MARKING SCHEME - HALF-YEARLY EXAMS 2017/2018
|
|
|
- Anthony Jordan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 S E C O N D A R Y S C H O O L M R I E H E L ST THOMAS MORE COLLEGE SECONDARY SCHOOL ZEJTUN MARKING SCHEME - HALF-YEARLY EXAMS 2017/2018 YEAR 10 Biology Time: 2hrs NOTE: / indicates alternative answers. Answers are an indication of what is acceptable. Accept other correct answers not indicated below after checking with other examiners. Section A: Answer ALL the questions in this section in the space provided. This section carries a total of 55 marks. 1. A balanced diet is one that gives your body the nutrients it needs to function correctly. a) Some of the nutrients included in a balanced diet are fat, fibre, mineral salts and vitamins. Name two other energy-releasing nutrients that should be part of a balanced diet. Carbohydrates and Proteins. b) Complete the table to show how each of the listed types of diet would affect the human body. Type of Diet Low vitamin D content High fat content Low iron content Effect on Human Body Lack of Calcium absorption / weak bones / rickets? Fat deposits under skin / obesity Anaemia / Lack of red blood cells (3) c) Calcium is a type of mineral salt present in all diets. i) What is the main role of calcium in the human body? For building bones & teeth / makes bones strong or hard / strong bones Biology Y10 HY Page 1 of 13
2 ii) Name the deficiency disease that results from lack of calcium in the diet. Rickets iii) Name a food item that helps to increase the calcium levels in our body. Milk / Cheese / leafy greens / nuts / small fishes with edible bones d) Many of the processes within your body depend on water, so it is important that you get enough of this essential nutrient in your diet. Write down two functions of water in the human body. Reactant / Reaction medium / Transport medium / Temperature regulation (Any 2 1 mark each) Total: 10 marks 2. Some people make use of diet supplements to lose weight. The diet supplements should include all the necessary nutrients normally present in a healthy diet. A group of Biology students investigated the nutrient content in a type of diet supplement. They carried out a number of food tests using the supplement, and recorded the results in the table below: Tested for Reagent(s) Used Colour of Mixture Before After Result Glucose Benedict s solution Blue Brick-red Present Starch Iodine solution Brown Yellowish brown Absent Protein Copper Sulphate and Sodium hydroxide (conc) Blue Purple Present a) Complete the table by writing the correct word(s) in each empty box. (½ mark each = 4) b) Write down the method the biology students used to carry out the test for glucose. Add a few drops of Benedict s solution to the food sample Heat in a water bath Biology Y10 HY Page 2 of 13
3 c) Glucose and starch are both carbohydrates. Write down two differences between these molecules. Soluble - insoluble / monosaccharide polysaccharide / simple sugar - complex sugar / sweet not sweet or tasteless (Any 2) d) Carbohydrates are used to build organic molecules. Explain. Glucose + nitrate Amino acids / proteins Total: 10 marks 3. A large fish, known as a pike, was caught from a lake. When it was opened, its stomach had many small fish known as roach. The roach feeds on the lake plants. a) Use the information above to draw a food chain of the mentioned organisms. Lake plants Roach Pike b) Draw and label a pyramid of biomass of these organisms. Pike Roach Lake plants c) Write the name of the organism that occupies the first trophic level. Lake plants d) The pike s stomach had already started digesting the small fish. Describe the process that occurs in the pike s stomach to digest the protein found in the small fish. Gastric juice is secreted / Contain HCl and pepsin/protease Pepsin breaks down proteins into polypeptides HCl provides acidic ph for pepsin (3) Biology Y10 HY Page 3 of 13
4 e) Further investigation of the pike s stomach revealed the presence of mucus. List one function of mucus within the stomach. Protects inner lining against acid / self-digestion by pepsin (Any 1) f) Explain how catching too many pike would affect the lake ecosystem. Less pike = more roaches = less lake plants Total:11 marks 4. The following diagram shows a few organisms present in a particular ecosystem. eagle hawk crow finch locust aphid grass tree a) Finches are also part of this ecosystem. Finches feed on the seeds produced by the tree, and are eaten by the hawks and eagles. Add this information to the food web above. (1 mark for each correct link = 3) b) Suggest two changes that might happen if all the eagles in this ecosystem died out. Change 1: More hawks = less crows Change 2: More finches = increased competition for seeds Biology Y10 HY Page 4 of 13
5 c) Match the type of organism to its correct definition. Two of the definitions are extra. Type of organism present in ecosystem Definition carnivore An animal that obtains its energy from eating other animals The position of an organism within the food web consumer An animal that obtains its energy from eating other plants decomposer An animal that obtains its energy from eating other organisms An animal that obtains its energy from dead or waste organic matter Herbivore An organism that makes its own organic nutrients (1 mark each = 4) Total: 9 marks 5. Bile is a dark green to yellowish brown fluid, produced by the liver of most vertebrates, which aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. a) In which structure is bile stored? Gall bladder b) Bile aids the digestion of lipids. Explain this biological statement. It breaks down large lipid droplets into smaller ones This increases surface area for digestion Emulsification (3) Biology Y10 HY Page 5 of 13
6 c) The following diagram shows the apparatus set at the start of an experiment that investigated the digestion of fat by an enzyme A. The apparatus is kept in a water bath at 40 C, for 30 minutes, during which the colour changes of the ph indicator are observed. The ph indicator changes colour as follows: ph value Below 7 Indicator colour Red 7 Green Above 7 Blue i) State the name of enzyme A. Lipase ii) Explain why the apparatus is kept in a water bath at 40 C. Optimum temperature / Close to body temperature (Any 1) iii) From the table above, suggest the colour which would be observed after 30 minutes. Give a reason for your answer. Red Lipids broken down into glycerol and fatty acids Fatty acids have an acidic ph - below 7 (3) Total: 9 marks Biology Y10 HY Page 6 of 13
7 6. The following diagram shows the villus (pl.villi). This structure is found in the ileum, which forms part of the small intestine. A B a) What is the main function of the villi in the ileum? Absorption of nutrients b) State two ways of how villi are adapted to perform their function. Large surface area / Network of blood vessels / Lacteal and Lymph ducts / Thin epithelium (Any 2) c) Name two substances which are normally absorbed into part A. Fatty acids and glycerol d) To which organ does the blood vessel B lead to? Liver e) Coeliac disease is a disease caused by intolerance to gluten, a chemical usually found in products such as wheat and oat. This intolerance is thought to cause damage to the villi. Suggest one effect of this disease. Less absorption / abdominal pain / weight loss (Any 1 or equivalent) Total: 6 marks Biology Y10 HY Page 7 of 13
8 Volume of juice obtained using 80% Section B: Answer question ONE and ANY OTHER TWO questions on the papers provided. This section carries a total of 45 marks. 1. Pectinase is an enzyme that breaks down pectin, a polysaccharide found in plant cell walls. Pectinase enzymes are commonly used in industrial processes involving the breakdown of plant materials, such as the extraction of fruit juice from fruit. Biology students investigated the effect of using different concentrations of pectinase on apples, by measuring the volume of apple juice obtained. The following table shows the results obtained: Time/hours Volume of juice obtained using 40% pectinase concentration/cm 3 Volume of juice obtained using 80% pectinase concentration/cm a) Plot a graph of the volume of juice collected at 80% pectinase concentration (y-axis) against the time (x-axis) (4) Volume of juice obtained using 80% pectinase concentration (cm 3 ) against time (hours) pectinase concentration/cm Time/hours Correct plotting Correct use of scales / graph Title Labels Deduct ½ mark if units are not included. Deduct 1 mark if both sets of data are plotted. Biology Y10 HY Page 8 of 13
9 b) Using the table of results, write down a suitable conclusion to clearly show the difference between 40% and 80% pectinase concentration. A higher concentration of enzyme results in a larger amount of juice / More juice is produced when 80% pectinase is used (Or equivalent) c) Throughout the experiment, the temperature was kept constant. Explain why. A change in temperature affects rate of reaction / Effect of temperature is not being investigated (Or equivalent = 1 mark) Only one factor should be changed at a time (1 mark) d) Write down one other factor that should have been kept constant throughout the experiment. The mass of apple used / Volume of enzyme solution used / Same apple / Same ph (Any 1) e) One of the students commented that fruit juice would still be extracted if the enzyme cellulase was used instead of pectinase. i) Is the student correct? ii) Give a reason for your answer. Yes. Cellulase breaks down cellulose present in the cell wall. f) Enzymes are commonly used in industrial processes. Write down three reasons why enzymes are normally included in industrial processes. (3) They are cheap / Do not need high temperatures to work / Less expensive to energy saving / Can be re-used / Only small amounts needed (Any 3) g) Besides extracting fruit juice, give one other example of enzyme use in industry. Biological washing powder / Fermentation / Breaking down blood clots / Making of chocolates or syrups / Making meat tender / Removing hair from animal skins / Skinning fish / Removing seed coats from cereal grains (Any 1 or equivalent) Total: 15 marks Biology Y10 HY Page 9 of 13
10 2. Green plants make their own food. They use simple substances from the air & soil, and build them into complex materials. This process is known as photosynthesis. a) Name one type of plant cell that performs photosynthesis and state where it can be found. Palisade mesophyll cell / Spongy mesophyll cell / guard cells (Any 1) Found in the leaf b) Name a plant cell that does not perform photosynthesis. Epidermal cell / Root cell (Any 1) c) Explain how each of the following helps a leaf to photosynthesise: i) There is an air space behind each stoma. ii) Leaves have a large surface area. iii) The veins in a leaf branch repeatedly. Air space allow gases to diffuse in and out / efficient gaseous exchange A large surface area allows leaf to absorb more light Veins bring water to the cells d) Two substances plants take up from the soil are magnesium and nitrogen (in the form of nitrates). For each of these minerals, state its function in plants, and the deficiency effect. (4) Mg: Part of chlorophyll molecule / helps activate growth enzymes Deficiency: Yellowing between leaf veins / Yellowing around leaf margins / Leaf death (Any 1) N: Synthesis of proteins and other complex chemicals Deficiency: Plants are stunted and yellow / No new shoots / Delayed flowering / reduced seed formation (Any 1) e) A limiting factor is something present in the environment in such short supplies that it restricts processes such as photosynthesis. List one limiting factor that might limit the rate of photosynthesis in the following situations: i) a plant growing on the forest floor; ii) a plant on a very hot, dry day. i) Amount of light ii) Amount of water / Temperature (Any 1) f) Although the setting up of greenhouses is very expensive, farmers still prefer to grow their plants and crops in greenhouses. Explain this statement. (3) Crops can be grown out of season / Can grow non-local species / Protection against weather / Control of factors for optimal growth / Cross pollination can be carried out manually as very little insects enter the greenhouse / Biological pest control is easier (Any 3) Total: 15 marks Biology Y10 HY Page 10 of 13
11 3. Explain each of the following biological statements: a) School canteens are encouraged to sell unsweetened cereals and fruit rather than sweets and chocolates. Sweets and chocolates have large amount of sugar Can cause damage to teeth / Diabetes / Obesity b) A nutritionist suggested to a vegetarian to include Soya beans in the diet. (3) Vegetarians do not eat meat Lack of protein Soya beans are rich in protein c) Food chains normally do not have more than 5 trophic levels. (3) 90% energy lost/used at each trophic level Only 10% is passed on Top organisms do not get enough energy to survive d) One of the secretions of the pancreas is sodium bicarbonate. Neutralises the acidity of chyme Provides the correct ph for pancreatic and intestinal enzymes e) The liver is considered to be a storage organ. (3) Stores food substances like glycogen, fat-soluble vitamins and iron f) Decomposers have an important role in all ecosystems. Break down remains of dead organisms / Cause decay / break down remains into simple chemical substance (Any 1) Responsible for recycling of nutrients from higher to lower trophic levels Total: 15 marks Biology Y10 HY Page 11 of 13
12 4. This question is about the human gut and the process of digestion. a) Digestion starts in the mouth. List: i) one mechanical (physical) way ii) and one chemical way in which digestion in the mouth takes place. Teeth chop and crush food Salivary amylase breaks down starch into maltose b) Explain how food reaches the stomach from the mouth. Waves of muscular contractions in wall of gullet push bolus down This is called peristalsis c) Name a region in the human gut with a: i) low ph ii) ph greater than 7 Low ph: Stomach High ph: Duodenum / ileum (Any 1) d) The mammalian body is capable of storing excess carbohydrates, but it cannot store excess proteins. i) Name the sugar that excess carbohydrates are stored as. ii) Name the organ in which excess carbohydrates are normally stored. iii) Explain how the mammalian body deals with extra proteins i) Glycogen ii) Liver iii) Deamination Amine group is removed from amino acid Remaining part is stored as a carbohydrate e) i) Explain the effect of a diet low in fibre. ii) Suggest one type of food that increases intake of fibre. i) Constipation / lack of bulk results in difficulty in pushing out faeces ii) Cereal grains / Bread / Vegetables (Any 1 or equivalent) (3) Total: 15 marks Biology Y10 HY Page 12 of 13
13 5. Many different species of ruminant animals are found around the world. Ruminants include cattle, sheep, goats, buffalo, deer, giraffes and camels. These animals all have a digestive system that is uniquely different from our own. a) What is a ruminant? Herbivores with a 4-chambered stomach b) Describe the importance of the following structures in the dentition of a ruminant: i) horny pad; ii) diastema; iii) flat molars and premolars i) Lower incisors act like pincers against it / Used for cropping grass (Any 1) ii) Allows the tongue to manipulate food easily iii) Allow crushing and grinding of food c) Explain why the molars and premolars of herbivores grow continuously throughout their life. d) Ruminants host cellulose-digesting bacteria in their stomach. Explain the importance of these bacteria. (3) Ruminants are not capable of digesting cellulose / No cellulase Bacteria break down cellulose into sugars Sugars can be absorbed by ruminant e) Lions are carnivores. Give three ways of how its dentition is expected to be different from that of a herbivore. (3) Pointed incisors used for nibbling meat from bones Large, pointed canines used for piercing skin and tearing flesh Carnissal teeth scrape flesh off bones with scissor-like action f) Carnivores normally have a large and active liver. Explain Carnivores have diet high in protein Liver is responsible for large amount of deamination g) Lions are referred to as predators. Give two reasons why predation is beneficial to the prey species. Controls number of prey / less competition within prey population Eliminates weak members Total: 15 marks Biology Y10 HY Page 13 of 13
Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition
 CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
CIE Biology GCSE 7: Human nutrition Notes Humans need many different nutrients to survive. To receive these nutrients in the correct quantities, a balanced diet must be eaten. A balanced diet includes
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
Objective 4- Digestion
 Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Objective 4- Digestion 1. Describe why cells require nutrients Supply energy for metabolism (cell activities), matter for synthesis of new materials, cell reproduction, secretion and to regulate cell processes
Human Digestive System
 3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
3.3.4 Human Digestive System Need to know The functions of the main parts of the alimentary canal and the associated glands Function of teeth. The human dental formula Role of mechanical digestion and
Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment
 _ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
_ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root. Tooth type and job. Why do humans have more than one type of tooth?
 Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Digestion & The Alimentary Canal
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013
 ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Look at nutrition in various animals o Herbivores, Carnivores and Omnivores Study the structure of the human digestive system Look
ANIMAL NUTRITION 24 APRIL 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Look at nutrition in various animals o Herbivores, Carnivores and Omnivores Study the structure of the human digestive system Look
Nutrition, part 2. Because 1 part isn t enough!
 Nutrition, part 2 Because 1 part isn t enough! 4. Calories and Caloric Intake Calories per gram of our Macro and Micro nutrients Macro Carbohydrates: 4 cal/g Fats: 9 cal/g Proteins: 4 cal/g Micro Vitamins:
Nutrition, part 2 Because 1 part isn t enough! 4. Calories and Caloric Intake Calories per gram of our Macro and Micro nutrients Macro Carbohydrates: 4 cal/g Fats: 9 cal/g Proteins: 4 cal/g Micro Vitamins:
Human Digestion. Junior Science
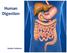 Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
At the end of this lesson, you should be able to:
 Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
Digestion Learning Objectives At the end of this lesson, you should be able to: Enzymes Explain enzyme action in terms of the lock and key hypothesis Explain the effects of temperature and ph on the rate
Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract
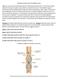 Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract Digestion is a process that break-down food into small molecule called nutrient. These small molecule called nutrients pass through the cell membrane or absorb
Reading Comprehension of the digestive tract Digestion is a process that break-down food into small molecule called nutrient. These small molecule called nutrients pass through the cell membrane or absorb
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Digestive System. Part A Multiple Choice. 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin.
 Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
Digestive System Part A Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following is NOT a digestive enzyme? A. Pepsin. B. Ptyalin. C. Gastrin. D. Trypsin. 2. The presence of large numbers of mitochondria in the cells
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013
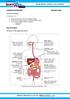 HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
Digestive System. Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy
 Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
Biology: 4. The Digestive System
 Biology: 4. The Digestive System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB6 OB7 OB8 Syllabus Identify and locate the major parts of
Biology: 4. The Digestive System Please remember to photocopy 4 pages onto one sheet by going A3 A4 and using back to back on the photocopier OB6 OB7 OB8 Syllabus Identify and locate the major parts of
Summary of chemical breakdown of food by hydrolytic enzymes (Protein enzymes).
 Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
7.4 Digestion. Highlight the definition of mechanical digestion.
 7.4 Digestion Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The large food molecules are starch,
7.4 Digestion Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The large food molecules are starch,
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by. broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Characteristics of living organism
 At a glance : Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Living organisms are bundles of cells that carry out specialized functions. 1. Life is uncertain because Organic Matter is born, it Organic / Biotic Matter
At a glance : Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Living organisms are bundles of cells that carry out specialized functions. 1. Life is uncertain because Organic Matter is born, it Organic / Biotic Matter
Nutrients and Digestion
 Nutrients and Digestion Nutrition what is needed to be taken in to keep the body healthy Essential Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Carbohydrates Types of sugars combined in
Nutrients and Digestion Nutrition what is needed to be taken in to keep the body healthy Essential Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Carbohydrates Types of sugars combined in
The Small Intestine. The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine.
 The Small Intestine The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine. approximately six metres (the longest section of your digestive
The Small Intestine The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine. approximately six metres (the longest section of your digestive
GOZO COLLEGE SECONDARY SCHOOL
 Embracing Diversity GOZO COLLEGE SECONDARY SCHOOL Half Yearly Exams 2014-2015 Subject: BIOLOGY TRACK 2 Form: 4 Time: 2 Hours Name: Class: Section A Section B Question No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 Max mark
Embracing Diversity GOZO COLLEGE SECONDARY SCHOOL Half Yearly Exams 2014-2015 Subject: BIOLOGY TRACK 2 Form: 4 Time: 2 Hours Name: Class: Section A Section B Question No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 4 5 Max mark
Animal Nutrition. Key Concepts. Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms. What do animals get from food?
 Key Concepts Animal Nutrition Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Key Concepts Animal Nutrition Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Key Concepts. Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory
 Animal Nutrition Key Concepts Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Animal Nutrition Key Concepts Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Nutrition. Why do humans need food? How do some animals get their food? ROUGHAGE NUTRIENTS. Animals make energy available using:
 Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
The Digestive System. 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers
 I. Type of food: The Digestive System 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers 1- Carbohydrates: are energy foods (sugars). They are made of C,H, and O atoms. They
I. Type of food: The Digestive System 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers 1- Carbohydrates: are energy foods (sugars). They are made of C,H, and O atoms. They
The digestive system consists of an alimentary canal and several accessory organs. The Digestive System
 The digestive system consists of an alimentary canal and several accessory organs. The Digestive System The Digestive System The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food. Mechanical
The digestive system consists of an alimentary canal and several accessory organs. The Digestive System The Digestive System The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaks down food. Mechanical
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Proteins their functions and uses revision 3
 Proteins their functions and uses revision 3 59 minutes 59 marks Page of 23 Q. The diagram gives information about some parts of the human digestive system. (a) (i) Name the organ which makes bile. Label
Proteins their functions and uses revision 3 59 minutes 59 marks Page of 23 Q. The diagram gives information about some parts of the human digestive system. (a) (i) Name the organ which makes bile. Label
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION
 ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Page 1. Chapter 34: Nutrition and Digestion
 Chapter 34: Nutrition and Digestion Nutrition: Process of acquiring / processing nutrients into usable form Function of Nutrients: 1) Fuel cellular metabolism Measured in calories (energy required to raise
Chapter 34: Nutrition and Digestion Nutrition: Process of acquiring / processing nutrients into usable form Function of Nutrients: 1) Fuel cellular metabolism Measured in calories (energy required to raise
Page 1. Electrolytes. Required to maintain certain functions. Imbalance causes death. Muscles, neurons, etc.
 Chapter 34: Nutrition and Digestion Nutrition: Process of acquiring / processing nutrients into usable form Function of Nutrients: 1) Fuel cellular metabolism Measured in calories (energy required to raise
Chapter 34: Nutrition and Digestion Nutrition: Process of acquiring / processing nutrients into usable form Function of Nutrients: 1) Fuel cellular metabolism Measured in calories (energy required to raise
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Learning Targets. The Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract. Also known as the alimentary canal. Hollow series of organs that food passes through
 Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating
 Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating Types of teeth Preventing tooth decay Dentition of other animals Digestive system By the end of this unit you should: Know the structure, function and care of the human teeth.
Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating Types of teeth Preventing tooth decay Dentition of other animals Digestive system By the end of this unit you should: Know the structure, function and care of the human teeth.
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that
 PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
PPL2O Human Digestion The human digestive system is a complex process that consists of breaking down large organic masses into smaller particles that the body can absorb and use. The breakdown of the nutrients
Digestion. I. What is digestion? II. Enzymes involved in digestion
 Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
Name: Enzymes. Class: Date: 101 minutes. Time: 100 marks. Marks: Level 1,2 and 3. Increasing demand. Comments:
 Enzymes Name: Class: Date: Time: 0 minutes Marks: 00 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. Catalase is an enzyme. Catalase controls the following reaction: hydrogen peroxide water + oxygen
Enzymes Name: Class: Date: Time: 0 minutes Marks: 00 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. Catalase is an enzyme. Catalase controls the following reaction: hydrogen peroxide water + oxygen
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010
 DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
NUTRITION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS
 NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE NUTRITION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS 1. 1989 Q1 P1 The diagram below shows chemical reactions I, and II which are controlled by enzymes respectively. GLUCOSE + FRUCTOSE Reaction
NAME SCHOOL INDEX NUMBER DATE NUTRITION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALS 1. 1989 Q1 P1 The diagram below shows chemical reactions I, and II which are controlled by enzymes respectively. GLUCOSE + FRUCTOSE Reaction
1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals a) Suspension feeders i) (1) Humpback whales b) Substrate feeders i)
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS
 2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3. Proteins 4. Minerals 5. Vitamins 6.
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3. Proteins 4. Minerals 5. Vitamins 6.
>>> FOCUS. Context. Digestion. The human digestive system
 Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS
 2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
FOOD. Why do we need food? What's in our food? There are 3 trace elements, Iron (Fe), Copper (Cu) and Zinc (Zn).
 Why do we need food? FOOD 1. As a source of energy keeps our cells and us alive. 2. To make chemicals for our metabolic reactions. 3. As raw materials for growth and repair of our cells and body. What's
Why do we need food? FOOD 1. As a source of energy keeps our cells and us alive. 2. To make chemicals for our metabolic reactions. 3. As raw materials for growth and repair of our cells and body. What's
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption. Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs
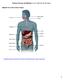 Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter26/animation organs_of_digestion.html
Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter26/animation organs_of_digestion.html
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology
 A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
GHS EOT 2 S. 2 BIOLOGY 553/1 (THEORY) AUGUST 2017 TIME: 2 HOURS. Attempt all the questions in section A and B and C in the spaces provided
 GHS EOT 2 S. 2 BIOLOGY 553/1 (THEORY) AUGUST 2017 TIME: 2 HOURS NAME: MARKING GUIDE INSTRUCTIONS Attempt all the questions in section A and B and C in the spaces provided ANSWERS TO SECTION A 1 A 7 C 13
GHS EOT 2 S. 2 BIOLOGY 553/1 (THEORY) AUGUST 2017 TIME: 2 HOURS NAME: MARKING GUIDE INSTRUCTIONS Attempt all the questions in section A and B and C in the spaces provided ANSWERS TO SECTION A 1 A 7 C 13
Digestive System Practice Test
 Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion 15.1A Food and Energy Functions of Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. Calories = amt. of energy in food RDA depends on age, gender, size and activity level Types of Nutrients (includes
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion 15.1A Food and Energy Functions of Nutrients 1. 2. 3. 4. Calories = amt. of energy in food RDA depends on age, gender, size and activity level Types of Nutrients (includes
Digestive and Excretory Systems
 Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) This section identifies the nutrients your body needs and explains why water is such an important nutrient Food
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) This section identifies the nutrients your body needs and explains why water is such an important nutrient Food
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System What is the digestive system? The digestive system is where the digestion of food and liquids occurs. Our bodies are not suited to absorbing the energy contained in food as they are
The Digestive System What is the digestive system? The digestive system is where the digestion of food and liquids occurs. Our bodies are not suited to absorbing the energy contained in food as they are
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion
 Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
Chapter 15 Food and Digestion Activity: Use Qualitative Observations (5 senses) to describe: What happens when you see candy? How does it smell? How do you chomp it into smaller pieces or swallow candy
a. parotid b. sublingual c. submandibular
 Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
Bozeman Science/ Nature The Digestive System Watch the videos, and answer the questions below. Please write your answers in complete sentences, and explain all concepts thoroughly. 1. What are the four
UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If you know what is
UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If you know what is
10/23/2013 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Slide 1 UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Slide 2 Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If
Slide 1 UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Slide 2 Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If
Nutrition and Deficiency Static GK Notes PDF 3
 Nutrition and Deficiency Static GK Notes PDF 3 Let us talk about nutrition and deficiency. Science and Technology form an integral part of our society. But we often forget age-old wisdom passed to us from
Nutrition and Deficiency Static GK Notes PDF 3 Let us talk about nutrition and deficiency. Science and Technology form an integral part of our society. But we often forget age-old wisdom passed to us from
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 www.xtremepapers.com Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *3022478872* BIOLOGY 0610/21 Paper 2 Core May/June 2015 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
www.xtremepapers.com Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *3022478872* BIOLOGY 0610/21 Paper 2 Core May/June 2015 1 hour 15 minutes Candidates
This section identifies the nutrients your body needs and explains why water is such an important nutrient.
 Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38-1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971-977) 44P TEKS FOCUS: 9A Structure and function of biomolecules; 11 C Importance of nutrition on health This section
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38-1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971-977) 44P TEKS FOCUS: 9A Structure and function of biomolecules; 11 C Importance of nutrition on health This section
The Digestive System Exam Questions
 The Digestive System Exam Questions 2012 - Higher Name an enzyme. Name the substrate that the enzyme you have named acts on. Name the product of the action of this enzyme. What reagent might you use, in
The Digestive System Exam Questions 2012 - Higher Name an enzyme. Name the substrate that the enzyme you have named acts on. Name the product of the action of this enzyme. What reagent might you use, in
Animal Nutrition Human Digestion
 Animal Nutrition Human Digestion 2006-2007 What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, O fats, nucleotides
Animal Nutrition Human Digestion 2006-2007 What do animals need to live? Animals make energy using: food food oxygen Animals build bodies using: food for raw materials amino acids, sugars, O fats, nucleotides
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM.
 1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
The Human Digestive Tract
 The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
Animal Nutrition Variations, Adaptations & Regulation
 Animal Nutrition Variations, Adaptations & Regulation This obese mouse (L) has defect in gene which normally produces leptin, an appetite-regulating protein. Many herbivores have diets deficient in mineral
Animal Nutrition Variations, Adaptations & Regulation This obese mouse (L) has defect in gene which normally produces leptin, an appetite-regulating protein. Many herbivores have diets deficient in mineral
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
SNC4M The Digestive System
 SNC4M The Digestive System What is digestion? Chemical and mechanical breakdown of organic molecules into units small enough for the body to absorb These molecules provide: 1. Energy resources 2. Essential
SNC4M The Digestive System What is digestion? Chemical and mechanical breakdown of organic molecules into units small enough for the body to absorb These molecules provide: 1. Energy resources 2. Essential
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
1b. Credit: State the chemical elements present in carbohydrates, proteins and fats. See table below
 1a. General: Explain in simple terms why food is required by animals. The main types of food are carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Carbohydrates and fats are required as sources of energy. Proteins are
1a. General: Explain in simple terms why food is required by animals. The main types of food are carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Carbohydrates and fats are required as sources of energy. Proteins are
Animal Survival. Standard Grade Biology
 Animal Survival Standard Grade Biology Give 5 reasons why the body needs food. The Need for Food The 3 main types of food are carbohydrate, fat and protein. State the chemical elements present in each.
Animal Survival Standard Grade Biology Give 5 reasons why the body needs food. The Need for Food The 3 main types of food are carbohydrate, fat and protein. State the chemical elements present in each.
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes
 Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
1 Small molecules are used as the basic units in the synthesis of large food molecules. Which statement is correct? A
 1 Small molecules are used as the basic units in the synthesis of large food molecules. Which statement is correct? mino acids are basic units of carbohydrates. Fatty acids are basic units of glycogen.
1 Small molecules are used as the basic units in the synthesis of large food molecules. Which statement is correct? mino acids are basic units of carbohydrates. Fatty acids are basic units of glycogen.
Lesson 1. Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition
 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems (Machalina song) Nutrition Let s figure out how many body systems there are! Draw a hollow body diagram Draw in each body part as it is mentioned in the song!!! Chorus:
AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST SUPPLY CHEMICAL ENERGY, ORGANIC MOLECULES, AND ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS
 1 ANIMAL NUTRITION 2 3 4 5 6 7 Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores
1 ANIMAL NUTRITION 2 3 4 5 6 7 Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores eat mainly plants and algae Carnivores
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C.
 There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C. The enzymes in biological washing powders do not work on the stains on clothes at temperatures
There are enzymes in biological washing powders. Biological washing powder has to be used at temperatures below 45 C. The enzymes in biological washing powders do not work on the stains on clothes at temperatures
Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Biology
 Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) Underline the correct answer: Part 1 1) Given below are some adapative features of plants: (i) It
Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 2 nd Term Examination March, 2018 Duration: 2.00 Hours 1) Underline the correct answer: Part 1 1) Given below are some adapative features of plants: (i) It
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
 Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
The small intestine THE DUODENUM
 4. The digestive system 4.2 The stages of digestion 4.2.7 The small intestine THE DUODENUM The duodenum is the first segment of the small intestine. It is an important segment because it receives pancreatic
4. The digestive system 4.2 The stages of digestion 4.2.7 The small intestine THE DUODENUM The duodenum is the first segment of the small intestine. It is an important segment because it receives pancreatic
BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min. Section B
 BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min INDEX NUMBER Total: 100 marks Section A Answer all questions in this section. Section A carries 55 marks. Question
BISHOP S CONSERVATORY SCHOOL ANNUAL EXAMINATIONS 2006 FORM 4 BIOLOGY TIME: 1hr 30 min INDEX NUMBER Total: 100 marks Section A Answer all questions in this section. Section A carries 55 marks. Question
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
BIOLOGY 30S: Digestion and Nutrition Mega-Review 1. What is the primary purpose of the process called cellular respiration?
 BIOLOGY 30S: Digestion and Nutrition Mega-Review 1. What is the primary purpose of the process called cellular respiration? 2. What is the powerhouse of the cell? 3. What is often described as the currency
BIOLOGY 30S: Digestion and Nutrition Mega-Review 1. What is the primary purpose of the process called cellular respiration? 2. What is the powerhouse of the cell? 3. What is often described as the currency
Warm-Up. Distinguish between an element and a compound. Element. Compound
 Warm-Up Distinguish between an element and a compound. Element Compound Warm-Up Distinguish between an element and a compound. Element Cannot be broken down into anything smaller Found on the Periodic
Warm-Up Distinguish between an element and a compound. Element Compound Warm-Up Distinguish between an element and a compound. Element Cannot be broken down into anything smaller Found on the Periodic
