Male median raphe cysts: serial retrospective analysis and histopathological classification
|
|
|
- Jewel Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Shao et al. Diagnostic Pathology 2012, 7:121 RESEARCH Open Access Male median raphe cysts: serial retrospective analysis and histopathological classification I-Hung Shao 1, Tai-Di Chen 2, Hsiang-Te Shao 3 and Hsiao-Wen Chen 1* Abstract Background: To review the clinical and pathological characteristics of median raphe cysts and to classify the lesions according to pathogenesis and histopathological findings. Methods: The medical records of patients who were diagnosed with median raphe cysts between 2001 and 2010 were reviewed to document the clinical presentation and pathological findings of the cysts. Results: Most patients were asymptomatic; however, 9 patients had inflammatory or infectious cysts that were tender or painful. Four patients who had cysts on the parameatus and distal prepuce had difficulty voiding. Hematuria and hematospermia were noted in 2 cases. Thirty-one cysts were lined with an urothelium-like epithelium, and a squamous epithelium lining was found in 3 cases. In 2 cases, a well-formed mucinous glandular structure was observed. The other 20 cysts consisted of mixed epithelia. After excision of the cysts under local or general anesthesia, an urethral fistula developed as a complication in only 1 case. Conclusions: Median raphe cysts are benign lesions formed due to tissue trapping during the development of urethral folds. The cysts can be defined into 4 types based on pathological findings: urethral, epidermoid, glandular, and mixed. The associated symptoms and signs should be taken into consideration when determining the treatment for the cysts. Virtual slides: The virtual slide(s) for this article can be found here: http// vs/ Keywords: Median raphe cyst, Paraurethral cyst, Male genitalia cyst, Penile cyst, Genitoperineal cysts, Pathological classification Background Median raphe cysts can develop at any site along the midline of the ventral side of the male genital area, from the meatus to the scrotum and perineum (Figure 1). In most patients, the cysts, which are asymptomatic or unrecognized during childhood, may progress later and become symptomatic during adolescence or adulthood. Although these cysts were first identified decades ago, only a few have been reported to date, mostly in case reports. The clinic pathological characteristics and pathogenesis of the disease are not well understood by physicians. In this study, we reviewed the medical records of patients with median raphe cysts to analyze * Correspondence: mhc1211@cgmh.org.tw 1 Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital and Chang Gung University College of Medicine, No.5, Fusing St., Gueishan Township, Taoyuan County 333, Taiwan Full list of author information is available at the end of the article the clinical characteristics and classify the histopathological findings. Methods We retrospectively reviewed the medical records, including the pathological diagnoses, of all patients with cysts on the median raphe (from the meatus to the perineum) diagnosed between 2001 and 2010 in our institution. Patients with epidermal inclusion cysts, skin tags, or cysts located anywhere other than the median raphe were excluded. Medical charts were reviewed to document the clinical presentation, characteristics of the cysts (including the occurrence site, cyst size, and histopathological findings), and patients outcomes. This study was approved by our institutional review board in Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Shao et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
2 Shao et al. Diagnostic Pathology 2012, 7:121 Page 2 of 5 Figure 1 Two synchronous cysts at the ventral side of the penile shaft of a 16-year-old patient. Results and discussion A total of 69 genital cysts from 68 patients were reviewed from 2001 to Ten epidermal inclusion cysts and 3 cystic tumors were excluded. A total of 55 patients (including a 16-year-old patient with synchronous cysts) had 56 median raphe cysts. The clinical characteristics are summarized in Table 1. The mean age of the patients was 26.7 years (range from newborn to 66 years), with a bimodal distribution at approximately 1 10 and years old (Figure 2). Most (72.7%) of the patients were asymptomatic, whereas 9 patients (16.4%) had inflammatory or infectious cysts, that were painful or tender. Another 4 patients with cysts on the parameatal site and distal prepuce had difficulty voiding. Hematuria or hematospermia occurred in 2 cases. Cysts were predominantly found on the parameatal site and penile shaft in 19 (33.9%) and 24 cases (42.9%). Lesions were found on the glands penis in 4 cases (7.1%) and on the scrotum and prepuce in 2 (3.6%) and 7 cases (12.7%), respectively. The mean size of the cysts was Table 1 General data and characteristics of patient Average age (range) 26.7 y/o (1 y/o 66 y/o) No. Age distribution (%) 0 ~ 10 y/o 14 (25.5) 11 ~ 20 y/o 6 (10.9) 21 ~ 30 y/o 11 (20.0) 31 ~ 40 y/o 12 (21.8) 41 ~ 50 y/o 6 (10.9) 51 ~ 60 y/o 4 (7.3) 61 ~ 70 y/o 2 (3.6) No. symptom/total No. (%) Pain / inflammation 9/55 (16.4) Difficult voiding 4/55 (7.3) Hematuria 1/55 (1.8) Hematospermia 1/55 (1.8) Asymptomatic 40/55 (72.7) No. location/total (%) Parameatus 19 (33.9) Glans penis 4 (7.1) Penile shaft 24 (42.9) Scrotum 2 (3.6) Prepuce 7 (12.7) Average diameter of the cyst in cetimeter (range) Parameatus 0.80 (0.2 ~ 3.0) Glans penis 0.95 (0.6 ~ 11.3) Penile shaft 0.79 (0.2 ~ 1.5) Scrotum 2.0 (1.9 ~ 2.1) Prepuce 0.92 (0.5 ~ 1.2) No. pathological type (%) Urethral type epithelium 31 (55.4) Epidermoid type epithelium 3 (5.4) Glandular type epithelium 2 (3.4) Mixed type epithelium 20 (35.7) No. complication / recurrence (%) Fistula 1 (1.8) None 54 (98.2) 0.88 cm, ranging from 0.2 to 2.1 cm. On histopathological examination, all the cysts were centered in the dermis and were not connected with either the epidermis or urethra. They exhibited cystic dilation and were irregularly shaped with clear mucinous content. The histological findings relating to the epithelium lining were varied, as 31 (55.4%) of 56 cysts were lined entirely with a urothelium-like epithelium (Figure 3), which is composed of a layer of columnar cells overlaid with uniform small cells arranged in stratified layers (1 to >10
3 Shao et al. Diagnostic Pathology 2012, 7:121 Page 3 of 5 Figure 2 Age distribution with bimodal characteristic. Figure 4 Squamous eputhelium in the median raphe cyst (Hematoxylin and eosin stain, 400X). layers). Apart from the absence of umbrella cells, the histological features of the epithelium were similar to those of the urothelium. A pure squamous epithelium lining was found in 3 cases (5.4%; Figure 4), and a wellformed intraepithelial mucinous glandular structure was found in 2 cases (3.4%; Figure 5). Twenty cases (35.7%) were of the mixed type, that is, the epithelial lining either coexisted with squamous metaplasia or was scattered with mucinous cells. Two cases had focal ciliated cell metaplasia (Figure 6). No surgical complications were encountered, except in 1 case where urethrocutaneous fistula formation occurred owing to long-term chronic inflammation adjacent to the urethra. Among the 55 patients, 1 underwent cyst aspiration, and recurrence was noted several months later. No signs of malignancy were found in any of the patients, either clinically or pathologically. Median raphe cysts develop along the median raphe of the male external genitalia, and such cysts have been described in case reports; however, serial reports of such cases are rare. In early studies, some cases were reported under varied terms including mucoid cyst, genitoperineal cyst, parameatal cyst, hydrocystoma, and apocrine cystadenoma. [1] The cysts can occur at any site on the ventral side of the genital area, including the parameatus, glans penis, penile shaft, scrotum, or perineum. Most of the cysts are diagnosed in young patients. Although referred to as median raphe cysts, they can also present as a cordlike or canaliform induration on the median raphe. Reports on such cases are even rarer in the literature [2]. The cysts should be differentiated from other genital lesions such as the glomus tumor, dermoid cyst, pilonidal cyst, epidermal inclusion cyst, urethral diverticulum, and steatocystoma [3]. Epidermal inclusion cysts, the most Figure 3 Urethral type epithelium, consisted with one layer of columnar cells overlying varying stratified layers of uniform small cells (Hematoxylin and eosin stain, 400X). Figure 5 A well-formed intraepithelial glandular structure in the lining of median raphe cyst, resembling Littré gland (Hematoxylin and eosin stain, 400X).
4 Shao et al. Diagnostic Pathology 2012, 7:121 Page 4 of 5 Figure 6 Ciliated cells in median raphe cysts, probably a metaplastic change secondary to local irritation (Hematoxylin and eosin stain, 400X). common genital cystic lesion, can occur anywhere on the body in adult men and women. Unlike the median raphe cyst, the epithelium of the epidermal inclusion cyst is lined and filled with keratin. The median raphe cyst can be easily differentiated from other skin tumors by its clinical presentation or pathological features. Median raphe cysts mostly present at birth and may remain asymptomatic or unrecognized during childhood [3]. As the patient grows older, the cyst may also progress slowly. Later in adolescence or adulthood, the cyst may appear as a solitary and movable cystic nodule on the ventral surface of the penis. In some cases, the cyst may progress rapidly or become symptomatic owing to infections or trauma, which could make diagnosis difficult [4,5]. In contrast, some cyts may grow rapidly even in the absence of trauma or infection [6]. However, in most cases, the lesions remain asymptomatic and do not interfere with urinary or sexual function [3]. This could be the reason for the bimodal distribution of the presentation: the patients were either presented to the physicians by their parents during childhood or they visited the physician themselves later in their 20s and 30s because they developed symptoms or mostly for cosmetic reasons. We also found that 12 of 18 cysts were located in the parameatus in the groups younger than 18 years, whereas only 7 of 38 cysts were found on the parameatal site in the group older than 18 years (Figure 7). A possible reason for this is that the cysts on the parameatal site could be easily noticed or were more likely to induce symptoms such as voiding difficulty, prompting parents or patients to seek treatment earlier. The cysts were asymptomatic in 72% of the patients, as most cysts were located on the proximal portion of the genitalia. The more distal the location of the cysts, the greater was the manifestation of symptoms, such as pain or difficulty voiding. Based on the histopathological Figure 7 Relationship between the age being diagnosed and the occurrence site. findings of our serial review, median raphe cysts can be classified into 4 types: urethral, epidermoid, glandular, and mixed. The urethral type is composed of a urothelium-like epithelium, with a layer of columnar cells overlaid with several stratified layers of uniform small cells; this is the most common type, accounting for 55% of all cases. The epidermoid type comprises a squamous epithelium and was noted in 5% of cases. The glandular type, consisting of a well-formed intraepithelial glandular structure in the lining of the urethral epithelium, accounted for 3% of cases. The second most common type, the mixed type, consists of more than 1 type of epithelium, including the urethral epithelium with partial squamous metaplasia, urethral epithelium with scattered or isolated mucinous cells, or all 3 occurring simultaneously, and was found in 35.7% of all cases. Nagore et al [3]. stated that the histomorphological features of the median raphe cyst are related to its embryonic origin and pathogenesis. The urethra forms as a result of fusion of the urethral folds and envelopment of the urethral groove during development. Tissue trapping could occur at this time or at a later stage either due to defective fusion of the urethral folds or anomalous outgrowths of the epithelium after primary closure [4]. The fossa navicularis is lined by a non keratinizing squamous epithelium that is similar and continuous to the epithelium covering the glands penis. The histogenesis of this squamous epithelium is explained by either ectodermal in growth or endodermal differentiation [7]. The epithelium of the distal urethra, except the fossa navicularis, is composed of a layer of columnar cells overlying 4 15 stratified layers of uniform small cells, usually categorized as a stratified or pseudo stratified epithelium. Differing from the classical features of the transitional urothelium of the proximal urethra, the nature of the anterior urethral lining appears to be related to that of the squamous epithelium. However, another theory proposed that median raphe cysts could also be caused during
5 Shao et al. Diagnostic Pathology 2012, 7:121 Page 5 of 5 development of the ectopic periurethral glands of Littre, which have clear mucinous cytoplasms and basally compressed nuclei resembling pyloric glands of the gastrointestinal tract [8]. This theory explains the presence of intraepithelial mucus cells and glandular structures in some cases. Median raphe cysts are supposed to be formed during the fusion of the urethral folds. Any trapped tissue outside the urethral groove may lead to anomalous outgrowths, thus resulting in the formation of cyst- or canal-like lesions in the median raphe of the genitalia. If the trapped tissue contains urothelium cells, the lining of the formed cyst would contain urethral epithelium. If non keratinizing squamous epithelium cells in the distal urethra are trapped, then we can expect the cyst to consist of an epidermoid epithelium. If the trapped tissue includes the periurethral glands, then the epithelium appears to be glandular. When 2 or more tissues are trapped and develop into outgrowths, cysts with mixed epithelia are formed. Ciliated cells in median raphe cysts are a rare finding, with only 5 cases reported in the English literature. The pathogenesisisprobablyametaplasticchangesecondarytoa local irritation [9,10]. Excision followed by primary closure, which establishes hemostasis and prevents infection or cosmetic sequelae, remains the optimal treatment. Given that oneofourpatientsdevelopedafistulaaftertheoperation, excision must be performed with caution when inflammation or adhesion is noted. However, spontaneous regression of the cyst has also been reported, [11] and observation can be considered for those who hesitate to undergo surgery for small and asymptomatic lesions. One patient received aspiration, and recurrence of the cyst was noted a few months later. Thus, simple aspiration alone is not recommended as a treatment for median raphe cysts. Further, marsupialization or unroofing performed in cases of deeply located large cysts, will result in a gaping sinus, which is cosmetically unsatisfactory, and these procedures should be avoided [12]. Conclusions The histopathological features of median raphe cysts are varied and can be classified into 4 types of cell manifestations. The diversification of the epithelium may be due to a congenital anomaly of the genitalia, with remnants of embryogenesis or acquired metaplasia of the genitalia. However, no malignant potentiality was observed during long-term follow-up in our study. The associated symptoms and signs should be considered in the treatment of these cysts. Competing interests There are no competing interests in this study. Author s contributions IHS carried out the preparation of the manuscript draft and participated in the analysis and interpretation of the data. TDC reviewed the pathological results and analyzed and interpreted the data. STS participated in the data collection. HWC participated in the revision and editing of the manuscript. IHS and TDC contributed equally to this study. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript. Author details 1 Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital and Chang Gung University College of Medicine, No.5, Fusing St., Gueishan Township, Taoyuan County 333, Taiwan. 2 Department of Pathology, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital and Chang Gung University College of Medicine, No.5, Fusing St., Gueishan Township, Taoyuan County 333, Taiwan. 3 Division of Dermatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Taipei City Hospital, Renai Branch, No.145, Zhengzhou Rd., Datong Dist., Taipei City 103, Taiwan. Received: 17 June 2012 Accepted: 2 September 2012 Published: 14 September 2012 References 1. Otsuka T, Ueda Y, Terauchi M, Kinoshita Y: Median raphe (parameatal) cysts of the penis. J Urol 1998, 159: Verma SB: Canal-like median raphe cysts: an unusual presentation of an unusual condition. Clin Exp Dermatol 2009, 34:e857 e Nagore E, Sanchez-Motilla JM, Febrer MI, Aliaga A: Median raphe cysts of the penis: a report of five cases. Pediatr Dermatol 1998, 15: Krauel L, Tarrado X, Garcia-Aparicio L, Lerena J, Sunol M, Rodo J, Ribo JM: Median raphe cysts of the perineum in children. Urology 2008, 71: Soendjojo A, Pindha S: Trichomonas vaginalis infection of the median raphe of the penis. Sex Transm Dis 1981, 8: Cardoso R, Freitas JD, Reis JP, Tellechea O: Median raphe cyst of the penis. Dermatol Online J 2005, 11: Kurzrock EA, Baskin LS, Cunha GR: Ontogeny of the male urethra: theory of endodermal differentiation. Differentiation 1999, 64: Dini M, Baroni G, Colafranceschi M: Median raphe cyst of the penis: a report of two cases with immunohistochemical investigation. Am J Dermatopathol 2001, 23: Koga K, Yoshida Y, Koga M, Takeshita M, Nakayama J: Median raphe cyst with ciliated cells of the penis. Acta Derm Venereol 2007, 87: Romani J, Barnadas MA, Miralles J, Curell R, de Moragas JM: Median raphe cyst of the penis with ciliated cells. J Cutan Pathol 1995, 22: Willis HL, Snow BW, Cartwright PC, Wallis MC, Oottamasathien S, DeVries C: Parameatal urethral cysts in prepubertal males. J Urol 2011, 185: Shiraki IW: Parametal cysts of the glans penis: a report of 9 cases. J Urol 1975, 114: doi: / Cite this article as: Shao et al.: Male median raphe cysts: serial retrospective analysis and histopathological classification. Diagnostic Pathology :121. Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Epithelial abnormalities and precancerous lesions of anterior urethra in patients with penile carcinoma: a report of 89 cases
 & 2005 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/05 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Epithelial abnormalities and precancerous lesions of anterior urethra in patients with penile carcinoma: a report of 89
& 2005 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/05 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Epithelial abnormalities and precancerous lesions of anterior urethra in patients with penile carcinoma: a report of 89
Normal Morphology. Anatomic Considerations. Normal Urothelial Histology and Cytology
 1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
1 Normal Morphology Anatomic Considerations The urinary tract can be divided into three regions: the kidney; the calyces, pelves and ureters (upper collecting system or upper tract); and the bladder and
Histology: Epithelial tissue
 Histology: Epithelial tissue Epithelial Tissue is presented in two forms: 1. Covering Epithelia: 2. Glandular Epithelia: 1. Simple Epithelium: contain only one layer of cells. 2. Stratified Epithelium:
Histology: Epithelial tissue Epithelial Tissue is presented in two forms: 1. Covering Epithelia: 2. Glandular Epithelia: 1. Simple Epithelium: contain only one layer of cells. 2. Stratified Epithelium:
CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT
 Mucocele and epidermoid cyst CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT Wen-Chen Wang, Li-Min Lin, Yee-Hsiung Shen, 1 Yu-Ju Lin, and Yuk-Kwan Chen Departments
Mucocele and epidermoid cyst CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT Wen-Chen Wang, Li-Min Lin, Yee-Hsiung Shen, 1 Yu-Ju Lin, and Yuk-Kwan Chen Departments
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Thyroglossal cyst our experience
 Volume 3 Issue 1 2013 ISSN: 2250-0359 Thyroglossal cyst our experience Balasubramanian Thiagarajan 1 Ulaganathan Venkatesan 2 Geetha Ramamoorthy 1 1 Stanley Medical College 2 Meenakshi Medical College
Volume 3 Issue 1 2013 ISSN: 2250-0359 Thyroglossal cyst our experience Balasubramanian Thiagarajan 1 Ulaganathan Venkatesan 2 Geetha Ramamoorthy 1 1 Stanley Medical College 2 Meenakshi Medical College
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the vulva
 Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
Diseases of the vulva 1. Bartholin Cyst - Infection of the Bartholin gland produces an acute inflammation within the gland (adenitis) and may result in an abscess. Bartholin duct cysts - Are relatively
Bio & 241 A&P Unit 1 / Lecture 3
 Bio & 241 A&P Unit 1 / Lecture 3 Tissues All body tissues arise from three fundamental embryonic tissues. Endoderm: forms epithelial tissues lining internal organs such as the GI tract Mesoderm: connective
Bio & 241 A&P Unit 1 / Lecture 3 Tissues All body tissues arise from three fundamental embryonic tissues. Endoderm: forms epithelial tissues lining internal organs such as the GI tract Mesoderm: connective
A CASE OF DUPLICATION OF PENILE URETHRA. Stoke Mandeville
 A CASE OF DUPLICATION OF PENILE URETHRA By J. P. REIDY, F.R.C.S. Stoke Mandeville THIS congenital deformity is of rare occurrence. Gross and Moore (195o) summarised the findings of eighty-three cases.
A CASE OF DUPLICATION OF PENILE URETHRA By J. P. REIDY, F.R.C.S. Stoke Mandeville THIS congenital deformity is of rare occurrence. Gross and Moore (195o) summarised the findings of eighty-three cases.
Epithelial Tissue. Functions include: 1. Protection 4. Absorption 2. Secretion 5. Filtration 3. Sensory reception
 Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
Epidermoid Cyst of the Ovary
 Epidermoid Cyst of the Ovary A eport of Three Cases with Comments on Histogenesis OBET H. YOUNG, M.B., JAIME PAT, M.D., AND OBET E. SCUY, M.D. Young, obert H., Prat, Jaime, and Scully, obert E.: Epidermoid
Epidermoid Cyst of the Ovary A eport of Three Cases with Comments on Histogenesis OBET H. YOUNG, M.B., JAIME PAT, M.D., AND OBET E. SCUY, M.D. Young, obert H., Prat, Jaime, and Scully, obert E.: Epidermoid
A classification of epithelial tissues
 A classification of epithelial tissues Ramray Bhat Molecular Reproduction Development and Genetics ramray@iisc.ac.in Textbooks for my portion Molecular Biology of the Cell (Bruce Alberts) 6 th Edition
A classification of epithelial tissues Ramray Bhat Molecular Reproduction Development and Genetics ramray@iisc.ac.in Textbooks for my portion Molecular Biology of the Cell (Bruce Alberts) 6 th Edition
Development of the urinary system
 Development of the urinary system WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. 3 sets of kidneys developing in succession (temporally and spatially) : Pronephros ] Mesonephros ]- Intermediate
Development of the urinary system WSO School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. 3 sets of kidneys developing in succession (temporally and spatially) : Pronephros ] Mesonephros ]- Intermediate
Case Report Müllerian Serous Cystadenoma of the Scrotum Following Orchiopexy
 Advances in Urology Volume 009, Article ID 610453, 4 pages doi:10.1155/009/610453 Case Report Müllerian Serous Cystadenoma of the Scrotum Following Orchiopexy Sebastian C. J. van der Putte, 1 Johan Toonstra,
Advances in Urology Volume 009, Article ID 610453, 4 pages doi:10.1155/009/610453 Case Report Müllerian Serous Cystadenoma of the Scrotum Following Orchiopexy Sebastian C. J. van der Putte, 1 Johan Toonstra,
Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy: a case report
 Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
Hypospadias. Laurence S. Baskin, M.D. Chief, Pediatric Urology University of California, San Francisco
 UCSF Pediatric Urology Center for the Study and Treatment of Hypospadias Written for Pediatricians, Family Practitioners, Nurse Practitioners, Health Care Workers and Families of Patients with Hypospadias
UCSF Pediatric Urology Center for the Study and Treatment of Hypospadias Written for Pediatricians, Family Practitioners, Nurse Practitioners, Health Care Workers and Families of Patients with Hypospadias
Redo hypospadias surgery; experience with 27 patients with prior distal or proximal hypospadias repair failure
 Redo hypospadias surgery; experience with 27 patients with prior distal or proximal hypospadias repair failure Ula Al-Kawaz FIBMS; FEBU. Abstract Background :Urethral reconstruction in failed hypospadias
Redo hypospadias surgery; experience with 27 patients with prior distal or proximal hypospadias repair failure Ula Al-Kawaz FIBMS; FEBU. Abstract Background :Urethral reconstruction in failed hypospadias
Cell and Tissue Types. Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve
 Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Development of the Urinary System
 Development of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Understand the development of the kidney and related organs of the urinary system. Define the pronephrons, mesonephrons and metanephrons. Understand
Development of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Understand the development of the kidney and related organs of the urinary system. Define the pronephrons, mesonephrons and metanephrons. Understand
Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts
 77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
77 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 47, No. 2, 77-81, 2005 Original Mucous and ciliated cell metaplasia in epithelial linings of odontogenic inflammatory and developmental cysts Yasunori Takeda, Yuko Oikawa,
PRACTICAL ROADMAP EPITHELIUM A. JOVANOVIĆ
 PRACTICAL ROADMAP EPITHELIUM A. JOVANOVIĆ Epithelia Simple epithelia Stratified epithelia Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Pseudostratified Stratified squamous - non keratinized - keratinized
PRACTICAL ROADMAP EPITHELIUM A. JOVANOVIĆ Epithelia Simple epithelia Stratified epithelia Simple squamous Simple cuboidal Simple columnar Pseudostratified Stratified squamous - non keratinized - keratinized
THE USE OF DEEPITHELIALIZATION
 THE USE OF DEEPITHELIALIZATION IN URETHROPLASTY - Deepithelialization Stratum corneum - Epidermis Papillary dermis Reticular dermis Skin Healing in any reconstructive surgery depends on not only the intact
THE USE OF DEEPITHELIALIZATION IN URETHROPLASTY - Deepithelialization Stratum corneum - Epidermis Papillary dermis Reticular dermis Skin Healing in any reconstructive surgery depends on not only the intact
Snodgrass Urethroplasty for Mid and Distal Penile Hypospadias. Ahmed Z. Zain FIBMS
 Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine P-ISSN 68-659 E-ISSN 2224-49 Email: iraqijms@colmed-alnahrain.edu.iq http://www.colmed-alnahrain.edu.iq http://www.iraqijms.net Iraqi JMS 2; Vol. 5(3)
Iraqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine P-ISSN 68-659 E-ISSN 2224-49 Email: iraqijms@colmed-alnahrain.edu.iq http://www.colmed-alnahrain.edu.iq http://www.iraqijms.net Iraqi JMS 2; Vol. 5(3)
Combined Use of Mathieu and Incised Plate Technique for Repair of Distal Hypospadias
 Original Article Annals of Pediatric Surgery Vol 5, No 2, April 2009, PP 141-145 Combined Use of Mathieu and Incised Plate Technique for Repair of Distal Hypospadias Hisahm Fayad Aly Pediatric Surgery
Original Article Annals of Pediatric Surgery Vol 5, No 2, April 2009, PP 141-145 Combined Use of Mathieu and Incised Plate Technique for Repair of Distal Hypospadias Hisahm Fayad Aly Pediatric Surgery
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors
 Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Origin of Odontogenic Cysts & Tumors Odontogenic Apparatus Remnants of dental lamina Reduced enamel epithelium Odontogenic rests Basal cell layer
Epithelium-1. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Epithelium-1 Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD General features Epithelium is an avascular tissue composed of cells that cover the exterior body surfaces and line internal closed cavities and tubes. It also forms
Epithelium-1 Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD General features Epithelium is an avascular tissue composed of cells that cover the exterior body surfaces and line internal closed cavities and tubes. It also forms
CASE 4 21/07/2017. Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix. Female 31. LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities
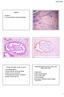 Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
Female 31 CASE 4 LLETZ for borderline nuclear abnormalities PSA Ectopic Prostatic Tissue in Cervix AJSP 2006;30;209-215 usually incidental microscopic finding usually in ectocervical stroma? developmental
Symptomatic Male Urethral Diverticula- Presentation, Diagnosis and Management
 Original article Symptomatic Male Urethral Diverticula- Presentation, Diagnosis and Management Ratkal JM 1, Elias Sharma 2 1Associate Professor, Department of Urology, KIMS, Hubli 2Asst Professor, Department
Original article Symptomatic Male Urethral Diverticula- Presentation, Diagnosis and Management Ratkal JM 1, Elias Sharma 2 1Associate Professor, Department of Urology, KIMS, Hubli 2Asst Professor, Department
Neck lumps in children
 Neck lumps in children Midline Lateral Midline neck lumps Thyroglossal cyst - 80% Dermoid cyst Submental lymph node Ectopic thyroid Some rare lesions Thyroglossal cyst Diagnosis: midline, usually overlying
Neck lumps in children Midline Lateral Midline neck lumps Thyroglossal cyst - 80% Dermoid cyst Submental lymph node Ectopic thyroid Some rare lesions Thyroglossal cyst Diagnosis: midline, usually overlying
PRACTICAL HISTOLOGY LAB
 PRACTICAL HISTOLOGY LAB.1 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- INTRODUCTION Cells are the smallest units of life, and are named according to their function. Cells
PRACTICAL HISTOLOGY LAB.1 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- INTRODUCTION Cells are the smallest units of life, and are named according to their function. Cells
CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Biology Histology: Histology: is the study of the tissues of the body. Tissue: group of similar cells combined to perform a common function. The human body is composed of only 4 basic
Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Biology Histology: Histology: is the study of the tissues of the body. Tissue: group of similar cells combined to perform a common function. The human body is composed of only 4 basic
Schwannomas (also known as neurilemmomas)
 Case Report 555 Schwannoma of the Penis: A Report of Two Cases Chi-Ju Yeh, MD; Wen-Yu Chuang, MD; Shih-Tsung Huang 1, MD; Shih-Ming Jung, MD Schwannomas are benign nerve sheath tumors, which can occur
Case Report 555 Schwannoma of the Penis: A Report of Two Cases Chi-Ju Yeh, MD; Wen-Yu Chuang, MD; Shih-Tsung Huang 1, MD; Shih-Ming Jung, MD Schwannomas are benign nerve sheath tumors, which can occur
TISSUES. Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 TISSUES Dr. Gary Mumaugh Tissues Tissues - Groups of cells similar in structure and function and perform a common function Histology The study of tissues The four types of tissues Epithelial Connective
TISSUES Dr. Gary Mumaugh Tissues Tissues - Groups of cells similar in structure and function and perform a common function Histology The study of tissues The four types of tissues Epithelial Connective
TISSUES TYPES. CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
Case MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve
 Case 12688 MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve Hidayatullah Hamidi Third year Resident of Radiology French medical institute for children Radiology Department; Kabul, Afghanistan;
Case 12688 MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve Hidayatullah Hamidi Third year Resident of Radiology French medical institute for children Radiology Department; Kabul, Afghanistan;
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Teratoma. Portion of a teratoma composed of neural tissue. The large cells in the central part correspond to ganglion cells.
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Teratoma. The tumor is composed predominantly of keratinizing squamous epithelium (Sq), which forms cysts filled with keratin (arrows). The tumor also contains
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Teratoma. The tumor is composed predominantly of keratinizing squamous epithelium (Sq), which forms cysts filled with keratin (arrows). The tumor also contains
Epithelial Lecture Test Questions
 Epithelial Lecture Test Questions 1. Which of the following free surfaces lack(s) epithelia: a. lung alveoli (air sacs) b. hard palate c. joint cavities d. abdominal cavity e. salivary gland ducts 2. Which
Epithelial Lecture Test Questions 1. Which of the following free surfaces lack(s) epithelia: a. lung alveoli (air sacs) b. hard palate c. joint cavities d. abdominal cavity e. salivary gland ducts 2. Which
Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD
 Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD SUNY-LICH Medical Center Department of Surgery Case Presentation xx year old male presents with sudden onset left lower neck swelling x 1 week Denies pain,
Congenital Neck Masses C. Stefan Kénel-Pierre, MD SUNY-LICH Medical Center Department of Surgery Case Presentation xx year old male presents with sudden onset left lower neck swelling x 1 week Denies pain,
Objectives. 1. Recognizing benign skin lesions. 2.Know which patients will likely need surgical intervention.
 The Joy of Pediatric Skin Dr. Claire Sanger University of Kentucky Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery Objectives 1. Recognizing benign skin lesions 2.Know which patients will likely need surgical intervention.
The Joy of Pediatric Skin Dr. Claire Sanger University of Kentucky Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery Objectives 1. Recognizing benign skin lesions 2.Know which patients will likely need surgical intervention.
Giant condyloma acuminata: Incidence among cases diagnosed as carcinoma of the penis
 J. clin. Path. (1965), 18, 142 Giant condyloma acuminata: Incidence among cases diagnosed as carcinoma of the penis SYLVIA W. DAVIES From the Department of Pathology, University of Liverpool SYNOPSIS Twenty-four
J. clin. Path. (1965), 18, 142 Giant condyloma acuminata: Incidence among cases diagnosed as carcinoma of the penis SYLVIA W. DAVIES From the Department of Pathology, University of Liverpool SYNOPSIS Twenty-four
Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
يراهظلا( يئلاطلا جيسنلا
 Epithelium النسيج الطالئي )الظهاري( Features of Epithelium Epithelium occurs in the body as a sheet of cells that covers a body surface, lines a cavity, or forms a gland. Coverings, linings, glands. Derived
Epithelium النسيج الطالئي )الظهاري( Features of Epithelium Epithelium occurs in the body as a sheet of cells that covers a body surface, lines a cavity, or forms a gland. Coverings, linings, glands. Derived
Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 742920, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/742920 Case Report A Rare Cutaneous Adnexal Tumor: Malignant Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor Omer Alici,
Vascular Related Torsion Venous compression Hemorrhagic infarct Young men At night Very painful Can be reduced Scrotal Masses Testicular Tumors (solid
 Pathology of the Male Reproductive System Testis and Epididymis Failure of Testis to Descend Testis are not always in scrotum at birth. Testes from in abdomen with kidneys Migrate to scrotum May get stuck
Pathology of the Male Reproductive System Testis and Epididymis Failure of Testis to Descend Testis are not always in scrotum at birth. Testes from in abdomen with kidneys Migrate to scrotum May get stuck
Japanese Neurogenic Bladder Society Meeting. Kofu - Japan. September 29th - October 1st, 2010
 Japanese Neurogenic Bladder Society Meeting Kofu - Japan September 29th - October 1st, 2010 Reconstruction of penile and bulbar urethra Evaluation of anterior urethral stricture Urethrography Retrograde
Japanese Neurogenic Bladder Society Meeting Kofu - Japan September 29th - October 1st, 2010 Reconstruction of penile and bulbar urethra Evaluation of anterior urethral stricture Urethrography Retrograde
Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric: Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and function Types of tissues Epithelial
ATLAS OF HEAD AND NECK PATHOLOGY METAPLASIA
 Metaplasia is the conversion of one adult differentiated cell type to another. Generally it is the result of persistent cellular trauma and serves as a protective mechanism. Thus anteriorly along the nasal
Metaplasia is the conversion of one adult differentiated cell type to another. Generally it is the result of persistent cellular trauma and serves as a protective mechanism. Thus anteriorly along the nasal
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Tissue: is a group of cells that serve the same function, they are surrounded by extra cellular matrix. The 4 basic types of tissue: 1. epithelial
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Tissue: is a group of cells that serve the same function, they are surrounded by extra cellular matrix. The 4 basic types of tissue: 1. epithelial
Dr. Abeer.c.Yousif. Histology -2 nd stage. What is histology?
 What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
CYTOMORPHOLOGY MODULE 28.1 INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 28.2 GENERAL GUIDELINES. Notes
 28 CYTOMORPHOLOGY 28.1 INTRODUCTION Light microscopic examination of stained cells in smears is the method of choice of diagnostic cytology. It allows classification of most normal cells as to type and
28 CYTOMORPHOLOGY 28.1 INTRODUCTION Light microscopic examination of stained cells in smears is the method of choice of diagnostic cytology. It allows classification of most normal cells as to type and
Diseases of the penis & testis
 Diseases of the penis & testis Done by : Saef B AL-Abbadi Diseases of penis, Condyloma Acuminatum A benign tumor *Tend to recur but only rarely progress into in situ or invasive cancers read this = genital
Diseases of the penis & testis Done by : Saef B AL-Abbadi Diseases of penis, Condyloma Acuminatum A benign tumor *Tend to recur but only rarely progress into in situ or invasive cancers read this = genital
Patient Information. Age: 8 y/o Sex: Female. Date of Admission: Date of Discharge:
 Patient Information Age: 8 y/o Sex: Female Date of Admission: 92-10-08 Date of Discharge: 92-10-18 Chief Complaint Severe admominal pain and vomiting with dysuria since last afternoon Present Illness Lower
Patient Information Age: 8 y/o Sex: Female Date of Admission: 92-10-08 Date of Discharge: 92-10-18 Chief Complaint Severe admominal pain and vomiting with dysuria since last afternoon Present Illness Lower
Trichofolliculoma of the Guinea Pig 1,2
 Trichofolliculoma of the Guinea Pig 1,2 Raymond D. Ediger, Garrett S. Dill, Jr., and Robert M. Kovatch, Aerobiology and Evaluation Laboratories and Medical Sciences Laboratories, Fort Detrick, Frederick,
Trichofolliculoma of the Guinea Pig 1,2 Raymond D. Ediger, Garrett S. Dill, Jr., and Robert M. Kovatch, Aerobiology and Evaluation Laboratories and Medical Sciences Laboratories, Fort Detrick, Frederick,
Histology = the study of tissues. Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function
 { EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
{ EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
Abstract. Keywords. Results of Onlay Flap Versus Durham Smith in Proximal Hypospadias. Ahmad Khaleghnejad Tabri 1
 33 Results of Onlay Flap Versus Durham... Noroozi et al. Original 33 Results of Onlay Flap Versus Durham Smith in Proximal Hypospadias Ahmad Khaleghnejad Tabri 1 Leily Mohajerzadeh 1 Saran Lotfollahzadeh
33 Results of Onlay Flap Versus Durham... Noroozi et al. Original 33 Results of Onlay Flap Versus Durham Smith in Proximal Hypospadias Ahmad Khaleghnejad Tabri 1 Leily Mohajerzadeh 1 Saran Lotfollahzadeh
Lichen Sclerosus and Isolated Bulbar Urethral Stricture Disease
 Lichen Sclerosus and Isolated Bulbar Urethral Stricture Disease Joceline S. Liu,* Kelly Walker, Daniel Stein, Sanjiv Prabhu, Matthias D. Hofer, Justin Han, Ximing J. Yang and Chris M. Gonzalez Departments
Lichen Sclerosus and Isolated Bulbar Urethral Stricture Disease Joceline S. Liu,* Kelly Walker, Daniel Stein, Sanjiv Prabhu, Matthias D. Hofer, Justin Han, Ximing J. Yang and Chris M. Gonzalez Departments
Basic Tissue Types and Functions
 Tissues Histology Basic Tissue Types and Functions 1) Epithelial tissue covering 2) Connective tissue support 3) Muscle tissue movement 4) Nervous tissue control Epithelial Tissue 1) Covers a body surface
Tissues Histology Basic Tissue Types and Functions 1) Epithelial tissue covering 2) Connective tissue support 3) Muscle tissue movement 4) Nervous tissue control Epithelial Tissue 1) Covers a body surface
Pathology Slides. [Pathology]
![Pathology Slides. [Pathology] Pathology Slides. [Pathology]](/thumbs/94/120604575.jpg) Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
Pathology Slides MedicoNotes provides real laboratory pathological slides to aid you to differentiate between different pathological structures under microscope. www.mediconotes.com Histology slides example
An Anteriorly Positioned Midline Prostatic Cyst Resulting in Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms
 Case Report INJ 2010;14:125-129 An Anteriorly Positioned Midline Prostatic Cyst Resulting in Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Joo-Yong Lee, Dong-Hyuk Kang, Hee-Young Park, Jung-Soo Park, Young-Woo Son, Hong-Sang
Case Report INJ 2010;14:125-129 An Anteriorly Positioned Midline Prostatic Cyst Resulting in Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Joo-Yong Lee, Dong-Hyuk Kang, Hee-Young Park, Jung-Soo Park, Young-Woo Son, Hong-Sang
Lecture Overview. Chapter 4 Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues. Epithelial Tissues. Glandular Epithelium
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Case Report The Cutaneous Ciliated Cyst in Young Male: The Possibility of Ciliated Cutaneous Eccrine Cyst
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 589831, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/589831 Case Report The Cutaneous Ciliated Cyst in Young Male: The Possibility of Ciliated Cutaneous Eccrine
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 589831, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/589831 Case Report The Cutaneous Ciliated Cyst in Young Male: The Possibility of Ciliated Cutaneous Eccrine
Histology Notes -Part 1: Epithelial Tissues
 Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Introduction Group of cells w/ similar structure & function = TISSUE Four Basic Tissue Types 1. Epithelial-covers 2. Connective-supports 3. Muscular*-produces movement (will discuss in the muscular system
Epithelium tissue system
 Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
Our Experience in Chordee without Hypospadias: Results
 PEDIATRIC UROLOGY Our Experience in Chordee without Hypospadias: Results of 102 Cases Emre Can Polat, 1 Mehmet Remzi Erdem, 2 Ramazan Topaktas, 3 Cevper Ersoz, 4 Sinasi Yavuz Onol 5 1 Department of Urology,
PEDIATRIC UROLOGY Our Experience in Chordee without Hypospadias: Results of 102 Cases Emre Can Polat, 1 Mehmet Remzi Erdem, 2 Ramazan Topaktas, 3 Cevper Ersoz, 4 Sinasi Yavuz Onol 5 1 Department of Urology,
Urethroplasty for Long Anterior Urethral Strictures Report of Long-term Results
 Reconstructive Surgery Urethroplasty for Long Anterior Urethral Strictures Report of Long-term Results Mahmoudreza Moradi, As ad Moradi Introduction: We reviewed the long-term outcome of substitution urethroplasty
Reconstructive Surgery Urethroplasty for Long Anterior Urethral Strictures Report of Long-term Results Mahmoudreza Moradi, As ad Moradi Introduction: We reviewed the long-term outcome of substitution urethroplasty
Pediatric Urology. Access Center 24/7 access for referring physicians (866) 353-KIDS (5437)
 Pediatric Urology The Urology practice at Valley Children s provides specialized care for infants, children and adolescents with genital and urological problems. In addition to pediatric urologists, the
Pediatric Urology The Urology practice at Valley Children s provides specialized care for infants, children and adolescents with genital and urological problems. In addition to pediatric urologists, the
Dorsal tunica vaginalis graft plus onlay preputial island flap urethroplasty: Experimental study in rabbits
 Journal of Pediatric Urology (2009) 5, 93e99 Dorsal tunica vaginalis graft plus onlay preputial island flap urethroplasty: Experimental study in rabbits Bruno Leslie a, Luiz L. Barboza a, Petrus O. Souza
Journal of Pediatric Urology (2009) 5, 93e99 Dorsal tunica vaginalis graft plus onlay preputial island flap urethroplasty: Experimental study in rabbits Bruno Leslie a, Luiz L. Barboza a, Petrus O. Souza
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Very late recurrence of sinus of Valsalva aneurysm rupture after patch repair
 Lin et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:73 CASE REPORT Open Access Very late recurrence of sinus of Valsalva aneurysm rupture after patch repair Ting-Tse Lin 1, Hsiao-En Tsai 2, Lin Lin 1, Tsung-Yan Chen 2, Cheng-Pin
Lin et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:73 CASE REPORT Open Access Very late recurrence of sinus of Valsalva aneurysm rupture after patch repair Ting-Tse Lin 1, Hsiao-En Tsai 2, Lin Lin 1, Tsung-Yan Chen 2, Cheng-Pin
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio 101 Laboratory 3. Epithelial Tissues and Integument
 Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
How I Do It - Evaluation of the Urethra
 How I Do It - Evaluation of the Urethra Parvati Ramchandani, MD Professor, Radiology and Surgery University of Pennsylvania Medical Center Philadelphia, PA, USA Disclosure of Commercial Interest Neither
How I Do It - Evaluation of the Urethra Parvati Ramchandani, MD Professor, Radiology and Surgery University of Pennsylvania Medical Center Philadelphia, PA, USA Disclosure of Commercial Interest Neither
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia
 Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
3/28/2017. Head and Neck/Endocrine Pathology Specialty Conference Case 4 Raja R. Seethala, M.D. University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
 Head and Neck/Endocrine Pathology Specialty Conference Case 4 Raja R. Seethala, M.D. University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships Disclosure of Relevant Financial
Head and Neck/Endocrine Pathology Specialty Conference Case 4 Raja R. Seethala, M.D. University of Pittsburgh Medical Center Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships Disclosure of Relevant Financial
Metachronous anterior urethral metastasis of prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma
 http://dx.doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2016.31.1.66 KMJ Case Report Metachronous anterior urethral metastasis of prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma Jeong Hyun Oh 1, Taek Sang Kim 1, Hyun Yul Rhew 1, Bong Kwon Chun
http://dx.doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2016.31.1.66 KMJ Case Report Metachronous anterior urethral metastasis of prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma Jeong Hyun Oh 1, Taek Sang Kim 1, Hyun Yul Rhew 1, Bong Kwon Chun
Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
 Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
Ann Dermatol Vol. 23, Suppl. 2, 2011 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.s2.s226 CASE REPORT Acantholytic Anaplastic Extramammary Paget s Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Literature Yu-Jin Oh,
OVARIES. MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L13 Dr: Ali Eltayb.
 OVARIES MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L13 Dr: Ali Eltayb. OBJECTIVES Recognize different disease of ovaries Classify ovarian cyst Describe the pathogenesis, morphology
OVARIES MLS Basic histological diagnosis MLS HIST 422 Semester 8- batch 7 L13 Dr: Ali Eltayb. OBJECTIVES Recognize different disease of ovaries Classify ovarian cyst Describe the pathogenesis, morphology
Midgut. Over its entire length the midgut is supplied by the superior mesenteric artery
 Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Cystoscopy in children presenting with hematuria should not be overlooked
 Ped Urol Case Rep 2015; 2(3):7-11 DOI: 10.14534/PUCR.2015310303 PUCR Ped Urol Case Rep PEDIATRIC UROLOGY CASE REPORTS ISSN: 2148 2969 Journal homepage: http://www.pediatricurologycasereports.com Cystoscopy
Ped Urol Case Rep 2015; 2(3):7-11 DOI: 10.14534/PUCR.2015310303 PUCR Ped Urol Case Rep PEDIATRIC UROLOGY CASE REPORTS ISSN: 2148 2969 Journal homepage: http://www.pediatricurologycasereports.com Cystoscopy
Mucin-producing urothelial-type adenocarcinoma of prostate: report of two cases of a rare and diagnostically challenging entity
 & 2005 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/05 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Mucin-producing urothelial-type adenocarcinoma of prostate: report of two cases of a rare and diagnostically challenging
& 2005 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/05 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Mucin-producing urothelial-type adenocarcinoma of prostate: report of two cases of a rare and diagnostically challenging
BASAL CELL CARCINOMA WITH ECCRINE DIFFERENTIATION: A RARE ENTITY Divvya B 1, Rehana Tippoo 2, P. Viswanathan 3, B. Krishnaswamy 4, A.
 BASAL CELL CARCINOMA WITH ECCRINE DIFFERENTIATION: A RARE ENTITY Divvya B 1, Rehana Tippoo 2, P. Viswanathan 3, B. Krishnaswamy 4, A. Anvar Ali 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Divvya B, Rehana Tippoo, P. Viswanathan,
BASAL CELL CARCINOMA WITH ECCRINE DIFFERENTIATION: A RARE ENTITY Divvya B 1, Rehana Tippoo 2, P. Viswanathan 3, B. Krishnaswamy 4, A. Anvar Ali 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Divvya B, Rehana Tippoo, P. Viswanathan,
A adipose cells. B capillary. C epithelium
 EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
Concurrent Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma and Leiomyoma in the Same Kidney: Previously Unreported Association
 218 Concurrent Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma and Leiomyoma in the Same Kidney: Previously Unreported Association Min Su Cheong a Dong Hun Koo a In-Sung Kim a Kyung Chul Moon b Ja Hyeon Ku a
218 Concurrent Multilocular Cystic Renal Cell Carcinoma and Leiomyoma in the Same Kidney: Previously Unreported Association Min Su Cheong a Dong Hun Koo a In-Sung Kim a Kyung Chul Moon b Ja Hyeon Ku a
41 st Scientific Congress. Gdańsk Poland
 41 st Scientific Congress Gdańsk Poland 8 10 September 2011 The Team Sl Salvatore Sansalone Giuseppe Romano Sofia Balò Problems of urethral stricture in adult male after penile and urethral reconstructive
41 st Scientific Congress Gdańsk Poland 8 10 September 2011 The Team Sl Salvatore Sansalone Giuseppe Romano Sofia Balò Problems of urethral stricture in adult male after penile and urethral reconstructive
Tissue: The Living Fabric
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb Chapter 4 Tissue: The Living Fabric Part A Tissues Groups of cells similar in structure and
B. Cystic Teratoma: Refer to virtual microscope slide p_223 ovary, teratoma and compare to normal virtual microscope slide 086 ovary.
 LAB 2: THE CONNECTIVE TISSUE AND EPITHELIUM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of connective tissue and epithelium. The lab will introduce you to the four basic tissue types: epithelium, connective
LAB 2: THE CONNECTIVE TISSUE AND EPITHELIUM The focus of this week s lab will be pathology of connective tissue and epithelium. The lab will introduce you to the four basic tissue types: epithelium, connective
Introduction. Results. Discussion. Histopathologic and immunohistochemical findings. Results. conclusions,
 1/5 2/5 Carcinoma distinctive carcinoma. form erysipeloides (CE), metastasis. which clinically Itfrom has resembles been termed erysipelas, is an uncommon, but may extend It164 toclassically back, presents
1/5 2/5 Carcinoma distinctive carcinoma. form erysipeloides (CE), metastasis. which clinically Itfrom has resembles been termed erysipelas, is an uncommon, but may extend It164 toclassically back, presents
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas
 CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
CINtec p16 INK4a Staining Atlas Rating Rating Positive The rating positive will be assigned if the p16 INK4a -stained slide shows a continuous staining of cells of the basal and parabasal cell layers of
Muco-epidermoid tumours of the anal canal
 J. clin. Path. (1963), 16, 200 Muco-epidermoid tumours of the anal canal B. C. MORSON AND H. VOLKSTADT From the Research Department, St. Mark's Hospital, London SYNOPSIS The pathology of 21 cases of muco-epidermoid
J. clin. Path. (1963), 16, 200 Muco-epidermoid tumours of the anal canal B. C. MORSON AND H. VOLKSTADT From the Research Department, St. Mark's Hospital, London SYNOPSIS The pathology of 21 cases of muco-epidermoid
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad. Lab 1
 Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad Lab 1 1 Tissues are groups of cells with a common structure (form) and function (job). There are (4) types of tissue: 1. Epithelial 2. Connective 3. Muscle 4. Nervous 2 Epithelial cells
Center for Reconstructive Urethral Surgery Guido Barbagli Center for Reconstructive Urethral Surgery Arezzo - Italy
 Guido Barbagli Arezzo - Italy E-mail: info@urethralcenter.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it SHANGHAI February 6 8, 2009 Prof. Qiang FU Professor FU day Professor FU and night Anterior urethroplasty using
Guido Barbagli Arezzo - Italy E-mail: info@urethralcenter.it Website: www.urethralcenter.it SHANGHAI February 6 8, 2009 Prof. Qiang FU Professor FU day Professor FU and night Anterior urethroplasty using
Rates of thyroid malignancy by FNA diagnostic category
 Williams et al. Journal of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery 2013, 42:61 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Rates of thyroid malignancy by diagnostic category Blair A Williams 1*, Martin J Bullock
Williams et al. Journal of Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery 2013, 42:61 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Rates of thyroid malignancy by diagnostic category Blair A Williams 1*, Martin J Bullock
Journal of International Academy of Forensic Science & Pathology (JIAFP)
 Journal of International Academy of Forensic Science & Pathology (JIAFP) ISSN 2395-0722 MICROCYSTIC ADNEXAL CARCINOMA-A CASE REPORT WITH REVIEW OF LITERATURE Case Report Sulakshana M S 1,Natarajan M 2
Journal of International Academy of Forensic Science & Pathology (JIAFP) ISSN 2395-0722 MICROCYSTIC ADNEXAL CARCINOMA-A CASE REPORT WITH REVIEW OF LITERATURE Case Report Sulakshana M S 1,Natarajan M 2
BIOH111. o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
Development of Respiratory System. Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra
 Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
Development of Respiratory System Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy& Dr. Saeed Vohra OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture the students should be able to: Identify the development of the laryngeotracheal (respiratory)
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
-The cause of testicular neoplasms remains unknown
 - In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - include: I. Germ cell tumors : (95%); all are malignant. II. Sex cord-stromal tumors: from Sertoli or Leydig cells; usually
- In the 15- to 34-year-old age group, they are the most common tumors of men. - include: I. Germ cell tumors : (95%); all are malignant. II. Sex cord-stromal tumors: from Sertoli or Leydig cells; usually
Histopathological Study of Skin Adnexal Tumors - A Ten Years Study
 Original Research Article Histopathological Study of Skin Adnexal Tumors - A Ten Years Study V. Srinivas Kumar 1, V. Geeta 1*, Nikhil Kumar Voruganti 2, O. Shravan Kumar 3, Tamilarasi 4 1 Associate Professor
Original Research Article Histopathological Study of Skin Adnexal Tumors - A Ten Years Study V. Srinivas Kumar 1, V. Geeta 1*, Nikhil Kumar Voruganti 2, O. Shravan Kumar 3, Tamilarasi 4 1 Associate Professor
