Familial resemblance of body composition in prepubertal girls and their biological parents 1 4
|
|
|
- Brett Roland Clarke
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Familial resemblance of body composition in prepubertal girls and their biological parents 1 4 Margarita S Treuth, Nancy F Butte, Kenneth J Ellis, Lisa J Martin, and Anthony G Comuzzie ABSTRACT Background: Heritability estimates for body mass index (BMI; in kg/m 2 ) in children generally have been derived from twin and adoption studies. However, BMI does not reflect total or regional body composition. Objective: We evaluated the familial resemblance of body composition between prepubertal girls of normal weight and body fatness and their parents by using state-of-the-art technology. Design: The subjects were 101 girls [mean age: 8.5 ± 0.4 y; percentage body fat (%BF): 12 30%] and their biological parents. Weight, height, and body composition [fat mass (FM), fat-free mass (FFM), and %BF] were measured with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) and total body potassium (TBK). Results: Weight, height, and BMI showed low-to-moderate similarity between the girls and both their parents (r = , P < 0.01). The girls FM, FFM, and %BF were significantly related to both parents body composition. Cross-generational equations were developed for DXA, eg, child s %BF = (0.158 paternal %BF) + (0.145 maternal %BF) (adjusted r 2 = 0.16, P < 0.001). Regional analysis with DXA showed that the adjusted r 2 values for the arm, trunk, and leg regions, respectively, were 0.17, 0.33, and 0.31 for lean tissue mass and 0.11, 0.14, and 0.09 for FM. TBK showed a similar relation between parents and girls (r = , P < 0.01). Significant heritability (h 2 ± SE) was detected for BMI (0.35 ± 0.17, P = 0.03) and %BF measured with DXA (0.50 ± 0.12, P = ). Conclusion: The body composition of prepubertal girls of normal weight and body fatness is significantly related to the body composition of both biological parents. Am J Clin Nutr 2001;74: KEY WORDS Obesity, girls, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, familial resemblance, total body potassium, body composition, heritability, fat mass, fat-free mass, body mass index, body fat INTRODUCTION Evidence suggests that both environmental and genetic factors play important roles in the development of obesity. Studies of twins reported heritability estimates for body mass index (BMI; weight in kg divided by the square of height in m) of 50 70% (1, 2), whereas adoption studies reported somewhat lower estimates of 20 30% (3 5). Four large family studies reported familial correlations for BMI ranging from 0.20 to 0.23 (6 9). Most of the studies that estimated the heritability of obesity used BMI as the measure of adiposity. However, BMI does not provide information about total or regional body composition, ie, the proportions of fat and lean tissue. Two studies overcame this limitation of BMI by using hydrodensitometry to measure percentage body fat (%BF) in Pima Indians (10) and in Canadians enrolled in the Quebec Family Study (6). The heritability estimates were reported as 0.76 and 0.20, respectively. The studies that examined body-composition correlations between parents and offspring were done primarily with adult offspring. One study of a large sample of 6- to 12-y-old children reported significant relations (no r value given, P = 0.04) between the BMI of the children and their parents (11). Family studies of body composition measured with sophisticated techniques are lacking. Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) provides accurate, precise measurements of bone mineral content (BMC), fat mass (FM), and fat-free mass (FFM). DXA can be used to examine both total body and regional (arms, legs, and trunk) values of these body-composition components. Because of its accuracy, DXA is being used more frequently for body-composition assessments in children. An older technique, total body potassium (TBK), can also be used to measure lean body mass but requires an instrument that typically is not available outside research settings. Thus, few facilities have the capability to measure body composition with both DXA and TBK in children. We used the DXA and TBK technology available at the US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, 1 From the Center for Human Nutrition, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore; the US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service, Children s Nutrition Research Center, Department of Pediatrics, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston; and the Department of Genetics, Southwest Foundation for Biomedical Research, San Antonio, TX. 2 The contents of this publication do not necessarily reflect the views or policies of the US Department of Agriculture, nor does mention of trade names, commercial products, or organizations imply endorsement by the US government. 3 Supported by NIH R29 HD34029 (to MT) and US Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service Cooperative Agreement D/01 (to MT, NB, and KE). 4 Address reprint requests to MS Treuth, Center for Human Nutrition, School of Hygiene and Public Health, Johns Hopkins University, 615 North Wolfe Street, Baltimore, MD mtreuth@jhsph.edu. Received October 20, Accepted for publication January 12, Am J Clin Nutr 2001;74: Printed in USA American Society for Clinical Nutrition 529
2 530 TREUTH ET AL TABLE 1 Characteristics of the prepubertal girls and their mothers and fathers 1 Girls Mothers Fathers (n = 101) (n = 101) (n = 101) Age (y) 8.5 ± ± ± 5.8 Weight (kg) 28.2 ± ± ± 17.1 Height (cm) ± ± ± 8.7 BMI (kg/m 2 ) 16.5 ± ± ± x ± SD. Children s Nutrition Research Center at Baylor College of Medicine to determine whether a familial resemblance of body composition could be found in biological parents and their prepubertal children. The specific aim of this study was to examine the total and regional BMC, FM, FFM, and %BF of prepubertal girls of normal weight and body fat and to compare these body-composition components with those of the girls biological parents. SUBJECTS AND METHODS Subjects Healthy prepubertal girls aged 8 9 y (n = 101) were recruited from the Houston area to participate in the study. All the girls were at Tanner stage I as confirmed by their mothers, who were shown drawings of the different Tanner stages. The girls were screened and had to be below the 90th percentile of weight for height (12) and have a %BF between 12% and 30% (as measured with DXA) to be included in the study. Girls with cardiovascular disease, anemia, diabetes, significant renal or hepatic disease, hypothyroidism, or musculoskeletal problems were excluded. The children and their parents provided written, informed consent to participate in the study, which was approved by the Institutional Review Board for Human Subject Research for Baylor College of Medicine and Affiliated Hospitals. Study protocol Body weight was measured to the nearest 0.1 kg with a digital balance (Scale-Tronix, Dallas). Height was measured to the nearest 1 cm with a stadiometer (Holtain Ltd, Crymych, United Kingdom). BMI was calculated as weight (kg) divided by height 2 (m). Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry Body composition was measured by using DXA (model QDR 2000, pencil beam mode; software 5.56; Hologic, Madison, WI;). The subject lay supine on a bed and was scanned from head to toe in min. DXA allows for determination of bone mineral density (BMD), lean tissue mass (LTM), FM, and BMC. For the total body, FFM was defined as the sum of LTM and BMC. For each body-composition compartment, we determined separate regional values for the arms, legs, and trunk. Total body potassium TBK was measured with a low-background, multidetector, whole-body counter as described previously (13). 40 K, a radioactive isotope, is an intrinsic tracer (0.012%) for natural potassium. It decays, emitting a 1.46-MeV gamma ray that can be detected external to the body. For the weight range of the children and adults examined in this study, the precision of the TBK measurement is 1 2%. For healthy subjects, the intracellular potassium content can be assumed to be constant at 150 mmol/l (14). Furthermore, the ratio of TBK (mmol) to FFM (kg) for healthy adults can be assumed constant (60 and 64 for women and men, respectively) (15). The ratio of TBK to FFM changes during the growth of children (16); however, for the age group of the girls in this study, the ratio was assumed to be Statistical analysis Data are presented as means ± SDs. MICROSOFT ACCESS (version 7.0; Microsoft Corp, Seattle) was used for database management. Statistical analyses were performed with MINITAB (version 12.2; Minitab Inc, State College, PA); significance was set at P < Pearson s product-moment correlation coefficients were determined to examine the relations between the child s body composition and the paternal and maternal body composition separately. Regression analysis was used to determine the combined effect of paternal and maternal body composition. The independent variables included weight; height; BMI; total and regional BMC, FM, FFM, and %BF measured with DXA; and TBK, FM, FFM, and %BF measured with TBK. The model (y = P + 2 M + 3 P M) included the paternal (P) and maternal (M) measures of the variable of interest and the interaction term. Univariate quantitative genetic analysis was used to partition the phenotypic variance for each of the body-composition phenotypes into additive genetic and environmental variance components. The additive genetic heritability (h 2 ) of a trait represents the portion of the total phenotypic variance accounted for by the effects of genes (ie, h 2 = 2 genetic / 2 phenotypic ). The heritabilities were estimated by using the maximum likelihood variance decomposition method (17, 18) implemented in the computer program FISHER (19). Such an approach makes it possible to test whether correlations among family members for a specific trait (eg, BMI) are solely the result of the environment or whether genetic effects are also involved. In addition, the effects of sex and age and their interaction were simultaneously estimated as part of the analysis. RESULTS Subject characteristics Of the 101 prepubertal girls, 52 were white, 30 were African American, and 19 were Hispanic. We used the ethnicity of the mother to classify the ethnicity of the daughter. The ethnic distribution of the fathers was 56 white, 29 African American, and 16 Hispanic. Weight, height, and BMI values are shown in Table 1. The girls were all of normal weight and body fatness because of the selection criteria. Parental BMI varied greatly, ranging from normal weight to severely obese (range: for mothers and for fathers). Body-composition values (FM, FFM, and %BF) measured with DXA and TBK are shown in Table 2. Correlations between the girls and parents body-composition measures are shown in Table 3. The girls weight, height, and BMI were correlated with the weight, height, and BMI of both mothers and fathers. The highest correlation was observed between the girls BMI and the fathers BMI. Similarly, for FM, FFM, and %BF obtained with DXA, the girls values were correlated with both the mothers and the fathers values. The girls FM, FFM, and %BF values obtained with TBK were significantly related to both the mothers and fathers values.
3 BODY COMPOSITION IN GIRLS AND THEIR PARENTS 531 TABLE 2 Body composition measured with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) and total body potassium (TBK) in the prepubertal girls and their mothers and fathers 1 Fat mass Fat-free mass Percentage body fat kg kg % Girls DXA (n = 101) 6.1 ± ± ± 4.7 ( ) ( ) ( ) TBK (n = 99) 6.8 ± ± ± 5.5 ( ) ( ) ( ) Mothers DXA (n = 100) 31.1 ± ± ± 8.9 ( ) ( ) ( ) TBK (n = 101) 31.1 ± ± ± 9.1 ( ) ( ) ( ) Fathers DXA (n = 94) 21.6 ± ± ± 7.8 ( ) ( ) ( ) TBK (n = 93) 27.3 ± ± ± 7.9 ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 x ± SD; range in parentheses. The results of regression analysis showed no significant interactions between paternal and maternal values for weight or height; however, a significant interaction was observed for BMI. The regression equations for weight, height, and BMI are as follows: Weight of child = P M (adjusted r 2 = 0.22) (1) Height of child = P M (adjusted r 2 = 0.24) (2) BMI of child (with interaction term) = P M ( P M) (adjusted r 2 = 0.26) (3) BMI of child (without interaction term) = P M (adjusted r 2 = 0.22) (4) where all were significant at P < Significant heritability was detected for BMI (x ± SE: 0.35 ± 0.17; P = 0.03) and for %BF measured with DXA (0.50 ± 0.12; P = ). The proportion of the variance that resulted from the 2 covariates (sex and age) was 0.44 for BMI and 0.54 for %BF. No significant heritabilities were detected for FFM and FM. The regression equations relating the girls and parents values for total-body BMC and BMD measured with DXA, and for FM, FFM, and %BF measured with DXA and TBK are shown in Table 4. The BMC and BMD of the girls were significantly related to the BMC and BMD of both parents. There were no significant interactions between maternal and paternal values for total-body FM, FFM, and %BF measured with DXA or TBK (adjusted r 2 = ). The effect of paternal and maternal %BF measured with DXA on the girls %BF measured with DXA was significant (adjusted r 2 = 0.16). When parental age was entered, the adjusted r 2 values were 0.37 for total-body FFM and 0.16 for %BF measured with DXA. With the TBK method, the FFM of the father and mother had a significant influence on the girl s FFM measured with TBK (adjusted r 2 = 0.32; interaction included adjusted r 2 = 0.36). Also shown in Table 4 are the regression equations for BMC, FM, and LTM of the arms, trunk, and legs measured with DXA. There were significant effects of both paternal and maternal BMC (adjusted r 2 = ) on the BMC of the girls arms and trunk. For the arms, trunk, and legs, the adjusted r 2 values were lower for FM (0.11, 0.14, and 0.09, respectively) than for LTM (0.17, 0.33, and 0.37, respectively). The strongest predictive power was for the leg region, specifically for LTM (adjusted r 2 = 0.37). The maternal trunk FM did not significantly influence the girls trunk FM. The paternal FM, LTM, and %BF of the legs did not significantly influence the girls leg values. DISCUSSION In this study we examined the relations between the body composition of prepubertal girls and that of their mothers and fathers; %BF ranged from 12% to 30% in the girls. The heritability estimate was significant for BMI and %BF measured with DXA, with a higher heritability estimate for the %BF than for BMI. Our analyses showed that the body composition of the girls was significantly related to both their fathers and mothers body composition. This observation also held true in the analyses of specific body regions, except for FM of the legs and trunk. Our study examined the familial resemblance between parent and child of an anthropometric index, BMI. BMI was one trait that had a significant heritability estimate (0.35 ± 0.17) in our sample of prepubertal girls and their parents. In studies of twins, heritability estimates for BMI were reported to be 50 70% (1, 2). The correlations of BMI observed between the girls and their mothers (r = 0.34) and fathers (r = 0.44) were slightly higher than the values of that were reported previously in 4 large family studies (6 9). The relative strength of the correlations we found may indicate that a large proportion of the interindividual differences in BMI is the result of additional environmental influences, such as dietary energy intake and macronutrient composition and physical activity levels. The influence TABLE 3 Correlations between the prepubertal girls and their mothers and fathers for body-composition components measured with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) and total body potassium (TBK) 1 Mother Father Girls r P r P Weight Height BMI FM DXA TBK FFM DXA TBK %BF DXA TBK TBK FM, fat mass; FFM, fat-free mass; %BF, percentage body fat. n values were as follows: girls, 101 for DXA and 99 for TBK; mothers, 100 for DXA and 101 for TBK; fathers, 94 for DXA and 93 for TBK.
4 532 TREUTH ET AL TABLE 4 Linear regression analysis of fat mass (FM), fat-free mass (FFM), and percentage body fat (%BF) determined with dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) and total body potassium (TBK) in the prepubertal girls and their mothers and their fathers 1 Equation Adjusted r 2 P (Father) P (Mother) P (Interaction) DXA: total body BMC P BMC M BMC BMD P BMD M BMD FM P FM M FM FFM P FFM M FFM %BF P %BF M %BF DXA: arms BMC P BMC + 95 M BMC FM P FM M FM LTM P LTM M LTM %BF P %BF M %BF DXA: trunk BMC P BMC M BMC FM P FM M FM LTM P LTM M LTM %BF P %BF M %BF DXA: legs BMC P BMC 624 M BMC P M BMC FM P FM M FM LTM P LTM 444 M LTM P M LTM %BF P %BF M %BF TBK TBK P TBK M TBK P M TBK FM P FM M FM FFM P FFM M FFM %BF P %BF M %BF Equations are shown without the interaction term unless it was significant. Kg is the unit for all the variables in all the equations. P, paternal; M, maternal; BMC, bone mineral content; BMD, bone mineral density; LTM, lean tissue mass. n values were as follows: girls, 101 for DXA and 99 for TBK; mothers, 100 for DXA and 101 for TBK; fathers, 94 for DXA and 93 for TBK. of the environment was also examined in a unique way in several studies of twins (20, 21). These studies suggested that there is an environmental gene interaction affecting an individual s response to changes in energy balance induced by exercise and overfeeding. In an adoption study, the genetic influence on BMI was unaffected by several different environmental conditions that may be associated with obesity (22). The heritability estimate for %BF analyzed with DXA was 0.50 in our study of prepubertal girls and their parents. Two studies that examined %BF with hydrodensitometry in Pima Indians (10) and in Canadians enrolled in the Quebec Family Study (6) reported heritability estimates of 0.76 and 0.20, respectively. Sample sizes in these studies were larger than those in the present study and as a result, the former may reflect better point estimates of the heritabilities. However, better characterized phenotypes could lead to improved estimations of heritability. For FFM and FM, our low statistical power is most likely the reason why we failed to find significant heritability estimates. With regard to regional body composition, correlations between girls values and parental values for FM were quite low (adjusted r ), whereas those for LTM were higher (adjusted r 2 = ). This indicates that at an early age, variations in LTM trace better than do variations in FM, in part because the child has not yet accumulated large stores of excess fat. In family studies in which the offspring were adults, it was shown that for extreme BMI values (extreme obesity or leanness), skinfold-thickness measures of the biceps and triceps showed significant correlations between mother and daughter (r = 0.31 and 0.26, respectively) and father and daughter (r = 0.26 and 0.33, respectively) (23). In our study, we observed the highest correlations for FFM and TBK, rather than for FM. Among the body regions, the highest correlations between the girls and their parents were for the legs, the largest muscle region of the body. Our measures of the girl s %BF in the trunk were influenced by both the father s and mother s values. In the Quebec Family Study, a heritability estimate for total abdominal fat area (visceral and subcutaneous fat combined, measured by computed tomography) was 70%, with correlations between father and daughter and mother and daughter of 0.35 (24). Thus, these studies support the theory that both regional fat tissue and fat-free tissue in the offspring are influenced by the body composition of the parents. The higher adjusted r 2 values ( ) for regional and total BMC than for FFM and FM in our sample may indicate that bone growth and mineralization are under stronger genetic influences than are FFM or FM. The total and regional BMC of the girls were influenced by both their mothers and fathers values. Other studies have examined the genetic determinants of bone mass by studying parent-offspring relations (25, 26). The BMC of the spine, femoral neck, and midfemoral diaphysis of 8-y-old prepubertal girls was significantly correlated (r = ) with their
5 BODY COMPOSITION IN GIRLS AND THEIR PARENTS 533 mothers BMC, with 18 37% of bone traits directly determined by maternal descent (26). Thus, it appears that the results of our study agree with those of other investigations, indicating a significant relation between the bone status of parent and child. In this family study, which was restricted to girls with a %BF of 12 30%, we found that the girl s body composition at 8 9 y of age is related to their biological parents body composition. Familial resemblance of parental obesity and leanness is clearly evident in daughters at prepubertal ages. We thank the children who participated in the study, the Metabolic Research Unit staff and body-composition staff of the Baylor College of Medicine for technical assistance, and B Kertz for subject recruitment. REFERENCES 1. Stunkard AJ, Harris JR, Pedersen NL, McClearn GE. The bodymass index of twins who have been reared apart. N Engl J Med 1990;322: Allison DB, Kaprio J, Korkeila N, Koskenvuo M, Neale MC, Hayakawa K. The heritability of body mass index among an international sample of monozygotic twins reared apart. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1996;20: Price RA, Cadoret RJ, Stunkard AJ, Troughton E. Genetic contributions to human fatness: an adoption study. Am J Psychiatry 1987; 144: Sorensen TIA, Holst C, Stunkard AJ. Childhood body mass index genetic and familial environmental influences assessed in a longitudinal adoption study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1992;16: Stunkard AJ, Sorensen TI, Hanis C, et al. An adoption study of human obesity. N Engl J Med 1986;314: Bouchard C, Perusse L, Leblanc C, Tremblay A, Theriault G. Inheritance of the amount and distribution of human body fat. Int J Obes 1988;12: Heller R, Garrison RJ, Havlik RJ, Feinleib M, Padgett S. Family resemblances in height and relative weight in the Framingham Heart Study. Int J Obes 1984;8: Perusse L, Leblanc C, Bouchard C. Inter-generation transmission of physical fitness in the Canadian population. Can J Sport Sci 1988; 13: Tambs K, Moum T, Eaves L, et al. Genetic and environmental contributions to the variance of the body mass index in a Norwegian sample of first- and second-degree relatives. Am J Hum Biol 1991; 3: Sakul H, Pratley R, Cardon L, Ravussin E, Mott D, Bogardus C. Familiality of physical and metabolic characteristics that predict the development of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in Pima Indians. Am J Hum Genet 1997;60: Guillaume M, Lapidus L, Beckers F, Lambert A, Bjorntorp P. Familial trends of obesity through three generations: the Belgian-Luxembourg child study. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1995;19(suppl):S Najjar MF, Rowland M. Anthropometric reference data and prevalence of overweight, United States, Vital Health Stat ;238: Ellis KJ, Shypailo RJ. Whole-body potassium measurements independent of body size. Basic Life Sci 1993;60: Moore FD, Olesen KH, McMurrey JD, Parker HV, Ball MR, Boyden CM, eds. The body cell mass and its supporting environment. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co, 1963: Forbes GB. Human body composition: growth, aging, nutrition, and activity. New York: Springer, 1987: Fomom SJ, Haschke F, Ziegler EE, Nelson SE. Body composition of reference children from birth to age 10 years. Am J Clin Nutr 1982;35: Hopper JL, Mathews JD. Extensions to multivariate normal models for pedigree analysis. Ann Hum Genet 1982;46: Lange K, Boehnke M. Extensions to pedigree analysis. IV. Covariance components models for multivariate traits. Am Med Genet 1983;14: Lange K, Weeks D, Boehnke M. Programs for Pedigree Analysis: MENDEL, FISHER, and dgene. Genet Epidemiol 1988;5: Bouchard C, Tremblay A, Despres JP, et al. The response to long-term overfeeding in identical twins. N Engl J Med 1990;322: Bouchard C, Tremblay A, Despres JP, et al. The response to exercise with constant energy intake in identical twins. Obes Res 1994;2: Sorensen TIA, Holst C, Stunkard AJ. Adoption study of environmental modifications of the genetic influences of obesity. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998;22: Price RA, Reed DR, Lee JH. Obesity related phenotypes in families selected for extreme obesity and leanness. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 1998;22: Perusse L, Despres JP, Lemieux S, Rice T, Rao DC, Bouchard C. Familial aggregation of abdominal visceral fat level: results from the Quebec family study. Metabolism 1996;45: Danielson ME, Cauley JA, Baker CE, et al. Familial resemblance of bone mineral density (BMD) and calcaneal ultrasound attenuation: the BMD in Mothers and Daughters Study. J Bone Miner Res 1999;14: Ferrari S, Rizzoli R, Slosman D, Bonjour JP. Familial resemblance for bone mineral mass is expressed before puberty. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998;83:
Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment
 Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott,
Chapter 17: Body Composition Status and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott,
Bone Mineral and Body Composition Measurements: Cross-Calibration of Pencil-Beam and Fan-Beam Dual- Energy X-Ray Absorptiometers*
 JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH Volume 13, Number 10, 1998 Blackwell Science, Inc. 1998 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Bone Mineral and Body Composition Measurements: Cross-Calibration
JOURNAL OF BONE AND MINERAL RESEARCH Volume 13, Number 10, 1998 Blackwell Science, Inc. 1998 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research Bone Mineral and Body Composition Measurements: Cross-Calibration
Growth of Visceral Fat, Subcutaneous Abdominal Fat, and Total Body Fat in Children
 Growth of Visceral Fat, Subcutaneous Abdominal Fat, and Total Body Fat in Children Terry T.-K. Huang,* Maria S. Johnson,* Reinaldo Figueroa-Colon, James H. Dwyer,* and Michael I. Goran* Abstract HUANG,
Growth of Visceral Fat, Subcutaneous Abdominal Fat, and Total Body Fat in Children Terry T.-K. Huang,* Maria S. Johnson,* Reinaldo Figueroa-Colon, James H. Dwyer,* and Michael I. Goran* Abstract HUANG,
Longitudinal Study of Total Body Potassium in Healthy Men
 Original Research Longitudinal Study of Total Body Potassium in Healthy Men Angela Andreoli, MD, PhD, Stella L. Volpe, PhD, Sarah J. Ratcliffe, PhD, Nicola Di Daniele, MD, Antonio Imparato, PhD, Luigi
Original Research Longitudinal Study of Total Body Potassium in Healthy Men Angela Andreoli, MD, PhD, Stella L. Volpe, PhD, Sarah J. Ratcliffe, PhD, Nicola Di Daniele, MD, Antonio Imparato, PhD, Luigi
In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in
 1 2 In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in adults: the influence of body mass index 3 4 Running title: Precision of the idxa for the measurement of visceral
1 2 In-vivo precision of the GE Lunar idxa for the measurement of visceral adipose tissue in adults: the influence of body mass index 3 4 Running title: Precision of the idxa for the measurement of visceral
Potassium per kilogram fat-free mass and total body potassium: predictions from sex, age, and anthropometry
 Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 284: E416 E423, 2003. First published October 15, 2002; 10.1152/ajpendo.00199.2001. Potassium per kilogram fat-free mass and total body potassium: predictions from sex, age,
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 284: E416 E423, 2003. First published October 15, 2002; 10.1152/ajpendo.00199.2001. Potassium per kilogram fat-free mass and total body potassium: predictions from sex, age,
Visceral fat in white and African American prepubertal children13
 Original Research Communications Visceral fat in white and African American prepubertal children13 Michael I Goran, Tim R Nagy, Margarita S Treuth, Chris Trowbridge, Carl Dezenberg, Aileen McGloin, and
Original Research Communications Visceral fat in white and African American prepubertal children13 Michael I Goran, Tim R Nagy, Margarita S Treuth, Chris Trowbridge, Carl Dezenberg, Aileen McGloin, and
Fat Mass. Baseline. (lbs) (lbs) Composition Trend: Total. Aug 17. Apr 17. May 17. Jun 17. Jul 17. Measured Date
 Name Sample Report Birth Date: 00/00/000 Height: 74.0 in. Gender Male Age: 54.7 Input Weight: 165.0 lbs. Body Composition Analysis (BCA) DXA or DEXA is a three component model, which means it quantifies
Name Sample Report Birth Date: 00/00/000 Height: 74.0 in. Gender Male Age: 54.7 Input Weight: 165.0 lbs. Body Composition Analysis (BCA) DXA or DEXA is a three component model, which means it quantifies
Aggregation of psychopathology in a clinical sample of children and their parents
 Aggregation of psychopathology in a clinical sample of children and their parents PA R E N T S O F C H I LD R E N W I T H PSYC H O PAT H O LO G Y : PSYC H I AT R I C P R O B LEMS A N D T H E A S SO C I
Aggregation of psychopathology in a clinical sample of children and their parents PA R E N T S O F C H I LD R E N W I T H PSYC H O PAT H O LO G Y : PSYC H I AT R I C P R O B LEMS A N D T H E A S SO C I
DEXA Bone Mineral Density Tests and Body Composition Analysis Information for Health Professionals
 DEXA Bone Mineral Density Tests and Body Composition Analysis Information for Health Professionals PERFORMANCE DEXA is an advanced technology originally used to, and still capable of assessing bone health
DEXA Bone Mineral Density Tests and Body Composition Analysis Information for Health Professionals PERFORMANCE DEXA is an advanced technology originally used to, and still capable of assessing bone health
Shared genetic influence of BMI, physical activity and type 2 diabetes: a twin study
 Diabetologia (2013) 56:1031 1035 DOI 10.1007/s00125-013-2859-3 SHORT COMMUNICATION Shared genetic influence of BMI, physical activity and type 2 diabetes: a twin study S. Carlsson & A. Ahlbom & P. Lichtenstein
Diabetologia (2013) 56:1031 1035 DOI 10.1007/s00125-013-2859-3 SHORT COMMUNICATION Shared genetic influence of BMI, physical activity and type 2 diabetes: a twin study S. Carlsson & A. Ahlbom & P. Lichtenstein
Visceral Fat in Prepubertal Children: Influence of Obesity, Anthropometry, Ethnicity, Gender, Diet, and Growth
 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF HUMAN BIOLOGY 11:201 207 (1999) Visceral Fat in Prepubertal Children: Influence of Obesity, Anthropometry, Ethnicity, Gender, Diet, and Growth MICHAEL I. GORAN* Division of Physiology
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF HUMAN BIOLOGY 11:201 207 (1999) Visceral Fat in Prepubertal Children: Influence of Obesity, Anthropometry, Ethnicity, Gender, Diet, and Growth MICHAEL I. GORAN* Division of Physiology
Adult BMI Calculator
 For more information go to Center for Disease Control http://search.cdc.gov/search?query=bmi+adult&utf8=%e2%9c%93&affiliate=cdc-main\ About BMI for Adults Adult BMI Calculator On this page: What is BMI?
For more information go to Center for Disease Control http://search.cdc.gov/search?query=bmi+adult&utf8=%e2%9c%93&affiliate=cdc-main\ About BMI for Adults Adult BMI Calculator On this page: What is BMI?
Segmental Body Composition Assessment for Obese Japanese Adults by Single-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with 8-point Contact Electrodes
 Segmental Body Composition Assessment for Obese Japanese Adults by Single-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with 8-point Contact Electrodes Susumu Sato 1), Shinichi Demura 2), Tamotsu Kitabayashi
Segmental Body Composition Assessment for Obese Japanese Adults by Single-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis with 8-point Contact Electrodes Susumu Sato 1), Shinichi Demura 2), Tamotsu Kitabayashi
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry to Determine Body Composition
 Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Determine Body Composition Description Using low dose x-rays of two different energy levels, whole body dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measures lean tissue
Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: March 2015 Determine Body Composition Description Using low dose x-rays of two different energy levels, whole body dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) measures lean tissue
Does Body Mass Index Adequately Capture the Relation of Body Composition and Body Size to Health Outcomes?
 American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 1998 by The Johns Hopkins University School of Hygiene and Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 147, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A A BRIEF ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Does
American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 1998 by The Johns Hopkins University School of Hygiene and Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 147, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A A BRIEF ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Does
Association of Lean Tissue and Fat Mass with Bone Mineral Content in Children and Adolescents
 Association of Lean Tissue and Fat Mass with Bone Mineral Content in Children and Adolescents Angelo Pietrobelli,* Myles S. Faith,* Jack Wang,* Paolo Brambilla, Giuseppe Chiumello, and Steven B. Heymsfield*
Association of Lean Tissue and Fat Mass with Bone Mineral Content in Children and Adolescents Angelo Pietrobelli,* Myles S. Faith,* Jack Wang,* Paolo Brambilla, Giuseppe Chiumello, and Steven B. Heymsfield*
Evaluation of body fat in fatter and leaner 10-y-old African American and white children: the Baton Rouge Children s Study 1 3
 Original Research Communications Evaluation of body fat in fatter and leaner 10-y-old African American and white children: the Baton Rouge Children s Study 1 3 George A Bray, James P DeLany, David W Harsha,
Original Research Communications Evaluation of body fat in fatter and leaner 10-y-old African American and white children: the Baton Rouge Children s Study 1 3 George A Bray, James P DeLany, David W Harsha,
CHAPTER 9. Anthropometry and Body Composition
 CHAPTER 9 Anthropometry and Body Composition 9.1 INTRODUCTION Ageing is characterized by reduction in fat free mass (FFM), primarily via loss of muscle mass, loss of bone mineral in women, redistribution
CHAPTER 9 Anthropometry and Body Composition 9.1 INTRODUCTION Ageing is characterized by reduction in fat free mass (FFM), primarily via loss of muscle mass, loss of bone mineral in women, redistribution
Suprailiac or Abdominal Skinfold Thickness Measured with a Skinfold Caliper as a Predictor of Body Density in Japanese Adults
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2007, Measurement 213, 51-61Error Characteristics of Skinfold Caliper 51 Suprailiac or Abdominal Skinfold Thickness Measured with a Skinfold Caliper as a Predictor of Body Density
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2007, Measurement 213, 51-61Error Characteristics of Skinfold Caliper 51 Suprailiac or Abdominal Skinfold Thickness Measured with a Skinfold Caliper as a Predictor of Body Density
Client Sex Facility Birth Date Height Weight Measured ####, #### #### (not specified) #### #### #### ####
 SUMMARY RESULTS This table provides an overview of your total body composition, broken down into total body fat %, total mass, fat tissue, lean tissue, and bone mineral content. These metrics establish
SUMMARY RESULTS This table provides an overview of your total body composition, broken down into total body fat %, total mass, fat tissue, lean tissue, and bone mineral content. These metrics establish
Frequency of church attendance in Australia and the United States: models of family resemblance
 Twin Research (1999) 2, 99 107 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 1369 0523/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/tr Frequency of church attendance in Australia and the United States: models of
Twin Research (1999) 2, 99 107 1999 Stockton Press All rights reserved 1369 0523/99 $12.00 http://www.stockton-press.co.uk/tr Frequency of church attendance in Australia and the United States: models of
ADOLESCENT OBESITY: IS IT BAD FOR THE BONES
 ADOLESCENT OBESITY: IS IT BAD FOR THE BONES Babette S. Zemel, PhD Director, Nutrition And Growth Laboratory Division Of Gastroenterology, Hepatology And Nutrition The Children s Hospital Of Philadelphia
ADOLESCENT OBESITY: IS IT BAD FOR THE BONES Babette S. Zemel, PhD Director, Nutrition And Growth Laboratory Division Of Gastroenterology, Hepatology And Nutrition The Children s Hospital Of Philadelphia
Heredity and Health-Related Fitness
 Heredity and Health-Related Fitness A Note From the Editors In the February Issue of the Physical Activity and Fitness Research Digest we noted the importance of heredity as a factor affecting the development
Heredity and Health-Related Fitness A Note From the Editors In the February Issue of the Physical Activity and Fitness Research Digest we noted the importance of heredity as a factor affecting the development
Impact of infant feeding on growth trajectory patterns in childhood and body composition in young adulthood
 Impact of infant feeding on growth trajectory patterns in childhood and body composition in young adulthood WP10 working group of the Early Nutrition Project Peter Rzehak*, Wendy H. Oddy,* Maria Luisa
Impact of infant feeding on growth trajectory patterns in childhood and body composition in young adulthood WP10 working group of the Early Nutrition Project Peter Rzehak*, Wendy H. Oddy,* Maria Luisa
Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics differ between manufacturers
 European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 449±454 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition (1997) 51, 449±454 ß 1997 Stockton Press. All rights reserved 0954±3007/97 $12.00 Body composition analysis by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry in female diabetics
DUAL ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY (DXA) GOLD STANDARD FOR BONE HEALTH AND BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT
 DUAL ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY (DXA) GOLD STANDARD FOR BONE HEALTH AND BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT Prof d-r Slavica Šubeska Stratrova Clinic of Endocrinology, Skopje, Macedonia Definition and classification
DUAL ENERGY X-RAY ABSORPTIOMETRY (DXA) GOLD STANDARD FOR BONE HEALTH AND BODY COMPOSITION ASSESSMENT Prof d-r Slavica Šubeska Stratrova Clinic of Endocrinology, Skopje, Macedonia Definition and classification
BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES. Abstract. Introduction. Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, UDC :572.
 EXERCISE AND QUALITY OF LIFE Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, 43-48 UDC 796.034.6-051:572.087 Research article BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES Jelena Popadiã Gaãeša *, Otto Barak, Dea Karaba
EXERCISE AND QUALITY OF LIFE Volume 3, No. 2, 2011, 43-48 UDC 796.034.6-051:572.087 Research article BODY MASS INDEX AND BODY FAT CONTENT IN ELITE ATHLETES Jelena Popadiã Gaãeša *, Otto Barak, Dea Karaba
Assessing Overweight in School Going Children: A Simplified Formula
 Journal of Applied Medical Sciences, vol. 4, no. 1, 2015, 27-35 ISSN: 2241-2328 (print version), 2241-2336 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2015 Assessing Overweight in School Going Children: A Simplified Formula
Journal of Applied Medical Sciences, vol. 4, no. 1, 2015, 27-35 ISSN: 2241-2328 (print version), 2241-2336 (online) Scienpress Ltd, 2015 Assessing Overweight in School Going Children: A Simplified Formula
This study may not be disseminated, reproduced in whole or in part without the written permission of Roduve Healthcare Solutions.
 This study may not be disseminated, reproduced in whole or in part without the written permission of Roduve Healthcare Solutions. A Randomized Controlled Trial for Roduve Healthcare Solutions on the Efficacy
This study may not be disseminated, reproduced in whole or in part without the written permission of Roduve Healthcare Solutions. A Randomized Controlled Trial for Roduve Healthcare Solutions on the Efficacy
PAPER Segregation analysis of waist circumference, hip circumference and waist-to-hip ratio in the Korean Nationwide Family Study
 (2002) 26, 228 233 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0307 0565/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/ijo PAPER, hip circumference and waist-to-hip ratio in the Korean Nationwide Family Study SH Jee
(2002) 26, 228 233 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0307 0565/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/ijo PAPER, hip circumference and waist-to-hip ratio in the Korean Nationwide Family Study SH Jee
Body-composition assessment in infancy: air-displacement plethysmography compared with a reference 4-compartment model 1 4
 Body-composition assessment in infancy: air-displacement plethysmography compared with a reference 4-compartment model 1 4 Kenneth J Ellis, Manjiang Yao, Roman J Shypailo, Alessandro Urlando, William W
Body-composition assessment in infancy: air-displacement plethysmography compared with a reference 4-compartment model 1 4 Kenneth J Ellis, Manjiang Yao, Roman J Shypailo, Alessandro Urlando, William W
EXTRACELLULAR WATER REFERENCE VALUES. Extracellular Water: Reference values for Adults
 CHAPTER 5 Extracellular Water: Reference values for Adults Analiza M. Silva, Jack Wang, Richard N. Pierson Jr., ZiMian Wang, David B. Allison Steven B. Heymsfield, Luis B. Sardinha, Stanley Heshka ABSTRACT
CHAPTER 5 Extracellular Water: Reference values for Adults Analiza M. Silva, Jack Wang, Richard N. Pierson Jr., ZiMian Wang, David B. Allison Steven B. Heymsfield, Luis B. Sardinha, Stanley Heshka ABSTRACT
ARTICLE. Diabetologia (2011) 54:87 92 DOI /s
 Diabetologia (2011) 54:87 92 DOI 10.1007/s00125-010-1925-3 ARTICLE Association of exposure to diabetes in utero with adiposity and fat distribution in a multiethnic population of youth: the Exploring Perinatal
Diabetologia (2011) 54:87 92 DOI 10.1007/s00125-010-1925-3 ARTICLE Association of exposure to diabetes in utero with adiposity and fat distribution in a multiethnic population of youth: the Exploring Perinatal
EXERCISE SUPPRESSES HERITABILITY ESTIMATES FOR OBESITY IN MEXICAN-AMERICAN FAMILIES
 Addictive Behaviors, Vol. 14, pp. 581-588, 1989 0306-4603/89 $3.00 +.00 Printed in the USA. All rights reserved. Copyright 1989 Pergamon Press plc BRIEF REPORT EXERCISE SUPPRESSES HERITABILITY ESTIMATES
Addictive Behaviors, Vol. 14, pp. 581-588, 1989 0306-4603/89 $3.00 +.00 Printed in the USA. All rights reserved. Copyright 1989 Pergamon Press plc BRIEF REPORT EXERCISE SUPPRESSES HERITABILITY ESTIMATES
A Pilot Study of Exercise Training to Reduce Trunk Fat in Adults With HIV Associated Fat Redistribution
 A Pilot Study of Exercise Training to Reduce Trunk Fat in Adults With HIV Associated Fat Redistribution Ronenn Roubenoff, Lauren Weiss, Ann McDermott, Tanya Heflin, Gregory J. Cloutier, Michael Wood and
A Pilot Study of Exercise Training to Reduce Trunk Fat in Adults With HIV Associated Fat Redistribution Ronenn Roubenoff, Lauren Weiss, Ann McDermott, Tanya Heflin, Gregory J. Cloutier, Michael Wood and
Common Genetic Components of Obesity Traits and Serum Leptin
 nature publishing group articles Common Genetic Components of Obesity Traits and Serum Leptin nn L. Hasselbalch, Beben Benyamin 2, Peter M. Visscher 2, Berit L. Heitmann,3, Kirsten O. Kyvik 4 and Thorkild
nature publishing group articles Common Genetic Components of Obesity Traits and Serum Leptin nn L. Hasselbalch, Beben Benyamin 2, Peter M. Visscher 2, Berit L. Heitmann,3, Kirsten O. Kyvik 4 and Thorkild
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017
 ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Paediatric specificities of nutritional assessment Body composition measurement in children N. Mehta (US) 39 th ESPEN Congress The Hague, Netherlands Body Composition Measurement
ESPEN Congress The Hague 2017 Paediatric specificities of nutritional assessment Body composition measurement in children N. Mehta (US) 39 th ESPEN Congress The Hague, Netherlands Body Composition Measurement
Is percentage body fat differentially related to body mass index in Hispanic Americans, African Americans, and European Americans?
 Is percentage body fat differentially related to body mass index in Hispanic Americans, African Americans, and European Americans? 1 3 José R Fernández, Moonseong Heo, Steven B Heymsfield, Richard N Pierson
Is percentage body fat differentially related to body mass index in Hispanic Americans, African Americans, and European Americans? 1 3 José R Fernández, Moonseong Heo, Steven B Heymsfield, Richard N Pierson
BMI may underestimate the socioeconomic gradient in true obesity
 8 BMI may underestimate the socioeconomic gradient in true obesity Gerrit van den Berg, Manon van Eijsden, Tanja G.M. Vrijkotte, Reinoud J.B.J. Gemke Pediatric Obesity 2013; 8(3): e37-40 102 Chapter 8
8 BMI may underestimate the socioeconomic gradient in true obesity Gerrit van den Berg, Manon van Eijsden, Tanja G.M. Vrijkotte, Reinoud J.B.J. Gemke Pediatric Obesity 2013; 8(3): e37-40 102 Chapter 8
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in Dexa Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Birth Date: 24.7 years Height / Weight: 8.0 cm 79.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 40% 30% 20% 0% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 00 Centile
Birth Date: 24.7 years Height / Weight: 8.0 cm 79.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 40% 30% 20% 0% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 00 Centile
Heritability estimation of conventional cardiovascular disease risk factors in Asian Indian families: The Calcutta family study
 Brief Report Heritability estimation of conventional cardiovascular disease risk factors in Asian Indian families: The Calcutta family study Arnab Ghosh, Rupak Dutta, Angshuman Sarkar 1 Biomedical Research
Brief Report Heritability estimation of conventional cardiovascular disease risk factors in Asian Indian families: The Calcutta family study Arnab Ghosh, Rupak Dutta, Angshuman Sarkar 1 Biomedical Research
Energy Expenditure in Lean and Obese Prepubertal Children
 Energy Expenditure in Lean and Obese Prepubertal Children James P. DeLany*f, David W. Harsha*, James C. Kime*, Julie Kumler*, Louis Melancon*, George A. Bray*f Abstract DELANY, JAMES P, DAVID W HARSHA,
Energy Expenditure in Lean and Obese Prepubertal Children James P. DeLany*f, David W. Harsha*, James C. Kime*, Julie Kumler*, Louis Melancon*, George A. Bray*f Abstract DELANY, JAMES P, DAVID W HARSHA,
Physique Science. Suite 2a, 76 Commercial Road Newstead, QLD 4006
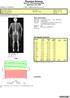 :3 Image not for diagnostic use k = 1.178, d0 = 40.3 327 x 150 DAP: 13.1 cgy*cm² Region Area (cm²) BMC (g) BMD (g/cm²) T - Z - L Arm 252.57 280.11 1.109 R Arm 269.81 288.33 1.069 L Ribs 155.55 154.55 0.994
:3 Image not for diagnostic use k = 1.178, d0 = 40.3 327 x 150 DAP: 13.1 cgy*cm² Region Area (cm²) BMC (g) BMD (g/cm²) T - Z - L Arm 252.57 280.11 1.109 R Arm 269.81 288.33 1.069 L Ribs 155.55 154.55 0.994
The Assessment of Body Composition in Health and Disease
 The Assessment of Body Composition in Health and Disease Giorgio Bedogni, Paolo Brambilla, Stefano Bellentani and Claudio Tiribelli CHAPTER 3 BODY AND NUTRITIONAL STATUS Nutritional status can be operationally
The Assessment of Body Composition in Health and Disease Giorgio Bedogni, Paolo Brambilla, Stefano Bellentani and Claudio Tiribelli CHAPTER 3 BODY AND NUTRITIONAL STATUS Nutritional status can be operationally
Cross-calibration of fat and lean measurements by dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry to pig carcass analysis in the pediatric body weight range13
 Cross-calibration of fat and lean measurements by dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry to pig carcass analysis in the pediatric body weight range13 Stephen J Pintauro, Tim R Nagy, Christa M Duthie, and Michael
Cross-calibration of fat and lean measurements by dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry to pig carcass analysis in the pediatric body weight range13 Stephen J Pintauro, Tim R Nagy, Christa M Duthie, and Michael
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Birth Date: 40.2 years Height / Weight: 158.0 cm 52.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 50% 40% 30% 20% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Birth Date: 40.2 years Height / Weight: 158.0 cm 52.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female Patient ID: Total Body Tissue Quantitation Composition Reference: Total Tissue 50% 40% 30% 20% 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Jackson Heart Study Manuscript Proposal Form
 Jackson Heart Study Manuscript Proposal Form Submission Date: 2/15/2017 Proposal ID: P0859 I. TITLE I. Title Information A. Proposal Title: Age related variations in obesity and diabetes correlates in
Jackson Heart Study Manuscript Proposal Form Submission Date: 2/15/2017 Proposal ID: P0859 I. TITLE I. Title Information A. Proposal Title: Age related variations in obesity and diabetes correlates in
Purpose. Methods and Materials
 Prevalence of pitfalls in previous dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans according to technical manuals and International Society for Clinical Densitometry. Poster No.: P-0046 Congress: ESSR 2014
Prevalence of pitfalls in previous dual energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scans according to technical manuals and International Society for Clinical Densitometry. Poster No.: P-0046 Congress: ESSR 2014
Validation of bioimpedance body composition assessment by TANITA BC-418 in 7 years-
 Validation of bioimpedance body composition assessment by TANITA BC-418 in 7 years- old children vs. Dual X-ray absorptiometry Veronica Luque on behalf to URV Team 18th November 2012 Milano, 10th Bi-annual
Validation of bioimpedance body composition assessment by TANITA BC-418 in 7 years- old children vs. Dual X-ray absorptiometry Veronica Luque on behalf to URV Team 18th November 2012 Milano, 10th Bi-annual
JEPonline Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline
 Estimating Intra-abdominal Fat 1 JEPonline Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline Official Journal of The American Society of Exercise Physiologists (ASEP) ISSN 1097-9751 An International Electronic Journal
Estimating Intra-abdominal Fat 1 JEPonline Journal of Exercise Physiologyonline Official Journal of The American Society of Exercise Physiologists (ASEP) ISSN 1097-9751 An International Electronic Journal
Medical Policy. MP Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry to Determine Body Composition
 Medical Policy MP 6.01.40 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 6.01.40 Last Review: 09/28/2017 Effective Date: 09/28/2017 Section: Radiology End Date: 09/18/2018 Related Policies 6.01.44 Vertebral Fracture Assessment With
Medical Policy MP 6.01.40 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 6.01.40 Last Review: 09/28/2017 Effective Date: 09/28/2017 Section: Radiology End Date: 09/18/2018 Related Policies 6.01.44 Vertebral Fracture Assessment With
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 48.2 years Height / Weight: 150.0 cm 72.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 48.2 years Height / Weight: 150.0 cm 72.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) to Determine Body Composition
 Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) to Determine Body Composition Policy Number: 6.01.40 Last Review: 4/2018 Origination: 4/2005 Next Review: 4/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City
Whole Body Dual X-Ray Absorptiometry (DXA) to Determine Body Composition Policy Number: 6.01.40 Last Review: 4/2018 Origination: 4/2005 Next Review: 4/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City
Clinical Study Body Fat Mass Assessment: A Comparison between an Ultrasound-Based Device and a Discovery A Model of DXA
 ISRN Obesity Volume 2013, Article ID 462394, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/462394 Clinical Study Body Fat Mass Assessment: A Comparison between an Ultrasound-Based Device and a Discovery A Model
ISRN Obesity Volume 2013, Article ID 462394, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/462394 Clinical Study Body Fat Mass Assessment: A Comparison between an Ultrasound-Based Device and a Discovery A Model
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 43.4 years Height / Weight: 170.0 cm 66.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in DEXA Scanning 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1 Patient: Birth Date: 43.4 years Height / Weight: 170.0 cm 66.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Female
Twin study of genetic and environmental influences on adult body size, shape, and composition
 (2004) 28, 39 48 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0307-0565/04 $25.00 www.nature.com/ijo PAPER Twin study of genetic and environmental influences on adult body size, shape, and composition
(2004) 28, 39 48 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0307-0565/04 $25.00 www.nature.com/ijo PAPER Twin study of genetic and environmental influences on adult body size, shape, and composition
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), body composition assessment 62
 Subject Index 3 -Adrenergic receptor, gene polymorphisms and obesity 10 Aging, body composition effects 64, 65 Air-displacement plethysmography, body composition assessment 62 Bioelectrical impedance analysis
Subject Index 3 -Adrenergic receptor, gene polymorphisms and obesity 10 Aging, body composition effects 64, 65 Air-displacement plethysmography, body composition assessment 62 Bioelectrical impedance analysis
Genetic parameters for M. longissimus depth, fat depth and carcass fleshiness and fatness in Danish Texel and Shropshire
 58th Annual Meeting of the European Association for Animal Production in Dublin, Ireland Session 25.5, Abstract 444 Genetic parameters for M. longissimus depth, fat depth and carcass fleshiness and fatness
58th Annual Meeting of the European Association for Animal Production in Dublin, Ireland Session 25.5, Abstract 444 Genetic parameters for M. longissimus depth, fat depth and carcass fleshiness and fatness
The Bone Wellness Centre - Specialists in Dexa Total Body 855 Broadview Avenue Suite # 305 Toronto, Ontario M4K 3Z1
 Patient: Obese, Sample Birth Date: 0/Jan/966 44.4 years Height / Weight: 72.0 cm 95.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Referring Physician: DR. SMITH Measured: 07/Jun/200 7:0:52 PM (.40) Analyzed: 02/Apr/203
Patient: Obese, Sample Birth Date: 0/Jan/966 44.4 years Height / Weight: 72.0 cm 95.0 kg Sex / Ethnic: Male Patient ID: Referring Physician: DR. SMITH Measured: 07/Jun/200 7:0:52 PM (.40) Analyzed: 02/Apr/203
Metabolic precursors and effects of obesity in children: a decade of progress,
 Special Article Norman Kretchmer Memorial Award in Nutrition and Development Lecture, 2000 Metabolic precursors and effects of obesity in children: a decade of progress, 1990 1999 1 4 Michael I Goran ABSTRACT
Special Article Norman Kretchmer Memorial Award in Nutrition and Development Lecture, 2000 Metabolic precursors and effects of obesity in children: a decade of progress, 1990 1999 1 4 Michael I Goran ABSTRACT
Measures of body composition in blacks and whites: a comparative review 1,2
 Review Article Measures of body composition in blacks and whites: a comparative review 1,2 Dale R Wagner and Vivian H Heyward See corresponding editorial on page 1387. ABSTRACT Biological differences exist
Review Article Measures of body composition in blacks and whites: a comparative review 1,2 Dale R Wagner and Vivian H Heyward See corresponding editorial on page 1387. ABSTRACT Biological differences exist
GENETIC INFLUENCES ON APPETITE AND CHILDREN S NUTRITION
 GENETIC INFLUENCES ON APPETITE AND CHILDREN S NUTRITION DR CLARE LLEWELLYN Lecturer in Behavioural Obesity Research Health Behaviour Research Centre, University College London Tuesday 8 th November, 2016
GENETIC INFLUENCES ON APPETITE AND CHILDREN S NUTRITION DR CLARE LLEWELLYN Lecturer in Behavioural Obesity Research Health Behaviour Research Centre, University College London Tuesday 8 th November, 2016
Validation Study of Multi-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance with Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Among Obese Patients
 OBES SURG (2014) 24:1476 1480 DOI 10.1007/s11695-014-1190-5 OTHER Validation Study of Multi-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance with Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Among Obese Patients Silvia L. Faria
OBES SURG (2014) 24:1476 1480 DOI 10.1007/s11695-014-1190-5 OTHER Validation Study of Multi-Frequency Bioelectrical Impedance with Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Among Obese Patients Silvia L. Faria
GROWTH AND ADIPOSITY OF CHILDREN WITH DOWN SYNDROME: EFFECT OF TOTAL ENERGY EXPENDITURE. Rosemary K. DeLuccia
 GROWTH AND ADIPOSITY OF CHILDREN WITH DOWN SYNDROME: EFFECT OF TOTAL ENERGY EXPENDITURE by Rosemary K. DeLuccia A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial fulfillment of
GROWTH AND ADIPOSITY OF CHILDREN WITH DOWN SYNDROME: EFFECT OF TOTAL ENERGY EXPENDITURE by Rosemary K. DeLuccia A thesis submitted to the Faculty of the University of Delaware in partial fulfillment of
THE PREVALENCE OF OVERweight
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Prevalence and Trends in Overweight Among US Children and Adolescents, 1999-2000 Cynthia L. Ogden, PhD Katherine M. Flegal, PhD Margaret D. Carroll, MS Clifford L. Johnson, MSPH THE
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Prevalence and Trends in Overweight Among US Children and Adolescents, 1999-2000 Cynthia L. Ogden, PhD Katherine M. Flegal, PhD Margaret D. Carroll, MS Clifford L. Johnson, MSPH THE
Differences in body composition between Singapore Chinese, Beijing Chinese and Dutch children
 ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION (2003) 57, 405 409 ß 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954 3007/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/ejcn Differences in body composition between Singapore Chinese, Beijing Chinese
ORIGINAL COMMUNICATION (2003) 57, 405 409 ß 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954 3007/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/ejcn Differences in body composition between Singapore Chinese, Beijing Chinese
This is a digitised version of a dissertation submitted to the University of Bedfordshire. It is available to view only.
 Title The Validity of Two Compartment Model Methods of Body Composition as Compared to Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Asian Indian Versus Caucasian Males Name Ben Davies This is a digitised version of a
Title The Validity of Two Compartment Model Methods of Body Composition as Compared to Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Asian Indian Versus Caucasian Males Name Ben Davies This is a digitised version of a
Norland Densitometry A Tradition of Excellence
 Norland Densitometry A Tradition of Excellence Norland DXA Bone Density Measurement Osteoporosis is a disease marked by reduced bone strength leading to an increased risk of fractures. About 54 million
Norland Densitometry A Tradition of Excellence Norland DXA Bone Density Measurement Osteoporosis is a disease marked by reduced bone strength leading to an increased risk of fractures. About 54 million
The Relationship of BMI, Fat Percentage, and Waist-Hip Ratio to Physical Fitness Factors in Female Students
 J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res., 3(3)1273-1278, 2013 2013, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-4304 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com The Relationship of BMI, Fat Percentage, and Waist-Hip
J. Basic. Appl. Sci. Res., 3(3)1273-1278, 2013 2013, TextRoad Publication ISSN 2090-4304 Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research www.textroad.com The Relationship of BMI, Fat Percentage, and Waist-Hip
Body-composition differences between African American and white women: relation to resting energy requirements 1 3
 Body-composition differences between African American and white women: relation to resting energy requirements 1 3 Alfredo Jones Jr, Wei Shen, Marie-Pierre St-Onge, Dympna Gallagher, Stanley Heshka, ZiMian
Body-composition differences between African American and white women: relation to resting energy requirements 1 3 Alfredo Jones Jr, Wei Shen, Marie-Pierre St-Onge, Dympna Gallagher, Stanley Heshka, ZiMian
Body Composition and Fatness Patterns in Prader-Willi Syndrome: Comparison with Simple Obesity
 Original Research as Short Communication Body Composition and Fatness Patterns in Prader-Willi Syndrome: Comparison with Simple Obesity Mariana F. Theodoro, Zohreh Talebizadeh, and Merlin G. Butler Abstract
Original Research as Short Communication Body Composition and Fatness Patterns in Prader-Willi Syndrome: Comparison with Simple Obesity Mariana F. Theodoro, Zohreh Talebizadeh, and Merlin G. Butler Abstract
Trends in adult obesity
 53 by Margot Shields and Michael Tjepkema Keywords: body mass index, body weight, income, smoking In recent years, the percentage of Canadian adults with excess weight has increased considerably, part
53 by Margot Shields and Michael Tjepkema Keywords: body mass index, body weight, income, smoking In recent years, the percentage of Canadian adults with excess weight has increased considerably, part
Unique Effect of Visceral Fat on Insulin Sensitivity in Obese Hispanic Children With a Family History of Type 2 Diabetes
 Pathophysiology/Complications O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Unique Effect of Visceral Fat on Insulin Sensitivity in Obese Hispanic Children With a Family History of Type 2 Diabetes MARTHA L. CRUZ, PHD
Pathophysiology/Complications O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Unique Effect of Visceral Fat on Insulin Sensitivity in Obese Hispanic Children With a Family History of Type 2 Diabetes MARTHA L. CRUZ, PHD
Programming of lean body mass: a link between birth weight, obesity, and cardiovascular disease? 1 3
 Programming of lean body mass: a link between birth weight, obesity, and cardiovascular disease? 1 3 Atul Singhal, Jonathan Wells, Tim J Cole, Mary Fewtrell, and Alan Lucas ABSTRACT Background: A high
Programming of lean body mass: a link between birth weight, obesity, and cardiovascular disease? 1 3 Atul Singhal, Jonathan Wells, Tim J Cole, Mary Fewtrell, and Alan Lucas ABSTRACT Background: A high
C H A P T E R 14 BODY WEIGHT, BODY COMPOSITION, AND SPORT
 C H A P T E R 14 BODY WEIGHT, BODY COMPOSITION, AND SPORT Learning Objectives Differentiate among body build, body size, and body composition. Find out what tissues of the body constitute fat-free mass.
C H A P T E R 14 BODY WEIGHT, BODY COMPOSITION, AND SPORT Learning Objectives Differentiate among body build, body size, and body composition. Find out what tissues of the body constitute fat-free mass.
PhenX Measure: Body Composition (#020300) PhenX Protocol: Body Composition - Body Composition by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (#020302)
 PhenX Measure: Body Composition (#020300) PhenX Protocol: Body Composition - Body Composition by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (#020302) Date of Interview/Examination (MM/DD/YYYY): A downloadable PDF
PhenX Measure: Body Composition (#020300) PhenX Protocol: Body Composition - Body Composition by Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry (#020302) Date of Interview/Examination (MM/DD/YYYY): A downloadable PDF
Evaluating body fat in girls and female adolescents: advantages and disadvantages of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry 1 4
 Evaluating body fat in girls and female adolescents: advantages and disadvantages of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry 1 4 William W Wong, Albert C Hergenroeder, Janice E Stuff, Nancy F Butte, E O Brian
Evaluating body fat in girls and female adolescents: advantages and disadvantages of dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry 1 4 William W Wong, Albert C Hergenroeder, Janice E Stuff, Nancy F Butte, E O Brian
THE FIRST NINE MONTHS AND CHILDHOOD OBESITY. Deborah A Lawlor MRC Integrative Epidemiology Unit
 THE FIRST NINE MONTHS AND CHILDHOOD OBESITY Deborah A Lawlor MRC Integrative Epidemiology Unit d.a.lawlor@bristol.ac.uk Sample size (N of children)
THE FIRST NINE MONTHS AND CHILDHOOD OBESITY Deborah A Lawlor MRC Integrative Epidemiology Unit d.a.lawlor@bristol.ac.uk Sample size (N of children)
The Impact Of Adiposity And Insulin Resistance On Endothelial Function In Middle-Aged Subjects
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Cardiovascular Research Volume 1 Number 1 The Impact Of Adiposity And Insulin Resistance On Endothelial Function In Middle-Aged Subjects L Zhu, K Liu Citation L Zhu, K
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Cardiovascular Research Volume 1 Number 1 The Impact Of Adiposity And Insulin Resistance On Endothelial Function In Middle-Aged Subjects L Zhu, K Liu Citation L Zhu, K
BODY mass index (BMI) is a measure of
 Body Mass Index in Bengali Adolescents I. Banerjee, * N. Ghia, S. Bandopadhyay, H.N. Sayed and + D. Mukherjee From Royal Manchester Children s Hospital, UK; *Ramakrishna Mission Seva Pratishthan, Kolkata;
Body Mass Index in Bengali Adolescents I. Banerjee, * N. Ghia, S. Bandopadhyay, H.N. Sayed and + D. Mukherjee From Royal Manchester Children s Hospital, UK; *Ramakrishna Mission Seva Pratishthan, Kolkata;
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies
 Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Femur Bone Measurements Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: DXXFEM_D.XPT January 2009 NHANES 2005 2006 Data
Documentation, Codebook, and Frequencies Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry Femur Bone Measurements Examination Survey Years: 2005 to 2006 SAS Transport File: DXXFEM_D.XPT January 2009 NHANES 2005 2006 Data
Genetic and Environmental Contributions to Obesity and Binge Eating
 Genetic and Environmental Contributions to Obesity and Binge Eating Cynthia M. Bulik,* Patrick F. Sullivan, and Kenneth S. Kendler Virginia Institute for Psychiatric and Behavioral Genetics of Virginia
Genetic and Environmental Contributions to Obesity and Binge Eating Cynthia M. Bulik,* Patrick F. Sullivan, and Kenneth S. Kendler Virginia Institute for Psychiatric and Behavioral Genetics of Virginia
Location of body fat and body size impacts DXA soft tissue measures: a simulation study
 (2008) 62, 553 559 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954-3007/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Location of body fat and body size impacts DXA soft tissue measures: a simulation
(2008) 62, 553 559 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0954-3007/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/ejcn ORIGINAL ARTICLE Location of body fat and body size impacts DXA soft tissue measures: a simulation
Body Composition Changes Following a Very Low Calorie Pre-Operative Diet in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery
 Body Composition Changes Following a Very Low Calorie Pre-Operative Diet in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery 03 September 2018 Jonathan Sivakumar, Lynn Chong, Salena Ward, Tom R Sutherland, Michael
Body Composition Changes Following a Very Low Calorie Pre-Operative Diet in Patients Undergoing Bariatric Surgery 03 September 2018 Jonathan Sivakumar, Lynn Chong, Salena Ward, Tom R Sutherland, Michael
Downloaded from ijem.sbmu.ac.ir at 20: on Sunday February 24th 2019
 ( ) ( ). :. :. - -.. -. ( ) %/ :. SPSS %/. %/. %/ :.(r= / p
( ) ( ). :. :. - -.. -. ( ) %/ :. SPSS %/. %/. %/ :.(r= / p
Body composition. Body composition models Fluid-metabolism ECF. Body composition models Elemental. Body composition models Anatomic. Molnár Dénes.
 Body composition models Fluid-metabolism Fat Body composition ECF Molnár Dénes BCM ICF ICS ECS FFM Body composition models Anatomic Fat NSMST SM Body composition models Elemental Miscellaneous Calcium
Body composition models Fluid-metabolism Fat Body composition ECF Molnár Dénes BCM ICF ICS ECS FFM Body composition models Anatomic Fat NSMST SM Body composition models Elemental Miscellaneous Calcium
Do Measures of Body Fat Distribution Provide Information on the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Addition to Measures of General Obesity?
 Epidemiology/Health Services/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Do Measures of Body Fat Distribution Provide Information on the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Addition to Measures of General
Epidemiology/Health Services/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Do Measures of Body Fat Distribution Provide Information on the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes in Addition to Measures of General
Consistent with trends in other countries,1,2 the
 9 Trends in weight change among Canadian adults Heather M. Orpana, Mark S. Tremblay and Philippe Finès Abstract Objectives Longitudinal analyses were used to examine the rate of change of self-reported
9 Trends in weight change among Canadian adults Heather M. Orpana, Mark S. Tremblay and Philippe Finès Abstract Objectives Longitudinal analyses were used to examine the rate of change of self-reported
Evaluation of DXA against the four-component model of body composition in obese children and adolescents aged 5 to 21 years
 Europe PMC Funders Group Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Int J Obes (Lond). 2010 April ; 34(4): 649 655. doi:10.1038/ijo.2009.249. Evaluation of DXA against the four-component model
Europe PMC Funders Group Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: Int J Obes (Lond). 2010 April ; 34(4): 649 655. doi:10.1038/ijo.2009.249. Evaluation of DXA against the four-component model
TITLE: Breast Density Assessment by Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry in Women and Girls. Rachel Novotny, Ph.D. Honolulu, HI 96822
 AD AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-07-1-0489 TITLE: Breast Density Assessment by Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry in Women and Girls PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Gertraud Maskarinec, M.D., Ph.D. Rachel Novotny, Ph.D.
AD AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-07-1-0489 TITLE: Breast Density Assessment by Dual Energy X-ray Absorptiometry in Women and Girls PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Gertraud Maskarinec, M.D., Ph.D. Rachel Novotny, Ph.D.
Michael B Zimmermann, Carolyn Gübeli, Claudia Püntener, and Luciano Molinari
 Detection of overweight and obesity in a national sample of 6 12-y-old Swiss children: accuracy and validity of reference values for body mass index from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Detection of overweight and obesity in a national sample of 6 12-y-old Swiss children: accuracy and validity of reference values for body mass index from the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
An evaluation of body mass index, waist-hip ratio and waist circumference as a predictor of hypertension across urban population of Bangladesh.
 An evaluation of body mass index, waist-hip ratio and waist circumference as a predictor of hypertension across urban population of Bangladesh. Md. Golam Hasnain 1 Monjura Akter 2 1. Research Investigator,
An evaluation of body mass index, waist-hip ratio and waist circumference as a predictor of hypertension across urban population of Bangladesh. Md. Golam Hasnain 1 Monjura Akter 2 1. Research Investigator,
Abdominal fat distribution (subcutaneous vs. visceral abdominal fat compartments): correlation with gender, age, BMI and waist circumference
 Abdominal fat distribution (subcutaneous vs. visceral abdominal fat compartments): correlation with gender, age, BMI and waist circumference Poster No.: C-934 Congress: ECR 202 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Abdominal fat distribution (subcutaneous vs. visceral abdominal fat compartments): correlation with gender, age, BMI and waist circumference Poster No.: C-934 Congress: ECR 202 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Familial Resemblance in Fatness and Fat Distribution in Nuclear Families from Biscay (Basque Country)
 Familial Resemblance in Fatness and Fat Distribution in Nuclear Families from Biscay (Basque Country) Esther Rebato, Itziar Salces, Aline Jelenkovic and Charles Susanne CHAPTER 4 INTRODUCTION Researches
Familial Resemblance in Fatness and Fat Distribution in Nuclear Families from Biscay (Basque Country) Esther Rebato, Itziar Salces, Aline Jelenkovic and Charles Susanne CHAPTER 4 INTRODUCTION Researches
Understanding Body Composition
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines 7 Understanding Body Composition Objectives Define body composition. Explain why the assessment of body size, shape, and composition is useful. Explain how to perform assessments
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines 7 Understanding Body Composition Objectives Define body composition. Explain why the assessment of body size, shape, and composition is useful. Explain how to perform assessments
DXA Body Composition Scan + Visceral Fat Analysis
 DXA Body Composition Scan + Visceral Fat Analysis Charles B. Christian, Jr. M.D. Medical Director Inside Outside Wellness Center & Medical Spa 4499 Medical Drive #225 San Antonio, Texas 78229 210.616.0836
DXA Body Composition Scan + Visceral Fat Analysis Charles B. Christian, Jr. M.D. Medical Director Inside Outside Wellness Center & Medical Spa 4499 Medical Drive #225 San Antonio, Texas 78229 210.616.0836
THE PERENNIAL STRUGGLE TO LOSE WEIGHT AND MAINTAIN: WHY IS IT SO DIFFICULT?
 THE PERENNIAL STRUGGLE TO LOSE WEIGHT AND MAINTAIN: WHY IS IT SO DIFFICULT? Robert Ferraro, MD Medical Director Southwest Endocrinology Associates, PA Diabetes and Weight Management Center OBESITY The
THE PERENNIAL STRUGGLE TO LOSE WEIGHT AND MAINTAIN: WHY IS IT SO DIFFICULT? Robert Ferraro, MD Medical Director Southwest Endocrinology Associates, PA Diabetes and Weight Management Center OBESITY The
Heritability of somatotype components: a multivariate analysis
 (2007) 31, 1295 1301 & 2007 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0307-0565/07 $30.00 www.nature.com/ijo ORIGINAL ARTICLE : a multivariate analysis MW Peeters 1, MA Thomis 1, RJF Loos 1,2, CA Derom
(2007) 31, 1295 1301 & 2007 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0307-0565/07 $30.00 www.nature.com/ijo ORIGINAL ARTICLE : a multivariate analysis MW Peeters 1, MA Thomis 1, RJF Loos 1,2, CA Derom
Regional Subcutaneous-Fat Loss Induced by Caloric Restriction in Obese Women
 Regional Subcutaneous-Fat Loss Induced by Caloric Restriction in Obese Women Jack Wang, Blandine Laferrère, John C. Thornton, Richard N. Pierson, Jr., and F. Xavier Pi-Sunyer Abstract WANG, JACK, BLANDINE
Regional Subcutaneous-Fat Loss Induced by Caloric Restriction in Obese Women Jack Wang, Blandine Laferrère, John C. Thornton, Richard N. Pierson, Jr., and F. Xavier Pi-Sunyer Abstract WANG, JACK, BLANDINE
