Outline. Ruminant Nutrition. Digestive Tract Anatomy. Digestive Tract Anatomy Digestion of nutrients AS 1124
|
|
|
- Antonia Jenkins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Outline Ruminant Nutrition Digestive Tract Anatomy Digestion of nutrients AS 1124 Digestive Tract Anatomy Many organic components of feed are in the form of large insoluble molecules, hence has to be broken down Depending on the type of feed animals consume, they are classified as 1- Carnivores consume meat and meat like products 2- Herbivores depend on forages or plat material 3- Omnivores - consume either plant material or animal product Anatomic structure of digestive system vary depending on the feeding habit Carnivores have simple and short Herbivores have most complicated and long Omnivores have intermediated anatomical structure of the gut Digestive system include all organs involved directly or indirectly to the process of reception of feed or food particles, digestion of feed or food nutrients, absorption of digested nutrients & excretion or elimination of waste material. 1- Alimentary tract, or gastrointestinal tract (GIT), or gut or digestive tract: which is a tube that runs from the mouth to anus (mouth, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, and anus). Depending up on this general definition two groups of organs belong to the digestive system. 1
2 2- Accessory digestive organs: these organs involve in indirect manner to digestive process. E.g. liver, pancreas that produce enzymes to or have some help to facilitate the digestion process and are essential components of the digestive system. Digestion is a process whereby large insoluble feed particles are broken to simple, soluble and absorbable particles. Absorption is the passage of the digested nutrients though the mucous membrane into blood circulation or lymph. Three forms digestion 1- Mechanical digestion: the mechanical activities are mastication and the muscular contraction of the gut. This involves mechanical or physical breakdown of feed particles to decrease particle size. 2- Chemical digestion: this refers to digestion brought about by enzymes secreted by the animal in the various digestive juices. Ruminants can convert fibrous food into meat, milk and fiber Do not compete with humans for food supply 3- Microbial digestion: this is also enzymatic, but is brought about by the action of bacteria, protozoa and fungi. Microbes are of special significance in ruminant digestion. In monogastrics microbial activity occurs in the large intestine. Digestive Tract Anatomy Mouth Food is mechanically broken down by chewing (mastication) Saliva starts the digestion process and lubricates the food (no carbohydrase in saliva). No incisors on the upper jaw ruminants chew very little initially but will rechew food later (regurgitate or ruminate) 2
3 Mouth The relative importance of the mouth and its component teeth, lips, tongue, cheeks, salivary glands, varies with species. The function include: 1- Prehension or bring in feed (lips more important in horses and tongue for cattle) 2- Mastication- mechanical digestion accomplished by teeth 3- Insalivation - mixing the feed with saliva Mouth Ruminants are more efficient in grinding grasses and other forages although much of this occurs during rumination. This is due to special modification in that ruminants normally grind the feed by the type of lateral movement of the upper and lower jaw. Some ruminants such as cattle usually swallow small grain seeds with very little chewing, so their grain should be ground or cracked before feeding. Mouth All ruminants ruminate, time spent for rumination depend on the fiber content of the feed. Grazing cattle commonly spend about 8 hours/day for rumination, 8 hr/d for grazing the 8 hrs for rest. Each bolus of feed regurgitated receive a through mastication than during eating. Different phases of rumination: 1- Small boluses are brought to the mouth called regurgitation. The content of the rumen are continually mixed by the rhythmic contraction of its wall, and material at the anterior end is drawn back into the esophagus & returned by a wave of contraction to the mouth. 2- Reswallowing liquids. The bolus regurgitated contain liquid and solid portion, liquid will be squeezed and reswallowed 3- Remastication and reinsalivation. 4- Reswallowing of bolus. This decrease feed physical size. Insalivation Mouth Mixing feed with saliva secreted into the mouth by three pairs of salivary glands. The salivary glands are: 1- Parotid glands - situated in front of each ear. 2- Submaxillary (submandibular) glands - which lie on each side of the lower jaw 3- Sublingual glands - located underneath the tongue. Function of saliva Mouth 1- Facilitate effective mastication and swallowing - softens the feed 2- Saliva contains 99% water, the remaining 1% consists of mucin (mucous materials), inorganic salts, enzyme, lysozymes. Ruminants saliva has lipase. 3- The enzyme lysozyme breaks the cell membrane of different species of bacteria - is important disinfectant 3
4 Mouth 4- Buffering effect: help to neutralize fermentation acid saliva is alkaline and is a source of bicarbonate phosphate buffer which buffer rumen action. Esophagus 5. Saliva has antifrothing agent. Ruminants require fiber for proper digestion which has get pinching effect on the internal environment of reticulo rumen. When ruminants graze on young clover rich pasture or pasture rich in legumes, there will be high production of gases like CH4, CO2, H2 which may not be lost by eructation and the gas is trapped in the rumen in a foam which may result to bloat and death of the animal. Esophagus transports feed from the mouth to the rumen/reticulum. Four compartments Rumen Reticulum Omasum Abomasum. Ruminant Stomach In young ruminants (calves) the 1 st two parts are undeveloped and milk reaching the stomach is channelled to omasum & mainly abomasum through a tube like fold of tissue called oesophageal groove or reticular groove. Because fermentation of milk in foregut is not essential. When young animals start to eat solid food (fibrous feed) the 1st two compartments enlarge until in the adult they comprise 85% of the total capacity of the stomach. The proportion of the 1st two and the last two compartments at three ages New born calf Two months age Adult Rumen and Reticulum Omasum and abomasum
5 Located predominately on the left side. The largest proportion of the stomach called fermentation bags Rumen and reticulum accounts for more than 50 % of the total digestive tract. This large capacity is essential to allow feed retention to give enough time to break cellulose and other complex carbohydrates, done by microbial enzymes. Rumen and reticulum are only separated by a fold in the wall and there is no specific orifice which joins the two organs together. However, there is a considerable difference in the appearance of the wall of the rumen and reticulum. The reticulo-rumen provides a continuous culture system for anaerobic bacteria, protozoa, and some fungi that produce enzymes that hydrolyse various nutrients. Rumen contents contain 85-93% water on average, but they often exist in two phases. A lower liquid phase, in which fine feed particles are suspended and a drier upper layer of coarse solid material (floating fibrous food). Bacteria and protozoa are responsible for fermentation in the reticulo-rumen. Bacteria number per ml of rumen content Protozoa number 10 6 ml rumen Number of microbes is variable depending diet type. High concentrate feed decreases number of protozoa due to low rumen ph (5.5. to 6.5 is an ideal ph for bacteria and protozoa) The waste products from the bacteria are called VFA's (volatile fatty acids: acetic, propionic and butyric acids), and these are absorbed through the rumen wall (villi) into the animal's bloodstream. These VFA's provide energy for the animal to live on and are the only nutrient absorbed through the rumen. Proportion of bacterial species also change with diet type. 5
6 A by-product of microbial fermentation is methane gas. Methane is released by belching but if this process is impeded then bloat occurs. 50 gallon capacity bolus (cud) is formed by the reticulum cud is forced up the esophagus and back into the mouth cud is thoroughly chewed and reswallowed rumen is ph neutral, so regurgitation is not bitter Due to the honeycomb structure of the reticulum, foreign objects will lodge there. If these objects puncture the reticulum, then a situation called hardware disease occurs. Calves, lambs and kids are functional nonruminants. Milk flows directly from the esophagus to the abomasum by means of an esophageal groove. Rumen fermentation is inefficient use of high-quality feed such as milk. Rumen contains A lot of small infoldings to increase the internal surface area Small projections in internal side of rumen called rumen papillae Running from side to side across the rumen are a series of muscular pillars capable of contraction. The rhythmic movement of these pillars causes the whole rumen to contract and expand leading to a through mixing of its contents. Reticulum Reticulum is most cranial compartment, honeycomb like Location is just behind the heart. Materials enter the rumen from oesophagus at the junction of rumen & reticulum. For this reason foreign bodies such as stone or nails accumulate in the reticulum & is in a very good position to penetrate into the heart. Materials passes freely between the rumen and reticulum, so they are often considered being parts of one large organ, termed the reticulo- rumen. 6
7 Omasum Omasum Digesta leaves the reticulo-rumen though a small passage called the reticulo-omasal orifice, and enters omasum which is about 6% of digestive tract in capacity. The omasum is located to right of rumen & reticulum just caudal to liver. Omasum Contains leaf like structure or folding (manyplies) that increase the internal surface area. Abomasum Water is absorbed from the digesta as it passes through the omasum. So the content of omasum is dry. Omasum contains short, blunt papillae which help in physical degradation as they are in constant motion Abomasum Small Intestine The omaso-abomasal orifice leads to abomasum from omasum, which is about 8% of gut capacity. The abomasum, often called the true stomach, secretes hydrochloric acid, which is a strong acid that begins chemical digestion and also kills bacteria. This is more or less equivalent in function to stomach of monogastric animals. 7
8 Small Intestine The small intestine is where most digestion occurs (by enzymes secreted into the small intestine) of everything except fiber. More importantly, the small intestine is where nutrients such as amino acids are absorbed into the bloodstream. Any nutrients that are not absorbed into the bloodstream are lost in the feces! Small Intestines The microorganisms (bacteria and protozoa) that pass from the rumen and destroyed by the strong acids in the abomasum are digested in the small intestines. The digested microorganisms provide amino acids and energy Cecum Cecum In the cecum, fiber can be fermented (digested) if it was not digested the first time in the rumen. That means ruminants have "two shots" at digesting fiber! Fiber digestion in the cecum is also by microbes; no animals can digest fiber unless microbes are there to do it for them. Large Intestine Large Intestine In the large intestine, some fermentation occurs. Mostly what happens is that water is absorbed back into the animal's body. 8
9 Digestive Pathway mouth esophagus rumen/reticulum abomasum small intestine omasum regurgitated, rechewed reensalivated, reswallowed cecum --- anus rumen/reticulum large intestine rectum A lot of digestion take place in the ruminant stomach, as well as at different sites of the gut. To study these processes researchers do surgical modification or surgical opening at different sites of the gut Such studies will help to understand how digestion takes place, and to device means for more efficient digestion and better productivity. 1. Rumen fistulation Make small hole or opening on the rumen and fix it with fistula. Make opening between the hip bone and lumbar vertebrae which you find rumen. This special point is called paralumbar fosa. Open skin next rumen, join the side of the outer skin and the rumen and fix the outer skin to internal rumen. When fixed it is permanent opening to be used for study. 9
10 2. Oesophageal fisula This is fistula on the oesophagus. Farm animals are selective eaters. We find many plant species on grazing land. To exactly know what type of plant species animal eat & their nutritive value, when animal grazes & swallows representative samples could be taken through oesophageal fistula. 3. Tracheal fistula Fermentation in the reticulo-rumen produce different gases. To study the quantity of these gases, measure gas exhaled through nose and mouth. But the gases coming through mouth and nose are mixture from reticulo-rumen and lungs. To separate gases of the two origin, tracheal fistula is made, whereby the trachea leads to lungs and oesophagus to GIT. Gas from lungs goes through opening while gases from oesophagus goes through mouth and nose. 4. Abomasal and intestinal cannulas Are tubes fitted to any part of gut. You may fit one point of cannula at the abomasum other at the duodenum or you may fit both points in the small intestine and can measure different things such as flow of digesta across the gut, how much nutrients digested, etc. Digestion of carbohydrates in the reticulo-rumen (Fermentation of carbohydrates) This is important as ruminants depend upon diets rich in carbohydrates, thus carbohydrate degradation impact utilisation of feeds. Carbohydrates in diet of ruminats include cellulose, hemicellulose, starch & water soluble carbohydrates (fructans, pentosans, xylans) Type of carbohydrates Structural Carbohydrates Include cellulose, and hemicellulose It is the support structure of the plant Nonstructural Carbohydrates Digestion of carbohydrates in the rumen may be divided into two stages. 1. Digestion of complex carbohydrates into simple sugars Cellulose Hemicellulose Starch Pectin Glucose Composed primarily of sugar, starch, and pectin. 10
11 2. The simple sugars are metabolised by intracellular enzymes of micro-organisms. Simple sugars Pyruvate Under aerobic condition pyruvate oxidised to CO 2 and H 2 O Under anaerobic environment of the rumen, pyruvate is oxidised to VFA. The main VFA are acetic, propionic and butyric acids, and gasses CO2 and methane. Volatile Fatty Acids (VFA's) Much VFA (>90%) is absorbed through rumen, retiulum and omasal walls. Rest through lower gut Acetic acid is used as a source of energy and synthesis of fatty acids. Propionic acid is mainly changed into glucose in the liver may serve for energy and fatty acids synthesis. Butyrate also serves as source of energy and fatty acids synthsesis. Stage 1 Digestion of protein in the reticulo-rumen Rumen microbes synthesise protein from proteins, non protein nitrogen ( NPN) such as urea, uric acid, etc. Monogastric animals could only utilise true protein Stage 2 Food proteins Peptides Extracellular microbial proteases Amino acids Ammonia + VFA Intracellular microbial deaminases Digestion of protein in the reticulo-rumen Ammonia + small peptides + amino acids is utilised to synthesise microbial proteins. Microbes are carried through to the abomasum and small intestine, will be digested and absorbed as amino acids. Microbes synthesize essential and nonessential amino acids, thus the host not need dietary supplies of the former. Digestion of protein in the reticulo-rumen Because of forgut fermentation, ruminants are provided with two major sources of proteins. 1. The protein synthesised by the microbes (microbial protein) 2. The UDP, which escapes microbial digestion in the rumen. Digestion of these two mixtures of microbial protein & UDP in the abomasum and small intestine supplies the amino acid for the host animal. 11
12 12
Ruminant Digestion 8/7/2014 1
 Ruminant Digestion 8/7/2014 1 Different Digestive Systems The three different types of digestive systems are: Monogastric Modified Monogastric Ruminant 8/7/2014 2 A few animals with ruminant digestive
Ruminant Digestion 8/7/2014 1 Different Digestive Systems The three different types of digestive systems are: Monogastric Modified Monogastric Ruminant 8/7/2014 2 A few animals with ruminant digestive
Rumenology 101. Dr. Matt Hersom Dept. of Animal Sciences, UF-IFAS
 Rumenology 101 Dr. Matt Hersom Dept. of Animal Sciences, UF-IFAS Ruminants are cool. They have a diverse body size from the small mouse deer that weighs 4 to 11 lbs and stands 14 inches tall to the giraffe
Rumenology 101 Dr. Matt Hersom Dept. of Animal Sciences, UF-IFAS Ruminants are cool. They have a diverse body size from the small mouse deer that weighs 4 to 11 lbs and stands 14 inches tall to the giraffe
AF 1201 Digestive System. Dr. A.M.J.B. Adikari Dept. of Animal and Food Sciences
 AF 1201 Digestive System Dr. A.M.J.B. Adikari Dept. of Animal and Food Sciences Complex / Compound Stomach Large structure, located on the left side 4 parts Rumen, Reticulum, Omasum Abomasum Fore stomach
AF 1201 Digestive System Dr. A.M.J.B. Adikari Dept. of Animal and Food Sciences Complex / Compound Stomach Large structure, located on the left side 4 parts Rumen, Reticulum, Omasum Abomasum Fore stomach
The digestion system and nutrient requirements
 Principles of nutrition 1 TechNote 1 The digestion system and nutrient requirements IN THIS TECHNOTE 1.1 Functions of the ruminant digestive system 1.2 Requirements of the dairy cow 1.3 Further reading
Principles of nutrition 1 TechNote 1 The digestion system and nutrient requirements IN THIS TECHNOTE 1.1 Functions of the ruminant digestive system 1.2 Requirements of the dairy cow 1.3 Further reading
The four stomachs of a dairy cow
 The four stomachs of a dairy cow Left side view 1) Rumen 2) Reticulum 3) Omasum 4) Abomasum Reticulo-omasal orifice (reticulo-rumen exit) (on the right side of the cow) (on the right side of the cow) Esophagus
The four stomachs of a dairy cow Left side view 1) Rumen 2) Reticulum 3) Omasum 4) Abomasum Reticulo-omasal orifice (reticulo-rumen exit) (on the right side of the cow) (on the right side of the cow) Esophagus
Chapter 2 Anatomy of Digestive System of Dairy Animals: digestion, absorption and utilization of different nutrients
 Chapter 2 Anatomy of Digestive System of Dairy Animals: digestion, absorption and utilization of different nutrients OBJECTIVE 1. To study the different organs and their role in digestion and absorption
Chapter 2 Anatomy of Digestive System of Dairy Animals: digestion, absorption and utilization of different nutrients OBJECTIVE 1. To study the different organs and their role in digestion and absorption
Unit Title: Digestive Systems. Instructor: Ms. Hutchinson. Objectives: After completion of this unit of instruction, students will:
 Course: Livestock Production TEKS: 130.3(c)(5)(a) Unit Title: Digestive Systems Instructor: Ms. Hutchinson Objectives: After completion of this unit of instruction, students will: A. Define what a digestive
Course: Livestock Production TEKS: 130.3(c)(5)(a) Unit Title: Digestive Systems Instructor: Ms. Hutchinson Objectives: After completion of this unit of instruction, students will: A. Define what a digestive
Unit C: Meeting Nutritional Needs of Animals. Lesson 2: Understanding Animal Digestion
 Unit C: Meeting Nutritional Needs of Animals Lesson 2: Understanding Animal Digestion Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives:
Unit C: Meeting Nutritional Needs of Animals Lesson 2: Understanding Animal Digestion Student Learning Objectives: Instruction in this lesson should result in students achieving the following objectives:
Monogastric. SIMPLE stomach Examples PIGS HUMANS
 Monogastric SIMPLE stomach Examples PIGS HUMANS Mouth, part of digestive system. The mouth contains the TEETH, TONGUE, and SALIVARY GLAND. Chewing action or MASTICATION. Food is cut and torn in the mouth,
Monogastric SIMPLE stomach Examples PIGS HUMANS Mouth, part of digestive system. The mouth contains the TEETH, TONGUE, and SALIVARY GLAND. Chewing action or MASTICATION. Food is cut and torn in the mouth,
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
Animal Digestion and Nutrition. Objective 7.02: Understand the digestive process
 Animal Digestion and Nutrition Objective 7.02: Understand the digestive process RUMINANTS Ruminant Animals Animals with complex digestive systems Capable of digesting material with a high fiber concentration
Animal Digestion and Nutrition Objective 7.02: Understand the digestive process RUMINANTS Ruminant Animals Animals with complex digestive systems Capable of digesting material with a high fiber concentration
2015 SENIOR DIGESTIVE
 2015 SENIOR DIGESTIVE EASY 2495 (easy) TH190/HIH705-1 Q: In reference to digestion, describe 2 main functions of the horse's mouth. A: Intake food, chew food, wet food with saliva 2496 (easy) TH93/HIH405-1,2
2015 SENIOR DIGESTIVE EASY 2495 (easy) TH190/HIH705-1 Q: In reference to digestion, describe 2 main functions of the horse's mouth. A: Intake food, chew food, wet food with saliva 2496 (easy) TH93/HIH405-1,2
Proceedings, The Range Beef Cow Symposium XXI December 1, 2 and , Casper, WY. Rumen Physiology for the Rancher
 Proceedings, The Range Beef Cow Symposium XXI December 1, 2 and 3 2009, Casper, WY Rumen Physiology for the Rancher Ivan G. Rush Beef Specialist Emeriti, University of Nebraska Panhandle Research and Extension
Proceedings, The Range Beef Cow Symposium XXI December 1, 2 and 3 2009, Casper, WY Rumen Physiology for the Rancher Ivan G. Rush Beef Specialist Emeriti, University of Nebraska Panhandle Research and Extension
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION
 Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Chapter 21 NUTRITION AND DIGESTION Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion: The act of eating. Usually involves placing food in mouth or oral cavity. 2. Digestion: Macromolecules in food (fats, proteins,
Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2015 page 1 of 7 Assessment Schedule 2015 Demonstrate understanding of biological relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement ONE NØ N1 N2 A3 A4 M5
Human Biology. Digestive System
 Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Human Biology Digestive System Digestion - Defined Prepares food for use by all body cells The physical and/or chemical breakdown of food Did you know: the average person eats more than 500kg of food per
Ch41 Animal Nutrition
 Ch41 Animal Nutrition Digestive system Purpose = break down food into smaller nutrients to be used in the body for energy and raw materials for biosynthesis Overview of food processing Ingestion: act of
Ch41 Animal Nutrition Digestive system Purpose = break down food into smaller nutrients to be used in the body for energy and raw materials for biosynthesis Overview of food processing Ingestion: act of
Unit 2: Animals on the land
 GCSE Animal Nutrition Unit 2: Animals on the land For first teaching from September 2013 For first award in Summer 2015 Animal Nutrition Learning Outcomes At the end of this unit students should be able
GCSE Animal Nutrition Unit 2: Animals on the land For first teaching from September 2013 For first award in Summer 2015 Animal Nutrition Learning Outcomes At the end of this unit students should be able
10/23/2013 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body
 Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
Digestive System What is Digestion? The break down of food into molecules that are small enough to be absorbed and used by the body What is Digestion? This involves: Ingestion and propulsion of food along
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
10/18/2017 ANIMAL NUTRITION ANIMAL NUTRITION ESSENTIAL NUTRIENTS AN ANIMAL S DIET MUST STUPPLY: AMINO ACIDS
 ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
ANIMAL NUTRITION Food is taken in, taken apart, and taken up in the process of animal nutrition In general, animals fall into three categories: Herbivores Carnivores Omnivores ANIMAL NUTRITION Chapter
Animal Digestion and Nutrition
 Animal Digestion and Nutrition Competency: Analyze the parts and functions of the digestive system of farm animals By : ARI WIBOWO, S.Pt.,M.Si & SUHARDI, S.Pt.,MP Ruminants Objective: Describe the function
Animal Digestion and Nutrition Competency: Analyze the parts and functions of the digestive system of farm animals By : ARI WIBOWO, S.Pt.,M.Si & SUHARDI, S.Pt.,MP Ruminants Objective: Describe the function
Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41. Nutritional Requirements pp Essential Amino Acids p.939. Essential Fatty Acids p.
 Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41 Nutritional Requirements pp.939-941 Diets for animals must satisfy three needs : 1. Metabolic fuel Energy needed to do cellular work. E.g. glucose 2. Materials for
Topic 10: Nutrition & Digestion Ch. 41 Nutritional Requirements pp.939-941 Diets for animals must satisfy three needs : 1. Metabolic fuel Energy needed to do cellular work. E.g. glucose 2. Materials for
Digestive System. How your body obtains nutrients. Wednesday, March 2, 16
 Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System How your body obtains nutrients Vocabulary Ingestion: food enters the system Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins Digestion: Further breakdown Chemical/enzymatic Vocabulary Absorption:
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System. Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy
 Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Digestive System Why do we need to eat? Growth Maintenance (repair tissue) Energy Nutrients Nutrient = chemical that must be obtained by an organism from it s environment in order to survive; nutrients
Animal Anatomy and Physiology Part 2. By : ARI WIBOWO, S.Pt.,M.Si & SUHARDI, S.Pt.,MP
 Animal Anatomy and Physiology Part 2 By : ARI WIBOWO, S.Pt.,M.Si & SUHARDI, S.Pt.,MP Digestive System Ruminant System Rumen Largest compartment Food is soaked, mixed. Microorganisms ferment the feed. Carbohydrates
Animal Anatomy and Physiology Part 2 By : ARI WIBOWO, S.Pt.,M.Si & SUHARDI, S.Pt.,MP Digestive System Ruminant System Rumen Largest compartment Food is soaked, mixed. Microorganisms ferment the feed. Carbohydrates
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Animal Nutrition. Chapter 41. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Chapter 41 Animal Nutrition PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp
Lesson Overview The Digestive System
 30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
30.3 THINK ABOUT IT The only system in the body that food actually enters is the digestive system. So how does food get to the rest of the body after the process of digestion? Functions of the Digestive
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Digestion. I. What is digestion? II. Enzymes involved in digestion
 Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
Overview. Herbivore Digestive Anatomy. Herbivory. Fraction of Primary Production Consumed By Various Herbivores
 Herbivore Digestive Anatomy Integrated Rangeland Management REM 456 Sergio Arispe, Ph.D. Overview Comparative Digestive Anatomy Herbivory Anatomy Digestive End-Products Foregut Fermenters http://www.lelylife.com
Herbivore Digestive Anatomy Integrated Rangeland Management REM 456 Sergio Arispe, Ph.D. Overview Comparative Digestive Anatomy Herbivory Anatomy Digestive End-Products Foregut Fermenters http://www.lelylife.com
Learning Targets. The Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract. Also known as the alimentary canal. Hollow series of organs that food passes through
 Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
Digestion the multistep process of breaking down food into molecules the body can use Learning Targets Describe the path food takes through the digestive system. Identify the major organs of the digestive
The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION
 ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
ABSORPTION AS RELATED TO DIGESTION The process by which nutrient molecules pass through the wall of your digestive system into your blood. 3 FUNCTIONS OF DIGESTION Breaks down food into molecules the body
The digestive tract of the pig
 The digestive tract of the pig 2010-11-26 J.P. Rowan1, K.L. Durrance2, G.E. Combs3 and L.Z. Fisher4 1Extension Agent - Agriculture, 4-h, Suwannee County 2professor, Animal Science Department 3professor,
The digestive tract of the pig 2010-11-26 J.P. Rowan1, K.L. Durrance2, G.E. Combs3 and L.Z. Fisher4 1Extension Agent - Agriculture, 4-h, Suwannee County 2professor, Animal Science Department 3professor,
All nutrients fall into one of; proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins and minerals
 Essential nutrients; - must be supplied to an animal because the animal cannot synthesise them - needed to satisfy the requirements of its cells * if the amount of essential nutrients supplied is insufficient
Essential nutrients; - must be supplied to an animal because the animal cannot synthesise them - needed to satisfy the requirements of its cells * if the amount of essential nutrients supplied is insufficient
Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root. Tooth type and job. Why do humans have more than one type of tooth?
 Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
Tooth type and job Enamel Dentine Pulp cavity nerves & blood vessels Gums & Bone Crown & root Be able to sketch & label this Tooth type and job Why do humans have more than one type of tooth? Omnivores
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Composed of two parts: 1. 2. There are 4 main parts of digestion: 1. Ingestion: 2. Digestion: a. Mechanical Digestion: Example: b. Chemical Digestion: Example: 3. Absorption: 4. Egestion:
Characteristics of living organism
 At a glance : Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Living organisms are bundles of cells that carry out specialized functions. 1. Life is uncertain because Organic Matter is born, it Organic / Biotic Matter
At a glance : Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Living organisms are bundles of cells that carry out specialized functions. 1. Life is uncertain because Organic Matter is born, it Organic / Biotic Matter
Rumination or cud chewing consists of regurgitation, remastication, reinsalvation, and reswallowing.
 Nutrition 115 Midterm Exam 2 February 25, 2000 Name Please be sure to put your name at the top of each page. Any page without a name in the appropriate place will not be graded. Read each question carefully,
Nutrition 115 Midterm Exam 2 February 25, 2000 Name Please be sure to put your name at the top of each page. Any page without a name in the appropriate place will not be graded. Read each question carefully,
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Grass to Glass Amazing Dairy Cows
 Purpose: Students learn how the complex digestive system of dairy cows allows these animals to eat grass and other forages to produce milk for humans to drink. Time: 60 min Level: 3-6 Materials: Diagram
Purpose: Students learn how the complex digestive system of dairy cows allows these animals to eat grass and other forages to produce milk for humans to drink. Time: 60 min Level: 3-6 Materials: Diagram
Department of Animal Science; University of Nebraska; Lincoln, NE
 BASICS OF RUMINANT ANIMAL NUTRITION Pablo L. Loza, MS and Jess L. Miner, PhD* Department of Animal Science; University of Nebraska; Lincoln, NE 68583-0908 Introduction Cellulose is the main constituent
BASICS OF RUMINANT ANIMAL NUTRITION Pablo L. Loza, MS and Jess L. Miner, PhD* Department of Animal Science; University of Nebraska; Lincoln, NE 68583-0908 Introduction Cellulose is the main constituent
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System What is the digestive system? The digestive system is where the digestion of food and liquids occurs. Our bodies are not suited to absorbing the energy contained in food as they are
The Digestive System What is the digestive system? The digestive system is where the digestion of food and liquids occurs. Our bodies are not suited to absorbing the energy contained in food as they are
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
NURSE-UP DIGESTIVE SYSTEM AKA G.I. SYSTEM The digestive system is used for breaking down food into nutrients which then pass into the circulatory system and are taken to where they are needed in the body.
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 1. The Teeth 5/18/2015
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
U S C on, hns Jo a elin C
 What do animals eat? What do feeds provide? What is a nutrient? Chemical substance that provides Chemical substance that provides nourishment for the body What types of nutrients are there? What types
What do animals eat? What do feeds provide? What is a nutrient? Chemical substance that provides Chemical substance that provides nourishment for the body What types of nutrients are there? What types
1 The Digestive System
 CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
CHAPTER 24 1 The Digestive System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What are the parts of the digestive
e. Undigested material is compacted and stored until the colon is full. When the colon is full, a signal to empty it is sent by sensors in the walls
 Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
The Digestive System. Basic process of digestion. Mouth and Teeth 10/30/2016
 The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
The Digestive System Basic process of digestion 1. Ingestion: animal eats food. 2. Digestion: animal body breaks food down. Mechanical digestion: chewing (mastication). Chemical digestion: enzymes and
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013
 HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
HUMAN NUTRITION 08 MAY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we: Study the structure of the human digestive system Look at the processes used in the human digestive system Look at the two different types
UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If you know what is
UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If you know what is
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis but needs source of nitrogen
 All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
All organisms must obtain and process essential nutrients (food) AUTOTROPHS self feeder makes their own food eg. Plants do not require a digestive tract *** Exception: Venus Fly Traps undergo photosynthesis
The horse's digestive system
 The horse's digestive system The horse is a nonruminant herbivore. Non-ruminant means that horses do not have multi-compartmented stomachs as cattle do. Instead, the horse has a simple stomach that works
The horse's digestive system The horse is a nonruminant herbivore. Non-ruminant means that horses do not have multi-compartmented stomachs as cattle do. Instead, the horse has a simple stomach that works
7.4 Digestion. Highlight the definition of mechanical digestion.
 7.4 Digestion Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The large food molecules are starch,
7.4 Digestion Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. The large food molecules are starch,
Digestive Systems of Livestock. A basic Look. To understand the basic anatomy of livestock digestive systems.
 Digestive Systems of Livestock A basic Look Goal: To understand the basic anatomy of livestock digestive systems. Objectives: To understand methods of prehension. To understand the different types of digestive
Digestive Systems of Livestock A basic Look Goal: To understand the basic anatomy of livestock digestive systems. Objectives: To understand methods of prehension. To understand the different types of digestive
UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Slide 1 UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Slide 2 Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If
Slide 1 UNDERSTANDING THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Slide 2 Understanding Digestion The key to solving food and digestive issues starts with an understanding of how the digestive and intestinal system works If
The Digestive System. Parts and Functions
 The Digestive System Parts and Functions Mechanical Digestion A process of digestion in which food is cut, torn, mashed, and churned into smaller bits. This process starts in the mouth and ends in the
The Digestive System Parts and Functions Mechanical Digestion A process of digestion in which food is cut, torn, mashed, and churned into smaller bits. This process starts in the mouth and ends in the
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
SNC4M The Digestive System
 SNC4M The Digestive System What is digestion? Chemical and mechanical breakdown of organic molecules into units small enough for the body to absorb These molecules provide: 1. Energy resources 2. Essential
SNC4M The Digestive System What is digestion? Chemical and mechanical breakdown of organic molecules into units small enough for the body to absorb These molecules provide: 1. Energy resources 2. Essential
Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929)
 NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
NCEA Level 1 Biology (90929) 2017 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2017 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of biological ideas relating to a mammal(s) as a consumer(s) (90929) Evidence Statement QUESTION
* Produces various chemicals to break. down the food. * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes
 * * Produces various chemicals to break down the food * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes * *Mouth *Pharynx *Oesophagus *Stomach *Small and large intestines * *Changes the physical
* * Produces various chemicals to break down the food * Filters out harmful substances * Gets rid of solid wastes * *Mouth *Pharynx *Oesophagus *Stomach *Small and large intestines * *Changes the physical
Nutrition. Why do humans need food? How do some animals get their food? ROUGHAGE NUTRIENTS. Animals make energy available using:
 Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
Nutrition the activities by which organisms Why do humans need food? Animals make energy available using: obtain and process material needed for energy, growth, repair, and to maintain homeostasis humans
Digestive System Practice Test
 Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
Name: Class Period: Section 1: Digestive System Practice Test Directions: Match the items in Column B to the definitions or explanations offered in Column A. Write the matching letter, on the line provided
UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM.
 1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
1 UNIT 3. DIGESTIVE AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 2 1. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1) Which are the relationships between cellular respiration and the systems that perform nutrition in human body? Digestive system processes
Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes
 Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes In a nutshell... The body uses a variety of small molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, glucose) for its metabolic needs. Food is mechanically and chemically
Biology 12 - The Digestive System - Chapter Notes In a nutshell... The body uses a variety of small molecules (amino acids, fatty acids, glucose) for its metabolic needs. Food is mechanically and chemically
1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals a) Suspension feeders i) (1) Humpback whales b) Substrate feeders i)
 1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
1 AP Biology March 2008 Digestion Chapter 41 Homeostatic mechanisms manage an animal s energy budget. 1) Four main feeding mechanisms of animals Suspension feeders (1) Humpback whales Substrate feeders
1 ANIMALS Digestive System Oral Cavity and Esophagus.notebook January 06, 2016
 The Human Digestive System 1 The Human Digestive System 2 You are a tube inside a tube 3 The Digestive System The Four Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion the taking in or eating of food 2. Digestion
The Human Digestive System 1 The Human Digestive System 2 You are a tube inside a tube 3 The Digestive System The Four Stages of Food Processing 1. Ingestion the taking in or eating of food 2. Digestion
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
The Digestive System s Big Book of Handouts Digestion and nutrition Specific Learning outcomes B11-2-01: Identify major structures and functions of the human digestive system from a diagram, model, or
4/8/16. Digestive System. When you are hungry it is because your brain receives a signal from your cells that they need energy
 When you are hungry it is because your brain receives a signal from your cells that they need energy Section 1 Digestive System A group of organs that work together to digest food so that it can be used
When you are hungry it is because your brain receives a signal from your cells that they need energy Section 1 Digestive System A group of organs that work together to digest food so that it can be used
Goals. The Hindgut 4/10/2014. Equine Digestive Tract. Week 2 Lecture 4
 Equine Digestive Tract Week 2 Lecture 4 Clair Thunes, PhD Animal Science 126 Equine Nutrition Goals Know the main anatomical sections of the hindgut, their functions and purpose Sites of potential impactions
Equine Digestive Tract Week 2 Lecture 4 Clair Thunes, PhD Animal Science 126 Equine Nutrition Goals Know the main anatomical sections of the hindgut, their functions and purpose Sites of potential impactions
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1. Digestion 101 & H.O.P.E.
 Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
Digestive Care Advisor Training #1 & H.O.P.E. The Digestive System in Brief The Process of Digestion The human digestive system is a complex series of organs and glands that process food and excrete waste.
Monday, October Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page.
 1. Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page. 2. Answer the following question on the same page: How do proteins, lipids and carbs impact
1. Pick up a little man from the front table. Color and glue it into your journal on the next available page. 2. Answer the following question on the same page: How do proteins, lipids and carbs impact
CARBOHYDRATES. Created for BCLM Pony Club Nutrition #14
 CARBOHYDRATES Created for BCLM Pony Club Nutrition #14 Carbohydrates Collective term for starches, sugars and dietary fibres The dietary fibres are cellulose and hemicellulose Glycogen is how energy is
CARBOHYDRATES Created for BCLM Pony Club Nutrition #14 Carbohydrates Collective term for starches, sugars and dietary fibres The dietary fibres are cellulose and hemicellulose Glycogen is how energy is
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes
 Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Animal Nutrition. Key Concepts. Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms. What do animals get from food?
 Key Concepts Animal Nutrition Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Key Concepts Animal Nutrition Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Key Concepts. Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory
 Animal Nutrition Key Concepts Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
Animal Nutrition Key Concepts Why eat? Eat what? Design of digestive systems Processing steps and their hormonal control Challenge of herbivory Animals are heterotrophs, obtain nutrition from other organisms
The Digestive System. 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers
 I. Type of food: The Digestive System 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers 1- Carbohydrates: are energy foods (sugars). They are made of C,H, and O atoms. They
I. Type of food: The Digestive System 1- Carbohydrates 2- Proteins 3- Lipids 4- Water 5- Vitamins 6- Minerals 7- Fibers 1- Carbohydrates: are energy foods (sugars). They are made of C,H, and O atoms. They
Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating
 Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating Types of teeth Preventing tooth decay Dentition of other animals Digestive system By the end of this unit you should: Know the structure, function and care of the human teeth.
Unit 6L.4: Teeth and Eating Types of teeth Preventing tooth decay Dentition of other animals Digestive system By the end of this unit you should: Know the structure, function and care of the human teeth.
Human Digestion. Junior Science
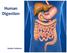 Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
The Human Digestive Tract
 The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
The Human Digestive Tract The Mouth salivary glands (parotid, sublingual, submaxillary) - produces saliva --->lubricate food ---> dissolves food particles ---> allows us to taste food --->contains amylase
Digestion of the Bison
 Digestion of the Bison Roll Call: Because the stomachs of the ruminant and monogastric animals are so different, their diets also vary. Let's compare the diets. Tell me what foods each of these animals
Digestion of the Bison Roll Call: Because the stomachs of the ruminant and monogastric animals are so different, their diets also vary. Let's compare the diets. Tell me what foods each of these animals
Name Date Class. 2. Is the following sentence true or false? Food is required for the body to. maintain homeostasis, keeping a steady internal state.
 CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
CHAPTER 11 FOOD AND DIGESTION SECTION 11 1 Food and Energy (pages 370-380) This section tells about the six nutrients needed by the body. It also describes the Food Guide Pyramid and how to read labels
Modified Monogastric Digestive System
 Modified Monogastric Digestive System Digestive System of the Horse 8/7/2014 1 The Digestive Tract Horses and rabbits are modified monogastric herbivores. Horses are able to utilize large amounts of roughage
Modified Monogastric Digestive System Digestive System of the Horse 8/7/2014 1 The Digestive Tract Horses and rabbits are modified monogastric herbivores. Horses are able to utilize large amounts of roughage
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
The Digestive System
 Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Digestive System 1 Name The Digestive System Purpose: To describe how food moves through the digestive system. To identify the parts of the digestive system. Background Information: Food provides us with
Harvesting energy from food. Digestion: A Closer Look. Where digestion begins. Salivary Glands 4/17/13. Or how food gets from
 Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010
 DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
DIGESTION SBI 3C: NOVEMBER 2010 DIAGRAM OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEM: Mouth Esophagus Liver Gallbladder Large Intestine Appendix Stomach Pancreas Small Intestine Rectum Anus STAGES OF DIGESTION: 1. INGESTION Taking
1. Three Main Functions. Chapter 19: 2. Two Groups of digestive organs. 2. Two Groups of digestive organs 6/1/2015. The Wall of the Digestive Tract
 1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
1. Three Main Functions Chapter 19: General Structure and Function of the Digestive System Digestion-breakdown of food into small particles for transport to blood Absorption- into bloodstream to take to
Weeks: Dates: 3/23 4/17 Unit: Animal Nutrition
 Name: clementaged.weebly.com Period: Weeks: 31 33 Dates: 3/23 4/17 Unit: Animal Nutrition Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 23 E *Vocabulary *Intro to Dig. Systems *digestive System Diagrams 30
Name: clementaged.weebly.com Period: Weeks: 31 33 Dates: 3/23 4/17 Unit: Animal Nutrition Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday 23 E *Vocabulary *Intro to Dig. Systems *digestive System Diagrams 30
Glencoe Health. Lesson 3 The Digestive System
 Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
Glencoe Health Lesson 3 The Digestive System Health espotlight Video BIG IDEA The digestive system provides nutrients and energy for your body through the digestion of food. New Vocabulary mastication
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
Digestive System Anatomy
 Digestive System Anatomy The Process of Digestion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j84pqg 8nf0M Parts of the Digestive System The digestive system begins at the mouth, where food enters the body. The mouth
Digestive System Anatomy The Process of Digestion http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=j84pqg 8nf0M Parts of the Digestive System The digestive system begins at the mouth, where food enters the body. The mouth
Digestive System. Physical and breakdown begins. : Further breakdown, chemical/enzymatic
 SBI 3C Digestive System : food enters the system Physical and breakdown begins : Further breakdown, chemical/enzymatic : Nutrients enter system, delivered to tissues of the body Elimination of Waste (
SBI 3C Digestive System : food enters the system Physical and breakdown begins : Further breakdown, chemical/enzymatic : Nutrients enter system, delivered to tissues of the body Elimination of Waste (
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
