The Journal of Physiology
|
|
|
- Berenice Heath
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Physiol (2013) pp Preserved fertility despite erectile dysfunction in mice lacking the nitric oxide receptor Dieter Groneberg 1, Barbara Lies 1,PeterKönig 2, Ronald Jäger 1 and Andreas Friebe 1 1 Physiologisches Institut I, Universität Würzburg, Germany 2 Institut für Anatomie, Zentrum für medizinische Struktur- und Zellbiologie, Universität zu Lübeck, Lübeck, Airway Research Center North (ARCN), Member of the German Center for Lung Research (DZL), Germany The Journal of Physiology Key points Erectile dysfunction may result from reduced or non-functional nitric oxide (NO)/cGMP-mediated signalling. Mice lacking NO synthases are fertile whereas mice deficient in cgmp-dependent protein kinase I suffer from erectile dysfunction. To clarify this discrepancy we performed studies on the corpus cavernosum of male mice lacking the NO receptor NO-sensitive guanylyl cyclase (NO-GC) either globally or specifically in smooth muscle cells. NO released from NO donors as well as from nitrergic neurons failed to relax precontracted corpus cavernosum from mice lacking NO-GC either globally or specifically in smooth muscle; to our surprise, males from both knockout lines were fertile. Our data show that deletion of the NO receptor specifically in smooth muscle cells abolishes NO-induced corpus cavernosum relaxation but does not lead to infertility. Abstract Nitric oxide (NO) and cgmp have been shown to be important mediators of penile erection. Erectile dysfunction may result from reduced or non-functional signal transduction within this cascade. There is, however, some inconsistency in the available data as mice lacking NO synthases (endothelial and neuronal nitric oxide synthase, or both) appear to be fertile whereas mice deficient in cgmp-dependent protein kinase I (PKGI) suffer from erectile dysfunction. To clarify this discrepancy we performed studies on mice lacking the NO receptor NO-sensitive guanylyl cyclase (NO-GC). In addition, we generated cell-specific NO-GC knockout (KO) lines to investigate the function of NO in individual cell types. NO-GC was specifically deleted in smooth muscle or endothelial cells (SM-guanylyl cyclase knockout (SM-GCKO) and EC-GCKO, respectively) and these KO lines were compared with total knockouts (GCKO) and wild-type animals. We investigated expression of NO-GC, NO-induced relaxation of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle and their ability to generate offspring. NO-GC-positive immunostaining was detected in smooth muscle and endothelial cells of murine corpus cavernosum but not in interstitial cells of Cajal. NO released from NO donors as well as from nitrergic neurons failed to relax precontracted corpus cavernosum from GCKO mice in organ bath experiments. Similar results were obtained in corpus cavernosum from SM-GCKO mice whereas deletion of NO-GC in endothelial cells did not affect relaxation. The lack of NO-induced relaxation in GCKO animals was not compensated for by guanosine 3,5 -cyclic monophosphate (cgmp) signalling. To our surprise, GCKO males were fertile although their ability to produce offspring was decreased. Our DOI: /jphysiol
2 492 D. Groneberg and others J Physiol data show that deletion of NO-GC specifically in smooth muscle cells abolishes NO-induced corpus cavernosum relaxation but does not lead to infertility. (Received 25 September 2012; accepted after revision 31 October 2012; first published online 5 November 2012) Corresponding author A. Friebe: Physiologisches Institut I, Universität Würzburg, Röntgenring 9, Würzburg, Germany. andreas.friebe@uni-wuerzburg.de Abbreviations CC, corpus cavernosum; DEA-NO, 2-(N,N-diethylamino)-diazenolate-2-oxide-diethylammonium salt; ECs, endothelial cells; EC-GCKO, EC-specific guanylyl cyclase knockout; EFS, electric field stimulation; enos, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; GCKO, guanylyl cyclase knockout; IBMX, 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine; ICC, interstitial cells of Cajal; NO, nitric oxide; NO-GC, nitric oxide-sensitive guanylyl cyclase; nnos, neuronal nitric oxide synthase; ODQ, 1H-[1,2,4]oxadiazolo[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one; PKG, cgmp-dependent protein kinase; α-sma, α-smooth muscle actin; SMCs, smooth muscle cells; SM-GCKO, smooth muscle-specific guanylyl cyclase knockout; WT, wild-type. Introduction To date, it is widely accepted that nitric oxide (NO) is the main neurotransmitter mediating penile erection. It can be produced either by neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nnos) from nitrergic nerves or by endothelial nitric oxide synthase (enos) from sinusoidal endothelial cells (Burnett, 1997; Lue, 2000; Musicki et al. 2009; Andersson, 2011). By activation of its main receptor NO-sensitive guanylyl cyclase (NO-GC), NO leads to production of guanosine 3,5 -cyclic monophosphate (cgmp) in different cell types (Friebe & Koesling, 2003). In turn, cgmp activates cgmp-dependent kinase (Hofmann, 2005) resulting in relaxation of the resistance vessels and trabecular smooth muscle; the resulting arteriolar vasodilatation induces an increase in blood flow, which expands the sinusoidal spaces leading to erection. Previous studies in knockout (KO) mouse models have already shown the importance of the NO/cGMP cascade in corpora cavernosa (CC) relaxation. All three NOS isozymes have been deleted on the genomic level, either alone or in double or triple combinations (Huang et al. 1993, 1995; Tranguch & Huet-Hudson, 2003; Morishita et al. 2005). Mice lacking nnos were shown to be fertile and maintain erectile function. This indicates that NO from enos is important for erectile function as inducible NOS (inos) was not detected in penile tissue (Burnett et al. 1996). Nevertheless, mice lacking enos alone or in combination with nnos or nnos plus inos were still fertile. Making this issue even more complicated, data from another nnos knockout in which exon 6 was deleted, indicate infertility of male mice attributed to central hormonal dysregulation but not to erectile dysfunction (Gyurko et al. 2002). Deletion of cgmp-dependent protein kinase I (PKGI), however, was shown to result in erectile dysfunction (Hedlund et al. 2000). The CC of male PKGI-deficient mice failed to relax upon stimulation of the NO/cGMP cascade; in addition, a very low ability to reproduce was observed. To resolve this paradox we first investigated erectile function in mice lacking NO-GC globally. Neither pharmacological NO nor electrical field stimulation (EFS)-induced NO release from cavernosal neurons led to relaxation of precontracted CC from guanylyl cyclase knockout (GCKO) mice; yet, camp-induced relaxation was unchanged. Immunohistochemical analysis reveals NO-GC expression in smooth muscle cells (SMCs) and endothelial cells (ECs) but not in interstitial cells of Cajal. Cell-specific deletion of NO-GC revealed a total loss of NO-induced CC relaxation in smooth muscle GCKO (SM-GCKO) whereas that from endothelial cell GCKO (EC-GCKO) animals was unperturbed. Surprisingly, male GCKO mice were fertile and able to produce offspring albeit with a reduced number of litters. We conclude that NO-GC in smooth muscle is the main contributor to CC relaxation and that, in line with the data on NOS knockout mice, NO/cGMP signalling is not necessary for fertility. Methods All experiments were conducted in accordance with the German legislation on protection of animals and were approved by the local animal care committee. Generation of GCKO, SM-GCKO and EC-GCKO mice Mice lacking NO-GC globally were generated as described previously (Friebe et al. 2007). SM-GCKO and EC-GCKO mice carry a floxed exon (exon 10 of the β 1 subunit of NO-GC; NO-GC-β flox/flox 1 ) and are transgenic for either the inducible (SMMHC-CreER T2 ) or the constitutive Cre recombinase (Tie2-Cre). SM-GCKO mice aged 6 8 weeks were injected with tamoxifen (1 mg I.P.) on five consecutive days to remove the floxed exon. The last day of tamoxifen injection was defined as day 0. SM-GCKO mice were analysed 20, 50 and 150 days after the last tamoxifen injection. In the relevant figures, pre indicates mice without tamoxifen injection. NO-dependent CC relaxation did not differ between SM-GCKO pre (Fig. 3B) and wild-type (WT) controls (Fig. 2B and C), indicating that the SMMHC-CreER T2 itself did not
3 J Physiol Fertility in mice lacking the NO receptor 493 influence NO signalling. After 50 days, deletion of NO-GC was considered complete as judged by the cessation in time-dependent reduction of NO relaxation in SM-GCKO mice. Thus, for experiments with SM-specific knockout CC we used animals >50 days after tamoxifen treatment. In each experiment, wherever feasible WT littermates or respective tamoxifen-injected littermates were used as controls. Isometric force studies The animals were killed by inhalation of an overdose of isoflurane. The tunica albuginea was carefully opened and the two CCs were microsurgically excised. Both CCs were immediately transferred to Krebs Henseleit solution (118 mm NaCl, 4.7 mm KCl, 2.5 mm CaCl 2, 1.2 mm KH 2 PO 4, 1.2 mm MgSO 4, 25mM NaHCO 3, 7.5 mm glucose, ph 7.4) and bubbled with 95% O 2 and 5% CO 2. The CCs were mounted longitudinally on fixed segment support pins in two four-chamber myographs (Myograph 610; Danish Myo Technology, Aarhus, Denmark) containing 5 ml of the Krebs Henseleit solution and bubbled with 95% O 2 and 5% CO 2. Resting tension was set to 3 mn. For pharmacological studies the strips were contracted with phenylephrine (PE; 3 μm). To investigate the effect of NO and cgmp on the CC of the different mouse strains, 2-(N,N-diethylamino)-diazenolate-2-oxide-diethylammonium salt (DEA-NO; 10 nm 10 μm), 8-Br-cGMP (10 μm), carbachol (1μM) or forskolin (1 nm 10 μm) were applied into the Krebs Henseleit solution. To specifically inhibit NO-GC, 1H-[1,2,4]oxadiazolo[4,3-a]quinoxalin-1-one (ODQ; 10 μm) was administered 20 min before relaxation. To determine maximal relaxation, 3-isobutyl-1-methylxanthine (IBMX; 100 μm) was added at the end of each experiment. Electrophysiological studies EFS was measured in CC strips precontracted with PE (3 μm). EFS was applied through two platinum wire electrodes (5 mm distance; supramaximal voltage, 0.5 ms, Hz, 15 s). Immunohistochemistry Mice were killed by inhalation of an overdose of isoflurane and tissues were fixed by transcardiac perfusion with 3% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 M phosphate buffer, ph 7.4, and tissue was cryoprotected using 20% sucrose and snap frozen. Cryosections (10 μm thick)werecut, air-dried and incubated overnight with an antibody generated in our lab (Friebe et al. 2007) against the β 1 subunit of NO-GC raised in rabbit (1:800) together either with a FITC-conjugated mouse anti-α-smooth muscle actin antibody (1:500, clone 1A4; Sigma-Aldrich, Munich, Germany), with a rat anti-ckit antibody (1:1600, clone ACK4; Linaris, Wertheim-Bettingen, Germany) or with a goat anti-caveolin 1 antibody (1:100, polyclonal; Abcam, Cambridge, UK) all diluted in Tris-buffered saline (TBS). Antibodies were detected by incubating the sections for 1 h with the appropriate secondary antibodies diluted in TBS. The following reagents were used for the rabbit antibody: Alexa 555-conjugated or Alexa 488-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody raised in donkey (both 1:800; Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA); for the rat antibody: Alexa 488-conjugated donkey anti-rat IgG antibody (1:400; Invitrogen); for the goat antibody: Alexa 555-conjugated anti-goat IgG antibody (1:100; Invitrogen). The sections were coverslipped using Mowiol and were evaluated using an epifluorescence microscope equipped with appropriate filter sets for Alexa 555 and FITC/Alexa 488. Materials 8-Br-cGMP, DEA-NO and ODQ were purchased from Axxora (Lörrach, Germany). Carbachol, IBMX, PE and tamoxifen were from Sigma (Taufkirchen, Germany). Individual statistical analyses For calculation of statistical tests, GraphPad Prism version 4.00 for Windows (GraphPad Software, San Diego California USA), was used. The Mann Whitney U test was used for the data in Figs 3C,5B,5D and6inapredefined sequence and comparison was stopped if P was >0.05 to prevent α inflation. In Figs 2B, 3B, 4B, 4D and 4F, all groups were compared by the Kruskal Wallis test. If P was 0.05 for the global test, two groups were compared by Mann Whitney U test (Figs 4B, 4D and 4F). In Figs 2B and 3B, P was 0.05 for the Kruskal Wallis test and two groups were compared by the Mann Whitney U test in a predefined sequence and comparison was stopped if p was >0.05 to prevent alpha inflation. Results Immunohistochemical localization of NO-GC in CC To visualize the expression of NO-GC in murine CC we performed immunohistochemistry using an antibody against the β 1 subunit as the obligatory subunit for both NO-GC isoforms (Friebe et al. 2007). Figure 1A shows intense staining in SMCs of the central and helicine artery walls and in smooth muscle cells of the trabecular
4 494 D. Groneberg and others J Physiol Figure 1. Immunohistochemical analysis of NO-GC expression Expression of NO-GC (β 1 subunit) in the CC of WT animals. Tissues were co-stained with specific antibodies for α-smooth muscle actin (A), caveolin 1 (B)or ckit(c). Indicated in the merged imagesare trabecular smooth muscle (a), sinusoidal caverns (b), sinusoidal endothelium (c) and mast cells (d). DIC = differential interference contrast.
5 J Physiol Fertility in mice lacking the NO receptor 495 septa surrounding the cavernous spaces. In addition, endothelial cells lining the cavernosal sinusoids were positive for NO-GC and caveolin-1 was highly expressed in endothelial cells (Fig. 1B; enlargement in Fig. 1D). In contrast to previous reports, ckit-positive interstitial cells were not detected. The only ckit-immunoreactive cells had the morphology of mast cells, which are known to express ckit (Fig. 1C). Taken together, in murine CC, NO-GC is expressed in SMCs and, surprisingly strongly, in ECs. Lack of NO-induced relaxation in CC from GCKO mice The functionality of the NO signalling in CC was investigated in organ bath experiments. CCs were isolated and precontracted with PE (3 μm). CC from WT mice showed a concentration-dependent relaxation in response to the NO donor DEA-NO (original trace in Fig. 2A, statistical analysis in Fig. 2B). The specific NO-GC inhibitor ODQ (10 μm) abolished this NO-induced relaxation, indicating cgmp dependence of NO-induced relaxation. In CC from GCKO animals, DEA-NO up to 10 μm did not lead to relaxation. NO-induced relaxation in SM-GCKO and EC-GCKO mice As NO-GC was detected in both SMCs and ECs of the murine CC we next aimed to clarify the contribution of either cell type to NO-mediated relaxation. Mice lacking NO-GC specifically in SMCs (Groneberg et al. 2010) and ECs were generated using smooth muscle myosin heavy chain promoter-driven (SM-MHC) and Tie2 promoter-driven Cre expression. In contrast to the constitutively active Tie2 promoter the SMC-specific knockout needed tamoxifen induction as shown in Fig. 3A: CCs of homozygous floxed mice carrying the SM-MHC-Cre transgene were investigated before (pre) and 20, 50 and 150 days after tamoxifen injection (indicated as a subscript, e.g. SM-GCKO 50 ). In previous reports we have shown that quantitative SMC-specific deletion of NO-GC was reached only after >50 days (Groneberg et al. 2010, 2011). NO-induced relaxation of CC from SM-GCKO mice was reduced 20 days and fully abolished 50 days after tamoxifen treatment (Fig. 3B) when compared to the control (SM-GCKO pre ). The relaxing response did not recover as even 150 days after tamoxifen treatment NO still had no effect. As shown in Fig. 3C, endothelium-specific deletion of NO-GC did not influence NO-induced CC relaxation. The effective deletionofno-gcinbothkomodelsisshowninfig. 3D: incctissuefromsm-gcko 50 mice, NO-GC only stains endothelial cells (see also Fig. 1B) but not SMCs positive for α-smooth muscle actin (αsma), whereas in EC-GCKO tissue, endothelial staining is absent and NO-GC colocalizes with αsma. Thus, NO-induced CC relaxation invariably depends on NO-GC in SMCs. Consequently, further analyses were performed only in the SM-GCKO animals. Effect of endogenously released NO on CC from GCKO and SM-GCKO mice Next, we studied whether endogenously produced NO still had an effect on CC tension. To stimulate cholinergic Figure 2. Lack of NO-induced relaxation in CC from GCKO mice A, original traces of organ bath experiments showing DEA-NO-dependent relaxation in CC from WT and GCKOmice after precontraction with 3 μm PE. The difference between WT and GCKO reached statistical significance (P < 0.05, Mann Whitney U test) from 0.1 μmol l 1 to 10 μmol l 1. B, quantitative analysis of the experiments carried out in A. In addition, CC from WT animals was pre-incubated with ODQ (10 μm) to specifically inhibit NO-GC. The difference between WT and WT + ODQ reached statistical significance (P < 0.05, Mann Whitney U test) from 0.1 μmol l 1 to 10 μmol l 1. Data shown are means ± SEM of n = 5 6 per genotype.
6 496 D. Groneberg and others J Physiol Figure 3. Lack of NO-induced relaxation in CC from SM-GCKO animals and preserved relaxation in EC-GCKO mice A, time scheme for the generation of SM-GCKO mice. Male mice (6 8 weeks old) were injected with tamoxifen (1 mg I.P.) on five consecutive days. The last day of tamoxifen injection was defined as day 0; mice were analysed 20, 50 or 150 days after tamoxifen injection. Control animals used did not receive tamoxifen (SM-GCKO pre ). B, CCs were mounted into the organ bath. After pre-contraction with PE (3 μm), increasing concentrations of the NO donor DEA-NO were applied. In SM-GCKO animals, NO-induced relaxation decreased with increasing time distance from the last tamoxifen injection; unresponsiveness to NO was seen after approximately 50 days and did not recover even after 150 days. The differences between SM-GCKOpre and SM-GCKO20, SM-GCKO50 or SM-GCKO150 reached statistical significance (P < 0.05, Mann Whitney U test) from 0.1 μmol l 1 to 10 μmol l 1 (SM-GCKOpre vs SM-GCKO20), from 0.03 μmol l 1 to 10 μmol l 1 (SM-GCKOpre vs SM-GCKO50) and from 0.03 μmol l 1 to 10 μmol l 1 (SM-GCKOpre vs SM-GCKO150). C, quantitative analysis of DEA-NO-induced relaxation of CC from EC-GCKO mice precontracted with PE (3 μm). Data shown are means ± SEM of n = 4 8 per genotype. No statistical significance was reached in either comparison (P = 0.24 to 1.00, Mann Whitney U test). Data shown are means ± SEM of n = 4 8 per genotype. D, expression of NO-GC (β 1 subunit) in the CC of SM-GCKO 50 and EC-GCKO animals. Tissues were co-stained with an antibody specific for α-smooth muscle actin. Both sets indicate effective cell-specific deletion of NO-GC.
7 J Physiol Fertility in mice lacking the NO receptor 497 Figure 4. Effects of NOS and PKGI stimulation and PDE inhibition CCs were mounted into the organ bath. After pre-contraction with PE (3 μm), relaxation was induced. A and B, representative original recordings (A) and quantitative analysis (B) of carbachol (1 μm)-induced relaxation of CC from WT and GCKO mice. Comparison of the data from WT animals to the data from GCKO animals or WT + ODQ reached statistical significance (P = and , respectively, Mann Whitney U test). Comparison of the data from SM-GCKOpre animals to the data from the SM-GCKO50 reached statistical significance (P = , Mann Whitney U test). C and D, representative original recordings (C) and quantitative analysis (D) of sildenafil (100 nm)-induced relaxation of CC from SM-GCKO pre and SM-GCKO 50 mice. Specific inhibition of NO-GC by ODQ (10 μm) blocked carbachol- and sildenafil-induced relaxation of WT CC as shown in B and D. Comparison of the data from WT animals to the data from GCKO animals or WT + ODQ reached statistical significance (P = and , respectively, Mann Whitney U test). Comparison of the data from SM-GCKOpre animals to the data from SM-GCKO50 reached statistical significance (P = , Mann Whitney U test). E and F, representative original recordings (E) and quantitative analysis (F) of 8-Br-cGMP (10 μm)-induced relaxation of CC from SM-GCKO pre and SM-GCKO 50 mice. No significant difference was detected between WT, GCKO, SM-GCKOpre and SM-GCKO50 (P = 0.66, Kruskal Wallis test). Data shown are means ± SEM of n = 3 8 per genotype.
8 498 D. Groneberg and others J Physiol receptors, carbachol (1 μm) was applied to pre-contracted CC (PE; 3 μm). Original traces of this experiment are shown in Fig. 4A (statistical analyses in Fig. 4B). CC from controls (WT and SM-GCKO pre animals) showed an almost 75% relaxation upon administration of carbachol. Contraction rather than relaxation was observed in CC from GCKO and SM-GCKO 50 animals as well as in CC from WT treated with ODQ. Thus, relaxation by endogenous NO is conveyed exclusively by smooth muscle NO-GC. Effects of sildenafil and 8-Br-cGMP on CC tension Sildenafil is a specific inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) which is the major cgmp-degrading enzyme in SMCs (Rybalkin et al. 2003). Administration of sildenafil (100 nm) to PE-precontracted CC produced similar results to carbachol (Figs 4C and D): CC from WT and SM-GCKO pre animals relaxed upon sildenafil treatment whereas PDE5 inhibition did not induce relaxation in CC from GCKO, SM-GCKO 50 mice and WT in the presence of ODQ. To exclude a possible change in signalling downstream of NO-GC we treated precontracted CC with the membrane-permeable cgmp analogue 8-Br-cGMP (10 μm). Relaxation by direct PKG activation was identical in CC from WT, GCKO, SM-GCKO pre and SM-GCKO 50 animals demonstrating PKG-mediated signal transduction to be undisturbed by the GC knockout (Figs 4E and F). camp-mediated CC relaxation Similar to cgmp, camp is known to relax CC smooth muscle. To investigate a possible camp-mediated Figure 5. Preserved camp cascade in CC from GCKO and SM-GCKO mice After pre-contraction (PE, 3 μm), CC relaxation was induced with increasing concentrations of forskolin (FSK). A and B, representative original recordings (A) and quantitative analysis (B) of CC from WT and GCKO mice. Comparison of the data from WT animals to the data from the GCKO animals did not reach statistical significance (P = 0.2 to 1.00, Mann Whitney U test). C and D, representative original recordings (C) and quantitative analysis (D) ofccfromsm-gcko pre and SM-GCKO 50 mice. No statistical significance was reached in either comparison. Comparison of the data from SM-GCKOpre animals to the data from SM-GCKO50 animals did not reach statistical significance (P = 0.7 to 1.00, Mann Whitney U test). Data shown are means ± SEM of n = 3 per genotype.
9 J Physiol Fertility in mice lacking the NO receptor 499 compensation in the NO-GC knockout models we studied the effect of forskolin, an activator of adenylyl cyclase. Forskolin-dependent relaxation of PE-contracted CC was identical in GCKO and SM-GCKO 50 animals and the respective controls (Figs 5A and B). These data clearly demonstrate that camp signalling is not affected by and does not compensate for the absence of NO-GC. Lack of EFS-induced CC relaxation in GCKO and SM-GCKO mice We then used EFS to stimulate release of neurotransmitters from nerve terminals onto CC smooth muscle. Relaxation of PE-contracted CC from WT and SM-GCKO pre was frequency dependent ( Hz; Fig. 6). In contrast, EFS up to 1 Hz did not relax CC strips from GCKO mice; at higher stimulation frequencies (2 8 Hz), we Table 1. Litter sizes and pup numbers of WT and GCKO mice WT GCKO Number of litters Number of pups Litters per week (mean ± SEM) 4.5 ± ± 1.1 Pups per litter (mean ± SEM) 5.1 ± ± 2.1 Four males of each genotype were mated to two females. Males were rotated to new females on a weekly basis for 12 weeks. saw EFS-induced contraction, as also noted by Hedlund et al. (2000). Similar results were observed in SM-GCKO >50 animals. Fertility of KO models To study the impact of the absence of NO-GC we crossed male mice of the different genotypes with WT females. We did not see any differences in fertility between EC-GCKO and WT animals. Although all GCKO males tested were capable of producing offspring, their fecundity was reduced. Table 1 shows the direct comparison of litter numbers and sizes between WT and GCKO. GCKO males produced only 25% of the number of litters compared to WT although the average size of the litters was similar. Crossing five SM-GCKO males with WT females over a period of 8 weeks resulted in only three litters with an mean size of 5.7 ± 2.3 pups. Taken together, deletion of NO-GC results in the loss of NO-mediated relaxation of CC smooth muscle but does not abolish fertility. Figure 6. EFS-induced relaxation of CC from GCKO and SM-GCKO mice After pre-contraction (PE, 3 μm), CC relaxation was induced by electric field stimulation. Quantitative analysis for EFS-induced relaxation of CC from WT, SM-GCKO pre, GCKO and SM-GCKO 50 mice. The difference between WT and GCKO animals reached statistical significance (P < 0.05, Mann Whitney U test) from Hz to 8 Hz. The difference between SM-GCKOpre animals and SM-GCKO50 animals reached statistical significance (P < 0.05, Mann Whitney U test) from Hz to 8 Hz. Data shown are means ± SEM of n = 4 8 per genotype. Discussion NOreleasedfromnitrergicnervesaswellasfromECs of the sinusoids is the major signalling molecule for inducing and sustaining penile erection (Burnett et al. 1992). A central nervous stimulus is thought to elicit a burst of neuronal NO release to relax cavernosal smooth muscle and increase blood flow. The resulting increase in shear stress then leads to activation of enos providing a sustained NO release which promotes maximal relaxation and thus erection (Hurt et al. 2002). Unexpectedly, deletion of either enos or nnos did not result in erectile dysfunction (Huang et al. 1993, 1995; Burnett et al. 1996), and even double or triple deletion including inos did not impair the production of offspring of mutant mice (Son et al. 1996; Tranguch & Huet-Hudson, 2003; Morishita et al. 2005). These data are in stark contrast to those collected from mice lacking PKGI: Hedlund et al. (2000) clearly showed that lack of PKGI resulted in erectile dysfunction in combination with strongly reduced fertility.
10 500 D. Groneberg and others J Physiol To resolve this discrepancy we investigated CC relaxation and fertility in mice lacking NO-GC. In the current model NO-GC, as receptor for NO, integrates endothelial and neuronal NO-based signals to convey these via changes of the intracavernosal cgmp concentration on to PKGI. CC from NO-GC-deficient males failed to relax upon stimulation with exogenous or endogenous NO but relaxation was unperturbed when induced by camp. The lack of NO/cGMP signalling did, however, only partly impair the production of offspring. Over a period of 12 weeks (rotation to two females on a weekly basis) WT mice produced a large number of litters/pups (54/273, respectively). To our surprise, fertility of GCKO males was not totally abrogated but they still were able to produce approximately 25% of the litter/pup numbers seen for WT (14/69, respectively). How can the difference in fertility between all these knockout lines be explained? Health conditions and survival rates in enos and nnos knockouts appear to be WT-like, which is in contrast to the PKGIand NO-GC-deficient mice. The general phenotype of animals lacking PKGI deteriorates between 5 and 6 weeks of age. Eighty per cent of them die before reaching 8 weeks(pfeifer et al. 1998), probably because of gastrointestinal malfunction (Singh et al. 2012). GCKO mice are even worse off than mice lacking PKGI. Eighty per cent of the NO-GC-deficient mice die of unknown reason within 2 days after birth, the remaining mice dying after weaning between weeks 3 and 4. Using an omeprazole-supplemented fibre-free diet, we were able to greatly improve the survival and the general condition of the NO-GC-knockouts. It appears conceivable that a better overall fitness (on fibre-free diet) is responsible for the higher fertility rates in GCKO compared to PKGI-KO animals (without special diet). Thus, fertility measurements in animals with reduced health status should not be used for the estimation of erectile dysfunction. In our case, reduced fertility may arise from erectile dysfunction but also be due to a reduced fertilizing capability. Although the number of litters produced by GCKO males was only 25% of that by WT males, the number of pups per litter was unaltered. This indicates that the functional competence of sperm, e.g. maturation and motility, was probably not affected by the absence of the NO receptor. The normal fertility rates in enos and nnos knockout mice may well be explained by the presence of the alternatively spliced β variant of nnos which is present in all mentioned NOS-deficient strains (Hurt et al. 2006) or by a compensatory increase in enos expression in the case of nnos deficiency (Burnett et al. 1996). Deletion of the α 1 subunit of NO-GC also led to reduced but not abolished CC relaxation to exogenous and endogenous NO (Nimmegeers et al. 2008). As NO-GC inhibition by ODQ abrogated the residual NO effect the α 2 -containing isoforms (which are not deleted in the α 1 -NO-GC knockout) obviously play a role in erectile function. The absence of nitrergic relaxation of CC from GCKO mice did not impair effective mating. Thus, an alternative, NO/cGMP-independent mechanism to allow copulation has to exist. Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and VIP-related peptides have been shown to relax CC and cavernosal vessels in vitro (Andersson & Wagner, 1995; Mizusawa et al. 2001) but their role in vivo is questioned. It is worth noting that camp-induced CC relaxation appears to be different in PKGI- and NO-GC-deficient animals. Concentration response curves for forskolin were identical between WT and GCKO animals, whereas a difference was documented for WT and PKGI-deficient animals, at least for elevated forskolin concentrations (Hedlund et al. 2000). So far, we have no explanation for this difference but it may indicate that besides PKGI, camp/cgmp may partially signal through some other effector, possibly PDEs in murine CC. Similar to Hedlund et al. we were unable to see EFS-induced relaxation in knockout CC. Other putative neurotransmitters involved in the initiation of penile erection thus appear to play a minor role. A different explanation for the preserved fertility may be based on the presence of a penis bone present in many mammals including mice (Ramm, 2007). The baculum (os penis) is normally kept in the abdomen. During intercourse, it provides stiffness and thus allows entry and sperm deposition in the female reproductive tract. Therefore, it is conceivable that penile erection may be helpful but not absolutely necessary in mice for effective fertilization. The discrepancy between in vivo and in vitro observations in our and in other labs may also be explained by different degrees of endothelial dysfunction in the respective animals, which was shown to be linked to reduction in fertility (Visioli & Hagen, 2011). Endothelial dysfunction regarding a reduced production of NO will probably not affect fertility in our mice as the effect of other signalling molecules (e.g. prostaglandins, sphingosine derivatives, reactive oxygen species) will probably be unaffected. NO signalling through a non-gc effector or a reduced effect of endothelium-derived non-no mediators would possibly affect erectile function and thus fertility. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed expression of NO-GC in cavernosal smooth muscle and in ECs, but not in ckit-positive interstitial cells. Absence of nitrergic relaxation in CC from smooth muscle-specific knockout mice clearly demonstrated that erectility is a function of NO/cGMP in SMCs. In endothelium-specific knockout animals, fertility (data not shown) as well as NO-induced relaxationwasidenticaltowt.wehavenotyetdetected a functional difference between the EC-GCKO and WT mice, and thus the function of NO-GC in the cavernosal endothelium is still enigmatic. A role of interstitial cells of
11 J Physiol Fertility in mice lacking the NO receptor 501 Cajal in penile function including nitrergic CC relaxation has been proposed in humans and guinea pigs (Uckert et al. 2010; Fu et al. 2011); the existence of interstitial cells of CajalinmurineCC,however,hasnotyetbeenreported. We only saw minor staining for ckit, a marker of interstitial cells of Cajal, in murine cavernosal tissue, resembling mast cells. As no co-staining for ckit and NO-GC was detected, we rule out a possible contribution of interstitial cells in nitrergic relaxation of the murine CC. In summary, our data provide evidence that nitrergic relaxation leading to penile erection is dependent on NO-GC in SMCs and that mice lacking nitrergic signalling are capable of producing offspring by a secondary mechanism. Our mice provide useful models for investigation of camp/non-cgmp-induced regulation of erectile function. References Andersson KE (2011). Mechanisms of penile erection and basis for pharmacological treatment of erectile dysfunction. Pharmacol Rev 63, Andersson KE & Wagner G (1995). Physiology of penile erection. Physiol Rev 75, Burnett AL (1997). Nitric oxide in the penis: physiology and pathology. JUrol157, Burnett AL, Lowenstein CJ, Bredt DS, Chang TS & Snyder SH (1992). Nitric oxide: a physiologic mediator of penile erection. Science 257, Burnett AL, Nelson RJ, Calvin DC, Liu JX, Demas GE, Klein SL, Kriegsfeld LJ, Dawson VL, Dawson TM & Snyder SH (1996). Nitric oxide-dependent penile erection in mice lacking neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Mol Med 2, Friebe A & Koesling D (2003). Regulation of nitric oxide-sensitive guanylyl cyclase. Circ Res 93, Friebe A, Mergia E, Dangel O, Lange A & Koesling D (2007). Fatal gastrointestinal obstruction and hypertension in mice lacking nitric oxide-sensitive guanylyl cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104, Fu W, Song B, Li W, Shen W, Ji H, Wang Y, Zhen J, Zhou Z & Yan J (2011). Ultrastructural features and possible functional role of kit-positive interstitial cells in the guinea pig corpus cavernosum. Int J Impot Res 23, Groneberg D, Konig P, Koesling D & Friebe A (2011). Nitric oxide-sensitive guanylyl cyclase is dispensable for nitrergic signaling and gut motility in mouse intestinal smooth muscle. Gastroenterology 140, Groneberg D, Konig P, Wirth A, Offermanns S, Koesling D & Friebe A (2010). Smooth muscle-specific deletion of nitric oxide-sensitive guanylyl cyclase is sufficient to induce hypertension in mice. Circulation 121, Gyurko R, Leupen S, Huang PL (2002). Deletion of exon 6 of the neuronal nitric oxide synthase gene in mice results in hypogonadism and infertility. Endocrinology 143, HedlundP,AszodiA,PfeiferA,AlmP,HofmannF,AhmadM, Fassler R & Andersson KE (2000). Erectile dysfunction in cyclic GMP-dependent kinase I-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97, Hofmann F (2005). The biology of cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinases. J Biol Chem 280,1 4. Huang PL, Dawson TM, Bredt DS, Snyder SH & Fishman MC (1993). Targeted disruption of the neuronal nitric oxide synthase gene. Cell 75, Huang PL, Huang Z, Mashimo H, Bloch KD, Moskowitz MA, Bevan JA & Fishman MC (1995). Hypertension in mice lacking the gene for endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Nature 377, Hurt KJ, Musicki B, Palese MA, Crone JK, Becker RE, Moriarity JL, Snyder SH & Burnett AL (2002). Akt-dependent phosphorylation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase mediates penile erection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99, Hurt KJ, Sezen SF, Champion HC, Crone JK, Palese MA, Huang PL, Sawa A, Luo X, Musicki B, Snyder SH & Burnett AL (2006). Alternatively spliced neuronal nitric oxide synthase mediates penile erection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103, Lue TF (2000). Erectile dysfunction. New Engl J Med 342, Mizusawa H, Hedlund P, Hakansson A, Alm P & Andersson KE (2001). Morphological and functional in vitro and in vivo characterization of the mouse corpus cavernosum. Br J Pharmacol 132, Morishita T, Tsutsui M, Shimokawa H, Sabanai K, Tasaki H, Suda O, Nakata S, Tanimoto A, Wang KY, Ueta Y, Sasaguri Y, Nakashima Y & Yanagihara N (2005). Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus in mice lacking all nitric oxide synthase isoforms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102, 10,616 10,621. Musicki B, Ross AE, Champion HC, Burnett AL & Bivalacqua TJ (2009). Posttranslational modification of constitutive nitric oxide synthase in the penis. JAndrol30, NimmegeersS,SipsP,BuysE,DecaluweK,BrouckaertP& Van de Voorde J (2008). Role of the soluble guanylyl cyclase α 1 -subunit in mice corpus cavernosum smooth muscle relaxation. Int J Impot Res 20, Pfeifer A, Klatt P, Massberg S, Ny L, Sausbier M, Hirneiss C, Wang GX, Korth M, Aszodi A, Andersson KE, Krombach F, Mayerhofer A, Ruth P, Fassler R & Hofmann F (1998). Defective smooth muscle regulation in cgmp kinase I-deficient mice. EMBO J 17, Ramm SA (2007). Sexual selection and genital evolution in mammals: a phylogenetic analysis of baculum length. Am Nat 169, Rybalkin SD, Yan C, Bornfeldt KE & Beavo JA (2003). Cyclic GMP phosphodiesterases and regulation of smooth muscle function. Circ Res 93, Singh AK, Spiessberger B, Zheng W, Xiao F, Lukowski R, Wegener JW, Weinmeister P, Saur D, Klein S, Schemann M, Krueger D, Seidler U & Hofmann F (2012). Neuronal cgmp kinase I is essential for stimulation of duodenal bicarbonate secretion by luminal acid. FASEB J 26,
12 502 D. Groneberg and others J Physiol Son H, Hawkins RD, Martin K, Kiebler M, Huang PL, Fishman MC & Kandel ER (1996). Long-term potentiation is reduced in mice that are doubly mutant in endothelial and neuronal nitric oxide synthase. Cell 87, Tranguch S & Huet-Hudson Y (2003). Decreased viability of nitric oxide synthase double knockout mice. Mol Reprod Dev 65, Uckert S, Kedia GT, Satzger I, Geismar U, Sohn M, Kuczyk MA, Hedlund P & Waldkirch ES (2010). C-kit-positive multipolar cells in human penile erectile tissue: expression of connexin 43 and relation to trabecular smooth muscle cells. Georgian Med News 180, Visioli F & Hagen TM (2011). Antioxidants to enhance fertility: role of enos and potential benefits. Pharmacol Res 64, Author contributions Study concept and design: D.G. and A.F.; acquisition of data: D.G., P.K., B.L., R.J. and A.F.; analysis and interpretation of data: D.G., B.L. and A.F.; critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: D.G., B.L. and A.F.; obtained funding: P.K. and A.F.; study supervision: A.F. Acknowledgements The excellent technical help of Michaela Kümmel and Kathy Budler is gratefully acknowledged. The work was supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (FR 1725/1 3) and Medizinische Fakultät der Universität zu Lübeck (A ). We are grateful to Stefan Offermanns, Max-Planck-Institut Bad Nauheim, for kind donation of the SMMHC-CreER T2 mouse strain. The authors declare no conflicting interests.
The enteric nervous system controls the motor function
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2011;140:1608 1617 Nitric Oxide Sensitive Guanylyl Cyclase Is Dispensable for Nitrergic Signaling and Gut Motility in Mouse Intestinal Smooth Muscle DIETER GRONEBERG,* PETER KÖNIG, DORIS
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2011;140:1608 1617 Nitric Oxide Sensitive Guanylyl Cyclase Is Dispensable for Nitrergic Signaling and Gut Motility in Mouse Intestinal Smooth Muscle DIETER GRONEBERG,* PETER KÖNIG, DORIS
The exact mechanism of nitrergic relaxation of gastrointestinal BASIC AND TRANSLATIONAL ALIMENTARY TRACT
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2013;145:188 196 TRANSLATIONAL ALIMENTARY TRACT Cell-Specific Deletion of Nitric OxideLSensitive Guanylyl Cyclase Reveals a Dual Pathway for Nitrergic Neuromuscular Transmission in the
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2013;145:188 196 TRANSLATIONAL ALIMENTARY TRACT Cell-Specific Deletion of Nitric OxideLSensitive Guanylyl Cyclase Reveals a Dual Pathway for Nitrergic Neuromuscular Transmission in the
Nitric Oxide in the Penis: Scientific Discoveries and Clinical Applications
 Nitric Oxide in the Penis: Scientific Discoveries and Clinical Applications Arthur L. (Bud) Burnett, M.D., M.B.A., F.A.C.S. Patrick C. Walsh Professor of Urology The James Buchanan Brady Urological Institute
Nitric Oxide in the Penis: Scientific Discoveries and Clinical Applications Arthur L. (Bud) Burnett, M.D., M.B.A., F.A.C.S. Patrick C. Walsh Professor of Urology The James Buchanan Brady Urological Institute
Arterial hypertension is a condition of chronically elevated
 Hypertension Smooth Muscle Specific Deletion of Nitric Oxide Sensitive Guanylyl Cyclase Is Sufficient to Induce Hypertension in Mice Dieter Groneberg, MSc; Peter König, MD; Angela Wirth, PhD; Stefan Offermanns,
Hypertension Smooth Muscle Specific Deletion of Nitric Oxide Sensitive Guanylyl Cyclase Is Sufficient to Induce Hypertension in Mice Dieter Groneberg, MSc; Peter König, MD; Angela Wirth, PhD; Stefan Offermanns,
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 593.2 (215) pp 43 414 43 Dominant role of interstitial cells of Cajal in nitrergic relaxation of murine lower oesophageal sphincter Dieter Groneberg 1,EugenZizer 2, Barbara Lies 1, Barbara Seidler
J Physiol 593.2 (215) pp 43 414 43 Dominant role of interstitial cells of Cajal in nitrergic relaxation of murine lower oesophageal sphincter Dieter Groneberg 1,EugenZizer 2, Barbara Lies 1, Barbara Seidler
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 593.2 (215) pp 4589 461 4589 Nitrergic signalling via interstitial cells of Cajal regulates motor activity in murine colon Barbara Lies 1, Katharina Beck 1, Jonas Keppler 1, Dieter Saur 2,DieterGroneberg
J Physiol 593.2 (215) pp 4589 461 4589 Nitrergic signalling via interstitial cells of Cajal regulates motor activity in murine colon Barbara Lies 1, Katharina Beck 1, Jonas Keppler 1, Dieter Saur 2,DieterGroneberg
Novel nitric oxide signaling mechanisms regulate the erectile response
 (2004) 16, S15 S19 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/04 $30.00 www.nature.com/ijir Novel nitric oxide signaling mechanisms regulate the erectile response Department of Urology,
(2004) 16, S15 S19 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/04 $30.00 www.nature.com/ijir Novel nitric oxide signaling mechanisms regulate the erectile response Department of Urology,
Supplemental Figure I
 Supplemental Figure I Kl ( mmol/l)-induced Force orta M (mn) 1 (mn) 1 Supplemental Figure I. Kl-induced contractions. and, Kl ( mmol/l)-induced contractions of the aorta () and those of mesenteric arteries
Supplemental Figure I Kl ( mmol/l)-induced Force orta M (mn) 1 (mn) 1 Supplemental Figure I. Kl-induced contractions. and, Kl ( mmol/l)-induced contractions of the aorta () and those of mesenteric arteries
for ED and LUTS/BPH Pierre Sarkis, M.D. Assistant Professor Fellow of the European Board of Urology
 Tadalafil 5 mg once daily for ED and LUTS/BPH Pierre Sarkis, M.D. Assistant Professor Fellow of the European Board of Urology Why this conference? Not promotional but educational The pharmacist regularly
Tadalafil 5 mg once daily for ED and LUTS/BPH Pierre Sarkis, M.D. Assistant Professor Fellow of the European Board of Urology Why this conference? Not promotional but educational The pharmacist regularly
The effect of sildenafil on electrostimulation-induced erection in the rat model
 (2002) 14, 251 255 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/ijir The effect of sildenafil on electrostimulation-induced erection in the rat model N Ueno 1,
(2002) 14, 251 255 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/ijir The effect of sildenafil on electrostimulation-induced erection in the rat model N Ueno 1,
Topical application of a Rho-kinase inhibitor in rats causes penile erection
 (2004) 16, 294 298 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/04 $30.00 www.nature.com/ijir Topical application of a Rho-kinase inhibitor in rats causes penile erection Y Dai 1,2,3, K
(2004) 16, 294 298 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/04 $30.00 www.nature.com/ijir Topical application of a Rho-kinase inhibitor in rats causes penile erection Y Dai 1,2,3, K
Light-controlled relaxation of the rat penile corpus cavernosum using NOBL-1, a novel nitric oxide releaser
 Original Article - Basic and Translational Research ICUrology 216;57:215-22. http://dx.doi.org/1.4111/icu.216.57.3.215 pissn 2466-493 eissn 2466-54X Light-controlled relaxation of the rat penile corpus
Original Article - Basic and Translational Research ICUrology 216;57:215-22. http://dx.doi.org/1.4111/icu.216.57.3.215 pissn 2466-493 eissn 2466-54X Light-controlled relaxation of the rat penile corpus
Intracavernous administration of SIN-1 þ VIP in an in vivo rabbit model for erectile function
 (2002) 14, 44 49 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/ijir Intracavernous administration of SIN-1 þ VIP in an in vivo rabbit model for erectile function
(2002) 14, 44 49 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/ijir Intracavernous administration of SIN-1 þ VIP in an in vivo rabbit model for erectile function
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE
 455..466 BJP British Journal of Pharmacology DOI:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01569.x www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPERbph_1569 Amplified NO/cGMP-mediated relaxation and ryanodine receptor-to-bk Ca channel
455..466 BJP British Journal of Pharmacology DOI:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01569.x www.brjpharmacol.org RESEARCH PAPERbph_1569 Amplified NO/cGMP-mediated relaxation and ryanodine receptor-to-bk Ca channel
Excess adenosine in murine penile erectile tissues contributes to priapism via A 2B adenosine receptor signaling
 Research article Excess adenosine in murine penile erectile tissues contributes to priapism via A 2B adenosine receptor signaling Tiejuan Mi, 1 Shahrzad Abbasi, 1 Hong Zhang, 2 Karen Uray, 3 Janci L. Chunn,
Research article Excess adenosine in murine penile erectile tissues contributes to priapism via A 2B adenosine receptor signaling Tiejuan Mi, 1 Shahrzad Abbasi, 1 Hong Zhang, 2 Karen Uray, 3 Janci L. Chunn,
Product Introduction
 Product Introduction 康達生命科學有限公司 Contek Life Science Co., Ltd. Red Algae Peptide Hydrolysate-EDpeptide The Next Generations of Erectile Dysfunction Cure Introduction of small peptides Erectile dysfunction
Product Introduction 康達生命科學有限公司 Contek Life Science Co., Ltd. Red Algae Peptide Hydrolysate-EDpeptide The Next Generations of Erectile Dysfunction Cure Introduction of small peptides Erectile dysfunction
Cell Communication CHAPTER 11
 Cell Communication CHAPTER 11 What you should know: The 3 stages of cell communication: reception, transduction, and response. How a receptor protein recognizes signal molecules and starts transduction.
Cell Communication CHAPTER 11 What you should know: The 3 stages of cell communication: reception, transduction, and response. How a receptor protein recognizes signal molecules and starts transduction.
Eliades, Erlandson, Ruiz UW-L Journal of Undergraduate Research XVII (2014)
 Effects of Hibernation on the Enteric Nervous System of the Thirteenlined Ground Squirrels. Lauren Eliades, Martin Erlandson, Amelia Ruiz Faculty Sponsors: Dr. Sumei Liu and Dr. Scott Cooper, Department
Effects of Hibernation on the Enteric Nervous System of the Thirteenlined Ground Squirrels. Lauren Eliades, Martin Erlandson, Amelia Ruiz Faculty Sponsors: Dr. Sumei Liu and Dr. Scott Cooper, Department
Cell Signaling part 2
 15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.
 Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
Supplementary Figure 1: Hsp60 / IEC mice are embryonically lethal (A) Light microscopic pictures show mouse embryos at developmental stage E12.5 and E13.5 prepared from uteri of dams and subsequently genotyped.
Defined as the consistent inability to attain and maintain an erection adequate for sexual intercourse Usually qualified by being present for several
 Defined as the consistent inability to attain and maintain an erection adequate for sexual intercourse Usually qualified by being present for several months and occurring at least half the time. Vinik
Defined as the consistent inability to attain and maintain an erection adequate for sexual intercourse Usually qualified by being present for several months and occurring at least half the time. Vinik
ChronicSildenafilImprovesErectileFunctionand Endothelium-dependent Cavernosal Relaxations in Rats: Lack oftachyphylaxis $
 European Urology European Urology 47 (2005) 87 91 ChronicSildenafilImprovesErectileFunctionand Endothelium-dependent Cavernosal Relaxations in Rats: Lack oftachyphylaxis $ Delphine Behr-Roussel a, Diane
European Urology European Urology 47 (2005) 87 91 ChronicSildenafilImprovesErectileFunctionand Endothelium-dependent Cavernosal Relaxations in Rats: Lack oftachyphylaxis $ Delphine Behr-Roussel a, Diane
Managing the Patient with Erectile Dysfunction: What Would You Do?
 Managing the Patient with Erectile Dysfunction: What Would You Do? Florida A & M University College of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences 42 nd Annual Clinical Symposium Wayne A. Sampson, M.D. Cross
Managing the Patient with Erectile Dysfunction: What Would You Do? Florida A & M University College of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences 42 nd Annual Clinical Symposium Wayne A. Sampson, M.D. Cross
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
CHRONIC HYPOXIA MODULATES ENDOTHELIUM- DEPENDENT VASORELAXATION THROUGH MULTIPLE INDEPENDENT MECHANISMS IN OVINE CRANIAL ARTERIES
 CHRONIC HYPOXIA MODULATES ENDOTHELIUM- DEPENDENT VASORELAXATION THROUGH MULTIPLE INDEPENDENT MECHANISMS IN OVINE CRANIAL ARTERIES William J. Pearce, James M. Williams, Mohammad W. Hamade, Melody M. Chang,
CHRONIC HYPOXIA MODULATES ENDOTHELIUM- DEPENDENT VASORELAXATION THROUGH MULTIPLE INDEPENDENT MECHANISMS IN OVINE CRANIAL ARTERIES William J. Pearce, James M. Williams, Mohammad W. Hamade, Melody M. Chang,
Receptors Families. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Receptors Families Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Receptor Families 1. Ligand-gated ion channels 2. G protein coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-linked
Receptors Families Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Receptor Families 1. Ligand-gated ion channels 2. G protein coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-linked
Warm-Up. Warm-Up. Warm-Up. Cell Communication. Cell Signaling 03/06/2018. Do bacteria communicate?
 Warm-Up 1. Why do you communicate? 2. How do you communicate? 3. How do you think cells communicate? 4. Do you think bacteria can communicate? Explain. Warm-Up 1. Why are scientists studying how bacteria
Warm-Up 1. Why do you communicate? 2. How do you communicate? 3. How do you think cells communicate? 4. Do you think bacteria can communicate? Explain. Warm-Up 1. Why are scientists studying how bacteria
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA. Lumen area ( m 2 )
 Elastin Lumen area ( m 2 ) Media to lumen ratio (x1) H.E. Medium thickness ( m) Medium area ( m 2 ) SUPPLEMENTAL DATA A (Bmal1 flox/flox ) (SM-Bmal1 -/- ) B 1 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 1µm 5 8 4 6 3 2 4 1 2 Supplemental
Elastin Lumen area ( m 2 ) Media to lumen ratio (x1) H.E. Medium thickness ( m) Medium area ( m 2 ) SUPPLEMENTAL DATA A (Bmal1 flox/flox ) (SM-Bmal1 -/- ) B 1 8 8 6 6 4 4 2 2 1µm 5 8 4 6 3 2 4 1 2 Supplemental
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Rationale for the Combination of PGE 1 and S-Nitrosoglutathione to Induce Relaxation of Human Penile Smooth Muscle 1
 0022-3565/00/2952-0586$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 295, No. 2 Copyright 2000 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2715/853843
0022-3565/00/2952-0586$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 295, No. 2 Copyright 2000 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2715/853843
Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators
 Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators Introduction about chemical mediators in inflammation Mediators may be Cellular mediators cell-produced or cell-secreted derived from circulating inactive precursors,
Cell-Derived Inflammatory Mediators Introduction about chemical mediators in inflammation Mediators may be Cellular mediators cell-produced or cell-secreted derived from circulating inactive precursors,
UNIT 3: Signal transduction. Prof K Syed Department of Biochemistry & Microbiology University of Zululand Room no. 247
 UNIT 3: Signal transduction Prof K Syed Department of Biochemistry & Microbiology University of Zululand Room no. 247 SyedK@unizulu.ac.za Topics Signal transduction Terminology G-protein signaling pathway
UNIT 3: Signal transduction Prof K Syed Department of Biochemistry & Microbiology University of Zululand Room no. 247 SyedK@unizulu.ac.za Topics Signal transduction Terminology G-protein signaling pathway
Relaxation mechanisms of neferine on the rabbit corpus cavernosum tissue in vitro
 Asian J Androl 2007; 9 (6): 795 800 DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-7262.2007.00321.x www.asiaandro.com. Original Article. Relaxation mechanisms of neferine on the rabbit corpus cavernosum tissue in vitro Jun Chen
Asian J Androl 2007; 9 (6): 795 800 DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-7262.2007.00321.x www.asiaandro.com. Original Article. Relaxation mechanisms of neferine on the rabbit corpus cavernosum tissue in vitro Jun Chen
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Information for Patients. Priapism. English
 Information for Patients Priapism English Table of contents What is priapism?... 3 What causes priapism?... 3 Diagnosing priapism... 3 Treating priapism... 4 Conservative, first- and second-line treatments...
Information for Patients Priapism English Table of contents What is priapism?... 3 What causes priapism?... 3 Diagnosing priapism... 3 Treating priapism... 4 Conservative, first- and second-line treatments...
H 2 S: Synthesis and functions
 H 2 S: Synthesis and functions 1 Signaling gas molecules: O 2, NO and CO Then, H 2 S - Fourth singling gas molecule after O 2, NO and CO 2 Nothing Rotten About Hydrogen Sulfide s Medical Promise Science
H 2 S: Synthesis and functions 1 Signaling gas molecules: O 2, NO and CO Then, H 2 S - Fourth singling gas molecule after O 2, NO and CO 2 Nothing Rotten About Hydrogen Sulfide s Medical Promise Science
Cell Signaling (part 1)
 15 Cell Signaling (part 1) Introduction Bacteria and unicellular eukaryotes respond to environmental signals and to signaling molecules secreted by other cells for mating and other communication. In multicellular
15 Cell Signaling (part 1) Introduction Bacteria and unicellular eukaryotes respond to environmental signals and to signaling molecules secreted by other cells for mating and other communication. In multicellular
MALE SEXUAL DYSFUNCTION. Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 MALE SEXUAL DYSFUNCTION Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara DEFINITION The inability to achieve a satisfactory sexual relationship May involve : - inadequacy
MALE SEXUAL DYSFUNCTION Urology Division, Surgery Department Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara DEFINITION The inability to achieve a satisfactory sexual relationship May involve : - inadequacy
The dynamic regulation of blood vessel caliber
 INVITED BASIC SCIENCE REVIEW The dynamic regulation of blood vessel caliber Colleen M. Brophy, MD, Augusta, Ga BACKGROUND The flow of blood to organs is regulated by changes in the diameter of the blood
INVITED BASIC SCIENCE REVIEW The dynamic regulation of blood vessel caliber Colleen M. Brophy, MD, Augusta, Ga BACKGROUND The flow of blood to organs is regulated by changes in the diameter of the blood
Effects and Mechanism of Action of a Tribulus terrestris Extract on Penile Erection
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.3.183 Sexual Dysfunction Effects and Mechanism of Action of a Tribulus terrestris Extract on Penile Erection Jungmo Do, Seemin Choi, Jaehwi Choi,
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.3.183 Sexual Dysfunction Effects and Mechanism of Action of a Tribulus terrestris Extract on Penile Erection Jungmo Do, Seemin Choi, Jaehwi Choi,
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.
 Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
Figure S1. Generation of inducible PTEN deficient mice and the BMMCs (A) B6.129 Pten loxp/loxp mice were mated with B6.129-Gt(ROSA)26Sor tm1(cre/ert2)tyj /J mice. To induce deletion of the Pten locus,
8-Br-cAMP SQ/DDA NKH477 AC IBMX PDE AMP. camp IP 3 R. Control + ESI-09. Control + H89. peak [Ca 2+ ] c (nm) log [PTH(1-34)] (/M) log [PTH(1-34)] (/M)
![8-Br-cAMP SQ/DDA NKH477 AC IBMX PDE AMP. camp IP 3 R. Control + ESI-09. Control + H89. peak [Ca 2+ ] c (nm) log [PTH(1-34)] (/M) log [PTH(1-34)] (/M) 8-Br-cAMP SQ/DDA NKH477 AC IBMX PDE AMP. camp IP 3 R. Control + ESI-09. Control + H89. peak [Ca 2+ ] c (nm) log [PTH(1-34)] (/M) log [PTH(1-34)] (/M)](/thumbs/83/88758039.jpg) peak [Ca 2+ ] c peak [Ca 2+ ] c A 8-Br- peak [Ca 2+ ] c peak [Ca 2+ ] c AC IBMX SQ/DDA NKH477 PDE AMP PKA EPAC IP 3 R B 5 + SQ/DDA H89 ESI-9 C 5 + H89 25 25-9 -7-5 log [PTH(1-34)] -9-7 -5 log [PTH(1-34)]
peak [Ca 2+ ] c peak [Ca 2+ ] c A 8-Br- peak [Ca 2+ ] c peak [Ca 2+ ] c AC IBMX SQ/DDA NKH477 PDE AMP PKA EPAC IP 3 R B 5 + SQ/DDA H89 ESI-9 C 5 + H89 25 25-9 -7-5 log [PTH(1-34)] -9-7 -5 log [PTH(1-34)]
27 part 2. Laith Abu Shekha. Mamoon Al-qatameen
 27 part 2 Laith Abu Shekha Mamoon Al-qatameen Ebaa Alzayadneh In this sheet we will continue talking about second messengers for hormone that can t cross PM. D. Ca +2 as a second messenger: Another second
27 part 2 Laith Abu Shekha Mamoon Al-qatameen Ebaa Alzayadneh In this sheet we will continue talking about second messengers for hormone that can t cross PM. D. Ca +2 as a second messenger: Another second
Influence of different concentrations of Sildenafil Citrate on histological parameters of mice epididymis
 Influence of different concentrations of Sildenafil Citrate on histological parameters of mice epididymis Muhammad-Baqir M-R. Fakhrildin Usama I. M. Al-Zubaidi Institute of Embryo Research and Infertility
Influence of different concentrations of Sildenafil Citrate on histological parameters of mice epididymis Muhammad-Baqir M-R. Fakhrildin Usama I. M. Al-Zubaidi Institute of Embryo Research and Infertility
Effects of ethanol treatment on the neurogenicand endothelium-dependent relaxation of corpus cavernosum smooth muscle in the mouse
 Pharmacological Reports 2008, 60, 725 734 ISSN 1734-1140 Copyright 2008 by Institute of Pharmacology Polish Academy of Sciences Effects of ethanol treatment on the neurogenicand endothelium-dependent relaxation
Pharmacological Reports 2008, 60, 725 734 ISSN 1734-1140 Copyright 2008 by Institute of Pharmacology Polish Academy of Sciences Effects of ethanol treatment on the neurogenicand endothelium-dependent relaxation
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Cellular Messengers. Intracellular Communication
 Cellular Messengers Intracellular Communication Most common cellular communication is done through extracellular chemical messengers: Ligands Specific in function 1. Paracrines Local messengers (neighboring
Cellular Messengers Intracellular Communication Most common cellular communication is done through extracellular chemical messengers: Ligands Specific in function 1. Paracrines Local messengers (neighboring
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Managing Erectile Dysfunction
 Managing Erectile Dysfunction Lewis E. Harpster MD, FACS Urology of Central PA 4/23/16 1 Objectives 1. Review physiologic mechanism of erection 2. Discuss medical management of ED 3. Discuss surgical management
Managing Erectile Dysfunction Lewis E. Harpster MD, FACS Urology of Central PA 4/23/16 1 Objectives 1. Review physiologic mechanism of erection 2. Discuss medical management of ED 3. Discuss surgical management
Effect of chronic hypoxia on penile erectile function in rats
 Effect of chronic hypoxia on penile erectile function in rats D.P. Yu 1, X.H. Liu 2 and A.Y. Wei 3 1 Department of Urology, The First People s Hospital of Jining City in Shandong Province, Jining, Shandong,
Effect of chronic hypoxia on penile erectile function in rats D.P. Yu 1, X.H. Liu 2 and A.Y. Wei 3 1 Department of Urology, The First People s Hospital of Jining City in Shandong Province, Jining, Shandong,
Relaxation responses of aortic rings from salt-loaded high calcium fed rats to potassium chloride, calcium chloride and magnesium sulphate
 Pathophysiology 4 (1998) 275 280 Relaxation responses of aortic rings from salt-loaded high calcium fed rats to potassium chloride, calcium chloride and magnesium sulphate B.J. Adegunloye, O.A. Sofola
Pathophysiology 4 (1998) 275 280 Relaxation responses of aortic rings from salt-loaded high calcium fed rats to potassium chloride, calcium chloride and magnesium sulphate B.J. Adegunloye, O.A. Sofola
ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION. & Current Therapies. GP Conference, Rotorua 7-10 June 2012
 ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION & Current Therapies GP Conference, Rotorua 7-10 June 2012 Jan Burns & Annie Woodsford Jan: EN, RCpN, BHSc, RPN (USA),MHSc, Member of the Sexual Medicine Society Urology Nurse Specialist
ERECTILE DYSFUNCTION & Current Therapies GP Conference, Rotorua 7-10 June 2012 Jan Burns & Annie Woodsford Jan: EN, RCpN, BHSc, RPN (USA),MHSc, Member of the Sexual Medicine Society Urology Nurse Specialist
Reactivity of the isolated perfused rat tail vascular bed
 Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1997) 30: 891-895 Perfused rat tail vascular bed ISSN 0100-879X 891 Reactivity of the isolated perfused rat tail vascular bed A.S. França, L.V. Rossoni,
Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research (1997) 30: 891-895 Perfused rat tail vascular bed ISSN 0100-879X 891 Reactivity of the isolated perfused rat tail vascular bed A.S. França, L.V. Rossoni,
MMM. Topic The use of Tadalafil 5mg daily for the treatment of BPH-LUTS
 Dr Tan & Partners MMM Vol. 1 No. 1 Morbidity & Mortality Meeting 14 th November 2014 Introduction Topic The use of Tadalafil 5mg daily for the treatment of BPH-LUTS Tadalafil 5mg daily is a well established
Dr Tan & Partners MMM Vol. 1 No. 1 Morbidity & Mortality Meeting 14 th November 2014 Introduction Topic The use of Tadalafil 5mg daily for the treatment of BPH-LUTS Tadalafil 5mg daily is a well established
IC351 (tadalafil, Cialis): update on clinical experience
 (2002) 14, Suppl 1, S57 S64 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/ijir IC351 (tadalafil, Cialis): update on clinical experience 1 * 1 Urological practice,
(2002) 14, Suppl 1, S57 S64 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/ijir IC351 (tadalafil, Cialis): update on clinical experience 1 * 1 Urological practice,
Prenatal hypoxia causes long-term alterations in vascular endothelin-1 function in aged male but not female offspring
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 Supplementary information for: Prenatal hypoxia causes long-term alterations in vascular endothelin-1 function in aged male but not female offspring Stephane L Bourque,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 11 12 13 14 Supplementary information for: Prenatal hypoxia causes long-term alterations in vascular endothelin-1 function in aged male but not female offspring Stephane L Bourque,
ONLINE SUPPLEMENT Title: CFTR dysfunction induces vascular endothelial growth factor synthesis in airway epithelium
 ONLINE SUPPLEMENT Title: CFTR dysfunction induces vascular endothelial growth factor synthesis in airway epithelium Martin C, Coolen N, Wu YZ, Thévenot G, Touqui L, PrulièreEscabasse V, Papon JF, Coste
ONLINE SUPPLEMENT Title: CFTR dysfunction induces vascular endothelial growth factor synthesis in airway epithelium Martin C, Coolen N, Wu YZ, Thévenot G, Touqui L, PrulièreEscabasse V, Papon JF, Coste
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
BCOR 011 Lecture 19 Oct 12, 2005 I. Cell Communication Signal Transduction Chapter 11
 BCOR 011 Lecture 19 Oct 12, 2005 I. Cell Communication Signal Transduction Chapter 11 External signal is received and converted to another form to elicit a response 1 Lecture Outline 1. Types of intercellular
BCOR 011 Lecture 19 Oct 12, 2005 I. Cell Communication Signal Transduction Chapter 11 External signal is received and converted to another form to elicit a response 1 Lecture Outline 1. Types of intercellular
INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that adrenaline may
 REVERSAL OF THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND G. L. BROWN. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that
REVERSAL OF THE ACTION OF ADRENALINE. BY B. A. McSWINEY AND G. L. BROWN. (From the Department of Physiology, University of Manchester.) INTRODUCTION. IN a previous paper(l) we have been able to show that
Testosterone and PDE5 inhibitors in the aging male
 Testosterone and PDE5 inhibitors in the aging male Francesco Romanelli Department of Experimental Medicine Medical Pathophysiology, Food Science and Endocrinology Section Sapienza University of Rome 3005
Testosterone and PDE5 inhibitors in the aging male Francesco Romanelli Department of Experimental Medicine Medical Pathophysiology, Food Science and Endocrinology Section Sapienza University of Rome 3005
Supplementary Material and Methods
 Online Supplement Kockx et al, Secretion of Apolipoprotein E from Macrophages 1 Supplementary Material and Methods Cloning of ApoE-GFP Full-length human apoe3 cdna (pcdna3.1/zeo + -apoe) was kindly provided
Online Supplement Kockx et al, Secretion of Apolipoprotein E from Macrophages 1 Supplementary Material and Methods Cloning of ApoE-GFP Full-length human apoe3 cdna (pcdna3.1/zeo + -apoe) was kindly provided
Interaction between interstitial cells and smooth muscles in the lower urinary tract and penis
 J Physiol 576.3 (2006) pp 707 714 707 SYMPOSIUM REPORT Interaction between interstitial cells and smooth muscles in the lower urinary tract and penis Hikaru Hashitani Department of Regulatory Cell Physiology,
J Physiol 576.3 (2006) pp 707 714 707 SYMPOSIUM REPORT Interaction between interstitial cells and smooth muscles in the lower urinary tract and penis Hikaru Hashitani Department of Regulatory Cell Physiology,
Chapter 9. Cellular Signaling
 Chapter 9 Cellular Signaling Cellular Messaging Page 215 Cells can signal to each other and interpret the signals they receive from other cells and the environment Signals are most often chemicals The
Chapter 9 Cellular Signaling Cellular Messaging Page 215 Cells can signal to each other and interpret the signals they receive from other cells and the environment Signals are most often chemicals The
THE ACTION OF PHYSOSTIGMINE AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF CHOLINESTERASES IN THE CHICKEN OESOPHAGUS
 Br. J. Phannac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 531-536. THE ACTION OF PHYSOSTIGMINE AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF CHOLINESTERASES IN THE CHICKEN OESOPHAGUS BY A. L. BARTLET AND T. HASSAN From the Department of Veterinary
Br. J. Phannac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 531-536. THE ACTION OF PHYSOSTIGMINE AND THE DISTRIBUTION OF CHOLINESTERASES IN THE CHICKEN OESOPHAGUS BY A. L. BARTLET AND T. HASSAN From the Department of Veterinary
The rabbit femoral artery was prepared and each arterial ring was permeabilized
 Online Supplement Nakmura et al. cgmp-dependent relaxation of smooth muscle Materials and Methods Measurement of tension The rabbit femoral artery was prepared and each arterial ring was permeabilized
Online Supplement Nakmura et al. cgmp-dependent relaxation of smooth muscle Materials and Methods Measurement of tension The rabbit femoral artery was prepared and each arterial ring was permeabilized
Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Keeps Erection Regulatory Function Balance in the Penis
 european urology 51 (2007) 1732 1740 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Sexual Medicine Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Keeps Erection Regulatory Function Balance
european urology 51 (2007) 1732 1740 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Sexual Medicine Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase Keeps Erection Regulatory Function Balance
Cystic Fibrosis. Na+ 2Cl - K+ Na+ Na+
 1 Cystic Fibrosis I. Overview of cystic fibrosis Among Caucasians, about one out of twenty people carry the gene for cystic fibrosis (CF), and one of 2,000 to 4,000 people is afflicted with the recessive
1 Cystic Fibrosis I. Overview of cystic fibrosis Among Caucasians, about one out of twenty people carry the gene for cystic fibrosis (CF), and one of 2,000 to 4,000 people is afflicted with the recessive
Onset and duration of action of sildena l citrate for the treatment of erectile dysfunction
 Onset and duration of action of sildena l citrate for the treatment of erectile dysfunction Ian Eardley, 1 Peter Ellis, 2 Mitradev Boolell 2 & Maria Wulff 2 1 Department of Urology, St James University
Onset and duration of action of sildena l citrate for the treatment of erectile dysfunction Ian Eardley, 1 Peter Ellis, 2 Mitradev Boolell 2 & Maria Wulff 2 1 Department of Urology, St James University
Lactate and force production in skeletal muscle
 J Physiol 562.2 (2005) pp 521 526 521 Lactate and force production in skeletal muscle Michael Kristensen, Janni Albertsen, Maria Rentsch and Carsten Juel Copenhagen Muscle Research Centre, University of
J Physiol 562.2 (2005) pp 521 526 521 Lactate and force production in skeletal muscle Michael Kristensen, Janni Albertsen, Maria Rentsch and Carsten Juel Copenhagen Muscle Research Centre, University of
Erectile Dysfunction in Hypertensive Rats Results from Impairment of the Relaxation Evoked by Neurogenic Carbon Monoxide and Nitric Oxide
 253 Original Article Erectile Dysfunction in Hypertensive Rats Results from Impairment of the Relaxation Evoked by Neurogenic Carbon Monoxide and Nitric Oxide Masayuki USHIYAMA, Toshisuke MORITA, Tomoya
253 Original Article Erectile Dysfunction in Hypertensive Rats Results from Impairment of the Relaxation Evoked by Neurogenic Carbon Monoxide and Nitric Oxide Masayuki USHIYAMA, Toshisuke MORITA, Tomoya
CD14 + S100A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CD14 + S1A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Po-Hao, Feng M.D., Kang-Yun, Lee, M.D. Ph.D., Ya-Ling Chang, Yao-Fei Chan, Lu- Wei, Kuo,Ting-Yu
CD14 + S1A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Po-Hao, Feng M.D., Kang-Yun, Lee, M.D. Ph.D., Ya-Ling Chang, Yao-Fei Chan, Lu- Wei, Kuo,Ting-Yu
The Role of Testosterone in the Sexual Function. Luiz Otavio Torres President Elect of ISSM Belo Horizonte - Brazil
 The Role of Testosterone in the Sexual Function Luiz Otavio Torres President Elect of ISSM Belo Horizonte - Brazil Hormones and Sexual Function Paraventricular Nucleus Stimuli visual Sexual Desire Melatonine
The Role of Testosterone in the Sexual Function Luiz Otavio Torres President Elect of ISSM Belo Horizonte - Brazil Hormones and Sexual Function Paraventricular Nucleus Stimuli visual Sexual Desire Melatonine
Potentiation of Penile Tumescence by T-1032, a New Potent and Specific Phosphodiesterase Type V Inhibitor, in Dogs
 0022-3565/00/2943-0870$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 294, No. 3 Copyright 2000 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2623/843022
0022-3565/00/2943-0870$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 294, No. 3 Copyright 2000 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2623/843022
The Effect of Alcohol Administration on the Corpus Cavernosum
 pissn: 2287-4208 / eissn: 2287-4690 World J Mens Health 2017 April 35(1): 34-42 https://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.2017.35.1.34 Original Article The Effect of Alcohol Administration on the Corpus Cavernosum
pissn: 2287-4208 / eissn: 2287-4690 World J Mens Health 2017 April 35(1): 34-42 https://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.2017.35.1.34 Original Article The Effect of Alcohol Administration on the Corpus Cavernosum
Oral phentolamine: an alpha-1, alpha-2 adrenergic antagonist for the treatment of erectile dysfunction
 (2000) 12, Suppl 1, S75±S80 ß 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0955-9930/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/ijir Oral phentolamine: an alpha-1, alpha-2 adrenergic antagonist for the treatment of
(2000) 12, Suppl 1, S75±S80 ß 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0955-9930/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/ijir Oral phentolamine: an alpha-1, alpha-2 adrenergic antagonist for the treatment of
Effects of plant extract neferine on cyclic adenosine monophosphate and cyclic guanosine monophosphate levels in rabbit corpus cavernosum in vitro
 Asian J Androl 2008; 10 (2): 307 312 DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-7262.2008.00342.x www.asiaandro.com. Original Article. Effects of plant extract neferine on cyclic adenosine monophosphate and cyclic guanosine
Asian J Androl 2008; 10 (2): 307 312 DOI: 10.1111/j.1745-7262.2008.00342.x www.asiaandro.com. Original Article. Effects of plant extract neferine on cyclic adenosine monophosphate and cyclic guanosine
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1
 GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
 http://noodlemaz.wordpress.com/category/science/cancer/ Outline Introduction Serious nature of Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) How to prevent CVD? The disease process Damage and plaque development Current
http://noodlemaz.wordpress.com/category/science/cancer/ Outline Introduction Serious nature of Cardiovascular Disease (CVD) How to prevent CVD? The disease process Damage and plaque development Current
Smooth muscle pathology and erectile dysfunction
 (2002) 14, Suppl 1, S17 S21 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/ijir and erectile dysfunction 1 * 1 Department of Urology, C.H.U. de Charleroi, Charleroi,
(2002) 14, Suppl 1, S17 S21 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/ijir and erectile dysfunction 1 * 1 Department of Urology, C.H.U. de Charleroi, Charleroi,
Reactive oxygen species: Importance for ischemia/reperfusion (injury)
 Physiologisches Institut Reactive oxygen species: Importance for ischemia/reperfusion (injury) Prof. Dr. Rainer Schulz Reactive oxygen species (ROS) in ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI) ROS GOOD: Endogenous
Physiologisches Institut Reactive oxygen species: Importance for ischemia/reperfusion (injury) Prof. Dr. Rainer Schulz Reactive oxygen species (ROS) in ischemia/reperfusion injury (IRI) ROS GOOD: Endogenous
- Biosignaling: Signal transduction. References: chapter 8 of Lippincots chapter 1 3 of Lehningers
 Basic concepts of Metabolism Metabolism and metabolic pathway Metabolic Map Catabolism Anabolism - Regulation of Metabolism Signals from within the cell (Intracellular) Communication between cells. - Biosignaling:
Basic concepts of Metabolism Metabolism and metabolic pathway Metabolic Map Catabolism Anabolism - Regulation of Metabolism Signals from within the cell (Intracellular) Communication between cells. - Biosignaling:
Supplemental Information. Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate. into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling. in Developing Skin Vasculature
 Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
Cell Reports, Volume 18 Supplemental Information Tissue Myeloid Progenitors Differentiate into Pericytes through TGF-b Signaling in Developing Skin Vasculature Tomoko Yamazaki, Ani Nalbandian, Yutaka Uchida,
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Mouse GLP-2 EIA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY
 YK142 Mouse GLP-2 EIA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY Kasumigaseki place, 3-6-7, Kasumigaseki, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-0013 Japan http://www.sceti.co.jp/english/export e-mail exp-pet@sceti.co.jp
YK142 Mouse GLP-2 EIA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY Kasumigaseki place, 3-6-7, Kasumigaseki, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-0013 Japan http://www.sceti.co.jp/english/export e-mail exp-pet@sceti.co.jp
Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy
 Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jiali Luo 1, 2, 3, 4, a, Shanshan Feng 1, 2, 3, 4, b 1Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jinan University,
Comparison of Young and Old Cardiac Telocytes Using Atomic Force Microscopy Jiali Luo 1, 2, 3, 4, a, Shanshan Feng 1, 2, 3, 4, b 1Key Laboratory of Regenerative Medicine, Ministry of Education, Jinan University,
Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes
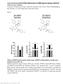 Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes T Jourdan, G Godlewski, R Cinar, A Bertola, G Szanda, J Liu, J Tam, T Han, B Mukhopadhyay,
Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes T Jourdan, G Godlewski, R Cinar, A Bertola, G Szanda, J Liu, J Tam, T Han, B Mukhopadhyay,
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents Question No. 1 of 10 1. Vascular smooth muscle contraction is triggered by a rise in. Question #01 (A) Luminal calcium (B) Extracellular calcium (C) Intracellular
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents Question No. 1 of 10 1. Vascular smooth muscle contraction is triggered by a rise in. Question #01 (A) Luminal calcium (B) Extracellular calcium (C) Intracellular
Title: Tadalafil Preserves Penile Nitric Oxide Synthase from Detrimental Effect of Paroxetine in Rats
 DOI: 10.5152/eurasianjmed.2018.18160 Manuscript Type: Original Article Title: Tadalafil Preserves Penile Nitric Oxide Synthase from Detrimental Effect of Paroxetine in Rats Authors: 1 Abdullah Gul, 2 Alexander
DOI: 10.5152/eurasianjmed.2018.18160 Manuscript Type: Original Article Title: Tadalafil Preserves Penile Nitric Oxide Synthase from Detrimental Effect of Paroxetine in Rats Authors: 1 Abdullah Gul, 2 Alexander
Erection Capability Is Potentiated by Long-Term Sildenafil Treatment: Role of Blood Flow-Induced Endothelial Nitric-Oxide Synthase Phosphorylation
 0026-895X/05/6801-226 232$20.00 MOLECULAR PHARMACOLOGY Vol. 68, No. 1 Copyright 2005 The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 10678/3040759 Mol Pharmacol 68:226 232, 2005 Printed
0026-895X/05/6801-226 232$20.00 MOLECULAR PHARMACOLOGY Vol. 68, No. 1 Copyright 2005 The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 10678/3040759 Mol Pharmacol 68:226 232, 2005 Printed
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Endothelial and neuronal-derived nitric oxide mediated relaxation of corpus cavernosal smooth muscle in a rat, in vitro, model of erectile function
 (2000) 12, 213±221 ß 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0955-9930/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/ijir Endothelial and neuronal-derived nitric oxide mediated relaxation of corpus cavernosal smooth
(2000) 12, 213±221 ß 2000 Macmillan Publishers Ltd All rights reserved 0955-9930/00 $15.00 www.nature.com/ijir Endothelial and neuronal-derived nitric oxide mediated relaxation of corpus cavernosal smooth
Application of Outlier Robust Nonlinear Mixed Effect Estimation in Examining the Effect of Phenylephrine in Rat Corpus Cavernosum
 Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2016: 12 (3): 47-54 www.ijps.ir Original Article Application of Outlier Robust Nonlinear Mixed Effect Estimation in Examining the Effect of Phenylephrine in Rat
Iranian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2016: 12 (3): 47-54 www.ijps.ir Original Article Application of Outlier Robust Nonlinear Mixed Effect Estimation in Examining the Effect of Phenylephrine in Rat
Acommon consequence of the clinical use of
 Sildenafil and a Compound Stimulating Endothelial NO Synthase Modify Sexual Incentive Motivation and Copulatory Behavior in Male Wistar and Fisher 344 Rats 2085 Xi Chu, MSc,* Ekaterina S. Zhavbert, MSc,
Sildenafil and a Compound Stimulating Endothelial NO Synthase Modify Sexual Incentive Motivation and Copulatory Behavior in Male Wistar and Fisher 344 Rats 2085 Xi Chu, MSc,* Ekaterina S. Zhavbert, MSc,
Vascular reactivity in sepsis and platelet dysfunction in septic shock
 Vascular reactivity in sepsis and platelet dysfunction in septic shock Benjamin Reddi Discipline of Physiology School of Medical Science University of Adelaide Thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor
Vascular reactivity in sepsis and platelet dysfunction in septic shock Benjamin Reddi Discipline of Physiology School of Medical Science University of Adelaide Thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor
2402 : Anatomy/Physiology
 Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 2 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology The Endocrine System G proteins and Adenylate Cyclase /camp TextBook Readings Pages 405 and 599 through 603. Make use of the figures in your textbook
Dr. Chris Doumen Lecture 2 2402 : Anatomy/Physiology The Endocrine System G proteins and Adenylate Cyclase /camp TextBook Readings Pages 405 and 599 through 603. Make use of the figures in your textbook
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1327 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1327 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Spring balance evaluation of the ischiocavernosus muscle
 International Journal of Impotence Research (2001) 13, 294 297 ß 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/01 $15.00 www.nature.com/ijir Spring balance evaluation of the ischiocavernosus
International Journal of Impotence Research (2001) 13, 294 297 ß 2001 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/01 $15.00 www.nature.com/ijir Spring balance evaluation of the ischiocavernosus
Learning Outcomes. Systems Pharmacology PHAR3320. Nerves of the Respiratory Tract. Dr Fernandes
 Systems Pharmacology PHAR3320 Nerves of the Respiratory Tract Dr Fernandes Learning Outcomes By the end of this lecture, students should be able to describe nerve pathways that innervate the airways discuss
Systems Pharmacology PHAR3320 Nerves of the Respiratory Tract Dr Fernandes Learning Outcomes By the end of this lecture, students should be able to describe nerve pathways that innervate the airways discuss
Epithelial cell death is an important contributor to oxidant-mediated acute lung injury SUPPORTING INFORMATION 60611, USA
 Epithelial cell death is an important contributor to oxidant-mediated acute lung injury SUPPORTING INFORMATION G.R. Scott Budinger 1,2 *, Gökhan M. Mutlu 1 *, Daniela Urich 2, Saul Soberanes 1, Leonard
Epithelial cell death is an important contributor to oxidant-mediated acute lung injury SUPPORTING INFORMATION G.R. Scott Budinger 1,2 *, Gökhan M. Mutlu 1 *, Daniela Urich 2, Saul Soberanes 1, Leonard
