ISSN Volume 5, Number 3 September 2013
|
|
|
- Wilfred Bennett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ISSN Volume 5, Number 3 September
2 Editor-in-Chief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in- Chief Radoslav Slavov Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Editors and Sections Genetics and Breading Atanas Atanasov (Bulgaria) Ihsan Soysal (Turkey) Max Rothschild (USA) Stoicho Metodiev (Bulgaria) Nutrition and Physiology Nikolai Todorov (Bulgaria) Peter Surai (UK) Zervas Georgios (Greece) Ivan Varlyakov (Bulgaria) Production Systems Dimitar Pavlov (Bulgaria) Dimitar Panaiotov (Bulgaria) Banko Banev (Bulgaria) Georgy Zhelyazkov (Bulgaria) Agriculture and Environment Georgi Petkov (Bulgaria) Ramesh Kanwar (USA) Product Quality and Safety Marin Kabakchiev (Bulgaria) Stefan Denev (Bulgaria) Vasil Atanasov (Bulgaria) English Editor Yanka Ivanova (Bulgaria) Scope and policy of the journal Agricultural Science and Technology /AST/ an International Scientific Journal of Agricultural and Technology Sciences is published in English in one volume of 4 issues per year, as a printed journal and in electronic form. The policy of the journal is to publish original papers, reviews and short communications covering the aspects of agriculture related with life sciences and modern technologies. It will offer opportunities to address the global needs relating to food and environment, health, exploit the technology to provide innovative products and sustainable development. Papers will be considered in aspects of both fundamental and applied science in the areas of Genetics and Breeding, Nutrition and Physiology, Production Systems, Agriculture and Environment and Product Quality and Safety. Other categories closely related to the above topics could be considered by the editors. The detailed information of the journal is available at the website. Proceedings of scientific meetings and conference reports will be considered for special issues. Submission of Manuscripts All manuscripts written in English should be submitted as MS-Word file attachments via to ascitech@uni-sz.bg. Manuscripts must be prepared strictly in accordance with the detailed instructions for authors at the website and the instructions on the last page of the journal. For each manuscript the signatures of all authors are needed confirming their consent to publish it and to nominate on author for correspondence. They have to be presented by a submission letter signed by all authors. The form of the submission letter is available upon from request from the Technical Assistance or could be downloaded from the website of the journal. Manuscripts submitted to this journal are considered if they have submitted only to it, they have not been published already, nor are they under consideration for publication in press elsewhere. All manuscripts are subject to editorial review and the editors reserve the right to improve style and return the paper for rewriting to the authors, if necessary. The editorial board reserves rights to reject manuscripts based on priorities and space availability in the journal. The articles appearing in this journal are indexed and abstracted in: EBSCO Publishing, Inc. and AGRIS (FAO). The journal is accepted to be indexed with the support of a project BG051PO Science and business financed by Operational Programme Human Resources Development of EU. The title has been suggested to be included in SCOPUS (Elsevier) and Electronic Journals Submission Form (Thomson Reuters). Internet Access This journal is included in the Trakia University Journals online Service which can be found at Address of Editorial office: Agricultural Science and Technology Faculty of Agriculture, Trakia University Student's campus, 6000 Stara Zagora Bulgaria Telephone.: Technical Assistance: Nely Tsvetanova Telephone.: ascitech@uni-sz.bg
3 Volume 5, Number 3 September 2013 ISSN
4
5 AGRICULTURAL SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 5, No 3, pp , 2013 Reproductive performance of weaning sows after treatment with Fertipig S. Dimitrov*, G. Bonev Department of Genetics, Breeding and Reproduction, Faculty of Agriculture, Trakia University, 6000 Stara Zagora, Bulgaria Abstract. The aim of this study was to examine the efficacy of hormonal treatment of lactating sows with a combination of 400 UI PMSG and 200 UI hcg one day before weaning. The treatment with Fertipig of a total of 88 sows induced estrus with an average period of 4.54±0.64 days after injection. It was established that the interval from the injection to the beginning of estrus had no significant effect on the main reproductive parameters. The animals with estrus up to 5 days after hormonal treatment had low percent of farrowing rate in comparison with sows showing estrus after 5 days 87.80% and 93.61%, respectively. The significant effect was found in the sow's parity number regarding live born piglets. More piglets were obtained from animals with up to 6 parities 11.00±1.51 in comparison with sows with over 6 parities 10.15±2.22 (р< 0.05). This factor does not have significant influence on the time of estrus appearance after hormonal injection and other reproductive parameters. This hormonal therapy is an effective way to improve the reproductive performance on commercial pig farms. Keywords: sows, weaning, hormonal treatment, reproductive parameters Introduction An important element of reproductive and economic efficiency of modern swine farms is the weaning-to-estrus interval. Estrus occurs within 4 to 7 days after weaning, but the practical experience shows that the short suckling period (4 5 weeks), the combination of long photoperiod with high daily temperature (especially during summer season) and other factors have a negative effect on the reproductive functions of the sows following weaning. In this case it is necessary to apply pharmacological treatment in order to stimulate the ovarian development and estrus in weaning sows. Induction of estrus in sows using exogenous gonadotropins is the common practice to decrease the number of non-productive days by decreasing the time to the post weaning heat in sows that are weaned in a conventional production system (Benaglia et al., 2012). Various pharmacological strategies exist to induce ovarian development and estrus behaviour in weaning sows. The studies of Gordon (1997), Kirkwood et al. (1998), Cassar et al. (2005) find that the gonadotropin therapy (a combination of equine chorionic gonadotropin and human chorionic gonadotropin) during weaning period induces the fertile estrus in weaned sows. The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of Fertipigon some reproductive parameters in sows after weaning. Material and methods Animals and Treatment The experiment was carried out in a commercial pig farm in May June Еighty-eight multiparous sows (Camborough 23, PIC) with an average parity number of were kept in the farrowing house with controlled ventilation and cooling systems. The animals were fed with a diet formulated for farrowing sows and they had access to water ad libitum. The lactating period was days. The day before weaning the sows were treated with Fertipig /Ceva Sante Animale, France (based on the combination of 400 I.U. of PMSG and 200 I.U. of hcg) at an individual single dose of 5 ml i.m. in the neck region. After weaning the animals were checked for estrus with mature boars two times per day. The sows were inseminated three times after beginning of estrus by cervical manner with doses of 80 ml containing 3.5 х 109 spermatozoa. Pregnancy rate was determined at days after insemination with mature boars. Data recorder The days from injection to onset of estrus were recorded for each animals after treatment. Farrowing rate was calculated as percentage of the number of farrowing sows to the number of breed sows. The total born piglets and live born piglets in litter were counted at farrowing. The farrowing index was calculated as percentage of the number of farrowing sows multipled by the total number of piglets born per litter. Prior to data analysis the animals were categorized in the following groups: 1) weaning-to-estrus interval up to 3rd day, at 4th day, at 5th day and 6th day after treatment, 2) weaning-to-estrus interval up to 5th day and after 5th day, and 3) animals up to 6th parity and over 6th parity. Statistical analysis A one-way ANOVA statistical analysis was used. The post hoc comparisons were done by LSD test. All calculations were made with statistical package StatSoft (STATISTICA, Tulsa, OK). Results and discussion The dynamics of the estrus in the weaning sows after treatment with Fertipig is shown in Figure 1. The mean interval from injection to the beginning of estrus was days. The percentage of animals which showed the signs of estrus up to 3rd day was 3,40%, at 4th day it was 43.18%, at 5th day % and 4.55% of the animals had a standing reflex at 6th day after treatment (р<0.05). The reproductive parameters of the weaning sows after treatment with Fertipig depending of the time from injection to * dimitrov@af.uni-sz.bg 269
6 % Days after injection 6 Figure 1. Dynamics of estrus of weaning sows afrer treatment with Fertipig beginning of the estrus is indicated in Table 1. The animals with estrus up to 5 days after hormonal treatment had low percentage of farrowing rate compared to sows showing estrus after 5 days 87.80% and 93.61%, respectively. The total born piglets and live born piglets per litter had the opposite tendency the values of these parameters were high in the animals with estrus up to 5 days after hormonal injection. This tendency confirmed the hypothesis that weaned sows with short weaning-to-estrus interval have long time of estrus with high fertility. Table 1. Reproductive parameters in weaning sows after treatment with Fertipig depending on weaning-to-estrus interval. (Mean ± SD) Reproductive parameters Mean weaning-to-estrus interval < 5 days 41 Number of sows Weaning-to-estrus interval, days 3.93 ± Farrowing rate, % ± 1.64 Total born piglets per litter, n ± 1.52 Live born piglets per litter, n Farrowing index short suckling period (4 5 weeks) which could increase the frequency of farrowing and to receive more piglets per sow. In normal functioning of the reproductive system and good body condition of the sows after weaning the animals show estrus between 3to 9days. In this experiment the animals were weaned at 28th day after farrowing and this period coincides with the afterfarrowing ovulatory wave, then the swine's ovaries had growing follicules, but at high level of prolactine in the blood they do not ovulate. The main idea of this experiment was to establish the effect of hormonal treatment of the sows with Fertipig on the main reproductive parameters (the interval from injection to the estrus, farrowing rate, total and live born piglets per litter and farrowing index). Fertipig has a combination of 400 U.I. PMSG and 200 U.I. HCG and if it is administered one day before weaning of the animals, that stimulates the oocytes growth, and induces rapid and synchronous postweaning estrus, i.e. there is short weaning-toestrus interval. Koketsu and Dial (1997) find that the reproductive parameters of weaning sows after hormonal treatment are in immediate dependence with the number of parity, length of suckling period and season. The reproductive problems of the sows in this case are connected with low or lack of ovarian function because of dearth of gonadotropin stimulation and the high level of prolactin in the blood (Britt, 1986; Van de Wiel and Booman, 1993; Kermabon et al., 1995). The mechanism of action of the combination of 400 UI PMSG and 200 UI HCG is not fully understood, but probably after injection there is an increase of estrogen concentration in the blood which provokes LH surge (Bates et al., 1991; Saoulidis et al., 1995; Estienne and Hartsock, 1998; Kirkwood et al., 1998). Table 2. Reproductive parameters in weaning sows after treatment with Fertipig depending on parities (Mean±SD) Reproductive parameters > 5 days ± ± ± Number of parity < 6 parity 45 Number of sows Weaning-to-estrus interval, days 4.44 ± Farrowing rate, % ± 1.59 Total born piglets per litter, n Live born piglets per litter, n ± 1.51A Farrowing index > 6 parity ± ± ± 2.22А A The differences between means are not statistically significant р< 0.05 the same superscripts within columns indicate statistically significant differences The idea of this study was to establish the influence of the number of parity on the reproductive performance of weaning sows after injection with Fertipig (Table 2). The data showed that the parities of the animals do not have significant effect on the interval injection-beginning of estrus days (sows with up to 6 parities) and days (sows over 6 parities). Regarding another reproductive parameter the farrowing rate was not significant more in the animals with over 6 parities, in comparison with the sows with up to 6 parities. For the total born piglets and live born piglets there was the opposite dependence the data were high in the animals with up to 6parities. The difference in the number of live born piglets per litter was significant (р<0.05). An important element in commercial pig production is to apply Data analysis showed that after hormonal treatment of a total of 88 sows, % manifest estrus sings up to 5 days after weaning (average period days). In another experiment Pabst (2011) applied Fertipig 24 hours after weaning and he received a shorter weaning to estrus interval days depending on the length of the suckling period. Similar data were obtained by Knox et al. (2001), Manjarin et al. (2011) when using another gonadotropin product (PG600 ). They found that the average weaning-to-estrus interval was days after injection. In our experiment the farrowing rate was % depending on the interval of hormonal treatment-beginning of estrus and the parity of the animals. The sow's parity number had a significant effect on live born piglets per litter only. 270
7 Conclusion Hormonal treatment with Fertipig one day before weaning in farrowing sows induces estrus with an average period 4.54 ± 0.64 days after injection. There is a tendency for higher farrowing rate in sows with up to 5 days of weaning-to-estrus interval and in the animals with over 6 parities. The litter's parameters (total born piglets and live born piglets) were higher in animals with up to 5 days of weaning-to-estrus interval and in sows with up to 6 parities. This hormonal product is able to be implemented in the reproductive management of commercial pig farms. References Bates RO, Day BN, Britt JH, Clark LK and Brauer MA, Reproductive performance of sows treated with a combination of pregnant mare's serum gonadotropin and human chorionic gonadotropin at weaning in the summer. Journal of Animal Science, 69, Benaglia P, Krejci R, Lopez A and Casappa P, Effect of the synchronisation of estrus in sows after weaning using Fertipig in comparison with another gonadotropin product. 22rd International pig veterinary society congress, June 10-13, Jeju, Korea, p. 12. Britt JH, Improving sow productivity through management during gestation, lactation and after weaning. Journal of Animal Science, 63, Cassar G, Kirkwood RN, Poljak Z, Bennett-Steward K and Friendship RM, Effect of single or double insemination on fertility of sows bred at an induced estrus and ovulation. Journal of Swine Health Production,13, Estienne MJ and Hartsock, TG, Effect of exogenous gonadotropins on the weaning-to-estrus interval in sows. Theriogenology, 49, Gordon I, Controlled Reproduction in Pigs. CAB International, Wallingford, UK. Saoulidis KJ, Kyriakis SK, Samouilidis S, Tsinas A and Chizios K, Ein eitrag zur brunstauslosung und erhohter fruchtbarkeit bei zuchtsauen durch die verabreichung gonadotroper hormone (PMSG und HCG). Tierärztl Umschau, 50, Kermabon AY, Prunier A, Djine J and Salesse R, Gonadotropins in lactating sows exposed to long or short days during pregnancy and lactation: serum concentrarion and ovarian receptors. Biology of Reproduction, 53, Kirkwood RN, Aherne FX and Foxcroft GR, Effect of gonadotropin at weaning on reproductive performance of primiparous sows. Swine Health Production, 6, Knox RV, Rodriguez-Zas SL, Miller GM, Willenburg KL and Robb JA, Administration of PG 600 to sows at weaning and the time of ovulation as determined by transrectal ultrasound. Journal of Animal Science, 79, Koketsu Y and Dial GD, Factors influencing the postweaning reproductive performance of sows on commercial farms. Theriogenology, 47, Manjarin R, Steibel JP, Zamora V, Am-in N, Kirkwood RN, Ernst CW, Weber PS, Taylor NP and Trottier NL, Transcript abundance of amino acid transporters, β-casein, and α-lactalbumin in mammary tissue of periparturient, lactating and postweaned sows. Journal of Dairy Science, 94, 7, Pabst T, Diagnostics in herds with reproductive problems and the use of Fertipig as a part of the hormonal control of reproduction. Proceedings of Trend in sow reproduction, April 11-12, Madrid, Spain, Van de Wiel DFM and Bootman P, Post weaning anoestrus in primiparous sows: LH patterns and effects of gonadotropin injection and boar exposure. Veterinary Quarterly, 15, 4,
8 AGRICULTURAL SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 5, No 3, 2013 CONTENTS 1/2 Review Fibromelanosis in domestic chickens H. Lukanov, A. Genchev 239 Genetics and Breeding Rumi and IPK Nelina new cotton varieties A. Stoilova, Hr. Meluca 247 Drying of seeds from common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) by using Silica gel for ex situ storage P. Chamurlyisky, N. Tsenov, S. Stoyanova 252 Breeding evaluation of newly stabilized lines of maize V. Valkova 257 Apricot breeding for resistance to Sharka V. Bozhkova, S. Milusheva 261 Dry matter accumulation in the varieties of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) according to previous crop A. Ivanova, N. Tsenov 264 Reproductive performance of weaning saws after treatment with Fertipig S. Dimitrov, G. Bonev 269 Reproductive performance of Polish Large White and Polish Landrace sows B. Szostak, V. Katsarov 272 Nutrition and Physiology Effect of the feeding of products stimulating the development of bee colonies R. Shumkova, I. Zhelyazkova 276 Investigations on kidney function in mulard ducklings with experimental aflatoxicosis I. Valchev, N. Grozeva, L. Lazarov, D. Kanakov, Ts. Hristov, R. Binev, Y. Nikolov 282 Rumen fermentation in yearling rams fed different rations V. Radev 290 Effect of different lipid and protein dietary levels on rumen ciliate fauna and cellulolytic activity in yearling rams V. Radev, I. Varlyakov, R. Mihaylov 294
9 AGRICULTURAL SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 5, No 3, 2013 CONTENTS 2/2 Production Systems Efficacy and selectivity of antibroadleaved herbicides at durum wheat against volunteers of coriander, Clearfield canola, Clearfield sunflower and ExpressSun sunflower G. Delchev 299 Investigations on friction coefficients of cow hooves with different dairy farm floor types T. Penev, Z. Manolov, I. Borissov, V. Dimova, Tch. Miteva, Y. Mitev, V. Kirov 305 Productivity of irrigation cotton cultivated under different inter-row spaces I. Saldzhiev, A. Muhova 309 Stability evaluation of mixtures among preparations with different biological effect on the basis of grain yield in spring vetch G. Delchev, N. Georgieva, I. Nikolova 313 Biological activity of plant protection products against Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) in tomato grown in greenhouses N. Valchev, V. Yankova, D. Markova 318 Agriculture and Environment Changes of some agro-chemical parameters of Pellic Vertisol (FAO) soil type in growing cereal crops under organic system of agriculture V. Koteva 322 Product Quality and Safety Carcass composition and meat quality in lambs reared indoors and on pasture T. Popova, P. Marinova 325 Fatty acids and lipid indices of buffalo milk yogurt N. Naydenova, T. Iliev, G. Mihaylova 331 Effect of supplementary honey and artificial sugar feeding of bees on the composition of royal jelly R. Balkanska, I. Zhelyazkova, M. Ignatova, B. Kashamov 335 Influence of the amount of milk clotting enzyme with microbial and camel origin on the coagulation time of cow's milk P. Panayotov, K. Yoanidu, P. Boyanova, B. Milenkov 339 Determining chlorophyll and carrotenoid content in Bombyx mori L. excreta by Near Infrared Spectroscopy S. Atanasova, M. Panayotov, D. Pavlov, M. Duleva 343
10 Instruction for authors Preparation of papers Papers shall be submitted at the editorial office typed on standard typing pages (A4, 30 lines per page, 62 characters per line). The editors recommend up to 15 pages for full research paper ( including abstract references, tables, figures and other appendices) The manuscript should be structured as follows: Title, Names of authors and affiliation address, Abstract, List of keywords, Introduction, Material and methods,results, Discussion, Conclusion, Acknowledgements (if any), References, Tables, Figures. The title needs to be as concise and informative about the nature of research. It should be written with small letter /bold, 14/ without any abbreviations. Names and affiliation of authors The names of the authors should be presented from the initials of first names followed by the family names. The complete address and name of the institution should be stated next. The affiliation of authors are designated by different signs. For the author who is going to be corresponding by the editorial board and readers, an address and telephone number should be presented as footnote on the first page. Corresponding author is indicated with *. Abstract should be not more than 350 words. It should be clearly stated what new findings have been made in the course of research. Abbreviations and references to authors are inadmissible in the summary. It should be understandable without having read the paper and should be in one paragraph. Keywords: Up to maximum of 5 keywords should be selected not repeating the title but giving the essence of study. The introduction must answer the following questions: What is known and what is new on the studied issue? What necessitated the research problem, described in the paper? What is your hypothesis and goal? Material and methods: The objects of research, organization of experiments, chemical analyses, statistical and other methods and conditions applied for the experiments should be described in detail. A criterion of sufficient information is to be possible for others to repeat the experiment in order to verify results. Results are presented in understandable tables and figures, accompanied by the statistical parameters needed for the evaluation. Data from tables and figures should not be repeated in the text. Tables should be as simple and as few as possible. Each table should have its own explanatory title and to be typed on a separate page. They should be outside the main body of the text and an indication should be given where it should be inserted. Figures should be sharp with good contrast and rendition. Graphic materials should be preferred. Photographs to be appropriate for printing. Illustrations are supplied in colour as an exception after special agreement with the editorial board and possible payment of extra costs. The figures are to be each in a single file and their location should be given within the text. Discussion: The objective of this section is to indicate the scientific significance of the study. By comparing the results and conclusions of other scientists the contribution of the study for expanding or modifying existing knowledge is pointed out clearly and convincingly to the reader. Conclusion: The most important consequences for the science and practice resulting from the conducted research should be summarized in a few sentences. The conclusions shouldn't be numbered and no new paragraphs be used. Contributions are the core of conclusions. References: In the text, references should be cited as follows: single author: Sandberg (2002); two authors: Andersson and Georges (2004); more than two authors: Andersson et al.(2003). When several references are cited simultaneously, they should be ranked by chronological order e.g.: (Sandberg, 2002; Andersson et al., 2003; Andersson and Georges, 2004). References are arranged alphabetically by the name of the first author. If an author is cited more than once, first his individual publications are given ranked by year, then come publications with one co-author, two co-authors, etc. The names of authors, article and journal titles in the Cyrillic or alphabet different from Latin, should be transliterated into Latin and article titles should be translated into English. The original language of articles and books translated into English is indicated in parenthesis after the bibliographic reference (Bulgarian = Bg, Russian = Ru, Serbian = Sr, if in the Cyrillic, Mongolian = Мо, Greek = Gr, Georgian = Geor., Japanese = Jа, Chinese = Ch, Arabic = Аr, etc.) The following order in the reference list is recommended: Journal articles: Author(s) surname and initials, year. Title. Full title of the journal, volume, pages. Example: Simm G, Lewis RM, Grundy B and Dingwall WS, Responses to selection for lean growth in sheep. Animal Science, 74, Books: Author(s) surname and initials, year. Title. Edition, name of publisher, place of publication. Example: Oldenbroek JK, Genebanks and the conservation of farm animal genetic resources, Second edition. DLO Institute for Animal Science and Health, Netherlands. Book chapter or conference proceedings: Author(s) surname and initials, year. Title. In: Title of the book or of the proceedings followed by the editor(s), volume, pages. Name of publisher, place of publication. Example: Mauff G, Pulverer G, Operkuch W, Hummel K and Hidden C, C3variants and diverse phenotypes of unconverted and converted C3. In: Provides of the Biological Fluids (ed. H. Peters), vol. 22, , Pergamon Press. Oxford, UK. Todorov N and Mitev J, Effect of level of feeding during dry period, and body condition score on reproductive performance in dairy cows,ixth International Conference on Production Diseases in Farm Animals, Sept.11 14, Berlin, Germany, p. 302 (Abstr.). Thesis: Penkov D, Estimation of metabolic energy and true digestibility of amino acids of some feeds in experiments with muscus duck (Carina moshata, L). Thesis for DSc. Agrarian University, Plovdiv, 314 pp. The Editorial Board of the Journal is not responsible for incorrect quotes of reference sources and the relevant violations of copyrights. Ethics Studies performed on experimental animals should be carried out according to internationally recognized guidelines for animal welfare. That should be clearly described in the respective section Material and methods.
11 Volume 5, Number 3 September 2013
ISSN Volume 5, Number 3 September 2013
 ISSN 11-88 Volume 5, Number September 1 1 Editor-in-Chief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in- Chief Radoslav Slavov Faculty of Agriculture Trakia
ISSN 11-88 Volume 5, Number September 1 1 Editor-in-Chief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in- Chief Radoslav Slavov Faculty of Agriculture Trakia
Online Version ISSN: X Volume 4, Number 2 June 2012
 Online Version ISSN: 1314-412X Volume 4, Number 2 June 2012 2012 Editor-inChief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in- Chief Radoslav Slavov Faculty
Online Version ISSN: 1314-412X Volume 4, Number 2 June 2012 2012 Editor-inChief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in- Chief Radoslav Slavov Faculty
ISSN Volume 5, Number 3 September 2013
 ISSN 1313-8820 Volume 5, Number 3 September 2013 2013 Editor-in-Chief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in- Chief Radoslav Slavov Faculty of Agriculture
ISSN 1313-8820 Volume 5, Number 3 September 2013 2013 Editor-in-Chief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in- Chief Radoslav Slavov Faculty of Agriculture
Online Version ISSN: X Volume 4, Number 3 September 2012
 Online Version ISSN: 1314-412X Volume 4, Number 3 September 2012 2012 Editor-inChief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in- Chief Radoslav Slavov
Online Version ISSN: 1314-412X Volume 4, Number 3 September 2012 2012 Editor-inChief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in- Chief Radoslav Slavov
Fertipig. Power with Control. i t s. ec o. ys a. 2 o
 Fertipig Power with Control da 8 2 o t Stable for up rr e t f ys a n o i ut t i t s n ec o Fertipig Power with Control Meet breeding targets The main goal of breeding herds is to consistently meet breeding
Fertipig Power with Control da 8 2 o t Stable for up rr e t f ys a n o i ut t i t s n ec o Fertipig Power with Control Meet breeding targets The main goal of breeding herds is to consistently meet breeding
ISSN Volume 7, Number 4 December 2015
 ISSN 1313-8820 Volume 7, Number 4 December 2015 2015 Editor-in-Chief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in-Chief Radoslav Slavov Faculty of Agriculture
ISSN 1313-8820 Volume 7, Number 4 December 2015 2015 Editor-in-Chief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in-Chief Radoslav Slavov Faculty of Agriculture
ISSN Volume 1, Number 4 December 2009
 ISSN 1313-8820 Volume 1, Number 4 December 2009 Scope and policy of the journal Agricultural Science and Technology /AST/ an International Scientific Journal of Agricultural and Technology Sciences is
ISSN 1313-8820 Volume 1, Number 4 December 2009 Scope and policy of the journal Agricultural Science and Technology /AST/ an International Scientific Journal of Agricultural and Technology Sciences is
Timing of A.I. Swine AI 9/6/12
 Breeding Herd Education Series 20 Timely, relevant & convenient learning Thank you for participating in SowBridge 20. To start this presentation, advance one slide by pressing enter or the down or right
Breeding Herd Education Series 20 Timely, relevant & convenient learning Thank you for participating in SowBridge 20. To start this presentation, advance one slide by pressing enter or the down or right
Online Version ISSN: X Volume 3, Number 3 September 2011
 Online Version ISSN: 1314-4X Volume 3, Number 3 September 2011 2011 Georgi Zhelyazkov (Bulgaria) Scope and policy of the journal Agricultural Science and Technology /AST/ an International Scientific Journal
Online Version ISSN: 1314-4X Volume 3, Number 3 September 2011 2011 Georgi Zhelyazkov (Bulgaria) Scope and policy of the journal Agricultural Science and Technology /AST/ an International Scientific Journal
Effect of Frequency of Boar Exposure on Estrus and Ovulation in Weaned Sows as Determined by Real-Time Ultrasound.
 Effect of Frequency of Boar Exposure on Estrus and Ovulation in Weaned Sows as Determined by Real-Time Ultrasound. Robert V. Knox, Kilby Willenburg, Gina Miller, Sandra Rodriguez-Zas Department of Animal
Effect of Frequency of Boar Exposure on Estrus and Ovulation in Weaned Sows as Determined by Real-Time Ultrasound. Robert V. Knox, Kilby Willenburg, Gina Miller, Sandra Rodriguez-Zas Department of Animal
Online Version ISSN: X Volume 5, Number 1 March 2013
 2013 Online Version ISSN: 1314-412X Volume 5, Number 1 March 2013 Editor-in-Chief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in-Chief Radoslav Slavov Faculty
2013 Online Version ISSN: 1314-412X Volume 5, Number 1 March 2013 Editor-in-Chief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in-Chief Radoslav Slavov Faculty
ISSN Volume 6, Number 3 September 2014
 ISSN 1313-88 Volume 6, Number 3 September 14 14 Editor-in-Chief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in-Chief Radoslav Slavov Faculty of Agriculture
ISSN 1313-88 Volume 6, Number 3 September 14 14 Editor-in-Chief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in-Chief Radoslav Slavov Faculty of Agriculture
ISSN Volume 3, Number 2 June, 2011
 2011 ISSN 1313-8820 Volume 3, Number 2 June, 2011 Georgi Zhelyazkov (Bulgaria) Scope and policy of the journal Agricultural Science and Technology /AST/ an International Scientific Journal of Agricultural
2011 ISSN 1313-8820 Volume 3, Number 2 June, 2011 Georgi Zhelyazkov (Bulgaria) Scope and policy of the journal Agricultural Science and Technology /AST/ an International Scientific Journal of Agricultural
ISSN Volume 2, Number 4 December 2010
 2010 ISSN 1313-8820 Volume 2, Number 4 December 2010 Scope and policy of the journal Agricultural Science and Technology /AST/ an International Scientific Journal of Agricultural and Technology Sciences
2010 ISSN 1313-8820 Volume 2, Number 4 December 2010 Scope and policy of the journal Agricultural Science and Technology /AST/ an International Scientific Journal of Agricultural and Technology Sciences
Online Version ISSN: X Volume 3, Number 3 September 2011
 Online Version ISSN: 1314-4X Volume 3, Number 3 September 2011 2011 Georgi Zhelyazkov (Bulgaria) Scope and policy of the journal Agricultural Science and Technology /AST/ an International Scientific Journal
Online Version ISSN: 1314-4X Volume 3, Number 3 September 2011 2011 Georgi Zhelyazkov (Bulgaria) Scope and policy of the journal Agricultural Science and Technology /AST/ an International Scientific Journal
LYSINE AND METABOLIZABLE ENERGY REQUIREMENT FOR PROLIFIC LACTATING SOWS
 LYSINE AND METABOLIZABLE ENERGY REQUIREMENT FOR PROLIFIC LACTATING SOWS Chung Wen Liao Livestock Research Institute, Council of Agriculture Nutrition Division, COA-LRI, Hsinhua, Tainan 712, Taiwan, R.O.C.
LYSINE AND METABOLIZABLE ENERGY REQUIREMENT FOR PROLIFIC LACTATING SOWS Chung Wen Liao Livestock Research Institute, Council of Agriculture Nutrition Division, COA-LRI, Hsinhua, Tainan 712, Taiwan, R.O.C.
REPRONET NEWSLETTER. How does PG600 induce
 U NIVERSITY OF I LLINOIS EXTENSION N0. 1 FALL, 1999 REPRONET NEWSLETTER from the U NIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS, URBANA-CHAMPAIGN In This Issue: USING PG600 IN THE SWINE BREEDING HERD Improves synchrony of estrus
U NIVERSITY OF I LLINOIS EXTENSION N0. 1 FALL, 1999 REPRONET NEWSLETTER from the U NIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS, URBANA-CHAMPAIGN In This Issue: USING PG600 IN THE SWINE BREEDING HERD Improves synchrony of estrus
ISSN (print) ISSN X (online) Volume 10, Number 1 March 2018
 ISSN 1313-8820 (print) ISSN 1314-412X (online) Volume 10, Number 1 March 2018 2018 Editor-in-Chief Georgi Petkov Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria E-mail: gpetkov@af.uni.sz.bg
ISSN 1313-8820 (print) ISSN 1314-412X (online) Volume 10, Number 1 March 2018 2018 Editor-in-Chief Georgi Petkov Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria E-mail: gpetkov@af.uni.sz.bg
Online Version ISSN: X Volume 4, Number 3 September 2012
 Online Version ISSN: 1314-412X Volume 4, Number 3 September 2012 2012 Editor-inChief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in- Chief Radoslav Slavov
Online Version ISSN: 1314-412X Volume 4, Number 3 September 2012 2012 Editor-inChief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in- Chief Radoslav Slavov
ISSN Volume 6, Number 2 June 2014
 ISSN 1313-8820 Volume 6, Number 2 June 2014 2014 Editor-in-Chief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in-Chief Radoslav Slavov Faculty of Agriculture
ISSN 1313-8820 Volume 6, Number 2 June 2014 2014 Editor-in-Chief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in-Chief Radoslav Slavov Faculty of Agriculture
ISSN Volume 2, Number 2 June 2010
 2010 ISSN 1313-8820 Volume 2, Number 2 June 2010 Scope and policy of the journal Agricultural Science and Technology /AST/ an International Scientific Journal of Agricultural and Technology Sciences is
2010 ISSN 1313-8820 Volume 2, Number 2 June 2010 Scope and policy of the journal Agricultural Science and Technology /AST/ an International Scientific Journal of Agricultural and Technology Sciences is
Syncrostim. The second chance for open cows. Presented for single cow treatment
 Syncrostim The second chance for open cows Presented for single cow treatment Syncrostim Equine chorionic gonadotrophin (ecg) for single cow treatment The active compound in Syncrostim is ecg, previously
Syncrostim The second chance for open cows Presented for single cow treatment Syncrostim Equine chorionic gonadotrophin (ecg) for single cow treatment The active compound in Syncrostim is ecg, previously
ONTARIO PORK RESEARCH PROPOSAL FINAL REPORT
 PROPOSAL # 04/16 ONTARIO PORK RESEARCH PROPOSAL FINAL REPORT Project Leader: R.N. Kirkwood/ R.M. Friendship Project Title: Effect of addition of seminal plasma to thawed semen on sow fertility Objectives
PROPOSAL # 04/16 ONTARIO PORK RESEARCH PROPOSAL FINAL REPORT Project Leader: R.N. Kirkwood/ R.M. Friendship Project Title: Effect of addition of seminal plasma to thawed semen on sow fertility Objectives
ISSN Volume 2, Number 2 June 2010
 0 ISSN 1313 880 Volume, Number June 0 Scope and policy of e journal Agricultural Science and Technology /AST/ an International Scientific Journal of Agricultural and Technology Sciences is published in
0 ISSN 1313 880 Volume, Number June 0 Scope and policy of e journal Agricultural Science and Technology /AST/ an International Scientific Journal of Agricultural and Technology Sciences is published in
Five-day Resynch Programs in Dairy Cows Including Controlled Internal Drug Release at Two Stages Post- Artificial Insemination
 Five-day Resynch Programs in Dairy Cows Including Controlled Internal Drug Release at Two Stages Post- Artificial Insemination S. L. Pulley, S. L. Hill, and J. S. Stevenson Summary Two experiments were
Five-day Resynch Programs in Dairy Cows Including Controlled Internal Drug Release at Two Stages Post- Artificial Insemination S. L. Pulley, S. L. Hill, and J. S. Stevenson Summary Two experiments were
Georgi Zhelyazkov (Bulgaria)
 Georgi Zhelyazkov (Bulgaria) Scope and policy of the journal Agricultural Science and Technology /AST/ an International Scientific Journal of Agricultural and Technology Sciences is published in English
Georgi Zhelyazkov (Bulgaria) Scope and policy of the journal Agricultural Science and Technology /AST/ an International Scientific Journal of Agricultural and Technology Sciences is published in English
Sow Reproduction and Seasonal Infertility. Darlington Pig Discussion Group 13 th March 2014 Richard Bull
 Sow Reproduction and Seasonal Infertility Darlington Pig Discussion Group 13 th March 2014 Richard Bull Richard Bull Taurus Concepts Ltd Sow Reproduction Endogenous Hormones Gland Hormone Function Hypothalamus
Sow Reproduction and Seasonal Infertility Darlington Pig Discussion Group 13 th March 2014 Richard Bull Richard Bull Taurus Concepts Ltd Sow Reproduction Endogenous Hormones Gland Hormone Function Hypothalamus
THE SWINE PRODUCTIVE CAPACITY DEPENDING ON USED BREEDS FOR THE HYBRID PRODUCTION
 Abstract Scientific Papers. Series D. Animal Science. Vol. LVIII, 2015 ISSN 2285-5750; ISSN CD-ROM 2285-5769; ISSN Online 2393-2260; ISSN-L 2285-5750 THE SWINE PRODUCTIVE CAPACITY DEPENDING ON USED BREEDS
Abstract Scientific Papers. Series D. Animal Science. Vol. LVIII, 2015 ISSN 2285-5750; ISSN CD-ROM 2285-5769; ISSN Online 2393-2260; ISSN-L 2285-5750 THE SWINE PRODUCTIVE CAPACITY DEPENDING ON USED BREEDS
Title. Author(s)Am-In, Nutthee; Roongsitthichai, Atthaporn. CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 65(1): Issue Date DOI
 Title Ameliorative effects of exogenous gonadotropins on r a farm in Thailand Author(s)Am-In, Nutthee; Roongsitthichai, Atthaporn CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 65(1): 45-5 Issue Date
Title Ameliorative effects of exogenous gonadotropins on r a farm in Thailand Author(s)Am-In, Nutthee; Roongsitthichai, Atthaporn CitationJapanese Journal of Veterinary Research, 65(1): 45-5 Issue Date
ISSN Volume 8, Number 1 March 2016
 2016 ISSN 1313-8820 Volume 8, Number 1 March 2016 Editor-in-Chief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in-Chief Dimitar Panaiotov Faculty of Agriculture
2016 ISSN 1313-8820 Volume 8, Number 1 March 2016 Editor-in-Chief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in-Chief Dimitar Panaiotov Faculty of Agriculture
REPRODUCTIVE INNOVATIONS: CONTROL OF SOW ESTRUS AND BREEDING
 REPRODUCTIVE INNOVATIONS: CONTROL OF SOW ESTRUS AND BREEDING Roy Kirkwood Department of Large Animal Clinical Sciences Michigan State University Lansing, Michigan 48824-1314 E-mail: kirkwood@cvm.msu.edu
REPRODUCTIVE INNOVATIONS: CONTROL OF SOW ESTRUS AND BREEDING Roy Kirkwood Department of Large Animal Clinical Sciences Michigan State University Lansing, Michigan 48824-1314 E-mail: kirkwood@cvm.msu.edu
Online Version ISSN: X Volume 5, Number 1 March 2013
 2013 Online Version ISSN: 1314-412X Volume 5, Number 1 March 2013 Editor-in-Chief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in-Chief Radoslav Slavov Faculty
2013 Online Version ISSN: 1314-412X Volume 5, Number 1 March 2013 Editor-in-Chief Tsanko Yablanski Faculty of Agriculture Trakia University, Stara Zagora Bulgaria Co-Editor-in-Chief Radoslav Slavov Faculty
Why Cycle Control?" Manipulating Ovulation and Estrous Synchronization" Manipulating Ovulation" Cattle" Principle of PGF 2α Use"
 Why Cycle Control?" Manipulating Ovulation and Estrous Synchronization" John Parrish 1. Group females for parturition: " a) Decrease labor, calving period Reduce calving season" b) More uniform weaning
Why Cycle Control?" Manipulating Ovulation and Estrous Synchronization" John Parrish 1. Group females for parturition: " a) Decrease labor, calving period Reduce calving season" b) More uniform weaning
METRIC Technical Bulletin MANAGING CHOICE GENETICS CG PARENT GILT REPLACEMENT THROUGH PARITY ONE
 METRIC Technical Bulletin MANAGING CHOICE GENETICS CG PARENT GILT REPLACEMENT THROUGH PARITY ONE Emphasizing proper CG parent gilt development and herd introduction will yield rewards in total herd output
METRIC Technical Bulletin MANAGING CHOICE GENETICS CG PARENT GILT REPLACEMENT THROUGH PARITY ONE Emphasizing proper CG parent gilt development and herd introduction will yield rewards in total herd output
Homeorhesis is orchestrated changes in metabolism of body tissue required to sustain a specific physiological status.
 Interaction Between Nutrition and Reproduction in Dairy Cows Amin Ahmadzadeh Animal and Veterinary Science Department University of Idaho Homeorhesis is orchestrated changes in metabolism of body tissue
Interaction Between Nutrition and Reproduction in Dairy Cows Amin Ahmadzadeh Animal and Veterinary Science Department University of Idaho Homeorhesis is orchestrated changes in metabolism of body tissue
The gestating and lactating sow
 The gestating and lactating sow The gestating and lactating sow edited by: Chantal Farmer Wageningen Academic P u b l i s h e r s Buy a print copy of this book at: www.wageningenacademic.com/sowlactation
The gestating and lactating sow The gestating and lactating sow edited by: Chantal Farmer Wageningen Academic P u b l i s h e r s Buy a print copy of this book at: www.wageningenacademic.com/sowlactation
The effect of feeding strategy during the pre-follicular phase on subsequent follicular development in the pig
 Domestic Animal Endocrinology 29 (2005) 362 370 The effect of feeding strategy during the pre-follicular phase on subsequent follicular development in the pig W. Hazeleger, N.M. Soede, B. Kemp Department
Domestic Animal Endocrinology 29 (2005) 362 370 The effect of feeding strategy during the pre-follicular phase on subsequent follicular development in the pig W. Hazeleger, N.M. Soede, B. Kemp Department
Interval between PMSG Priming and hcg Injection in Superovulation of the Mongolian Gerbil
 J. Mamm. Ova Res. Vol. 21, 105 109, 2004 105 Original Interval between PMSG Priming and hcg Injection in Superovulation of the Mongolian Gerbil Yuichi Kameyama 1 *, Kaori Arai 1 and Yoshiro Ishijima 1
J. Mamm. Ova Res. Vol. 21, 105 109, 2004 105 Original Interval between PMSG Priming and hcg Injection in Superovulation of the Mongolian Gerbil Yuichi Kameyama 1 *, Kaori Arai 1 and Yoshiro Ishijima 1
Feeding the modern sow; the next step
 Feeding the modern sow; the next step ir. P.R.T. Bonekamp Swine Specialist EMEA Brasil, December 2015 Modern swine farming does not differ that much from the past as the main goal is still to produce as
Feeding the modern sow; the next step ir. P.R.T. Bonekamp Swine Specialist EMEA Brasil, December 2015 Modern swine farming does not differ that much from the past as the main goal is still to produce as
Why Cycle Control? Manipulating Ovulation and Estrous Synchronization. Manipulating Ovulation. Cattle. Principle of PGF 2a Use
 Why Cycle Control? Manipulating and Estrous Synchronization John Parrish 1. Group females for parturition: a) Decrease labor, calving period Reduce calving season b) More uniform weaning weights. 2. Reduce
Why Cycle Control? Manipulating and Estrous Synchronization John Parrish 1. Group females for parturition: a) Decrease labor, calving period Reduce calving season b) More uniform weaning weights. 2. Reduce
Solving the Heat Stress Problem
 Breeding Herd Education Series 2012-2013 Timely, relevant & convenient learning Thank you for participating in SowBridge 2012-13. To start this presentation, advance one slide by pressing enter or the
Breeding Herd Education Series 2012-2013 Timely, relevant & convenient learning Thank you for participating in SowBridge 2012-13. To start this presentation, advance one slide by pressing enter or the
The Diploma in Ruminant Nutrition
 Further Information on the Modules that Make Up The Diploma in Ruminant Nutrition Taken from the Module Descriptors Ruminant Animal Production and the Feed Industry A4057 Academic Level 4 Rationale and
Further Information on the Modules that Make Up The Diploma in Ruminant Nutrition Taken from the Module Descriptors Ruminant Animal Production and the Feed Industry A4057 Academic Level 4 Rationale and
Feeding the High Producing Sow
 Feeding the High Producing Sow ESTIMATING ENERGY AND PROTEIN REQUIREMENTS OF THE HIGH PRODUCING SOW John F. Patience INTRODUCTION Much more is expected of the sow today than was the case even a decade
Feeding the High Producing Sow ESTIMATING ENERGY AND PROTEIN REQUIREMENTS OF THE HIGH PRODUCING SOW John F. Patience INTRODUCTION Much more is expected of the sow today than was the case even a decade
understood as achieving highest possible efficiency (combined pigs produced per sow per
 Bio-markers measuring health status and management tools to improve productive performance and animal health on swine commercial farms CARLOS PIÑEIRO NOGUERA Current swine production is led by competitiveness
Bio-markers measuring health status and management tools to improve productive performance and animal health on swine commercial farms CARLOS PIÑEIRO NOGUERA Current swine production is led by competitiveness
Nutri Products for Pigs
 The Formula for Success Nutri Products for Pigs Contents: Nutri Products for Pigs...40 Rations for Piglets...41 2103 Nutri Pig Creep...41 2105 Nutri Pig Starter...43 Growing Pigs...44 2220 Nutri Pig Grower...44
The Formula for Success Nutri Products for Pigs Contents: Nutri Products for Pigs...40 Rations for Piglets...41 2103 Nutri Pig Creep...41 2105 Nutri Pig Starter...43 Growing Pigs...44 2220 Nutri Pig Grower...44
The use of laser to improve semen quality and reproduction performance of sows. Dr. Ivan Sheyko, Bielorussia ; ;
 use of laser to improve semen quality and reproduction performance of sows. Dr. Ivan Sheyko, Bielorussia ; ; In Belarus pig breeding is based on commercial technologies providing for artificial insemination.
use of laser to improve semen quality and reproduction performance of sows. Dr. Ivan Sheyko, Bielorussia ; ; In Belarus pig breeding is based on commercial technologies providing for artificial insemination.
INFLUENCE OF FOLLICULAR ABLATION DURING LACTATION ON POSTWEANING INTERVAL TO ESTRUS, OVULATION RATE, AND ENDOCRINE FUNCTION IN SOWS
 INFLUENCE OF FOLLICULAR ABLATION DURING LACTATION ON POSTWEANING INTERVAL TO ESTRUS, OVULATION RATE, AND ENDOCRINE FUNCTION IN SOWS N.M. Cox, J.D. Armstrong and J.H. Britt ABSTRACT Duroc sows farrowed
INFLUENCE OF FOLLICULAR ABLATION DURING LACTATION ON POSTWEANING INTERVAL TO ESTRUS, OVULATION RATE, AND ENDOCRINE FUNCTION IN SOWS N.M. Cox, J.D. Armstrong and J.H. Britt ABSTRACT Duroc sows farrowed
Advanced Non-Cycling Program. Health
 Advanced Non-Cycling Program Health Why Treat Non-Cycling Cows? Treating cows that have not been detected in oestrus ( non-cycling ) prior to the planned start of mating with DIB-Synch provides a return
Advanced Non-Cycling Program Health Why Treat Non-Cycling Cows? Treating cows that have not been detected in oestrus ( non-cycling ) prior to the planned start of mating with DIB-Synch provides a return
Ovarian Characteristics, Serum Hormone Concentrations, and Fertility in Lactating Dairy Cows in Response to Equine Chorionic Gonadotropin
 Ovarian Characteristics, Serum Hormone Concentrations, and Fertility in Lactating Dairy Cows in Response to quine Chorionic Gonadotropin S. L. Pulley, L. D. Wallace, H. I. Mellieon, and J. S. Stevenson
Ovarian Characteristics, Serum Hormone Concentrations, and Fertility in Lactating Dairy Cows in Response to quine Chorionic Gonadotropin S. L. Pulley, L. D. Wallace, H. I. Mellieon, and J. S. Stevenson
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 7 Understanding Animal Reproduction
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 7 Understanding Animal Reproduction 1 Terms Anestrus Artificial insemination Castration Cervix Copulation Diestrus Egg Ejaculation Estrous cycle Estrus Fertilization
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 7 Understanding Animal Reproduction 1 Terms Anestrus Artificial insemination Castration Cervix Copulation Diestrus Egg Ejaculation Estrous cycle Estrus Fertilization
The Influence of Amaferm on Swine Breeding Performance. Thesis. Partial Fulfillment of Requirements for Undergraduate Research Distinction
 The Influence of on Swine Breeding Performance Thesis Partial Fulfillment of Requirements for Undergraduate Research Distinction By Melinda Blake Hess The Ohio State University 2014 Project Advisor: Dr.
The Influence of on Swine Breeding Performance Thesis Partial Fulfillment of Requirements for Undergraduate Research Distinction By Melinda Blake Hess The Ohio State University 2014 Project Advisor: Dr.
ASC 321 DAIRY CATTLE EVALUATION. (2) Evaluation of dairy cattle for type characteristics. Laboratory, four hours.
 106 INTRODUCTION TO ANIMAL SCIENCES. (3) Relationships of food production and consumption to income of humans throughout the world; major livestock (beef and dairy cattle, sheep, swine, poultry and horses)
106 INTRODUCTION TO ANIMAL SCIENCES. (3) Relationships of food production and consumption to income of humans throughout the world; major livestock (beef and dairy cattle, sheep, swine, poultry and horses)
Animal Science: Isotopes and Nuclear Techniques
 Animal Science: Isotopes and Nuclear Techniques by John E. Vercoe In many regions of the world, animal production is limited by poor growth, reproductive performance and milk output of livestock, thus
Animal Science: Isotopes and Nuclear Techniques by John E. Vercoe In many regions of the world, animal production is limited by poor growth, reproductive performance and milk output of livestock, thus
Product Purpose Statement for Commercial Feed Eli Miller University of Kentucky Lexington, KY May 15, 1997
 Product Purpose Statement for Commercial Feed Eli Miller University of Kentucky Lexington, KY May 15, 1997 The AAFCO Model Feed Regulations requires the label for most livestock feeds to include a product
Product Purpose Statement for Commercial Feed Eli Miller University of Kentucky Lexington, KY May 15, 1997 The AAFCO Model Feed Regulations requires the label for most livestock feeds to include a product
W.L. Flowers Department of Animal Science North Carolina State University
 Sow and Piglet Performance during Lactation and Sow Rebreeding Performance for Self Feeders and Hand Feeding Final Report W.L. Flowers Department of Animal Science North Carolina State University The main
Sow and Piglet Performance during Lactation and Sow Rebreeding Performance for Self Feeders and Hand Feeding Final Report W.L. Flowers Department of Animal Science North Carolina State University The main
Sponsors. w. Christopher Scruton Stephen Claas. Editors. Layout David Brown
 Sponsors University of Minnesota College of Veterinary Medicine College of Agricultural, Food and Environmental Sciences Extension Service Swine Center Editors w. Christopher Scruton Stephen Claas Layout
Sponsors University of Minnesota College of Veterinary Medicine College of Agricultural, Food and Environmental Sciences Extension Service Swine Center Editors w. Christopher Scruton Stephen Claas Layout
The Effect of Aspergillus oryzae on Performance of Swine
 The Texas Journal of Agriculture and Natural Resource 19:1-7 (2006) 1 The Effect of Aspergillus oryzae on Performance of Swine Jared E. Jackson Randal M. Harp Department of Animal Science, Tarleton State
The Texas Journal of Agriculture and Natural Resource 19:1-7 (2006) 1 The Effect of Aspergillus oryzae on Performance of Swine Jared E. Jackson Randal M. Harp Department of Animal Science, Tarleton State
PGF PGF. ecg. hcg PGF PGF PGF.
 F h h h h h hh h h h h h h h F PGF AI AI PGF.... AI AI AI AI AI,,, AI AI F PGF PGF AI, PGF AI PGF h h h hh FAX hh E-mail : tomoko_nakata@pref.aichi.lg.jp 119 AI AI Ln ; Wn ;LW n mm PGF.. PGF mg PG n PGF
F h h h h h hh h h h h h h h F PGF AI AI PGF.... AI AI AI AI AI,,, AI AI F PGF PGF AI, PGF AI PGF h h h hh FAX hh E-mail : tomoko_nakata@pref.aichi.lg.jp 119 AI AI Ln ; Wn ;LW n mm PGF.. PGF mg PG n PGF
Effects of exogenous gonadotrophins at farrowing on incidence of ovulation
 Effects of exogenous gonadotrophins at farrowing on incidence of ovulation by Jessica Zemitis A thesis submitted for the partial fulfilment of the requirements of the Bachelor of Science (Animal Science)
Effects of exogenous gonadotrophins at farrowing on incidence of ovulation by Jessica Zemitis A thesis submitted for the partial fulfilment of the requirements of the Bachelor of Science (Animal Science)
Abstracts for the KSAR and JSAR Joint Symposium. Fertility control in female domestic animals: From basic understanding to application
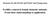 Abstracts for the KSAR and JSAR Joint Symposium Fertility control in female domestic animals: From basic understanding to application Current Research Orientation in Livestock Reproduction in Korea Choong-Saeng
Abstracts for the KSAR and JSAR Joint Symposium Fertility control in female domestic animals: From basic understanding to application Current Research Orientation in Livestock Reproduction in Korea Choong-Saeng
Chapter-6 Feed formulation - nutrients requirement for different category of dairy animals, balanced/complete ration, methods of feed formulation
 Chapter-6 Feed formulation - nutrients requirement for different category of dairy animals, balanced/complete ration, methods of feed formulation Objectives 1. To study the nutrient requirements of different
Chapter-6 Feed formulation - nutrients requirement for different category of dairy animals, balanced/complete ration, methods of feed formulation Objectives 1. To study the nutrient requirements of different
The ECO-FCE project is funded by the European Union Seventh Framework Programme (FP7 2007/2013) under grant agreement No
 ECO-FCE: Lifetime performance of low birth weight piglets from hyperprolific sows is affected by peri-natal nutrition Work package title (WP2): Identification and optimization of feed strategies Task 2.3:
ECO-FCE: Lifetime performance of low birth weight piglets from hyperprolific sows is affected by peri-natal nutrition Work package title (WP2): Identification and optimization of feed strategies Task 2.3:
Feed Management to Improve Nitrogen and Phosphorus Efficiency. Charles C. Stallings Professor and Extension Dairy Scientist Virginia Tech
 Feed Management to Improve Nitrogen and Phosphorus Efficiency Charles C. Stallings Professor and Extension Dairy Scientist Virginia Tech The two nutrients that have the greatest potential for negative
Feed Management to Improve Nitrogen and Phosphorus Efficiency Charles C. Stallings Professor and Extension Dairy Scientist Virginia Tech The two nutrients that have the greatest potential for negative
EFFECT OF P.G. 600 ON THE TIMING OF OVULATION IN GILTS TREATED WITH REGU-MATE. Brandon Ryan Horsley. Thesis submitted to the faculty of the
 EFFECT OF P.G. 600 ON THE TIMING OF OVULATION IN GILTS TREATED WITH REGU-MATE by Brandon Ryan Horsley Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial
EFFECT OF P.G. 600 ON THE TIMING OF OVULATION IN GILTS TREATED WITH REGU-MATE by Brandon Ryan Horsley Thesis submitted to the faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial
Balanced nutritional solutions for optimal animal performance
 Balanced nutritional solutions for optimal animal performance Maxcare ruminant mineral range Add performance to nutrition Introduction The Maxcare mineral range has been formulated to help meet the requirements
Balanced nutritional solutions for optimal animal performance Maxcare ruminant mineral range Add performance to nutrition Introduction The Maxcare mineral range has been formulated to help meet the requirements
Checking Heat and Managing the Heat Cycle
 Checking Heat and Managing the Heat Cycle Dr. Tim Safranski University of Missouri-Columbia SafranskiT@Missouri.edu Presented at Ohio Show Pig Producer Symposium August 25, 2018, Plain City, OH Outline
Checking Heat and Managing the Heat Cycle Dr. Tim Safranski University of Missouri-Columbia SafranskiT@Missouri.edu Presented at Ohio Show Pig Producer Symposium August 25, 2018, Plain City, OH Outline
OVARIAN RESPONSES AND CONCEPTION RATES IN RESPONSE TO GnRH, hcg, AND PROGESTERONE 1
 Dairy Research 2006 OVARIAN RESPONSES AND CONCEPTION RATES IN RESPONSE TO GnRH, hcg, AND PROGESTERONE 1 J. S. Stevenson, M. A. Portaluppi, D. E. Tenhouse, A. Lloyd, D. R. Eborn, S. Kacuba 2 and J. M. DeJarnette
Dairy Research 2006 OVARIAN RESPONSES AND CONCEPTION RATES IN RESPONSE TO GnRH, hcg, AND PROGESTERONE 1 J. S. Stevenson, M. A. Portaluppi, D. E. Tenhouse, A. Lloyd, D. R. Eborn, S. Kacuba 2 and J. M. DeJarnette
COMPARISON OF HCG VS GNRH EFFECTS IN DOUBLE OVSYNCH ON FIRST-SERVICE CONCEPTION RATES IN ANESTRUS DAIRY COWS
 TRADITION AND MODERNITY IN VETERINARY MEDICINE, 2018, vol. 3, No 1(4): 70 76 COMPARISON OF HCG VS GNRH EFFECTS IN DOUBLE OVSYNCH ON FIRST-SERVICE CONCEPTION RATES IN ANESTRUS DAIRY COWS Gundars Naglis
TRADITION AND MODERNITY IN VETERINARY MEDICINE, 2018, vol. 3, No 1(4): 70 76 COMPARISON OF HCG VS GNRH EFFECTS IN DOUBLE OVSYNCH ON FIRST-SERVICE CONCEPTION RATES IN ANESTRUS DAIRY COWS Gundars Naglis
Program 2 Improving Whole Herd Feed Efficiency
 Program 2 Improving Whole Herd Feed Efficiency The Pork CRC Targets 1. Reduce HFC from 4.3 to 3.6 Improving HFC reduces feed/ grain usage and will optimise efficiency through improved health, metabolic
Program 2 Improving Whole Herd Feed Efficiency The Pork CRC Targets 1. Reduce HFC from 4.3 to 3.6 Improving HFC reduces feed/ grain usage and will optimise efficiency through improved health, metabolic
Optimizing dietary lipid use to improve essential fatty acid status and reproductive performance of the modern lactating sow: a review
 Rosero et al. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology (2016) 7:34 DOI 10.1186/s40104-016-0092-x REVIEW Optimizing dietary lipid use to improve essential fatty acid status and reproductive performance
Rosero et al. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology (2016) 7:34 DOI 10.1186/s40104-016-0092-x REVIEW Optimizing dietary lipid use to improve essential fatty acid status and reproductive performance
Nutritional requirements
 Nutritional requirements Foraging behavior Rooting : Seeds, roots, rhizomes, tubers, acorns, nuts, fruit, berries, fungi, insects, earthworms and small animals as snakes and toads. Grazing: Vegetation.
Nutritional requirements Foraging behavior Rooting : Seeds, roots, rhizomes, tubers, acorns, nuts, fruit, berries, fungi, insects, earthworms and small animals as snakes and toads. Grazing: Vegetation.
1. Describe the importance and process of animal reproduction. 2. List the sexual classification of animals for major species.
 Unit B: Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 7: Understanding Animal Reproduction Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives:
Unit B: Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 7: Understanding Animal Reproduction Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives:
Exercise 2 Feed Composition and Nutrient Requirements 20 Points
 Exercise 2 Feed Composition and Nutrient Requirements 20 Points The objective of this laboratory exercise is to familiarize the student with the feed composition and nutrient requirement tables in the
Exercise 2 Feed Composition and Nutrient Requirements 20 Points The objective of this laboratory exercise is to familiarize the student with the feed composition and nutrient requirement tables in the
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission
 2012. M40 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2012 AGRICULTURAL SCIENCE - HIGHER LEVEL THURSDAY, 21 JUNE MORNING, 9.30 12.00 Answer any six questions.
2012. M40 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission LEAVING CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2012 AGRICULTURAL SCIENCE - HIGHER LEVEL THURSDAY, 21 JUNE MORNING, 9.30 12.00 Answer any six questions.
Genotype by environment interactions between pig populations in Australia and Indonesia
 Genotype by environment interactions between pig populations in Australia and Indonesia Tiffany Mote 1, Susanne Hermesch 1 and Julius van der Werf 2 1 Animal Genetic and Breeding Unit; 2 Department of
Genotype by environment interactions between pig populations in Australia and Indonesia Tiffany Mote 1, Susanne Hermesch 1 and Julius van der Werf 2 1 Animal Genetic and Breeding Unit; 2 Department of
Proceedings of the Annual Resort Symposium of the American Association of Equine Practitioners AAEP
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Annual Resort Symposium of the American Association of Equine Practitioners AAEP Jan. 19-21, 2006 Rome, Italy www.ivis.org Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the Annual Resort Symposium of the American Association of Equine Practitioners AAEP Jan. 19-21, 2006 Rome, Italy www.ivis.org Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission
ENHANCED OMEGA 3 ESSENTIAL FATTY ACID SUPPLEMENT
 AGROMEGA ENHANCED OMEGA 3 ESSENTIAL FATTY ACID SUPPLEMENT In nature the pig would consume an extremely wide variety of different things ranging from seeds and roots to insects and animals. This diet would
AGROMEGA ENHANCED OMEGA 3 ESSENTIAL FATTY ACID SUPPLEMENT In nature the pig would consume an extremely wide variety of different things ranging from seeds and roots to insects and animals. This diet would
DETERMINING THE THREONINE REQUIREMENT OF THE LACTATING SOW 1
 Swine Research 2005 DETERMINING THE THREONINE REQUIREMENT OF THE LACTATING SOW 1 J. D. Schneider, J. L. Nelssen, M. D. Tokach, S. S. Dritz 2, R. D. Goodband, and J. M. DeRouchey Summary A total of 182
Swine Research 2005 DETERMINING THE THREONINE REQUIREMENT OF THE LACTATING SOW 1 J. D. Schneider, J. L. Nelssen, M. D. Tokach, S. S. Dritz 2, R. D. Goodband, and J. M. DeRouchey Summary A total of 182
Energy requirements of swine
 Energy requirements of swine The energy requirements of swines are presented as megajoules (MJ) net energy (NE) per day, MJ NE/d separately for growing pigs (weight under 150, MJ NE k ) and for adult pigs
Energy requirements of swine The energy requirements of swines are presented as megajoules (MJ) net energy (NE) per day, MJ NE/d separately for growing pigs (weight under 150, MJ NE k ) and for adult pigs
Understanding Natural Animal Reproduction
 Lesson B4 2 Understanding Natural Animal Reproduction Unit B. Animal Science and the Industry Problem Area 4. Understanding Animal Reproduction and Biotechnology Lesson 2. Understanding Natural Animal
Lesson B4 2 Understanding Natural Animal Reproduction Unit B. Animal Science and the Industry Problem Area 4. Understanding Animal Reproduction and Biotechnology Lesson 2. Understanding Natural Animal
College of Agriculture. Animal Sciences
 101 DOMESTIC ANIMAL BIOLOGY. (3) The first in a sequence of two courses providing an introduction to the subject of animal science. Emphasis is placed on a fundamental understanding of anatomy, physiology,
101 DOMESTIC ANIMAL BIOLOGY. (3) The first in a sequence of two courses providing an introduction to the subject of animal science. Emphasis is placed on a fundamental understanding of anatomy, physiology,
Evaluation and Economic Impact of Boar Fertility
 Evaluation and Economic Impact of Boar Fertility A. Minton 1, A. Johnson 2, T. Werner 2, E. Triemert 2, N. Holden 2, G. Foxcroft 3, J. Patterson 3 and M. Dyck 3 1 PIC North America100 Bluegrass Commons
Evaluation and Economic Impact of Boar Fertility A. Minton 1, A. Johnson 2, T. Werner 2, E. Triemert 2, N. Holden 2, G. Foxcroft 3, J. Patterson 3 and M. Dyck 3 1 PIC North America100 Bluegrass Commons
Milk Urea Nitrogen Evaluation in Louisiana Dairy Herds
 Milk Urea Nitrogen Evaluation in Louisiana Dairy Herds Michael E. McCormick, Associate Professor, Southeast Research Station, Franklinton, La Angelica M. Chapa, Graduate Assistant, Animal Science Department,
Milk Urea Nitrogen Evaluation in Louisiana Dairy Herds Michael E. McCormick, Associate Professor, Southeast Research Station, Franklinton, La Angelica M. Chapa, Graduate Assistant, Animal Science Department,
FEEDING and MANAGEMENT OF DAMASCUS GOATS CYPRUS EXPERIENCE By Miltiades Hadjipanayiotou
 DAMASCUS GOAT FEEDING and MANAGEMENT OF DAMASCUS GOATS CYPRUS EXPERIENCE By Miltiades Hadjipanayiotou Damascus goat is a breed originating from Syria, and is found as pure breed in many M.E. & N. African
DAMASCUS GOAT FEEDING and MANAGEMENT OF DAMASCUS GOATS CYPRUS EXPERIENCE By Miltiades Hadjipanayiotou Damascus goat is a breed originating from Syria, and is found as pure breed in many M.E. & N. African
Science & Technologies INVESTIGATION OF SOME HOOF DISEASE PREVENTION PRACTICES ON CLAW HORN HARDNESS AND FRICTIONAL PROPERTIES IN DAIRY CATTLE
 INVESTIGATION OF SOME HOOF DISEASE PREVENTION PRACTICES ON CLAW HORN HARDNESS AND FRICTIONAL PROPERTIES IN DAIRY CATTLE T. Penev 1 *, Z. Manolov 2, D. Dimov 1, V. Kirov 3, K. Uzunova 4, V. Dimova 5, V.
INVESTIGATION OF SOME HOOF DISEASE PREVENTION PRACTICES ON CLAW HORN HARDNESS AND FRICTIONAL PROPERTIES IN DAIRY CATTLE T. Penev 1 *, Z. Manolov 2, D. Dimov 1, V. Kirov 3, K. Uzunova 4, V. Dimova 5, V.
Do pigs benefit from omega-3 fatty acids?
 Do pigs benefit from omega-3 fatty acids? Denise Beaulieu Assistant Professor Animal & Poultry Science Introduction What are omega-3 fatty acids? Outline Why would we consider augmenting the diet of growing
Do pigs benefit from omega-3 fatty acids? Denise Beaulieu Assistant Professor Animal & Poultry Science Introduction What are omega-3 fatty acids? Outline Why would we consider augmenting the diet of growing
Final Report APL Project 2012/ June 2014
 Specific Carbohydrate Formulation in Late Lactation Diets for Primiparous Sows to Enhance Early Antral Follicle Development, Oocyte Quality and Post- Weaning Fertility Final Report APL Project 2012/1033.496
Specific Carbohydrate Formulation in Late Lactation Diets for Primiparous Sows to Enhance Early Antral Follicle Development, Oocyte Quality and Post- Weaning Fertility Final Report APL Project 2012/1033.496
EFFECT OF INCIDENTS ASSOCIATED TO POST-CERVICAL ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION ON REPRODUCTIVE PERFORMANCE OF SOWS
 Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2018, 21, No 2, 198 205 ISSN 1311-1477; DOI: 10.15547/bjvm.1031 Original article EFFECT OF INCIDENTS ASSOCIATED TO POST-CERVICAL ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION ON REPRODUCTIVE
Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 2018, 21, No 2, 198 205 ISSN 1311-1477; DOI: 10.15547/bjvm.1031 Original article EFFECT OF INCIDENTS ASSOCIATED TO POST-CERVICAL ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION ON REPRODUCTIVE
Keeping Control of Feed Costs in an Uncertain Market
 Keeping Control of Feed Costs in an Uncertain Market Presented To: Iowa Pork Producers Association Regional Meetings February, 2009 John F. Patience Iowa State University Ames, IA Outline What s new in
Keeping Control of Feed Costs in an Uncertain Market Presented To: Iowa Pork Producers Association Regional Meetings February, 2009 John F. Patience Iowa State University Ames, IA Outline What s new in
Estimating Manure Nutrient Excretion
 Feed Management Estimating Manure Nutrient Excretion A Key Ingredient in Livestock and Poultry Nutrient Management Rick Koelsch, Livestock Environmental Engineer, University of Nebraska Disclaimer This
Feed Management Estimating Manure Nutrient Excretion A Key Ingredient in Livestock and Poultry Nutrient Management Rick Koelsch, Livestock Environmental Engineer, University of Nebraska Disclaimer This
Sponsors. Editors W. Christopher Scruton Stephen Claas. Layout David Brown
 Sponsors University of Minnesota College of Veterinary Medicine College of Agricultural, Food and Environmental Sciences Extension Service Swine Center Editors W. Christopher Scruton Stephen Claas Layout
Sponsors University of Minnesota College of Veterinary Medicine College of Agricultural, Food and Environmental Sciences Extension Service Swine Center Editors W. Christopher Scruton Stephen Claas Layout
INDUCTIONS OF SUPEROVULATION USING SEVERAL FSH REGIMENS IN HOLSTEIN-FRIESIAN HEIFERS
 lpn. l. Vet. Res., 33, 45-50 (1985) INDUCTIONS OF SUPEROVULATION USING SEVERAL FSH REGIMENS IN HOLSTEIN-FRIESIAN HEIFERS Yoshiyuki TAKAHASHI and Hiroshi KANAGAWA (Received for publication, February 2,
lpn. l. Vet. Res., 33, 45-50 (1985) INDUCTIONS OF SUPEROVULATION USING SEVERAL FSH REGIMENS IN HOLSTEIN-FRIESIAN HEIFERS Yoshiyuki TAKAHASHI and Hiroshi KANAGAWA (Received for publication, February 2,
TECH EXTENSION. How low can we go? Finding a practical path to produce more pigs from fewer and better boars.
 TECH EXTENSION How low can we go? Finding a practical path to produce more pigs from fewer and better boars www.fastgenetics.com Artificial insemination (AI) has become the standard breeding method for
TECH EXTENSION How low can we go? Finding a practical path to produce more pigs from fewer and better boars www.fastgenetics.com Artificial insemination (AI) has become the standard breeding method for
GONADOTROPHIN (LUTEINISING)- RELEASING HORMONE AND ANALOGUES (GnRH OR LHRH)
 GONADOTROPHIN (LUTEINISING)- RELEASING HORMONE AND ANALOGUES (GnRH OR LHRH) Naturally occurring hormone, produced by the hypothalamus and transferred to the anterior pituitary gland in the hypophyseal
GONADOTROPHIN (LUTEINISING)- RELEASING HORMONE AND ANALOGUES (GnRH OR LHRH) Naturally occurring hormone, produced by the hypothalamus and transferred to the anterior pituitary gland in the hypophyseal
Impact of increased energy and amino acids in sow lactation diets on piglet performance in large litters
 Impact of increased energy and amino acids in sow lactation diets on piglet performance in large litters Aimee-Louise Craig* 1, 2 and Dr. Elizabeth Magowan 1, 2 *Corresponding author: aimee-louise.leslie@afbini.gov.uk
Impact of increased energy and amino acids in sow lactation diets on piglet performance in large litters Aimee-Louise Craig* 1, 2 and Dr. Elizabeth Magowan 1, 2 *Corresponding author: aimee-louise.leslie@afbini.gov.uk
DESCRIPTIVE ANALYSIS OF RABBIT SEXUAL RECEPTIVITY AND ITS SOURCES OF VARIATION
 World Rabbit Science Association Proceedings 0 th World Rabbit Congress September 3-6, 202 Sharm El- Sheikh Egypt, 447 45 DESCRIPTIVE ANALYSIS OF RABBIT SEXUAL RECEPTIVITY AND ITS SOURCES OF VARIATION
World Rabbit Science Association Proceedings 0 th World Rabbit Congress September 3-6, 202 Sharm El- Sheikh Egypt, 447 45 DESCRIPTIVE ANALYSIS OF RABBIT SEXUAL RECEPTIVITY AND ITS SOURCES OF VARIATION
Aflatoxin Material Properties
 Aflatoxin Material Properties Aflatoxin is a kind of mycotoxin that was discovered from the mass poisoning of turkeys in UK in 1960, and has strong carcinogenicity. The typical mold that produces this
Aflatoxin Material Properties Aflatoxin is a kind of mycotoxin that was discovered from the mass poisoning of turkeys in UK in 1960, and has strong carcinogenicity. The typical mold that produces this
Consequences of selection for lean growth and prolificacy on piglet survival and sow attribute traits
 Consequences of selection for lean growth and prolificacy on piglet survival and sow attribute traits Susanne Hermesch Animal Genetics and Breeding Unit (AGBU), University of New England, Armidale, NSW,
Consequences of selection for lean growth and prolificacy on piglet survival and sow attribute traits Susanne Hermesch Animal Genetics and Breeding Unit (AGBU), University of New England, Armidale, NSW,
OVULATION INDUCTION METHODS COMPARED AMONG NON-CYCLING BEEF COWS. D. G. Landblom, J.L. Nelson and D. Redmer
 OVULATION INDUCTION METHODS COMPARED AMONG NON-CYCLING BEEF COWS By D. G. Landblom, J.L. Nelson and D. Redmer INTRODUCTION In the spring of 1987, an experiment was initiated to evaluate several ovulation
OVULATION INDUCTION METHODS COMPARED AMONG NON-CYCLING BEEF COWS By D. G. Landblom, J.L. Nelson and D. Redmer INTRODUCTION In the spring of 1987, an experiment was initiated to evaluate several ovulation
