Mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the cervix:! [INS][c] C! [/INS] ase report and literature review
|
|
|
- Poppy Nash
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Accepted Manuscript Mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the cervix:! [INS][c] C! [/INS] ase report and literature review A. Dierickx, M. Göker, G. Braems, P. Tummers, R. Van Den Broecke PII: S (16)30025-X DOI: doi: /j.gore Reference: GORE 122 To appear in: Received date: 16 February 2016 Revised date: 27 April 2016 Accepted date: 4 May 2016 Please cite this article as: Dierickx, A., Göker, M., Braems, G., Tummers, P., Van Den Broecke, R., Mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the cervix:! [INS][c] C! [/INS] ase report and literature review, (2016), doi: /j.gore This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
2 Mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the cervix: case report and literature review A.Dierickx 1, M.Göker 1, G. Braems 1, P.Tummers 1, R. Van Den Broecke 1 1. Department of gynecology and obstetrics, University Hospital of Ghent, De Pintelaan 185, 9000 Ghent, Belgium. anneloor.dierickx@ugent.be, telephone number: (+32) The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest. No financial support. 1
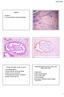
3 Abstract A mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the cervix is a very rare tumor deriving from remnants of the mesonephric duct. Differential diagnosis from other cervical carcinomas is difficult and little is known regarding its biological behavior, prognosis, and the optimal management strategy. We present a case of a mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the cervix with a comprehensive review of the existing literature. In this case a 66-year-old woman presented with postmenopausal vaginal bleeding. She was diagnosed with a FIGO stage IIB mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the cervix and treated with neo-adjuvant chemoradiotherapy and a Wertheim hysterectomy. The recovery from surgery was uneventful and the patient remains with no evidence of disease with 2 years of follow-up. Keywords Cervical cancer; mesonephric carcinoma; mesonephric adenocarcinoma; adenocarcinoma cervix. Case Clinical presentation A 66-year-old woman with no medical history presented with postmenopausal vaginal bleeding. In speculo a small punctiform orifice on the right side of the cervical ostium was observed. Transvaginal ultrasound revealed a mass of 2 by 2 cm in de right lateral cervical wall, palpable as a hard nodule without extension to the pelvic wall. Taking into consideration there was a mass in a suspiciouslooking cervix an immediate conization was performed. The patient had a normal PAP smear 2 years before. The pathological examination of the conus revealed the presence of an invasive mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the cervix, characterized by infiltrating tubular structures containing eosinophilic, hyaline secretions in their lumens (Fig. 1A). The tubular structures were lined by cuboidal epithelium exhibiting mild to moderate nuclear atypia. Immunohistochemical stainings for PAX8, p16 and CD10 were positive (Fig. 1C). 2
4 There was extension of tumor cells in all resection margins. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) performed after the conization showed a mass in the right side of the cervix, measuring 38 x 35 x 38 mm, with extension to the uterus, the right parametrium and the upper part of the vagina (figure 2). These clinical findings corresponded with an International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) stage IIB. A Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scan showed no evidence of pathological lymphadenopathies or distant metastases. The CA-125 blood serum level was normal. Treatment Given the presence of a bulky tumor with parametrial invasion, the patient underwent neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy: 50 Gray (Gy) of Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) in 25 fractions of 2 Gy daily and concomitant chemotherapy (Cisplatin) once a week. There was a limited reduction in size of the cervical mass to a volume of 37 x 23 x 30 mm. After the neoadjuvant therapy the patient underwent a type 2 Wertheim hysterectomy without pelvic lymphadenectomy. Histopathologic examination confirmed the presence of a mesonephric adenocarcinoma, predominantly on the right side, however, with almost complete circumferential extension. The lesion measured 3 cm in greatest dimension. There was extension to the isthmus and the paracervical fat tissue. The resection margins were free of tumor. The lesion stained for cytokeratin 7, EMA and vimentin. Stainings for calretinin, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), estrogen- and progesterone receptor (ER/PR) were negative. The final diagnosis was a mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the cervix, FIGO stage IIB. Tumor cells expressed p16, but chromogenic in situ hybridization did not demonstrate low- or high-risk Human Papillomavirus (HPV). 3
5 Outcome and follow up The patient did not receive adjuvant therapy and she remains with no evidence of disease with 2 years of follow-up, with follow-up every 3 months and MRI- and PET-scans every 12 months. Review of the literature Definition In order to understand the origin of this tumor we recapitulate the embryology in the supplementary material. Incidence To the best of our knowledge there are only 40 cases of this tumor reported in the literature to date, including present case (table 2). The incidence of this neoplasm is uncertain since it is often confused with more common adenocarcinomas or mistaken for benign florid mesonephric hyperplasia [1-3]. Diagnosis The mean age at the time of diagnosis was 52 years in this literature review. Unlike the more common squamous epithelial carcinoma, this type of cervical cancer is rarely discovered by PAP smear [4]. Most patients present with abnormal vaginal bleeding, often with a visible cervical lesion [1]. The diagnosis is usually made on biopsy specimens, endometrial curettings or hysterectomy specimens. A common finding on endometrial biopsy is a coexisting endometroid adenocarcinoma [4]. Most tumors exhibit a widely infiltrative and confluent pattern of growth and extension into the lower uterine segment is common [5]. Because of the widespread distribution within the cervix at the time of diagnosis the initial site of origin in the lateral part of the cervix is often no longer apparent [3], as was in this case. 4
6 Pathology One of the most characteristic features of a mesonephric adenocarcinoma is that it exhibits a mixture of morphologic patterns. Therefore they are often confused with serous, clear cell or endometroid adenocarcinomas [4,5]. In this literature review 23% of the reported mesonephric carcinomas were associated with a spindled cell component (malignant mixed mesonephric tumor, MMMT). This is a biphasic variant of a mesonephric carcinoma with sarcomatoid features [6,7]. The typical background lesion of a mesonephric carcinoma is florid mesonephric hyperplasia, characterized by a densely eosinophilic luminal secretion [8]. In contrast to mesonephric hyperplasia, a mesonephric carcinoma does not have a lobular architecture and the nuclei appear cytological malignant. The Ki-67 proliferation index is less than 1% in mesonephric hyperplasia compared to 15-20% in mesonephric carcinoma [9]. Immunohistochemistry Given its potential mimicry of other neoplasms, immunohistochemistry can be helpful in the differential diagnosis. Positive immunostaining for CD10, CK7 and calretinin along with a negative immunostaining for CEA is suggestive for a mesonephric origin [9]. Mesonephric adenocarcinoma is also usually positive for epithelial membrane antigen (EMA) [9] and vimentin [6,9,10] whereas ER/PR are usually absent [9]. Mesonephric adenocarcinoma is one of the few subtypes of cervical cancer that is not related to HPV [3]. PAX8 staining is usually positive in mesonephric carcinomas [3,11. CA125 is also usually positive in mesonephric carcinoma but negative in benign mesonephric structures [3]. 5
7 Treatment In the 39 cases described in the literature, treatment depended on the stage of the disease and consisted of hysterectomy (HRT) with or without bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (BSO), pelvic lymphadenectomy (LA) and (neo-) adjuvant chemo- or radiation therapy. In the present literature review the vast majority of patients (70%) were diagnosed at a stage I. All patients with stage I carcinoma, except for two, were treated with HRT and BSO, and LA was performed in eighteen patients (64%). No adjuvant treatment was given in patients with stage I disease except for radiotherapy in five patients with adenocarcinoma (AC) and chemotherapy in one patient with a mesonephric adenocarcinoma with spindled cell component (MMMT). There seems to be no difference in disease recurrence and mean recurrence interval between the patients with stage I mesonephric AC of the cervix treated merely surgically and those who received adjuvant therapy afterwards (table 2). However, the biological behavior of this unusual tumor remains unclear and until there are sufficient data to recommend a particular course of therapy it seems reasonable to manage patients with mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the cervix according to current guidelines for cervical adenocarcinoma of similar stage. Prognosis Owing to the small number of cases with adequate follow-up, prognosis cannot be accurately predicted but it seems that mesonephric carcinomas carry a worse prognosis. Patients with a stage I mesonephric AC had a recurrence rate of 32% and a mean recurrence interval of 24 months (table 2), compared to a reported recurrence rate of 11% for squamous cell carcinomas and 16% for adenocarcinomas in early stage cervical cancer [10]. However, these results should be interpreted with caution given the small number of patients. 6
8 Four out of 24 patients diagnosed at stage I with adequate follow up available died of the disease, with a mean survival of 50 months. All of the patients diagnosed at stage IV had a spindled cell component. Only five of the nine reported cases of MMMT were diagnosed at stage I, two were stage II and two were stage IV. It seems that mesonephric carcinomas with a spindled cell component are diagnosed at a more advanced stage, implying a worse prognosis. Conclusion A mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the cervix arises from remnants of the mesonephric (Wolffian) duct in the lateral wall of the cervix. It is a rare type of cervical cancer, to the best of our knowledge only 40 cases have been reported in literature. The most common symptom is postmenopausal bleeding. Because of its localization, this type of cervical cancer is rarely discovered on PAP smear. Diagnosis is made for the most part on biopsy or hysterectomy specimens. Because of its widely infiltrative growth potential a barrel-shaped cervix can occur. If a barrel-shaped cervix is palpated during pelvic examination, an adenocarcinoma of the cervix should be considered. It is a pathologically challenging diagnosis since a mesonephric adenocarcinoma typically exhibits a mixture of morphologic patterns. Therefore they are often confused with more common adenocarcinomas. The incidence of mesonephric carcinoma is probably underestimated because of this frequent misclassification. The possibility of a mesonephric carcinoma of the cervix should be considered when encountering a histological unusual-appearing carcinoma or MMMT. In this case a targeted search for associated mesonephric hyperplasia is required, characterized by small glands or tubules with eosinophilic luminal secretions. In questionable cases, immunohistochemical profiling can be helpful. 7
9 Prognosis cannot be accurately predicted owing to the small number of cases with sufficient follow up but it seems that mesonephric carcinomas carry a worse prognosis. In this review the majority of patients (70%) were diagnosed at stage IB with a mean age of 52 years. Treatment consisted of hysterectomy, bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy in the majority of these patients. The recurrence rate in these patients was 32% and the mean recurrence interval 24 months. Acknowledgments I would like to thank Kathleen Lambein and Jo Van Dorpe for reviewing the pathology content and providing the pathology slides. I would like to thank Julie Vercauteren for providing the illustrations. Conflicts of interest None. References [1] Hart WR. Symposium part II: special types of adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix. Int J Gynecol Pathol Oct;21(4): [2] Ferry JA, Scully RE. Mesonephric remnants, hyperplasia, and neoplasia in the uterine cervix. A study of 49 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 1990;14(12). [3] Kenny SL, McBride HA, Jamison J, McCluggage WG. Mesonephric adenocarcinomas of the uterine cervix and corpus: HPV-negative neoplasms that are commonly PAX8, CA125, and HMGA2 positive and that may be immunoreactive with TTF1 and hepatocyte nuclear factor 1-β. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012;36(6): [4] Anagnostopoulos A, Ruthven S, Kingston R. Mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix and literature review. BMJ Case Rep
10 [5] Nomoto K, Hayashi S, Tsuneyama K, Hori T, Ishizawa S. Cytopathology of cervical mesonephric adenocarcinoma: a report of two cases. Cytopathology. 2013;24(2): [6] Clement PB, Young RH, Keh P, Ostör AG, Scully RE. Malignant mesonephric neoplasms of the uterine cervix. A report of eight cases, including four with a malignant spindle cell component. Am J Surg Pathol. 1995;19(10): [7] Yap OW, Hendrickson MR, Teng NN, Kapp DS. Mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the cervix: a case report and review of the literature. Gynecol Oncol. 2006;103(3): [8] Menon S, Kathuria K, Deodhar K, Kerkar R. Mesonephric adenocarcinoma (endometrioid type) of endocervix with diffuse mesonephric hyperplasia involving cervical wall and myometrium: an unusual case report. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2013;56(1):51-3. [9] Silver SA, Devouassoux-Shisheboran M, Mezzetti TP, Tavassoli FA. Mesonephric adenocarcinomas of the uterine cervix. A study of 11 cases with immunohistochemical findings. Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25: [10] Lang G, Dallenbach-Hellweg G. The histogenetic origin of cervical mesonephric hyperplasia and mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix studied with immunohistochemical methods. Int J Gynecol Pathol 1990;9: [11] Fregnani JH, Soares FA, Novik PR, Lopes A, Latorre MR. Comparison of biological behavior between early-stage adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2008;136(2): [12] McGee CT, Cromer DW, Greene RR. Mesonephric carcinoma of the cervix-differentiation from endocervical adenocarcinoma. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1962;84: [13] Buntine DW. Adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix of probable wolffian origin. Pathology 1979;11:
11 [14] Valente PT, Susin M. Cervical adenocarcinoma arising in florid mesonephric hyperplasia: report of a case with immunocytochemical studies. Gynecol Oncol 1987;27: [15] Stewart CJR, Taggart CR, Brett F, Mutch AF. Mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix with focal endocrine cell differentiation. Int J Gynecol Pathol 1993;12: [16] Angeles, R., August, C., Weisenberg,E. Pathologic Quiz Case. An Incidentally Detected Mass of the Uterine Cervix. Arch Pathol Lab Med ;128(10): [17] Bague S, Rodriguez IM, Prat J. Malignant mesonephric tumors of the female genital tract. A clinicopathologic study of 9 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28: [18] Fukunaga M., Takahashi H., Yasuda M. Mesonephric adenocarcinoma of the uterine cervix: a case report with immunohistochemical and ultrastructural studies. Pathol Res pract. 2008;204(9): [19] Meguro S, Yasuda M, Shimizu M, Kurosaki A, Fujiwara K. Mesonephric adenocarcinoma with a sarcomatous component, a notable subtype of cervical carcinosarcoma: a case report and review of the literature. Diagn Pathol. 2013;8:74. 10
12 A A B 11
13 C D Fig. 1. A, The lesion shows infiltrating tubular structures containing eosinophilic, hyaline secretions (original magnification, x200). B, The tubular structures are lined by cuboidal tumor cells demonstrating mild to moderate nuclear atypia (original magnification, x400). C, The tumor cells show strong nuclear expression of the transcription factor PAX8 (immunohistochemistry for PAX8, original magnification x200). D, There is nuclear and cytoplasmic expression of the tumor suppressor p16 (immunohistochemistry for p16, original magnification x200). 12
14 Fig. 2. Axial and sagittal T2 MRI image of the patient before treatment. Arrows indicate the cervical tumor on the right side of the cervix, measuring 38 x 35 x 38 mm, with extension to the uterus, the right parametrium and the upper part of the vagina. 13
15 Table 1 Immunohistochemical staining profile of mesonephric, endocervical and endometroid adenocarcinoma of the cervix and the present case. Present case Mesonephric adenocarcinoma Endocervical adenocarcinoma Endometroid adenocarcinoma PAX Calretinin CD CK Vimentin EMA CEA ER/PR HPV
16 Author Year Case Age Symptoms Table 2: summary of the 40 cases of mesonephric carcinoma of the cervix reported in the literature, including present case. Tumor type Stage Treatment Clinical course Outcome McGee PC VBV AC IB HRT Pelvic R (6yr) :NFT DOD 7yr Buntine fibroids AC / HRT+BSO Vaginal R (7yr):NFT DOD 9yr Valente&Susin PMP VBV AC IB1 HRT+BSO+LA Pelvis, sacral R (2yr):RT DOD 2,8yr Lang Cervical polyp AC / HRT RT NED 10mo 5 55 / AC IB HRT / / Ferry&Scully Pelvic relaxation AC / HRT+BSO RT NED 5yr Stewart Constipation, menorrhagia AC I HRT+BSO+LA NFT NED 10yr Clement Menorrhagia, "fibroid uterus" AC IB HRT+BSO+LA NFT NED 2yr 9 34 Menometrorrhagia AC IB HRT+BSO+LA Abd R (1yr) : CT NED 2yr AC on PAP smear, pelvic mass AC IB HRT+BSO+LA RT, abd R (4 mo) : CT DOD 8,5mo PMP VB AC IB HRT+BSO+LA / / 15
17 12 37 PC VB MMMT IB HRT+BSO+LA Adj CT, abd R (9&11yr) : CT AWD 13yr PMP VB MMMT IB HRT+BSO RT NED 3yr Menorrhagia, cervical polyp MMMT IB HRT+BSO RT NED 2,3yr Silver PMP VB AC IB HRT+USO NFT NED 1,5yr Uterine prolaps AC IB HRT+BSO NFT NED 2,1yr SIL on PAP smear AC IB HRT+BSO NFT NED 3,2yr PMP VB AC IB HRT+BSO+LA NFT NED 6,1yr PMP VB AC IB HRT+BSO NFT NED 8,3yr AGC on PAP smear AC IB HRT+BSO+LA Menorrhagia, cervical "fibroid" MMMT IB HRT+BSO RT, rectovaginal R (1,7yr) : CT Mediastinal metastasis (5,6 yr) : CT PMP VB AC IB HRT+BSO+LA NFT / NED 2,5yr DOD 6,2yr Righ ovarian cystadenoma AC / HRT+BSO NFT NED 7,4yr VB, pelvic pain AC IIB RT Pelvic R (2,2yr):CT DOD 3,2yr Metrorrhagia, anemia MMMT IVB HRT+BSO+LA+O CT, bladder & pelvic R (8mo):RT DOD 10mo Angeles Menometrorrhagia, pelvic pain AC IIA HRT+BSO RT NED 1yr 16
18 Bagué Abnormal VB AC IB HRT+BSO+LA+A RT NED 11,4yr / AC IIA / / / PC VB AC IB1 HRT+USO NFT NED 3,1yr PMP VB MMMT IIA HRT+BSO+LA+O NFT DOD 7mo / MMMT IVB HRT+BSO CT & RT, bone R AWD 3,3yr / MMMT IB1 HRT+BSO+LA+O NFT NED 1,1yr Yap PMP VB AC IB1 HRT+BSO+LA RT NED 3,1yr Fukunaga Abnormal VB AC IB HRT+BSO+LA+O NFT NED 4mo Anagnostopoulos Suspicous looking cervix AC IB1 HRT+BSO+LA NFT NED 6mo Nomoto PMP VB AC IB1 HRT+BSO+LA Multifocal lung metastases (1yr):CT PMP VB AC IB1 HRT+BSO+LA NFT / Meguro PMP VB MMMT IIA HRT+BSO+LA Local R (7 mo) : CRT NED 7mo Menon PMP VB AC IB1 HRT+BSO+LA RT NED 6mo / Present case PMP VB AC IIB CRT+HRT+BSO NFT NED 2yr PMP VB: postmenopausal vaginal bleeding. PC VB: postcoital vaginal bleeding. HRT: hysterectomy. BSO: bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy. USO: unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy LA: lymphadenectomy. O: omentectomy. A: appendectomy. AC: adenocarcinoma. MMMT: malignant mixed mesonephric tumour. CT: chemotherapy. RT: radiotherapy. CRT: chemo- and radiotherapy. NFT: no further treatment. R: recurrence. Yr: year. Mo: month. NED: no evidence of disease. AWD: alive with disease. DOD: dead of disease. 17
19 Highlights A mesonephric adenocarcinoma is a rare tumor deriving from remnants of the Wolffian duct Challenging diagnosis since this tumor can mimic more common adenocarcinomas Immunohistochemistry can be helpful in questionable cases Rational to base treatment on current guidelines for adenocarcinoma until more data It seems mesonephric carcinomas carry a worse prognosis 18
Mesonephric carcinoma of the uterine corpus: A report of two cases
 ONCOLOGY LETTERS 11: 335-339, 2016 Mesonephric carcinoma of the uterine corpus: A report of two cases JIANGUO ZHAO 1,2, CAIYAN LIU 2, JI QI 2 and PENGPENG QU 2 1 Clinical College of Central Gynecology
ONCOLOGY LETTERS 11: 335-339, 2016 Mesonephric carcinoma of the uterine corpus: A report of two cases JIANGUO ZHAO 1,2, CAIYAN LIU 2, JI QI 2 and PENGPENG QU 2 1 Clinical College of Central Gynecology
MPH Quiz. 1. How many primaries are present based on this pathology report? 2. What rule is this based on?
 MPH Quiz Case 1 Surgical Pathology from hysterectomy performed July 11, 2007 Final Diagnosis: Uterus, resection: Endometrioid adenocarcinoma, Grade 1 involving most of endometrium, myometrial invasion
MPH Quiz Case 1 Surgical Pathology from hysterectomy performed July 11, 2007 Final Diagnosis: Uterus, resection: Endometrioid adenocarcinoma, Grade 1 involving most of endometrium, myometrial invasion
New Cancer Cases By Site Breast 28% Lung 14% Colo-Rectal 10% Uterus 6% Thyroid 5% Lymphoma 4% Ovary 3%
 Uterine Malignancy New Cancer Cases By Site 2010 Breast 28% Lung 14% Colo-Rectal 10% Uterus 6% Thyroid 5% Lymphoma 4% Ovary 3% Cancer Deaths By Site 2010 Lung 26% Breast 15% Colo-Rectal 9% Pancreas 7%
Uterine Malignancy New Cancer Cases By Site 2010 Breast 28% Lung 14% Colo-Rectal 10% Uterus 6% Thyroid 5% Lymphoma 4% Ovary 3% Cancer Deaths By Site 2010 Lung 26% Breast 15% Colo-Rectal 9% Pancreas 7%
In situ and Invasive Endocervical Carcinoma: Problems and Pitfalls in Diagnosis
 In situ and Invasive Endocervical Carcinoma: Problems and Pitfalls in Diagnosis Rouba Ali-Fehmi,MD The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine Global incidence of cervical
In situ and Invasive Endocervical Carcinoma: Problems and Pitfalls in Diagnosis Rouba Ali-Fehmi,MD The Karmanos Cancer Institute, Wayne State University School of Medicine Global incidence of cervical
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER CERVIX
 PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER CERVIX Site Group: Gynecology Cervix Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION 3 3. SCREENING AND
PRINCESS MARGARET CANCER CENTRE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES GYNECOLOGIC CANCER CERVIX Site Group: Gynecology Cervix Author: Dr. Stephane Laframboise 1. INTRODUCTION 3 2. PREVENTION 3 3. SCREENING AND
Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology
 Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Eric C. Huang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of California, Davis Medical Center Case 1 Presentation 38
Diagnostically Challenging Cases in Gynecologic Pathology Eric C. Huang, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of California, Davis Medical Center Case 1 Presentation 38
05/07/2018. Types of challenges. Challenging cases in uterine pathology. Case 1 ` 65 year old female Post menopausal bleeding Uterine Polyp
 Types of challenges Challenging cases in uterine pathology Nafisa Wilkinson Gynaecological Pathologist UCLH London Lack of complete history often, NO clinical history at all! Cases from other centres often
Types of challenges Challenging cases in uterine pathology Nafisa Wilkinson Gynaecological Pathologist UCLH London Lack of complete history often, NO clinical history at all! Cases from other centres often
Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
 Question 1. Each of the following statements about cervical adenocarcinoma is true except: Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix SAMS a) A majority of women with cervical adenocarcinoma have stage I tumors at diagnosis.
Question 1. Each of the following statements about cervical adenocarcinoma is true except: Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix SAMS a) A majority of women with cervical adenocarcinoma have stage I tumors at diagnosis.
3/25/2019. Rare uterine cancers ~3% Leiomyosarcoma Carcinosarcoma (MMMT) Endometrial Stromal Sarcomas Aggressive tumors High Mortality Rates
 J. Anthony Rakowski D.O., F.A.C.O.O.G. MSU SCS Board Review Coarse Rare uterine cancers ~3% Leiomyosarcoma Carcinosarcoma (MMMT) Endometrial Stromal Sarcomas Aggressive tumors High Mortality Rates Signs
J. Anthony Rakowski D.O., F.A.C.O.O.G. MSU SCS Board Review Coarse Rare uterine cancers ~3% Leiomyosarcoma Carcinosarcoma (MMMT) Endometrial Stromal Sarcomas Aggressive tumors High Mortality Rates Signs
What is endometrial cancer?
 Uterine cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the uterus. The lining is called the endometrium. Endometrial cancer usually occurs in women
Uterine cancer What is endometrial cancer? Endometrial cancer is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the uterus. The lining is called the endometrium. Endometrial cancer usually occurs in women
Intravascular Endometrium Mimicking Vascular Invasion
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 A Papanicolau, G Lin Citation A Papanicolau, G Lin.. The Internet Journal of Pathology. 2010 Volume 12 Number 1. Abstract Intravascular endometrium
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 12 Number 1 A Papanicolau, G Lin Citation A Papanicolau, G Lin.. The Internet Journal of Pathology. 2010 Volume 12 Number 1. Abstract Intravascular endometrium
CASE 4 21/07/2017. Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix. Female 31. LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities
 Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
Chapter 8 Adenocarcinoma
 Page 80 Chapter 8 Adenocarcinoma Overview In Japan, the proportion of squamous cell carcinoma among all cervical cancers has been declining every year. In a recent survey, non-squamous cell carcinoma accounted
Page 80 Chapter 8 Adenocarcinoma Overview In Japan, the proportion of squamous cell carcinoma among all cervical cancers has been declining every year. In a recent survey, non-squamous cell carcinoma accounted
Cervical Cancer: 2018 FIGO Staging
 Cervical Cancer: 2018 FIGO Staging Jonathan S. Berek, MD, MMS Laurie Kraus Lacob Professor Stanford University School of Medicine Director, Stanford Women s Cancer Center Senior Scientific Advisor, Stanford
Cervical Cancer: 2018 FIGO Staging Jonathan S. Berek, MD, MMS Laurie Kraus Lacob Professor Stanford University School of Medicine Director, Stanford Women s Cancer Center Senior Scientific Advisor, Stanford
Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE
 Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES PHYSICAL EXAMINATION CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE 3/5 Patient presents through the emergency room with
Please complete prior to the webinar. HOSPITAL REGISTRY WEBINAR FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM EXERCISES PHYSICAL EXAMINATION CASE 1: FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE 3/5 Patient presents through the emergency room with
The PAX8 gene is a member of the paired-box family of
 Assessment of the Utility of PAX8 Immunohistochemical Stain in Diagnosing Endocervical Glandular Lesions Li Liang, MD, PhD; Wenxin Zheng, MD; Jinsong Liu, MD, PhD; Sharon X. Liang, MD, PhD Context. PAX8,
Assessment of the Utility of PAX8 Immunohistochemical Stain in Diagnosing Endocervical Glandular Lesions Li Liang, MD, PhD; Wenxin Zheng, MD; Jinsong Liu, MD, PhD; Sharon X. Liang, MD, PhD Context. PAX8,
Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia
 Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia The terminology and pathology of VAIN are analogous to those of CIN (VAIN I-III). The main difference is that vaginal epithelium does not normally have crypts, so the
Vaginal intraepithelial neoplasia The terminology and pathology of VAIN are analogous to those of CIN (VAIN I-III). The main difference is that vaginal epithelium does not normally have crypts, so the
Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies
 Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies Bunja Rungruang, MD Medical College of Georgia No disclosures 4 th most common new cases of cancer in women 5 th and 6 th leading cancer deaths
Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies Bunja Rungruang, MD Medical College of Georgia No disclosures 4 th most common new cases of cancer in women 5 th and 6 th leading cancer deaths
Mody. AIS vs. Invasive Adenocarcinoma of the Cervix
 Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Michael T. Deavers, M.D. Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, Texas Common Problems in Gynecologic Pathology Adenocarcinoma in-situ (AIS) of the Cervix vs. Invasive
Article begins on next page
 Pseudopapillary Granulosa Cell Tumor: A Case of This Rare Subtype Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. [https://rucore.libraries.rutgers.edu/rutgers-lib/50622/story/]
Pseudopapillary Granulosa Cell Tumor: A Case of This Rare Subtype Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. [https://rucore.libraries.rutgers.edu/rutgers-lib/50622/story/]
Article begins on next page
 Primary Carcinosarcoma of the Uterine Cervix-Report of a case and review of the literature Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Primary Carcinosarcoma of the Uterine Cervix-Report of a case and review of the literature Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
Cervical cancer presentation
 Carcinoma of the cervix: Carcinoma of the cervix is the second commonest cancer among women worldwide, with only breast cancer occurring more commonly. Worldwide, cervical cancer accounts for about 500,000
Carcinoma of the cervix: Carcinoma of the cervix is the second commonest cancer among women worldwide, with only breast cancer occurring more commonly. Worldwide, cervical cancer accounts for about 500,000
Gynecologic Malignancies. Kristen D Starbuck 4/20/18
 Gynecologic Malignancies Kristen D Starbuck 4/20/18 Outline Female Cancer Statistics Uterine Cancer Adnexal Cancer Cervical Cancer Vulvar Cancer Uterine Cancer Endometrial Cancer Uterine Sarcoma Endometrial
Gynecologic Malignancies Kristen D Starbuck 4/20/18 Outline Female Cancer Statistics Uterine Cancer Adnexal Cancer Cervical Cancer Vulvar Cancer Uterine Cancer Endometrial Cancer Uterine Sarcoma Endometrial
UTERINE SARCOMAS CURRENT THERAPEUTIC OPTIONS
 Review Journal of Translational Medicine and Research, volume 19, no. 1-2, 2014 UTERINE SARCOMAS CURRENT THERAPEUTIC OPTIONS N. Bacalbaæa 1, A. Traistaru 2, I. Bãlescu 3 1 Carol Davila University of Medicine
Review Journal of Translational Medicine and Research, volume 19, no. 1-2, 2014 UTERINE SARCOMAS CURRENT THERAPEUTIC OPTIONS N. Bacalbaæa 1, A. Traistaru 2, I. Bãlescu 3 1 Carol Davila University of Medicine
North of Scotland Cancer Network Clinical Management Guideline for Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix
 THIS DOCUMENT North of Scotland Cancer Network Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED DOCUMENT CONTROL Prepared by A Kennedy/AG Macdonald/Others Approved by NOT APPROVED Issue date April
THIS DOCUMENT North of Scotland Cancer Network Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED DOCUMENT CONTROL Prepared by A Kennedy/AG Macdonald/Others Approved by NOT APPROVED Issue date April
PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT
 PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT QUESTION #1 WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS NOT A RISK FACTOR FOR CERVICAL CANCER? A. HIGH RISK HPV B. CIGARETTE SMOKING C.
PRE TEST CERVICAL SCREENING MANAGEMENT COLPOSCOPY PATHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT QUESTION #1 WHICH OF THE FOLLOWING IS NOT A RISK FACTOR FOR CERVICAL CANCER? A. HIGH RISK HPV B. CIGARETTE SMOKING C.
Most common cancer Africans & Asians more prone because of poor socioeconomic condition Drastic decline in west as more detection of preinvasive
 CANCER CERVIX Most common cancer Africans & Asians more prone because of poor socioeconomic condition Drastic decline in west as more detection of preinvasive leison by PAP Smears. Etiology: Age - 2 peaks
CANCER CERVIX Most common cancer Africans & Asians more prone because of poor socioeconomic condition Drastic decline in west as more detection of preinvasive leison by PAP Smears. Etiology: Age - 2 peaks
When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box?
 When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box? Teri A. Longacre, MD Stanford Medicine Stanford California pi6 in Gynecologic Pathology: Panacea or Pandora
When Immunostains Can Get You in Trouble: Gynecologic Pathology p16: Panacea or Pandora s Box? Teri A. Longacre, MD Stanford Medicine Stanford California pi6 in Gynecologic Pathology: Panacea or Pandora
An Unusual Case of Cervical Cancer with Inguinal Lymph Node Metastasis: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.9655003 Volume 1, Issue 1 Case Report An Unusual Case of Cervical Cancer with Inguinal Lymph Node Metastasis: A Case Report and Review
Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.9655003 Volume 1, Issue 1 Case Report An Unusual Case of Cervical Cancer with Inguinal Lymph Node Metastasis: A Case Report and Review
Annual report of Gynecologic Oncology Committee, Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 2013
 bs_bs_banner doi:10.1111/jog.12360 J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. Vol. 40, No. 2: 338 348, February 2014 Annual report of Gynecologic Oncology Committee, Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 2013 Daisuke
bs_bs_banner doi:10.1111/jog.12360 J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. Vol. 40, No. 2: 338 348, February 2014 Annual report of Gynecologic Oncology Committee, Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology, 2013 Daisuke
Hiroyuki Hanakawa, Nobuya Monden, Kaori Hashimoto, Aiko Oka, Isao Nozaki, Norihiro Teramoto, Susumu Kawamura
 Accepted Manuscript Radiation-induced laryngeal angiosarcoma: Case report Hiroyuki Hanakawa, Nobuya Monden, Kaori Hashimoto, Aiko Oka, Isao Nozaki, Norihiro Teramoto, Susumu Kawamura PII: S2468-5488(18)30005-5
Accepted Manuscript Radiation-induced laryngeal angiosarcoma: Case report Hiroyuki Hanakawa, Nobuya Monden, Kaori Hashimoto, Aiko Oka, Isao Nozaki, Norihiro Teramoto, Susumu Kawamura PII: S2468-5488(18)30005-5
C ORPUS UTERI C ARCINOMA STAGING FORM (Carcinosarcomas should be staged as carcinomas)
 CLINICAL C ORPUS UTERI C ARCINOMA STAGING FORM PATHOLOGIC Extent of disease before S TAGE C ATEGORY D EFINITIONS Extent of disease through any treatment completion of definitive surgery y clinical staging
CLINICAL C ORPUS UTERI C ARCINOMA STAGING FORM PATHOLOGIC Extent of disease before S TAGE C ATEGORY D EFINITIONS Extent of disease through any treatment completion of definitive surgery y clinical staging
Unusual Osteoblastic Secondary Lesion as Predominant Metastatic Disease Spread in Two Cases of Uterine Leiomyosarcoma
 49 Unusual Osteoblastic Secondary Lesion as Predominant Metastatic Disease Spread in Two Cases of Uterine Leiomyosarcoma Loredana Miglietta a Maria Angela Parodi b Luciano Canobbio b Luca Anselmi c a Medical
49 Unusual Osteoblastic Secondary Lesion as Predominant Metastatic Disease Spread in Two Cases of Uterine Leiomyosarcoma Loredana Miglietta a Maria Angela Parodi b Luciano Canobbio b Luca Anselmi c a Medical
Endometrial Cancer. Incidence. Types 3/25/2019
 Endometrial Cancer J. Anthony Rakowski DO, FACOOG MSU SCS Board Review Coarse Incidence 53,630 new cases yearly 8,590 deaths yearly 4 th most common malignancy in women worldwide Most common GYN malignancy
Endometrial Cancer J. Anthony Rakowski DO, FACOOG MSU SCS Board Review Coarse Incidence 53,630 new cases yearly 8,590 deaths yearly 4 th most common malignancy in women worldwide Most common GYN malignancy
Article begins on next page
 Scalp metastasis as a presenting symptom of Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. [https://rucore.libraries.rutgers.edu/rutgers-lib/50623/story/]
Scalp metastasis as a presenting symptom of Cervical Squamous Cell Carcinoma Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. [https://rucore.libraries.rutgers.edu/rutgers-lib/50623/story/]
Index. B Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy (BSO), 69
 A Advanced stage endometrial cancer diagnosis, 92 lymph node metastasis, 92 multivariate analysis, 92 myometrial invasion, 92 prognostic factors FIGO stage, 94 histological grade, 94, 95 histologic cell
A Advanced stage endometrial cancer diagnosis, 92 lymph node metastasis, 92 multivariate analysis, 92 myometrial invasion, 92 prognostic factors FIGO stage, 94 histological grade, 94, 95 histologic cell
UPDATE IN THE MANAGEMENT OF INVASIVE CERVICAL CANCER
 UPDATE IN THE MANAGEMENT OF INVASIVE CERVICAL CANCER Susan Davidson, MD Professor Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Division of Gynecologic Oncology University of Colorado- Denver Anatomy Review
UPDATE IN THE MANAGEMENT OF INVASIVE CERVICAL CANCER Susan Davidson, MD Professor Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Division of Gynecologic Oncology University of Colorado- Denver Anatomy Review
Port-Site Metastases After Robotic Surgery for Gynecologic Malignancy
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Port-Site Metastases After Robotic Surgery for Gynecologic Malignancy Noah Rindos, MD, Christine L. Curry, MD, PhD, Rami Tabbarah, MD, Valena Wright, MD ABSTRACT Background and Objectives:
SCIENTIFIC PAPER Port-Site Metastases After Robotic Surgery for Gynecologic Malignancy Noah Rindos, MD, Christine L. Curry, MD, PhD, Rami Tabbarah, MD, Valena Wright, MD ABSTRACT Background and Objectives:
Disclosure. Case. Mixed Tumors of the Uterine Corpus and Cervix. I have nothing to disclose
 Mixed Tumors of the Uterine Corpus and Cervix Marisa R. Nucci, M.D. Division of Women s and Perinatal Pathology Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston, MA UCSF Current Issues in Anatomic
Mixed Tumors of the Uterine Corpus and Cervix Marisa R. Nucci, M.D. Division of Women s and Perinatal Pathology Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital Boston, MA UCSF Current Issues in Anatomic
One of the commonest gynecological cancers,especially in white Americans.
 Gynaecology Dr. Rozhan Lecture 6 CARCINOMA OF THE ENDOMETRIUM One of the commonest gynecological cancers,especially in white Americans. It is a disease of postmenopausal women with a peak incidence in
Gynaecology Dr. Rozhan Lecture 6 CARCINOMA OF THE ENDOMETRIUM One of the commonest gynecological cancers,especially in white Americans. It is a disease of postmenopausal women with a peak incidence in
Case Report Osteoclastic Giant Cell Rich Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Case Reports in Pathology, Article ID 415328, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/415328 Case Report Osteoclastic Giant Cell Rich Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix: A Case Report and Review
Case Reports in Pathology, Article ID 415328, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/415328 Case Report Osteoclastic Giant Cell Rich Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix: A Case Report and Review
of 20 to 80 and subsequently declines [2].
![of 20 to 80 and subsequently declines [2]. of 20 to 80 and subsequently declines [2].](/thumbs/80/81450506.jpg) - - According to the 2014 World Health Organization (WHO) classification and tumor morphology, primary ovarian tumors are subdivided into three categories: epithelial (60%), germ cell (30%), and sex-cord
- - According to the 2014 World Health Organization (WHO) classification and tumor morphology, primary ovarian tumors are subdivided into three categories: epithelial (60%), germ cell (30%), and sex-cord
PORTEC-4. Patient seqnr. Age at inclusion (years) Hospital:
 May 2016 Randomisation Checklist Form 1, page 1 of 2 Patient seqnr. Age at inclusion (years) Hospital: Eligible patients should be registered and randomised via the Internet at : https://prod.tenalea.net/fs4/dm/delogin.aspx?refererpath=dehome.aspx
May 2016 Randomisation Checklist Form 1, page 1 of 2 Patient seqnr. Age at inclusion (years) Hospital: Eligible patients should be registered and randomised via the Internet at : https://prod.tenalea.net/fs4/dm/delogin.aspx?refererpath=dehome.aspx
Algorithms for management of Cervical cancer
 Algithms f management of Cervical cancer Algithms f management of cervical cancer are based on existing protocols and guidelines within the ESGO comunity and prepared by ESGO Educational Committe as a
Algithms f management of Cervical cancer Algithms f management of cervical cancer are based on existing protocols and guidelines within the ESGO comunity and prepared by ESGO Educational Committe as a
North of Scotland Cancer Network Clinical Management Guideline for Endometrial Cancer
 THIS DOCUMENT North of Scotland Cancer Network Clinical Management Guideline for Endometrial Cancer Based on WOSCAN CMG with further extensive consultation within NOSCAN UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED DOCUMENT
THIS DOCUMENT North of Scotland Cancer Network Clinical Management Guideline for Endometrial Cancer Based on WOSCAN CMG with further extensive consultation within NOSCAN UNCONTROLLED WHEN PRINTED DOCUMENT
Chapter 2: Initial treatment for endometrial cancer (including histologic variant type)
 Chapter 2: Initial treatment for endometrial cancer (including histologic variant type) CQ01 Which surgical techniques for hysterectomy are recommended for patients considered to be stage I preoperatively?
Chapter 2: Initial treatment for endometrial cancer (including histologic variant type) CQ01 Which surgical techniques for hysterectomy are recommended for patients considered to be stage I preoperatively?
Wendy L Frankel. Chair and Distinguished Professor
 1 Wendy L Frankel Chair and Distinguished Professor Case 1 59 y/o woman Abdominal pain No personal or family history of cancer History of colon polyps Colonoscopy Polypoid rectosigmoid mass Biopsy 3 4
1 Wendy L Frankel Chair and Distinguished Professor Case 1 59 y/o woman Abdominal pain No personal or family history of cancer History of colon polyps Colonoscopy Polypoid rectosigmoid mass Biopsy 3 4
C ORPUS UTERI C ARCINOMA STAGING FORM (Carcinosarcomas should be staged as carcinomas)
 C ORPUS UTERI C ARCINOMA STAGING FORM CLINICAL Extent of disease before any treatment y clinical staging completed after neoadjuvant therapy but before subsequent surgery Tis * T1 I T1a IA NX N0 N1 N2
C ORPUS UTERI C ARCINOMA STAGING FORM CLINICAL Extent of disease before any treatment y clinical staging completed after neoadjuvant therapy but before subsequent surgery Tis * T1 I T1a IA NX N0 N1 N2
Atypical Hyperplasia/EIN
 EIN Atypical Hyperplasia/EIN Based on scientific and diagnostic advances, in 2014 the WHO moved that the precursor lesion for endometrioid carcinoma be atypical hyperplasia/ein, rather than what was previously
EIN Atypical Hyperplasia/EIN Based on scientific and diagnostic advances, in 2014 the WHO moved that the precursor lesion for endometrioid carcinoma be atypical hyperplasia/ein, rather than what was previously
Department of Pathology, Royal Group of Hospitals Trust, Belfast, Northern Ireland.
 UTERINE ADENOSARCOMA W Glenn McCluggage Department of Pathology, Royal Group of Hospitals Trust, Belfast, Northern Ireland. Definition of Adenosarcoma: A mixed tumor composed of benign neoplastic glandular
UTERINE ADENOSARCOMA W Glenn McCluggage Department of Pathology, Royal Group of Hospitals Trust, Belfast, Northern Ireland. Definition of Adenosarcoma: A mixed tumor composed of benign neoplastic glandular
Ovarian mucinous borderline tumor accompanied by LGESS with myxoid change: a case report and literature review
 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-017-0295-4 European Journal of Medical Research CASE REPORT Open Access Ovarian mucinous borderline tumor accompanied by LGESS with myxoid change: a case report and literature
https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-017-0295-4 European Journal of Medical Research CASE REPORT Open Access Ovarian mucinous borderline tumor accompanied by LGESS with myxoid change: a case report and literature
Malignant transformation in benign cystic teratomas, dermoids of the ovary
 European JournalofObstetrics& Gynecology andreproductivebiology, 29 (1988) 197-206 197 Elsevier EJO 00716 Malignant transformation in benign cystic teratomas, dermoids of the ovary S. Chadha 1 and A. Schaberg
European JournalofObstetrics& Gynecology andreproductivebiology, 29 (1988) 197-206 197 Elsevier EJO 00716 Malignant transformation in benign cystic teratomas, dermoids of the ovary S. Chadha 1 and A. Schaberg
Mu ath M.A. Rjoub Supervised by: Dr. Huda Zahawi, FRCPath. King Abdullah University Hospital )KAUH(
 Mu ath M.A. Rjoub Supervised by: Dr. Huda Zahawi, FRCPath. King Abdullah University Hospital )KAUH( Clinical History A 56 year old single female, presented complaining of postmenopausal bleeding. She underwent
Mu ath M.A. Rjoub Supervised by: Dr. Huda Zahawi, FRCPath. King Abdullah University Hospital )KAUH( Clinical History A 56 year old single female, presented complaining of postmenopausal bleeding. She underwent
64 YO lady THBSO for prolapse At gross : A 3 cm endometrial polyp in the fundus
 Case 6 64 YO lady THBSO for prolapse At gross : A 3 cm endometrial polyp in the fundus Numerous irregular, large glands with leaf-like pattern Large glands with broad-based papillary infolding into the
Case 6 64 YO lady THBSO for prolapse At gross : A 3 cm endometrial polyp in the fundus Numerous irregular, large glands with leaf-like pattern Large glands with broad-based papillary infolding into the
Vagina. 1. Introduction. 1.1 General Information and Aetiology
 Vagina 1. Introduction 1.1 General Information and Aetiology The vagina is part of internal female reproductive system. It is an elastic, muscular tube that connects the outside of the body to the cervix.
Vagina 1. Introduction 1.1 General Information and Aetiology The vagina is part of internal female reproductive system. It is an elastic, muscular tube that connects the outside of the body to the cervix.
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
ARROCase: Locally Advanced Endometrial Cancer
 ARROCase: Locally Advanced Endometrial Cancer Charles Vu, MD (PGY-3) Faculty Advisor: Peter Y. Chen, MD, FACR Beaumont Health (Royal Oak, MI) November 2016 Case 62yo female with a 3yr history of vaginal
ARROCase: Locally Advanced Endometrial Cancer Charles Vu, MD (PGY-3) Faculty Advisor: Peter Y. Chen, MD, FACR Beaumont Health (Royal Oak, MI) November 2016 Case 62yo female with a 3yr history of vaginal
Disclosure. Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None. Off Label Usage None MFMER slide-1
 Disclosure Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 2013 MFMER slide-1 Case Presentation A 43 year old male, with partial nephrectomy for a right kidney mass 2013 MFMER slide-2 2013
Disclosure Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 2013 MFMER slide-1 Case Presentation A 43 year old male, with partial nephrectomy for a right kidney mass 2013 MFMER slide-2 2013
Index. Cytoplasm, nonepithelial malignant tumor features 70
 Accurette device 23 Adenosarcoma, differential diagnosis 80, 81 Arias-Stella reaction 65 Atypical endocervical cells 8 Atypical endometrial cells 8 Atypical glandular cells (AGC) 8, 9 Atypical glandular
Accurette device 23 Adenosarcoma, differential diagnosis 80, 81 Arias-Stella reaction 65 Atypical endocervical cells 8 Atypical endometrial cells 8 Atypical glandular cells (AGC) 8, 9 Atypical glandular
The Primary Squamous Cell Carcinoma of The Endometrium: A Case Report and Literature Review
 May, 2018 2018; Vol2; Issue5 http://iamresearcher.online The Primary Squamous Cell Carcinoma of The Endometrium: A Case Report and Literature Review Ahmed Guennoun, Yousra Krimou, Chahrazad Bouchikhi,
May, 2018 2018; Vol2; Issue5 http://iamresearcher.online The Primary Squamous Cell Carcinoma of The Endometrium: A Case Report and Literature Review Ahmed Guennoun, Yousra Krimou, Chahrazad Bouchikhi,
Cervical Cancer 3/25/2019. Abnormal vaginal bleeding
 Cervical Cancer Abnormal vaginal bleeding Postcoital, intermenstrual or postmenopausal Vaginal discharge Pelvic pain or pressure Asymptomatic In most patients who are not sexually active due to symptoms
Cervical Cancer Abnormal vaginal bleeding Postcoital, intermenstrual or postmenopausal Vaginal discharge Pelvic pain or pressure Asymptomatic In most patients who are not sexually active due to symptoms
Uterine Tumors Resembling Ovarian Sex Cord Tumor in Postmenopausal Woman
 DOI 10.1007/s13224-014-0545-0 CASE REPORT in Postmenopausal Woman Byun Jung Mi Kim Ki Tae Yoon Hye Kyoung Jeong Dae Hoon Kim Young Nam Lee Kyung Bok Sung Moon Su Received: 14 January 2014 / Accepted: 22
DOI 10.1007/s13224-014-0545-0 CASE REPORT in Postmenopausal Woman Byun Jung Mi Kim Ki Tae Yoon Hye Kyoung Jeong Dae Hoon Kim Young Nam Lee Kyung Bok Sung Moon Su Received: 14 January 2014 / Accepted: 22
ENODMETRIAL CARCINOMA: SPECIAL & NOT SO SPECIAL VARIANTS
 ENODMETRIAL CARCINOMA: SPECIAL & NOT SO SPECIAL VARIANTS Pacific Northwest Society of Pathologists Vancouver, B.C. September 26, 2015 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu Stanford University, Stanford,
ENODMETRIAL CARCINOMA: SPECIAL & NOT SO SPECIAL VARIANTS Pacific Northwest Society of Pathologists Vancouver, B.C. September 26, 2015 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu Stanford University, Stanford,
Histopathological Study of Spectrum of Lesions Seen in Surgically Resected Specimens of Fallopian Tube
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/613 Histopathological Study of Spectrum of Lesions Seen in Surgically Resected Specimens of Fallopian Tube Pratima
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/613 Histopathological Study of Spectrum of Lesions Seen in Surgically Resected Specimens of Fallopian Tube Pratima
A Rare Case of Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix Extending to Endometrium and Right Fallopian Tube
 A Rare Case of Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix Extending to Endometrium and Right Fallopian Tube Kate Madhuri S 1, Gulhane Sushma R 2, Mane Sheetal V 3 1 Professor and Head, 2 Specialist cum
A Rare Case of Invasive Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Cervix Extending to Endometrium and Right Fallopian Tube Kate Madhuri S 1, Gulhane Sushma R 2, Mane Sheetal V 3 1 Professor and Head, 2 Specialist cum
Basement membrane in lobule.
 Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
Bahram Memar, MD Basement membrane in lobule. Normal lobule-luteal phase Normal lobule-follicular phase Lactating breast Greater than 95% are adenocarcinomas in situ carcinomas and invasive carcinomas.
Case Report Ovarian Seromucinous Borderline Tumor and Clear Cell Carcinoma: An Unusual Combination
 Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 2015, Article ID 690891, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/690891 Case Report Ovarian Seromucinous Borderline Tumor and Clear Cell Carcinoma: An Unusual
Case Reports in Obstetrics and Gynecology Volume 2015, Article ID 690891, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/690891 Case Report Ovarian Seromucinous Borderline Tumor and Clear Cell Carcinoma: An Unusual
CARCINOMA CERVIX. Dr. PREETHI REDDY. B. M S OBG II yr POST GRADUATE.
 CARCINOMA CERVIX Dr. PREETHI REDDY. B M S OBG II yr POST GRADUATE. Introduction Cervical cancer is the second most common female malignancy worldwide. It is responsible for 4,66,000 deaths annually worldwide
CARCINOMA CERVIX Dr. PREETHI REDDY. B M S OBG II yr POST GRADUATE. Introduction Cervical cancer is the second most common female malignancy worldwide. It is responsible for 4,66,000 deaths annually worldwide
Ph.D. THESIS ENDOMETRIAL HYPERPLASIAS IN PERIMENOPAUSE SUMMARY
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE Ph.D. THESIS ENDOMETRIAL HYPERPLASIAS IN PERIMENOPAUSE SUMMARY SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: PROF. DR. MIHAI B. BRĂILA, Ph.D. Ph.D. Graduand:
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY OF CRAIOVA FACULTY OF MEDICINE Ph.D. THESIS ENDOMETRIAL HYPERPLASIAS IN PERIMENOPAUSE SUMMARY SCIENTIFIC COORDINATOR: PROF. DR. MIHAI B. BRĂILA, Ph.D. Ph.D. Graduand:
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID. Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles
 GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID
 GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
GOBLET CELL CARCINOID Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD University of California Los Angeles Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners (Education Committee) in a position to
NAACCR Webinar Series /7/17
 COLLECTING CANCER DATA: UTERUS 2017 2018 NAACCR WEBINAR SERIES Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this webinar
COLLECTING CANCER DATA: UTERUS 2017 2018 NAACCR WEBINAR SERIES Q&A Please submit all questions concerning webinar content through the Q&A panel. Reminder: If you have participants watching this webinar
Case 1. Gynaecology Case Presentation. Objectives. Disclosures 22/10/ year old female Clinical history: Assess right ovarian cyst
 Gynaecology Case Presentation Organ Imaging 2016 University of Toronto Sarah Johnson 39 year old female Clinical history: Assess right ovarian cyst Clinically diagnosed endometriosis Started fertility
Gynaecology Case Presentation Organ Imaging 2016 University of Toronto Sarah Johnson 39 year old female Clinical history: Assess right ovarian cyst Clinically diagnosed endometriosis Started fertility
Papillary serous carcinoma of the uterine cervix: a clinicopathological analysis of 4 cases and a literature review
 Oncology and Translational Medicine DOI 10.1007/s10330-017-0233-3 October 2017, Vol. 3, No. 5, P197 P202 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Papillary serous carcinoma of the uterine cervix: a clinicopathological analysis
Oncology and Translational Medicine DOI 10.1007/s10330-017-0233-3 October 2017, Vol. 3, No. 5, P197 P202 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Papillary serous carcinoma of the uterine cervix: a clinicopathological analysis
Clear cell carcinoma arising from abdominal wall endometriosis: a unique case with bladder and lymph node metastasis
 Liu et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2014, 12:51 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY CASE REPORT Open Access Clear cell carcinoma arising from abdominal wall endometriosis: a unique case with bladder
Liu et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology 2014, 12:51 WORLD JOURNAL OF SURGICAL ONCOLOGY CASE REPORT Open Access Clear cell carcinoma arising from abdominal wall endometriosis: a unique case with bladder
Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Beirut, Lebanon. Anaís Malpica, M.D. Professor Department of Pathology
 Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Beirut, Lebanon Anaís Malpica, M.D. Professor Department of Pathology Primary Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Cystadenoma Borderline (Tumor of Low Malignant Potential/Atypical
Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Beirut, Lebanon Anaís Malpica, M.D. Professor Department of Pathology Primary Mucinous Tumors of the Ovary Cystadenoma Borderline (Tumor of Low Malignant Potential/Atypical
CPC on Cervical Pathology
 CPC on Cervical Pathology Dr. W.K. Ng Senior Medical Officer Department of Clinical Pathology Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital Cervical Smear: High Grade SIL (CIN III) Cervical Smear: High Grade
CPC on Cervical Pathology Dr. W.K. Ng Senior Medical Officer Department of Clinical Pathology Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital Cervical Smear: High Grade SIL (CIN III) Cervical Smear: High Grade
Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix.
 Cervical Cancer Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where
Cervical Cancer Cervical cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the cervix. The cervix is the lower, narrow end of the uterus (the hollow, pear-shaped organ where
BCCCP Approved ICD-9 Code List Fiscal Year 2010
 BCCCP Approved ICD-9 List Fiscal Year 2010 Diagnosis Description 174.0 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; Nipple and areola 174.1 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; Central portion 174.2 Malignant
BCCCP Approved ICD-9 List Fiscal Year 2010 Diagnosis Description 174.0 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; Nipple and areola 174.1 Malignant neoplasm of female breast; Central portion 174.2 Malignant
ARRO Case: Early-stage Endometrial Cancer
 ARRO Case: Early-stage Endometrial Cancer Ankit Modh, MD (PGY-4) Faculty Advisor: Mohamed A Elshaikh, MD Department of Radiation Oncology Henry Ford Cancer Institute Case Presentation 70 y/o African American
ARRO Case: Early-stage Endometrial Cancer Ankit Modh, MD (PGY-4) Faculty Advisor: Mohamed A Elshaikh, MD Department of Radiation Oncology Henry Ford Cancer Institute Case Presentation 70 y/o African American
Janjira Petsuksiri, M.D
 GYN malignancies Janjira Petsuksiri, M.D Outlines Cervical cancer Endometrial cancer Ovarian cancer Vaginal cancer Vulva cancer 2 CA Cervix Epidemiology - Second most common female cancer Risk factors
GYN malignancies Janjira Petsuksiri, M.D Outlines Cervical cancer Endometrial cancer Ovarian cancer Vaginal cancer Vulva cancer 2 CA Cervix Epidemiology - Second most common female cancer Risk factors
The role of immunohistochemistry in surgical pathology of the uterine corpus and cervix
 The role of immunohistochemistry in surgical pathology of the uterine corpus and cervix Prof. Ben Davidson, MD PhD Department of Pathology, Norwegian Radium Hospital, Oslo University Hospital, Oslo, Norway
The role of immunohistochemistry in surgical pathology of the uterine corpus and cervix Prof. Ben Davidson, MD PhD Department of Pathology, Norwegian Radium Hospital, Oslo University Hospital, Oslo, Norway
Villoglandular adenocarcinoma of cervix a tumour with bland cytological features: report of a case missed on cytology
 Malaysian J Pathol 2003; 25(2) : CERVICAL 139 143 VILLOGLANDULAR ADENOCARCINOMA CYTOLOGY CASE REPORT Villoglandular adenocarcinoma of cervix a tumour with bland cytological features: report of a case missed
Malaysian J Pathol 2003; 25(2) : CERVICAL 139 143 VILLOGLANDULAR ADENOCARCINOMA CYTOLOGY CASE REPORT Villoglandular adenocarcinoma of cervix a tumour with bland cytological features: report of a case missed
Gynecologic Oncologist. Surgery Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy Hormonal Therapy Immunotherapy. Cervical cancer
 Gynecologic Oncology Pre invasive vulvar, vaginal, & cervical disease Vulvar Cervical Endometrial Uterine Sarcoma Fallopian Tube Ovarian GTD Gynecologic Oncologist Surgery Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy
Gynecologic Oncology Pre invasive vulvar, vaginal, & cervical disease Vulvar Cervical Endometrial Uterine Sarcoma Fallopian Tube Ovarian GTD Gynecologic Oncologist Surgery Chemotherapy Radiation Therapy
Uterine Cervix. Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the cervix.
 Uterine Cervix Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the cervix. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition and FIGO 2001 Annual Report Procedures Cytology (No Accompanying
Uterine Cervix Protocol applies to all invasive carcinomas of the cervix. Protocol revision date: January 2005 Based on AJCC/UICC TNM, 6 th edition and FIGO 2001 Annual Report Procedures Cytology (No Accompanying
Prof. Dr. Aydın ÖZSARAN
 Prof. Dr. Aydın ÖZSARAN Adenocarcinomas of the endometrium Most common gynecologic malignancy in developed countries Second most common in developing countries. Adenocarcinomas, grade 1 and 2 endometrioid
Prof. Dr. Aydın ÖZSARAN Adenocarcinomas of the endometrium Most common gynecologic malignancy in developed countries Second most common in developing countries. Adenocarcinomas, grade 1 and 2 endometrioid
Adjuvant Therapies in Endometrial Cancer. Emma Hudson
 Adjuvant Therapies in Endometrial Cancer Emma Hudson Endometrial Cancer Most common gynaecological cancer Incidence increasing in Western world 1-2% cancer deaths 75% patients postmenopausal 97% epithelial
Adjuvant Therapies in Endometrial Cancer Emma Hudson Endometrial Cancer Most common gynaecological cancer Incidence increasing in Western world 1-2% cancer deaths 75% patients postmenopausal 97% epithelial
Ritu Salani, M.D., M.B.A. Assistant Professor, Dept. of Obstetrics & Gynecology Division of Gynecologic Oncology The Ohio State University
 Cervical Cancer Ritu Salani, M.D., M.B.A. Assistant Professor, Dept. of Obstetrics & Gynecology Division of Gynecologic Oncology The Ohio State University Estimated gynecologic cancer cases United States
Cervical Cancer Ritu Salani, M.D., M.B.A. Assistant Professor, Dept. of Obstetrics & Gynecology Division of Gynecologic Oncology The Ohio State University Estimated gynecologic cancer cases United States
Coversheet for Network Site Specific Group Agreed Documentation
 Coversheet for Network Site Specific Group Agreed Documentation This sheet is to accompany all documentation agreed by Pan Birmingham Cancer Network Site Specific Groups. This will assist the Network Governance
Coversheet for Network Site Specific Group Agreed Documentation This sheet is to accompany all documentation agreed by Pan Birmingham Cancer Network Site Specific Groups. This will assist the Network Governance
Annual report of the Committee on Gynecologic Oncology, the Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology
 bs_bs_banner doi:10.1111/jog.12596 J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. Vol. 41, No. 2: 167 177, February 2015 Annual report of the Committee on Gynecologic Oncology, the Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology
bs_bs_banner doi:10.1111/jog.12596 J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. Vol. 41, No. 2: 167 177, February 2015 Annual report of the Committee on Gynecologic Oncology, the Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology
MRI in Cervix and Endometrial Cancer
 28th Congress of the Hungarian Society of Radiologists RCR Session Budapest June 2016 MRI in Cervix and Endometrial Cancer DrSarah Swift St James s University Hospital Leeds, UK Objectives Cervix and endometrial
28th Congress of the Hungarian Society of Radiologists RCR Session Budapest June 2016 MRI in Cervix and Endometrial Cancer DrSarah Swift St James s University Hospital Leeds, UK Objectives Cervix and endometrial
Female Genital Tract Lab. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan
 Female Genital Tract Lab Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan Ovarian Pathology A 20-year-old female presented with vague left pelvic pain. Pelvic exam revealed
Female Genital Tract Lab Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin Assistant Professor of Pathology University of Jordan Ovarian Pathology A 20-year-old female presented with vague left pelvic pain. Pelvic exam revealed
The Role of Radiation in the Management of Gynecologic Cancers. Scott Glaser, MD
 The Role of Radiation in the Management of Gynecologic Cancers Scott Glaser, MD Nothing to disclose DISCLOSURE Outline The role of radiation in: Endometrial Cancer Adjuvant Medically inoperable Cervical
The Role of Radiation in the Management of Gynecologic Cancers Scott Glaser, MD Nothing to disclose DISCLOSURE Outline The role of radiation in: Endometrial Cancer Adjuvant Medically inoperable Cervical
Presenter: Yeh-Han Wang M.D.
 Korea-Taiwan-Japan Joint Meeting for Gynecological Pathology Mini-lecture Female Adnexal Tumor of Probable Wolffian Origin (FATWO) in Taiwan: A Small Case Series and Literature Review Presenter: Yeh-Han
Korea-Taiwan-Japan Joint Meeting for Gynecological Pathology Mini-lecture Female Adnexal Tumor of Probable Wolffian Origin (FATWO) in Taiwan: A Small Case Series and Literature Review Presenter: Yeh-Han
Cytological Features of Cervical Smears in Serous Adenocarcinoma of the Endometrium
 Jpn J Clin Oncol 2003;33(12)636 641 Cytological Features of Cervical Smears in Serous Adenocarcinoma of the Endometrium Yukiharu Todo, Shinichirou Minobe, Kazuhira Okamoto, Mahito Takeda, Yasuhiko Ebina,
Jpn J Clin Oncol 2003;33(12)636 641 Cytological Features of Cervical Smears in Serous Adenocarcinoma of the Endometrium Yukiharu Todo, Shinichirou Minobe, Kazuhira Okamoto, Mahito Takeda, Yasuhiko Ebina,
Objectives. Atypical Glandular Cells. Atypical Endocervical Cells. Reactive Endocervical Cells
 2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
2013 California Society of Pathologists 66 th Annual Meeting San Francisco, CA Atypical Glandular Cells to Early Invasive Adenocarcinoma: Cervical Cytology and Histology Christina S. Kong, MD Associate
Endometrial Metaplasia, Hyperplasia & Other Cancer Mimics: a Consultant s Experience
 Endometrial Metaplasia, Hyperplasia & Other Cancer Mimics: a Consultant s Experience Pacific Northwest Society of Pathologists Vancouver, B.C. September 26, 2015 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu
Endometrial Metaplasia, Hyperplasia & Other Cancer Mimics: a Consultant s Experience Pacific Northwest Society of Pathologists Vancouver, B.C. September 26, 2015 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu
MR Findings of Extrauterine Mu llerian Adenosarcoma Associated with Deep Pelvic Endometriosis 1
 MR Findings of Extrauterine Mullerian Adenosarcoma Associated with Deep Pelvic Endometriosis 1 Dae Kun Oh, M.D., Chan Kyo Kim, M.D., Byung Kwan Park, M.D., Ji Young Kim, M.D. 2 Extrauterine mu llerian
MR Findings of Extrauterine Mullerian Adenosarcoma Associated with Deep Pelvic Endometriosis 1 Dae Kun Oh, M.D., Chan Kyo Kim, M.D., Byung Kwan Park, M.D., Ji Young Kim, M.D. 2 Extrauterine mu llerian
Gynecologic Cancer InterGroup Cervix Cancer Research Network. Management of Cervical Cancer in Resource Limited Settings.
 Management of Cervical Cancer in Resource Limited Settings Linus Chuang MD Conflict of Interests None Cervical cancer is the fourth most common malignancy in women worldwide 530,000 new cases per year
Management of Cervical Cancer in Resource Limited Settings Linus Chuang MD Conflict of Interests None Cervical cancer is the fourth most common malignancy in women worldwide 530,000 new cases per year
