Enzyme Activity Lecture. Every reaction has energy requirement. The minimum amount of energy required is termed activation energy.
|
|
|
- Jayson Nicholson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Enzyme Activity Lecture Every reaction has energy requirement. The minimum amount of energy required is termed activation energy. Living organisms have optimum temperature requirement so elevating the temperature to increase incidence of molecular collision will harm the biological structure. Increasing the concentration of the reactants also increases the likelihood of collisions, however concentrations are normally low. Enzymes are used by biological systems to lower the activation energy. The enzymes provide another pathway that requires less energy and increases the rate of reaction. Enzyme Properties: 1. Show remarkable specificity for their reactants, called substrates. 2. Nearly all enzymes are protein. 3. Each enzyme has a unique, intricately shaped binding surface called the active site. 4. Most enzymes often contain non-protein components such as metal ions called cofactor. Co-enzymes are organic nom-protein component (example: vitamins) 5. The protein component of an enzyme is called the apoenzyme and an enzyme that has the cofactor intact is called the haloenzyme. 6. The non-covalent forces that bind substrate to the active site are the same forces that account for the conformations of protein themselves: van der Waals forces, electrostatic forces, hydrogen bonding and hydrophobic interactions.
2 7. How do enzymes work? The Induced Fit Model. The enzyme and the substrate combine to form an enzyme-substrate complex. The formation of the complex often induces a conformational change in that allows it to bind to the substrate. Binding the substrate also often causes certain of its bond to become strained, and therefore is easily broken. The product of the reaction usually has a different shape from the substrate, and the altered shape or the intervention of another molecule causes the complex to dissociate. The enzyme can then accept another molecule of substrate, repeating the whole process. 1. How is enzyme activity regulated? The reaction is stopped by enzyme inhibition: competitive, non-competitive and feedback inhibition. In competitive inhibition, another substance other than the substrate competes for the active site of the enzyme. This type of inhibition slows down the reaction and is reversible.
3 In non-competitive inhibition, the inhibitors with portions of the active site which results in the changing of its shape. Once the active site's shape is changed, it can no longer attach to the substrate In allosteric inhibition another substance bind to the enzyme in a spot other than the active site, altering the conformation of the enzyme. The enzyme is left non-functional.
4 In feedback inhibition, the amount of product present or absent determines enzyme activity. 2. Factors that affect the enzyme activity. a. Substrate Concentration Rate of reaction initially increases as substrate concentration is increased. At a certain concentration the substrate, the rate of reaction reaches a maximum. b. Enzyme Concentration Rate of reaction increases with increased enzyme concentration. There will be a leveling off as the substrate is used up. 3. Effect of Temperature and ph Enzymes function most effectively at neutral ph. The rate of reaction falls rapidly as the solution is made acidic or alkaline. At extreme ph the enzyme actually looses it biological active conformation and is denatured. Enzymes are rapidly destroyed if the temperature rise above 37 o C but remain stable at much lower temperatures.
5 Experiment: Part A Extraction of polypheloxidase Extract polyphenoloxidase from potato. Polyphenoloxidase catalyses oxidation of dihydroxyphenols to quinones. Colorless Reddish Brown Part B Enzyme specificity Will compounds that have similar structure as cathechol also be catalyzed by polyphenoxidase? Phenol 1,4 cyclohexanediol Cathecol
6 For the remainder of the experiment: Keep test tube A from Part B as your negative control. Keep test tube B from Part B as your positive control Part C Substrate Concentration Because the enzyme extracted for the potato is not quantified, a qualitative measure is done. You must be able to differentiate the color among the different enzyme concentrations. If no difference in intensity is observed in Part C, the enzyme might be too concentrated. Dilute enzyme stock solution 2:1 (8 ml enzyme + 4 ml 2% NaF) and repeat the Part C with the diluted enzyme. If this is still too concentrated, dilute the enzyme 1:1 with the NaF solution. Once the optimum concentration is achieved, use the same enzyme concentration for the remaining parts of the experiment. Part D Enzyme Concentration Part E Effect of ph Part F Effect of Temperature Part G Inhibitors When a ppt is observed, the protein has denatured. Phenylthiourea combines with the copper cofactor. Is it a competitive or noncompetitive inhibitor. Data Analysis Recommendation: Graph with Excel. Determine the relative intensity among the samples for each part of the experiment only. What do Parts B and G determine. Plot graph for Part C and D Part C plot Intensity VS Relative Substrate Concentration Part D plot Intensity VS Relative Enzyme Concentration Connect the points in the graph. Do not do a best fit. For Part E and F A bar graph would represent the data best.
7
Organic molecules are the molecules in living things There are four types of organic (carbon-based) molecules: Carbohydrates Lipids (fats) Proteins
 Organic molecules are the molecules in living things There are four types of organic (carbon-based) molecules: Carbohydrates Lipids (fats) Proteins Nucleic Acids Protein Muscles are made of proteins Enzymes
Organic molecules are the molecules in living things There are four types of organic (carbon-based) molecules: Carbohydrates Lipids (fats) Proteins Nucleic Acids Protein Muscles are made of proteins Enzymes
CHAPTER 2- ENZYMES PROTEINS B. AMINO ACID- 10/4/2016
 CHAPTER 2- ENZYMES BIOL. 1 AB KENNEDY PROTEINS A. DEFINITION- LARGE MACROMOLECULES MADE OF CARBON, HYDROGEN, NITROGEN, OXYGEN, AND SULFUR THEIR PRIMARY BUILDING BLOCK IS THE AMINO ACID THEY FUNCTION AS
CHAPTER 2- ENZYMES BIOL. 1 AB KENNEDY PROTEINS A. DEFINITION- LARGE MACROMOLECULES MADE OF CARBON, HYDROGEN, NITROGEN, OXYGEN, AND SULFUR THEIR PRIMARY BUILDING BLOCK IS THE AMINO ACID THEY FUNCTION AS
ENZYMES: BIOLOGICAL CATALYSTS OF LIFE
 Potential Energy Lab 6 ENZYMES: BIOLOGICAL CATALYSTS OF LIFE OBJECTIVES Define catalyst, enzyme, activation energy, enzyme-substrate complex, substrate, product, active site, denaturation, and cofactor;
Potential Energy Lab 6 ENZYMES: BIOLOGICAL CATALYSTS OF LIFE OBJECTIVES Define catalyst, enzyme, activation energy, enzyme-substrate complex, substrate, product, active site, denaturation, and cofactor;
Review of Energetics Intro
 Review of Energetics Intro Learning Check The First Law of Thermodynamics states that energy can be Created Destroyed Converted All of the above Learning Check The second law of thermodynamics essentially
Review of Energetics Intro Learning Check The First Law of Thermodynamics states that energy can be Created Destroyed Converted All of the above Learning Check The second law of thermodynamics essentially
AP BIOLOGY Enzyme Catalysis
 AP BIOLOGY Enzyme Catalysis Introduction In general, enzymes are proteins produced by living cells; they act as catalysts in biochemical reactions. A catalyst affects the rate of a chemical reaction. One
AP BIOLOGY Enzyme Catalysis Introduction In general, enzymes are proteins produced by living cells; they act as catalysts in biochemical reactions. A catalyst affects the rate of a chemical reaction. One
6.5 Enzymes. Enzyme Active Site and Substrate Specificity
 180 Chapter 6 Metabolism 6.5 Enzymes By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts Discuss enzyme
180 Chapter 6 Metabolism 6.5 Enzymes By the end of this section, you will be able to: Describe the role of enzymes in metabolic pathways Explain how enzymes function as molecular catalysts Discuss enzyme
Chapter 6. Flow of energy through life. Chemical reactions of life. Examples. Examples. Chemical reactions & energy 9/7/2012. Enzymes & Metabolism
 Flow of energy through life Chapter 6 Life is built on chemical reactions Enzymes & Metabolism Chemical reactions of life Examples Metabolism Forming bonds between molecules Dehydration synthesis Anabolic
Flow of energy through life Chapter 6 Life is built on chemical reactions Enzymes & Metabolism Chemical reactions of life Examples Metabolism Forming bonds between molecules Dehydration synthesis Anabolic
BIOCHEMISTRY Unit 2 Part 4 ACTIVITY #7 (Chapter 8.4) Enzymes. A. Is this reaction dehydration synthesis or hydrolysis?
 AP BIOLOGY BIOCHEMISTRY Unit 2 Part 4 ACTIVITY #7 (Chapter 8.4) NAME DATE PERIOD Enzymes 8.4 1. Enzymes are an important type of protein. For now, use this sketch to review what you know about enzymes.
AP BIOLOGY BIOCHEMISTRY Unit 2 Part 4 ACTIVITY #7 (Chapter 8.4) NAME DATE PERIOD Enzymes 8.4 1. Enzymes are an important type of protein. For now, use this sketch to review what you know about enzymes.
Studying the Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide Substrate Concentration on Catalase Induced Reaction
 Studying the Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide Substrate Concentration on Catalase Induced Reaction Submitted by: [Student Name] [Course Name] [University Name] Table of Contents 1.0 Aim... 3 2.0 Background
Studying the Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide Substrate Concentration on Catalase Induced Reaction Submitted by: [Student Name] [Course Name] [University Name] Table of Contents 1.0 Aim... 3 2.0 Background
Enzymes. Enzyme Structure. How do enzymes work?
 Page 1 of 6 Enzymes Enzymes are biological catalysts. There are about 40,000 different enzymes in human cells, each controlling a different chemical reaction. They increase the rate of reactions by a factor
Page 1 of 6 Enzymes Enzymes are biological catalysts. There are about 40,000 different enzymes in human cells, each controlling a different chemical reaction. They increase the rate of reactions by a factor
Review of Biochemistry
 Review of Biochemistry Chemical bond Functional Groups Amino Acid Protein Structure and Function Proteins are polymers of amino acids. Each amino acids in a protein contains a amino group, - NH 2,
Review of Biochemistry Chemical bond Functional Groups Amino Acid Protein Structure and Function Proteins are polymers of amino acids. Each amino acids in a protein contains a amino group, - NH 2,
Terminology-Amino Acids
 Enzymes 1 2 Terminology-Amino Acids Primary Structure: is a polypeptide (large number of aminoacid residues bonded together in a chain) chain of amino acids linked with peptide bonds. Secondary Structure-
Enzymes 1 2 Terminology-Amino Acids Primary Structure: is a polypeptide (large number of aminoacid residues bonded together in a chain) chain of amino acids linked with peptide bonds. Secondary Structure-
Life and the Flow of Energy. Chapter 6. The Flow of Energy
 Life and the Flow of Energy Chapter 6 Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes Energy is the ability to do work Cells (and organisms) need a constant supply of Life on Earth is dependent on solar Solar The Flow
Life and the Flow of Energy Chapter 6 Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes Energy is the ability to do work Cells (and organisms) need a constant supply of Life on Earth is dependent on solar Solar The Flow
Notes 2-4. Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
 Notes 2-4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chemical Reaction: A process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals Reactants: Elements entered into the reaction Products: Elements or
Notes 2-4 Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chemical Reaction: A process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals Reactants: Elements entered into the reaction Products: Elements or
Unit 7 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 7 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 7 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Chapter 6. Metabolism & Enzymes. AP Biology
 Chapter 6. Metabolism & Enzymes Flow of energy through life Life is built on chemical reactions Chemical reactions of life Metabolism forming bonds between molecules dehydration synthesis anabolic reactions
Chapter 6. Metabolism & Enzymes Flow of energy through life Life is built on chemical reactions Chemical reactions of life Metabolism forming bonds between molecules dehydration synthesis anabolic reactions
Examples. Chapter 8. Metabolism & Enzymes. Flow of energy through life. Examples. Chemical reactions of life. Chemical reactions & energy
 WH Examples dehydration synthesis Chapter 8 Metabolism & Enzymes + H 2 O hydrolysis + H 2 O Flow of energy through life Life is built on chemical reactions Examples dehydration synthesis hydrolysis 2005-2006
WH Examples dehydration synthesis Chapter 8 Metabolism & Enzymes + H 2 O hydrolysis + H 2 O Flow of energy through life Life is built on chemical reactions Examples dehydration synthesis hydrolysis 2005-2006
Chapter 5- Enzymes. State Standard Standard 1.b.
 Chapter 5- Enzymes State Standard Standard 1.b. Enzymes Speed Up Chemical Reactions Most of the essential chemical reactions in cells must occur quickly and precisely for the cell to survive For a chemical
Chapter 5- Enzymes State Standard Standard 1.b. Enzymes Speed Up Chemical Reactions Most of the essential chemical reactions in cells must occur quickly and precisely for the cell to survive For a chemical
Chapter 23 Enzymes 1
 Chapter 23 Enzymes 1 Enzymes Ribbon diagram of cytochrome c oxidase, the enzyme that directly uses oxygen during respiration. 2 Enzyme Catalysis Enzyme: A biological catalyst. With the exception of some
Chapter 23 Enzymes 1 Enzymes Ribbon diagram of cytochrome c oxidase, the enzyme that directly uses oxygen during respiration. 2 Enzyme Catalysis Enzyme: A biological catalyst. With the exception of some
increase rate of reaction without being consumed reduce activation energy don t change free energy ( G) released or required
 Enzymes Enzymes Biological catalysts proteins (& RNA) facilitate chemical reactions increase rate of reaction without being consumed reduce activation energy don t change free energy ( G) released or required
Enzymes Enzymes Biological catalysts proteins (& RNA) facilitate chemical reactions increase rate of reaction without being consumed reduce activation energy don t change free energy ( G) released or required
Multiple Choice Review- Membranes & Enzymes
 Multiple Choice Review- Membranes & Enzymes 1. Cell membranes are and regulate the materials moving into and out of the cell, in order to maintain equilibrium. a. completely permeable b. ionically permeable
Multiple Choice Review- Membranes & Enzymes 1. Cell membranes are and regulate the materials moving into and out of the cell, in order to maintain equilibrium. a. completely permeable b. ionically permeable
Enzymes - Exercise 3 - Germantown
 Enzymes - Exercise 3 - Germantown Objectives -Understand the function of an enzyme. -Know where catechol oxidase (enzyme) used in today s experiment came from. -Understand why enzymes require a cofactor.
Enzymes - Exercise 3 - Germantown Objectives -Understand the function of an enzyme. -Know where catechol oxidase (enzyme) used in today s experiment came from. -Understand why enzymes require a cofactor.
BACKGROUND INFORMATION:
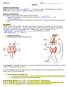 BIOLOGY 12 ENZYMES NAME: BACKGROUND INFORMATION: Energy: is defined as the ability to do or bring about change. A living organism must constantly perform work in order to maintain its organization, to
BIOLOGY 12 ENZYMES NAME: BACKGROUND INFORMATION: Energy: is defined as the ability to do or bring about change. A living organism must constantly perform work in order to maintain its organization, to
Energy and catalysts. Enzymes. Contents. 1 Energy and catalysts 2 Enzymes
 Contents 1 Energy and catalysts 2 Enzymes Energy and catalysts In Biological systems, energy is roughly defined as the capacity to do work. Molecules are held together by electrons. Breaking and building
Contents 1 Energy and catalysts 2 Enzymes Energy and catalysts In Biological systems, energy is roughly defined as the capacity to do work. Molecules are held together by electrons. Breaking and building
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Chapter 5- Enzymes. State Standard. Enzymes Speed Up Chemical Reactions. Standard 1.b.
 Slide 1 Chapter 5- Enzymes Slide 2 State Standard Standard 1.b. Slide 3 Enzymes Speed Up Chemical Reactions Most of the essential chemical reactions in cells must occur quickly and precisely for the cell
Slide 1 Chapter 5- Enzymes Slide 2 State Standard Standard 1.b. Slide 3 Enzymes Speed Up Chemical Reactions Most of the essential chemical reactions in cells must occur quickly and precisely for the cell
Name: Date: AP Biology LAB : FACTORS INFLUENCING ENZYME ACTIVITY
 LAB : FACTORS INFLUENCING ENZYME ACTIVITY Background Enzymes are biological catalysts capable of speeding up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy. One benefit of enzyme catalysts is that the
LAB : FACTORS INFLUENCING ENZYME ACTIVITY Background Enzymes are biological catalysts capable of speeding up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy. One benefit of enzyme catalysts is that the
Chemistry 107 Exam 4 Study Guide
 Chemistry 107 Exam 4 Study Guide Chapter 10 10.1 Recognize that enzyme catalyze reactions by lowering activation energies. Know the definition of a catalyst. Differentiate between absolute, relative and
Chemistry 107 Exam 4 Study Guide Chapter 10 10.1 Recognize that enzyme catalyze reactions by lowering activation energies. Know the definition of a catalyst. Differentiate between absolute, relative and
Energy. Energy is the ability to do work or bring about a change. Energy transactions must follow the laws of Thermodynamics
 Chapter 6 Energy Energy is the ability to do work or bring about a change Kinetic Energy: Energy of motion Potential Energy: Stored energy Energy transactions must follow the laws of Thermodynamics 1 st
Chapter 6 Energy Energy is the ability to do work or bring about a change Kinetic Energy: Energy of motion Potential Energy: Stored energy Energy transactions must follow the laws of Thermodynamics 1 st
Concept 8.3: ATP powers cellular work by coupling exergonic reactions to endergonic reactions
 Concept 8.3: ATP powers cellular work by coupling exergonic reactions to endergonic reactions A cell does three main kinds of work: Chemical Transport Mechanical To do work, cells manage energy resources
Concept 8.3: ATP powers cellular work by coupling exergonic reactions to endergonic reactions A cell does three main kinds of work: Chemical Transport Mechanical To do work, cells manage energy resources
Enzymes: The Catalysts of Life
 Chapter 6 Enzymes: The Catalysts of Life Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Activation Energy and the Metastable State Many thermodynamically feasible reactions in a cell that could
Chapter 6 Enzymes: The Catalysts of Life Lectures by Kathleen Fitzpatrick Simon Fraser University Activation Energy and the Metastable State Many thermodynamically feasible reactions in a cell that could
Biological Molecules B Lipids, Proteins and Enzymes. Triglycerides. Glycerol
 Glycerol www.biologymicro.wordpress.com Biological Molecules B Lipids, Proteins and Enzymes Lipids - Lipids are fats/oils and are present in all cells- they have different properties for different functions
Glycerol www.biologymicro.wordpress.com Biological Molecules B Lipids, Proteins and Enzymes Lipids - Lipids are fats/oils and are present in all cells- they have different properties for different functions
Enzymes. Ms. Paxson. From food webs to the life of a cell. Enzymes. Metabolism. Flow of energy through life. Examples. Examples
 From food webs to the life of a cell energy energy energy Flow of energy through life Life is built on chemical reactions sun transforming energy from one form to another solar energy ATP & organic molecules
From food webs to the life of a cell energy energy energy Flow of energy through life Life is built on chemical reactions sun transforming energy from one form to another solar energy ATP & organic molecules
fossum/files/2012/01/10 Enzymes.pdf
 http://www.laney.edu/wp/cheli fossum/files/2012/01/10 Enzymes.pdf Enzyme Catalysis Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts for biological reactions. Enzymes, like all catalysts, speed up reactions without
http://www.laney.edu/wp/cheli fossum/files/2012/01/10 Enzymes.pdf Enzyme Catalysis Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts for biological reactions. Enzymes, like all catalysts, speed up reactions without
Unit 7 Part I: Introductions to Biochemistry
 Unit 7 Part I: Introductions to Biochemistry Chemical Reactions, Enzymes and ATP 19 March 2014 Averett 1 Reaction Graphs Every chemical reaction involves bond breaking and bond forming. In order for bonds
Unit 7 Part I: Introductions to Biochemistry Chemical Reactions, Enzymes and ATP 19 March 2014 Averett 1 Reaction Graphs Every chemical reaction involves bond breaking and bond forming. In order for bonds
AP Biology Summer Assignment Chapter 3 Quiz
 AP Biology Summer Assignment Chapter 3 Quiz 2016-17 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. All of the following are found in a DNA nucleotide
AP Biology Summer Assignment Chapter 3 Quiz 2016-17 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. All of the following are found in a DNA nucleotide
Microbial Metabolism. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 5 Microbial Metabolism Big Picture: Metabolism Metabolism is the buildup and breakdown of nutrients
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Bradley W. Christian, McLennan Community College C H A P T E R 5 Microbial Metabolism Big Picture: Metabolism Metabolism is the buildup and breakdown of nutrients
AP Biology. Metabolism & Enzymes
 Metabolism & Enzymes From food webs to the life of a cell energy energy energy Flow of energy through life Life is built on chemical reactions transforming energy from one form to another organic molecules
Metabolism & Enzymes From food webs to the life of a cell energy energy energy Flow of energy through life Life is built on chemical reactions transforming energy from one form to another organic molecules
Enzymes Topic 3.6 & 7.6 SPEED UP CHEMICAL REACTIONS!!!!!!!
 Enzymes Topic 3.6 & 7.6 SPEED UP CHEMICAL REACTIONS!!!!!!! Key Words Enzyme Substrate Product Active Site Catalyst Activation Energy Denature Enzyme-Substrate Complex Lock & Key model Induced fit model
Enzymes Topic 3.6 & 7.6 SPEED UP CHEMICAL REACTIONS!!!!!!! Key Words Enzyme Substrate Product Active Site Catalyst Activation Energy Denature Enzyme-Substrate Complex Lock & Key model Induced fit model
A cell s metabolism is all the organism s chemical reactions. Metabolism manages the material and energy resources of the cell.
 Enzymes Metabolism Metabolism A cell s metabolism is all the organism s chemical reactions. Metabolism manages the material and energy resources of the cell. Energy is the capacity to do work. Metabolism
Enzymes Metabolism Metabolism A cell s metabolism is all the organism s chemical reactions. Metabolism manages the material and energy resources of the cell. Energy is the capacity to do work. Metabolism
Enzymes Biological Catalysts Review
 Enzymes Biological Catalysts Review Catalyst a substance that speeds up a reaction but is not actually a part of the reaction nor changes because of the reaction Catalysis the process of speeding a chemical
Enzymes Biological Catalysts Review Catalyst a substance that speeds up a reaction but is not actually a part of the reaction nor changes because of the reaction Catalysis the process of speeding a chemical
Metabolism & Enzymes. From food webs to the life of a cell. Flow of energy through life. Life is built on chemical reactions
 Metabolism & Enzymes 2007-2008 From food webs to the life of a cell energy energy energy Flow of energy through life Life is built on chemical reactions transforming energy from one form to another organic
Metabolism & Enzymes 2007-2008 From food webs to the life of a cell energy energy energy Flow of energy through life Life is built on chemical reactions transforming energy from one form to another organic
Microbial Metabolism (Chapter 5) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Microbial Metabolism (Chapter 5) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Source for figures and content: Tortora, G.J. Microbiology An Introduction
Microbial Metabolism (Chapter 5) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Source for figures and content: Tortora, G.J. Microbiology An Introduction
Chapter 5 Microbial Metabolism: The Chemical Crossroads of Life
 Chapter 5 Microbial Metabolism: The Chemical Crossroads of Life Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The Metabolism of Microbes metabolism all chemical
Chapter 5 Microbial Metabolism: The Chemical Crossroads of Life Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The Metabolism of Microbes metabolism all chemical
GRU3L1 Metabolism & Enzymes. AP Biology
 GRU3L1 Metabolism & Enzymes From food webs to the life of a cell energy energy energy Flow of energy through life Life is built on chemical reactions u transforming energy from one form to organic molecules
GRU3L1 Metabolism & Enzymes From food webs to the life of a cell energy energy energy Flow of energy through life Life is built on chemical reactions u transforming energy from one form to organic molecules
Chapter 8.4, 8.5. Enzymes. AP Biology
 Chapter 8.4, 8.5 Enzymes Activation energy Breaking down large molecules requires an initial input of energy activation energy large biomolecules are stable must absorb energy to break bonds cellulose
Chapter 8.4, 8.5 Enzymes Activation energy Breaking down large molecules requires an initial input of energy activation energy large biomolecules are stable must absorb energy to break bonds cellulose
Biochem sheet (5) done by: razan krishan corrected by: Shatha Khtoum DATE :4/10/2016
 Biochem sheet (5) done by: razan krishan corrected by: Shatha Khtoum DATE :4/10/2016 Note about the last lecture: you must know the classification of enzyme Sequentially. * We know that a substrate binds
Biochem sheet (5) done by: razan krishan corrected by: Shatha Khtoum DATE :4/10/2016 Note about the last lecture: you must know the classification of enzyme Sequentially. * We know that a substrate binds
The MOLECULES of LIFE
 The MOLECULES of LIFE Physical and Chemical Principles Solutions Manual Prepared by James Fraser and Samuel Leachman Chapter 16 Principles of Enzyme Catalysis Problems True/False and Multiple Choice 1.
The MOLECULES of LIFE Physical and Chemical Principles Solutions Manual Prepared by James Fraser and Samuel Leachman Chapter 16 Principles of Enzyme Catalysis Problems True/False and Multiple Choice 1.
Chapter 8. Metabolism. Topics in lectures 15 and 16. Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis
 Chapter 8 Topics in lectures 15 and 16 Metabolism Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis 1 Metabolism Chemical Foundations Enzymes REDOX Catabolism Pathways Anabolism Principles and pathways 2 Chemical
Chapter 8 Topics in lectures 15 and 16 Metabolism Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis 1 Metabolism Chemical Foundations Enzymes REDOX Catabolism Pathways Anabolism Principles and pathways 2 Chemical
Chapter 11 Enzymes and Metabolic Pathways
 Chapter 11 Enzymes and Metabolic Pathways 11.1. Metabolism Metabolism comes from the Greek metabole, meaning "change". It is an emergent property of life. It includes all the chemical processes needed
Chapter 11 Enzymes and Metabolic Pathways 11.1. Metabolism Metabolism comes from the Greek metabole, meaning "change". It is an emergent property of life. It includes all the chemical processes needed
ENZYME ACTIVITY. Introduction
 ENZYME ACTIVITY This activity is an alternative to the titration proposed for Enzyme Catalysis (AP Bio Lab #2, Biology Lab Manual). There are numerous alternative lab activities that measure the rate of
ENZYME ACTIVITY This activity is an alternative to the titration proposed for Enzyme Catalysis (AP Bio Lab #2, Biology Lab Manual). There are numerous alternative lab activities that measure the rate of
Section 5. Enzymes, Equilibrium, Energy and the Sulfonamides
 Section 5 Enzymes, Equilibrium, Energy and the Sulfonamides Monday: ESKAPE handout describing them (Tiffany will provide). M-W Tie the metabolism back to the nutritional requirements and media choice,
Section 5 Enzymes, Equilibrium, Energy and the Sulfonamides Monday: ESKAPE handout describing them (Tiffany will provide). M-W Tie the metabolism back to the nutritional requirements and media choice,
Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition
 Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 8 An Introduction to Microbial Metabolism Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Lecture PowerPoint to accompany Foundations in Microbiology Seventh Edition Talaro Chapter 8 An Introduction to Microbial Metabolism Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
ENZYMES: CLASSIFICATION, STRUCTURE
 ENZYMES: CLASSIFICATION, STRUCTURE Enzymes - catalysts of biological reactions Accelerate reactions by a millions fold Common features for enzymes and inorganic catalysts: 1. Catalyze only thermodynamically
ENZYMES: CLASSIFICATION, STRUCTURE Enzymes - catalysts of biological reactions Accelerate reactions by a millions fold Common features for enzymes and inorganic catalysts: 1. Catalyze only thermodynamically
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 5, part A Microbial Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation prepared by Christine L. Case Microbial
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 5, part A Microbial Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation prepared by Christine L. Case Microbial
Part 1: Energy and Metabolism
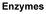 Part 1: Energy and Metabolism Life is highly organized rganisms need free energy to survive, grow, and reproduce In each system, the arrow is pointing in the direction of spontaneous change. Why? 1 2 More
Part 1: Energy and Metabolism Life is highly organized rganisms need free energy to survive, grow, and reproduce In each system, the arrow is pointing in the direction of spontaneous change. Why? 1 2 More
Amylase: a sample enzyme
 Amylase: a sample enzyme Objectives: After completion of this laboratory exercise you will be able to: 1. Explain the importance of enzymes in biology. 2. Explain the basic properties of an enzyme as a
Amylase: a sample enzyme Objectives: After completion of this laboratory exercise you will be able to: 1. Explain the importance of enzymes in biology. 2. Explain the basic properties of an enzyme as a
Chapter 5 Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes
 Biology 12 Name: Cell Biology Per: Date: Chapter 5 Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 154-175 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 533) 1. B 2. B 3. C
Biology 12 Name: Cell Biology Per: Date: Chapter 5 Metabolism: Energy and Enzymes Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 154-175 Diagnostic Questions (mark using the answer key on page 533) 1. B 2. B 3. C
ENZYME ACTIVITY. Readings: Review pp , and in your text (POHS, 5 th ed.).
 ENZYME ACTIVITY Readings: Review pp. 51-58, and 128-139 in your text (POHS, 5 th ed.). Introduction Enzymes are biological catalysts; that is, enzymes are able to mediate the conversion of substrate into
ENZYME ACTIVITY Readings: Review pp. 51-58, and 128-139 in your text (POHS, 5 th ed.). Introduction Enzymes are biological catalysts; that is, enzymes are able to mediate the conversion of substrate into
Enzymes - Exercise 3 - Rockville
 Enzymes - Exercise 3 - Rockville Objectives -Understand the function of an enzyme. -Know what the substrate, enzyme, and the product of the reaction for this lab. -Understand how at various environments
Enzymes - Exercise 3 - Rockville Objectives -Understand the function of an enzyme. -Know what the substrate, enzyme, and the product of the reaction for this lab. -Understand how at various environments
Enzymes. Ch 3: Macromolecules
 Enzymes Ch 3: Macromolecules Living things use different chemical reactions to get the energy needed for life Chemical Reactions Reactants = substance that is changed Products = new substance that forms
Enzymes Ch 3: Macromolecules Living things use different chemical reactions to get the energy needed for life Chemical Reactions Reactants = substance that is changed Products = new substance that forms
Chemical Basis For Life Open Ended Questions:
 Chemical Basis For Life Open Ended Questions: Answer the following questions to the best of your ability: Make sure you read each question carefully and provide answers to all of the parts of the question.
Chemical Basis For Life Open Ended Questions: Answer the following questions to the best of your ability: Make sure you read each question carefully and provide answers to all of the parts of the question.
DNA and Protein Synthesis Practice
 Biology 12 DNA and Protein Synthesis Practice Name: 1. DNA is often called the "code of life". Actually it contains the code for a) the sequence of amino acids in a protein b) the sequence of base pairs
Biology 12 DNA and Protein Synthesis Practice Name: 1. DNA is often called the "code of life". Actually it contains the code for a) the sequence of amino acids in a protein b) the sequence of base pairs
An Introduction to Enzyme Structure and Function
 An Introduction to Enzyme Structure and Function Enzymes Many reactions in living systems are similar to laboratory reactions. 1. Reactions in living systems often occur with the aid of enzymes. 2. Enzymes
An Introduction to Enzyme Structure and Function Enzymes Many reactions in living systems are similar to laboratory reactions. 1. Reactions in living systems often occur with the aid of enzymes. 2. Enzymes
BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE
 BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION MOST ENZYMES ARE PROTEINS ENZYME CLASSIFICATION AND NUMENCLATURE HOW ENZYMES WORK: ACTIVE SITE STRUCTURE OF THE ACTIVE SITE MODELS OF SUBSTRATE BINDING
BY: RASAQ NURUDEEN OLAJIDE LECTURE CONTENT INTRODUCTION MOST ENZYMES ARE PROTEINS ENZYME CLASSIFICATION AND NUMENCLATURE HOW ENZYMES WORK: ACTIVE SITE STRUCTURE OF THE ACTIVE SITE MODELS OF SUBSTRATE BINDING
Enzyme Action. Intermediate 2 Biology Unit 1: Living Cells
 Enzyme Action Intermediate 2 Biology Unit 1: Living Cells Learning Objectives Describe 2 ways in which chemical reactions can be speeded up. Name the products of the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide. State
Enzyme Action Intermediate 2 Biology Unit 1: Living Cells Learning Objectives Describe 2 ways in which chemical reactions can be speeded up. Name the products of the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide. State
Chapter 5. The Working Cell. Lecture by Richard L. Myers
 Chapter 5 The Working Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Richard L. Myers MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
Chapter 5 The Working Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Richard L. Myers MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS
 SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS Course Number: BIOL 140 Department: Biology Course Title: Biochemistry/Health Sciences Semester: Spring Year: 1997 Objectives/ Course Number: BIOL
SPRINGFIELD TECHNICAL COMMUNITY COLLEGE ACADEMIC AFFAIRS Course Number: BIOL 140 Department: Biology Course Title: Biochemistry/Health Sciences Semester: Spring Year: 1997 Objectives/ Course Number: BIOL
Biochemistry Department. Level 1 Lecture No : 3 Date : 1 / 10 / Enzymes kinetics
 Biochemistry Department Level 1 Lecture No : 3 Date : 1 / 10 / 2017 Enzymes kinetics 1 Intended Learning Outcomes By the end of this lecture, the student will be able to: 1.Understand what is meant by
Biochemistry Department Level 1 Lecture No : 3 Date : 1 / 10 / 2017 Enzymes kinetics 1 Intended Learning Outcomes By the end of this lecture, the student will be able to: 1.Understand what is meant by
Cofactors and coenzymes. Reversible, irreversible, competitive, and noncompetitive inhibitors. Allosteric enzymes. Feedback inhibition.
 Enzyme regulation Cofactors and coenzymes. Reversible, irreversible, competitive, and noncompetitive inhibitors. Allosteric enzymes. Feedback inhibition. Introduction The genome of a typical organism,
Enzyme regulation Cofactors and coenzymes. Reversible, irreversible, competitive, and noncompetitive inhibitors. Allosteric enzymes. Feedback inhibition. Introduction The genome of a typical organism,
An organic catalysts that enhances the speed or likelihood of a bio-chemical reaction by lowering the energy of activation.
 Micro 260 Fall 2009 Name: Allan Keys Tools: You may use your notes and or book for this assignment 1) What is an enzyme? (4 pts) An organic catalysts that enhances the speed or likelihood of a bio-chemical
Micro 260 Fall 2009 Name: Allan Keys Tools: You may use your notes and or book for this assignment 1) What is an enzyme? (4 pts) An organic catalysts that enhances the speed or likelihood of a bio-chemical
Chapter 8 Microbial Metabolism: The Chemical Crossroads of Life
 Chapter 8 Microbial Metabolism: The Chemical Crossroads of Life / Building Your Knowledge 1) What are the two branches of metabolism? a. b. Which branch synthesizes large molecules from small subunits?
Chapter 8 Microbial Metabolism: The Chemical Crossroads of Life / Building Your Knowledge 1) What are the two branches of metabolism? a. b. Which branch synthesizes large molecules from small subunits?
AP Biology Protein Structure and Enzymes
 AP Biology Protein Structure and Enzymes Connection to the Nitrogen-cycle Amino acids (protein) Nucleic acids (RNA and DNA) ATP 78% 1. Assimilation of nitrate by photosynthetic eukaryotes 2. Nitrogen fixation
AP Biology Protein Structure and Enzymes Connection to the Nitrogen-cycle Amino acids (protein) Nucleic acids (RNA and DNA) ATP 78% 1. Assimilation of nitrate by photosynthetic eukaryotes 2. Nitrogen fixation
Topic 4: Enzymes and metabolism
 Topic 4: Enzymes and metabolism 1. An is a living molecule produced by glands to digest food in the alimentary canal. living molecule produced by cells to synthesise complex molecules from simpler ones.
Topic 4: Enzymes and metabolism 1. An is a living molecule produced by glands to digest food in the alimentary canal. living molecule produced by cells to synthesise complex molecules from simpler ones.
Life s molecular diversity is based on the. properties of carbon. Chain Ring Branching chain
 Carbon Compounds Life s molecular diversity is based on the properties of carbon Chain Ring Branching chain The Chemistry of Carbon : carbon based Carbon can make 4 covalent bonds The foundation of organic
Carbon Compounds Life s molecular diversity is based on the properties of carbon Chain Ring Branching chain The Chemistry of Carbon : carbon based Carbon can make 4 covalent bonds The foundation of organic
MONDAY Review ( SL 2.5)
 Enzymes 8.1 MONDAY Review ( SL 2.5) -Active site to which specific substrate binds -Enzymes are catalysts: bring about biochemical reactions! -Optimal environment: affected by ph, temp, and substrate concentration
Enzymes 8.1 MONDAY Review ( SL 2.5) -Active site to which specific substrate binds -Enzymes are catalysts: bring about biochemical reactions! -Optimal environment: affected by ph, temp, and substrate concentration
INTERACTION DRUG BODY
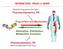 INTERACTION DRUG BODY What the drug does to the body What the body does to the drug Receptors - intracellular receptors - membrane receptors - Channel receptors - G protein-coupled receptors - Tyrosine-kinase
INTERACTION DRUG BODY What the drug does to the body What the body does to the drug Receptors - intracellular receptors - membrane receptors - Channel receptors - G protein-coupled receptors - Tyrosine-kinase
Biology 2180 Laboratory #3. Enzyme Kinetics and Quantitative Analysis
 Biology 2180 Laboratory #3 Name Introduction Enzyme Kinetics and Quantitative Analysis Catalysts are agents that speed up chemical processes and the catalysts produced by living cells are called enzymes.
Biology 2180 Laboratory #3 Name Introduction Enzyme Kinetics and Quantitative Analysis Catalysts are agents that speed up chemical processes and the catalysts produced by living cells are called enzymes.
How Cells Work. Chapter 4
 How Cells Work Chapter 4 Energy Laws Energy is the capacity to do work The total amount of energy in the universe is constant-energy can t be created or destroyed..only transferred! Energy is flowing from
How Cells Work Chapter 4 Energy Laws Energy is the capacity to do work The total amount of energy in the universe is constant-energy can t be created or destroyed..only transferred! Energy is flowing from
Enzymes. Biology Gr10. Complete the concept map showing the characteristics of enzymes. They Act as. They Are. Examples are. They cause.
 Name: Class: Date: Grade 10 Science Related Reading/Biology Enzymes Biology Gr10 Complete the concept map showing the characteristics of enzymes. They Are They Act as They cause Examples are Affected by
Name: Class: Date: Grade 10 Science Related Reading/Biology Enzymes Biology Gr10 Complete the concept map showing the characteristics of enzymes. They Are They Act as They cause Examples are Affected by
Tala Saleh. Ahmad Attari. Mamoun Ahram
 23 Tala Saleh Ahmad Attari Minna Mushtaha Mamoun Ahram In the previous lecture, we discussed the mechanisms of regulating enzymes through inhibitors. Now, we will start this lecture by discussing regulation
23 Tala Saleh Ahmad Attari Minna Mushtaha Mamoun Ahram In the previous lecture, we discussed the mechanisms of regulating enzymes through inhibitors. Now, we will start this lecture by discussing regulation
LAB 5 - Enzymes BACKGROUND INFORMATION
 LAB 5 - Enzymes BACKGROUND INFORMATION Chemical Reactions The cells of organisms, from bacteria to plants to animals, carry out hundreds to thousands of chemical reactions that must be properly coordinated
LAB 5 - Enzymes BACKGROUND INFORMATION Chemical Reactions The cells of organisms, from bacteria to plants to animals, carry out hundreds to thousands of chemical reactions that must be properly coordinated
[BCH 322] Some Factors Affec.ng Polyphenol Oxidase Ac.vity
![[BCH 322] Some Factors Affec.ng Polyphenol Oxidase Ac.vity [BCH 322] Some Factors Affec.ng Polyphenol Oxidase Ac.vity](/thumbs/94/119524662.jpg) [BCH 322] Some Factors Affec.ng Polyphenol Oxidase Ac.vity Polyphenol Oxidase (PPO): Is a copper- containing enzyme with an op4mum ph of 6.7. It catalyzes the oxida4on of di- and tri- hydroxyl phenol to
[BCH 322] Some Factors Affec.ng Polyphenol Oxidase Ac.vity Polyphenol Oxidase (PPO): Is a copper- containing enzyme with an op4mum ph of 6.7. It catalyzes the oxida4on of di- and tri- hydroxyl phenol to
Microbial Metabolism
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 5 Microbial Metabolism Microbial Metabolism The sum total of chemical reactions that take place within cells (of an organism) Metabolic
PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 5 Microbial Metabolism Microbial Metabolism The sum total of chemical reactions that take place within cells (of an organism) Metabolic
Browning Reactions. Maillard browning. Caramelization high temps. Enzymatic browning. + flavors. brown pigments. + flavors.
 Browning Reactions Maillard browning reducing sugar + amine Caramelization sugar high temps Enzymatic browning phenolics polyphenoloxidase brown pigments + flavors brown pigments + flavors brown pigments
Browning Reactions Maillard browning reducing sugar + amine Caramelization sugar high temps Enzymatic browning phenolics polyphenoloxidase brown pigments + flavors brown pigments + flavors brown pigments
3/1/2011. Enzymes. Enzymes and Activation Energy. Enzymes Enzyme Structure and Action. Chapter 4 Outline. Enzymes
 Free content 3/1/2011 Chapter 4 Outline Enzymes as catalysts Control of enzyme activity Bioenergetics Enzymes 4-2 4-3 Enzymes Enzymes - function as biological catalysts permit reactions to occur rapidly
Free content 3/1/2011 Chapter 4 Outline Enzymes as catalysts Control of enzyme activity Bioenergetics Enzymes 4-2 4-3 Enzymes Enzymes - function as biological catalysts permit reactions to occur rapidly
Copyright 2016 Dan Dill 1
 carbonate These solutions are mixed and a precipitate forms. After the precipitation, the solution 1. will be positively charged 2. will be electrically neutral 3. will be negatively charged 4. More information
carbonate These solutions are mixed and a precipitate forms. After the precipitation, the solution 1. will be positively charged 2. will be electrically neutral 3. will be negatively charged 4. More information
Question Expected Answers Mark Additional Guidance 1 (a) (enzymes are) proteins / used in metabolism / used in named metabolic pathway ;
 Question Expected Answers Mark Additional Guidance (a) (enzymes are) proteins / used in metabolism / used in named metabolic pathway ; ACCEPT used in reactions, in organisms / in the body IGNORE biological
Question Expected Answers Mark Additional Guidance (a) (enzymes are) proteins / used in metabolism / used in named metabolic pathway ; ACCEPT used in reactions, in organisms / in the body IGNORE biological
Enzymes. Enzymes accelerate chemical reactions as the engine accelerates this drag race.
 Chapter 30 Enzymes Enzymes accelerate chemical reactions as the engine accelerates this drag race. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison,
Chapter 30 Enzymes Enzymes accelerate chemical reactions as the engine accelerates this drag race. Introduction to General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 10e John Wiley & Sons, Inc Morris Hein, Scott Pattison,
Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions
 Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells. They are instrumental in almost everything an organism does. Protein
Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells. They are instrumental in almost everything an organism does. Protein
1. Most organisms are active in a limited temperature range
 1. Most organisms are active in a limited temperature range Identify the role of enzymes in metabolism, describe their chemical composition and use a simple model to describe their specificity on substrates
1. Most organisms are active in a limited temperature range Identify the role of enzymes in metabolism, describe their chemical composition and use a simple model to describe their specificity on substrates
QUALITATIVE TEST OF PROTEIN
 QUALITATIVE TEST F PRTEIN UTLINE Experment2 To detect the presence of peptide bonds or proteins in the sample Using Biuret Method Protein precipitation and denaturation Salt Strong Acid Heavy metals Heating
QUALITATIVE TEST F PRTEIN UTLINE Experment2 To detect the presence of peptide bonds or proteins in the sample Using Biuret Method Protein precipitation and denaturation Salt Strong Acid Heavy metals Heating
About Science Prof Online PowerPoint Resources
 About Science Prof Online PowerPoint Resources Science Prof Online (SPO) is a free science education website that provides fully-developed Virtual Science Classrooms, science-related PowerPoints, articles
About Science Prof Online PowerPoint Resources Science Prof Online (SPO) is a free science education website that provides fully-developed Virtual Science Classrooms, science-related PowerPoints, articles
Analysis of Polyphenoloxidase Enzyme Activity from Potato Extract Biochemistry Lab I (CHEM 4401)
 Analysis of Polyphenoloxidase Enzyme Activity from Potato Extract Biochemistry Lab I (CHEM 4401) Background Enzymes are protein molecules (primarily) that serve as biological catalysts. They are responsible
Analysis of Polyphenoloxidase Enzyme Activity from Potato Extract Biochemistry Lab I (CHEM 4401) Background Enzymes are protein molecules (primarily) that serve as biological catalysts. They are responsible
Lecture 6: Allosteric regulation of enzymes
 Chem*3560 Lecture 6: Allosteric regulation of enzymes Metabolic pathways do not run on a continuous basis, but are regulated according to need Catabolic pathways run if there is demand for ATP; for example
Chem*3560 Lecture 6: Allosteric regulation of enzymes Metabolic pathways do not run on a continuous basis, but are regulated according to need Catabolic pathways run if there is demand for ATP; for example
Biological Science 101 General Biology
 Lecture Seven: Cellular Respiration Ch. 9, Pgs. 163-181 Figs. 9.2-9.20 Biological Science 101 General Biology Cellular Respiration: - A series of processes that is involved in converting food to energy
Lecture Seven: Cellular Respiration Ch. 9, Pgs. 163-181 Figs. 9.2-9.20 Biological Science 101 General Biology Cellular Respiration: - A series of processes that is involved in converting food to energy
UNIT #3: Enzymes. What is an enzyme? How do enzymes work?
 UNIT #3: Enzymes What is an enzyme? How does an enzyme work? How is an enzyme structured? What are some factors that affect enzyma8c reac8ons? How are enzymes controlled in the body? What is an enzyme?
UNIT #3: Enzymes What is an enzyme? How does an enzyme work? How is an enzyme structured? What are some factors that affect enzyma8c reac8ons? How are enzymes controlled in the body? What is an enzyme?
Do Now #1. Name: Enzymes & ph. 1. Enzymes, hormones and cell receptors are examples of which type of macromolecule?
 Name: Do Now #1 Enzymes & ph 1. Enzymes, hormones and cell receptors are examples of which type of macromolecule? 2. What do you think enzymes do for the body? Chemical reactions with enzymes are used
Name: Do Now #1 Enzymes & ph 1. Enzymes, hormones and cell receptors are examples of which type of macromolecule? 2. What do you think enzymes do for the body? Chemical reactions with enzymes are used
Qualitative test of protein-lab2
 1- Qualitative chemical reactions of amino acid protein functional groups: Certain functional groups in proteins can react to produce characteristically colored products. The color intensity of the product
1- Qualitative chemical reactions of amino acid protein functional groups: Certain functional groups in proteins can react to produce characteristically colored products. The color intensity of the product
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Practice Quiz 1 AP Bio Sept 2016 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The element present in all organic molecules is A) hydrogen.
Practice Quiz 1 AP Bio Sept 2016 Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The element present in all organic molecules is A) hydrogen.
BIOCHEMISTRY I HOMEWORK III DUE 10/15/03 66 points total + 2 bonus points = 68 points possible Swiss-PDB Viewer Exercise Attached
 BIOCHEMISTRY I HOMEWORK III DUE 10/15/03 66 points total + 2 bonus points = 68 points possible Swiss-PDB Viewer Exercise Attached 1). 20 points total T or F (2 points each; if false, briefly state why
BIOCHEMISTRY I HOMEWORK III DUE 10/15/03 66 points total + 2 bonus points = 68 points possible Swiss-PDB Viewer Exercise Attached 1). 20 points total T or F (2 points each; if false, briefly state why
