Can Treatment and Occurrence Research Keep up with the CCL Process? The case of DBPs (and PPCPs)
|
|
|
- Eustacia Judith Sharp
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Research ommittee Seminar on L3 VA Section AWWA an Treatment and ccurrence Research Keep up with the L Process? The case of DBPs (and PPPs) Dave Reckhow University of Massachusetts 20 ct 2008
2 utline Introduction DBPs: regulated vs emerging Deductive vs bservational approach Predictions from Structure Toxicity Models Biopolymers and DBP pathways New Analytical Methods onclusions
3 DBP Formation The THMs H The Precursors! H + natural organics (NM) Br H Br Br H xidized NM and inorganic chloride Aldehydes hlorinated rganics TX THMs HAAs Br Br H Br hloroform Bromodichloromethane hlorodibromomethane Bromoform 3
4 The Haloacetic Acids Br Br Br Br Br Br Trichloroacetic Bromodichloroacetic hlorodibromoacetic Tribromoacetic Acid Acid Acid Acid (TAA) H H Br Br H Br Dichloroacetic Bromochloroacetic Dibromoacetic Acid Acid Acid (DAA)
5 The DBP Iceberg DHAAs THMs, THAAs IR ompounds 50 MWDS DBPs Stuart Krasner ~700 Known DBPs Susan Richardson Halogenated ompounds Non-halogenated ompounds
6 DBPs on L3 Aldehydes Formaldehyde Acetaldehyde Nitrosamines Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) Nitrosodiethylamine (NDEA) Nitroso-di-n-propylamine (NDPA) Nitrosodiphenylamine Nitrosopyrrolidine (NPYR) Hydrazine
7 ther DBPs on PL hloropicrin Halophenols hlorophenol 2,4,5-trichlorophenol 2,4,6-trichlorophenol Benzoic acid, 3,6-dichloro-2-hydroxy Haloamines 1,2-benzenediamine, 4-chloro 2,4-Imidazolidinedione, 1,3-dibromo-5,5-dimethyl 1,2-propanediol, 3-chloro Many oxidation products
8 Epidemiology Bladder ancer DBPs linked to 9,300 US cases every year ther ancers Rectal, colon Reproductive & developmental effects Neural tube defects Miscarriages & Low birth weight eft palate ther Kidney & spleen disorders Immune system problems, neurotoxic effects 137,000 at risk in US?
9 TX: Known & Unknown Data from the Mills Plant (A) August 1997 (courtesy of Stuart Krasner) Haloketones hloropicrin Trihalomethanes 20% Regulated DBPs But, the Bad Stuff is somewhere here Unknown rganic Halogen 64% Haloacetonitriles 2% hloral Hydrate 1% Sum of 5 Haloacetic Acids 10% Bromochloroacetic Acid 3%
10 IR data 140 Are regulated DBPs good surrogates? TTHM (µg/l) Unknown TX (µg/l)
11 Species Model Simple competitive kinetic model From: MacNeill, 1993; owan & Singer, Probabilistic model THM Mole Fraction (THM4 only) H 3 HBr 2 HBr 2 HBr Dave Reckhow, UMass 11 THM Br/(+Br)
12 Bromo speciation 1.2 Full-scale data (small symbols) from Weinberg et al., 2002 (All 12 plants) THM Mole Fraction (THM4 only) Lab data (large symbols) from Hua & Reckhow, 2004 Lines are geometric model H3 HBr2 HBr2 HBr3 H3 Lab tests HBr2 Lab tests HBr2 Lab tests HBr3 Lab tests Dave Reckhow, UMass THM Br/(+Br) 12
13 Brominated 3 & 4-carbon acids Brominated 3-carbon and 4-carbon acids: like the HAAs, these are maximized with chlorine Examples from Weinberg et al., 2002: Propanoic acid (2,2-Br 2 ; Br) Butanoic acid (2-Br) Propenoic acid (3,3-2 ; 3,3-Br 2 ; cis-2,3-br 2 ; Br 3 ; BrI) Buten-2-oic acid (trans&cis-4-br; 2,3-Br 2 ; Br 2 ) Butenedoic acid (2-Br; trans-2,3-br 2 ) Dave Reckhow, UMass 13
14 Iodo speciation nly low THM I data available from field sites Suggestions of departure from probabilistic model at high THM I Higher iodoform than expected Possible decomposition of larger TI structures THM Mole Fraction (&I only) Full-scale data (small symbols) from Weinberg et al., 2002 Lab data (large symbols) from Hua & Reckhow, 2004 Lines are geometric model (All 12 plants) H3 HI2 HI2 HI3 H3 Lab tests HI2 Lab tests HI2 Lab tests HI3 Lab tests THM I/(+I) Dave Reckhow, UMass 14
15 Iodo-acids ompounds from chloramine system (Weinberg et al., 2002) Iodoacetic acid Bromoiodoacetic acid (E)-3,3-bromoiodopropenoic acid (Z)-3,3-bromoiodopropenoic acid (E)-2-iodo-3-methylbutenedioic acid Lab Data suggests Less TI formation than TBr formation at same molar halide levels Due to iodate formation Without iodate formation, TI forms as readily as TBr onclusion Iodoacids probably track Iodomethanes Dave Reckhow, UMass 15
16 MX Several isomers, congeners and related forms pen (ZMX, EMX) and closed (MX) xidized (ox-mx, ox- EMX) and reduced (red-mx) Brominated (BMX1-3, BEMX1-3) Dave Reckhow, UMass 16 Fig. 1. Ring and open forms of targeted halogenated furanones (MX-analogues); from nstad & Weinberg, 2005.
17 MX ompounds (cont.) MX ccurrence studies Kronberg and other early studies Generally < 60 ng/l Wright et al., 2002 [Env. Hlth. Pers.] Up to 80 ng/l Weinberg et al., 2002 Median = 20 ng/l; 75%ile = 60 ng/l; max = 310 ng/l ther forms BMX1 (170 ng/l) and BMX3 (200 ng/l) High Br plant using chlorine dioxide, chlorine and chloramines Dave Reckhow, UMass 17
18 MX Behavior Lab degradation studies Slow hydrolysis at neutral ph t ½ ~ 9 days Accelerated degradation in presence of sulfite t ½ ~ 9 hrs at 25 µm [S(IV)] Weinberg et al., 2002 zone destroys MX precursors, but 2 doesn t Apparent MX degradation in DS of Plant #2 Dave Reckhow, UMass 18
19 N-DBPs Nitrosamines NDMA etc. rganic chloramines N-haloamino acids, etc. Haloquinones Halonitriles DHANs and many others
20 H ytotoxicity Work of Michael Plewa DBP hemical ass IAA BAA TBAA hloroacetamide Trichloroacetonitrile 3-Iodo-3-bromopropenoic Acid DBAA MX DIAA DBAA BDAA BIAA BAA AA 2-Bromobutenedioic Acid 2,3-Dibromopropenoic Acid TAA DAA DBNM DBNM BNM TBNM BDNM 3,3-Dibromo-4-oxopentanoic Acid BNM 2-Iodo-3-bromopropenoic Acid 3,3-Dibromopropenoic Acid DNM NM TNM Tribromopropenoic Acid 2-Bromo-3-methylbutenedioic Acid hlorodibromomethane Bromoacetamide Dibromoacetamide Tribromopyrrole Bromate Dichloroacetamide Trichloroacetamide EMS +ontrol ther DBPs Iodoacetamide Haloacetamides Dibromoacetonitrile Bromoacetonitrile Iodoacetonitrile Bromochloroacetonitrile Haloacetonitriles Dichloroacetonitrile hloroacetonitrile Iodoform Halomethanes Halonitromethanes 3,3-Bromochloro-4-oxopentanoic Acid Bromoform hloroform Halo Acids Haloacetic Acids H ell ytotoxicity as %½ Values (~L 50 ) Log Molar oncentration (72 h Exposure) July
21 N-DBPs we know about: end products ertain to come from N-organics when using free chlorinen & NBr Major types: yanogen Halides Haloacetonitriles Halonitromethanes N hloropicrin 9 species (HP) 2 H Br Br N H N H N Br Dichloroacetonitrile Bromochloroacetonitrile Dibromoacetonitrile (DAN) (BAN) Special focus on these compounds because of large data set (DBAN) Trichloroacetonitrile (TAN) N
22 ccurrence DHANs are typically 10% of THM level Krasner et al., 2002 [WQT] 12 plant survey IR (mean for all) HAN4: 2.7 µg/l P: <0.5 µg/l N: 2.1 µg/l
23 Pathway to NDMA Role of Dichloramine and oxygen Based on recent work by Bill Mitch and colleagues Dichloramine H N N H 3 R H 3 Dimethyl(xx)amine PRDUTS R H N H N N Monochloro Unsymmetric Dimethylhydrazine (UDMH-) N H 3 H 3 N Nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA) xygen H 3 H 3
24 Reaction of UDMH Abbreviations DMD: dimethyldiazene TMT: tetramethyltetrazene FMMH: formaldehyde monomethylhydrazone FDMH: formaldehyde dimethylhydrazone DM: dimethylcyanamide DMF: dimethylformamide From: Mitch & Sedlak, 2002 [ES&T, 36:588]
25 The Unnatural Precursor? Ranitidine (Zantac) 63% conversion to NDMA Schmidt et al., 2006 [WQT] Introduced in 1981, largest selling prescription drug by 1988 Stomach ulcers and esophageal reflux Mean concentration of 3000 ng/l estimated for raw municipal WW (national average) Sedlak 2005 AWWARF report 450 ng/l formation in raw WW expected Unknowns: how much does this persist in treatment and in the environment? 25
26 Hunting for the bad DBPs bservational/empirical Multifaceted analysis of treated waters ompanion toxicity testing Deductive/theoretical Postulate DBPs from known NM substructures Exploit Structure-toxicity models Also allows us to probe NM contributions to regulated DBPs
27 g hemical Models to Prioritize DBP Research AWWARF funded study ( ) Richard Bull, Dave Reckhow Background Health risks associated with disinfection in epidemiology studies are poorly represented in the toxicology data of individual DBPs Effects specific to epidemiology, and/or Projected risks are much higher than sum of individual by-products studied in toxicology studies Toxicology data has identified the compounds in current regulations (e.g. THMs & HAAs) omplying with these MLs does not necessarily result in decreases in major health risks which are those identified in epidemiology studies
28 An Aquatic Humic Structure From Thurman, 1985 Hydroxy Acid H H H Phenolic- Aliphatic Dicarboxylic Acid Aromatic Dicarboxylic Acid H H 3 Aliphatic Acid Aromatic Acid
29 Aliphatics: Haloform Reaction RLS is deprotonation (k 1 ) under many conditions Many LFERs exist for estimating K a s E.g., Perrin et al., 1982 Then relate k 1 to K a H 3 H 3 H 3 H 2 H H 2 H + - H 3 H 2 H - H 3 H 2 H H 2 [ ] H 3 H 2 H H 3-3 H 3 H H 29 3
30 arbonaceous biopolymers ellulose Lignin Phenyl-propane units ross-linked Radical polymerization Ill defined structure Hemicellulose Terpeniods
31 H Lignin Monomers Aromatic structures from u degradation Syringyl Vanillyl innamyl 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid H Vanillin H 3 Vanillic acid H 3 H 3 H H 3 H 3 Syringaldehyde H 3 H 3 H 3 Syringic acid H 3 Acetovanilione H 3 H 3 H 3 H 3 4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydroxyacetophenone 4-Hydroxycinnamic acid Acetosyringone Ferulic acid
32 Demand TX Unkn TX 2.0 hlorine Demand (M/M-compound) TX Speciation hydroxy benzoic acid 4-hydroxy benzaldehyde 4-hydroxy acetophenone TX Formation (M-/M-compound) TTHM THAA DHAA DHAN Unkn TX 4-hydroxy benzenes Among the most reactive structures tested H H 3
33 Mining the literature to postulate new DBPs hlorination of p- hydroxybenzoic acid based on Larson and Rockwell (1979). A represents electrophilic aromatic substitution, B is oxidative decarboxylation H B H H A H H H H H H H H B H H H A 1 B 3 Haloquinones are likely intermediates 2 A A 4 5
34 horine + Aromatics hlorination of Resorcinol From Boyce & Hornig, 1983 All structures identified by G/MS except those in brackets Dave Reckhow, UMass 34
35 ther plant products Steroids Porphyrins Nucleic Acids Terpenoids Water Soluble Acids Mevalonic acid Acetate Amino Acids Misc. N & S compounds Unsaponifiable Liquids Flavonoids Saponifiable Liquids Pyruvate arbohydrates Shikimic Acid Aromatic ompounds Proteins Nitrogenous precursors Activated non-n precursors From: Robinson, 1991
36 Amino Acids: Estimated Abundance assification 50%ile 90%ile 99%ile DN Free AA ombined AA Nucleic acids Amino Sugars Humic-N From: Bull et al., 2007 Estimates in µg-n/l Amino Abun- Acid dance Glycine 11.7% Alanine 11.7% Valine 5.2% Isoleucine 4.4% Leucine 5.6% Serine 10.8% Threonine 7.0% Methionine 1.0% Aspartic Acid 10.2% Glutamic Acid 10.0% Lysine 1.6% rnithine 2.0% Arginine 7.4% Histidine 2.5% Asparagine 0.4% Glutamine 0.5% Tryptophan 2.5% Phenylalanine 3.4% Tryrosine 2.2% SUM 100.0% [1] Based on an average of: Isle Bay water (Yamashita & Tanoue, 2003), Lake Biwa (Wu et al., 2003), and water column values, summer, from Thomas,
37 R N-chloro-organics Reactions of chlorine with organic amines Primary amines H H NH 2 R NH R N 2 Secondary amines R 2 H NH R2 N Inorganic chloramines can transfer their active chlorine in a similar fashion
38 Degradation pathways R 1 H N R2 R 4 R 3 X + Nu R 1 X N R2 R 4 R 3 R 1 =H X + Nu X X N R2 R 4 R 3 R 2 =H or I II R 2 =H or HX ( 2 ) R 1 =H HX ( 2 ) General scheme for carbonyl and cyano formation from chlorination of amines and amino acids (adapted from Nweke and Scully, 1989, and Armesto et al., 1998). R 1 NH 2 R 1 R 4 N III R 3 R 4 R 3 V NH 2 X X + Nu X R 4 N IV R 4 =H N R 3 HX R 3 VI Monohalamine Pathway Dihalamine Pathway
39 assic Mechanism Isoleucine 2 Pathways Formation of nitriles with excess chlorine Formation of aldehydes with under-chlorination Froese, Kenneth L., Wolanski, Alina, and Hrudey, Steve E. Factors Governing dorous Aldehyde Formation as Disinfection By-Products in Drinking Water. Water Research 33[6], Aldehyde Nitrile
40 Phenylalanine Stable N-chloroaldimine Pathway favored at lower phs Half-life of onyers & Scully, 1993 [ES&T 27:261]
41 Aspartic Acid Early Recognition of DHAN pathway From Trehy, 1980 (MS Thesis)
42 H DAN N Asp (cont) k 2 k 1 k 4 H N H N H 2 fast DAN continues to degrade There is a direct pathway to DAA There is an important oxidation & deamination pathway too H 2 fast DAD H H k 1-1 H NH 2 NH 3 NH 2 fast fast NH (+II) S (+IV) H fast H H NH 2 H N pka = 3.7 k 1-2 N--DAD anion N--DAD NH H NH DAA
43 Polypeptide linkages # of AAs Amide nitrogen thought to react slowly About 5% under conditions used Based on Jensen et al., 1999 More reactive than expected 2 Demand (mg/mg-n) Demands calculated from component AAs both with and without amide reactivity Asp-Asp-Asp-Asp L-Aspartyl-L-Phenylalanine Albumin Measured al w/ amide al w/o amide Hemoglobin Lysozyme Insulin Demand (M/M-N) ompound
44 Larger Proteins omparison to free AAs Less dihalo; more trihalo Similar TX; maybe less UTX Hemoglobin Albumin DBP Formation (µg/mg-n) bserved Predicted DBP Formation (µg/mg-) DBP Formation (µg/mg-n) bserved Predicted DBP Formation (µg/mg-) 0 TTHM TAA DAA TX UnKn TX DBP 0 0 TTHM TAA DAA TX UnKn TX DBP 0
45 onclusions: from QSTR From: Bull et al., 2008, AwwaRF Report Research needs Group Example ccurrence Toxicology Haloquinones rganic N- haloamines Alkaloidal nitrosamines 2,6-dichloro-3-methyl-1,2- benzoquinone (DMBQ) Prioritize on range of stabilities and mutagenic activity N-nitrosonornicotine 1-Noxide yclopentenoic acids & MX-related 3,5-dichloro 1-hydroxy-4- ketocyclopent-2-enoic acid 1 2 MF 2 1 Halonitriles 2,3-Dichloropropenal (arc) 2,3-dibromopropionitrile (DT) 1 1
46 Higher MW DBPs NM research ESI with Ultra High- Resolution Fourier Transform Ion yclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry Benefits Unambiguous molecular formulae
47 Raw Water - Winnipeg 4.00E E E+02 -ve ion + ve ion Intensity ESI-TF MS 2.50E E E E E+01 ESI-FTIR MS Abundance 0.00E m/z Same: comparison side-by-side 500 m/z
48 hlorinated Water + Br Winnipeg 7 6 Abundance m/z Abundance m/z
49 Ultra-high resolution MS Reemtsma et al., 2006 [ES&T: 40:19:5839] Zone of low solubility Area of predicted fulvic acid molecules in a - vs molecular mass diagram for the mass range m/z (marked by the lines) and fulvic acid molecules detected by SE-FTIRMS in the river isolate (dots (island no. 24) and triangles (island no. 25)). 49
50 Some examples hlorination of Winnipeg RW in presence of Iodide Possible structures H I 2 H Mass Mass H H I Mass
51 onclusions: DBPs The most toxicologically important DBPs have not yet been proposed for regulation Many biopolymers can produce important DBPs Amino acids and proteins produce substantial amounts of DBPs that may be of toxicological significance, especially N- DBPs Lignin and monomers probably produce haloquinones that are suspected to be carcinogenic DBPs for future Ls should be examined using deductive methods as well as the more conventional approaches
52 Acknowledgements Research Support American Waterworks Association Research Foundation Massachusetts Division of onservation and Recreation Many UMass students, post-docs and faculty Paula Rees, Klaus Nusslein, John Tobiason Darlene Bryan, Greg Devine, Junsung Kim, Gladys Makdissy, Teresa onneely, ynthia astellon, Alison Boutin Many Drinking Water Utilities
53 The End Suspect apprehended? 53
Proteins as Important Reactive Compounds in Drinking Water Treatment
 Proteins as Important Reactive ompounds in Drinking Water Treatment Junsung Kim, Guanghui Hua, Gladys Dave Makdissy, Reckhow John Mcellan, ynthia astellon, Darlene Amherst Buttrick University of Massachusetts
Proteins as Important Reactive ompounds in Drinking Water Treatment Junsung Kim, Guanghui Hua, Gladys Dave Makdissy, Reckhow John Mcellan, ynthia astellon, Darlene Amherst Buttrick University of Massachusetts
CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater
 Print version CEE 697z rganic Compounds in Water and Wastewater NM and DBPs Special Lecturer: Rassil El Sayess Lecture #9 http://www.ecs.umass.edu/eve/research/nyc_chloramines/literature.html Dave Reckhow
Print version CEE 697z rganic Compounds in Water and Wastewater NM and DBPs Special Lecturer: Rassil El Sayess Lecture #9 http://www.ecs.umass.edu/eve/research/nyc_chloramines/literature.html Dave Reckhow
CEE 690K ENVIRONMENTAL REACTION KINETICS
 Updated: 12 April 2008 EE690K Lecture #16 1 Print version EE 690K EVIROMETAL REATIO KIETIS Lecture #16 ase Study: itrogenous Disinfection Byproducts Primary Literature as noted David A. Reckhow Introduction
Updated: 12 April 2008 EE690K Lecture #16 1 Print version EE 690K EVIROMETAL REATIO KIETIS Lecture #16 ase Study: itrogenous Disinfection Byproducts Primary Literature as noted David A. Reckhow Introduction
CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater
 Print version CEE 697z rganic Compounds in Water and Wastewater NM and DBPs Special Lecturer: Rassil El Sayess Lecture #9 http://www.ecs.umass.edu/eve/research/nyc_chloramines/literature.html Dave Reckhow
Print version CEE 697z rganic Compounds in Water and Wastewater NM and DBPs Special Lecturer: Rassil El Sayess Lecture #9 http://www.ecs.umass.edu/eve/research/nyc_chloramines/literature.html Dave Reckhow
Safe Drinking Water? Effect of Wastewater Inputs and Source Water Impairment and Implications for Water Reuse. Susan D. Richardson
 Safe Drinking Water? Effect of Wastewater Inputs and Source Water Impairment and Implications for Water Reuse Susan D. Richardson Safe Drinking Water: What are the Issues? Chemical risk: Exposure to hazardous
Safe Drinking Water? Effect of Wastewater Inputs and Source Water Impairment and Implications for Water Reuse Susan D. Richardson Safe Drinking Water: What are the Issues? Chemical risk: Exposure to hazardous
Nitrogenous Disinfection By-Products Formation Potential from Molecular Weight Fractions of Natural Organic Matter
 Nitrogenous Disinfection By-Products Formation Potential from Molecular Weight Fractions of Natural Organic Matter Ina Kristiana, Jace Tan, Suzanne McDonald, Rino Trolio, Cynthia Joll, Anna Heitz and Jeffrey
Nitrogenous Disinfection By-Products Formation Potential from Molecular Weight Fractions of Natural Organic Matter Ina Kristiana, Jace Tan, Suzanne McDonald, Rino Trolio, Cynthia Joll, Anna Heitz and Jeffrey
Induction of Mammalian Cell Chronic Cytotoxicity and Acute Genomic DNA Damage by Drinking Water Disinfection Byproducts
 Induction of Mammalian Cell Chronic Cytotoxicity and Acute Genomic DNA Damage by Drinking Water Disinfection Byproducts Michael J. Plewa, Elizabeth D. Wagner University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
Induction of Mammalian Cell Chronic Cytotoxicity and Acute Genomic DNA Damage by Drinking Water Disinfection Byproducts Michael J. Plewa, Elizabeth D. Wagner University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
The Next Generation of Drinking Water Disinfection By-Products: Occurrence, Formation, and Toxicity
 The Next Generation of Drinking Water Disinfection By-Products: Occurrence, Formation, and Toxicity Susan D. Richardson U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, National Exposure Research Laboratory, Athens,
The Next Generation of Drinking Water Disinfection By-Products: Occurrence, Formation, and Toxicity Susan D. Richardson U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, National Exposure Research Laboratory, Athens,
Overview of Drinking Water Treatment and Byproduct
 verview of Drinking Water Treatment and Byproduct Compounds David Cwiertny Associate Professor Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Director, Sustainable Water Development Graduate Program
verview of Drinking Water Treatment and Byproduct Compounds David Cwiertny Associate Professor Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Director, Sustainable Water Development Graduate Program
Chlorinated Disinfection By-Products (CDBPs) Prepared for the CDBP Task Group
 Chlorinated Disinfection By-Products (CDBPs) Prepared for the CDBP Task Group Introduction The goal of water disinfection is the inactivation of microorganisms, such as viruses, bacteria and protozoa,
Chlorinated Disinfection By-Products (CDBPs) Prepared for the CDBP Task Group Introduction The goal of water disinfection is the inactivation of microorganisms, such as viruses, bacteria and protozoa,
CEE 697K ENVIRONMENTAL REACTION KINETICS
 Updated: 7 October 2013 1 Print version CEE 697K ENVIRONMENTAL REACTION KINETICS Lecture #8 Special Topics: Pharmaceuticals in Water I Primary Literature (e.g., Westerhoff et al., 2005) Introduction 2
Updated: 7 October 2013 1 Print version CEE 697K ENVIRONMENTAL REACTION KINETICS Lecture #8 Special Topics: Pharmaceuticals in Water I Primary Literature (e.g., Westerhoff et al., 2005) Introduction 2
Scientific Facts on. Water Disinfectants. & disinfectant by-products
 page 1/13 Scientific Facts on Water Disinfectants & disinfectant by-products Source document: IPCS (2000) Summary & Details: GreenFacts Level 2 - Details on Water Disinfectants 1. What disinfectants and
page 1/13 Scientific Facts on Water Disinfectants & disinfectant by-products Source document: IPCS (2000) Summary & Details: GreenFacts Level 2 - Details on Water Disinfectants 1. What disinfectants and
CEE 697K ENVIRONMENTAL REACTION KINETICS
 Updated: 7 October 2013 1 Print version CEE 697K ENVIRONMENTAL REACTION KINETICS Lecture #8 Special Topics: Pharmaceuticals in Water I Primary Literature (e.g., Westerhoff et al., 2005) Introduction Boston
Updated: 7 October 2013 1 Print version CEE 697K ENVIRONMENTAL REACTION KINETICS Lecture #8 Special Topics: Pharmaceuticals in Water I Primary Literature (e.g., Westerhoff et al., 2005) Introduction Boston
Aeration to remove THMs from drinking water. Ron Hofmann Susan Andrews Arash Zamyadi Hong Zhang
 Aeration to remove THMs from drinking water Ron Hofmann Susan Andrews Arash Zamyadi Hong Zhang DBPs: a distribution system issue (too!) Distribution system strategies to minimize DBPs Chlorine chloramines
Aeration to remove THMs from drinking water Ron Hofmann Susan Andrews Arash Zamyadi Hong Zhang DBPs: a distribution system issue (too!) Distribution system strategies to minimize DBPs Chlorine chloramines
CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater
 Print version CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater NOM and MS Methods Lecture #10 NOM Characterization Analytical Tests elemental analysis spectral properties functional group chemistry Separation/Fractionation
Print version CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater NOM and MS Methods Lecture #10 NOM Characterization Analytical Tests elemental analysis spectral properties functional group chemistry Separation/Fractionation
CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater
 Print version CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater NOM and MS Methods Lecture #10 NOM Characterization Analytical Tests elemental analysis spectral properties functional group chemistry Separation/Fractionation
Print version CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater NOM and MS Methods Lecture #10 NOM Characterization Analytical Tests elemental analysis spectral properties functional group chemistry Separation/Fractionation
Science Dossier. Human health aspects of halogenated organic by-products from use of active chlorine
 Science Dossier Human health aspects of halogenated organic by-products from use of active chlorine January 2017 This publication is the seventeenth in a series of Science Dossiers providing the scientific
Science Dossier Human health aspects of halogenated organic by-products from use of active chlorine January 2017 This publication is the seventeenth in a series of Science Dossiers providing the scientific
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 9. AMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 9. AMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND
FinalReport. Study into the formation of disinfection by-products of chloramination, potential health implications and techniques for minimisation
 FinalReport Study into the formation of disinfection by-products of chloramination, potential health implications and techniques for minimisation i ii STUDY INTO THE FORMATION OF DISINFECTION BY- PRODUCTS
FinalReport Study into the formation of disinfection by-products of chloramination, potential health implications and techniques for minimisation i ii STUDY INTO THE FORMATION OF DISINFECTION BY- PRODUCTS
CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater
 Print version CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater Isolation of NOM Lecture #3 A USGS Preparative-based method Leenheer, J.A. and Noyes, T.I. (1984) A Filtration and Column- Adsorption System
Print version CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater Isolation of NOM Lecture #3 A USGS Preparative-based method Leenheer, J.A. and Noyes, T.I. (1984) A Filtration and Column- Adsorption System
Danielle Westerman, Hannah K. Liberatore, Kristin H. Cochran Cassiana Montagner, Dion D. Dionysiou, Leslie H. Cizmas, Susan Richardson
 Danielle Westerman, Hannah K. Liberatore, Kristin H. Cochran Cassiana Montagner, Dion D. Dionysiou, Leslie H. Cizmas, Susan Richardson Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of South Carolina
Danielle Westerman, Hannah K. Liberatore, Kristin H. Cochran Cassiana Montagner, Dion D. Dionysiou, Leslie H. Cizmas, Susan Richardson Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry University of South Carolina
N-CHLORAMINES. Somprasong Laingam (MBiotech) Discipline of Pharmacology. The University of Adelaide. (Faculty of Health Science) July, 2009
 GENOTOXICITY INVESTIGATION OF ORGANIC N-CHLORAMINES Somprasong Laingam (MBiotech) Discipline of Pharmacology The University of Adelaide (Faculty of Health Science) July, 2009 A thesis submitted for the
GENOTOXICITY INVESTIGATION OF ORGANIC N-CHLORAMINES Somprasong Laingam (MBiotech) Discipline of Pharmacology The University of Adelaide (Faculty of Health Science) July, 2009 A thesis submitted for the
Uptake of Water Disinfection By-Products Into Food
 Methods Report Uptake of Water Disinfection By-Products Into Food James H. Raymer and Larry C. Michael August 2010 RTI Press About the Authors James H. Raymer, PhD, is a senior research analytical chemist
Methods Report Uptake of Water Disinfection By-Products Into Food James H. Raymer and Larry C. Michael August 2010 RTI Press About the Authors James H. Raymer, PhD, is a senior research analytical chemist
Identification of Novel Brominated Disinfection By-Products of Concern in Drinking Water by Use of DIPIC-Frag Untargeted Screening
 Identification of Novel Brominated Disinfection By-Products of Concern in Drinking Water by Use of DIPIC-Frag Untargeted Screening Tena Watts November 9, 2016 Hui Peng, Paul D. Jones & John P. Giesy Title
Identification of Novel Brominated Disinfection By-Products of Concern in Drinking Water by Use of DIPIC-Frag Untargeted Screening Tena Watts November 9, 2016 Hui Peng, Paul D. Jones & John P. Giesy Title
DISINFECTION BY-PRODUCTS (DBPS) IN DRINKING WATER AND THEIR ASSOCIATED HEALTH RISK: A REVIEW
 DISINFECTION BY-PRODUCTS (DBPS) IN DRINKING WATER AND THEIR ASSOCIATED HEALTH RISK: A REVIEW F. Khan & M. F. R Zuthi * Department of Civil Engineering, Chittagong University of Engineering and Technology,
DISINFECTION BY-PRODUCTS (DBPS) IN DRINKING WATER AND THEIR ASSOCIATED HEALTH RISK: A REVIEW F. Khan & M. F. R Zuthi * Department of Civil Engineering, Chittagong University of Engineering and Technology,
1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids
 Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
9/6/2011. Amino Acids. C α. Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups
 Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Lecture 11 AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS
 Lecture 11 AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS The word "Protein" was coined by J.J. Berzelius in 1838 and was derived from the Greek word "Proteios" meaning the first rank. Proteins are macromolecular polymers composed
Lecture 11 AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS The word "Protein" was coined by J.J. Berzelius in 1838 and was derived from the Greek word "Proteios" meaning the first rank. Proteins are macromolecular polymers composed
Formation of emerging DBPs from the chlorination and chloramination of seawater algal organic matter and related model compounds.
 Formation of emerging DBPs from the chlorination and chloramination of seawater algal organic matter and related model compounds Thesis by Maolida Nihemaiti In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements For
Formation of emerging DBPs from the chlorination and chloramination of seawater algal organic matter and related model compounds Thesis by Maolida Nihemaiti In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements For
Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids.
 Today we begin our discussion of the structure and properties of proteins. Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids. Conjugated proteins contain
Today we begin our discussion of the structure and properties of proteins. Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids. Conjugated proteins contain
AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS
 AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine
AMINO ACIDS STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION, PROPERTIES. PRIMARY STRUCTURE OF PROTEINS Elena Rivneac PhD, Associate Professor Department of Biochemistry and Clinical Biochemistry State University of Medicine
Organic Chemistry. Chapter 23. Hill, Petrucci, McCreary & Perry 4 th. Ed. Alkane to Substituent Group methane CH 4 methyl CH 3
 hapter 23 rganic hemistry ill, Petrucci, Mcreary & Perry 4 th Ed. Alkane to Substituent Group methane 4 methyl 3 ethane 3 3 ethyl 3 2 propane 3 2 3 propyl 3 2 2 isopropyl ( 3 ) 2 or 3 3 butyl 3 2 2 2 butane
hapter 23 rganic hemistry ill, Petrucci, Mcreary & Perry 4 th Ed. Alkane to Substituent Group methane 4 methyl 3 ethane 3 3 ethyl 3 2 propane 3 2 3 propyl 3 2 2 isopropyl ( 3 ) 2 or 3 3 butyl 3 2 2 2 butane
Amino acids. You are required to know and identify the 20 amino acids : their names, 3 letter abbreviations and their structures.
 Amino acids You are required to know and identify the 20 amino acids : their names, 3 letter abbreviations and their structures. If you wanna make any classification in the world, you have to find what
Amino acids You are required to know and identify the 20 amino acids : their names, 3 letter abbreviations and their structures. If you wanna make any classification in the world, you have to find what
Page 8/6: The cell. Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products)
 Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Page 8/6: The cell Where to start: Proteins (control a cell) (start/end products) Page 11/10: Structural hierarchy Proteins Phenotype of organism 3 Dimensional structure Function by interaction THE PROTEIN
Biomolecules: amino acids
 Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Lecture 3: 8/24. CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids
 Lecture 3: 8/24 CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids 1 Chapter 3 Outline 2 Amino Acid Are Biomolecules and their Atoms Can Be Visualized by Two Different Ways 1) Fischer projections: Two dimensional representation of
Lecture 3: 8/24 CHAPTER 3 Amino Acids 1 Chapter 3 Outline 2 Amino Acid Are Biomolecules and their Atoms Can Be Visualized by Two Different Ways 1) Fischer projections: Two dimensional representation of
Formation of Halogenated C-, N-DBPs from Chlor(am)ination. and UV Irradiation of Tyrosine in Drinking Water
 1 2 Formation of Halogenated C-, N-DBPs from Chlor(am)ination and UV Irradiation of Tyrosine in Drinking Water 3 Wenhai Chu a, Naiyun Gao a,*, Stuart W. Krasner b, Michael R Templeton c, Daqiang Yin a
1 2 Formation of Halogenated C-, N-DBPs from Chlor(am)ination and UV Irradiation of Tyrosine in Drinking Water 3 Wenhai Chu a, Naiyun Gao a,*, Stuart W. Krasner b, Michael R Templeton c, Daqiang Yin a
cyclobutane Benzene Ring phenyl
 ow many carbons and hydrogens in the following? More rganic Today eview hydrocarbons Functional Groups Condensation eaction Biopolymers A. 6 C, 14 B. 6 C, 15 C. 6 C, 16 3 1 2 D. 7 C, 15 3 1 1 3 E. 7 C,
ow many carbons and hydrogens in the following? More rganic Today eview hydrocarbons Functional Groups Condensation eaction Biopolymers A. 6 C, 14 B. 6 C, 15 C. 6 C, 16 3 1 2 D. 7 C, 15 3 1 1 3 E. 7 C,
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids. Table of a-amino Acids Found in Proteins
 Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Molecular Biology. general transfer: occurs normally in cells. special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions.
 Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Alehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid
 Alehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Aldehydes and Ketones: Introduction Aldedydes and ketones are organic compounds that contain carbon-oxygen doule bonds. The general formula for aldehydes is O C R
Alehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid Aldehydes and Ketones: Introduction Aldedydes and ketones are organic compounds that contain carbon-oxygen doule bonds. The general formula for aldehydes is O C R
Introduction to Proteomics Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay
 Introduction to Proteomics Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay Lecture 01 Introduction to Amino Acids Welcome to the proteomic course.
Introduction to Proteomics Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay Lecture 01 Introduction to Amino Acids Welcome to the proteomic course.
Update on Special Flint Sampling: Flushing and Lead, Disinfection By- Product and Legionella Sampling. U-Mass, Wayne State, Virginia Tech
 Update on Special Flint Sampling: Flushing and Lead, Disinfection By- Product and Legionella Sampling U-Mass, Wayne State, Virginia Tech 1 Forma&on of scale within the distribu&on system Lead-bearing plumbing
Update on Special Flint Sampling: Flushing and Lead, Disinfection By- Product and Legionella Sampling U-Mass, Wayne State, Virginia Tech 1 Forma&on of scale within the distribu&on system Lead-bearing plumbing
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1)
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 7. CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 7. CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR
Reactions and amino acids structure & properties
 Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Lecture 2: Reactions and amino acids structure & properties Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Common Functional Groups Common Biochemical Reactions AH + B A + BH Oxidation-Reduction A-H + B-OH + energy ª A-B + H
Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives
 arboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Families ontaining the arbonyl Group Family Y Z Y Z aldehyde or ketone carboxylic acid or -- ester or -- acid halide or -F,-l,-Br,-I acid anhydride or amide or -N
arboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Families ontaining the arbonyl Group Family Y Z Y Z aldehyde or ketone carboxylic acid or -- ester or -- acid halide or -F,-l,-Br,-I acid anhydride or amide or -N
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles شیمی آلی 2
 Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition The
Chapter 20: Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles شیمی آلی 2 Dr M. Mehrdad University of Guilan, Department of Chemistry, Rasht, Iran m-mehrdad@guilan.ac.ir Based on McMurry s Organic Chemistry, 7 th edition The
Lecture Notes Chemistry Mukund P. Sibi Lecture 31 Reactions at the Alpha-Carbon of Carbonyl Compounds
 Lecture Notes hemistry 342-2008 Mukund P. Sibi eactions at the Alpha-arbon of arbonyl ompounds Enolates are nucleophilic and undergo reaction with electrophiles. For example, one can do halogenation under
Lecture Notes hemistry 342-2008 Mukund P. Sibi eactions at the Alpha-arbon of arbonyl ompounds Enolates are nucleophilic and undergo reaction with electrophiles. For example, one can do halogenation under
Biochemistry - I. Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I
 Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry
 Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Amino acids. (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi
 Amino acids (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi Learning outcomes What are the amino acids? General structure. Classification of amino acids. Optical properties. Amino acid configuration. Non-standard amino
Amino acids (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi Learning outcomes What are the amino acids? General structure. Classification of amino acids. Optical properties. Amino acid configuration. Non-standard amino
Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition- Elimination at the Acyl Carbon
 Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition- Elimination at the Acyl Carbon Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO 2 H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl
Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition- Elimination at the Acyl Carbon Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO 2 H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl
Chapter 18. Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination at the Acyl Carbon
 Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination at the Acyl Carbon Carboxylic Acids Organic compounds characterized by their acidity Contains COOH group (must be at
Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination at the Acyl Carbon Carboxylic Acids Organic compounds characterized by their acidity Contains COOH group (must be at
Risk of Birth Defects in Australian Communities with High Levels of Brominated Disinfection By-products
 Risk of Birth Defects in Australian Communities with High Levels of Brominated Disinfection By-products Kimberly Chisholm, Angus Cook, Carol Bower, & Philip Weinstein Environmental Health Perspectives
Risk of Birth Defects in Australian Communities with High Levels of Brominated Disinfection By-products Kimberly Chisholm, Angus Cook, Carol Bower, & Philip Weinstein Environmental Health Perspectives
Prelab 6: Carboxylic Acids
 The Structure of Carboxylic Acids Prelab 6: Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl functional group attached to a hydrocarbon (alkyl group) part. Carboxyl groups contain both a carbonyl group,
The Structure of Carboxylic Acids Prelab 6: Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl functional group attached to a hydrocarbon (alkyl group) part. Carboxyl groups contain both a carbonyl group,
Org/Biochem Final Lec Form, Spring 2012 Page 1 of 6
 Page 1 of 6 Missing Complete Protein and Question #45 Key Terms: Fill in the blank in the following 25 statements with one of the key terms in the table. Each key term may only be used once. Print legibly.
Page 1 of 6 Missing Complete Protein and Question #45 Key Terms: Fill in the blank in the following 25 statements with one of the key terms in the table. Each key term may only be used once. Print legibly.
Date: EXERCISE 4. Figure 1. Amino acid structure.
 Student s name: Date: Points: Assistant s signature: Index numer: /6 EXERISE 4 AMIN AIDS AND PRTEINS. Amino acids are structural units (monomers) of proteins. There are 20 different amino acids coded for
Student s name: Date: Points: Assistant s signature: Index numer: /6 EXERISE 4 AMIN AIDS AND PRTEINS. Amino acids are structural units (monomers) of proteins. There are 20 different amino acids coded for
Chapter 10. Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives. Naming Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives. Carboxylic Acids: RCOOH (RCO 2 H)
 Chapter 10 Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Naming Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Carboxylic Acids: RCH (RC 2 H) The functional group of a carboxylic acid is a carboxyl group (carbonyl & hydroxyl group)
Chapter 10 Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Naming Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Carboxylic Acids: RCH (RC 2 H) The functional group of a carboxylic acid is a carboxyl group (carbonyl & hydroxyl group)
Proteins are sometimes only produced in one cell type or cell compartment (brain has 15,000 expressed proteins, gut has 2,000).
 Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Fatty acids and phospholipids
 PYS 4xx Intro 2 1 PYS 4xx Intro 2 - Molecular building blocks We now describe in more detail the nomenclature and composition of several classes of compounds of relevance to the cell, including: membrane
PYS 4xx Intro 2 1 PYS 4xx Intro 2 - Molecular building blocks We now describe in more detail the nomenclature and composition of several classes of compounds of relevance to the cell, including: membrane
Section 1 Proteins and Proteomics
 Section 1 Proteins and Proteomics Learning Objectives At the end of this assignment, you should be able to: 1. Draw the chemical structure of an amino acid and small peptide. 2. Describe the difference
Section 1 Proteins and Proteomics Learning Objectives At the end of this assignment, you should be able to: 1. Draw the chemical structure of an amino acid and small peptide. 2. Describe the difference
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins
 Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Amino acids. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester,
 Amino acids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.66-76) General structure (Chiral carbon) The amino acids that occur in
Amino acids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.66-76) General structure (Chiral carbon) The amino acids that occur in
Amino Acid Metabolism
 Amino Acid Metabolism Last Week Most of the Animal Kingdom = Lazy - Most higher organisms in the animal kindom don t bother to make all of the amino acids. - Instead, we eat things that make the essential
Amino Acid Metabolism Last Week Most of the Animal Kingdom = Lazy - Most higher organisms in the animal kindom don t bother to make all of the amino acids. - Instead, we eat things that make the essential
Carboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl Chlorides
 R hemistry A 432 arboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl hlorides arboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl hlorides arboxylic acids contain the functional group, attached to an alkyl stem. They are widely found in nature,
R hemistry A 432 arboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl hlorides arboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl hlorides arboxylic acids contain the functional group, attached to an alkyl stem. They are widely found in nature,
1/3/2011. Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition- Elimination at the Acyl Carbon
 Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO 2 H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl compounds or carboxylic acid derivatives Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic
Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO 2 H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl compounds or carboxylic acid derivatives Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic
DERIVATIVES OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
 13 Rl RH RNH 2 RR RR DERIVATIVES F ARBXYLI AIDS HAPTER SUMMARY 13.1 Structure and Nomenclature of arboxylic Acid Derivatives A. Structure arboxylic acids and their derivatives can be expressed as variations
13 Rl RH RNH 2 RR RR DERIVATIVES F ARBXYLI AIDS HAPTER SUMMARY 13.1 Structure and Nomenclature of arboxylic Acid Derivatives A. Structure arboxylic acids and their derivatives can be expressed as variations
Relative Reactivity of Amino Acids with Chlorine in Mixtures
 Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3220-3225 Relative Reactivity of Amino Acids with Chlorine in Mixtures CHONGZHENG NA AND TERESE M. OLSON* Environmental and Water Resource Engineering, Department of Civil
Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3220-3225 Relative Reactivity of Amino Acids with Chlorine in Mixtures CHONGZHENG NA AND TERESE M. OLSON* Environmental and Water Resource Engineering, Department of Civil
PROTEIN. By: Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM
 PROTEIN By: Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM OBJECTIVES OF THE LECTURE By the end of this lecture, student can: Define
PROTEIN By: Shamsul Azahari Zainal Badari Department of Resource Management and Consumer Studies Faculty of Human Ecology UPM OBJECTIVES OF THE LECTURE By the end of this lecture, student can: Define
H 2 C H 2 N C CH O N C CH 3 CH 2 H O. aspartame
 1 The addition of sucrose, table sugar, to food and drink has been linked to the increased risk of obesity and insulin resistance. Aspartame is used as an alternative to sugar. The structure of aspartame
1 The addition of sucrose, table sugar, to food and drink has been linked to the increased risk of obesity and insulin resistance. Aspartame is used as an alternative to sugar. The structure of aspartame
CS612 - Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Lecture 10 - Protein Turnover and Amino Acid Catabolism
 Lecture 10 - Protein Turnover and Amino Acid Catabolism Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction 2 Proteins are degraded into amino acids. Protein
Lecture 10 - Protein Turnover and Amino Acid Catabolism Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction 2 Proteins are degraded into amino acids. Protein
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids. Introduction
 hapter 20 arboxylic Acids Introduction arbonyl (-=) and hydroxyl (-H) on the same carbon is carboxyl group. arboxyl group is usually written -H or 2 H. Aliphatic acids have an alkyl group bonded to -H.
hapter 20 arboxylic Acids Introduction arbonyl (-=) and hydroxyl (-H) on the same carbon is carboxyl group. arboxyl group is usually written -H or 2 H. Aliphatic acids have an alkyl group bonded to -H.
CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater
 Print version CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater Origins of NOM II Lecture #5 Dave Reckhow - Organics In W & WW Carbohydrates empirical formula: C x (H 2 O) y CH 2 OH H H O H OH H OH OH
Print version CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater Origins of NOM II Lecture #5 Dave Reckhow - Organics In W & WW Carbohydrates empirical formula: C x (H 2 O) y CH 2 OH H H O H OH H OH OH
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy
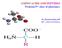 AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
AMINO ACIDS AND PEPTIDES Proteins/3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry MEDICAL AND BIOLOGICAL IMPORTANCE 1. building blocks of proteins. Some amino acids are found in
Recent Developments in Coffee Flavour Formation Using In-Bean Experiments
 23 rd ASIC Conference, Bali (Indonesia), ctober 3-8, 2010 Coffee Chemistry Recent Developments in Coffee Flavour Formation Using In-Bean Experiments L. Poisson, J. Kerler, T. Davidek, and I. Blank (estle
23 rd ASIC Conference, Bali (Indonesia), ctober 3-8, 2010 Coffee Chemistry Recent Developments in Coffee Flavour Formation Using In-Bean Experiments L. Poisson, J. Kerler, T. Davidek, and I. Blank (estle
Disinfection methods and by-products formation
 Desalination and Water Treatment ISSN: 1944-3994 (Print) 1944-3986 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tdwt20 Disinfection methods and by-products formation I. Voukkali & A.A. Zorpas
Desalination and Water Treatment ISSN: 1944-3994 (Print) 1944-3986 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tdwt20 Disinfection methods and by-products formation I. Voukkali & A.A. Zorpas
Tala Saleh. Tamer Barakat. Diala Abu-Hassan
 13 Tala Saleh Tamer Barakat Diala Abu-Hassan Biochemical application of monosodium glutamate MSG MSG is a glutamic acid derivative, used as a flavor enhancer in Asian food. Chinese restaurant syndrome
13 Tala Saleh Tamer Barakat Diala Abu-Hassan Biochemical application of monosodium glutamate MSG MSG is a glutamic acid derivative, used as a flavor enhancer in Asian food. Chinese restaurant syndrome
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination #5: Section Five December 7, Name: (print) Section:
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination #5: Section Five December 7, 2011 Name: (print) Section: alkene < alkyne < amine < alcohol < ketone < aldehyde < amide
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2011 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination #5: Section Five December 7, 2011 Name: (print) Section: alkene < alkyne < amine < alcohol < ketone < aldehyde < amide
AMINO ACIDS NON-ESSENTIAL ESSENTIAL
 Edith Frederika Introduction A major component of food is PROTEIN The protein ingested as part of our diet are not the same protein required by the body Only 40 to 50 gr of protein is required by a normal
Edith Frederika Introduction A major component of food is PROTEIN The protein ingested as part of our diet are not the same protein required by the body Only 40 to 50 gr of protein is required by a normal
Drinking Water Disinfection Byproducs: Review and Approach
 Drinking Water Disinfection Byproducs: Review and Approach to Toxicity Evaluation Gary A. Boorman,1 Vicki Dellarco,2 June K. Dunnick,1 Robert E. Chapin,1 Sid Hunter,3 Fred Hauchman,3 Hank Gardner,4 Mike
Drinking Water Disinfection Byproducs: Review and Approach to Toxicity Evaluation Gary A. Boorman,1 Vicki Dellarco,2 June K. Dunnick,1 Robert E. Chapin,1 Sid Hunter,3 Fred Hauchman,3 Hank Gardner,4 Mike
Amino acids. Dr. Mamoun Ahram and Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan Summer semester,
 Amino acids Dr. Mamoun Ahram and Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan Summer semester, 2017-2018 dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.66-76) General structure
Amino acids Dr. Mamoun Ahram and Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan Summer semester, 2017-2018 dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.66-76) General structure
PHAR3316 Pharmacy biochemistry Exam #2 Fall 2010 KEY
 1. How many protons is(are) lost when the amino acid Asparagine is titrated from its fully protonated state to a fully deprotonated state? A. 0 B. 1 * C. 2 D. 3 E. none Correct Answer: C (this question
1. How many protons is(are) lost when the amino acid Asparagine is titrated from its fully protonated state to a fully deprotonated state? A. 0 B. 1 * C. 2 D. 3 E. none Correct Answer: C (this question
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Biochemistry Lec #1 Dr. Nafith AbuTarboush- (30.6.2014) Amino Acids 1 Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 3 (pp.66-76) Introduction: Biochemistry is two courses; one is
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Biochemistry Lec #1 Dr. Nafith AbuTarboush- (30.6.2014) Amino Acids 1 Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 3 (pp.66-76) Introduction: Biochemistry is two courses; one is
Carboxylic Acids. The Importance of Carboxylic Acids (RCO 2 H)
 Carboxylic Acids The Importance of Carboxylic Acids (RCO 2 H) Starting materials for acyl derivatives (esters, amides, and acid chlorides) Abundant in nature from oxidation of aldehydes and alcohols in
Carboxylic Acids The Importance of Carboxylic Acids (RCO 2 H) Starting materials for acyl derivatives (esters, amides, and acid chlorides) Abundant in nature from oxidation of aldehydes and alcohols in
COO - l. H 3 N C a H l R 1
 COO - l + H 3 N C a H l R 1 Amino acids There are 20 standard amino acids. All proteins are built from the same amino acids. The most important criteria for classification is affinity to water: hydrophilic
COO - l + H 3 N C a H l R 1 Amino acids There are 20 standard amino acids. All proteins are built from the same amino acids. The most important criteria for classification is affinity to water: hydrophilic
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Organic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
 rganic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins No. 1 of 10 1. Which amino acid does not contain a chiral center? (A) Serine (B) Proline (C) Alanine (D) Phenylalanine (E) Glycine
rganic Chemistry - Problem Drill 23: Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins No. 1 of 10 1. Which amino acid does not contain a chiral center? (A) Serine (B) Proline (C) Alanine (D) Phenylalanine (E) Glycine
Charting a New Path To Resolve the Adverse Health Effects of DBPs
 Chapter 1 Downloaded via 148.251.232.83 on November 12, 2018 at 08:26:09 (UTC). See https://pubs.acs.org/sharingguidelines for options on how to legitimately share published articles. Charting a New Path
Chapter 1 Downloaded via 148.251.232.83 on November 12, 2018 at 08:26:09 (UTC). See https://pubs.acs.org/sharingguidelines for options on how to legitimately share published articles. Charting a New Path
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell
 A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
A Chemical Look at Proteins: Workhorses of the Cell A A Life ciences 1a Lecture otes et 4 pring 2006 Prof. Daniel Kahne Life requires chemistry 2 amino acid monomer and it is proteins that make the chemistry
Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]
![Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version]](/thumbs/84/90818314.jpg) Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Earth/matriX: SCIENCE TODAY Towards a New Paradigm in Scientific Notation Patterns of Periodicity among Proteinogenic Amino Acids [Abridged Version] By Charles William Johnson Earth/matriX Editions P.O.
Mass Spectrometry Introduction
 Mass Spectrometry Introduction Chem 744 Spring 2013 What MS is and is not MS is NOT a spectroscopic method. Molecules are not absorbing EM radiation MS is the generation, separation and characterization
Mass Spectrometry Introduction Chem 744 Spring 2013 What MS is and is not MS is NOT a spectroscopic method. Molecules are not absorbing EM radiation MS is the generation, separation and characterization
I) Choose the best answer: 1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine.
 1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine. 2- The egg white protein, ovalbumin, is denatured in a hard-boiled egg. Which of the
1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine. 2- The egg white protein, ovalbumin, is denatured in a hard-boiled egg. Which of the
(65 pts.) 27. (10 pts.) 28. (15 pts.) 29. (10 pts.) TOTAL (100 points) Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring Instructor: Professor Gopal
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Spring 2012 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 1, 2012 Name: (print) GOOD LUCK! Directions: Make sure your examination contains TWELVE total pages
Amino Acids. Amino Acids. Fundamentals. While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an NH. 3 and CO NH 3
 Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Fundamentals While their name implies that amino acids are compounds that contain an 2 group and a 2 group, these groups are actually present as 3 and 2 respectively. They are classified as α, β, γ, etc..
Short polymer. Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond. Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer
 HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
HO 1 2 3 H HO H Short polymer Dehydration removes a water molecule, forming a new bond Unlinked monomer H 2 O HO 1 2 3 4 H Longer polymer (a) Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of a polymer HO 1 2 3
Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
 Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction Biosynthetic pathways for amino acids, nucleotides and lipids
Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction Biosynthetic pathways for amino acids, nucleotides and lipids
Organic. Carbon Chemistry
 Today Organic Carbon Chemistry Organic You know more than you think already What you will need Lewis dot, VSEPR VB, hybrid orbitals, MO electronegativity intermolecular forces Two hurdles we will deal
Today Organic Carbon Chemistry Organic You know more than you think already What you will need Lewis dot, VSEPR VB, hybrid orbitals, MO electronegativity intermolecular forces Two hurdles we will deal
