Chalcogen ( kal-ka-jen) chemistry and biochemistry: The many faces of O, S, and Se in proteins and enzymes Garry R. Buettner and Freya Q.
|
|
|
- Barrie Murphy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chalcogen ( kal-ka-jen) chemistry and biochemistry: The many faces of, S, and Se in proteins and enzymes Garry R. Buettner and Freya Q. Schafer Free Radical and Radiation Biology Program and ESR Facility The University of Iowa Iowa City, IA Tel: garry-buettner@uiowa.edu
2 e e Chalcogen Pronunciation: 'kal-ka-jen; Function: noun What is a Chalcogen? Etymology: International Scientific Vocabulary chalkbronze, ore (from Greek chalkos) + -gen; from the occurrence of oxygen and sulfur in many ores Date: circa 1961 ('kal-k -j n) : any of the elements oxygen, sulfur, selenium, and tellurium From - Merriam-Webster's Collegiate Dictionary
3 What is a Chalcogen? Group 16
4 Chalcogens, essential in biology xygen Sulfur Selenium Tellurium g (in std 70 kg human) 140 g g 0 g (toxic) 8 1s 2 2s 2 2p 4 16 S 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 4 34 Se 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 6 3d 10 4s 2 4p 4
5 x xygen Sulfur Selenium State -2 xides H 2 Sulfides H 2 S Selenides H 2 Se Thiols Cys-SH, GSH Selenocysteine Cys-SeH Some Chalcogen xidation States in Biology -1 Peroxides H---H R---H xyl radical R -0.5 Superoxide - 2 Thiolethers R-S-R Methionine Disulfides RSSR Thiyl radical RS Disulfide radical anion RSSR - Selenylsulfides Cys-Se-S-Cys Selenyl radical RSe
6 0 xygen 2 Sulfur S Sulfenic acid R-SH, (R-S + ) Sulfoxide RS()R +2 Sulfinic acid RS()H +4 Sulfonic acid R-S() 2 H Sulfone R-S() 2 R Selenium Se Selenocysteine selenol Cys-SeH, Selenocysteine selenic acid Cys-Se()H Chalcogen xidation States, continued
7 Reduction of Dioxygen 2 + 4e - + 4H + 2H 2 ne electron at a time: 2 + e E = -160 mv or (-330 mv) H + H 2 pk a = is, in general, reducing H 2 is, in general, oxidizing E = mv
8 The second electron: Reduction of Dioxygen, the 2 nd electron 2 + 4e - + 4H + 2H e - + 2H + H 2 2 E = +940 mv H 2 2 H H + pk a = 11.6 H 2 2 is, in general, oxidizing E 2e - = mv
9 Reduction of Dioxygen, the 3 rd electron 2 + 4e - + 4H + 2H 2 The 3 rd electron: H e - + H + H + H 2 E = +320 mv H is very oxidizing E = mv H - + H + pk a = 11.9
10 Reduction of Dioxygen, the 4 th electron 2 + 4e - + 4H + 2H 2 The 4 th electron: H + e - + H + H 2 E = mv H 2 is quite stable.
11 Sulfur in Biology Found in two amino acids: Cysteine and Methionine H S CH 2 + NH 3 C C H H 3 C + NH 3 S CH 2 CH 2 C C H cysteine methionine pk a (S-H) = 8.3
12 Formula Name x state of S R-SH thiol -2 RS thiyl radical -1 RSSR disulfide -1 RSSR - disulfide radical anion -0.5 R-SH (RS + ) sulfenic acid 0 R-S()H sulfinic acid +2 R-S()2H sulfonic acid +4 H 2 S hydrogen sulfide -2 S sulfur 0 S sulfur monoxide +2 S 2 sulfur dioxide +4 S 3 2- /H 2 S 3 sulfite/sulfurous acid +4 S 3 sulfur trioxide +6 S 4 2- /H 2 S 4 sulfate/sulfuric acid +6 Some oxidation states of sulfur
13 C H 3 N C H CH 2 S H cysteine sulfonic acid +4 C xidation of Cysteine H 3 N C H CH 2 S H cysteine sulfinic acid +2 H 3 N C C H CH 2 S H cysteine sulfenic acid 0 C H 3 N C H CH 2 S cysteinyl radical -1 C H 3 N C H CH 2 SH cysteine -2
14 H 3 N C C H H 3 N C C H CH 2 S CH 2 S -1-1 cystine H 3 N C C H H 3 N C C H CH 2 CH 2 S S +1-1 H 3 N Cystine and its oxidation C C H CH 2 S H 3 N +3-1 cystine-smonoxide cystine-sdioxide C C H CH 2 S
15 Disulfides Disulfide formation is an important redox reaction of cysteine Used: 2 RSH fi RSSR + 2H + + 2e - to form structure of proteins as redox buffer in signaling H 3 N to change activity of enzymes C C H CH 2 S H 3 N C C H CH 2 S
16 Protein Disulfides When cysteine residues are oxidized to disulfides, they can form: P S S P 1 S S P 2 G S S P intraprotein crosslink interprotein crosslink mixed disulfide adduct of GSH
17 Glutathione, GSH Note: GSH = N-(N-L-γ-glutamyl-L-cysteinyl)glycine (C.A.S. NUMBER: ) Tripeptide with unusual structure. R 1 H 3 N C C + H H H 3 N C C R 2 NH 3 C CH CH 2 CH 2 C - H + H 3 N C C + H 3 N CH 2 C CH 2 SH (N-terminal) N H R 1 H H C C N C C R 2 H peptide bond (C-terminal) C NH 3 CH CH 2 CH 2 C l-glutamate H NH C C CH 2 SH cysteine NH CH 2 C glycine Standard Peptide Bond glutathione Glutathione (GSH)
18 Some general reactions of thiols RSH+ GSSG RSSG + GSH thiol/disulfide exchange 2RSH RSSR + 2H + + 2e - two-electron transfer RSH RS + H + + e - single-electron transfer RSH RS + H hydrogen-atom transfer RSH+GSH RSSG + H 2 nucleophilic substitution RSH+R CH [RSCH(H)R ] nucleophilic addition [RSCH(H)R ] RSC()R +2H + + 2e - RSH+R -X R-SR + HX S-conjugation (R -X is electrophilic)
19 The thiol-disulfide exchange reaction Example: RSH + GSSG RSSG + GSH These reactions are probably the most common reactions of cysteine residues in vivo. However, the actual reaction may be better written as: RS - + GSSG + H + RSSG + GSH It is the ionized form that is often the dominant player in the reaction.
20 Redox Couple (2-electron reductions) E '/mv at 25 C DTTox, 2H + /DTT 317 a NADP +, H + /NADPH 315 Lipoic acid, 2H + /Dihydro-LA acid 290 Trx(SS), 2H + /Trx(SH) GSSG, 2H + /2GSH 240 Grx-1(SS), 2H + /Grx-1(SH) Cys-S-S-Cys, 2H + /2Cys-SH 230 Grx-3(SS), 2H + /Grx-3(SH) PDI(SS), 2H + /PDI(SH) DHA, H + /Ascorbate +54 CoQ, 2H + /(CoQH 2 ) +84 Some twoelectron reduction potentials
21 Vicinal thiols, Vicinal Vicinal: from Latin vicinalis, neighboring. In chemistry, vicinal means neighboring groups, e.g. vicinal alcohol groups.
22 Vicinal thiols In a protein, vicinal has been translated to mean two intervening amino acids, e.g., -CXXC- would be two cysteines separated by two intervening amino acids. The -CXXC- motif of thiol:disulfide oxidoreductases is now widely recognized as being essential for the catalysis of thiol redox reactions: Thioredoxin Glutaredoxin -Cys-Gly-Pro-Cys- -Cys-Pro-Try-Cys- Cys Cys PDI -Cys-Gly-His-Cys- X X DsbA -Cys- Pro-His-Cys-
23 The reduction potential and the pk a of the active thiol is key in the function of di-thiol proteins (circles) DsbA (triangles) Trx pk 1 of the active thiol Chivers PT, Prehoda KE, Raines RT. (1997) The CXXC motif: a rheostat in the active site. Biochemistry. 36:4061.
24 A primary function of the thiol system is to remove hydroperoxides RH + 2(-Cys-SH) RH + H 2 + -(Cys-S) 2
25 GSH system and peroxide removal GSH synthetic enzymes inhibits RH RH + H 2 GPx 2 GSH 2e - GSSG GSSG reductase NADPH 2e - NADP + stimulates 6-P-G G-6-P dehydrogenase G-6-P electron flow Freya Q. Schafer 2003
26 Thioredoxin- Peroxiredoxin system H 2 H 2 2 GPx 2 GSH Grx S 2 R'SSR RSH R'SH 6-P-G NADPH GR GSSG Grx (SH) 2 G-6-PD G-6-P Trx S 2 TrxR Glucose NADP + Trx (SH) 2 RSSR (RS 2 ) 2 RSH (R(SH) 2 ) Prx (SH) 2 Prx S 2 H 2 H 2 2 Freya Q. Schafer 2003
27 Thiols as switches Thiols are major contributors to the redox environment of cells. They are involved in the function and control of many proteins.
28 Thiols and disulfides as nano-switches A nano-switch is a very small, operating on a nanometer scale. For example, the distance between two sulfhydryls in a protein with two intervening amino acids, such as in thioredoxin. The redox environment of the cell, or regions within a cell, could be viewed as a means to activate a cellular switchboard, thereby changing the message of cellular signals. By changing the reduction potential, a series of nano-switches are activated/de-activated that move the cell from proliferation through various stages of proliferation, differentiation or into apoptosis. Necrosis is the complete loss of the ability to activate/de-activate and respond to changes in these nano-switches.
29 Type I switch GSSG + PSH PSSG + GSH (Type I) K = [GSH] [PSSG] [GSSG] [PSH] For the GSSG, 2H + /2GSH couple E hc = (59.1/2) log ([GSH] 2 /[GSSG]) mv at 25 C, ph 7.0 If [GSH] = 5 mm and [GSSG] = 25 µm, then E hc = 240 mv. If [GSH] decreases to 2.5 mm and [GSSG] increases to 100 µm, a +35 mv change will occur resulting in E hc = 205 mv. The [PSSG]/[PSH] ratio will change by a factor of 8, resulting in an 8-fold change in the status of the switch.
30 Type II switch GSSG + P(SH) 2 PSS + 2GSH (Type II) K = [GSH] 2 [PSS] [GSSG] [P(SH) 2 ] Using the example for the Type I switch, this same +35 mv change in the GSSG/2GSH couple will result in a change of the [PSS]/[P(SH) 2 ] ratio by a factor of 16. Thus, a Type II switch translates changes in reduction potential into a 2-fold greater change in the status of the nano-switch, compared to a Type I switch. Schafer FQ, Buettner GR. (2001) Redox state of the cell as viewed though the glutathione disulfide/glutathione couple. Free Radic Biol Med. 30: Schafer FQ, Buettner GR. (2003) Redox state and redox environment in Biology. In Signal Transduction by Reactive xygen and Nitrogen Species: Pathways and Chemical Principles. Eds Forman HJ, Torres M, Fukuto J. Kluwer academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Netherlands, Chapter 1, pp
31 Summary GSSG + PSH PSSG + GSH (Type I) P 1 (SH) 2 + P 2 S 2 P 1 S 2 + P 2 (SH) 2 GSSG + P(SH) 2 PSS + 2GSH (Type II) In a cell there is are many copies of proteins, and several components to a signal. Thus, the state of a switch is due to the ensemble. It is the ensemble that results in an action like a rheostat. verviews: Nathan, Carl (2003) Specificity of a third kind: reactive oxygen and nitrogen intermediates in cell signaling. J. Clin. Invest. 111: Cooper CE, Patel RP, Brookes PS, Darley-Usmar, VM, (2002) Nanotransducers in cellular redox signaling: modification of thiols by reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, Trends in Biochemical Sciences. 27:
32 Methionine H 3 N C C H H 3 N C C H H 3 N C C H CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 S CH 3 methionine CH 2 S CH 3 methionine sulfoxide CH 2 S CH 3 (-2) (0) (+2) xidation methionine sulfone
33 xidation of methionine The start codon AUG for protein synthesis encodes methionine, thus this amino acid is found in most proteins. Methionine is considered to be an antioxidant. Methionine residues on protein surfaces can protect against oxidation of other amino acids that are important for the function of the proteins. If a protein with a spherical diameter of 60 Å has 8 methionine residues, then the concentration of methionine in that volume is >100 mm (cellular [GSH] is 1 10 mm). Jacob C, Giles GI, Giles NM, Sies H. (2003) Sulfur and Selenium: The Role of xidation State in Protein Structure and Function. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 42:
34 xidation of methionine In some enzymes methionine can play the role of a sacrificial lamb, e.g. glutamine synthetase; oxidation of 8 of the 16 methionine residues to Met() did not effect the activity of the enzyme. They were on the surface and appeared to guard the active site of the enzyme. Methionine residues can also be essential for the activity of proteins. H 3 N C C H CH 2 CH 2 S CH 3 methionine sulfoxide Met() Levine RL, Mosoni L, Berlett BS, Stadtman ER. (1996) Methionine residues as endogenous antioxidants in proteins. PNAS. 93:
35 Repair of Met() H 2 H 2 2 GPx 2 GSH Grx S 2 R'SSR RSH R'SH 6-P-G NADPH GR GSSG Grx (SH) 2 G-6-P Glucose G-6-PD Trx S 2 TrxR NADP + Trx (SH) 2 Met() MsrA Met Methionine sulfoxide reductase, MsrA and MsrB Weissbach H, Etienne F, Hoshi T, Heinemann SH, Lowther WT, Matthews B, St John G, Nathan C, Brot N. (2002) Peptide methionine sulfoxide reductase: structure, mechanism of action, and biological function. Arch Biochem Biophys. 397: Prx (SH) 2 Prx S 2 H 2 H 2 2 Freya Q. Schafer 2003
36 Selenium in proteins H + NH 3 Se CH 2 C C H seleno-cysteine H 3 C + NH 3 Se CH 2 CH 2 C C H seleno-methionine
37 Selenocysteine Selenocysteine: Cys-SeH Cys-SH Cys-S - + H + pk a = 8.3 Cys-SeH Cys-Se - + H + pk a = 5.2 The low pk a, and the much greater nucleophilicity of Cys-Se - renders selenocysteine catalytically much more reactive than Cys-SH. Cys-Se - is at the active site of GPx, TrxR, At ph Cys-SH»90%, Cys-Se -»99.9%
38 xidation of selenocysteine When oxidized, selenocysteine forms a selenol or selenenic acid rather than di-selenides. H NH 3 + Se CH 2 C C H selenocysteine oxidation H Se CH 2 C C H NH 3 + NH 3 + H Se CH 2 C C H selenocysteine selenol selenocysteine selenenic acid
39 Selenylsulfides -Cys-Se-S-Cys- However, selenylsulfides (-Cys-Se-S-Cys-) are found in proteins, e.g. GPx and TrxR. They are intermediates formed during enzyme function. For example, with GPx the intermediate with GSH is, -Cys-Se-S-G.
40 Reduction of a seleno-cysteine Trx S S FADH 2 HS SeH TrxR HS SH NAD + NADPH + H + HS HS FAD TrxR SeH SH FADH 2 FADH 2 Trx SH SH HS HS TrxR Se S S S TrxR A selenylsulfide in a protein is reduced by a cysteineexchange reaction and the resulting disulfide is then reduced by electron transfer. This example shows the reduction of thioredoxin (Trx) by thioredoxin reductase (TrxR). Jacob C, Giles GI, Giles NM, Sies H. (2003) Sulfur and Selenium: The Role of xidation State in Protein Structure and Function. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 42: SeH SH
41 H 3 C + NH 3 Se CH 2 CH 2 C C H seleno-methionine Selenomethinonine is randomly found in proteins and not specifically incorporated as is selenocysteine. Intake of selenomethionine in animals increases the amount of selenomethionine-containing proteins. xidized to selenosulfoxide or selenosulfones, which can be reduced spontaneously by GSH. Thus, selenomethionine it might be a defense against permanent protein damage.
42 Reactive Species RS - Reactive xygen Species RNS RSS - Reactive Nitrogen Species - Reactive Sulfur Species The difference is in what element undergoes changes in oxidation state,? N? or S?
43 Reactive Sulfur Species (RSS) Sulfur can exist in higher oxidation states in biological systems than the 2 of Cys and Met. Sulfenic acids Sulfenic acids (Cys-SH) found in various proteins, such as GR, FS and Jun. Formation of Cys-SH is reversible (role in signal transduction, oxygen metabolism and transcriptional regulation. Sulfenic acids seem to be transient intermediates. They react with other thiols to form disulfides.
44 Reactive Sulfur Species (RSS) Disulfide-S-oxides H 2 C S S CH 2 diallyldisulfide-s-monoxide ne sulfur of a disulfide bond can be further oxidized increasing the reactivity of the compound towards sulfur-sulfur exchange reaction. The garlic component allicin contains a diallyldisulfide- S-monoxide that is thought to be responsible for the antimicrobial properties of garlic.
45 Reactive Sulfur Species (RSS) oxidation 2 R 1 SH oxidation R 1 S R 1 S disulfide oxidation R 1 S S R 1 S R 1 R 1 S disulfide-smonoxide disulfide-sdioxide R 2 SH R 2 SH R 1 SH S R 2 R 1 S mixed disulfide R 1 S 2 H Formation of disulfide-s-oxide and subsequent sulfur-sulfur exchange. These RSS can be formed by reaction with various RS and RNS (e.g. peroxides, peroxynitrite). The oxidation of one sulfur in the disulfide makes the bond more labile and enhances the reaction with a reduced thiol.
46 Thiol reagents as research tools DTT Diamide Lipoic acid Arsenic
47 Thiol reagents, Dithiothreitol H H HS CH 2 CH CH CH 2 SH dithiothreitol DTT Dithiothreitol, also known as Cleland s Reagent, is one of the most common agents used to reduce disulfide bonds. DTT is used at low concentrations to stabilize enzymes, antibodies etc. that have thiol groups. At high concentrations it is used to cleave disulfide bonds and thereby denature proteins. However, reagents that react faster than DTT are now available.
48 Thiol reagents, diamide H 3 C CH 3 H 3 C N C N N C N H + GS N C N N C N H 3 C CH 3 H 3 C GS H H 3 C CH 3 H H 3 C N C N N C N + GS GSSG + N C N H 3 C GS H CH 3 H 3 C H CH 3 CH 3 N C N H CH 3 CH 3 Acidic, low molecular weight thiols are oxidized in preference to protein thiols. Protein thiols are in general less acidic and sterically hindered. Some proteins such as hemoglobin A or albumin, react very slowly with diamide if at all, while other proteins such as thioredoxin or rat hemoglobin react with diamide or the diamide-sg intermediate to form disulfides or mixed disulfides. Diamide penetrates cell membranes within seconds. The activation energy for the reaction of thiols with diamide is low. Thus, diamide can be used at low temperatures. Glutathione, as the major non-protein thiol in cells, will preferentially react with diamide. At higher diamide concentration protein thiols will also be oxidized.
49 S Lipoic acid is not quite a vicinal thiol S H 2 C CH2 CH CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 C 2e, 2H Lipoate H 2 C SH CH 2 SH CH CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 2 C Dihydrolipoic acid
50 Arsenite, a vicinal thiol reagent Arsenite (As(III)): Arsenic has been used as a therapeutic agent and poison for over 2000 years. The solid form As 4 6, generally referred to as arsenic trioxide, dissolves in base to yield arsenite ions such as [As(H) 2 ] -, [As 2 (H)] 2-, and [As 3 ] 3-. (Arsenic (group 15 element) is under N and P in the periodic table.) Arsenite binds to vicinal thiols and this may well be central to its mechanism of action.
51 The End H 2 H 2 S Essential for life; we swim in it. IDLH*» 100 ppm H 2 Se IDLH» 1 ppm What a difference a few electrons make. *IDLH = Immediately dangerous to life and health
THIOL REDOX SYSTEMS SOPHIA CEDER, LUU THANH THUY, STEPHENIE BAILEY, TIMOTHY NICODEMUS & ELLIN-KRISTINA HILLERT
 THIOL REDOX SYSTEMS SOPHIA CEDER, LUU THANH THUY, STEPHENIE BAILEY, TIMOTHY NICODEMUS & ELLIN-KRISTINA HILLERT THIOL REDOX SYSTEMS Thioredoxin system Glutaredoxin system Redundant, but not identical THIOREDOXIN
THIOL REDOX SYSTEMS SOPHIA CEDER, LUU THANH THUY, STEPHENIE BAILEY, TIMOTHY NICODEMUS & ELLIN-KRISTINA HILLERT THIOL REDOX SYSTEMS Thioredoxin system Glutaredoxin system Redundant, but not identical THIOREDOXIN
What is an antioxidant? How do antioxidants work?
 What is an antioxidant? How do antioxidants work? Garry R. Buettner and Freya Q. Schafer Free Radical and Radiation Biology Program and ESR Facility The University of Iowa Iowa City, IA 52242-1101 Tel:
What is an antioxidant? How do antioxidants work? Garry R. Buettner and Freya Q. Schafer Free Radical and Radiation Biology Program and ESR Facility The University of Iowa Iowa City, IA 52242-1101 Tel:
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
NST 160 Theil Selenium Lecture 1 October 27, 2004 Selenium Nutrition and Physiology
 NST 160 Theil Selenium Lecture 1 October 27, 2004 Selenium Nutrition and Physiology Reading Chapter 12: Insel, P., R.E. Turner, and D. Ross. Nutrition, 2nd Ed. Chapter 34: (Reserve BioSci Library) Stipanuk
NST 160 Theil Selenium Lecture 1 October 27, 2004 Selenium Nutrition and Physiology Reading Chapter 12: Insel, P., R.E. Turner, and D. Ross. Nutrition, 2nd Ed. Chapter 34: (Reserve BioSci Library) Stipanuk
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
Thiol redox systems. Chao Sun (CCK KI) Ting Jia (RBC UNL) Saeed Eshtad (MBB KI) Weishu Fan (RBC UNL)
 Thiol redox systems Chao Sun (CCK KI) Ting Jia (RBC UNL) Saeed Eshtad (MBB KI) Weishu Fan (RBC UNL) Questions What is the function of thioredoxin? Questions What is the function of thioredoxin? How many
Thiol redox systems Chao Sun (CCK KI) Ting Jia (RBC UNL) Saeed Eshtad (MBB KI) Weishu Fan (RBC UNL) Questions What is the function of thioredoxin? Questions What is the function of thioredoxin? How many
Redox regulated transcription factors
 Redox regulated transcription factors, MD PhD Division of Biochemistry Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden Elias.Arner@ki.se Redox regulation A process of regulated
Redox regulated transcription factors, MD PhD Division of Biochemistry Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden Elias.Arner@ki.se Redox regulation A process of regulated
OH-selenomethionine: an efficient source of Se in fattening pigs
 OH-selenomethionine: an efficient source of Se in fattening pigs S. GREEN, K. COPPENS, P.-A. GERAERT Adisseo France SAS and Denkavit BV, Netherlands What are our challenges at the animal level? Pork: Transform
OH-selenomethionine: an efficient source of Se in fattening pigs S. GREEN, K. COPPENS, P.-A. GERAERT Adisseo France SAS and Denkavit BV, Netherlands What are our challenges at the animal level? Pork: Transform
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
Glutathione / Thioredoxin Nrf2 & Hyperoxia
 Glutathione / Thioredoxin Nrf2 & Hyperoxia Trent E. Tipple, MD Principal Investigator, Center for Perinatal Research The Research Institute at Nationwide Children s Hospital Assistant Professor of Pediatrics,
Glutathione / Thioredoxin Nrf2 & Hyperoxia Trent E. Tipple, MD Principal Investigator, Center for Perinatal Research The Research Institute at Nationwide Children s Hospital Assistant Professor of Pediatrics,
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 pring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, pring 2001) offered
77:222 pring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, pring 2001) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
Kit for assay of thioredoxin
 FkTRX-02-V2 Kit for assay of thioredoxin The thioredoxin system is the major protein disulfide reductase in cells and comprises thioredoxin, thioredoxin reductase and NADPH (1). Thioredoxin systems are
FkTRX-02-V2 Kit for assay of thioredoxin The thioredoxin system is the major protein disulfide reductase in cells and comprises thioredoxin, thioredoxin reductase and NADPH (1). Thioredoxin systems are
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
Biological Chemistry of Hydrogen Peroxide
 Biological Chemistry of Hydrogen Peroxide Christine Winterbourn Department of Pathology University of Otago, Christchurch New Zealand Hydrogen Peroxide Intermediate in reduction of oxygen to water A major
Biological Chemistry of Hydrogen Peroxide Christine Winterbourn Department of Pathology University of Otago, Christchurch New Zealand Hydrogen Peroxide Intermediate in reduction of oxygen to water A major
Molecular Biology. general transfer: occurs normally in cells. special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions.
 Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
Antioxidant Enzymes. - Superoxide dismutases (SODs) - Catalases - Peroxiredoxins - Glutathione peroxidases
 Antioxidant Enzymes - Superoxide dismutases (SODs) - Catalases - Peroxiredoxins - Glutathione peroxidases Eva Maria Steiner, Samantha Swenson, Mattias Günther and Xiaoxiao Peng 1 Eva Maria Steiner June
Antioxidant Enzymes - Superoxide dismutases (SODs) - Catalases - Peroxiredoxins - Glutathione peroxidases Eva Maria Steiner, Samantha Swenson, Mattias Günther and Xiaoxiao Peng 1 Eva Maria Steiner June
Role of Thioredoxin System in Cell Death Caused by Toxic Compounds Xu Zhang
 From the Division of Biochemistry Department of Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden Role of Thioredoxin System in Cell Death Caused by Toxic Compounds Xu Zhang
From the Division of Biochemistry Department of Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden Role of Thioredoxin System in Cell Death Caused by Toxic Compounds Xu Zhang
Thiol Redox Systems June 2014 Aida Rodriguez Garcia, Brenna Zimmer, Jus:n Prigge, Shelby Bickford, Tom Reichenbach, and Rakesh Basavalingappa
 Thiol Redox Systems June 2014 Aida Rodriguez Garcia, Brenna Zimmer, Jus:n Prigge, Shelby Bickford, Tom Reichenbach, and Rakesh Basavalingappa Introduc6on Thioredoxin func:on, isoforms, localiza:on, structure,
Thiol Redox Systems June 2014 Aida Rodriguez Garcia, Brenna Zimmer, Jus:n Prigge, Shelby Bickford, Tom Reichenbach, and Rakesh Basavalingappa Introduc6on Thioredoxin func:on, isoforms, localiza:on, structure,
Effects of selenium in the intracellular peroxideremoval
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Fall 2011 Effects of selenium in the intracellular peroxideremoval system Weipeng Bian University of Iowa Copyright 2011 Weipeng Bian This
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Fall 2011 Effects of selenium in the intracellular peroxideremoval system Weipeng Bian University of Iowa Copyright 2011 Weipeng Bian This
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids. Table of a-amino Acids Found in Proteins
 Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
3. AMINO ACID AND PEPTIDES
 3. AMINO ACID AND PEPTIDES 3.1 Amino Acids and Peptides General structure - Only 20 amino-acids are found in proteins - Amino group and carboxyl group - α-carbon and side chain group 3.1 Amino Acids and
3. AMINO ACID AND PEPTIDES 3.1 Amino Acids and Peptides General structure - Only 20 amino-acids are found in proteins - Amino group and carboxyl group - α-carbon and side chain group 3.1 Amino Acids and
Vadim Gladyshev. Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School
 Selenium and Redox Systems Vadim Gladyshev Center for Redox Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School June 13, 2011 Genome Transcriptome Metabolome Ionome Proteome Trace Elements Metals
Selenium and Redox Systems Vadim Gladyshev Center for Redox Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School June 13, 2011 Genome Transcriptome Metabolome Ionome Proteome Trace Elements Metals
H 2 S: Synthesis and functions
 H 2 S: Synthesis and functions 1 Signaling gas molecules: O 2, NO and CO Then, H 2 S - Fourth singling gas molecule after O 2, NO and CO 2 Nothing Rotten About Hydrogen Sulfide s Medical Promise Science
H 2 S: Synthesis and functions 1 Signaling gas molecules: O 2, NO and CO Then, H 2 S - Fourth singling gas molecule after O 2, NO and CO 2 Nothing Rotten About Hydrogen Sulfide s Medical Promise Science
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
GLUTATHIONE TRANSFERASES. Ralf Morgenstern Institute of Environmental Medicine Karolinska Institutet
 GLUTATHIONE TRANSFERASES Ralf Morgenstern Institute of Environmental Medicine Karolinska Institutet GSTs How many enzymes Structures THREE SUPERFAMILIES SOLUBLE GLUTATHIONE-TRANSFERASES (25 kda, dimers)
GLUTATHIONE TRANSFERASES Ralf Morgenstern Institute of Environmental Medicine Karolinska Institutet GSTs How many enzymes Structures THREE SUPERFAMILIES SOLUBLE GLUTATHIONE-TRANSFERASES (25 kda, dimers)
Biomolecules: amino acids
 Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Plasmodium and host glutathione reductase: molecular function and biological process
 Plasmodium and host glutathione reductase: molecular function and biological process Viroj Wiwanitkit Department of Laboratory Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok Thailand
Plasmodium and host glutathione reductase: molecular function and biological process Viroj Wiwanitkit Department of Laboratory Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok Thailand
Redox regulated transcription factors
 Redox regulated transcription factors Katarina Johansson, PhD Division of Biochemistry Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden Outline General introduction How is a
Redox regulated transcription factors Katarina Johansson, PhD Division of Biochemistry Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden Outline General introduction How is a
Lecture Sixteen: METABOLIC ENERGY: [Based on GENERATION Chapter 15
 Lecture Sixteen: METABOLIC ENERGY: [Based on GENERATION Chapter 15 AND STORAGE Berg, (Figures in red are for the 7th Edition) Tymoczko (Figures in Blue are for the 8th Edition) & Stryer] Two major questions
Lecture Sixteen: METABOLIC ENERGY: [Based on GENERATION Chapter 15 AND STORAGE Berg, (Figures in red are for the 7th Edition) Tymoczko (Figures in Blue are for the 8th Edition) & Stryer] Two major questions
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
77:222 Spring 2003 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2003) offered
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
Erythrocytes. Dr. MOHAMED SAAD DAOUD BCH 471 1
 Red blood cells Erythrocytes Circulating erythrocytes are derived from erythropoietic cells (the precursors of erythrocytes). RBCs arise from mesenchymal cells present in bone marrow. RBCs lack nucleus
Red blood cells Erythrocytes Circulating erythrocytes are derived from erythropoietic cells (the precursors of erythrocytes). RBCs arise from mesenchymal cells present in bone marrow. RBCs lack nucleus
UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH CHEM 4540 ENZYMOLOGY Winter 2005 Quiz #2: March 24, 2005, 11:30 12:50 Instructor: Prof R. Merrill ANSWERS
 UNIVERSITY F GUELPH CHEM 4540 ENZYMLGY Winter 2005 Quiz #2: March 24, 2005, 11:30 12:50 Instructor: Prof R. Merrill ANSWERS Instructions: Time allowed = 80 minutes. Total marks = 30. This quiz represents
UNIVERSITY F GUELPH CHEM 4540 ENZYMLGY Winter 2005 Quiz #2: March 24, 2005, 11:30 12:50 Instructor: Prof R. Merrill ANSWERS Instructions: Time allowed = 80 minutes. Total marks = 30. This quiz represents
OxisResearch A Division of OXIS Health Products, Inc.
 OxisResearch A Division of OXIS Health Products, Inc. BIOXYTECH GSH/GSSG-412 TM Colorimetric Determination of Reduced and Oxidized Glutathione For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
OxisResearch A Division of OXIS Health Products, Inc. BIOXYTECH GSH/GSSG-412 TM Colorimetric Determination of Reduced and Oxidized Glutathione For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures.
Cellular functions of protein degradation
 Protein Degradation Cellular functions of protein degradation 1. Elimination of misfolded and damaged proteins: Environmental toxins, translation errors and genetic mutations can damage proteins. Misfolded
Protein Degradation Cellular functions of protein degradation 1. Elimination of misfolded and damaged proteins: Environmental toxins, translation errors and genetic mutations can damage proteins. Misfolded
Iron Chelates and Unwanted Biological Oxidations
 The Virtual Free Radical School Iron Chelates and Unwanted Biological Oxidations Kevin D. Welch and Steven D. Aust Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Biotechnology Center Utah State University Logan,
The Virtual Free Radical School Iron Chelates and Unwanted Biological Oxidations Kevin D. Welch and Steven D. Aust Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Biotechnology Center Utah State University Logan,
Polypeptides. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017
 Polypeptides Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.72-78) and 4 Definitions and concepts A residue: each amino acid in a (poly)peptide
Polypeptides Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer, 2017 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.72-78) and 4 Definitions and concepts A residue: each amino acid in a (poly)peptide
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
77:222 Spring 2005 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2005) offered
Oxidation and Methylation in Human Brain: Implications for vaccines
 Oxidation and Methylation in Human Brain: Implications for vaccines 1 Life can be viewed through the perspective of oxidation and reduction, which involves the loss and gain of electrons, respectively.
Oxidation and Methylation in Human Brain: Implications for vaccines 1 Life can be viewed through the perspective of oxidation and reduction, which involves the loss and gain of electrons, respectively.
Chapter 2 Biosynthesis of Enzymes
 Chapter 2 Biosynthesis of Enzymes 2.1 Basic Enzyme Chemistry 2.1.1 Amino Acids An amino acid is a molecule that has the following formula: The central carbon atom covalently bonded by amino, carboxyl,
Chapter 2 Biosynthesis of Enzymes 2.1 Basic Enzyme Chemistry 2.1.1 Amino Acids An amino acid is a molecule that has the following formula: The central carbon atom covalently bonded by amino, carboxyl,
Biochemical properties of human glutaredoxins
 The Medical Nobel Institute for Biochemistry Department of Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics Karolinska Institutet, SE-171 77 Stockholm, Sweden Biochemical properties of human glutaredoxins Catrine Johansson
The Medical Nobel Institute for Biochemistry Department of Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics Karolinska Institutet, SE-171 77 Stockholm, Sweden Biochemical properties of human glutaredoxins Catrine Johansson
Mechanistic Toxicology
 SECOND EDITION Mechanistic Toxicology The Molecular Basis of How Chemicals Disrupt Biological Targets URS A. BOELSTERLI CRC Press Tavlor & France Croup CRC Press is an imp^t o* :H Taylor H Francn C'r,,jpi
SECOND EDITION Mechanistic Toxicology The Molecular Basis of How Chemicals Disrupt Biological Targets URS A. BOELSTERLI CRC Press Tavlor & France Croup CRC Press is an imp^t o* :H Taylor H Francn C'r,,jpi
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy
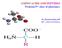 AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
Redox and Methyla.on in the Gut, Brain and Immune System. Part I: General Principles. Viewing Life Through Redox Glasses
 Overview Redox and in the Gut, Brain and Immune System Part I: General Principles Richard Deth, PhD Northeastern University Boston, MA - Oxidation and antioxidant metabolism - Epigenetic regulation of
Overview Redox and in the Gut, Brain and Immune System Part I: General Principles Richard Deth, PhD Northeastern University Boston, MA - Oxidation and antioxidant metabolism - Epigenetic regulation of
Ionization of amino acids
 Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Mechanism of Detoxification
 Mechanism of Detoxification Prof.Dr. Hedef Dhafir El-Yassin 1 Objectives: 1. To list the detoxification pathways 2. To describe detoxification pathways and phases in the liver, 2 3 4 o Xenobiotics are
Mechanism of Detoxification Prof.Dr. Hedef Dhafir El-Yassin 1 Objectives: 1. To list the detoxification pathways 2. To describe detoxification pathways and phases in the liver, 2 3 4 o Xenobiotics are
Mouse&Models&for&Studies&of&Redox&Systems&
 Mouse&Models&for&Studies&of&Redox&Systems& Thursday, 5 June 2014 Course: Redox Regulation, Oxidative Stress, and Selenoproteins Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, 2-6 June 2014 Ed Schmidt, Professor Department
Mouse&Models&for&Studies&of&Redox&Systems& Thursday, 5 June 2014 Course: Redox Regulation, Oxidative Stress, and Selenoproteins Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, 2-6 June 2014 Ed Schmidt, Professor Department
Amino acids. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester,
 Amino acids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.66-76) General structure (Chiral carbon) The amino acids that occur in
Amino acids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.66-76) General structure (Chiral carbon) The amino acids that occur in
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures a b c d PDI activity in % ERp72 activity in % 4 3 2 1 1 1 ERp activity in % e ΔRFU min -1 1 1 ERp7 activity in % 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Selectivity of the bepristat-mediated
Supplementary Figures a b c d PDI activity in % ERp72 activity in % 4 3 2 1 1 1 ERp activity in % e ΔRFU min -1 1 1 ERp7 activity in % 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Selectivity of the bepristat-mediated
Role of metabolism in Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):
 Role of metabolism in Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):159-234 Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):159-234 Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):159-234 A schematic representation of the most relevant
Role of metabolism in Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):159-234 Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):159-234 Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):159-234 A schematic representation of the most relevant
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell
 A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
Distribution of the amino acids in Nature Frequency in proteins (%)
 Distribution of the amino acids in ature Amino Acid Frequency in proteins (%) Leucine Alanine Glycine erine Valine Glutamic acid Threonine Arginine Lysine Aspartic acid Isoleucine Proline Asparagine Glutamine
Distribution of the amino acids in ature Amino Acid Frequency in proteins (%) Leucine Alanine Glycine erine Valine Glutamic acid Threonine Arginine Lysine Aspartic acid Isoleucine Proline Asparagine Glutamine
CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins
 CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins Learning goals: Structure and naming of amino acids Structure and properties of peptides Ionization behavior of amino acids and peptides Methods to characterize
CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids, Peptides, Proteins Learning goals: Structure and naming of amino acids Structure and properties of peptides Ionization behavior of amino acids and peptides Methods to characterize
Biologic Oxidation BIOMEDICAL IMPORTAN
 Biologic Oxidation BIOMEDICAL IMPORTAN Chemically, oxidation is defined as the removal of electrons and reduction as the gain of electrons. Thus, oxidation is always accompanied by reduction of an electron
Biologic Oxidation BIOMEDICAL IMPORTAN Chemically, oxidation is defined as the removal of electrons and reduction as the gain of electrons. Thus, oxidation is always accompanied by reduction of an electron
1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids
 Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Drug Metabolism Phase 2 conjugation reactions. Medicinal chemistry 3 rd stage
 Drug Metabolism Phase 2 conjugation reactions Medicinal chemistry 3 rd stage 1 Phase II or Conjugation reactions 1. Glucuronic acid conjugation 2. Sulfate conjugation 3. Glycine and Glutamine conjugation
Drug Metabolism Phase 2 conjugation reactions Medicinal chemistry 3 rd stage 1 Phase II or Conjugation reactions 1. Glucuronic acid conjugation 2. Sulfate conjugation 3. Glycine and Glutamine conjugation
Glutathione Regulation
 The Virtual Free Radical School Glutathione Regulation Dale A. Dickinson 1, Henry Jay Forman 1 and Shelly C. Lu 2 1 University of California, Merced, School of Natural Sciences, P.O. Box 2039, Merced,
The Virtual Free Radical School Glutathione Regulation Dale A. Dickinson 1, Henry Jay Forman 1 and Shelly C. Lu 2 1 University of California, Merced, School of Natural Sciences, P.O. Box 2039, Merced,
Glutathione Is a Key Player in Metal-Induced Oxidative Stress Defenses
 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 3145-3175; doi:10.3390/ijms13033145 Review OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Glutathione Is a Key Player in Metal-Induced
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 3145-3175; doi:10.3390/ijms13033145 Review OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Glutathione Is a Key Player in Metal-Induced
THIOREDOXIN REDUCTASE AS A TARGET ENZYME FOR ELECTROPHILIC ANTICANCER DRUGS
 From the Division of Biochemistry, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden THIOREDOXIN REDUCTASE AS A TARGET ENZYME FOR ELECTROPHILIC ANTICANCER DRUGS
From the Division of Biochemistry, Department of Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden THIOREDOXIN REDUCTASE AS A TARGET ENZYME FOR ELECTROPHILIC ANTICANCER DRUGS
Reactions and amino acids structure & properties
 Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Pro-Oxidant Environmental Exposures: Implications of Redox Imbalance in Autism S. Jill James, Ph.D.
 Pro-Oxidant Environmental Exposures: Implications of Redox Imbalance in Autism S. Jill James, Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pediatrics Director, Autism Metabolic Genomics Laboratory Arkansas Children
Pro-Oxidant Environmental Exposures: Implications of Redox Imbalance in Autism S. Jill James, Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pediatrics Director, Autism Metabolic Genomics Laboratory Arkansas Children
Glutathione Peroxidase Assay Kit
 Glutathione Peroxidase Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0882 100 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4
Glutathione Peroxidase Assay Kit Catalog Number KA0882 100 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4
Polar bodies are either introduced or unmasked, which results in more polar metabolites Phase I reactions can lead either to activation or
 Polar bodies are either introduced or unmasked, which results in more polar metabolites Phase I reactions can lead either to activation or inactivation of the drug (i.e. therapeutic effects or toxicity)
Polar bodies are either introduced or unmasked, which results in more polar metabolites Phase I reactions can lead either to activation or inactivation of the drug (i.e. therapeutic effects or toxicity)
9/11/18. Cell Function & Chemistry. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2. Bio-Chemical Foundations & Key Molecules of a Cell
 Molecular and Cellular Biology Cell Function & Chemistry 2. Bio-Chemical Foundations & Key Molecules of a Cell Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Interaction Molecular Bonds Define Cellular Functions Water H 2 O Interactions
Molecular and Cellular Biology Cell Function & Chemistry 2. Bio-Chemical Foundations & Key Molecules of a Cell Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Interaction Molecular Bonds Define Cellular Functions Water H 2 O Interactions
Glutathione Assay Kit
 Glutathione Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1649 250 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Glutathione Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1649 250 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Non-reciprocal regulation of the redox state of the glutathione glutaredoxin and thioredoxin systems
 scientificreport Non-reciprocal regulation of the redox state of the glutathione glutaredoxin and thioredoxin systems Eleanor W. Trotter & Chris M. Grant + University of Manchester Institute of Science
scientificreport Non-reciprocal regulation of the redox state of the glutathione glutaredoxin and thioredoxin systems Eleanor W. Trotter & Chris M. Grant + University of Manchester Institute of Science
Human Biochemistry Option B
 Human Biochemistry Option B A look ahead... Your body has many functions to perform every day: Structural support, genetic information, communication, energy supply, metabolism Right now, thousands of
Human Biochemistry Option B A look ahead... Your body has many functions to perform every day: Structural support, genetic information, communication, energy supply, metabolism Right now, thousands of
Chapter 4. Drug Biotransformation
 Chapter 4 Drug Biotransformation Drug Biotransformation 1 Why is drug biotransformation necessary 2 The role of biotransformation in drug disposition 3 Where do drug biotransformation occur 4 The enzymes
Chapter 4 Drug Biotransformation Drug Biotransformation 1 Why is drug biotransformation necessary 2 The role of biotransformation in drug disposition 3 Where do drug biotransformation occur 4 The enzymes
Amino acids. Dr. Mamoun Ahram and Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan Summer semester,
 Amino acids Dr. Mamoun Ahram and Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan Summer semester, 2017-2018 dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.66-76) General structure
Amino acids Dr. Mamoun Ahram and Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan Summer semester, 2017-2018 dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.66-76) General structure
3 The abbreviations used are: MeHg or CH 3 HgCl, methylmercury; DTNB, 5,5 dithiobis-(2-nitrobenzoic
 THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 283, NO. 18, pp. 11913 11923, May 2, 2008 2008 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in the U.S.A. Inhibition of the Human
THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 283, NO. 18, pp. 11913 11923, May 2, 2008 2008 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Printed in the U.S.A. Inhibition of the Human
This dissertation is available at Iowa Research Online:
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Spring 2016 Toward absolute quantitation in cell culture: expression of dose of xenobiotics and capacity of cells to remove hydrogen peroxide
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations Spring 2016 Toward absolute quantitation in cell culture: expression of dose of xenobiotics and capacity of cells to remove hydrogen peroxide
Hind Abu Tawileh. Moh Tarek & Razi Kittaneh. Ma moun
 26 Hind Abu Tawileh Moh Tarek & Razi Kittaneh... Ma moun Cofactors are non-protein compounds, they are divided into 3 types: Protein-based. Metals: if they are bounded tightly (covalently) to the enzyme
26 Hind Abu Tawileh Moh Tarek & Razi Kittaneh... Ma moun Cofactors are non-protein compounds, they are divided into 3 types: Protein-based. Metals: if they are bounded tightly (covalently) to the enzyme
Thioredoxin structure and mechanism: conformational changes on oxidation of the active-site sulfhydryls to a disulfide
 ARNE HOLMGREN MINIREVIEW Thioredoxin structure and mechanism: conformational changes on oxidation of the active-site sulfhydryls to a disulfide The recent high-resolution solution structures of human and
ARNE HOLMGREN MINIREVIEW Thioredoxin structure and mechanism: conformational changes on oxidation of the active-site sulfhydryls to a disulfide The recent high-resolution solution structures of human and
Previous Class. Today. Detection of enzymatic intermediates: Protein tyrosine phosphatase mechanism. Protein Kinase Catalytic Properties
 Previous Class Detection of enzymatic intermediates: Protein tyrosine phosphatase mechanism Today Protein Kinase Catalytic Properties Protein Phosphorylation Phosphorylation: key protein modification
Previous Class Detection of enzymatic intermediates: Protein tyrosine phosphatase mechanism Today Protein Kinase Catalytic Properties Protein Phosphorylation Phosphorylation: key protein modification
Computational Insights into the Structural Properties and Catalytic Functions of Selenoprotein Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx)
 1 1 Computational Insights into the Structural Properties and Catalytic Functions of Selenoprotein Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx) Rajeev Prabhakar, Keiji Morokuma, and Djamaladdin G. Musaev 1.1 Introduction
1 1 Computational Insights into the Structural Properties and Catalytic Functions of Selenoprotein Glutathione Peroxidase (GPx) Rajeev Prabhakar, Keiji Morokuma, and Djamaladdin G. Musaev 1.1 Introduction
UNIT 2 Amino acids and Proteins
 UNIT 2 Amino acids and Proteins Significance of Proteins 1. Keep the cells and tissues growing, renewing and mending 2. Take part in some kinds of important physiological activities 3. Oxidation and supply
UNIT 2 Amino acids and Proteins Significance of Proteins 1. Keep the cells and tissues growing, renewing and mending 2. Take part in some kinds of important physiological activities 3. Oxidation and supply
Proteins are sometimes only produced in one cell type or cell compartment (brain has 15,000 expressed proteins, gut has 2,000).
 Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Biochemistry 2 Recita0on Amino Acid Metabolism
 Biochemistry 2 Recita0on Amino Acid Metabolism 04-20- 2015 Glutamine and Glutamate as key entry points for NH 4 + Amino acid catabolism Glutamine synthetase enables toxic NH 4 + to combine with glutamate
Biochemistry 2 Recita0on Amino Acid Metabolism 04-20- 2015 Glutamine and Glutamate as key entry points for NH 4 + Amino acid catabolism Glutamine synthetase enables toxic NH 4 + to combine with glutamate
Protein oxidation: concepts, mechanisms and new insights. Michael J. Davies The Heart Research Institute Sydney
 Protein oxidation: concepts, mechanisms and new insights Michael J. Davies The eart Research Institute Sydney utline of talk Mechanisms of oxidation of proteins by radical oxidants. Mechanisms of oxidation
Protein oxidation: concepts, mechanisms and new insights Michael J. Davies The eart Research Institute Sydney utline of talk Mechanisms of oxidation of proteins by radical oxidants. Mechanisms of oxidation
Activation of Chemical Biological Defense Mechanisms and Remission of Vital Oxidative Injury by Low Dose Radiation
 Activation of Chemical Biological Defense Mechanisms and Remission of Vital Oxidative Injury by Low Dose Radiation K.Yamaoka 1, T.Nomura 2 and S.Kojima 3 1 Okayama University Medical School, Okayama 700-8558,
Activation of Chemical Biological Defense Mechanisms and Remission of Vital Oxidative Injury by Low Dose Radiation K.Yamaoka 1, T.Nomura 2 and S.Kojima 3 1 Okayama University Medical School, Okayama 700-8558,
Y. Hong 1, S. Hong 1, Y. H. Chang 1, S. H. Cho 2. Republic of Korea,
 INFLUENCE OF AN ORALLY EFFECTIVE SUPEROXIDE DISMUTASE (GLISODIN ) ON STRENUOUS EXERCISE-INDUCED CHANGES OF BLOOD ANTIOXIDANT ENZYMES AND PLASMA LACTATE Y. Hong 1, S. Hong 1, Y. H. Chang 1, S. H. Cho 2
INFLUENCE OF AN ORALLY EFFECTIVE SUPEROXIDE DISMUTASE (GLISODIN ) ON STRENUOUS EXERCISE-INDUCED CHANGES OF BLOOD ANTIOXIDANT ENZYMES AND PLASMA LACTATE Y. Hong 1, S. Hong 1, Y. H. Chang 1, S. H. Cho 2
This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is worth 2 points.
 MBB 407/511 Molecular Biology and Biochemistry First Examination - October 1, 2002 Name Social Security Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is
MBB 407/511 Molecular Biology and Biochemistry First Examination - October 1, 2002 Name Social Security Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions is
Chemistry 20 Chapter 14 Proteins
 Chapter 14 Proteins Proteins: all proteins in humans are polymers made up from 20 different amino acids. Proteins provide structure in membranes, build cartilage, muscles, hair, nails, and connective tissue
Chapter 14 Proteins Proteins: all proteins in humans are polymers made up from 20 different amino acids. Proteins provide structure in membranes, build cartilage, muscles, hair, nails, and connective tissue
The Role of Glutathione in Cell Defense, with References to Clinical Deficiencies and Treatment. Thomas A. Kwyer, M.D.
 The Role of Glutathione in Cell Defense, with References to Clinical Deficiencies and Treatment Thomas A. Kwyer, M.D. Glutathione Precursors: Amino Acids L-Glutamate L-Cysteine the rate-limiting substrate
The Role of Glutathione in Cell Defense, with References to Clinical Deficiencies and Treatment Thomas A. Kwyer, M.D. Glutathione Precursors: Amino Acids L-Glutamate L-Cysteine the rate-limiting substrate
This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course
 77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
77:222 Spring 2001 Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine Page 0 This student paper was written as an assignment in the graduate course Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine (77:222, Spring 2001) offered
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, Name: (print)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Cornstarch
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary data : Supplementary Table 1: Diet composition (g/kg) on the basis of the
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Supplementary data : Supplementary Table 1: Diet composition (g/kg) on the basis of the
Chemistry 121 Winter 17
 Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
7.014 Quiz I Handout. Quiz I announcements: **This will be a closed book exam**
 MIT Department of Biology 7.014 Introductory Biology, Spring 2005 7.014 Quiz I Handout Quiz I announcements: **This will be a closed book exam** Below is last year s Quiz I (solutions at the end). It should
MIT Department of Biology 7.014 Introductory Biology, Spring 2005 7.014 Quiz I Handout Quiz I announcements: **This will be a closed book exam** Below is last year s Quiz I (solutions at the end). It should
Chapter 10. Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives. Naming Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives. Carboxylic Acids: RCOOH (RCO 2 H)
 Chapter 10 Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Naming Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Carboxylic Acids: RCH (RC 2 H) The functional group of a carboxylic acid is a carboxyl group (carbonyl & hydroxyl group)
Chapter 10 Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Naming Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Carboxylic Acids: RCH (RC 2 H) The functional group of a carboxylic acid is a carboxyl group (carbonyl & hydroxyl group)
Imbalance in Protein Thiol Redox Regulation and Cancer-Preventive Efficacy of Selenium
 Imbalance in Protein Thiol Redox Regulation and Cancer-Preventive Efficacy of Selenium Rayudu Gopalakrishna 1, Usha Gundimeda 1, Sarah Zhou 1, Kristen Zung 1, Kaitlyn Forell 1, and Arne Holmgren 2 1 Department
Imbalance in Protein Thiol Redox Regulation and Cancer-Preventive Efficacy of Selenium Rayudu Gopalakrishna 1, Usha Gundimeda 1, Sarah Zhou 1, Kristen Zung 1, Kaitlyn Forell 1, and Arne Holmgren 2 1 Department
Glutathione Homeostasis & Glutathione S- Transferases
 Glutathione Homeostasis & Glutathione S- Transferases So why do we even need to worry about ANTIoxidants? Oxidative damage has been linked with many human pathologies: aging; heart disease; diabetes; neurodegenerative
Glutathione Homeostasis & Glutathione S- Transferases So why do we even need to worry about ANTIoxidants? Oxidative damage has been linked with many human pathologies: aging; heart disease; diabetes; neurodegenerative
