Zackary Johnson Department of Oceanography
|
|
|
- Sybil Lyons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Zackary Johnson Department of Oceanography Application of Bioenergetics to Biological Oceanography Biochemical parameters indicative of stock sizes and process rates dc 1 /dt = growth Standing Stock C 1 transfer efficiency dc 2 /dt C 2 1. MEASUREMENT OF STANDING STOCKS: Carbon = the "standard unit" of measurement, basic to all organic molecules. Bulk measurements straightforward, but difficult to separate community components: "dead" carbon (detritus) >> living C [cells] biovolume / cell carbon = population carbon microscope work is tedious carbon / biovolume varies with nutritional status, taxa, etc. 1
2 [Chl a] C:Chl a = phytoplankton carbon C:Chl varies with nutritional state, light range 25:1 (high nutrient, low light) 200:1 moretypical50 100:1 [ATP] C:ATP = living carbon C:ATP 250:1, varies with nutritional state, taxa, etc. Other bulk measurable possible: lipopolysaccharide (LPS) bacterial cell wall component taxa specific photosynthetic accessory pigments DNA (specific) Holm Hansen 1969 L/O 14: Holm Hansen and Paerl 1972 Mem. Ist. Ital. Idrobiol. 29: 2. Measurement of Rate Processes: Isotope (Tracer) Methods: 14 C-CO 2 Primary Production 18 O-O 2 Respiration 2 P-PO 4-15 N-NH 4 + (NO - ) H-thymidine H-adenine Phosphorous uptake & cycling Nitrogen uptake & cycling Bacterial growth H-amino acids 14 C-amino acids Protein synthesis 2
3 2. Measurement of Rate Processes: other approaches primary production: oxygen evolution, CO 2 consumption, ΔpH, heat production, fluorescence, change in abundance secondary production: oxygen consumption, CO 2 production, ΔpH, change in abundance PP: light bottle/dark bottle O 2 evolution grazing dilution experiments growth rate dilution Biochemical Indices: enzymes can be induced by need (substrate availability) assumes energy economy in production of cell components ex. RUBISCO enzyme in photosynthetic dark reaction ETS activity: King and Packard 1975 L/O 20: RNA:DNA ratio protein synthesis/biomass ~ growth digestive enzymes substrate specific
4 . Relationship among cell constituents: Carbon energy content Lipid (fat) has greater than twice the energy content per carbon molecule (or per unit mass) than protein or carbohydrate. ATP energy content ATP content is the pool of immediately available energy. The process of energy utilization can be assessed by the turnover rate of the ATP pool. Respiratory Quotient = RQ = CO 2 evolved/o 2 used a RQ b calories/g Carbohydrate Protein Lipid (Fatty Acid) a relevant to carbon budgets, given respiration measured as O 2 utilization. Conversion from stoichiometry b relveant to energy budgets, derived from chemistry. Elemental composition of organic molecules: Carbon Nitrogen Phosphorous Carbohydrates Trace Proteins Lipids 100 Nucleic Acids Redfield Ratio (C:N:P) (molar ratio) = 106:16:1 average of all living material 4. Energetic Efficiency no process can occur with 100% conservation of energy Respiration Given: Glucose yields 686 Kcal/mole 8 moles of ATP/mole glucose respired ATP phosphate bond liberates 10 kcal/mole 8 ATP 10 kcal/atp = 55% efficiency 686 Kcal/mole glucose Biosynthesis Given: Heterotroph starts with amino acids Glycine (AA) = 24 Kcal/mole Peptide linkage: cost = ATP = 0 Kcal/mole bond energy = 5.5 Kcal/mole Needed ATP is generated with 55% efficiency 24 Kcal/mole glycine 0.55 =4. 0 Kcal/mole peptide bond About one out of every 5 assimilated glycine molecules must be fully oxidized in respiration to provide enough energy to link the other 4 molecules with peptide bonds. THEORETICAL MAXIMUM EFFICIENCY: All life processes 70% 4
5 5. Energetic Implications of Adaptations Short term Within physiological limits, organisms adjust biochemical systems to the external environment in a manner that promotes energetic efficiency (e.g., enzymes, C:Chl). Long term (evolutionary) (morphological specializations, physiological tolerances). Additional capabilities and structures have energetic costs that must be offset, in the long term, by energetic advantages (e.g., homeotherm metabolism). EXAMPLE: TEMPERATURE TOLERANCE Temperature enhances all enzymecatalyzed biochemical reactions. The enzyme systems for different species are adapted to specific temperature ranges. Growth vs. temperature for 5 unicellular algae (Eppley 1972 Fish. Bull. 70) Phytoplankton Biomass 1: Quantifying Phytoplankton Biomass a. carbon (nitrogen, phosphorous, etc.) dead carbon > live carbon what fraction is phytoplankton specific? b. counting cells (microscope, flow cytometry) 5
6 1/25/2008 Phytoplankton Biomass c. chlorophyll (pigments) most abundant phytoplankton pigment present in all oxygenic phytoplankton two strong absorption bands (Soret blue & Qy red band), reflected light is green strong fluorescence at ~680nm 680nm (red) strong can be measured remotely, in situ, or extracted absorption sensitive, simple, rapid fluorescence Phytoplankton Biomass c. chlorophyll pigments (cont): extracted in situ remotely sensed 6
7 c. chlorophyll pigments (cont): Beer Lambert law (absorption): a Phytoplankton Biomass = clε a is the absorption, c is the concentration, l is the path length, and ε is extinction coefficient rearranging: c = a lε similarly for fluorescence: ( mgchla / m = 11.85E 1.54E 0.08E ) c = fls φ where fluorescence is directly proportional to c by fluorescence yield, φ for both techniques, extracted pigments (ex. acetone, methanol) work best, because they can be dissociated from contaminants or other sources of intereference and 100% of absorbed energy leads to fluorescence (vs. ~% in intact cells) in situ and remotely sensed values can be compromised from non chlorophyll contamination of the absorption or fluorescence wavebands. Phytoplankton Production 2: Quantifying Primary Production bulk properties photosynthesis: CO 2 + H 2 O CH 2 O + O 2 natural concentrations of CO 2 and O 2 in seawater: carbonate buffer system: CO 2 HCO CO 2 oxygen saturation: 0.21mM (25 o C), 0.6mM (0 o C) [TCO 2 ] 2.0mM typical range primary production values: μmol CO 2 L 1 d μmol O 2 L 1 d 1 sensitivity of methods: CO 2 1μM (Coulometry) O μM (Microwinkler) so, direct measurement of CO 2 not sensitive enough O 2 possible, but only ~10% resolution (not good for precise comparison) 7
8 1/25/2008 Phytoplankton Production 2: Quantifying Primary Production: incubations with tracers photosynthesis: CO2 + H2O Æ CH2O + O2 carbon incorporation p g bottle technique q dark bottle / light 14CO2 uptake: Phytoplankton Production 2: Quantifying Primary Production (cont). carbon uptake 14CO 2 + H2O Æ 14CH2O + O2 measure radioactive decay using liquid scintillation counter counts per minute (CPM) Æ disintegrations per minute (DPM) photosynthetic rate = 1.05 (DPM sample DPM dark ) [CO2 ] DPM added time notes: 1.05 for preferential uptake of C 12 over C 14 (heavier) DPM always positive, very sensitive DPMdark measures non specific incorporation (including adsorption) incubation time period shapes whether net or gross measurement can be b d done in i situ, it simulated i l t d light li ht incubators, i b t or short h t term t photosynthetrons h t th t 8
9 Phytoplankton Production 2: Quantifying Primary Production (cont). oxygen evolution CO 2 + H 2 O CH 2 O + O 2 measure production of oxygen in light bottle relative to dark bottle difference is net primary production ([ O ] [ O ]) 2 ([ O ] [ O ]) net production = respiration = light 2initial time notes: gross=net+respiration can be negative low sensitivity can be done in situ incubations, simulated light incubators derivatives include stable isotopes: 2 dark 2initial time CO 2 + H 2 18 O CH 2 O + 18 O 2 used to differentiate net and gross photosynthesis 9
OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Bioenergetics-III
 OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Bioenergetics-III Guangyi Wang POST 103B guangyi@hawaii.edu http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/oceanography/zij/education/ocn621/ dc 1 /dt = growth Standing Stock C 1 Overview
OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Bioenergetics-III Guangyi Wang POST 103B guangyi@hawaii.edu http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/oceanography/zij/education/ocn621/ dc 1 /dt = growth Standing Stock C 1 Overview
OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Bioenergetics-II
 OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Bioenergetics-II Zackary Johnson MSB614 zij@hawaii.edu Chemosynthesis (Chemolithotrophy) Use of small inorganic
OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Bioenergetics-II Zackary Johnson MSB614 zij@hawaii.edu Chemosynthesis (Chemolithotrophy) Use of small inorganic
In steady state, new production = carbon export
 In steady state, new production = carbon export Where does primary production go? Export Bacteria Dissolved organic matter Grazing What other components of the biological pump are important? The majority
In steady state, new production = carbon export Where does primary production go? Export Bacteria Dissolved organic matter Grazing What other components of the biological pump are important? The majority
Guangyi Wang. Chemosynthesis (Chemolithotrophy)
 OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Bioenergetics-II Guangyi Wang POST 103B guangyi@hawaii.edu http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/oceanography/zij/education/ocn621/ Chemosynthesis (Chemolithotrophy) Use of small
OCN621: Biological Oceanography- Bioenergetics-II Guangyi Wang POST 103B guangyi@hawaii.edu http://www.soest.hawaii.edu/oceanography/zij/education/ocn621/ Chemosynthesis (Chemolithotrophy) Use of small
BIOCHEMISTRY. There are 4 major types of organic compounds each with unique characteristics: A. CARBOHYDRATES Contain,, and. Ratio of H:O is always
 BIOCHEMISTRY All organic compounds must contain and Are the following organic? Why or why not? H2O CO2 CH4 There are 4 major types of organic compounds each with unique characteristics: A. CARBOHYDRATES
BIOCHEMISTRY All organic compounds must contain and Are the following organic? Why or why not? H2O CO2 CH4 There are 4 major types of organic compounds each with unique characteristics: A. CARBOHYDRATES
AP Biology Review: Theme 3- Energy
 AP Biology Review: Theme 3- Energy 3.1: All living systems require constant input of free energy. 3.2: Interactions between molecules affect their structure and function. 3.3: Organisms capture and store
AP Biology Review: Theme 3- Energy 3.1: All living systems require constant input of free energy. 3.2: Interactions between molecules affect their structure and function. 3.3: Organisms capture and store
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2.
 BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2. A possible explanation for an event that occurs in nature is
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2. A possible explanation for an event that occurs in nature is
Bioenergetics. Finding adequate sources of energy is a constant challenge for all living organisms, including this bear.
 33 Bioenergetics Finding adequate sources of energy is a constant challenge for all living organisms, including this bear. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc
33 Bioenergetics Finding adequate sources of energy is a constant challenge for all living organisms, including this bear. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc
Feeding Measurements
 Feeding Measurements Measures of Feeding Rates (or specific mortality rate) Clearance Rate Concept Clearance Rate (F) = Volume cleared of prey pred -1 time -1 predator prey A consumer may have different
Feeding Measurements Measures of Feeding Rates (or specific mortality rate) Clearance Rate Concept Clearance Rate (F) = Volume cleared of prey pred -1 time -1 predator prey A consumer may have different
Chapter 8. An Introduction to Microbial Metabolism
 Chapter 8 An Introduction to Microbial Metabolism The metabolism of microbes Metabolism sum of all chemical reactions that help cells function Two types of chemical reactions: Catabolism -degradative;
Chapter 8 An Introduction to Microbial Metabolism The metabolism of microbes Metabolism sum of all chemical reactions that help cells function Two types of chemical reactions: Catabolism -degradative;
Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC.
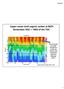 Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Analysis & Interpretation. Analysis Questions answer questions on a separate sheet of paper. Name(s): Period: Date:
 Name(s): Period: Date: Dehydration Synthesis and Hydrolysis The chemical reactions that bond together macromolecules are similar and require water. When macromolecules are consumed, they must be broken
Name(s): Period: Date: Dehydration Synthesis and Hydrolysis The chemical reactions that bond together macromolecules are similar and require water. When macromolecules are consumed, they must be broken
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis!
 Factors Affecting Photosynthesis! Temperature Eppley (1972) Light Sverdrup s Critical Depth Model Nutrients Limitations Uptake Kinetics Temperature! The oceans vary much less than the land does, both seasonally
Factors Affecting Photosynthesis! Temperature Eppley (1972) Light Sverdrup s Critical Depth Model Nutrients Limitations Uptake Kinetics Temperature! The oceans vary much less than the land does, both seasonally
Student Number: To form the polar phase when adsorption chromatography was used.
 Name: Student Number: April 14, 2001, 1:30 AM - 4:30 PM Page 1 (of 4) Biochemistry II Lab Section Final Examination Examiner: Dr. A. Scoot 1. Answer ALL questions in the space provided.. 2. The last page
Name: Student Number: April 14, 2001, 1:30 AM - 4:30 PM Page 1 (of 4) Biochemistry II Lab Section Final Examination Examiner: Dr. A. Scoot 1. Answer ALL questions in the space provided.. 2. The last page
Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher Section 3 Chemistry of Cells
 Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher Section 3 Chemistry of Cells Objectives Summarize the characteristics of organic compounds. Compare the structures and function of different types of biomolecules.
Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher Section 3 Chemistry of Cells Objectives Summarize the characteristics of organic compounds. Compare the structures and function of different types of biomolecules.
Chemical Formulas. Chemical Formula CH 3 COCHCHOCHClCHNH Lewis Dot Structure
 Biochemistry . Chemical Formulas A chemical formula represents the chemical makeup of a compound. It shows the numbers and kinds of atoms present in a compound. It is a kind of shorthand that scientists
Biochemistry . Chemical Formulas A chemical formula represents the chemical makeup of a compound. It shows the numbers and kinds of atoms present in a compound. It is a kind of shorthand that scientists
A. There are about 100 elements; 25 of them are necessary for life. B. Carbon atoms can form long chains, leading to a huge number of possible
 Ch. 2 How Cells Function 2.1 Chemical reactions take place inside cells. 1. All cells are made of the same elements. A. There are about 100 elements; 25 of them are necessary for life. B. The smallest
Ch. 2 How Cells Function 2.1 Chemical reactions take place inside cells. 1. All cells are made of the same elements. A. There are about 100 elements; 25 of them are necessary for life. B. The smallest
Standard B-3: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the flow of energy within and between living systems.
 B-3.1 Summarize the overall process by which photosynthesis converts solar energy into chemical energy and interpret the chemical equation for the process. Taxonomy Level: 2.4-B and 2.1-B Understand Conceptual
B-3.1 Summarize the overall process by which photosynthesis converts solar energy into chemical energy and interpret the chemical equation for the process. Taxonomy Level: 2.4-B and 2.1-B Understand Conceptual
Chemistry 1506: Allied Health Chemistry 2. Section 13: Biosynthetic Pathways. Making Complex Biomolecules. Outline
 Chemistry 1506 Dr. Hunter s Class Section 13 Notes - Page 1/9 Chemistry 1506: Allied Health Chemistry 2 Section 13: Biosynthetic Pathways Making Complex Biomolecules utline SECTIN 13.1 INTRDUCTIN...2 SECTIN
Chemistry 1506 Dr. Hunter s Class Section 13 Notes - Page 1/9 Chemistry 1506: Allied Health Chemistry 2 Section 13: Biosynthetic Pathways Making Complex Biomolecules utline SECTIN 13.1 INTRDUCTIN...2 SECTIN
To be able to answer a question
 1. State Problem or question 2. Gather information 3. State a hypothesis 4. Conduct Experiment 5. Observe, collect, & analyze data 6. State a conclusion7. Repeat many times Observation =Recognizing a FACT
1. State Problem or question 2. Gather information 3. State a hypothesis 4. Conduct Experiment 5. Observe, collect, & analyze data 6. State a conclusion7. Repeat many times Observation =Recognizing a FACT
Bioenergetics. Chapter 3. Objectives. Objectives. Introduction. Photosynthesis. Energy Forms
 Objectives Chapter 3 Bioenergetics Discuss the function of cell membrane, nucleus, & mitochondria Define: endergonic, exergonic, coupled reactions & bioenergetics Describe how enzymes work Discuss nutrients
Objectives Chapter 3 Bioenergetics Discuss the function of cell membrane, nucleus, & mitochondria Define: endergonic, exergonic, coupled reactions & bioenergetics Describe how enzymes work Discuss nutrients
Aim: What are the molecules of life?
 Aim: What are the molecules of life? Do Now: List the elements & compounds cycled through ecosystems. Homework: Read pp. 59 63 P. 63 # 1,2,3,4,5 Vocabulary: Carbohydrate, lipid, protein, amino acid, nucleic
Aim: What are the molecules of life? Do Now: List the elements & compounds cycled through ecosystems. Homework: Read pp. 59 63 P. 63 # 1,2,3,4,5 Vocabulary: Carbohydrate, lipid, protein, amino acid, nucleic
Living Environment. Scientific Inquiry Exam
 Name: Class: 1. Which elements are present in all organic compounds? 1) nitrogen and carbon 3) hydrogen and oxygen 2) nitrogen and oxygen 4) hydrogen and carbon 2. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
Name: Class: 1. Which elements are present in all organic compounds? 1) nitrogen and carbon 3) hydrogen and oxygen 2) nitrogen and oxygen 4) hydrogen and carbon 2. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
Biochemistry Name: Practice Questions
 Name: Practice Questions 1. Carbohydrate molecules A and B come in contact with the cell membrane of the same cell. Molecule A passes through the membrane readily, but molecule B does not. It is most likely
Name: Practice Questions 1. Carbohydrate molecules A and B come in contact with the cell membrane of the same cell. Molecule A passes through the membrane readily, but molecule B does not. It is most likely
Assignment #1: Biological Molecules & the Chemistry of Life
 Assignment #1: Biological Molecules & the Chemistry of Life A. Important Inorganic Molecules Water 1. Explain why water is considered a polar molecule. The partial negative charge of the oxygen and the
Assignment #1: Biological Molecules & the Chemistry of Life A. Important Inorganic Molecules Water 1. Explain why water is considered a polar molecule. The partial negative charge of the oxygen and the
Microbial nutrition. Nutrients. Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology and Growth. Chapter 7
 Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology and Growth Chapter 7 Microbial nutrition Macronutrients required in large quantities; play principal roles in cell structure & metabolism proteins, carbohydrates
Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology and Growth Chapter 7 Microbial nutrition Macronutrients required in large quantities; play principal roles in cell structure & metabolism proteins, carbohydrates
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 2: Cellular Chemistry
 Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 2: Cellular Chemistry NC Essential Standard: 1.2.1 Explain how cells use buffers to regulate cell ph 4.1.1 Compare the structure and functions
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 2: Cellular Chemistry NC Essential Standard: 1.2.1 Explain how cells use buffers to regulate cell ph 4.1.1 Compare the structure and functions
Biomolecules. Unit 3
 Biomolecules Unit 3 Atoms Elements Compounds Periodic Table What are biomolecules? Monomers vs Polymers Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Minerals Vitamins Enzymes Triglycerides Chemical Reactions
Biomolecules Unit 3 Atoms Elements Compounds Periodic Table What are biomolecules? Monomers vs Polymers Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Minerals Vitamins Enzymes Triglycerides Chemical Reactions
Jeopardy Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400
 Jeopardy Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids Energy & Reactions Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400
Jeopardy Proteins Carbohydrates Lipids Nucleic Acids Energy & Reactions Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400
The building blocks for this molecule are A) amino acids B) simple sugars C) fats D) molecular bases
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a portion of a starch molecule. The building blocks for this molecule are A)
1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. The diagram represents a portion of a starch molecule. The building blocks for this molecule are A)
2: Describe glycolysis in general terms, including the molecules that exist at its start and end and some intermediates
 1 Life 20 - Glycolysis Raven & Johnson Chapter 9 (parts) Objectives 1: Know the location of glycolysis in a eukaryotic cell 2: Describe glycolysis in general terms, including the molecules that exist at
1 Life 20 - Glycolysis Raven & Johnson Chapter 9 (parts) Objectives 1: Know the location of glycolysis in a eukaryotic cell 2: Describe glycolysis in general terms, including the molecules that exist at
Molecules of Life. Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids
 Molecules of Life Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Molecules of Life All living things are composed of the following basic elements: Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Phosphorous Sulfur Remember
Molecules of Life Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Molecules of Life All living things are composed of the following basic elements: Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Phosphorous Sulfur Remember
The chemistry of life
 The chemistry of life All living organisms are comprised of organic molecules. Organic molecules contain CARBON and HYDROGEN which is not true of inorganic molecules. Carbon is central to life on Earth
The chemistry of life All living organisms are comprised of organic molecules. Organic molecules contain CARBON and HYDROGEN which is not true of inorganic molecules. Carbon is central to life on Earth
Chemistry 506: Allied Health Chemistry 2. Chapter 22: Biosynthetic Pathways. Making Complex Biomolecules
 Chemistry 506: Allied Health Chemistry 2 1 Chapter 22: Biosynthetic Pathways Making Complex Biomolecules Introduction to General, rganic & Biochemistry, 5 th Edition by Bettelheim and March: Chapter 22,
Chemistry 506: Allied Health Chemistry 2 1 Chapter 22: Biosynthetic Pathways Making Complex Biomolecules Introduction to General, rganic & Biochemistry, 5 th Edition by Bettelheim and March: Chapter 22,
Chapter 2 Part 3: Organic and Inorganic Compounds
 Chapter 2 Part 3: Organic and Inorganic Compounds Objectives: 1) List the major groups of inorganic chemicals common in cells. 2) Describe the functions of various types of inorganic chemicals in cells.
Chapter 2 Part 3: Organic and Inorganic Compounds Objectives: 1) List the major groups of inorganic chemicals common in cells. 2) Describe the functions of various types of inorganic chemicals in cells.
Introduction to Biochemistry
 Life is Organized in Increasing Levels of Complexity Introduction to Biochemistry atom simple molecule What is the chemical makeup of living things? macromolecule organ organ system organism organelle
Life is Organized in Increasing Levels of Complexity Introduction to Biochemistry atom simple molecule What is the chemical makeup of living things? macromolecule organ organ system organism organelle
Lecture Notes 2: Protiens
 Lecture Notes 2: Protiens BY/ARSHED ABD ALI SHIHAD Proteins and Amino Acids What Are Proteins? Large molecules Made up of chains of amino acids Are found in every cell in the body Are involved in most
Lecture Notes 2: Protiens BY/ARSHED ABD ALI SHIHAD Proteins and Amino Acids What Are Proteins? Large molecules Made up of chains of amino acids Are found in every cell in the body Are involved in most
Biochemical Concepts. Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water. Pre-View 4.6. A Covalent Polar Molecule
 Biochemical Concepts Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water Pre-View 4.6 Polar molecule a molecule that has a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other end Hydrogen bond
Biochemical Concepts Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water Pre-View 4.6 Polar molecule a molecule that has a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other end Hydrogen bond
Biology 12 - Biochemistry Practice Exam
 Biology 12 - Biochemistry Practice Exam Name: Water: 1. The bond between water molecules is a (n) a. ionic bond b. covalent bond c. polar covalent bond d. hydrogen bond 2. The water properties: good solvent,
Biology 12 - Biochemistry Practice Exam Name: Water: 1. The bond between water molecules is a (n) a. ionic bond b. covalent bond c. polar covalent bond d. hydrogen bond 2. The water properties: good solvent,
Carbon & Energy Utilization OCN 621
 Carbon & Energy Utilization OCN 621 Lecture Outline 1) Materials Balance Approach defined 2) Sloppy Feeding 3) Egestion: as relates to Assimilation efficiency 4) Metabolism: Allometric Equation 1) Temperature
Carbon & Energy Utilization OCN 621 Lecture Outline 1) Materials Balance Approach defined 2) Sloppy Feeding 3) Egestion: as relates to Assimilation efficiency 4) Metabolism: Allometric Equation 1) Temperature
Organic Molecules. 8/27/2004 Mr. Davenport 1
 Organic Molecules 8/27/2004 Mr. Davenport 1 Carbohydrates Commonly called sugars and starches Consist of C, H, O with H:O ration 2:1 Usually classified as to sugar units Monosaccharide are single sugar
Organic Molecules 8/27/2004 Mr. Davenport 1 Carbohydrates Commonly called sugars and starches Consist of C, H, O with H:O ration 2:1 Usually classified as to sugar units Monosaccharide are single sugar
Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism)
 Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism) Large food molecules contain a lot of potential energy in the form of chemical bonds but it requires a lot of work to liberate the energy. Cells need
Energy Production In A Cell (Chapter 25 Metabolism) Large food molecules contain a lot of potential energy in the form of chemical bonds but it requires a lot of work to liberate the energy. Cells need
Macromolecules Chapter 2.3
 Macromolecules Chapter 2.3 E.Q. What are the 4 main macromolecues found in living things and what are their functions? Carbon-Based Molecules Why is carbon called the building block of life? Carbon atoms
Macromolecules Chapter 2.3 E.Q. What are the 4 main macromolecues found in living things and what are their functions? Carbon-Based Molecules Why is carbon called the building block of life? Carbon atoms
Unit 2 - Characteristics of Living Things
 Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. A fully functioning enzyme molecule is arranged in a complex three-dimensional shape. This shape determines the A) specific type of molecule
Living Environment Answer Key to Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. A fully functioning enzyme molecule is arranged in a complex three-dimensional shape. This shape determines the A) specific type of molecule
ANSC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism
 I. verall concepts A. Definitions ANSC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose and lactate) 1) Uses glucose
I. verall concepts A. Definitions ANSC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose and lactate) 1) Uses glucose
Metabolism III. Aim: understand gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, photosynthesis and amino acid synthesis
 Metabolism III Aim: understand gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, photosynthesis and amino acid synthesis Anabolism From a carbon source and inorganic molecules, microbes synthesize new organelles
Metabolism III Aim: understand gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, photosynthesis and amino acid synthesis Anabolism From a carbon source and inorganic molecules, microbes synthesize new organelles
Microbial Metabolism (Chapter 5) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Microbial Metabolism (Chapter 5) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Source for figures and content: Tortora, G.J. Microbiology An Introduction
Microbial Metabolism (Chapter 5) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Source for figures and content: Tortora, G.J. Microbiology An Introduction
The Carbon Atom (cont.)
 Organic Molecules Organic Chemistry The chemistry of the living world. Organic Molecule a molecule containing carbon and hydrogen Carbon has 4 electrons in its outer shell and can share electrons with
Organic Molecules Organic Chemistry The chemistry of the living world. Organic Molecule a molecule containing carbon and hydrogen Carbon has 4 electrons in its outer shell and can share electrons with
The Atoms of Life. What are other elements would you expect to be on this list? Carbon Hydrogen Nitrogen Oxygen Phosphorous Sulfur (sometimes)
 Macromolecules The Atoms of Life The most frequently found atoms in the body are Carbon Hydrogen Nitrogen Oxygen Phosphorous Sulfur (sometimes) What are other elements would you expect to be on this list?
Macromolecules The Atoms of Life The most frequently found atoms in the body are Carbon Hydrogen Nitrogen Oxygen Phosphorous Sulfur (sometimes) What are other elements would you expect to be on this list?
Biology Unit 2 Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Date/Hour
 Biology Unit 2 Name Elements & Macromolecules in rganisms Date/our Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body
Biology Unit 2 Name Elements & Macromolecules in rganisms Date/our Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body
9/17/2009. HPER 3970 Dr. Ayers. (courtesy of Dr. Cheatham)
 REVIEW: General Principles II What is the RDA? Level of intake for essential nutrients determined on the basis of scientific knowledge to be adequate to meet the known nutrient needs of practically all
REVIEW: General Principles II What is the RDA? Level of intake for essential nutrients determined on the basis of scientific knowledge to be adequate to meet the known nutrient needs of practically all
Chapter 2: Biochemistry
 Chapter 2: Biochemistry Biochemistry Biochemistry is the study of chemical makeup and reactions of living matter All chemicals in the body are either organic & inorganic Organic compounds contain carbon
Chapter 2: Biochemistry Biochemistry Biochemistry is the study of chemical makeup and reactions of living matter All chemicals in the body are either organic & inorganic Organic compounds contain carbon
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules I. Polymers What is a polymer? Poly = many; mer = part. A polymer is a large molecule consisting of many smaller sub-units bonded together. What is a monomer?
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules I. Polymers What is a polymer? Poly = many; mer = part. A polymer is a large molecule consisting of many smaller sub-units bonded together. What is a monomer?
Warm-Up. Distinguish between an element and a compound. Element. Compound
 Warm-Up Distinguish between an element and a compound. Element Compound Warm-Up Distinguish between an element and a compound. Element Cannot be broken down into anything smaller Found on the Periodic
Warm-Up Distinguish between an element and a compound. Element Compound Warm-Up Distinguish between an element and a compound. Element Cannot be broken down into anything smaller Found on the Periodic
Life s molecular diversity is based on the. properties of carbon. Chain Ring Branching chain
 Carbon Compounds Life s molecular diversity is based on the properties of carbon Chain Ring Branching chain The Chemistry of Carbon : carbon based Carbon can make 4 covalent bonds The foundation of organic
Carbon Compounds Life s molecular diversity is based on the properties of carbon Chain Ring Branching chain The Chemistry of Carbon : carbon based Carbon can make 4 covalent bonds The foundation of organic
: -CH2O - anadph + bproduct + catp + dnadh + eco2 2O + 2NADPH + CO 2 2O ATP + CO 2
 Supplementary Notes In the calculations below metabolism is assumed to be respiro-fermentative in nature, which is generally the case under high glycolytic flux and is the best case scenario for pathways
Supplementary Notes In the calculations below metabolism is assumed to be respiro-fermentative in nature, which is generally the case under high glycolytic flux and is the best case scenario for pathways
Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms
 Name: Period: Date: Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight.
Name: Period: Date: Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight.
Photosynthesis Digestion Respiration. ., proteins. ... Glucose,.., fatty acids and glycerol, respectively.
 BIOMOLECULES Dear Reader In the previous chapter you have read about DNA present in the chromosomes. It is one of the many organic chemical compounds present in all living organisms. The organic compounds
BIOMOLECULES Dear Reader In the previous chapter you have read about DNA present in the chromosomes. It is one of the many organic chemical compounds present in all living organisms. The organic compounds
EH1008 Biomolecules. Inorganic & Organic Chemistry. Water. Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry.
 EH1008 Biomolecules Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Inorganic & Organic Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry: generally, substances that do not contain carbon Inorganic molecules:
EH1008 Biomolecules Lecture 2: Inorganic and organic chemistry limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Inorganic & Organic Chemistry Inorganic Chemistry: generally, substances that do not contain carbon Inorganic molecules:
2 3 Carbon Compounds Slide 1 of 37
 1 of 37 The Chemistry of Carbon The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon atoms have four valence electrons that can join with
1 of 37 The Chemistry of Carbon The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon atoms have four valence electrons that can join with
Cellular Respiration Chapter 5 Notes
 Cellular Respiration Chapter 5 Notes Some Terms to Know Aerobic = WITH oxygen Anaerobic = without oxygen NAD+ electron carrier = NADH FAD electron carrier = FADH 2 Cellular Respiration a way for cells
Cellular Respiration Chapter 5 Notes Some Terms to Know Aerobic = WITH oxygen Anaerobic = without oxygen NAD+ electron carrier = NADH FAD electron carrier = FADH 2 Cellular Respiration a way for cells
ANSC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism
 Fatty Acid ynthesis I. verall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism Fatty Acid ynthesis 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors
Fatty Acid ynthesis I. verall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism Fatty Acid ynthesis 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors
Standard 2 Exam Biology. 2. This macromolecule is responsible for short term energy storage and structural support in plants
 1. This macromolecule is responsible for structural support, movement, enzymatic activity, cell communication, and is made of amino acids. a. Lipids b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Nucleic Acids e. ATP
1. This macromolecule is responsible for structural support, movement, enzymatic activity, cell communication, and is made of amino acids. a. Lipids b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Nucleic Acids e. ATP
I. Polymers & Macromolecules Figure 1: Polymers. Polymer: Macromolecule: Figure 2: Polymerization via Dehydration Synthesis
 I. Polymers & Macromolecules Figure 1: Polymers Polymer: Macromolecule: Figure 2: Polymerization via Dehydration Synthesis 1 Dehydration Synthesis: Figure 3: Depolymerization via Hydrolysis Hydrolysis:
I. Polymers & Macromolecules Figure 1: Polymers Polymer: Macromolecule: Figure 2: Polymerization via Dehydration Synthesis 1 Dehydration Synthesis: Figure 3: Depolymerization via Hydrolysis Hydrolysis:
Chapter 5. Microbial Metabolism
 Chapter 5 Microbial Metabolism Metabolism Collection of controlled biochemical reactions that take place within a microbe Ultimate function of metabolism is to reproduce the organism Metabolic Processes
Chapter 5 Microbial Metabolism Metabolism Collection of controlled biochemical reactions that take place within a microbe Ultimate function of metabolism is to reproduce the organism Metabolic Processes
Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition
 Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 7 Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology, and Growth Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 7 Elements of Microbial Nutrition, Ecology, and Growth Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required
Life and the Flow of Energy. Chapter 6. The Flow of Energy
 Life and the Flow of Energy Chapter 6 Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes Energy is the ability to do work Cells (and organisms) need a constant supply of Life on Earth is dependent on solar Solar The Flow
Life and the Flow of Energy Chapter 6 Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes Energy is the ability to do work Cells (and organisms) need a constant supply of Life on Earth is dependent on solar Solar The Flow
2-2 Properties of Water
 2-2 Properties of Water 1 A. The Water Molecule o o o Water is polar Hydrogen bonds form between water molecules Properties of Water: cohesion adhesion capillary action high specific heat ice floats good
2-2 Properties of Water 1 A. The Water Molecule o o o Water is polar Hydrogen bonds form between water molecules Properties of Water: cohesion adhesion capillary action high specific heat ice floats good
The Structure and Function of Biomolecules
 The Structure and Function of Biomolecules The student is expected to: 9A compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
The Structure and Function of Biomolecules The student is expected to: 9A compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
Competitive Inhibitor
 is a substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by entering the active site in place of the substrate whose structure it mimics. Competitive Inhibitor Identify the following molecule: Polysaccharide
is a substance that reduces the activity of an enzyme by entering the active site in place of the substrate whose structure it mimics. Competitive Inhibitor Identify the following molecule: Polysaccharide
Chemistry Regents Review A. A B. B C. C D. D
 hemistry Regents Review Name: ate: 1. Nitrogenous wastes result from the metabolism of 4. Which sugar solution was the first to liberate a measurable volume of O 2?. amino acids. glucose molecules. fatty
hemistry Regents Review Name: ate: 1. Nitrogenous wastes result from the metabolism of 4. Which sugar solution was the first to liberate a measurable volume of O 2?. amino acids. glucose molecules. fatty
Ch 2 Molecules of life
 Ch 2 Molecules of life Think about (Ch 2, p.2) 1. Water is essential to life. If there is water on a planet, it is possible that life may exist on the planet. 2. Water makes up the largest percentage by
Ch 2 Molecules of life Think about (Ch 2, p.2) 1. Water is essential to life. If there is water on a planet, it is possible that life may exist on the planet. 2. Water makes up the largest percentage by
Chapter 11 Nutrition: Food for Thought
 Chapter 11 Nutrition: Food for Thought Do you think about the food that goes into your body and how it affects you? How can you interpret the various nutrition information found in the press? What are
Chapter 11 Nutrition: Food for Thought Do you think about the food that goes into your body and how it affects you? How can you interpret the various nutrition information found in the press? What are
The. Crash Course. Basically, almost all living things are made up of these 4 Elements: - Carbon (C) - Nitrogen (N) - Hydrogen (H) - Oxygen (O)
 The Biochemistry Crash Course Basically, almost all living things are made up of these 4 Elements: - Carbon (C) - Nitrogen (N) - Hydrogen (H) - Oxygen (O) This exercise is designed to familiarize you with
The Biochemistry Crash Course Basically, almost all living things are made up of these 4 Elements: - Carbon (C) - Nitrogen (N) - Hydrogen (H) - Oxygen (O) This exercise is designed to familiarize you with
Sverdrup s Critical Depth Revisited
 Sverdrup s Critical Depth Revisited For Homework 2, question 4, you need some additional information. Sverdrup assumed that the Compensation Depth (Ec) includes respiration from both phytoplankton and
Sverdrup s Critical Depth Revisited For Homework 2, question 4, you need some additional information. Sverdrup assumed that the Compensation Depth (Ec) includes respiration from both phytoplankton and
Chapter 5: Major Metabolic Pathways
 Chapter 5: Major Metabolic Pathways David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: Introduction to Metabolism Glucose Metabolism Glycolysis, Kreb s Cycle, Respiration Biosysthesis
Chapter 5: Major Metabolic Pathways David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: Introduction to Metabolism Glucose Metabolism Glycolysis, Kreb s Cycle, Respiration Biosysthesis
Topic 3: The chemistry of life (15 hours)
 Topic : The chemistry of life (5 hours). Chemical elements and water.. State that the most frequently occurring chemical elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen...2 State that
Topic : The chemistry of life (5 hours). Chemical elements and water.. State that the most frequently occurring chemical elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen...2 State that
Water: 1. The bond between water molecules is a(n) a. ionic bond b. covalent bond c. polar covalent bond d. hydrogen bond
 Biology 12 - Biochemistry Practice Exam KEY Water: 1. The bond between water molecules is a(n) a. ionic bond b. covalent bond c. polar covalent bond d. hydrogen bond 2. The water properties: good solvent,
Biology 12 - Biochemistry Practice Exam KEY Water: 1. The bond between water molecules is a(n) a. ionic bond b. covalent bond c. polar covalent bond d. hydrogen bond 2. The water properties: good solvent,
N.S. Lecture 3 Biochemistry is broken up into 3 parts - this is part 3b
 N.S. Lecture 3 Biochemistry is broken up into 3 parts - this is part 3b Hemoglobin carries oxygen 33 PROTEINS PROVIDE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION TO LIFE Antibodies fight disease Fibers clot blood Fibers gives
N.S. Lecture 3 Biochemistry is broken up into 3 parts - this is part 3b Hemoglobin carries oxygen 33 PROTEINS PROVIDE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION TO LIFE Antibodies fight disease Fibers clot blood Fibers gives
Biomolecule: Carbohydrate
 Biomolecule: Carbohydrate This biomolecule is composed of three basic elements (carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen) in a 1:2:1 ratio. The most basic carbohydrates are simple sugars, or monosaccharides. Simple
Biomolecule: Carbohydrate This biomolecule is composed of three basic elements (carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen) in a 1:2:1 ratio. The most basic carbohydrates are simple sugars, or monosaccharides. Simple
Respiration: Allometric Relationship
 Metabolism Defined as: all energy transformations, chemical reactions and pathways that make possible the properties of living organisms Measured as: the Respiration Rate, assumes all organism s energy
Metabolism Defined as: all energy transformations, chemical reactions and pathways that make possible the properties of living organisms Measured as: the Respiration Rate, assumes all organism s energy
Cell Processes Review
 1. Most green algae are able to obtain carbon dioxide from the environment and use it to synthesize organic compounds. This activity is an example of 1) hydrolysis 2) saprophytism 3) cellular respiration
1. Most green algae are able to obtain carbon dioxide from the environment and use it to synthesize organic compounds. This activity is an example of 1) hydrolysis 2) saprophytism 3) cellular respiration
OVERVIEW OF ENERGY AND METABOLISM
 Biochemistry 5. Bio-Energetics & ATP 5.1) ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration OVERVIEW OF ENERGY AND METABOLISM 1. The food we eat, (carbohydrates/ glucose /sugar, lipids/fat, proteins), are our only source
Biochemistry 5. Bio-Energetics & ATP 5.1) ADP, ATP and Cellular Respiration OVERVIEW OF ENERGY AND METABOLISM 1. The food we eat, (carbohydrates/ glucose /sugar, lipids/fat, proteins), are our only source
CHAPTER 5 MICROBIAL METABOLISM
 CHAPTER 5 MICROBIAL METABOLISM I. Catabolic and Anabolic Reactions A. Metabolism - The sum of all chemical reactions within a living cell either releasing or requiring energy. (Overhead) Fig 5.1 1. Catabolism
CHAPTER 5 MICROBIAL METABOLISM I. Catabolic and Anabolic Reactions A. Metabolism - The sum of all chemical reactions within a living cell either releasing or requiring energy. (Overhead) Fig 5.1 1. Catabolism
Macromolcules, Enzymes, & Cells Intro
 Name: Date: 1. The distortion (change in shape) of enzyme molecules which occurs at high temperatures is known as 5. A characteristic shared by all enzymes, hormones, and antibodies is that their function
Name: Date: 1. The distortion (change in shape) of enzyme molecules which occurs at high temperatures is known as 5. A characteristic shared by all enzymes, hormones, and antibodies is that their function
Respiration. Respiration. Respiration. How Cells Harvest Energy. Chapter 7
 How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs: live on
How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs: live on
Biological Molecules. Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, and Nucleic Acids
 Biological Molecules Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, and Nucleic Acids Organic Molecules Always contain Carbon (C) and Hydrogen (H) Carbon is missing four electrons Capable of forming 4 covalent bonds
Biological Molecules Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, and Nucleic Acids Organic Molecules Always contain Carbon (C) and Hydrogen (H) Carbon is missing four electrons Capable of forming 4 covalent bonds
Organic Compounds: Carbohydrates
 Organic Compounds: Carbohydrates Carbohydrates include sugars and starches Contain the elements C,H,O (H & O ratio like water, 2 H s to 1O), ex. glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 Word means hydrated carbon Classified
Organic Compounds: Carbohydrates Carbohydrates include sugars and starches Contain the elements C,H,O (H & O ratio like water, 2 H s to 1O), ex. glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 Word means hydrated carbon Classified
FARM MICROBIOLOGY 2008 PART 3: BASIC METABOLISM & NUTRITION OF BACTERIA I. General Overview of Microbial Metabolism and Nutritional Requirements.
 FARM MICROBIOLOGY 2008 PART 3: BASIC METABOLISM & NUTRITION OF BACTERIA I. General Overview of Microbial Metabolism and Nutritional Requirements. Under the right physical conditions, every microorganism
FARM MICROBIOLOGY 2008 PART 3: BASIC METABOLISM & NUTRITION OF BACTERIA I. General Overview of Microbial Metabolism and Nutritional Requirements. Under the right physical conditions, every microorganism
Prerequisite Knowledge: Students should have already been introduced to the inputs and outputs of photosynthesis.
 www.ngsslifescience.com. Topic: Metabolism Chemistry Model Summary: Students will learn act out polymerization by performing dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis using chemistry models. Students will also
www.ngsslifescience.com. Topic: Metabolism Chemistry Model Summary: Students will learn act out polymerization by performing dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis using chemistry models. Students will also
2.3 Carbon Compounds 12/19/2011 BIOLOGY MRS. MICHAELSEN. Lesson Overview. Carbon Compounds The Chemistry of Carbon. Lesson Overview.
 2.3 The Chemistry of Carbon A. Carbon atoms have four valence electrons 1. Form strong covalent bonds with many other elements: H, O, P, S, N. 2. Living organisms are made up of carbon and these other
2.3 The Chemistry of Carbon A. Carbon atoms have four valence electrons 1. Form strong covalent bonds with many other elements: H, O, P, S, N. 2. Living organisms are made up of carbon and these other
What is an atom? An atom is the smallest component of all living and nonliving materials.
 What is an atom? An atom is the smallest component of all living and nonliving materials. It is composed of protons (+), neutrons (0), and electrons (-). The Periodic Table Elements are composed of all
What is an atom? An atom is the smallest component of all living and nonliving materials. It is composed of protons (+), neutrons (0), and electrons (-). The Periodic Table Elements are composed of all
Chapter 5-7, 10. Read P , , and
 Chapter 5-7, 10 Read P. 75-82, 91-100, 107-117 and 173-185 Introduction to Metabolism and Enzymes Catabolic reactions (also called catabolism ) break down larger, more complex molecules into smaller molecules
Chapter 5-7, 10 Read P. 75-82, 91-100, 107-117 and 173-185 Introduction to Metabolism and Enzymes Catabolic reactions (also called catabolism ) break down larger, more complex molecules into smaller molecules
FOOD. Why do we need food? What's in our food? There are 3 trace elements, Iron (Fe), Copper (Cu) and Zinc (Zn).
 Why do we need food? FOOD 1. As a source of energy keeps our cells and us alive. 2. To make chemicals for our metabolic reactions. 3. As raw materials for growth and repair of our cells and body. What's
Why do we need food? FOOD 1. As a source of energy keeps our cells and us alive. 2. To make chemicals for our metabolic reactions. 3. As raw materials for growth and repair of our cells and body. What's
Carbon. Has four valence electrons Can bond with many elements. Can bond to other carbon atoms. Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Nitrogen
 Organic Compounds Carbon Has four valence electrons Can bond with many elements Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Nitrogen Can bond to other carbon atoms Gives carbon the ability to form chains
Organic Compounds Carbon Has four valence electrons Can bond with many elements Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Nitrogen Can bond to other carbon atoms Gives carbon the ability to form chains
How Cells Harvest Energy. Chapter 7. Respiration
 How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Respiration Organisms classified on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs: live on organic compounds
How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Respiration Organisms classified on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs: live on organic compounds
All living things are mostly composed of 4 elements: H, O, N, C honk Compounds are broken down into 2 general categories: Inorganic Compounds:
 Biochemistry Organic Chemistry All living things are mostly composed of 4 elements: H, O, N, C honk Compounds are broken down into 2 general categories: Inorganic Compounds: Do not contain carbon Organic
Biochemistry Organic Chemistry All living things are mostly composed of 4 elements: H, O, N, C honk Compounds are broken down into 2 general categories: Inorganic Compounds: Do not contain carbon Organic
Name: Per. HONORS: Molecules of Life
 Name: Per. HONORS: Molecules of Life Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are classes of organic molecules that are essential to the life processes of all living things. All three classes of molecules are
Name: Per. HONORS: Molecules of Life Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are classes of organic molecules that are essential to the life processes of all living things. All three classes of molecules are
Carbon. p Has four valence electrons p Can bond with many elements p Can bond to other carbon atoms
 Organic Compounds Carbon p Has four valence electrons p Can bond with many elements p Can bond to other carbon atoms n Gives carbon the ability to form chains that are almost unlimited in length. p Organic
Organic Compounds Carbon p Has four valence electrons p Can bond with many elements p Can bond to other carbon atoms n Gives carbon the ability to form chains that are almost unlimited in length. p Organic
1. The diagram shows the flow of energy through a marine ecosystem. The units are kj m 2 year 1. Light energy measured at sea surface 12.
 1. The diagram shows the flow of energy through a marine ecosystem. The units are kj m 2 year 1. Light energy measured at sea surface 12.5 10 5 6250 1000 Producers Respiration 1250 500 4000 Primary consumers
1. The diagram shows the flow of energy through a marine ecosystem. The units are kj m 2 year 1. Light energy measured at sea surface 12.5 10 5 6250 1000 Producers Respiration 1250 500 4000 Primary consumers
