departments.agri.huji.ac.il/entomology/ STAFF Professors Emeriti: Gerson, U., Ph.D. Lensky, Y., Ph.D. Applebaum, S.W., Ph.D. 1 Professors:
ENTOMOLOGY Tel: 972-8-948-9223; Fax: 972-8-946-6768 URL: http://departments.agri.huji.ac.il/entomology/ STAFF Professors Emeriti: Gerson, U., Ph.D. Lensky, Y., Ph.D. Applebaum, S.W., Ph.D. 1 Professors:
Mediterranean fruit fly
 Common names: medfly, Mediterreense vrugtevlieg Higher taxon: Insecta: Diptera: Tephritidae EPPO code: CERTCA The is one of the most destructive fruit pests in the world. It is native to sub-saharan Africa
Common names: medfly, Mediterreense vrugtevlieg Higher taxon: Insecta: Diptera: Tephritidae EPPO code: CERTCA The is one of the most destructive fruit pests in the world. It is native to sub-saharan Africa
Improved postharvest market access treatments for horticultural commodities (3097)
 Improved postharvest market access treatments for horticultural commodities (3097) Ms L. Jamieson (Plant and Food Research) and Ms P. Wyatt (Department of Agriculture and Fisheries). The disruption to
Improved postharvest market access treatments for horticultural commodities (3097) Ms L. Jamieson (Plant and Food Research) and Ms P. Wyatt (Department of Agriculture and Fisheries). The disruption to
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine: Current Supply & Demand Outlook. UNICEF Supply Division
 Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine: Current Supply & Demand Outlook UNICEF Supply Division Update: October 2013 0 Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) Supply & Demand Outlook October 2013 Update Key updates
Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine: Current Supply & Demand Outlook UNICEF Supply Division Update: October 2013 0 Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) Supply & Demand Outlook October 2013 Update Key updates
Scaling Up Nutrition Action for Africa
 Scaling Up Nutrition Action for Africa Where are we and what challenges are need to be addressed to accelerate malnutrition? Lawrence Haddad Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition Why should African political
Scaling Up Nutrition Action for Africa Where are we and what challenges are need to be addressed to accelerate malnutrition? Lawrence Haddad Global Alliance for Improved Nutrition Why should African political
Successful Utilization of the Area-Wide Approach for the Management of Fruit Flies in Hawaii
 1 Successful Utilization of the Area-Wide Approach for the Management of Fruit Flies in Hawaii Roger I. Vargas 1, Ronald F. L. Mau 2, Lyle Wong 3, and Eric B. Jang 1 1 United States Department of Agriculture
1 Successful Utilization of the Area-Wide Approach for the Management of Fruit Flies in Hawaii Roger I. Vargas 1, Ronald F. L. Mau 2, Lyle Wong 3, and Eric B. Jang 1 1 United States Department of Agriculture
Africa s slow fertility transition
 Africa s slow fertility transition John Bongaarts Population Council, New York Süssmilch Lecture Max Planck Institute, Rostock 3 Sep 215 Billions 4 3 Population projections for sub-saharan Africa 215 projection
Africa s slow fertility transition John Bongaarts Population Council, New York Süssmilch Lecture Max Planck Institute, Rostock 3 Sep 215 Billions 4 3 Population projections for sub-saharan Africa 215 projection
COLD CHAIN EQUIPMENT OPTIMISATION PLATFORM (CCEOP)
 COLD CHAIN EQUIPMENT OPTIMISATION PLATFORM (CCEOP) Sushila Maharjan Senior Manager, Innovative Finance International Conference on Sustainable Cooling World Bank Washington DC - 29 November 2018 Reach
COLD CHAIN EQUIPMENT OPTIMISATION PLATFORM (CCEOP) Sushila Maharjan Senior Manager, Innovative Finance International Conference on Sustainable Cooling World Bank Washington DC - 29 November 2018 Reach
Food Production and Violent Conflict in Sub-Saharan Africa. - Supplementary Information -
 Food Production and Violent Conflict in Sub-Saharan Africa - Supplementary Information - Halvard Buhaug a,b,1, Tor A. Benaminsen c,a, Espen Sjaastad c & Ole Magnus Theisen b,a a Peace Research Institute
Food Production and Violent Conflict in Sub-Saharan Africa - Supplementary Information - Halvard Buhaug a,b,1, Tor A. Benaminsen c,a, Espen Sjaastad c & Ole Magnus Theisen b,a a Peace Research Institute
UNAIDS 2013 AIDS by the numbers
 UNAIDS 2013 AIDS by the numbers 33 % decrease in new HIV infections since 2001 29 % decrease in AIDS-related deaths (adults and children) since 2005 52 % decrease in new HIV infections in children since
UNAIDS 2013 AIDS by the numbers 33 % decrease in new HIV infections since 2001 29 % decrease in AIDS-related deaths (adults and children) since 2005 52 % decrease in new HIV infections in children since
Institute/Country. Universidad de Costa Rica, COSTA RICA. Plant Protection Directorate, Madeira, PORTUGAL
 1. CRP Title "Development of Female Medfly Attractant Systems for Trapping and Sterility Assessment" 2. Section/Division: Insect Pest Control / Joint FAO/IAEA Division (NAFA) 3. Project Officer: Jorge
1. CRP Title "Development of Female Medfly Attractant Systems for Trapping and Sterility Assessment" 2. Section/Division: Insect Pest Control / Joint FAO/IAEA Division (NAFA) 3. Project Officer: Jorge
Collaborators: Gration Rwegasira, Marc De Meyer, Massimiliano Virgilio and Richard Drew
 (a) Progress report (i) Contract number IAEA Technical contract Nr 16077/RO (ii) Title of the project Host utilization and genetic divergence among populations of Bactrocera invadens Drew Tsuruta and White
(a) Progress report (i) Contract number IAEA Technical contract Nr 16077/RO (ii) Title of the project Host utilization and genetic divergence among populations of Bactrocera invadens Drew Tsuruta and White
CONTENTS. Paragraphs I. BACKGROUND II. PROGRESS REPORT ON THE AFRICAN REGIONAL IMMUNIZATION STRATEGIC PLAN
 23 September 2013 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-third session Brazzaville, Republic of Congo, 2 6 September, 2013 Agenda item 14 IMMUNIZATION IN THE AFRICAN REGION: PROGRESS REPORT
23 September 2013 REGIONAL COMMITTEE FOR AFRICA ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Sixty-third session Brazzaville, Republic of Congo, 2 6 September, 2013 Agenda item 14 IMMUNIZATION IN THE AFRICAN REGION: PROGRESS REPORT
Prioritizing Emergency Polio Eradication Activities
 Prioritizing Emergency Polio Eradication Activities Managing the Financing Gap the other half of the Emergency Hamid Jafari GPEI Financing 2012-13: Budget = $2.23 b - Confirmed contributions = $1.14 b
Prioritizing Emergency Polio Eradication Activities Managing the Financing Gap the other half of the Emergency Hamid Jafari GPEI Financing 2012-13: Budget = $2.23 b - Confirmed contributions = $1.14 b
Efficacy of Protein Bait Sprays in Controlling Melon Fruit Fly [Bactrocera Cucurbitae (Coquillett)] in Vegetable Agro-ecosystems
![Efficacy of Protein Bait Sprays in Controlling Melon Fruit Fly [Bactrocera Cucurbitae (Coquillett)] in Vegetable Agro-ecosystems Efficacy of Protein Bait Sprays in Controlling Melon Fruit Fly [Bactrocera Cucurbitae (Coquillett)] in Vegetable Agro-ecosystems](/thumbs/85/92068826.jpg) Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences: B. Life and Environmental Sciences 54 (2): 111 115 (2017) Copyright Pakistan Academy of Sciences ISSN: 2518-4261 (print), ISSN 2518-427X (online) Pakistan
Proceedings of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences: B. Life and Environmental Sciences 54 (2): 111 115 (2017) Copyright Pakistan Academy of Sciences ISSN: 2518-4261 (print), ISSN 2518-427X (online) Pakistan
African Gender and Development Index
 African Gender and Development Index EXPERTS MEETING ON METHODOLOGIES FOR REGIONAL INTEGRATION INDEX 26 SEPTEMBER 2018 ADDIS ABABA, ETHIOPIA Outline 1. The African Gender and Development Index 2. Gender
African Gender and Development Index EXPERTS MEETING ON METHODOLOGIES FOR REGIONAL INTEGRATION INDEX 26 SEPTEMBER 2018 ADDIS ABABA, ETHIOPIA Outline 1. The African Gender and Development Index 2. Gender
Establishment of areas of low pest prevalence for fruit flies (Tephritidae)
 30 ISPM 30 International Standard for Phytosanitary Measures Establishment of areas of low pest prevalence for fruit flies (Tephritidae) eng This page is intentionally left blank INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS
30 ISPM 30 International Standard for Phytosanitary Measures Establishment of areas of low pest prevalence for fruit flies (Tephritidae) eng This page is intentionally left blank INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS
FRUIT FLY LURE AND TRAP FOR QUEENSLAND FRUIT FLY (Bactrocera tryoni) TECHNICAL MANUAL Innovation. Quality. Solutions.
 FRUIT FLY LURE AND TRAP FOR QUEENSLAND FRUIT FLY (Bactrocera tryoni) TECHNICAL MANUAL 2018 Innovation. Quality. Solutions. TECHNICAL MANUAL TRAPS CONTENTS Executive Summary Page 03 Background Page 05 Development
FRUIT FLY LURE AND TRAP FOR QUEENSLAND FRUIT FLY (Bactrocera tryoni) TECHNICAL MANUAL 2018 Innovation. Quality. Solutions. TECHNICAL MANUAL TRAPS CONTENTS Executive Summary Page 03 Background Page 05 Development
Putting Sterile Insect Technique into the Modern IPM Toolbox: Over 20 years of successful area-wide integrated pest management in Canadian pome fruit
 Putting Sterile Insect Technique into the Modern IPM Toolbox: Over 20 years of successful area-wide integrated pest management in Canadian pome fruit Cara Nelson, General Manager Okanagan-Kootenay Sterile
Putting Sterile Insect Technique into the Modern IPM Toolbox: Over 20 years of successful area-wide integrated pest management in Canadian pome fruit Cara Nelson, General Manager Okanagan-Kootenay Sterile
Management and Control: Queensland fruit fly (Bactrocera tryoni)
 Management and Control: Queensland fruit fly (Bactrocera tryoni) 1.0 EARLY DETECTION 2.0 COMBINED MANAGEMENT 3.0 CHEMICAL 3.1 GROUND SPRAYING 3.2 BAIT SPRAYING 3.3 COVER SPRAYING 3.4 MALE ANNIHILATION
Management and Control: Queensland fruit fly (Bactrocera tryoni) 1.0 EARLY DETECTION 2.0 COMBINED MANAGEMENT 3.0 CHEMICAL 3.1 GROUND SPRAYING 3.2 BAIT SPRAYING 3.3 COVER SPRAYING 3.4 MALE ANNIHILATION
Funding for AIDS: The World Bank s Role. Yolanda Tayler, WB Bi-regional Workshop for the Procurement of ARVs Phnom Penh, Cambodia
 Funding for AIDS: The World Bank s Role Yolanda Tayler, WB Bi-regional Workshop for the Procurement of ARVs Phnom Penh, Cambodia Outline New resources needs estimates Bridging the gap Global overview of
Funding for AIDS: The World Bank s Role Yolanda Tayler, WB Bi-regional Workshop for the Procurement of ARVs Phnom Penh, Cambodia Outline New resources needs estimates Bridging the gap Global overview of
ISPM No. 26 ESTABLISHMENT OF PEST FREE AREAS FOR FRUIT FLIES (TEPHRITIDAE) (2006)
 ISPM No. 26 INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR PHYTOSANITARY MEASURES ISPM No. 26 ESTABLISHMENT OF PEST FREE AREAS FOR FRUIT FLIES (TEPHRITIDAE) (2006) Produced by the Secretariat of the International Plant Protection
ISPM No. 26 INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS FOR PHYTOSANITARY MEASURES ISPM No. 26 ESTABLISHMENT OF PEST FREE AREAS FOR FRUIT FLIES (TEPHRITIDAE) (2006) Produced by the Secretariat of the International Plant Protection
1) SO1: We would like to suggest that the indicator used to measure vaccine hesitancy be DTP 1 to measles first dose dropout.
 To SAGE Secretariat, WHO Dear Professor Helen Rees, Dear Dr. Jean Marie Okwo-Bele, On behalf of the Civil Society Constituency of the GAVI Alliance, we would like to thank SAGE and its members for the
To SAGE Secretariat, WHO Dear Professor Helen Rees, Dear Dr. Jean Marie Okwo-Bele, On behalf of the Civil Society Constituency of the GAVI Alliance, we would like to thank SAGE and its members for the
Fruit Sampling Guidelines for Area-Wide Fruit Fly Programmes
 Fruit Sampling Guidelines for Area-Wide Fruit Fly Programmes DISCLAIMER The material in this document has been supplied by the authors. The views expressed remain the responsibility of the authors and
Fruit Sampling Guidelines for Area-Wide Fruit Fly Programmes DISCLAIMER The material in this document has been supplied by the authors. The views expressed remain the responsibility of the authors and
Excellence and Originality from Necessity: Palliative Care in Africa. Dr Emmanuel Luyirika Executive Director, African Palliative Care Association
 Excellence and Originality from Necessity: Palliative Care in Africa Dr Emmanuel Luyirika Executive Director, African Palliative Care Association Summary of the presentation 1. Introduction 2. Background
Excellence and Originality from Necessity: Palliative Care in Africa Dr Emmanuel Luyirika Executive Director, African Palliative Care Association Summary of the presentation 1. Introduction 2. Background
PHYTOSANITARY IRRADIATION TO CONTROL QUARANTINE PESTS
 PHYTOSANITARY IRRADIATION TO CONTROL QUARANTINE PESTS Peter Follett, Research Entomologist USDA-ARS U.S. Pacific Basin Agricultural Research Center Hilo, Hawaii Los huracanes de Mexico Hawaii Overview
PHYTOSANITARY IRRADIATION TO CONTROL QUARANTINE PESTS Peter Follett, Research Entomologist USDA-ARS U.S. Pacific Basin Agricultural Research Center Hilo, Hawaii Los huracanes de Mexico Hawaii Overview
All male strains and chemical stimulants: Two ways to boost sterile males in SIT programs. Abstract
 All male strains and chemical stimulants: Two ways to boost sterile males in SIT programs Drs. Donald O. McInnis 1, Todd E. Shelly 2, and Ronald F. L. Mau 3 1. USDA/ARS/PBARC, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2. USDA/APHIS/CPHST,
All male strains and chemical stimulants: Two ways to boost sterile males in SIT programs Drs. Donald O. McInnis 1, Todd E. Shelly 2, and Ronald F. L. Mau 3 1. USDA/ARS/PBARC, Honolulu, HI, USA, 2. USDA/APHIS/CPHST,
PILOT APPLICATION OF STERILE INSECT TECHNIQUE FOR THE ORIENTAL FRUIT FLY, BACTROCERA PHJLIPPJNENSIS, IN NAOWAY ISLET
 PH992 PILOT APPLICATION OF STERILE INSECT TECHNIQUE FOR THE ORIENTAL FRUIT FLY, BACTROCERA PHJLIPPJNENSIS, IN NAOWAY ISLET E. C. MANOTO, S. S. RESILVA, G. B. OBRA, M. R. REYES Philippine Nuclear Research
PH992 PILOT APPLICATION OF STERILE INSECT TECHNIQUE FOR THE ORIENTAL FRUIT FLY, BACTROCERA PHJLIPPJNENSIS, IN NAOWAY ISLET E. C. MANOTO, S. S. RESILVA, G. B. OBRA, M. R. REYES Philippine Nuclear Research
ATTACHMENT 5 CONSISTENCY CORRECTIONS IN RELATION TO HARMONIZATION OF FRUIT FLY STANDARDS
 ATTACHMENT 5 CONSISTENCY CORRECTIONS IN RELATION TO HARMONIZATION OF FRUIT FLY STANDARDS (Developed by the TPFF, October 2015; approved by SC May 2016 pending CPM-13 decision on reorganization) ANNEX 1
ATTACHMENT 5 CONSISTENCY CORRECTIONS IN RELATION TO HARMONIZATION OF FRUIT FLY STANDARDS (Developed by the TPFF, October 2015; approved by SC May 2016 pending CPM-13 decision on reorganization) ANNEX 1
Progress has been made with respect to health conditions.
 health Strong performers in reducing child mortality 199-2 Niger Guinea-Bissau Guinea Ethiopia Benin 2 199 Strong performers in reducing maternal mortality 199-2 Djibouti Madagascar Eritrea Comoros Somalia
health Strong performers in reducing child mortality 199-2 Niger Guinea-Bissau Guinea Ethiopia Benin 2 199 Strong performers in reducing maternal mortality 199-2 Djibouti Madagascar Eritrea Comoros Somalia
Foreword. For further information please contact Dr Nivo Ramanandraibe at and Dr Ahmed E. Ogwell Ouma at
 Bans on tobacco advertising, promotion and sponsorship in the African Region, 2013 Foreword Banning tobacco advertising, promotion and sponsorship is an obligation under Article 13 of the WHO Framework
Bans on tobacco advertising, promotion and sponsorship in the African Region, 2013 Foreword Banning tobacco advertising, promotion and sponsorship is an obligation under Article 13 of the WHO Framework
Relationship between Population Fluctuation of Oriental Fruit Fly Bactrocera dorsalis Hendel and Abiotic Factors in Yezin, Myanmar
 Journal of Life Sciences 12 (218) 141-149 doi: 1.17265/1934-7391/218.3.4 D DAVID PUBLISHING Relationship between Population Fluctuation of Oriental Fruit Fly Bactrocera dorsalis Hendel and Abiotic Factors
Journal of Life Sciences 12 (218) 141-149 doi: 1.17265/1934-7391/218.3.4 D DAVID PUBLISHING Relationship between Population Fluctuation of Oriental Fruit Fly Bactrocera dorsalis Hendel and Abiotic Factors
ONGOING PROJECT REPORT YEAR 1/3 WTFRC Project # CH
 ONGOING PROJECT REPORT YEAR 1/3 WTFRC Project # CH-6-63 Project title: Cherry Fruit Fly Control Options PI: Timothy J. Smith Organization: WSU Extension, North Central Washington Address, phone, e-mail:
ONGOING PROJECT REPORT YEAR 1/3 WTFRC Project # CH-6-63 Project title: Cherry Fruit Fly Control Options PI: Timothy J. Smith Organization: WSU Extension, North Central Washington Address, phone, e-mail:
SUMMARY: We are amending the fruits and vegetables regulations to allow the importation of
 This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 04/08/2016 and available online at http://federalregister.gov/a/2016-08191, and on FDsys.gov BILLING CODE: 3410-34-P DEPARTMENT OF
This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 04/08/2016 and available online at http://federalregister.gov/a/2016-08191, and on FDsys.gov BILLING CODE: 3410-34-P DEPARTMENT OF
Addressing climate change driven health challenges in Africa
 Addressing climate change driven health challenges in Africa Ednah N Ototo, Parasitologist, Climate Change and Health Kenyatta University, Kenya Kenya Medical Research Institute Outline The impact of climate
Addressing climate change driven health challenges in Africa Ednah N Ototo, Parasitologist, Climate Change and Health Kenyatta University, Kenya Kenya Medical Research Institute Outline The impact of climate
Cydia pomonella. Do You Know? Hosts. Orchard IPM Series HG/Orchard/08 Codling Moth. by Diane G. Alston and Michael E. Reding Adult Codling Moth
 Orchard IPM Series HG/Orchard/08 Codling Moth Cydia pomonella by Diane G. Alston and Michael E. Reding Adult Codling Moth Michigan State University Do You Know? Major pest of apple and pear in Utah. Damaging
Orchard IPM Series HG/Orchard/08 Codling Moth Cydia pomonella by Diane G. Alston and Michael E. Reding Adult Codling Moth Michigan State University Do You Know? Major pest of apple and pear in Utah. Damaging
Tree Fruit IPM Advisory: June 20 th, 2006
 Tree Fruit IPM Advisory: June 20 th, 2006 Past IPM advisories are archived at: http://extension.usu.edu/cooperative/ipm/index.cfm/cid.610/ **********News Alert!********** It is now time to put out pheromone
Tree Fruit IPM Advisory: June 20 th, 2006 Past IPM advisories are archived at: http://extension.usu.edu/cooperative/ipm/index.cfm/cid.610/ **********News Alert!********** It is now time to put out pheromone
Birth Control for Insects: The Sterile Insect Technique (SIT) for Controlling Fruit Fly (Tephritidae: Diptera) by Releasing Sterile Males
 International Journal of Animal Biology Vol. 1, No. 5, 2015, pp. 253-259 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/ijab Birth Control for Insects: The Sterile Insect Technique (SIT) for Controlling Fruit Fly (Tephritidae:
International Journal of Animal Biology Vol. 1, No. 5, 2015, pp. 253-259 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/ijab Birth Control for Insects: The Sterile Insect Technique (SIT) for Controlling Fruit Fly (Tephritidae:
Rift Valley Fever. What is Rift Valley Fever?
 Rift Valley Fever What is Rift Valley Fever? Rift Valley fever (RVF) is a peracute or acute insect-borne disease of man and animals, historically restricted to Africa. An outbreak of RVF in animals frequently
Rift Valley Fever What is Rift Valley Fever? Rift Valley fever (RVF) is a peracute or acute insect-borne disease of man and animals, historically restricted to Africa. An outbreak of RVF in animals frequently
