Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference
|
|
|
- Sydney Collins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Proceeding of the SEVC Southern European Veterinary Conference Oct , 2008 Barcelona, Spain Reprinted in the IVIS website with the permission of the SEVC
2 Reproduction Infertility in the Bitch Dr. S. Romagnoli Department of Veterinary Clinical Sciences Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Padova Canine infertility can be due to wrong breeding management, reproductive cycle disorders, non-infectious uterine disease, poor semen quality, failure of the male to achieve a complete breeding, infectious disease of the reproductive tract, or ovarian disease. From a practical standpoint, fertility means achieving conception, then establishing a pregnancy through implantation and carrying the pregnancy to term. This paper will briefly review the most common factors influencing conception and pregnancy in canines. FACTOR INFLUENCING CONCEPTION AND PREGNANCY IN THE BITCH Errors in breeding management, anovulatory cycles and ovarian/uterine problems are frequently encountered as a cause of infertility in bitches of all ages, while poor semen quality is often a feature of adult to older male dogs. The most common factors influencing conception and the establishment of a normal canine pregnancy are listed in order of incidence in Table n 1. Table n 1: The most common factors influencing conception and the establishment of pregnancy in dogs. Factors are listed in order of incidence. Collecting reproductive history - A complete database of information (Table n 2) should be recorded for all previous seasons for which information is available. Information collected through history can be used by the clinician to decide whether or not the bitch is cycling normally, whether or not she was bred/inseminated at the appropriate time and whether or not reproductive disease is present. Each of the questions on table n 2 addresses a specific issue which may be relevant for understanding the cause of failure to conceive.
3 Table n 2 Questions to be asked when collecting reproductive history for cases of canine female infertility and reasons for their importance. Breeding management - As most bitches ovulate on day 12 of their season, there is a widespread tendency of owners to assume that day 12 is the ideal breeding day for all bitches. As a matter of fact, some bitches ovulate early (such as on day 8, or 6 or even 4 from the onset of proestrus) while others may ovulate as late as on day 17, 19 or One should never assume that a given bitch will ovulate on day 12 unless proven. Also, incidence of early or late ovulation is probably higher in the
4 those bitches who are taken to the veterinarian with a presenting complaint of infertility with respect to the normal canine population; bitches ovulating on day 12 from the onset of proestrus will always conceive at the first mating and therefore will almost never be taken to the veterinarian because of fertility problems. Managing a canine breeding requires the client taking the bitch to the veterinary clinic as soon as the first signs of proestrus are displayed (vulvar discharge, male attractiveness) for a first check, and then coming back every 2-3 days to monitor how quickly the female is progressing towards ovulation through vaginal smears and serum progesterone assays. Vaginoscopy and ovarian ultrasound can be very helpful clinical tools in identifying and monitoring the ovulation process. When the first day of ovulation is identified, there are still a few days to achieve a breeding, thanks to longevity of canine oocytes (4-6 days following ovulation). Performing vaginal citology as well as checking the bitch s behavior to look for onset of male receptivity are the 2 most practical ways of determining the best time for breeding. Owners should be instructed to bring their bitch to a male dog to check her behavior regularly as soon as possible after proestrus onset as well as to have a vaginal smear taken from the veterinarian every 2-3 days. Breeding should be performed as soon as the bitch stand and/or as soon as her smear is fully cornified, in order not to miss early ovulators. However, behavior does not always correlate with vaginal citology: some bitches will not stand to be mounted even though their smear is fully cornified. Provided that vaginal abnormalities (strictures, bands of tissue, hymen) are ruled out, serum P4 as well as using different male dogs (to rule out male preference) are helpful in such cases, although some bitches become receptive to mating only in mid to late estrus. Ovulation should always be timed using serum P4 assay every 2-3 days and the bitch should be bred when a high P4 value is observed (>5.0 ng/ml). Vaginal cytology should also be used to confirm serum P4 data (serum P4 kits which use a semi-quantitative colorimetric system are only 80% accurate) during and (most importantly) after breeding until the first day of cytological diestrus (D1) is identified, which occurs 6-8 days after ovulation. Vaginal endoscopy is also a helpful tool to stage the estrous cycle. Estradiol stimulation causes vaginal mucosa to become edematous, therefore during proestrus and early estrus vaginal folds appear round and swollen with some blood-tinged fluid in between them. As soon as follicular estrogen production stops fluid is resorbed from the vaginal mucosal lining and therefore vaginal folds suddenly become wrinkled (a process called crenulation ). As the wrinkling process is associated with a decrease in estradiol rather than an increase in progesterone, the crenulation is only an indirect indicator of ovulation. Therefore, vaginal endoscopy is a good way of identifying and monitoring the estradiol curve, but cannot be used to identify ovulation directly: serum progesterone remains a vital indicator in this respect. Reproductive cycle disorders Prolonged lack of heat or anestrus is sometimes observed especially in older bitches. Frequent cycling (3-4 heats/year) is also observed in bitches of all ages, and has been associated with infertility, although the mechanism involved is not yet clear. Anovulatory cycles occur fairly frequently (although there are no reported figures on their incidence) both at puberty as well as in the adult bitch. When a bitch experiences an anovulatory cycle, her reproductive behavior is generally absolutely normal, i.e. she attracts male dogs, has a normal vulvar discharge and accepts breeding. Failure to ovulate can only be diagnosed by finding a low serum progesterone concentration after breeding. Non-ifectious uterine disease - Uterine pathology is a common cause of failure to conceive both in bitches and queens. The bitch experiences 2 estrous cycles/year, with spontaneous ovulation, development of corpus luteum and progesterone secretion for about 2 months. The progesterone stimulation on the uterine lining (the endometrium) causes accumulation of secretion of endometrial glands with formation of cystic structures (cystic endometrial hyperplasia = CEH). Such cystic structures are very important for feeding the embryos, and if the female is not pregnant they normally regress towards the end the luteal phase (also called progestational phase or diestrus), leaving the
5 endometrium free to regenerate and be ready for the next chance for a pregnancy. If the female is rarely if ever mated, these cystic structures will eventually persist, thereby making large sections of the endometrium unsuitable for the establishment of pregnancy. Uterine disease is not believed to be a problem in breeding establishments where bitches are bred and conceive on a regular basis, as pregnancy may have a protective effect on the endometrium. Unlike breeding bitches, the average intact bitch kept as a pet may experience problems in becoming pregnant if bred only as an adult dog, due to the deterioration of her uterine lining. For diagnosis and treatment of canine pyometra the reader is referred to the paper on How I treat pyometra. Poor semen quality Dogs ejaculate million spermatozoa diluted in 2-50 cc of seminal plasma. Quantity of spermatozoa as well as of seminal plasma varies according to body weight and testicular size, with Yorkshire terriers and Great Danes producing an average of 2-3 and cc of ejaculate, respectively. Semen quality depends on quantity of spermatozoa present, their motility and morphology. Assessing semen quality is an easy task which can be performed in any veterinary clinic, provided that the male dog is accustomed to the technique or a bitch in heat is available to help him concentrate on ejaculation. Semen collection is generally performed through manual stimulation of the dog s penis through an artificial vagina (a latex cone connected to a plastic tube) or just wearing a latex glove in one hand and a smooth glass or plastic container in the other hand. Once collected, the semen must be kept in a warm environment (holding the tube in one s hands is enough) while it is being checked for motility (under a light microscope at 100X), morphology (under light microscope at X following staining with any cytological stain such as Diff Quick, haematoxylin-eosin or Leishman blue) and number of spermatozoa (using a haemocytometer such as a Niebauer chamber, Thomas chamber or Makler chamber). Poor semen quality can be found in adult to older male dogs, especially if suffering from prostate disease or following orchitis/epidydimitis or scrotal trauma. Poor semen quality can be due to also to inbreeding causing early testicular degeneration. Failure to achieve a normal mating Young stud dogs at their first attempts at breeding may sometime apparently look not capable of mounting properly, e.g. they may approach the female from her flank or from her head, or may spend a considerable amount of time pelvic thrusting without achieving an intromission. Although this should be considered part of the normal process of learning reproductive behaviour in young animals, it is considered abnormal when displayed by adult male dogs. Sometimes a male dog may achieve an incomplete intromission in which the bulbus glandis will engorge outside of the vulva. When this occurs, ejaculation may take place more caudally in the vestibule instead of in the most cranial aspect of the vagina, with a consequent loss of semen due to a retrograde flow of spermatozoa outside the vulva or to a higher degeneration rate of spermatozoa due to the acidic ph of the vagina. Not achieving an inside tie in the dog may be due to lack of experience, disease of the penis or lack of libido. When collecting history for a case of infertility it is important to check whether or not a coital lock or an inside tie (penis engorged and temporarily blocked into the vagina) occurred. Although outside-tie breedings may be fertile, an outside tie should always be ruled out when investigating causes of canine infertility. Partial or complete failure to accept breeding can also prevent normal mating to occur. If the bitch does not accept to be bred she might not be at the proper time for breeding, might have a vaginal septum or persistent hymen which causes her to feel pain at penetration or might have a behavioural problem (mate preference). Infectious disease of the reproductive tract - Infectious diseases of the canine reproductive tract which can be responsible for infertility include bacterial infection such as brucellosis due to Brucella canis (rarely Brucella abortus or suis), infection due to salmonella species, streptococci and E. coli; viral diseases such as herpes virus, distemper, parvovirus 1 and 2, and to the parasites Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum. Incidence may vary depending on the country and the area/s within each country. Brucella canis and herpes virus are highly contagious. Other bacterial infections (salmonella, streptococcus, E. coli) and toxoplasmosis are less contagious and tend to be a feature of the individual bitch. Not much is known about the role of Neospora caninum in canine abortion. Herpes virus has always been known as a cause of abortion. A herpes virus vaccine has recently been introduced in Europe, to be used in pregnant bitches. The vaccine is supposed to be used repeatedly in pregnant bitches, initially during early pregnancy followed by a booster injection during the last third of
6 pregnancy. The company claims that such a use is improving fertility in bitches which, if confirmed, would further substantiate the role of canine herpes virus as a cause of failure to conceive. Noninfectious causes of embryonic-fetal death Endocrine diseases such as inadequate production of progesterone or thyroid hormones during pregnancy may cause abortion. Also, diabetes, adrenal insufficiency and other endocrine diseases may affect foetal viability. The improper use of drugs may also have an adverse effect on pregnancy. Chromosomal abnormalities are widely described as a cause of embryonic/fetal death in the dog. Collecting a whole blood sample and submitting it to a laboratory for karyotype should never be overlooked when dealing with an abortion case. Luteal insufficiency is a recognized cause of failure to carry a pregnancy to term in the bitch. The clinical approach to hypoluteoidism includes assessing maternal and fetal conditions, ruling out other possible causes of abortion and repeatedly measuring serum progesterone (P4) concentrations. Treatment includes administration of a natural or synthetic P4 compound to support pregnancy as long as needed. The use of synthetic P4 compounds prior to day 25 of gestation should be avoided since it may induce malformation of the genital system of female foetuses. Treatment should be withdrawn prior to the expected day of whelping as a prolonged P4 administration may inhibit the mechanism of parturition. However, there is not enough data to advice a specific time interval prior to the expected date of whelping during which P4 administration should be withdrawn. Progestin administration during pregnancy may negatively affect the canine lactation. Ovarian disease - Ovarian disease (ovarian cysts or ovarian tumors) is a rare cause of infertility in bitches due to the fact that incidence of ovarian cysts or tumors is higher is adult to older bitches (the older the bitch the less likely she is to be used for reproduction). The most common presenting complaint of ovarian cyst or tumor is prolonged heat due to a high estrogen production. Ovarian cysts and tumors have occasionally been reported in bitches as young as 2-3 years of age. SUGGESTED READINGS Eilts BE - Pregnancy maintenance in the bitch using regumate. Proc Annual Meeting Society for Theriogenology 1992, pp Fieni F, Martal J, Marnet PG, Siliart B, Bernard F, Riou M, Bruyas JF, Tainturier D Hormonal variation in bitches after early or mid-pregnancy termination with aglepristone. J Reprod Fert Suppl 57: Feldman RW, Nelson EC Infertility, associated breeding disorders and disorders of sexual development. In: Feldman and Nelson, Canine and Feline Endocrinology and Reproduction. 3rd edition, WB Saunders, 2004, pp Johnston SD, Root-Kustritz MV, Olson PNS Clinical approach to canine infertility. In: Canine and Feline Theriogenology. Editors SD Johnston, MV Root-Kustritz and Olson PNS, WB Saunders 2001, pp Meyers-Wallen VN - Unusual and abnormal canine estrous cycles. Theriogenology 68, Thomas PGA, Perkins NR History taking and diagnostic assessment of the subfertile bitch. Austr Vet Pract 23:34-43, 1993 Ramsey I, Herrtage M - Distinguishing normal, sick and hypothyroid dogs using total thyroxine and thyrotropin concentrations. Canine Practice 22:43-44, 1997 Reimers TJ Endocrine testing for infertility in the bitch. In: Kirk RW ed, Current Vet Therapy VIII, WB Saunders, 1983,
Canine breeding management optimising fertility in bitches
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Canine breeding management optimising fertility in bitches Author : STEFANO ROMAGNOLI Categories : Vets Date : March 10, 2014
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Canine breeding management optimising fertility in bitches Author : STEFANO ROMAGNOLI Categories : Vets Date : March 10, 2014
Breeding Management in the Bitch: Timing Really is Everything! Erin E. Runcan, DVM, DACT Fairfield Pet Hospital, Lancaster, OH
 Breeding Management in the Bitch: Timing Really is Everything! Erin E. Runcan, DVM, DACT Fairfield Pet Hospital, Lancaster, OH It is often surprising how many well-seasoned breeders will have little knowledge
Breeding Management in the Bitch: Timing Really is Everything! Erin E. Runcan, DVM, DACT Fairfield Pet Hospital, Lancaster, OH It is often surprising how many well-seasoned breeders will have little knowledge
Artificial Insemination in Swine
 Artificial Insemination in Swine Artificial Insemination in Swine Routinely practiced on swine farms More efficient and effective use of boars AI centers distribute semen from genetically valuable boars
Artificial Insemination in Swine Artificial Insemination in Swine Routinely practiced on swine farms More efficient and effective use of boars AI centers distribute semen from genetically valuable boars
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA) Australian Small Animal Veterinary Association (ASAVA)
TIMING THE FERTILE PERIOD OF THE BITCH: BRIEF REVIEW
 TIMING THE FERTILE PERIOD OF THE BITCH: BRIEF REVIEW Canine Reproduction Seminar Dr. Scarlette Gotwals Stages of the Estrous Cycle Proestrus: Estrus: Diestrus: Anestrus: Vulvar swelling and bloody vaginal
TIMING THE FERTILE PERIOD OF THE BITCH: BRIEF REVIEW Canine Reproduction Seminar Dr. Scarlette Gotwals Stages of the Estrous Cycle Proestrus: Estrus: Diestrus: Anestrus: Vulvar swelling and bloody vaginal
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems. Lesson 7 Understanding Animal Reproduction
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 7 Understanding Animal Reproduction 1 Terms Anestrus Artificial insemination Castration Cervix Copulation Diestrus Egg Ejaculation Estrous cycle Estrus Fertilization
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 7 Understanding Animal Reproduction 1 Terms Anestrus Artificial insemination Castration Cervix Copulation Diestrus Egg Ejaculation Estrous cycle Estrus Fertilization
Preparation for Breeding
 Preparation for Breeding Bitch Regardless of the type of semen being used, all bitches over 4 years of age should be screened for underlying health conditions by running a complete blood count; a serum
Preparation for Breeding Bitch Regardless of the type of semen being used, all bitches over 4 years of age should be screened for underlying health conditions by running a complete blood count; a serum
VM 744 THERIOGENOLOGY Spring 2013
 VM 744 THERIOGENOLOGY Spring 2013 Credits-3 Coordinator: Patrick M., DVM, PhD, Diplomate ACT Department of Clinical Sciences Office: Equine Reproduction Laboratory Phone: 491-8626 email: pmccue@colostate.edu
VM 744 THERIOGENOLOGY Spring 2013 Credits-3 Coordinator: Patrick M., DVM, PhD, Diplomate ACT Department of Clinical Sciences Office: Equine Reproduction Laboratory Phone: 491-8626 email: pmccue@colostate.edu
breeders really don t want to miss!!!
 Oestrus induction in the canine species: dream or reality? The bitch: a mono-oestrian species Most mammals In the bitch in seasons twice a year Restricted breeding Breed variations: periods breeders really
Oestrus induction in the canine species: dream or reality? The bitch: a mono-oestrian species Most mammals In the bitch in seasons twice a year Restricted breeding Breed variations: periods breeders really
Female Reproductive System. Justin D. Vidal
 Female Reproductive System Justin D. Vidal If you cannot identify the tissue, then it is probably part of the female reproductive system! Introduction The female reproductive system is constantly changing,
Female Reproductive System Justin D. Vidal If you cannot identify the tissue, then it is probably part of the female reproductive system! Introduction The female reproductive system is constantly changing,
Ovarian Remnant Syndrome
 Ovarian Remnant Syndrome Dawna L. Voelkl, DVM, Dipl ACT University of Missouri College of Veterinary Medicine Ovarian Remnant Syndrome Definition Incidence Clinically applicable anatomy and etiology Clinical
Ovarian Remnant Syndrome Dawna L. Voelkl, DVM, Dipl ACT University of Missouri College of Veterinary Medicine Ovarian Remnant Syndrome Definition Incidence Clinically applicable anatomy and etiology Clinical
Progesterone level does not distinguish the different course of canine ovulation determined by ultrasonography
 Polish Journal of Veterinary Sciences Vol. 17, No. 2 (2014), 293 297 DOI 10.2478/pjvs-2014-0040 Original article Progesterone level does not distinguish the different course of canine ovulation determined
Polish Journal of Veterinary Sciences Vol. 17, No. 2 (2014), 293 297 DOI 10.2478/pjvs-2014-0040 Original article Progesterone level does not distinguish the different course of canine ovulation determined
AUSTRALIAN AND NEW ZEALAND COLLEGE OF VETERINARY SCIENTISTS. FELLOWSHIP GUIDELINES Animal Reproduction (Dog and Cat)
 Approved 1999 AUSTRALIAN AND NEW ZEALAND COLLEGE OF VETERINARY SCIENTISTS FELLOWSHIP GUIDELINES Animal Reproduction (Dog and Cat) ELIGIBILITY 1. The candidate shall meet the eligibility prerequisites for
Approved 1999 AUSTRALIAN AND NEW ZEALAND COLLEGE OF VETERINARY SCIENTISTS FELLOWSHIP GUIDELINES Animal Reproduction (Dog and Cat) ELIGIBILITY 1. The candidate shall meet the eligibility prerequisites for
Page 1. A wide variety of ovarian abnormalities are encountered in clinical practice
 A wide variety of ovarian abnormalities are encountered in clinical practice Common Problems Anovulatory follicles Persistent anovulatory follicles Hemorrhagic/Luteinized follicles Persistent corpus luteum
A wide variety of ovarian abnormalities are encountered in clinical practice Common Problems Anovulatory follicles Persistent anovulatory follicles Hemorrhagic/Luteinized follicles Persistent corpus luteum
Understanding Natural Animal Reproduction
 Lesson B4 2 Understanding Natural Animal Reproduction Unit B. Animal Science and the Industry Problem Area 4. Understanding Animal Reproduction and Biotechnology Lesson 2. Understanding Natural Animal
Lesson B4 2 Understanding Natural Animal Reproduction Unit B. Animal Science and the Industry Problem Area 4. Understanding Animal Reproduction and Biotechnology Lesson 2. Understanding Natural Animal
Fertility and early embryonic development. Chris Willoughby, Huntingdon Life Sciences 11 October 2012
 Fertility and early embryonic development Chris Willoughby, Huntingdon Life Sciences 11 October 2012 Outline 2 What sort of compounds may affect fertility? What areas of reproduction are we assessing in
Fertility and early embryonic development Chris Willoughby, Huntingdon Life Sciences 11 October 2012 Outline 2 What sort of compounds may affect fertility? What areas of reproduction are we assessing in
Chris Davies & Greg Handley
 Chris Davies & Greg Handley Contents Definition Epidemiology Aetiology Conditions for pregnancy Female Infertility Male Infertility Shared infertility Treatment Definition Failure of a couple to conceive
Chris Davies & Greg Handley Contents Definition Epidemiology Aetiology Conditions for pregnancy Female Infertility Male Infertility Shared infertility Treatment Definition Failure of a couple to conceive
(Received 5th July 1968)
 EFFECT OF AN INTRA-UTERINE DEVICE ON CONCEPTION AND OVULATION IN THE RHESUS MONKEY W. A. KELLY, J. H. MARSTON and P. ECKSTEIN Department of Anatomy, Medical School, Birmingham 15 (Received 5th July 1968)
EFFECT OF AN INTRA-UTERINE DEVICE ON CONCEPTION AND OVULATION IN THE RHESUS MONKEY W. A. KELLY, J. H. MARSTON and P. ECKSTEIN Department of Anatomy, Medical School, Birmingham 15 (Received 5th July 1968)
Small Ruminant Reproductive Management Workshop
 Small Ruminant Reproductive Management Workshop Animal Nutrition and Physiology Center, North Dakota State University Sponsors: American Sheep and Goat Center, North Dakota State University, University
Small Ruminant Reproductive Management Workshop Animal Nutrition and Physiology Center, North Dakota State University Sponsors: American Sheep and Goat Center, North Dakota State University, University
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Domestic Animal Behavior ANSC 3318 SEXUAL BEHAVIOR. Image courtesy : USDA ARS Image Library
 SEXUAL BEHAVIOR Image courtesy : USDA ARS Image Library Importance of Sexual Behavior Without reproduction, life would come to an end! In production situations, it is economically important to have good
SEXUAL BEHAVIOR Image courtesy : USDA ARS Image Library Importance of Sexual Behavior Without reproduction, life would come to an end! In production situations, it is economically important to have good
AP Biology Ch ANIMAL REPRODUCTION. Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below.
 AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
FERTILITY & TCM. On line course provided by. Taught by Clara Cohen
 FERTILITY & TCM On line course provided by Taught by Clara Cohen FERTILITY & TCM FERTILITY AND TCM THE PRACTITIONER S ROLE CAUSES OF INFERTILITY RISK FACTORS OBJECTIVES UNDERSTANDING TESTS Conception in
FERTILITY & TCM On line course provided by Taught by Clara Cohen FERTILITY & TCM FERTILITY AND TCM THE PRACTITIONER S ROLE CAUSES OF INFERTILITY RISK FACTORS OBJECTIVES UNDERSTANDING TESTS Conception in
MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure.
 Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
Chapter 27 Exam Due NLT Thursday, July 31, 2015 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE: match the term(s) or description with the appropriate letter of the structure. Figure 27.1 Using Figure 27.1, match the following:
to ensure the. Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion of.
 The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
The Reproductive System Fill-In Notes Purpose of life: to ensure the. Stages of Human Development Sexual reproduction requires the (from the mother) by a (from the father). Fertilization is the fusion
Reproductive Endocrinology. Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007
 Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Animal Reproductive Systems. Chapter 42
 Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
Animal Reproductive Systems Chapter 42 Impacts, Issues Male or Female? Body or Genes? Body and genes don t always match male or female characteristics also depend on hormones mutations can result in intersex
REPRODUCTION & GENETICS. Hormones
 REPRODUCTION & GENETICS Hormones http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=np0wfu_mgzo Objectives 2 Define what hormones are; Compare and contrast the male and female hormones; Explain what each hormone in the mail
REPRODUCTION & GENETICS Hormones http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=np0wfu_mgzo Objectives 2 Define what hormones are; Compare and contrast the male and female hormones; Explain what each hormone in the mail
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction
 Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
Ch 20: Reproduction. Keypoints: Human Chromosomes Gametogenesis Fertilization Early development Parturition
 Ch 20: Reproduction Keypoints: Human Chromosomes Gametogenesis Fertilization Early development Parturition SLOs Contrast mitosis/meiosis, haploid/diploid, autosomes/sex chromosomes. Outline the hormonal
Ch 20: Reproduction Keypoints: Human Chromosomes Gametogenesis Fertilization Early development Parturition SLOs Contrast mitosis/meiosis, haploid/diploid, autosomes/sex chromosomes. Outline the hormonal
WHY INVESTIGATE FOR INFERTILITY
 WHY INVESTIGATE FOR INFERTILITY Intrauterine Insemination 1 About this booklet This series of booklets has been developed and written with the support of leading fertility clinics across Australia, and
WHY INVESTIGATE FOR INFERTILITY Intrauterine Insemination 1 About this booklet This series of booklets has been developed and written with the support of leading fertility clinics across Australia, and
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Canine infertility. Alfort National Veterinary College Paris - France. Alain Fontbonne. DVM, PhD, Dipl. ECAR
 Canine infertility Alain Fontbonne DVM, PhD, Dipl. ECAR Alfort National Veterinary College Paris - France Introduction Nowadays: vets are more often asked to manage fertility problems in the dog: increased
Canine infertility Alain Fontbonne DVM, PhD, Dipl. ECAR Alfort National Veterinary College Paris - France Introduction Nowadays: vets are more often asked to manage fertility problems in the dog: increased
1. Describe the importance and process of animal reproduction. 2. List the sexual classification of animals for major species.
 Unit B: Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 7: Understanding Animal Reproduction Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives:
Unit B: Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 7: Understanding Animal Reproduction Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives:
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE
 Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCCIÓN. La idea fija. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
Age and Fertility. A Guide for Patients Revised 2012 Copyright 2012 by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine
 1 Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients Revised 2012 Copyright 2012 by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine INTRODUCTION Fertility changes with age. Both males and females become fertile in
1 Age and Fertility A Guide for Patients Revised 2012 Copyright 2012 by the American Society for Reproductive Medicine INTRODUCTION Fertility changes with age. Both males and females become fertile in
STUDIES ON THE THERAPY WITH GONADOTROPIN- RELEASING HORMONE (GnRH) AND HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN (hcg) IN GENITAL DISORDERS IN BITCHES
 STUDIES ON THE THERAPY WITH GONADOTROPIN- RELEASING HORMONE (GnRH) AND HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN (hcg) IN GENITAL DISORDERS IN BITCHES Mihai Cristian Popescu, Maria Crivineanu, Mario Darius Codreanu
STUDIES ON THE THERAPY WITH GONADOTROPIN- RELEASING HORMONE (GnRH) AND HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN (hcg) IN GENITAL DISORDERS IN BITCHES Mihai Cristian Popescu, Maria Crivineanu, Mario Darius Codreanu
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System
 9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
9.4 Regulating the Reproductive System The Reproductive System to unite a single reproductive cell from a female with a single reproductive cell from a male Both male and female reproductive systems include
Information Booklet. Exploring the causes of infertility and treatment options.
 Information Booklet Exploring the causes of infertility and treatment options www.ptafertility.co.za info@ptafertility.co.za +27 12 998 8854 Faith is taking the first step even if you don t see the whole
Information Booklet Exploring the causes of infertility and treatment options www.ptafertility.co.za info@ptafertility.co.za +27 12 998 8854 Faith is taking the first step even if you don t see the whole
Reproductive physiology. About this Chapter. Case introduction. The brain directs reproduction 2010/6/29. The Male Reproductive System
 Section Ⅻ Reproductive physiology Ming-jie Wang E-Mail: mjwang@shmu.edu.cn About this Chapter The reproductive organs and how they work the major endocrine functions of sexual glands actions of sex hormones
Section Ⅻ Reproductive physiology Ming-jie Wang E-Mail: mjwang@shmu.edu.cn About this Chapter The reproductive organs and how they work the major endocrine functions of sexual glands actions of sex hormones
The beginning of puberty is marked by the progressive increase in the production of sex hormones.
 Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System
 Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Bio 12- Ch. 21: Reproductive System 21.1- Male Reproductive System o Male anatomy o Testes and how they relate to sperm production and male sex hormones o Hormone regulation in males 21.2- Female Reproductive
Female Reproductive System
 Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
In domestic animals, we have limited period of estrus (sexual receptivity) and the term estrous
 REPRODUCTIVE CYCLES 1. Estrous cycle 2. Menstrual cycle In domestic animals, we have limited period of estrus (sexual receptivity) and the term estrous cycle is used. The onset of proestrus defines the
REPRODUCTIVE CYCLES 1. Estrous cycle 2. Menstrual cycle In domestic animals, we have limited period of estrus (sexual receptivity) and the term estrous cycle is used. The onset of proestrus defines the
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
Female Reproductive System. Lesson 10
 Female Reproductive System Lesson 10 Learning Goals 1. What are the five hormones involved in the female reproductive system? 2. Understand the four phases of the menstrual cycle. Human Reproductive System
Female Reproductive System Lesson 10 Learning Goals 1. What are the five hormones involved in the female reproductive system? 2. Understand the four phases of the menstrual cycle. Human Reproductive System
Onset of sexual maturity in female Göttingen minipigs & consequences for toxicity studies
 Onset of sexual maturity in female Göttingen minipigs & consequences for toxicity studies Birgit Peter Eveline e Rijk Helle Lorentsen*, Adrian Zeltner* *Joint project with Ellegaard Göttingen Minipigs
Onset of sexual maturity in female Göttingen minipigs & consequences for toxicity studies Birgit Peter Eveline e Rijk Helle Lorentsen*, Adrian Zeltner* *Joint project with Ellegaard Göttingen Minipigs
Chapter 14 The Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment
 Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
STUDY GUIDE FOR PERSONAL HEALTH & MANAGEMENT ESSENTIAL UNIT 4 (E04) and SELECTIVE UNIT 1 (S01) (Human Development & Infectious Diseases)
 Name: STUDY GUIDE FOR PERSONAL HEALTH & MANAGEMENT ESSENTIAL UNIT 4 (E04) and SELECTIVE UNIT 1 (S01) (Human Development & Infectious Diseases) Chapter 16 Section 1 Pages 388-394 Section 2 Pages 395-402
Name: STUDY GUIDE FOR PERSONAL HEALTH & MANAGEMENT ESSENTIAL UNIT 4 (E04) and SELECTIVE UNIT 1 (S01) (Human Development & Infectious Diseases) Chapter 16 Section 1 Pages 388-394 Section 2 Pages 395-402
a. the tail disappears b. they become spermatids c. they undergo capacitation d. they have been stored in the uterus for several days
 (2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
(2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
Canine reproductive disorders
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Canine reproductive disorders Author : Jennifer Cartwright Categories : RVNs Date : November 1, 2011 Jennifer Cartwright RVN
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk Canine reproductive disorders Author : Jennifer Cartwright Categories : RVNs Date : November 1, 2011 Jennifer Cartwright RVN
Sperm production. Sperm production. Meiosis. Mitosis. The cells of Leydig in testes secrete
 Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Sperm production. Sperm production. Controlling sperm production. Meiosis. Mitosis. The cells of Leydig in testes secrete
 Ductus deferens Sperm production Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Ductus deferens Sperm production Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems. Chapter 39: Biology II
 Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
Endocrine and Reproductive Systems Chapter 39: Biology II The Endocrine System Made up of glands that release their products into the bloodstream These products broadcast messages throughout the body Chemicals
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
Neil Goodman, MD, FACE
 Initial Workup of Infertile Couple: Female Neil Goodman, MD, FACE Professor of Medicine Voluntary Faculty University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Scope of Infertility in the United States Affects
Initial Workup of Infertile Couple: Female Neil Goodman, MD, FACE Professor of Medicine Voluntary Faculty University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Scope of Infertility in the United States Affects
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction
 Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The human male and female reproductive cycles are controlled by the interaction of hormones from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary with
Hormonal Control of Human Reproduction Bởi: OpenStaxCollege The human male and female reproductive cycles are controlled by the interaction of hormones from the hypothalamus and anterior pituitary with
Evaluation of the Infertile Couple
 Overview and Definition Infertility is defined as the inability of a couple to fall pregnant after one year of unprotected intercourse. Infertility is a very common condition as in any given year about
Overview and Definition Infertility is defined as the inability of a couple to fall pregnant after one year of unprotected intercourse. Infertility is a very common condition as in any given year about
Reproduction and Development. Female Reproductive System
 Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Reproduction and Development Female Reproductive System Outcomes 5. Identify the structures in the human female reproductive system and describe their functions. Ovaries, Fallopian tubes, Uterus, Endometrium,
Canine reproduction : what s new in 2015?
 When you are a scientific communication officer, one day or another, you will have to do lectures. I am not complaining here since, in my current position, this is something I really enjoy! It gives me
When you are a scientific communication officer, one day or another, you will have to do lectures. I am not complaining here since, in my current position, this is something I really enjoy! It gives me
DATE: NAME: CLASS: Chapter 14 Test
 Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
Multiple Choice Questions Decide which of the choices best completes the statement or answers the question. Locate that question number on the separate answer sheet provided. Use the procedure described
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes
 Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Functions of male Reproductive System: produce gametes deliver gametes protect and support gametes Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes after puberty. From the testes they are deposited into the epididymas
Web Activity: Simulation Structures of the Female Reproductive System
 differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
differentiate. The epididymis is a coiled tube found along the outer edge of the testis where the sperm mature. 3. Testosterone is a male sex hormone produced in the interstitial cells of the testes. It
SAMPLE REPORT. Order Number: PATIENT. Age: 40 Sex: F MRN:
 Patient: Age: 40 Sex: F MRN: SAMPLE PATIENT Order Number: Completed: Received: Collected: SAMPLE REPORT Progesterone ng/ml 0.34 0.95 21.00 DHEA-S mcg/dl Testosterone ng/ml 48 35 0.10 0.54 0.80 430 Sex
Patient: Age: 40 Sex: F MRN: SAMPLE PATIENT Order Number: Completed: Received: Collected: SAMPLE REPORT Progesterone ng/ml 0.34 0.95 21.00 DHEA-S mcg/dl Testosterone ng/ml 48 35 0.10 0.54 0.80 430 Sex
Breeding & Kidding Management
 Breeding & Kidding Management Breeding Season Fall Decreasing day length 1:25 ratio (male:female) Length of estrous cycle: 21 days Length of breeding period: 35-45 days Percentage of Does Ovulating 120
Breeding & Kidding Management Breeding Season Fall Decreasing day length 1:25 ratio (male:female) Length of estrous cycle: 21 days Length of breeding period: 35-45 days Percentage of Does Ovulating 120
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom
 1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems. Male Reproductive Organs. Male Reproductive Organs. Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm)
 Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA
 Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S Congress Avenue 4631 N Congress Avenue Lake Worth, FL 33461 West Palm Beach, FL 33407 INSTRUCTIONS FOR INFERTILITY WORKUP Please read these handouts carefully.
Palm Beach Obstetrics & Gynecology, PA 4671 S Congress Avenue 4631 N Congress Avenue Lake Worth, FL 33461 West Palm Beach, FL 33407 INSTRUCTIONS FOR INFERTILITY WORKUP Please read these handouts carefully.
Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 36 Active Reading Guide Reproduction and Development Section 1 1. Distinguish between sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. 2. Which form of reproduction: a.
Outline OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
 UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
UNIT FIVE: PUBERTY HiTOPS, Inc./Princeton Center for Leadership Training OVERVIEW PUBERTY PRE-TESTS Outline PUBERTY WITH SAM AND SALLY MENSTRUATION: HOW DOES IT WORK? SPERMATOGENESIS: HOW DOES IT WORK?
Manipulation of Ovarian Function for the Reproductive Management of Dairy Cows
 Veterinary Research Communications,28(2004) 111 119 2004 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands Manipulation of Ovarian Function for the Reproductive Management of Dairy Cows W.W. Thatcher1*,
Veterinary Research Communications,28(2004) 111 119 2004 Kluwer Academic Publishers. Printed in the Netherlands Manipulation of Ovarian Function for the Reproductive Management of Dairy Cows W.W. Thatcher1*,
Lesson 3: Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology
 Lesson 3: Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology 1 Terms Artificial insemination Cloning Donor female Embryo transfer Estrous synchronization Genetic engineering Progestin Prostaglandin Recipient
Lesson 3: Understanding Animal Reproduction Technology 1 Terms Artificial insemination Cloning Donor female Embryo transfer Estrous synchronization Genetic engineering Progestin Prostaglandin Recipient
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction
 Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
Sample Provincial exam Q s: Reproduction 11. Functions Testosterone Makes the male sex organs function normally, and also inhibits hypothalamus s release of GnRH and thus LH & FSH and thus testosterone
6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction
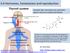 6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Thyroxin is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. It's key role is in controlling
6.6 Hormones, homeostasis and reproduction Essential idea: Hormones are used when signals need to be widely distributed. Thyroxin is a hormone produced by the thyroid gland. It's key role is in controlling
Animal and Veterinary Science Department University of Idaho. REGULATION OF REPRODUCTION AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) Chapter 5
 Animal and Veterinary Science Department University of Idaho REGULATION OF REPRODUCTION AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) Chapter 5 I. DEFINITIONS A. Endocrine Gland B. Hormone Chemical messenger
Animal and Veterinary Science Department University of Idaho REGULATION OF REPRODUCTION AVS 222 (Instructor: Dr. Amin Ahmadzadeh) Chapter 5 I. DEFINITIONS A. Endocrine Gland B. Hormone Chemical messenger
Why Cycle Control? Manipulating Ovulation and Estrous Synchronization. Manipulating Ovulation. Cattle. Principle of PGF 2a Use
 Why Cycle Control? Manipulating and Estrous Synchronization John Parrish 1. Group females for parturition: a) Decrease labor, calving period Reduce calving season b) More uniform weaning weights. 2. Reduce
Why Cycle Control? Manipulating and Estrous Synchronization John Parrish 1. Group females for parturition: a) Decrease labor, calving period Reduce calving season b) More uniform weaning weights. 2. Reduce
PERIPARTURIENT DISORDERS IN DAIRY COWS. J.S. Stevenson. Introduction
 5 a PERIPARTURIENT DISORDERS IN DAIRY COWS J.S. Stevenson I! e Introduction The economic climate in the dairy industry requires producers to operate efficiently to remain competitive. Attention to details
5 a PERIPARTURIENT DISORDERS IN DAIRY COWS J.S. Stevenson I! e Introduction The economic climate in the dairy industry requires producers to operate efficiently to remain competitive. Attention to details
VETERINARY CONSIDERATIONS MALE BREEDING SOUNDNESS EXAMS AND
 VETERINARY CONSIDERATIONS MALE BREEDING SOUNDNESS EXAMS AND VENEREAL DISEASES IN BULLS Bret McNabb, DVM, MPVM, DACT University of California, Davis School of Veterinary Medicine Physical Examination A
VETERINARY CONSIDERATIONS MALE BREEDING SOUNDNESS EXAMS AND VENEREAL DISEASES IN BULLS Bret McNabb, DVM, MPVM, DACT University of California, Davis School of Veterinary Medicine Physical Examination A
Why Cycle Control?" Manipulating Ovulation and Estrous Synchronization" Manipulating Ovulation" Cattle" Principle of PGF 2α Use"
 Why Cycle Control?" Manipulating Ovulation and Estrous Synchronization" John Parrish 1. Group females for parturition: " a) Decrease labor, calving period Reduce calving season" b) More uniform weaning
Why Cycle Control?" Manipulating Ovulation and Estrous Synchronization" John Parrish 1. Group females for parturition: " a) Decrease labor, calving period Reduce calving season" b) More uniform weaning
Examining Breeding Soundness of Beef Bulls
 Examining Breeding Soundness of Beef Bulls A herd bull that will serve a higher percentage of cows during a limited breeding season is essential to a successful cow-calf operation. In many of these operations,
Examining Breeding Soundness of Beef Bulls A herd bull that will serve a higher percentage of cows during a limited breeding season is essential to a successful cow-calf operation. In many of these operations,
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Phases of the Ovarian Cycle
 OVARIAN CYCLE An ovary contains many follicles, and each one contains an immature egg called an oocyte. A female is born with as many as 2 million follicles, but the number is reduced to 300,000 to 400,000
OVARIAN CYCLE An ovary contains many follicles, and each one contains an immature egg called an oocyte. A female is born with as many as 2 million follicles, but the number is reduced to 300,000 to 400,000
Semen collection in domestic animals
 Reproductive Biotechnologies Andrology I Semen collection in domestic animals Prof. Alberto Contri Aims Technological aim Diagnostic aim Methods for semen collection Indirect collection post-coital method
Reproductive Biotechnologies Andrology I Semen collection in domestic animals Prof. Alberto Contri Aims Technological aim Diagnostic aim Methods for semen collection Indirect collection post-coital method
Plasma LH and Progesterone Levels before and after Ovulation and Observation of Ovarian Follicles by Ultrasonographic Diagnosis System in Dogs
 FULL PAPER Theriogenology Plasma LH and Progesterone Levels before and after Ovulation and Observation of Ovarian Follicles by Ultrasonographic Diagnosis System in Dogs Masayoshi HASE, Tatsuya HORI, Eiichi
FULL PAPER Theriogenology Plasma LH and Progesterone Levels before and after Ovulation and Observation of Ovarian Follicles by Ultrasonographic Diagnosis System in Dogs Masayoshi HASE, Tatsuya HORI, Eiichi
Basic Reproduction & Genetics. Steve Pritchard UNL Extension Educator Boone-Nance Counties
 Basic Reproduction & Genetics Steve Pritchard UNL Extension Educator Boone-Nance Counties Hormonal Regulation of the Estrous Cycle Several hormones regulate the estrous cycle Changes in the concentrations
Basic Reproduction & Genetics Steve Pritchard UNL Extension Educator Boone-Nance Counties Hormonal Regulation of the Estrous Cycle Several hormones regulate the estrous cycle Changes in the concentrations
Female Reproductive Physiology. Dr Raelia Lew CREI, FRANZCOG, PhD, MMed, MBBS Fertility Specialist, Melbourne IVF
 Female Reproductive Physiology Dr Raelia Lew CREI, FRANZCOG, PhD, MMed, MBBS Fertility Specialist, Melbourne IVF REFERENCE Lew, R, Natural History of ovarian function including assessment of ovarian reserve
Female Reproductive Physiology Dr Raelia Lew CREI, FRANZCOG, PhD, MMed, MBBS Fertility Specialist, Melbourne IVF REFERENCE Lew, R, Natural History of ovarian function including assessment of ovarian reserve
1.Abstinence no sex (Abstinence only education has been proven ineffective in preventing unwanted pregnancies)
 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Contraception 2. STDs 1. Ovary Transplants 2. Freezing Eggs 3. Choosing Gender 4. The Male Pill, parts 1&2 5. Male Birth Control: RISUG 6. Birth Control. 1.Abstinence
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Contraception 2. STDs 1. Ovary Transplants 2. Freezing Eggs 3. Choosing Gender 4. The Male Pill, parts 1&2 5. Male Birth Control: RISUG 6. Birth Control. 1.Abstinence
The Female Reproductive System
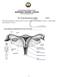 The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
The Female Reproductive System STD X The female reproductive system consists of a pair of ovaries, a pair of oviducts, uterus, a vagina and the outermost part - the vulva. 1 1. Ovaries The ovaries are
16 East 40 th St, 2 nd Fl, New York, NY Ph fax
 Page 1 of 9 16 East 40 th St, 2 nd Fl, New York, NY 10016 Ph 212-679-2289 fax 212-679-2288 Please complete the following: Fertility Evaluation Name: Date of birth: Age: Partner s Name: Date of birth: Age:
Page 1 of 9 16 East 40 th St, 2 nd Fl, New York, NY 10016 Ph 212-679-2289 fax 212-679-2288 Please complete the following: Fertility Evaluation Name: Date of birth: Age: Partner s Name: Date of birth: Age:
Article #1 CE Acquired Infertility in Male Dogs with Normal Libido ABSTRACT: SIGNALMENT
 Article #1 CE Acquired Infertility in Male Dogs with Normal Libido Cristina Gobello, DMV, DECAR Yanina Corrada, MV National University of La Plata, Argentina ABSTRACT: This article discusses the signalment,
Article #1 CE Acquired Infertility in Male Dogs with Normal Libido Cristina Gobello, DMV, DECAR Yanina Corrada, MV National University of La Plata, Argentina ABSTRACT: This article discusses the signalment,
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
