ENGLISH. 2. Write a speech on Child Labour to be delivered in your school assembly on the occasion of LABOUR DAY.
|
|
|
- Christopher Welch
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ENGLISH 1. The day Private Quelch was chosen for cookhouse duties, the writer felt very happy and contented. Write a diary-entry expressing your thoughts and feelings, imagining yourself to be in the writer s place. 2. Write a speech on Child Labour to be delivered in your school assembly on the occasion of LABOUR DAY. 3. You are Abhishek and you have noticed an advertisement of a Book Fair at Pragati Maidan, New Delhi. Send an to your brother, asking him to visit the fair. 4. Write an article on the topic Utility of Computers in Children s Education in about 150 words. 5. Write 20 Newspaper Headlines. 6. Write a notice for your School notice-board informing the students about the School Inspection to be held on 1 st December 2017 by the District Education Officer. The notice should be of 50 words asking for punctuality, discipline and cleanliness. Put the notice in a box. You are the School Captain. 7. You are Nitish Goel. Send a post-card to your friend Ajay inviting him to the sacred thread ceremony of your younger brother, who is 9 years old. Make the format for the purpose. 8. Write about your School Hostel using both active and passive voices. 9. Read the story Keeping It from Harold and note down the main incidents in your HW notebook. 10. Read the chapters 11 to 19 of the novel Three Men in a Boat and note down the main points in your HW copy. 11. Read the passages given in the Unit Mystery from your Main Course Book. HINDI 1. keàer eæ[ keàe keàej³e Heeþ kesà ÒeMveebs kesà GÊej efueefkes ~ 2. SkeÀ HetÀue keàer een keàefjelee keàes Heæ{keÀj GmekeÀe YeeJeeLe& efueefkes ~ 3. efjejece ef eúew kesà Yeso keàes efuekekeàj GvekeÀe Òe³eesie keàj Jeeke̳e yeveefs~ 4. GHemeie& Deewj Òel³e³e keàer HeefjYee<ee yeleeles ngs meyeer keàs GoenjCe efueefkes ~ 5. Deveg íso efueefkes onspe SkeÀ DeefYeMeeHe, ðeer efme#ee 6. íe$e - efme#ekeà, efhelee - Heg$e kesà yeer e mebjeeo efueefkes ~ 7. efje%eeheve lew³eej keàerefpes He$e efueefkes efòe³e efce$e keàes, DeHeves ceeceepeer keàes
2 icé _âgüe CZe û ODIA 1. bûezúd iõäézòe aûzðûaj Êûcú aòùakû^ 2. ùiaû I cczûe cìzðòc«_âzúk c\e ùuùeiû 3. ]cð eûr^úzòe _eò_^úú Kò? 4. Zêc _âòd _êék 5. icûrùe ù^ ZòK gòlû ûcôòk gòlûe _âùdûr^ 6. _fäúe gûe\úd i ýû 7. Kkòwe ae_êzâ aòrdû^ _ ^ûdk 8. iwÿk \ênðuyû GK ^òzò\ò^ò@û aýû_ûe 9. iûõ_âzòk ~ême gòlû iciýû I Zû e _âzòkûe 10. bûeze Kûgàúe iciýû GK RûZúd iciýû 11. GK Neù_ûWÿò i û\ _âkûg Keòaû ^òcù«ù\ ^òk i û\_zâkê i û\ ù_âey Ke û 12. ù\ ^òk i û\_zâùe _âkûgòz i û\e _âzòaû\ Keò _Zâ i û\ _ZâòKû iõ_û\ku ^òkukê ùfl û 13. aýûuùe LûZû ùlûfòaû ^òcù«aýûu cýûù^reu ^òkukê _Zâ û 14. Zêc Mâûcùe GK _ûvûmûe Méj ^òcðûy ^òcù«@û[ôðk ijûdzû ^òcò aòbûmúd cªúuê \elûé _â\û^ Ke û 15. aò\ýûkdùe ieêzú _ìrûùe ù~ûmù\aû ^òcù«^òcªy _Zâ ùfl û 16. Zêc Mâûcùe N^N^ ù eò ùjcqò, Gjûe ^òeûkey _ûañ ^òcù«ù\ ^òk i û\_zâkê GK i û\ ù_âey Ke û MATHEMATICS 1. Write the proofs of the following theorems. a) A diagonal of a parallelogram divides it into two congruent triangles. b) Opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal. c) If each pair of opposite sides of a quadrilateral are equal, prove that it is a parallelogram. d) Opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal, prove it. e) If each pair of opposite angles of a quadrilateral are equal, prove that it is a parallelogram. f) Prove that the diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other. g) I f the diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other, prove that it is a parallelogram. h) A quadrilateral is a parallelogram if a pair of its opposite sides are equal and parallel.
3 i) The line segment joining the mid points of any two sides of a triangle is parallel to the third side. Prove it. j) The line drawn through the midpoint of any side of a triangle and parallel to another side, bisects the third side. Prove it. k) Parallelograms on the same base and between the same parallels are equal in area. l) Triangles on the same base and between the same parallels are equal in area. m) Two triangles having the same base and equal areas lie between the same parallels. 2. Chapter 9 ( Areas of parallelograms & Triangles ) From NCERT Text Book Exercise questions, Exercise questions From any reference book of Class IX. At least 10 questions each on the following chapters. Chapter-1 : Number System Chapter-2 : Polynomials Chapter-6 : Lines & Angles Chapter-7 : Triangles Chapter-8 : Quadrilaterals PHYSICS Answer the following. 1. A particle is moving in a circle of diameter 5m. What is its displacement when it covers one and half revolutions? 2. Define (a) average speed and (b) average velocity 3. A runner presses the ground with his feet before he starts his run. Identify action and reaction in this situation. 4. A heavy and a light object have same momentum. Which of these is travelling faster? 5. Why does the weight of a body vary from poles to equator? 6. (a) What can be depicted from the graph regarding the motion of the object? (b) Find the value of acceleration from the graph. 50 Velocity (ms -1 ) time(s)
4 7. A bullet of mass 10g travelling horizontally with a velocity of 150ms -1 strikes stationary wooden block and comes to rest in 0.03s. Calculate the distance of penetration of bullet into the block. Also calculate the magnitude of force exerted by the wooden block on the bullet. 8. A force of 2N acting on a body changes its velocity uniformly from 2ms -1 to 5ms -1 in 10s. Calculate the mass of the body. 9. State and prove Law of conservation of Momentum. 10. The velocity time graph of a body is shown below: a. State the kind of motion represented by OA, AB and BC b. What is the acceleration for BC c. Find the distance travelled between 10 th and 30 th second. 15 A B Velocity (ms -1 ) 10 5 o C time(s) CHEMISTRY 1.Using Symbol and Valence given to you write the chemical formulae for the followings 1. Zinc oxide 2. Aluminium chloride 3. Calcium sulphide 4. Sodium carbonate 5. Magnesium nitrate 6. Barium sulphate 7. Potassium sulphate 8. Ammonium phosphate 9. Silver nitrate 10. Ferrous chloride 11. Aluminium phosphate 12. Calcium bicarbonate 13. Aluminium oxide 14. Potassium carbonate 15. Zinc chloride 16. Lead(II) nitrate 17. Silver bromide 18. Sodium sulphite 19. Magnesium oxide 20. Barium chloride 21. Ferric sulphate 22. Mercury(II) oxide 23. Copper(II)carbonate 24. Ferrous sulphate 25. Iron(II)sulphide
5 2.Write the name of the compounds whose chemical formulae are given below. 1. Zn 3 (PO 4 ) 2 2. Al 2 (CO 3 ) 3 3. K 2 SO 4 4. NH 4 NO 3 5. Ca(OH) 2 6. FeS 7. PbCO 3 8. Ag 2 O 9. BaSO NaHCO Fe(NO 3 ) Na 2 SO 3 IONS- Atoms or clusters of atoms carrying charge on them are called ions. Ions may be positive ( for metals) or negative(for non metals) EXAMPLES- Sodium ion- Na +, Calcium ion- Ca 2+, Aluminium ion- Al 3+, Chloride ion- Cl -, Oxide ion- O 2-, Nitride ion- N 3- ( Valence number of positive or negative charge) Now write to represent the following ions. 1. Calcium ion 2. Potassium ion 3. Sulphide ion 4. Bromide ion 5. Ferric ion 6. Copper(II)ion 7. Phosphide ion A. Read your text book chapter 1,2,3 thoroughly and then write exercise questions from each chapter. B. Read the chapter structure of the atom from your text book and write the answer of the exercise questions. BIOLOGY Attemp all the Questions/Exercises given below referring the Notes/concepts given in the class: Short Answer Questions 1. Why are lysosomes known as suicide-bags of a cell? 2. Do you agree that A cell is a building unit of an organism. If yes, explain why? 3. Why does the skin of your finger shrink when you wash clothes for a long time? 5
6 4. A person takes concentrated solution of salt, after sometime, he starts vomiting. What is the phenomenon responsible for such situation? Explain. 5. We eat food composed of all the nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals and water. After digestion, these are absorbed in the form of glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, glycerol etc. 6. If you are provided with some vegetables to cook. You generally add salt into the vegetables during cooking process. After adding salt, vegetables release water. What mechanism is responsible for this? 7. If cells of onion peel and RBC are separately kept in hypotonic solution, what among the following will take place? Explain the reason for your answer. (a) Both the cells will swell. (b) RBC will burst easily while cells of onion peel will resist the bursting to some extent. (c) a and b both are correct. (d) RBC and onion peel cells will behave similarly. 8. Bacteria do not have chloroplast but some bacteria are photoautotrophic in nature and perform photosynthesis. Which part of bacterial cell performs this? 9. How is a bacterial cell different from an onion peel cell? 10. Name the two organelles in a plant cell that contain their own genetic material and ribosomes. 11. Why are lysosomes also known as scavengers of the cells? 12. Which cell organelle controls most of the activities of the cell? 13. Which kind of plastid is more common in (a) roots of the plant (b) leaves of the plant (c) flowers and fruits 14. Why do plant cells possess large sized vacuole? 15. How are chromatin, chromatid and chromosomes related to each other? 16. What are the consequences of the following conditions? (a) A cell containing higher water concentration than the surrounding medium (b) A cell having low water concentration than the surrounding medium. (c) A cell having equal water concentration to its surrounding medium. 17. Animals of colder regions and fishes of cold water have thicker layer of subcutaneous fat. Describe why? 18. If a potted plant is covered with a glass jar, water vapours appear on the wall of glass jar. Explain why? 19. Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles. Give one example of each type. 20. Differentiate the following activities on the basis of voluntary (V) or involuntary (I V) muscles. (a) (b) (c) (d) Jumping of frog Pumping of the heart Writing with hand Movement of chocolate in your intestine 21. Water hyacinth floats on water surface. Explain. 22. Which structure protects the plant body against the invasion of parasites? Long Answer Questions 6
7 1. Describe the structure and function of different types of epithelial tissues. Draw diagram of each type of epithelial tissue. 2. Draw well labelled diagrams of various types of muscles found in human body. 3. Give reasons for (a) Meristematic cells have a prominent nucleus and dense cytoplasm but they lack vacuole. (b) Intercellular spaces are absent in sclerenchymatous tissues. (c) We get a crunchy and granular feeling, when we chew pear fruit. (d) Branches of a tree move and bend freely in high wind velocity. (e) It is difficult to pull out the husk of a coconut tree. 4. List the characteristics of cork. How are they formed? Mention their role. 5. Draw a plant cell and label the parts which (a) determines the function and development of the cell (b) packages materials coming from the endoplasmic reticulum (c) provides resistance to microbes to withstand hypotonic external media without bursting (d) is site for many biochemical reactions necessary to sustain life. (f) is a fluid contained inside the nucleus 6. Illustrate only a plant cell as seen under electron microscope. How is it different from animal cell? 7. Differentiate between rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum. How is endoplasmic reticulum important for membrane biogenesis? 8. In brief state what happens when (a) Dry apricots are left for sometime in pure water and later transferred to sugar solution? (b) A Red Blood Cell is kept in concentrated saline solution? (c) The Plasma-membrane of a cell breaks down? (d) Rheo leaves are boiled in water first and then a drop of sugar syrup is put on it? (e) Golgi apparatus is removed from the cell? HISTORY & CIVICS 1. Which is known as the supreme law of the country? What does it include? 2. Who was Nelson Mandela? Why was he imprisoned? 3. What does Segregation mean in South Africa? What was African National Congress? 4. What policies were changed by the White Regime in South Africa? 5. Write the significance of Constituent Assembly Debates. 6. Mention any three changes that were brought about in the Constitution of South Africa after Describe the steps taken to form the Constituent Assembly. 8. What are Constituent Assembly Debates? 9. What is the philosophy of Indian Constitution? 10. Describe how the Indian Constitution has embodied the basic values into institutional arrarangements? 11. Explain how did the White minority and the black majority agree to draw up a common constitution for South Africa? 12. Why do we need a constitution? 7
8 13. The familiarity with political institutions of the Colonial rule helped to develop an agreement over the institutional design. Justify the statement. 14. Explain the importance of Institutional design of the Constitution of India. 15. Explain any 5 major ideals enshrined in the Preamble to the Constitution. 16. What kind of inspiration do we get from the Constitution of South Africa? 17. The Preamble of Indian Constitution Provides a Philosophy and Value of Constitution. Explain any 3 values that you derived from it. 18. Give a brief description about any 2 members of the Constituent Assembly. 19. Which country Constitutional features inspired Indian Constitution makers? 20. Describe the term- -Sovereign -Republic -Fraternity -Secular GEOGRAPHY 1) Explain the factors affecting the climate of India? 2) What does monsoon imply? 3) Write a brief note on the south-west monsoon and its influence on the climate of India? 4) Why eastern coastal plains are prone to cyclone? 5) Define coriolis force and ENSO. --END-- 8
Unit 2 Warm Ups. Equilibrium
 Unit 2 Warm Ups Equilibrium 1. Cell wall 2. Mitochondria 3. Chloroplast 4. Vesicle 5. Vacuole 6. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 7. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 8. Cytoskeleton 9. Lysosomes 10.Cell Membrane
Unit 2 Warm Ups Equilibrium 1. Cell wall 2. Mitochondria 3. Chloroplast 4. Vesicle 5. Vacuole 6. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum 7. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum 8. Cytoskeleton 9. Lysosomes 10.Cell Membrane
Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized
 Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: Organelles 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized 2. Golgi apparatus Enzymes in this apparatus
Chapter 7: Cells Review Packet Name: Organelles 1. endoplasmic reticulum The organelle made up of internal membranes where lipids and proteins are synthesized 2. Golgi apparatus Enzymes in this apparatus
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
Cells & Cell Organelles The Building Blocks of Life AP Biology 2008-2009 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal
(a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. B... (2)
 1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5
 Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Class: Date: Study Guide for Biology Chapter 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following led to the discovery of cells? a.
Cells & Cell Organelles. Doing Life s Work
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work AP Biology 2009-2010 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote - no organelles Eukaryotes - organelles animal cells plant cells Cell size comparison Animal cell
Cells & Cell Organelles
 Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work 2009 2010 1 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote no organelles animal cells Eukaryotes organelles plant cells 2 Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial
Cells & Cell Organelles Doing Life s Work 2009 2010 1 Types of cells bacteria cells Prokaryote no organelles animal cells Eukaryotes organelles plant cells 2 Cell size comparison Animal cell Bacterial
1. Structure A is the a. Cell wall b. Cell membrane c. Vacuole d. Lysosome
 Figure 1 Use Figure 1 to answer the following questions: 1. Structure A is the a. Cell wall b. Cell membrane c. Vacuole d. Lysosome 2. Structure E controls cellular functions. It is the a. Nucleolus b.
Figure 1 Use Figure 1 to answer the following questions: 1. Structure A is the a. Cell wall b. Cell membrane c. Vacuole d. Lysosome 2. Structure E controls cellular functions. It is the a. Nucleolus b.
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I, Class IX
 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I, 0-6 SCIENCE Class IX Time Allowed : hours Maximum Marks : 90 General Instructions :. The question paper comprises of two Sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections..
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I, 0-6 SCIENCE Class IX Time Allowed : hours Maximum Marks : 90 General Instructions :. The question paper comprises of two Sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections..
Chapter 7 Notes. Section 1
 Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Chapter 7 Notes Section 1 Cells Cells remained out of sight during most of human history until the invention of the first microscopes. It was not until the mid 1600s that scientists began to use microscopes
Cells. Cell as a basic unit of life. Activity: Observing onion cells. Cells
 1 Cells Cell as a basic unit of life In the year 1665, Robert Hooke observed a honeycomb like structure consisting of many compartments in a thin slice of cork. He called these boxes as cells. Cell in
1 Cells Cell as a basic unit of life In the year 1665, Robert Hooke observed a honeycomb like structure consisting of many compartments in a thin slice of cork. He called these boxes as cells. Cell in
The Fundamental Unit of Life. Intext Exercise 1
 Intext Exercise 1 Who discovered cells and how? Cells were discovered in 1665 by an English Botanist, Robert Hooke. He used a primitive microscope to observe cells in a cork slice. Why is the cell called
Intext Exercise 1 Who discovered cells and how? Cells were discovered in 1665 by an English Botanist, Robert Hooke. He used a primitive microscope to observe cells in a cork slice. Why is the cell called
Journey to the World of Cells
 Journey to the World of Cells Starting Point for Life All living organisms on Earth are divided into pieces called cells. Formed from Proteins Organelles Make larger pieces called Tissues and systems Main
Journey to the World of Cells Starting Point for Life All living organisms on Earth are divided into pieces called cells. Formed from Proteins Organelles Make larger pieces called Tissues and systems Main
By: Brooke Sheppard
 By: Brooke Sheppard What is a Cell? Cells are the basic structure of life for all organisms. Cells are microscopic, which means we can only view cells under a microscope. There are animal cells and plant
By: Brooke Sheppard What is a Cell? Cells are the basic structure of life for all organisms. Cells are microscopic, which means we can only view cells under a microscope. There are animal cells and plant
The Fundamental Unit Of Life Notes
 The Fundamental Unit Of Life Notes Cell Cell is regarded as the structural and fundamental unit of living organisms. Discovery of the Cell The term cell was introduced by an English Scientist Robert Hooke.
The Fundamental Unit Of Life Notes Cell Cell is regarded as the structural and fundamental unit of living organisms. Discovery of the Cell The term cell was introduced by an English Scientist Robert Hooke.
BIOLOGY 111. CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life
 BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
BIOLOGY 111 CHAPTER 3: The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Learning Outcomes 3.1 Explain the similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Ch. 6: A Tour of the Cell
 Ch. 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Compare the 2 Types of Cells PROKARYOTES BOTH EUKARYOTES Domain: Domain: Relative Size & Complexity: Relative Size & Complexity: No DNA in No Examples: Has Has Examples: 2.
Ch. 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. Compare the 2 Types of Cells PROKARYOTES BOTH EUKARYOTES Domain: Domain: Relative Size & Complexity: Relative Size & Complexity: No DNA in No Examples: Has Has Examples: 2.
Class IX Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life Science
 1 Class IX Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life Science Question 1: Who discovered cells and how? Cells were discovered in 1665 by an English Botanist, Robert Hooke. He used a primitive microscope to
1 Class IX Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life Science Question 1: Who discovered cells and how? Cells were discovered in 1665 by an English Botanist, Robert Hooke. He used a primitive microscope to
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. Use the following words to label the backside of the flashcards. The words are not listed
10. The diagram below shows two different kinds of substances, A and B, entering a cell.
 1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
1. In the binomial system of nomenclature, which two classification groups provide the scientific name of an organism? A) kingdom and phylum B) phylum and species C) kingdom and genus D) genus and species
MY BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM WORKBOOK
 NAME PER DATE MY BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM WORKBOOK DIRECTIONS: This study work book is due on the day of your final exam. Start now! After you have completed this study guide, you need to memorize it! 1. Look
NAME PER DATE MY BIOLOGY FINAL EXAM WORKBOOK DIRECTIONS: This study work book is due on the day of your final exam. Start now! After you have completed this study guide, you need to memorize it! 1. Look
Lesson 1. Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions. Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
 Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Lesson 1 Cell Theory - Statements - Exceptions Categorizing Cells - Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes The Cell Theory The discovery of cells and their structure is linked to the development of the magnifying lenses,
Cell structure and function flash cards
 Process Cell structure and function flash cards involved in aerobic respiration releasing ATP / energy has a double membrane folded into cristae (to make large SA) mostly occurs in mitochondria; needing
Process Cell structure and function flash cards involved in aerobic respiration releasing ATP / energy has a double membrane folded into cristae (to make large SA) mostly occurs in mitochondria; needing
Cell Cell
 Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Organelles. copyright cmassengale 1
 Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Organelles copyright cmassengale 1 Organelles Very small (Microscopic) Perform various functions for a cell Found in the cytoplasm May or may not be membrane-bound 2 Animal Cell Organelles Nucleolus Nucleus
Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards
 Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
Mr. Powner Biology Cell Theory Vocabulary Flashcards Instructions: Cut out the flashcards from the following pages. The following word list is the vocabulary for studying cell theory. Write each word on
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Take Home Exam: Cell Parts, Membranes, Photosynthesis, Cell Respiration. You are allowed to use any resources you can find for this exam. You may also work with a partner. Multiple Choice Identify the
Take Home Exam: Cell Parts, Membranes, Photosynthesis, Cell Respiration. You are allowed to use any resources you can find for this exam. You may also work with a partner. Multiple Choice Identify the
Explain the reason for this difference in resolving power.
 1. (a) An electron microscope has a much greater resolving power than an optical microscope. (i) Explain the meaning of the term resolving power. Explain the reason for this difference in resolving power.
1. (a) An electron microscope has a much greater resolving power than an optical microscope. (i) Explain the meaning of the term resolving power. Explain the reason for this difference in resolving power.
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells.
 Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Notes Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function 7.1 Cell discovery and Theory 1665 Hooke looked at cork under a simple microscope and found tiny chambers he named cells. Cells are the basic structural and
Standard 2 Exam Biology. 2. This macromolecule is responsible for short term energy storage and structural support in plants
 1. This macromolecule is responsible for structural support, movement, enzymatic activity, cell communication, and is made of amino acids. a. Lipids b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Nucleic Acids e. ATP
1. This macromolecule is responsible for structural support, movement, enzymatic activity, cell communication, and is made of amino acids. a. Lipids b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Nucleic Acids e. ATP
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Review Facts About Living Things 2 What Are the Main Characteristics of organisms? 1. Made of CELLS 2. Require ENERGY (food) 3. REPRODUCE (species) 4. Maintain HOMEOSTASIS 5.
Name: Date: Block: Biology 12
 Name: Date: Block: Biology 12 Provincial Exam Review: Cell Processes and Applications January 2003 Use the following diagram to answer questions 1 and 2. 1. Which labelled organelle produces most of the
Name: Date: Block: Biology 12 Provincial Exam Review: Cell Processes and Applications January 2003 Use the following diagram to answer questions 1 and 2. 1. Which labelled organelle produces most of the
 Question 1: Who discovered cells and how? Cells were discovered in 1665 by an English Botanist, Robert Hooke. He used a primitive microscope to observe cells in a cork slice. Question 2: Why is the cell
Question 1: Who discovered cells and how? Cells were discovered in 1665 by an English Botanist, Robert Hooke. He used a primitive microscope to observe cells in a cork slice. Question 2: Why is the cell
Living Environment. Scientific Inquiry Exam
 Name: Class: 1. Which elements are present in all organic compounds? 1) nitrogen and carbon 3) hydrogen and oxygen 2) nitrogen and oxygen 4) hydrogen and carbon 2. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
Name: Class: 1. Which elements are present in all organic compounds? 1) nitrogen and carbon 3) hydrogen and oxygen 2) nitrogen and oxygen 4) hydrogen and carbon 2. Which substances are inorganic compounds?
Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells?
 Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells? Name the two different types of cells 1. Prokaryotic Cells 2. Eukaryotic Cells Unit 3: Cells Objective: To
Look at the following images, what are some similarities and differences between the cells? Name the two different types of cells 1. Prokaryotic Cells 2. Eukaryotic Cells Unit 3: Cells Objective: To
In the space provided, write the letter of the term or phrase that best completes each statement or best answers each question.
 CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
CHAPTER 3 TEST Cell Structure Circle T if the statement is true or F if it is false. T F 1. Small cells can transport materials and information more quickly than larger cells can. T F 2. Newly made proteins
Cells & Transport. Chapter 7.1, 7.2, & 7.4
 Cells & Transport Chapter 7.1, 7.2, & 7.4 Do Now How big is a cell? How many cells are we made of? How many cells is the smallest living organism made of? Objectives Describe how cells were discovered
Cells & Transport Chapter 7.1, 7.2, & 7.4 Do Now How big is a cell? How many cells are we made of? How many cells is the smallest living organism made of? Objectives Describe how cells were discovered
Parts (organelles) of the Cell
 Lesson 07 Cell Organelles.notebook Parts (organelles) of the Cell Parts that provide structure and support Cell Membrane 1) Is a barrier for the cell. It controls what goes in and out of the cell. 2) It
Lesson 07 Cell Organelles.notebook Parts (organelles) of the Cell Parts that provide structure and support Cell Membrane 1) Is a barrier for the cell. It controls what goes in and out of the cell. 2) It
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Look at the diagrams below. Label the prokaryotic cell and the
 Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Look at the diagrams below. Label the prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cell. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Nucleus Organelles Use the diagrams to answer the question.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Look at the diagrams below. Label the prokaryotic cell and the eukaryotic cell. Cell membrane Cytoplasm Cytoplasm Nucleus Organelles Use the diagrams to answer the question.
History of the Cell. History of the Cell 10/24/2013. Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function. Robert Hooke (1665) Robert Hooke (1665)
 Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function Mr. Hulse BVHS 2013-2014 Unit 3: Learning Targets 1-9 History of the Cell Robert Hooke (1665) 1 st person to see a cell Observed a piece of cork using a microscope
Unit 3: Cellular Structure and Function Mr. Hulse BVHS 2013-2014 Unit 3: Learning Targets 1-9 History of the Cell Robert Hooke (1665) 1 st person to see a cell Observed a piece of cork using a microscope
BIOLOGY. James Ruse Agricultural High School. Total marks for this paper: 37. This paper has two parts, Part A and Part B. General Instructions
 James Ruse Agricultural High School 2007 PRELIMINARY COURSE TERM 2 (Y11) ASSESSMENT TASK THEORY EXAMINATION (PATTERNS IN NATURE) BIOLOGY Total marks for this paper: 37 General Instructions Reading time
James Ruse Agricultural High School 2007 PRELIMINARY COURSE TERM 2 (Y11) ASSESSMENT TASK THEORY EXAMINATION (PATTERNS IN NATURE) BIOLOGY Total marks for this paper: 37 General Instructions Reading time
Basic Structure of a Cell
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Introduction to Cells Cells are the basic units of organisms Cells can only be observed under microscope Basic types of cells: Animal Cell Plant Cell Bacterial Cell 2 Number
Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is a specialized subunit within a cell that has a specific function.
 Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Plant and Animal Cells The Cell Theory All living things are made up of one or more cells. All cells come from other cells. Organization of Living Things Cell are made up of organelles. An ORGANELLE is
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Cell Structure and Function Agre and cells in the news Cells Smallest living unit Most are microscopic Discovery of Cells Robert Hooke (mid-1600s) Observed sliver of cork Saw row of empty boxes Coined
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function. Typical Animal Cell
 Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
Biology 12 Cell Structure and Function Typical Animal Cell Vacuoles: storage of materials and water Golgi body: a series of stacked disk shaped sacs. Repackaging centre stores, modifies, and packages proteins
What Are Cell Membranes?
 What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
Basic Structure of a Cell. copyright cmassengale
 Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Prokaryotes The first Cells Cells that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Includes bacteria Simplest type of cell Single, circular chromosome 2 Prokaryotes Nucleoid
Basic Structure of a Cell 1 Prokaryotes The first Cells Cells that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles Includes bacteria Simplest type of cell Single, circular chromosome 2 Prokaryotes Nucleoid
1. Finish textbook questions from chapter 1 2. Parts of the cell lesson 3. Parts of the cell assignment
 Science 10 Dec. 3 1. Finish textbook questions from chapter 1 2. Parts of the cell lesson 3. Parts of the cell assignment Chapter Two Structure and Cell Function 2.1 The Cell as an Efficient System Thought
Science 10 Dec. 3 1. Finish textbook questions from chapter 1 2. Parts of the cell lesson 3. Parts of the cell assignment Chapter Two Structure and Cell Function 2.1 The Cell as an Efficient System Thought
1. What is the difference between a scientific theory and a scientific law? (Hint: what do both explain?)
 Name: Per: Date: Semester Exam Study Guide Cell Size, Cell Cycle and Cell Division are not included in the following study guide, as you have just finished a study guide on those topics. Please use that
Name: Per: Date: Semester Exam Study Guide Cell Size, Cell Cycle and Cell Division are not included in the following study guide, as you have just finished a study guide on those topics. Please use that
Cells are the smallest units of life CH 3
 Cells are the smallest units of life CH 3 The Cell Theory 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function. 3. Cells are produced only from
Cells are the smallest units of life CH 3 The Cell Theory 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function. 3. Cells are produced only from
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved.
 Study Island Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 04/01/2014 Generated By: Cheryl Shelton Title: Science- biology Cells 1. Below is an image of a plant cell. What processes require
Study Island Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 04/01/2014 Generated By: Cheryl Shelton Title: Science- biology Cells 1. Below is an image of a plant cell. What processes require
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
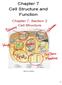 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 7, Section 2 Cell Structure Cell as a Factory 1 A. Cell Organization The Cell is like a Factory: Many different workers performing different functions in order
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 7, Section 2 Cell Structure Cell as a Factory 1 A. Cell Organization The Cell is like a Factory: Many different workers performing different functions in order
A Tour of the Cell. Ch. 7
 A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
3.2 Cell Structures. Lesson 3.2: True or False. Lesson 3.2: Critical Reading
 3.2 Cell Structures Lesson 3.2: True or False Write true if the statement is true or false if the statement is false. 1. The water-hating hydrophobic tails of the phospholipid bilayer face the outside
3.2 Cell Structures Lesson 3.2: True or False Write true if the statement is true or false if the statement is false. 1. The water-hating hydrophobic tails of the phospholipid bilayer face the outside
Looking Inside Cells
 Looking Inside Cells Inner Life of a Cell http://www.bing.com/videos/search?q=inside +cell+animation&form=hdrsc3#view=detail &mid=4ba834420ea307a061374ba834420ea 307A06137 Cell Defined Cells-Basic unit
Looking Inside Cells Inner Life of a Cell http://www.bing.com/videos/search?q=inside +cell+animation&form=hdrsc3#view=detail &mid=4ba834420ea307a061374ba834420ea 307A06137 Cell Defined Cells-Basic unit
Lesson Overview. 7.2 Cell Structure
 7.2 Cell Organization The eukaryotic cell can be divided into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus. Prokaryotes do not have
7.2 Cell Organization The eukaryotic cell can be divided into two major parts: the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus. Prokaryotes do not have
Renaissance Biology Midterm Study Guide Answers
 Renaissance Biology Midterm Study Guide Answers 2016-2017 LEARNING TARGET 1: List the characteristics of life Made of one or more cells Organization cells -> tissues -> organs -> organ systems -> organisms
Renaissance Biology Midterm Study Guide Answers 2016-2017 LEARNING TARGET 1: List the characteristics of life Made of one or more cells Organization cells -> tissues -> organs -> organ systems -> organisms
Exam 2 Practice Problems
 Exam 2 Practice Problems Cell Structure and Function Practice Questions 1. One of the relationships that exists between ribosomes and lysosomes is that a. ribosomes produce enzymes that could be stored
Exam 2 Practice Problems Cell Structure and Function Practice Questions 1. One of the relationships that exists between ribosomes and lysosomes is that a. ribosomes produce enzymes that could be stored
Name Date Class. Cellular Structure
 Concept Mapping Cellular Structure Complete the network tree about cellular structure. These terms may be used more than once: animals, bacteria, chloroplasts, eukaryotes, a large central vacuole, plants,
Concept Mapping Cellular Structure Complete the network tree about cellular structure. These terms may be used more than once: animals, bacteria, chloroplasts, eukaryotes, a large central vacuole, plants,
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What is the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell?
 CHAPTER 3 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
CHAPTER 3 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
Unit 2 Notes: Cells. What you need to know:
 1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
1 Unit 2 Notes: Cells What you need to know: 1. MC.2.B.1: Construct a hierarchy of life from cells to ecosystems. (ex: cell, tissue, organ etc) 2. NS.12.B.4: Relate the development of the cell theory to
Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Many Scientists Contributed to the Cell Theory! Hooke discovered cells while looking at cork under the microscope! Leewenhoek was the first to observe bacteria! Schleiden discovered
Cell Structure and Function Many Scientists Contributed to the Cell Theory! Hooke discovered cells while looking at cork under the microscope! Leewenhoek was the first to observe bacteria! Schleiden discovered
Cell Transport Unit Test
 Cell Transport Unit Test ~Please DO NOT write on the test~ I CAN describe the parts of cells. 1. The ideas that all living things are composed of cells come from other cells defines: a. Central dogma b.
Cell Transport Unit Test ~Please DO NOT write on the test~ I CAN describe the parts of cells. 1. The ideas that all living things are composed of cells come from other cells defines: a. Central dogma b.
Chapters 2 and 3. Pages and Pages Prayer Attendance Homework
 Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
Chapters 2 and 3 Pages 44-45 and Pages 59-62 Prayer Attendance Homework The Cell The cell is the basic unit of life on Earth, separated from its environment by a membrane and sometimes an outer wall. Prokaryotic
3.2 Cell Structures. Lesson Objectives. Vocabulary. Introduction. Overview of Cell Structures
 3.2 Cell Structures Lesson Objectives Describe the structure and function of the plasma membrane. Identify the roles of the cytoplasm and cytoskeleton. Outline the form and function of the nucleus and
3.2 Cell Structures Lesson Objectives Describe the structure and function of the plasma membrane. Identify the roles of the cytoplasm and cytoskeleton. Outline the form and function of the nucleus and
BALSIGER BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDES (SEMESTER 1)
 BALSIGER BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDES (SEMESTER 1) Table of Contents 1 III. Parts of an Experiment 1) Write a brief definition for each of these components of an experiment: manipulated variable, treatments, experimental
BALSIGER BIOLOGY STUDY GUIDES (SEMESTER 1) Table of Contents 1 III. Parts of an Experiment 1) Write a brief definition for each of these components of an experiment: manipulated variable, treatments, experimental
Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per:
 Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per: 1. Put the following in order according to blood flow through the body, starting with the lungs: Lungs, right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, aorta,
Test Review Worksheet 1 Name: Per: 1. Put the following in order according to blood flow through the body, starting with the lungs: Lungs, right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, left ventricle, aorta,
Study Guide A. Answer Key. Cell Structure and Function
 Cell Structure and Function Answer Key SECTION 1. CELL THEORY 1. b 2. e 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. i. cells; ii. living; iii. cell 7. biology 8. Surrounded by a cell membrane = Both; Contains cytoplasm = Both;
Cell Structure and Function Answer Key SECTION 1. CELL THEORY 1. b 2. e 3. d 4. a 5. c 6. i. cells; ii. living; iii. cell 7. biology 8. Surrounded by a cell membrane = Both; Contains cytoplasm = Both;
Cell Structure and Function. The Basic Unit of Life
 Cell Structure and Function The Basic Unit of Life The Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke The word " cell was first used in late 1665 by Robert Hooke. He looked at thin slices of cork (plant cells) under
Cell Structure and Function The Basic Unit of Life The Discovery of the Cell Robert Hooke The word " cell was first used in late 1665 by Robert Hooke. He looked at thin slices of cork (plant cells) under
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures
 7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
7-2 : Plasma Membrane and Cell Structures Plasma Membrane of aveolar sac But first... Let s Review What is cell theory? Light microscopes vs. electron microscopes Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic Basic Cell
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
 Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Comparing the Cell to a Factory Eukaryotic Cell Structures Structures within a eukaryotic cell that perform important cellular functions are known as organelles. Cell biologists divide the eukaryotic cell
Cell Structure and and Function Chapter 4
 Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Robert Hooke (1635-1703) 1703) Discovered cells by studying the cork layer of bark from an oak tree. Found cells when studied tree stems, roots, and leaves. Antony
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 4 Robert Hooke (1635-1703) 1703) Discovered cells by studying the cork layer of bark from an oak tree. Found cells when studied tree stems, roots, and leaves. Antony
LIFE IS CELLULAR. Cell Theory. Cells Are Small. Prokaryotic Cell 10/4/15. Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function The cell basic unit of life, all living things are made of a cell (unicellular) or more than one cell (multicellular). LIFE IS CELLULAR The invention of the microscope
Name Class Date. cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell. MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell theory.
 Section 1: Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell
Section 1: Cell Theory KEY CONCEPT Cells are the basic unit of life. VOCABULARY cell theory organelle eukaryotic cell cytoplasm prokaryotic cell MAIN IDEA: Early studies led to the development of the cell
Biochemical Concepts. Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water. Pre-View 4.6. A Covalent Polar Molecule
 Biochemical Concepts Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water Pre-View 4.6 Polar molecule a molecule that has a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other end Hydrogen bond
Biochemical Concepts Section 4.6 The Chemistry of Water Pre-View 4.6 Polar molecule a molecule that has a partial positive charge on one end and a partial negative charge on the other end Hydrogen bond
(impermeable; freely permeable; selectively permeable)
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
1. How many fatty acid molecules combine with a glycerol to form a phospholipid molecule? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
 Topic 3: Movement of substances across cell membrane 1. How many fatty acid molecules combine with a glycerol to form a phospholipid molecule? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Directions: Questions 2 and 3 refer to
Topic 3: Movement of substances across cell membrane 1. How many fatty acid molecules combine with a glycerol to form a phospholipid molecule? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Directions: Questions 2 and 3 refer to
Looking forward to an awesome year in IB Biology!
 WESTLAKE HIGH SCHOOL IB BIOLOGY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT INSTRUCTIONS IB Biology will be a very intensive course. Though we will have 90 minute periods every other day, there is still a lot of new material to
WESTLAKE HIGH SCHOOL IB BIOLOGY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT INSTRUCTIONS IB Biology will be a very intensive course. Though we will have 90 minute periods every other day, there is still a lot of new material to
3 Movement in and out of cells
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Movement in and out of cells Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 3 Movement
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ Movement in and out of cells Question Paper Level IGSE Subject iology Exam oard ambridge International Examinations Unit 3 Movement
Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell
 CELL TRANSPORT AND HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis Balanced internal condition of cells Also called equilibrium Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell Functions of Plasma Membrane
CELL TRANSPORT AND HOMEOSTASIS Homeostasis Balanced internal condition of cells Also called equilibrium Maintained by plasma membrane controlling what enters & leaves the cell Functions of Plasma Membrane
Maharashtra State Board Class IX Science and Technology Sample Paper 3
 Maharashtra State Board Class IX Science and Technology Sample Paper 3 Time: 3 hrs Max. Marks: 80 Note: 1. Use the same answer-sheet for Section A and Section B. 2. Draw well-labelled diagrams wherever
Maharashtra State Board Class IX Science and Technology Sample Paper 3 Time: 3 hrs Max. Marks: 80 Note: 1. Use the same answer-sheet for Section A and Section B. 2. Draw well-labelled diagrams wherever
Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided.
 Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided. 1. The type of electron microscope that gives 2 dimensional images. a) Scanning b) Condensing c) Transmission d) Multidimensional
Part 1 Multiple Choice Shade the correct answer on the SCANTRON sheet provided. 1. The type of electron microscope that gives 2 dimensional images. a) Scanning b) Condensing c) Transmission d) Multidimensional
Name Class Date. What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What is the function of each part of a eukaryotic cell?
 CHAPTER 2 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
CHAPTER 2 SECTION 2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life Eukaryotic Cells BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of a eukaryotic cell? What
CP Biology Semester 1 FINAL Study Guide
 Name: KEY CP Biology Semester 1 FINAL Study Guide Unit 1- Introduction to Biology Define each of the following: 1. Match the following vocabulary words on the left with their definition on the right. b
Name: KEY CP Biology Semester 1 FINAL Study Guide Unit 1- Introduction to Biology Define each of the following: 1. Match the following vocabulary words on the left with their definition on the right. b
6. What surrounds the nucleus? How many membranes does it have?
 Biology-R track Study Guide: 7.2 Cell Structure Cell Organization 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? 2. What part is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus?
Biology-R track Study Guide: 7.2 Cell Structure Cell Organization 1. What are the 2 major parts that you can divide the eukaryotic cell into? 2. What part is the fluid portion of the cell outside the nucleus?
Revision Question Bank
 Revision Question Bank Fundamental Unit of Life 1. What are the main functions of each of the following cell components? (a) Plasma membrane (b) Chromosomes (c) Lysosomes (d) Ribosome (e) Nucleus (f) Mitochondria
Revision Question Bank Fundamental Unit of Life 1. What are the main functions of each of the following cell components? (a) Plasma membrane (b) Chromosomes (c) Lysosomes (d) Ribosome (e) Nucleus (f) Mitochondria
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 3
 AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 3 128 minutes 128 marks Page 1 of 29 Q1. Plants need chemical energy for respiration and for active transport. (i) Write a balanced chemical equation
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 3 128 minutes 128 marks Page 1 of 29 Q1. Plants need chemical energy for respiration and for active transport. (i) Write a balanced chemical equation
CBSE SAMPLE PAPER 05 (Solved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Class-IX (SCIENCE) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 90
 CBSE SAMPLE PAPER 05 (Solved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Class-IX (SCIENCE) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 90 General Instructions (i) The question paper comprises of two Sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections.
CBSE SAMPLE PAPER 05 (Solved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Class-IX (SCIENCE) Time: 3 Hrs MM: 90 General Instructions (i) The question paper comprises of two Sections, A and B. You are to attempt both the sections.
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
 Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
Eukaryotic Cell Structure Vocabulary listed for Chapter 7.3: cell wall, chromatin, nucleolus, ribosome, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vacuole, lysosome, chloroplast, plastid, chlorophyll,
Chapter MEMBRANE TRANSPORT
 Chapter 3 I MEMBRANE TRANSPORT The cell membrane, or plasma membrane, is the outermost layer of the cell. It completely surrounds the protoplasm or living portion of the cell, separating the cell s interior
Chapter 3 I MEMBRANE TRANSPORT The cell membrane, or plasma membrane, is the outermost layer of the cell. It completely surrounds the protoplasm or living portion of the cell, separating the cell s interior
By Calypso Harmon Fall 2002
 By Calypso Harmon Fall 2002 This is an extremely thin slice through a plant cell. Are there any structures you recognize? Chloroplasts collect the energy from the sun and change it into chemical energy
By Calypso Harmon Fall 2002 This is an extremely thin slice through a plant cell. Are there any structures you recognize? Chloroplasts collect the energy from the sun and change it into chemical energy
Plant Weight Week g 1.3 g 1.5 g 1 1 g 1.7 g 2 g 2 1 g 1.6 g 1.8 g 3 1 g 1.3 g 1.5 g 4 1 g 1 g 1 g. Plant Weight Week 1. Plant Weight Week 2
 9/11-9/12 Sci 7 AGENDA 1. Lecture 2. Organelle Flip Page 3. Processing Task 4. Fix your notebooks LEVEL ZERO VOICE CATALYST (10 minutes, individual work): 1. List all of the characteristics of life and
9/11-9/12 Sci 7 AGENDA 1. Lecture 2. Organelle Flip Page 3. Processing Task 4. Fix your notebooks LEVEL ZERO VOICE CATALYST (10 minutes, individual work): 1. List all of the characteristics of life and
First to View Cells. copyright cmassengale
 CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
CELL THEORY All living things are made of cells Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in an organism (basic unit of life) Cells come from the reproduction of existing cells (cell division)
CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL
 AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
A small, membrane-bound compartment capable of performing all the basic functions of life
 AP Biology The Cell The Cell Cell: A small, membrane-bound compartment capable of performing all the basic functions of life Discovery of Cells: - 17 th century - A Dutch clothing dealer named Antonie
AP Biology The Cell The Cell Cell: A small, membrane-bound compartment capable of performing all the basic functions of life Discovery of Cells: - 17 th century - A Dutch clothing dealer named Antonie
Cell Category? Prokaryote
 CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
CELLS Cell Category? Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Cell Category? Cell Type? Cell Category? Cell Type? Endosymbiosis eukaryotic cells were formed from simpler prokaryotes Endo within Symbiosis together
Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell
 Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell 1. Cell Membrane 2. Cytoplasm 3. Nucleus 4. Nuclear Membrane 5. Nucleoplasm 6. Nucleolus 7. Chromosomes 8. Vacuole 9. Ribosomes 10. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Organelles Found in a Generalized Animal Cell 1. Cell Membrane 2. Cytoplasm 3. Nucleus 4. Nuclear Membrane 5. Nucleoplasm 6. Nucleolus 7. Chromosomes 8. Vacuole 9. Ribosomes 10. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Cell Structure and Function
 Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic Record your
Name Cell Structure and Function Date How do the structures and processes of a cell enable it to survive? Before You Read Before you read the chapter, think about what you know about the topic Record your
